Patents
Literature
586 results about "Substrate concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Substrate concentration is the number of substrate molecules found in a particular solution, while enzyme concentration is the number of enzymes.
Biosensor
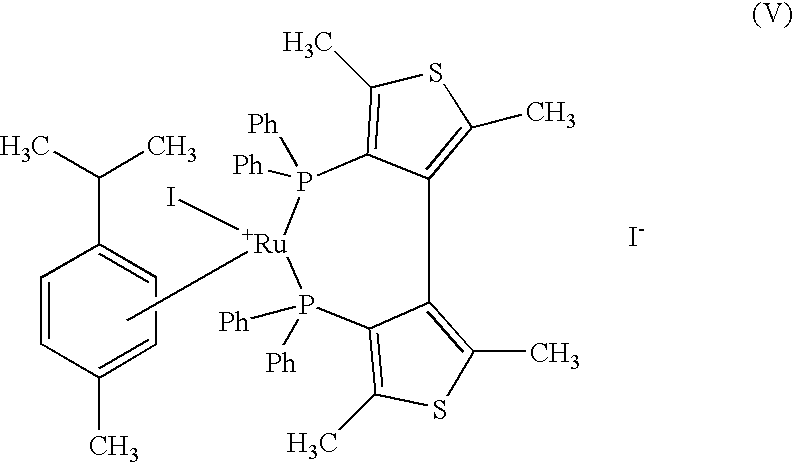
InactiveUS6911131B2Achieve effectImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic acidAlcohol sugars
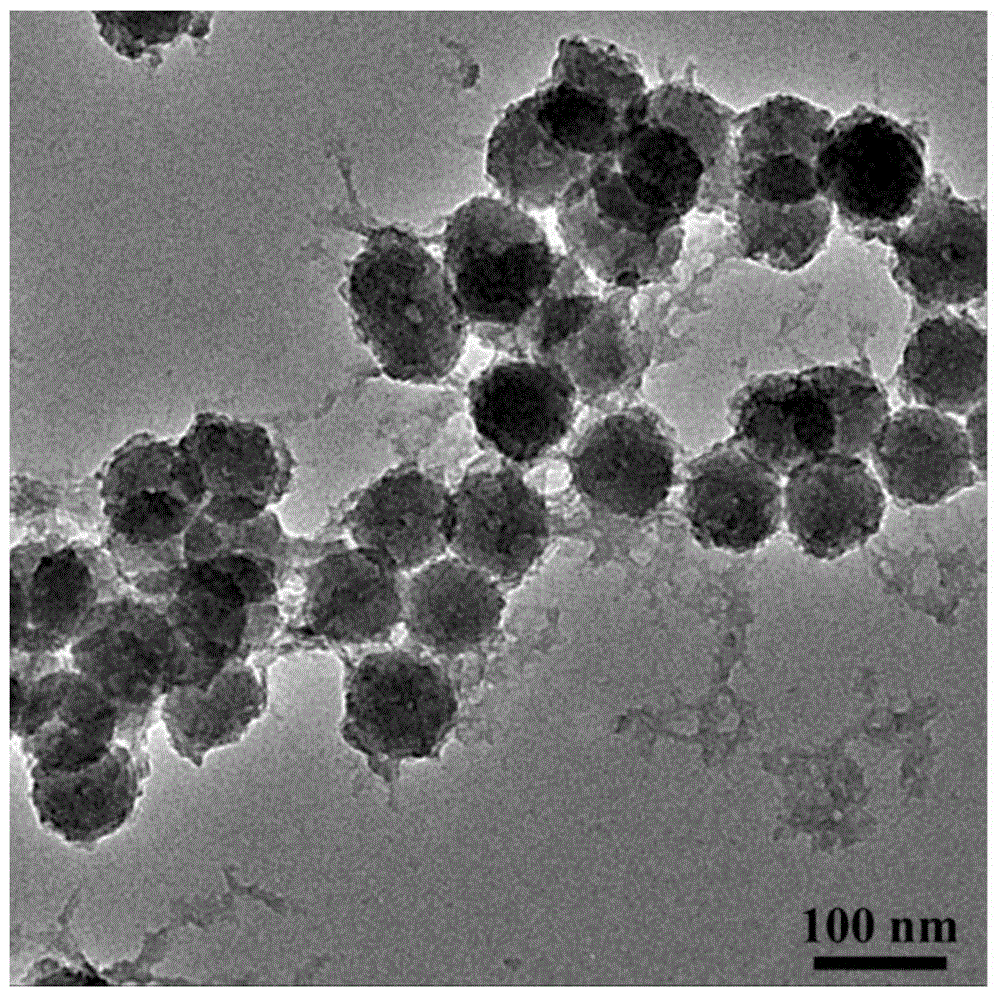
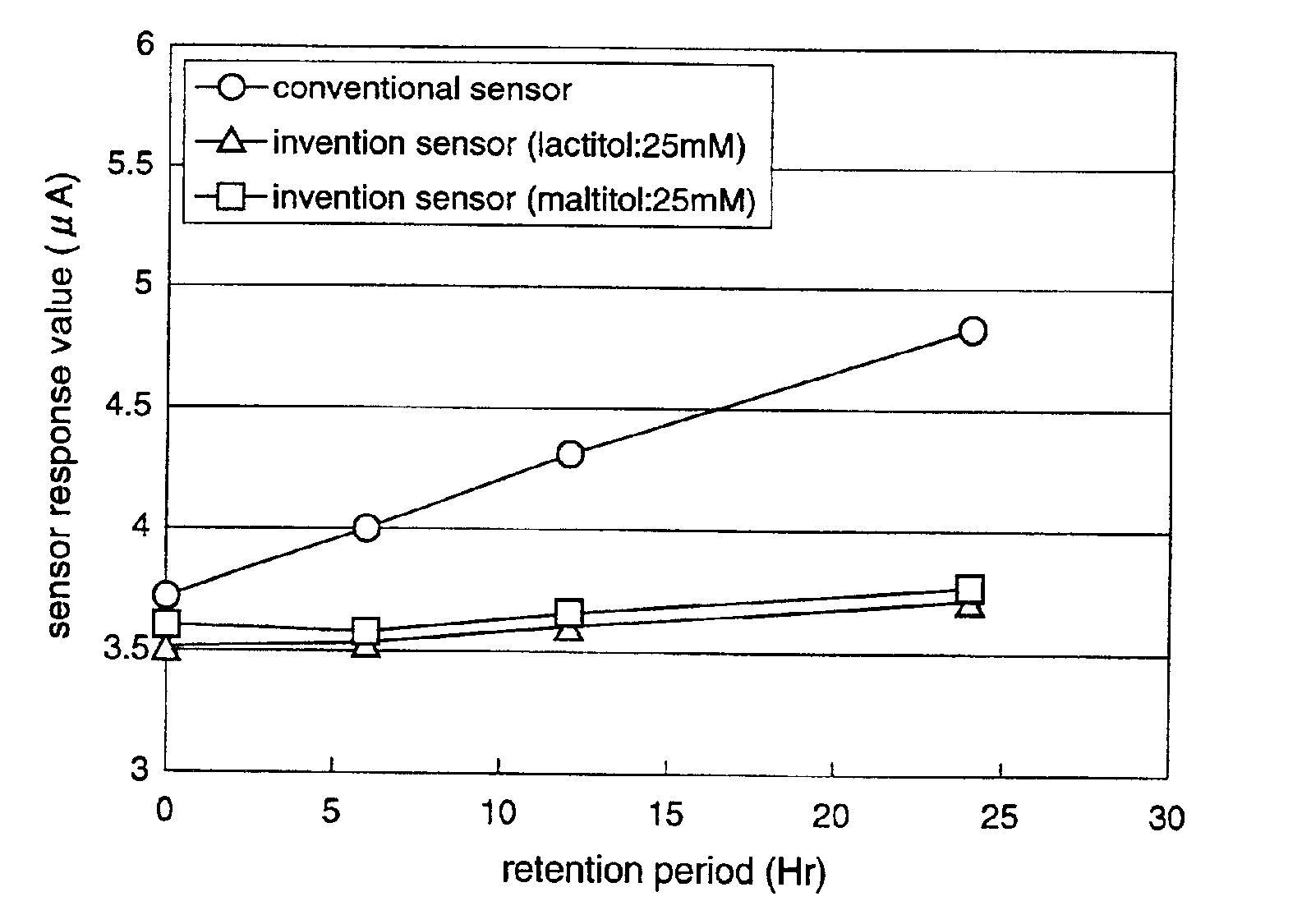
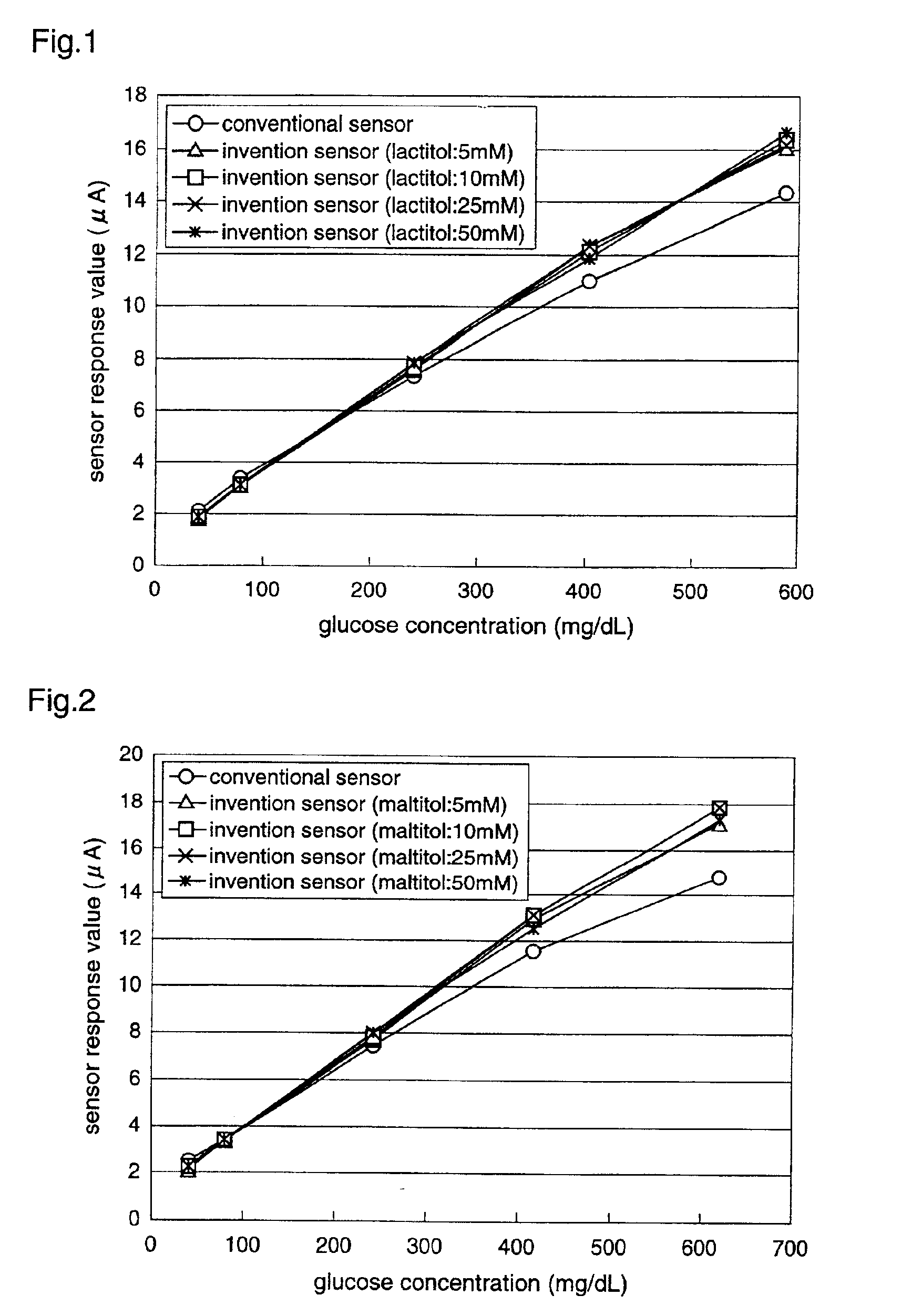
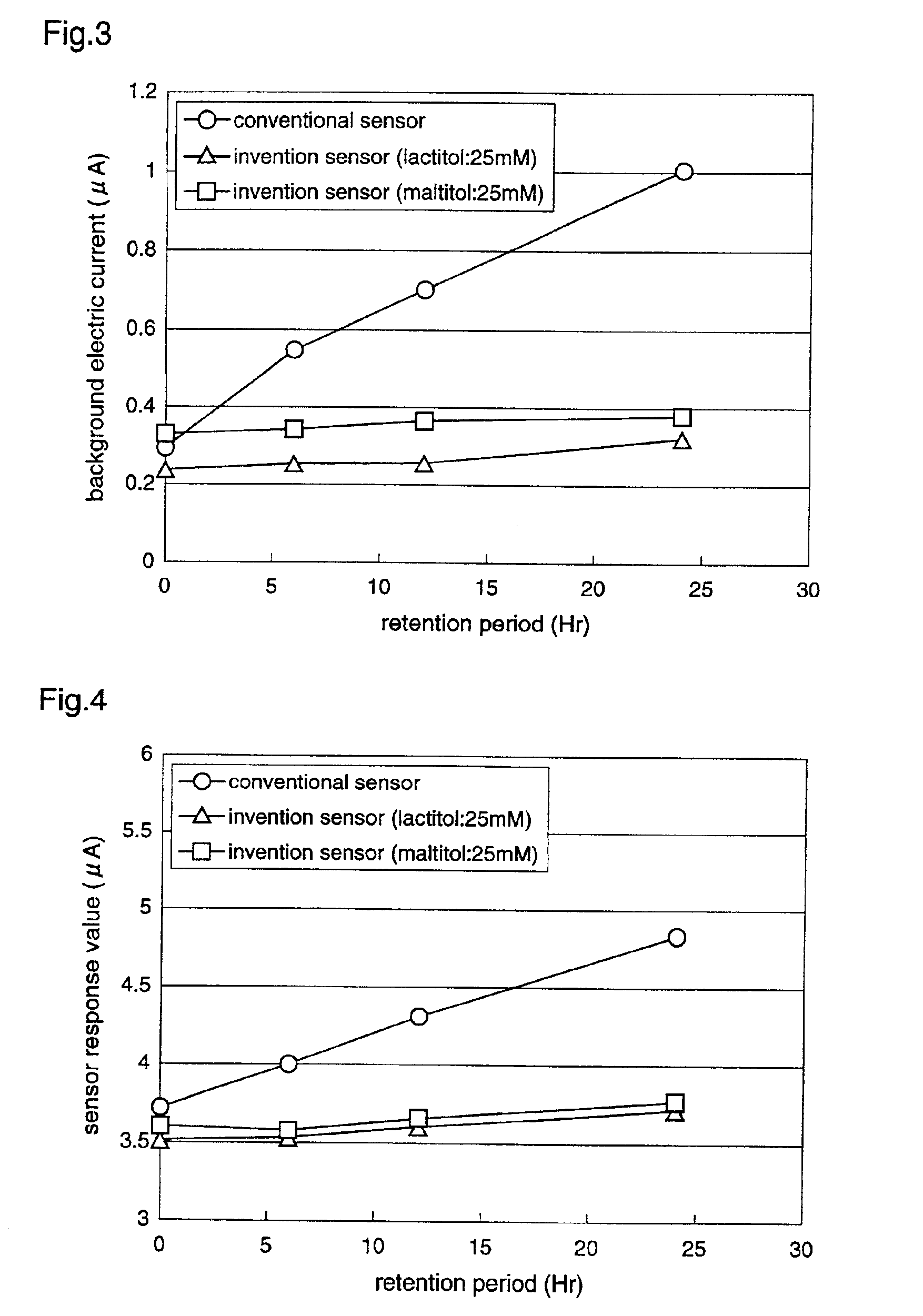
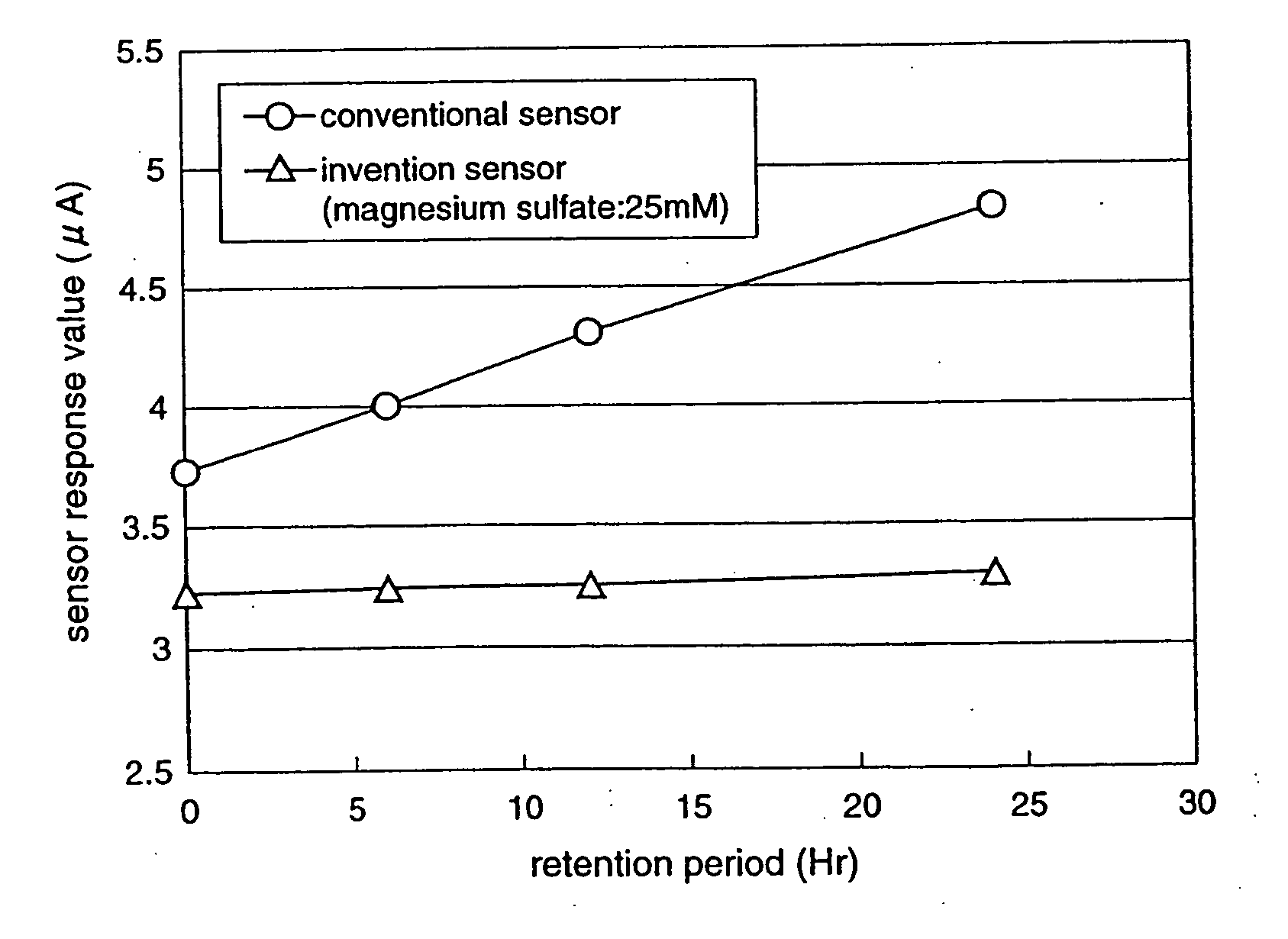
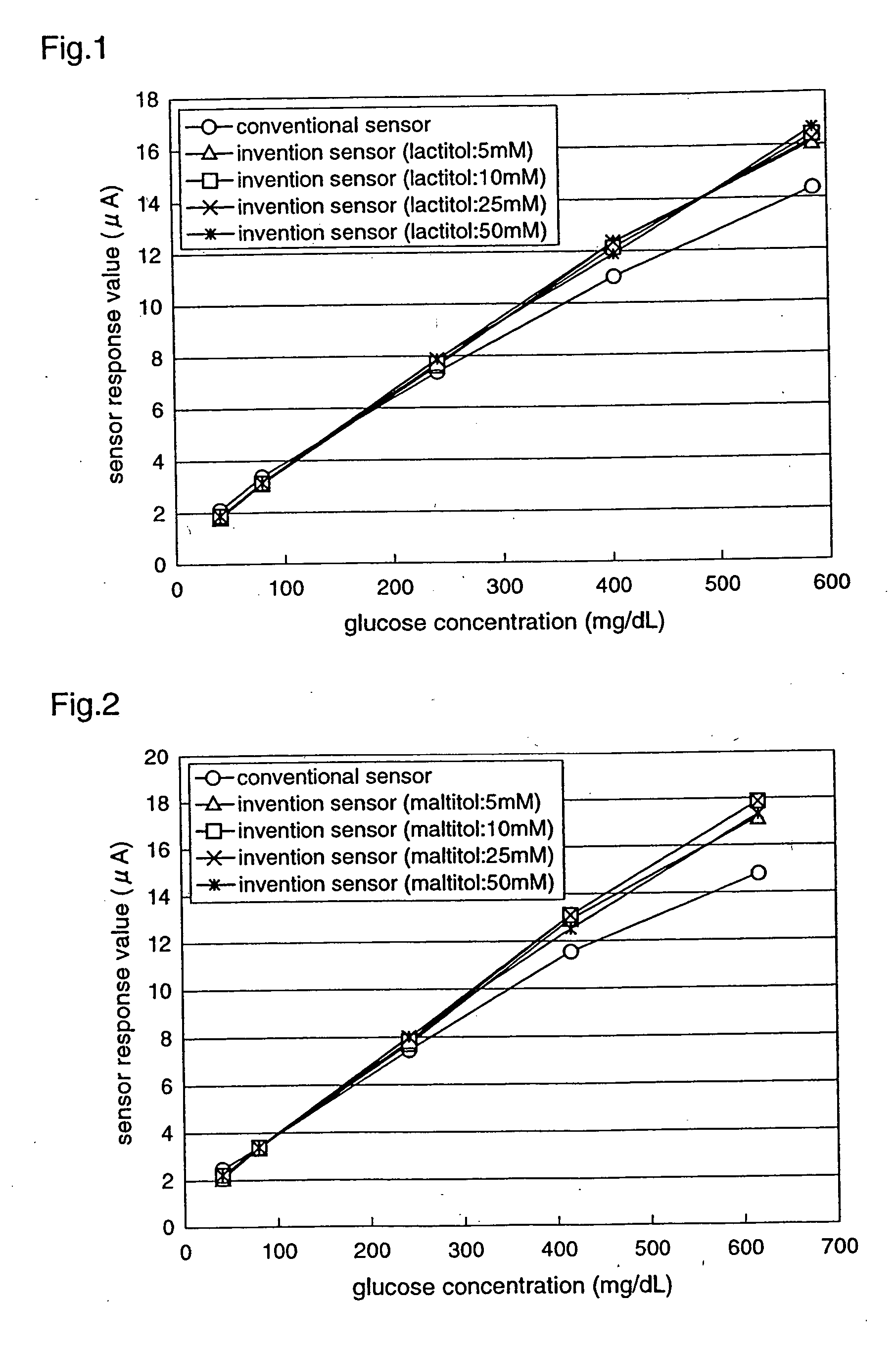
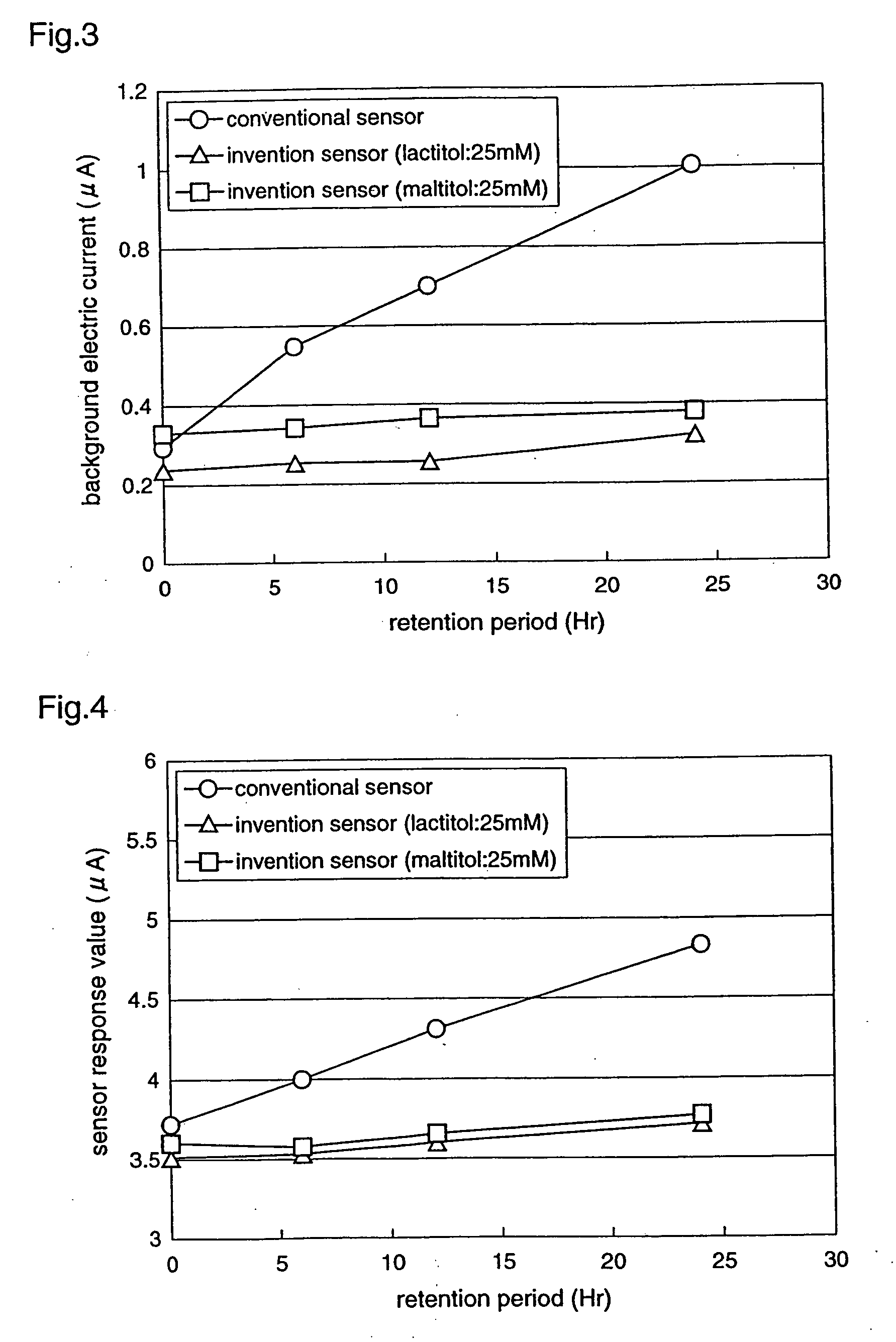
In a biosensor for measuring a specific substance in a liquid sample, one or a combination of sugar alcohol, metallic salt, organic acid or organic acid salt which has at least one carboxyl group in a molecule, and organic acid or organic acid salt which has at least one carboxyl group and one amino group in a molecule, is included in a reagent layer provided on electrodes, thereby providing a highly-accurate biosensor which is excellent in stability and has high response (sensitivity, linearity) of the sensor to the substrate concentration.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Thermophilic Organisms For Conversion Of Lignocellulosic Biomass To Ethanol
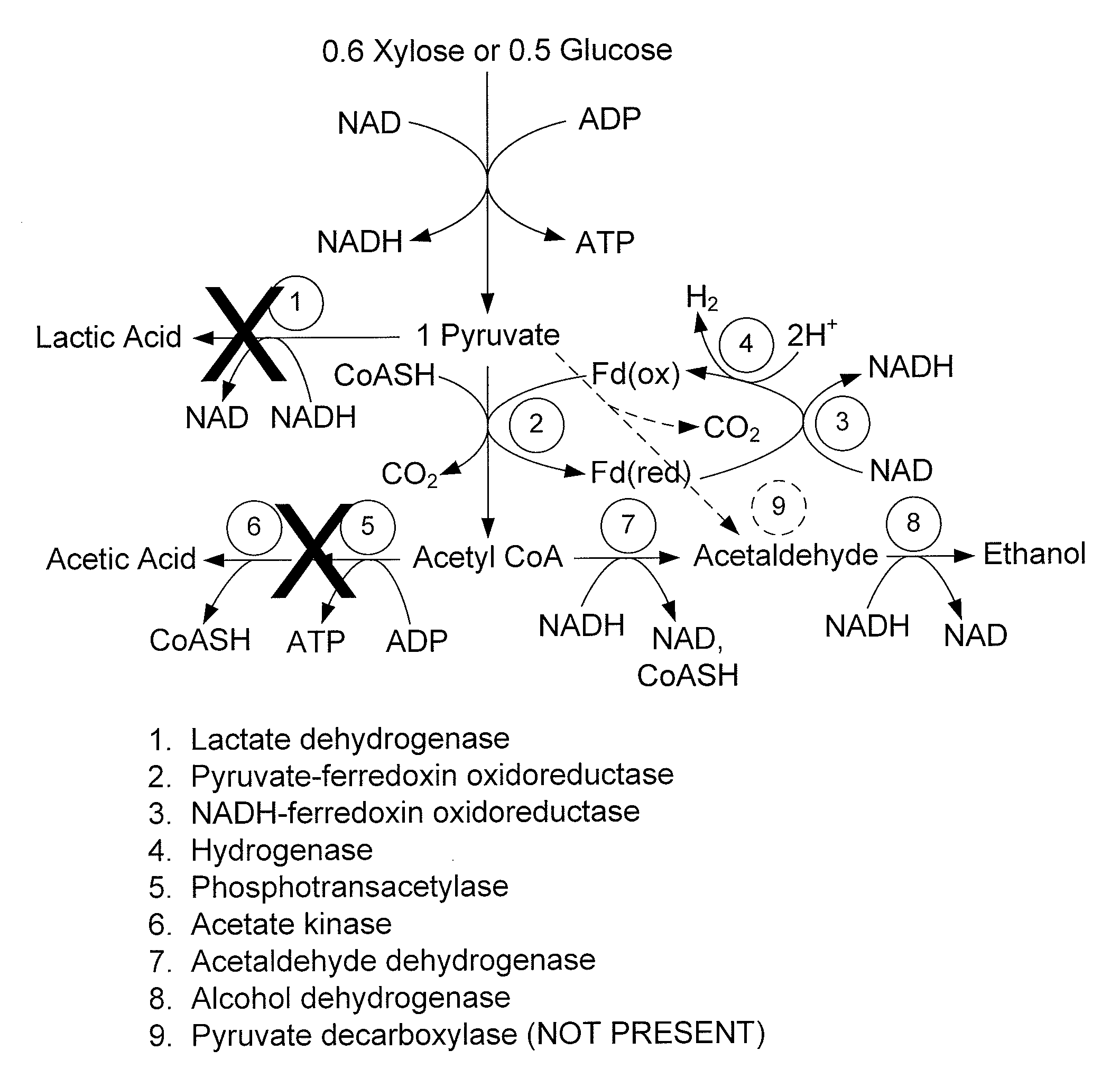
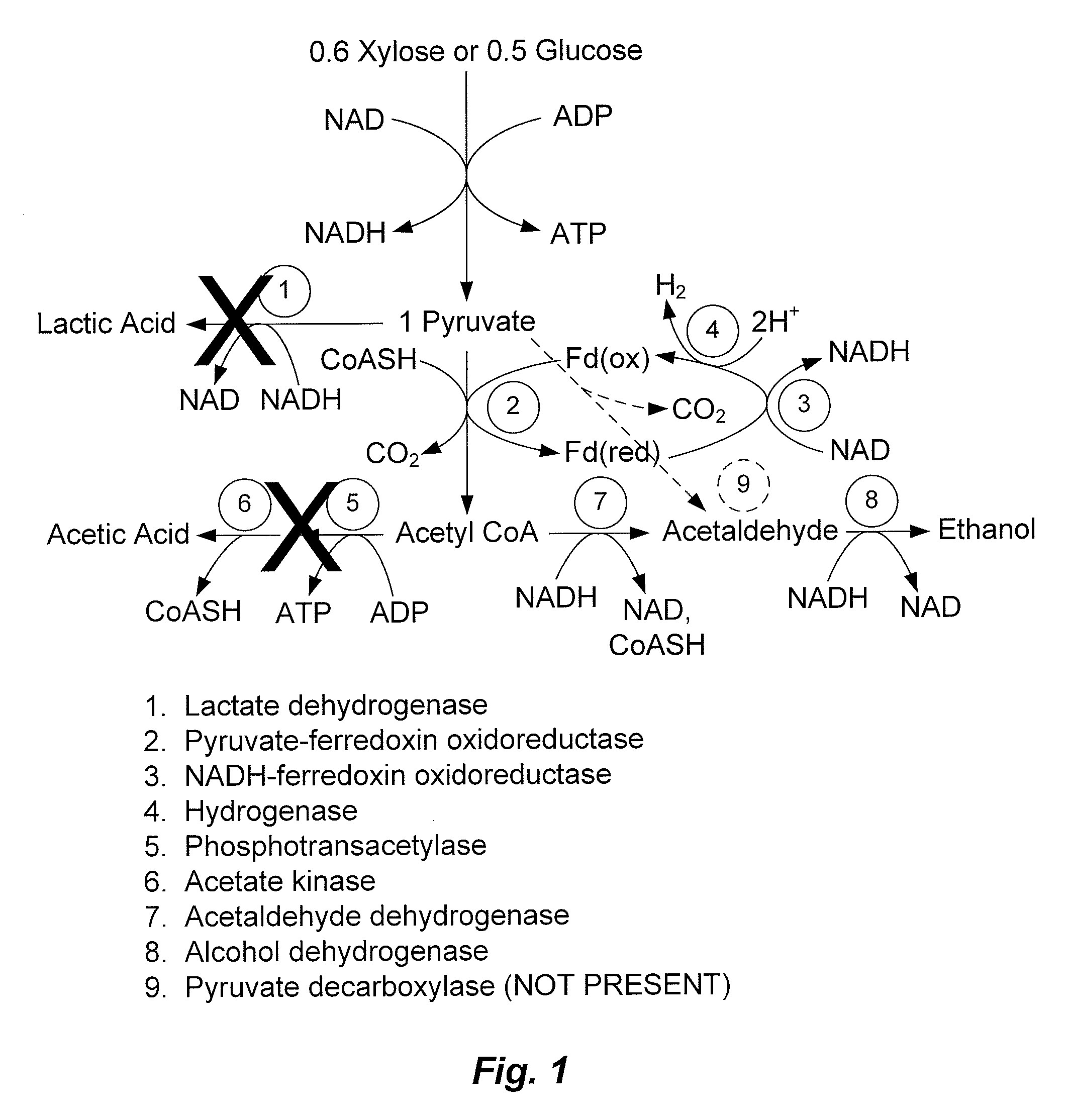
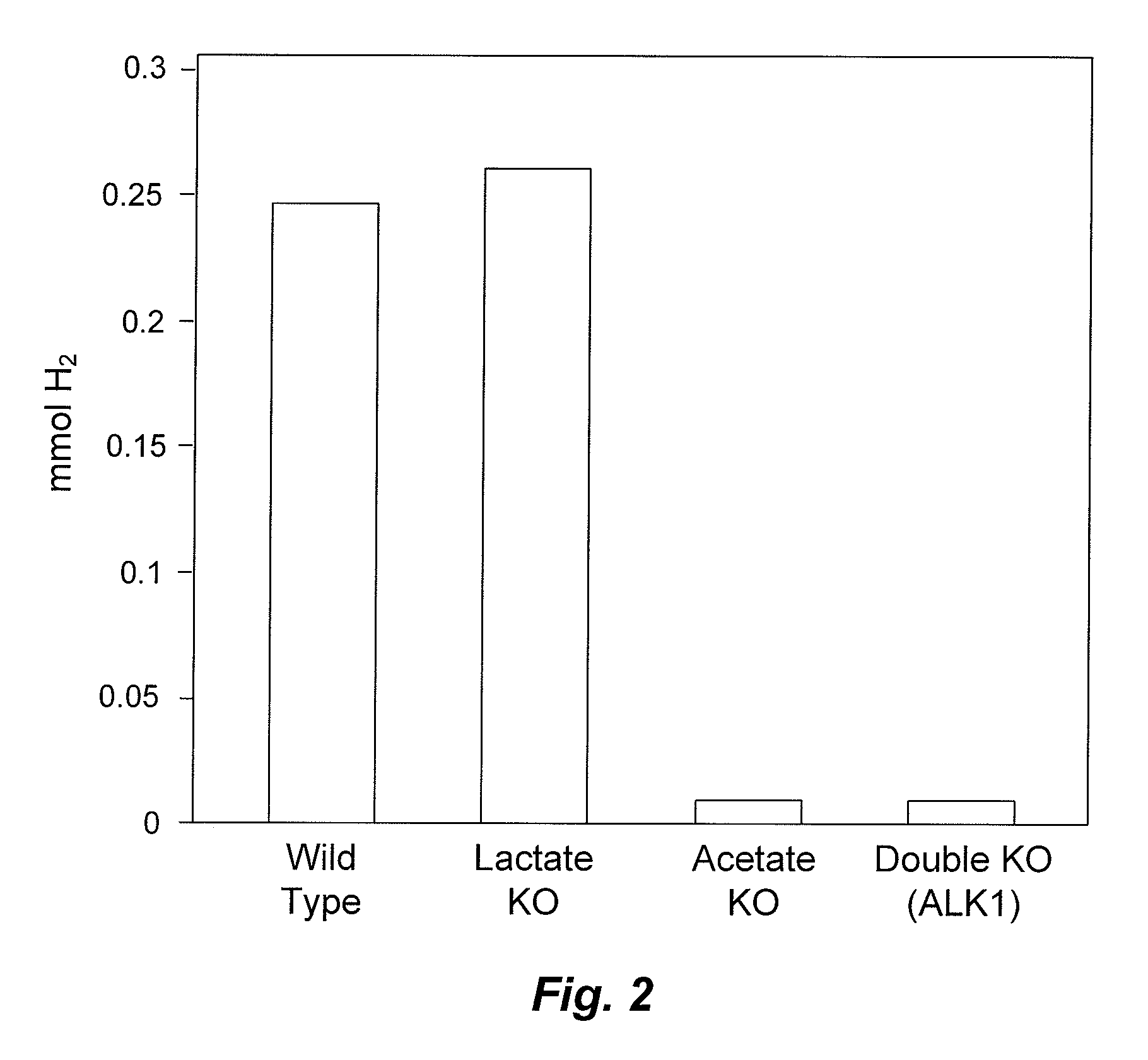
Mutant thermophilic organisms that consume a variety of biomass derived substrates are disclosed herein. Strains of Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum with acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase expression eliminated are disclosed herein. Further, strain ALK1 has been engineered by site directed homologous recombination to knockout both acetic acid and lactic acid production. Continuous culture involving a substrate concentration challenge lead to evolution of ALK1, and formation of a more robust strain designated ALK2. The organisms may be utilized for example in thermophilic SSF and SSCF reactions performed at temperatures that are optimal for cellulase activity to produce near theoretical ethanol yields without expressing pyruvate decarboxylase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
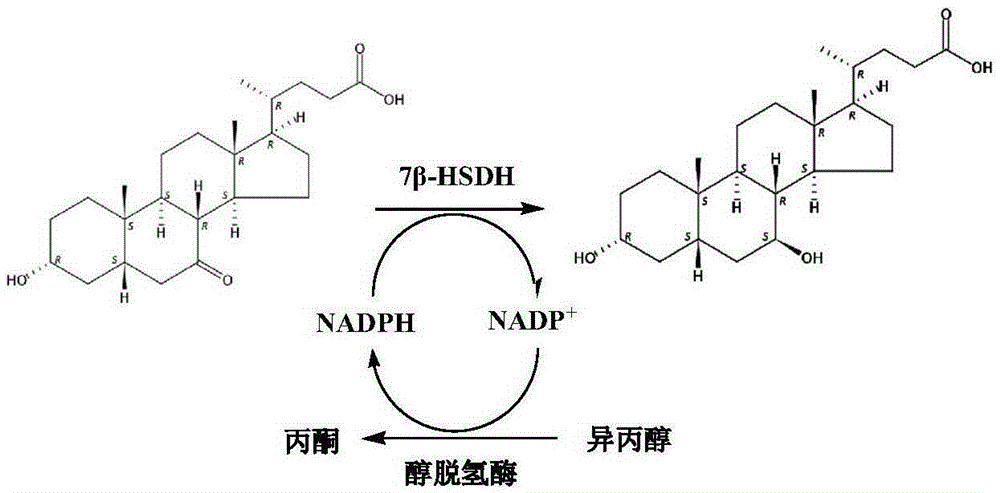
Mutant of 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, application of mutant and synthesis method
ActiveCN105274070ASuitable for industrial productionEasy to controlOxidoreductasesFermentationChemical synthesisCholic acid
The invention provides a mutant of 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, application of the mutant and a synthesis method. The mutant of the 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase is characterized in that amino acid sequences of the mutant are Seq ID NO:4, and coded nucleotide sequences are Seq ID NO:3; or amino acid sequences of the mutant are Seq ID NO:6, and coded nucleotide sequences are Seq ID NO:5. The mutant, the application and the synthesis method have the advantages that cholic acid compounds, particularly ursodeoxycholic acid, can be catalytically synthesized by the efficient 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, mutant enzymes of the 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase and coenzyme regeneration systems, accordingly, the substrate concentration can reach 100 g / L, the conversion rate is 99.2-99.5%, and the weight yield can reach 94-96%; and the enzymes can be inexpensively and easily obtained by the aid of a fermentation process, accordingly, the production cost and the product quality are superior to the production cost and the product quality of chemical synthesis methods, and the mutant and the synthesis method are applicable to industrial production.
