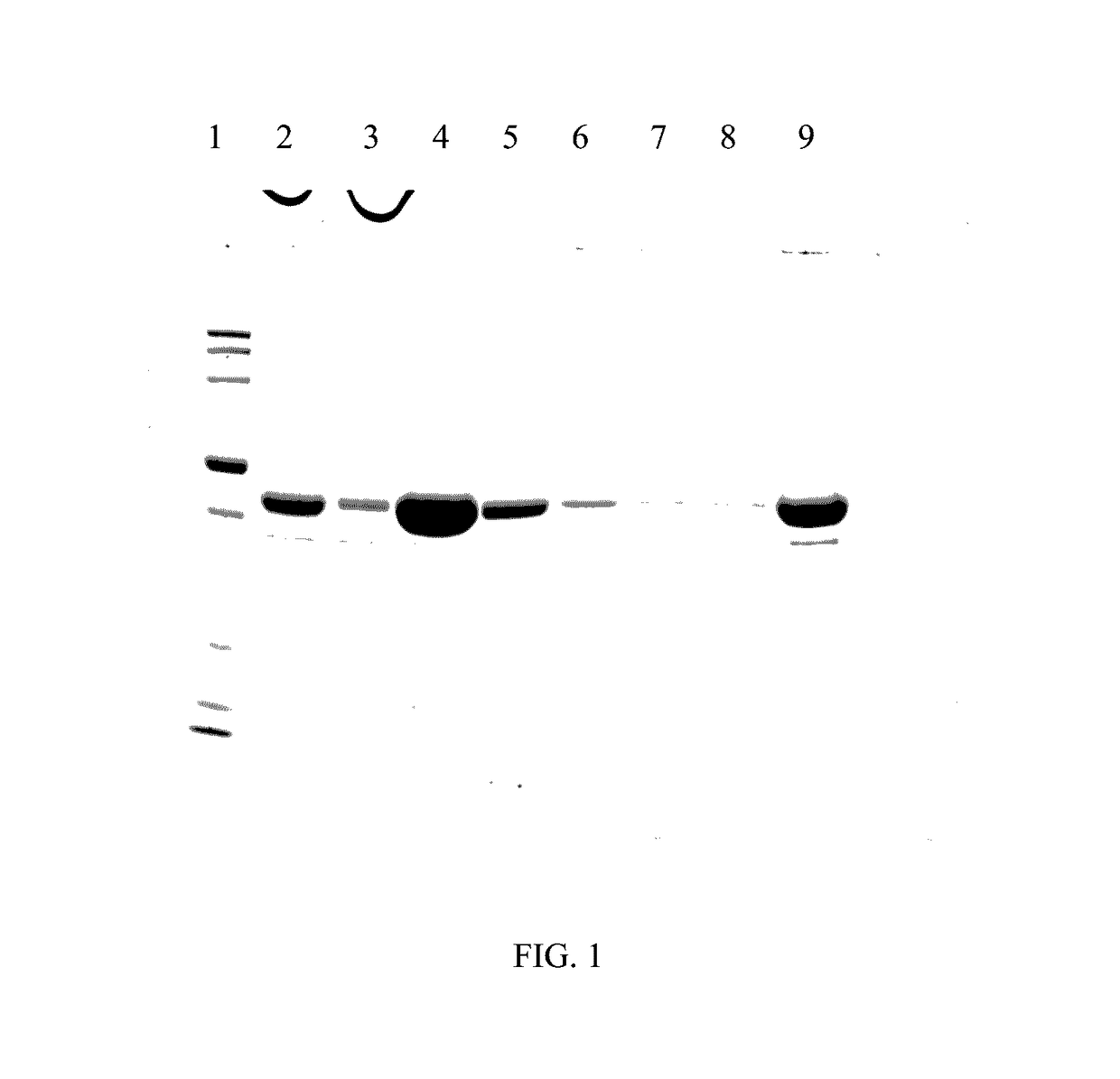
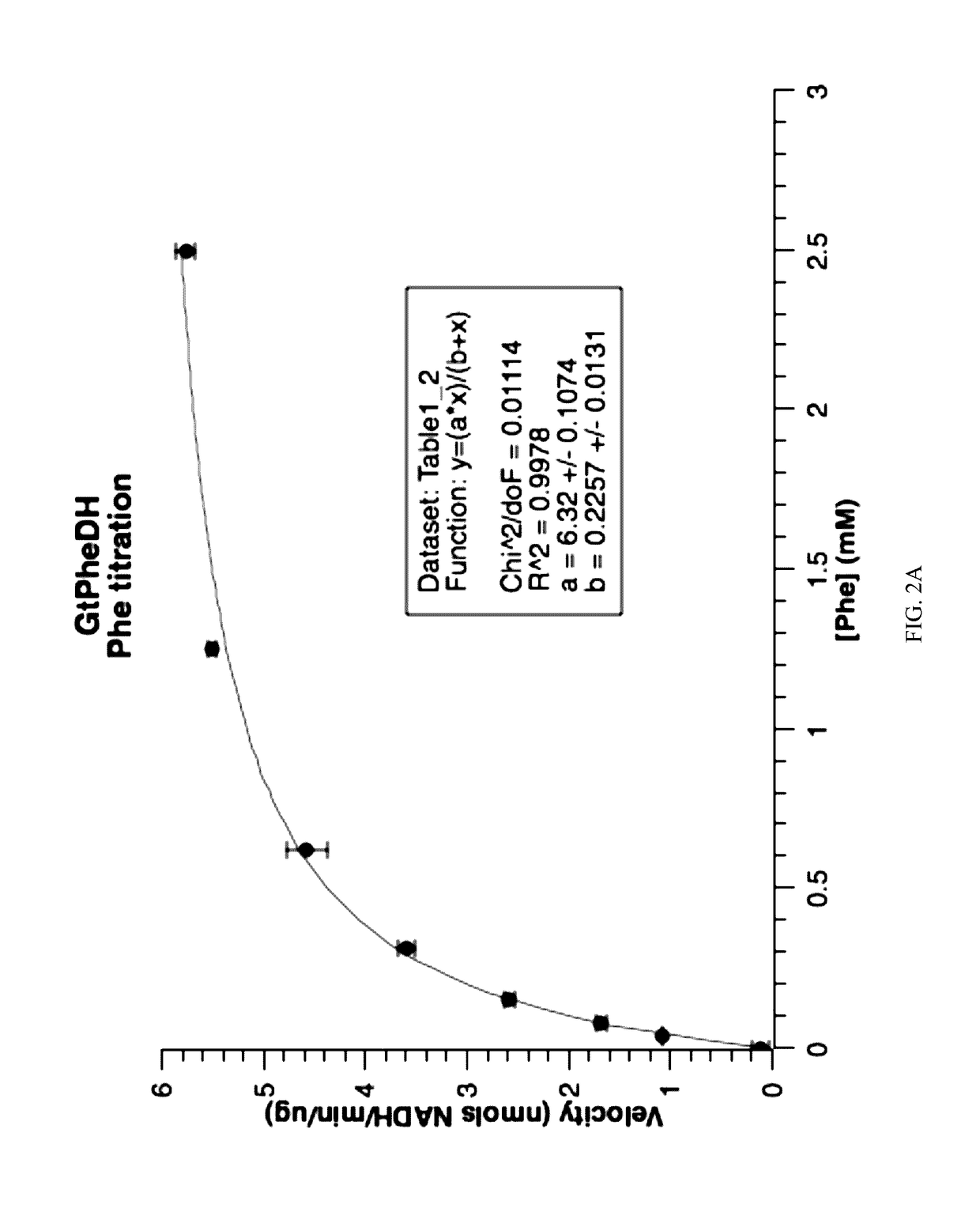
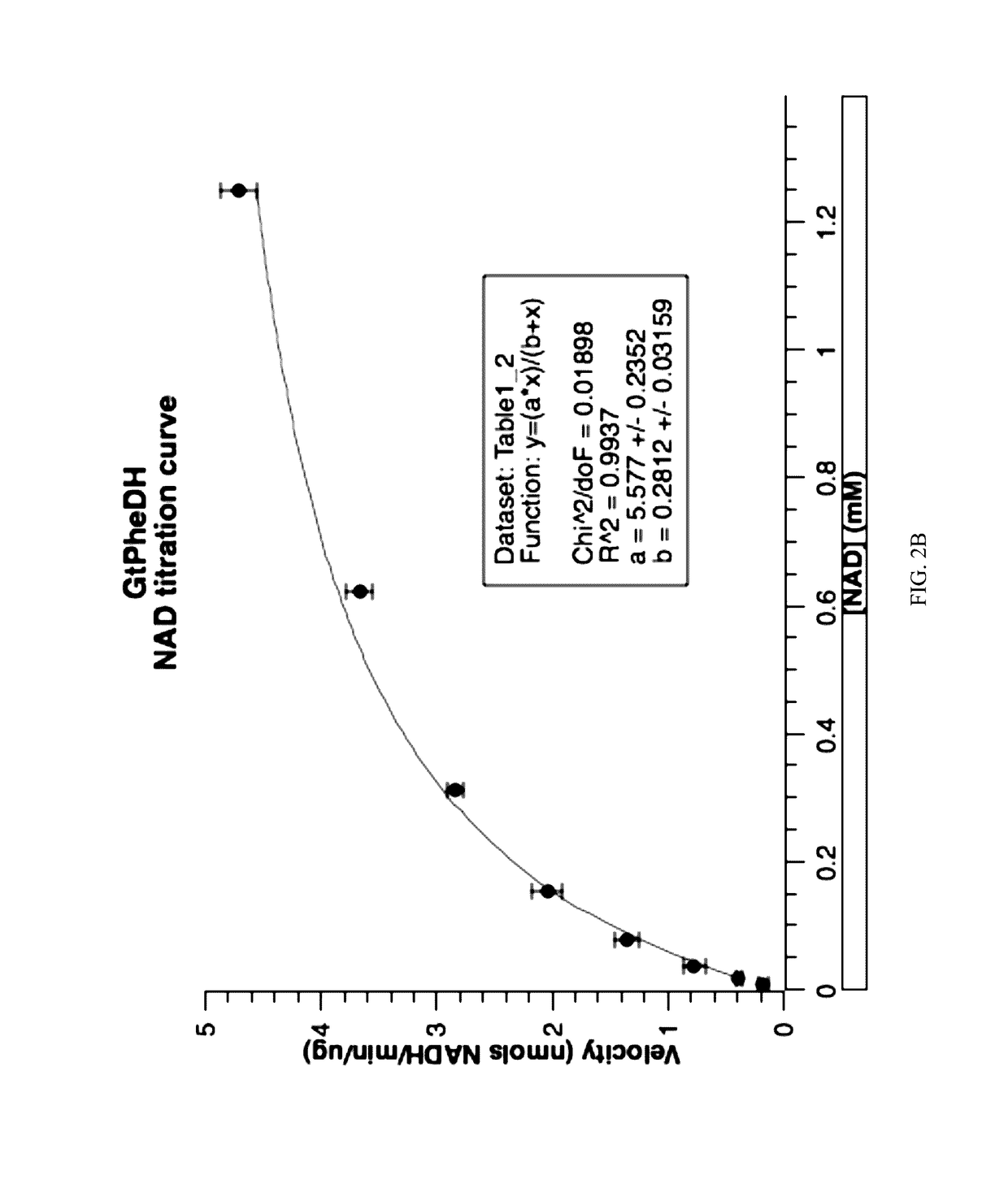
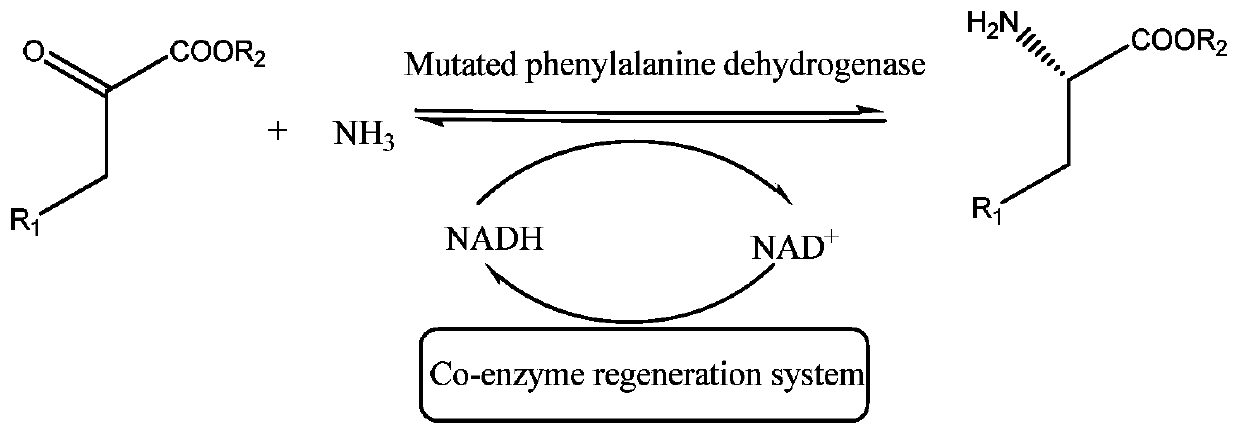
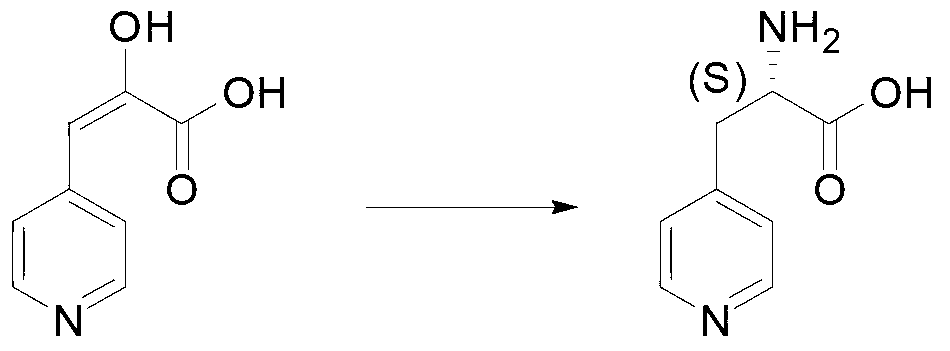
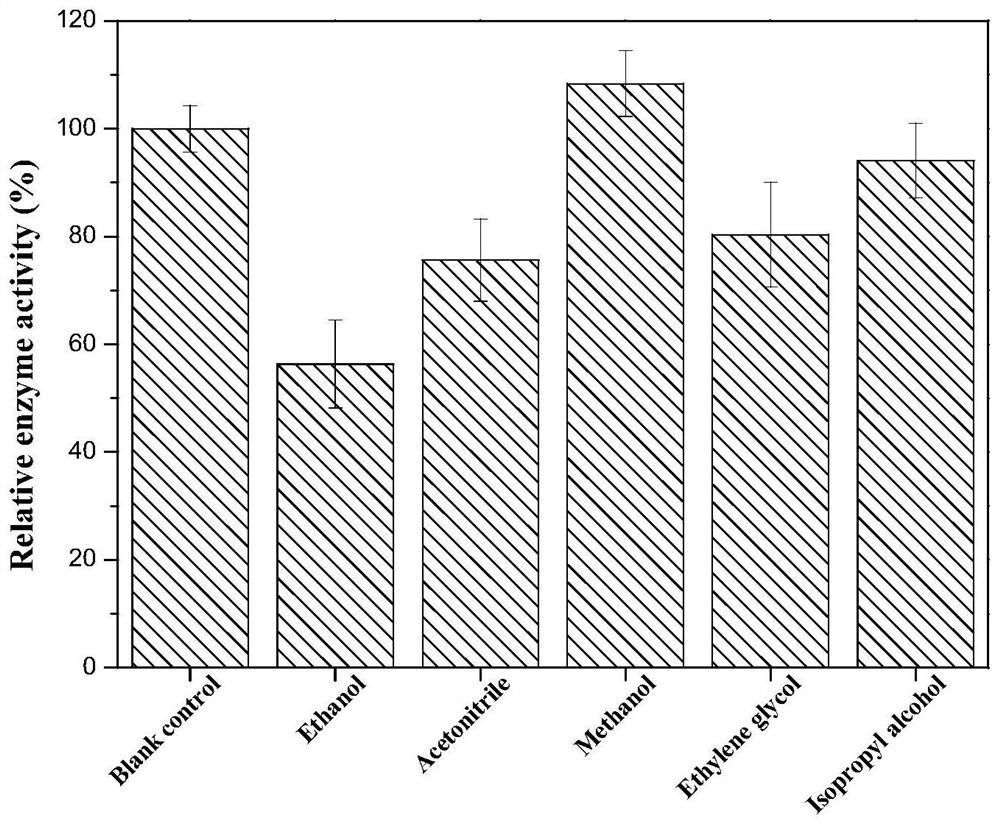
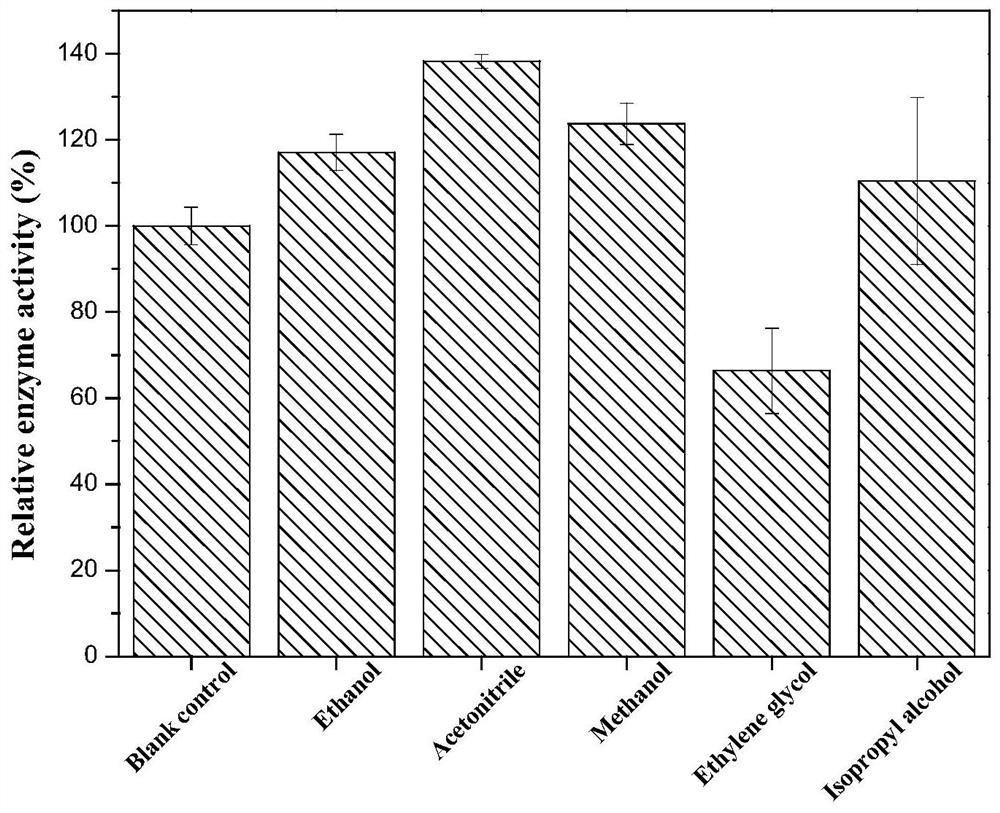
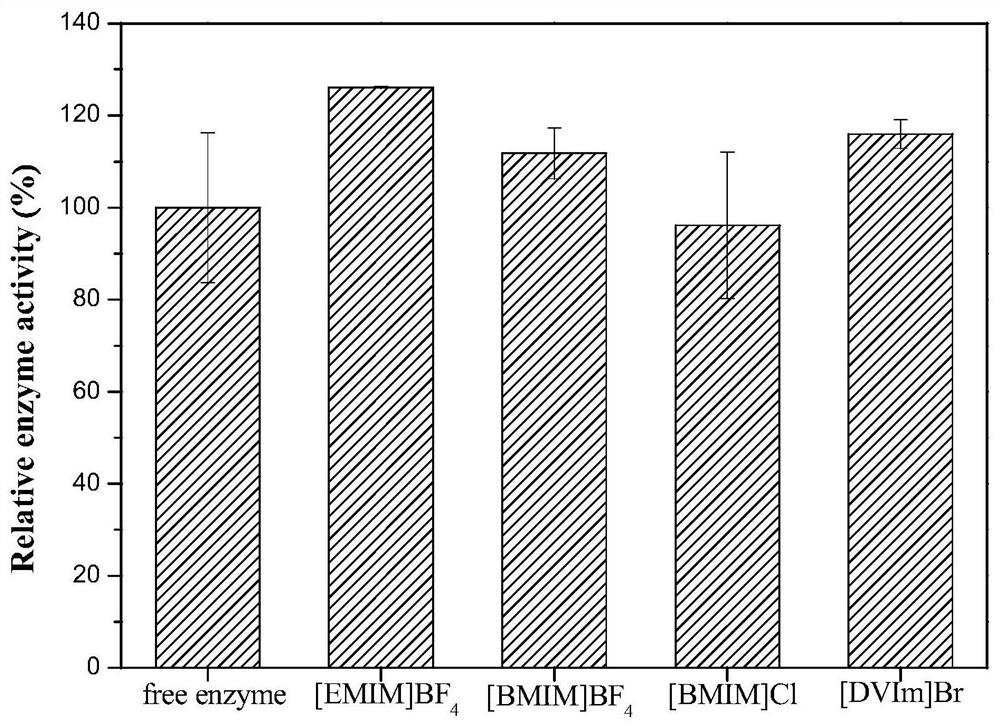
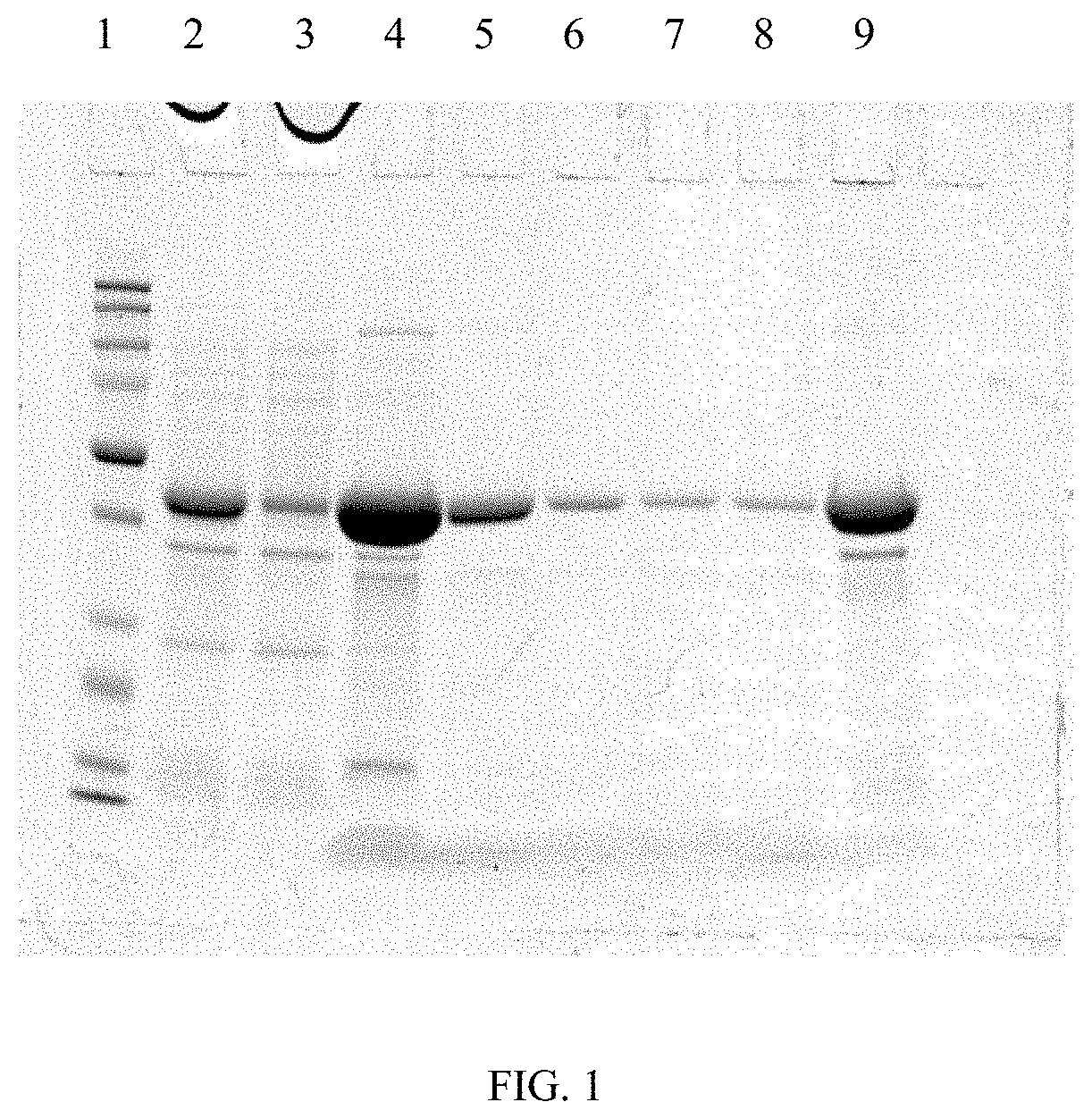
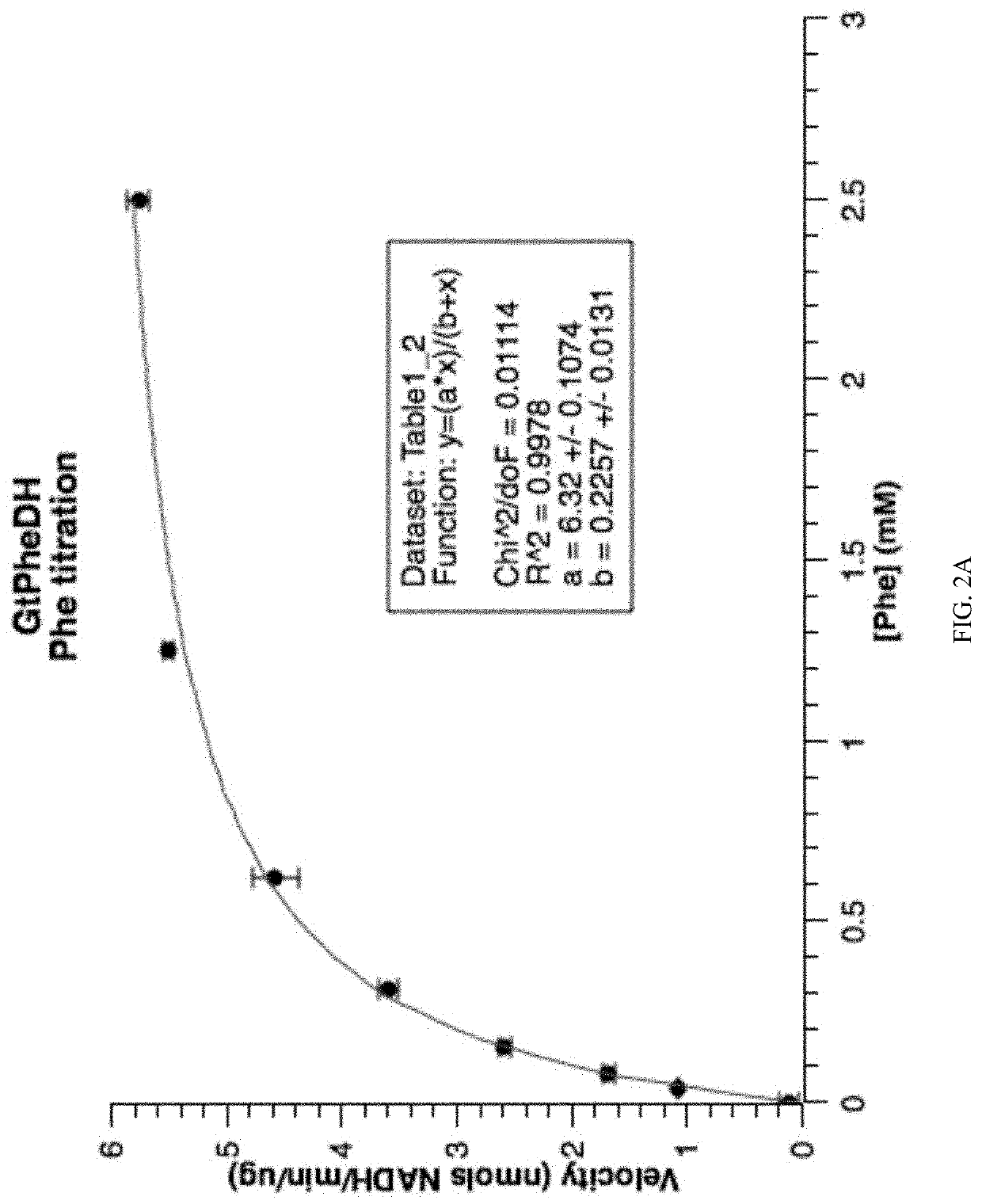
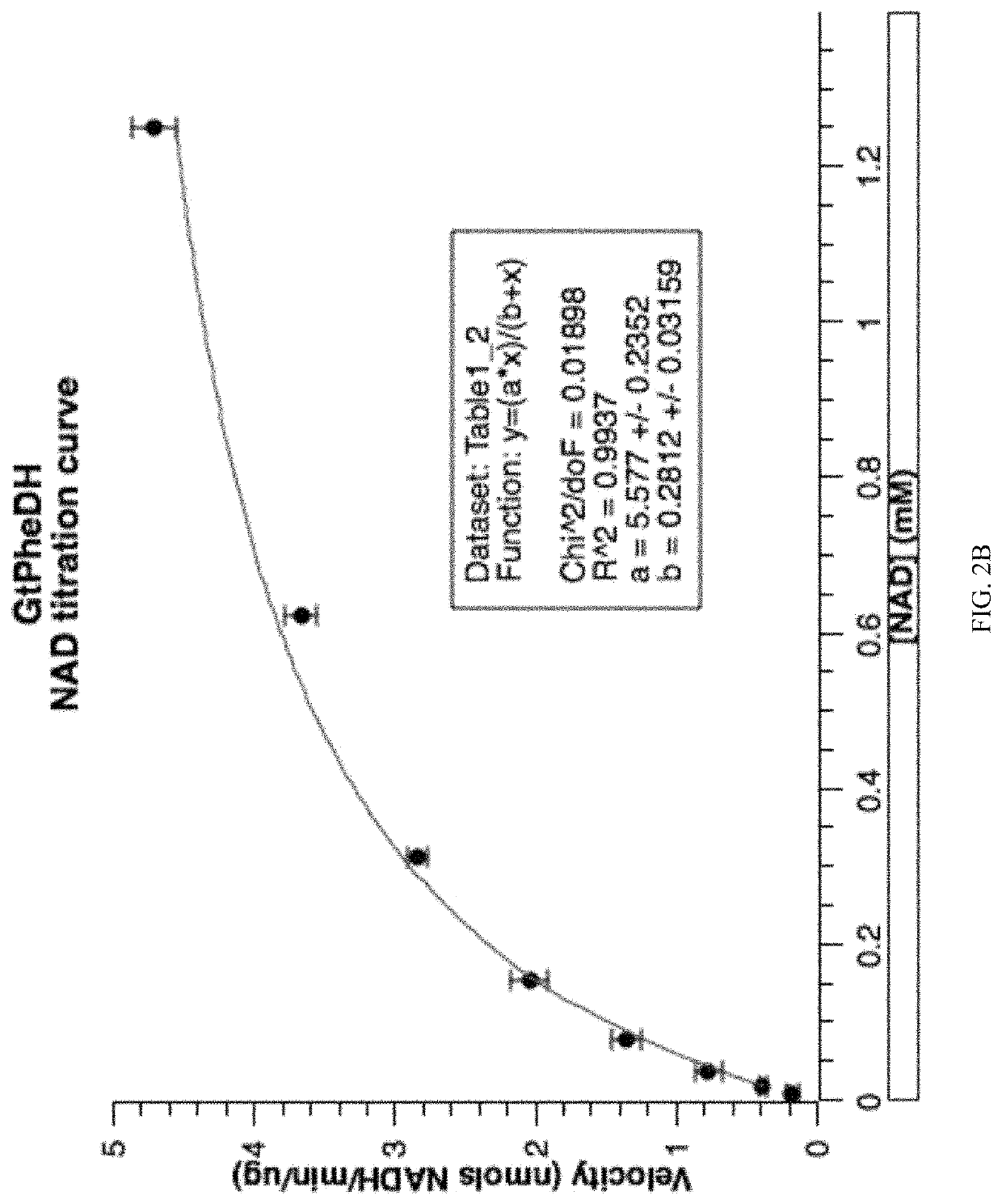
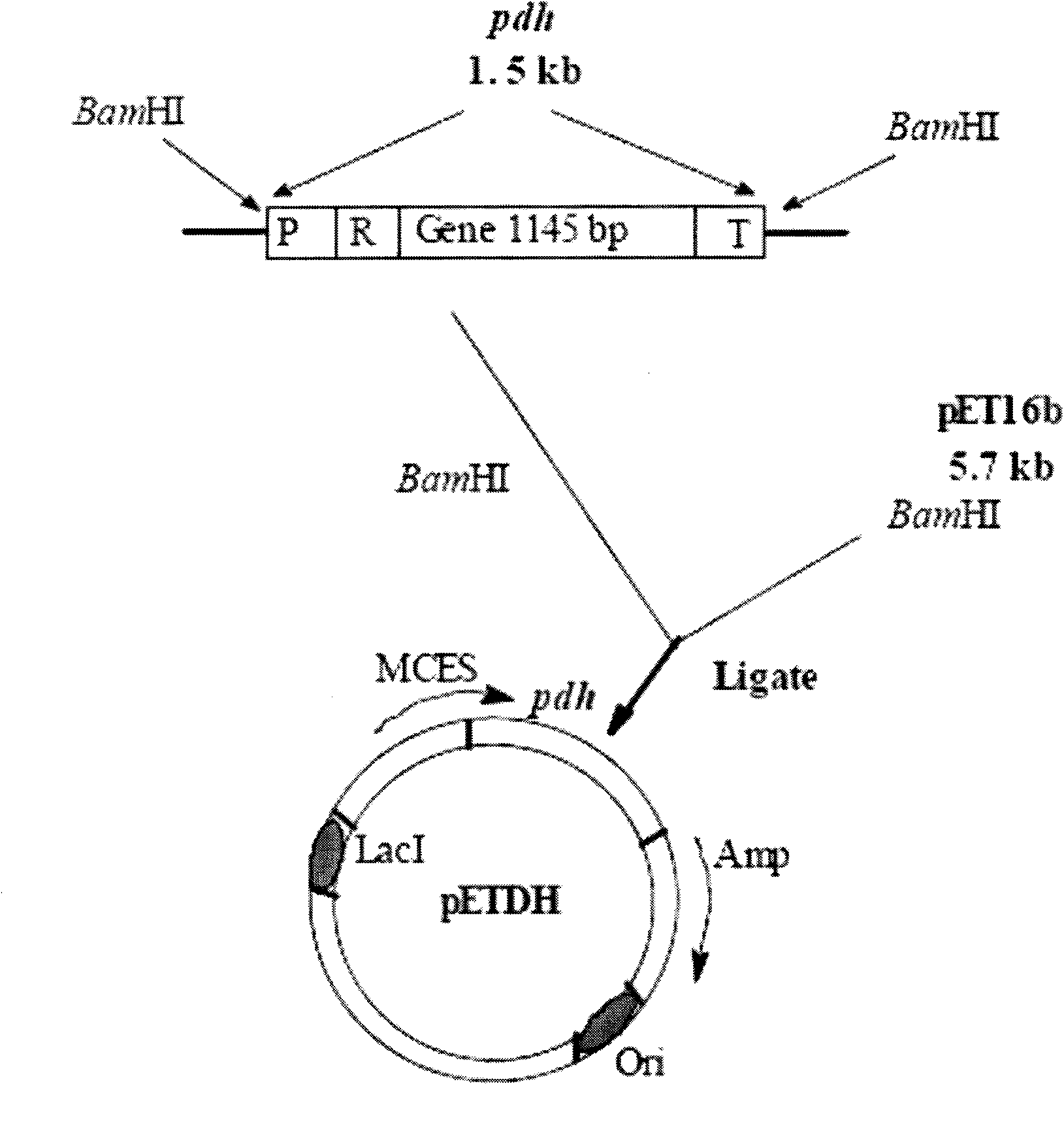
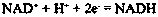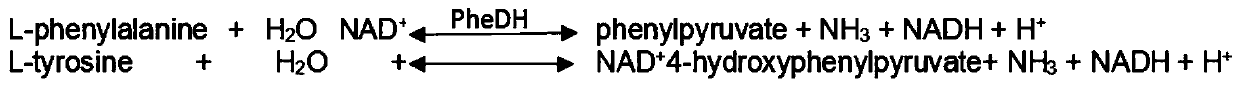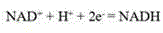Patents
Literature
38 results about "Phenylalanine dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
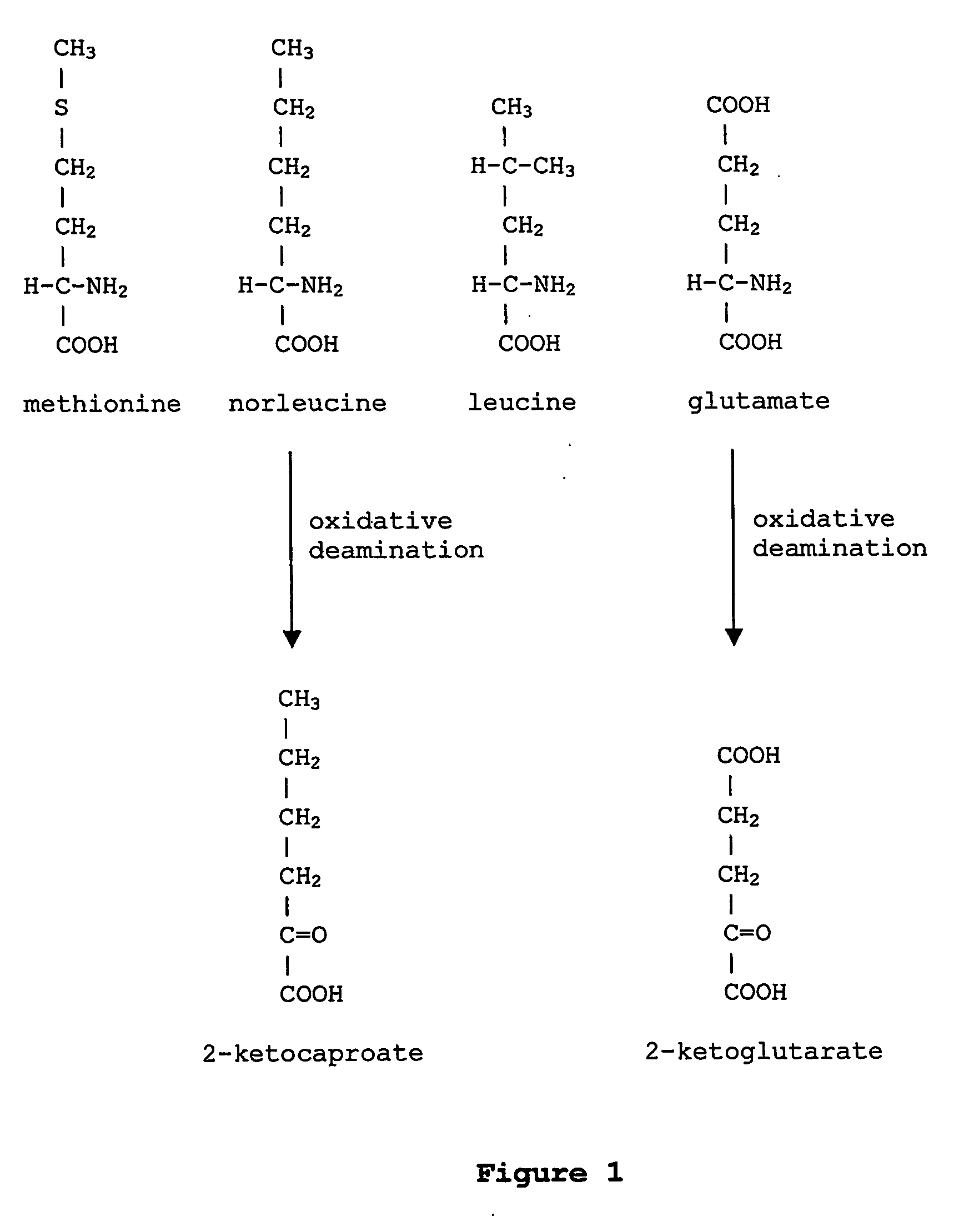
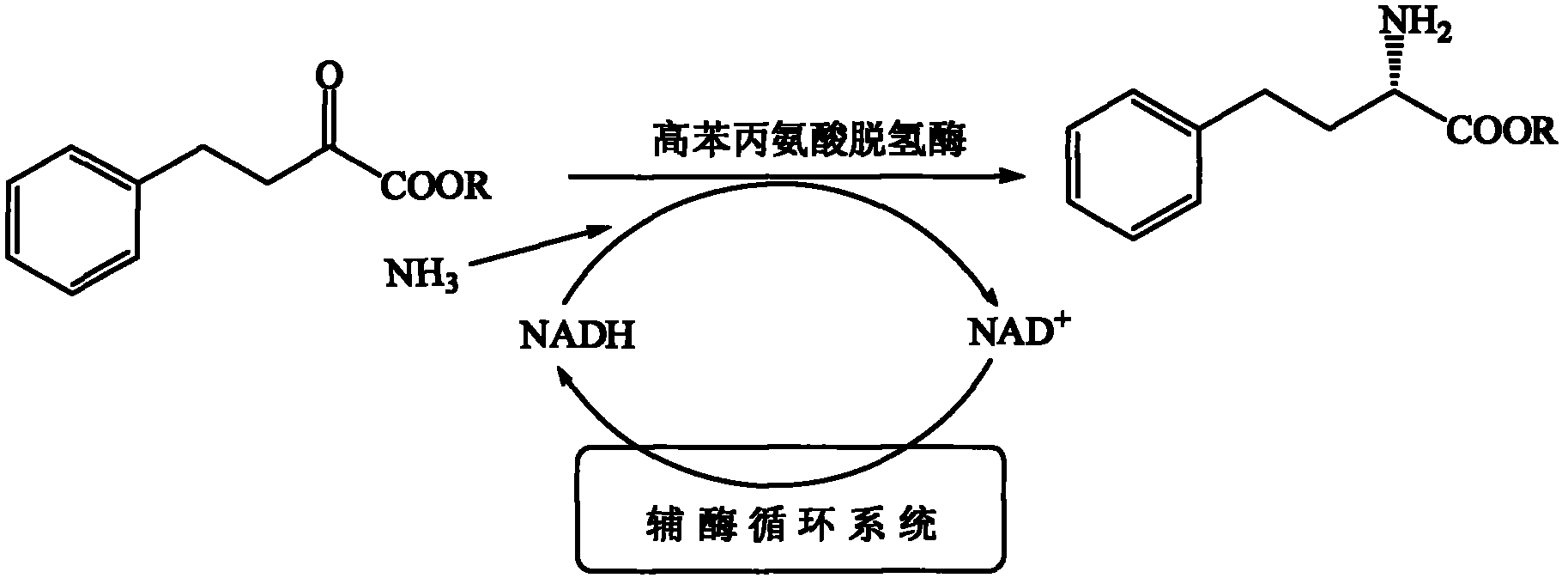
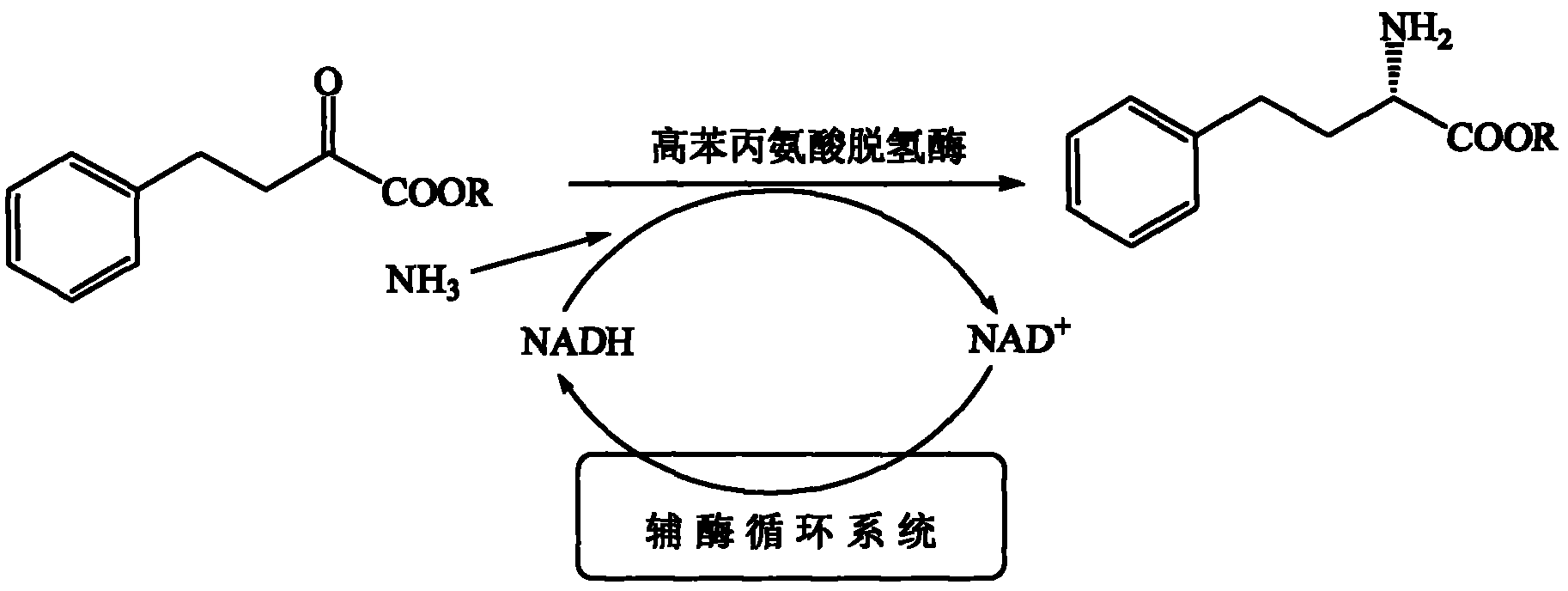
In enzymology, a phenylalanine dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction L-phenylalanine + H₂O + NAD⁺ ⇌ phenylpyruvate + NH₃ + NADH + H⁺ The 3 substrates of this enzyme are L-phenylalanine, H₂O, and NAD⁺, whereas its 4 products are phenylpyruvate, NH₃, NADH, and H⁺. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-NH2 group of donors with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor.
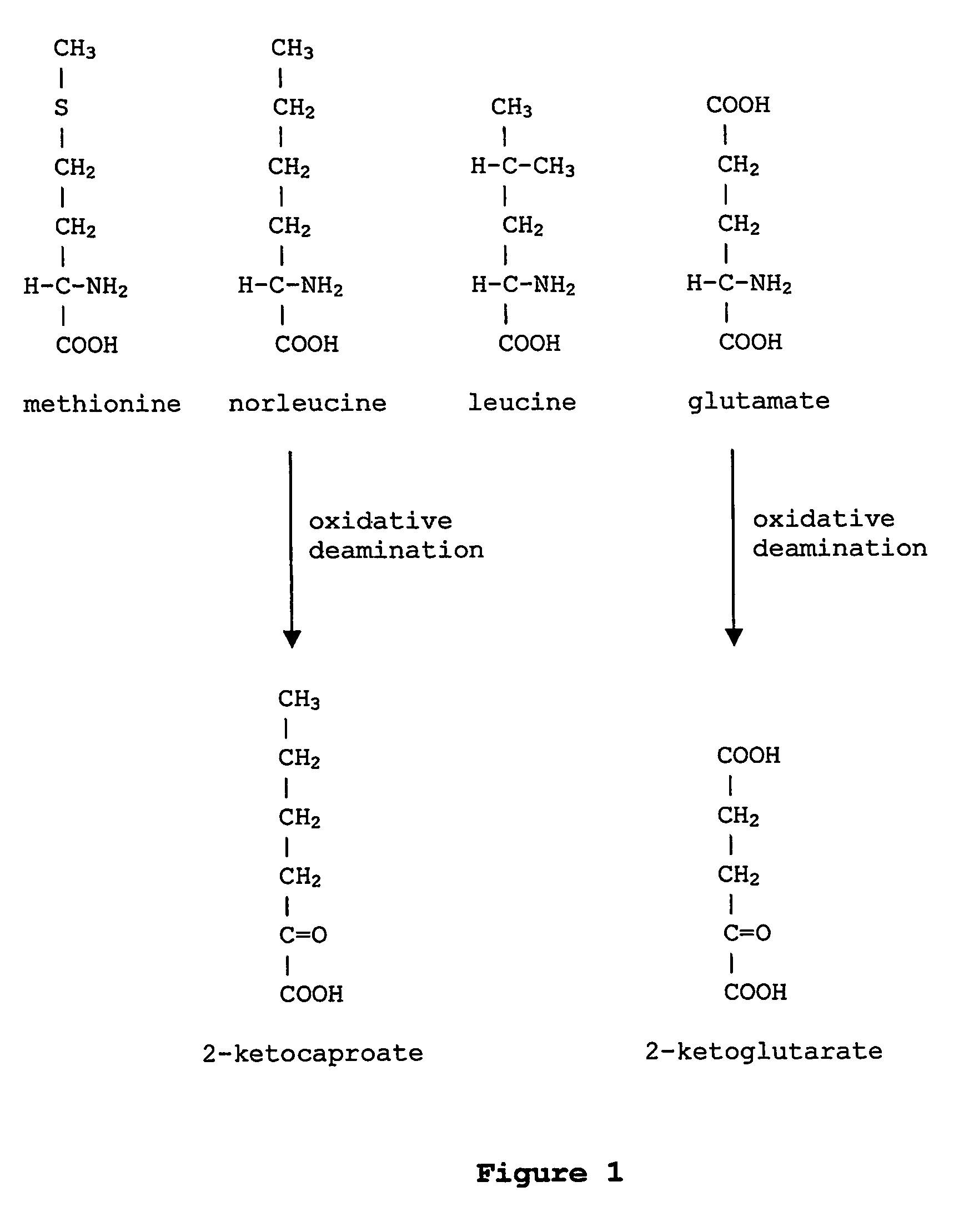
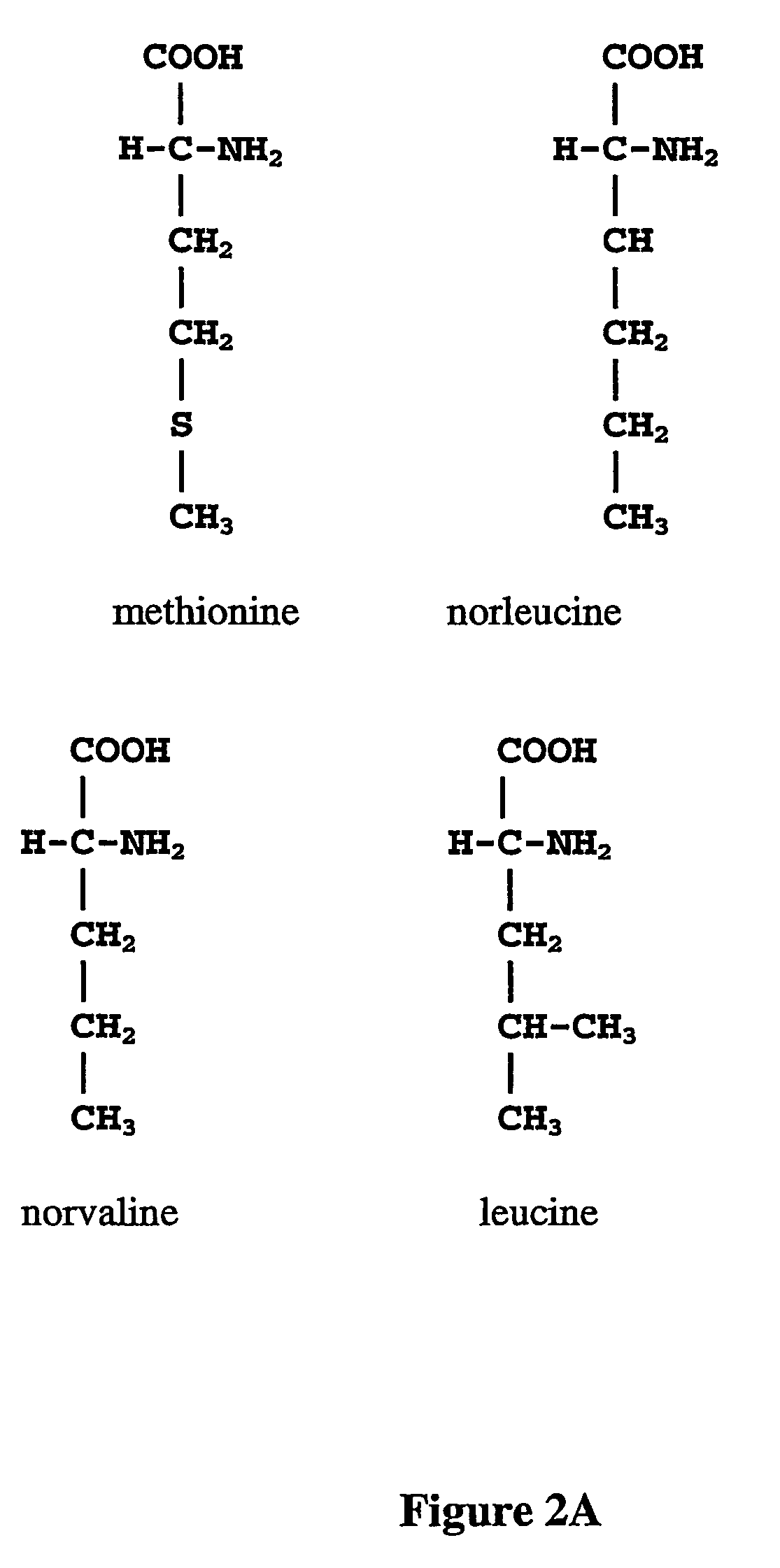
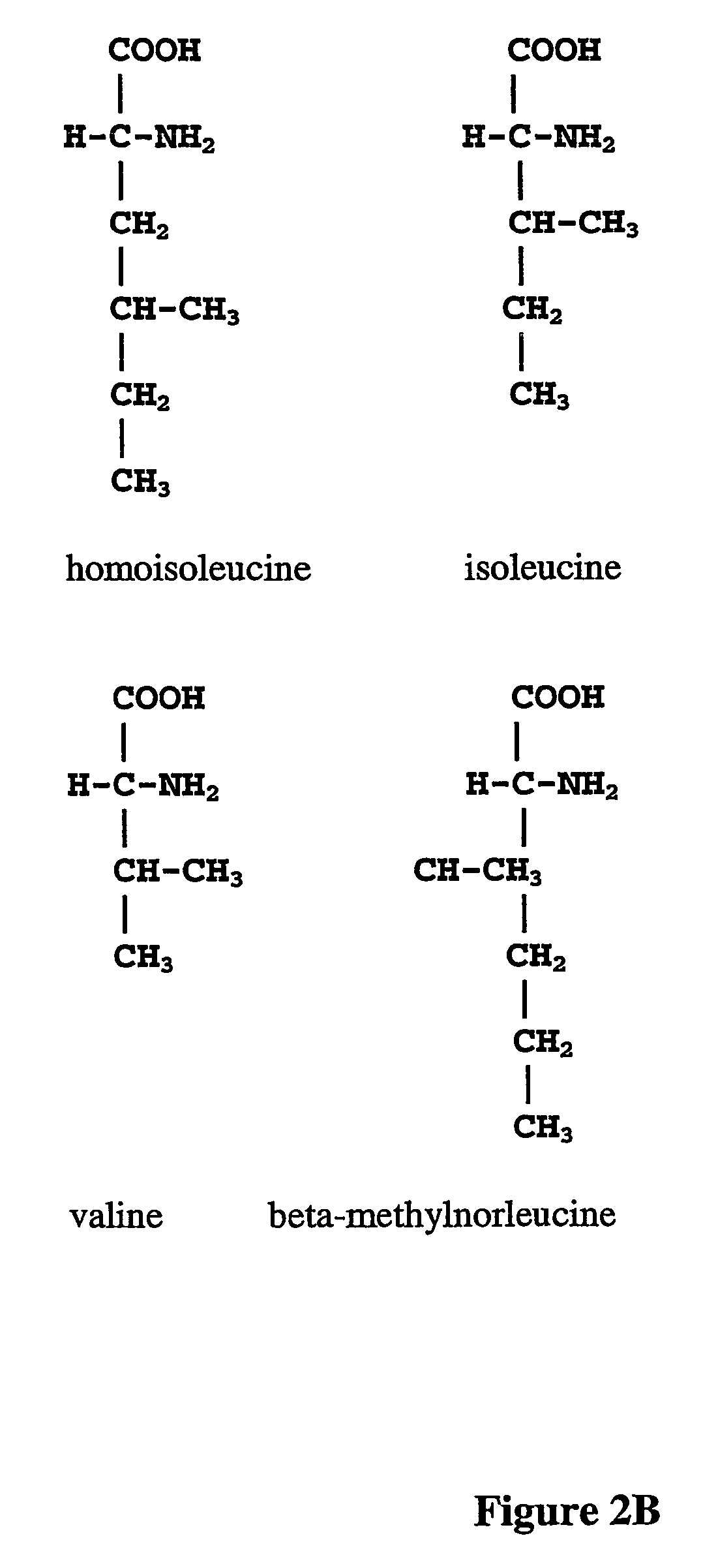
Prevention of incorporation of non-standard amino acids into protein
ActiveUS20070009995A1Cellular level is reducedReducing, or substantially eliminating, endogenous cellular levels of norleucineBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBeta-methylnorleucinePhenylalanine dehydrogenase
