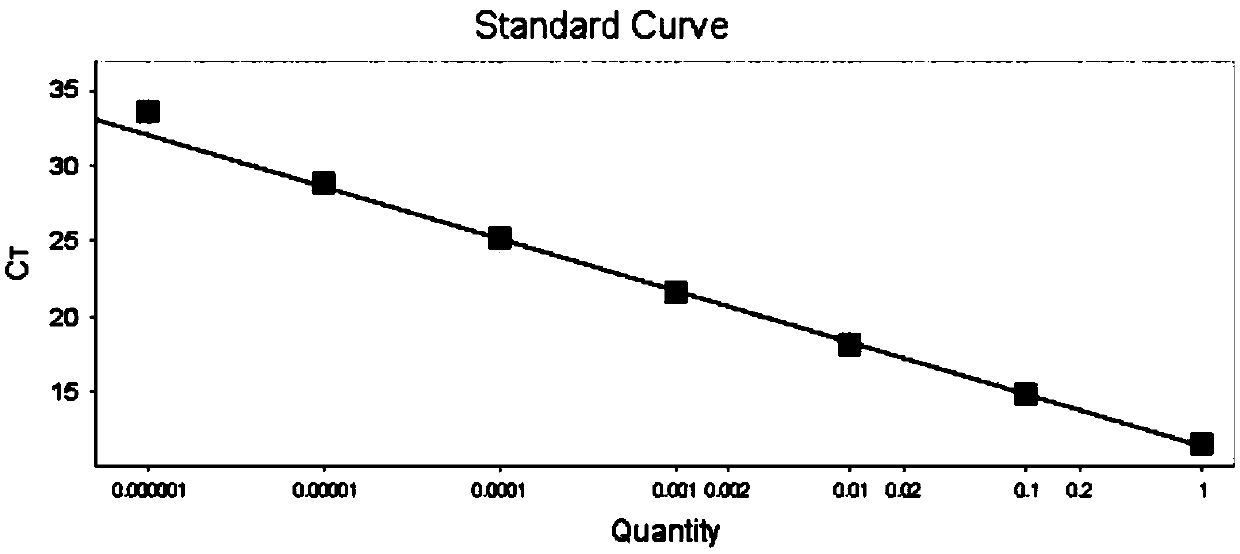
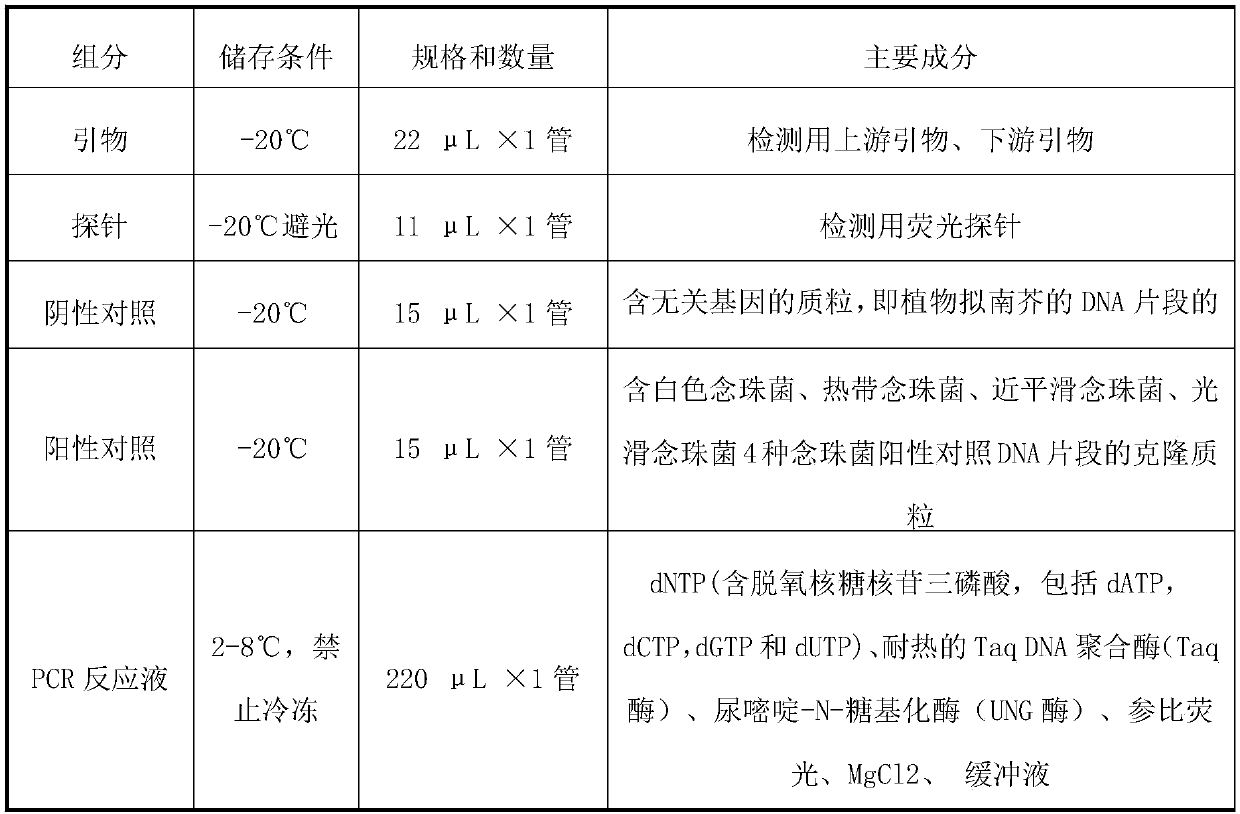
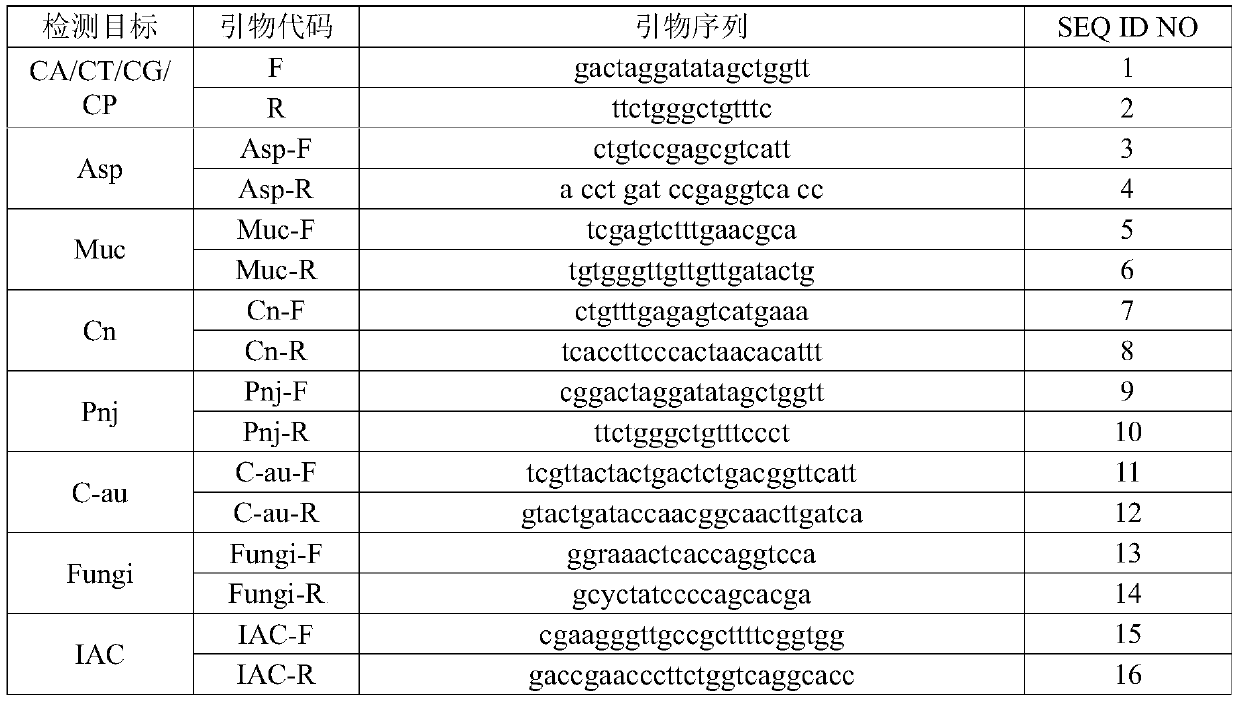
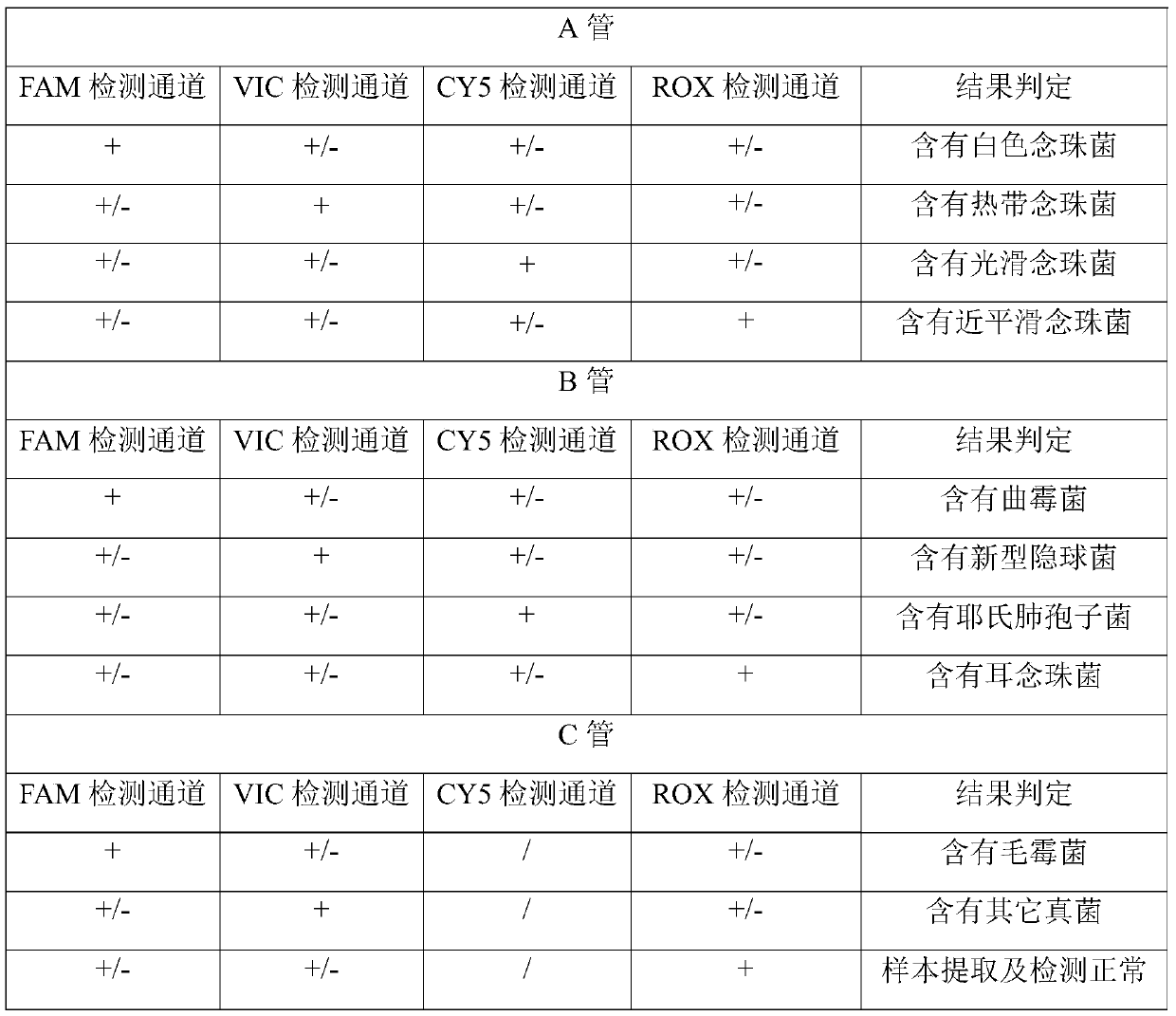
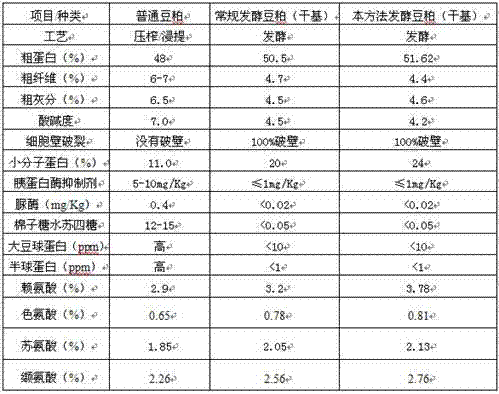
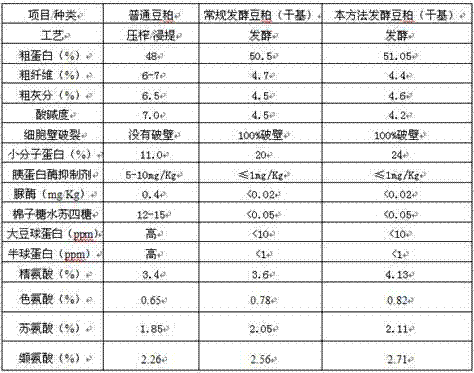
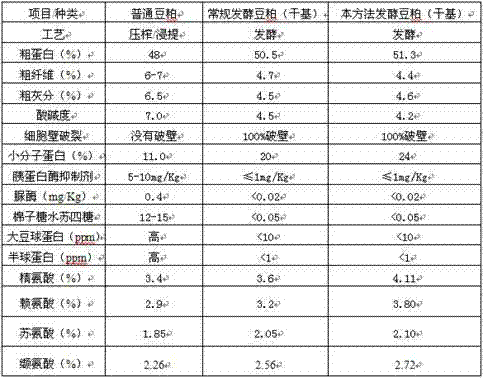
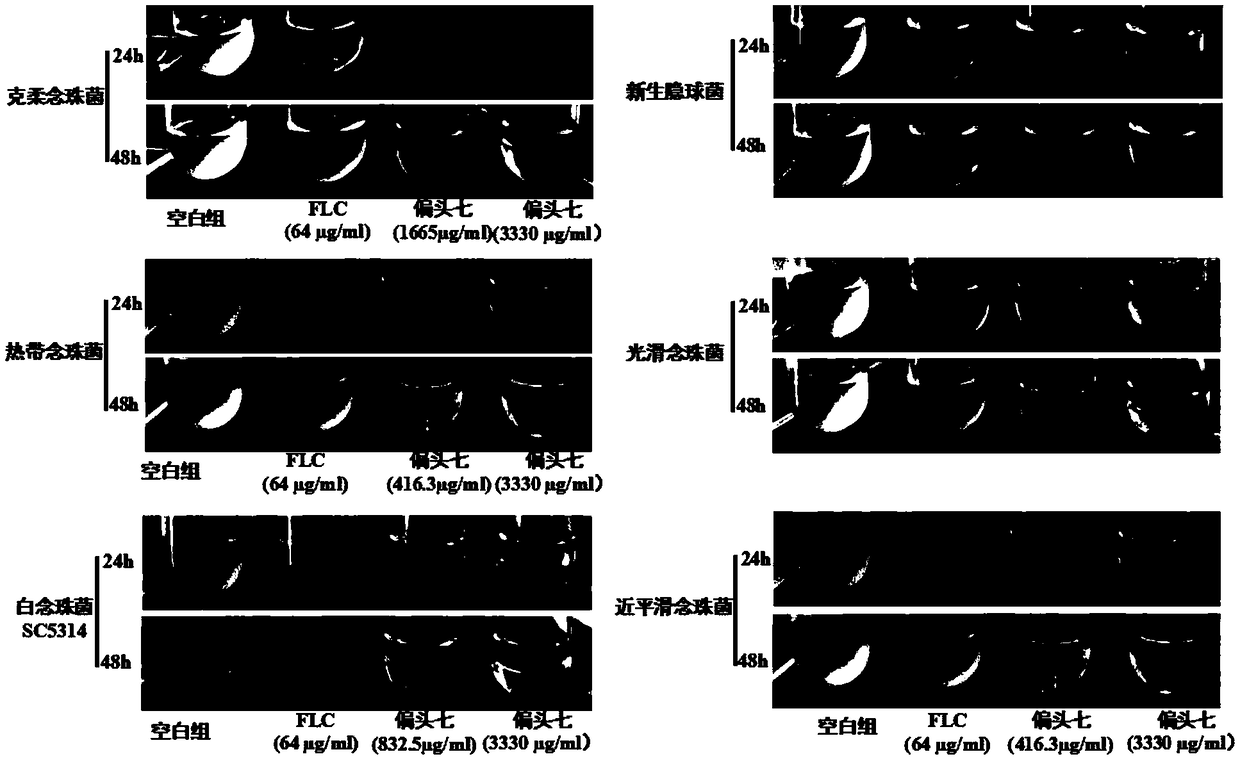
Patents
Literature
110 results about "Candida parapsilosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Candida parapsilosis is a fungal species of yeast that has become a significant cause of sepsis and of wound and tissue infections in immunocompromised people. Unlike Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis, C. parapsilosis is not an obligate human pathogen, having been isolated from nonhuman sources such as domestic animals, insects and soil. C. parapsilosis is also a normal human commensal and it is one of the fungi most frequently isolated from human hands. There are several risk factors that can contribute to C. parapsilosis colonization. Immunocompromised individuals and surgical patients, particularly those undergoing surgery of the gastrointestinal tract, are at high risk for infection with C. parapsilosis. There is currently no consensus on the treatment of invasive candidiasis caused by C. parapsilosis, although the therapeutic approach typically includes the removal of foreign bodies such as implanted prostheses and the administration of systemic antifungal therapy. Amphotericin B and Fluconazole are often used in the treatment of C. parapsilosis infection.