Owner:苏州天绿生物制药有限公司
Novel method for storing and brewing white spirit
ActiveCN101792709AFully agedAssociation stabilityAlcoholic beverage preparationAlcohol contentDistillation
The invention relates to a novel method for storing and brewing white spirit and aims to solve the defects that currently the storage of the white spirit at home and abroad adopts a mode that after being stored for a certain period, the white spirit of the original grade is subjected to design, alcohol content reduction, combination, seasoning, adsorption, filter and then is subjected to filling production; in the natural storage condition, the stimulating components and hazardous components in the white spirit cannot sufficiently react and volatilize; the stability of the association of the white spirit body is not good; the vinosity of the produced white spirit is lack of soft taste and clean aftertaste; and the quality of the produced white spirit is not stable. In the novel method for storing and brewing the white spirit of the invention, the double cellaring, namely the secondary ageing process is adopted, and according to the substrate concentration, the non-homogeneous substance motion characteristics and the permutation and combination principle, primitive base wine generated by carrying out solid-state fermentation and distillation in a mud cellar is subjected to twice physical and chemical changes, ageing, alcoholizing and bouquet spreading, and processing in a conventional wine storage container under a specific environment to generate the natural, hygiene and health white spirit.
Owner:重庆诗仙太白酒业有限公司
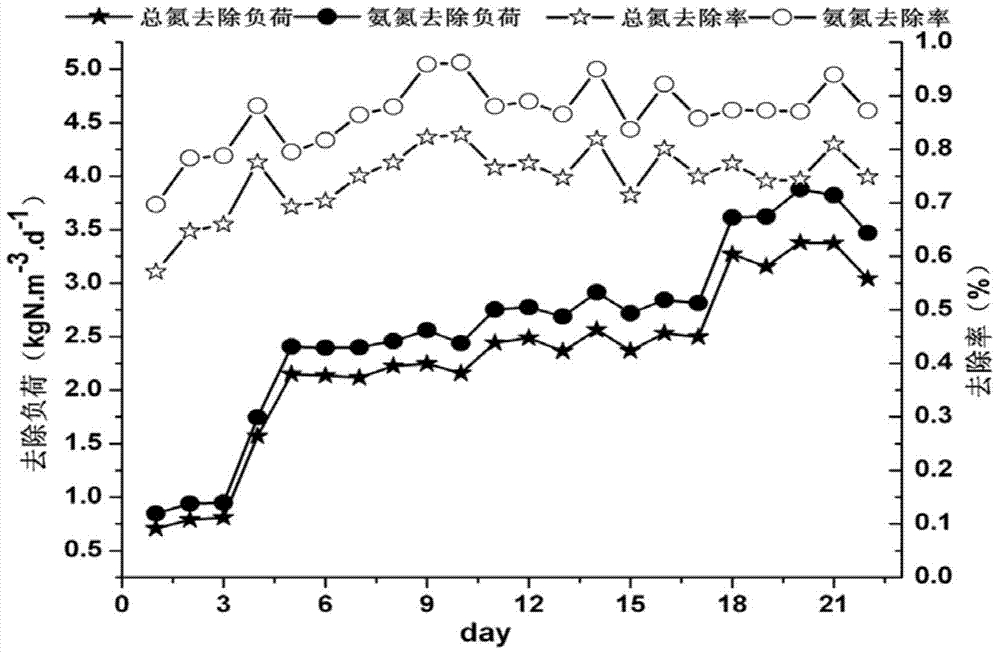
Quick starting method for technology for simultaneous denitrification and COD removal under condition of normal-temperature and low-C/N sewage
ActiveCN103482765AReduce startup timeHigh denitrification and COD removal effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrifying bacteriaHigh load
The invention belongs to the field of treatment and regeneration of urban sewage, and provides a quick starting method for a technology for simultaneous denitrification and COD removal under the condition of normal-temperature and low-C / N sewage. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly inoculating some mature CANON sludge, and enabling the CANON sludge to perform biofilm culturing on volcanic rock filtering material, and quickly constructing an aerobiotic AOB and anammox oriented microbial system; then reducing the inflowing water substrate concentration and adjusting the aeration and hydraulic retention time, so as to improve the nitrogen removal load, and realize the high-load stable operation of the CANON technology under the condition of a medium ammonia nitrogen substrate; finally adding an organic carbon source into the inflowing water, performing heterotrophy for the growth of denitrifying bacteria, and controlling the temperature, free ammonia, aeration and other conditions, so as to optimize the aerobiotic AOB, anammox and denitrifying bacteria coexisted micro-environment, and successfully start an SNAD technology. According to the invention, the difficult problems that a large amount of organic carbon sources are required to be added for biological denitrification in the long term and the cost is prodigious are solved, and a method is provided for starting of the SNAD technology under the condition of normal-temperature and low-C / N simulated wastewater.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase
ActiveCN101861909AOvercome hydrolysisOvercoming the problem of partial denaturation of proteinsVegetable proteins working-upFreeze-dryingReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for modification of rice protein and oryzenin with protein glutaminase, which comprises the following steps: adding the rice protein or oryzenin into a constant-temperature enzyme reactor with phosphate buffer solution while stirring to obtain protein dispersion solution with a certain substrate concentration; adding protein glutaminase to obtain a system with a certain proportion of enzyme and substrate, wherein the temperature of enzymatic reaction is 36-38 DEG C, the time of the enzymatic reaction is 0.1-48 hour(s), and the pH value of the enzymatic reaction is maintained 7.0; adding dialysis solution, i.e. acetic acid solution of 0.10mol / L, wherein the dialysis time is about 8 hours; and carrying out vacuum freeze-drying, thereby obtaining the product. The invention can improve the protein solubility of the rice protein or the oryzenin, and can also enhance the emulsification, foaming performance, gelation and other functional properties of the rice protein or the oryzenin.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for producing Chitosan oligosaccharide by using enzyme method to degrade chitosan
The invention discloses a method for preparing chitosan oligosaccharide by degrading chitose comprising steps removing extraneous constituents through fermentation culturing and separation purifying by utilizing shell dextranase bacillus TQK to obtain TQK enzyme liquor which enzyme activation is up to 718u / ml, putting TQK enzyme liquor into 10-20poncentration degrading liquor which uses chitose as bottom liquor, the ratio of TQK enzyme liquor to bottom object is 1:10, and the enzymolysis reaction condition is: mixing speed is 200-300 r / min, Ph is 4-5.5, temperature is 45-52 DEG C and time is 4-6 hours, then centrifugal separating, flocculating, fining, filtrating, ion exchanging, hyperfiltration stage treating, vacuum concentration disposing, sponging drying disposing to prepare chitosan oligosaccharide. The enzymolysis bubatrate concentration can be up to 15-20, enzymolysis time is only 4-6 hours, receiving rate is high, energy consumption is low, pollution is small, also the invention can prepare narrow molecular weight distribution chitosan oligosaccharide with average molecular weight D1500 in quack speed, low consumption and large mass.
Owner:WUHAN EAST ANGEL BIOENG
Icodextrin and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103467608AMolecular weight concentrationUniform particle sizeSubstrate concentrationHydrolysis
The invention discloses an icodextrin and a preparing method thereof. The preparing method comprises the first step of mixing cereal starch and water into a solution with the substrate concentration ranging from 20wt% to 50wt%, and adding acid to the mixture of the cereal starch and the water to form a reaction solution, wherein the final concentration of the acid ranges from 0.1% to 1.5% (V / V), the hydrolysis reaction is carried out at the temperature ranging from 70 DEG C to 93 DEG C, the reaction process is monitored at the same time, when the flow-out time duration of the reaction solution, measured with an Ubbelohde viscometer with the internal diameter of a capillary tube being 0.9mm to 1.0mm, is 2-4 minutes, the reaction solution is neutralized to pH7 through the aqueous alkali, the hydrolysis reaction is ended to obtain a product 1, and the reaction duration ranges from 0.5 hour to 4 hours; the second step of carrying out molecular weight screening on the product 1 to obtain a product 2 with the weight-average molecular weight ranging from 13 thousand Da to 19 thousand Da; the product 2 is dried and solidified to obtain the icodextrin. The distribution range of the molecular weight of the icodextrin is narrower, and the molecular weight distribution is more centralized.
