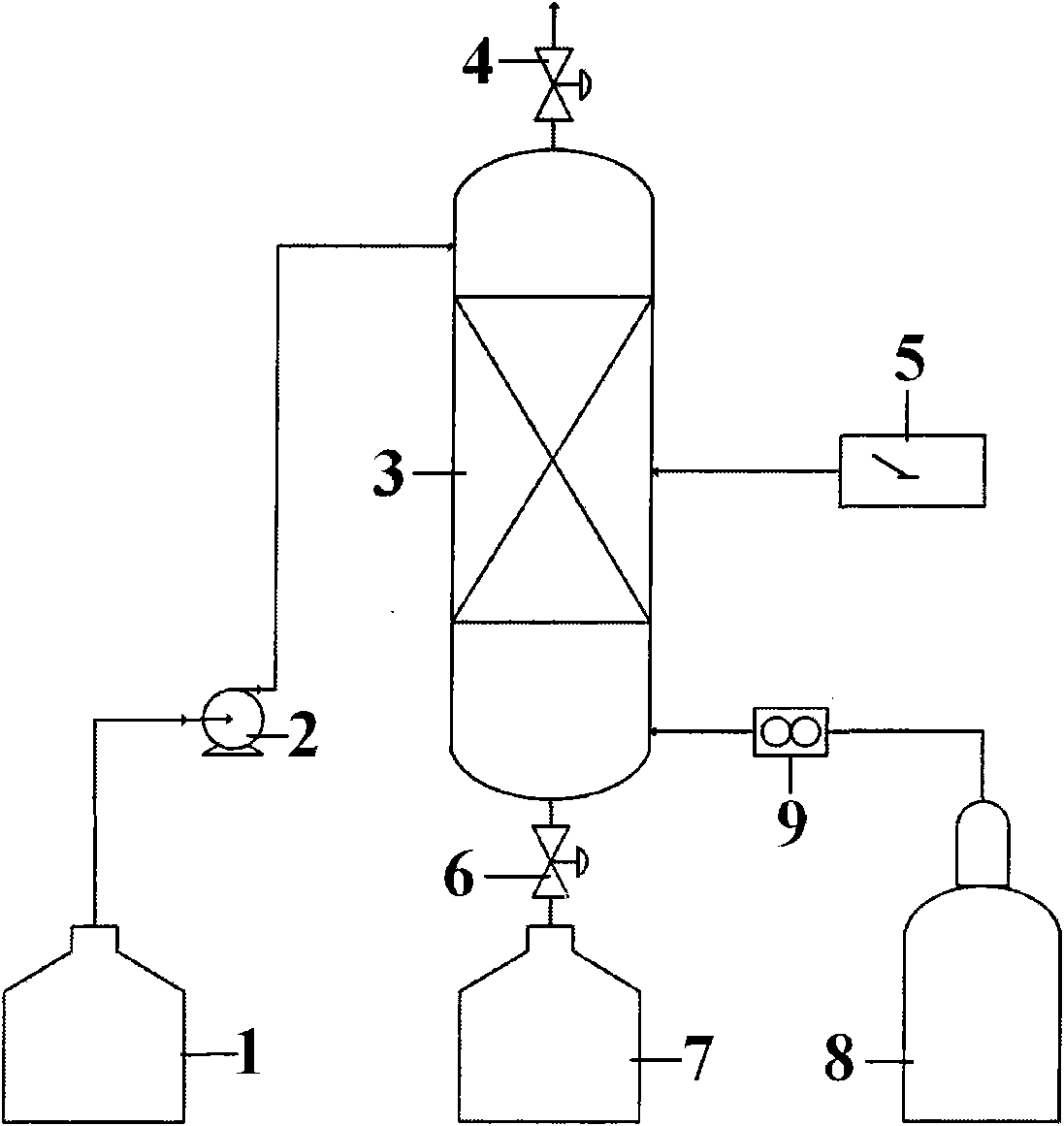
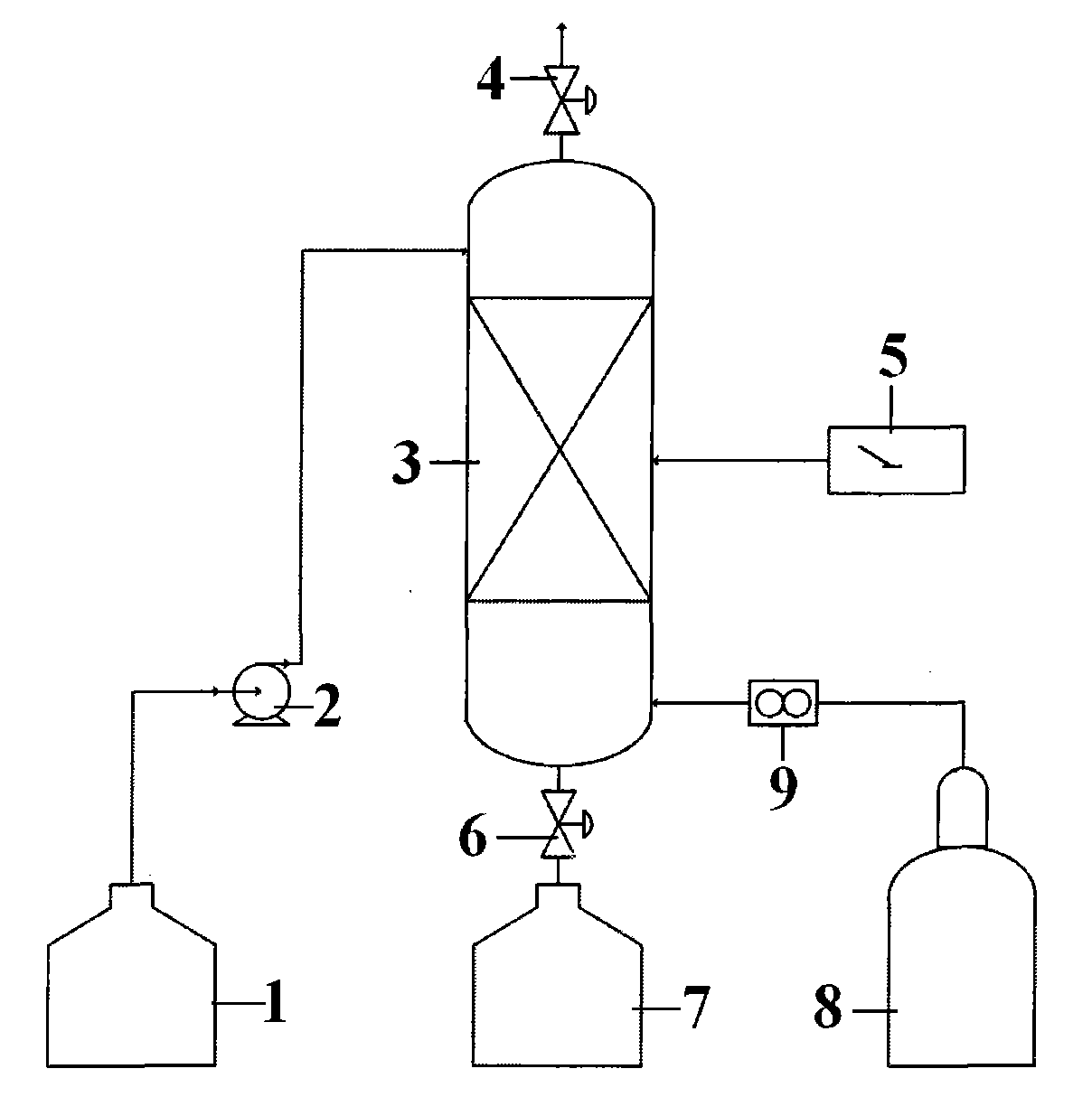
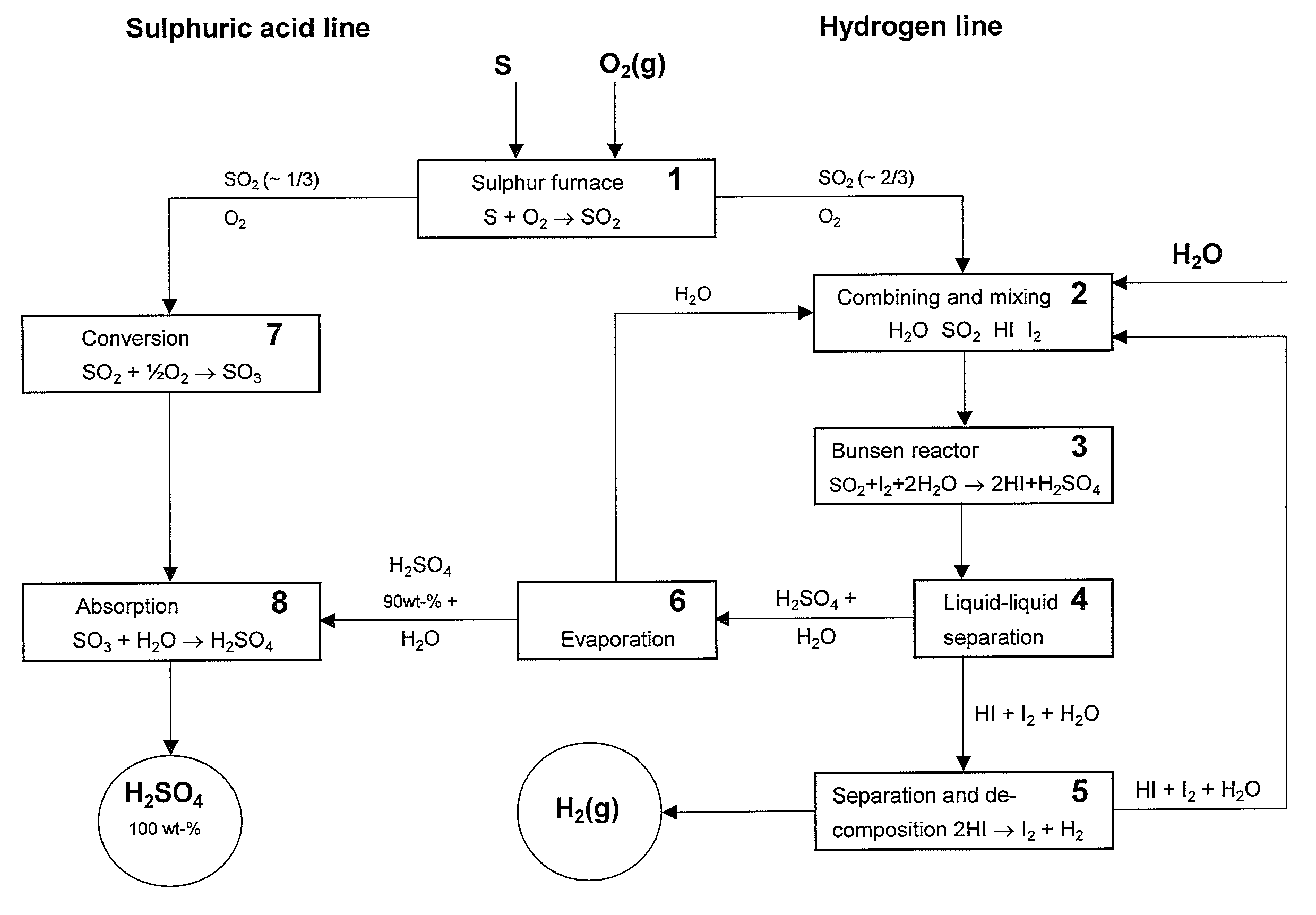
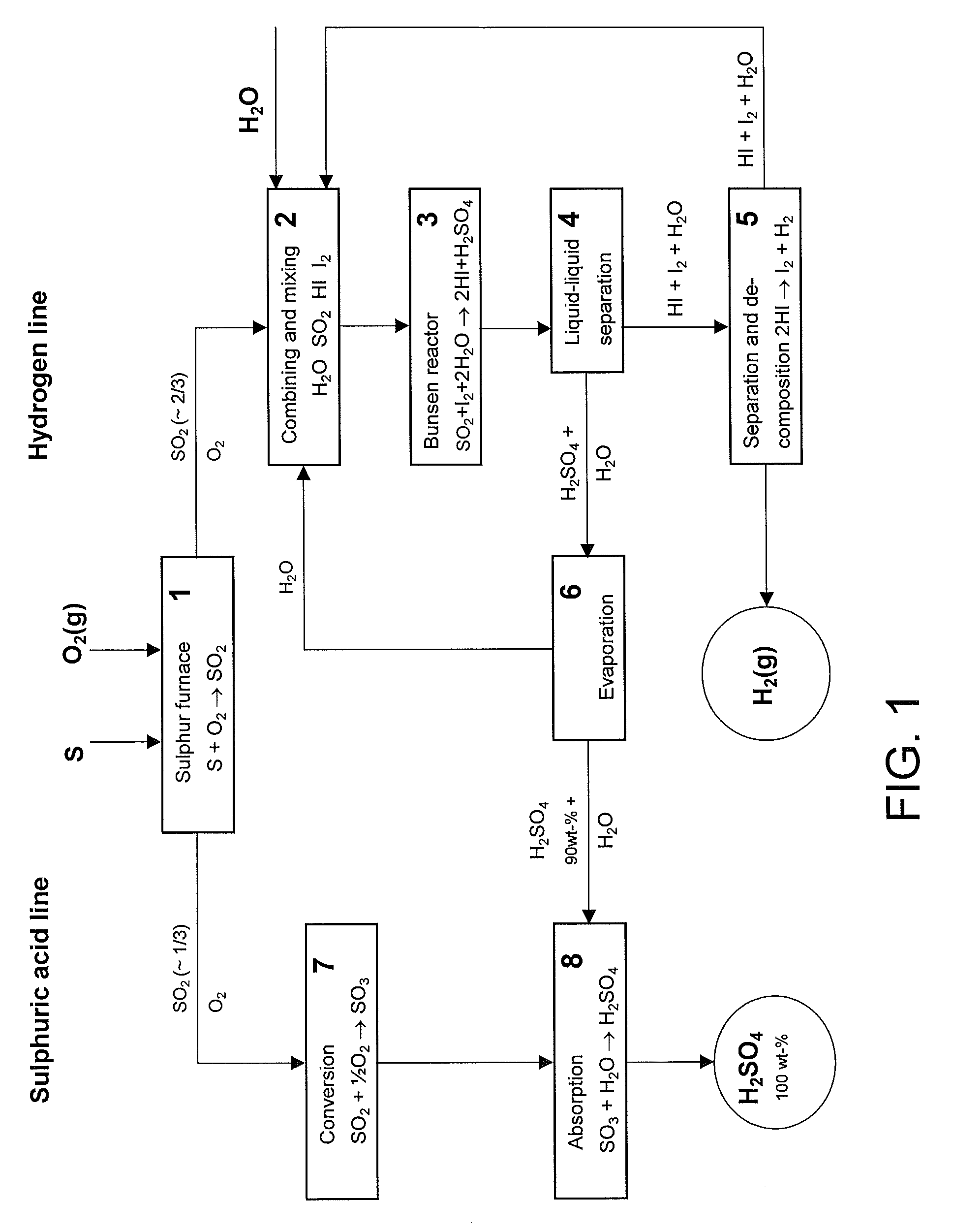
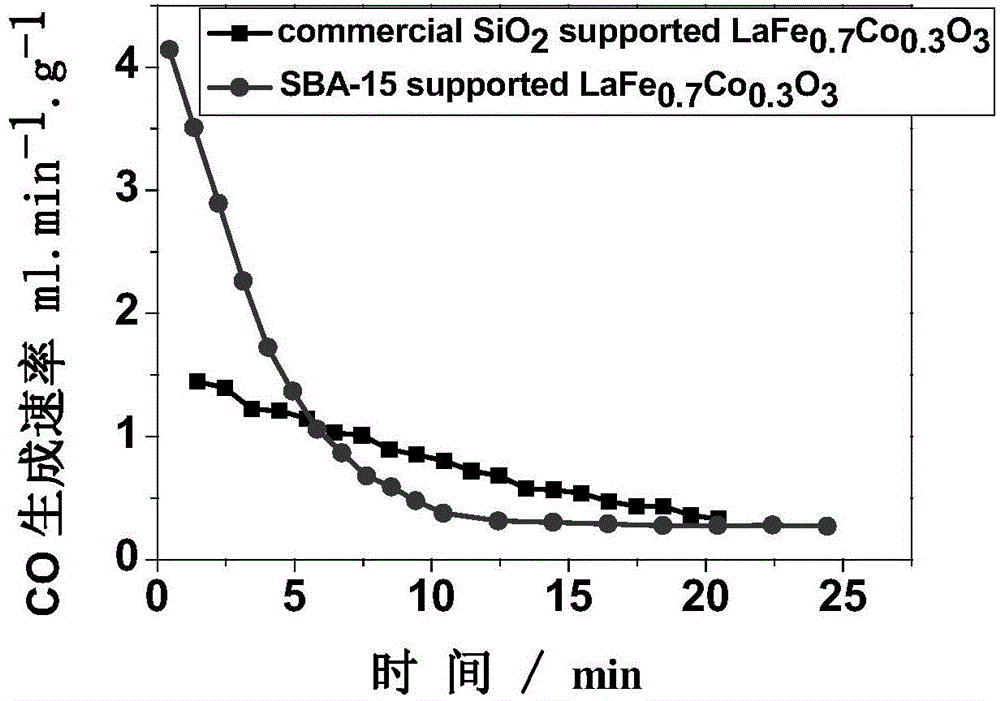
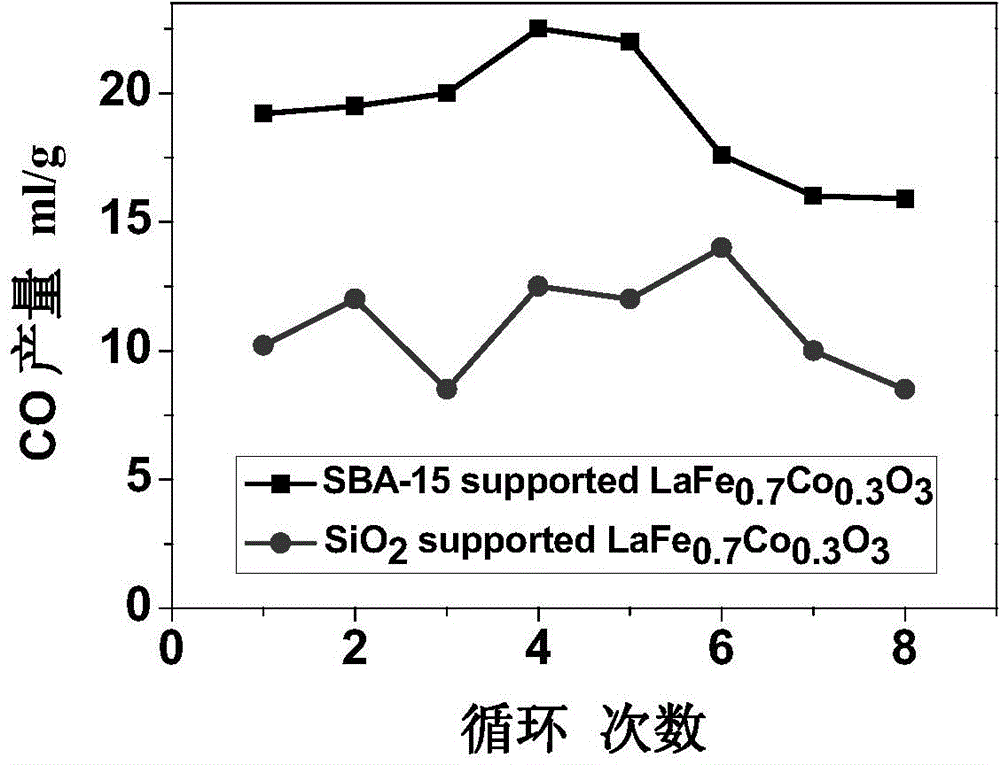
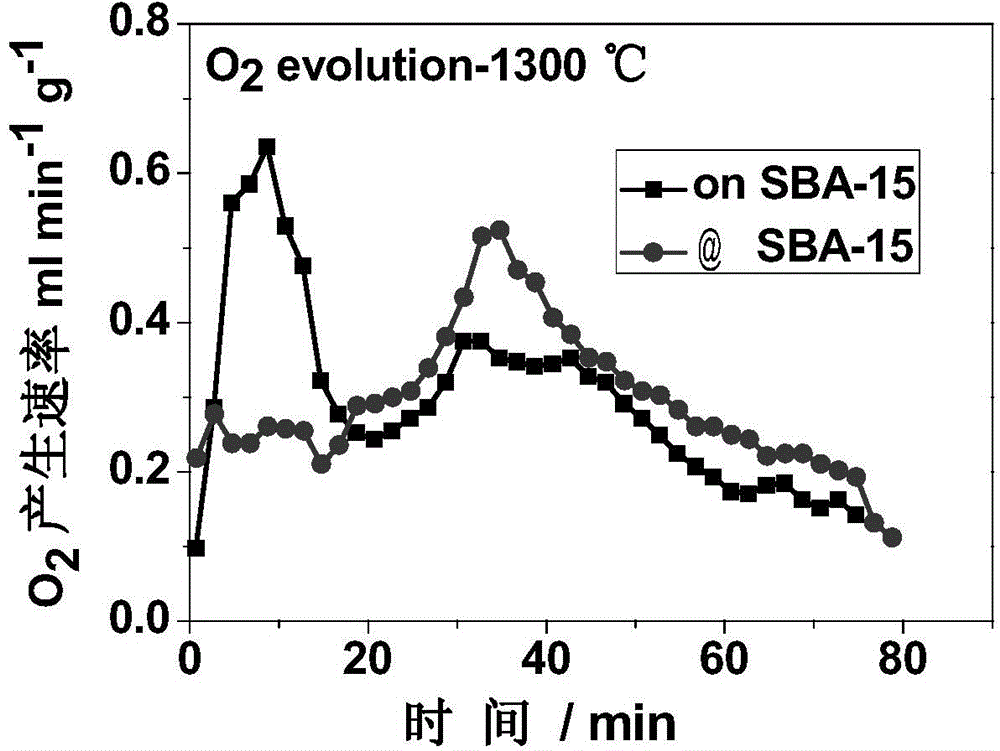
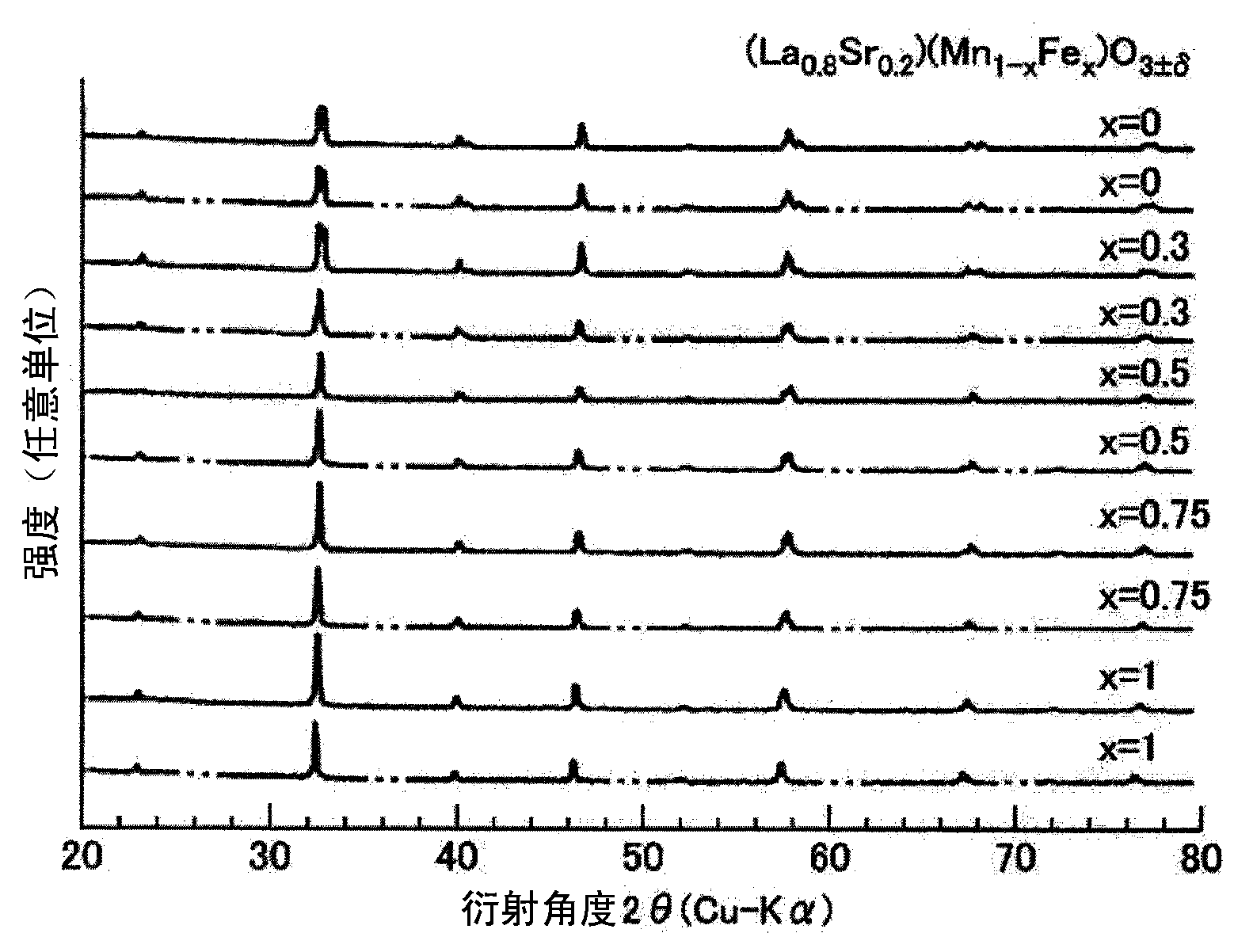
Patents
Literature
109 results about "Thermochemical cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
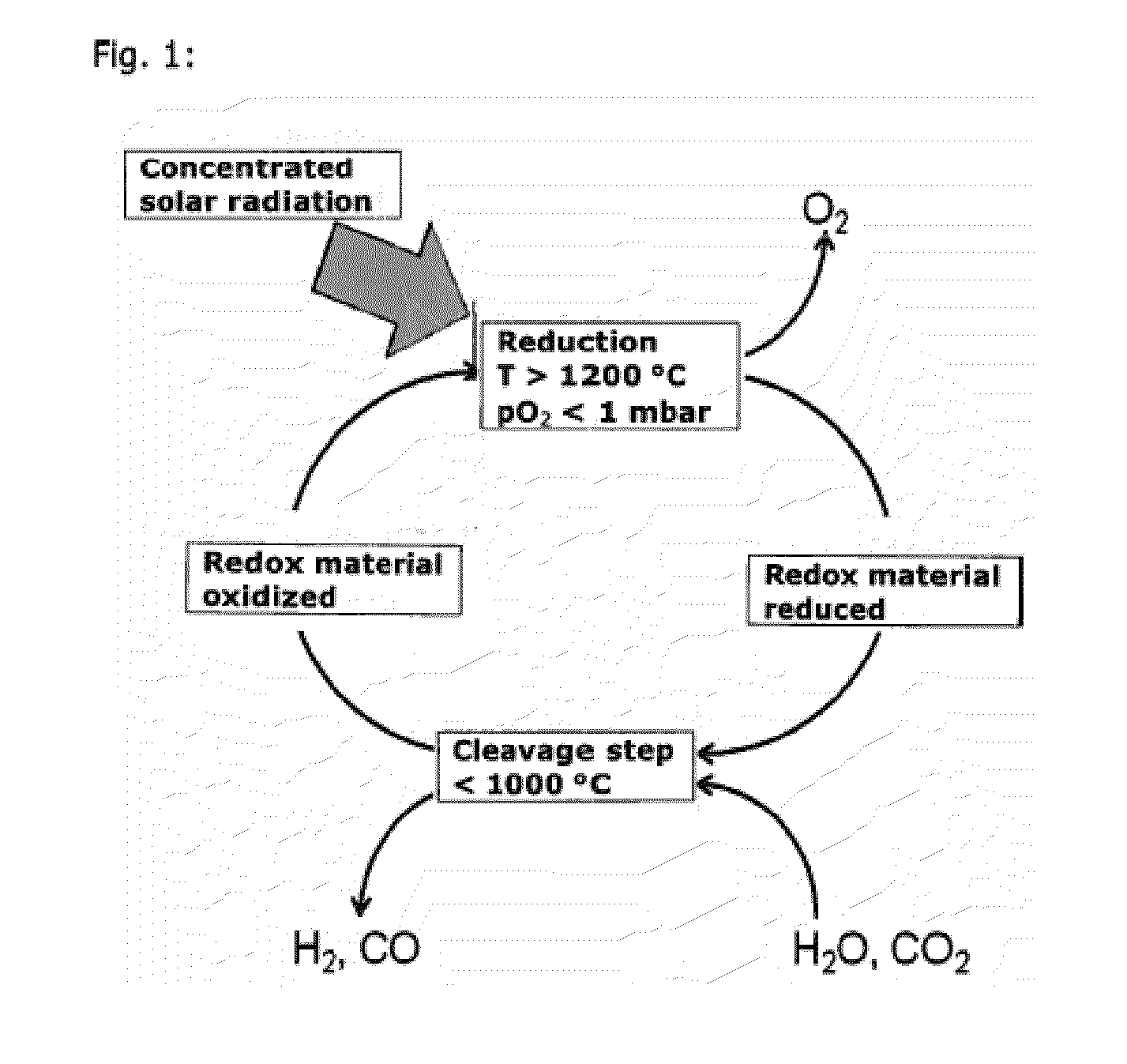
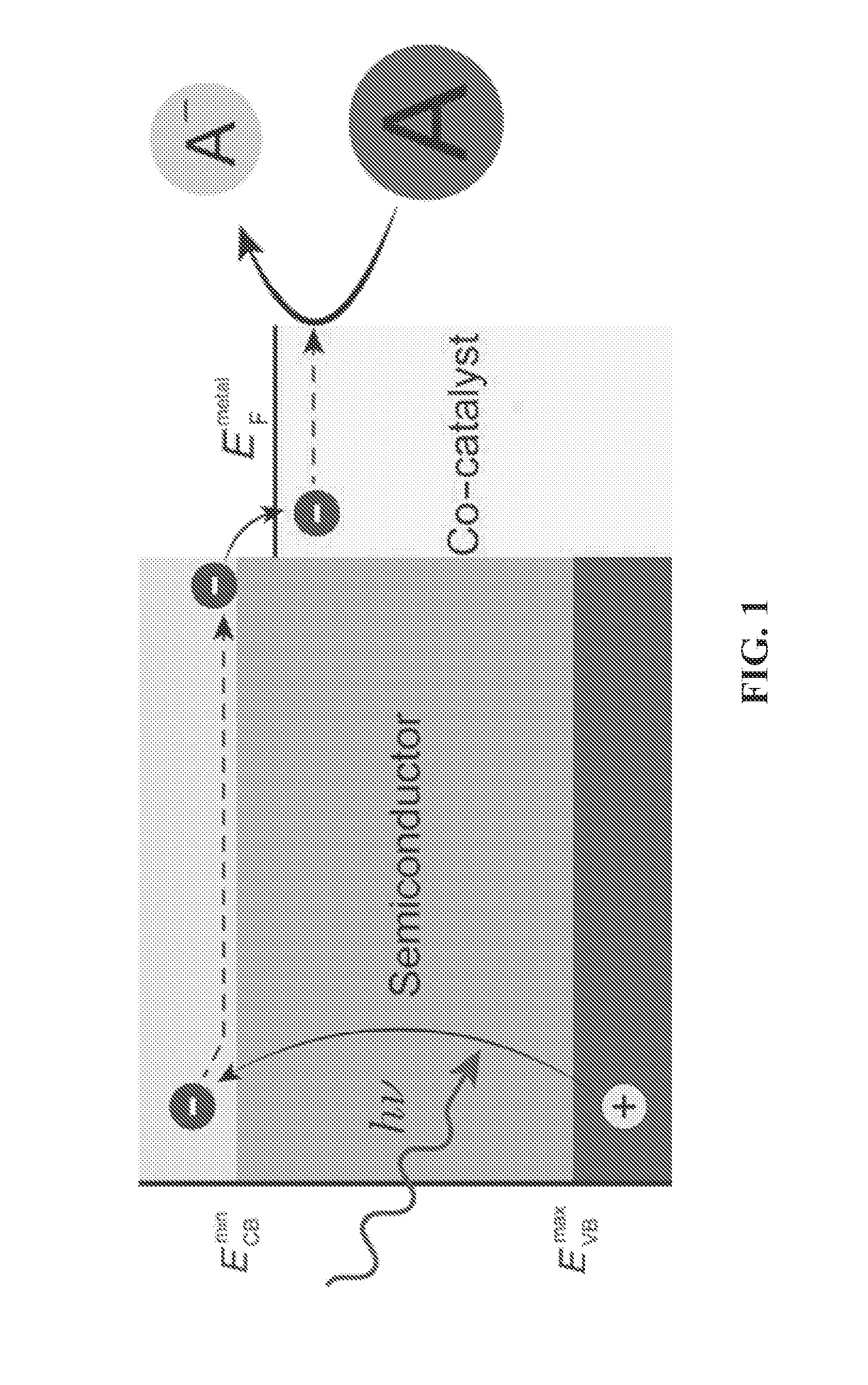
Thermochemical cycles combine solely heat sources (thermo) with chemical reactions to split water into its hydrogen and oxygen components. The term cycle is used because aside of water, hydrogen and oxygen, the chemical compounds used in these processes are continuously recycled.
