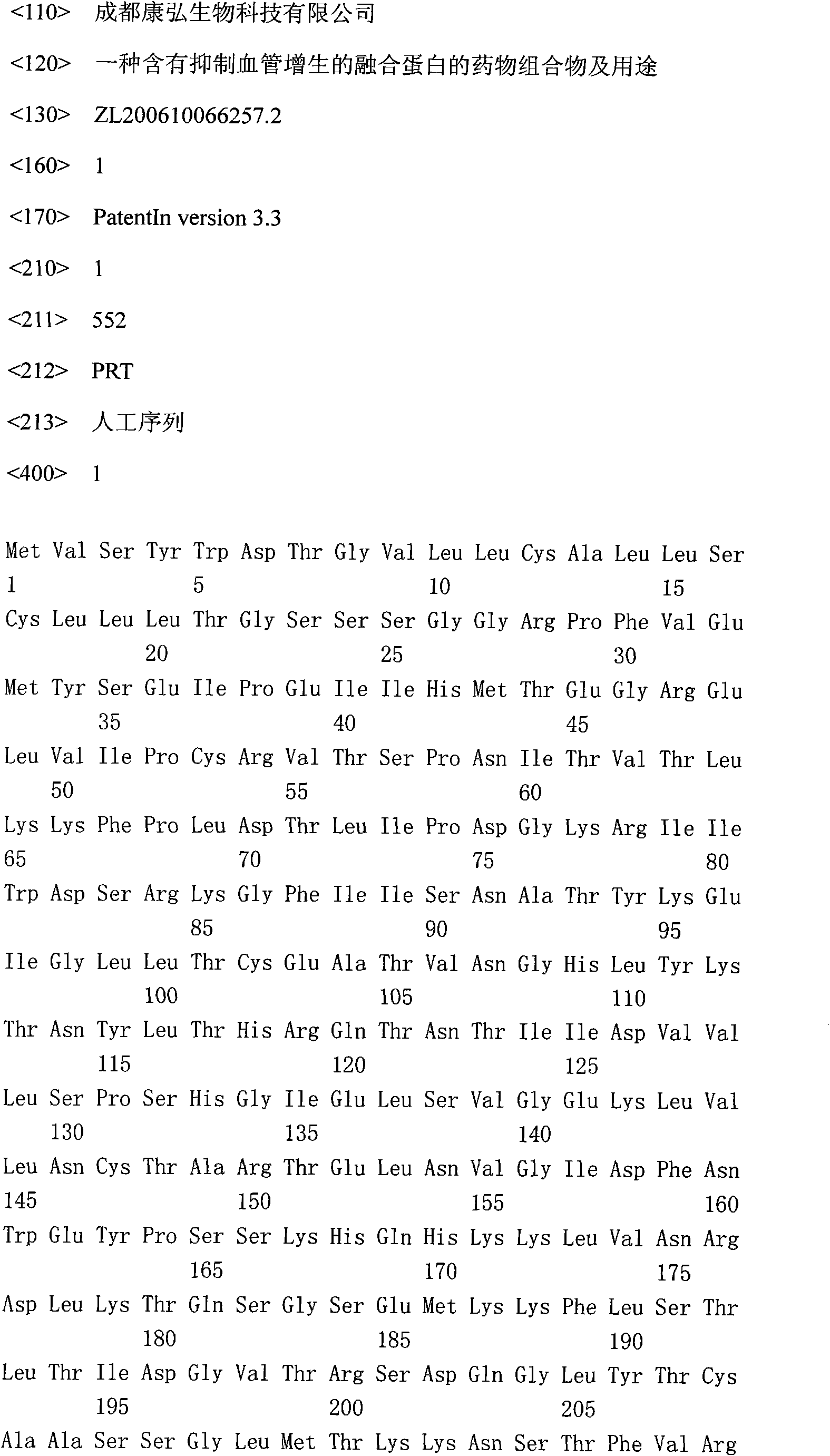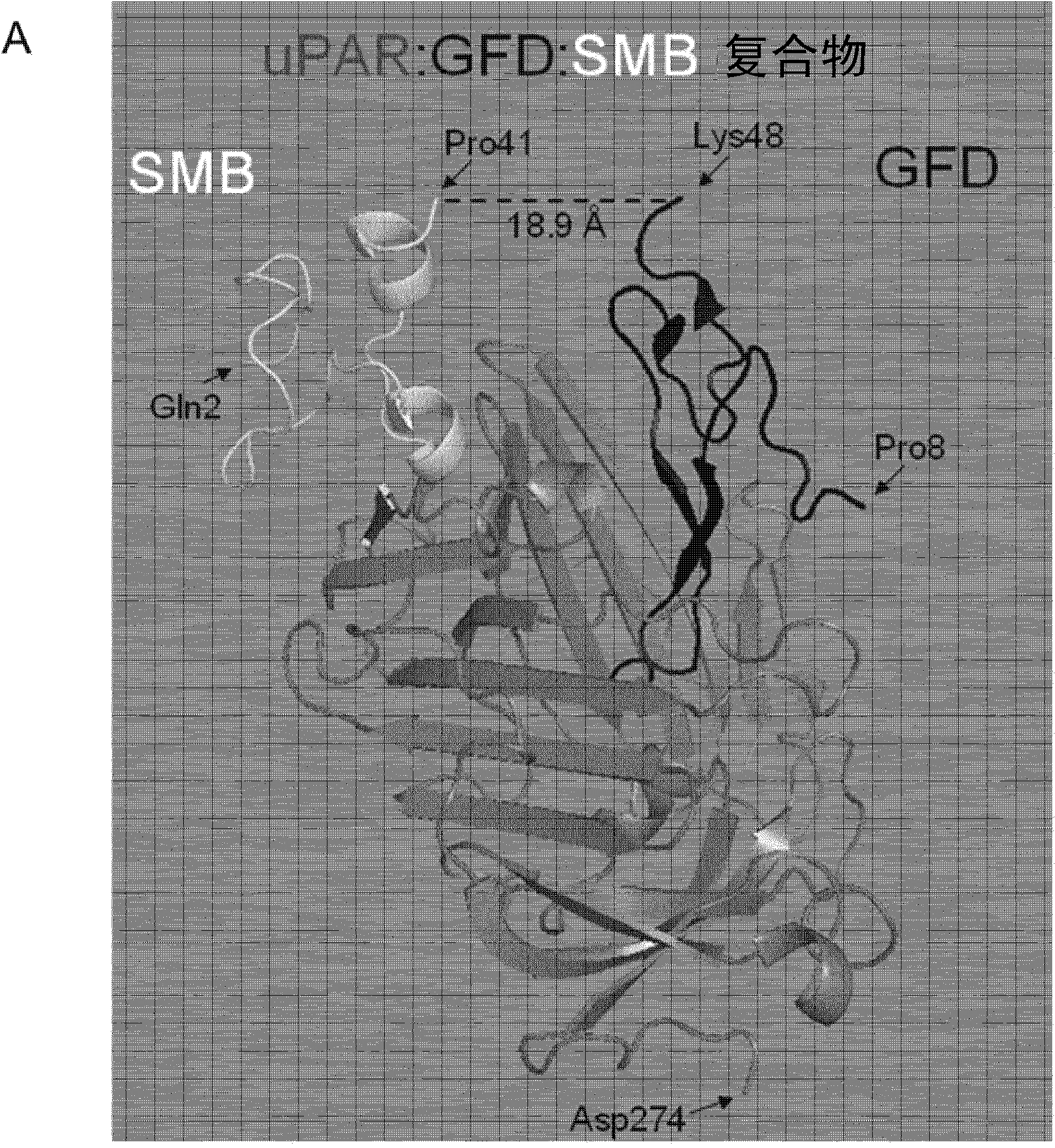Patents
Literature
121 results about "Extracellular proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An extracellular protein is a peptide that resides in body fluids outside of cells.
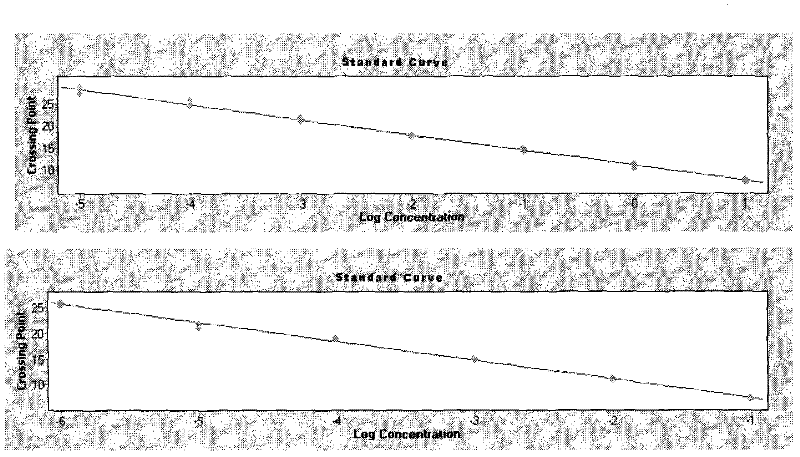
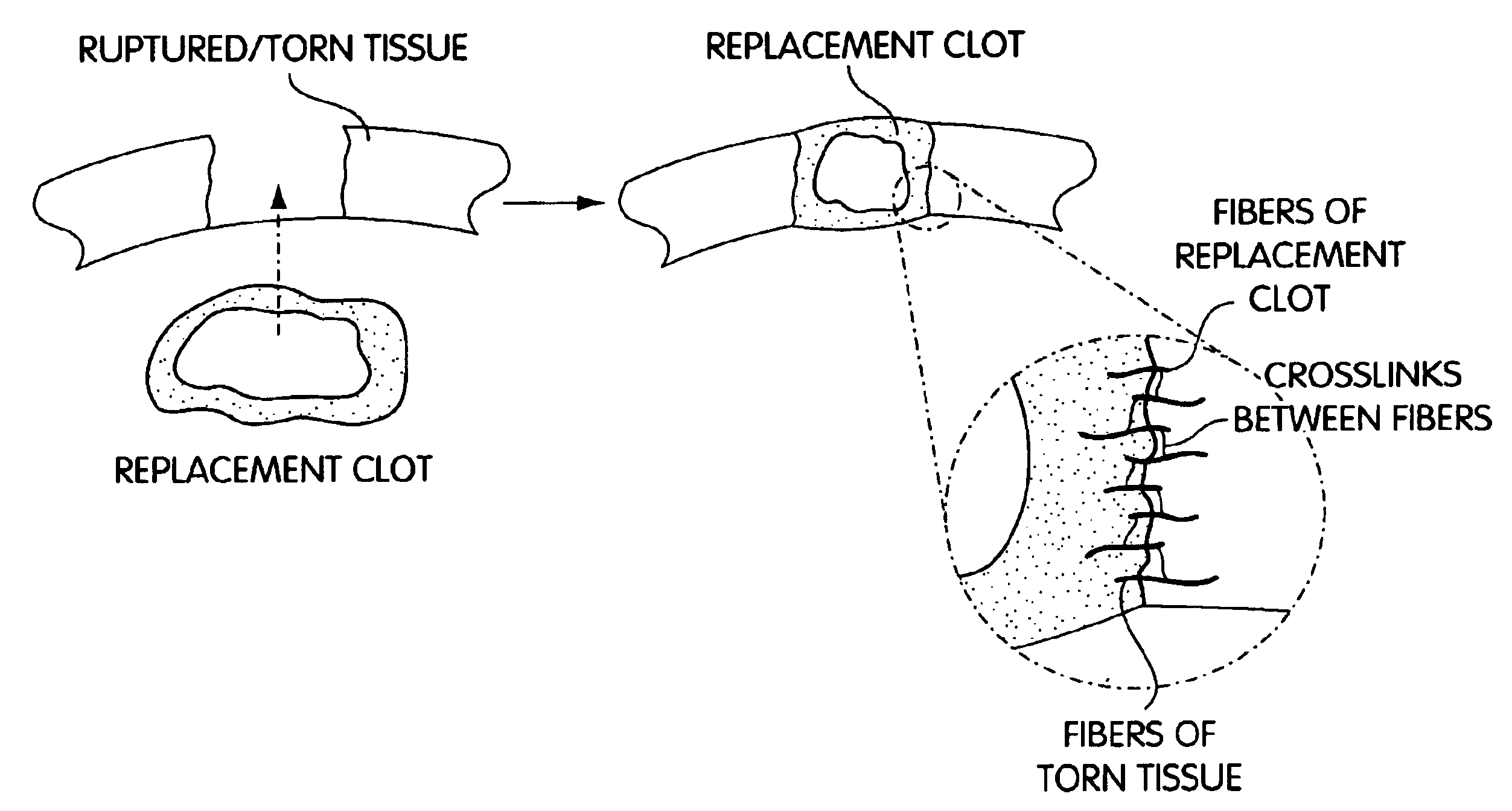
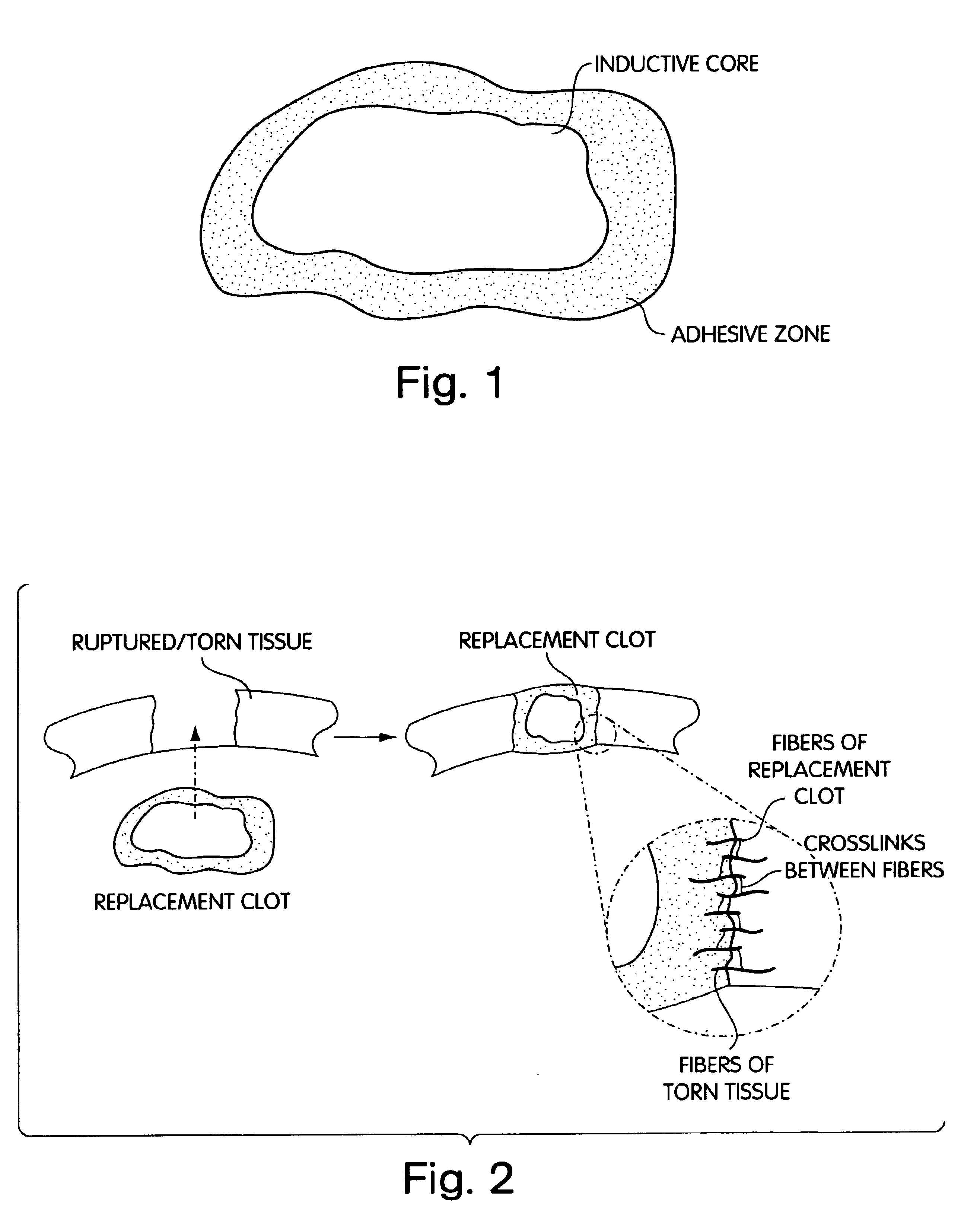
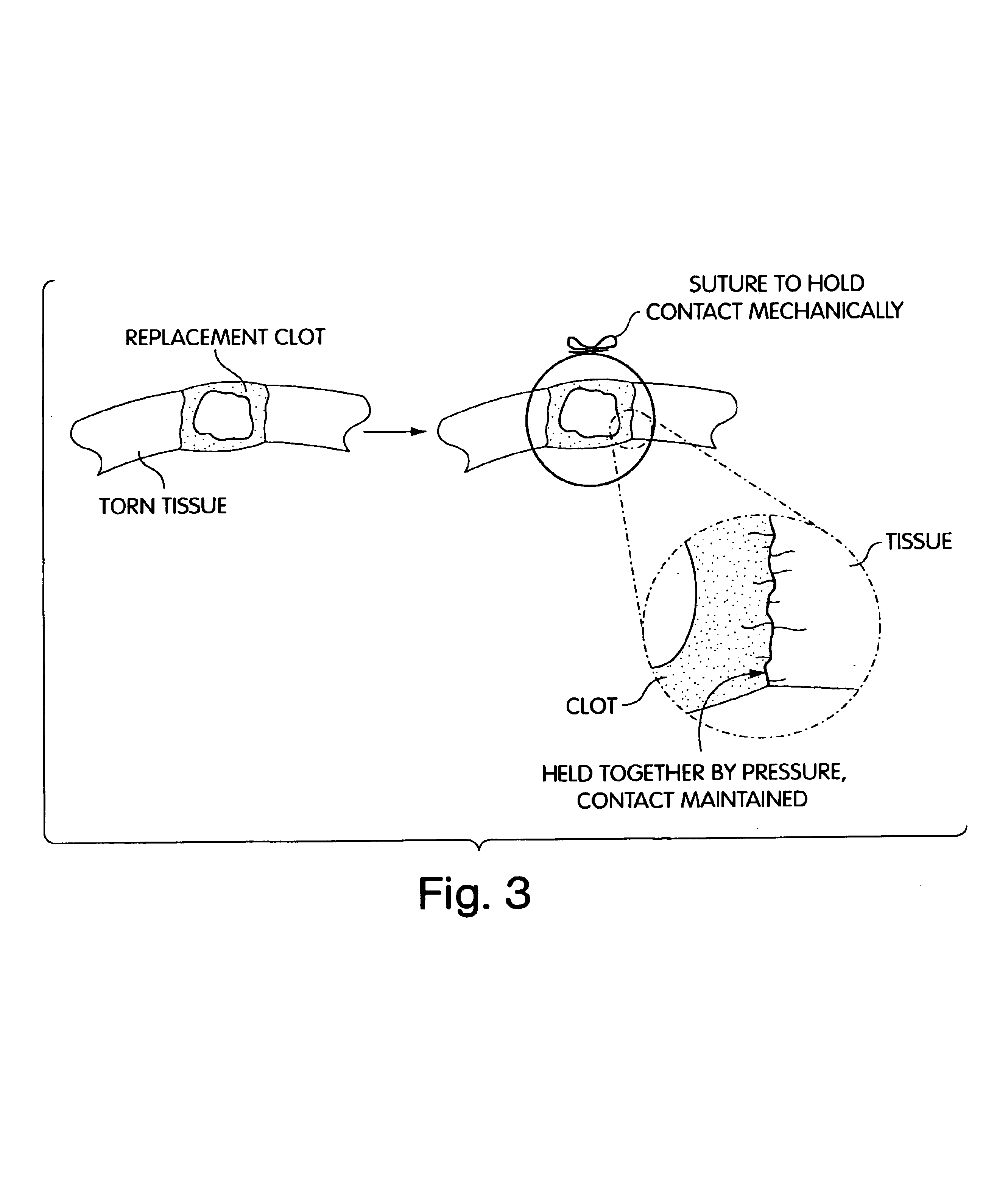
Biologic replacement for fibrin clot
InactiveUS6964685B2Increase contactResists premature degradationSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsExtra-ArticularExtracellular proteins
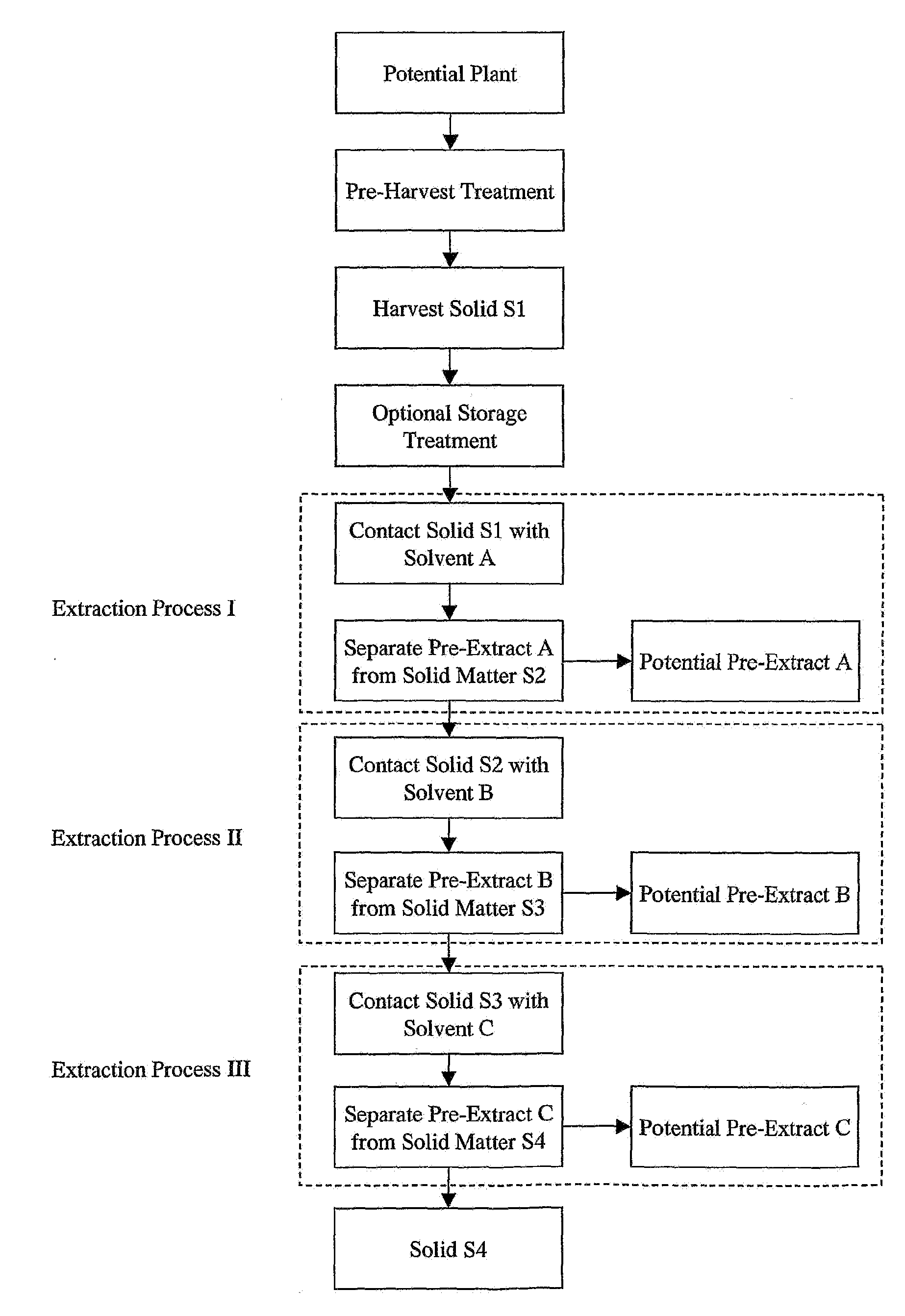
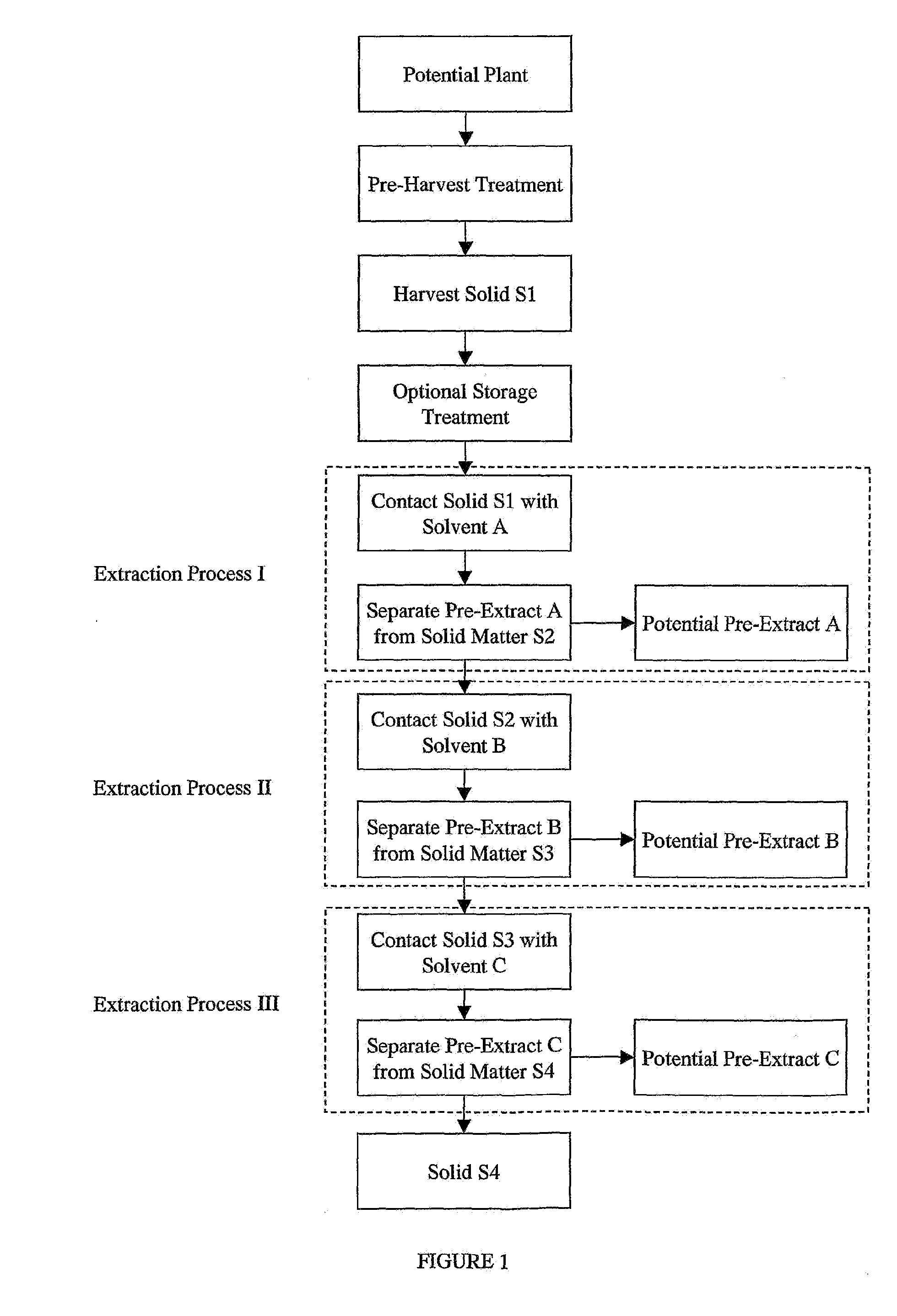
The invention provides compositions and methods for repairing intra-articular and extra-articular tissue including ligament, meniscus, cartilage, tendon, and bone. The method includes contacting the ends of an injured tissue from a patient with a composition. The repair composition includes soluble type 1 collagen, a platelet, and at least one of an extracellular protein and a neutralizing agent.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
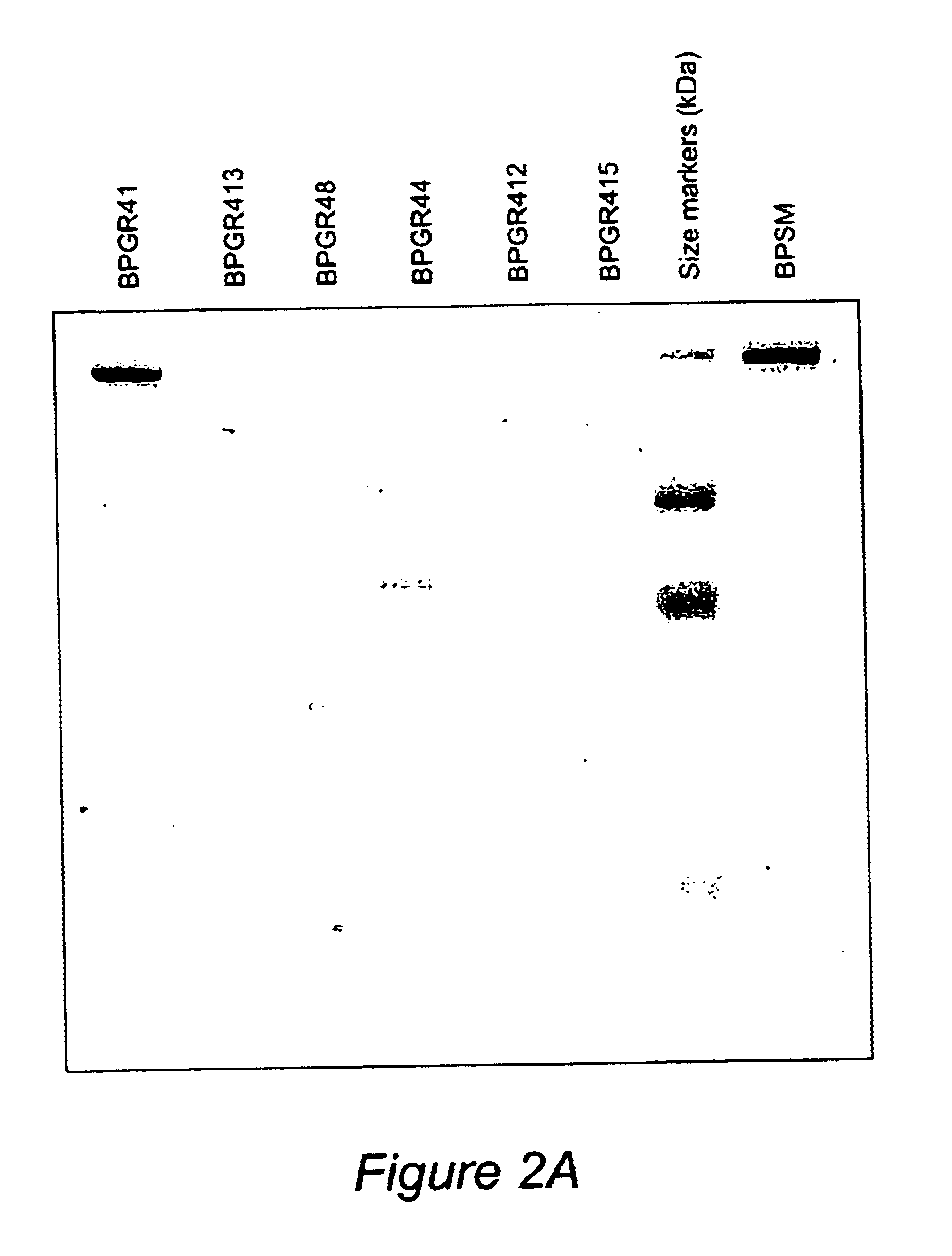
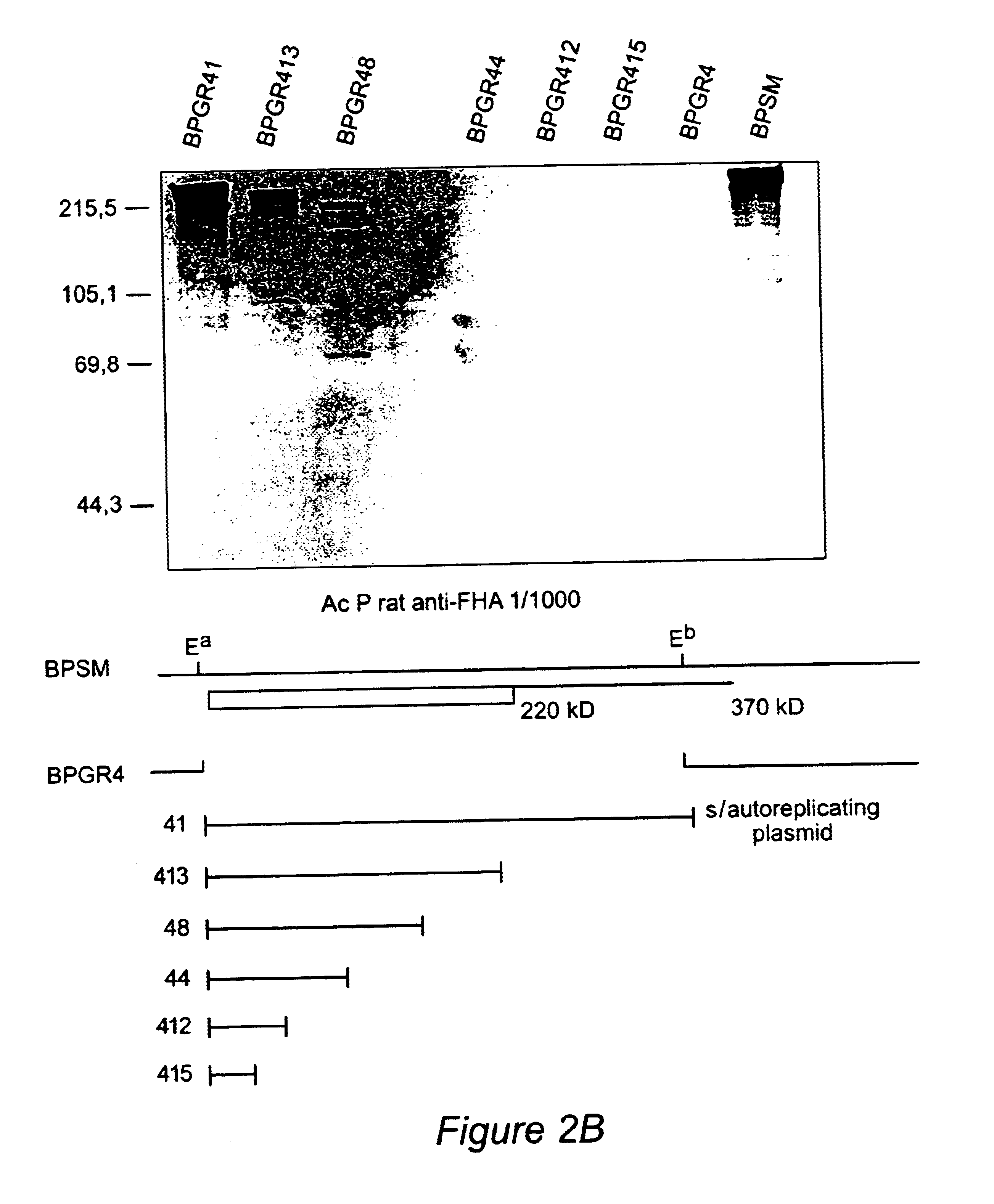
Recombinant proteins of filamentous haemagglutinin of bordetella, particularly bordetella pertussis, method for producing same, and uses thereof for producing foreign proteins of vaccinating active principles
InactiveUS6841358B1Easy to separateEasy to demonstrateBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsHeterologousPolymerase L
A recombinant DNA containing a sequence (1) coding for a polypeptide heterologous to a filamentous haemagglutinin of Bordetella (Fha) fused within the reading frame to a sequence (2) located upstream from the first sequence. Sequence (2) codes for at least part of the Fha precursor, which part