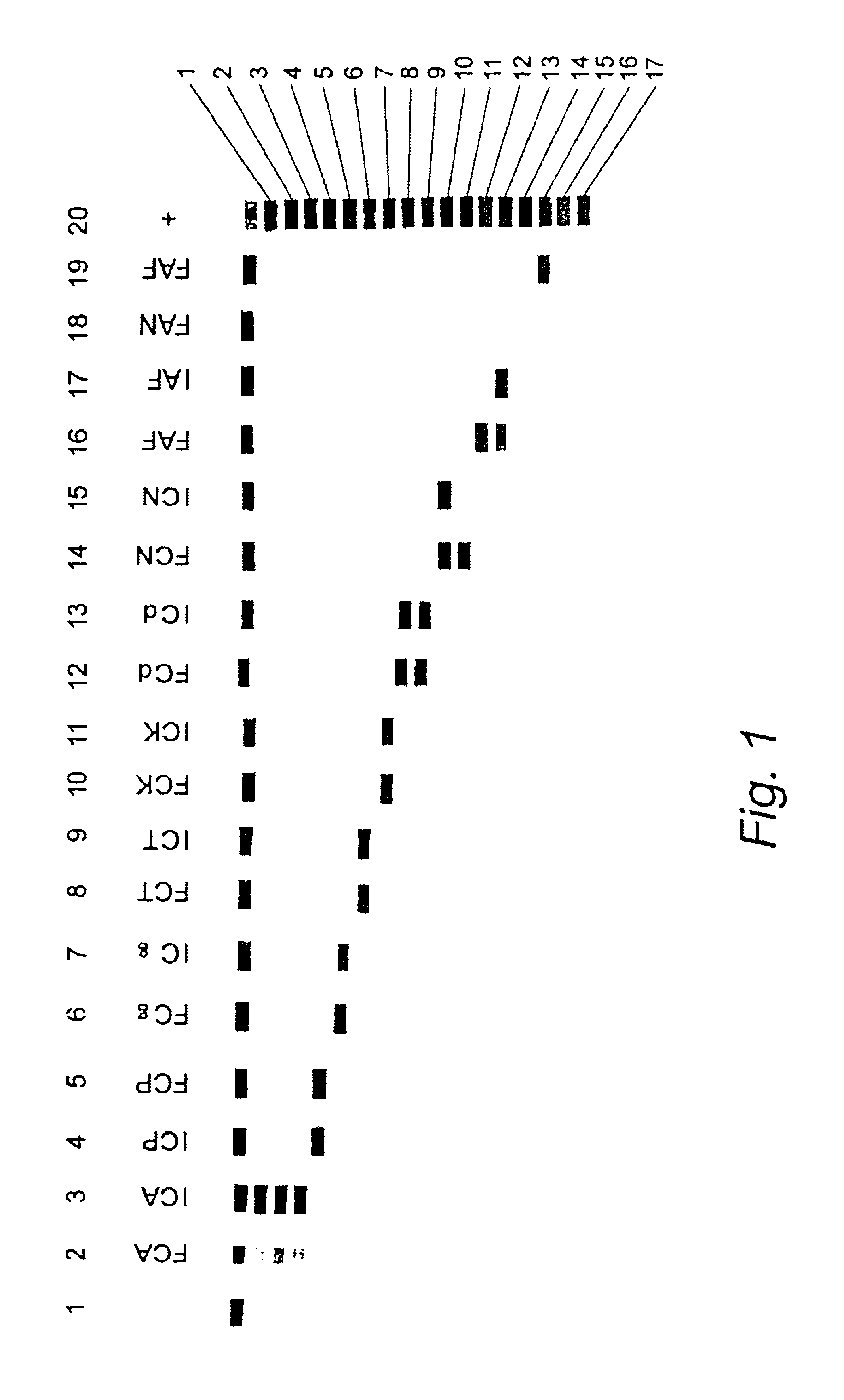
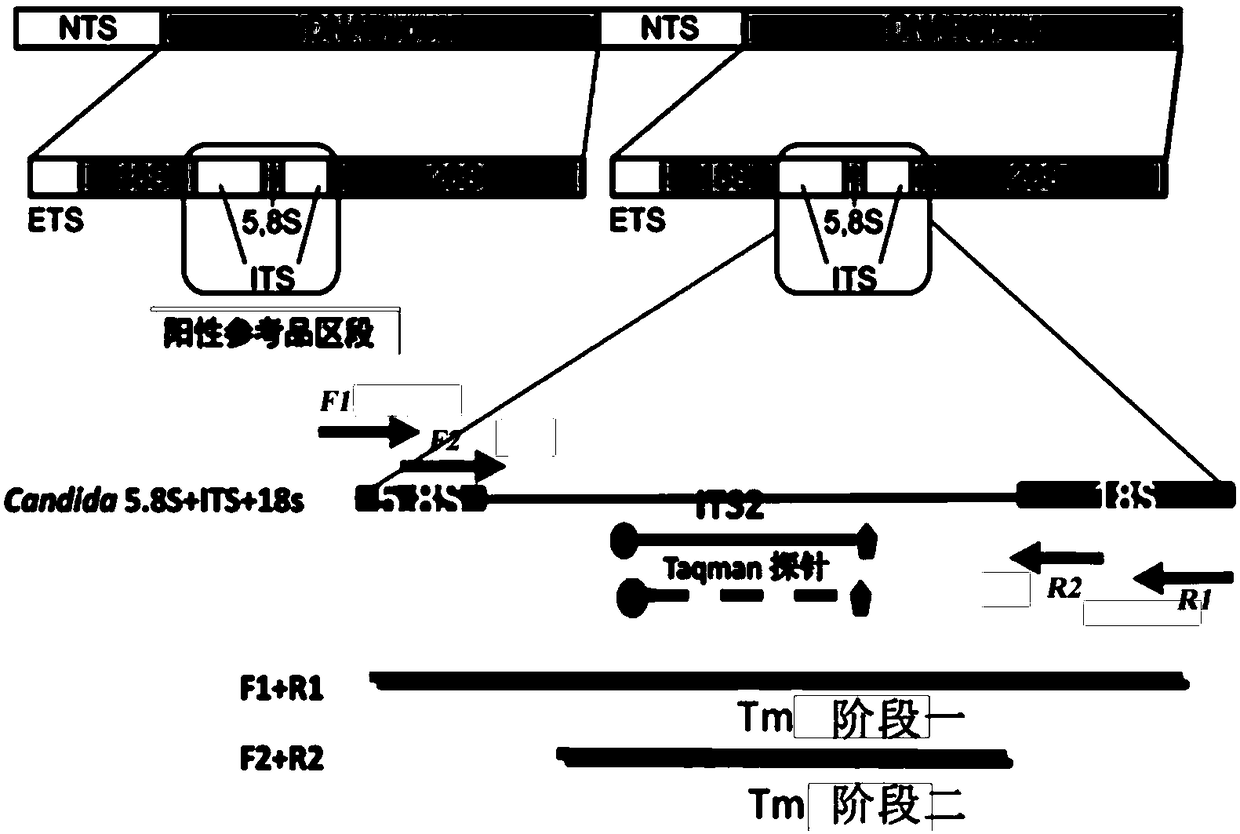
Nucleic acid probes and methods for detecting clinically important fungal pathogens
InactiveUS6858387B1Function increaseAttached with easeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesAspergillus flavus
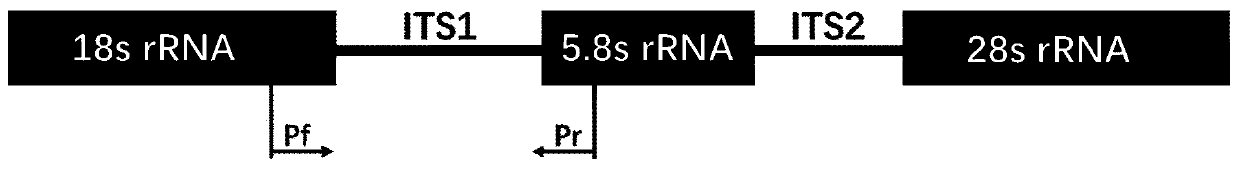
The current invention relates to the field of detection and identification of clinically important fungi. More particularely, the present invention relates to species specific probes originating from the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of rDNA for the detection of fungal species such as Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida kefyr, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata, Candida dubliniensis, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Cyptococcus neoformans and Pneumocystis carinii in clinical samples, and methods using said probes.