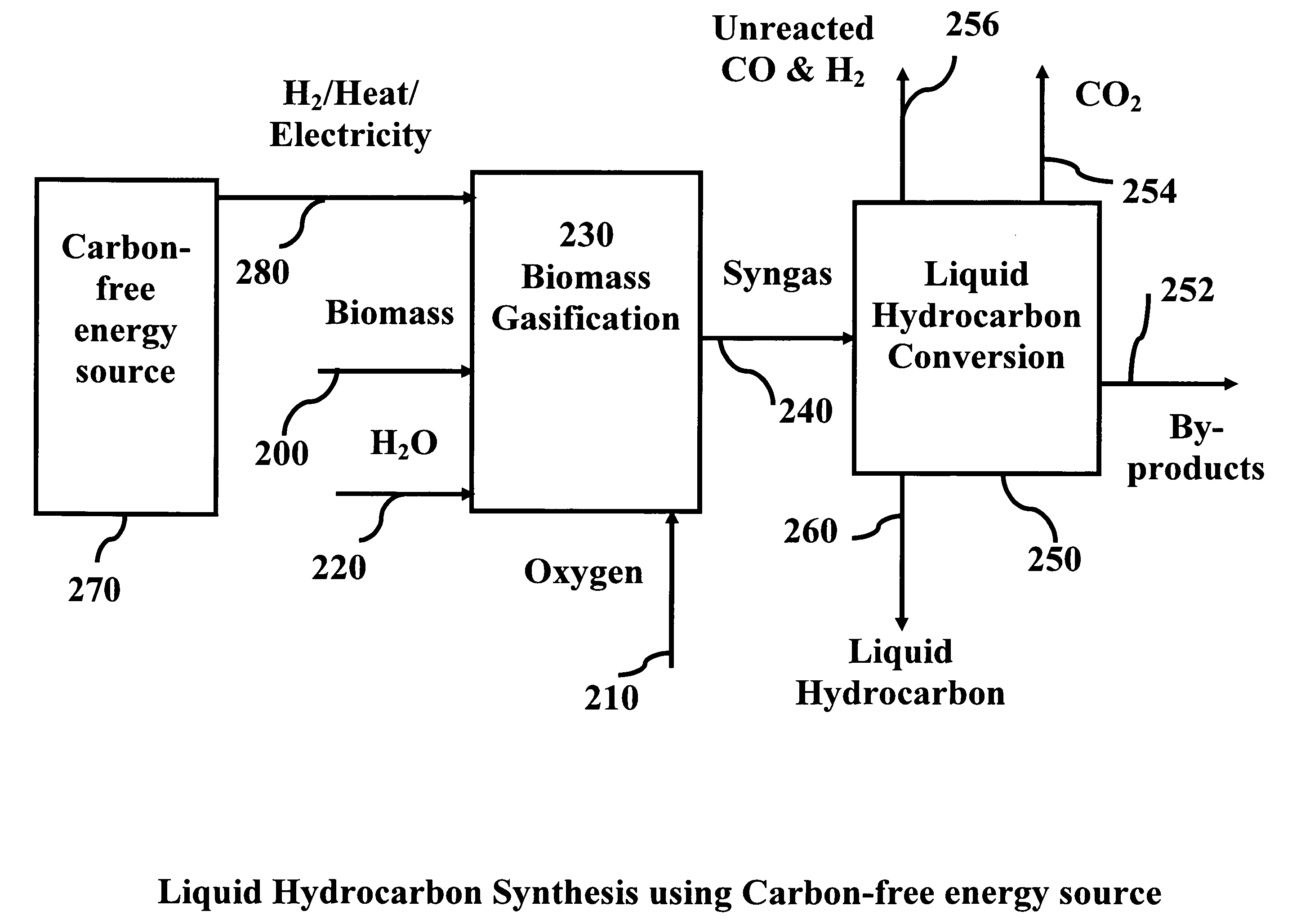
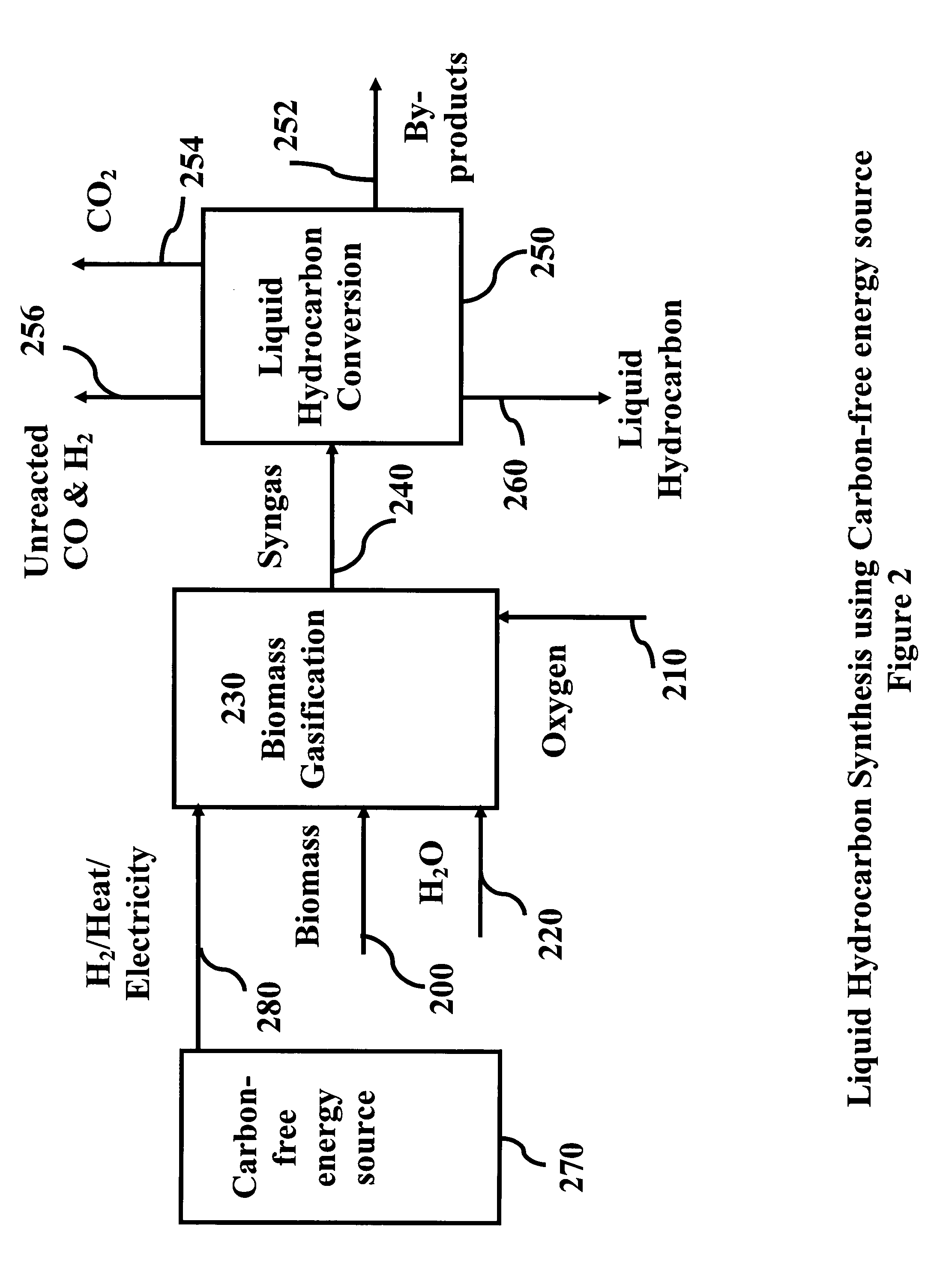
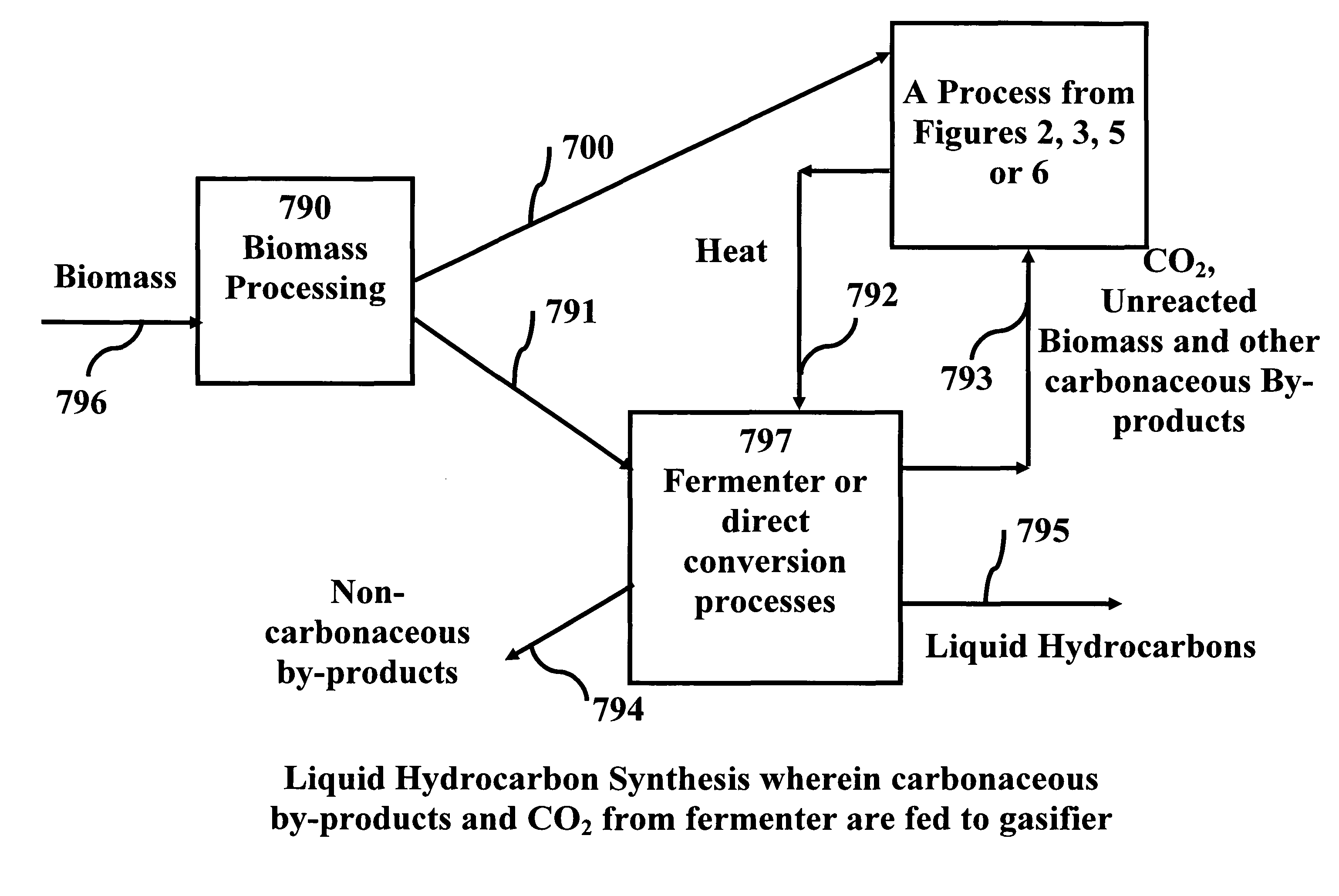
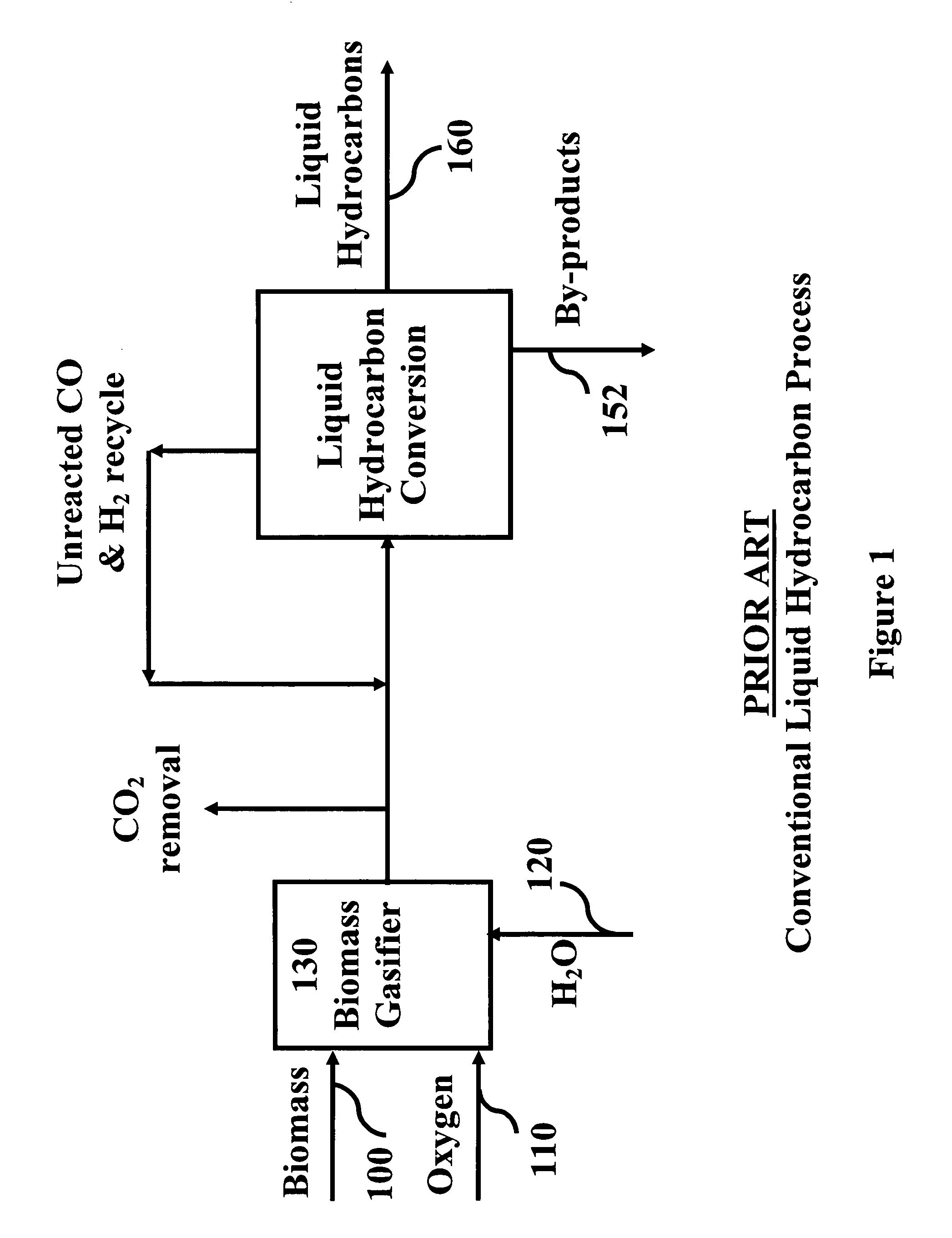
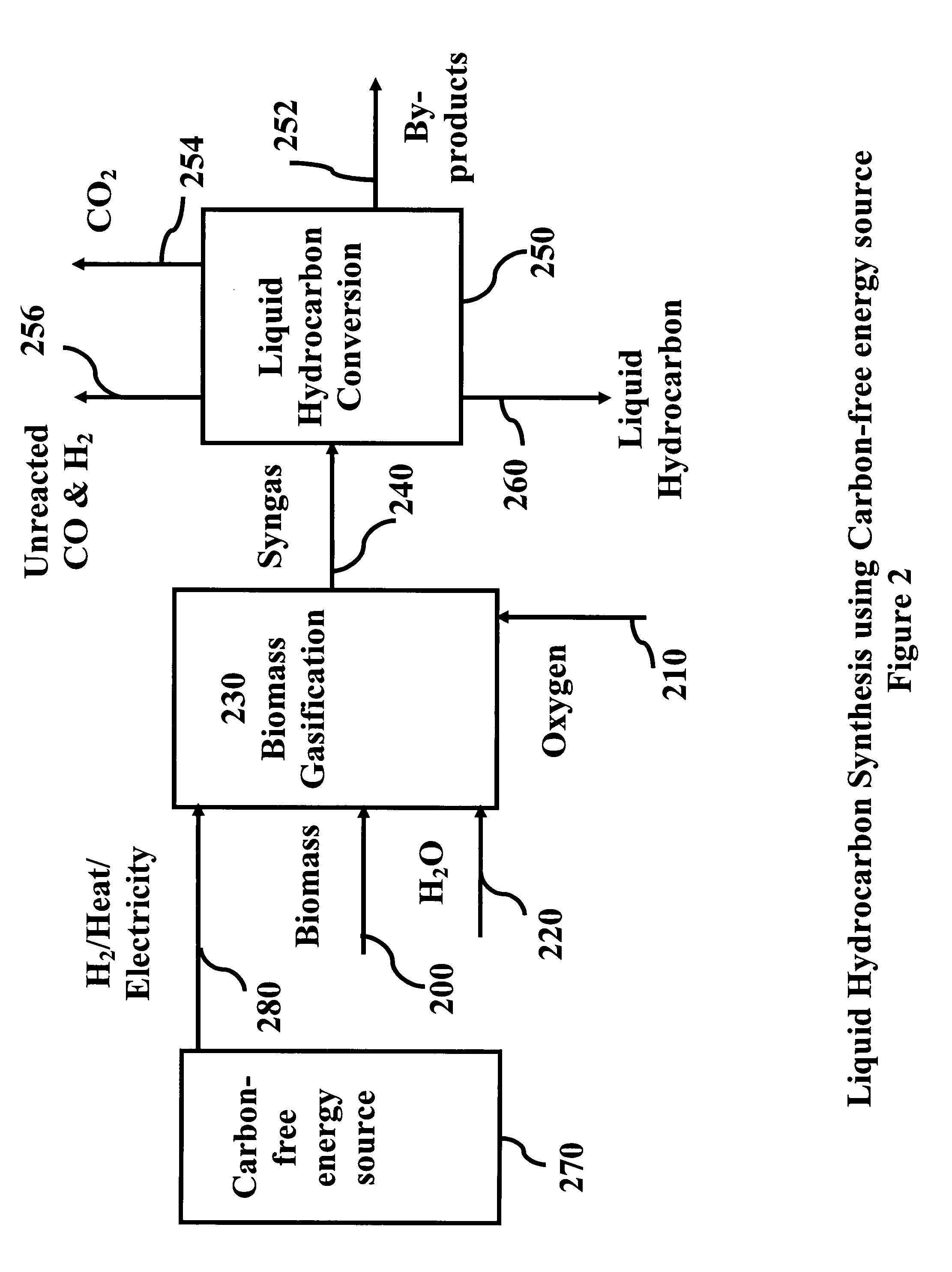
System and process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon
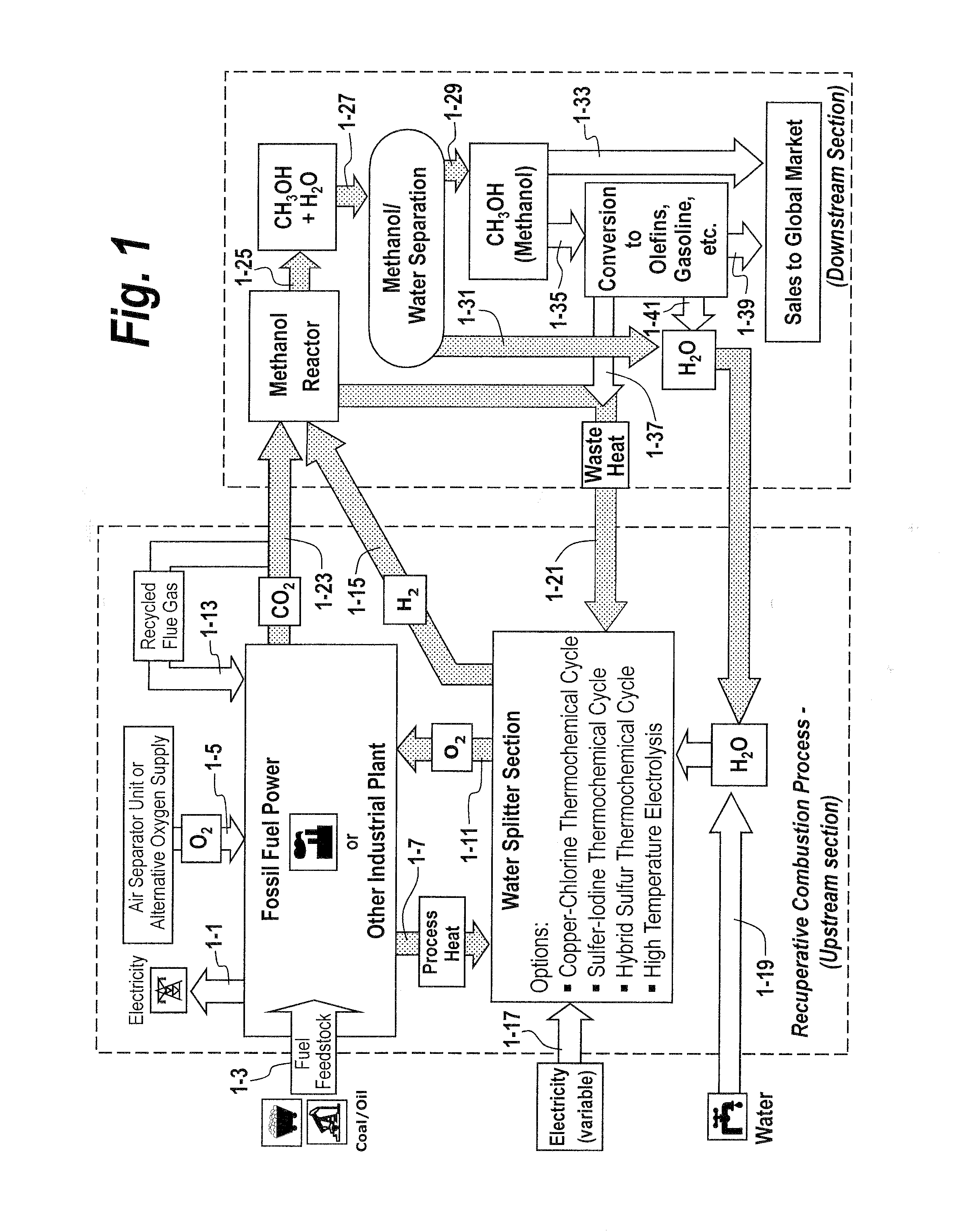
ActiveUS20080115415A1Improve carbon efficiencyReduce area requirementsMuffle furnacesCarbon compoundsOxygenElectrolysis of water
Production of synthetic liquid hydrocarbon fuel from carbon containing moieties such as biomass, coal, methane, naphtha as a carbon source and hydrogen from a carbon-free energy source is disclosed. The biomass can be fed to a gasifier along with hydrogen, oxygen, steam and recycled carbon dioxide. The synthesis gas from the gasifier exhaust is sent to a liquid hydrocarbon conversion reactor to form liquid hydrocarbon molecules. Unreacted CO & H2 can be recycled to the gasifier along with CO2 from the liquid hydrocarbon conversion reactor system. Hydrogen can be obtained from electrolysis of water, thermo-chemical cycles or directly by using energy from carbon-free energy sources.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
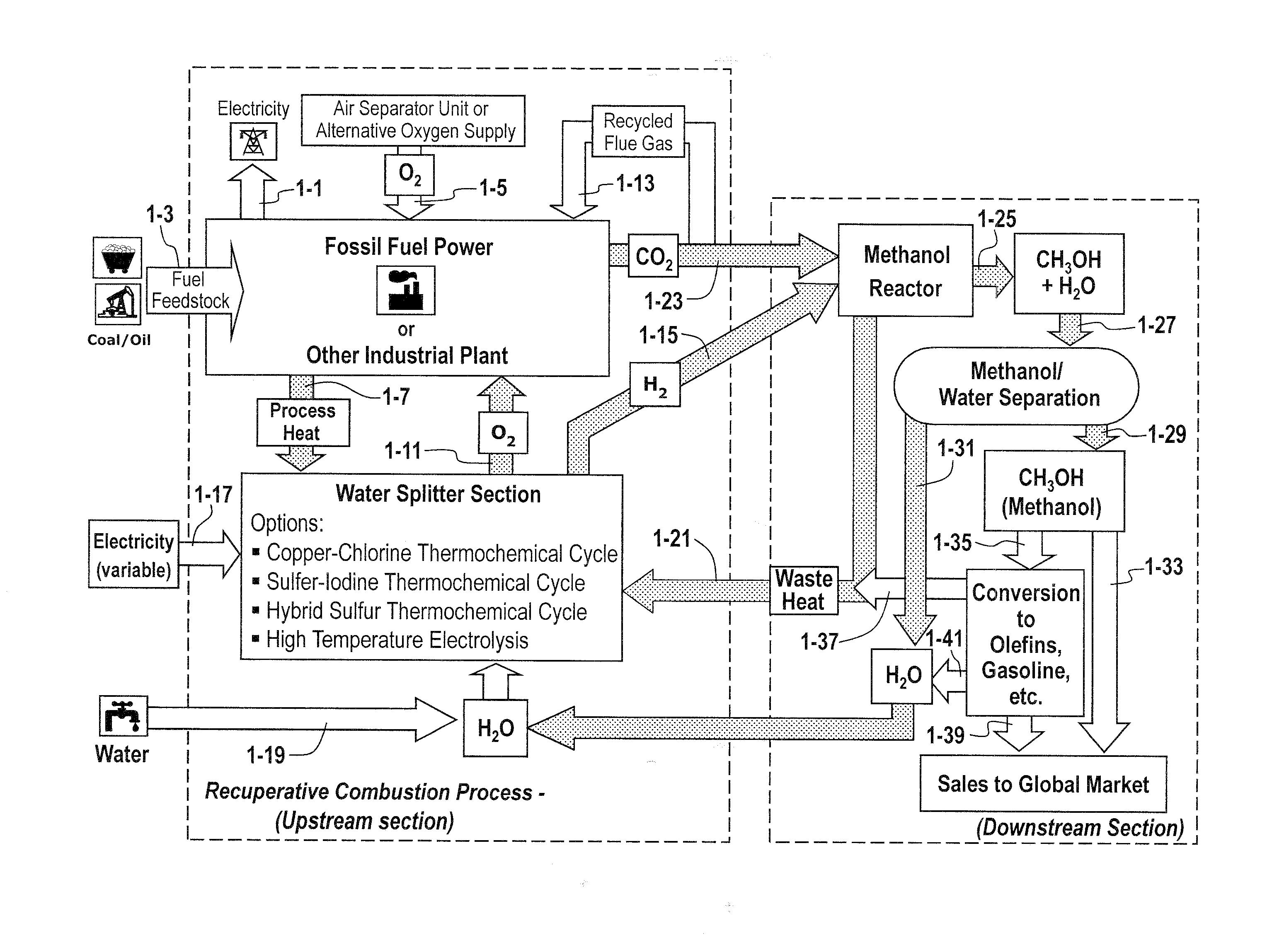
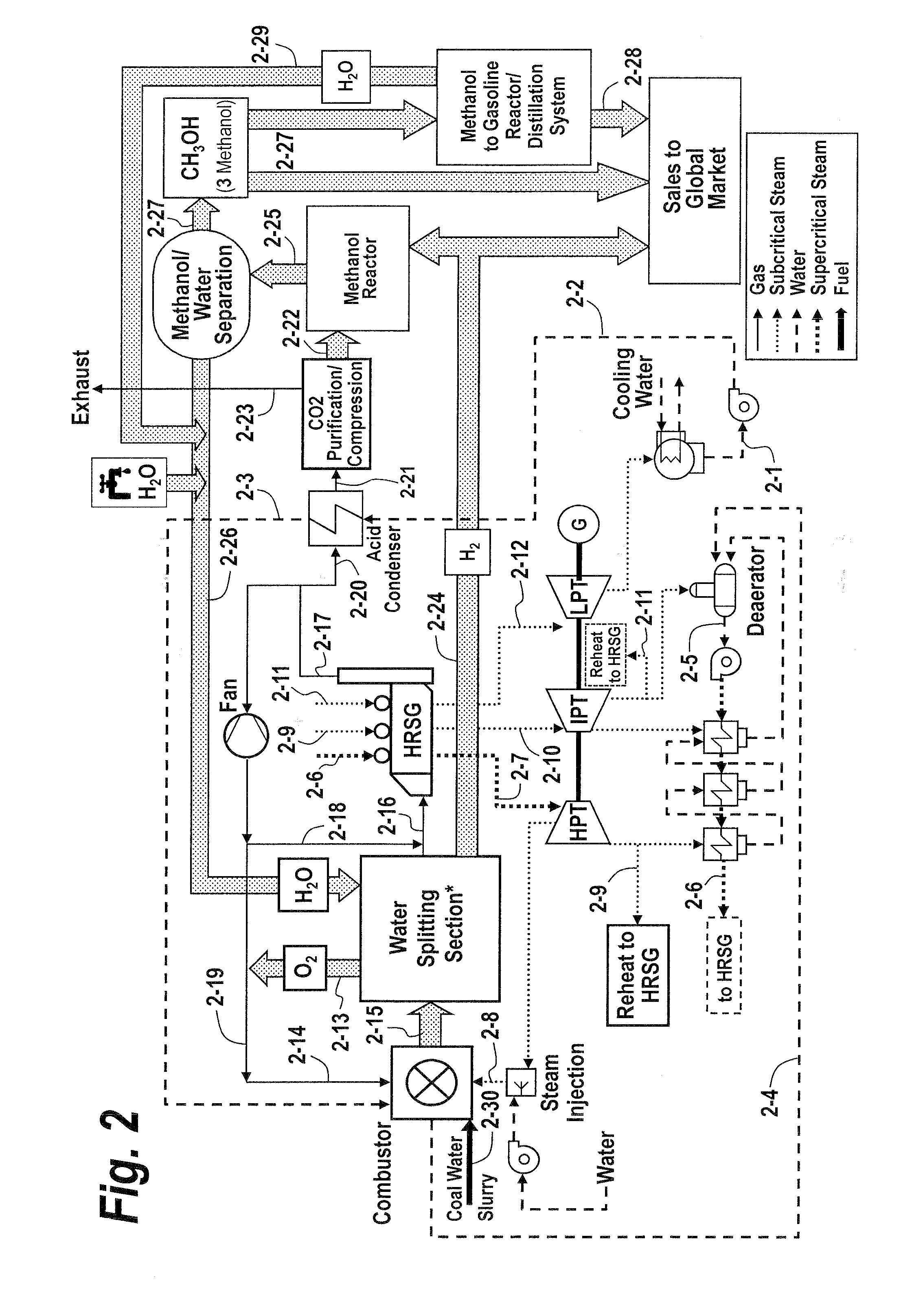
Recuperative combustion system
InactiveUS20110041740A1Reducing and eliminating amount of oxygenSolid fuel combustionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationOxygenDimethyl ether
The methods and systems described herein relate to a recuperative combustion system that recuperates energy from fuel combustion that would otherwise be lost. The recuperative combustion system minimizes or eliminates the need for an air separator unit through the use of a clean water splitter section, consisting of a thermochemical cycle or high-temperature electrolysis. Water is split into its component hydrogen and oxygen, primarily with process heat from the combustion process. The oxygen produced by the water splitter provides oxygen necessary for oxy-fuel combustion, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for the power intensive air separator unit and / or external oxygen source, significantly increasing the efficiency of the oxy-fuel combustion cycle. Hydrogen produced by the water splitter may be used for a variety of industrial uses, or combined with carbon dioxide (captured from the flue gases produced by said combustion process) to produce methanol. Methanol can further be refined in a methanol to gasoline reactor to produce dimethyl ether, olefins or high grade gasoline. Described herein are methods and systems that 1) increase oxy-fuel combustion efficiency, 2) produce hydrogen for a suite of industrial / energy uses, and 3) capture carbon dioxide and convert it to high value hydrocarbons.