comprises at least the N-terminal region of a truncated mature Fha protein, which contains the interaction site of Fha and heparin and the secretion domain. This Fha protein is under the control of a promoter recognized by the cell polymerases of B. pertussis and is inserted into a B. pertussis cell culture, is expressed in the culture and excreted into the cell culture medium. The invention uses both the abilities of Bordetella and particularly B. pertussis to secrete or surface expose the heterologous polypeptide fused to the Fha portion corresponding to sequence (2), which does not appear to produce extracellular proteases, and the ease with which filamentous haemagglutinins can be isolated from other Bordetella proteins.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
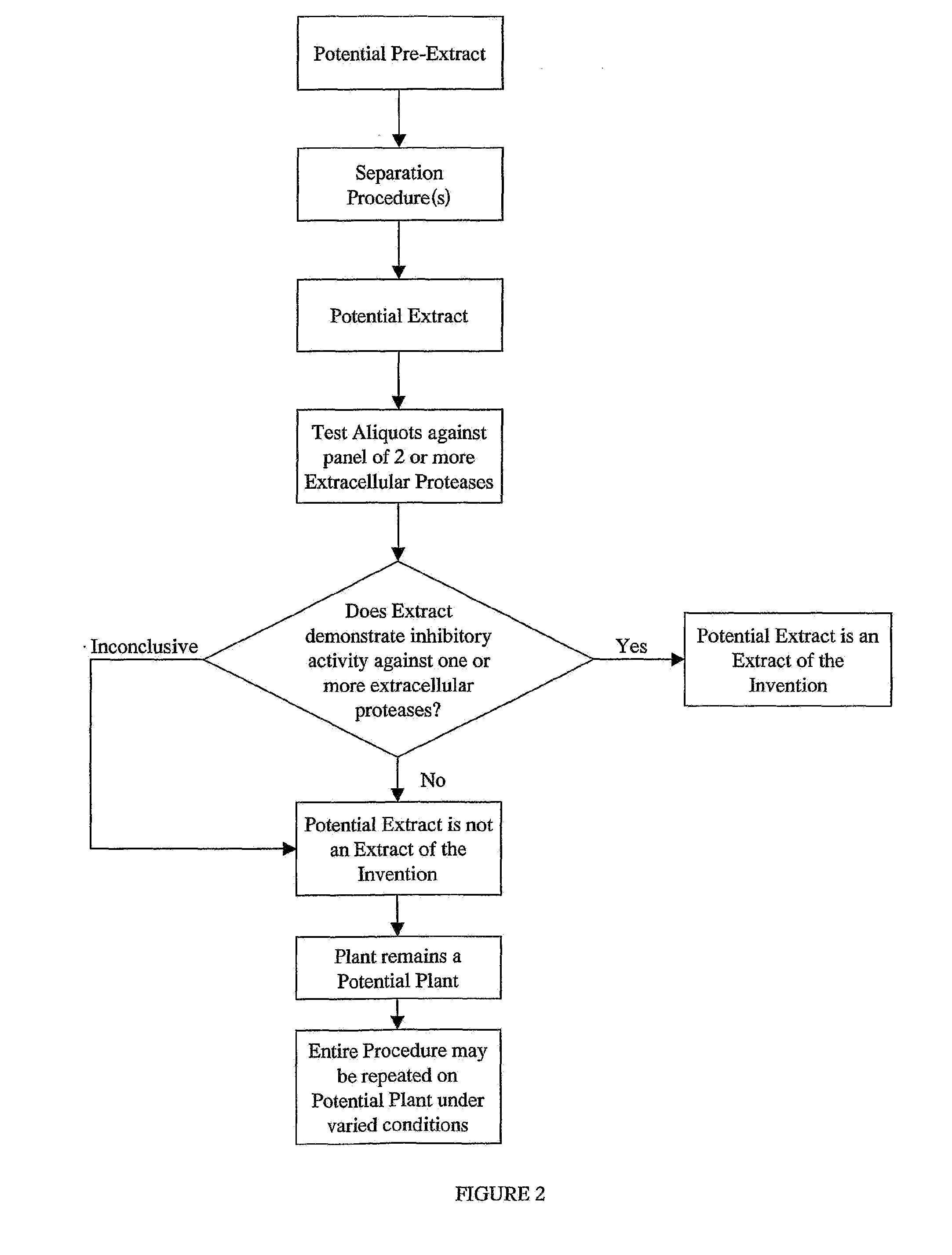
Inhibitors of extracellular proteases
InactiveUS20110217753A1Minimize degradationImprove fractionationCosmetic preparationsOther chemical processesExtracellular proteinsProtein purification
Provided is a plant derived extract including inhibitory activity against one or more extracellular proteases which degrade human tissue matrix. Moreover, the amount of inhibitory activity in an extract can be increased by stressing the plant prior to forming an extract. These extracts are each prepared by a process and demonstrate the ability to inhibit one or more extracellular proteases which degrade human tissue matrix. Libraries of extracts can be prepared from stressed and non-stressed plants, where each of the extracts demonstrate inhibitory activity against on or more extracellular protease inhibitors. Alternatively, semi-purified and purified inhibitory compounds can be isolated from the extracts. In one aspect, these extracts with inhibitory activity can be used during protein purification to minimize degradation due to extracellular proteases.