Owner:HUAREN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
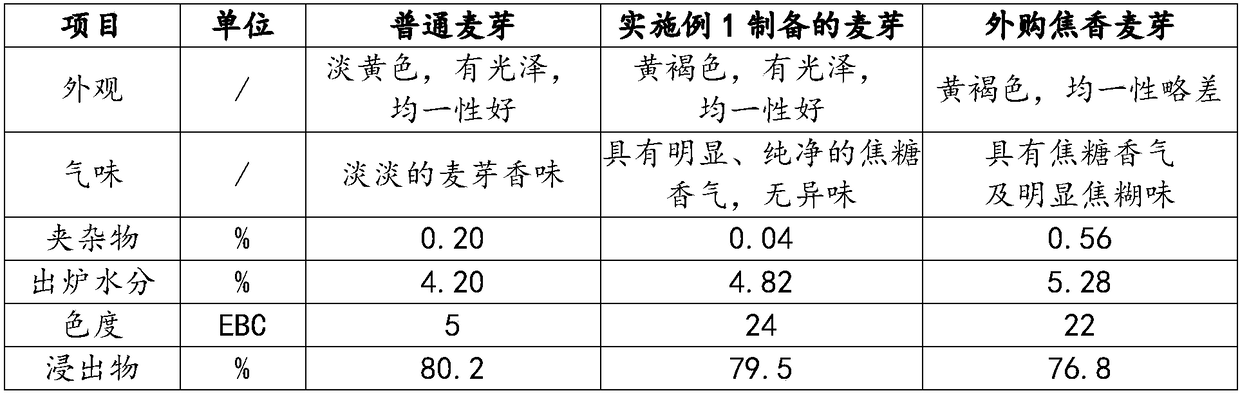
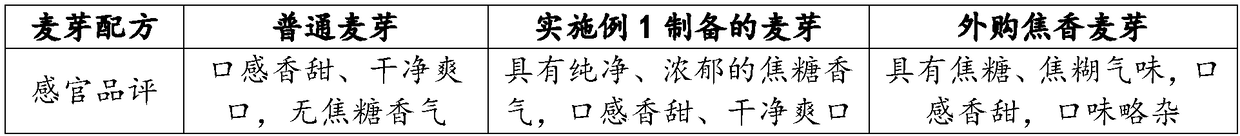
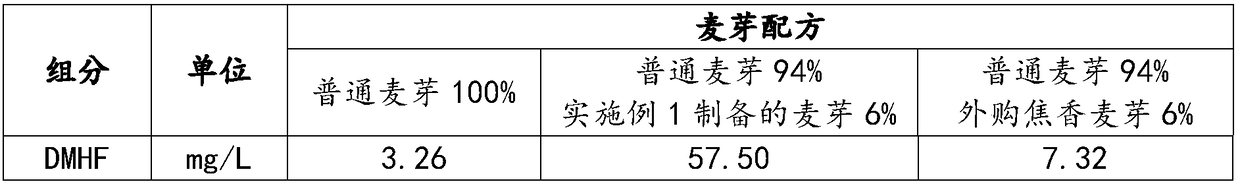
Preparation method of burnt malt with high caramel aroma and beer
ActiveCN108102825AFully stimulate vitalityIncrease concentrationMalt preparationMaillard reactionHordeum vulgare
Belonging to the malt manufacturing field, the invention provides a preparation method of burnt malt with high caramel aroma and beer. The malt preparation method includes the steps of: barley selection, raw material pretreatment, wheat dipping, germination, green malt saccharification, baking and root removal. Specifically, during barley selection, barley with moderate protein content is adoptedas the raw material; the wheat dipping process provides barley grains sufficient internal moisture content to fully stimulate the vitality of the endogenous enzyme system of malt, thus providing sufficient conditions for subsequent acquisition of a Maillard reaction substrate; the saccharification process is carried out in four stages, so that green malt can effectively degrade cellulose, proteinand starch under an appropriate water condition, and the concentration of the Maillard reaction substrate is increased; and then baking is carried out at an appropriate generation temperature of DMHFso as to enrich DMHF product substantially. The obtained malt has significant caramel aroma, the aroma is pure and strong, sensory evaluation indicates that the malt is free of scorched flavor, burntflavor and other foreign and miscellaneous smell, and can be used for production of beer with high caramel aroma.
Owner:TSINGTAO BREWERY
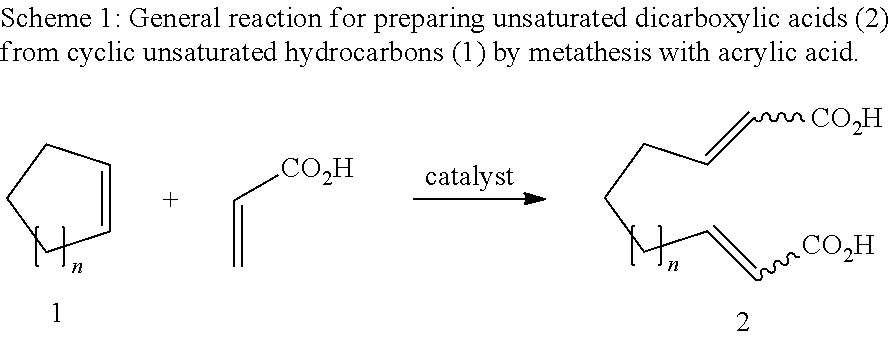
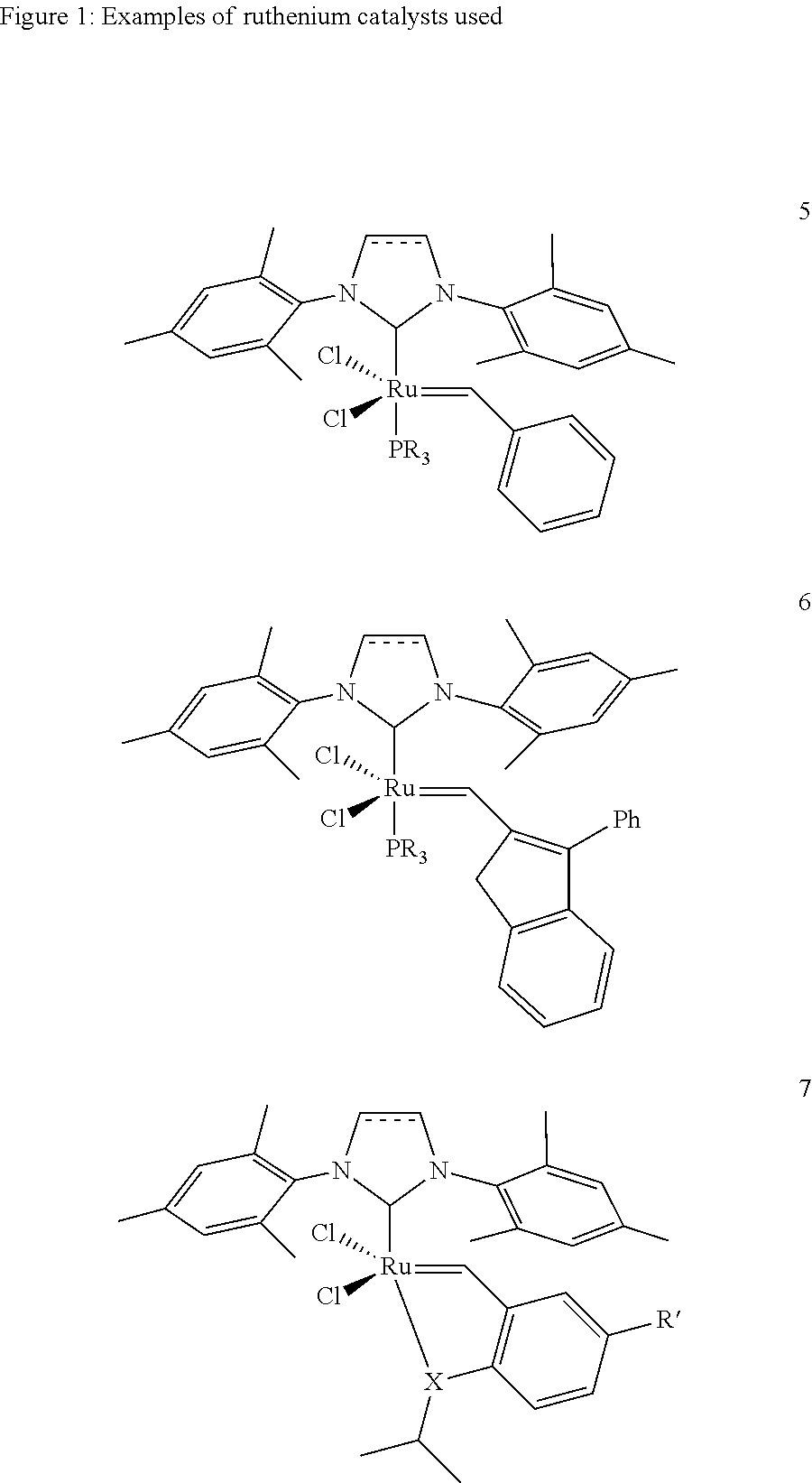
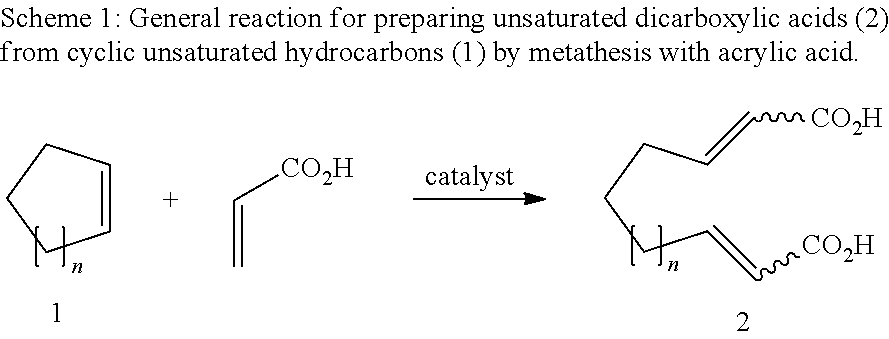
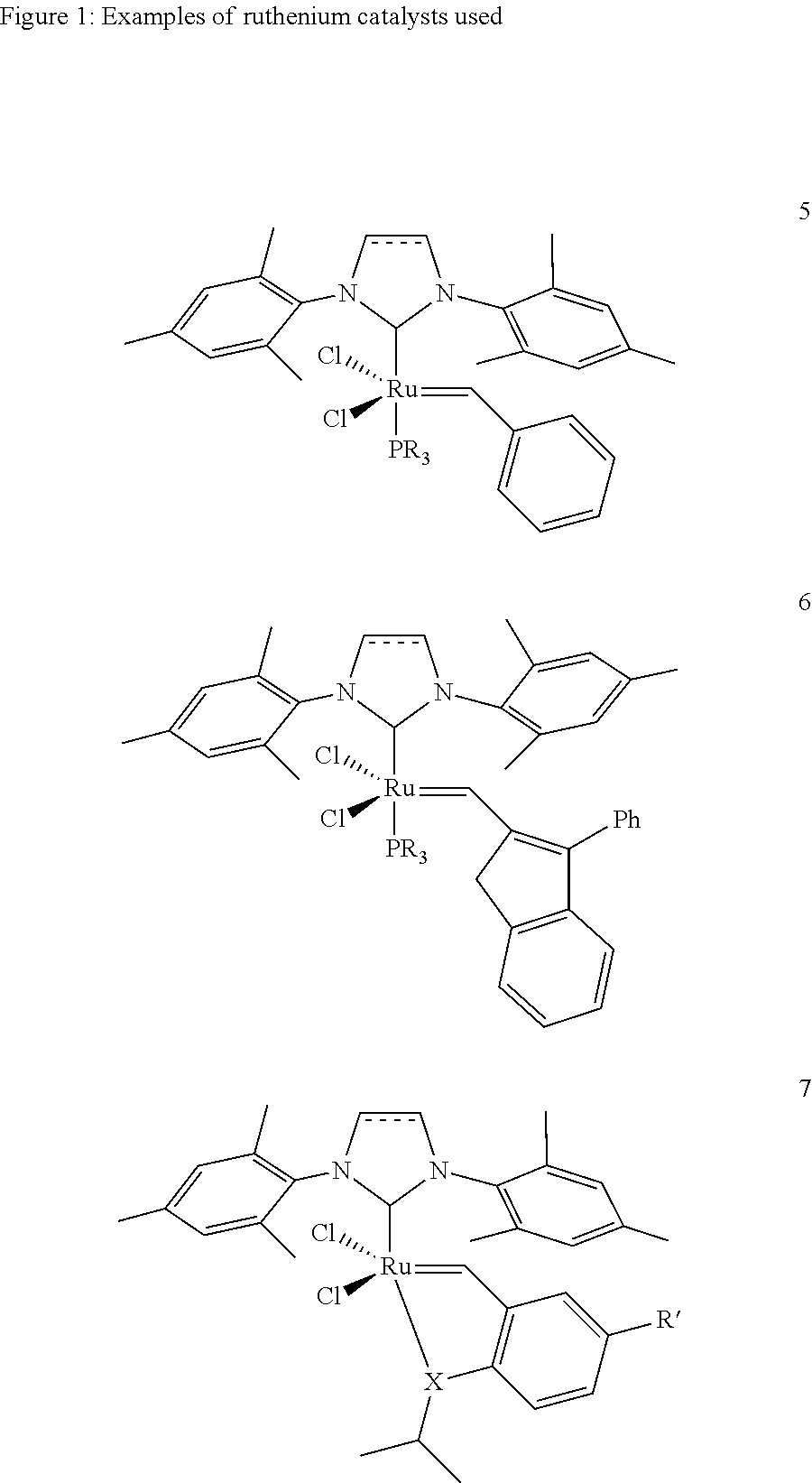
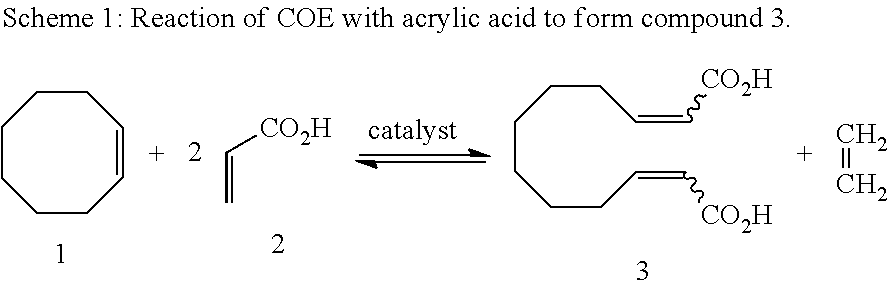
Unsaturated dicarboxylic acids from unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons and acrylic acid by way of metathesis, the use thereof as monomers for polyamides, polyesters and polyurethanes, and subsequent reaction to diols and diamines
InactiveUS8445720B2Organic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPolyesterPolyamide
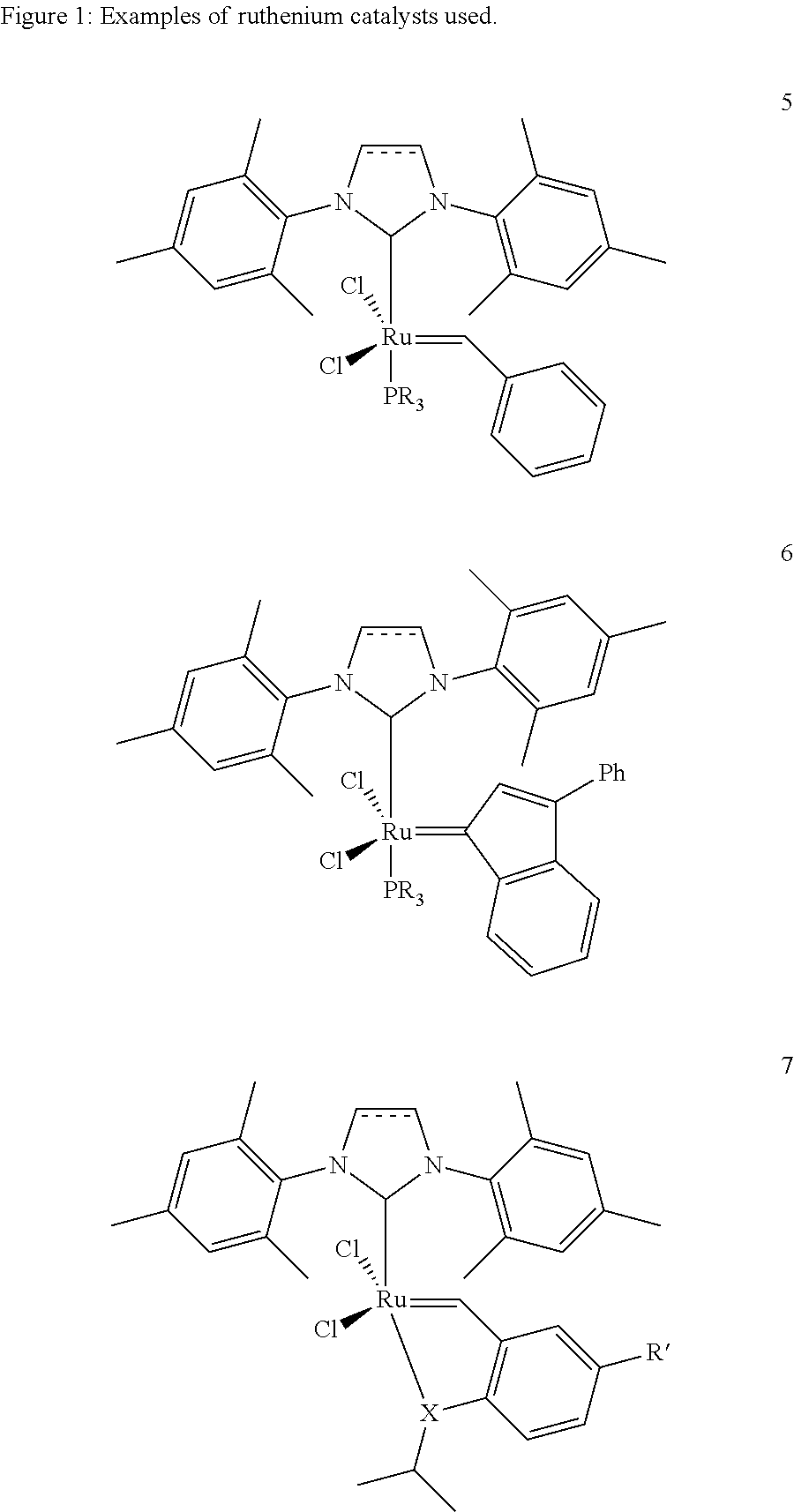
The invention relates to a method for producing α,β-unsaturated dicarboxylic acids and the corresponding saturated dicarboxylic acids, whereby the corresponding cycloalkene and acrylic acid are reacted with a ruthenium catalyst by way of a metathesis reaction at high substrate concentrations until the reaction takes place in substance, the resulting dicarboxylic acid being precipitated.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
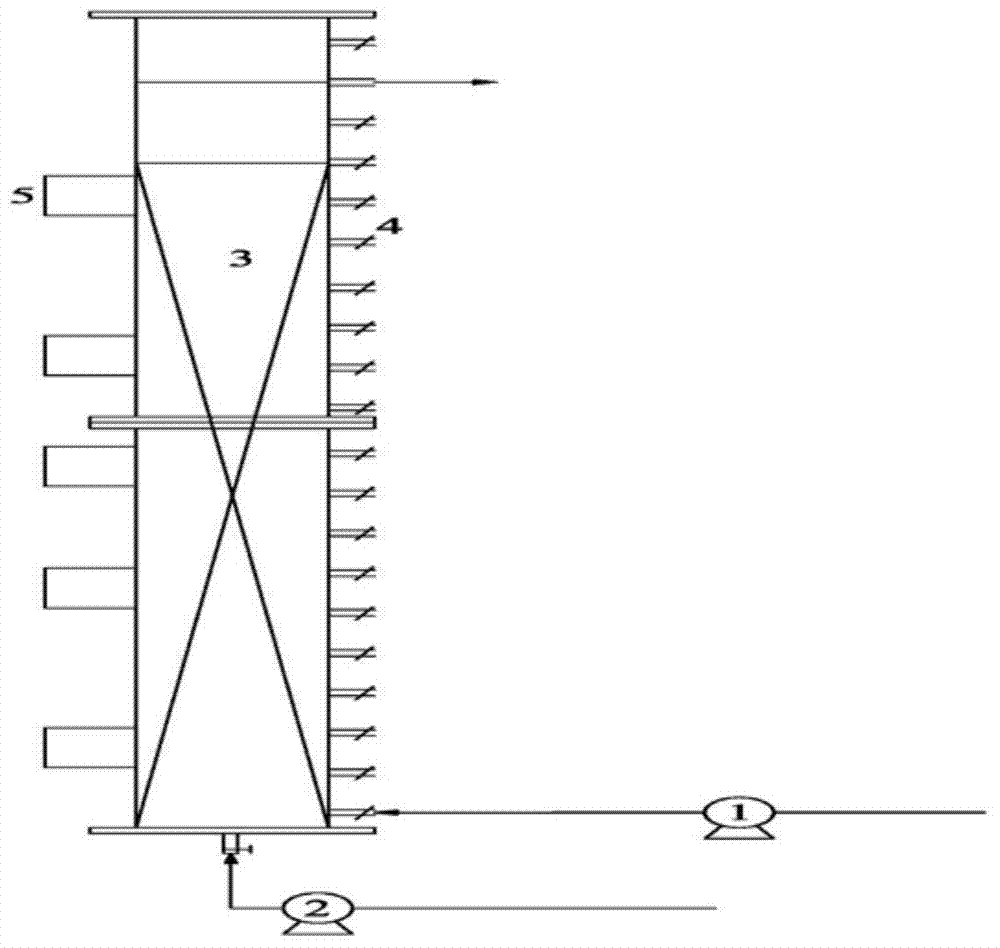
Room temperature nitrosation-anaerobic ammoxidation coupling symbiotic denitrification device for municipal sewage and sewage treatment method
InactiveCN102531172AReduce yieldReduce aerationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesChemical oxygen demandNitration
The invention provides a room temperature nitrosation-anaerobic ammoxidation coupling symbiotic denitrification device for municipal sewage and a sewage treatment method and relates to a sewage treatment method, solving the technical problems that in the existing nitration-anaerobic ammoxidation process, occupied area is large and operation cost is high. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out film formation with an intermittent film formation mode; introducing municipal sewage; completing the removal of COD (chemical oxygen demand) in the outer barrel and generating a small amount of NO2<-1>-N; and introducing mixed sludge subjected to nitrosation and anaerobic ammoxidation into the outer barrel so as to realize nitrosation-anaerobic ammoxidation coupling symbiotic denitrification. According to the invention, a continuous operation mode is adopted for the device; the device is small in occupied area, and the effective volume of a structure is reduced; and the device is simple and convenient in management, high in treatment efficiency, low in operation cost and the like, and specifically aims at domestic sewage having the characteristics of low substrate concentration and large water yield.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for pickling fresh water fish
InactiveCN101356981AIncreased concentration activates the enzymeSuppress generationMeat/fish preservation using acidsFood preparationPediococcus speciesBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for preserving fresh water fish. The method comprises the steps of killing, washing, preserving, drying and packing. The preserving steps comprise after being processed, round fish is placed in pickle at the temperature of 10-15 DEG C for 24-36 hours; wherein, the prepared pickle is of 4% salt solution containing 2%-3%(W / W) of glucose, 3 per thousand-4 per thousand (W / W) of zinc ion, 1%-2%(W / W) of a blended leaven; the blended leaven is selected from the mixture of two or more than two of Lactobacillus casei (L.casei), Lactobacillus plant arum (L.plantarum), Staphylococcus xylosus (S.xylosus) or Pediococcus pentosaceus (L.pentosaceus) with the same mass. In the method, the pickle with low baume degree is added with beneficial microbes and the zinc ion to increase substrate concentration activation enzyme, breed the beneficial microbes, and restrain the generation of molds. The preserved fish has low salt content and good flavor, and is easy to store.