Owner:REILLY TIMOTHY J
Solar Receivers for Use in Solar-Driven Thermochemical Processes
InactiveUS20130234069A1Improve efficiencyImprove system efficiencySolar heating energyHydrogenThermochemical cycleElectricity
Solar receivers which produce heat at very high temperatures (in excess of 1000° C.) are described herein. The receiver produces the high temperature heat and radiates the heat to a containment element (e.g., pipe) that contains a heat transfer fluid which absorbs the heat. The fluid is preferably a material which is thermally and chemically stable at the temperatures involved. The heat transfer fluid absorbs the heat and can deliver it to a reactor system to drive an endothermic reaction, such as thermochemical water splitting, CO2 capture, and / or syngas production. Alternatively, the heat can be used to directly generate electricity through a high temperature heat engine such as a Brayton or combined Brayton+Rankine cycle.
Owner:HENRY ASEGUN
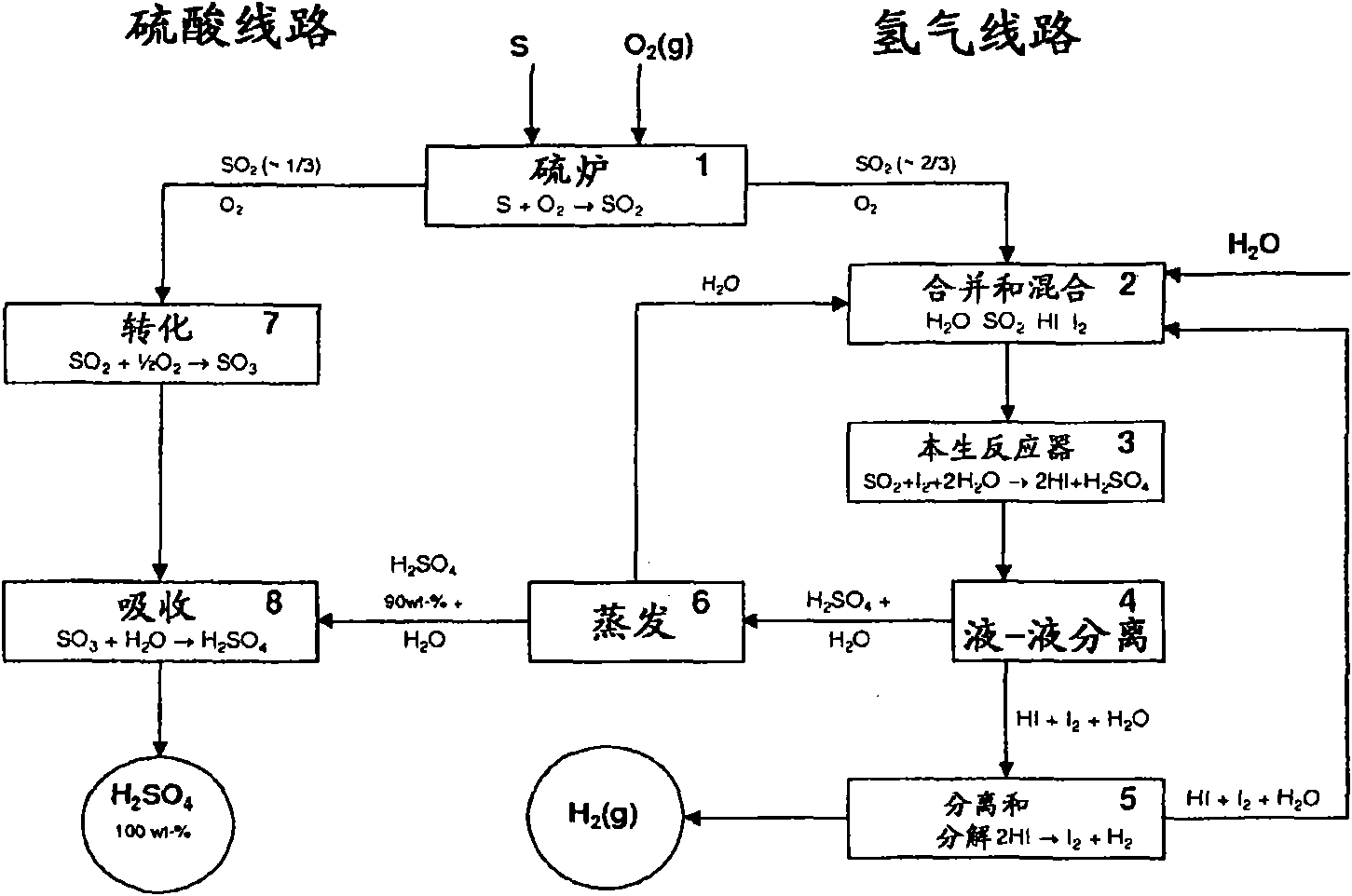
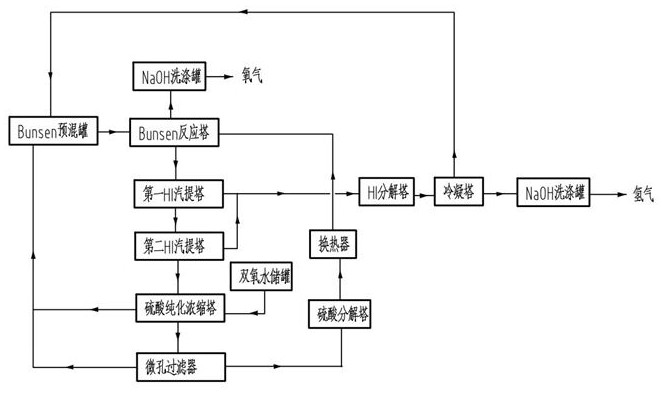
Process for purifying sulfuric acid phase and hydriodic acid phase in iodine-sulfur cycle
InactiveCN101830443AAchieve purificationSuppress generationIodine/hydrogen-iodideSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidThermochemical cycleSulfur cycle
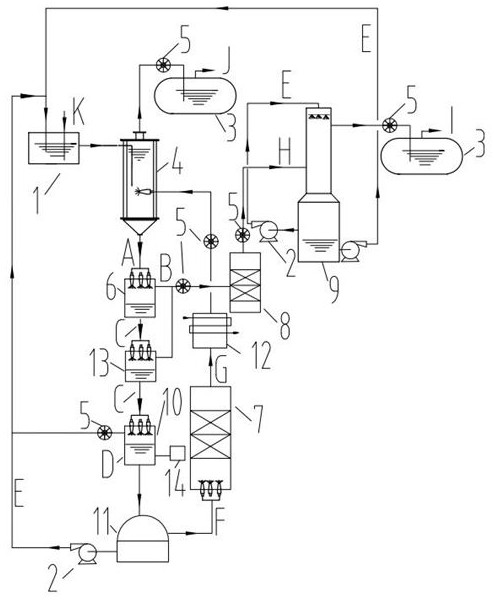
The invention relates to a process for purifying a sulfuric acid phase and a hydriodic acid phase in an iodine-sulfur cycle, which belongs to the technical field related to hydrogen production through an iodine-sulfur thermochemical cycle. The sulfuric acid phase and the hydriodic acid phase obtained through a Benson reaction in the iodine-sulfur cycle respectively contain a small amount of HI and a small amount of H2SO4, and a traditional purification process comprises the following steps of: using nitrogen gas as sweep gas, heating to promote the occurrence of the reverse reaction of the Benson reaction: 2HI+H2SO4=SO2+I2+2H2O, and removing impurity acid. The traditional purification process can consume main acid, and a side reaction often occurs together. In order to overcome the defect, the invention provides a two-phase purification process using the mixed gas of oxygen and inert gas as active sweep gas, and as for the purification of the sulfuric acid phase, the reaction principle is 4HI+O2=2I2+2H2O, sulfuric acid is not lost, and the reaction temperature is lower; and as for the purification of the hydriodic acid phase, the active sweep gas can inhabit the generation of S and H2S and promote the selectivity enhancement of converting H2SO4 into SO2.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
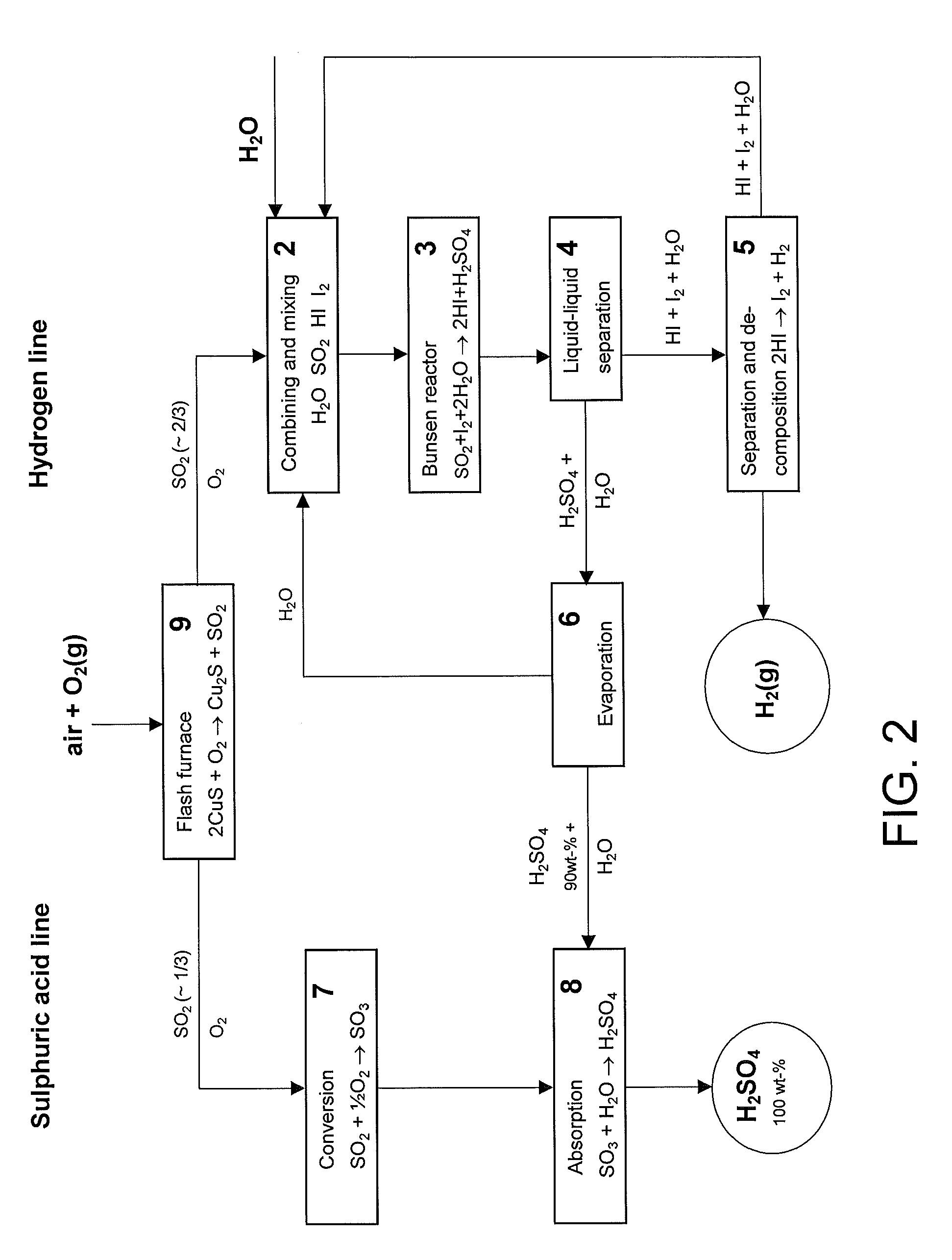
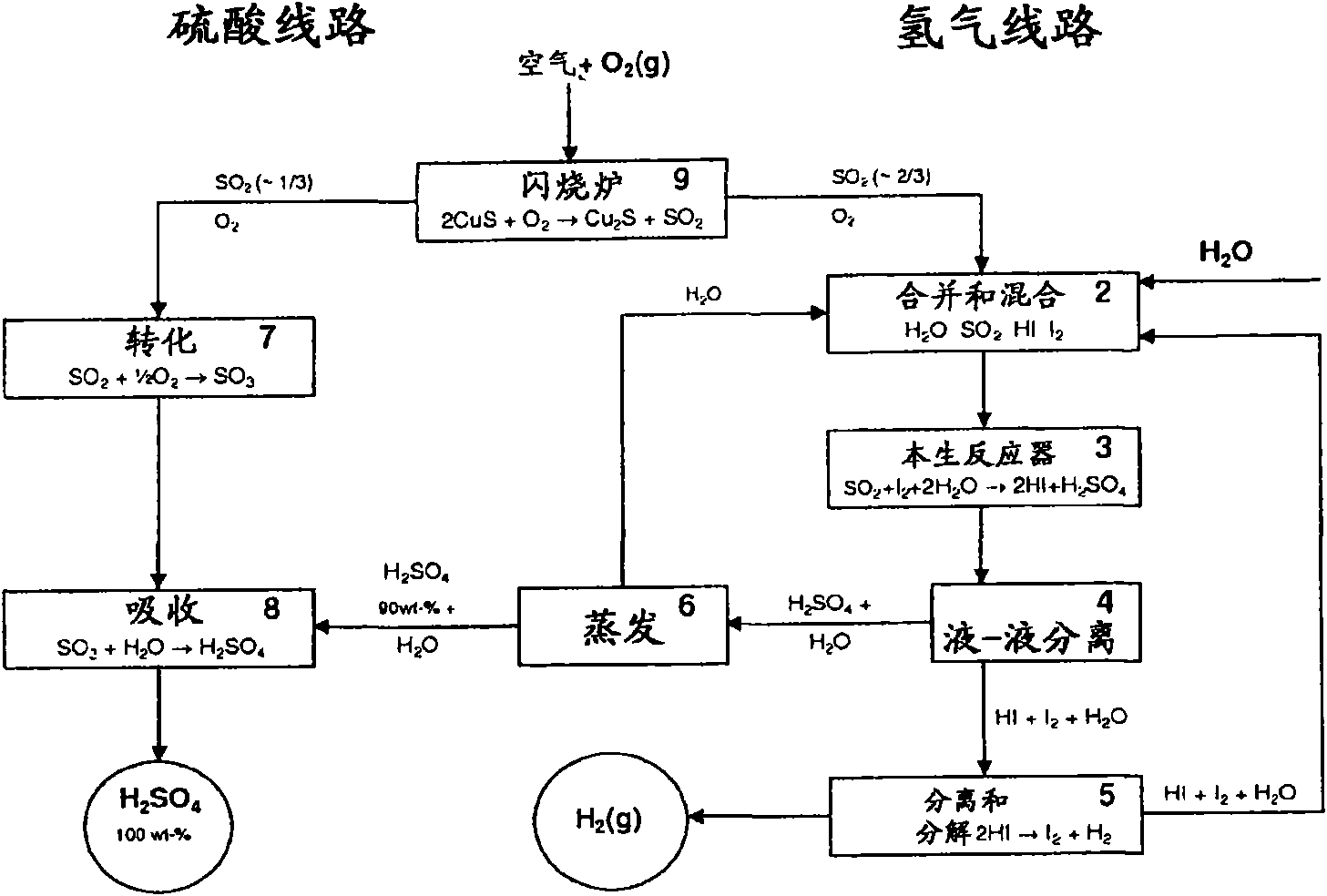
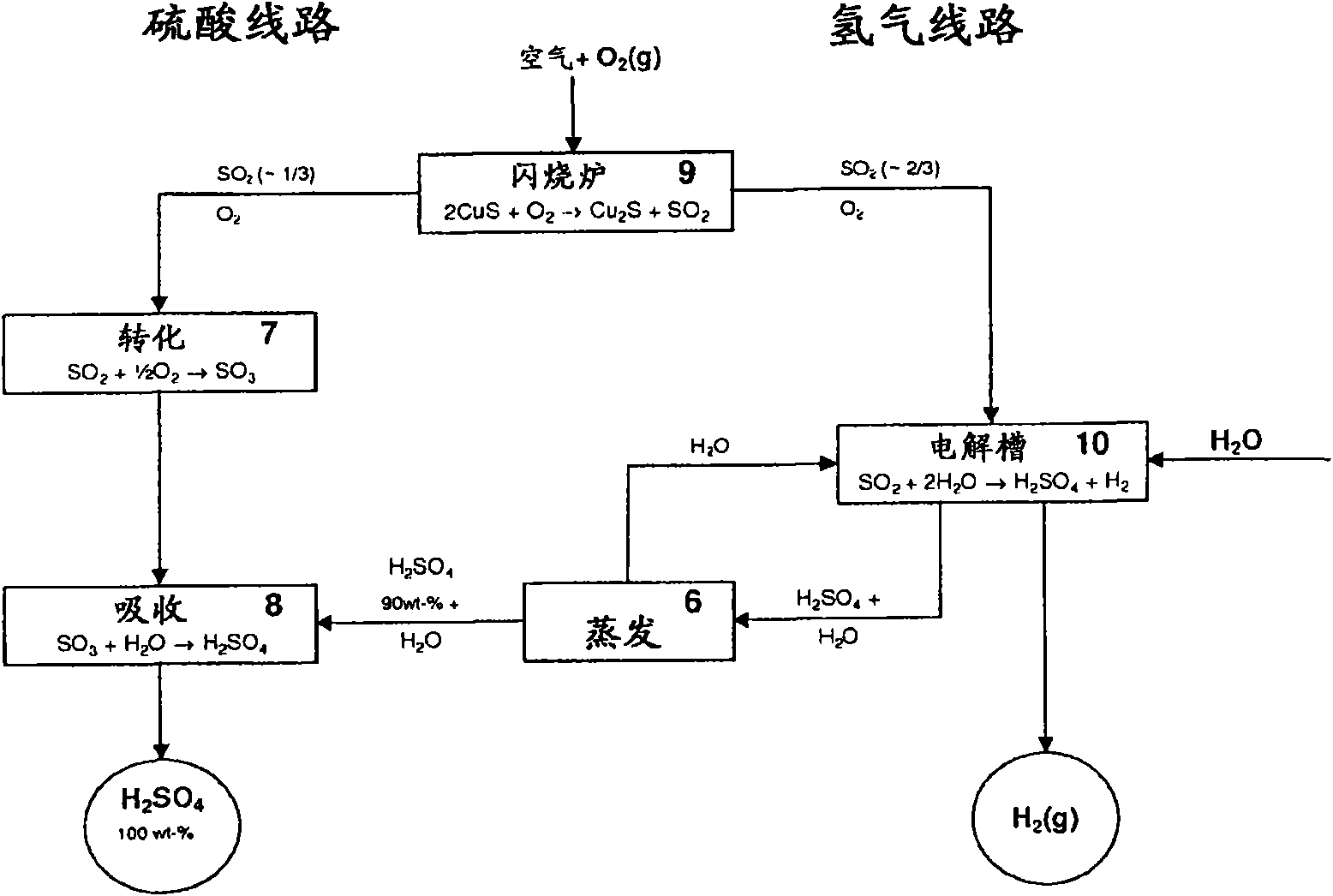
Method for producing hydrogen and sulphuric acid
InactiveUS20100061922A1Avoid recyclingAvoid decompositionHydrogen productionSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidThermochemical cycleDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for producing gaseous hydrogen and strong sulphuric acid (97-100 wt-%) simultaneously from sulphur dioxide gas and water. Sulphur dioxide gas stream is divided into two separate sub-streams, the first sub-stream is routed for water decomposition in a partial thermochemical cycle of the hydrogen and sulphuric acid production and the second sub-stream is fed to the oxidation of the sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide.
Owner:OUTOTEC OYJ
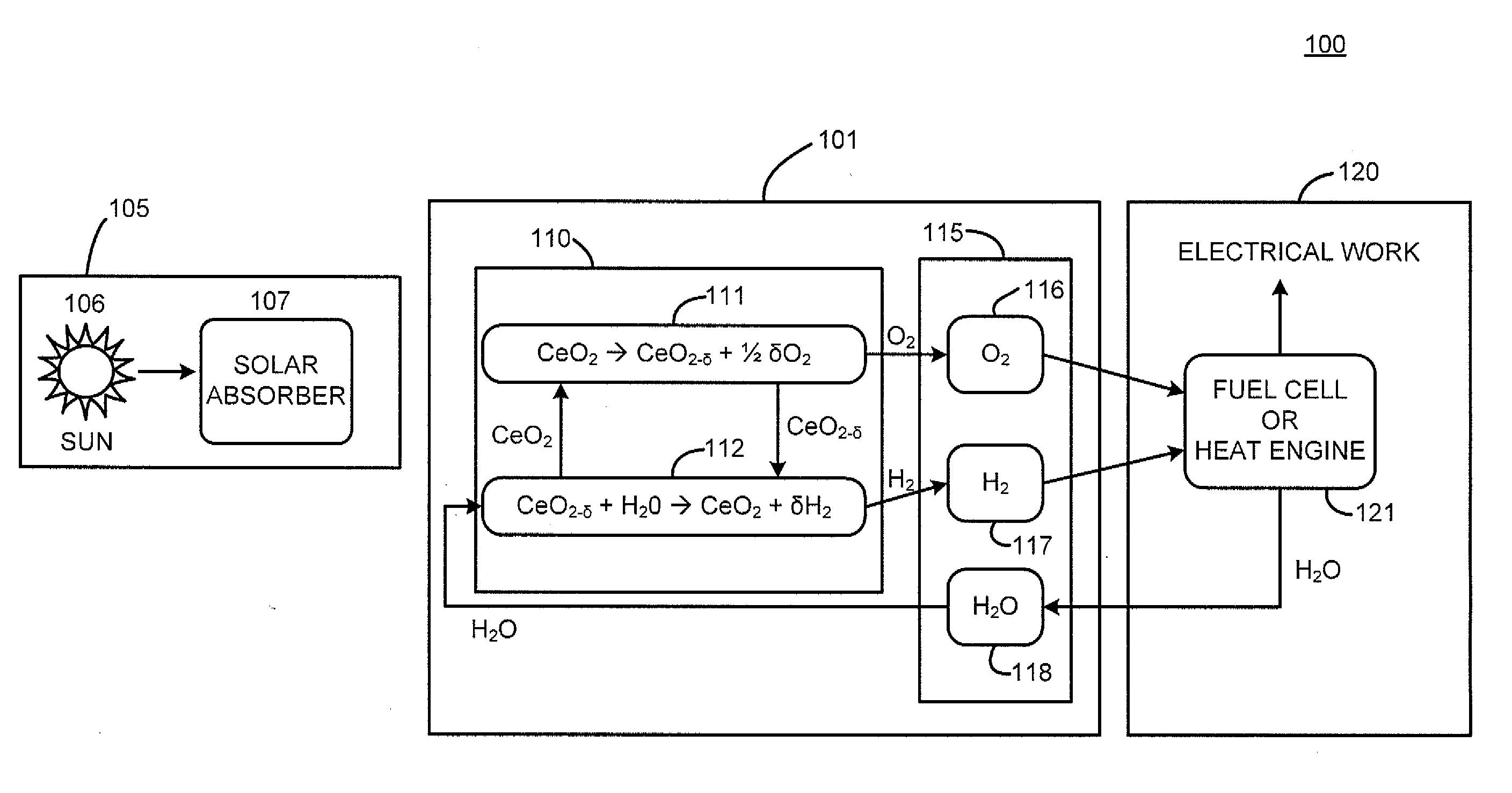
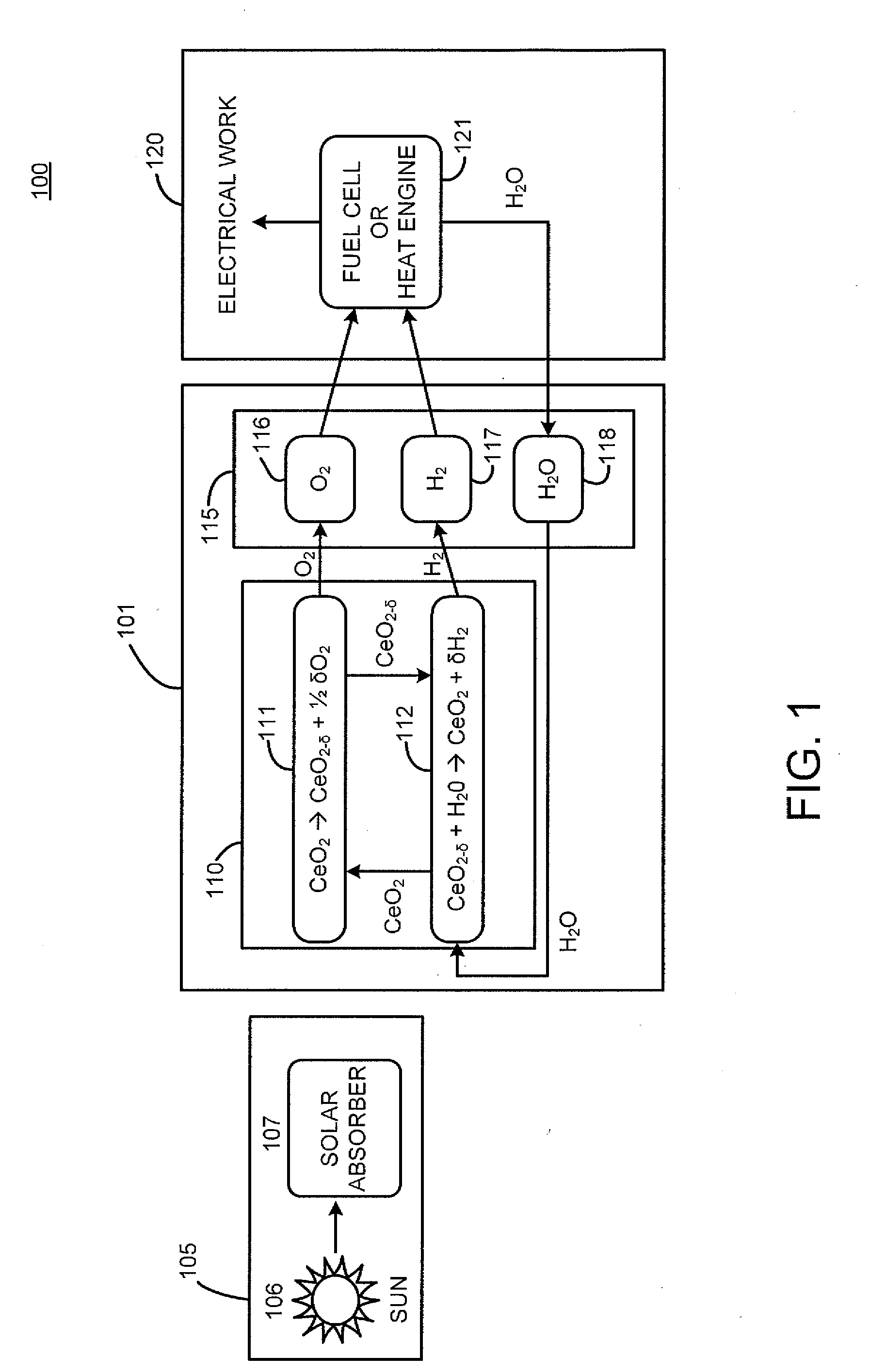
Reactor, system and method for solid reactant based thermochemical processes
A method and system for solid reactant based thermochemical process are disclosed. A metal oxide or solid reactant having a crystal structure associated with a characteristic state of high temperature engendering creation of oxygen vacancies is identified. The metal oxide is heated to the high temperature corresponding to the state of oxygen vacancies. Subsequently, the solid reactant is cooled to a temperature conducive to water splitting reaction. Steam is then introduced to react with the solid reactant to thereby re-oxidize the solid reactant producing hydrogen gas. Finally, the re-oxidized solid reactant is reheated to a reduction temperature completing the process of solid based reactant thermochemical solar power generation.The system includes one or more processors adapted to configure a solar absorption system, a thermochemical system, a gas storage system for storing product gases and a power generation system for processing the stored product gases into electrical power.