Owner:BIOPHARMACOPAE DESIGN INT
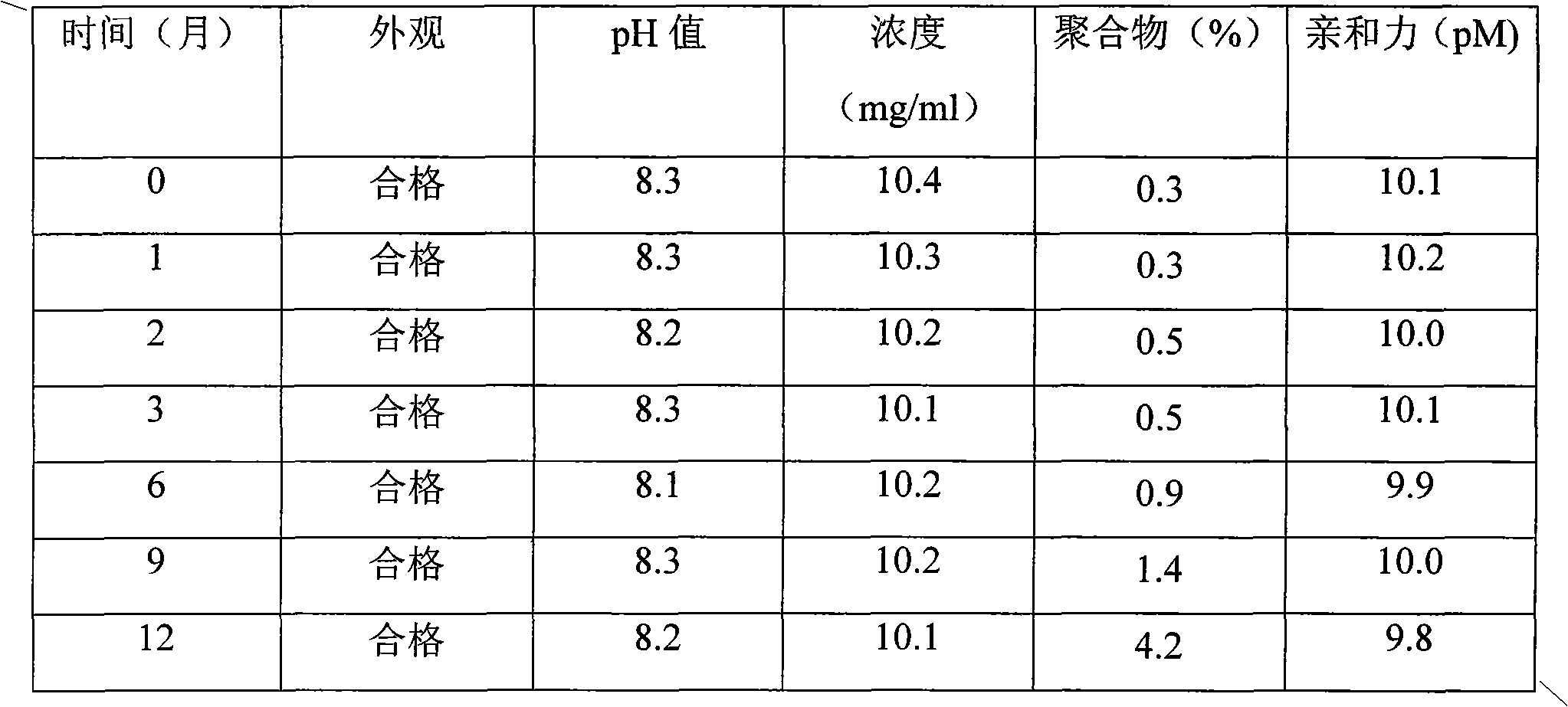
Medicine combination containing fusion protein for suppressing angiogenesis and application
ActiveCN102380096AInhibition of Purity DeclineSenses disorderAntibody ingredientsVascular proliferationVascular endothelium
The invention discloses a medicine combination containing fusion protein for suppressing angiogenesis and application, and particularly relates to a medicine combination containing fusion protein of an extracellular protein domain 2 (Flt-2) of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 1, extracellular protein domains 3 and 4 (KDR-3 and 4) of a VEGF receptor 2 and human normal immunoglobulin 1(G1) Fc. The medicine combination can keep the fusion protein stable, has the most outstanding advantage of capability of effectively suppressing fusion protein polymer so as to avoid reduction of purity, and accordingly keeps bioactivity of effective components.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG BIOTECH
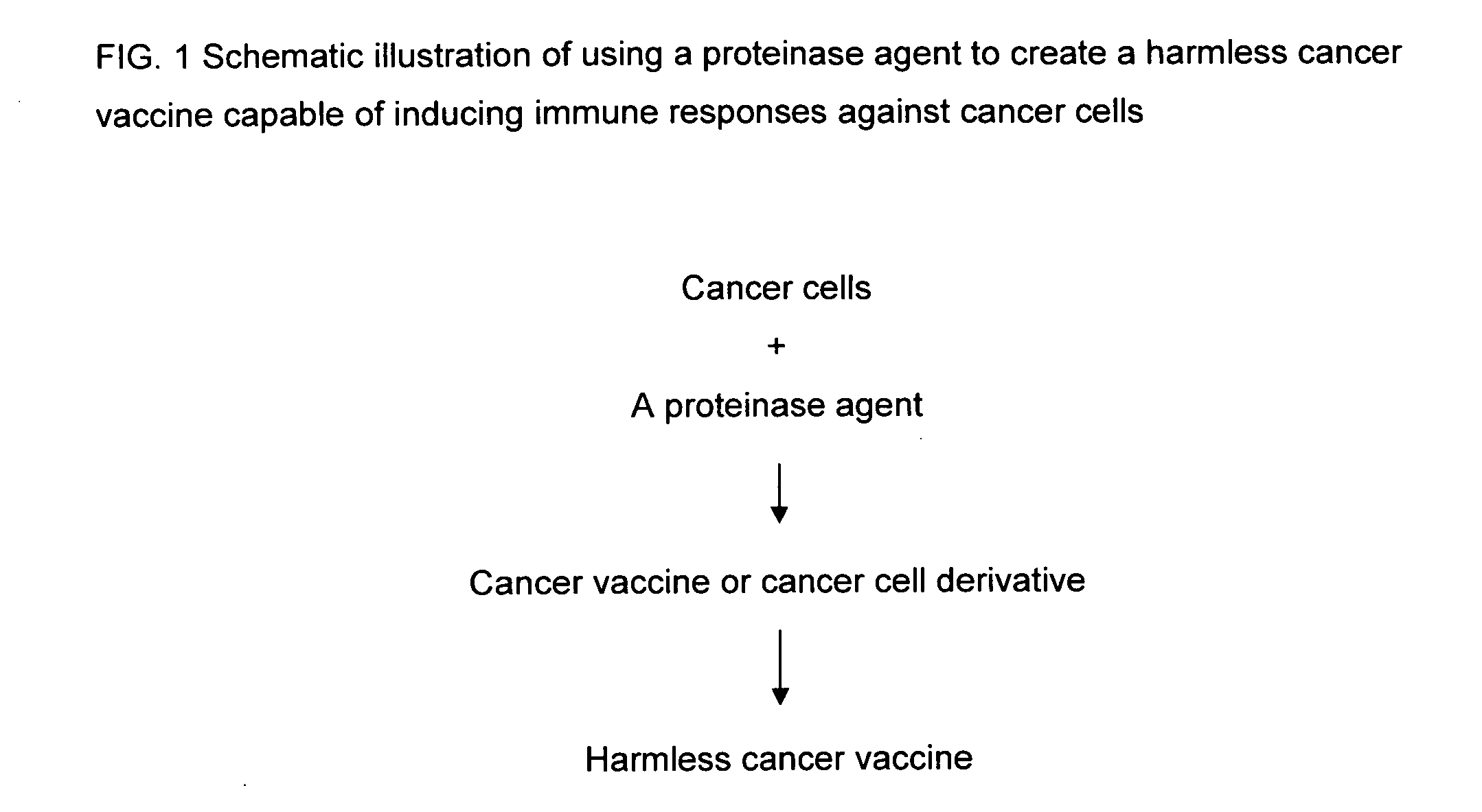
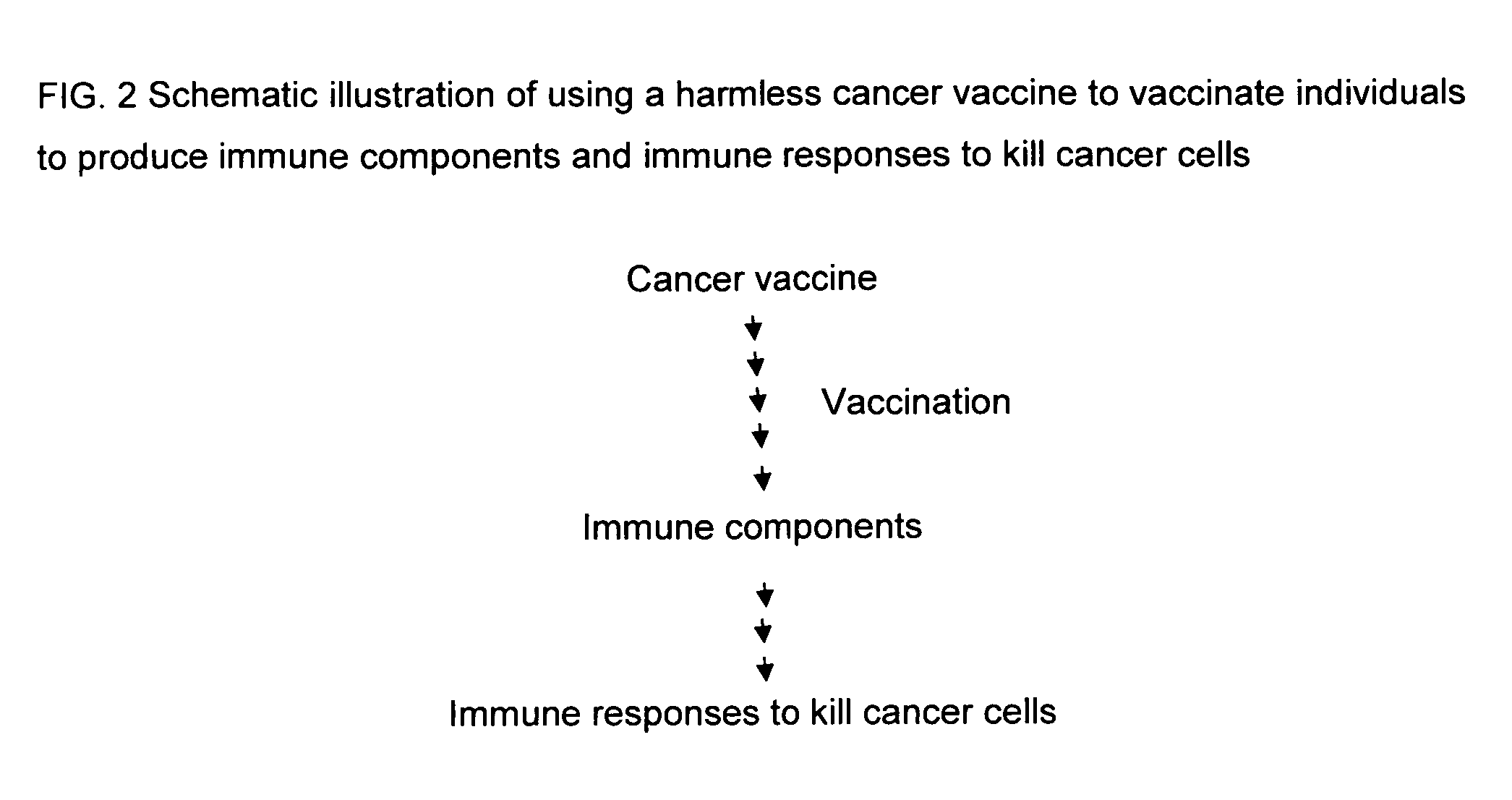
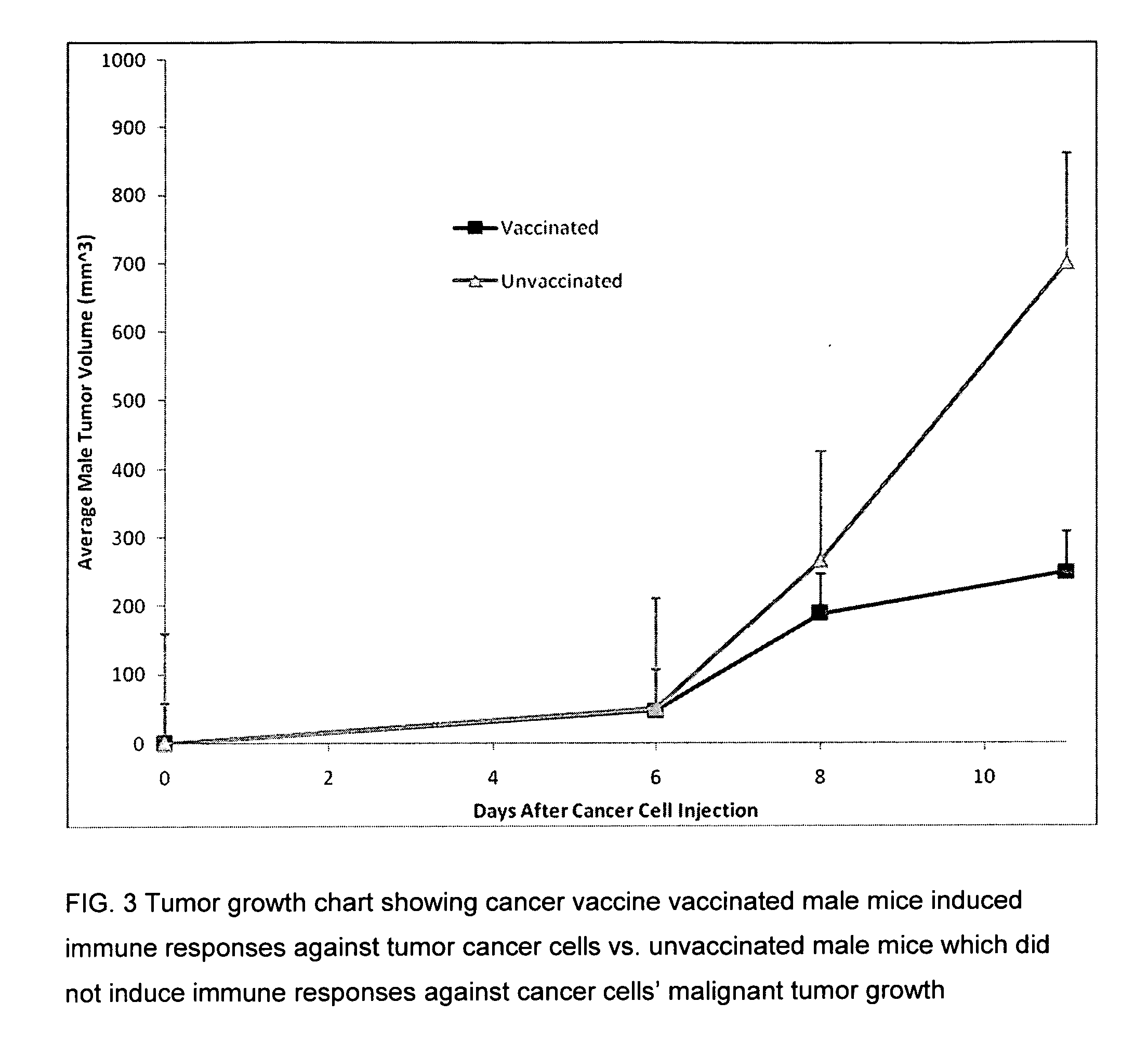
Proteinase-engineered cancer vaccine induces immune responses to prevent cancer and to systemically kill cancer cells
InactiveUS20090162405A1Induce immune responseVaccinesCancer antigen ingredientsCancer preventionCancer cell
A harmless cancer vaccine is made from cancer cells with extracellular proteins including self-recognition molecular patterns being digested by a proteinase. The cancer vaccine is used to vaccinate an individual to induce immune responses against cancer cells systemically. Cancer cells become harmless when they are digested by Tumorase™. Some proteinases including trypsin cannot kill cancer cells completely and treated cancer cells need to be further processed in order to be harmless and effective. Cancer cells may be from tissue-cultured human or animal cancer cell lines or cancer patients directly. Cancer vaccine vaccinated individuals produce cancer vaccine specific immune responses against cancer cells. Immune response components may be isolated and used to fight against cancer for a cancer patient with a suppressed immune system. Cancer vaccine specific immune components may include cancer vaccine specific polyclonal antibodies, B-cells, T-cells, natural killer cells, monocytes, macrophages and other lymphocytes.