Owner:KUSN ZHOUZHUANG LVERKANG FOOD
Biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its application
InactiveCN101020919AImprove solubilityPromote biotransformationMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolubilityMicroorganism
The present invention belongs to the field of biological sterol transforming technology, and is especially biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its derivative and its preparation. In a transforming system, cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain amount is added, or substrate and cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain ratio are made to form inclusion compound, so as to facilitate transformation. The process of the present invention is especially suitable for microbial transformation of hydrophobic compound, and can raise the solubility of reaction substrate in water solution, raise the substrate utilizing rate and reaction rate, release substrate and product inhibition and raise product converting rate. When the substrate concentration is 3-20g / L, the present invention has conversion period shorted to 3-4 days, conversion rate of 50-95 % and high industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Enzymology method for preparing polysaccharide bioflocculant
ActiveCN101392280AGood flocculation effectQuality improvementFermentationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationUltrafiltrationInternational market
The invention belongs to the technological field of environmentally-friendly water treatment, in particular to an enzymology method for preparing polysaccharide bio-flocculant. In the method, sucrose solution with different concentrations of substrate is prepared according to the requirements of products with different molecular weights; and then 1 percent of calcium chloride solution is added and 30 percent of acetic acid buffer solution is used for regulating the pH to be 5.2 to 5.4; the amount of enzyme added is regulated and the pH is regulated to range from 5.2 to 5.4; simultaneously, reaction conditions of temperature, stirring speed, reaction time and the like are controlled; termination is determined to stop the reaction by measuring kinetic viscosity, and then ethanol, methanol or isopropanol is adopted for precipitation, or a ultrafiltration membrane system is used for separation and purification so that various technological indexes of products with different molecular weights can fully reach the quality standard of international market on a novel polysaccharide bioflocculant. A controllable molecular weight can be synthesized by the method, particularly the polysaccharide bioflocculant with ultra-high molecular weight and also can be used for large scale industrialized production.
Owner:威海汉邦生物环保科技股份有限公司
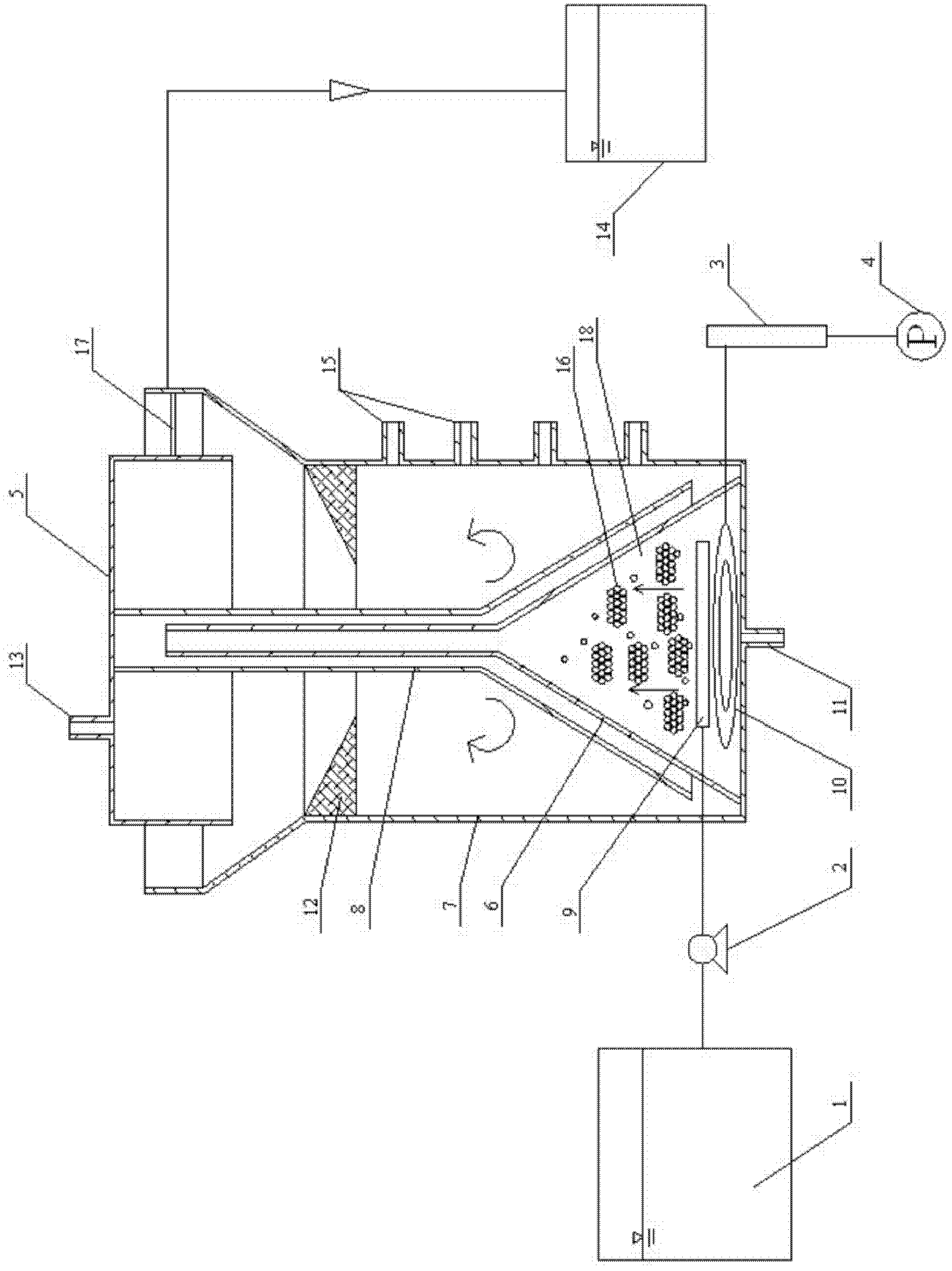
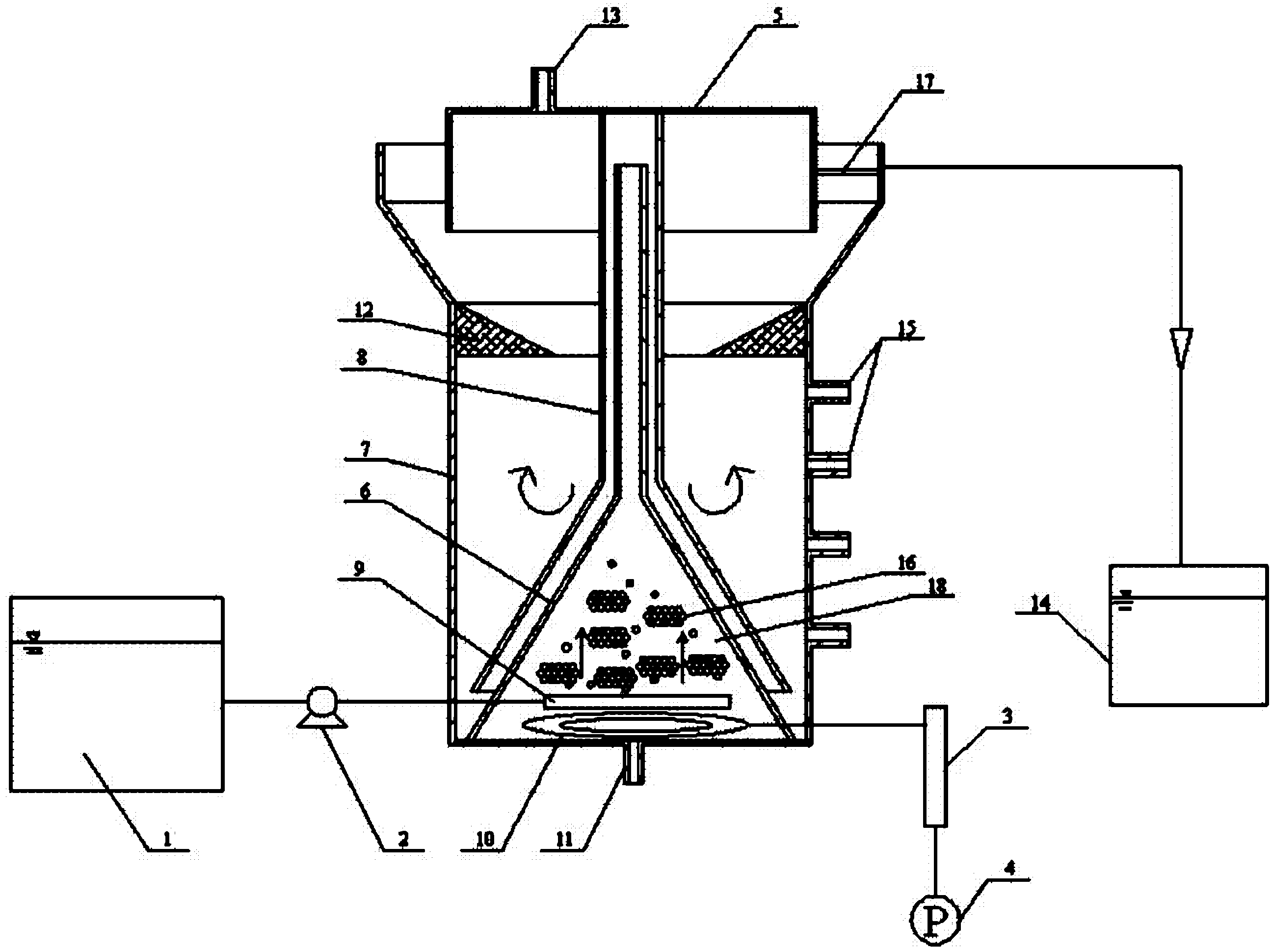
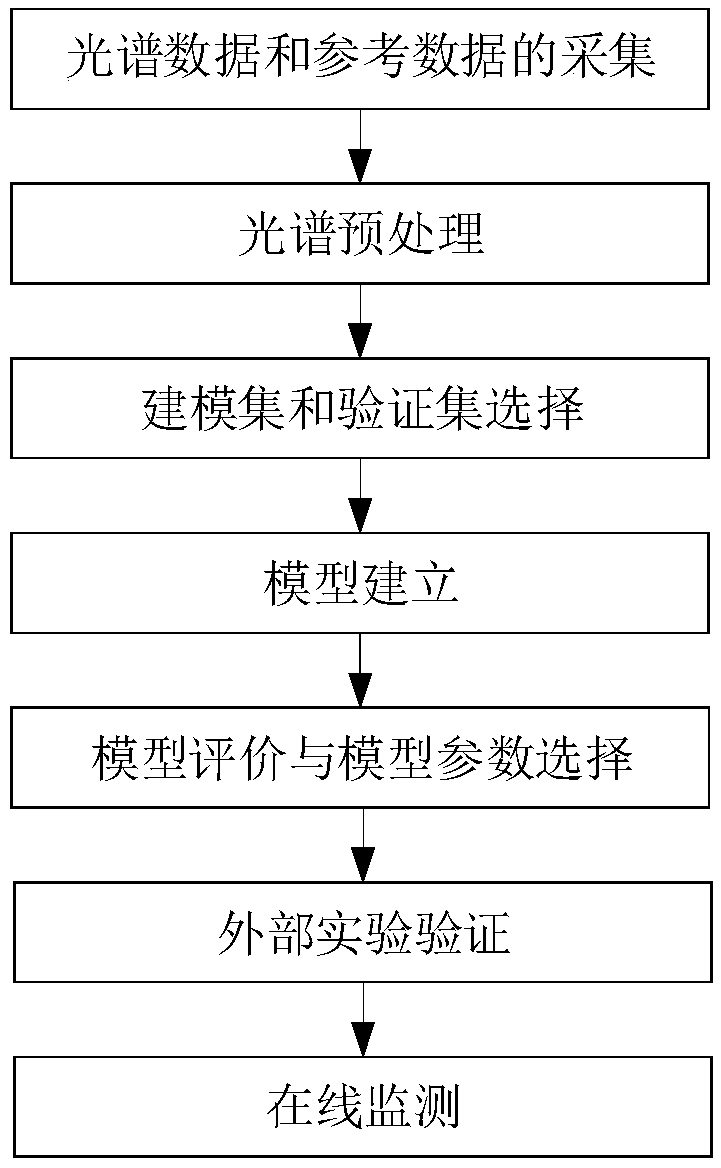
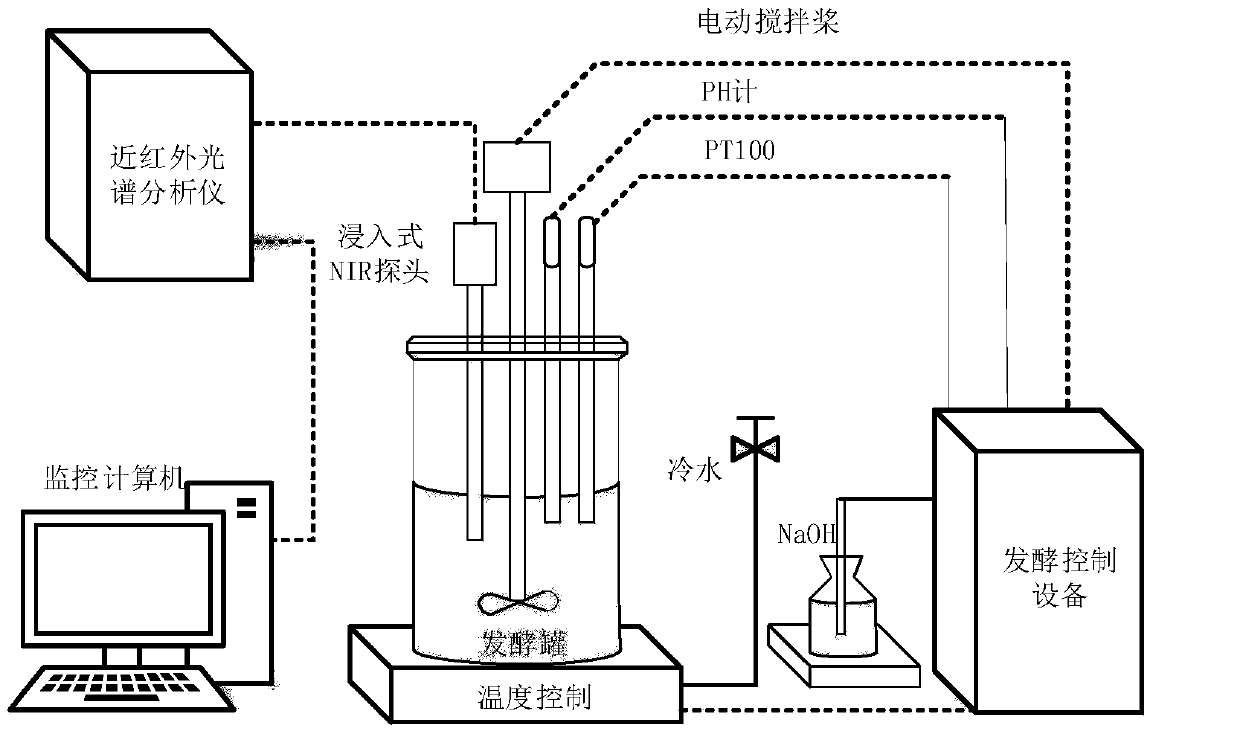
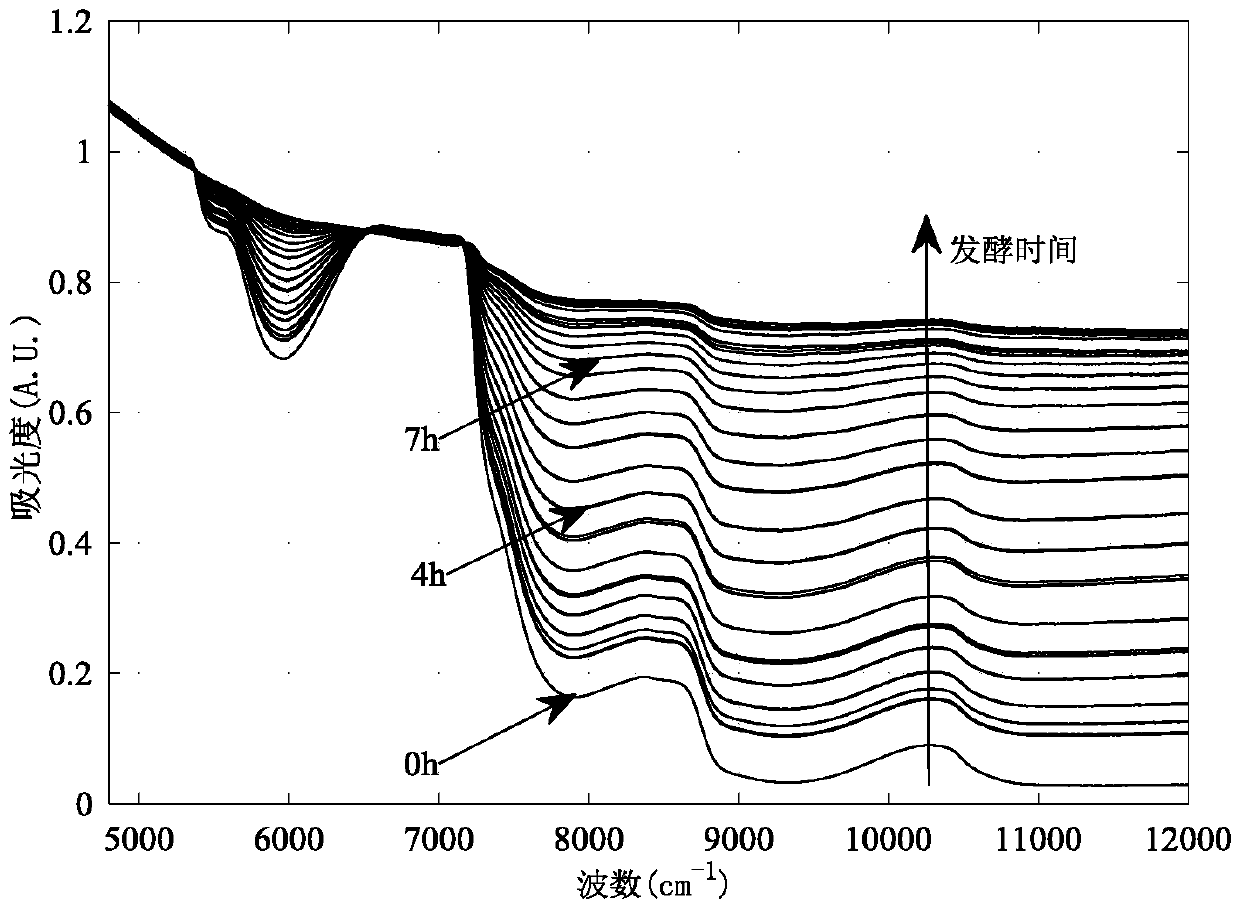
Method for detecting biomass and composition concentrations in fermentation process based on near-infrared spectrum
InactiveCN109668858AAutomatic detectionQuick checkMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredSpectrum analyzer
The invention belongs to the field of industrial process detection and relates to a method for detecting biomass and composition concentrations in a fermentation process based on a near-infrared spectrum. The method is characterized by building an on-line monitoring experiment platform of a biological fermentation process by using a near-infrared spectrum analyzer equipped with an immersion probe,so as to carry out real-time in-situ measurement of near-infrared spectrum data of fermentation liquid of the biological fermentation process. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting spectrum data and reference data; secondly, carrying out preprocessing operation on the measured near-infrared spectrum data, then dividing the data into a correction set and a validation set and building a joint calibration model, and selecting model parameters by using a grid searching and cross validation method; finally, validating the validity of the established model through external experiment, so as to carry out quantitative analysis of biomass, a substrate concentration and a product concentration of the fermentation process. The method is capable of automatically and rapidly detecting the biomass, the substrate concentration and the product concentration; practical industrial application and popularization of the method are facilitated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Unsaturated dicarboxylic acids from unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons and acrylic acid by way of metathesis, the use thereof as monomers for polyamides, polyesters and polyurethanes, and subsequent reaction to diols and diamines
InactiveUS20100312012A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by ozone oxidationPolyesterPolyamide