Owner:HENRY ASEGUN
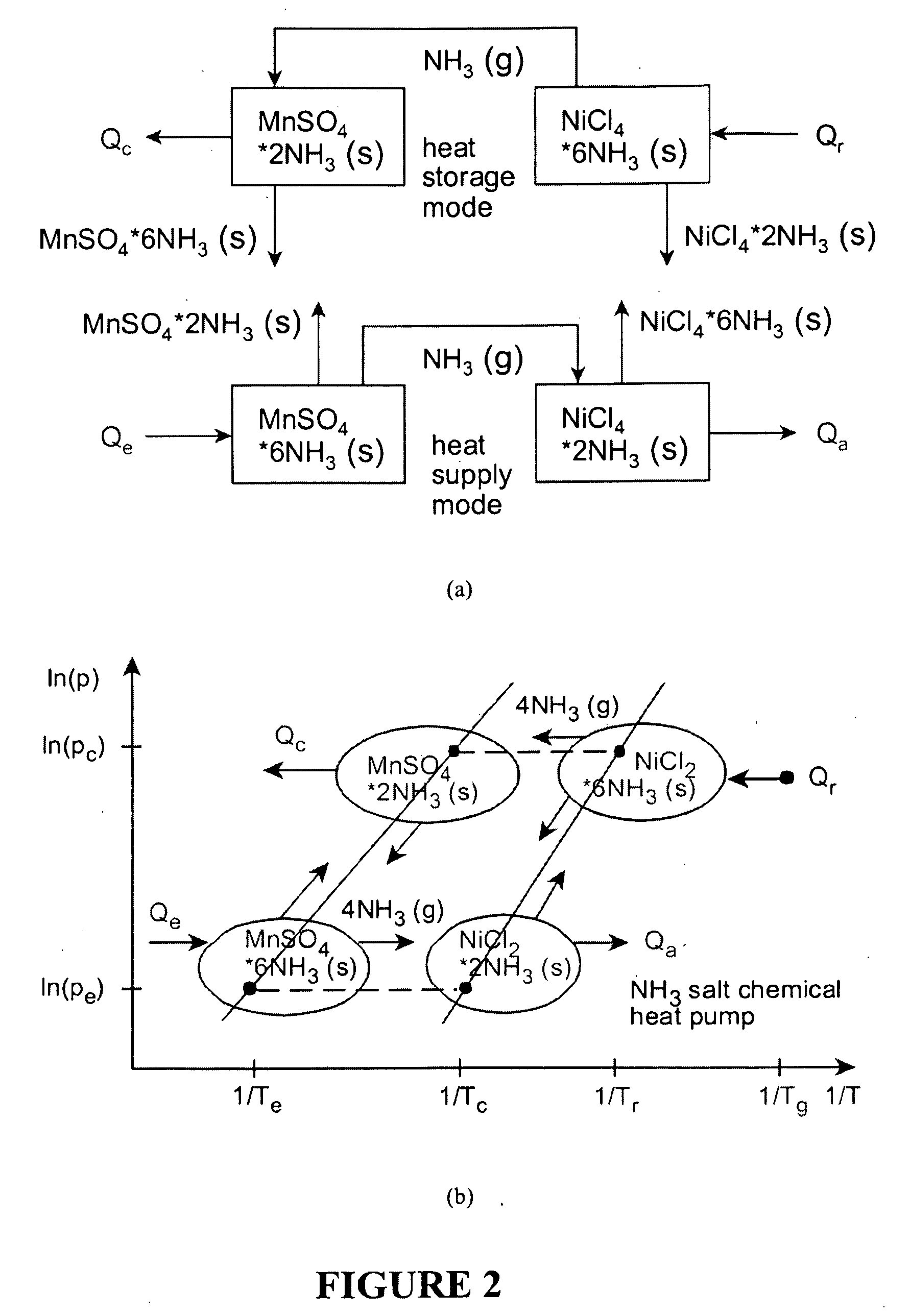
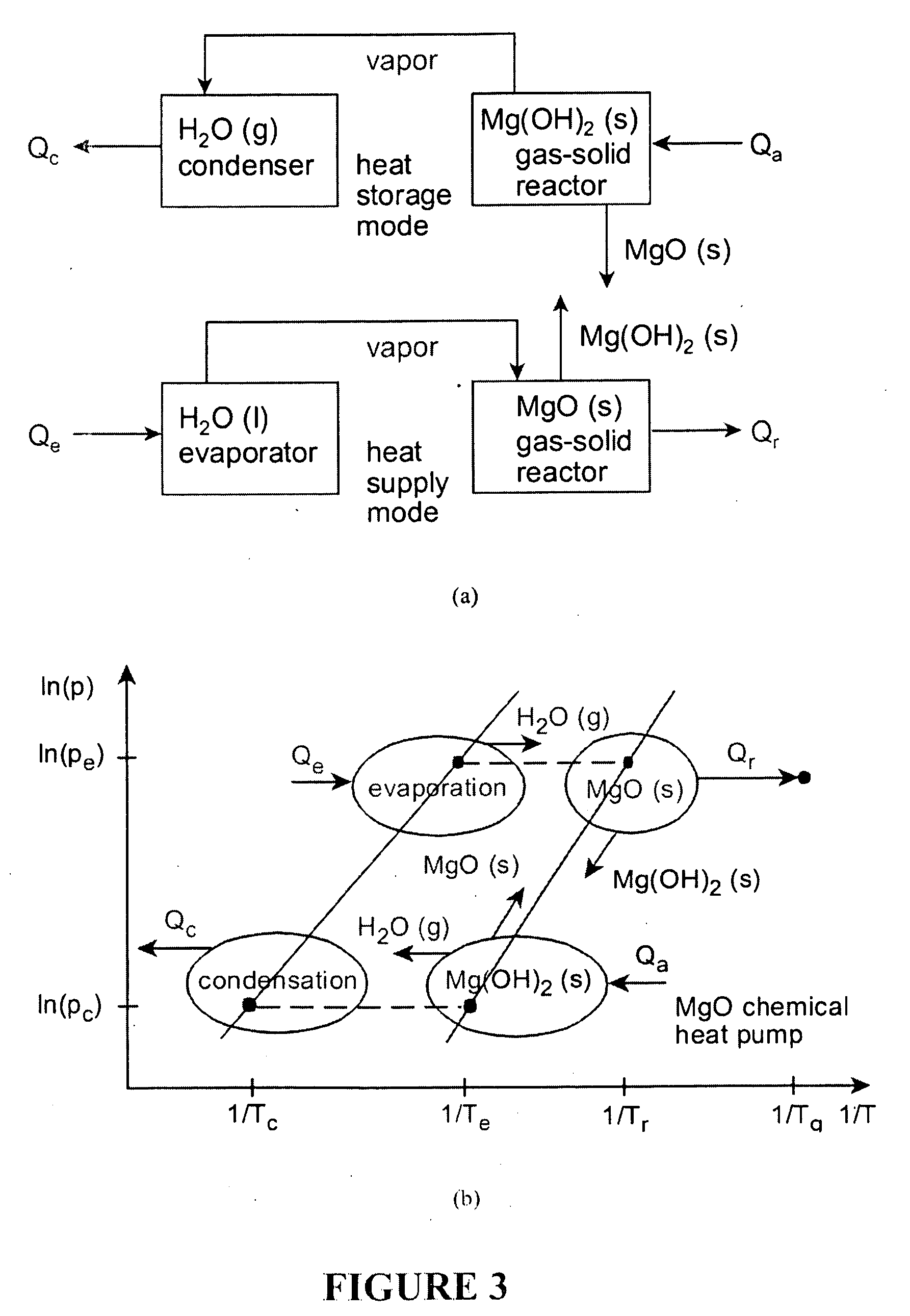
Upgrading waste heat with heat pumps for thermochemical hydrogen production
ActiveUS20100025260A1Reduce demandOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideElectrolysis componentsThermal energyThermochemical cycle
This invention relates to hydrogen production using combined heat pumps and a thermochemical cycle. Low grade waste heat can be upgraded to higher temperatures via salt / ammonia and / or MgO / vapour chemical heat pumps, which release heat at successively higher temperatures through exothermic reactions, or vapour compression heat pumps that upgrade thermal energy with phase change fluids. Using this new approach, low grade heat or waste heat from nuclear or other industrial sources can be transformed to a useful energy supply for thermochemical hydrogen production.
Owner:UNIV OF ONTARIO INST OF TECH
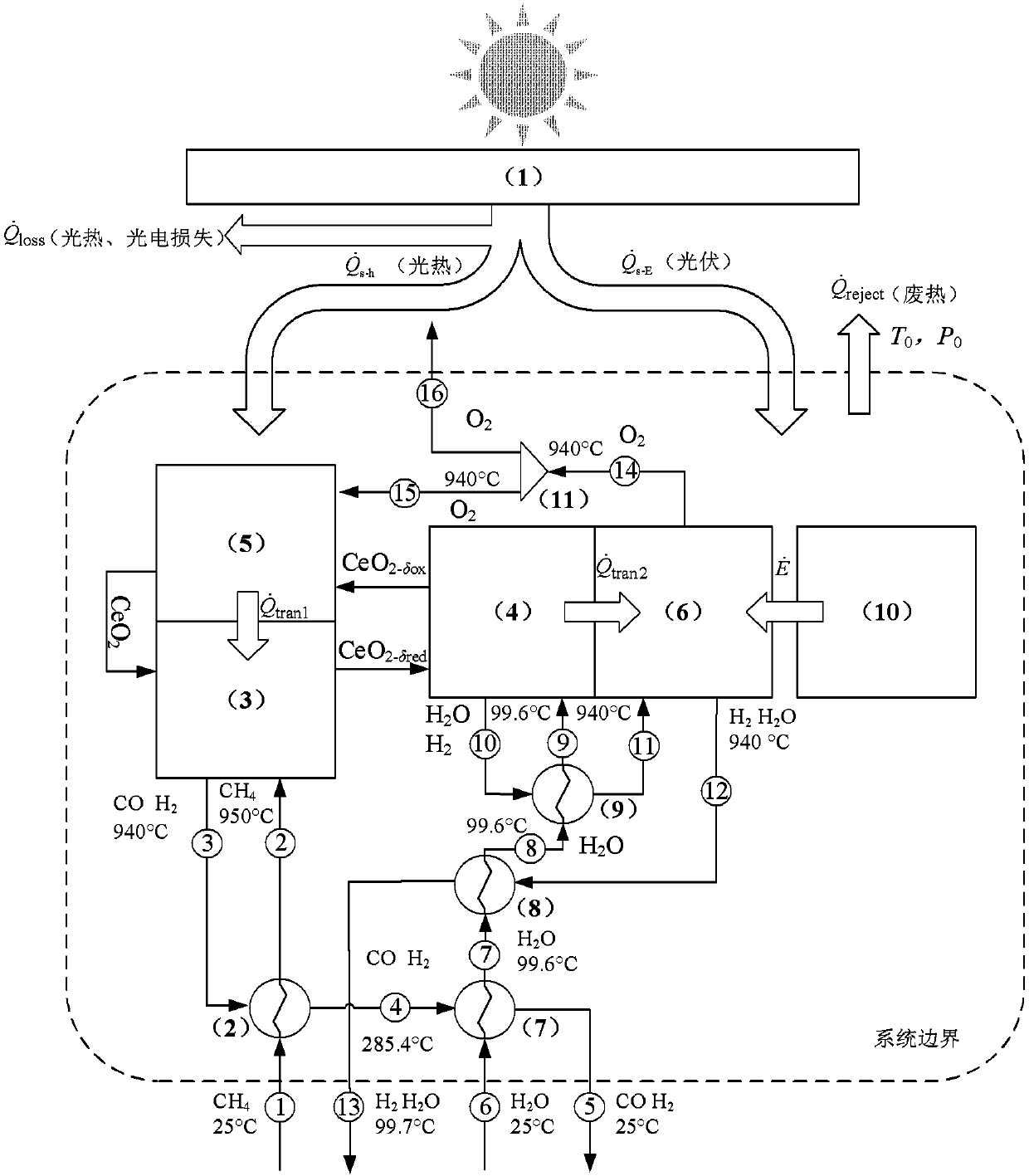
Electro-thermal chemical cycle coupled solar fuel preparation system and method
PendingCN108483396AImprove utilization efficiencyTake advantage ofSolar heating energyHydrogenThermal energySteam reforming
The invention discloses an electro-thermal chemical cycle coupled high-efficiency solar fuel preparation system and method. The system mainly comprises a light condensing and frequency dividing subsystem, a three-step methane steam reforming subsystem, and a high-temperature water electrolytic hydrogen producing subsystem, wherein a first solar spectrum obtained by the light condensing and frequency division subsystem drives the three-step methane steam reforming subsystem to perform a three-step methane water reforming reaction through heat collection; then a second spectrum drives the high-temperature water electrolytic hydrogen producing subsystem to perform reaction of producing H2 by electrolyzing water through a photovoltaic cell; the three-step methane steam reforming subsystem canprovide thermal energy, high-temperature steam source and reducing atmosphere to the high-temperature water electrolytic hydrogen producing subsystem, and pure O2 produced by the high-temperature water electrolytic hydrogen producing subsystem can be directly used in the three-step methane steam reforming subsystem. The high-efficiency solar fuel preparation system and method realize the synergistic coupling of solar thermochemical and electrochemical processes, and can efficiently produce pure hydrogen and high-quality syngas and efficiently convert solar energy into hydrocarbon and hydrogenfuel.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
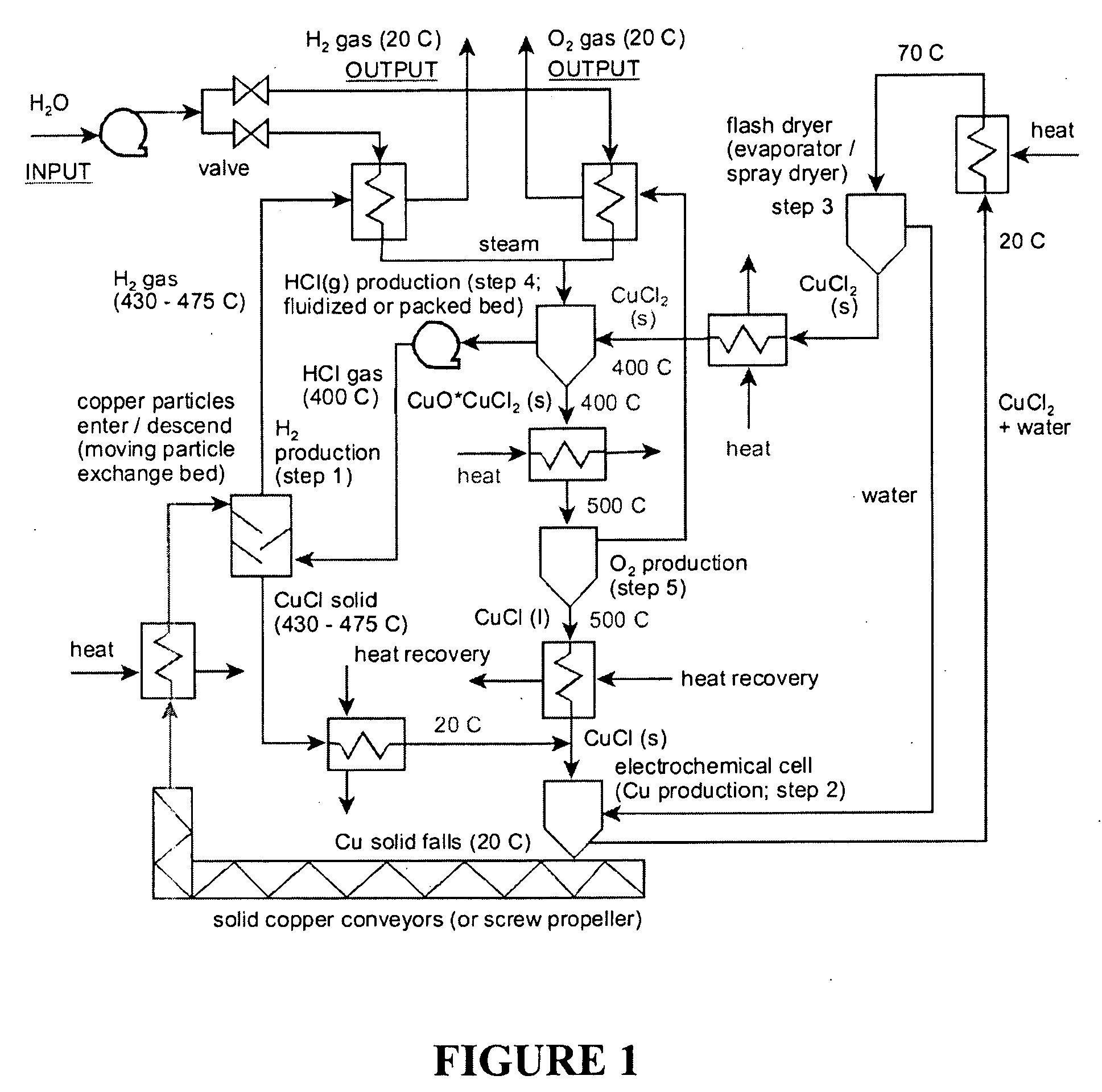
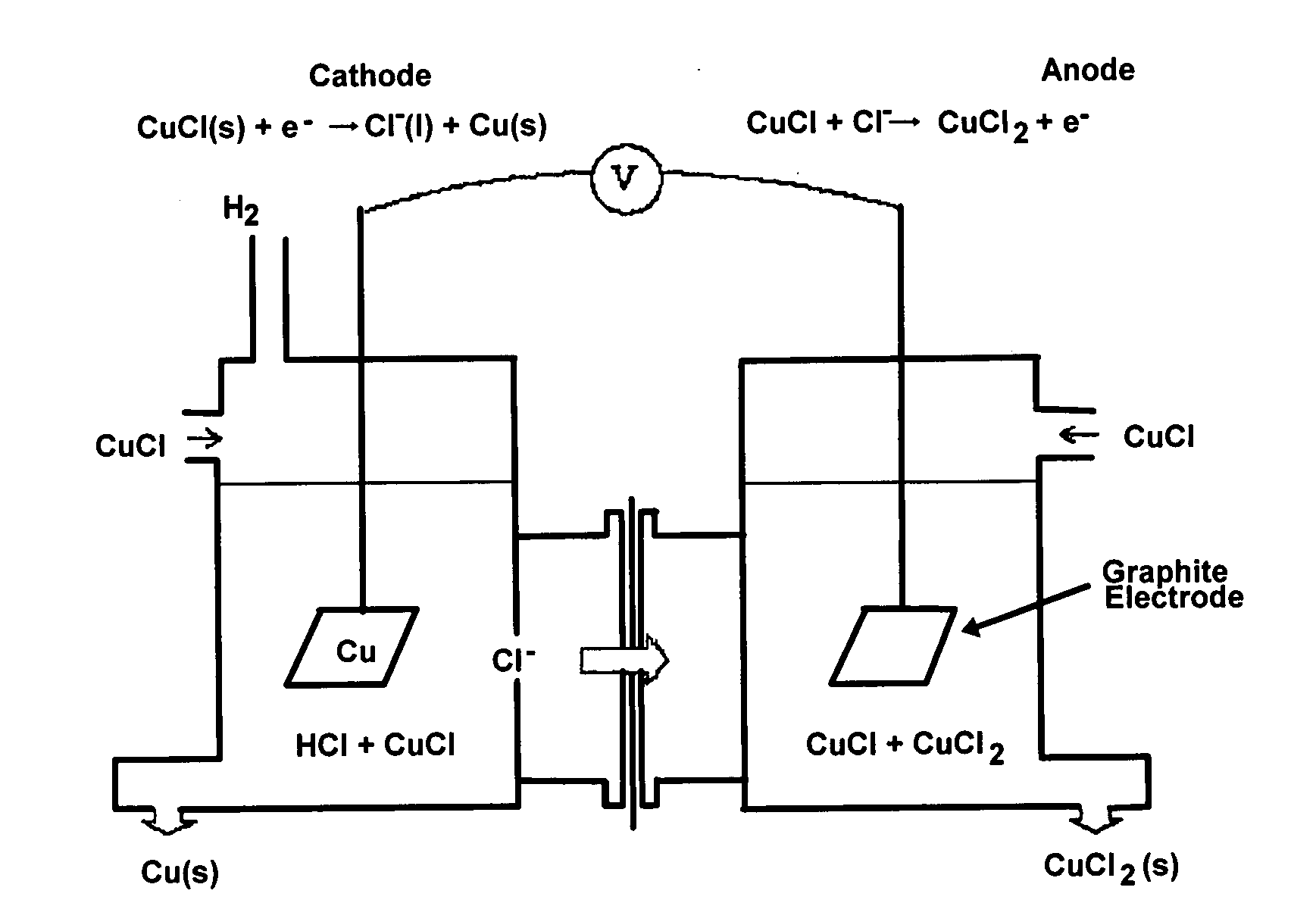
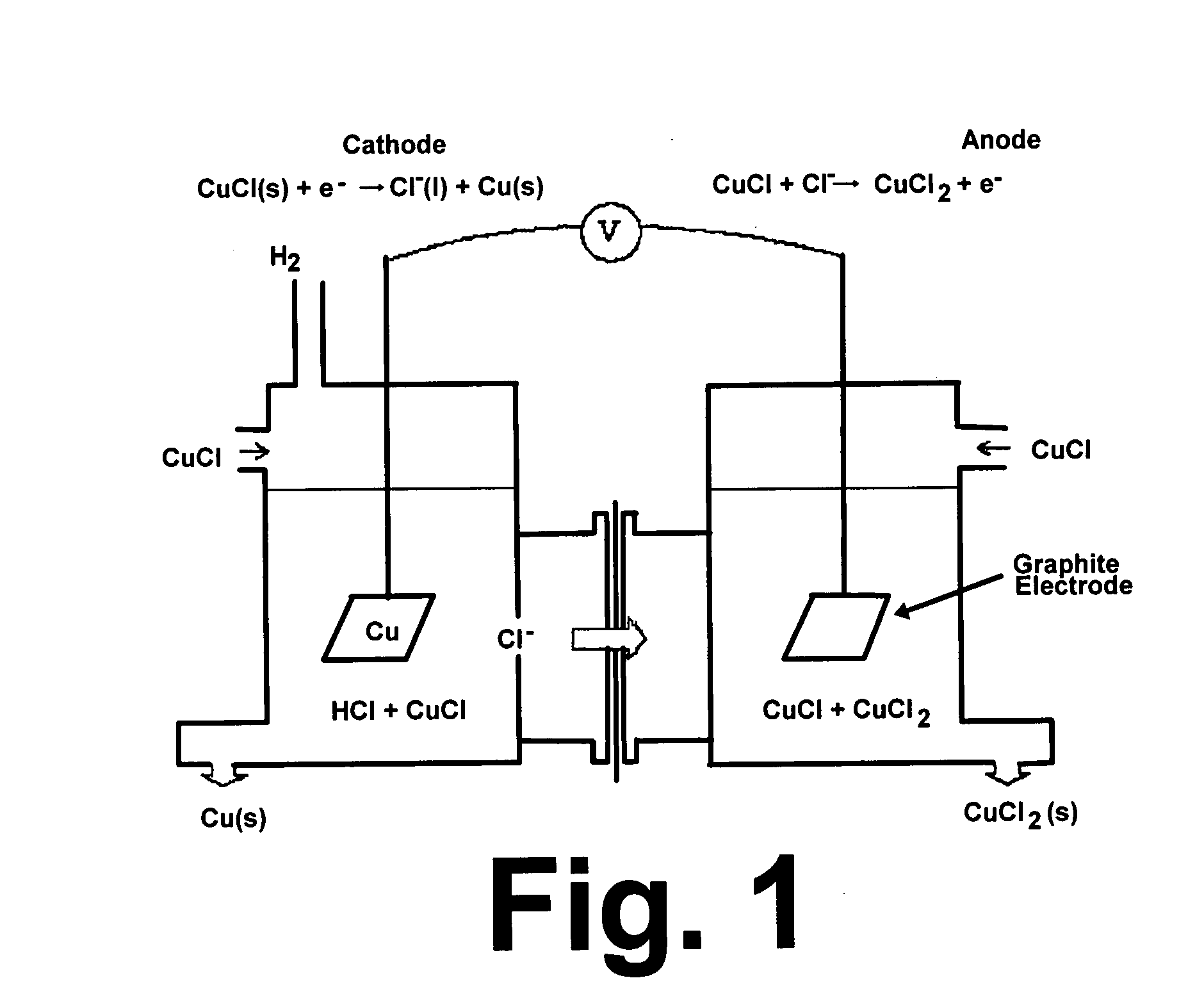
CuC1 thermochemical cycle for hydrogen production
InactiveUS20080283390A1Low corrosion rateLow production costSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsCross-linkEthylene vinyl alcohol copolymer
An electrochemical cell for producing copper having a dense graphite anode electrode and a dense graphite cathode electrode disposed in a CuCl solution. An anion exchange membrane made of poly(ethylene vinyl alcohol) and polyethylenimine cross-linked with a cross-linking agent selected from the group consisting of acetone, formaldehyde, glyoxal, glutaraldehyde, and mixtures thereof is disposed between the two electrodes.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Methods and apparatuses for removal and transport of thermal energy