Owner:ENTERPRISE IRELAND +2
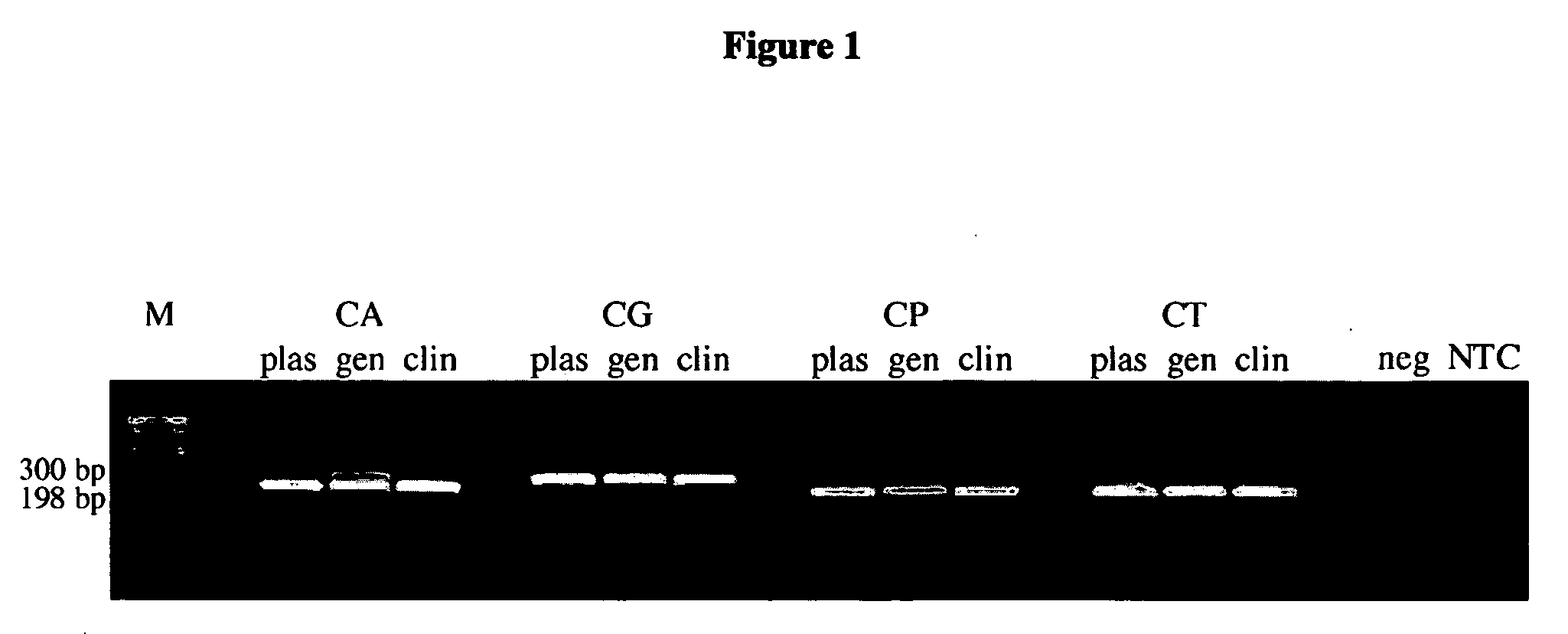
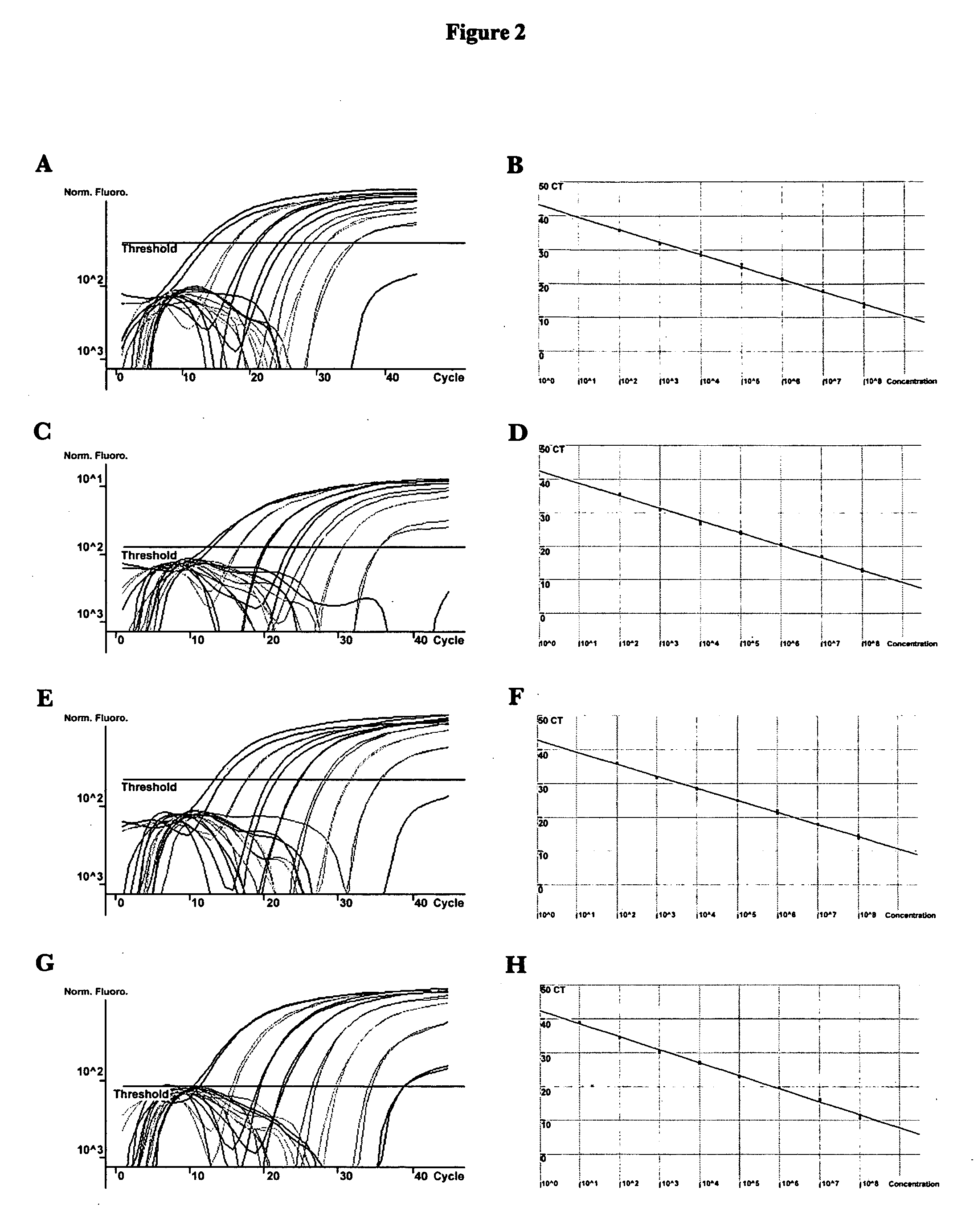
Methods and compositions for detecting and identifying species of Candida
ActiveUS20080102449A1Avoid disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerNucleotide
Methods and compositions useful in the detection and identification of species of Candida are disclosed. These species include Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, each of which is a causative agent for vaginal candidiasis. The compositions of the invention are combinations of oligonucleotides. These oligonucleotides include pairs of forward and reverse primers for polymerase chain reactions, wherein each primer pair is capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to one of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, but preferably is not capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to any of the other three species. In preferred embodiments, the forward primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each reverse primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other reverse primers; or the reverse primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each forward primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other forward primers. These unique primer sequences account for the species specificity of the resultant amplicons. The oligonucleotides also include probes capable of detecting these amplicons, and sequencing primers for determining, in primer extension reactions, the nucleotide sequences contained within the amplicons. In preferred methods of the invention, a biological sample is tested for the presence of at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis by isolating nucleic acid from the sample, attempting a polymerase chain reaction in a mixture containing this nucleic acid and a plurality of these primer pairs, ascertaining whether any amplicon is produced in the mixture using an oligonucleotide probe, and determining the sequence of any resultant amplicon using the sequencing primers. The detection of an amplicon indicates that the sample contains at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, or Candida tropicalis, and the nucleotide sequence data is used to determine which of these four Candida species is present.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
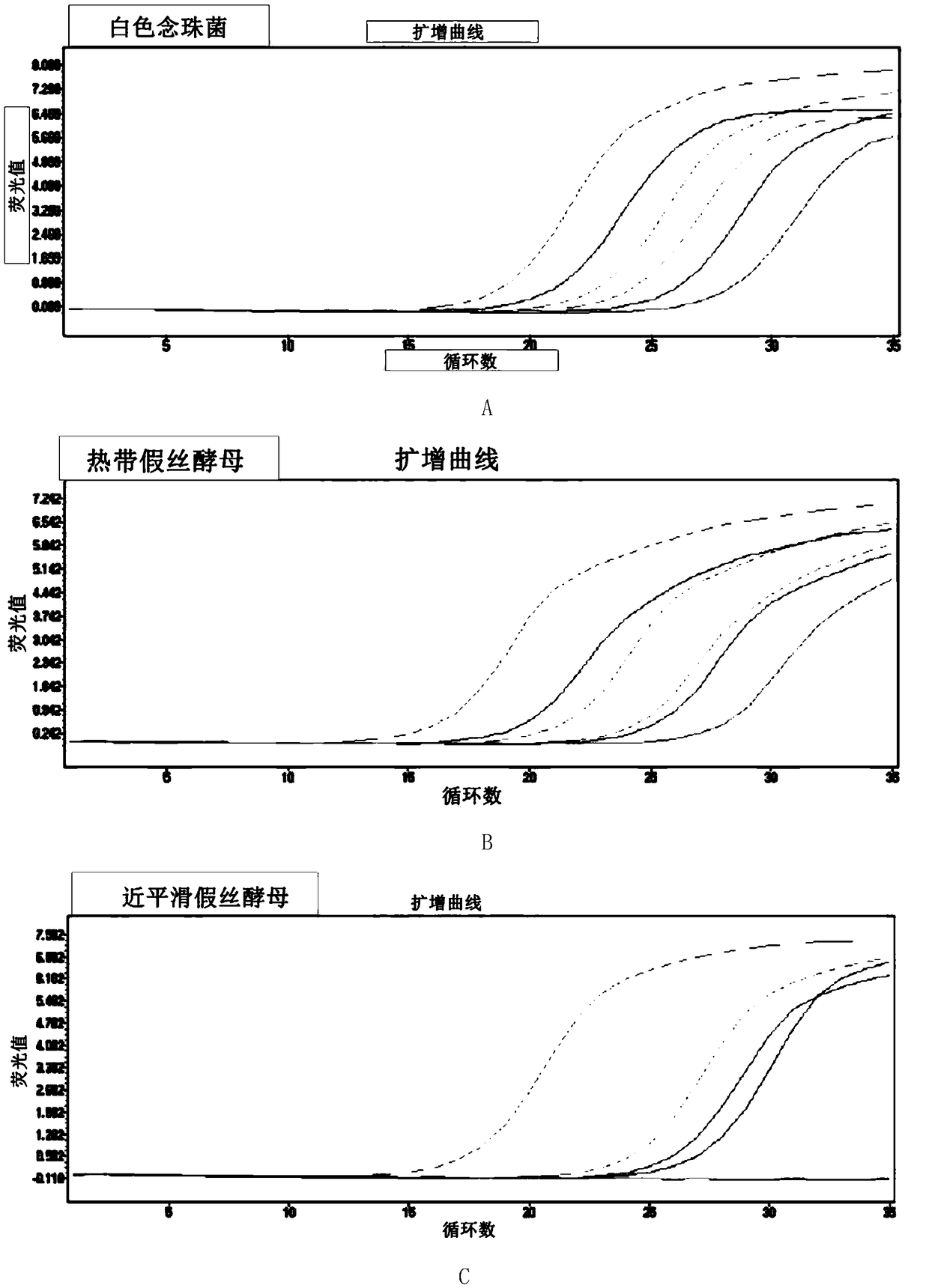
Fluorescence quantitative PCR primer, probe and kit for detecting ordinary pathogenic fungi
InactiveCN104450936AOvercome limitationsSolve the problem of fungal infectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceCandida tropicalis
The invention discloses a fluorescence quantitative PCR primer, a probe and a kit for detecting ordinary pathogenic fungi. A specific primer and a TaqMan probe are independently designed, and a fluorescence PCR detection method which can be used for simultaneously detecting 15 clinically ordinary pathogenic fungi, including 8 candida mycoderma bacteria (candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida parapsilosis, candida kefyr, candida sake, candida kruse, candida guilliermind and candida tropicalis), four aspergilli (aspergillus niger, aspergillus flavus, aspergillus terreus and aspergillus fumigates), cryptococcus, rhizopus oryzae and mucor circinelloides, is established. The method is relatively high in sensitivity and specificity, and has significant meanings for early diagnosis and treatment on invasive infections with fungi.
Owner:天津宝瑞生物技术有限公司
Detection method of invasive fungus infection, detection kit and application
ActiveCN109055502ASimplify detectionSimplify operabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCell freeFluorescence
The invention provides a fast multiplex PCR identification diagnosis detection method of invasive fungus infection based on cfDNA (cell free DNA). The method can be used for identifying the invasive infection caused by clinic common and high-incidence Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata and Aspergillus fumigtus. An amplification primer is designed according to characteristic genome segments of each fungus category and species; a detection fluorescence probe of a strain can be distinguished according to the amplification segment design; the real time PCR can be performed on a sample to be tested; high sensitivity of nested PCR and high specificity and multi-target performance advantages of multiple fluorescent hybrid probe PCR are integrated for identifying the fungus strain. The invention also provides a PCR diagnosis kit for the invasive fungus infection and application thereof.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST SHANGHAI
Nucleic acid probes and methods for detecting clinically important fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20050164243A1Faster and simpler to performSuitable for automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesAspergillus flavus
The current invention relates to the field of detection and identification of clinically important fungi. More particularely, the present invention relates to species specific probes originating from the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of rDNA for the detection of fungal species such as Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida kefyr, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata, Candida dubliniensis, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Cryptococcus neoformans and Pneumocystis carinii in clinical samples, and methods using said probes.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV +2
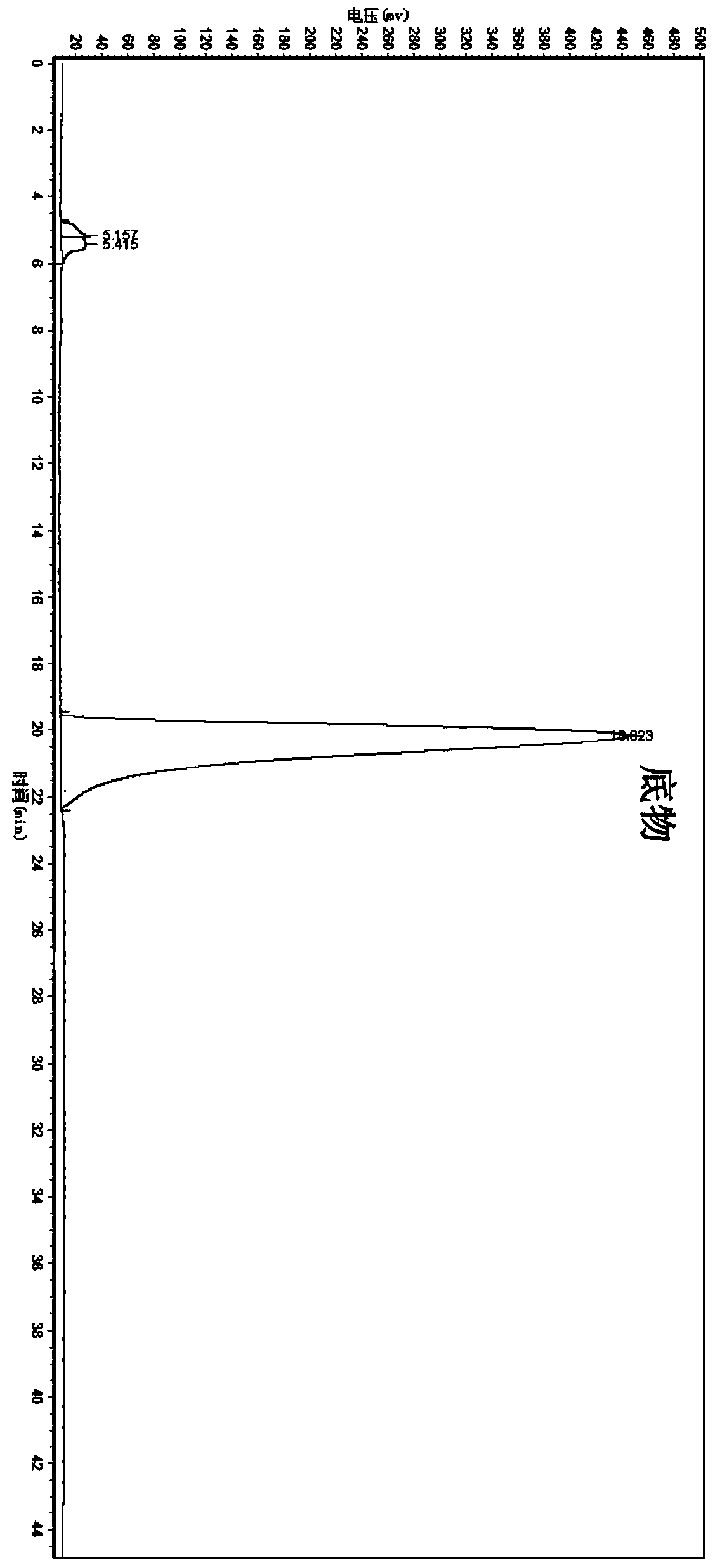
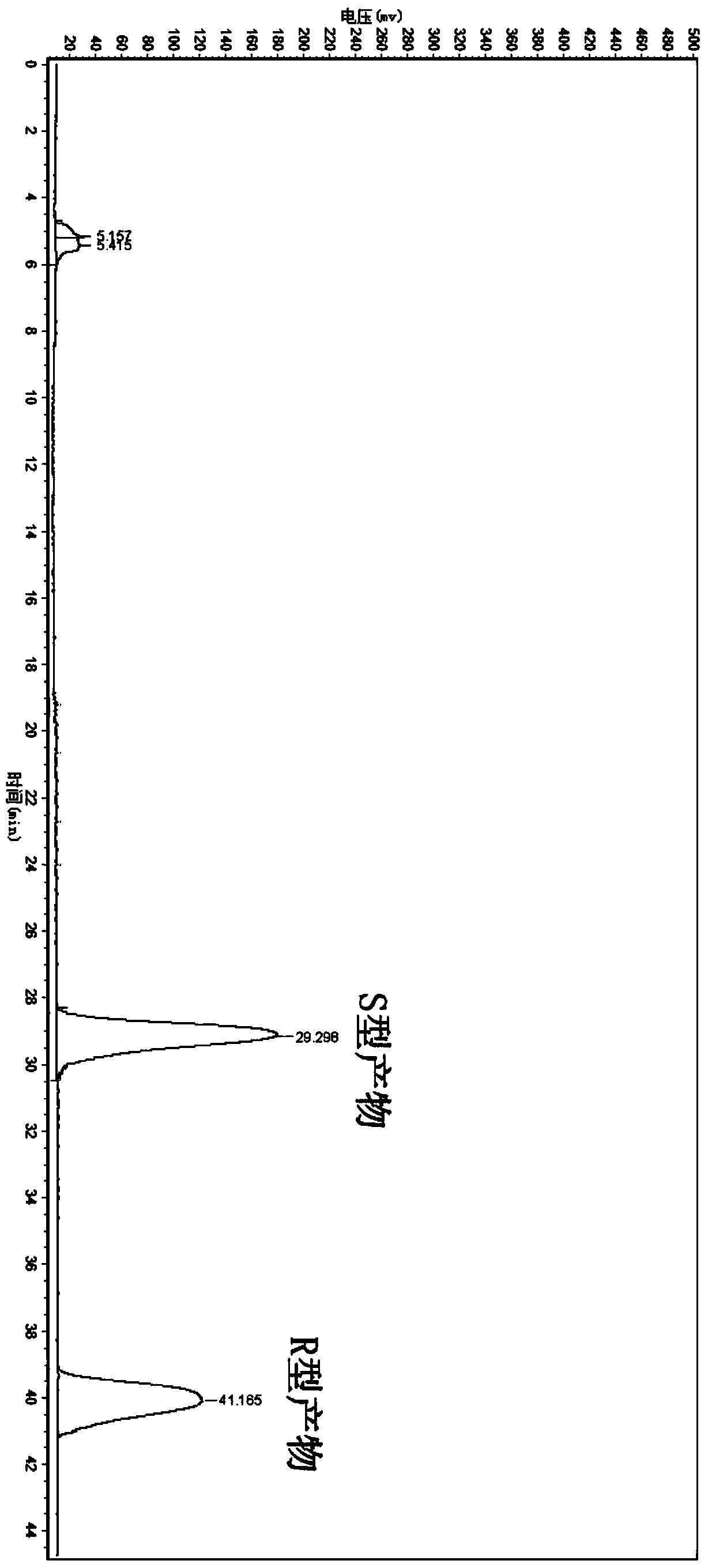
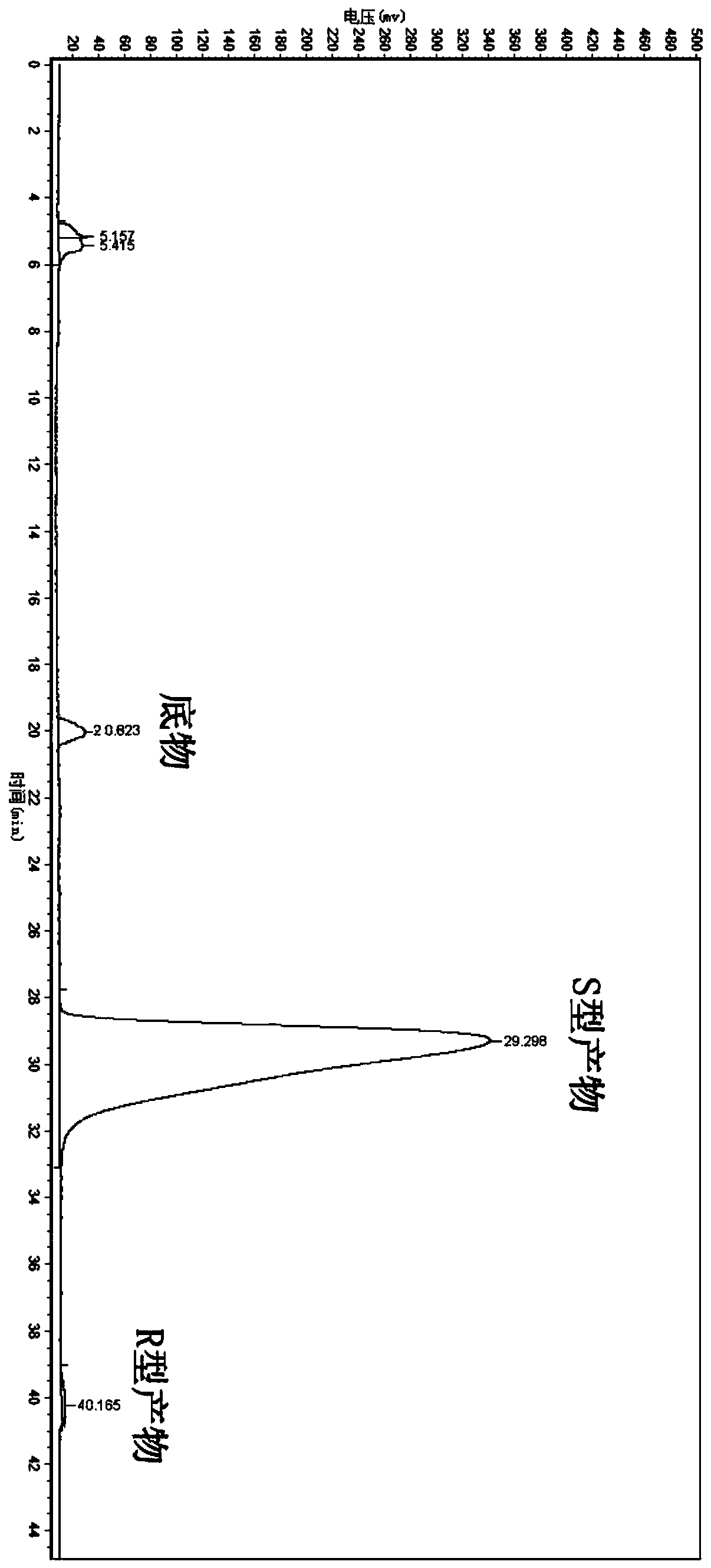
Candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 and application thereof in preparation of chiral alcohol
ActiveCN103849574AHigh optical purityHigh substrate concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAlcohol
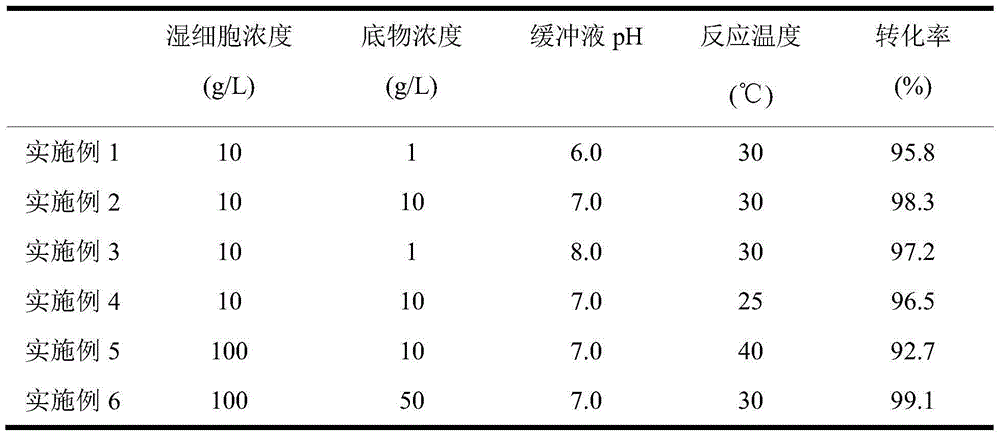
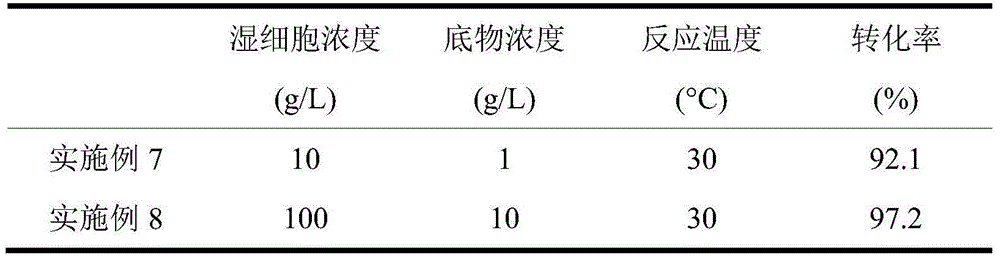