The invention relates to a method for producing α / β-unsaturated dicarboxylic acids and the corresponding saturated dicarboxylic acids, whereby the corresponding cycloalkene and acrylic acid are reacted with a ruthenium catalyst by way of a metathesis reaction at high substrate concentrations until the reaction takes place in substance, the resulting dicarboxylic acid being precipitated.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to synthesis of chiral biaryl alcohols
InactiveCN108359649AHigh stereoselectivityIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholMutant
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof to synthesis of chiral biaryl alcohols, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant has excellent catalytic activity and stereoselectivity and can be used for efficient catalysis for preparation of a series of R-configuration and S-configuration chiral biaryl alcohols. Alcohol dehydrogenase can be applied to synthesis of various chiral biaryl alcohol intermediates of antihistamine drugs by being coupled with glucose dehydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase. Compared withthe existing reports, a method for preparing the chiral biaryl alcohols from alcohol dehydrogenase through asymmetric catalytic reduction has the advantages of simple operation, high substrate concentration, complete reaction and high product purity, and has broad industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
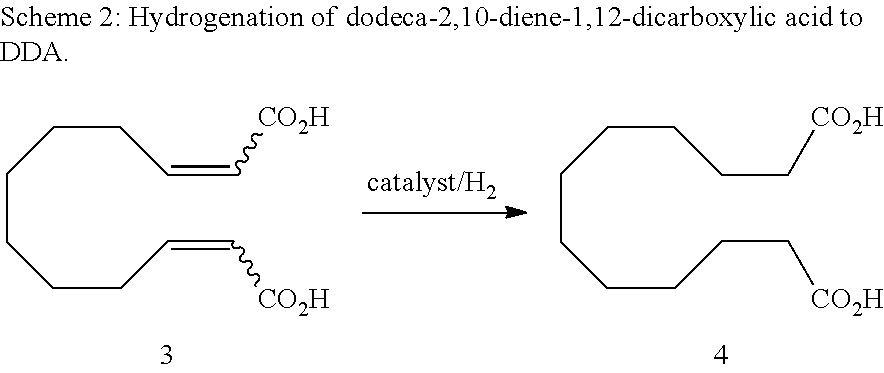
Method for producing dodeca-2,10-diene-1,12-dicarboxylic acid or 1,12-dodecane-dicarboxylic acid by way of ring-opening cross metathesis (ROCM) of cyclooctene with acrylic acid
InactiveUS20110015434A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by ozone oxidationDodecaneCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a method for producing 1,2-dodeca-2,10-diene diacid and 1,12-dodecanoic acid whereby cyclooctene and acrylic acid are reacted with a ruthenium catalyst by way of a metathesis reaction at high substrate concentrations until the reaction takes place in substance, the resulting unsaturated dicarboxylic acid being precipitated and being hydrated in a second reaction step.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
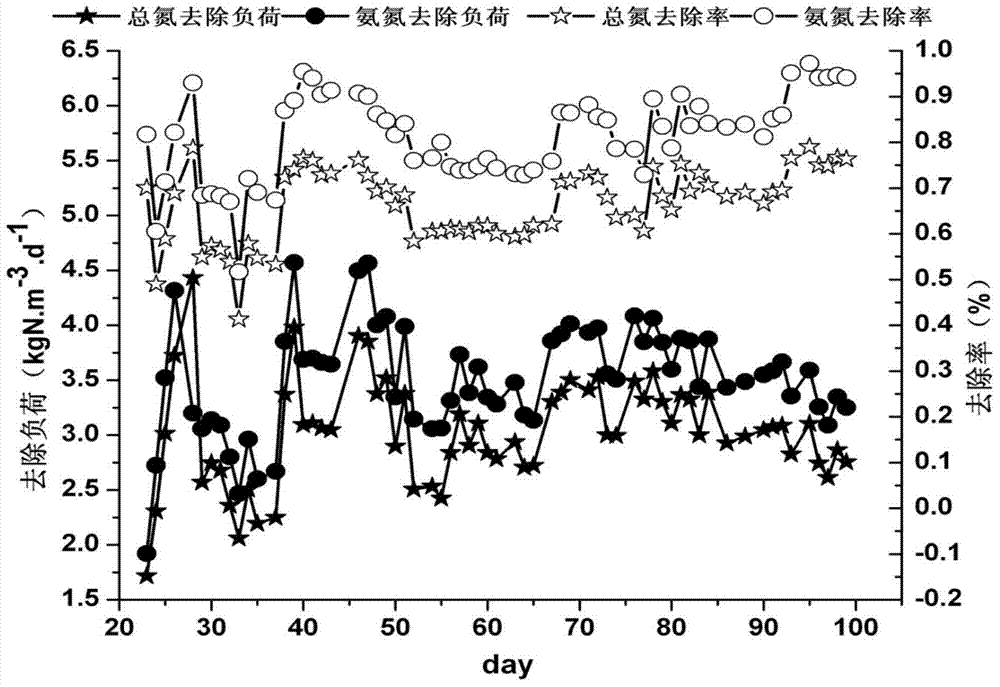
Method for operating anaerobic ammoxidation reactor capable of rapidly restarting heavy metal pollution
ActiveCN104891651AEfficient removalRapid recovery of denitrification performanceWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesInorganic saltsNitrogen removal
The invention discloses a method for operating an anaerobic ammoxidation reactor capable of rapidly restarting the heavy metal pollution. According to the invention, a chelating cleaning solution is added in the anaerobic ammoxidation sludge subjected to heavy metal contamination, and then the obtained product is oscillated and washed in a shaking bath. The obtained supernatant is removed, and the low-storied sludge is oscillated and washed in an inorganic salt solution. The washed sludge is inoculated into a reactor, and simulated wastewater is pumped into the reactor, wherein the substrate initial concentration in the simulated wastewater is 50-70 mg / L. When the heavy metal concentration in the effluent water of the reactor is smaller than the heavy metal concentration in the inflowing water of the reactor, a growth activator is added into the inflowing water of the reactor. When the nitrate nitrogen concentration in the effluent water of the reactor is smaller than 10 mg / L and the three-day mean variation of the nitrate nitrogen concentration in the effluent water of the reactor is smaller than 15%, the substrate concentration in the simulated wastewater is gradually increased. When the total nitrogen removal rate is larger than 80% and the molar reaction stoichiometric ratio of the substrate is stable, the growth activator is no longer added into the inflowing water of the reactor. In this way, the restarting function is successfully realized. According to the invention, heavy metals remaining in the sludge can be efficiently removed. Meanwhile, the nitrogen removal performance of the reactor and the particle characteristics of the anaerobic ammoxidation sludge can be rapidly recovered.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Process for hydrolyzing fish processing leftover using emzyme preparation
InactiveCN1943365AIncrease added valueMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsFresh fishNeutral proteinase
A process for treating tailings of processing fish with the enzymes, such as one of or the combination of two more of the neutral proteinase,alkali protease,papainase,flavor protease and trypsinase. The hydrolysis process includes 7 steps as following, adjusting the substance concentration, high temperature denaturalization, cooling down and adjusting the pH to 8.0-9.5, heat preservation at 35-6deg.C for 30-50min, enzymolysis for 2-6hr, enzyme destroyed at 85-100deg.C for 10-30min, then it will be separated to get the hydrolysis product. Such product can be used in the food industry with fresh fish flavor. The added value of the fish processing tailings will be greatly improved and it will make sense to the aquaculture and the environment.