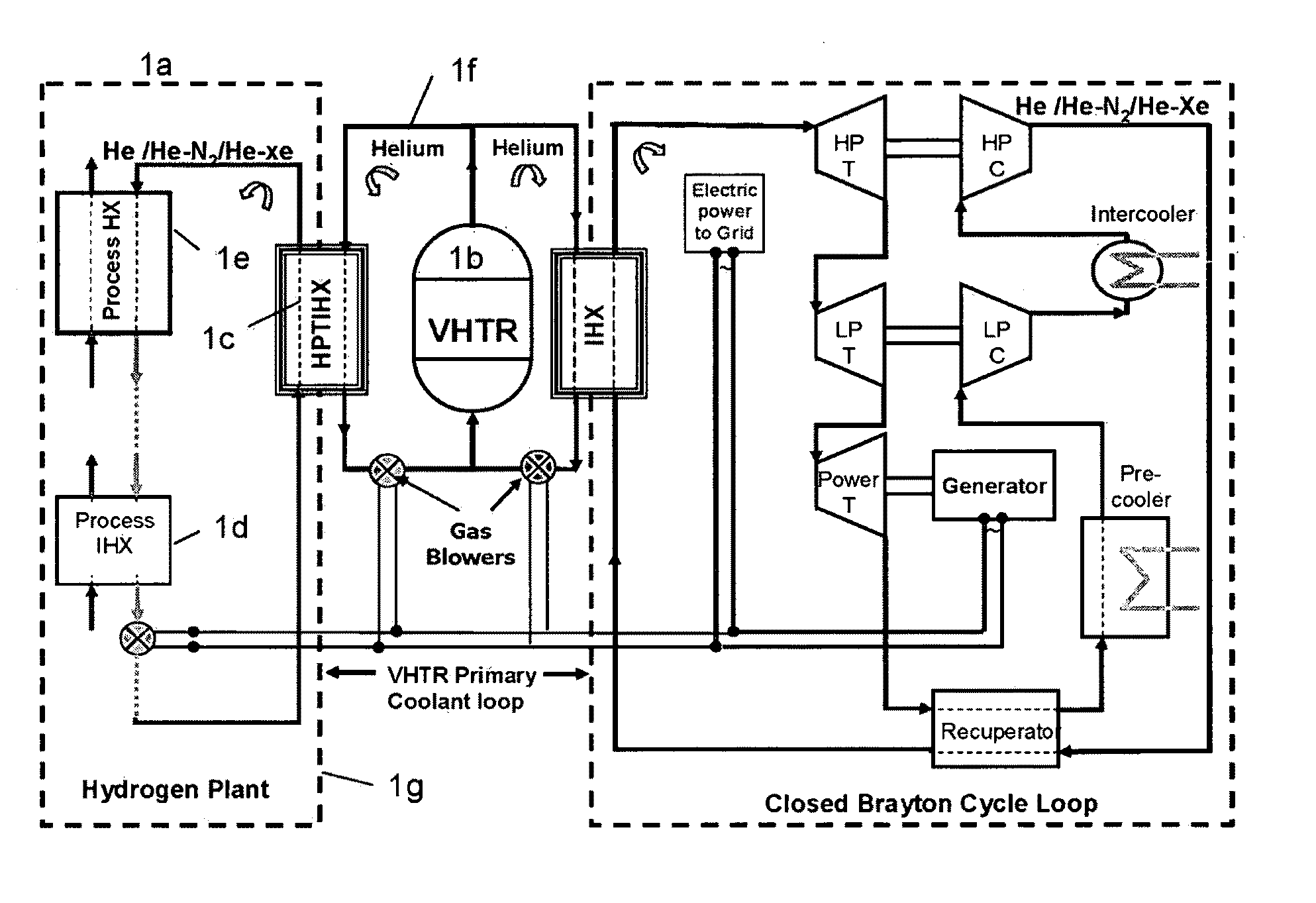
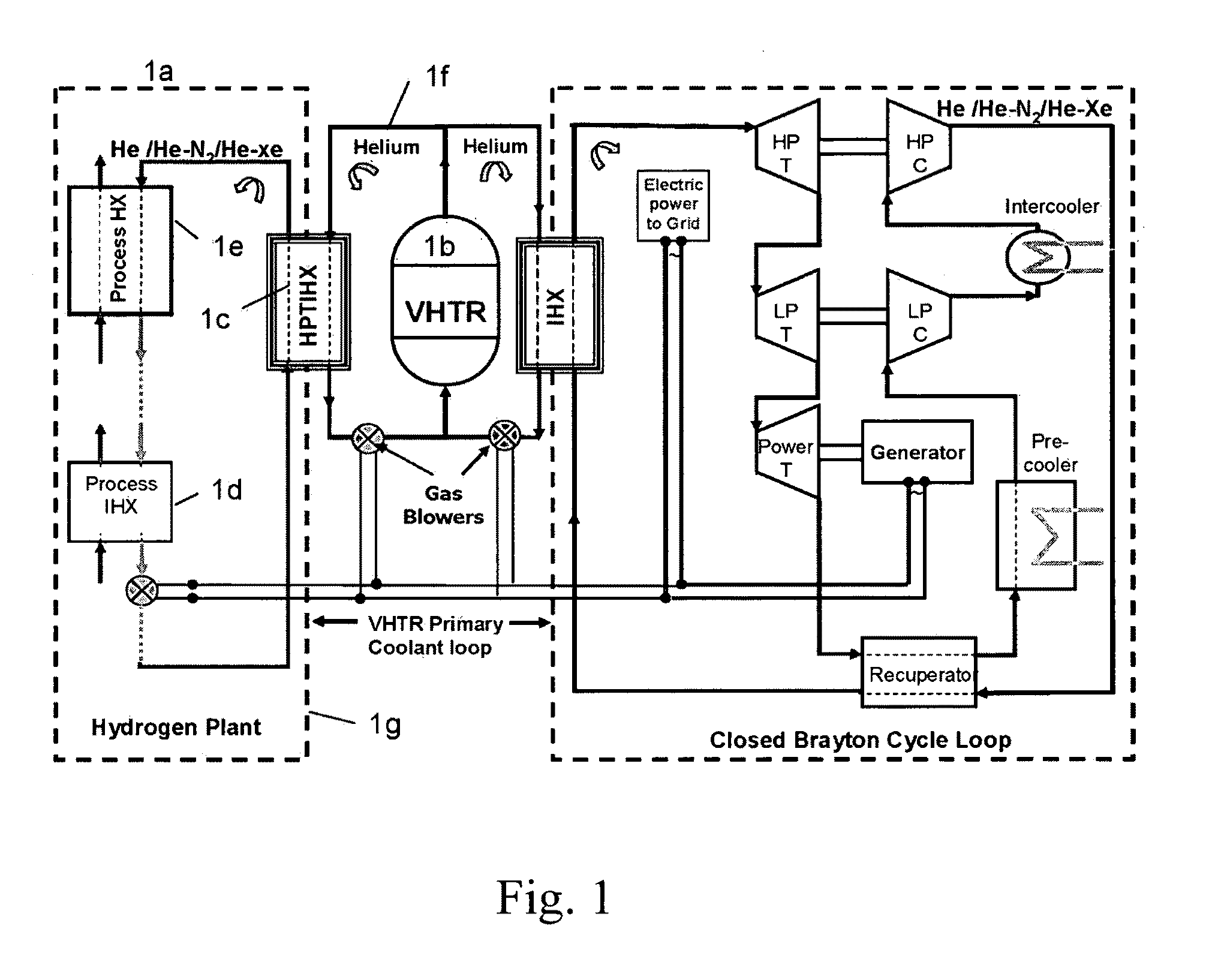
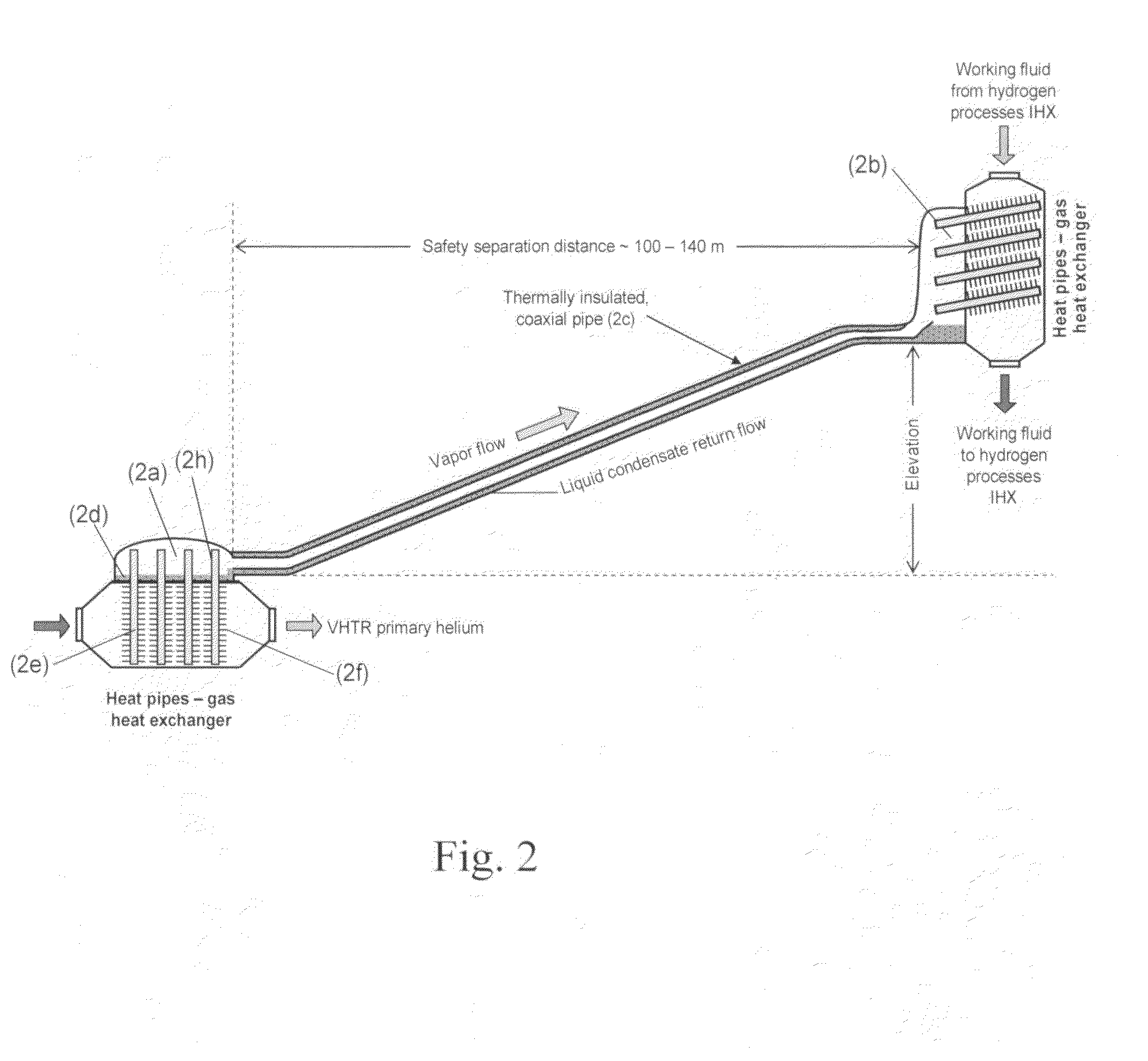
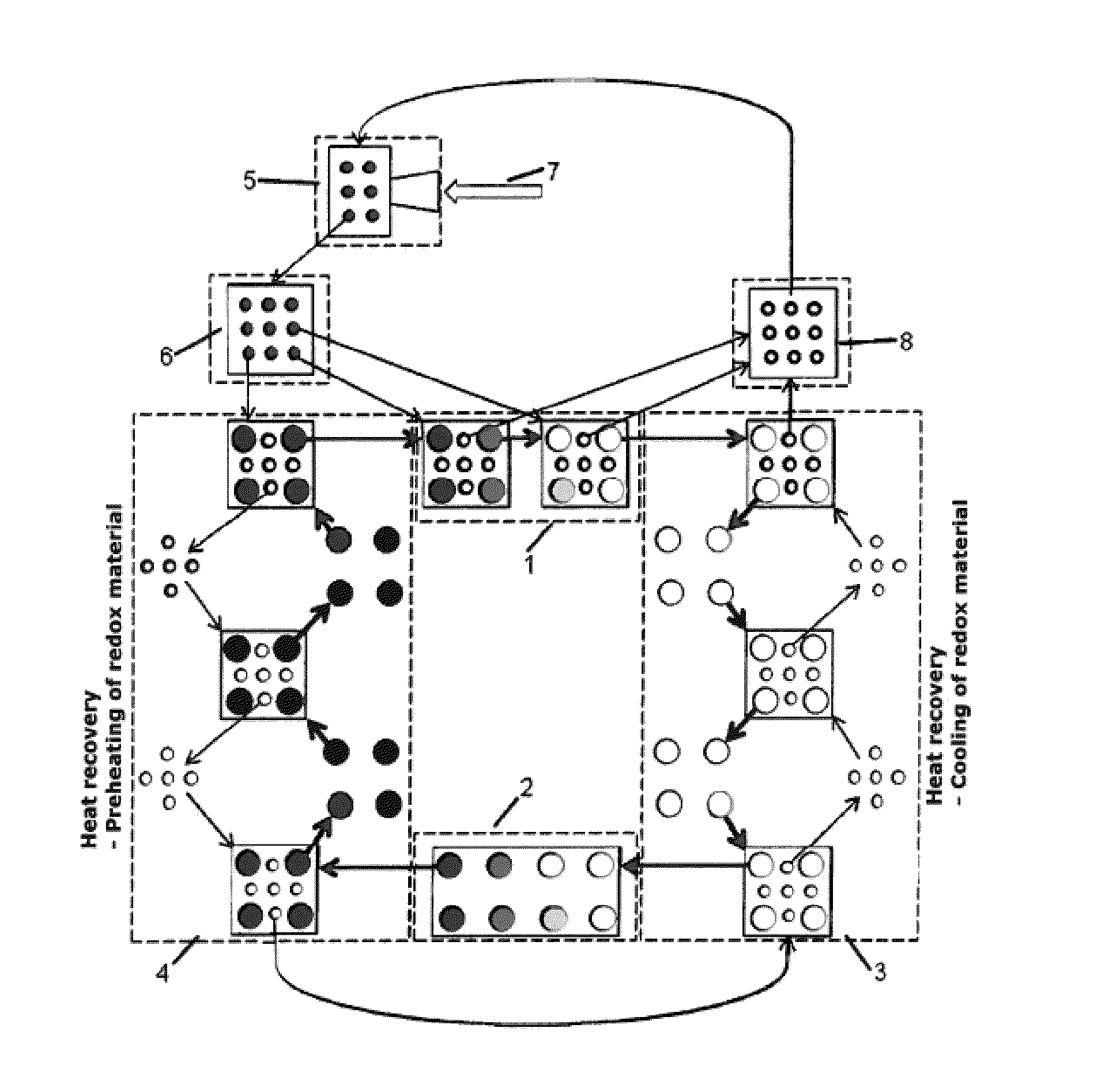
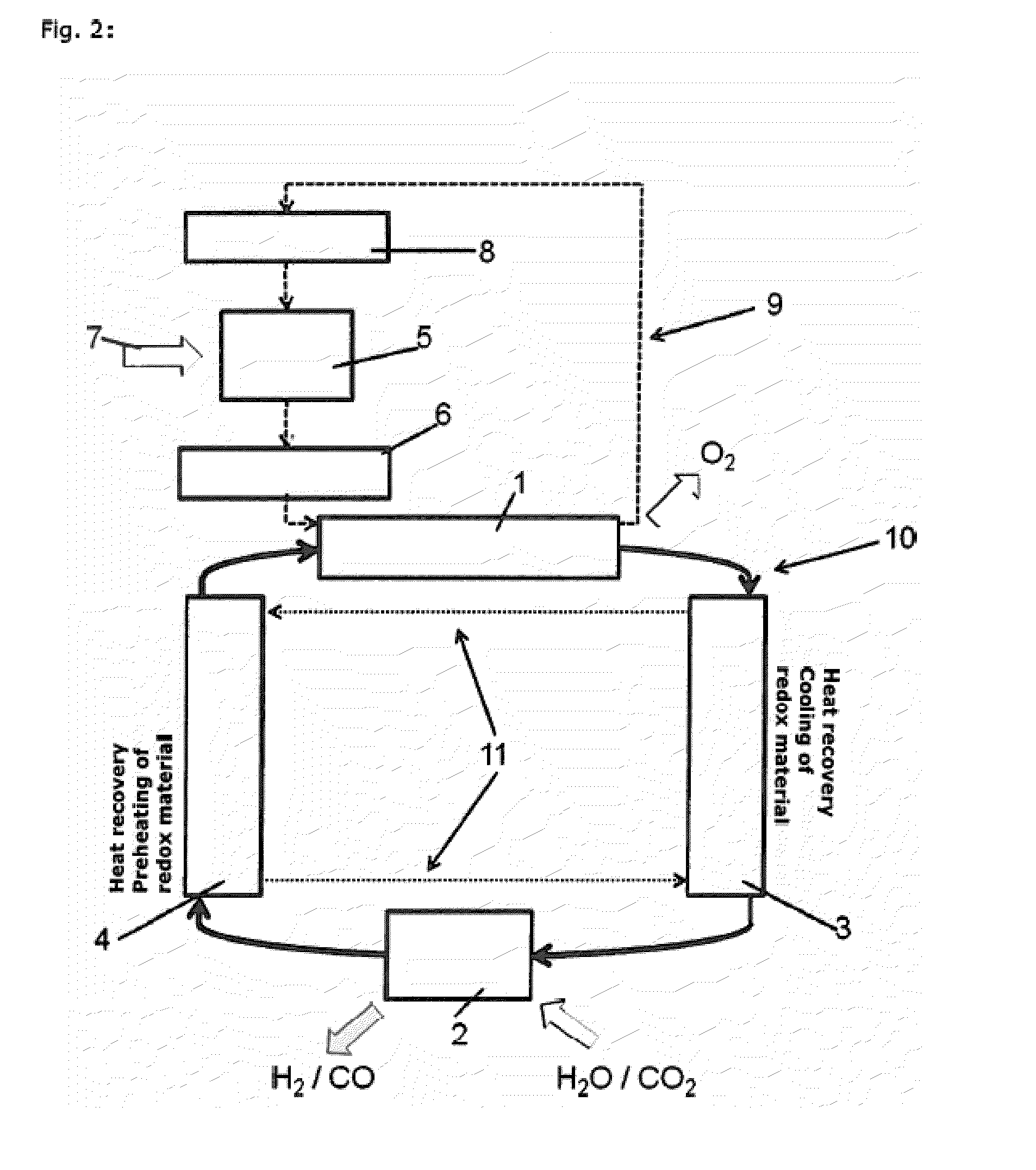
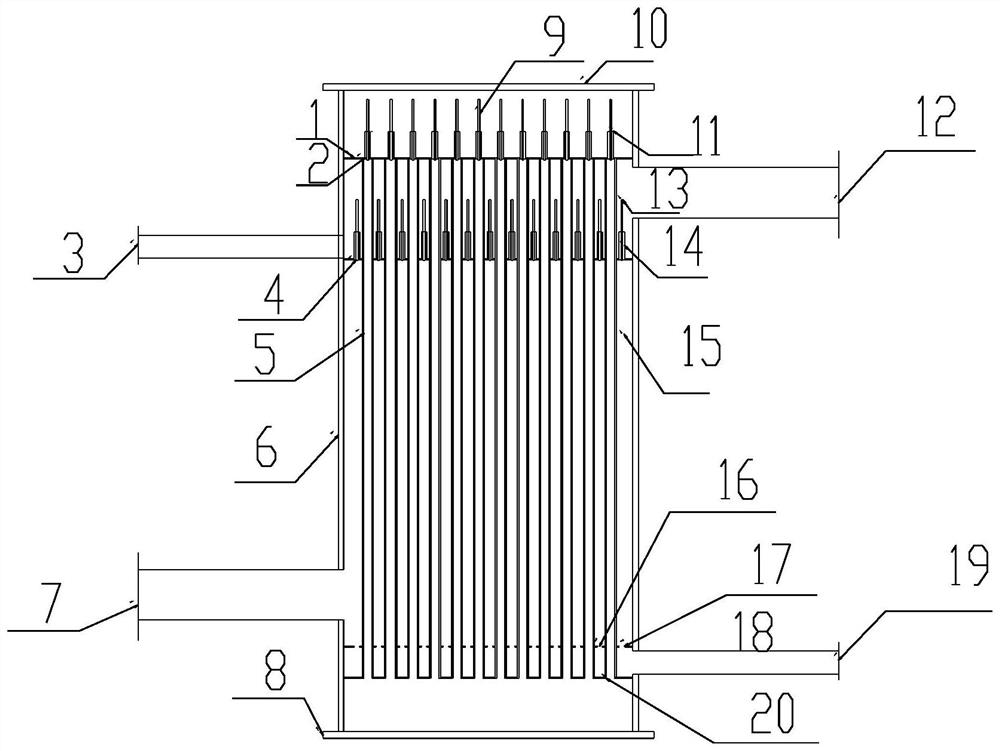
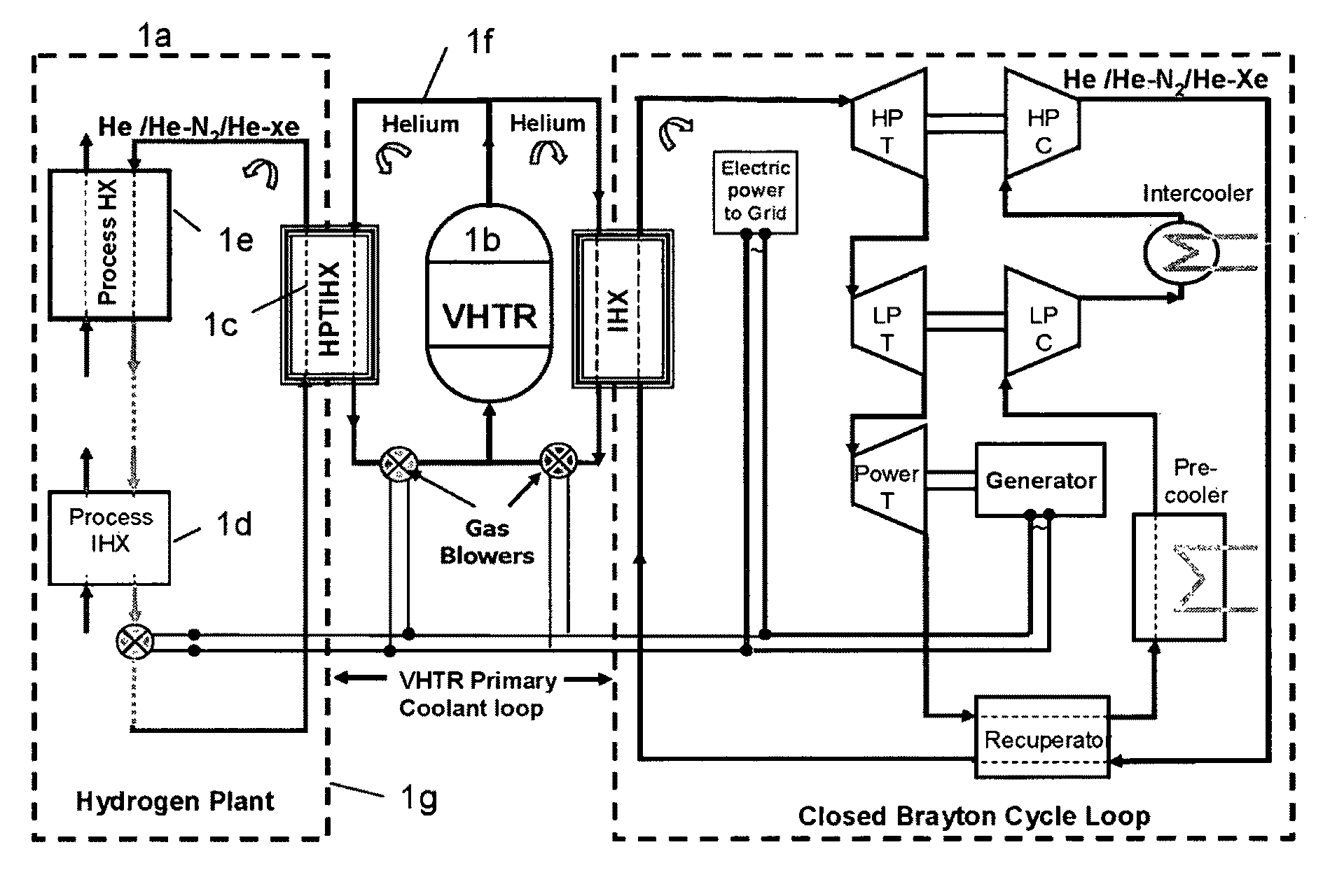
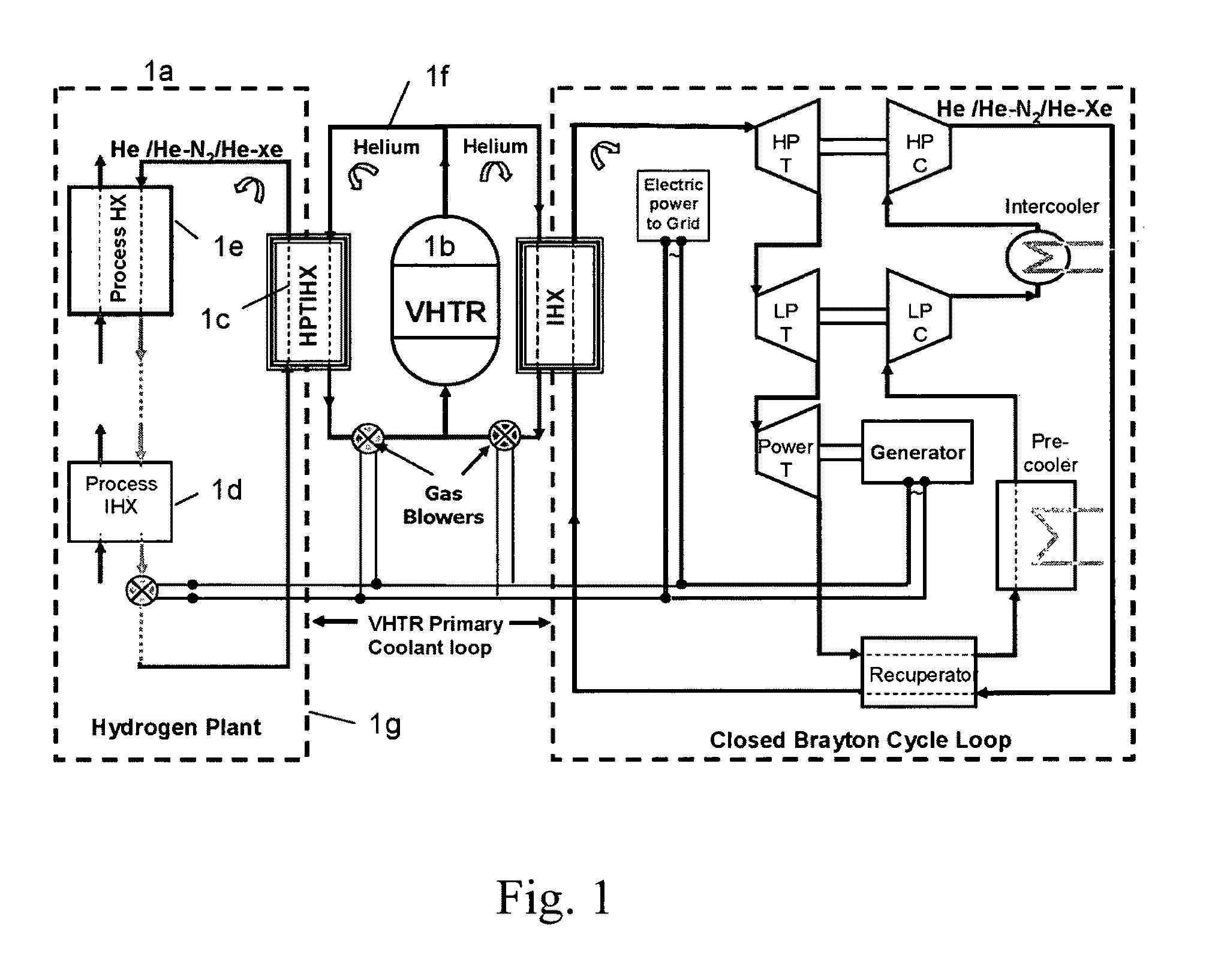
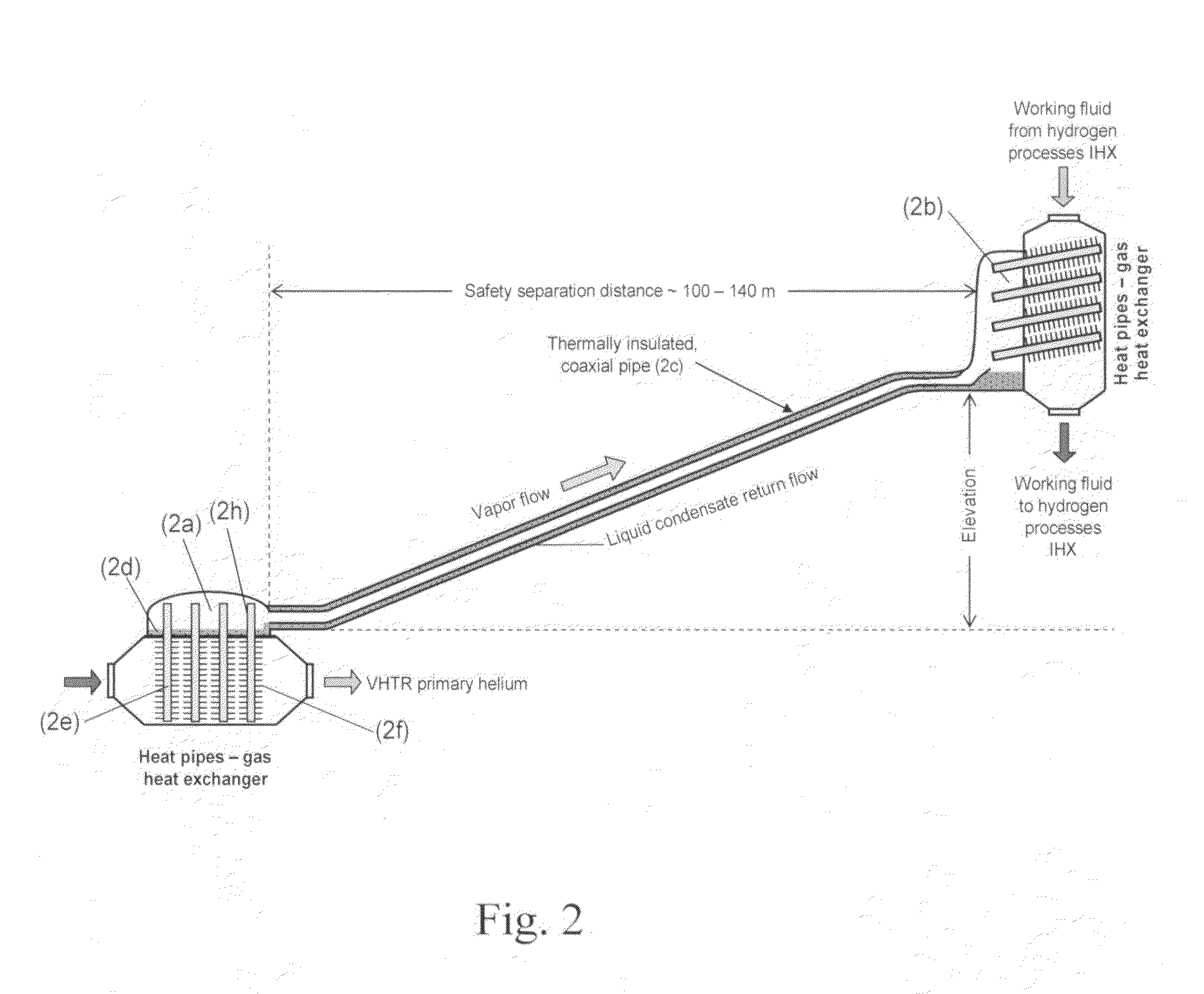
ActiveUS20090323886A1Minimum energy lossAir heatersIndirect heat exchangersThermochemical cycleThermal energy
Methods and apparatuses are provided for the removal and transportation of thermal energy from a heat source to a distant complex for use in thermochemical cycles or other processes. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a hybrid heat pipes / thermosyphon intermediate heat exchanger (HPTIHX) system that is divided into three distinct sections, namely: an evaporation chamber, a condensation chamber, and a working fluid transport section of liquid and vapor counter-current flows.
Owner:STC UNM
System and process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon
ActiveUS8444725B2Reduce area requirementsImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMuffle furnacesOxygenElectrolysis of water
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
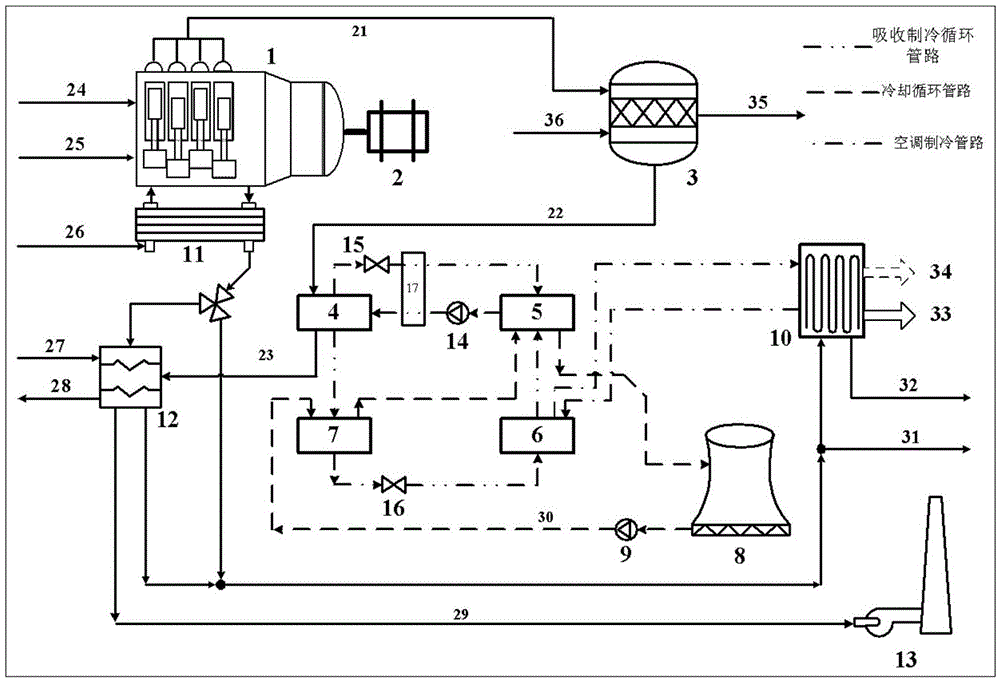
Complementary type distributed energy system integrating internal combustion engine tail gas into thermochemical process
ActiveCN105605827ATo achieve complementary useReduce utilization shareHydrogenClimate change adaptationChemical reactionInternal combustion engine
The invention provides a complementary type distributed energy system integrating internal combustion engine tail gas into the thermochemical process. The system comprises an internal combustion engine power generation subsystem, a thermochemistry waste heat utilization subsystem, an absorption refrigeration subsystem and a low-temperature exhaust waste heat utilization subsystem. According to the system, based on the energy utilization principle of parallel temperature and gradient utilization, exhaust waste heat recovery is conducted through thermochemical reaction, absorption refrigeration, heat supply and the like in sequence, high-temperature exhaust waste heat is utilized scientifically and reasonably in a gradient mode, heat, electric and cold diversified energy product output is achieved, and the energy utilization efficiency and grade of exhaust waste heat are improved greatly.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for producing hydrogen and sulphuric acid
The invention relates to a method for producing gaseous hydrogen and strong sulphuric acid (97 - 100 wt-%) simultaneously from sulphur dioxide gas and water. Sulphur dioxide gas stream is divided into two separate sub-streams, the first sub-stream is routed for water decomposition in a partial thermochemical cycle of the hydrogen and sulphuric acid production and the second sub-stream is fed to the oxidation of the sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide.