The invention discloses a novel strain, namely candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 and application thereof in preparation of high optical purity (5S)-(4-fluobenzene)-5-hydroxyvalerate by virtue of microbial catalytic asymmetric reduction of a 5-(4-fluobenzene)-5-keto pentanoic acid. The e.e value of a target product (5S)-(4-fluobenzene)-5-hydroxyvalerate achieves 99.9% and the yield achieves 95.37% when the concentration of a substrate is 47.62mmol / L and the final concentration of cosubstrate glucose is 100g / L by virtue of chiral biocatalysis of adopting the candida parapsilosis ZJPH1305 cell as a catalyst.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
Primer probe combination for simultaneously detecting four types of candida and kit thereof
ActiveCN108034745AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismFluorescence
The invention provides a primer probe combination for simultaneously detecting four types of candida, which belongs to the technical field of microbe detection. The primer probe combination comprisesprimers and a probe, the primer is an upstream primer and a downstream primer, a sequence of the upstream primer is shown as SEQ ID No.1; the sequence of the downstream primer is shown as SEQ ID No.2,and the probe is the sequence labeled with a report fluorescence group and a quenching fluorescence group shown as SEQ ID No.3. The invention provides a pair of primers and a probe which specificallyand simultaneously detect four types of candida such as Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, candida glabrata and candida parapsilosis.
Owner:杭州缔蓝生物技术有限公司
Candida parapsilosis CCTCC M203011 (S)- carbonyl reduction enzyme gene sequence and amino acid composition
The invention relates to gene order and amino acid component of (S)-carbonyl reductase of Candida parapsilosis CCTCC M203011, and the (S)-special carbonyl reductase gene can be used in separating recemic compound with biological method, which belongs to biological engineering sphere. The invention is to confirm (S)-special carbonyl reductase of Candida parapsilosis CCTCC M203011, its gene nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO:1, and its amino acid component is SEQ ID NO:2. By this gene, the recombination strain can be used in racemic chirality resolution and can arrange conditions for the heterogeneity, conversion approach and reaction mechanism of the microbial stereoselectivity oxidoreductase used in chirality resolution.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compound microbial inoculant for degrading COD (chemical oxygen demand) and preparation method of compound microbial inoculant
InactiveCN104894033AImprove adaptabilitySolve the problems of high cost of treatment process and unsatisfactory COD removal rateFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisCandida tropicalis
The invention discloses a compound microbial inoculant for degrading chemical oxygen demand and a preparation method of the compound microbial inoculant. The compound microbial inoculant comprises, by volume, 9-11% of candida tropicalis, 9-11% of candida parapsilosis, 28-32% of bacillus subtilis, 28-32% of bacillus licheniformis and 19-21% of enterococcus faecalis lactobacillus. The preparation method of the compound microbial inoculant includes that the candida tropicalis, the candida parapsilosis, the bacillus subtilis, the bacillus licheniformis and the enterococcus faecalis lactobacillus are respectively inoculated and cultured in sewage culturing media to obtain respective bacterium solutions, and the bacterium solutions are mixed according to the volume ratio to obtain the compound microbial inoculant, wherein the sewage culturing media are abundant in organic matter after being sterilized. The compound microbial inoculant is high in environment adaptability, applicable to microbial enhanced sewage treatment in different areas and various sewage including aquaculture sewage, domestic sewage, landfill leachate and the like which are abundant in organic matter, and capable of removing 95% of the COD in sewage.
Owner:湖北凌卓生物工程有限公司
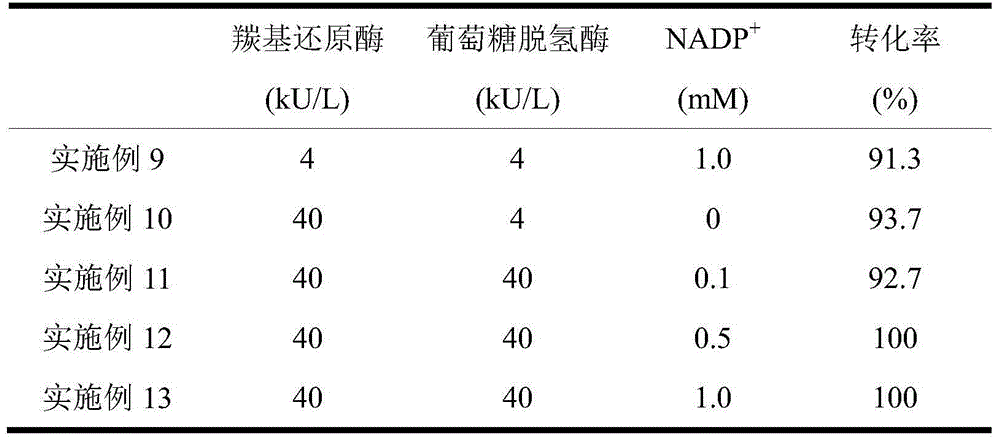
Method for improving transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase
The invention relates to a method for improving the transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase, belonging to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the method for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol by recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 and 2-hydroxyacetophenone catalyzed by the recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 in multiple batches. In the invention, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and the Candida parapsilosis (S)-carbonyl reductase gene are simultaneously integrated into the Pichia pastoris genome, under the participation of 5% (w / v) glucose, the whole cells are reused for 10 batches, and the optical purity and yield of the (S)-phenyl glycol prepared by asymmetric transformation are maintained at 100% and higher than 85% all the time. The recombinant strain improves the batch stability of full cell transformation of the (S)-phenyl glycol by polygene coexpression, which well relieves the limit of coenzyme regenerative cycle in a biological transformation reaction; and simultaneously an efficient approach for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol industrially in multiple batches at low cost is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nucleic acid reagent, kit, system and method for detecting invasive fungi
InactiveCN110551840AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCandida tropicalisCandida famata
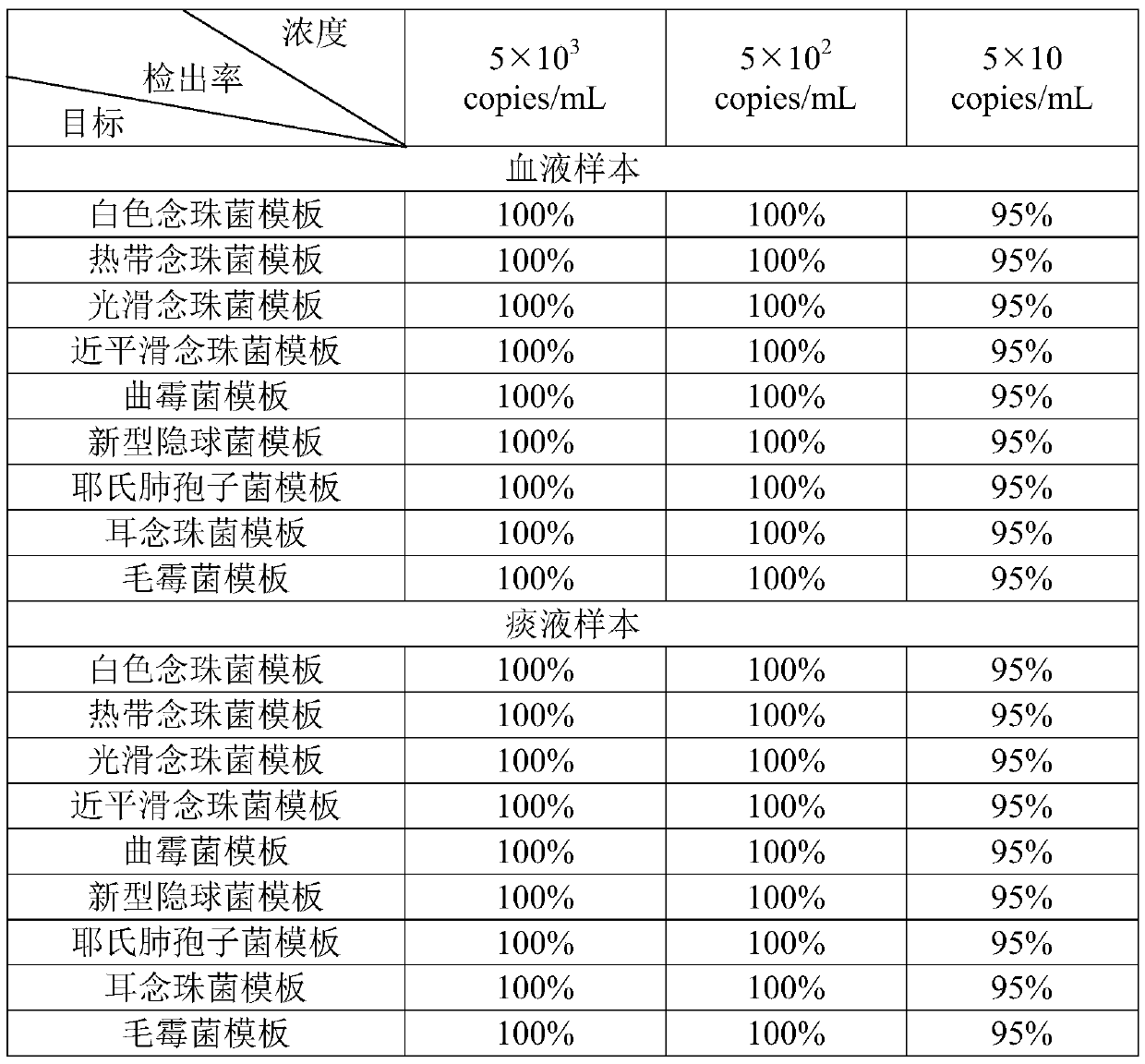
The invention relates to a nucleic acid reagent, kit, system and method for detecting invasive fungi. The nucleic acid reagent comprises a primer shown in SEQ ID NO.1-14 and a probe shown in SEQ ID NO.17-26, and the primer and the probe are stored independently with each other correspondingly or mixed with each other at will. Through the primer and the probe, the nucleic acid reagent, the kit, thesystem and the method of at least 9 invasive fungi of candida albicans, candida tropicalis, candida glabrata, candida parapsilosis, mucor, aspergillus, cryptococcus neoformans, pneumocystis jeroveciand candida auris, fast, comprehensive, sensitive, specific and automatic detection result determination can be achieved, and the sensitivity, specificity, simplicity and convenience of simultaneous detection of the detection target genome are significantly improved.