Owner:QIAN YONG
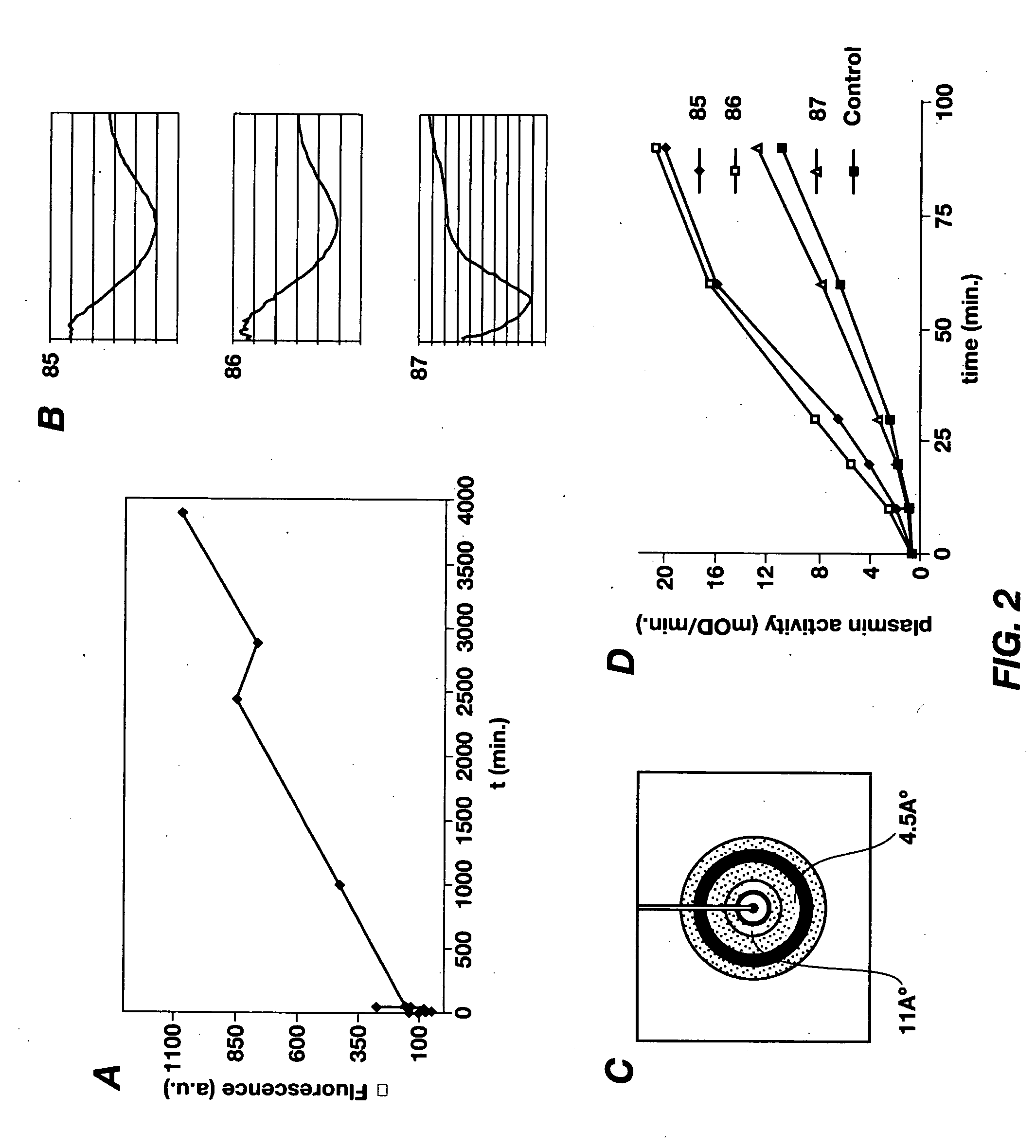
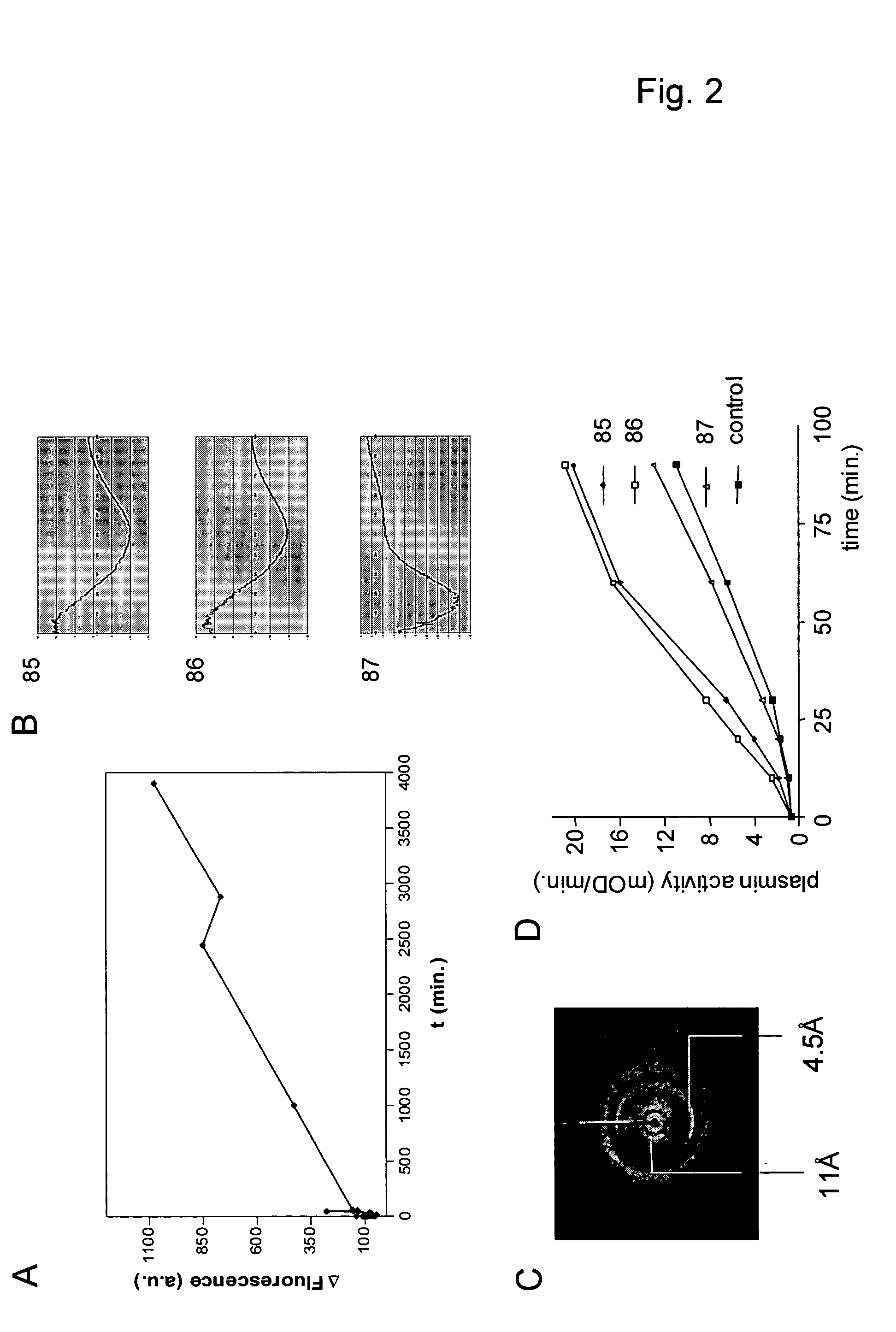
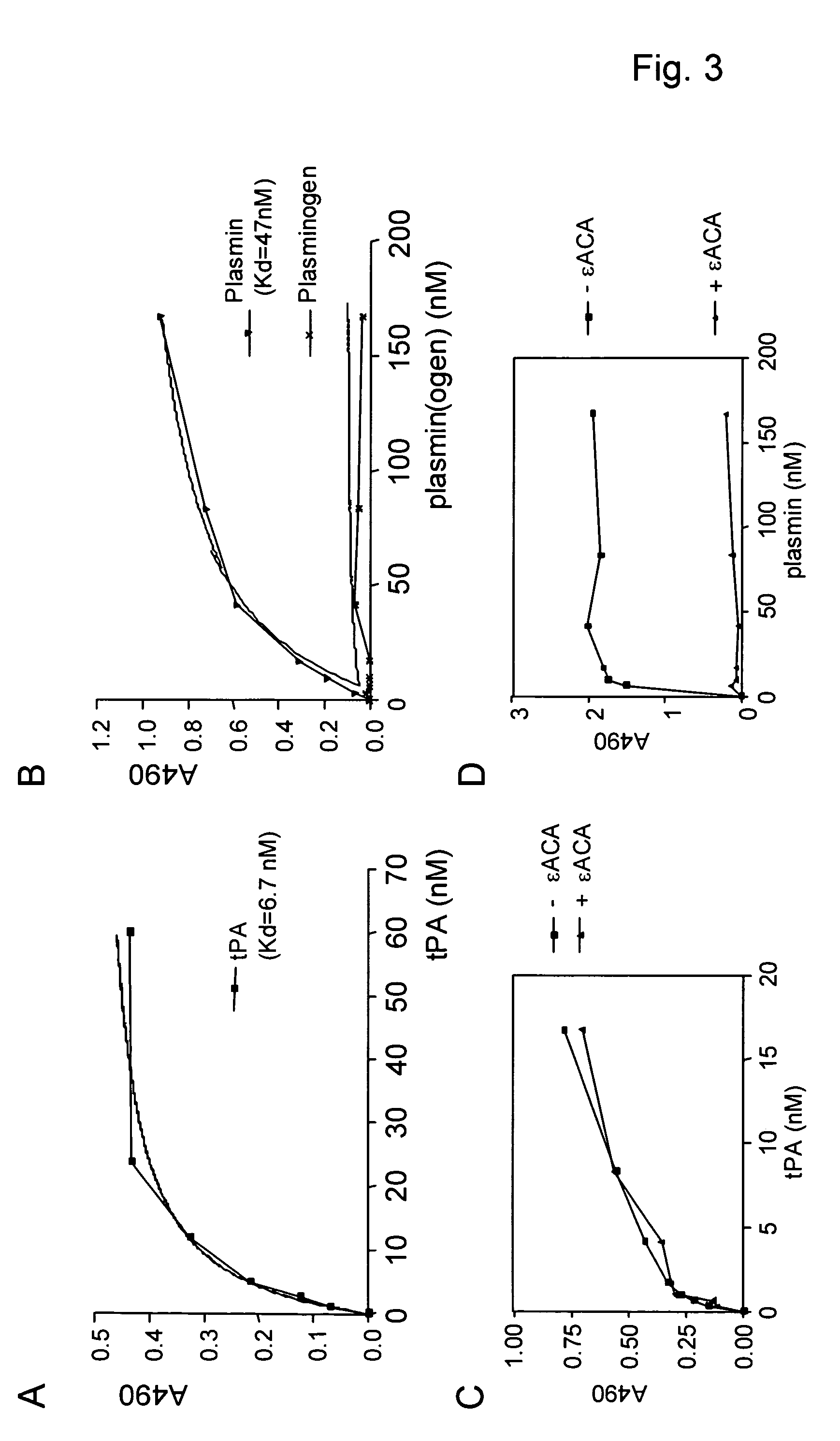
Cross-beta structure comprising amyloid-binding proteins and methods for detection of the cross-beta structure, for modulating cross-beta structures fiber formation and modulating cross-beta structure-mediated toxicity
The invention relates to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology and medicine. More in particular, the invention relates to cross-β structures and the biological role of these cross-β structures. In one embodiment, the invention discloses a method for modulating extracellular protein degradation and / or protein clearance comprising modulating cross-β(beta) structure formation (and / or cross-β structure-mediated activity) of the protein present in the circulation.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
Cross-beta structure comprising amyloid-binding proteins and methods for detection of the cross-beta structure, for modulating cross-beta structures fibril formation and for modulating cross-beta structure-mediated toxicity
The invention relates to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology and medicine. More in particular, the invention relates to cross-β structures and the biological role of these cross-β structures. In one embodiment, the invention discloses a method for modulating extracellular protein degradation and / or protein clearance comprising modulating cross-β(beta) structure formation (and / or cross-β structure-mediated activity) of the protein present in the circulation.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain capable of highly producing cellulase and application thereof
ActiveCN106978360AIncrease productionIncrease secretionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyExtracellular proteins
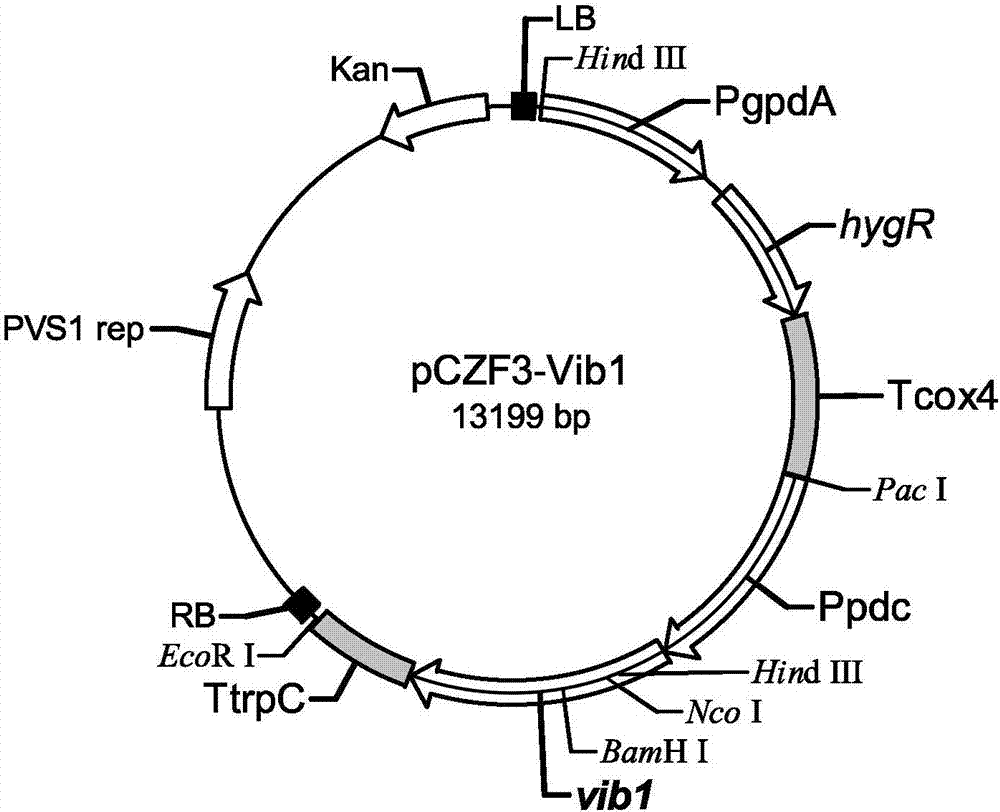
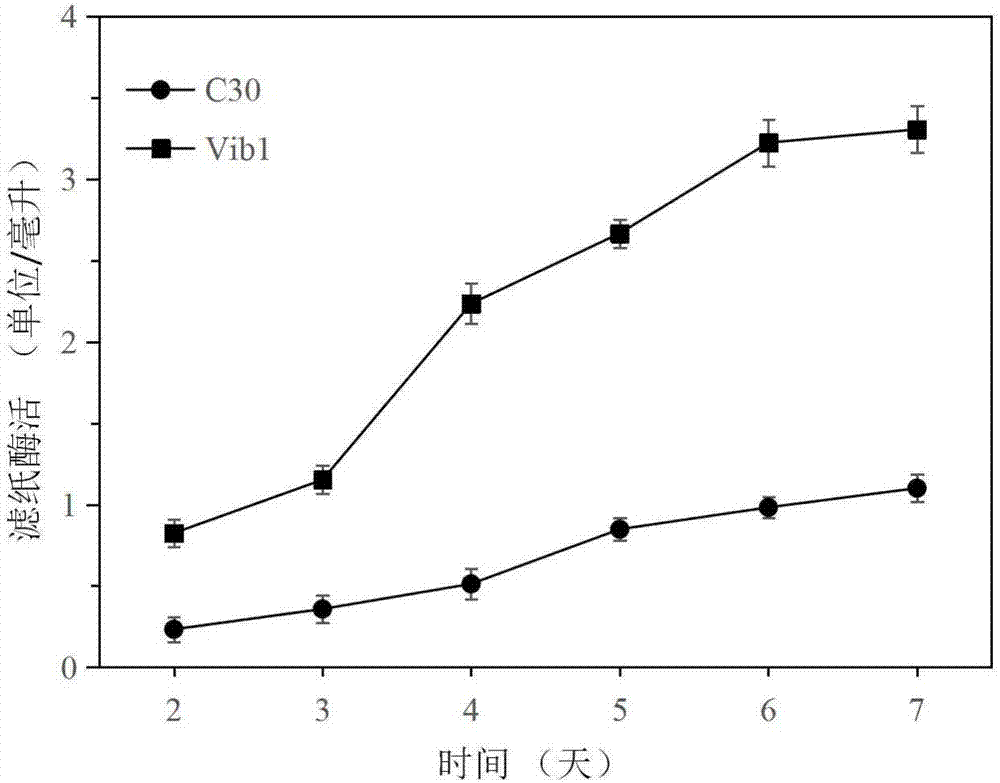
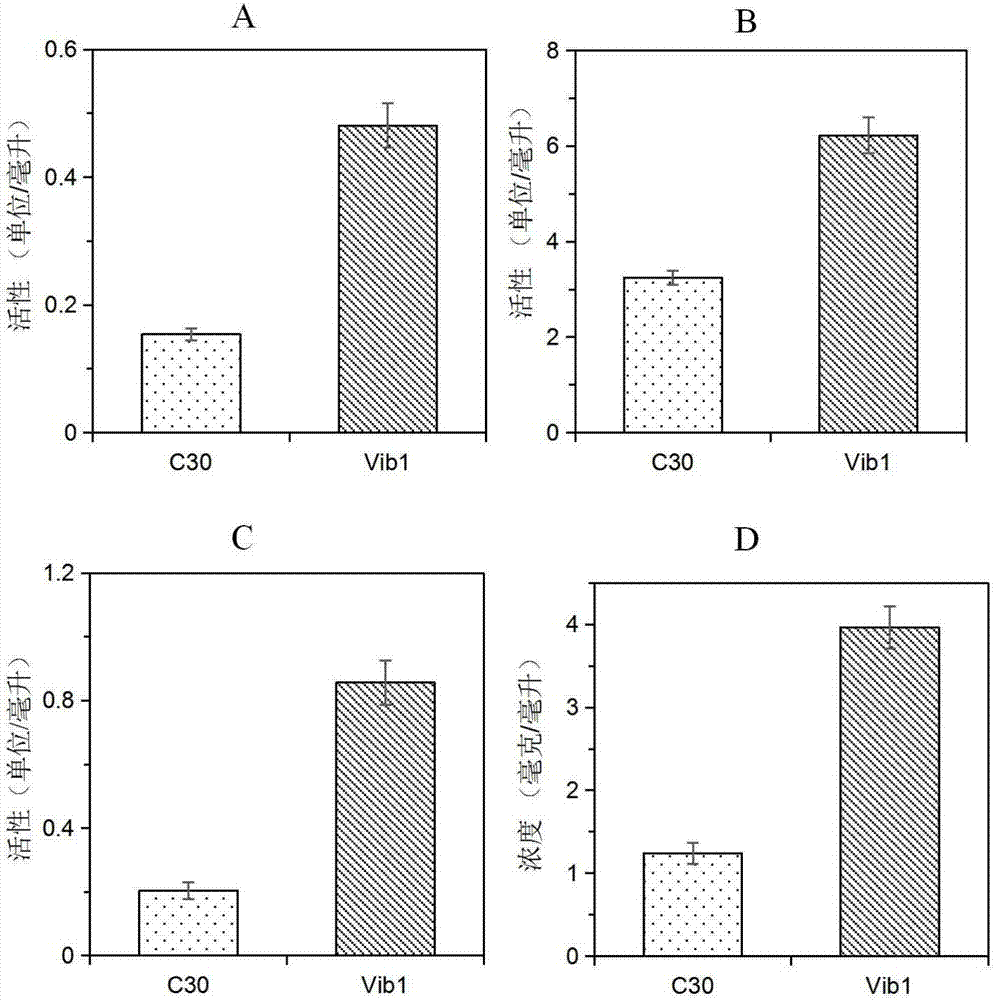
The invention discloses a trichoderma reesei recombinant strain capable of highly producing cellulase and application thereof. Vlbltr which grows an incompatible repression protein gene is transformed into trichoderma reesei Rut-C30, so as to obtain the trichoderma reesei Vib1 (CCMCC No.13578). Compared with the strain Vib1 and the trichoderma reesei Rut-C30, the trichoderma reesei recombinant strain has the advantages that the excretion of extracellular protein and the production of cellulase are obviously improved; compared with the trichoderma reesei Rut-C30, the activity of cellulase in the Vib1 in cellulose and bran culture mediums is increased by about 200%, and reaches 3.3U / ml; the enzyme activities of cellobiohydrolase, endo-cellulase and beta-glucosidase are respectively improved; the excretion amount of the extracellular protein in the Vib1 strain is equal to 2.19 times of the excretion amount of trichoderma reesei Rut-30; proved by the results of hydrolysis reaction of pretreated corn straw, compared with the Rut-30 strain, the output of glucose in the Vib1 strain cellulase hydrolyte is increased by 20%.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Soil protein extraction and intracellular protein separation method
InactiveCN101531708AHigh extraction rateImprove electrophoresisMicroorganismsDepsipeptidesBüchner funnelExtracellular proteins
The invention provides a high-efficiency soil protein extraction method, comprising the following steps: adding soil in a pre-cooling soil protein extraction buffer solution and blending and oscillating the mixture in a 4 DEG C shaking table over night; performing drawing and filtering of the shaken mixture in a buchner funnel using a crude filter paper; processing the drawing and filtering liquid by macroporous resin (D101), filtering the processed liquid through a 0.22 Mum microporous membrane, the filtered liquid being the extracellular protein mother liquid; processing the cells on the filter membrane by cleaning, crushing, centrifugalizing and vacuum drying to obtain the dried powder, namely intracellular soil protein sediment. The extracellular protein mother liquid is processed by centrifuging, separating and vacuum drying to obtain the intracellular soil protein dried powder; degrading the intracellular soil protein dried powder until the degraded intracellular soil protein dried powder is clearly separated on 10% polyacrylamide gel SDS-PAG electrophoresis, the method has high separation efficiency, microbial yield is 37.5%, which is higher than the yield of the traditional method 0.1-1%, simple operation flow, good SDS-PAGE resolution and good mass spectrum identification effect.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Expression equipment for expressing exogenous protein by secretion in trichoderma reesei and application of expression equipment
