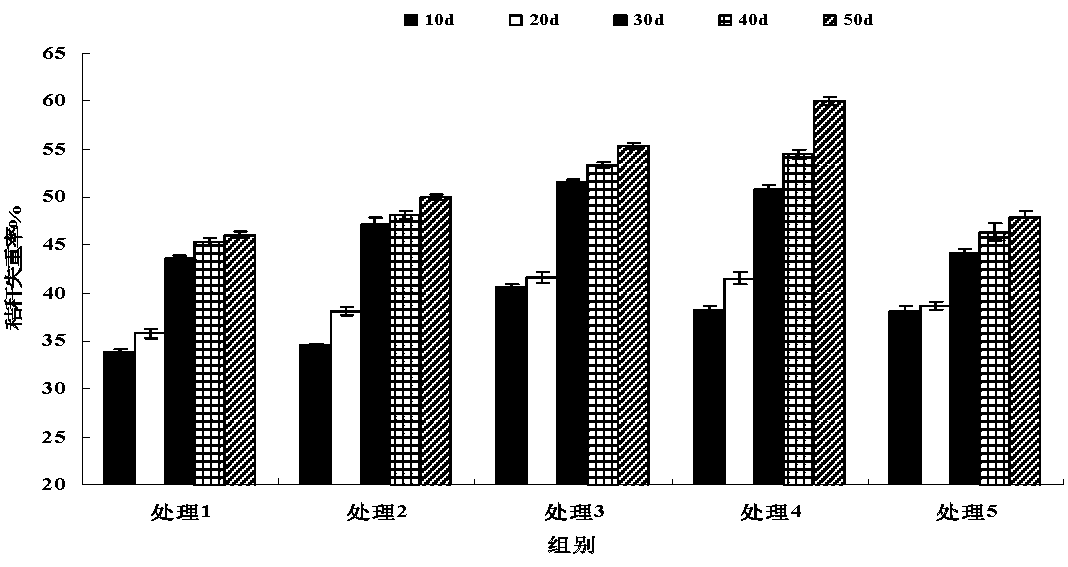
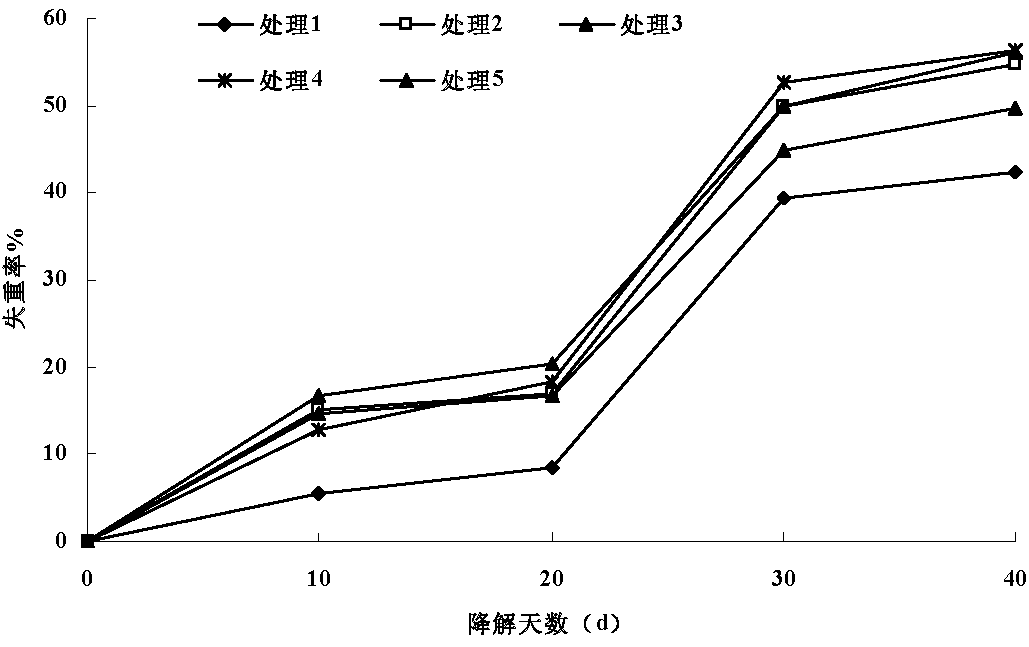
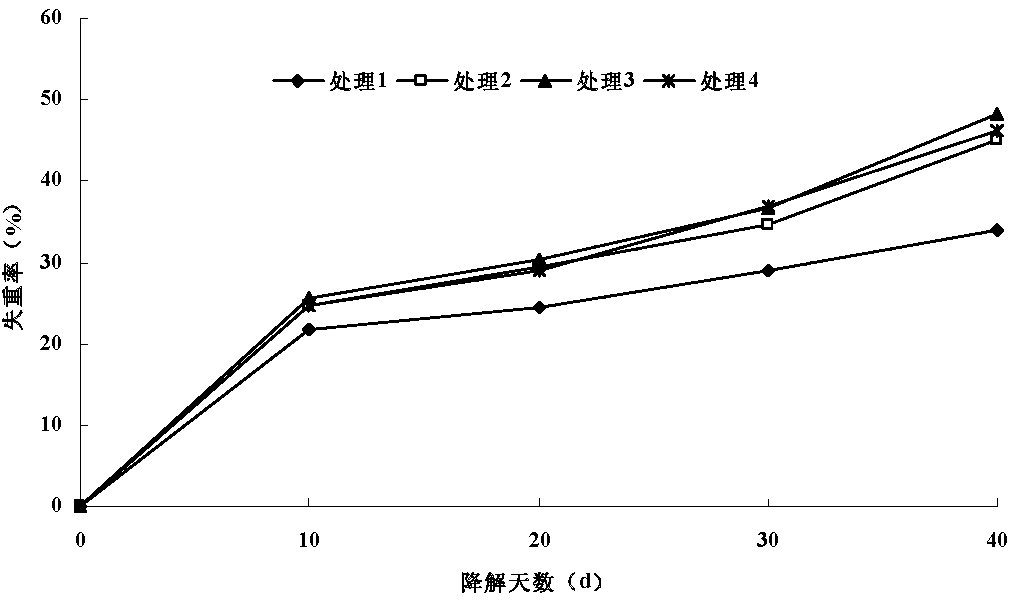
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Aspergillus nidulans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aspergillus nidulans (also called Emericella nidulans when referring to its sexual form, or teleomorph) is one of many species of filamentous fungi in the phylum Ascomycota. It has been an important research organism for studying eukaryotic cell biology for over 50 years, being used to study a wide range of subjects including recombination, DNA repair, mutation, cell cycle control, tubulin, chromatin, nucleokinesis, pathogenesis, metabolism, and experimental evolution. It is one of the few species in its genus able to form sexual spores through meiosis, allowing crossing of strains in the laboratory. A. nidulans is a homothallic fungus, meaning it is able to self-fertilize and form fruiting bodies in the absence of a mating partner. It has septate hyphae with a woolly colony texture and white mycelia. The green colour of wild-type colonies is due to pigmentation of the spores, while mutations in the pigmentation pathway can produce other spore colours.
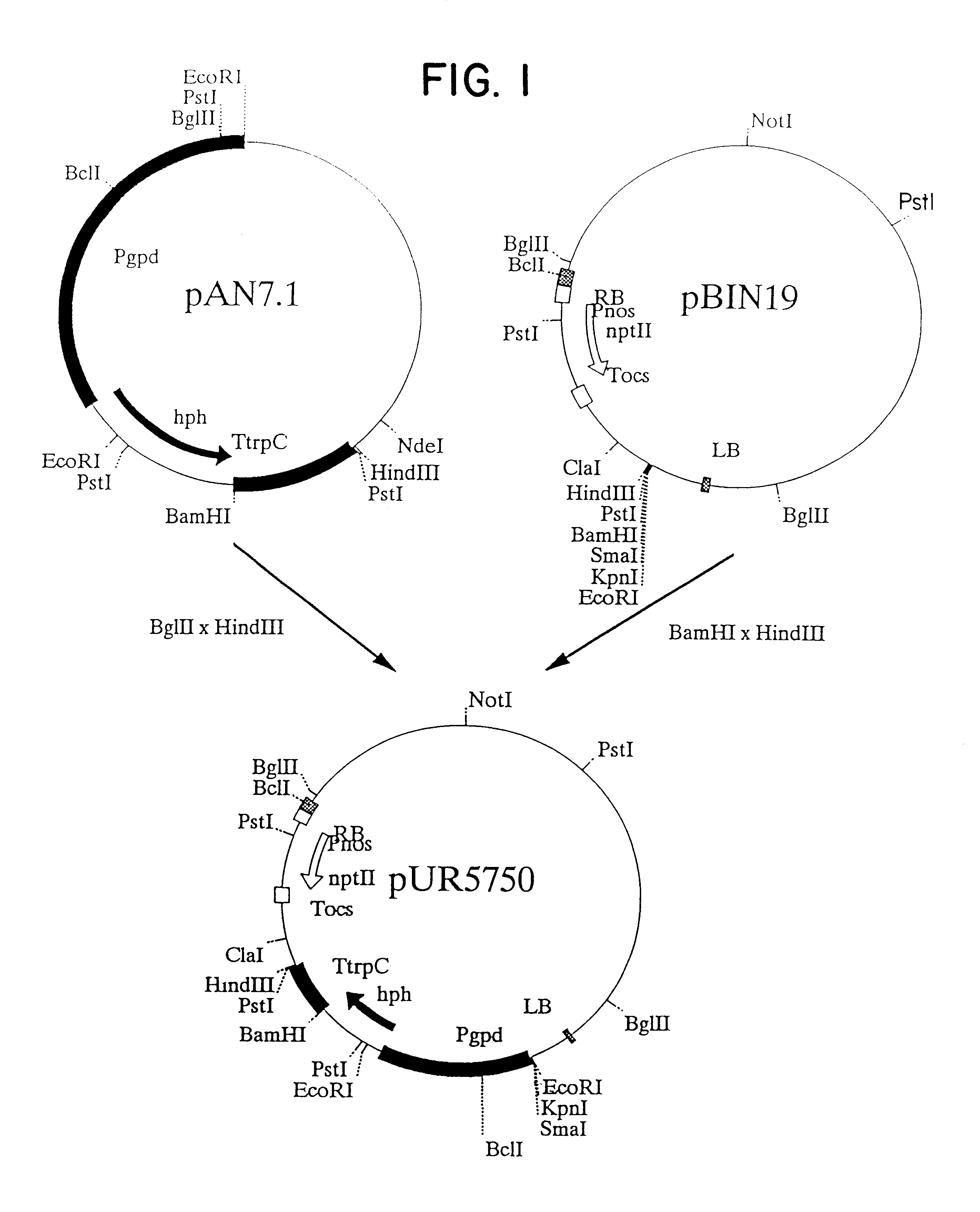
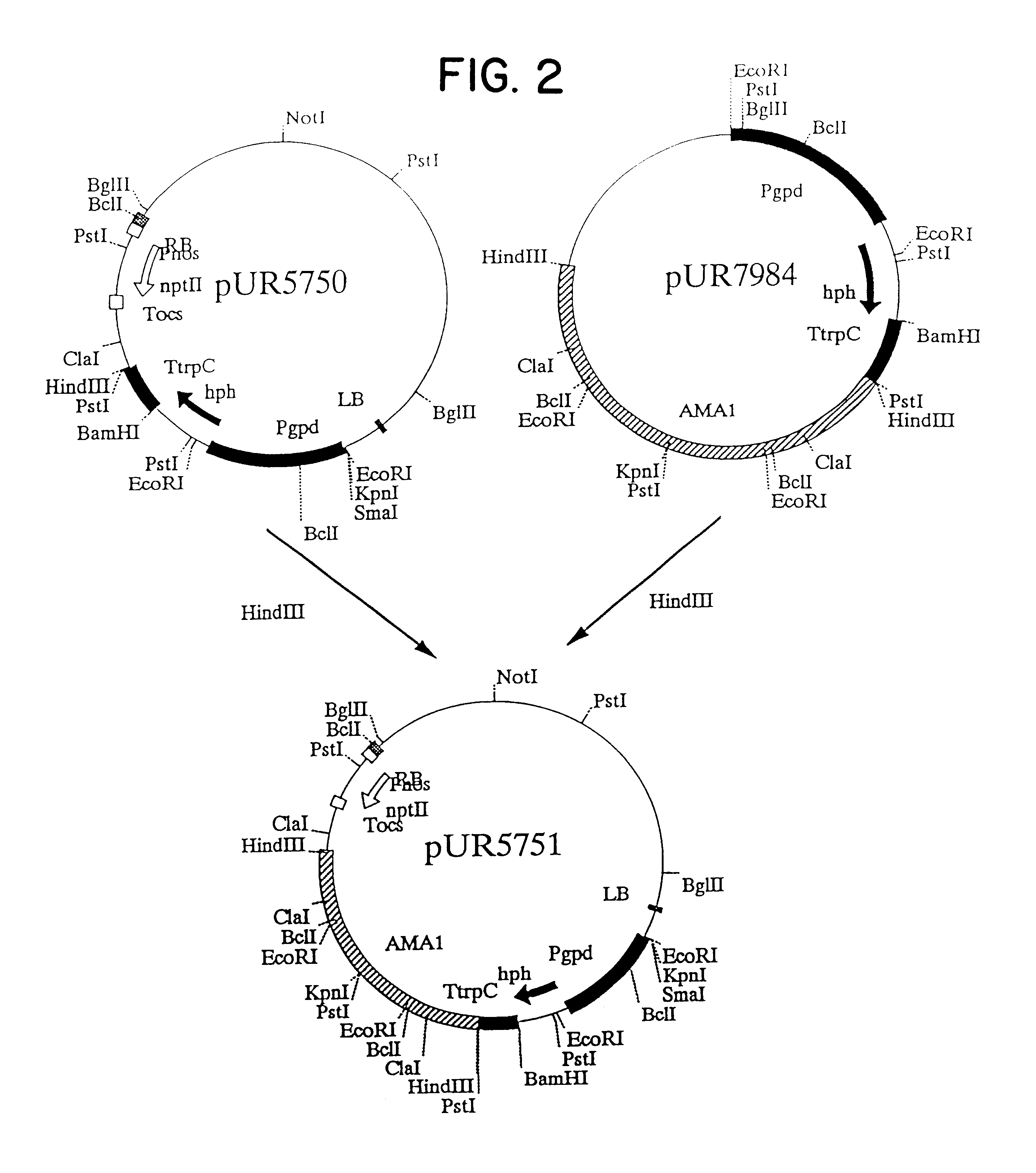
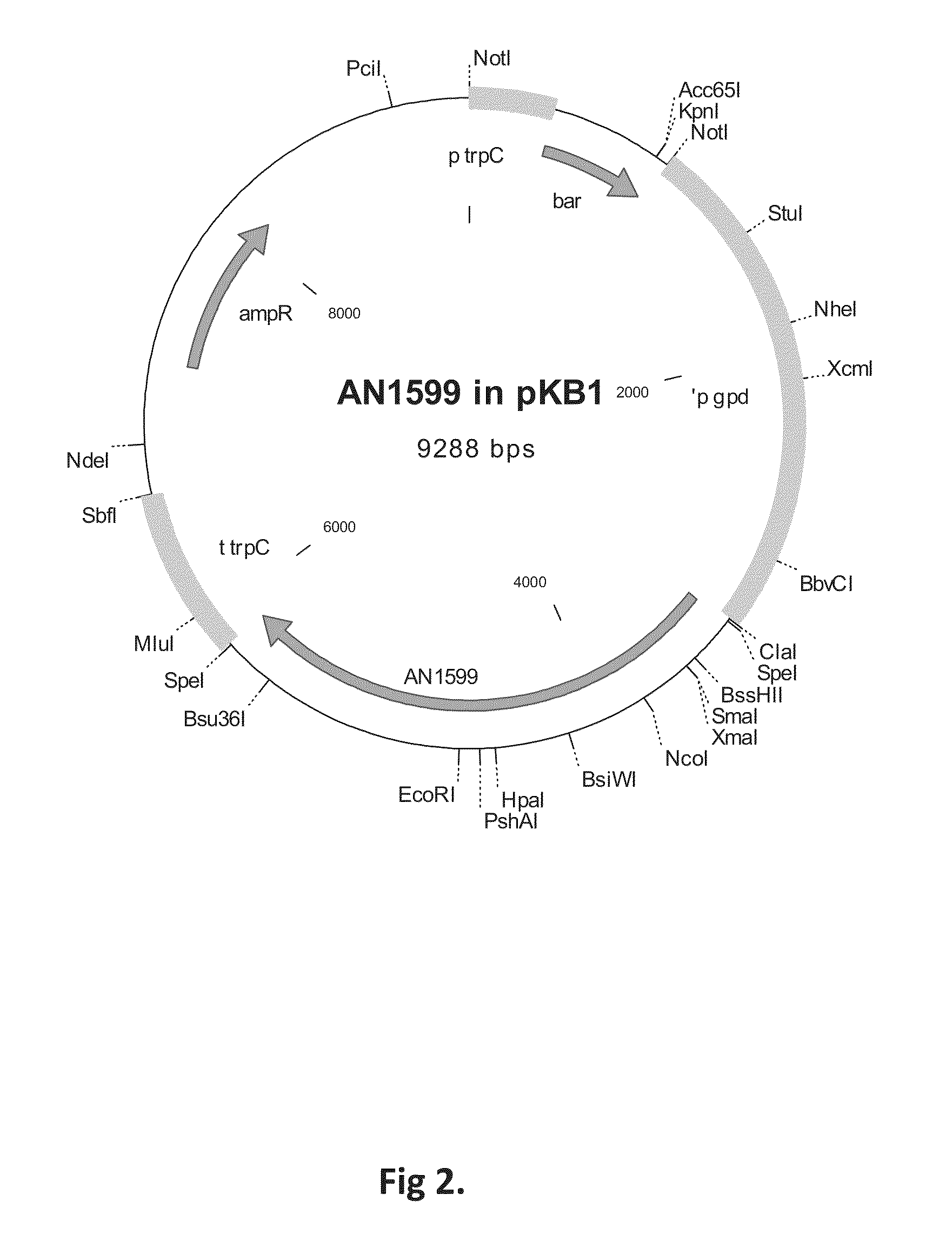
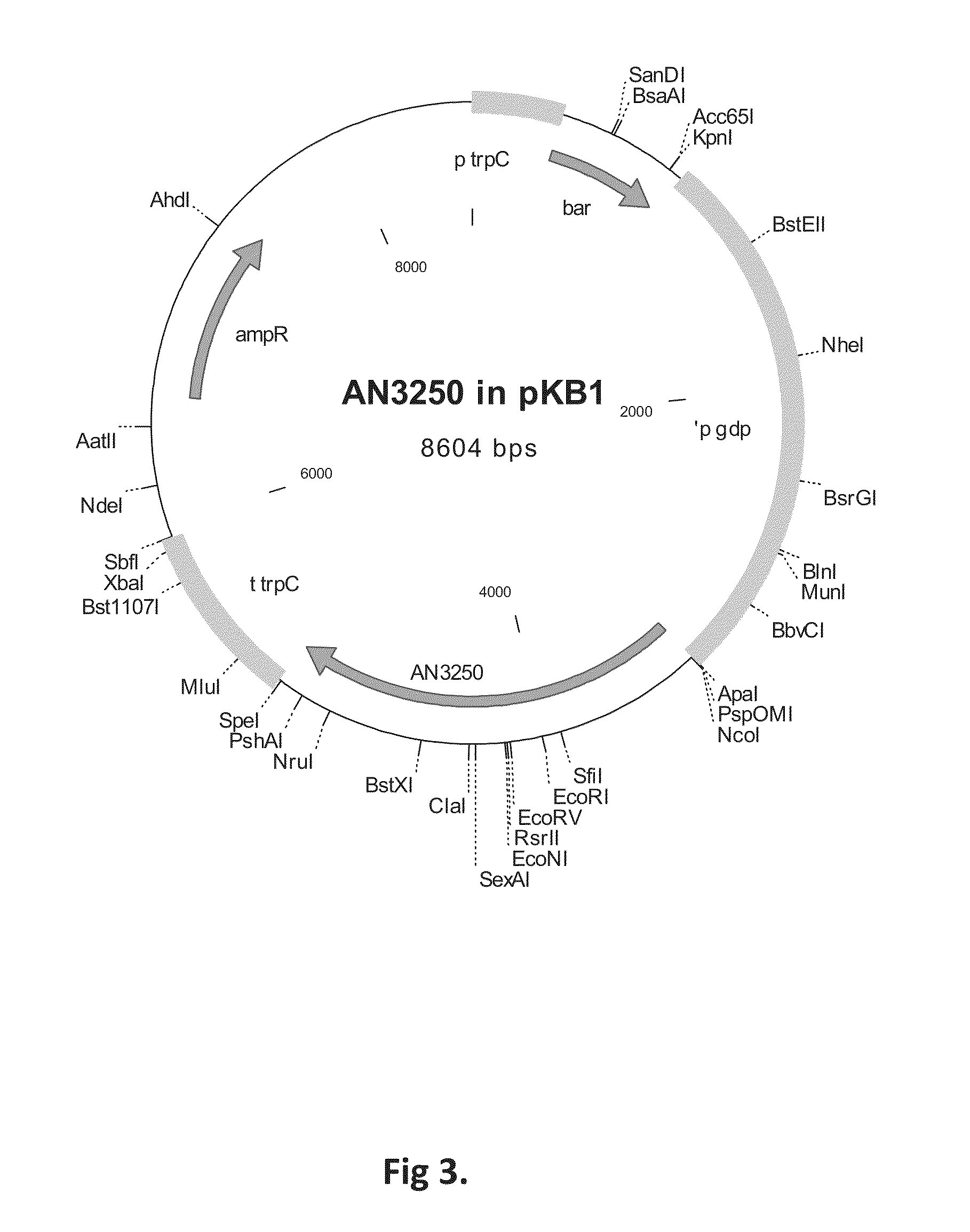
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
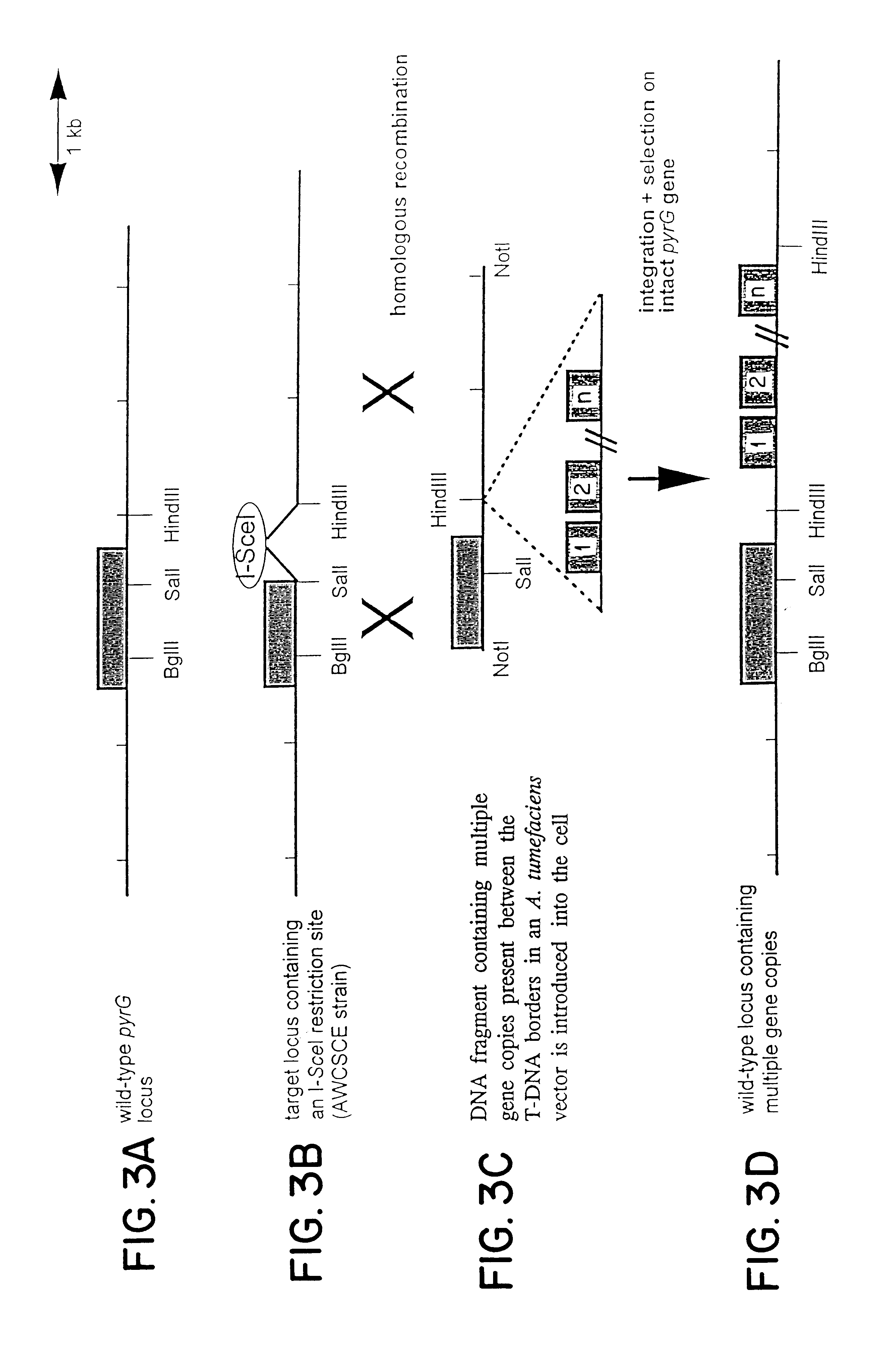
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Nucleic acid probes and methods for detecting clinically important fungal pathogens
InactiveUS6858387B1Function increaseAttached with easeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesAspergillus flavus
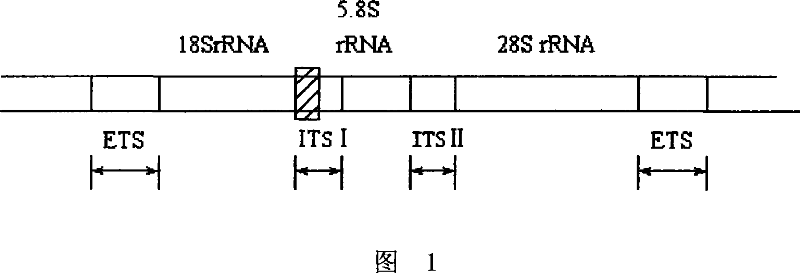
The current invention relates to the field of detection and identification of clinically important fungi. More particularely, the present invention relates to species specific probes originating from the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of rDNA for the detection of fungal species such as Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida kefyr, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata, Candida dubliniensis, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Cyptococcus neoformans and Pneumocystis carinii in clinical samples, and methods using said probes.
Owner:ENTERPRISE IRELAND +2
PCR kit for fluorescence quantitative detecting aspergilli
InactiveCN101038254AAccurate detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAspergillus nidulansFluorescence
The present invention provides a PCR reagent kit used for detecting quantificationally fluorescence of aspergillus. Said reagent kit contains primers such as 5'-CGGAAGGATCATTACCGAGTGA-3' (SEQ NO.1), 5'-CCCGCCGAAGCAACAAG-3' (SEQ NO.2) and a fluorescence probe 5'FAM-CCAACCTCCCACCCGTGTCTATYGT-BHQ-1 3' (SEQ NO.3). Said reagent kit in accordance with the present invention amplifies specifically gene in the interzone ITS I of aspergillus and generates a production with a size of 79 bp, is capable of quickly and correctly detecting a variety of common pathogenic aspergillus (such as aspergillus fumigatus, aspergillus flavus, aspergillus terreus, aspergillus niger and aspergillus nidulans) with a detection limit of 5-10 CFU / ml, and then is applied for a clinical diagnoses of invasive aspergillus infection with excellent sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid probes and methods for detecting clinically important fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20050164243A1Faster and simpler to performSuitable for automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesAspergillus flavus