Owner:北京卓诚惠生生物科技股份有限公司
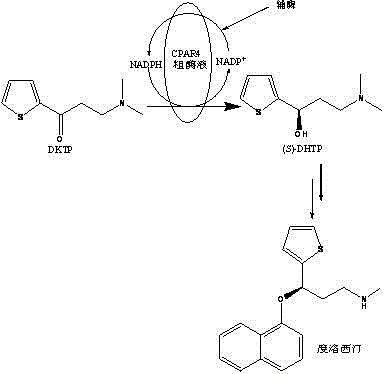
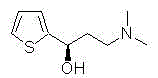
Method catalytically synthesizing (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-(2-thiofuran)-1-propylamine((S)-DHTP) by aldehyde ketone reductase recombinant strain crude enzyme system
The invention discloses a method catalytically synthesizing (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-(2-thiofuran)-1-propylamine((S)-DHTP) by aldehyde ketone reductase recombinant strain crude enzyme system, and belongs to the technical field of biological catalysis asymmetric conversion. An auxiliary substrate and original bulk coenzyme NADP<+> are added in the recombinant strain crude enzyme system to accelerate regeneration cycle of coenzyme NADPH in the system; the reaction substrate is N, N-dimethyl-3-ketone-(2-thiophene)-1-propylamine (DTKP); the recombinant strain is E. coliBL21(DE3)(pETCPAR4); aldehyde ketone reducing enzyme gene cpar4 comes from Candida parapsilosis; the gene coded aldehyde ketone reducing enzyme gene CPAR4 catalytically and asymmetrically reduces the DKTP into (S)-DHTP. The method utilizes the cell-free system to conduct catalytic reaction; coupling enzyme required by regeneration of the coenzyme is not extra added in the reaction system; direct acting efficiency of the enzyme and the substrate is improved; reaction time is shortened; the conversion effect is relatively good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Candida categorized detection primer and probe composition, kit, detection method and application of composition
ActiveCN109971883AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluorescenceCandida famata
The invention provides a Candida categorized detection primer and probe composition, a kit, a detection method and an application of the composition. The Candida categorized detection primer and probecomposition comprises specific primers, detection probes and complementary probes which are used for Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida krusei and Candida glabrata, and the complementary probes and the detection probes are incompletely complemented and paired. The primer and probe composition can detect and determine presence and absence of Candida infection onceand can distinguish the Candida albicans, the Candida tropicalis, the Candida parapsilosis, the Candida krusei and the Candida glabrata in the same fluorescent light channel.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
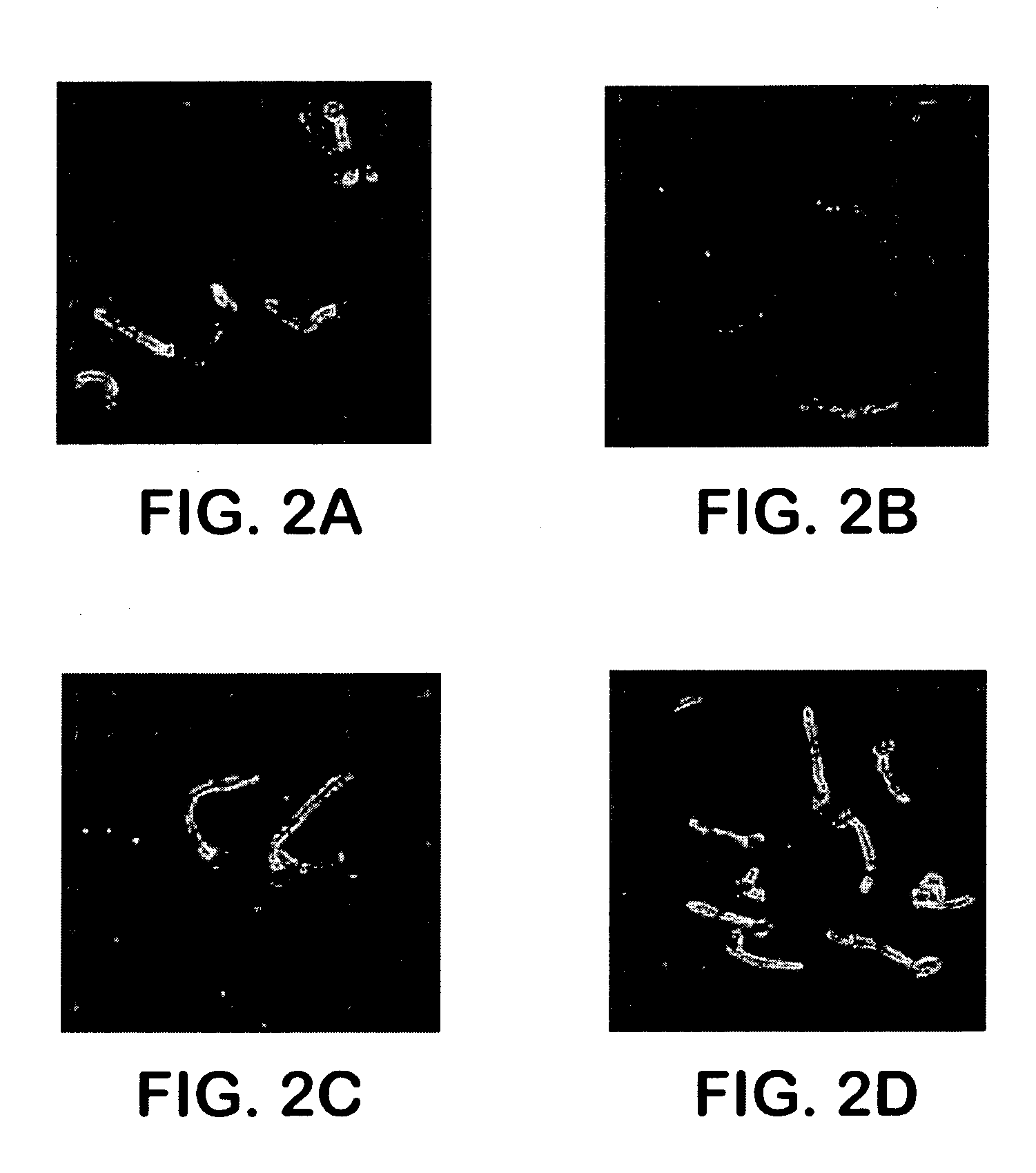
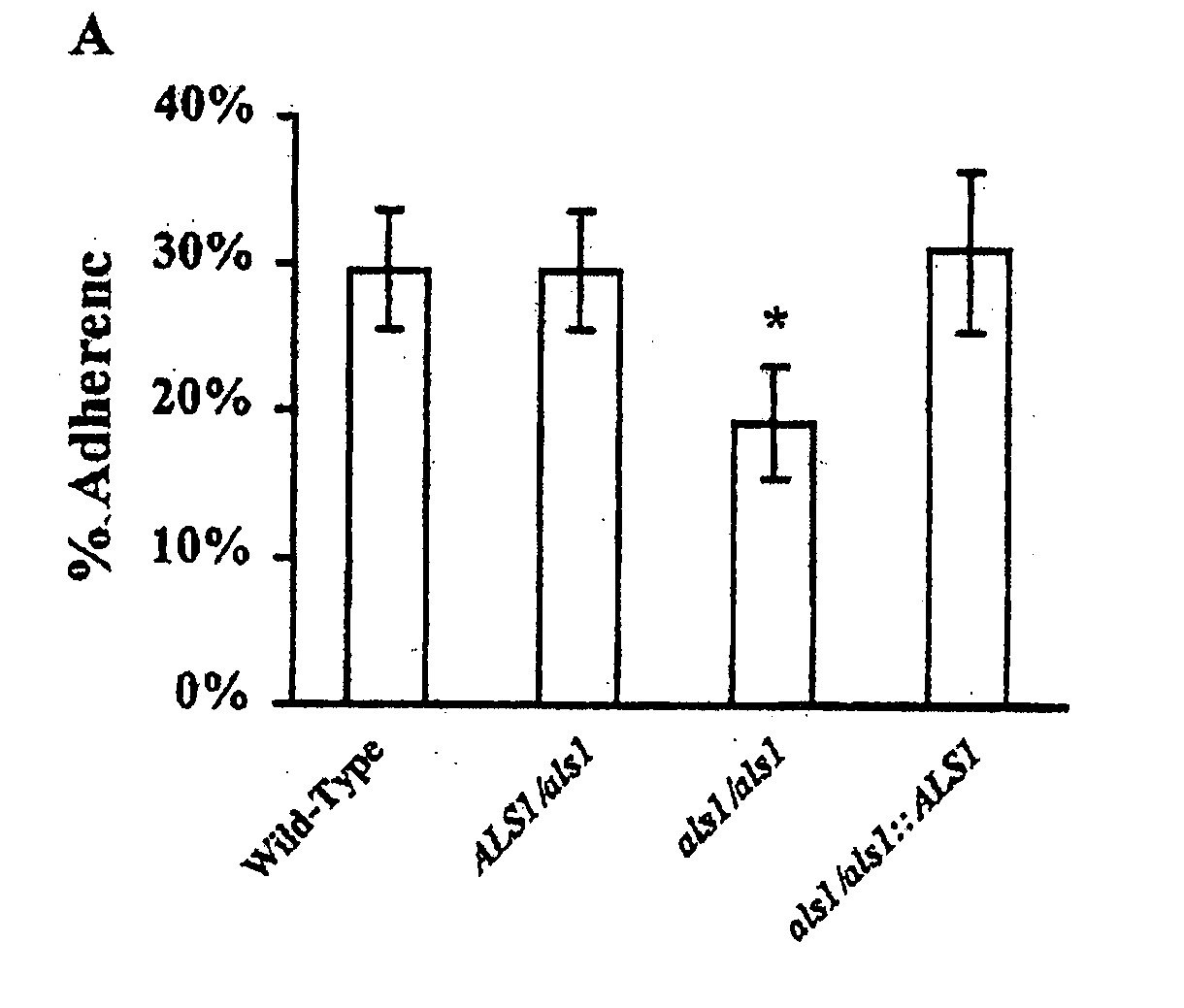
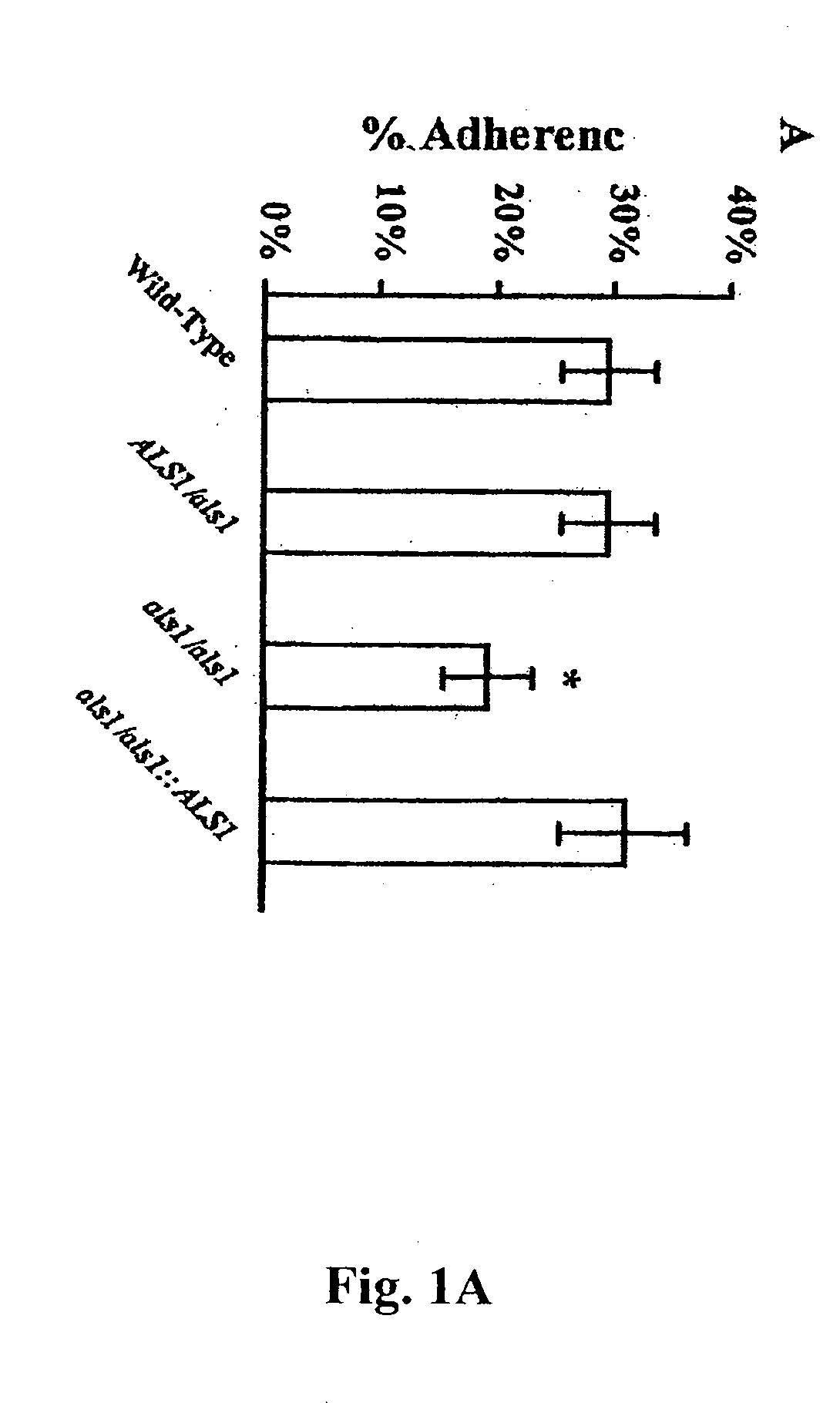
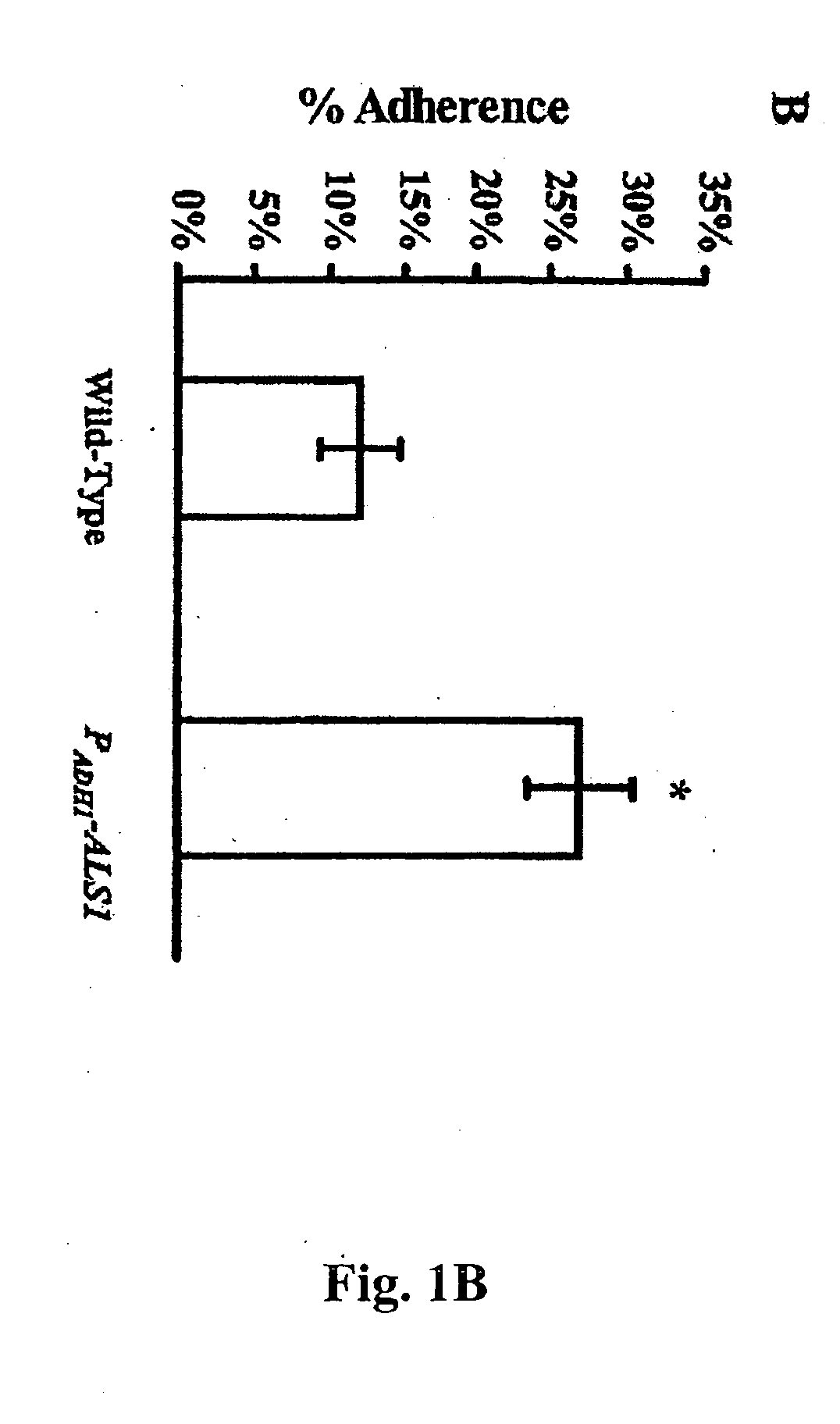
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods to vaccinate against disseminated candidiasis
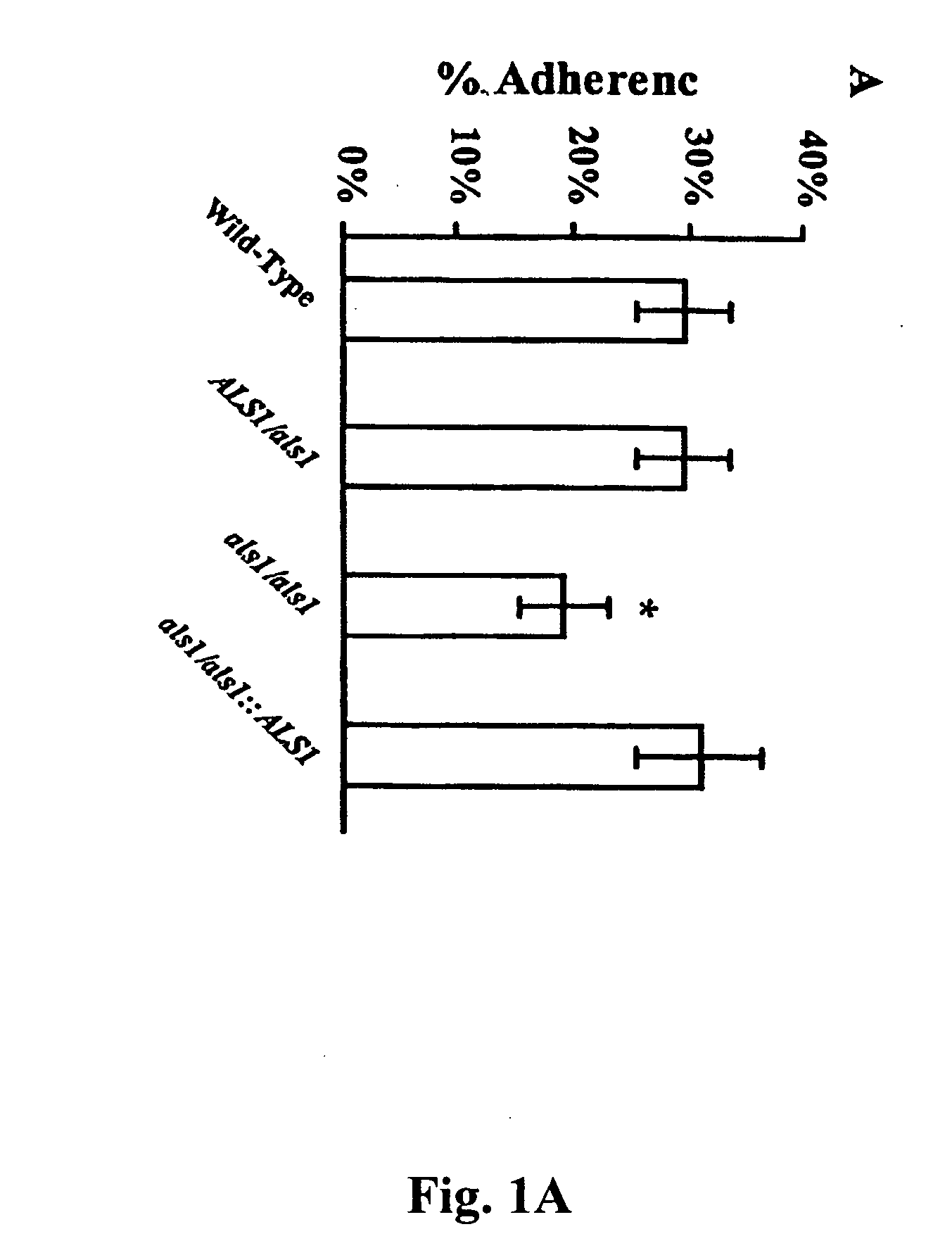
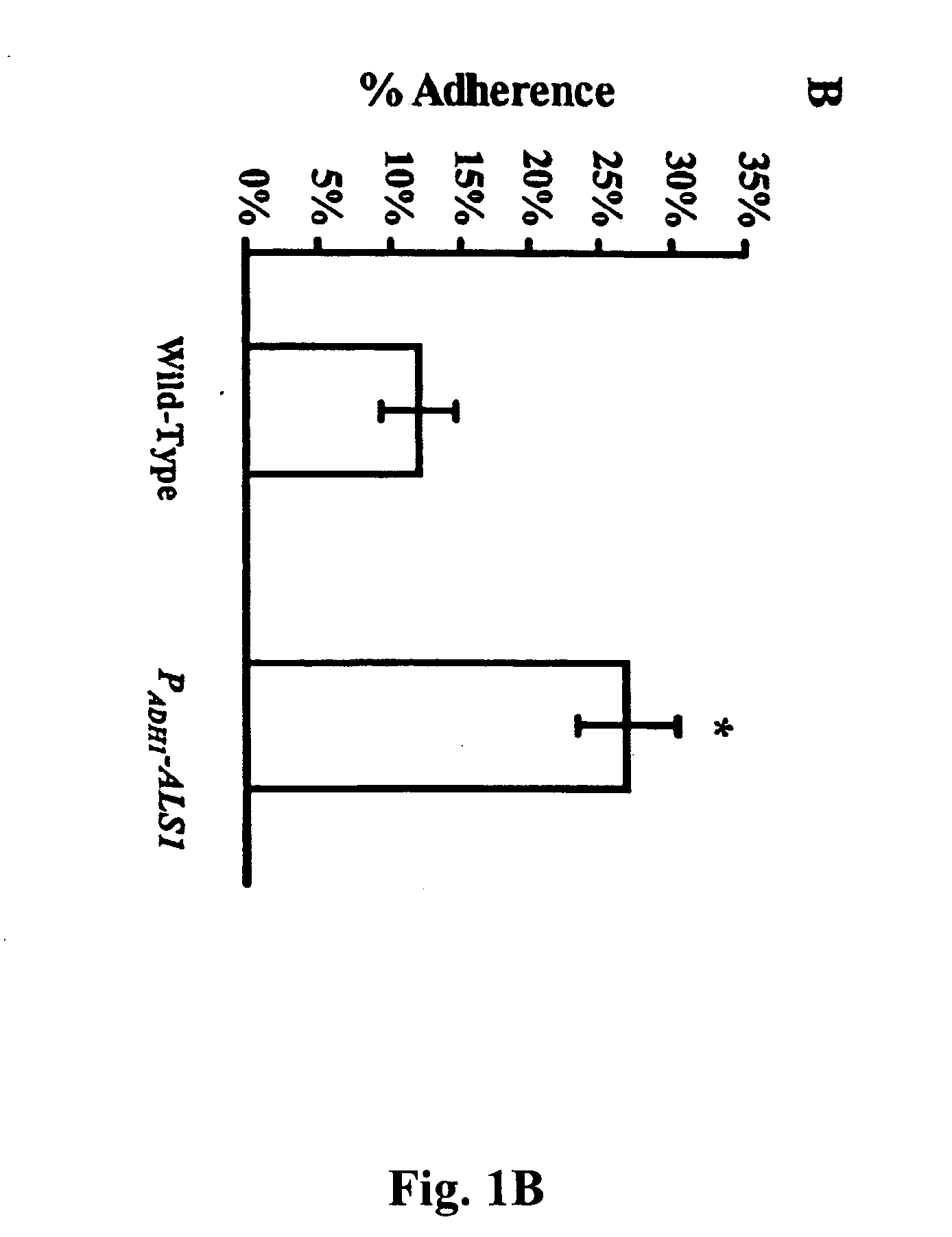
InactiveUS20060083750A1Treating preventingInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsFungiCell adhesionAdjuvant
The invention provides a vaccine including an isolated Als protein family member having cell adhesion activity, or an immunogenic fragment thereof, with an adjuvant in a pharmaceutically acceptable medium. The invention also provides a method of treating or preventing disseminated candidiasis. The method includes administering an immunogenic amount of a vaccine an isolated Als protein family member having cell adhesion activity, or an immunogenic fragment thereof, in a pharmaceutically acceptable medium. A method of treating or preventing disseminated candidiasis also is provided that includes administering an effective amount of an isolated Als protein family member having cell adhesion activity, or an functional fragment thereof, to inhibit the binding or invasion of Candida to a host cell or tissue. The Als protein family member can be derived from a Candida strain selected from the group consisting of Candida albicans, Candida krusei, Candida tropicalis, Candida glabrata and Candida parapsilosis and the Als protein family member includes Als1p, Als3p, Als5p, Als6p, Als7p or Als9p.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods to vaccinate against disseminated candidiasis and other infectious agents
InactiveUS20070077256A1Treating preventingInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCell adhesionAdjuvant
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
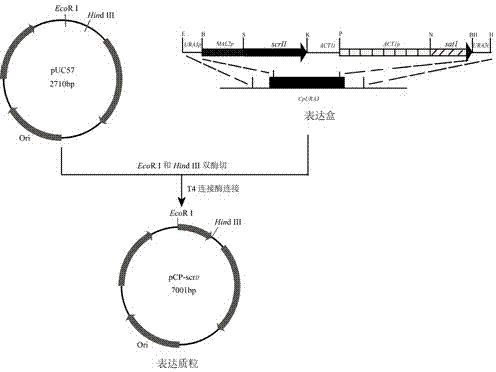
Method for using recombinant candida parapsilosis strain to efficiently prepare (S)-phenyl glycol
InactiveCN104774778AHelps understand the effect of stereoselectivityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhenyl glycolDrug biotransformation