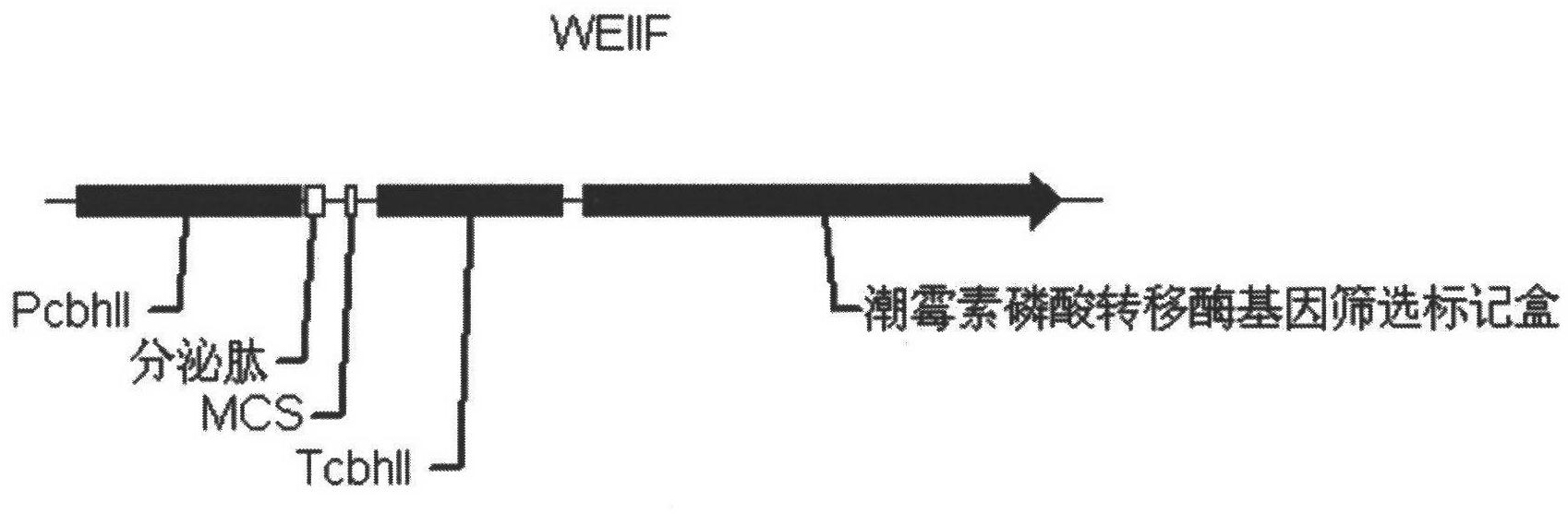
ActiveCN102304540AEasy to storeEase of DNA manipulationFungiBacteriaHeterologousExtracellular proteins
The invention discloses expression equipment for expressing exogenous protein by secretion in trichoderma reesei cells. The expression equipment comprises the following elements from 5' to 3': (1) an exo-glucan cellobiose hydrolase II promoter of trichoderma reesei; (2) a secretively-expressed signal peptide; (3) a polyclonal locus sequence; and (4) an exo-glucan cellobiose hydrolase II terminator of the trichoderma reesei. Exogenous genes are inserted into the expression equipment, agrobacterium tumefaciens is converted by a T-deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) binary vector and is jointed with thetrichoderma reesei to obtain trichoderma reesei genetic engineering bacteria which can express heterologous genes from animals, plants, fungi and the like efficiently by secretion, and a large amountof exogenous protein is obtained from the trichoderma reesei genetic engineering bacteria. The trichoderma reesei has an extensive culture condition, and is suitable for solid culture and liquid submerged fermentation; and mycotoxin and antibiotics cannot be generated under the zymogenic condition, and the generated extracellular protein is easy to separate and purify and low in cost.
Owner:百开盛(上海)生物科技有限公司
Alkaline pectic enzyme producing engineering strain and its construction and method for producing alkaline pectic enzyme with the same
InactiveCN101157900ASimple purification processReduce typesFungiMicroorganism based processesPectinaseExocytosis
An engineering bacterium of producing alkaline pectinase, a construction thereof and a method of producing alkaline pectinase by using the alkaline pertain to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention uses nonpathogenic bacillus sp WSHB04-02 genes group as a model and adopts amplification technology of PCR. And then the sequence pel containing 1.2kb coding alkaline pectinase genes section is obtained. At the same time from the point of the demand for industrial production, the invention makes use of a shuttle expression carrier to restructure yeast Pichiapastoris(pel), which means to produce engineering bacterium CGMCC No.2143 of alkaline pectinase (E.C.4.2.2.2). The invention also provides CGMCC No.2143 as the method of producing alkaline pectinase for fermented yeast strain. The genes engineering bacterium aims at exocytosis of protein and the species of extracellular protein is few, which simplifies the purification technique of producing alkaline pectinase by using microorganism and reduces the cost and shoetens the time for ferment. Besides, the invention improves the production efficiency and lays a foundation for industrialization of the ferment method of producing alkaline pectinase by using microorganism.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
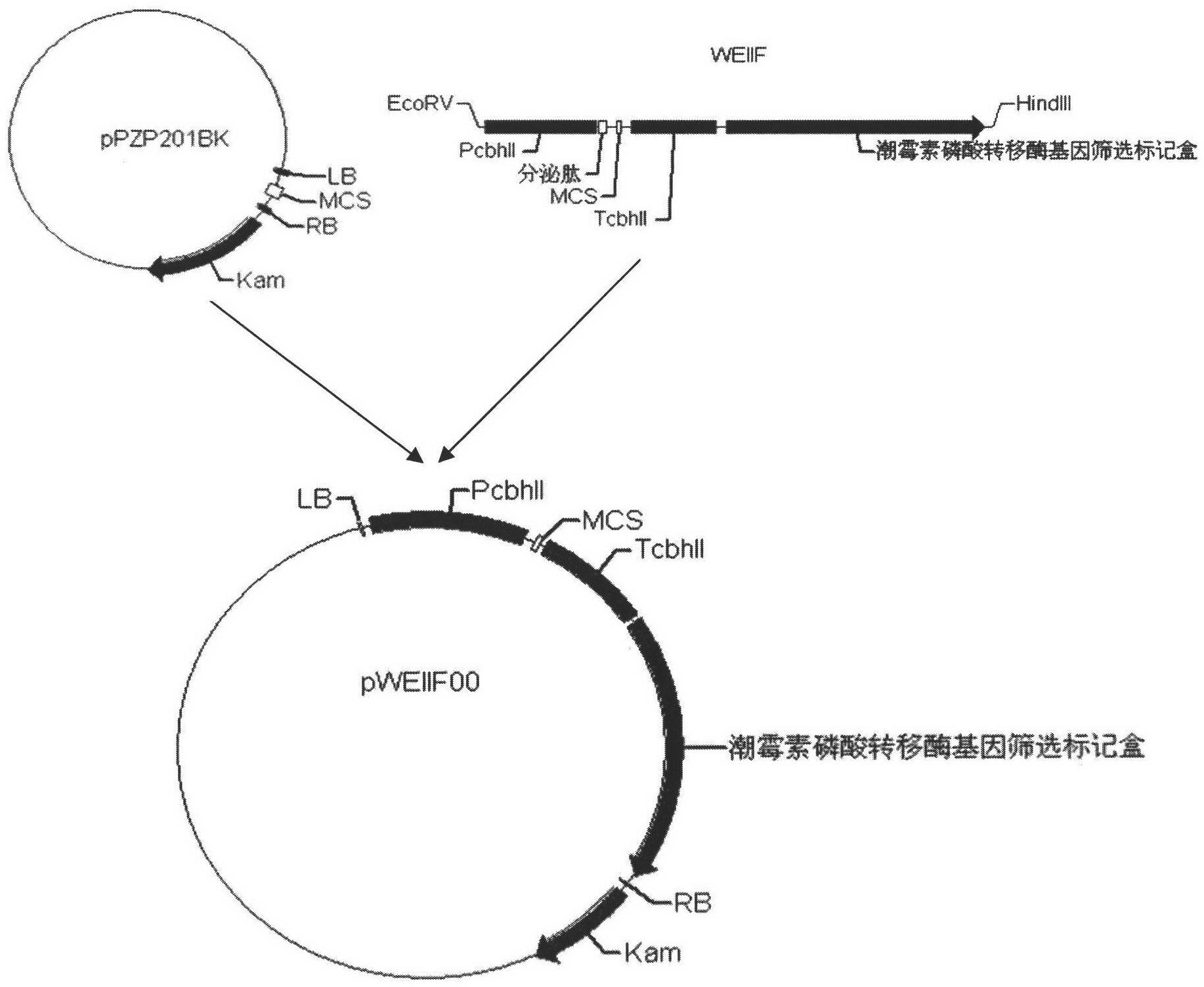
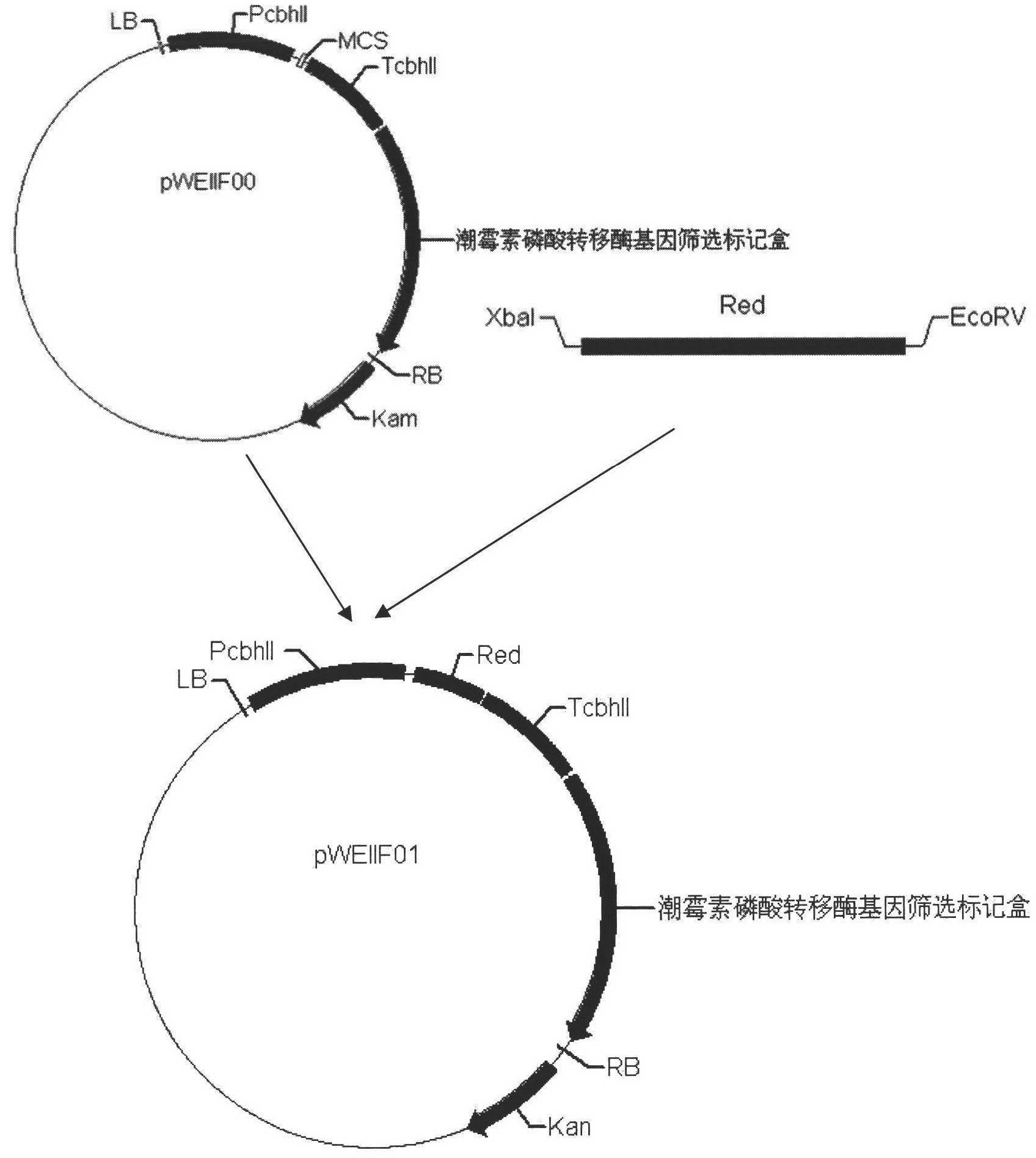
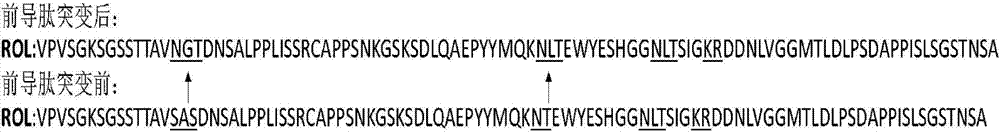
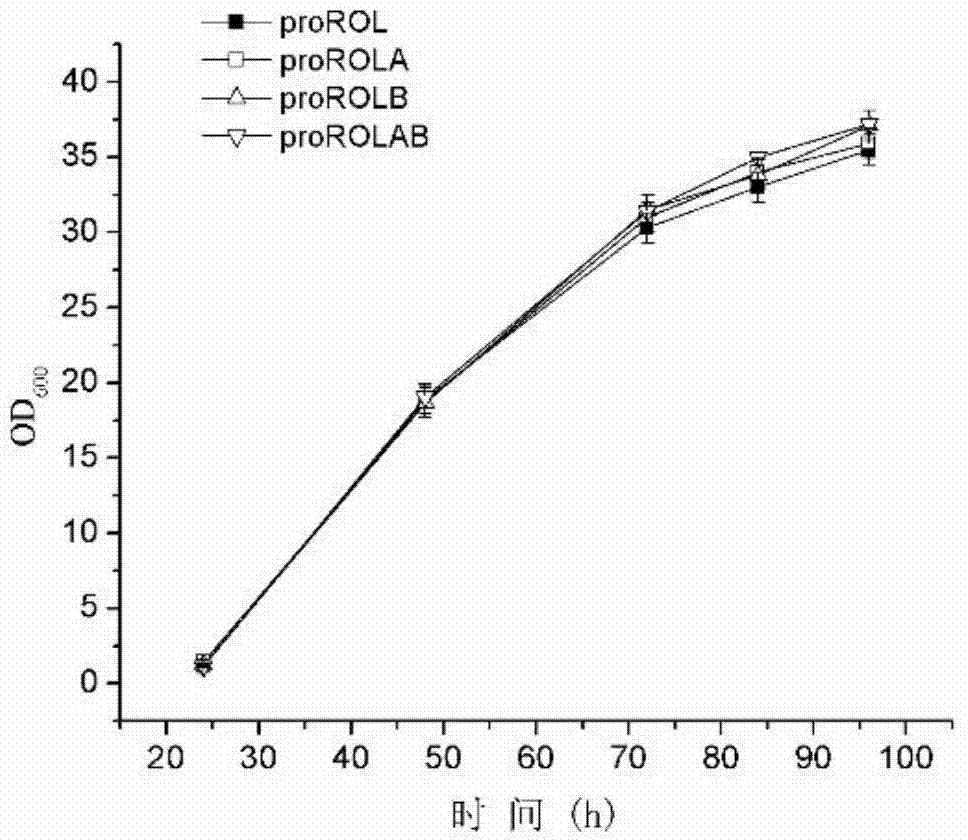
Method for increasing lipase expression through glycosylation modification as well as mutant enzyme and application thereof
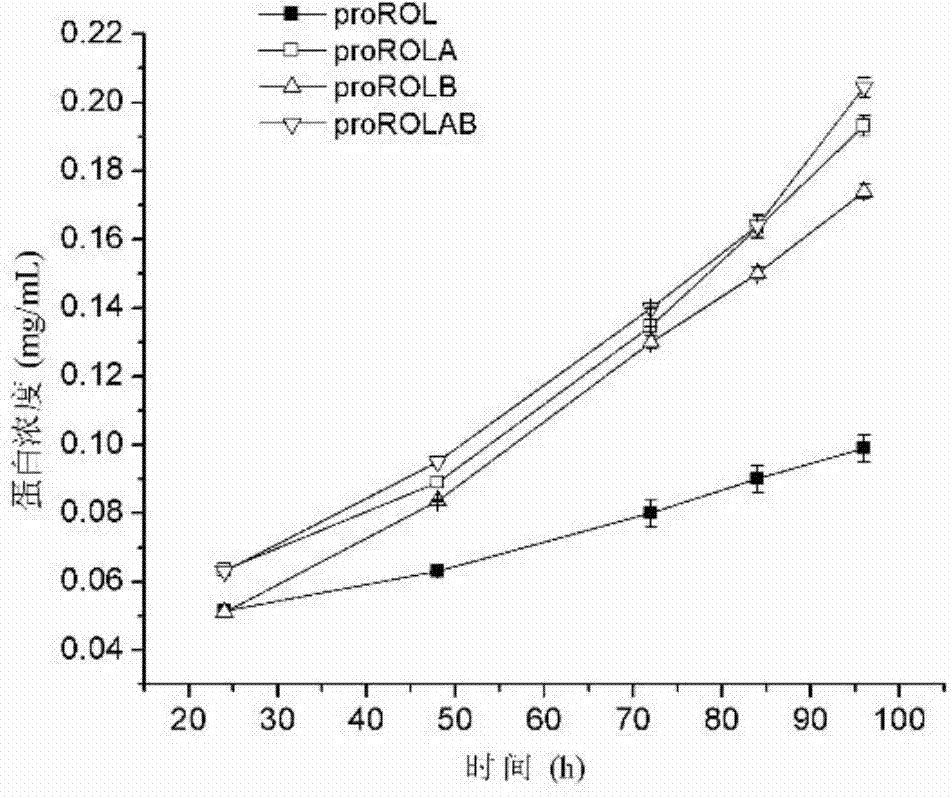
ActiveCN104762277ADoes not affect growthIncrease enzyme activityFungiHydrolasesExtracellular proteinsPeptide sequence
The invention discloses a method for increasing lipase expression through glycosylation modification as well as a mutant enzyme and an application thereof and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The N-glycosylation mutation is performed on a leading peptide sequence of rhizopus oryzae lipase, the SAS and / or NT amino acid are / is respectively modified to an N-glycosylation site NGT and / or NLT, the extracellular protein concentrations of the obtained mutant enzyme proROLA, proROLB and proROLAB are increased by 211%, 188% and 233% compared with those of the un-glycosylated proROL, the enzyme activities when culturing in a fermentation tank are respectively 8210 U.mL<-1>, 8457 U.ml<-1> and 9366 U.mL<-1>, and the un-mutated proROL extracellular enzyme activity is almost zero. The rhizopus oryzae lipase provided by the invention has obviously increased lipase enzyme activity and can be used in the fields such as food, chemical engineering and biological energy source.