The current invention relates to the field of detection and identification of clinically important fungi. More particularely, the present invention relates to species specific probes originating from the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region of rDNA for the detection of fungal species such as Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida kefyr, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata, Candida dubliniensis, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Cryptococcus neoformans and Pneumocystis carinii in clinical samples, and methods using said probes.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV +2
Alkaline pectate lyase producing gene engineering bacteria and construction and use thereof
InactiveCN102191212AIncrease productionShort fermentation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHybrid proteinGenetic engineering
The invention discloses alkaline pectate lyase producing gene engineering bacteria and construction and use thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. In the invention, the Escherichia coli pel engineering bacteria capable of secreting and expressing pectinase Pel in vitro with high efficiency are constructed from an industrial prospective by using a totally synthetic Aspergillus nidulans pel gene. The invention also provides a method for producing pectinase by using the engineering bacteria. When the engineering bacteria are used, the fermentation time is short, and at 37 DEG C, the total fermentation lasts for 6 hours, wherein the early fermentation lasts for 4 hours and post fermentation lasts for 6 hours; the enzyme active yield is as high as 400U / mL; in addition, the produced pectinase can be secreted in vitro directly, hybrid proteins are reduced, and the purification is easy. Therefore, the engineering bacteria have better industrial application prospect.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
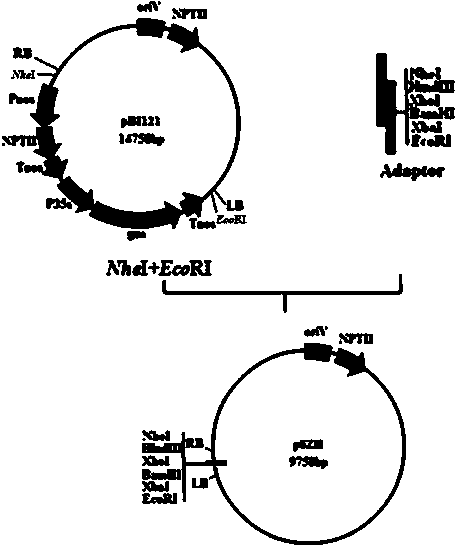
Ti plasmid aspergillus niger gene replacement expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN103409458AEliminate position effectEliminate competition effectsFungiMicroorganism based processesPosition effectTi plasmid
The invention provides a Ti plasmid aspergillus niger gene replacement expression vector and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The T-DNA (Triple helix Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) region elements of the Ti plasmid aspergillus niger gene replacement expression vector are arranged in the following sequence: an aspergillus niger target gene promoter, a multiple cloning site, an aspergillus niger target gene terminator, an aspergillus nidulans 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase gene promoter PgpdA, an aspergillus niger selection marker gene and an aspergillus niger target gene terminator. According to the invention, a target gene is integrated at the site of the aspergillus niger target gene through homologous recombination, and the target gene is regulated and controlled by a target gene promotor of high expression; therefore, the position effect of transgenosis is eliminated and the expression level is improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
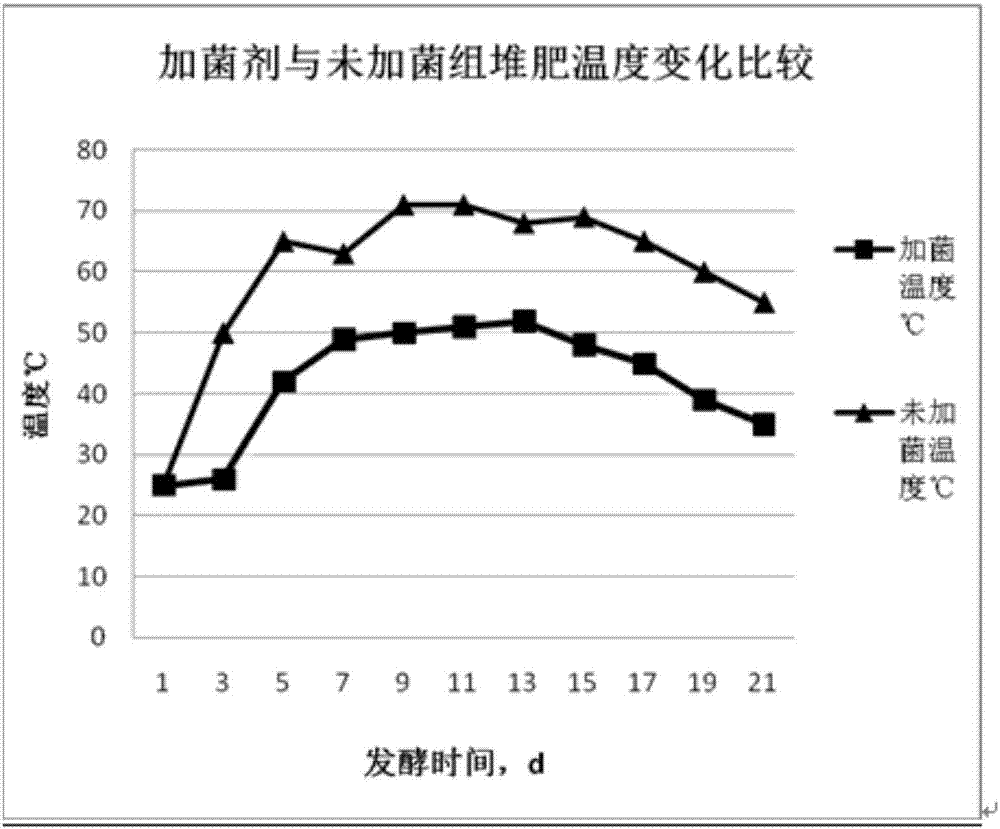
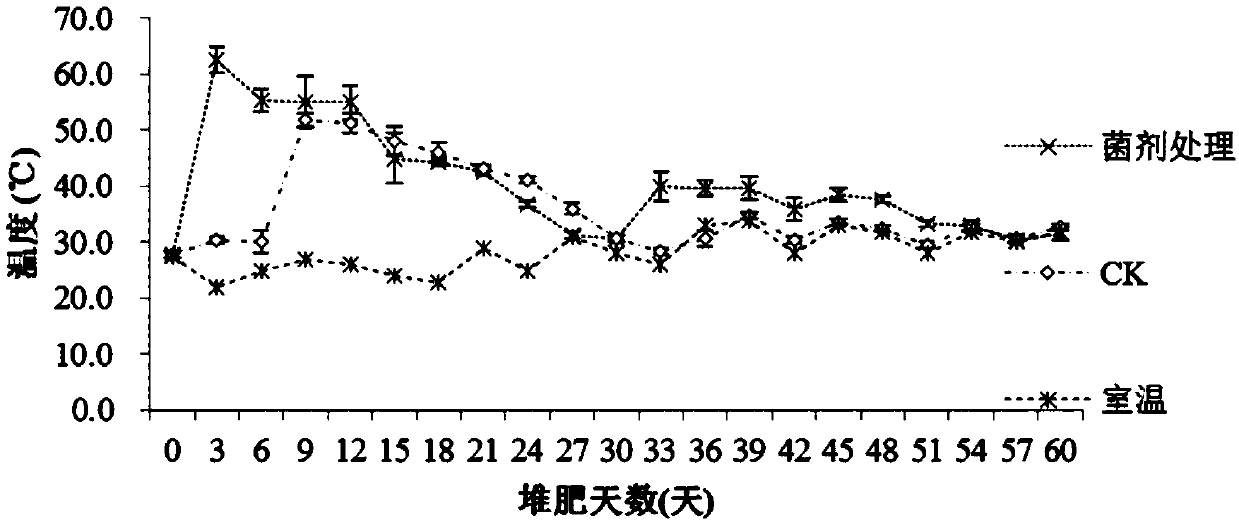
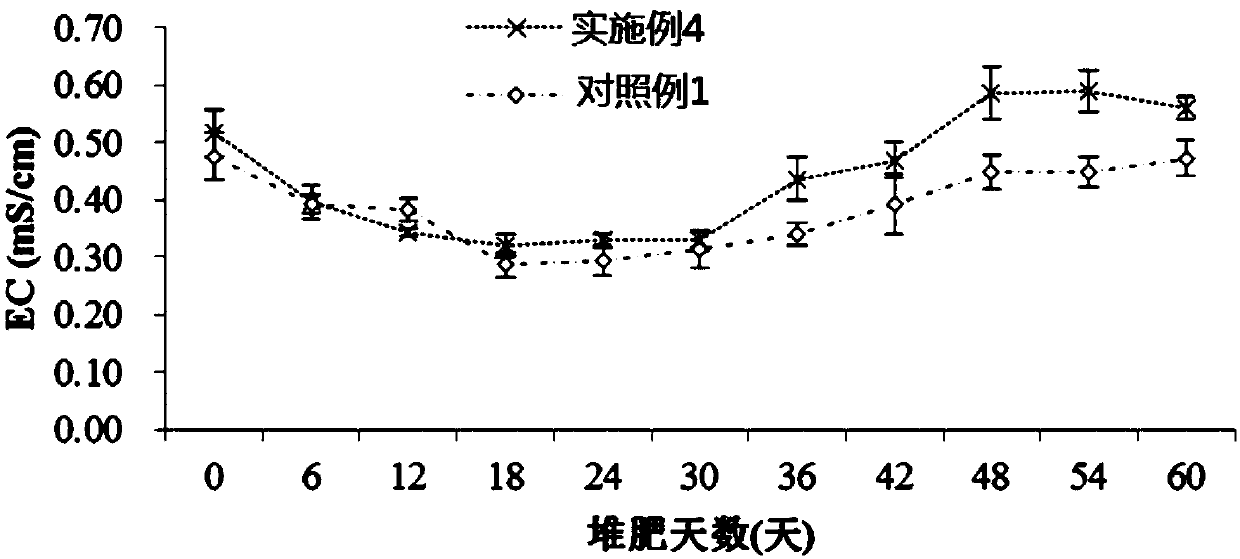
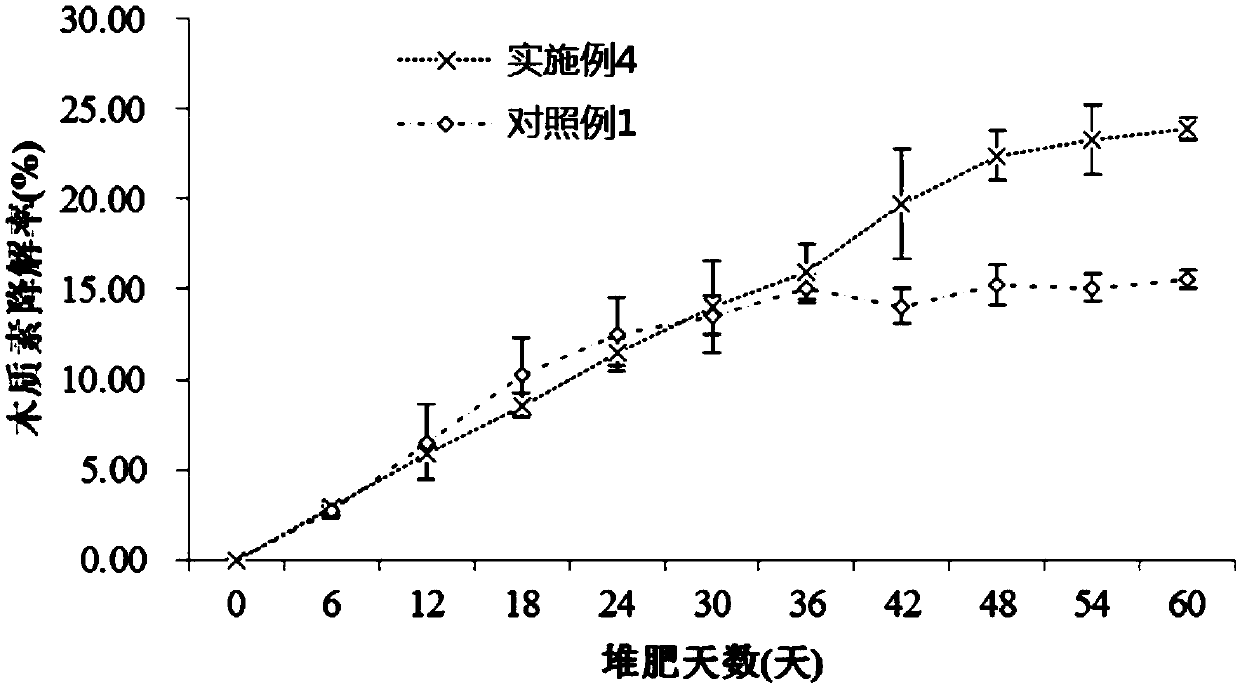
Composite microbial inoculum for composting organic materials and preparation method thereof
PendingCN106854633AAdaptableExtended shelf lifeFungiBio-organic fraction processingTrichoderma reeseiLactobacillus acidophilus
