High-magnesium phosphorite de-magging method with by-product magnesium ammonium phosphate
A technology of by-product ammonium phosphate and high-magnesium phosphate rock, which is applied in the fields of phosphate material treatment, chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, etc., can solve the problems of difficult promotion of chemical magnesium removal, large loss of phosphorus pentoxide, and low removal rate. Advanced problems, achieve the effect of improving foaming phenomenon and filtration performance, saving equipment investment and high removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
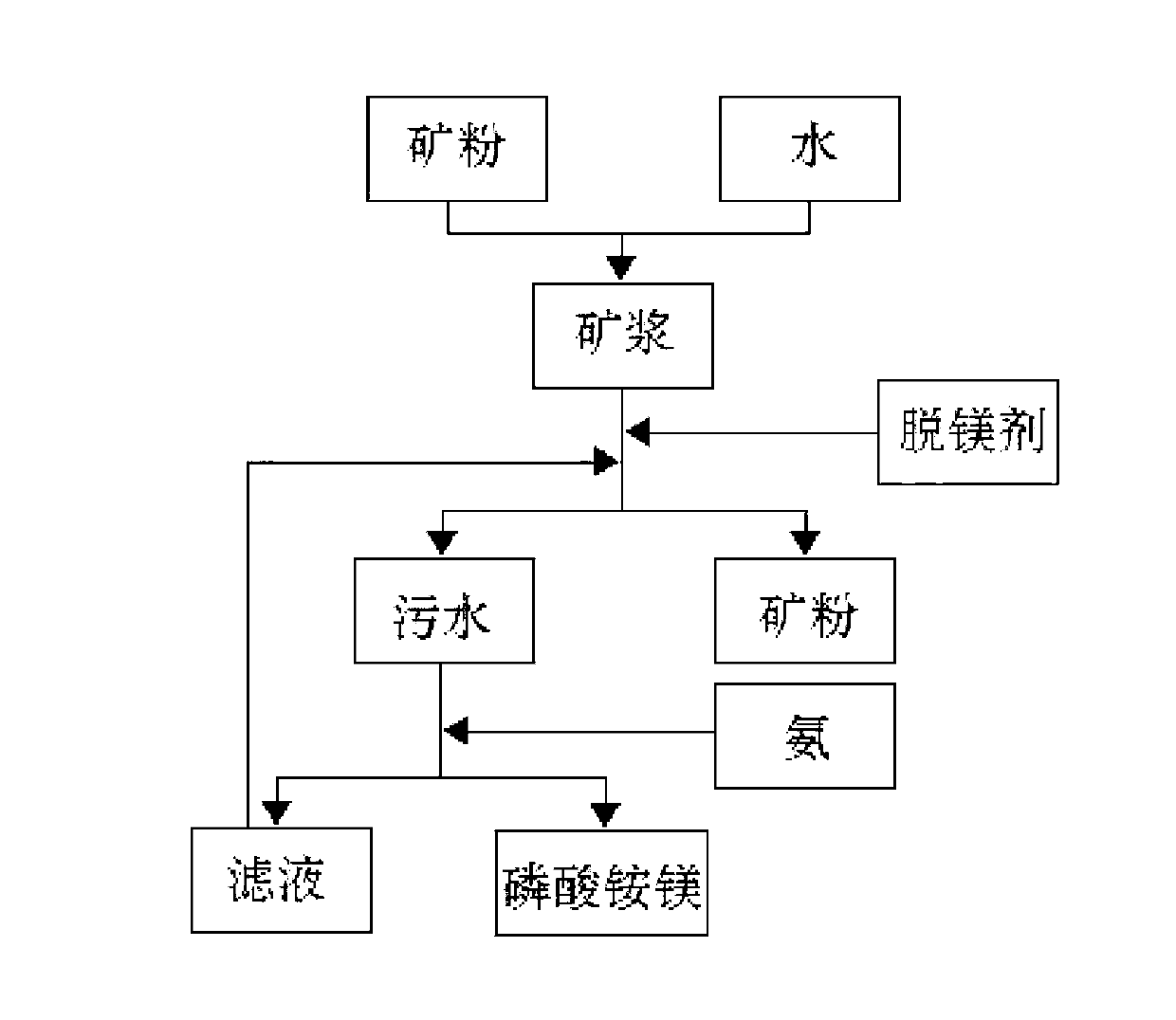
[0029] Grind 1Kg of phosphate sand with MgO content of 4.2% to 100 mesh, mix it with 1.2kg of water to prepare a slurry, slowly add 93% sulfuric acid while stirring, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 3.5, and add it dropwise while stirring Sulfuric acid kept the pH value of the solution unchanged, reacted for 90 minutes, filtered and dried, and analyzed the content of MgO in the ore powder to be 0.42%; the filtered sewage was adjusted to PH value to 8.5 with 25% ammonia water, stirred for 50 minutes, filtered, and solid-phase dried 120g of magnesium ammonium phosphate fertilizer was obtained by dry weighing, and 140g of phosphoric acid with a phosphoric acid concentration of 64% was added to the filtrate, which was sent to the separated sewage obtained after magnesium removal and continued to stir for 60 minutes, and filtered to obtain 155g of magnesium ammonium phosphate.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Mix 0.8kg of ore powder with MgO content of 3.6%, particle size of 200 mesh, and 0.8kg of water to make a slurry, adjust the pH of the slurry to 3.2 with phosphoric acid with an acid concentration of 50%, continue to stir and react, and adopt the method of adding phosphoric acid to maintain The PH value of the ore slurry was kept unchanged for 80 minutes, filtered and dried, and the MgO content in the slag powder was analyzed to be 0.51%; liquid ammonia was slowly introduced into the filtered sewage to adjust the pH value of the solution to 8.0, stirred and reacted for 60 minutes, filtered, filtered The cake was dried and weighed to obtain 167g of magnesium ammonium phosphate.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Use 0.6Kg of ore powder with a particle size of 200 mesh and a MgO content of 3.7% to prepare a slurry with a water content of 40%, and adjust the pH value of the slurry to 3.3 with a mixed acid made of sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid with a mass fraction of 50% each. Add mixed acid to keep the pH of the solution constant. Stir and react the pulp for 80 minutes, filter and dry. After analysis, the content of MgO in the ore powder is 0.47%. Slowly inject gas ammonia into the filtered sewage to adjust the pH value of the solution to 9.0. Stir the reaction for 45 minutes, filter, dry and weigh the filter cake to obtain 134 g of magnesium ammonium phosphate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com