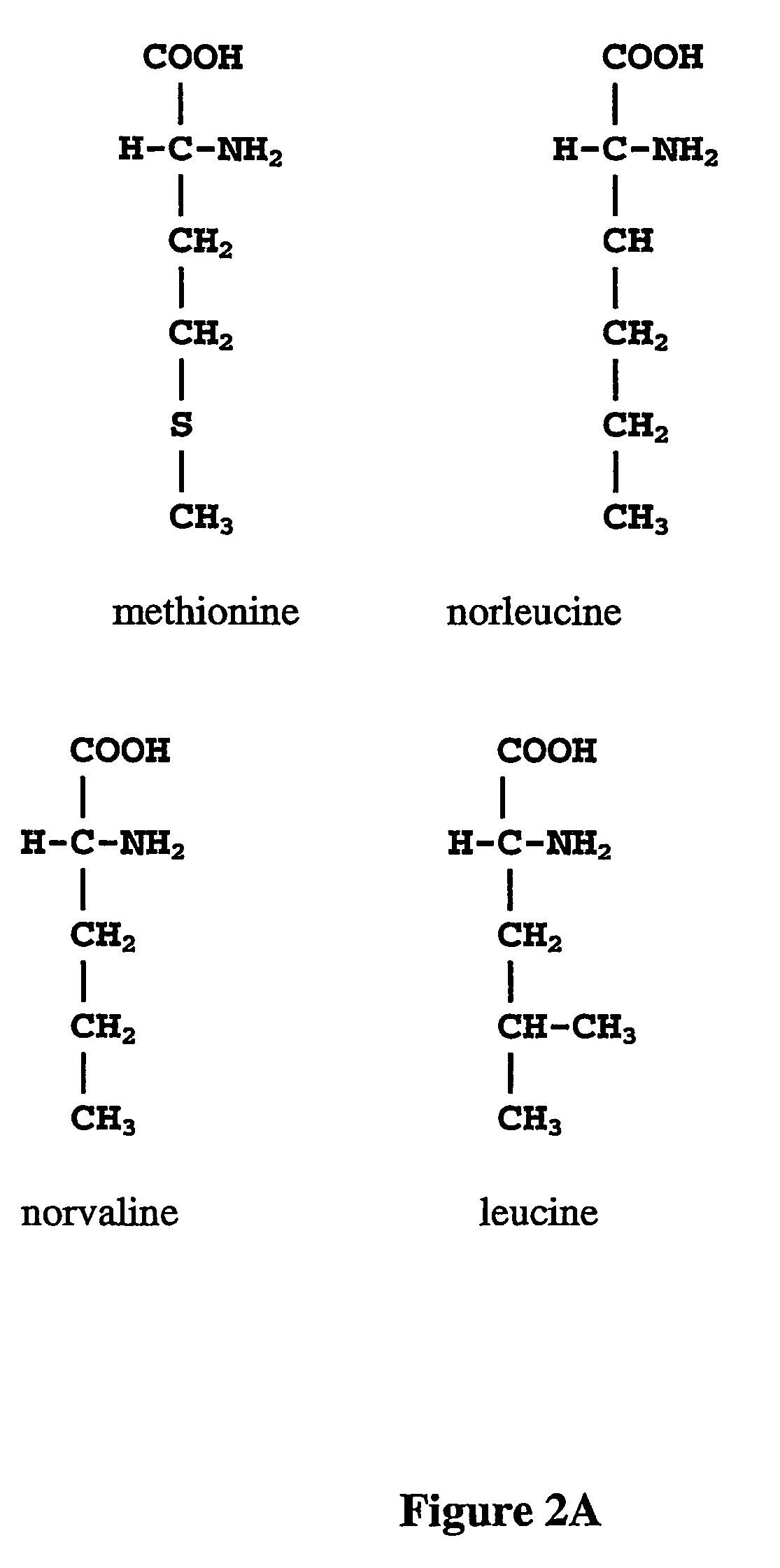
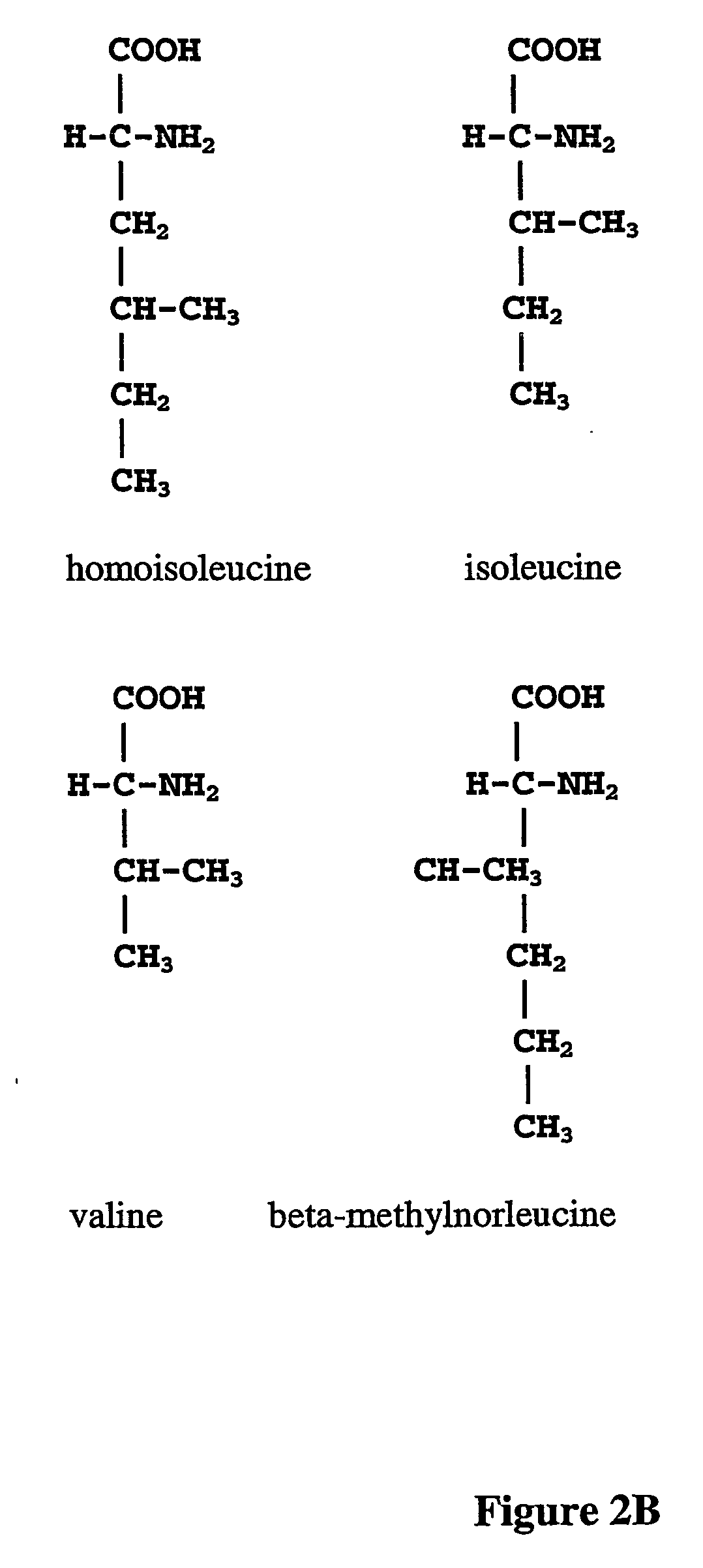
The instant invention is drawn to the methods and compositions necessary to provide recombinant proteins with a substantially reduced or eliminated content of norleucine or other non-standard amino acids. Various embodiments of the invention provide for the substantial elimination of the incorporation of non-standard amino acids into recombinant proteins by the co-expression or enhanced expression of a protein (or the enzymatically active portion thereof) capable of degrading norleucine or other non-standard amino acids, including norvaline, beta-methylnorleucine, and homoisoleucine. In certain particular embodiments of the invention, the norleucine is degraded by a glutamate dehydrogenase, a leucine dehydrogenase, a valine dehydrogenase, a phenylalanine dehydrogenase, a glutamate / leucine / phenylalanine / valine dehydrogenase, or an opine dehydrogenase. Also provided are the cells and DNA constructs for carrying out these methods.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Process for preparing dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors and intermediates therefor
InactiveUS20050260712A1Procedure of process can be improvedReduce processing timeSugar derivativesBacteriaPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseDipeptidyl peptidase