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum for composting organic materials and a preparation method thereof. The microbial inoculum mainly comprises pichia pastoris, lactobacillus acidophilus, bacillus coagulans, enterococcus faecalis, bacillus natto, bacillus subtilis, aspergillus nidulans, white-rot fungi, aspergillus usamii, trichoderma harzianum, trichoderma reesei and aspergillus niger. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first classifying the microorganisms into bacteria, yeasts and filamentous fungi, then performing mixed culture on the same class of microorganisms till quality requirements are met, and then compounding according to the following proportions: 20-70 parts of bacteria, 30-60 parts of yeasts and 50-80 parts of filamentous fungi. The compositing microbial inoculum prepared by the preparation method has the advantages of fast fermentation start during composting fermentation, high temperature in the composting process, a long high-temperature period and fast organic material decomposition. An organic fertilizer prepared by using the microbial inoculum is good in quality; compost has a fertility-retaining function, has high effective utilization rate of a large number of elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and has the effects of dissolving phosphorus, dissolving potassium and fixing nitrogen; compared with a control group which is not inoculated with the microbial inoculum, a product provided by the invention has the advantages as follows: the content of water-soluble organic carbon is increased by about 2 times, the total humic acid content is increased by about 1 times or above, and the content of biochemical fulvic acid is increased by about 2 times.
Owner:杨小波
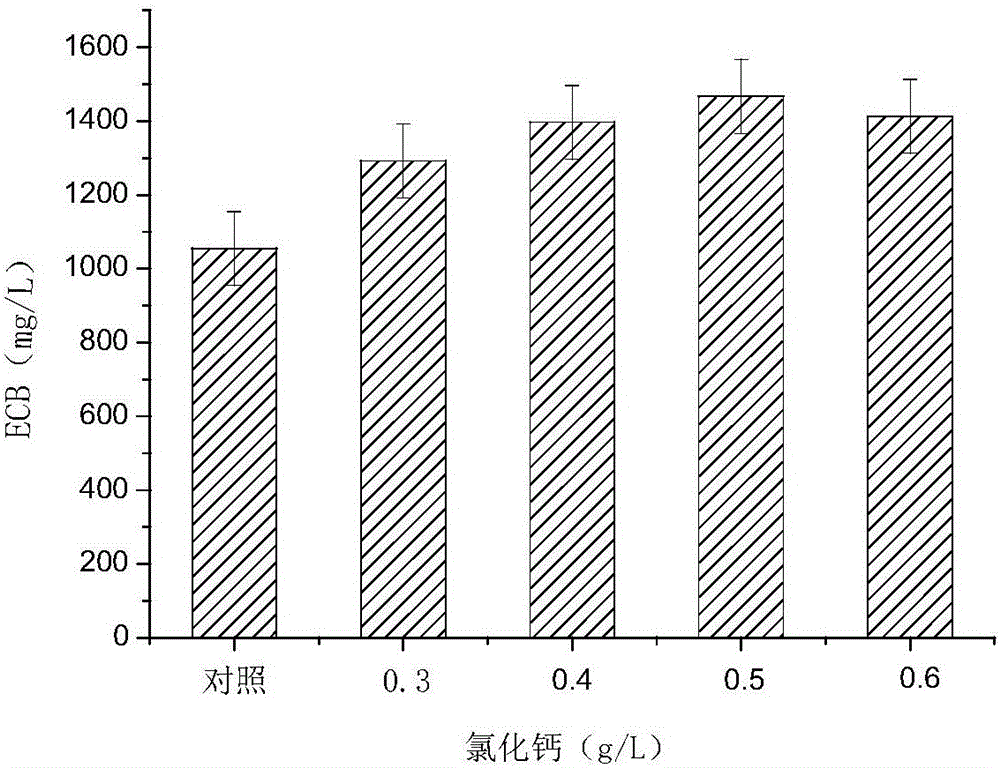
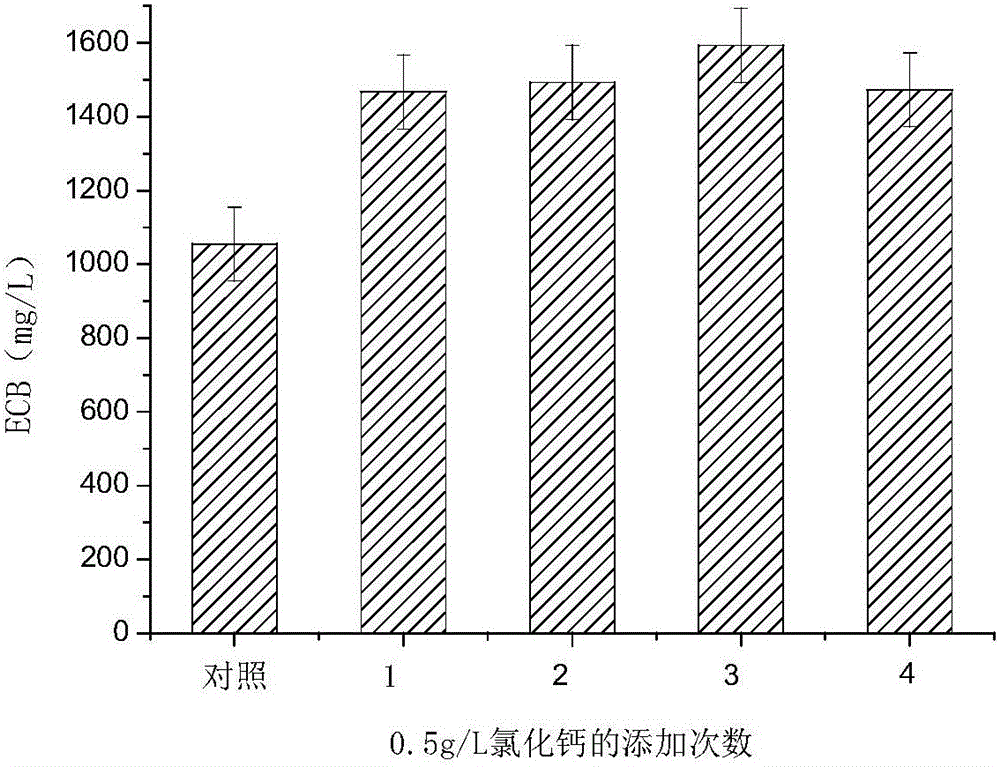
Method for improving yield of echimocandins B
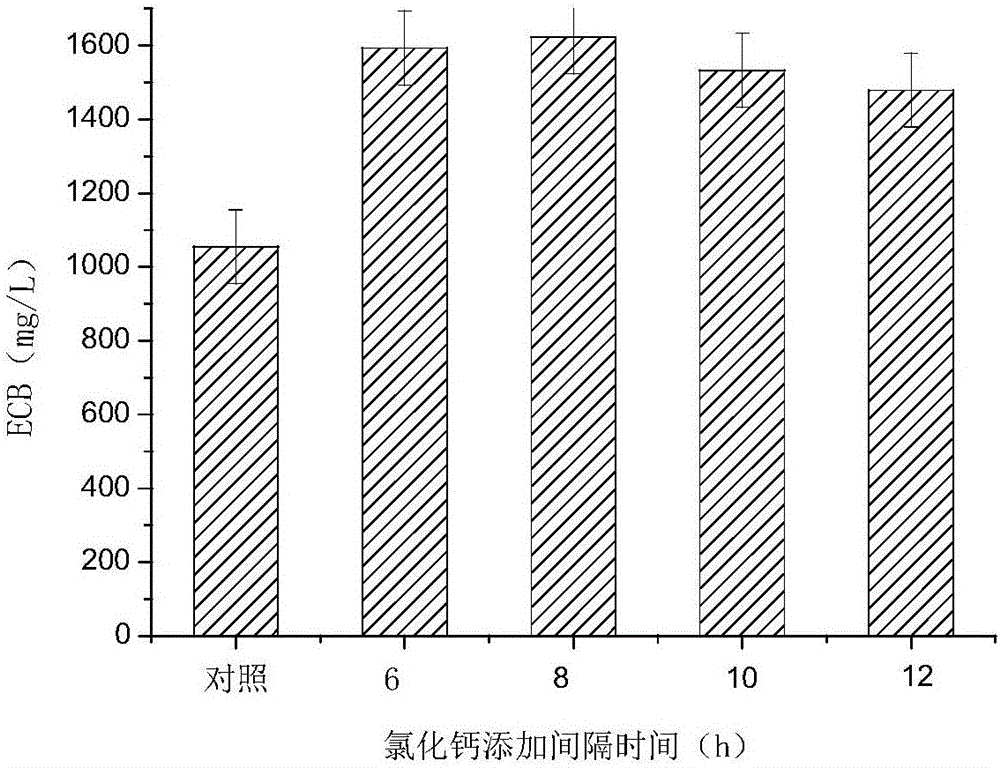
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of echinocandin B. The method comprises: using Aspergillus nidulans CCTCC M 2012300 as a production strain, inoculating Aspergillus nidulans CCTCC M 2012300 into a fermentation medium added with metal ions , cultured at 20-30°C and 220-280rpm for 7-12 days to obtain a fermented liquid, which was separated and purified to obtain echinocandin B; The method of echinocandin B output, by adding manganese sulfate, calcium chloride, cupric sulfate, ferrous chloride, magnesium sulfate etc. in fermentation medium, improves anidifungin precursor compound echinocandin B output; Result Show that in the fermentation culture system, the highest yield reaches 1738.6mg / L, which is 64.7% higher than that of the control group without metal ions. important meaning.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
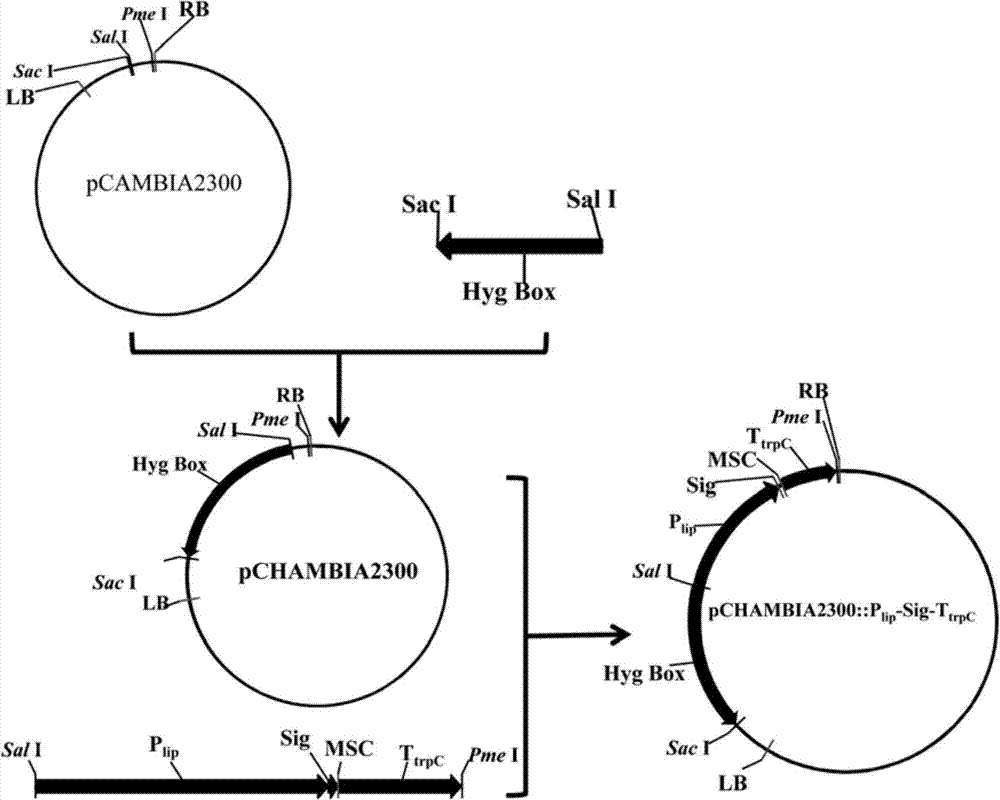
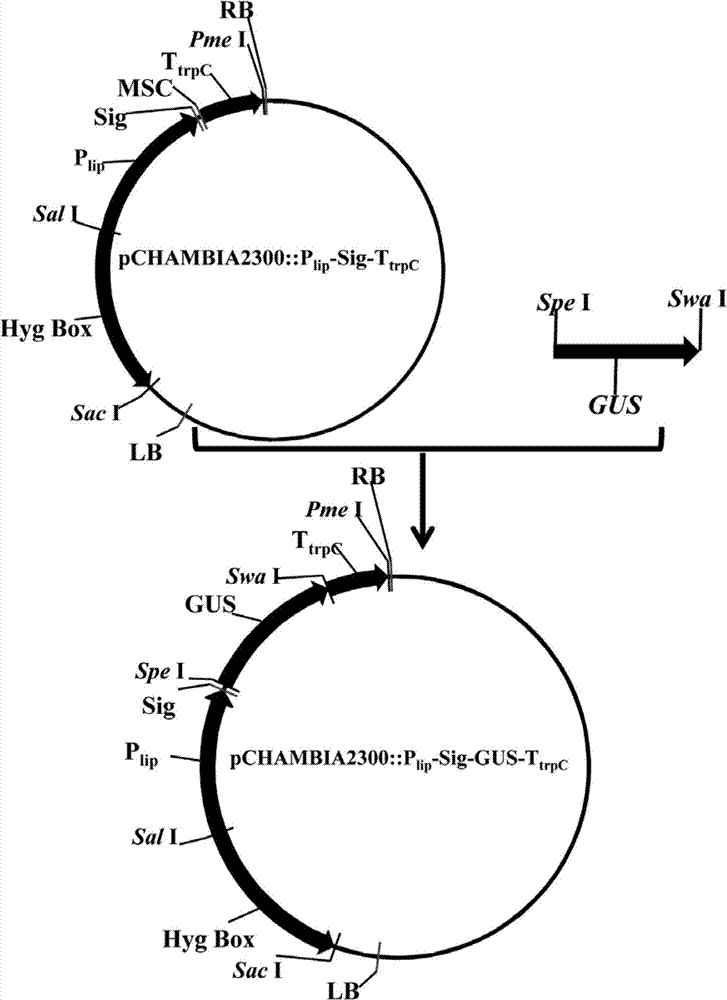
Construction method of efficiently-expressed plasmid for producing lipase gene
ActiveCN102154358AEfficient and stable expressionVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceTryptophan
The application of the invention provides a construction method of an efficiently-expressed plasmid for producing lipase gene. The method comprises the following steps: cloning an obtained hygromycin-resistant expression box on an objective plasmid so as to obtain a hygromycin-resistant recombinant plasmid; the respectively amplifying lipase gene (PEL) of blue mould, aspergillus nidulans strong promoter 3-phosphoglyceraldehydedehydrogenase promoter (PgpdA) and aspergillus nidulans tryptophan synzyme terminator (TtrpC) by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology to obtain a PEL gene expression box driven by a strong promoter; and inserting the PEL gene expression box into the hygromycin-resistant recombinant plasmid to obtain a hygromycin selection marker-containing PEL gene overexpression vector. The efficiently-expressed plasmid for producing lipase gene is transferred to obtain the genetic engineering penicillium of the efficiently-expressed plasmid, high-efficiency and stable in expression. Compared with conventional lipase production method, the construction method has great advantages.