Owner:天津市诺奥科技发展股份有限公司
Rhizopus microsporus root-shaped variant ZJPH1308 and application thereof in preparation of sitagliptin intermediate
ActiveCN104893989AHigh stereoselectivityHigh optical purityFungiMicroorganism based processesPyrazineButanone
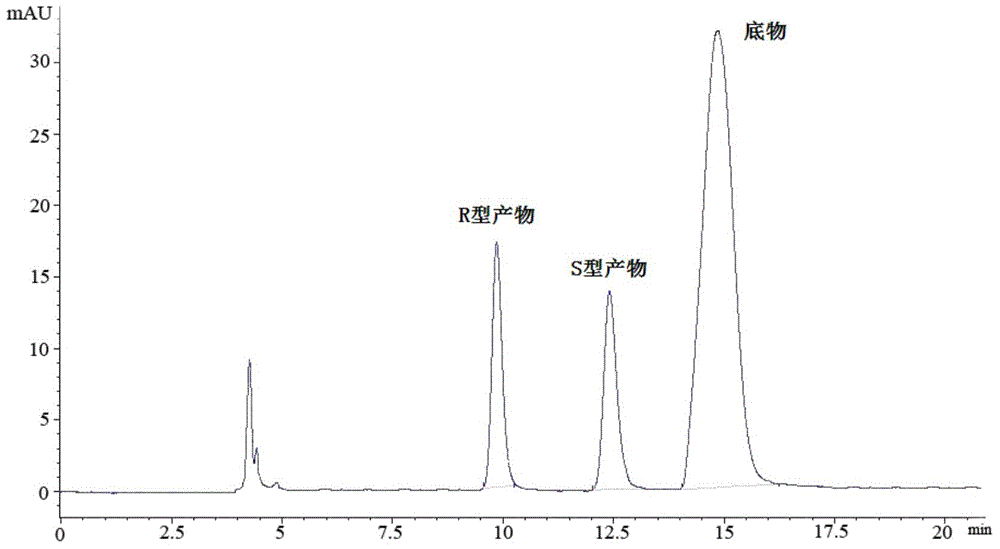
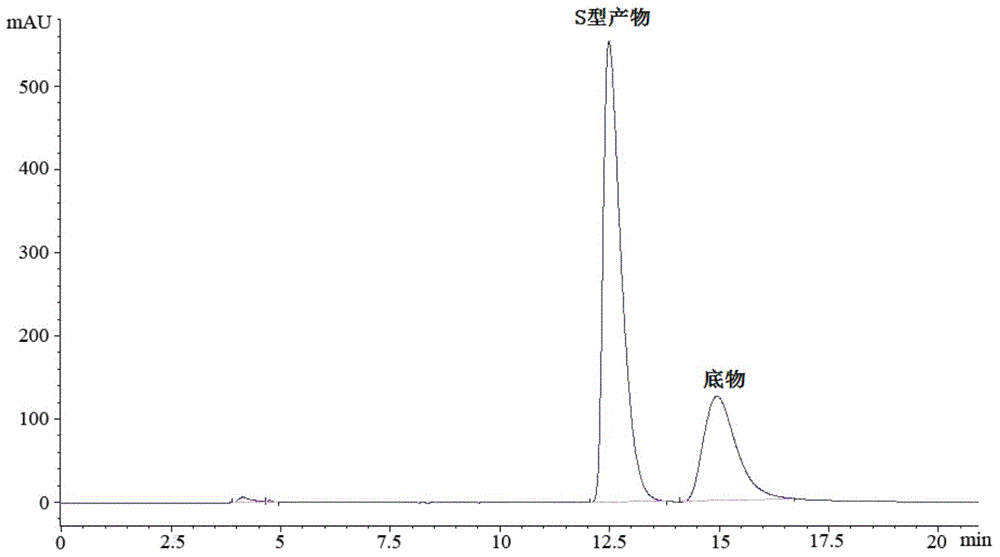
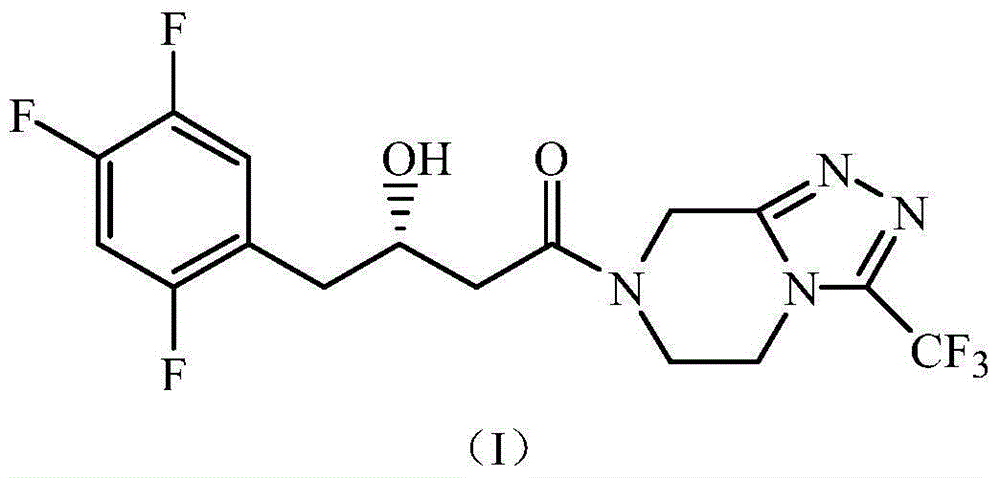
The invention discloses a rhizopus microsporus root-shaped variant ZJPH1308 and application thereof in preparation of a sitagliptin intermediate. A strain of the rhizopus microsporus root-shaped variant ZJPH1308 can be used for biologically and asymmetrically reducing 4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazol[4,3-a]pyrazine-7-(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanone so as to obtain (S)-3-hydroxyl-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazol[4,3-a]pyrazine-7-(8H)-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanone. The strain has the advantages of good three-dimensional selectivity, high product optical purity and the like. The rhizopus microsporus root-shaped variant ZJPH1308 is fermented and cultured to obtain a wet thallus which serves as chiral biological catalyst; when the substrate concentration is 10mmol / L, the reduction product yield is as high as 95%, and the e.e. value of the product is greater than 99.9%.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANHE PHARMA CO LTD
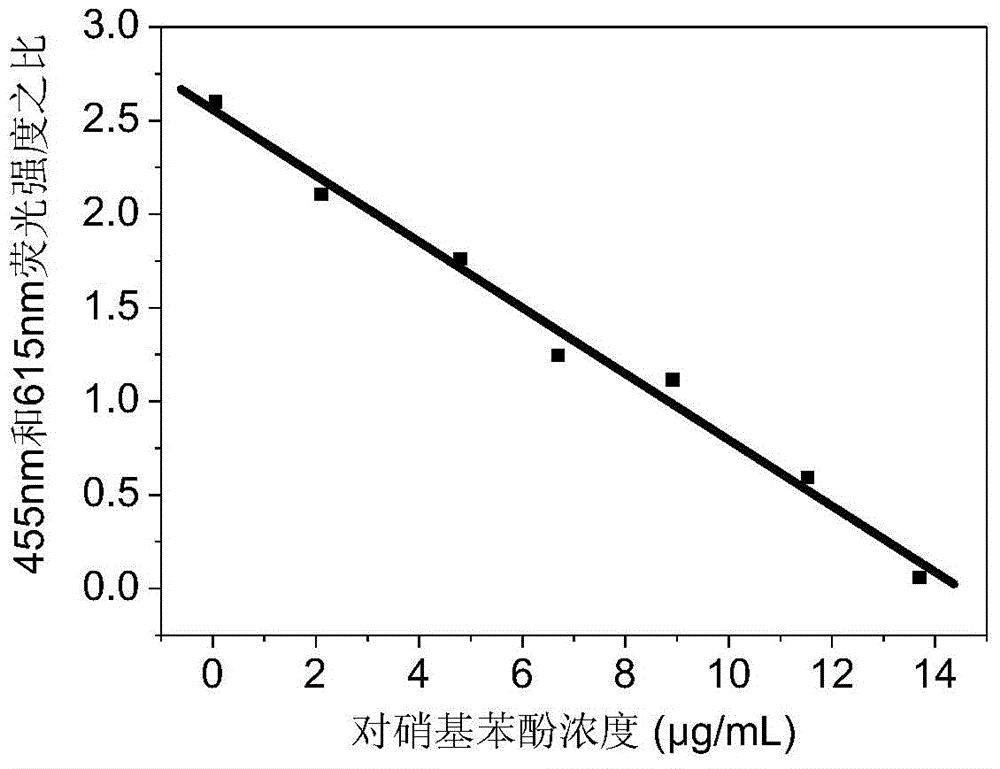
Method for detecting p-nitrophenol based on molecular imprinting ratio type fluorescent probe
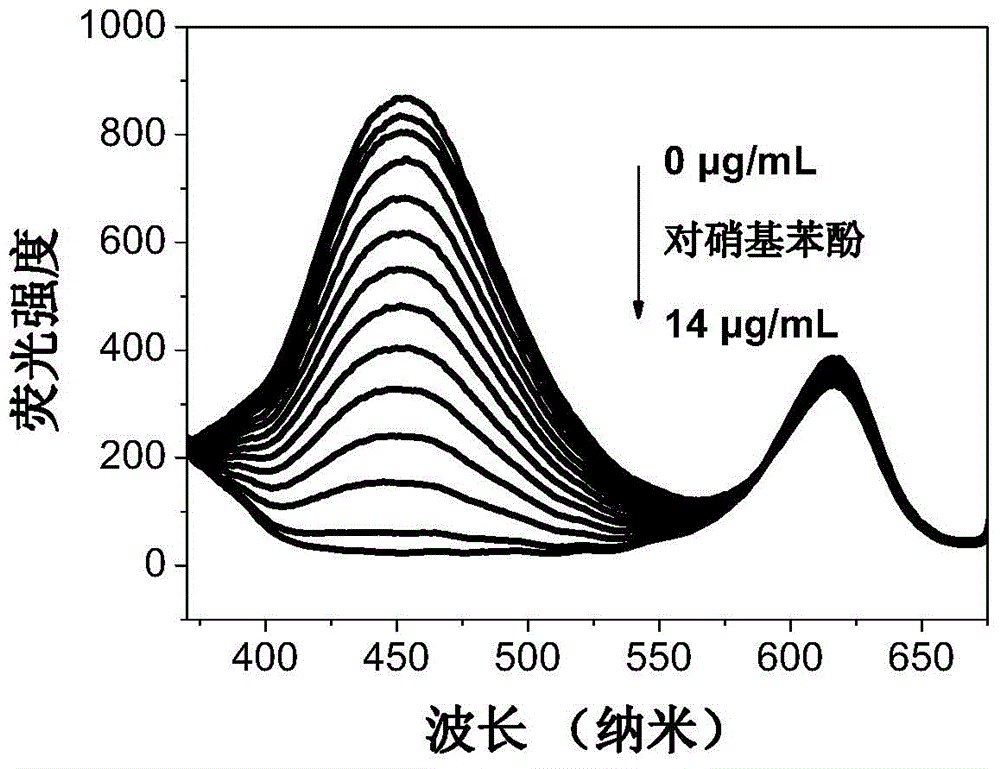
ActiveCN105092548ARealize determinationFix the leakFluorescence/phosphorescenceComposite nanoparticlesSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a method for detecting p-nitrophenol based on a molecular imprinting ratio type fluorescent probe. The molecular imprinting ratio type fluorescent probe is composed of a core-shell type double-emissivity molecular imprinting silicon dioxide nanoparticle, a quantum-dot-covering silicon dioxide nanoparticle and a siloxane functionalized carbon dot are employed for preparing the double-emissivity fluorescent nanoparticle, and then a silicon dioxide layer containing an imprinting molecule p-nitrophenol is grown on the surface of the double-emissivity fluorescent nanoparticle , so that the molecular imprinting double fluorescent composite nanoparticle is obtained. In the structure, the quantum dot in the silicon dioxide nanoparticle shell is taken as a reference fluorescent signal, and the carbon dot in the outer molecular imprinting layer is taken as a response fluorescent signal and is used for selective identification on p-nitrophenol. The method fully gives play to the advantages that molecular imprinting is resistant to interference, high in selectivity, high in sensitivity and the like, overcomes the disadvantage that a conventional single-fluorescent-signal analysis method is easily influenced by detection substrate concentration, external environment and other factors, and possesses significant meaning in the fields such as environment pollutant monitoring and control, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for producing konjac glucomannan
InactiveCN103060399AIncrease concentrationIncrease productivityFermentationHigh concentrationHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for producing konjac glucomannan, which comprises the following steps: firstly, adding konjac flour into citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution with pH of 6.0 to carry out enzymatic hydrolysis with beta-mannase for 2 to 6 h; carrying out heating treatment on enzymatic hydrolysate for 15 to 30 min by adopting a variable frequency microwave reactor; then placing the obtained enzymatic hydrolysate in a vacuum drying oven with the temperature of 45 DEG C for drying, and grinding and sieving the powder by 100 mesh sieves to obtain light yellow powder; and dissolving the light yellow powder in distilled water; and finally, executing the steps of centrifugation, vacuum evaporation and concentration, alcohol precipitation, drying, grinding and the like so as to obtain the konjac glucomannan finished product. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the enzymatic hydrolysis process adopts a semi-dry method; an enzymatic substrate has high concentration; production efficiency is greatly improved; and production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Composite anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction process and device based on granule sludge and biological films
InactiveCN104386812AGuaranteed uptimeStrong resilienceWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesHigh concentrationSequencing batch reactor
The invention discloses a composite anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction process based on granule sludge and biological films. A reactor main body is inoculated by adopting flocculent sludge, the hydraulic cutting force is improved by stirring, and an inorganic salt is added so that a crystal nucleus mode is formed, and thus anaerobic ammonia oxidation granule sludge is gradually formed; the reactor adopts an operating mode of a sequencing batch reactor, and the inflow water containing high-concentration ammonia nitrogen is diluted in a mode of regulating the drainage ratio, so that the substrate concentration in the reactor is in a proper range, and inhibition to anaerobic ammonia oxidation is avoided. According to the process disclosed by the invention, the anaerobic ammonia oxidation granule sludge can be rapidly cultured from the flocculent sludge, high-concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater is directly received, high-load operation is realized, the process has extremely high restorability, the activity of the reactor can be rapidly restored under extreme substrate inhibition conditions, and high-load stable operation is realized. The invention also provides a corresponding reaction device. Therefore, the occupied area is saved, the construction and operation are easy and convenient, the operation is stable and high-efficiency, and the operating energy consumption is greatly reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Process for preparing intestinal membrane protein powder by utilizing residual liquid sourced from heparin sodium production
InactiveCN102178050AReduce pollutionReduce production energy consumptionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffIntestinal membraneSubstrate concentration
The invention relates to a process for preparing intestinal membrane protein powder by utilizing residual liquid sourced from heparin sodium production, which comprises the following steps of: (1) raw material pretreatment: filtering heparin sodium residual liquid by nylon cloth of 180 meshes for removing impurities; (2) raw material desalination and dehydration: desalinating and dehydrating raw materials by the heparin sodium residual liquid obtained, after impurity removal, through nanofiltration membrane equipment; (3) enzymolysis: adding composite animal protein hydrolase which is 0.2-0.8 percent by substrate weight into the heparin sodium residual liquid with the substrate concentration of 3-6 percent, adjusting the pH value to 7.0 to 8.5 and carrying out enzymolysis at the constant temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 4-8 hours; (4) carrier addition: adding wheat bran which accounts for 20-50 percent by substrate weight into enzymolysis liquid, completely dissolving and uniformly stirring; and (5) spraying and drying. The method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, enzymolysis thoroughness, high product yield and high product quality, can be used for reducing the environmental pollution, changing the waste materials into valuable things and reducing the production energy consumption and the production cost.