The invention provides a method for using a recombinant candida parapsilosis strain to efficiently prepare (S)-phenyl glycol and belongs to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the recombinant candida parapsilosis strain Candida parapsilosis pCP-scrII preserved at the typical culture preservation center in China and marked with a preservation CCTCC NO: M2015107. According to the method, an expression plasmid of exogenous protein in candida parapsilosis is established, S-carbonyl reductase II is integrated to a candida parapsilosis genome to obtain the pCP-scrII, the candida parapsilosis is converted through electric shock to obtain the recombinant candida parapsilosis strain. By optimizing biotransformation reaction conditions, catalytic conversion is conducted on 2-hydroxyacetophenone through the recombinant strain to obtain the product S-phenyl glycol, the optical purity and yield of the product are up to 99.9%, an effective way is provided for efficient and low-cost preparation of the S-phenyl glycol, and a solid foundation is laid for industrial application of biological catalysis of chiral alcohol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms
ActiveCN102080127AWith monitoring functionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCandida tropicalisRhizopus oryzae
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms. The gene chip comprises specific detection probes fixed on a solid phase vector, wherein the probes are designed for 16SrRNA gene and ITS gene sequences of staphylococcus aureus, klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli, shigella, enterobacter aerogenes, pseudomonas fluorescens, candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida tropicalis, candida parapsilosis, aspergillus terreus, aspergillus flavus and rhizopus oryzae, and screened and verified by repeated tests, and have high hybridization specificity and accuracy. The chip provided by the invention ensures simple detection operations and relatively lower cost, saves time, is applied to the screening of the clinical common pathogenic microorganisms, the early rapid diagnosis of critical patients and the diagnosis of suddenly occurring infection event pathogens and favorable for clinically rapidly diagnosing infection sources and functions in the early detection and early diagnosis of clinical diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Strain for producing mannitol and method for producing mannitol through fermentation of strain
ActiveCN103131643AEfficient productionSuitable for mass productionFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastMANNITOL/SORBITOL
The invention discloses a strain for producing mannitol and a method for producing mannitol through fermentation of the strain, and belongs to the technical field of food biologics. The invention provides Candida parapsilosis SK26.003 which is screened from sugarcane juice and is preserved in the Chinese Typical Culture Collection Center with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2012491. The invention further provides a method for producing mannitol through fermentation of the Candida parapsilosis strain. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) fermenting the strain in a fermentation culture medium containing glucose so as to obtain a fermentation liquid containing mannitol; and (b) separating and purifying mannitol from the fermentation liquid. Mannitol produced by using the strain and the method is safe and reliable, is a functional product with much market potential, and is widely applied to industries such as food, cosmetics, medicament and the like. The strain can be used for producing mannitol in high efficiency and is applicable to large-scale production, and a new method is provided for the industrial preparation of mannitol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for Industrially Producing(s)-1,1,1-Trifluoro-2-Propanol
ActiveUS20130005007A1Economically and conveniently producingHigh optical purityFungiFermentationNatural stateCandida saitoana
Disclosed is a method for producing (S)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanol with high optical purity and high yield by having at least one kind of microorganism, which is selected from the group consisting of Hansenula polymorpha, Pichia anomala, Candida parapsilosis, Candida mycoderma, Pichia naganishii, Candida saitoana, Cryptococcus curvatus, Saturnospora dispora, Saccharomyces bayanus and Pichia membranaefaciens, act on 1,1,1-trifluoroacetone. Since microorganisms found in nature are made to act in a natural state, the problems to be raised when a transformant or the like is used can be avoided in this method. Consequently, the method can be easily put in industrial practice.