Owner:ANHUI LEVEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for obtaining strain capable of expressing lipase effectively
ActiveCN102154340ABreeding goals are clearImprove efficiencyFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyPenicillium cainii
Aiming at the drawbacks of the prior art, the invention applies for providing a method for breeding a penicillium gene engineering bacterium having high lipase synthesis capability. The method comprises: obtaining a hygromycin-resistance expression box and cloning to a target plasmid to obtain a hygromycin-resistance plasmid; amplifying the lipase gene, namely primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), of the penicillium and the strong promoter, namely glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter PgpdA, of Aspergillus nidulans and tryptophan synthetase terminator TtrpC of the Aspergillus nidulans respectively to obtain a PEL gene expression box driven by the strong promoter; inserting the PEL gene expression box into the hygromycin-resistance plasmid to obtain a PEL gene super expression vector containing a hygromycin screening marker; and finally, transferring Agrobacterium rhizogenes by using the PEL gene super expression vector containing the hygromycin screening marker, and transferring the PEL gene expression box into a penicillium strain by using a Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transfer method to obtain the penicillium gene engineering bacterium with high lipase expressing capability.
Owner:ANHUI LEVEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Construction and application of heterologous expression system of aspergillus nidulans
ActiveCN108795970AEfficient expression productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNatural product
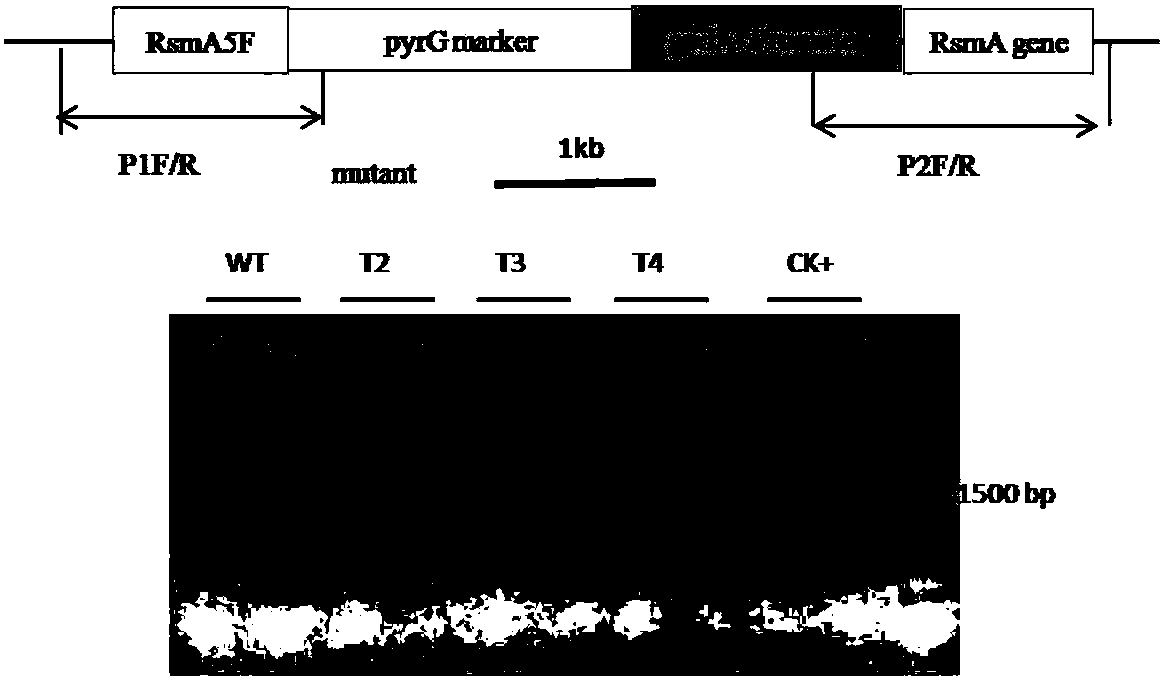
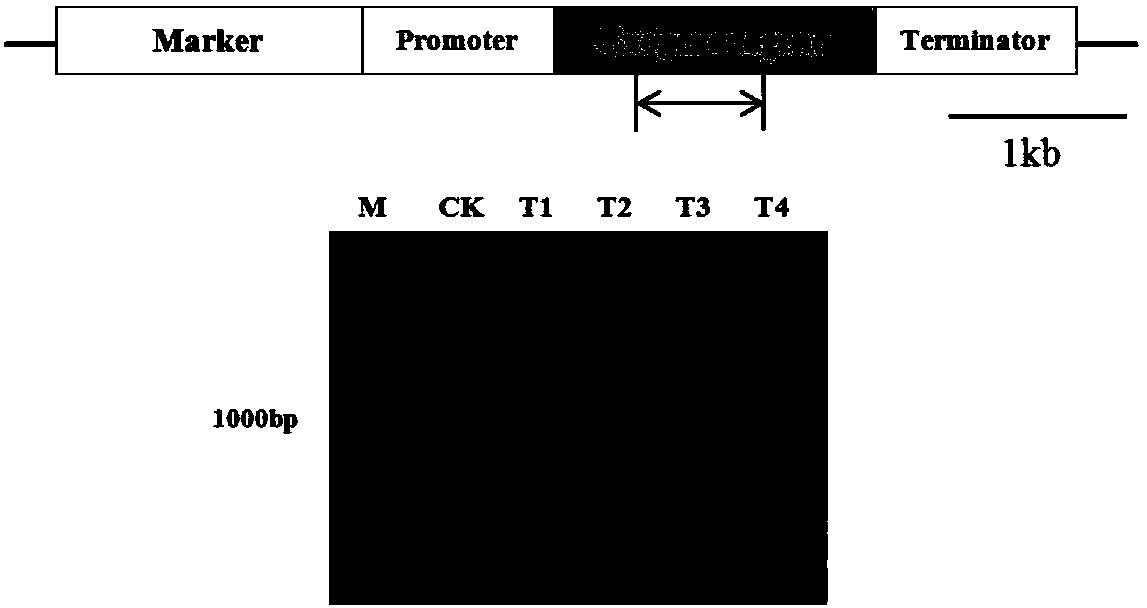
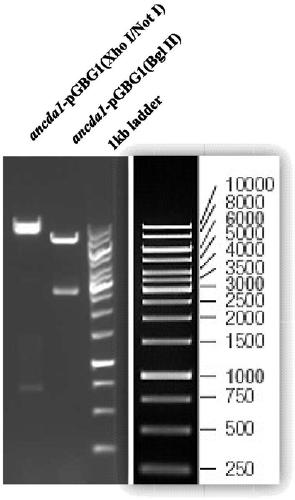
The invention relates to a construction method of a heterologous expression system of aspergillus nidulans. The method includes the following step (1) or step (2): (1) knocking out any one or two of an aspergillus nidulans dppV gene, an mnn9 gene or a pepA gene to construct a proteolytic enzyme knockout mutant strain of the aspergillus nidulans; or (2) overexpressing an RsmA gene in the aspergillus nidulans, and constructing a mutant strain of the aspergillus nidulans with the overexpressed RsmA gene. The proteolytic enzyme knockout mutant strain of the aspergillus nidulans and the mutant strain of the aspergillus nidulans with the overexpressed RsmA gene are helpful for efficient expression production of important industrial proteases. Expression elements of a gpdA promoter and a xylP promoter provided by the invention can regulate the generation direction of different compounds produced when the aspergillus nidulans heterologously expresses natural products of fungi, can be used formodifying or discovering compounds that can be used in medicine, and is of great significance for the research and development of the proteases with important industrial value and potential natural products of fungi.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
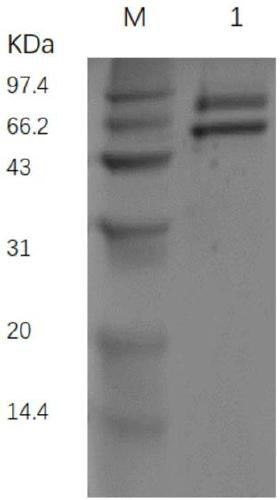
Aspergillus nidulans chitin deacetylase, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109022403AHigh deacetylation activityImprove biological activityHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses an Aspergillus nidulans chitin deacetylase, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The sequence of a chitin deacetylase coding gene in Aspergillus nidulans is obtained by a whole gene synthesis technology according to the codon preference of Pichia yeast, and the optimized nucleic acid sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. The optimized chitin deacetylase encoding gene is secreted and expressed by a Pichia pastoris expression system to obtain the Aspergillus nidulans chitin deacetylase, and the amino acid sequence of the Aspergillus nidulans chitin deacetylase is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The Aspergillus nidulans chitin deacetylase obtained in the invention can remove acetyl groups in chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides in order to obtain the chitosan or chitosan oligosaccharides with a specific structure. The modified chitosan or chitosan oligosaccharides have new or higher biological activities than unmodified chitosan or chitosan oligosaccharides. So the above enzyme and its deacelation product have good industrial application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Straw returning fast rot-promoting microbial inoculum
ActiveCN110846261AEasy to operateSimple cultivation conditionsFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisTrichoderma asperellum
The invention relates to a straw returning fast rot-promoting microbial inoculum, and effectively solves the problem that an existing straw returning microbial inoculum is low in degradation speed, poor in effect, high in cost and poor in usability. The straw returning fast rot-promoting microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing three of solid fermentation spore powder of Trichoderma asperellum SFC-3 and solid fermentation spore powder of aspergillus niger J4 without mutual antagonism, the solid adsorption microbial inoculum of Aspergillus nidulans QY5, the solid adsorption microbial inoculum of Rhizopus oryzae JG3, the solid adsorption microbial inoculum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CXMJ, the solid adsorption microbial inoculum of Bacillus subtilis nkkc and the solid adsorption microbial inoculum of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WS3-1 according to the weight ratio of 1-2: 1-2: 1: 1. The synergistic straw degradation effect of the Trichoderma asperellum SFC-3 and other strains is utilized,the carbon-nitrogen ratio is adjusted without additionally adding nitrogen sources such as urea, the practical application operation is simple and convenient, therefore, the production cost is saved,and a fermentation medium and the culture conditions are simple. The straw returning fast rot-promoting microbial inoculum is convenient to operate and easy for industrial production, and is the innovation of a straw returning technology.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
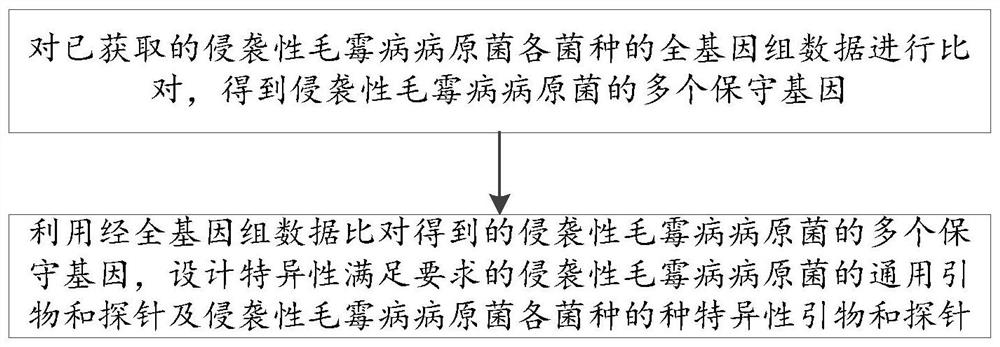
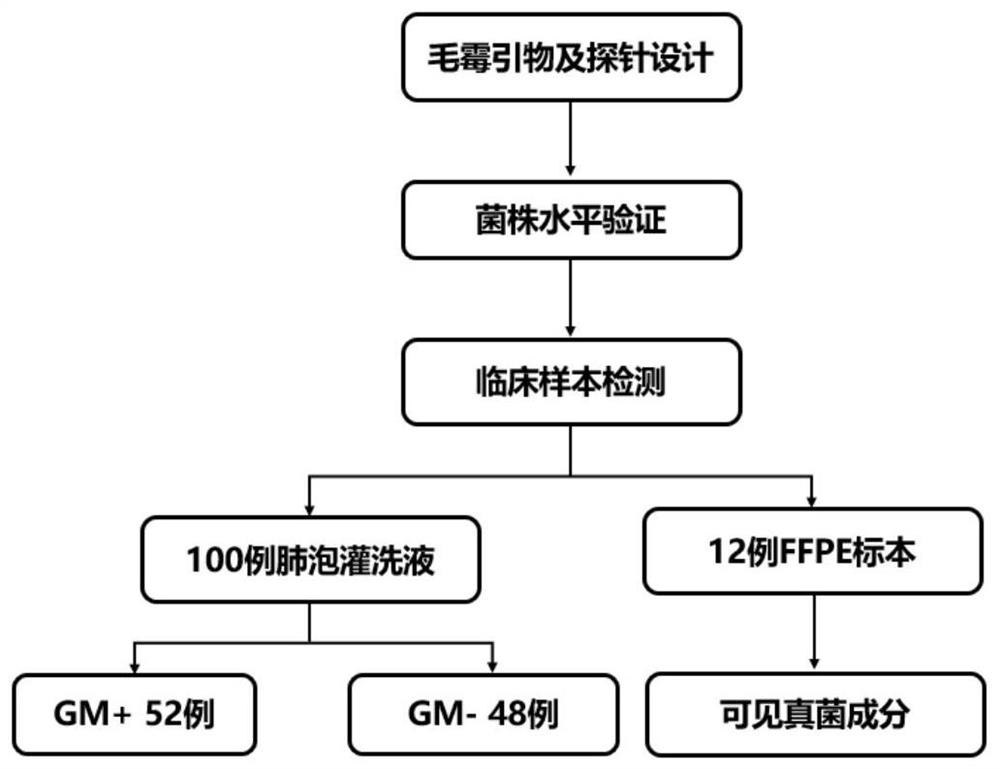
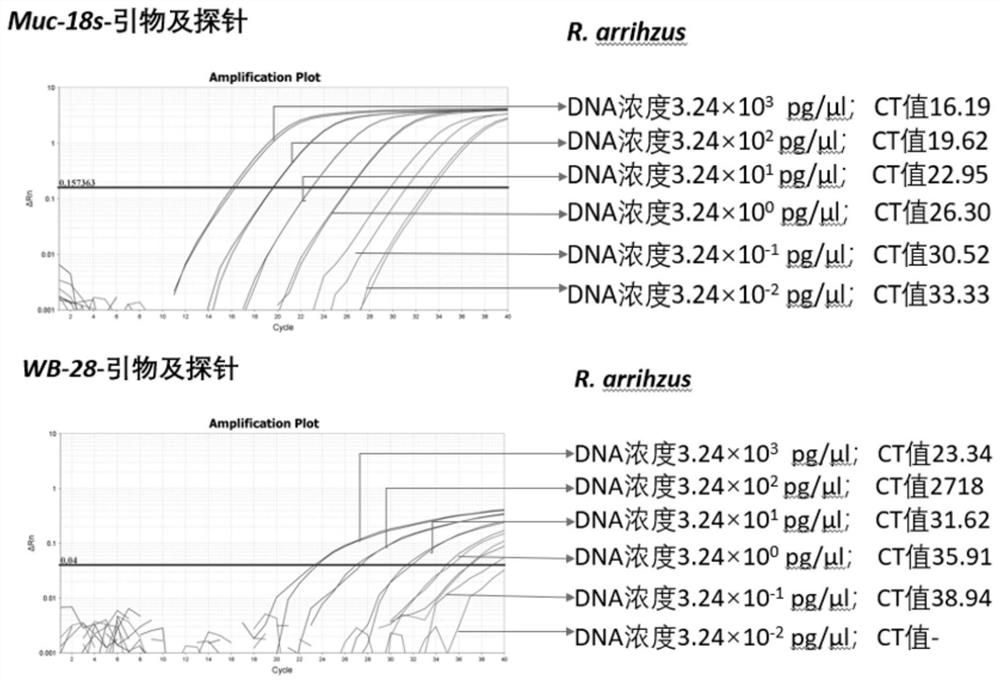
Primer and probe of invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria, implementation method and detection system thereof
ActiveCN112980997AAccurate identificationImprove diagnostic accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAspergillus flavusGenomic data
The invention discloses a primer and a probe of invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria, an implementation method and a detection system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: comparing whole genome data of all strains of the obtained invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria to obtain a plurality of conserved genes of the invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria; and designing a universal primer and a probe of the invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria with specificity meeting the requirement and a species-specific primer and a probe of all strains of the invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria by utilizing the plurality of conserved genes of the invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria obtained by whole genome data comparison. By utilizing the primer and the probe designed by the invention, the sensitivity and the specificity of detection of the invasive mucor pathogenic bacteria can be improved, and various strains including aspergillus fumigatus, aspergillus flavus, aspergillus terreus, aspergillus niger and aspergillus nidulans can be detected; and the primer and the probe are suitable for different clinical samples such as BALF and FFPE tissues and exudates (pus).