A process for production of cyclopropyl-fused pyrrolidine-based inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV is provided which employs a BOC-protected amine of the structure prepared by subjecting an acid of the structure to reduce amination by treating the acid with ammonium formate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dithiothreitol and partially purified phenylalanine dehydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase enzyme concentrate (PDH / FDH) and without isolating treating the resulting amine of the structure 2 with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate to form the BOC-protected amine.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Method for producing 2-phenylethanol under biological catalysis
ActiveCN106957878AImprove conversion rateIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseKetonic acids
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering and biotechnologies, and discloses a method for producing 2-phenylethanol under biological catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: adding wet cells of E.coli / Pdh, E.coli / Kdc and E.coli / ADH undergoing induced expression into a biological catalysis system taking L-phenylalanine as a substrate for performing a catalytic reaction; centrifuging after finishing the reaction; extracting supernatant to obtain the 2-phenylethanol. In the method, the L-phenylalanine is taken as the substrate, and recombinant escherichia coli transformed with a phenylalanine dehydrogenase gene, a 2-keto acid decarboxylase gene and an alcohol dehydrogenase gene is added into a reaction system for performing a biological deamination, decarboxylation and reduction three-step catalytic reaction in order to generate a product, namely, phenylethanol; a coenzyme, namely, NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is added once and can be recycled, excess ketonic acid and hydrogen sources do not need to be added, no unnecessary side products are generated, a high substrate transforming rate is achieved, and the yield of the phenylethanol is increased remarkably.
Owner:BOTON SHANGHAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Synthesis method of saxagliptin chiral intermediate
ActiveCN103555683AOrganic chemistryBacteriaPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
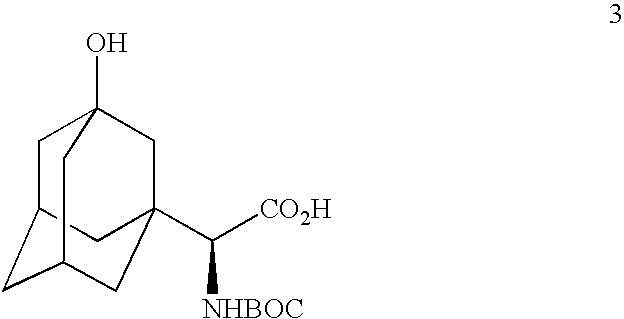
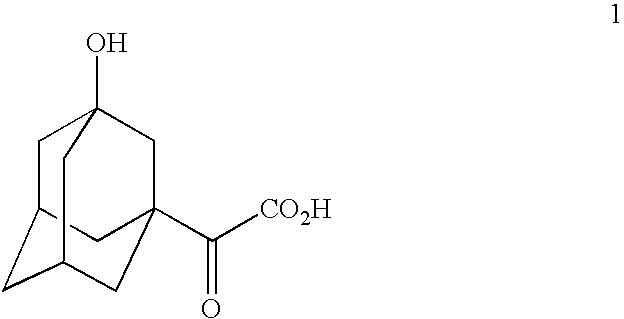
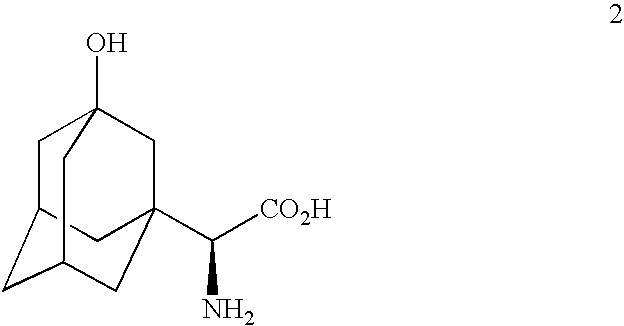
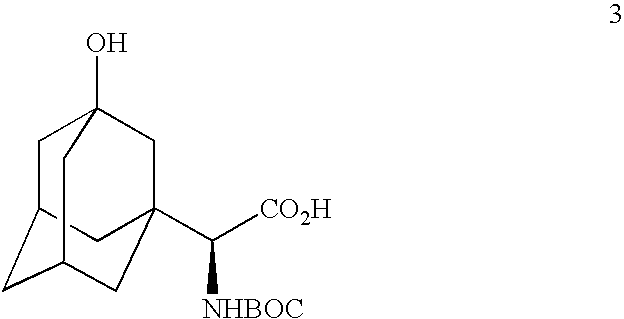
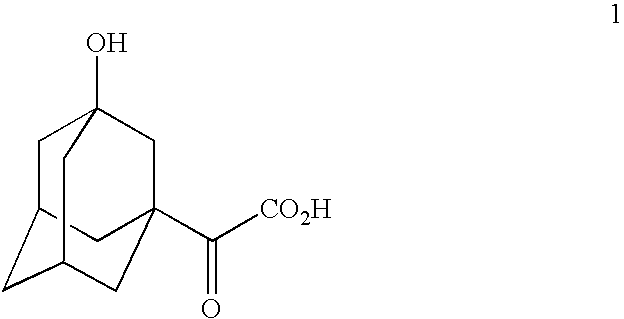
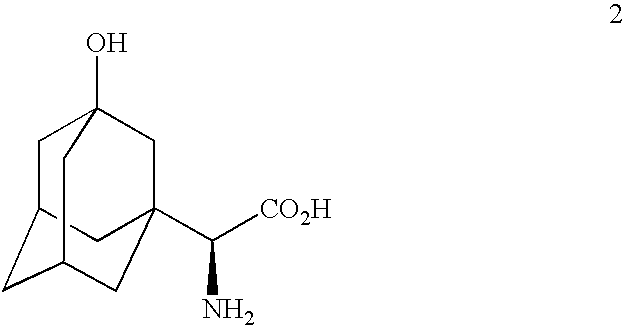
The invention provides a phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PDH) mutant derived from geobacillus, which is high in enzyme activity and thermal stability compared to wild PDH. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for catalytic synthesis of a saxagliptin chiral intermediate, namely (S)-N-t-butyloxycarbonyl-3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl-D-glycine (Boc-HAG) through the PDH mutant. According to the method provided by the invention, Boc-HAG can be directly prepared through a reaction in two steps, and e.e. (enantiomeric excess) value exceeds 99.9%; generation of side products can be reduced, yield of 95% can be achieved within 12 hours, catalysis time is greatly shortened, energy consumption is reduced and a post-treatment process is simplified.