Owner:OUTOTEC OYJ
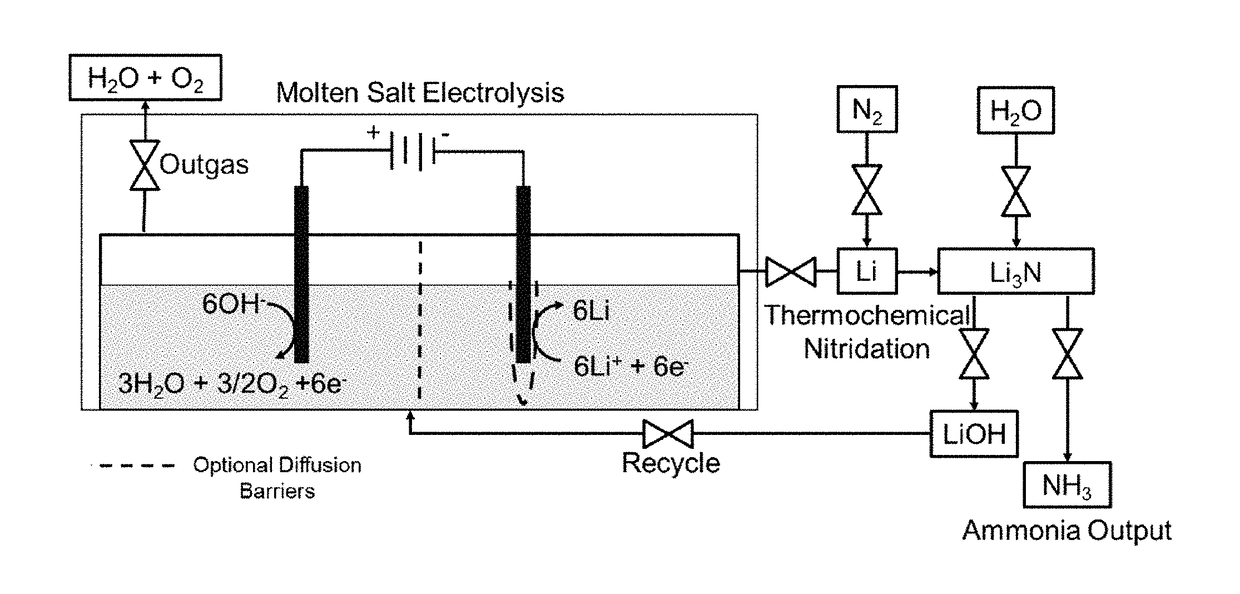
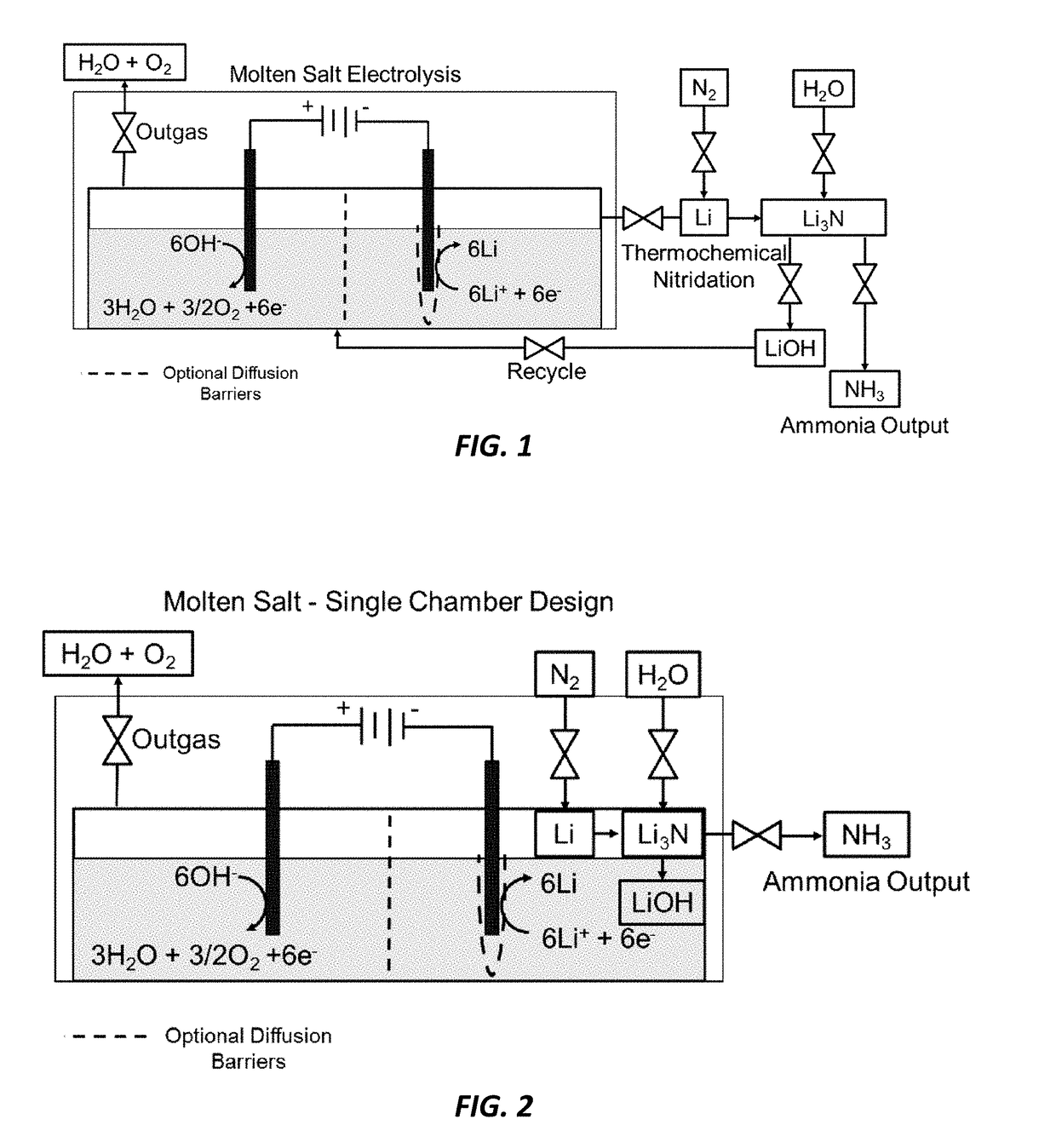
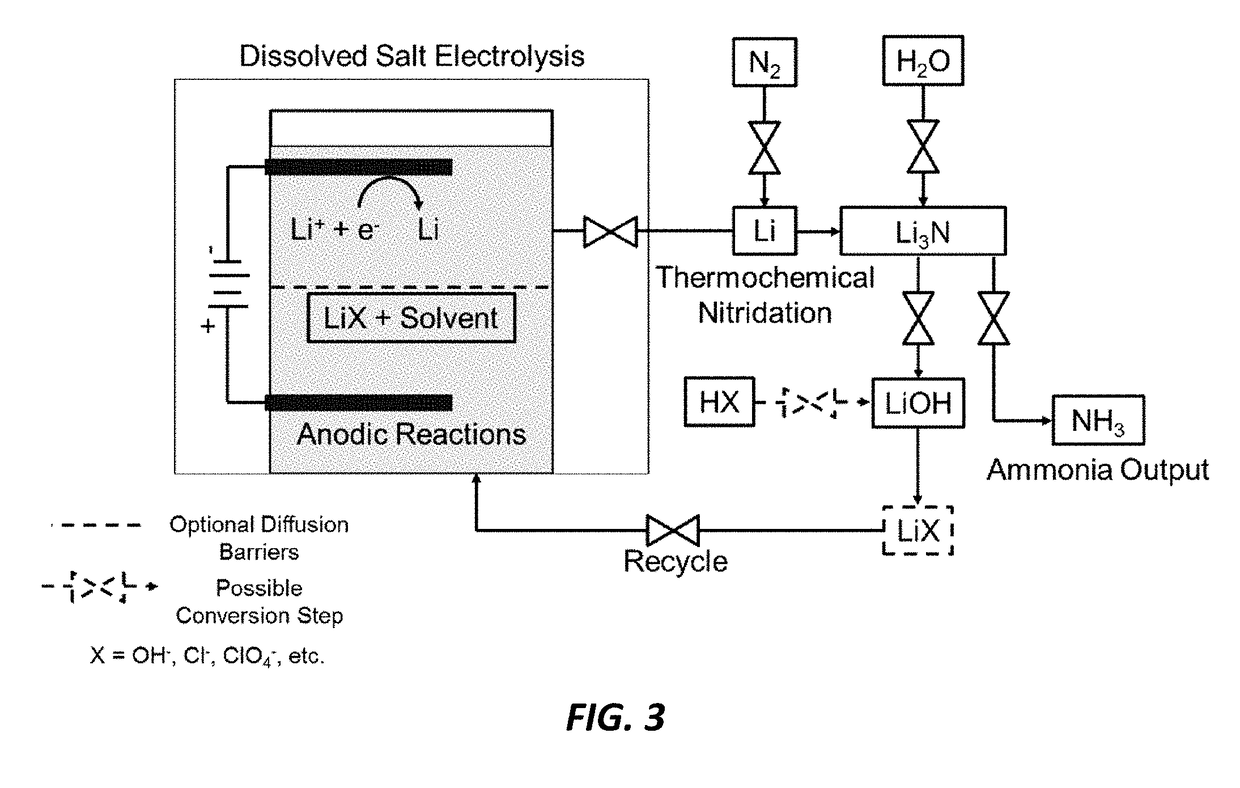
Electro-thermochemical Li Cycling for NH3 Synthesis from N2 and H2O
An electro-thermochemical cycling system for producing ammonia is provided that includes a reaction chamber having a metal compound input port, an anode suitable for oxidation in contact with the metal compound and configured for oxidation of hydroxide ions to water and oxygen, a cathode suitable for plating in contact with the metal compound and configured to electrolyze the metal compound to metal, a voltage source connecting the cathode and anode, a nitrogen port to the reaction chamber that combines nitrogen with the electrolyzed metal on the cathode to form a metal-nitrogen compound proximal to the nitrogen input, an atomic hydrogen port to the reaction chamber that combines with the metal-nitrogen compound to form ammonia, and an ammonia output port from the reaction chamber, where a metal compound input port inputs the metal compound to the reaction chamber according to a depletion rate of the metal compound in the reaction chamber.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
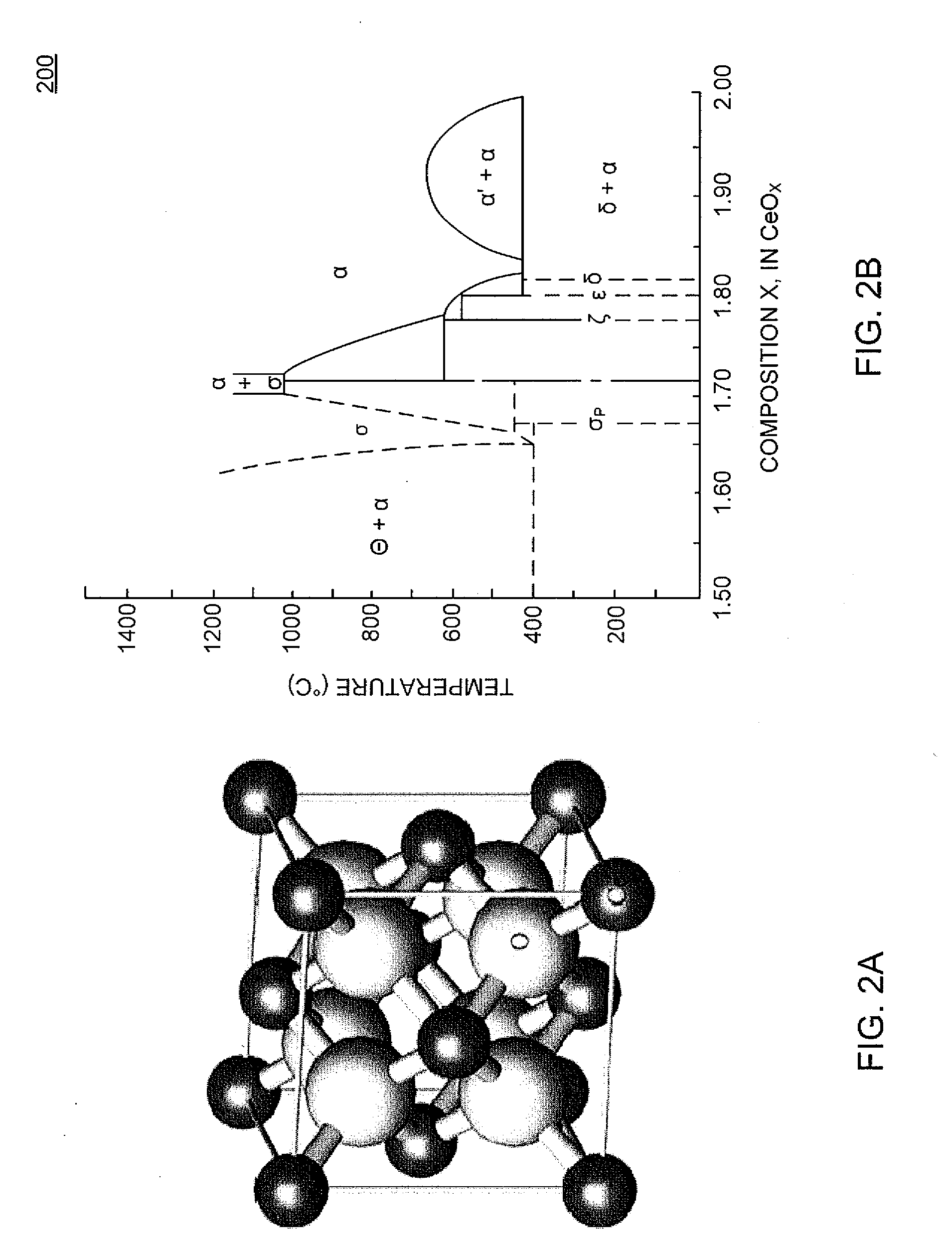
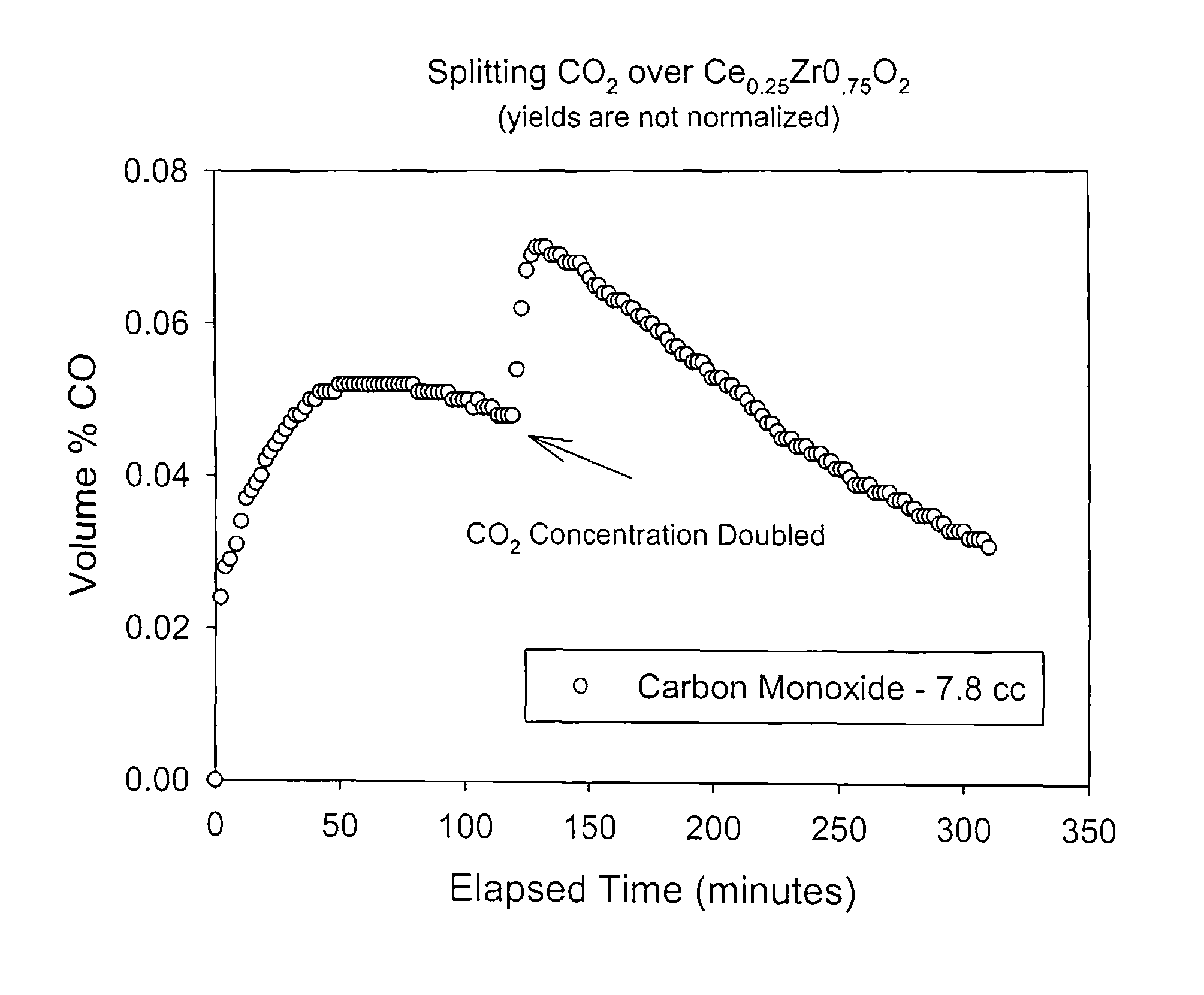
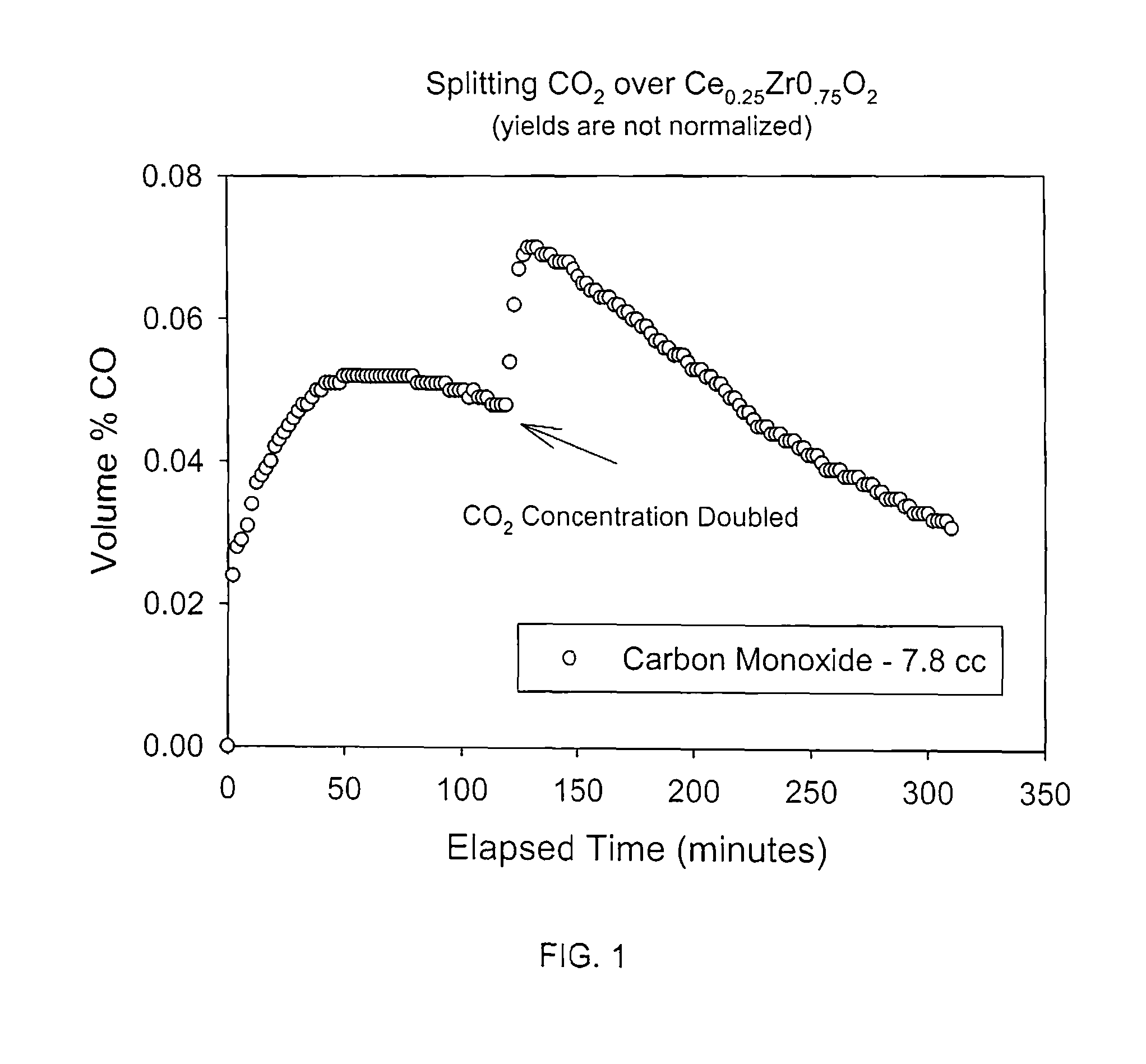
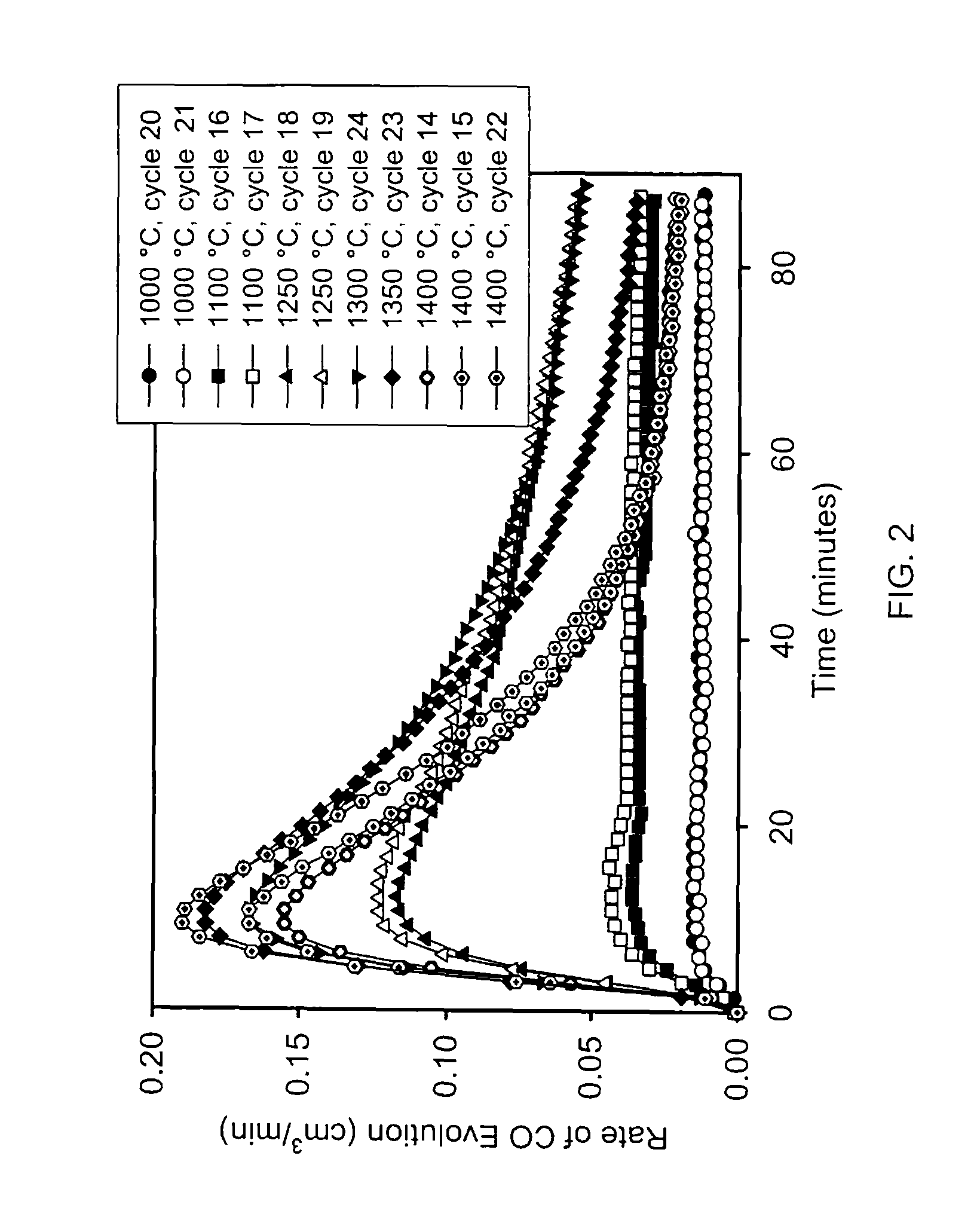
Application of CeO2-based active material to two-step thermochemical cycle decomposition of H2O and/or CO2
InactiveCN103172021AOptimal Reaction ConditionsNo pollution in the processEnergy inputHydrogen productionThermochemical cycleOxygen vacancy
The invention relates to a method for generating H2 and CO by the two-step thermochemical cycle decomposition of H2O and / or CO2 by taking a nano CexM1-xO2-delta (M is La, Y, Sm or Zr) sosoloid as an active material. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) enabling the active material to release oxygen at a high temperature, and (2) enabling the active material which comprises a large number of oxygen vacancies to react with H2O / CO2 at a low temperature to release H2 / CO. In the Ce0.75Zr0.25O2 system, the yield of H2 is 21ml / g and is higher than the yield of H2 of 11ml / g reported in a literature, and the yield of CO is 25.5ml / g and is higher than the yield of CO of 7ml / g reported in a literature, and in the Ce0.85M0.15O2-delta (M is La, Y or Sm) system, the yield of H2 is 12-13ml / g, and the yield of CO is 13ml / g. The active material can take the high-temperature heat generated from the concentration of solar energy as an energy source, and the H2O / CO2 can serve as a raw material to react to generate the H2 / CO. The method can not lead to the generation of other byproducts, is clean, can not cause pollution and is expected to be an effective technology for preparing a chemical fuel by using the solar energy.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
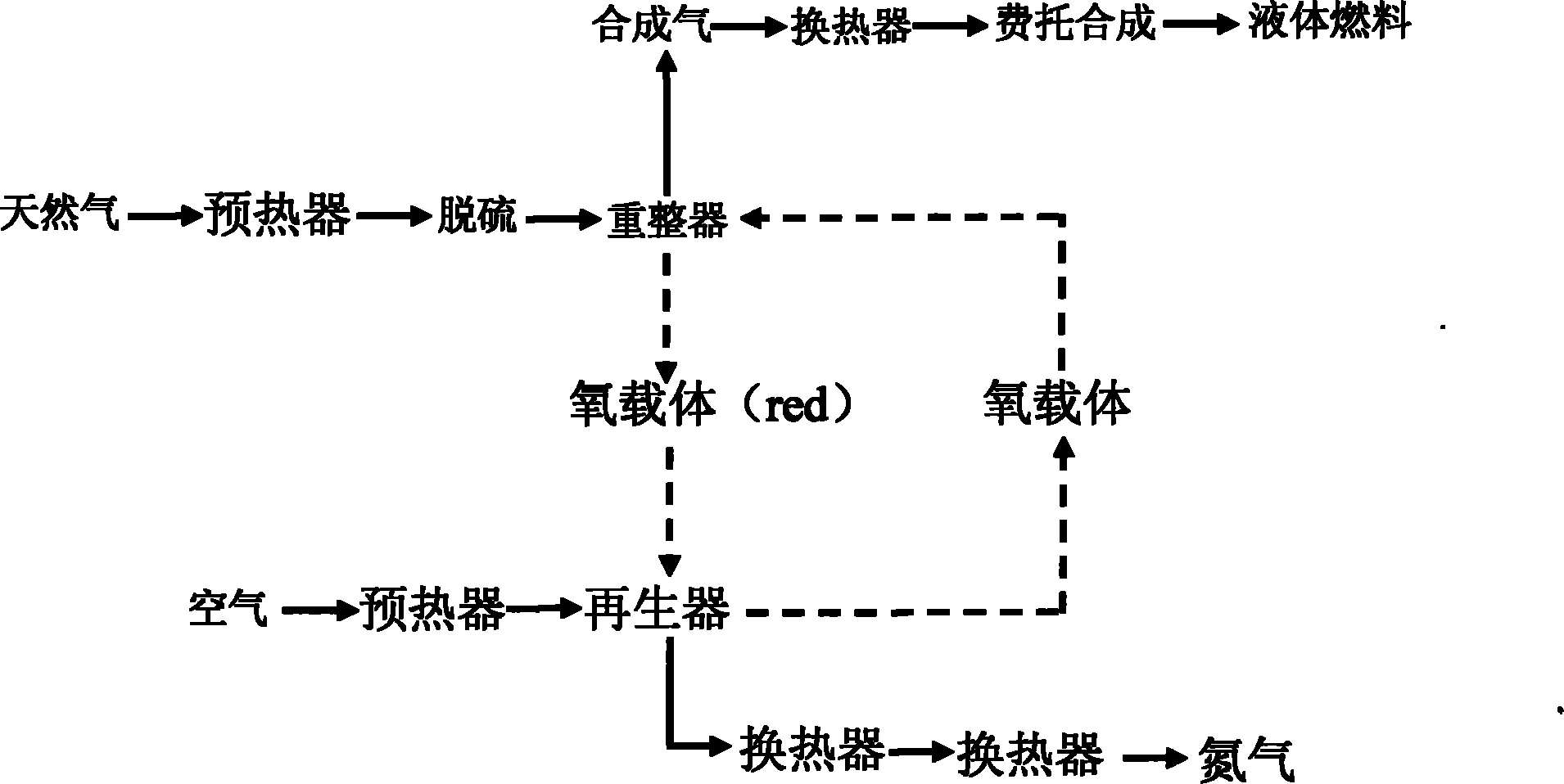
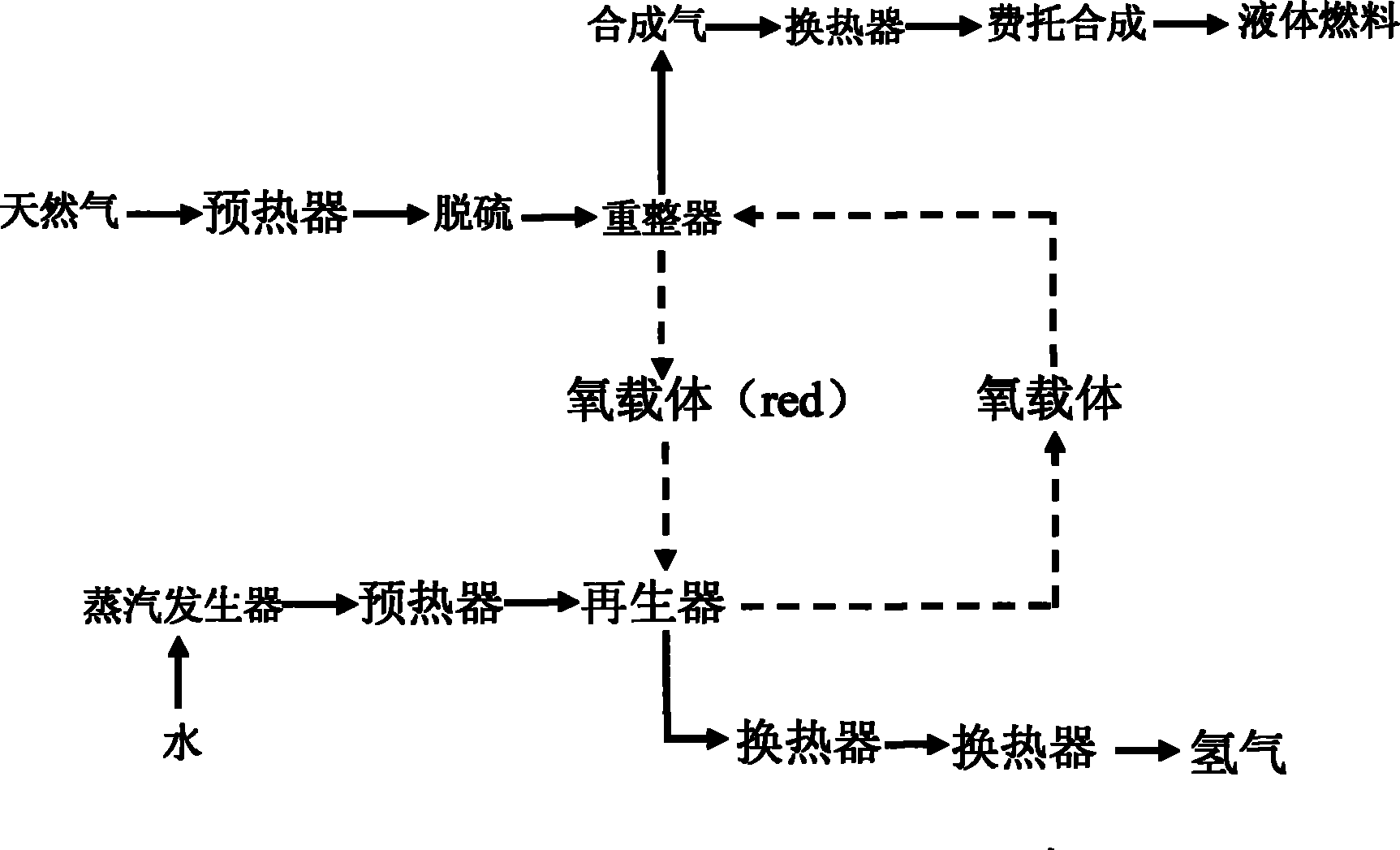
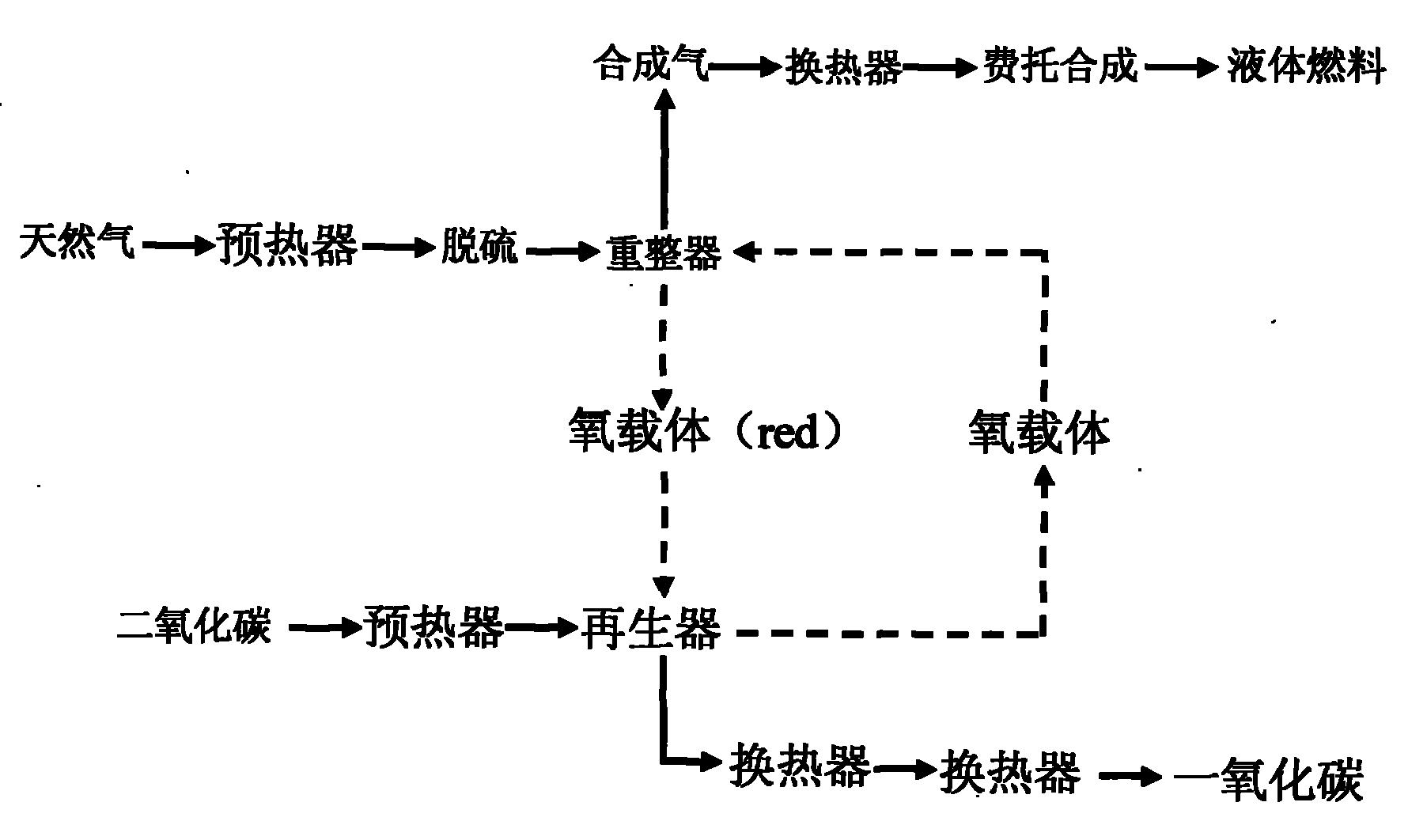
Method for producing synthetic gas by natural gas conversion
InactiveCN101830434AEfficient conversionContinuous conversionHydrogenThermochemical cycleLattice oxygen
The invention discloses a circulating fluidized bed technology-based oxygen carrier thermo-chemical circulation process aiming at the purpose of producing synthetic gas by natural gas scale conversion. Natural gas is introduced at the inlet of a reforming reactor of a circulating fluidized bed at a certain speed, the natural gas captures lattice oxygen of oxygen carriers in the reforming reactor, and the generated synthetic gas (H2 and CO) can be used for preparing liquid fuel by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis after heat exchange of a heat exchanger and purification; and meanwhile, the oxygen carriers losing the lattice oxygen rise along with airflow and drop and return to an oxygen carrier regenerating reactor to react with an oxygen source such as H2O, air or CO2 and the like introduced from the bottom so as to recover the lattice oxygen thereof, the generated H2, N2 and CO airflow take the regenerated oxygen carriers out of the regenerating reactor and drop the oxygen carriers to the reforming reactor, and the H2, N2 and CO are discharged from the top and used as products through heat exchange of the heat exchanger and purification. The oxygen carriers are circularly used in two reaction areas of the circulating fluidized bed. The technology provides an important path for producing the synthetic gas by the natural gas scale conversion.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
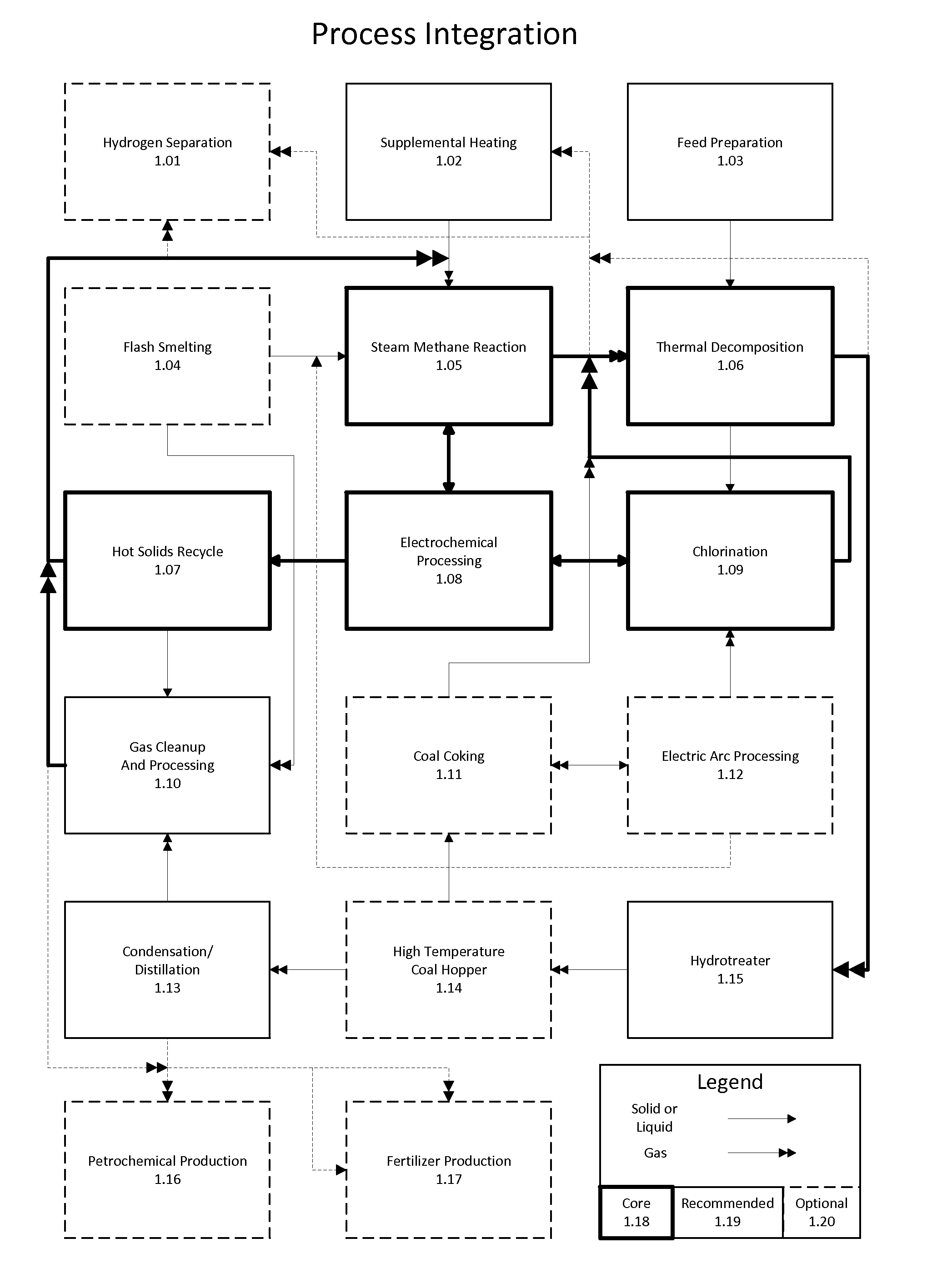
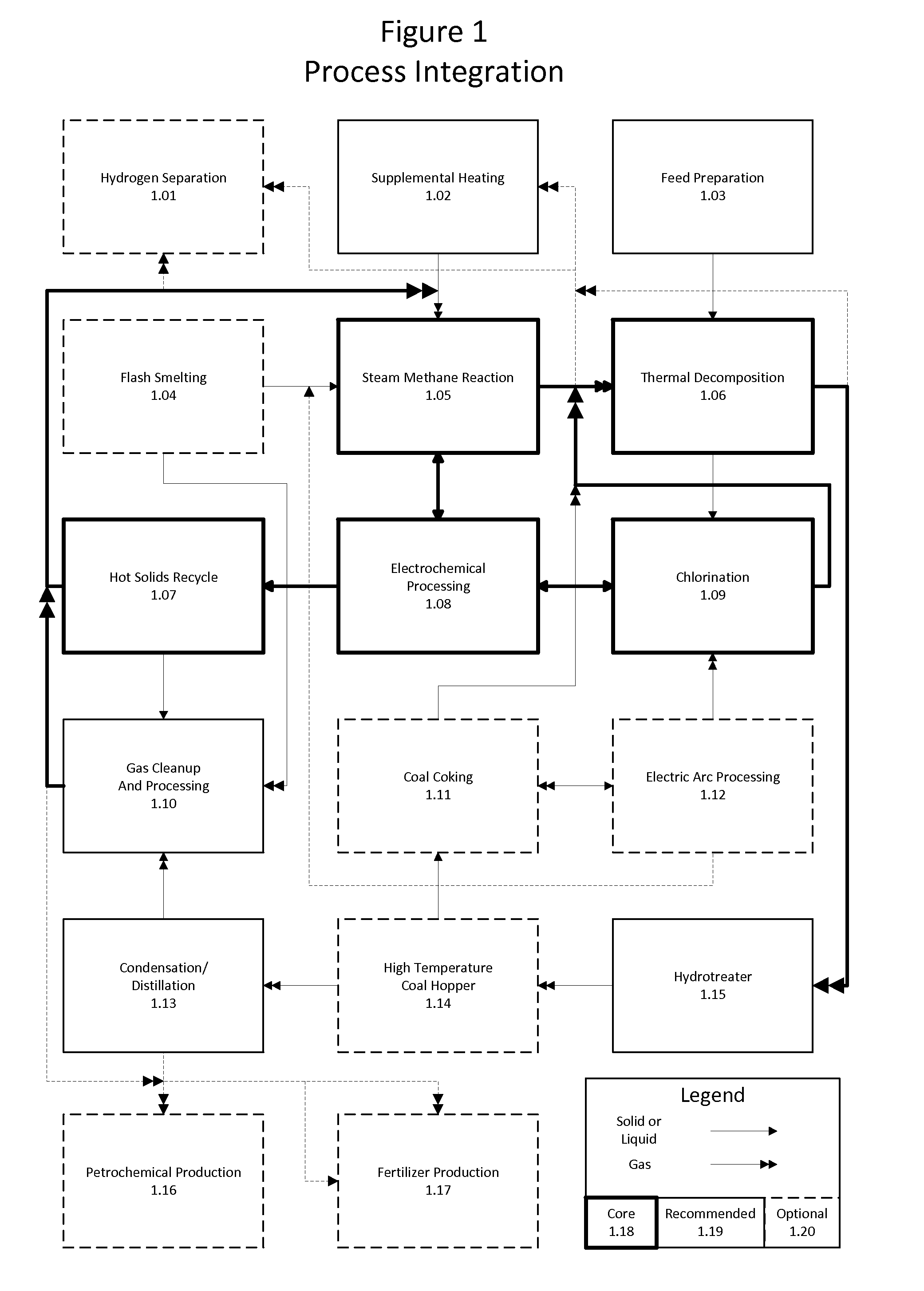
Method for the integration of carbochlorination into a staged reforming operation as an alternative to direct residue oxidation for the recovery of valuable metals