Owner:PEKING UNIV FIRST HOSPITAL
Preparation method and application of penicillium genetically engineering bacterium
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a penicillium genetically engineering bacterium. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining a hygromycin resistance expression cassette, cloning the hygromycin resistance expression cassette onto a target plasmid so as to obtain a hygromycin resistance recombinant plasmid; respectively cloning a penicillium lipase gene (PEL), a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter PgpdP of penicillium expansum and a aspergillus nidulans tryptophan synthetase terminator TtrPC so as to obtain a PEL gene expression cassette driven by a strong promoter; cloning the PEL gene expression cassette to the hygromycin resistance recombinant plasmid, thus obtaining a hygromycin selection marker containing a PEL gene over-expression vector; and converting the over-expression vector into an engineering agrobacterium, and converting the PEL gene expression cassette to a penicillium strain by using an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method, thus obtaining the penicillium genetically engineering bacterium. The penicillium genetically engineering bacterium obtained by the method has strong lipase production capacity; the enzyme activity of the lipase prepared by the penicillium genetically engineering bacterium is 100%-150% higher than that of a starting strain penicillium wild fungus.
Owner:ANHUI LEVEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for preparing straw-decomposing inoculant capable of inhibiting soil-borne diseases
ActiveCN103642782AEfficient killingIncrease the number ofBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganism based processesCelluloseBacillus aryabhattai
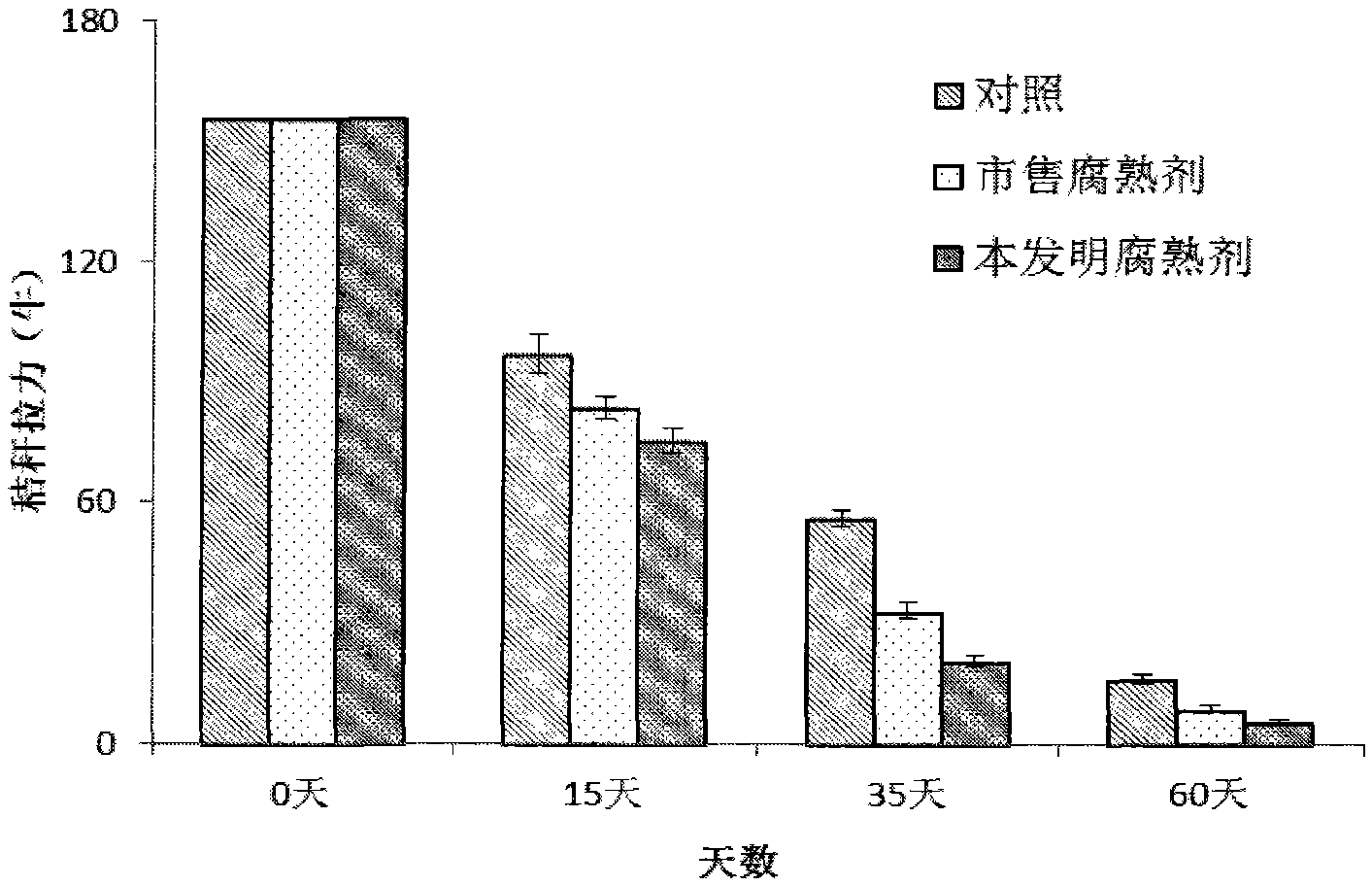
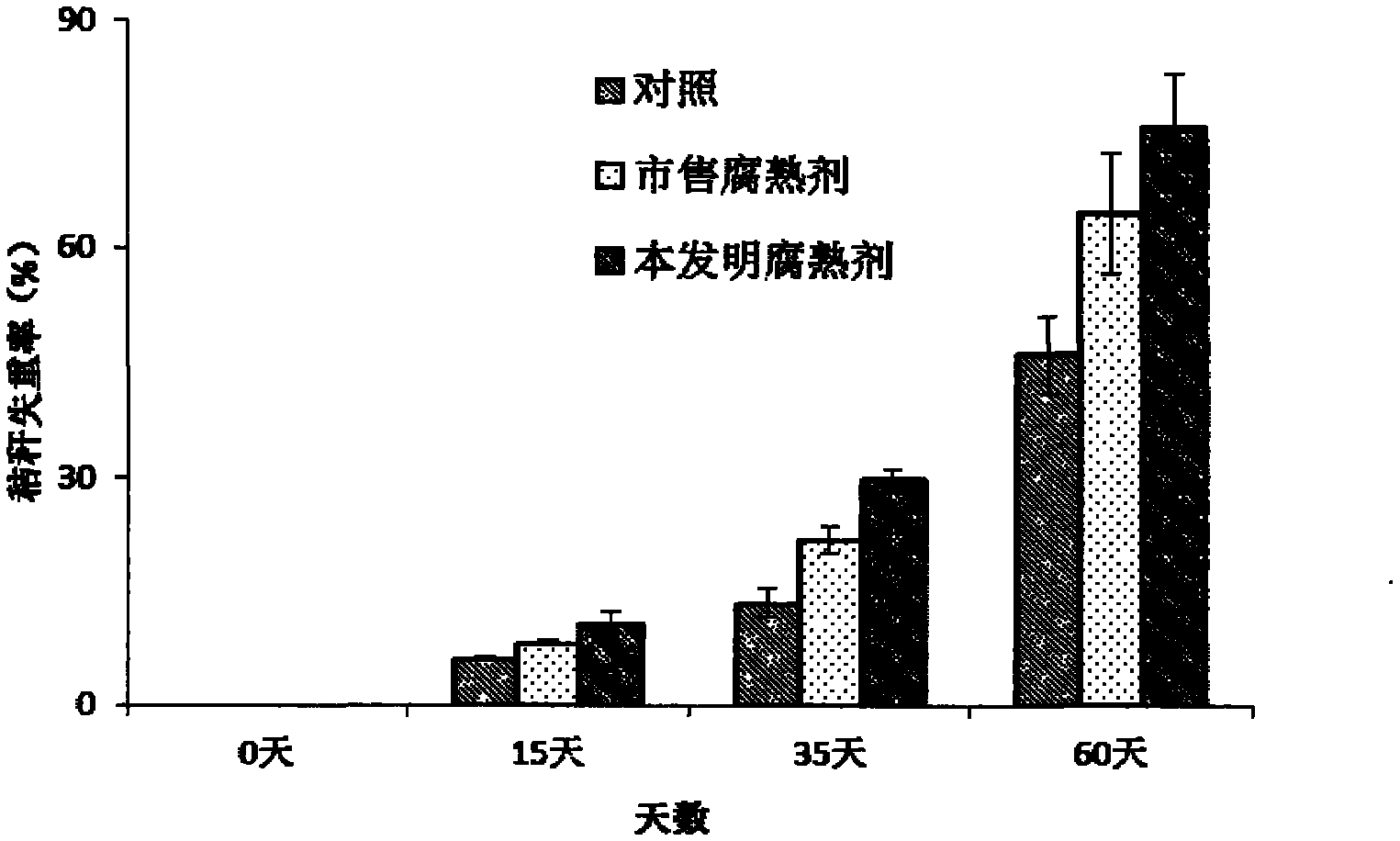
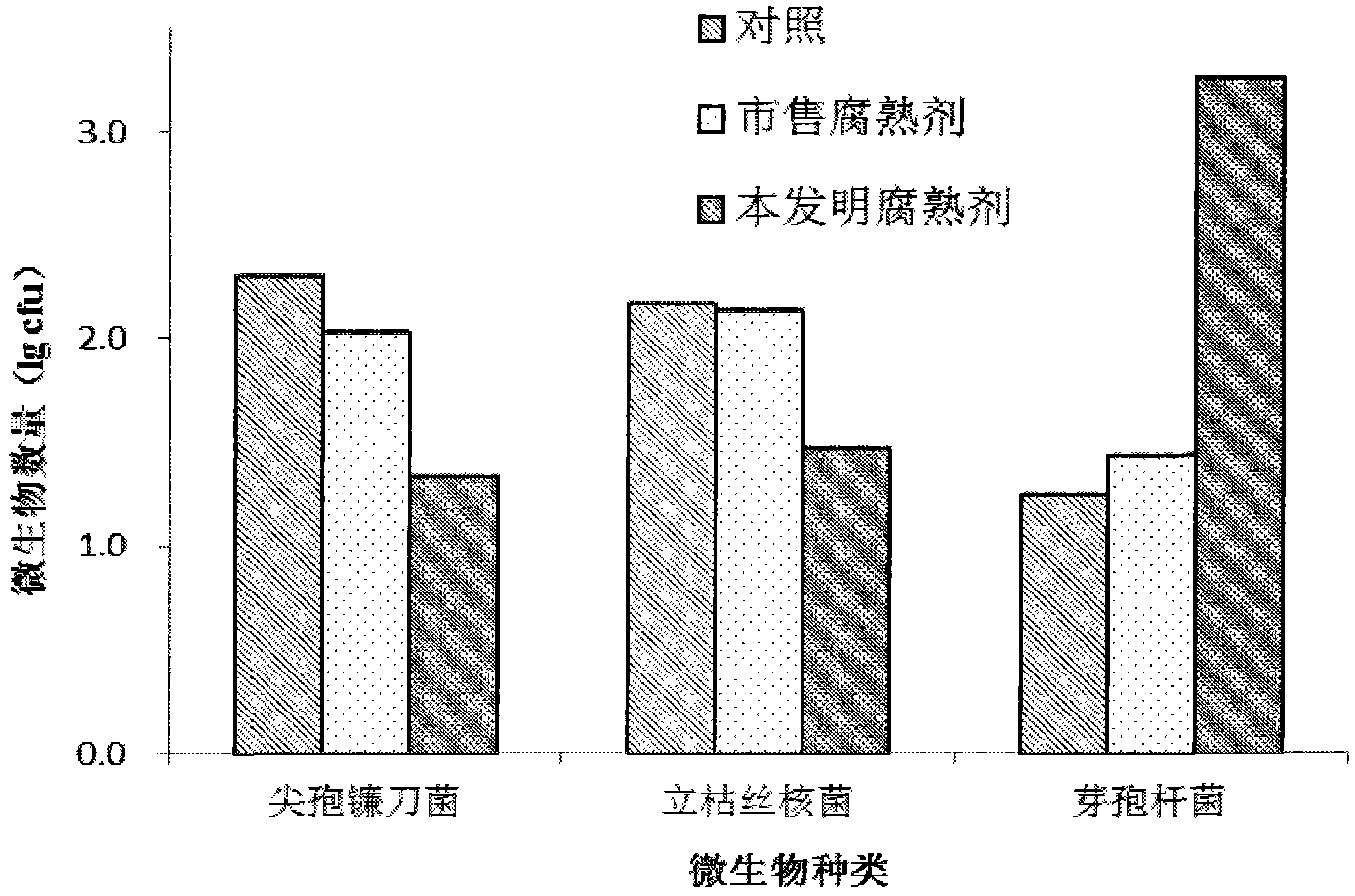
The invention discloses a method for preparing a straw-decomposing inoculant capable of inhibiting soil-borne diseases. The straw-decomposing inoculant capable is characterized by being prepared by compounding aspergillus nidulans with fibrinolysis function, aspergillus oryzae, bacillus subtilis, yeast and bacillus pumillus solid with biological control function. The product can be used for effectively accelerating the decomposing speed of returned straws, inhibiting growth of rice sheath blight disease, rice blast, wheat sharp eyespot and other pathogenic bacteria. When the straw-decomposing inoculant is applied to the field, the straw decomposing speed can be accelerated, the weight loss ratio of straws can be remarkably increased, and the straw tensile force can be remarkably reduced; the number of pathogenic bacterium antagonistic bacillus in the soil can be increased, and the number of pathogenic microbes can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:南京宁粮生物工程有限公司