Owner:弈柯莱(台州)药业有限公司
Method for preparing L-homophenylalanine
InactiveCN102373246AAchieve regenerationRealize repeated useChemical recyclingFermentationPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a process method for preparing single optical pure L-homophenylalanine by using L-homophenylalanine dehydrogenase as a biological catalyst. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: adding a substrate, ammonium formate, the L-homophenylalanine dehydrogenase and a formate dehydrogenase mediated coenzyme recycling and regenerating system into reaction liquid; after reacting under an oscillating or stirring condition, filtering from the reaction system to directly obtain an L-homophenylalanine product; and circulating the filtrate for the next reaction, wherein the reaction temperature is between 15 and 40 DEG C. The L-homophenylalanine is prepared by coordinating the L-homophenylalanine dehydrogenase with the coenzyme recycling and regenerating system and by adopting a simple filtering circulation process, wherein the substrate concentration reaches 560 mM; the NAD+ concentration of the required coenzyme is low; the coenzyme can be recycled and reused for many times, so that the cost of the coenzyme can be ignored; the yield excesses 95 percent; and important application value is achieved.
Owner:陈依军
Process for preparing dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors and intermediates therefor
A process for production of cyclopropyl-fused pyrrolidine-based inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV is provided which employs a BOC-protected amine of the structureprepared by subjecting an acid of the structureto reduce amination by treating the acid with ammonium formate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dithiothreitol and partially purified phenylalanine dehydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase enzyme concentrate (PDH / FDH) and without isolating treating the resulting amine of the structure 2with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate to form the BOC-protected amine.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Methods and Compositions for Treating Phenylketonuria
ActiveUS20170106054A1Reducing phenylalanine levelLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsCarbon-nitrogen lyasesIntestinal structurePhenylalanine dehydrogenase
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treating hyperphenylalaninemia (e.g., phenylketonuria) in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PheDH) polypeptide. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical formulations comprising PheDH for lowering the phenylalanine concentration in the subject (e.g., in the intestines and / or blood).
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
Method for realizing whole cell transformation to synthesize L-phenyllactic acid by genetic engineering strain
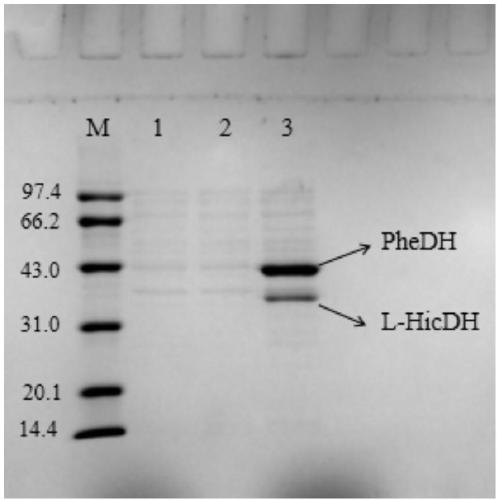
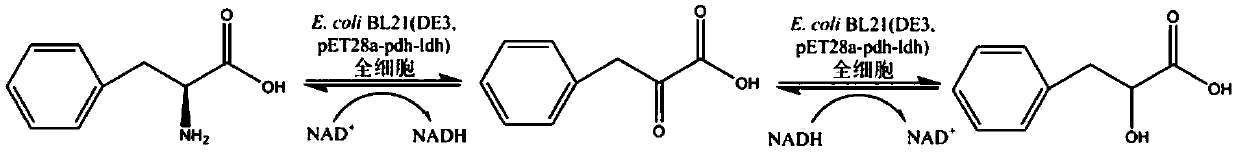
ActiveCN109593702ASolve the loop problemAdd lessBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseBio engineering
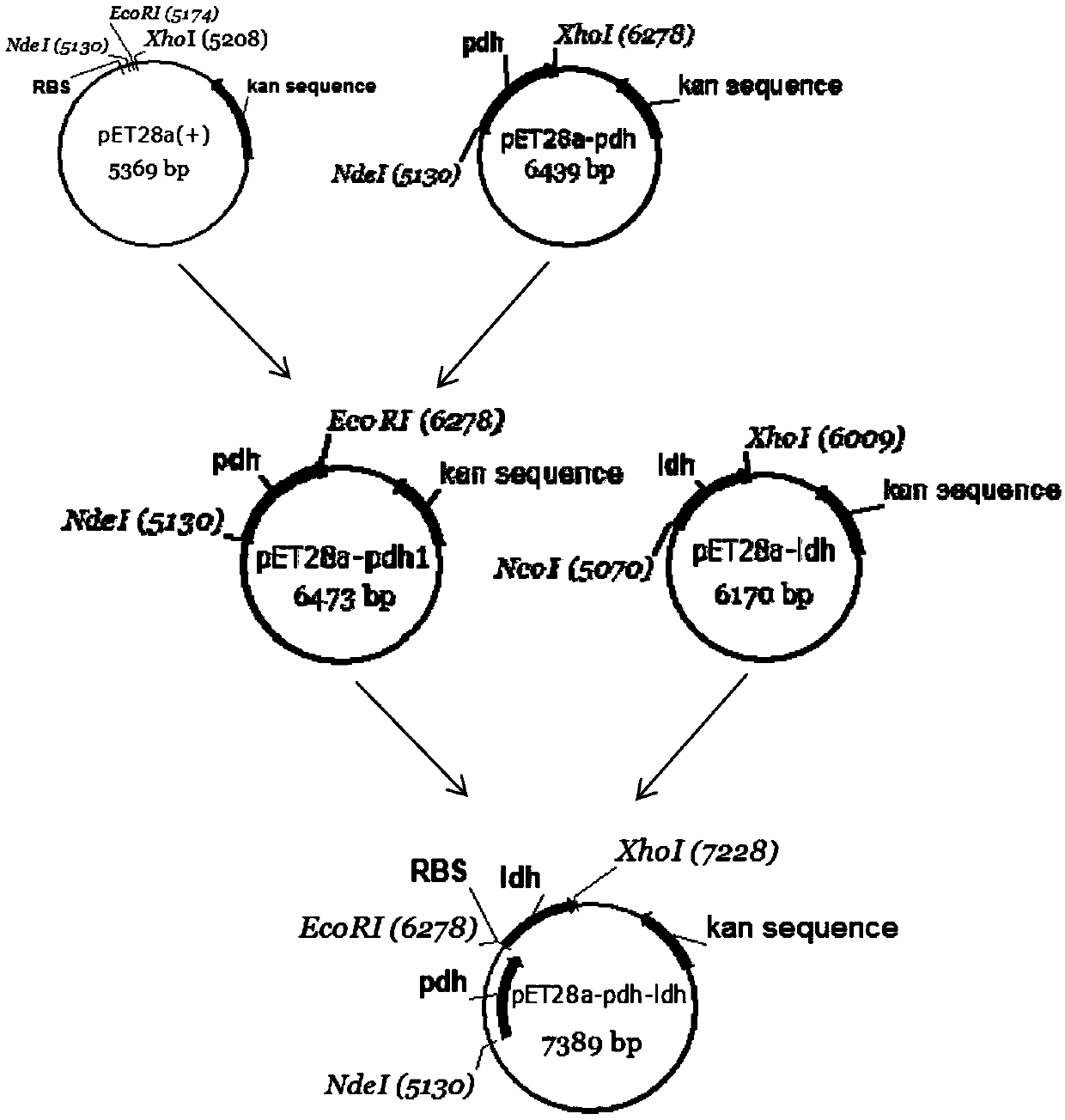
The invention discloses a method for realizing whole cell transformation to synthesize L-phenyllactic acid by a genetic engineering strain, in particular to a genetic engineering strain capable of co-expressing phenylalanine dehydrogenase and L-hydroxyisocaproic acid reductase to realize self-circulation of cofactors NAD<+> and NADH. The method for synthesizing L-phenyllactic acid by a whole celltransformation substrate L-phenylalanine belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. By using the whole cell transformation of a recombinant strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-pdh-ldh to synthesizeL-phenyllactic acid, the whole cell transformation rate can reach 88.9% to 95.6% under the action of an added surfactant. By adopting the method, the self-circulation of the cofactors NAD<+> and NADHis realized, the addition amount of the cofactors is reduced, the production cost is reduced, and the method has a broad application prospect in the field of industrial synthesis of L-phenyllactic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Quantitative detection kit and quantitative detection method for phenylalanine
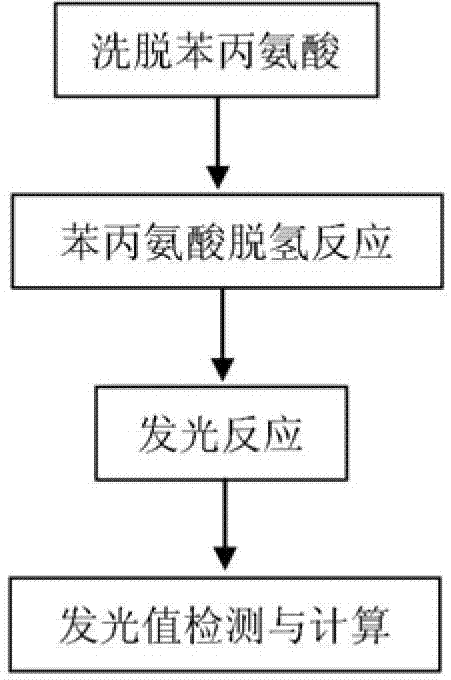
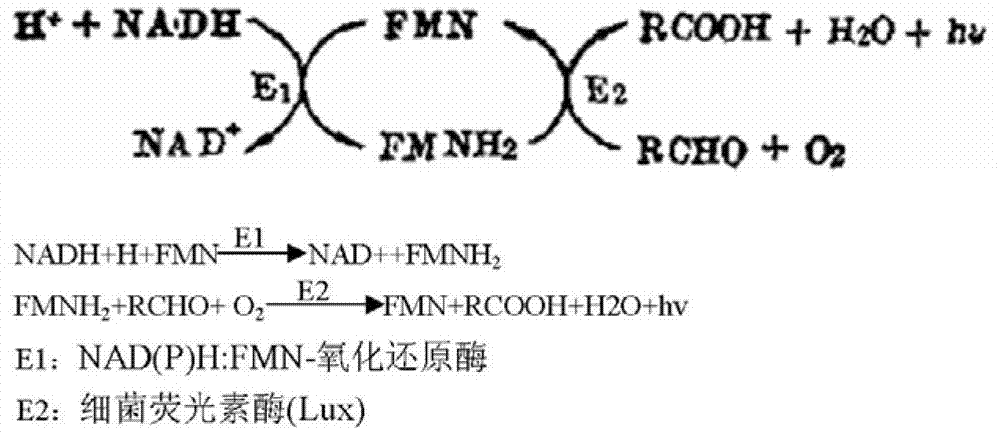
InactiveCN103196897AHigh detection sensitivityWide linear rangeChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhenylalanine dehydrogenaseLuminous intensity
The invention discloses a quantitative detection kit for of phenylalanine. The kit comprises phenylalanine dehydrogenase, coenzyme Beta-NAD, coenzyme FMN, long-chain aliphatic aldehyde, FMN-NADH oxidoreductase, bacteriofluorescein, a Gly-NaOH buffer with a concentration of 0 .05 mol / L and a pH value of 10.0 and a K2HPO4-KH2PO4 buffer with a concentration of 0.1 mol / L and a pH value of 7.0. The invention also discloses a quantitative detection method for phenylalanine. The method comprises the following steps: subjecting phenylalanine and Beta-NAD to a dehydrogenation reaction under the action of phenylalanine dehydrogenase so as to produce Beta-NADH; allowing Beta-NADH and FMN to undergo electron transfer under the action of bacteriofluorescein and FMN-NADH oxidoreductase so as to generate blue-green light; and calculating the content of phenylalanine in a sample according to luminous intensity. The detection method has the advantages of high sensitivity, a wide linear range, high precision and accuracy, short detection time, capacity of high-throughput detection, etc.