Owner:TOYAMA PREFECTURE +1
Production method of functional protein feed rich in four essential amino-acids
The invention discloses a production method of a functional protein feed rich in four essential amino-acids. The production method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out liquid fermentation on corynebacterium glutamicum, candida parapsilosis, lactobacillus plantarum and bacillus natto; mixing fermented liquid rich in metabolites and living bacteria to prepared the mixed fermented liquid; then, mixing with one or more than two of bean pulp, cottonseed meal, rapeseed dregs and peanut meal at a certain ratio, and carrying out solid fermentation; and finally drying and packaging the product, so as to obtain the final product in which the crude protein content is greater than 50% and four essential amino-acids are abundant. According to the production method, the fermented liquid is directly mixed and fermented together with a solid material; the probability of contamination with infectious microbes is reduced; the energy consumption is low; no waste is discharged; the content of anti-nutritional factors in meal materials is lowered; the content of the essential amino-acids and protein in the raw materials is improved; the added economic value of agricultural and sideline products is improved; the essential amino acids in the finished feed are high in content; the adding amount of exogenous essential amino acids can be replaced; and the feed cost is reduced.
Owner:河南双成生物科技有限公司 +1
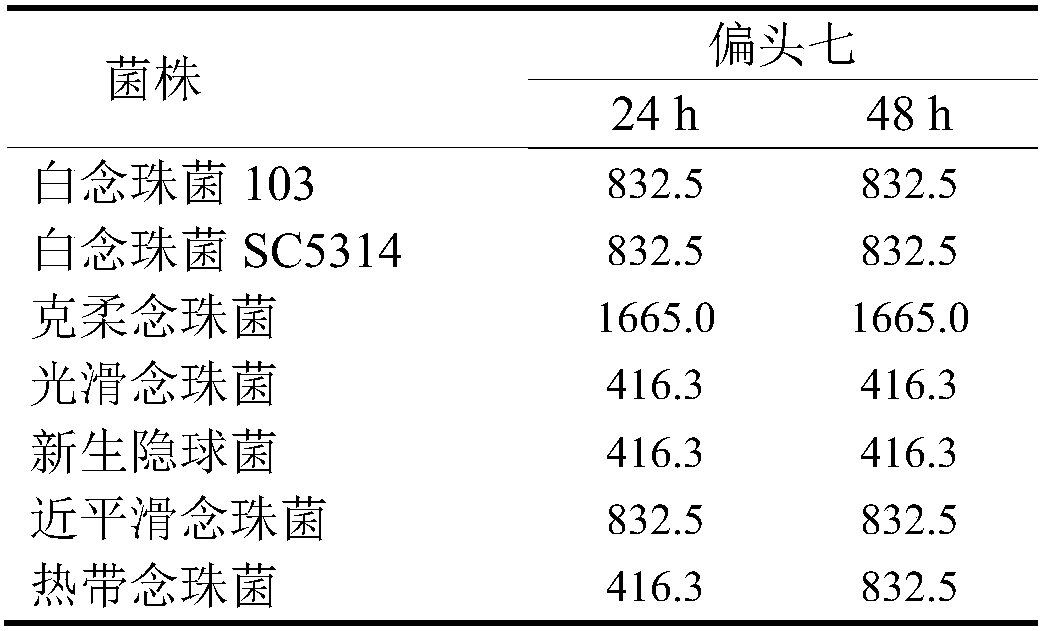
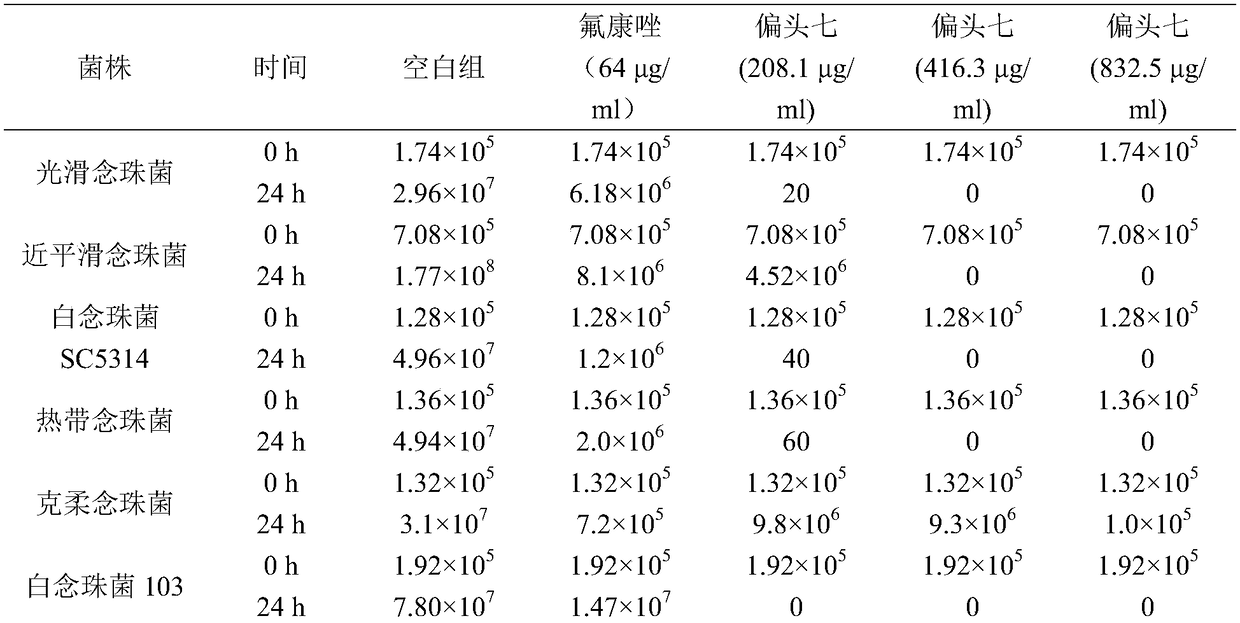
Use of rhizoma paridis chinensis for preparing antifungal drug
The invention discloses use of rhizoma paridis chinensis for preparing an antifungal drug, belonging to the technical field of medicines. In-vitro cell experiments show that rhizoma paridis chinensishas different levels of antifungal effects and even fungus-killing effect to drug-resistant candida albicans 103, candida albicans SC5314, cryptococcus neoformans, candida krusei, candida parapsilosis, candida glabrata and candida tropicalis and therefore can be taken as the antifungal drug. According to the use, new use of rhizoma paridis chinensis is opened up, rhizoma paridis chinensis is usedfor preparing the antifungal drug, and a new candidate drug is provided for the treatment of fungal infection. Currently, drugs with wide antifungal spectrums and fungus-killing activity on clinic arevery few, and a new way is provided for the clinical and efficient treatment of infection of fungi and even drug-resistant fungi by virtue of the characteristics of wide antifungal spectrums and fungus-killing activity of rhizoma paridis chinensis under the conditions that clinical fungus drug resistance becomes common increasingly and the drug resistance level becomes serious increasingly.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
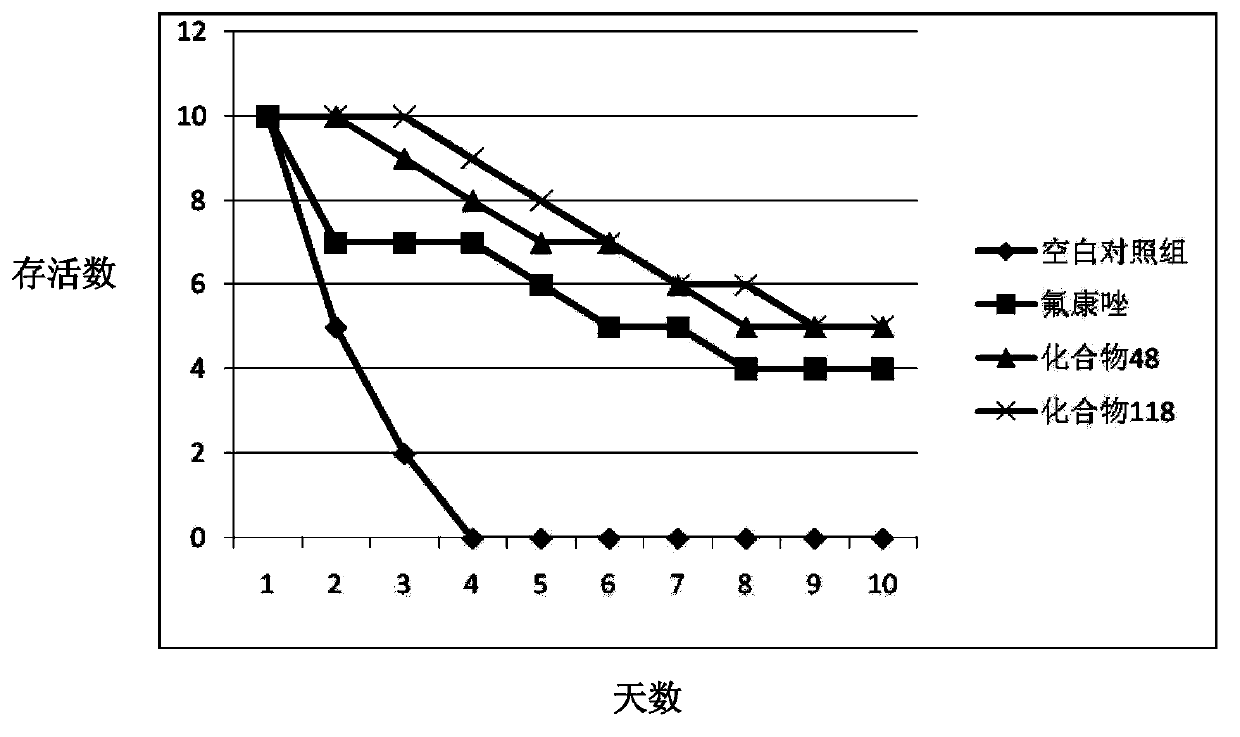
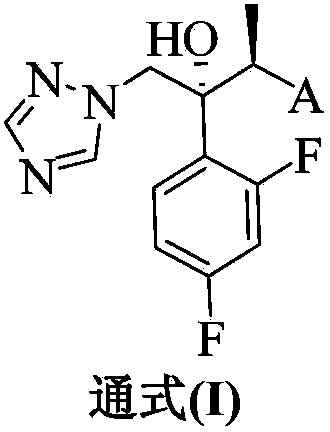
Novel triazole antifungal compound, pharmaceutical composition and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a triazole compound shown as a general formula (I), optical isomers or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and application of the compound, optical isomers or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof to preparation of medicaments for resisting fungi, especially Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida glabrata, Cryptococcus neoformans, Microsporum flavescens, Trichophyton rubrum and / or Aspergillus fumigatus. The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or more selected from the compound shown in the formula (I), optical isomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and pharmaceutic adjuvants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
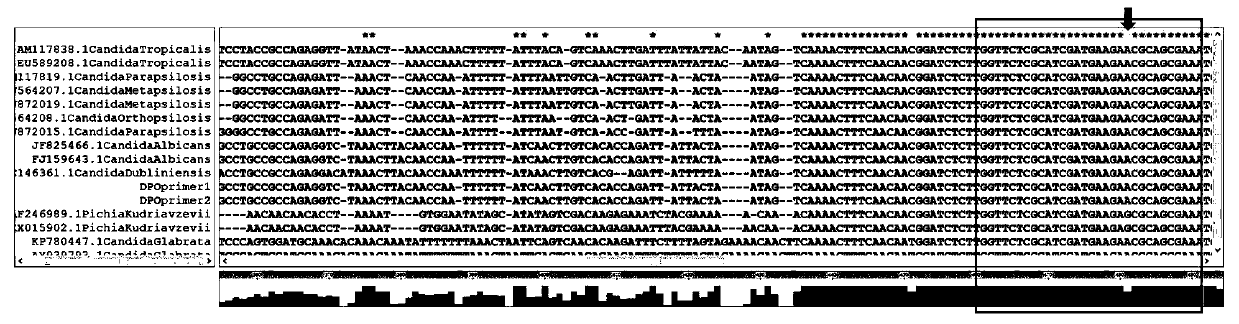
DPO primer pair, detection method and kit of candida classification detection and application of kit of candida classification detection
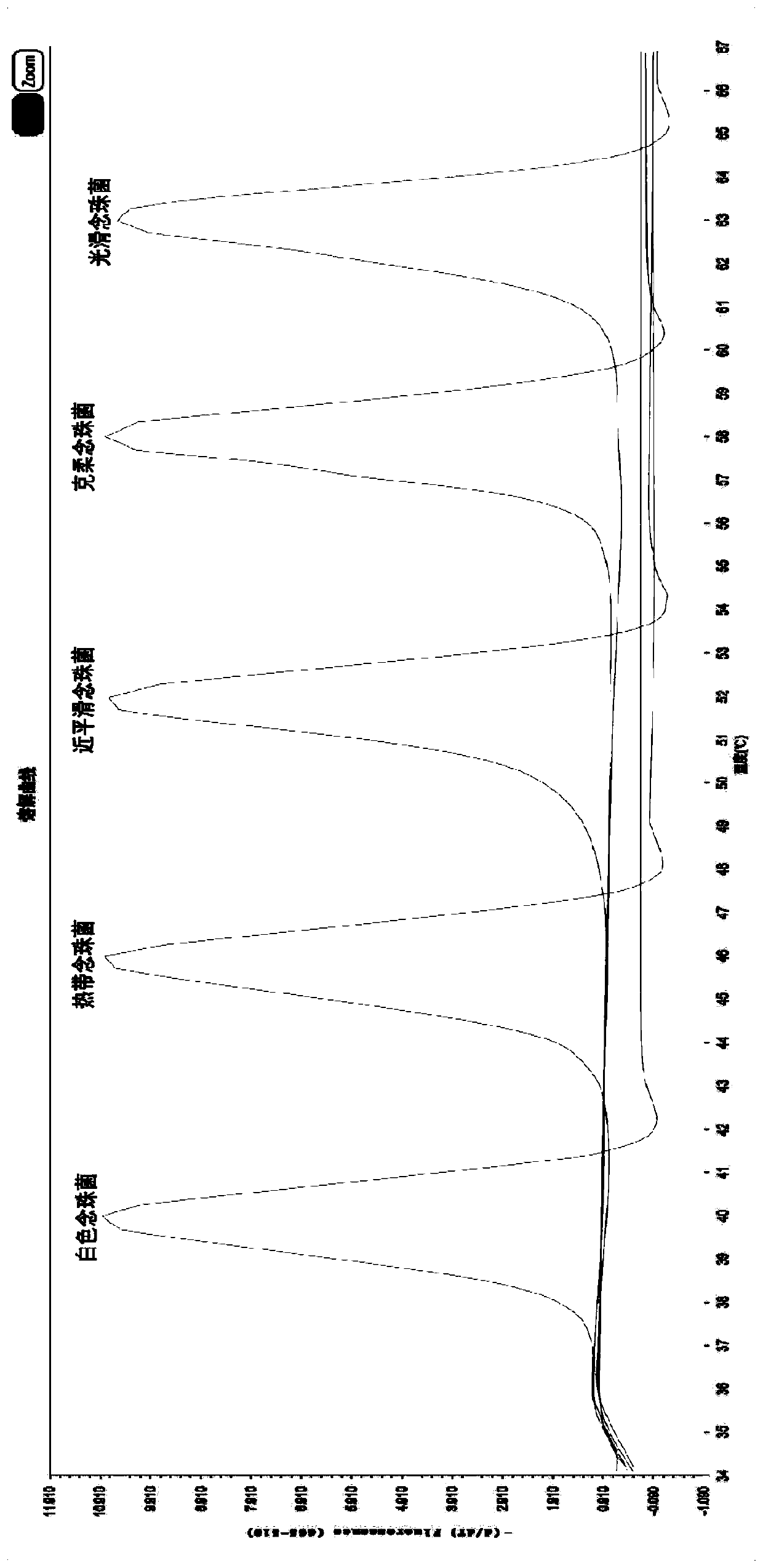
InactiveCN109811080AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention provides a DPO primer pair, detection method and kit of candida classification detection and application of the kit of candida classification detection. Nucleotide sequences of the DPO primer pair are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-2. The primer pair can specifically amplify candida, and is not crossed with other common pathogenic bacteria such as aspergillus, escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus, moreover, by designing the DPO primer pair, products of different candida strains have different annealing temperatures, through melting curve analysis of the products, candida albicans,candida tropicalis, candida parapsilosis, candida krusei and candida glabrata can be judged, only one pair of primers are used for achieving multiple detection, and compared with the prior art, the DPO primer pair is more simple, convenient and economic.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Method for biological catalyzed synthesis of optically active alkyl lactone
ActiveCN104651425AIncrease concentrationHigh optical purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationCapric Acid4-Butyrolactone
The invention relates to a method for biological catalyzed synthesis of optically active alkyl lactone. The method comprises the following steps: (1) catalyzing asymmetric reduction of a carbonyl acid to synthesize optically active hydroxy acid by using a biological catalyst; (2) in an acid environment, cyclizing the optically active hydroxy acid, thereby generating an optically active lactone compound. Freshly cultured candida parapsilosis cells or a cell-free extract is adopted as the biological catalyst for catalyzing stereoselective reduction of 4-carbonyl capric acid and 5-carbonyl capric acid, and subsequently the components are cyclized in the acid environment so as to obtain the lactone compound, so that (R)-(+)-4-hexyl-4-butyrolactone and (R)-(+)-5-amyl-5-valerolactone can be efficiently prepared. Compared with the prior art, the method is easy in preparing cells of the strain and extracts of the cells, high in stereoselectivity, simple in process for catalytic preparation of (R)-(+)-4-hexyl-4-butyrolactone and (R)-(+)-5-amyl-5-valerolactone, environment-friendly, and very good in industrial application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIFUAN ENZYME TECH +2