Method for increasing yield of anidulafungin precursor compound Echinocandin B
ActiveCN103509840ARaise the level of fermentationIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-threonineOrnithine synthesis
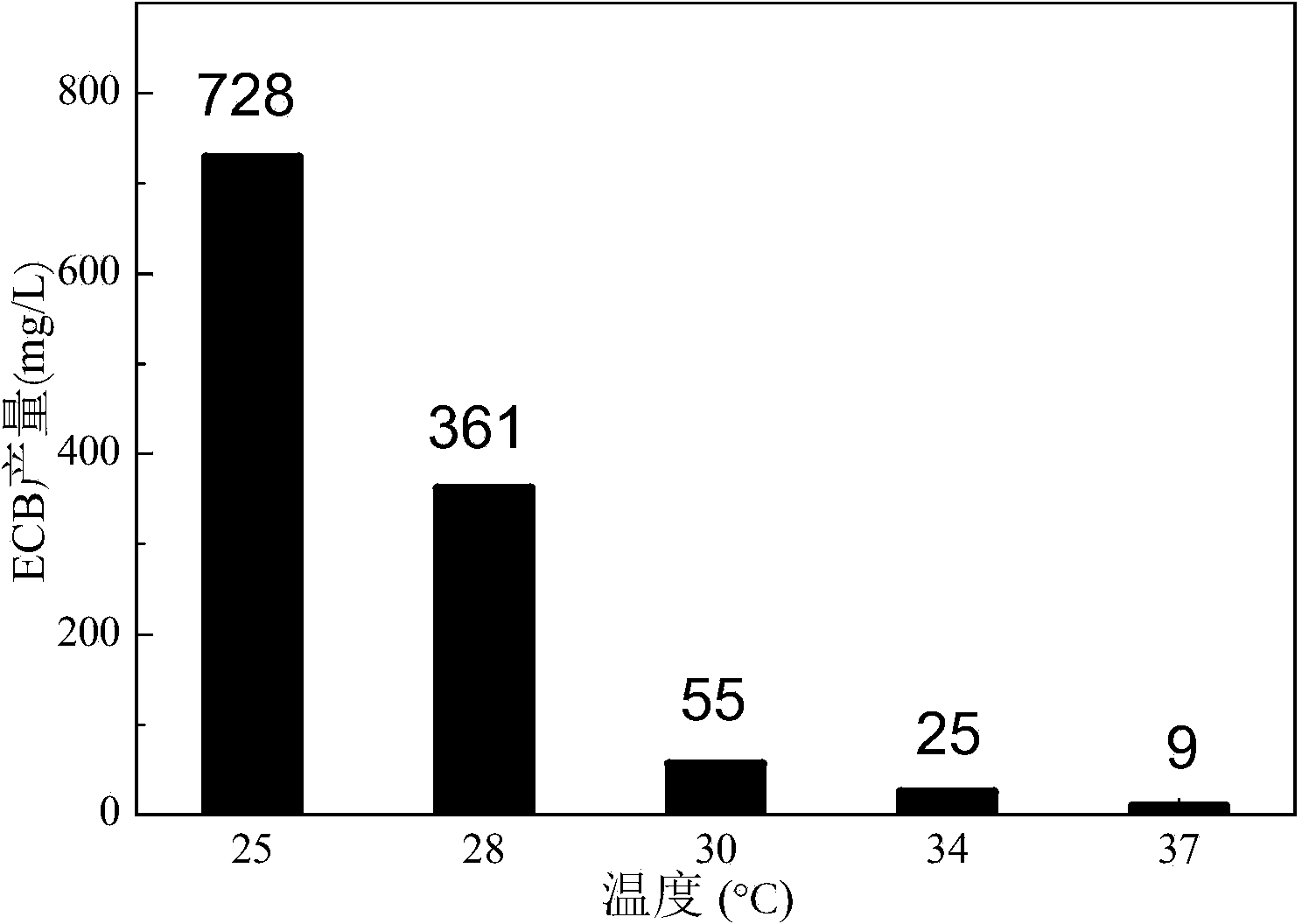
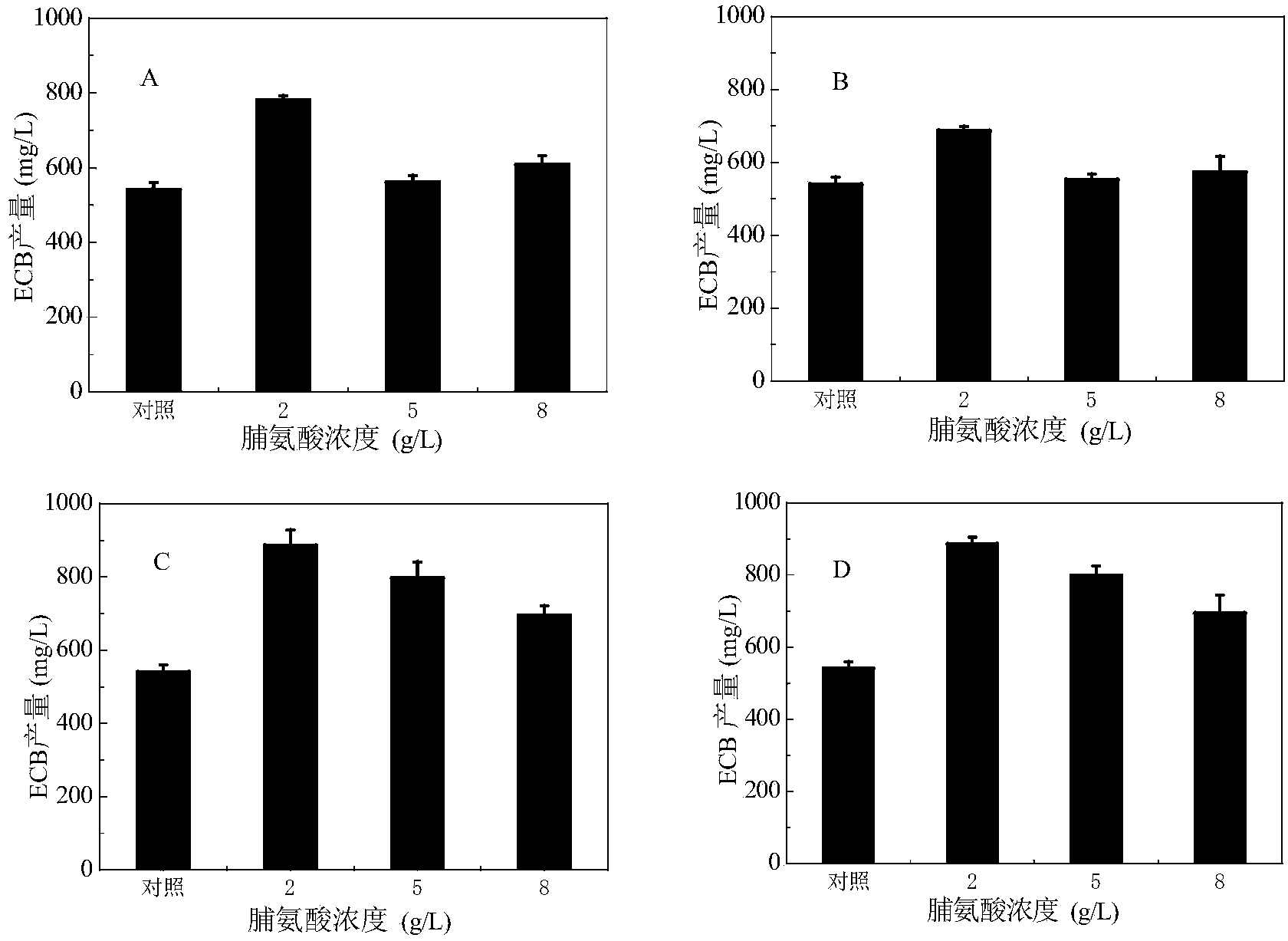
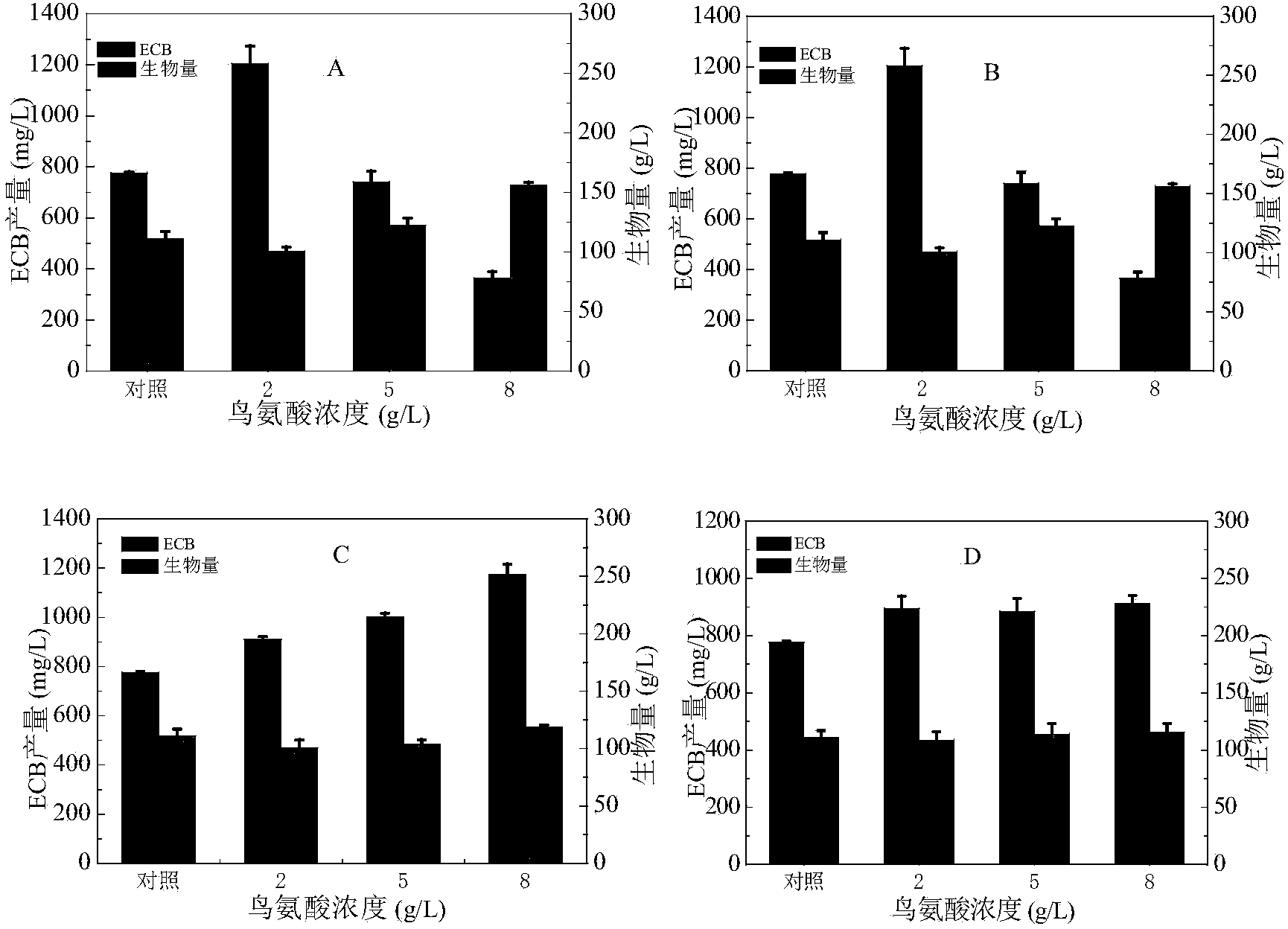
The invention provides a method for increasing the yield of an anidulafungin precursor compound Echinocandin B (ECB). The method comprises the following steps: preparing a fermentation culture medium for culturing Aspergillus nidulans for synthesizing ECB, inoculating aspergillus nidulans, culturing for 3 days at 28-37 DEG C, and continuously culturing at 25 DEG C till the fermentation is accomplished. Compared with constant temperature culture, the method adopts the strategy that the ECB is cultured at 37 DEG C at the early three days and is cultured at 25 DEG C at the later 9 days, so that the yield of the ECB is increased to be 1,237mg / L from 728mg / L; in addition, the yield of the ECB is increased to be 850mg / L from 540mg / L by adding 2g / L proline on the sixth day; and the yield of the ECB can be respectively increased by 21.9% and 55.2% by adding 2g / L threonine and 2g / L ornithine into the culture medium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
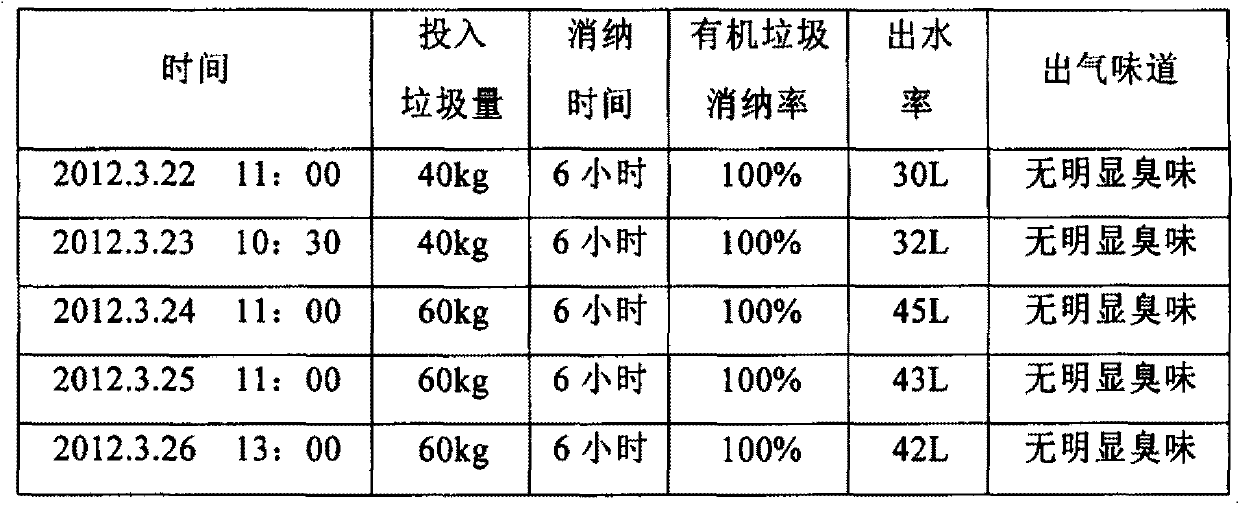
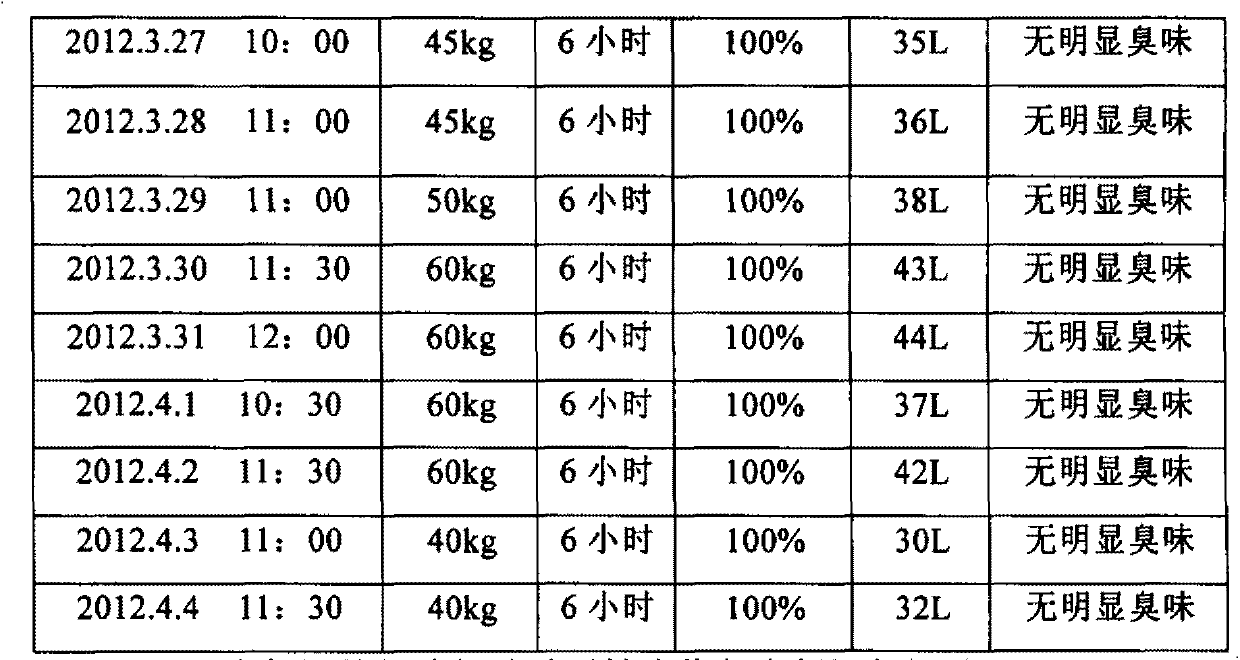
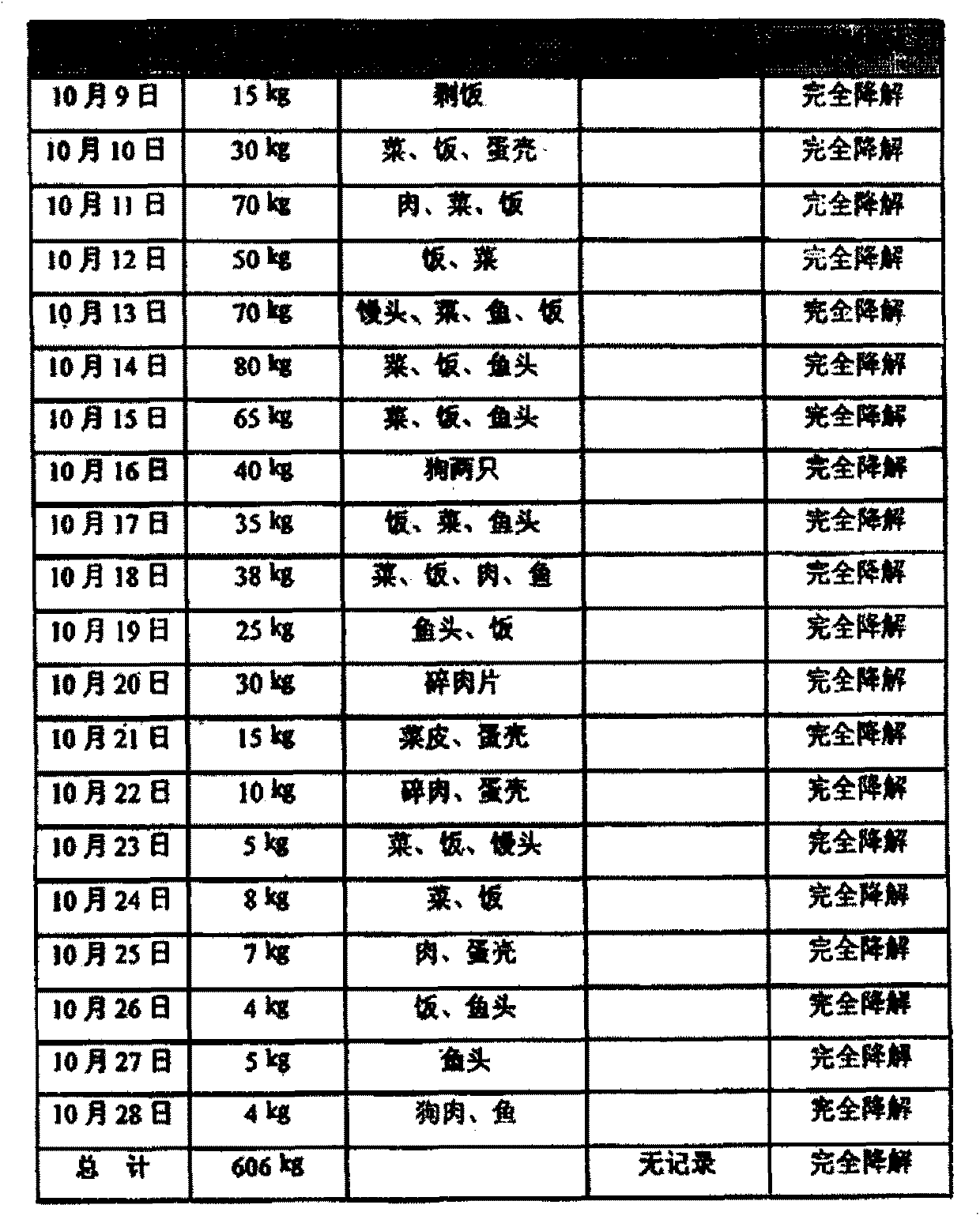
Active biological complexing agent for degradation and digestion of organic wet garbage and preparation method of active biological complexing agent
InactiveCN103272361AEfficient decompositionNo external heating requiredInorganic saltsPICHIA JADINII
The invention relates to an active biological complexing agent for degradation and digestion of organic wet garbage and a preparation method of the active biological complexing agent. The active biological complexing agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.6-1.0 percent of pichia jadinii solution, 0.6-1.0 percent of Japanese aspergillus solution, 0.6-1.0 percent of aspergillus terreus solution, 0.6-1.0 percent of bacillus cereus solution, 0.6-4.0 percent of Bacillus thermoliquefaciens-NL solution, 0.6-1.0 percent of geobacillus stearothermophilus solution, 0.6-1.0 percent of aspergillus nidulans solution, 50-60 percent of rice husks, 4-5 percent of swill and the balance of water. The active biological complexing agent for degradation and digestion of the organic wet garbage is prepared by carrying out mixed fermentation and domestication. Compared with the prior art, the active biological complexing agent organically combines the solutions together, has the capability of decomposing wet garbage into gases, water and inorganic salts within 8-24 hours and has the degradation rate of 75-99.9 percent; and no external heating is needed.