Owner:BEIJING YUANDE BIO MEDICAL ENG
Method for immobilization of phenylalanine dehydrogenase by chemical reduced graphene oxide
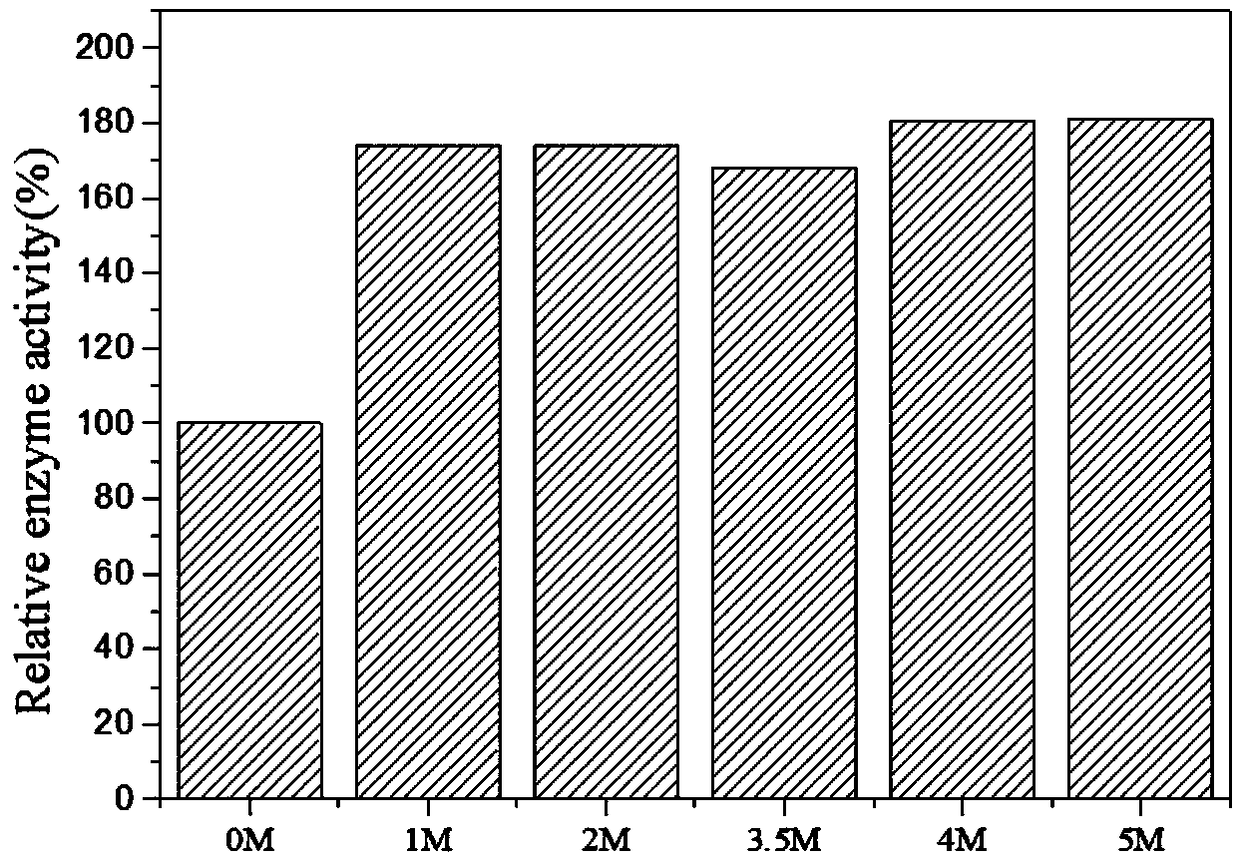
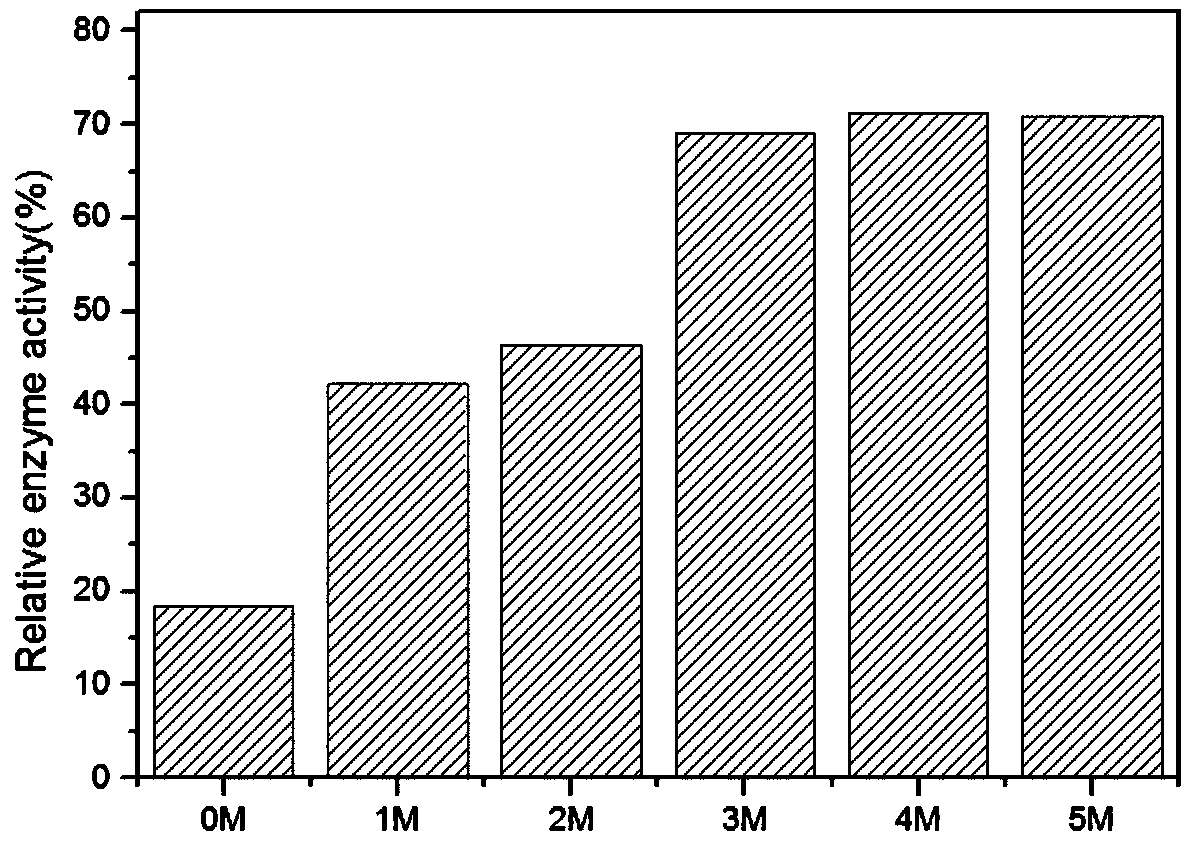
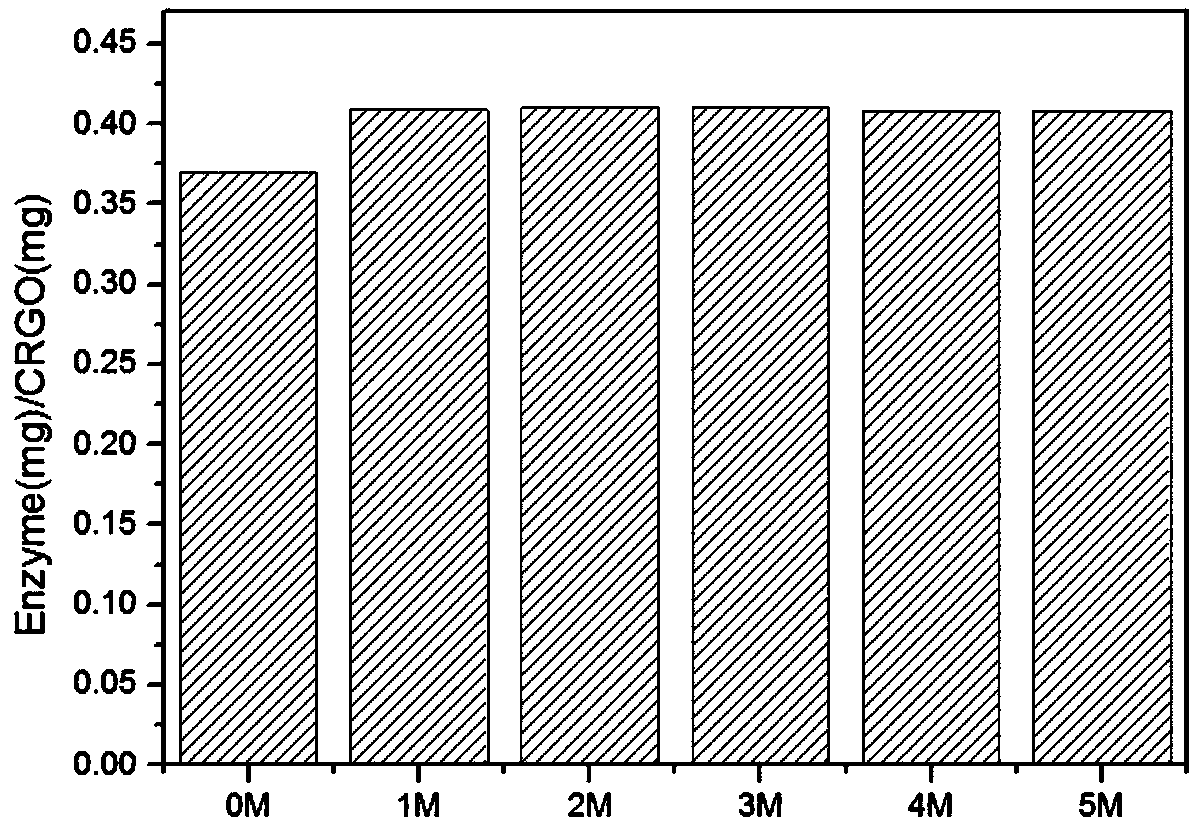
InactiveCN109456960ALess structural interferenceEnables controlled immobilizationMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for immobilization of phenylalanine dehydrogenase by chemical reduced graphene oxide, and belongs to the technical field of immobilized enzyme. The chemical reduced graphene oxide is stable in structure, is good in biocompatibility, and is a good enzyme immobilization carrier. The surface of the chemical reduced graphene oxide with a sheet-layer structure is lack of groups such as an epoxy group, a carbonyl group and a carboxyl group, is great in load area, and has hydrophobicity. The immobilization of phenylalanine dehydrogenase by the chemical reduced graphene oxide mainly has a hydrophobic effect; and in an immobilization process, the degree of reduction and salt concentration of the chemical reduced graphene oxide have influences on immobilization of enzyme by the chemical reduced graphene oxide. The obtained immobilized phenylalanine dehydrogenase is obviously improved in pH stability and repeated use stability, and meanwhile, has relatively high enzyme activity recovery rate. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the process is simple; the preparation conditions are mild; and the immobilization rate is high.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Beta-cypermethrin degrading bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a Beta-cypermethrin degrading bacterium. The bacterial strain is bacillus licheniformis B-1; the GenBank accession number of 16S rDNA is HQ009796. The strain is from soil of atea garden, and is obtained through Beta-cypermethrin concentration gradient domestication, preliminary screening, separation and purification and secondary screening. The bacterial colony edge of thestrain is reddish color; the center is white; the surface is dry and has drapes; the edge is irregular; the single thallus is in a rod shape and is gram positive; the spore is elliptical and is mesic; the sporocyst is slightly inflated; glucose, arabinose, xylose and mannite are positive; gelatin and starch can be hydrolyzed; phenylalanine dehydrogenase and yolk lecithin enzyme are negative; theanaerobic growth can be realized. Under the proper conditions, the degrading rate of the strain on the Beta-cypermethrin with the concentration being 16.5mu g / mL in a culture medium is 94.12 percent.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Phenylalanine dehydrogenase for catalytic preparation of non-natural amino acid and application of phenylalanine dehydrogenase
ActiveCN110592037AAchieve recyclingEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationBacillus nanhaiensisPhenylalanine dehydrogenase
The invention discloses phenylalanine dehydrogenase for catalytic preparation of non-natural amino acid and application of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase. Amino acid sequences of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase are shown in SEQ ID NO.01, SEQ ID NO.02 and SEQ ID NO.03 or SEQ ID NO.04. According to the phenylalanine dehydrogenase, the phenylalanine dehydrogenase obtained from a marine strain Bacillus nanhaiensis (CGMCC NO.8969) is subjected to C terminal area modification, the obtained variant amino acid dehydrogenase can catalyze a series of non-natural amino acid substrates, the ability of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase to catalyze the non-natural amino acid with large hydrophobic groups is improved, and a substrate spectrum is expanded.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Amino acid dehydrogenase and application thereof
ActiveCN110607289AExpand catalytic functionEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationBacillus nanhaiensisPhenylalanine dehydrogenase
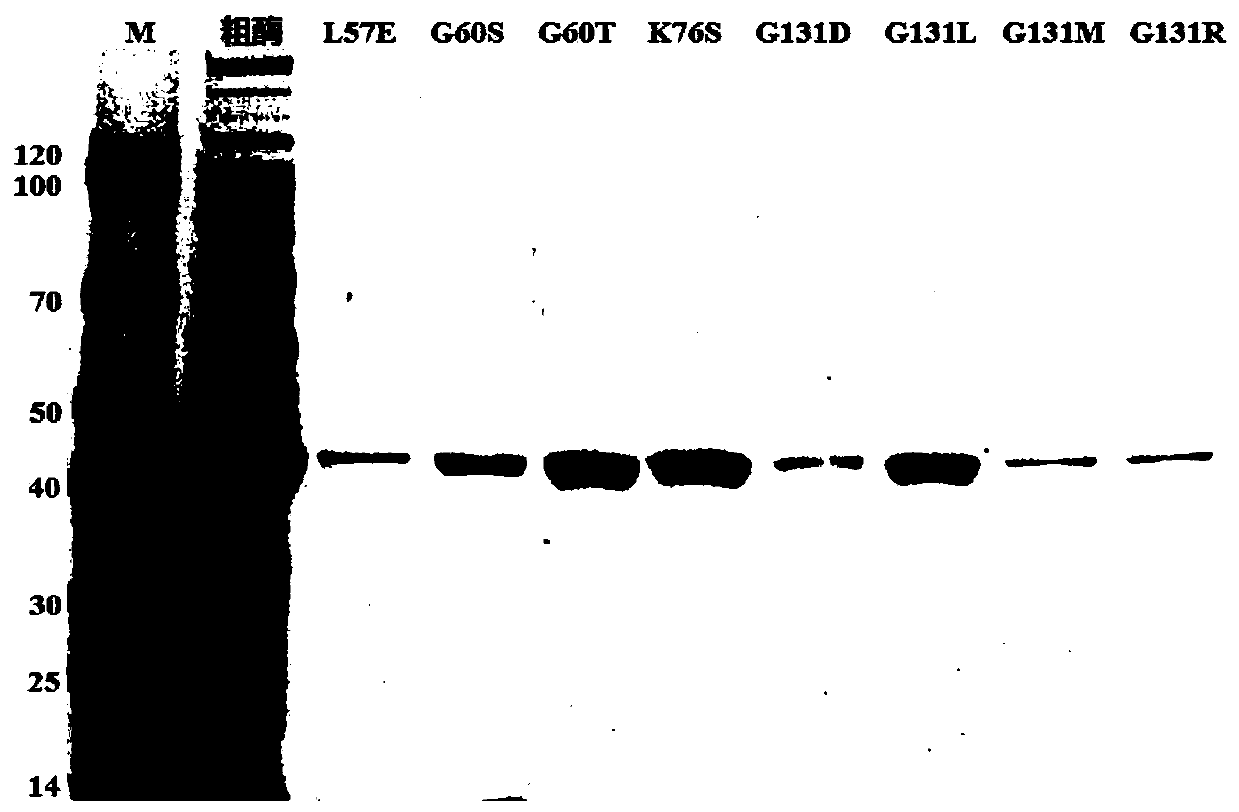
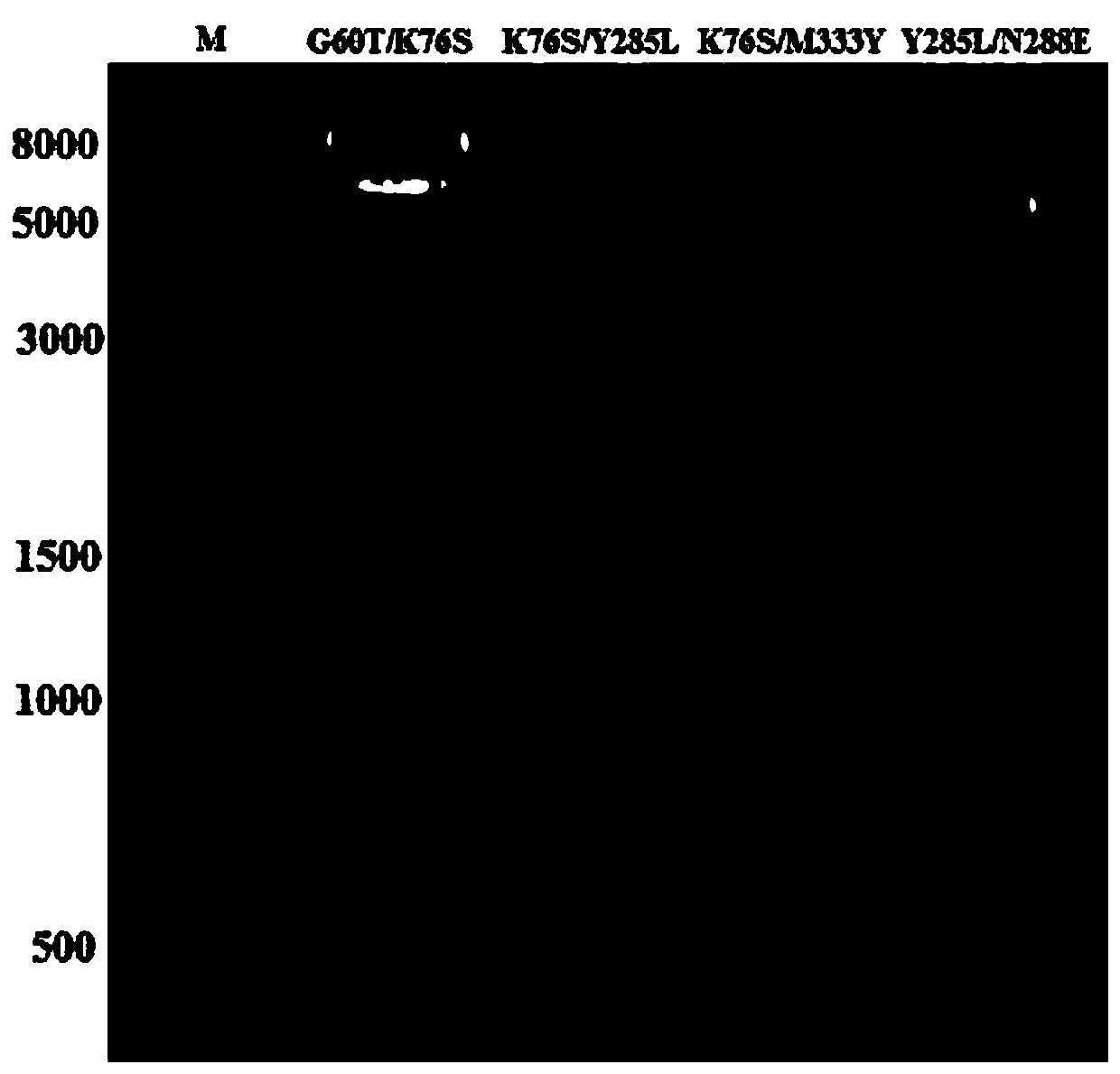
The invention discloses amino acid dehydrogenase and application thereof. The amino acid dehydrogenase is obtained by mutating amino acid dehydrogenase shown as SEQ ID NO.01, mutation includes at least one of the following: L at the 57 bit is mutated into E, G at the 60 bit is mutated into S or T, K at the 76 bit is mutated into S, Y at the 285 bit is mutated into L or M, N at the288 bit is mutated into E, and M at the 333<rd> bit is mutated into D or R. By modifying molecules of phenylalanine dehydrogenase obtained from a marine strain, namely bacillus nanhaiensis, a substrate binding pocket of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase is remodeled, large steric hindrance substrates can be accommodated, meanwhile, the substrates are brought closer to coenzyme, thus the amino acid dehydrogenase obtains catalytic activity to the large steric hindrance substrates, and the catalytic function of the amino acid dehydrogenase is expanded for the biosynthetic series of non-naturalamino acids with large steric hindrance hydrophobic side chains.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Synthetic method of L-heterocyclic amino acid and pharmaceutical composition with L-heterocyclic amino acid
ActiveCN103276025AThe synthesis process is simpleAdapt to industrial mass productionOrganic active ingredientsFermentationAlkyl transferPhenylalanine dehydrogenase
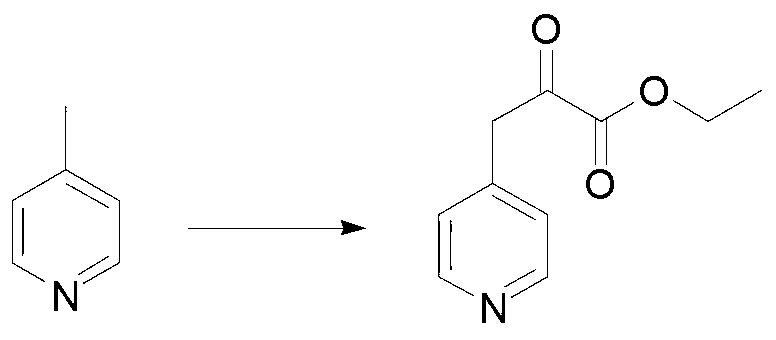
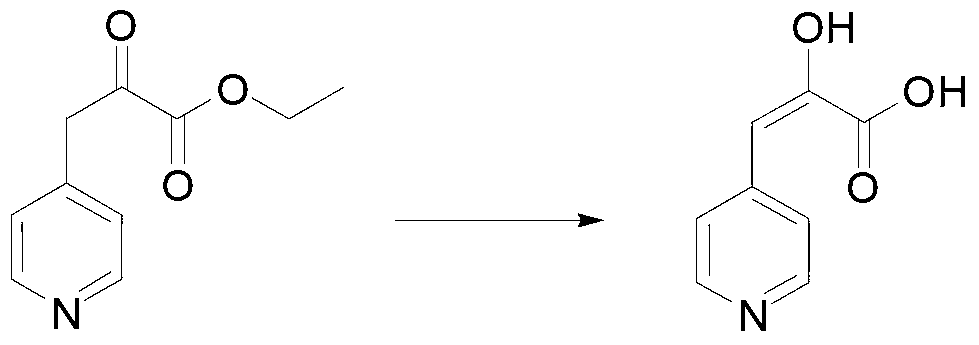
The invention provides a synthetic method of L-heterocyclic amino acid and a pharmaceutical composition with L-heterocyclic amino acid. The synthetic method comprises the steps that A, heterocyclic ketonic acid is prepared, wherein heterocycle in heterocyclic ketonic acid is selected from any one of pentabasic single heterocycle, hexabasic single heterocycle, heptabasic single heterocycle, pentabasic alkylation single heterocycle, hexabasic alkylation single heterocycle and heptabasic alkylation single heterocycle, and a structural formula of ketonic acid base in heterocyclic ketonic acid is as shown in the specification, and is positioned in any carbon position of heterocycle; and B, heterocyclic ketonic acid is mixed with ammonium formate, phenylalanine dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase and coenzyme NAD<+> to perform a reduced amination reaction to generate L-heterocyclic amino acid, wherein an amino acid sequence of phenylalanine dehydrogenase is SEQ ID No. 1 (sequence identifier number 1). Since special phenylalanine dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase and coenzyme NAD<+> are used for allowing heterocyclic ketonic acid to perform the reduced amination reaction to generate L-heterocyclic amino acid, the raw material conversion rate is high and the chiral selectivity is high.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN +4