Owner:ANHUI BAODI MEAT FOODS
Industrial process for the production of L-carnitine
InactiveUS6566552B2Easily appilcable on an industrial scaleReduce productionOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen pressureSubstrate concentration
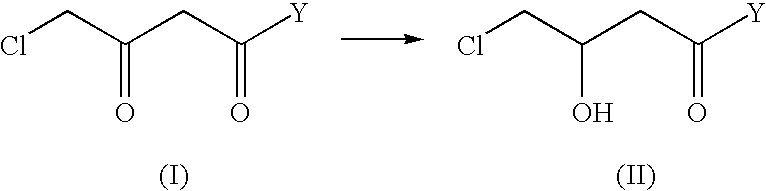
The present invention describes a process for the industrial production of L-carnitine, comprising the enantioselective reduction of an alkyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutyrate or 4-chloro-3-oxobutyramide. The optically active 3-hydroxy derivative thus obtained is reacted with trimethylamine, obtaining crude L-carnitine, which is then finally purified. The catalyst used for the reduction is a complex of ruthenium bound to a penta-atomic bis-heteroaromatic system. The reduction reaction, performed in controlled conditions of hydrogen pressure, substrate concentration, temperature, and substrate: catalyst molar ratio, enables 4-chloro-3-hydoxybutyrate or 4-chloro-hydroxybutyamide to be obtained in a high yield. The process described, which leads to L-carnitine being obtained, is easily applicable on an industrial scale.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Biosensor
InactiveUS20050194251A1Growth inhibitionAvoid reactionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic acidAlcohol sugars
In a biosensor for measuring a specific substance in a liquid sample, one or a combination of sugar alcohol, metallic salt, organic acid or organic acid salt which has at least one carboxyl group in a molecule, and organic acid or organic acid salt which has at least one carboxyl group and one amino group in a molecule, is included in a reagent layer provided on electrodes, thereby providing a highly-accurate biosensor which is excellent in stability and has high response (sensitivity, linearity) of the sensor to the substrate concentration.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110343676AHigh substrate concentrationLow costOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringL-glutamate dehydrogenaseEnzyme action
The invention discloses an L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. The sequence of the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant comprises a sequence obtained by mutating amino acid residue Aat position 166 and / or amino acid residue V at position 376 in a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 into a basic, hydrophilic or small hindered amino acid residue. The application comprises the followingsteps: subjecting 2-oxo-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butanoate to amination reaction in the presence of an L-amino acid dehydrogenase mutant, an inorganic amino donor and a reduced coenzyme NADPH to obtain L-glufosinate salt; and further acidifying the obtained L-glufosinate salt to obtain L-glufosinate. Compared with wild-type L-glutamate dehydrogenase, the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant of theinvention has a higher catalyzed substrate concentration when used for preparing the L-glufosinate, thus the enzyme action efficiency is improved, the reaction cost is reduced, and industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIZHOU ZIYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 and application thereof in preparation of chiral alcohol
ActiveCN103849574AHigh optical purityHigh substrate concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAlcohol
The invention discloses a novel strain, namely candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 and application thereof in preparation of high optical purity (5S)-(4-fluobenzene)-5-hydroxyvalerate by virtue of microbial catalytic asymmetric reduction of a 5-(4-fluobenzene)-5-keto pentanoic acid. The e.e value of a target product (5S)-(4-fluobenzene)-5-hydroxyvalerate achieves 99.9% and the yield achieves 95.37% when the concentration of a substrate is 47.62mmol / L and the final concentration of cosubstrate glucose is 100g / L by virtue of chiral biocatalysis of adopting the candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 cell as a catalyst.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
Nitrilase, encoding genes, carrier and application
InactiveCN104962540AAtom economy is highHigh potential for industrial applicationHydrolasesFermentationBrassica rapaBirdsrape Mustard
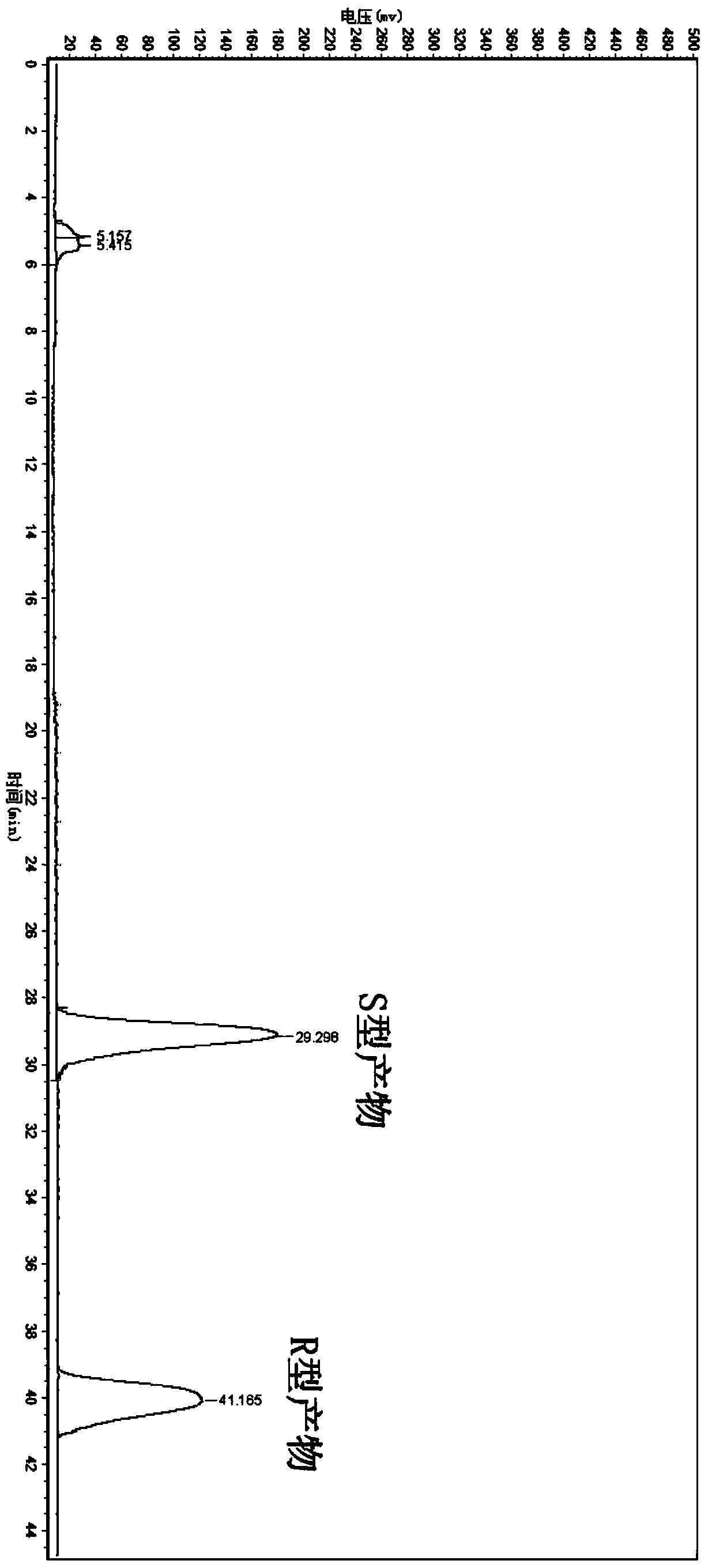
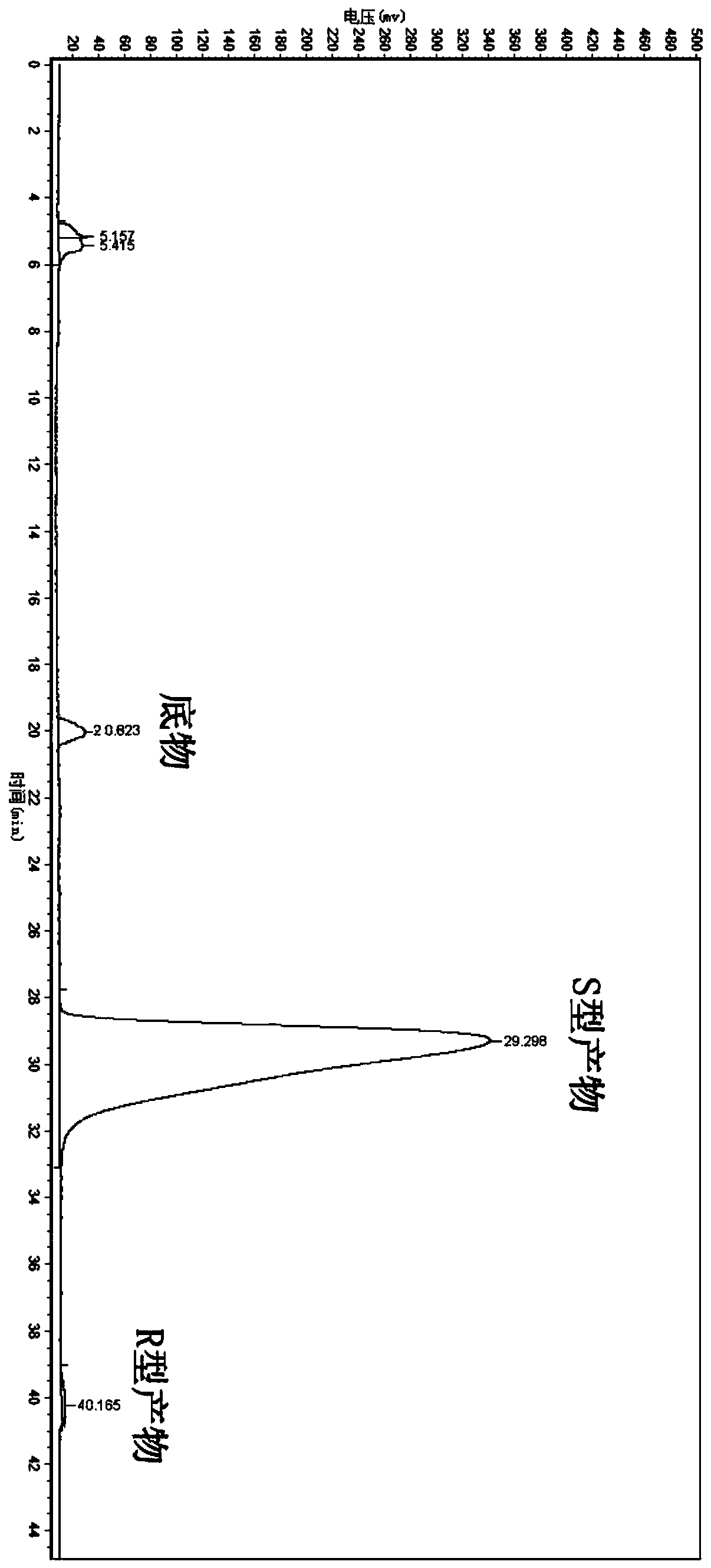
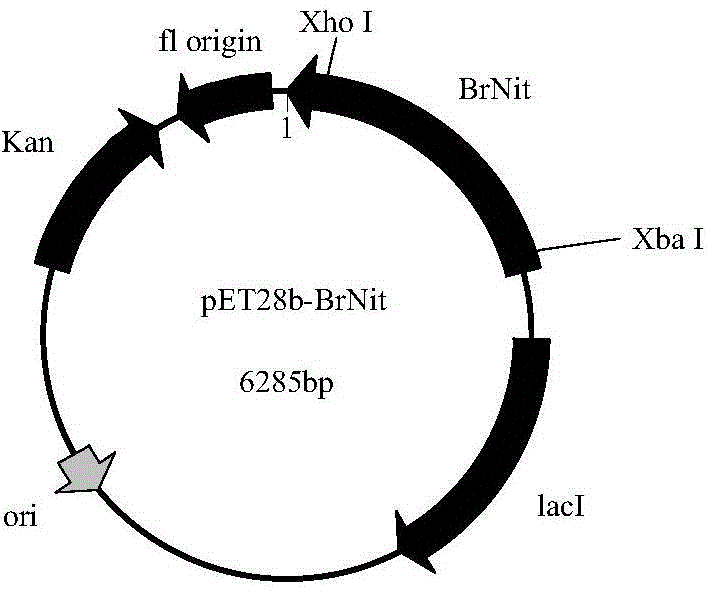
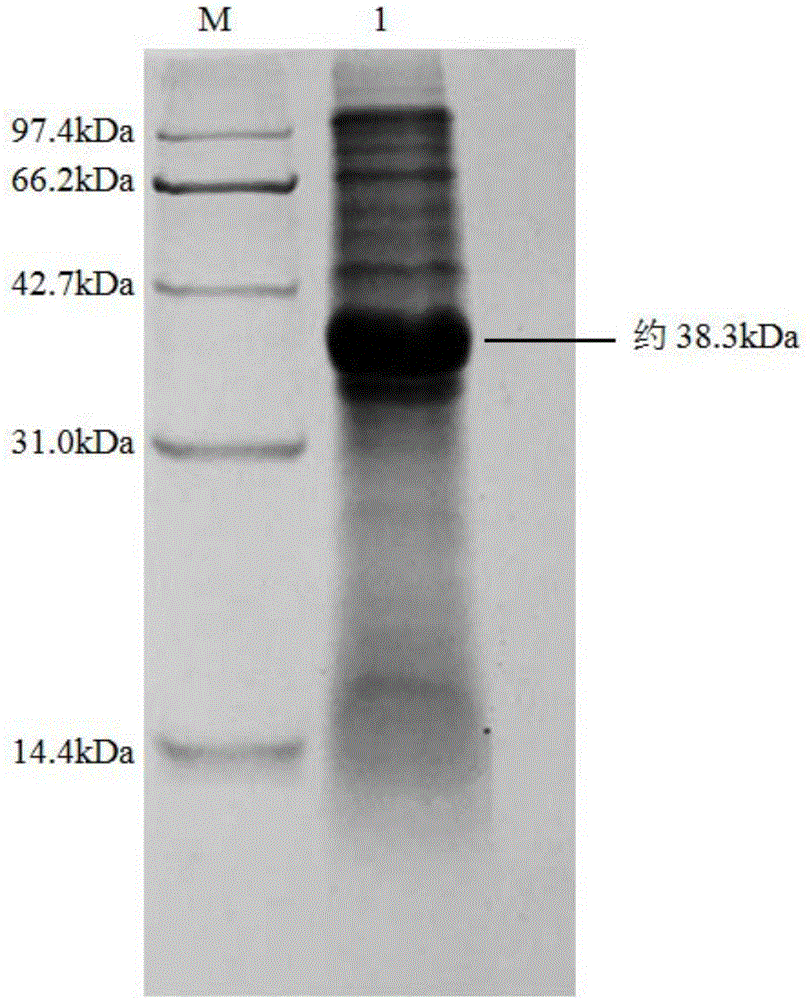
The invention discloses nitrilase from brassica rapa, encoding genes and an application of the encoding genes to the preparation of pregabalin chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid through biocatalysis, and an amino acid sequence of the nitrilase is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention provides novel nitrilase for preparing the (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid with high region and high stereoselectivity through hydrolysis, the concentration of hydrolysis substrates of the nitrilase can reach more than 1 M, and an ee (enantiomeric excess) value is kept more than 99 percent. The pregabalin important chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid can be prepared through the nitrilase; a preparation method of the (S)-3-cyan-5-methylhexanoic acid has the advantages of high atom economy, mild conditions, environmental friendliness and the like and has high industrial application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com