Owner:TAIXING YIMING BIOLOGICAL PRODS
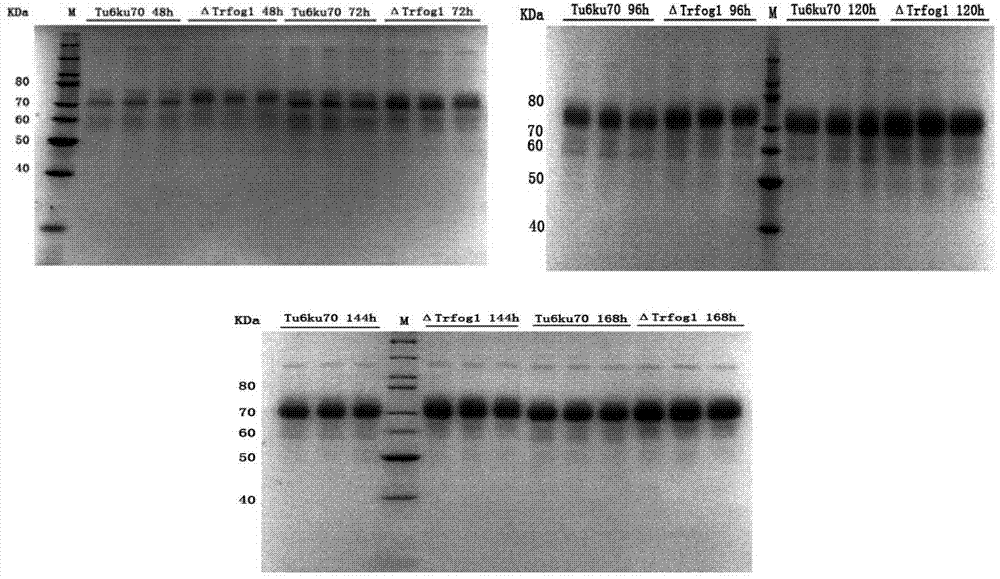
Protein derived from Trichoderma reesei and gene application thereof
The invention discloses a protein derived from Trichoderma reesei and application the gene of the protein. The application is the application of the Trfogl to controlling the extracellular protein secretion amount of the Trichoderma reesei, and the Trfogl is the protein shown by an amino acid sequence such as a sequence 2 in a sequence table. According to the invention, a technical base is provided for constructing Trichoderma reesei host bacteria and engineering bacteria with an increased extracellular protein secretion amount.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
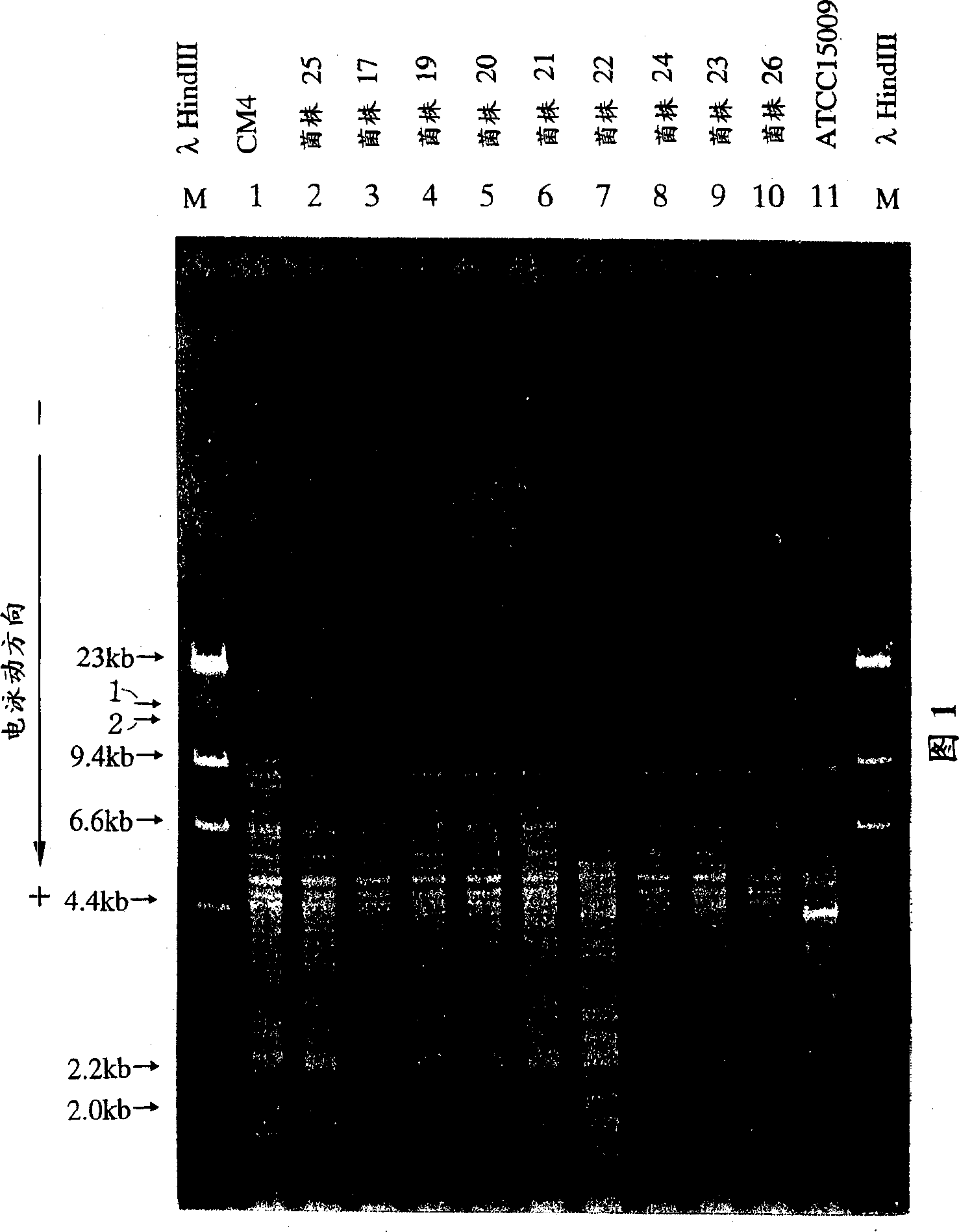
Lactobacillus helveticus bacterium having high capability of producing tripentide, fermented milk product, and preparing process thereof
There is provided a lactic acid bacteria capable of producing a large amount of lactotripeptide; also a fermented milk product that contains a large amount of active ingredient having hypotensive activity and anti-stress effect and can be taken pleasantly, is provided. More specifically, the present invention relates to Lactobacillus helveticus, that is, Lactobacillus helveticus CM4 strain (deposited at National Institute of Bioscience and Human-Technology Agency of Industrial Science and Technology, deposition number FERM BP-6060), characterized in having specific bacteriological properties, the bacteria, when cultured in a medium of animal milk containing 9 wt % solid of non-fat milk, producing tripeptides Val-Pro-Pro and Ile-Pro-Pro in an amount of 60 mu g in terms of Val-Pro-Pro per ml medium, and the bacteria exhibiting extracellular proteinase activity of not lower than 400U / OD590. The present invention also relates to a fermented milk product obtained by fermenting an animal milk with these lactic acid bacteria.
Owner:CALPIS
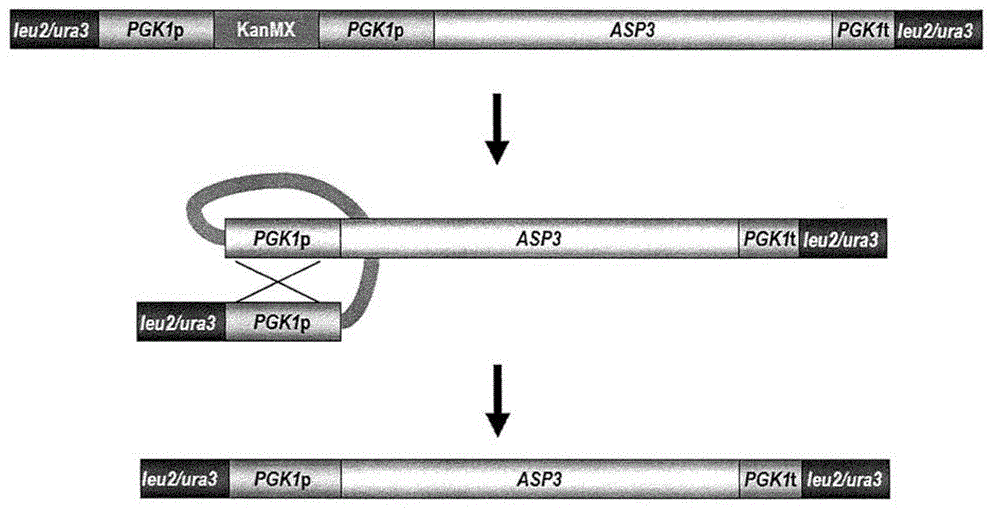
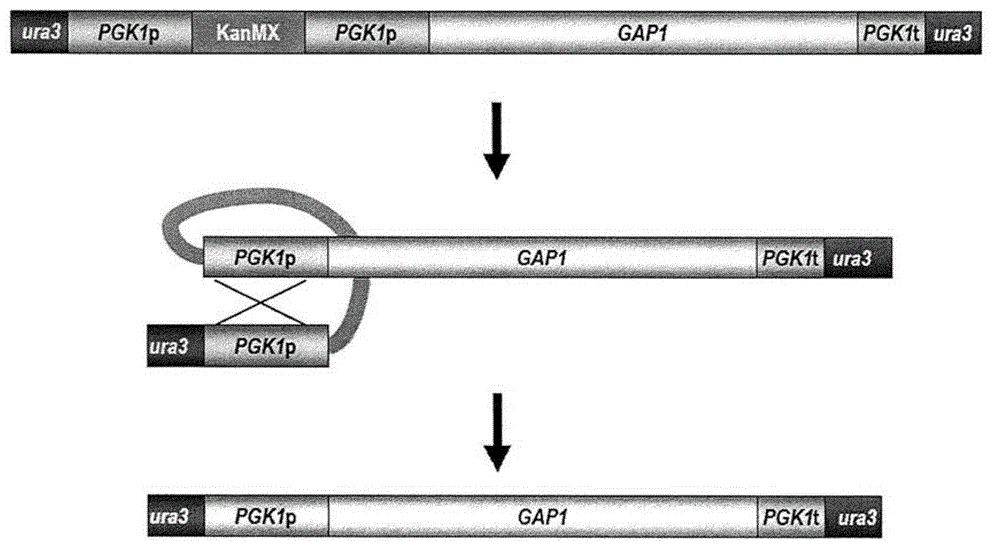
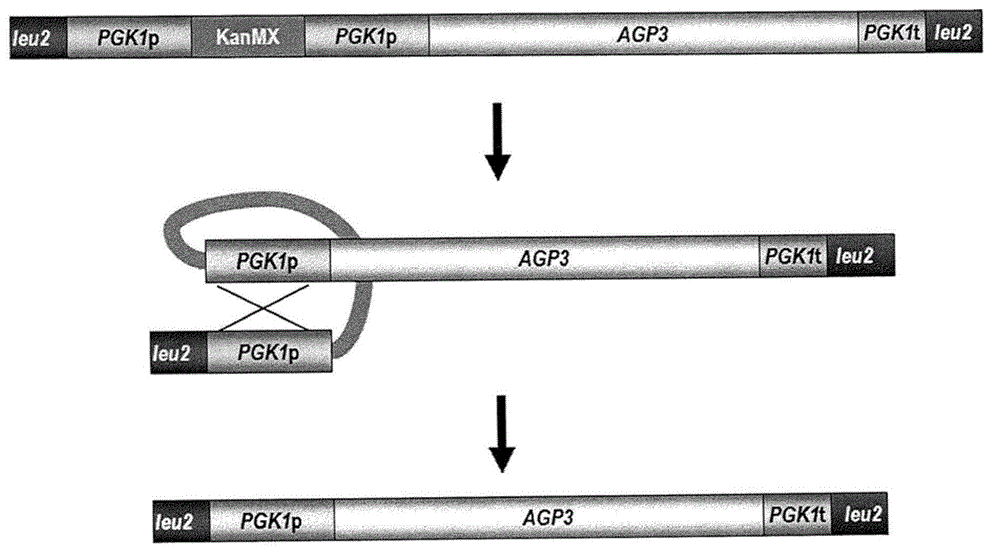
Functional enhancement of microorganisms to minimize production of acrylamide
ActiveCN102869765AFungiCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiotechnologyGlucose repression
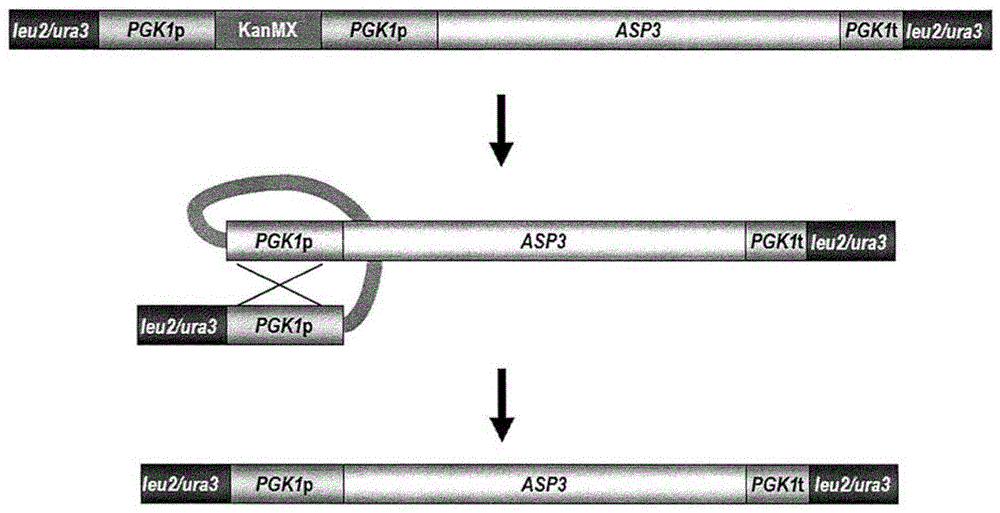
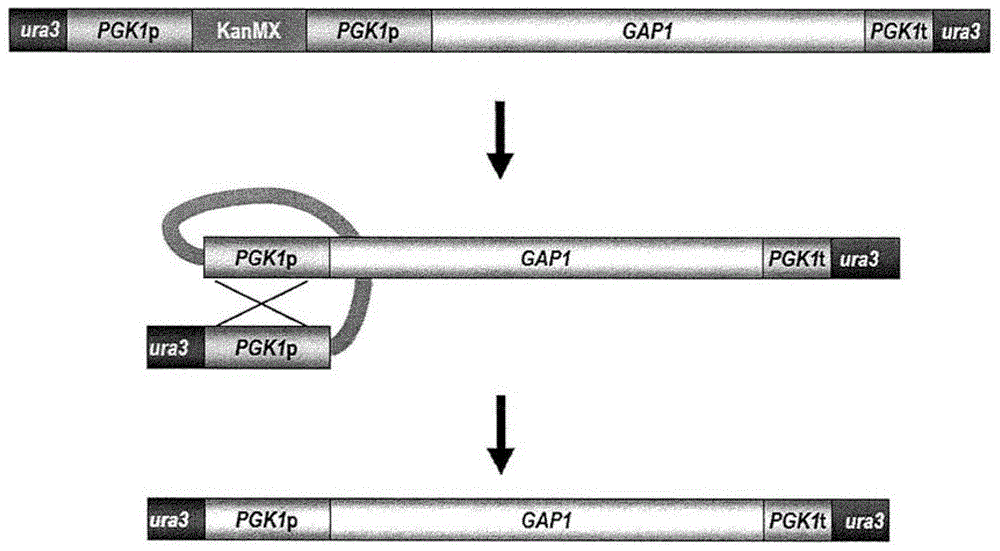
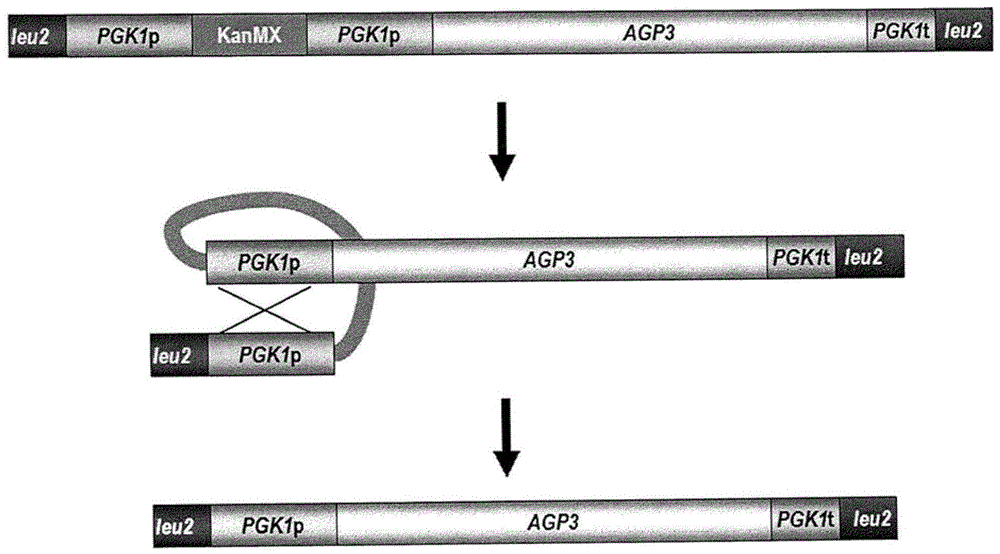
The present disclosure provides yeast transformed with a nucleic acid molecule (GAT1 ) to reduce nitrogen catabolite repression of asparagine transport / degradation and / or overexpress genes (ASP1 or ASP3) encoding cell- wall or extracellular proteins involved in asparagine degradation and / or genes (AGP1 or GNP1 or GAP1 ) encoding proteins involved in asparagine transport under food preparation / processing conditions. The genetically modified yeast has enhanced ability to reduce acnlamide concentration in foods prepared by heating. Also provided are methods and uses of the transgenic yeast for reducing acnlamide in a food product and food products having reduced acrylamide content prepared using the transgenic yeast.