Phenylalanine dehydrogenase as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111893098AMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseOrganic solvent
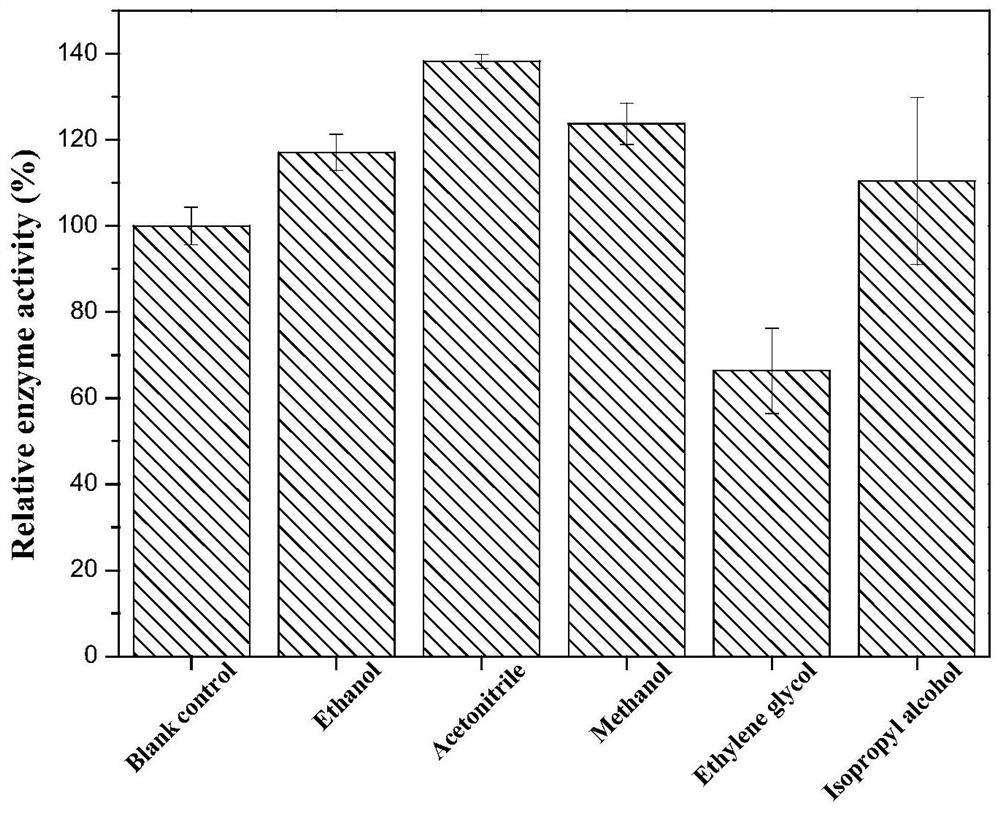
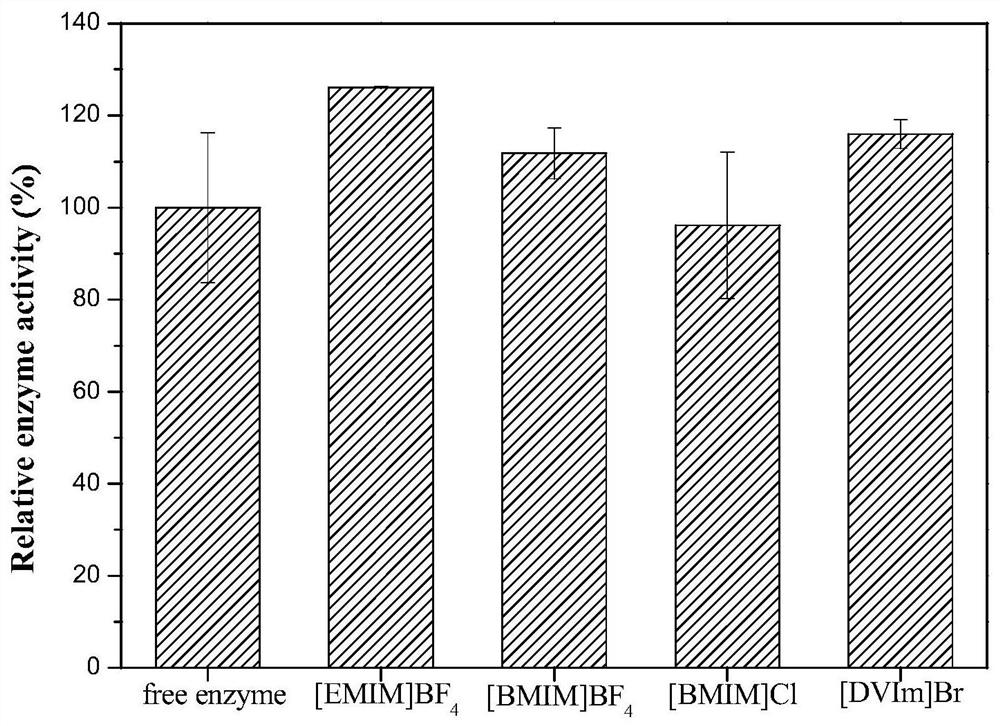
The invention discloses phenylalanine dehydrogenase as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to strain culture, enzyme expression, separation and purification, detection ofionic liquid tolerance and organic solvent system tolerance of enzymes and the like. According to the invention, high-stability phenylalanine dehydrogenase which is resistant to an organic solvent and an ionic liquid and is required by industrial biological catalysis application is obtained. The phenylalanine dehydrogenase has the characteristics of good stress resistance and high stability in anon-aqueous phase system, can effectively prolong the half-life period and improve the catalytic efficiency in industrial production, achieves the purpose of reducing the production cost, and has important industrial application value.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
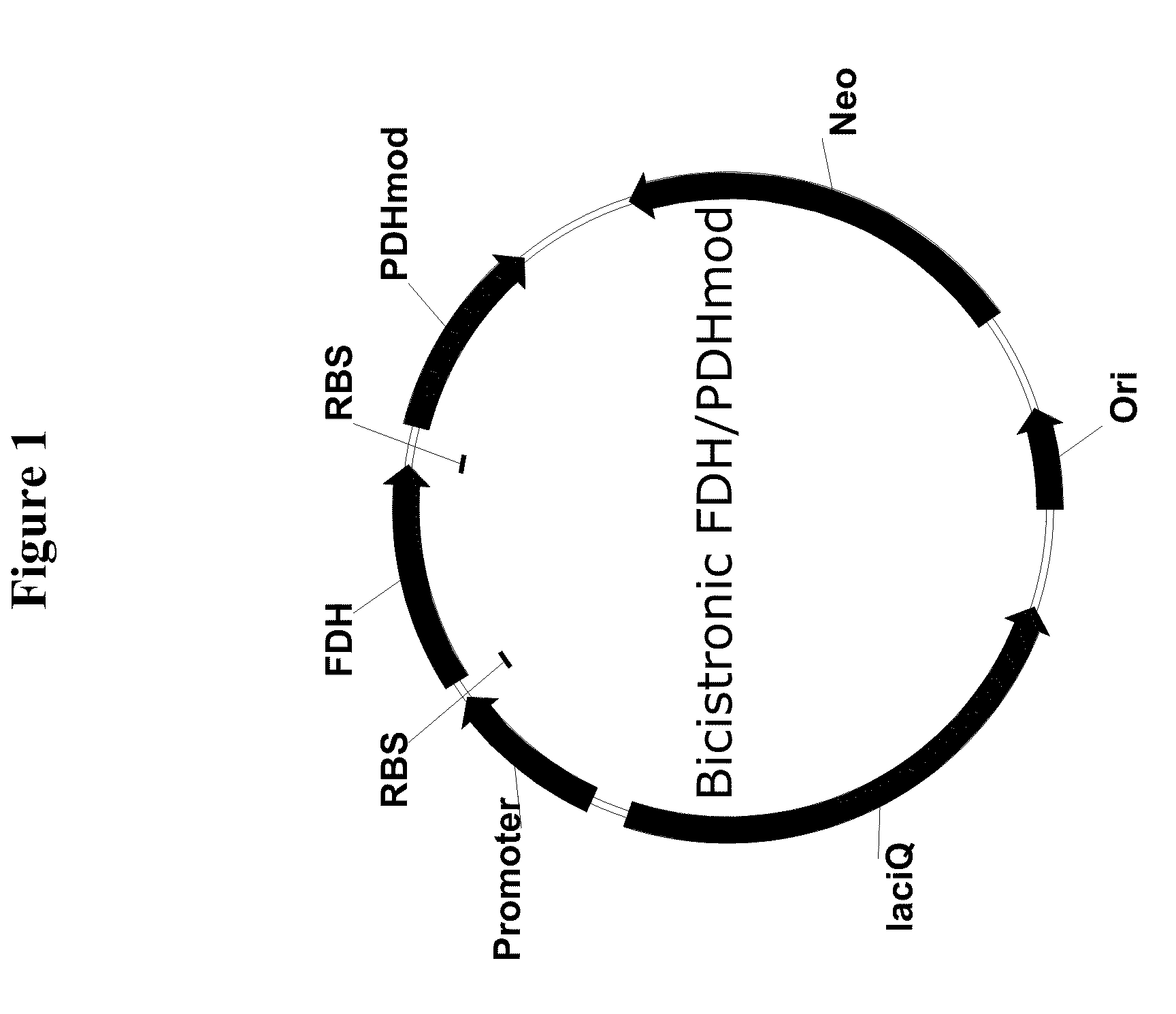
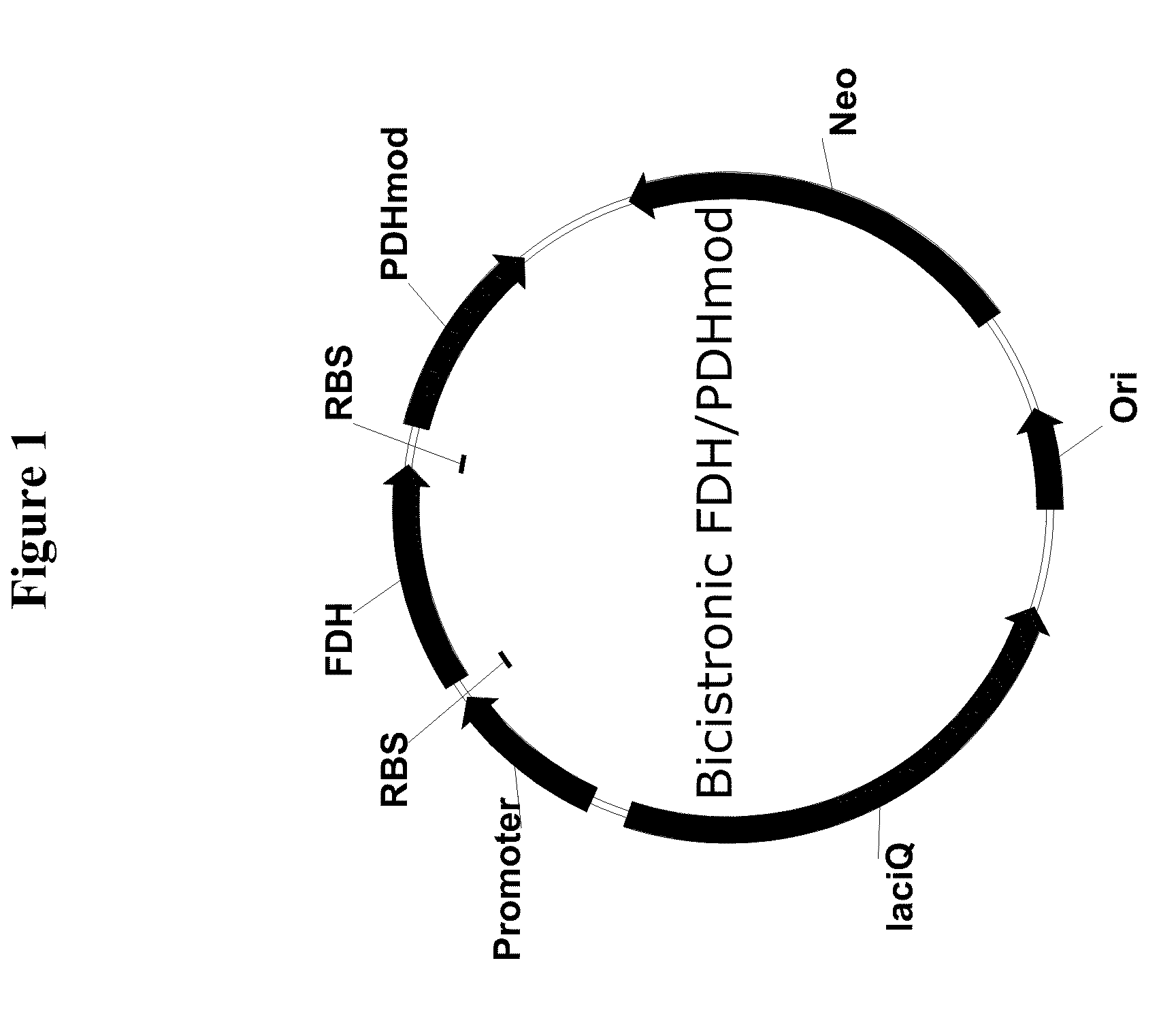
Genetically stable plasmid expressing PDH and FDH enzymes
Bi-cistronic plasmids used for the expression of formate dehydrogenase (FDH) and modified phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PDHmod) are provided.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Prevention of incorporation of non-standard amino acids into protein
ActiveUS8603781B2Reducing, or substantially eliminating, endogenous cellular levels of norleucineLower Level RequirementsBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBeta-methylnorleucinePhenylalanine dehydrogenase
The instant invention is drawn to the methods and compositions necessary to provide recombinant proteins with a substantially reduced or eliminated content of norleucine or other non-standard amino acids. Various embodiments of the invention provide for the substantial elimination of the incorporation of non-standard amino acids into recombinant proteins by the co-expression or enhanced expression of a protein (or the enzymatically active portion thereof) capable of degrading norleucine or other non-standard amino acids, including norvaline, beta-methylnorleucine, and homoisoleucine. In certain particular embodiments of the invention, the norleucine is degraded by a glutamate dehydrogenase, a leucine dehydrogenase, a valine dehydrogenase, a phenylalanine dehydrogenase, a glutamate / leucine / phenylalanine / valine dehydrogenase, or an opine dehydrogenase. Also provided are the cells and DNA constructs for carrying out these methods.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
A mutant of amine dehydrogenase and its application in the synthesis of chiral amines and aminoalcohols
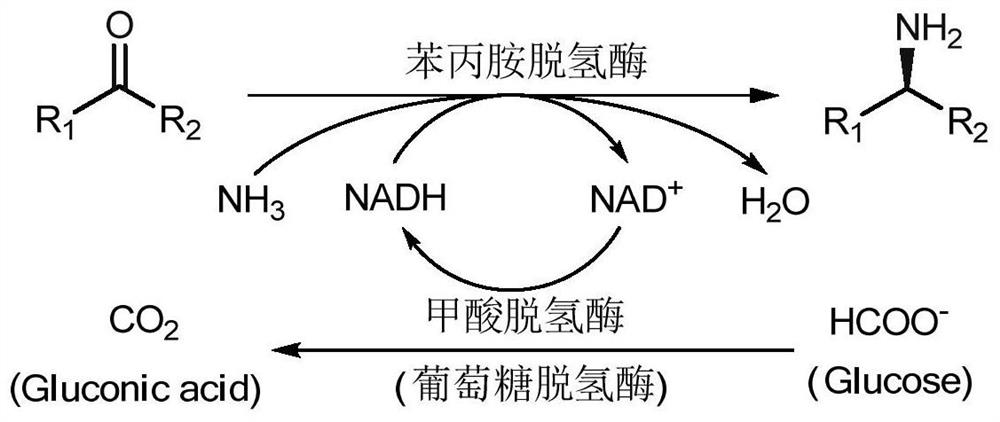
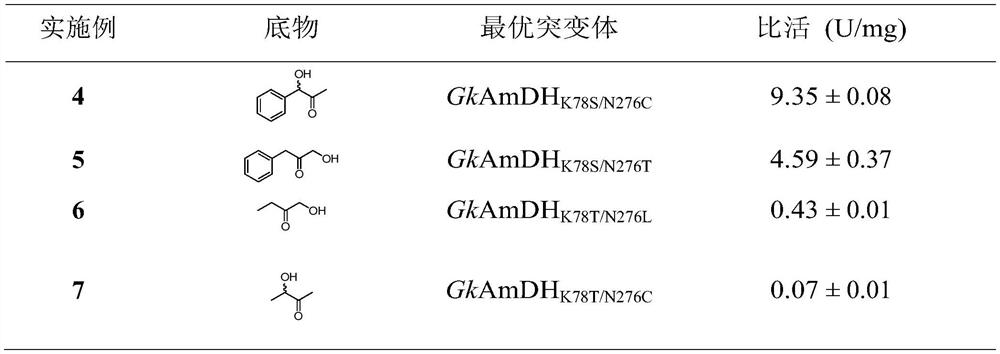
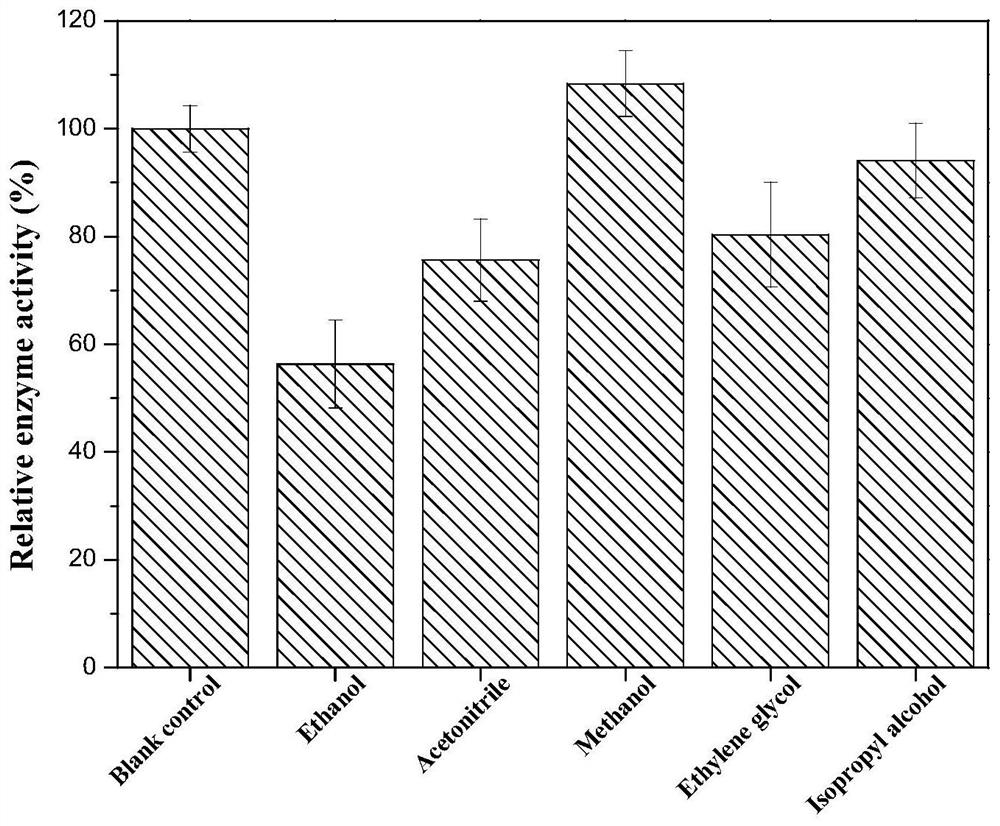
ActiveCN110628739BImprove catalytic performanceHigh optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseAmphetamine use
The invention relates to an amine dehydrogenase mutant and its application in the synthesis of chiral amine and aminoalcohol. Specifically, the present invention discloses an amphetamine dehydrogenase mutant and its corresponding amino acid sequence obtained by molecular engineering of Geobacillus kaustophilus phenylalanine dehydrogenase, and the amphetamine The use of dehydrogenase mutants in the synthesis of chiral amines and chiral amino alcohols by asymmetric reductive amination of latent chiral carbonyl compounds. Compared with the synthesis methods of other chiral amines and chiral amino alcohols, the ammonia donor used in the present invention is cheap ammonia water, the formed by-product is only clean water, and the optical purity of the products is >99%, so it represents A biosynthesis method with mild reaction, high stereoselectivity, and environmental protection has been developed, which has a good application prospect in the actual production of chiral amines and chiral amino alcohols.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
A kind of phenylalanine dehydrogenase and its preparation method and application
The invention discloses a phenylalanine dehydrogenase and a preparation method and application thereof. It involves strain culture, enzyme expression, separation and purification, detection of enzyme ionic liquid tolerance and organic solvent system tolerance, etc. The present invention obtains an organic solvent-resistant and ionic liquid-resistant high-stability phenylalanine dehydrogenase required for industrial biocatalysis applications. The enzyme has good stress resistance and relatively stable stability in a non-aqueous phase system. High characteristics can effectively prolong the half-life in industrial production, improve the catalytic efficiency, and achieve the purpose of reducing production costs, and have important industrial application value.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing saxagliptin chiral intermediate by enzyme-catalyzed asymmetric transamination reaction
The invention discloses a method for preparing a saxagliptin chiral intermediate through an enzyme-catalyzed asymmetric transamination reaction. The present invention couples phenylalanine dehydrogenase (phenylalanine dehydrogenase, PDH) and glycerol dehydrogenase (Glycerol dehydrogenase, GDH) in an aqueous solution containing amino groups, using saxagliptin intermediate and glycerol as substrates, and at the same time Generate 1,3-dihydroxyacetone (DHA) and saxagliptin chiral intermediates, and realize the cyclic regeneration of coenzyme NAD+, realizing the efficient synthesis of saxagliptin chiral intermediates.
