Method for removing mercury ions in water and regeneration method of adsorbent used in same
An adsorbent and mercury ion technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of poor adsorption selectivity and specificity, increase the difficulty of operation, and difficult solid-liquid separation, etc., to improve adsorption capacity and selectivity, enhance affinity, high The effect of environmental economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
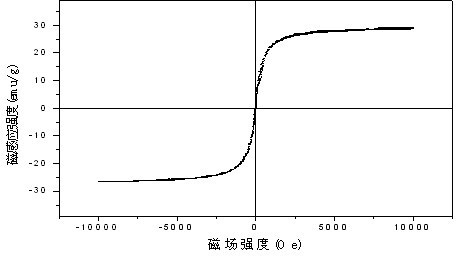
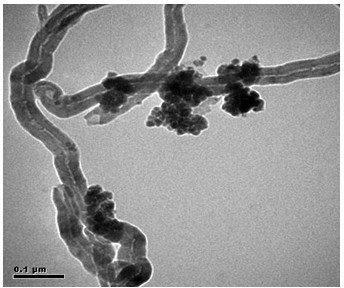
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Activation of carbon nanotubes
[0046] Take 1.0g of carbon nanotube composite material, put it in a 60mL autoclave, add 20mL of concentrated nitric acid with a mass fraction of 65-68%, and seal the autoclave; the autoclave used is a high-pressure airtight container, which is resistant to high pressure. The high-pressure reaction kettle is composed of a polytetrafluoroethylene lined tank and a stainless steel sealed jacket. The stainless steel sealed jacket is compacted up and down with threads, so that the lid and the tank of the lined tank can be sealed, and the internal reactants are sealed by heating. The reaction is carried out under the conditions of high temperature and high pressure in the environment;
[0047] ②Put the high-pressure reactor containing the above reactants in an oven, keep it at 100°C for 10 minutes, then rapidly raise the temperature to 150°C, and react for 1.0h. After the reaction is complete, stop heating and cool down to room temper...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 Magnetic modification of carbon nanotubes
[0051] The magnetic modification reaction is carried out under the condition of nitrogen protection, and the reaction temperature is 50°C;
[0052] ②Weigh 1.0g of the activated carbon nanotube composite material, suspend it in 200ml of aqueous solution containing 1.7g of (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O and 2.5g of NH4Fe(SO4)2·12H2O, and mix the solution of the reaction system The mass fraction of iron / (iron+carbon nanotubes) is 35%, and the synthetic product is recorded as 35% Fe magnetically modified carbon nanotubes;
[0053] The above system was reacted under ultrasonic conditions for 10 minutes. During the reaction process, 8mol / L ammonia water was added dropwise to keep the pH value of the mixture at 11-12; the ultrasonic frequency was 40KHz, the ultrasonic power was 250W, and the heating power was 400W;
[0054] ④ After the ultrasonic reaction, in order to further ensure that the reaction is complete, the reaction system ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3 Magnetic carbon nanotubes supported metal palladium
[0057] Weigh 1.0 g of 35% Fe magnetically modified carbon nanotube composite material, suspend it in 300 mL of PdCl2 aqueous solution containing 0.0825 g, and the mass fraction of palladium / (palladium+magnetically modified carbon nanotube) in the reaction system solution is 5%, The product is recorded as 5%Pd-35%Fe palladium nanoparticle-loaded / iron oxide magnetically modified carbon nanotube composite material;
[0058] ② Place the above system solution under ultrasonic conditions for 15 minutes; the ultrasonic frequency is 40KHz, the ultrasonic power is 250W, and the temperature is 20°C;
[0059] ③ After the ultrasonic reaction is over, add 8mol / L ammonia water drop by drop under the constant stirring condition of 300-400r / min to keep the pH value of the mixture at 8-9;
[0060] ④ Under constant stirring condition of 300-400r / min, add 50mL of newly prepared 0.05mol / L NaBH4 solution dropwise, and react fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com