Owner:上海盈成玉环境技术有限公司
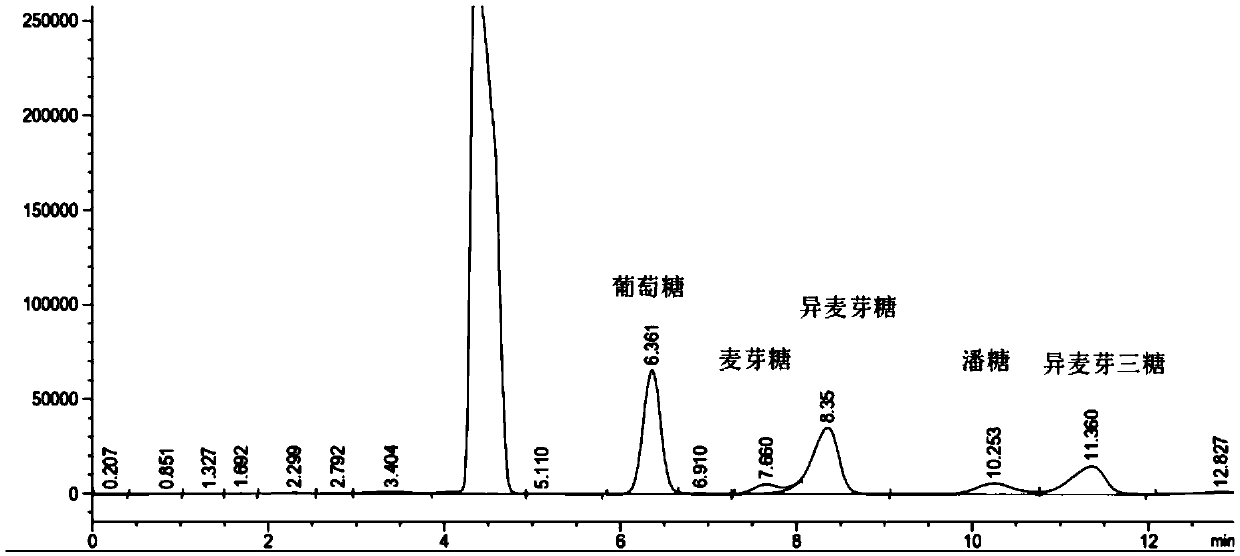
Alpha-glucosidase mutant and application thereof
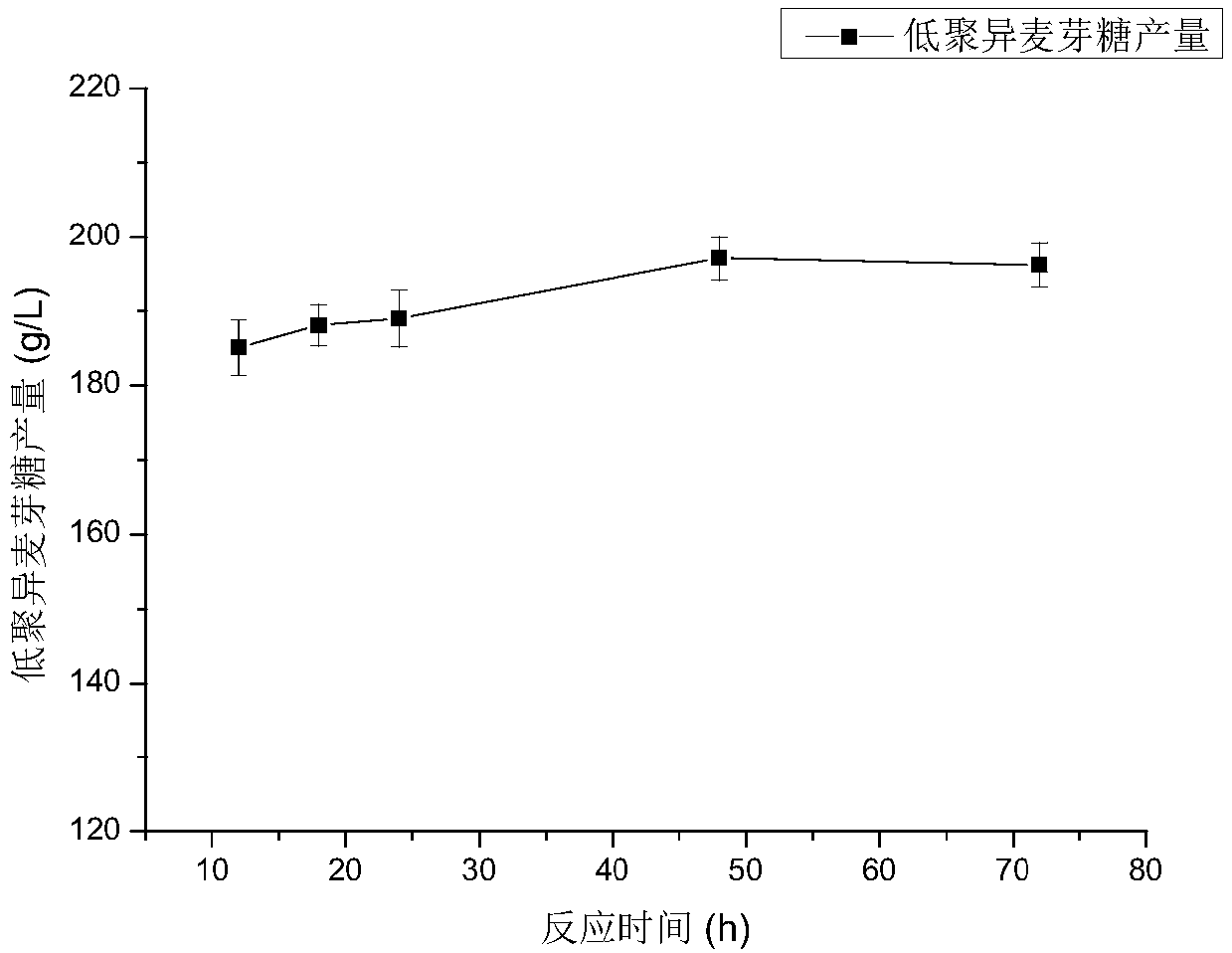
ActiveCN109576246AIncrease resistance dextrin compositionIncrease productivityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention relates to an alpha-glucosidase mutant and application thereof, in particular to an alpha-glucosidase mutant and application of the alpha-glucosidase mutant to production of isomaltooligosaccharide and resistant dextrin, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. An alpha-glucosidase mutant gene from aspergillus nidulans is transferred into pichia pastoris to be expressed; the recombinant alpha-glucosidase is used for preparing isomaltooligosaccharide and resistant dextrin; under the conditions of the temperature being 45 DEG C, the pH being 5.5, the enzyme adding quantity being 5 U / g and the substrate concentration being 300 g / L, the yield of the isomaltooligosaccharide reaches 216 g / L; the conversion rate is 72 percent. When pyrodextrin is used as a substrate,three enzymes of branching enzymes, alpha-CGT enzymes and alpha-glucosidase are compounded to improve the ingredients of resistant dextrin; the resistant ingredients of the pyrodextrin can be improvedto 70 percent from the original 44 percent. By the method, the production efficiency is effectively improved; the production cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for fermenting high-yield echinocandins B through aspergillus nidulans
ActiveCN108342437AControl the shape of bacteriaImprove and stabilize fermentation yieldMicroorganism based processesPeptidesMyceliumEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a method for fermenting high-yield echinocandins B through aspergillus nidulans. The method includes the steps that a fermentation culture medium is inoculated with the aspergillus nidulans, culture is carried out at the temperature of 25 DEG C, fermentation liquor containing echinocandins B is obtained, the fermentation liquor is separated and purified, and echinocandins Bare obtained; by optimizing the varieties of carbon sources, adding particles and the like, the forms of mycelia in the fermentation process of the aspergillus nidulans are controlled, the mycelia are coccoid, and the problems that as the mycelia are too long during fermentation, the viscosity is high, dissolved oxygen is low, and mass transfer is insufficient are solved; by analyzing key metabolism components in the ECB synthesis process and optimizing a precursor adding strategy in the fermentation process, the yield of fermentation products is further increased by one time or above, and broad application prospects are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Compound microbial inoculum used for waste composting, preparation method of compound microbial inoculum, and waste composting method
InactiveCN109251872ASignificant decomposition functionReduce usageFungiBio-organic fraction processingCelluloseMicroorganism
The invention discloses a compound microbial inoculum used for waste composting, a preparation method of the compound microbial inoculum, and a waste composting method adopting the compound microbialinoculum. The compound microbial inoculum comprises bacillus subtilis, bacillus thuringiensis and aspergillus nidulans. Microbes of the compound microbial inoculum have the obvious function of decomposing lignin and cellulose, the compound microbial inoculum prepared by compounding the microbes at a certain ratio (the microbes are separated out at the waste composting maturity stage) is used for carrying out landscaping waste composting, thus the contents of lignin and cellulose in the compost product are obvious reduced, and the degradation rates of lignin and cellulose are improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
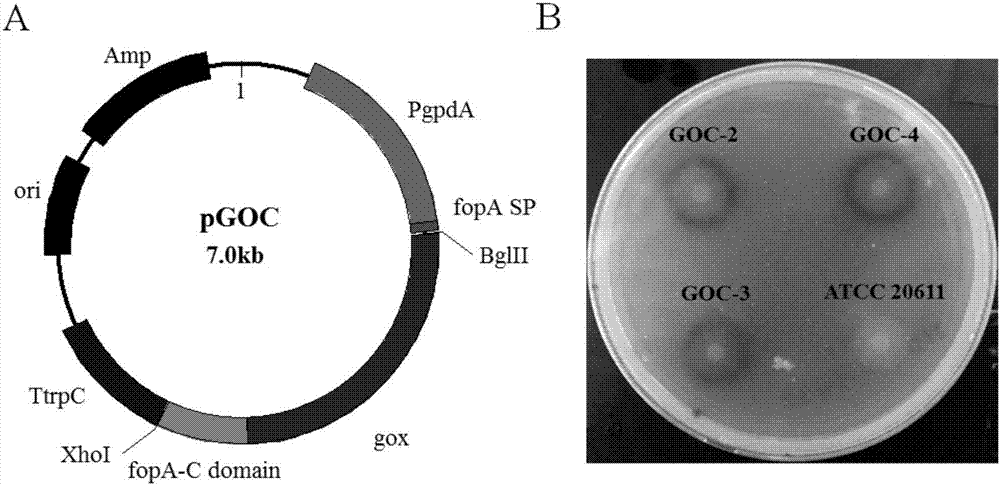
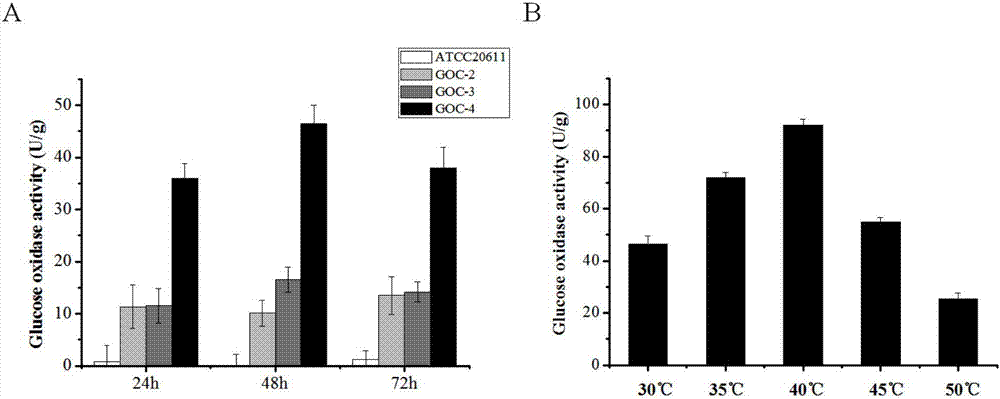
Glucose oxidase-expressing fructooligosaccharide-synthesizing engineered strain, and its construction method and application
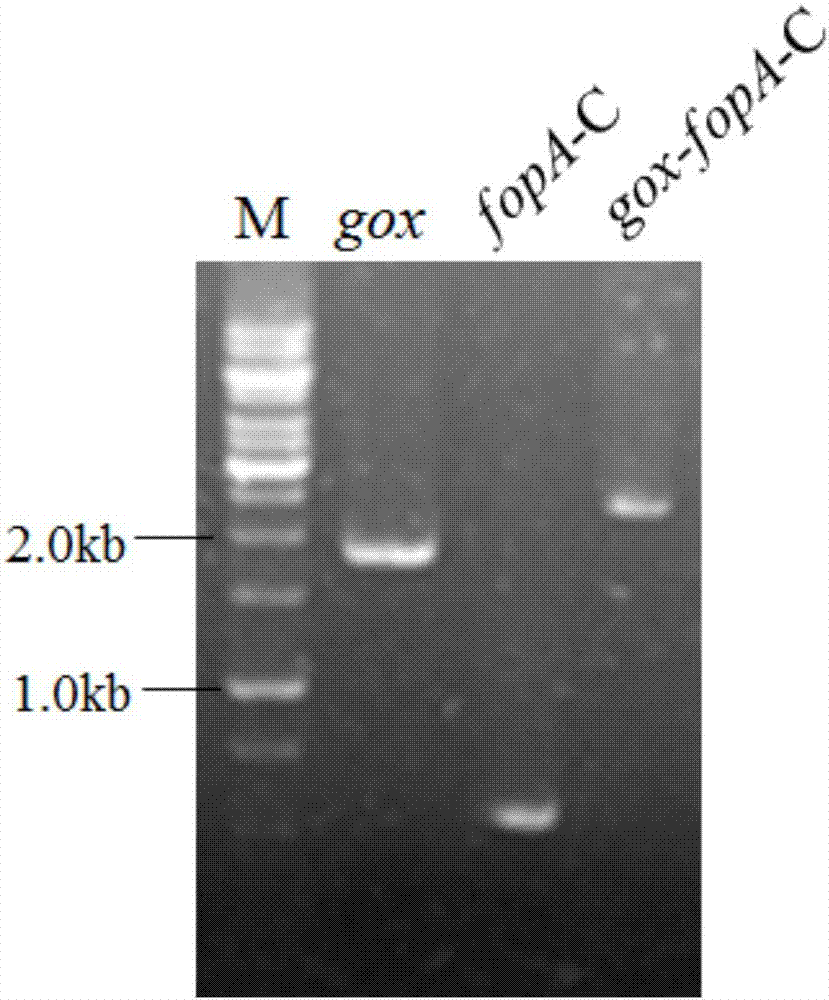
ActiveCN107418903APromote positive conversionHigh purityFungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAspergillus nidulansTryptophan
The invention discloses a glucose oxidase-expressing fructooligosaccharide-synthesizing engineered strain. The genome of the engineered strain contains the fusion gene gox-fopA-C; the starting strain of the engineered strain is Aspergillus niger ATCC 20611; the fusion gene gox-fopA-C is prepared through fusion of the gox gene coding glucose oxidase GOX and the fopA-C gene coding the FopA-C terminal domain of beta-fructofuranosidase; and the fusion gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, the upstream of the nucleotide sequence is a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter PgpdA of Aspergillus nidulans, and the downstream of the nucleotide sequence is a tryptophan terminator TtrpC of Aspergillus nidulans. The invention also discloses application of the engineered strain to preparation of fructooligosaccharide. Experimental results show that the activity of glucose oxidase in the engineered strain reaches 90.0 U / g, the activity of beta-fructofuranosidase reaches 380 U / g, mycelia are directly used for preparation of fructooligosaccharide, and the content of prepared fructooligosaccharide reaches 71.2%. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, capacity of realizing one-step enzymatic preparation of high-purity fructooligosaccharide and good industrial application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Organic pollution water body bioremediation agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103351061AImprove compactnessImprove water qualityFungiBacteriaBalance of natureEutrophication
The present invention relates to an organic pollution water body bioremediation agent and a preparation method thereof. The raw materials comprise, by weight, 0.6-1.0% of an Aspergillus oryzae liquid, 0.6-1.0% of a Bacillus cereus liquid, 0.6-1.0% of an Aspergillus terreus liquid, 0.6-1.0% of an Aspergillus nidulans liquid, 50-60% of hull, and the balance of nature river water, wherein mixing, fermentation, and acclimation preparation are performed to obtain the organic pollution water body bioremediation agent. Compared with the organic pollution water body bioremediation agent in the prior art, the organic pollution water body bioremediation agent of the present invention has the following characteristics that: black, odorous and eutrophicated organic pollutants are formed in a water body so as to be decomposed and be discharged out of the water, such that water quality is improved; and other technologies such as aquatic plants and animals, and the like are combined, such that the polluted water body can be restored to the ground surface IV-V class water.