Method of combining industrial processes having inherent carbon capture and conversion capabilities offering maximum flexibility, efficiency, and economics while enabling environmentally and sustainably sound practices. Maximum chemical energy is retained throughout feedstock processing. A hybrid thermochemical cycle couples staged reforming with hydrogen production and chlorination. Hydrogen generated is used to upgrade feedstocks including bitumen, shale, coal, and biomass. Residues of upgrading are chlorinated, metals of interest are removed, and the remainder is reacted with ammonia solution and carbon dioxide to form carbonate minerals. The combination provides emissions free production of synthetic crude oil and derivatives, as well as various metals and fertilizers. Sand and carbonate minerals are potentially the only waste streams. Through this novel processing, major carbon dioxide reduction is afforded byminimizing direct oxidation. Supplemental heat to run the reactions is obtained through external means such as concentrated solar, geothermal, or nuclear.
Owner:BLUE SKIES RES INC
Heat transfer particles for solar-driven thermochemical processes
The present invention relates to a process for performing a chemical reaction consisting of at least two sequential reversible steps characterized by being performed in a cycle, and to a reactor for performing such process.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Method for carrying out solar thermal decomposition on H2O and/or CO2 employing perovskite dispersed by different carriers
ActiveCN104418299AIncrease spawn rateLower initial reduction temperatureMolecular sieve catalystsEnergy inputThermochemical cycleAs Directed
The invention relates to a method for decomposing H2O and / or CO2 through a two-step thermochemical cycle to produce H2 and / or CO by taking a perovskite compound which is dispersed by SiO2 with different pore structures as an active material. The dispersion mode comprises the forms such as direct mechanical mixing, in-situ packaging and packaging in a mesoporous duct; SiO2 comprises SBA-15, MCM-41, MCF and other mesoporous structures; and the method comprises the following main steps: (1) firstly discharging oxygen from loaded active material at a high temperature (1100-1300 DEG C); and (2) enabling the active material containing a lot of oxygen vacancies to react with H2O and / or CO2 at a relatively low temperature (800-1100 DEG C), discharging H2 and / or CO. According to the method and the material provided by the invention, high-temperature heat generated by solar concentration can be utilized as an energy source; H2O and CO2 are taken as reaction materials; compared with the reported results, H2 and CO can be stably and quickly produced at a relatively low reduction temperature; and the method is clean and free of pollution, and is expected to become an effective technology for preparing chemical fuels by reducing CO2 through solar energy.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Catalyst for manufacturing thermochemical fuel, and method for manufacturing thermochemical fuel
ActiveCN104203403AReduce usageLow costNitrous oxide captureOrganic chemistry methodsRare-earth elementThermochemical cycle
To provide a catalyst, which is formed from a perovskite oxide, for thermochemical fuel production, and a method of producing fuel using thermochemical fuel production that is capable of allowing a fuel to be produced in a thermochemical manner. Provided is a catalyst for thermochemical fuel production, which is used for producing the fuel from thermal energy by using a two-step thermochemical cycle of a first temperature and a second temperature that is equal to or lower than the first temperature, wherein the catalyst is formed from a perovskite oxide having a compositional formula of AXO3±delta (provided that, 0@delta@1). Here, A represents one or more of a rare-earth element (excluding Ce), an alkaline earth metal element, and an alkali metal element, X represents one or more of a transition metal element and a metalloid element, and O represents oxygen.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
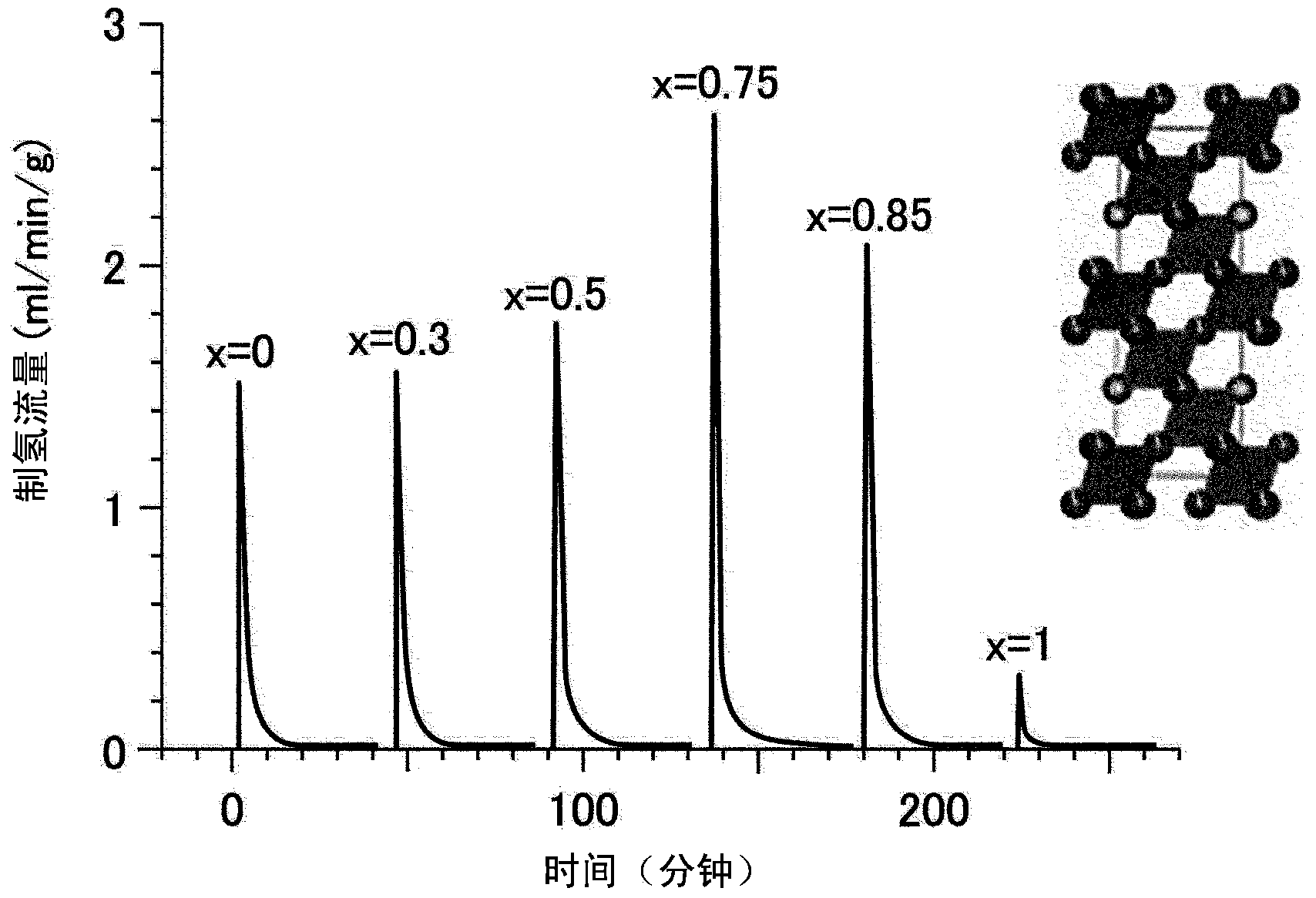
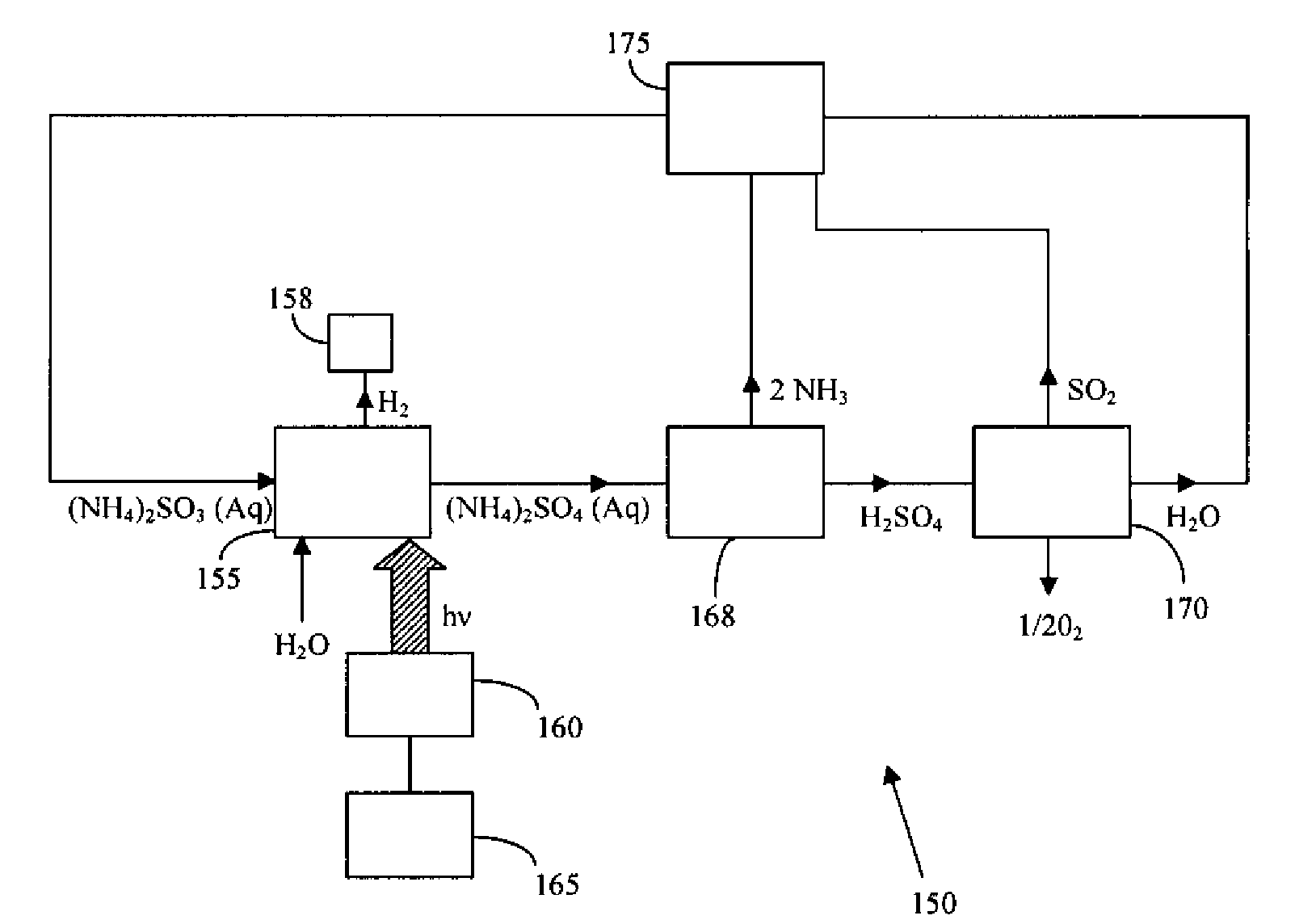
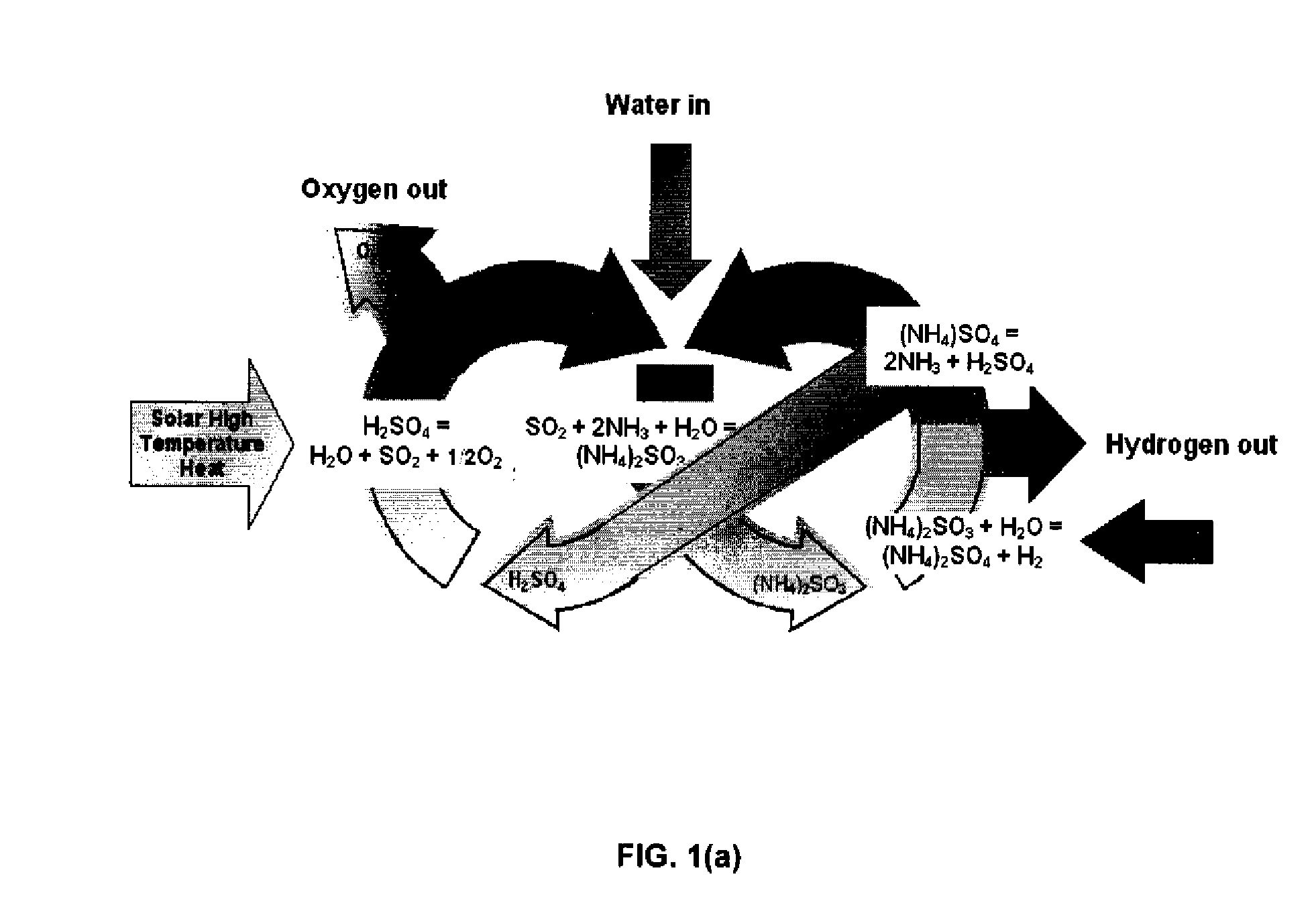
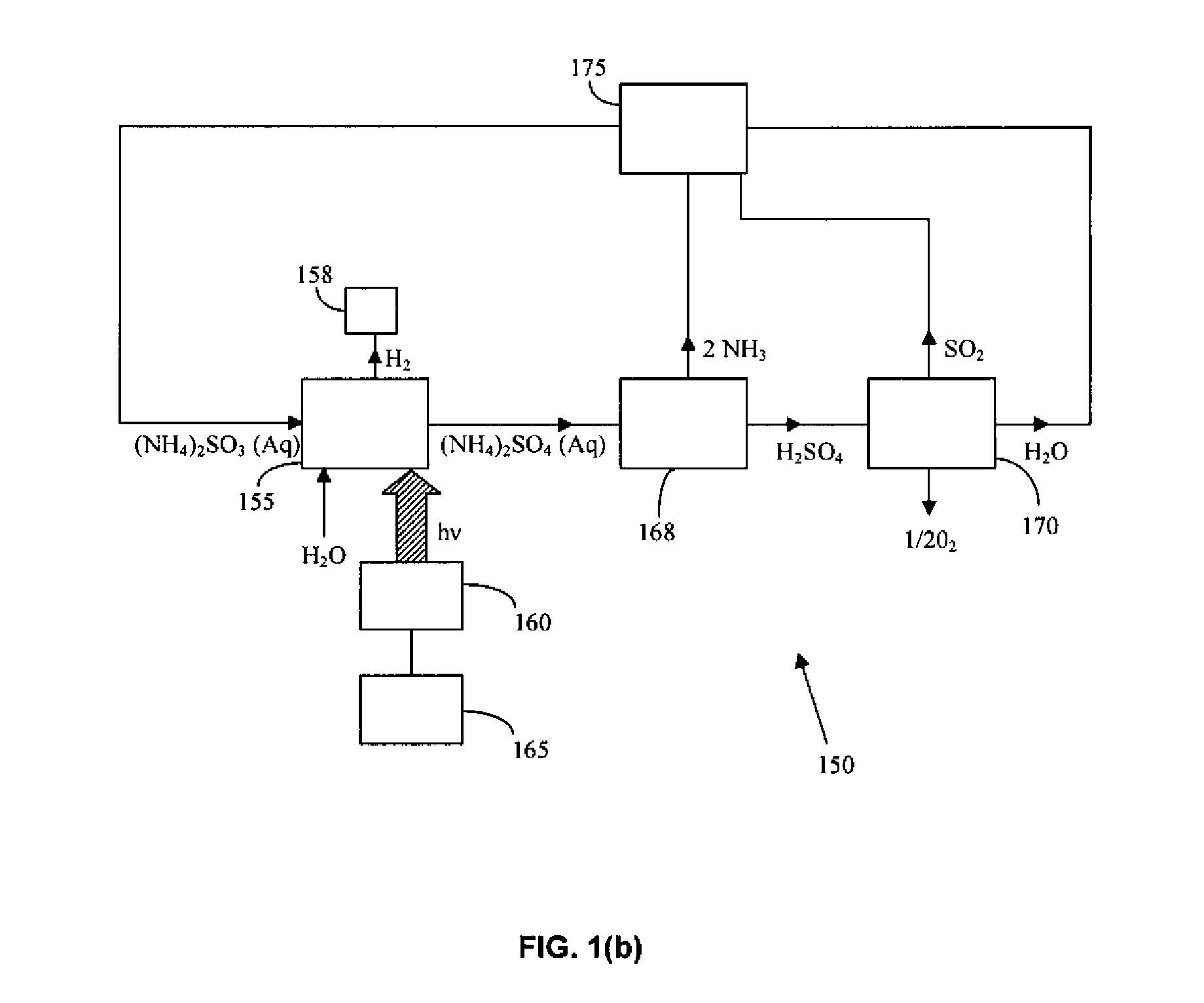
Thermochemical Cycle for Production of Hydrogen and/or Oxygen Via Water Splitting Processes
InactiveUS20080289951A1Hydrogen productionMagnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfidesWind drivenNuclear power
A method for the production of hydrogen via thermochemical water splitting includes the steps of providing an ammonium sulfite compound, dissolving the ammonium sulfite in water, and oxidizing the aqueous ammonium sulfite solution, wherein hydrogen is produced as a water reduction product associated with the oxidation. If purified air is used instead for the oxidation of aqueous ammonium sulfite solution, the method produces oxygen from the purified air. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the oxidation is a photooxidation. Light for the photoxidation can be provide by a direct light source, such as solar energy, or indirectly from conversion of electrical energy to light, such as using a UV or visible light lamp. Electrical energy can be provided by a variety of sources, including low cost sources comprising wind driven, water driven (hydroelectric), or nuclear power.