Method for improving the concentration of substrate in biological resolution L-menthol reaction
InactiveCN101545002AIncrease concentrationReduce inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationAcetic acidRhizopus oryzae
The invention relates to a method for improving the concentration of a substrate in a resolution L-menthol reaction, belonging to the technical field of the resolution of a racemic compound by a biological method. In the method, a pH value of an asymmetric resolution DL-acetic acid menthol reaction system is controlled to be from 5.0 to 8.0, conversion strains are obtained in Rhizopus chinensis CCTCC M201021, Rhizopus oryzae AS 3.41, Candida parapsilosis CICC 1676, Burkholderia cepacia ATCC 25416, Pseudomonas fluorescens AS1.823 or Pseudomonas.fluorescens AS 1.55, and any one of resin HZ-801, HZ-816, D-315, D-202, HD-81, NKA-II, D-406 and DA-201 is added to improve the concentration of the single-batch conversion substrate DL-acetic acid menthol up to 6 times.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of (R)-alpha-thioctic acid
ActiveCN106083811AHigh purityHigh yieldOrganic chemistryDipotassium hydrogen phosphateChemical synthesis
The invention relates to a preparation method of (R)-alpha-thioctic acid, and belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical chemical synthesis. The method comprises the following steps: introducing Candida parapsilosis to a fermentation medium, carrying out multiplication culture, and centrifuging; introducing above obtained reductase catalyst to a system composed of 6-carbonyl-8-chloroctanoic acid, glucose dehydrogenase, glucose, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate and water, and carrying out a chiral reduction reaction; adding above obtained (S)-6-hydroxy-8-chloroctanoic acid to a system composed of a chlorination reagent, a catalyst and a solvent, and carrying out a chlorination reaction; and adding obtained (R)-6,8-dichloroctanoic acid to a system composed of sulfur, sodium sulfide, a phase transfer catalyst and water, and carrying out a cyclization reaction to obtain the finished product. The method has the advantages of mild technologic conditions, low cost, realization of high purity, high yield and high optical purity of the product, easy obtaining of reagents used in the above technologic route, and reasonable and environmentally-friendly technical scheme.
Owner:SUZHOU FUSHILAI PHARMA CO LTD
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method for detecting DNA of Candida parapsilosis
InactiveUS7888026B2Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
LAMP primer composition used for detecting candida parapsilosis and LAMP detection kit and application method thereof
InactiveCN106521010AStrong strain specificitySmooth responseMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceMicrobiology
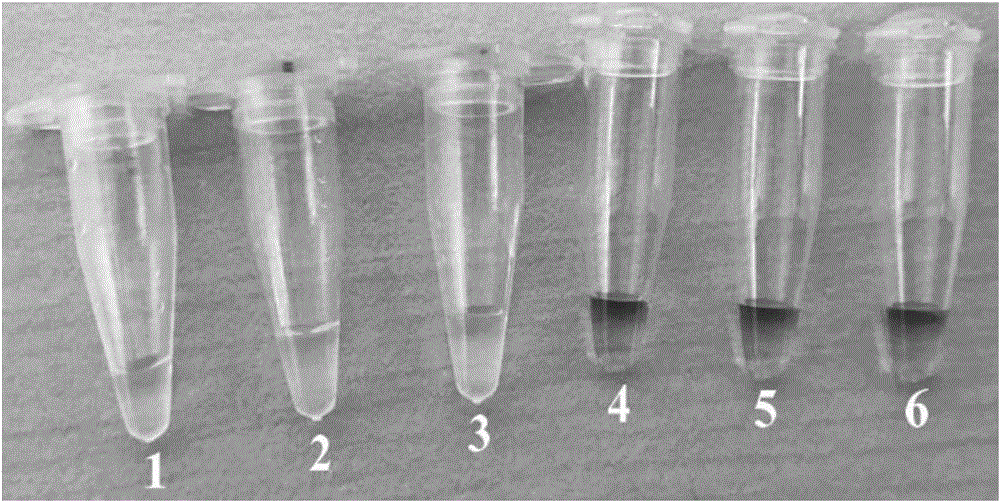
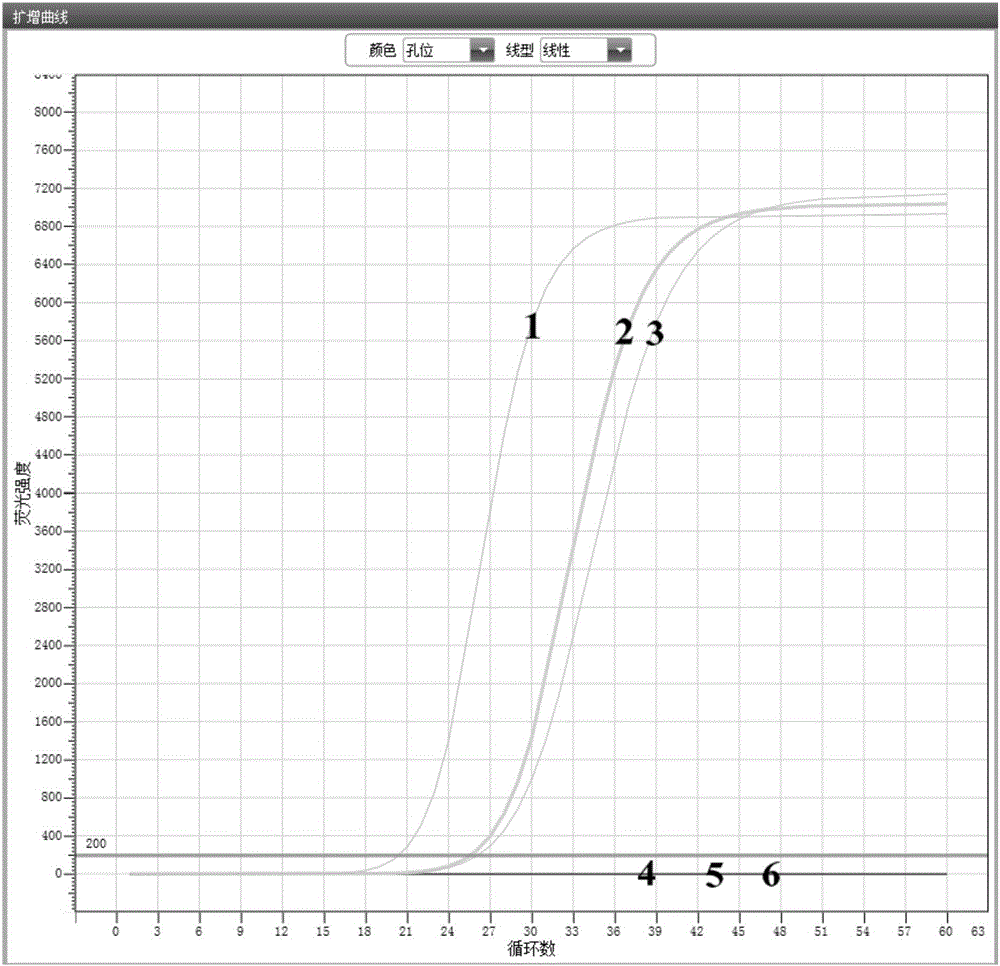
The invention discloses an LAMP primer composition used for detecting candida parapsilosis, an LAMP detection kit based on the primer composition and a detection method. The detection kit comprises the LAMP primer composition, Bst DNA polymerase, a color developing agent and the like; the color developing agent is fluorochrome SYBGreen or a fluorescent indicator Syto 9. According to the LAMP primer composition, four primers are designed on a peculiar endogenous gene place of the candida parapsilosis, thus the LAMP primer composition has very strong cultivar specificity, and successful proceeding of a reaction is guaranteed. In addition, the detection kit has the advantages of being convenient to operate, fast and efficient in reaction, high in specificity and sensitivity, various in identification method and the like, and is suitable for application and popularization in the clinical practice.
Owner:SHANGHAI IGENETEC DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +2
Gene chip and kit for detecting invasive fungal pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN101967507AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMonilinia laxaCandida tropicalis
The invention provides a gene chip and a kit for detecting invasive fungal pathogenic bacteria. The gene chip comprises a solid phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase vector, wherein the probe contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequences selected from 18S to 5.8S or 5.8S to 28S inside transcription regions (ITS) of rDNA and 5.8S rDNA of candida albicans, candida parapsilosis, candida tropicalis, candida kefyr, candida drusei, candida lusitaniae, candida glabrata, candida guilliermondii and cryptococcus neoformans as well as 5.8S rDNA of the nine fungus. The gene chip and the kit of the invention are utilized to detect nine kinds of common pathogenic bacteria, and have the advantages of simple and convenient operation, high accuracy and strong repeatability.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
All-weather composite photocatalysis synergy system and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108996709AEvenly dispersedSolve technical problems that cannot coexistWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMicrosphereTransmittance
The invention provides an all-weather composite photocatalysis synergy system. The all-weather composite photocatalysis synergy system is composed of titanium dioxide photocatalytic microspheres and sodium alginate embedded candida parapsilosis inocula. While treating phenol wastewater with deep depth and poor light transmittance, the system can effectively degrade phenol in wastewater and meet industrial demand, at the same time, an inventor found that in the research and development, the combination makes titanium dioxide not affect the biological activity of phenol degrading bacteria undernormal photocatalysis.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com