Owner:福州基石医药科技有限公司
Genetically Stable Plasmid Expressing PDH and FDH Enzymes
Bi-cistronic plasmids used for the expression of formate dehydrogenase (FDH) and modified phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PDHmod) are provided.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant with improved substrate specificity and application of phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant
ActiveCN110607290AIncreased substrate specificityReduced substrate specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPhenylpyruvic acidGlycine
The invention discloses a phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant with improved substrate specificity and application of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant and belongs to the technical field of enzymeengineering and microorganism engineering. The substrate specificity of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant disclosed by the invention upon phenylpyruvic acid is remarkably improved when being compared with that of a wild type, and meanwhile, the specificity of the mutant upon L-norvaline, L-leucine, L-valine and L-phenylglycine is remarkably degraded, so that when the phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant disclosed by the invention is applied to detection on the content of phenylalanine in samples such as blood, interference of other amino acids can be eliminated, the detection sensitivity can be improved, and the mutant has very good application prospects in preparing phenylalanine detection kits and phenylketonuria detection kits.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of phenylalanine dehydrogenase for catalyzing the preparation of unnatural amino acid and its application
ActiveCN110592037BAchieve recyclingEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationBacillus nanhaiensisPhenylalanine dehydrogenase
The invention discloses phenylalanine dehydrogenase for catalytic preparation of non-natural amino acid and application of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase. Amino acid sequences of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase are shown in SEQ ID NO.01, SEQ ID NO.02 and SEQ ID NO.03 or SEQ ID NO.04. According to the phenylalanine dehydrogenase, the phenylalanine dehydrogenase obtained from a marine strain Bacillus nanhaiensis (CGMCC NO.8969) is subjected to C terminal area modification, the obtained variant amino acid dehydrogenase can catalyze a series of non-natural amino acid substrates, the ability of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase to catalyze the non-natural amino acid with large hydrophobic groups is improved, and a substrate spectrum is expanded.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Escherichia coli biochemistry identification method
InactiveCN101140277ASimplify identification proceduresLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEscherichia coliPhenylalanine dehydrogenase
A colon bacillus biochemical authentication method belongs to the technical field of microbiology omits urease, phenyl alanine dehydrogenase and xylose from prior colon bacillus authentication items on the premise of having no impact on authentication accuracy and simplifies the biochemical authentication method, thus reducing authentication procedures, saving cost and particularly adapting to authentication of large-scale colon bacillus.
Owner:NATIONAL MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENTRE
Methods and compositions for treating phenylketonuria
ActiveUS10792339B2Lower Level RequirementsReducing phenylalanine levelCarbon-nitrogen lyasesOrganic active ingredientsPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseBiochemistry
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treating hyperphenylalaninemia (e.g., phenylketonuria) in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of a phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PheDH) polypeptide. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical formulations comprising PheDH for lowering the phenylalanine concentration in the subject (e.g., in the intestines and / or blood).
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
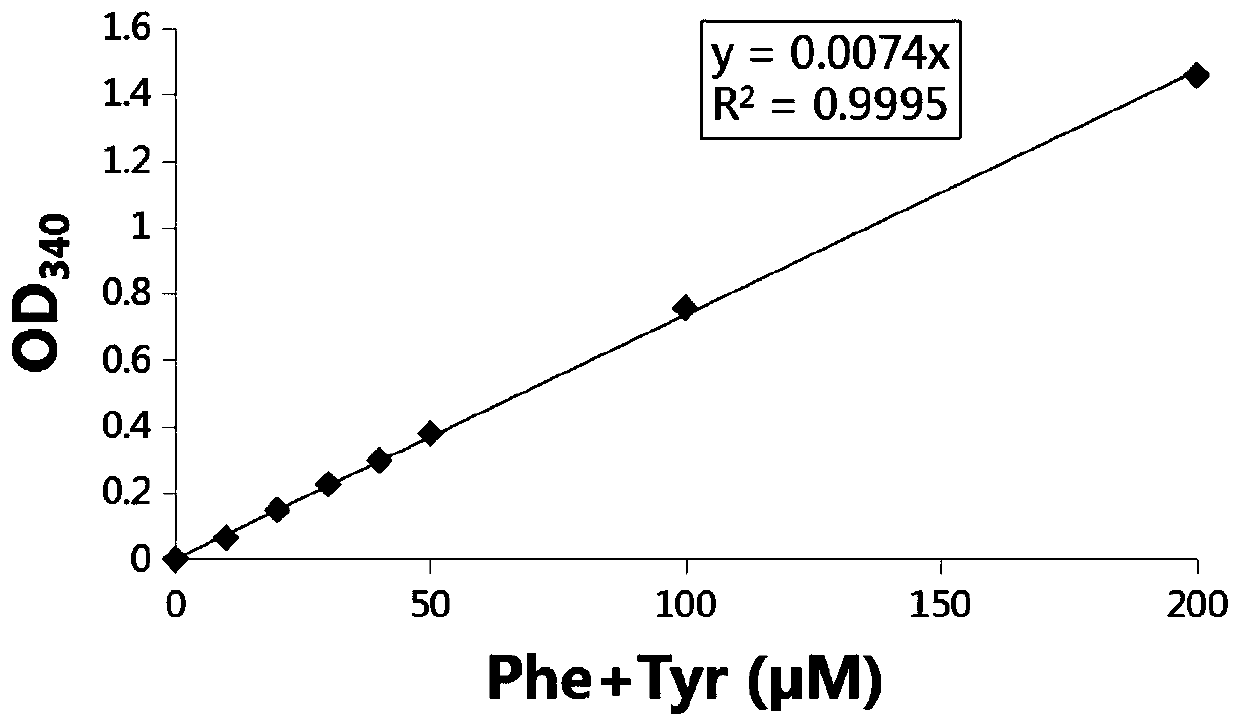
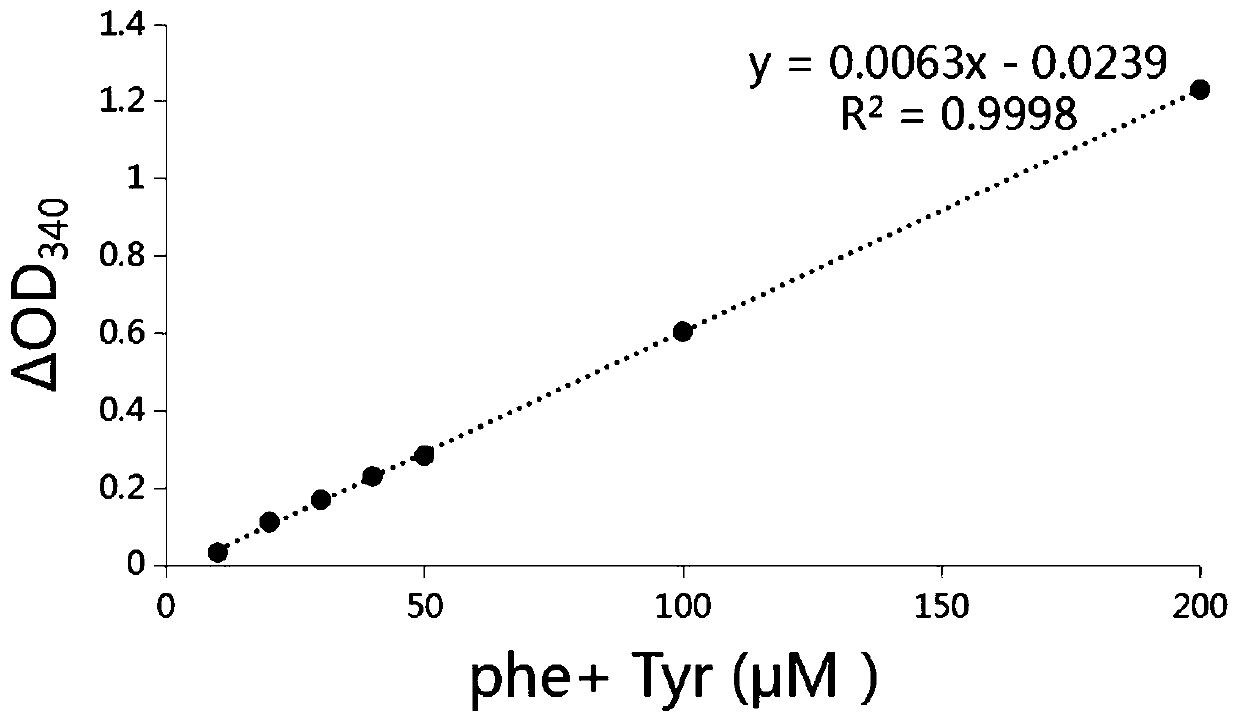
Method for detecting content of phenylalanine and tyrosine by enzyme method, and application thereof
PendingCN110819693AHigh sensitivityRapid and stable detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseCu-tyrosine
The invention relates to a method for detecting the content of phenylalanine and tyrosine by an enzyme method, and an application thereof. The method uses phenylalanine dehydrogenase to quickly and correctly characterize the content of phenylalanine and phenylalanine in a system by the increasing of the content of NADH. The total content of phenylalanine and tyrosine in a sample can be quickly determined by the end point method or the initial velocity method. The method has high sensitivity, rapid and stable detection, good repeatability, simple and convenient operation, relatively low cost and relatively wide application range.
Owner:申友基因组研究院(南京)有限公司 +1
Technical method for preparing phenylalanine hydroxylase
InactiveCN101899464AIncrease productionHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and relates to a method for preparing recombinant L-phenylalanine hydroxylase, in particular to a method for obtaining high-yield L-phenylalanine hydroxylase by embedding a programmable microorganism source L-phenylalanine hydroxylase gene into an appropriate expression vector to establish recombinant plasmid and a transformed cell and using a simple and effective affinity method. The L-phenylalanine hydroxylase obtained by the method has high yield, high activity and simple and convenient production method. The invention also comprises the new recombinant plasmid and transformed cell established in the method. The L-phenylalanine hydroxylase prepared by the method can be used for developing a screening reagent of newborn phenylketonuria and producing L-phenylalanine.
Owner:北京协和洛克生物技术有限责任公司
Method for preparing saxagliptin chiral intermediate through enzymatic-catalysis asymmetric transamination
The invention discloses a method for preparing a saxagliptin chiral intermediate through enzymatic-catalysis asymmetric transamination. The method includes that phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PDH) and glycerol dehydrogenase (GDH) are coupled in a water solution containing amino, and a saxagliptin intermediate and glycerol are used as substrates; 1, 3-dihydroxy acetone (DHA) and the saxagliptin chiral intermediate are generated at the same time, recycling of coenzyme NAD+ is realized, and efficient synthesis of the saxagliptin chiral intermediate is realized.
Owner:福州基石医药科技有限公司
A phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant with improved substrate specificity and application thereof
ActiveCN110607290BIncreased substrate specificityReduced substrate specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPhenylpyruvic acidGlycine
The invention discloses a mutant of phenylalanine dehydrogenase with improved substrate specificity and application thereof, belonging to the technical fields of enzyme engineering and microorganism engineering. The substrate specificity of the phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant of the present invention to phenylpyruvate has been significantly improved compared with the wild type, and at the same time, to L-norvaline, L-leucine, L-valine The specificity of acid and L-phenylglycine has significantly decreased compared with the wild type. Therefore, when the phenylalanine dehydrogenase mutant of the present invention is used for the detection of phenylalanine content in samples such as blood, it can be excluded The interference of other amino acids improves the detection sensitivity and has a very high application prospect in the preparation of phenylalanine detection kits and phenylketonuria detection kits.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
3-Phenoxy benzoic acid degrading bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN108148776APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBenzoic acidSphingomonas sp.
The invention discloses 3-phenoxy benzoic acid degrading bacterium which is Sphingomonas sp. SC-1, and GenBank login number for its 16S rDNA is JN857975. The 3-phenoxy benzoic acid degrading bacteriumis originated from pesticide manufacturer sludge and is obtained by 3-phenoxy benzoic acid concentration gradient domestication, primary screening, separating and screening, and secondary screening.A colony of the 3-phenoxy benzoic acid degrading bacterium is colorless and transaprent and has neat edge and moist surface; individuals of the 3-phenoxy benzoic acid degrading bacterium are rod shaped and gram negative, having no spore; both glucose and glycerol ferments show positiveness, and both acid and gas are produced; no gel or starch is hydrolyzed; the growth of the bacterium requires sodium chloride and potassium chloride; phenylalanine dehydrogenase is positive; the growth requires oxygen. The 3-phenoxy benzoic acid degrading bacterium can grow with 3-phenoxy benzoic acid as the unique carbon source and energy and can degrade 3-phenoxy benzoic acid having a concentration of 300 mu g / mL in a medium to the rate of 100%.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com