Owner:上海玉仑应用微生物研究所
Method for producing terpenes
ActiveUS20140045238A1Improve production yieldIncrease productionSugar derivativesMicroorganismsBiosynthetic genesGene cluster
The present invention relates to a method for producing terpenes in fungi, wherein a terpene biosynthetic gene cluster having terpene biosynthetic genes and regulatory regions operably linked to said genes is activated. The invention relates also to a terpene biosynthetic gene cluster and regulatory regions of such terpene biosynthetic gene cluster usable is production of terpenes, use of regulator for regulating the terpene production and use of Aspergillus nidulans FGSC A4 for producing terpenes. The method of invention provides higher yields of enriched terpene product without essential amount of side-products.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Method for producing chitosan oligosaccharide from home-made enzyme solution
InactiveCN105803019AReduce manufacturing costLow costHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesCellulaseTwo step
The invention relates to the technical field of enzymatic production of chitosan oligosaccharide and particularly relates to a low-cost method for producing chitosan oligosaccharide from a home-made enzyme solution. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out fermentation culture on an enzyme solution to prepare fungus aspergillus nidulans capable of highly producing deacetylase and obtain an enzyme solution A for preparing chitosan by virtue of deacetylation of chitin; and preparing an enzyme solution B capable of highly producing cellulose and amylase by virtue of liquid fermentation culture, and preparing chitosan oligosaccharide from the enzyme solution B by virtue of enzymolysis of chitosan. By virtue of a two-step enzymolysis process, chitin firstly reacts with the enzyme solution A to generate chitosan, and chitosan reacts with the enzyme solution B to generate chitosan oligosaccharide. The method has the advantages that the requirements of deacetylation and enzymolysis of chitosan are met by virtue of the home-made enzyme solution, so that the risk of enzyme inactivation of purchased commodities caused due to too many links of drying, storing and transportation is avoided; and a non-specific cheap enzyme source is provided, so that the production cost is lowered, the independence ability of an enterprise is improved, and the stable development of the chitosan oligosaccharide industry is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHUHAI JINLONG BIOTECH CO LTD
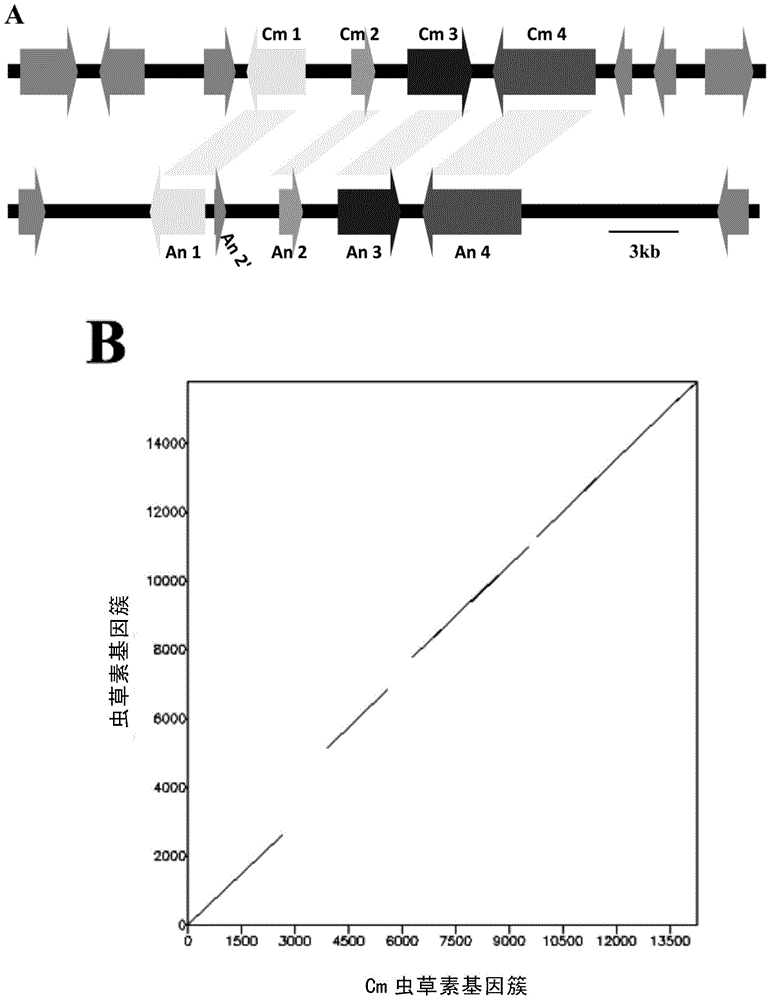
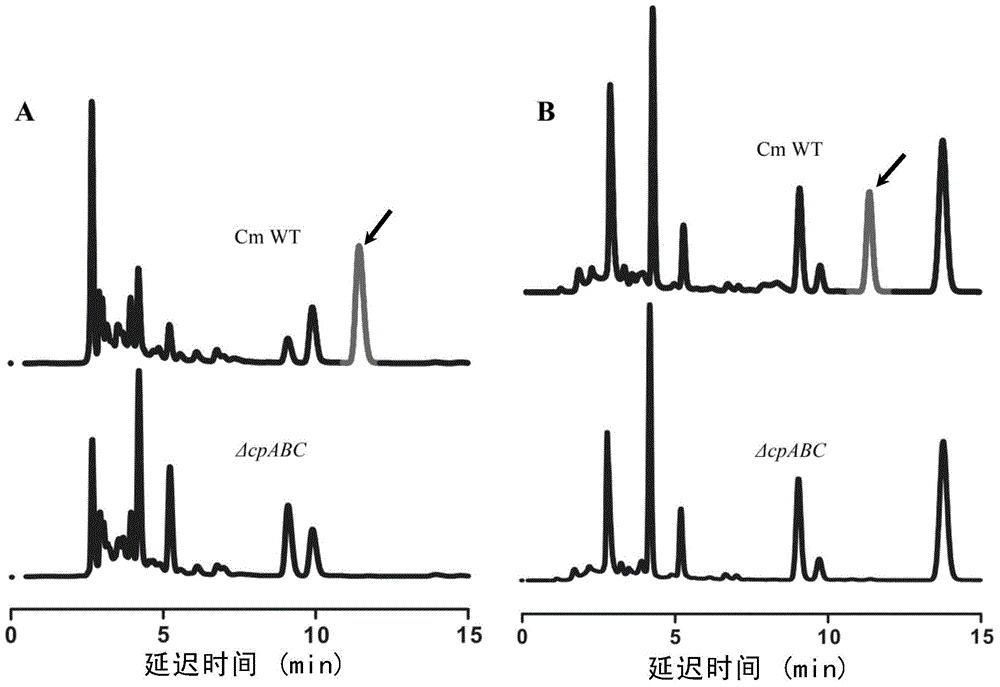
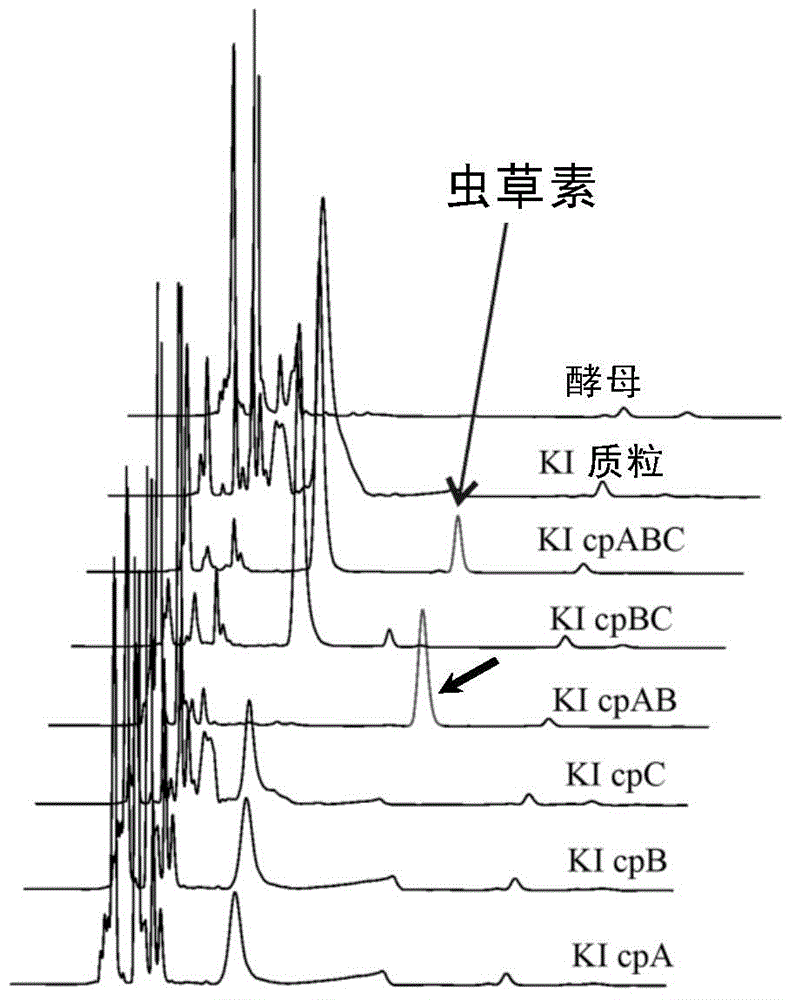
Identification and application of synthesis gene cluster of cordycepin
The invention relates to identification and application of a synthesis gene cluster of cordycepin that is a metabolite of cordyceps militaris (L.) link. The gene cluster of cordycepin biosynthesis is found for the first time. The gene cluster comprises Cm1 and Cm2 and / or Cm3, and corresponding homologous genes in aspergillus nidulans are An1, An2 and / or An3 respectively, and therefore a method of achieving efficient cordycepin biosynthesis is disclosed.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Modified penicillium expansum lipase gene, and construction and expression method thereof
InactiveCN103014036AEfficient and stable expressionHydrolasesFermentationAgricultural sciencePenicillium cainii
The present invention relates to an efficiently-expressed modified penicillium expansum lipase gene, and a plasmid construction method and a protein expression method of the gene. According to the present invention, an obtained hygromycin resistance expression cassette is cloned on target plasmid to obtain hygromycin resistance recombinant plasmid; a PCR technology is adopted to respectively amplify penicillium lipase gene (PEL), Aspergillus nidulans strong promoter glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter (PgpdA) and Aspergillus nidulans tryptophan synthetase terminator (TtrpC) to obtain a PEL gene expression cassette driven by a strong promoter, and finally the PEL gene expression cassette is inserted into the hygromycin resistance recombinant plasmid to obtain a PEL gene overexpression vector with a hygromycin screening marker. In addition, the obtained efficiently-expressed lipase gene production plasmid is transformed to obtain gene engineering penicillium with high lipase expression, wherein the expression is efficient and stable, and a plurality of advantages are provided compared to the conventional lipase production method.
Owner:SHENZHEN LEVEKING BIOLOGY ENG
Actinomycetes for resisting contamination fungi in grain feeds and grains
InactiveCN102206602AExtended shelf lifeImprove qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSnow moldAspergillus flavus
The invention relates to actinomycetes for resisting contamination fungi in grain feeds and grains, which is characterized in that: the strain is named TD-1 and is classified and named Streptomyces sp., which is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of Beijing on March 15, 2011 with the collection number of CGMCC No.4666. Autotrophic actinomyces for resisting growth of contamination fungi in the grain feeds and grains is separated and screened for the first time; and the strain has obvious inhibition effect on various fungi contaminating the grain feeds and grains, has obvious antagonism on aspergillus flavus, penicillium citrinum, fusarinm solani, aspergillus ochraceus, aspergillus oryzae, aspergillus nidulans, aspergillus niger, fusarium oxysporum, penicillium viridicatum and the like, can effectively prolong the retention period and improve the storing quality of the grain feeds and the grains, and lays a foundation for developing biological inhibitors for the fungi in the grain feeds and the grains.
Owner:天津市食品加工工程中心
Escherichia coli-bacillus subtilis shuttle expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102002509BStrong ability to secrete extracellular proteinsFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliExtracellular proteins
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli-bacillus subtilis shuttle expression vector and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The Escherichia coli-bacillus subtilis shuttle expression vector comprises a bacillus subtilis promoter sequence, a bacillus subtilis signal peptide coding sequence, an artificially designed ribosome binding sequence which can be identified by bacillus subtilis, the artificially designed enzyme cutting site of bacillus subtilis signal peptidase, an artificially designed multiple cloning site, a bacteriophage terminator sequence, a bacillus subtilis replicating initial sequence, and an Escherichia coli replicating initial sequence. The vector can be replicated in Escherichia coli and can also be replicated and expressed in the bacillus subtilis, so that vectors for a bacillus subtilis expression system are enriched; and the vector uses a B.subtilis deacetylated chitinase signal peptide for the first time, the signal peptide has high capability of guiding to secrete extracellular protein, a reporter gene is aspergillus nidulans pectate lyase gene, and the extracellular expression level reaches 600U / mL which is higher than that when the pectate lyase gene uses other vectors.
Owner:山东黄三角生物技术产业研究院有限公司
Expression equipment for secretory expression of foreign protein by penicillium expansum and genetically engineered bacterium thereof
The invention discloses expression equipment for secretory expression of a foreign protein by penicillium expansum and a genetically engineered bacterium thereof. The expression equipment sequentially comprises the following members from 5' to 3': (1) a lipase gene promoter of penicillium expansum; (2) a signal peptide of secretory expression; (3) multiple cloning sites; (4) a terminator of a gene C of aspergillus nidulans tryptophan synthetase. By inserting the foreign gene into the expression equipment, converting into agrobacterium tumefaciens by T-DNA (Transferred-Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and combining with penicillium expansum, the genetically engineered bacterium of penicillium expansum obtained can efficiently secretory-express heterologous genes originated from animals, plants and microorganisms, so that the foreign protein obtained can be produced on a large scale. The penicillium expansum is exuberant to grow, the condition of culture is extensive and cheap, both solid culture and liquid submerged fermentation are feasible, and the extracelluar protein produced is easy to separate and purify, so that the expression equipment is suitable for producing proteins with great industrial demands.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com