Owner:HUANG CUNPING +2
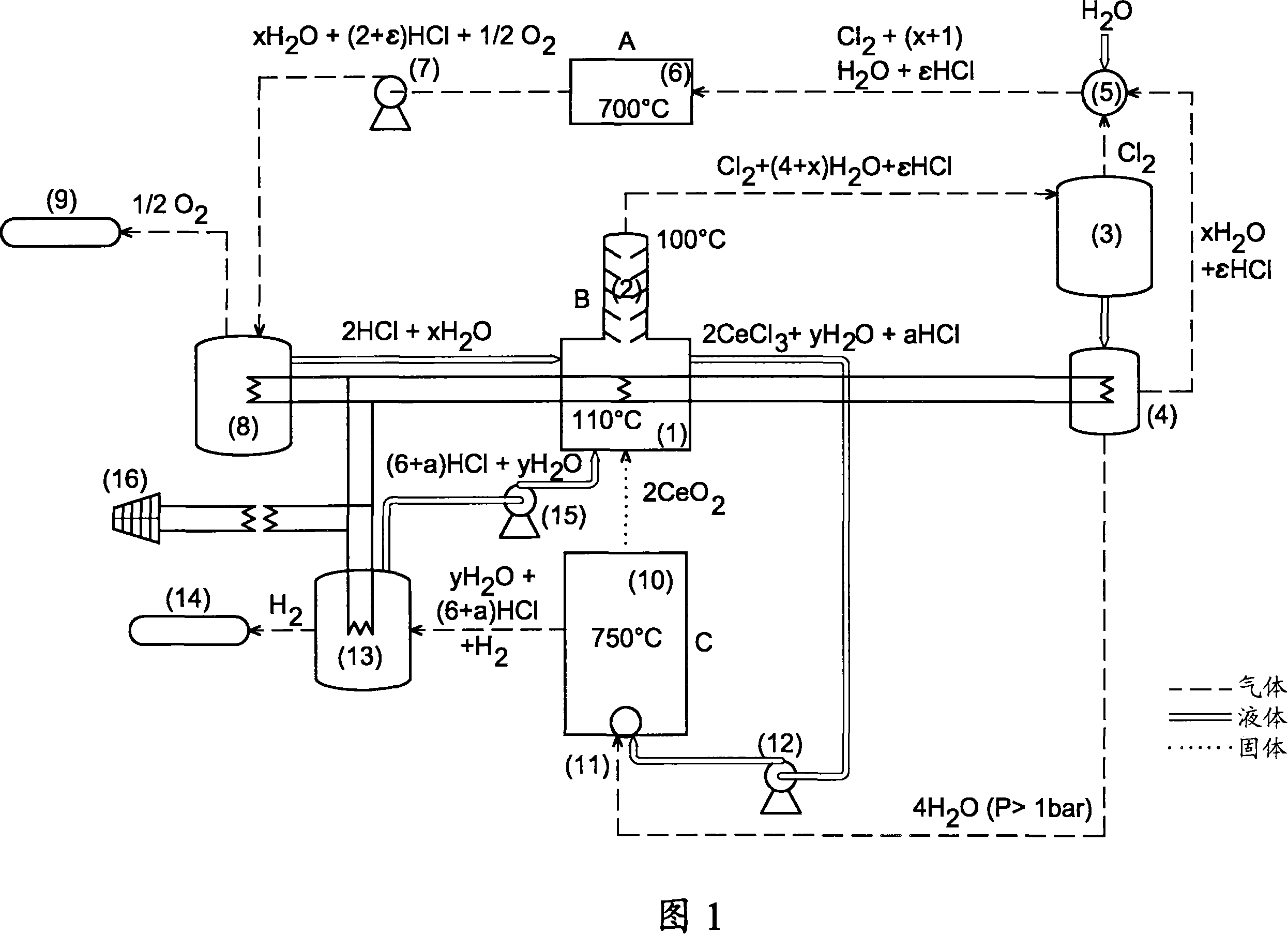
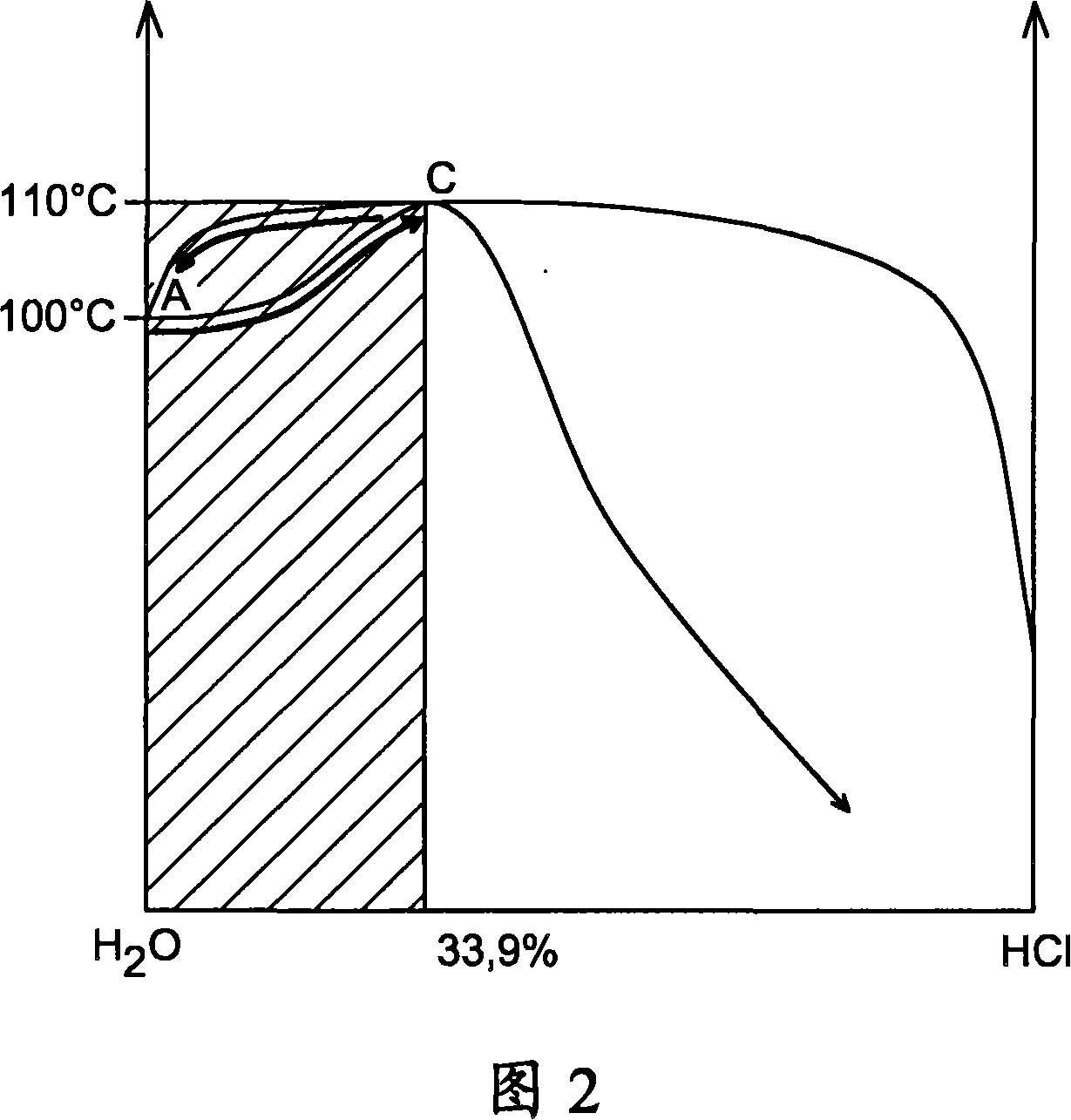
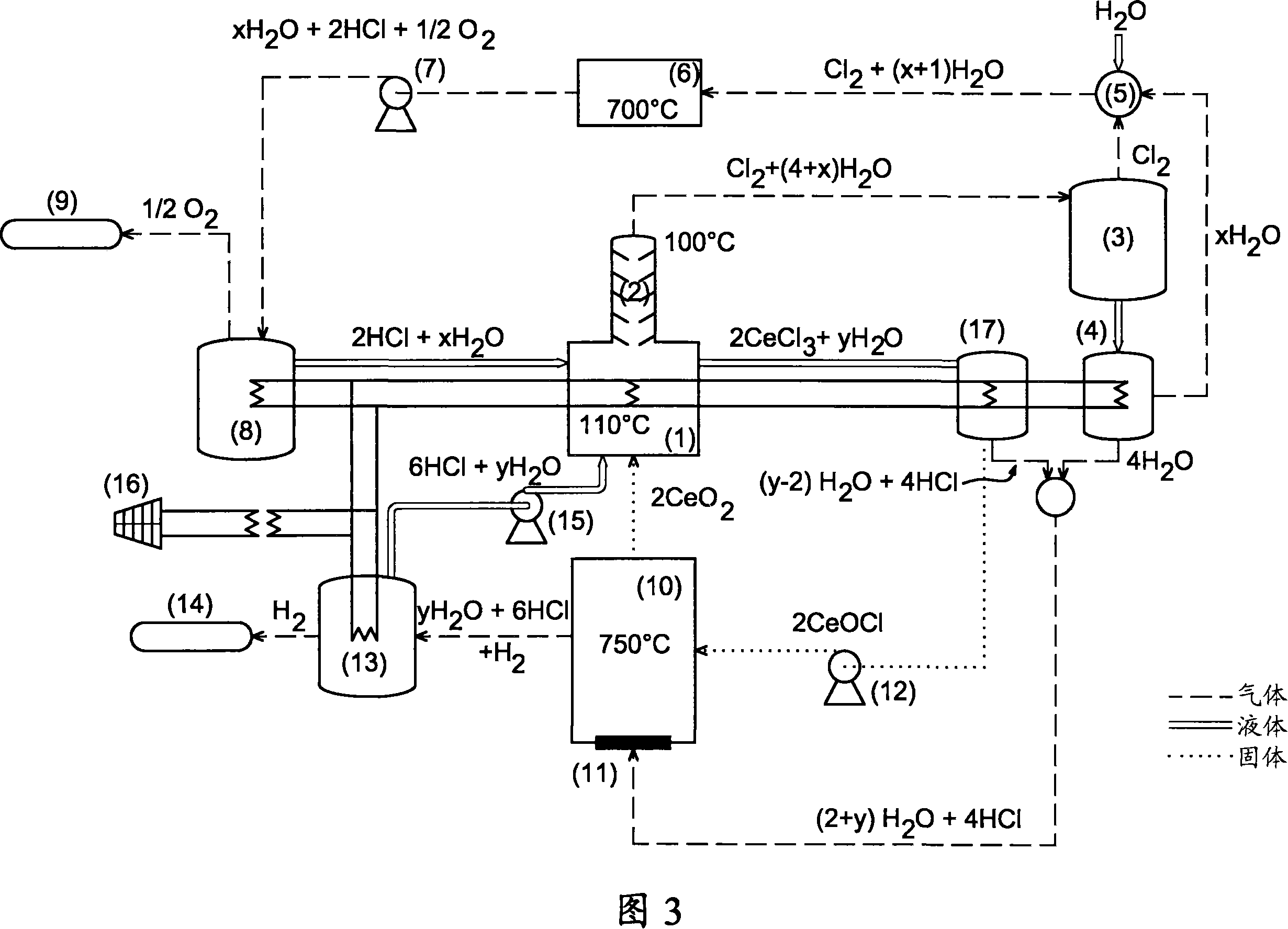
Method for producing hydrogen by thermochemical process based on hydrochlorination of cerium
Thermochemical production of hydrogen from water, based on cerium-chlorine cycle, comprises: a first reaction comprising reducing chlorine, chlorinating cerium oxide and oxidizing cerium chloride; and a second reaction comprising reducing chlorine, chlorinating cerium oxide, oxidizing cerium chloride and oxidizing cerium oxychloride. Thermochemical production of hydrogen from water, based on cerium-chlorine cycle, comprises: a first reaction (comprising: reducing chlorine by reacting water (1 mol) and chlorine (1 mol) to give hydrochloric acid (2 mol) and oxygen (0.5 mol); chlorinating cerium oxide by reacting hydrochloric acid (8 mol) and cerium oxide (2 mol) to give cerium chloride (2 mol), chlorine (1 mol) and water (4 mol); and oxidizing cerium chloride by reacting cerium chloride (2 mol) and water (4 mol) to give cerium oxide (2 mol), hydrochloric acid (6 mol) and hydrogen (1 mol)); and a second reaction (comprising: reducing chlorine by reacting water (1 mol) and chlorine (1 mol) to give hydrochloric acid (2 mol) and oxygen (0.5 mol); chlorinating cerium oxide by reacting hydrochloric acid (8 mol) and cerium oxide (2 mol) to give cerium chloride (2 mol), chlorine (1 mol) and water (4 mol); and oxidizing cerium chloride by reacting cerium chloride (2 mol) and water (2 mol) to give cerium oxychloride (2 mol) and hydrochloric acid (4 mol); and reacting cerium oxychloride (2 mol) and water (2 mol) to give cerium oxide (2 mol), hydrochloric acid (2 mol) and hydrogen (1 mol)), where the chlorination of cerium oxide is carried out in liquid phase by passing the cerium chloride in solution.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Perovskite oxide and preparation thereof, and application during photothermal chemical conversion of solar energy
ActiveCN108609643AThe synthesis method is simpleEase of large-scale synthesisEnergy inputHydrogen productionOxygen vacancyDecomposition
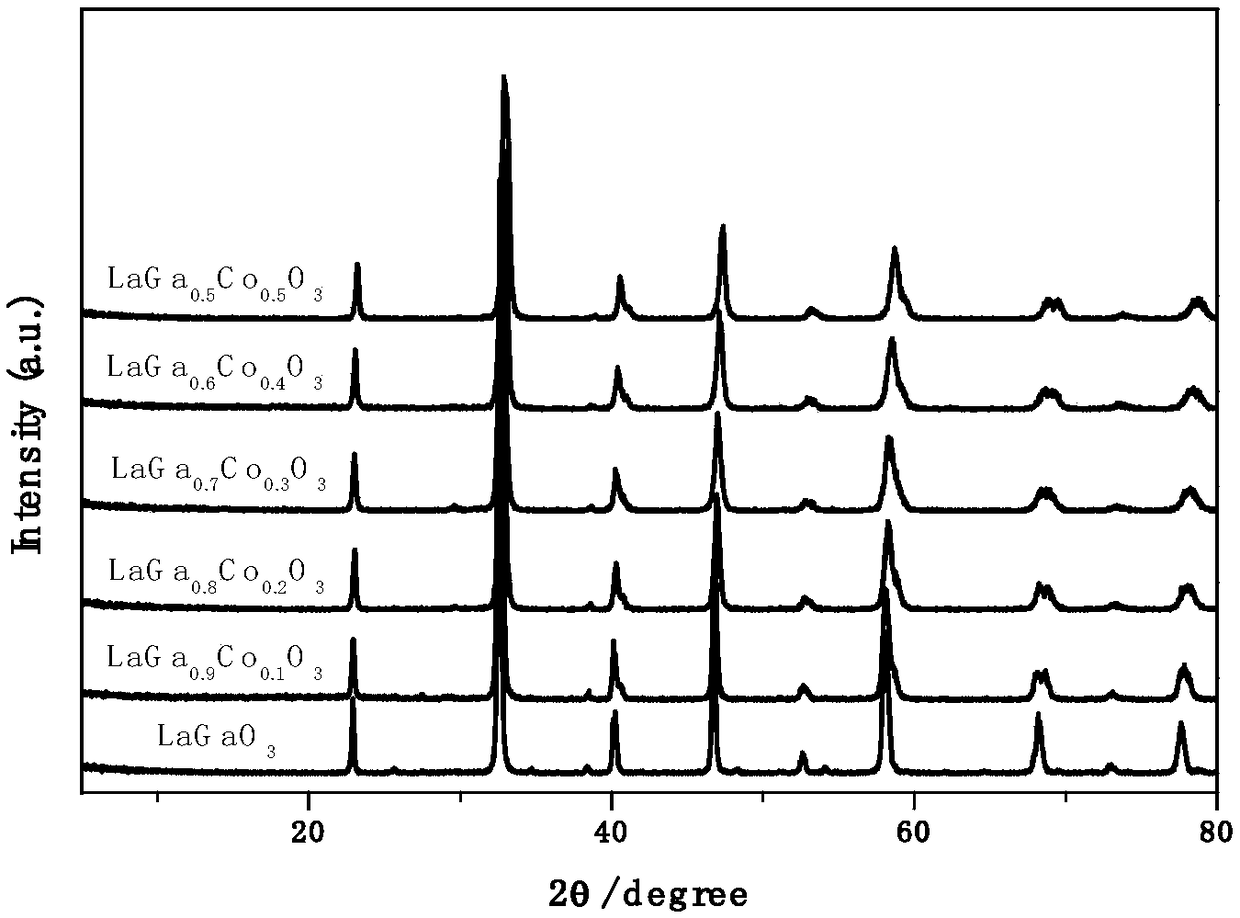
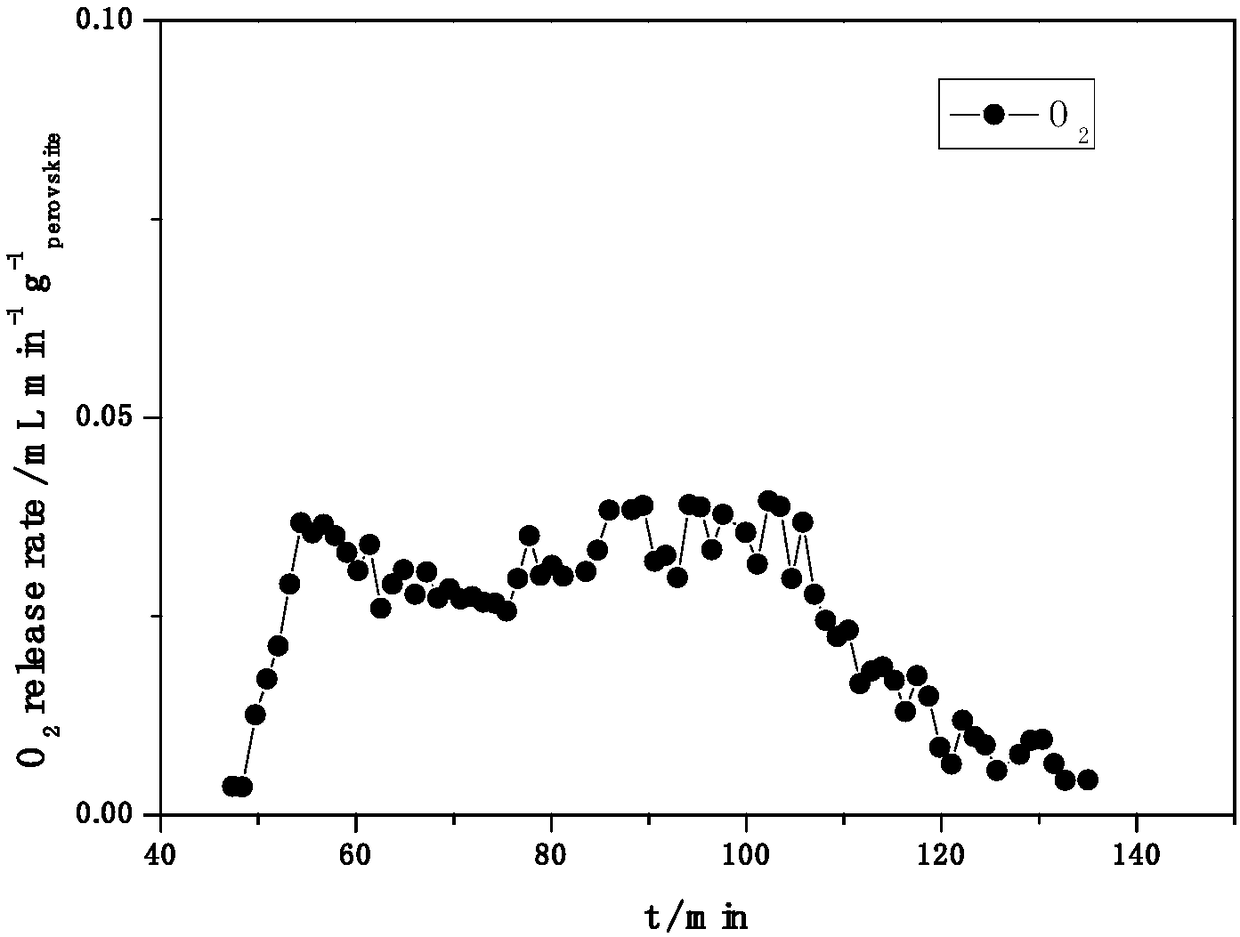
The invention relates to a method that takes a novel Ga based perovskite oxide as a redox cycle active material to decompose H2O and / or CO2 through a two-step thermochemical cycle so as to generate H2and / or CO. Oxygen vacancy formation energy of the Ga based perovskite oxide can be regulated through A-site and B-site wide doping. The thermochemical cycle reaction mainly includes the following steps: (1) reducing the active material to release oxygen at a high temperature; and (2) reacting the active material containing large amounts of oxygen vacancies with H2O and / or CO2 at a lower temperature to release H2 and / or CO. That the novel Ga based perovskite oxide can be used as the active material to realize the decomposition of H2O and / or CO2 through the thermochemical cycle is discovered for the first time. The active material can utilize the high temperature heat generated by solar energy focusing as energy sources, and takes H2O and / or CO2 as reaction raw materials to generate H2 and / or CO; and the perovskite oxide is clean and pollution-free, and is hopeful to become an effective material for preparing chemical fuel by reducing H2O and / or CO2 through the solar energy.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing synthetic gas through photo-thermal chemical circulation decomposition of carbon dioxide
ActiveCN105836703AReduce the temperatureImprove circulation conditionsEnergy inputHydrogen productionWater vaporDecomposition
The invention relates to the synthetic gas preparation technology, aims at providing a method for preparing synthetic gas through photo-thermal chemical circulation decomposition of carbon dioxide. The method includes the following steps: carrying out uniform ultrasonic vibration of a titanium dioxide nano powder and deionized water, pouring the obtained mixed suspension into a quartz glass ware, and drying; placing a prepared titanium dioxide thin film in a sealed cavity body, carrying out a reaction at normal temperature and pressure and by light source irradiation, then introducing CO2 with water vapor, heating the cavity body to 300 to 600 DEG C, carrying out a reaction, and finally, obtaining the synthetic gas including hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane. Photochemistry and thermochemistry are combined together, so the temperature required for the first step of thermochemical circulation is greatly reduced, and the circulation conditions are improved; operations required to be carried out are simpler and more convenient, the highest heat source temperature is relatively low, and the heat sources of solar energy, nuclear energy and other forms are adopted. The method can produce methane having more use value, prepares CO and H2 and the like at the same time, and has the potential for synthesis of a variety of chemical raw materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process and device for preparing oxygen through thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid phase in iodine-sulfur circulation
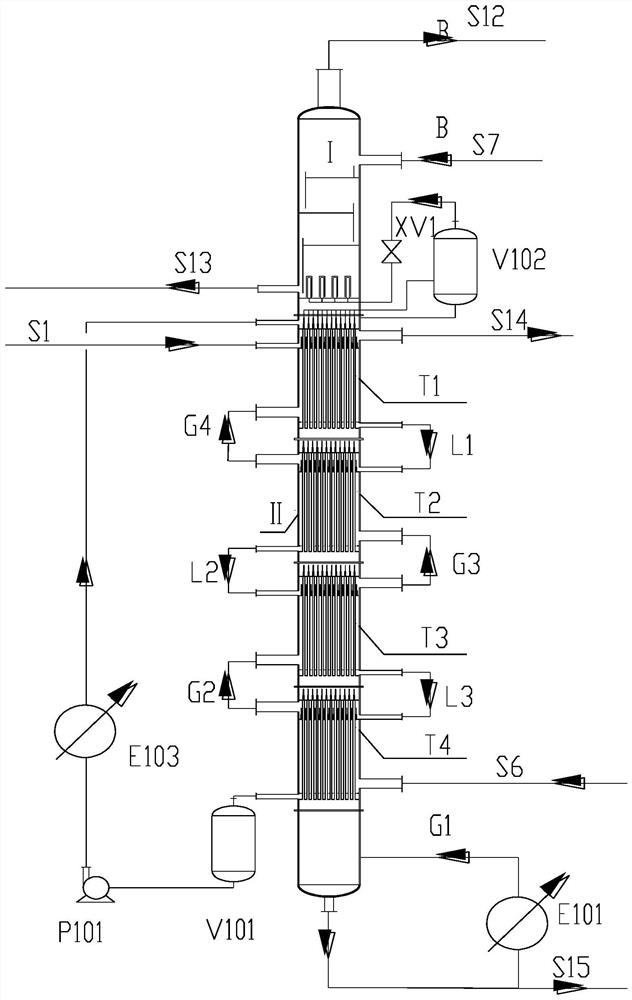
ActiveCN113274755AHigh recovery rateAvoid gasDistillation separationOxygen preparationSulfur cycleThermochemical cycle
The invention provides a process and a device for preparing oxygen through thermal decomposition of a sulfuric acid phase in iodine-sulfur circulation, and belongs to the related technical field of hydrogen preparation through thermal chemical circulation. The process comprises a sulfuric acid phase steam stripping purification section, a rectification concentration section, a washing section and a sulfuric acid thermal decomposition and mixed gas blending process and device. According to the invention, a shell pass and a tube pass of a novel shell-and-tube heat integration composite tower are filled with a 1# filler and a 2# filler respectively, N tower sections of a composite section are coaxially connected in a sealed mode, and a sulfuric acid phase steam stripping purification section, a reaction rectification section and a washing section are coupled together, so that gradient utilization of energy is achieved; a process gas containing O2 and SO2 decomposed by sulfuric acid is blended with O2 extracted by a system, and the blended gas is used as a steam stripping purification gas which respectively enters the steam stripping purification section of the shell pass of the composite tower and an HIX steam stripping purification tower; and compared with a traditional process for preparing oxygen through sulfuric acid phase thermal decomposition, the process of the invention has the advantages that the quality and the energy utilization rate of the system are improved, the purification efficiency is improved, and the energy consumption and the production cost are reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for carbon dioxide splitting
A method for splitting carbon dioxide via a two-step metal oxide thermochemical cycle by heating a metal oxide compound selected from an iron oxide material of the general formula AxFe3-xO4, where 0≦x≦1 and A is a metal selected from Mg, Cu, Zn, Ni, Co, and Mn, or a ceria oxide compound of the general formula MaCebOc, where 0<a<1, 0<b<1, and 0<c<2, where M is a metal selected from the group consisting of at least one of a rare earth metal and an alkaline earth metal, to a temperature greater than approximately 1400° C., thereby producing a first solid-gas mixture, adding carbon dioxide, and heating to a temperature less than approximately 1400 C, thereby producing carbon monoxide gas and the original metal oxide compound.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Tandem photochemical-thermochemical process for hydrocarbon production from carbon dioxide feedstock
InactiveUS20160340593A1Energy efficiencyHydroxy compound preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionThermochemical cycleWater use
The present invention is directed at an improved process for generating heavier hydrocarbons from carbon dioxide and / or carbon monoxide and water using tandem photochemical-thermochemical catalysis in a single reactor. Catalysts of the present disclosure can comprise photoactive material and deposits of conductive material interspersed on the surface thereof. The conductive material can comprise Fischer-Tropsch type catalysts.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Process and device for preparing hydrogen from hydrogen iodide in iodine-sulfur circulation
ActiveCN113233415AEnhanced mass transferImprove heat transfer performanceHydrogen iodideEnergy inputThermochemical cycleSulfur cycle
The invention belongs to the related technical field of hydrogen preparation through thermochemical circulation, and provides a process and a device for preparing hydrogen from hydrogen iodide in iodine-sulfur circulation. The device comprises an HIX steam stripping section, a reaction rectifying section, a reaction gas washing section and a steam stripping gas washing process and device. A shell pass and a tube pass of a novel shell-and-tube heat integration composite tower are filled with a 1# filler and a 2# filler respectively, N tower sections of a composite section are coaxially and hermetically connected, and the HIX steam stripping section, the reaction rectifying section and a water washing section are coupled together, so that gradient utilization of energy is realized; the system mixed gas containing O2 and SO2 is used as the circulating stripping gas of the stripping section of the composite tower, so that the generation of S, H2S and a small amount of H2SO4 mingled in an HIX system is inhibited, and the recovery rate of SO2 in HIX is improved; and the tower bottom material liquid of the reaction section of the heat integration composite tower and the acidic water of the washing section and the stripping gas washing tower are returned to the front mixing tank of the Bensen reactor, so that the quality utilization rate of the system is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for two-phase separation, concentration and purification in sulfur-iodine circulating hydrogen production
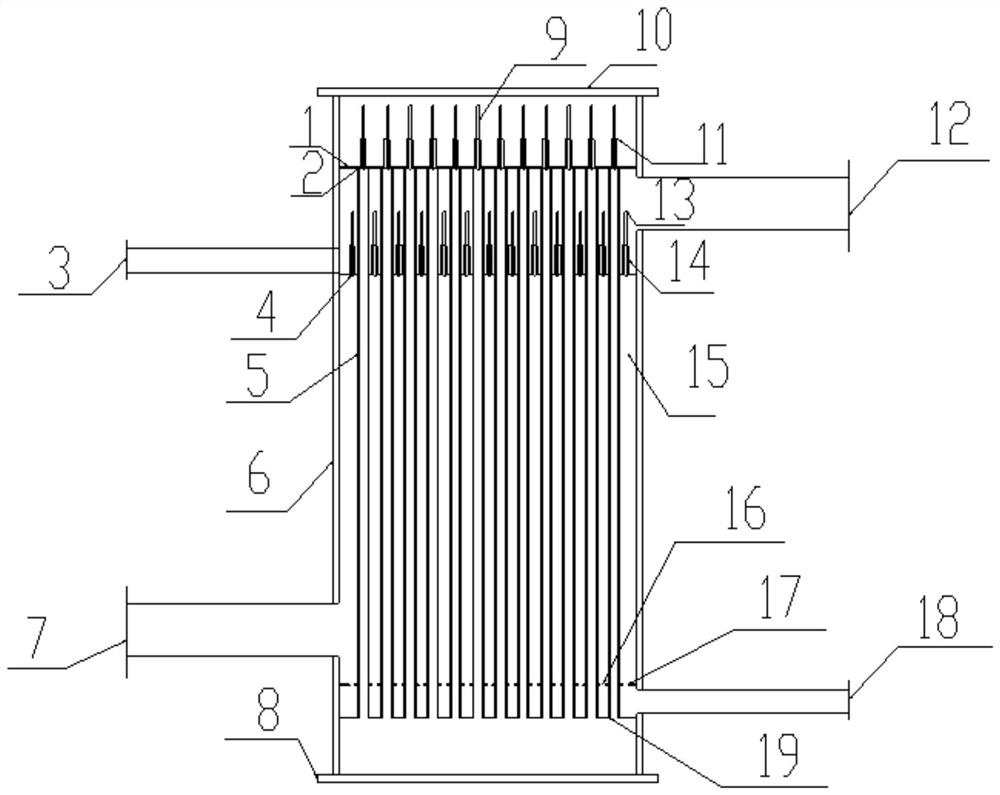
ActiveCN114852960AReduce energy consumptionRealize step separationEnergy inputHydrogen productionMicropore FilterThermochemical cycle
The invention discloses a two-phase separation, concentration and purification method and device in sulfur-iodine cycle hydrogen production, and belongs to the related technical field of hydrogen preparation through thermochemical cycle. According to the invention, gradient separation of HI gas is realized by utilizing gradual reduction of pressure, and the risk of subsequent I2 precipitation and the energy consumption of solution concentration are reduced; heat of high-temperature gas generated by decomposition of H2SO4 is collected through a heat exchanger, so that gradient utilization of energy of the process and the system is realized; the method comprises the following steps: feeding liquid subjected to HI steam stripping into an H2SO4 purification and concentration tower, rapidly vaporizing H2O under the conditions of low pressure and high temperature, reacting HI mixed in an H2SO4 system with H2O2 to generate I2 and H2O, removing I2 in a microporous filter, and achieving the purpose of purifying an H2SO4 solution under the condition of not introducing other impurities; a concentration section and a purification section of H2SO4 are coupled together, so that the whole system is greatly simplified.
Owner:浙江百能科技有限公司
Methods and apparatuses for removal and transport of thermal energy
ActiveUS8073096B2Minimum energy lossAir heatersIndirect heat exchangersThermal energyThermochemical cycle
Methods and apparatuses are provided for the removal and transportation of thermal energy from a heat source to a distant complex for use in thermochemical cycles or other processes. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a hybrid heat pipes / thermosyphon intermediate heat exchanger (HPTIHX) system that is divided into three distinct sections, namely: an evaporation chamber, a condensation chamber, and a working fluid transport section of liquid and vapor counter-current flows.
Owner:STC UNM
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com