Owner:复兴生物科技公司
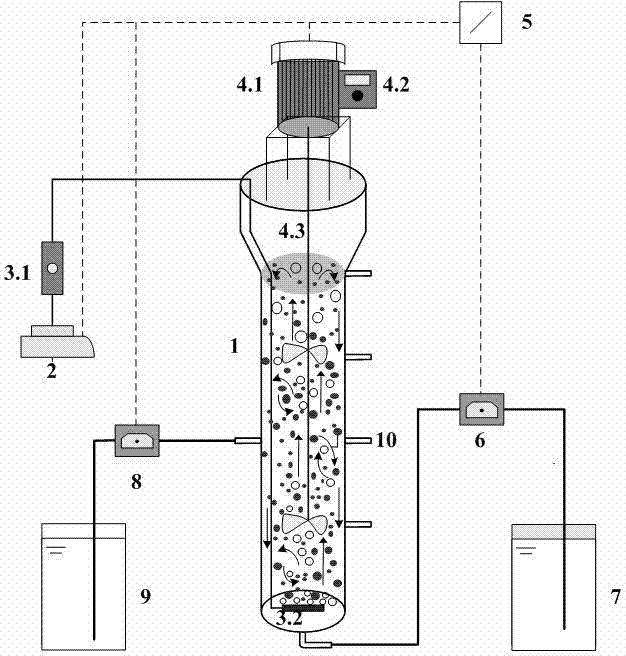
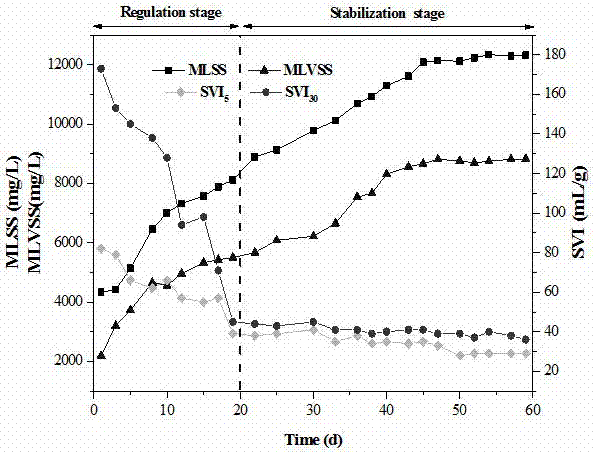
Method for restoring sticky expansion of aerobic granular sludge
InactiveCN106927562AFlat surfaceRegular shapeSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsFlocculationSludge
The invention discloses a method for restoring sticky expansion of aerobic granular sludge. According to the method, by appropriately increasing the concentration of metal ions Ca<2+>, Mg<2+> and Fe<2+> in inlet water of an aerobic granular sludge reactor, the micro-organism flocculation is facilitated on the surface of a compressive cell by virtue of double electrode layers, the secretion of hydrophobic extracellular proteins (PN) is increased, so that the sticky expansion problem of the granular sludge occurring in the long-term operation process can be solved. The granular sludge SVI having the sticky expansion can be reduced to 20 to 40 mL / g, and a stable structure and sedimentation performance of the granular sludge can be restored.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
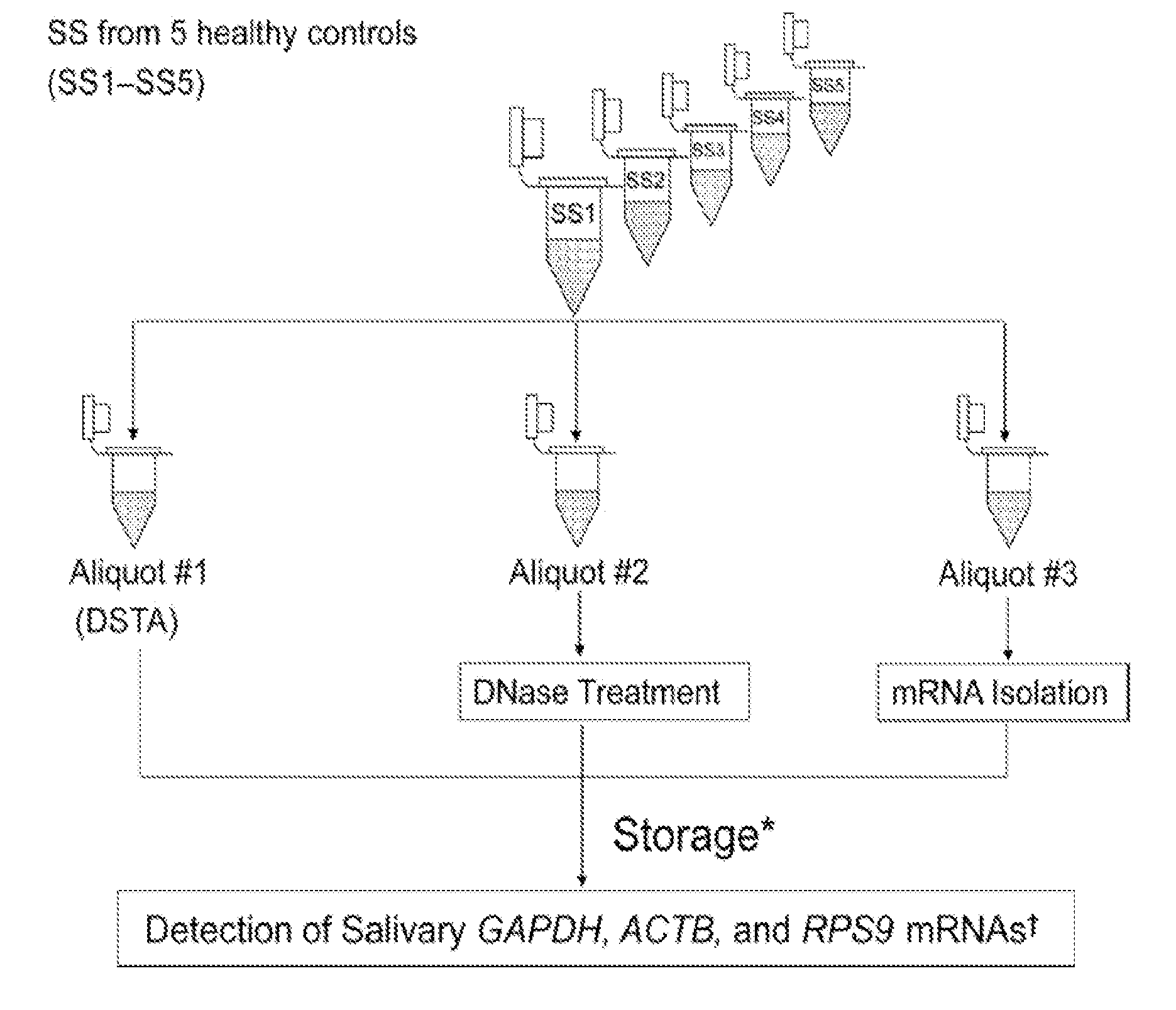
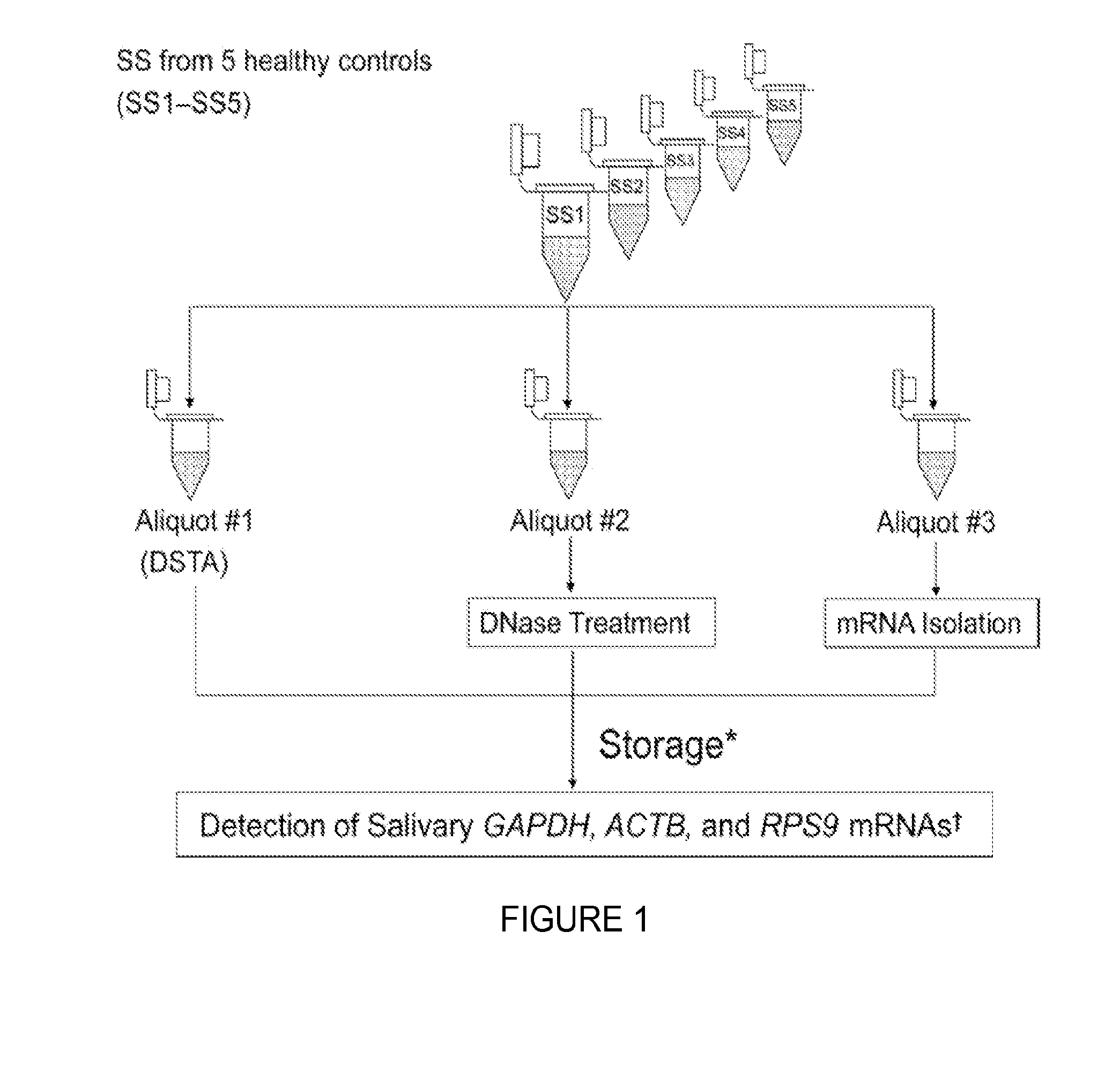
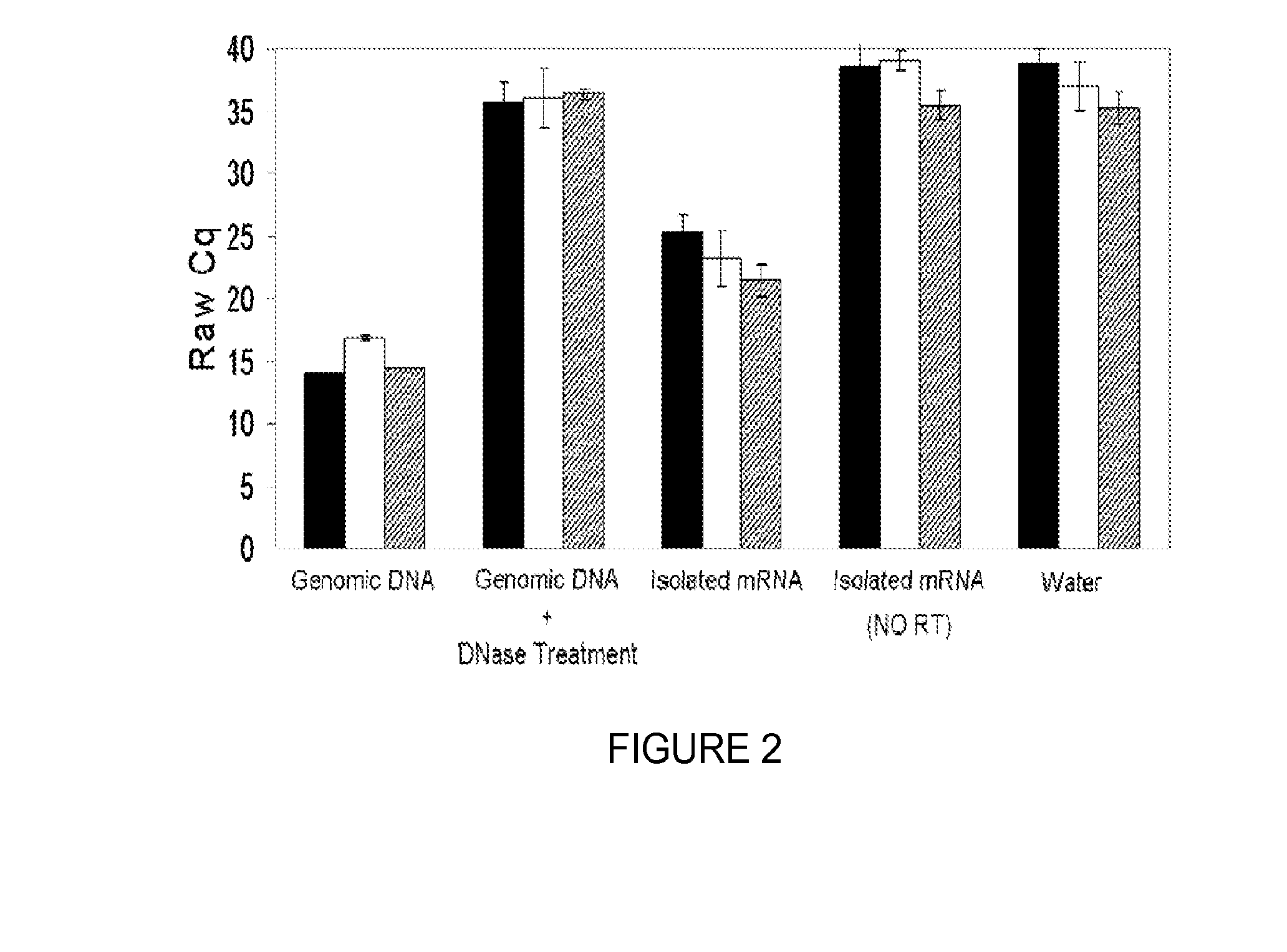
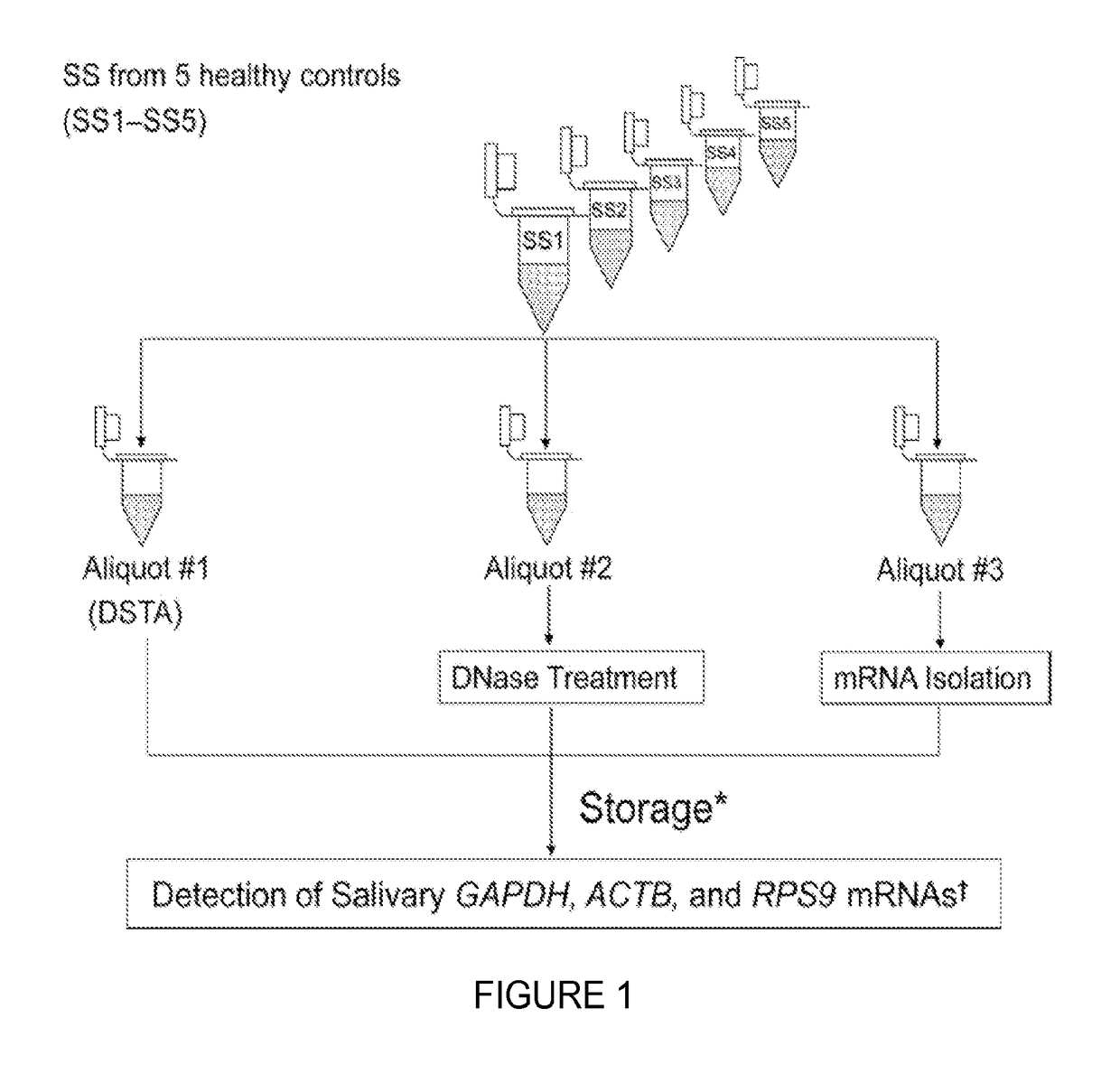
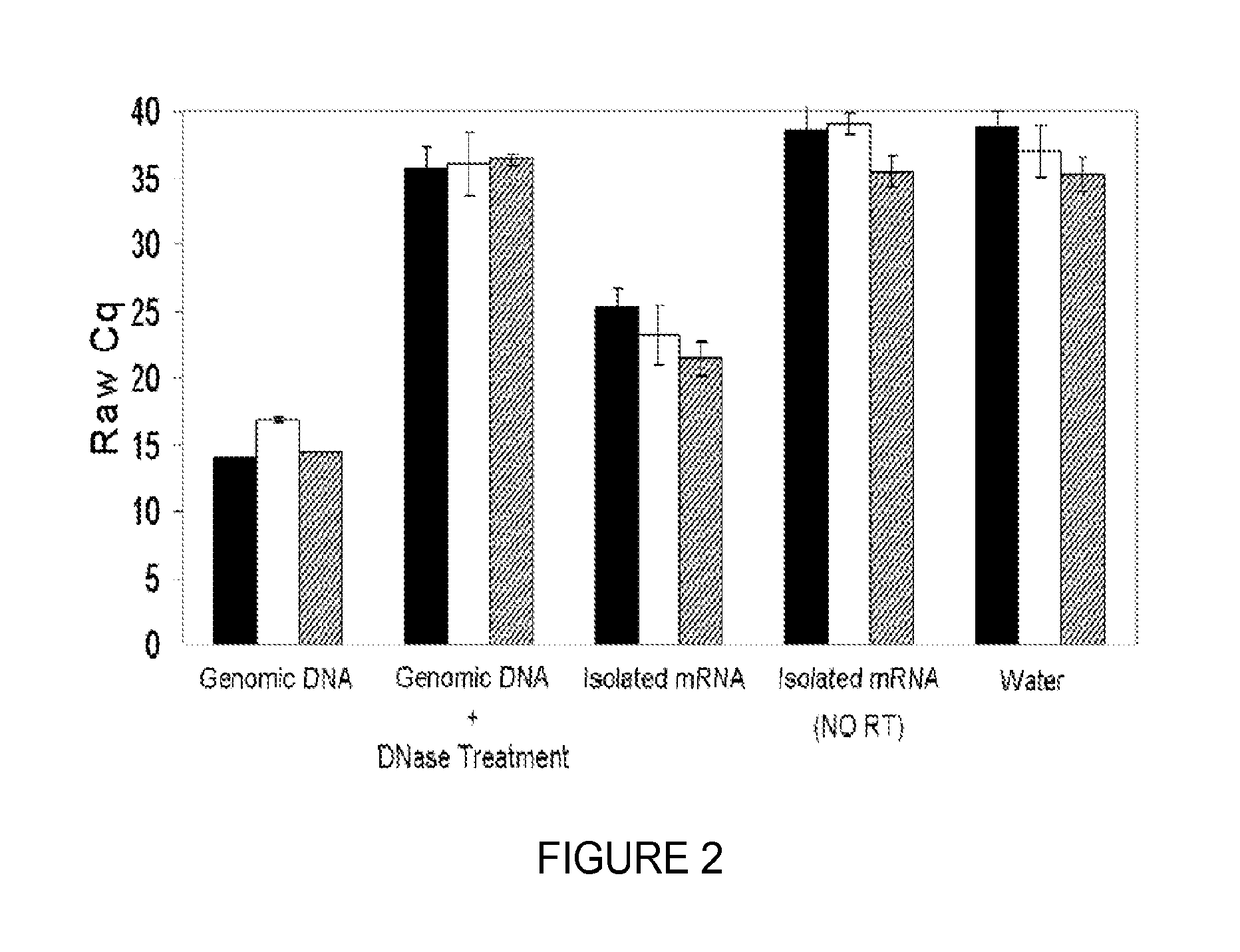
Saliva collection, processing, stabilization, and storage method
ActiveUS20140329705A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSaliva sampleCell free
Provided herein is an all-in-one saliva collection apparatus that collects saliva to allow for the filtration of saliva in order to separate saliva components, such as extracellular proteins and nucleic acids that are not present in intact cells, from the intact cells and debris remaining in the extracted sample. The filtered saliva samples can be aliquoted into two fractions for protein and / or nucleic acid analysis. The present invention further describes long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary nucleic acids, and long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary proteins added to an ethanol solution. The filtered cell-free saliva samples have diagnostic usefulness.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Full-humanized agonist single-chain antibody resistant to human death receptor 5 and application thereof
ActiveCN106397594AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood antitumor activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsEscherichia coliTumor target
The invention relates to a single-chain antibody capable of specific binding and capable of activating human death receptor 5 (DR5), and belongs to a full-humanized antibody; the single-chain antibody is obtained by performing quintuple screening in a high-capacity full-humanized phage antibody library by using human death receptor DR5 extracellular protein as a target antigen; the single-chain antibody may be acquired by induced expression in Escherichia coli, nickel ion affinity chromatography and molecular-exclusion chromatographic purification; pharmacodynamic experiments prove that the single-chain antibody is efficient in suppressing the growth of DR5 positive colon cancer cell COLO205 and breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231; the single-chain antibody and other antibodies modified therefrom, including full-length, bispecific or fusion protein forms, may act as drugs for positive tumor targeting therapy of death receptor DR5; the single-chain antibody has the advantages such as low immunogenicity, high specificity and high penetrability and is an ideal targeting tumor therapeutic drug.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for removing endotoxin in protein
InactiveCN105001299AEfficient removalEasy to operatePeptide preparation methodsUltrafiltrationFiltration
The invention provides a method for removing endotoxin in protein. The method adopts a sequential combination of chromatography, ultrafiltration and common filtration, and accords with a protein purification process flow. With the method, protein purification is realized while endotoxin is effectively removed, and the properties of protein is not influenced. The method is especially suitable to be used in treating various genetically engineered bacteria expressed intracellular and extracellular proteins. With optimized designs of the conditions of filtering mode, filtering pressure, membrane pore size and the like, operation steps and operation time are simplified, such that production cost is reduced, and processing capacity is improved. With the method provided by the invention, the endotoxin content can be reduced to an animal clinical application standard range, and the properties of the product is not influenced while the endotoxin is removed. The method is suitable for large-scale productions and applications.
Owner:TIANJIN RINGPU BIO TECH
Application of carborane derivatives, nano compound preparation and application of nano compound preparation
ActiveCN102327278AHigh antibacterial activitySuppress multidrug resistanceAntibacterial agentsInorganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial drugAcinetobacter baumannii
The invention provides carborane derivatives and application thereof. The structural formulas of three relative novel carborane derivatives are shown as (1), (2) and (3), and antibacterial medicines used as active ingredients of a medicine have the effects of resisting clinically common pathogenic bacteria (staphylococcus aureus, acinetobacter baumannii, klebsiella pneumonia, and proteus mirabilis), and also have the same-degree effect of resisting multidrug-resistant staphylococcus aureus strains and can inhibit multidrug resistance of the multidrug-resistant staphylococcus aureus strains, wherein a compound (2) can react with medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus extracellular proteins, so adhesion of bacteria on the surface of an organism is reduced, and the formation of a medicine-resistant strain biological film is inhibited. The toxicity and invasiveness of staphylococcus aureus are reduced, treatment efficiency is improved, an adverse effect caused by using a large amount ofantibiotics is avoided, and a novel compound is provided for finding a novel medicine for resisting medicine resistance bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Medicine combination containing fusion protein for suppressing angiogenesis and application
ActiveCN102380096BInhibition of Purity DeclineSenses disorderAntibody ingredientsVascular proliferationVascular endothelium
The invention discloses a medicine combination containing fusion protein for suppressing angiogenesis and application, and particularly relates to a medicine combination containing fusion protein of an extracellular protein domain 2 (Flt-2) of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 1, extracellular protein domains 3 and 4 (KDR-3 and 4) of a VEGF receptor 2 and human normal immunoglobulin 1(G1) Fc. The medicine combination can keep the fusion protein stable, has the most outstanding advantage of capability of effectively suppressing fusion protein polymer so as to avoid reduction of purity, and accordingly keeps bioactivity of effective components.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG BIOTECH
Saliva test for hemolytic streptococcus
A reagent for the detection of an extracellular enzymatically active protein produced by a beta-hemolytic streptococcus bacteria found in a host biological fluid includes a proteinaceous substrate or a cholesterol-containing membrane substrate for the extracellular protein. The substrate is nonspecific within the groups of beta-hemolytic streptococcus bacterium and is in contact with an inert solid matrix. Upon reaction between the streptococcus enzymatically activate protein and the substrate, a color change discernable by an unaided human eye results. Extracellular streptococcus protein found in saliva represents a less invasive source of biological fluid for the determination as to whether a host suffers acute pharyngitis.
Owner:MOSER LEROY E +2
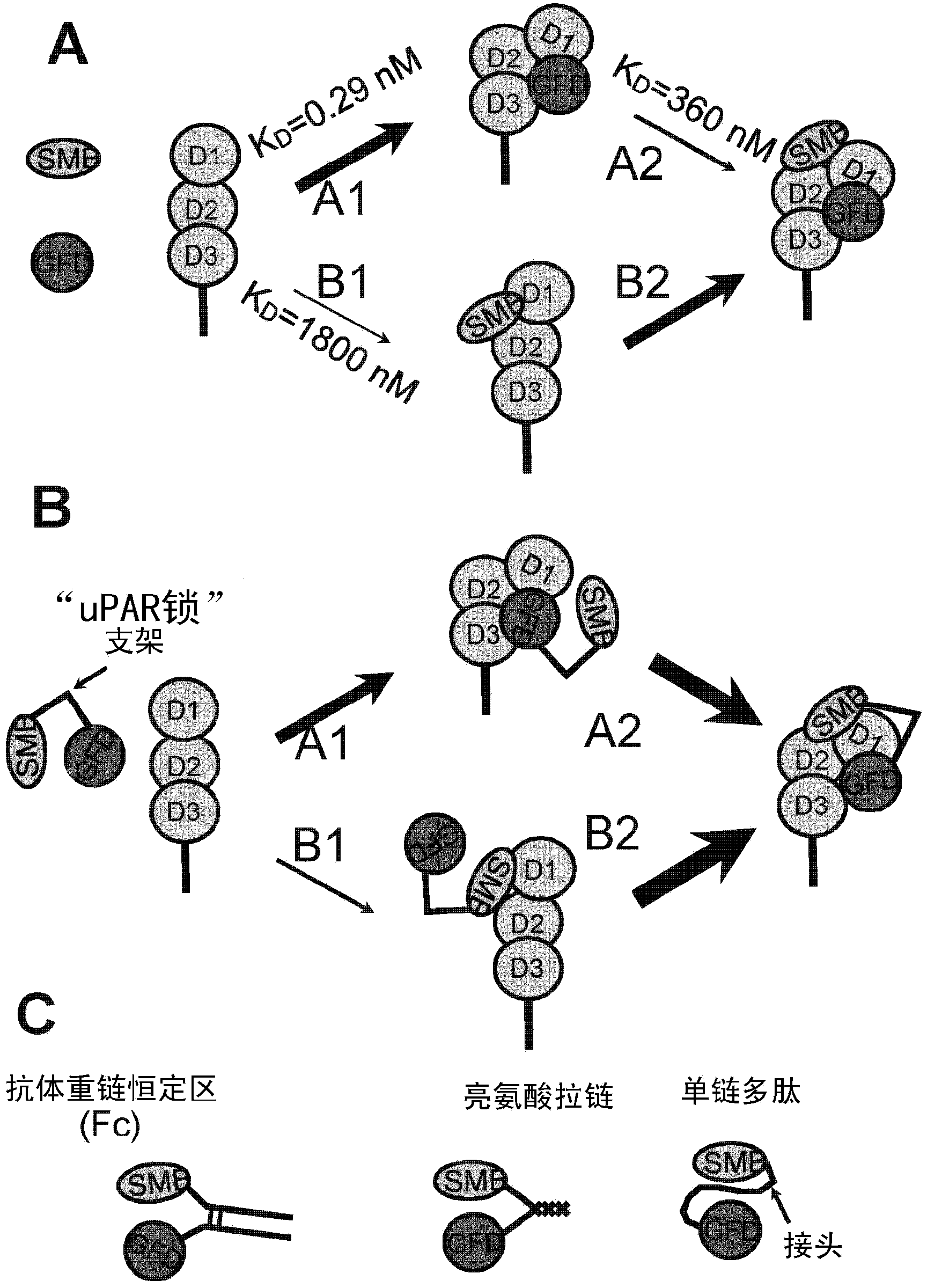
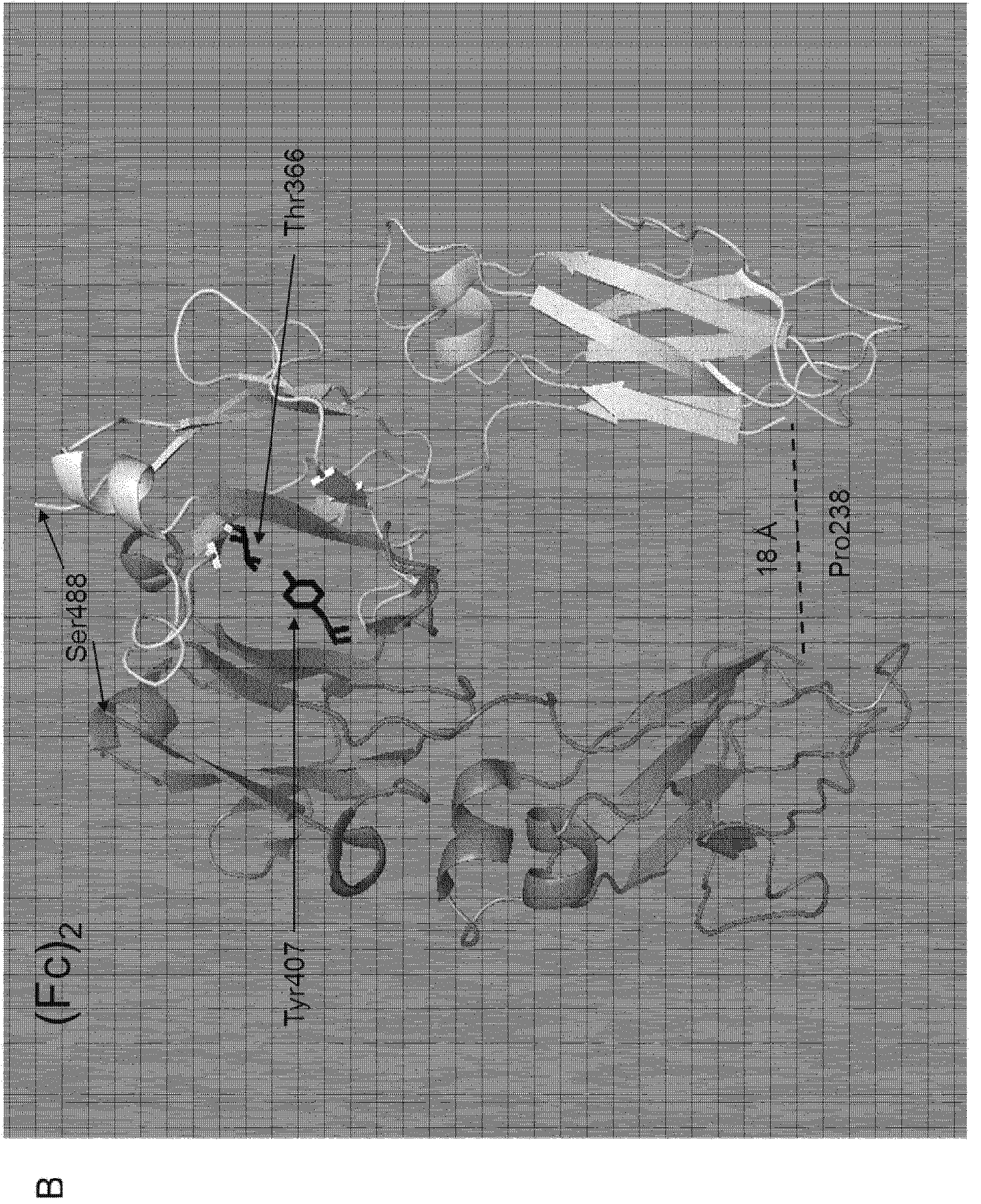
UPAR-antagonists and uses thereof
InactiveCN103391787AExcellent drug propertiesVarious clinical applicationsConnective tissue peptidesHydrolasesCell-Extracellular MatrixVitronectin
The invention relates to inhibitors of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR). The generated inhibitors are bivalent uPAR-ligands containing the receptor binding domains of the extracellular protease urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and of the extracellular matrix protein vitronectin (VN), in different configurations, linked by a scaffold. The present invention also refers to the above molecules for use as a medicament, in particular for treatment of cancer, and for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:IFOM FOND INST FIRC DI ONCOLOGIA MOLECOLARE
Extraction separation method for soil intracellular protein
The invention provides an extraction separation method for soil intracellular protein, which comprises the following steps: extracting with a sodium citrate extracting solution to remove soil extracellular protein; extracting and dissolving soil intracellular protein with an SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate) extracting solution, carrying out further extraction on the intracellular protein with Tris-saturated phenol, methanol-ammonium acetate and the like, and carrying out dielectrophoresis separation. The SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) detection indicates thatstripes and protein points of the extracted soil intracellular protein are clear, and the extraction separation method for soil intracellular protein is provided for the first time in the world.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Sludge dehydration conditioning method based on protein denaturant
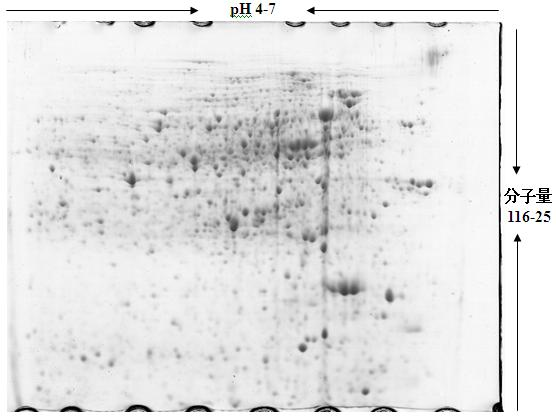
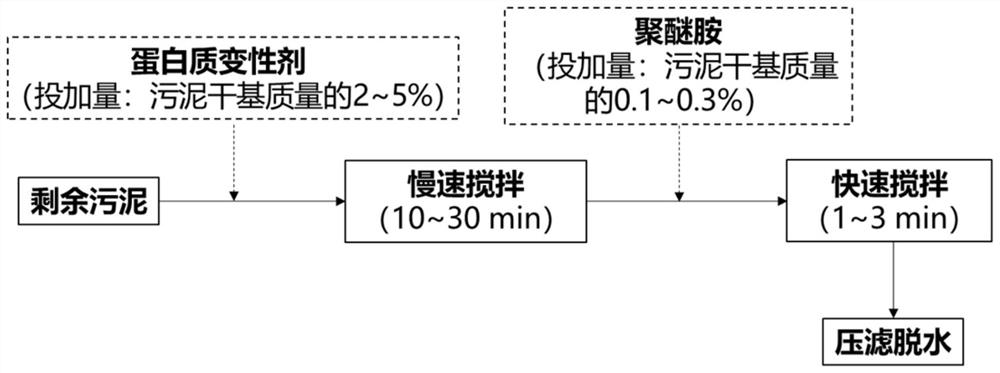
ActiveCN112047611AImprove dehydration effectNovel and efficient dehydration conditioning methodSludge treatmentExtracellular proteinsPulp and paper industry
The invention relates to a sludge dehydration conditioning method based on a protein denaturant, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: uniformly mixing sludge to be conditioned with the protein denaturant, carrying out protein denaturation reaction, adding a protein emulsifying coagulant, and quickly stirring to obtain a sludge conditioning solution; coagulation and aggregationof water-binding extracellular protein in the sludge are further promoted in an assisted manner, and the dispersion water-holding performance of the protein is reduced. Compared with the prior art, the method has the remarkable advantages of low dosage, mild reaction conditions, no toxicity or harm, no influence on the sludge incineration heat value and the like, provides a new technical way forenvironment-friendly sludge dehydration conditioning, and shows wide market application prospects and important social and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
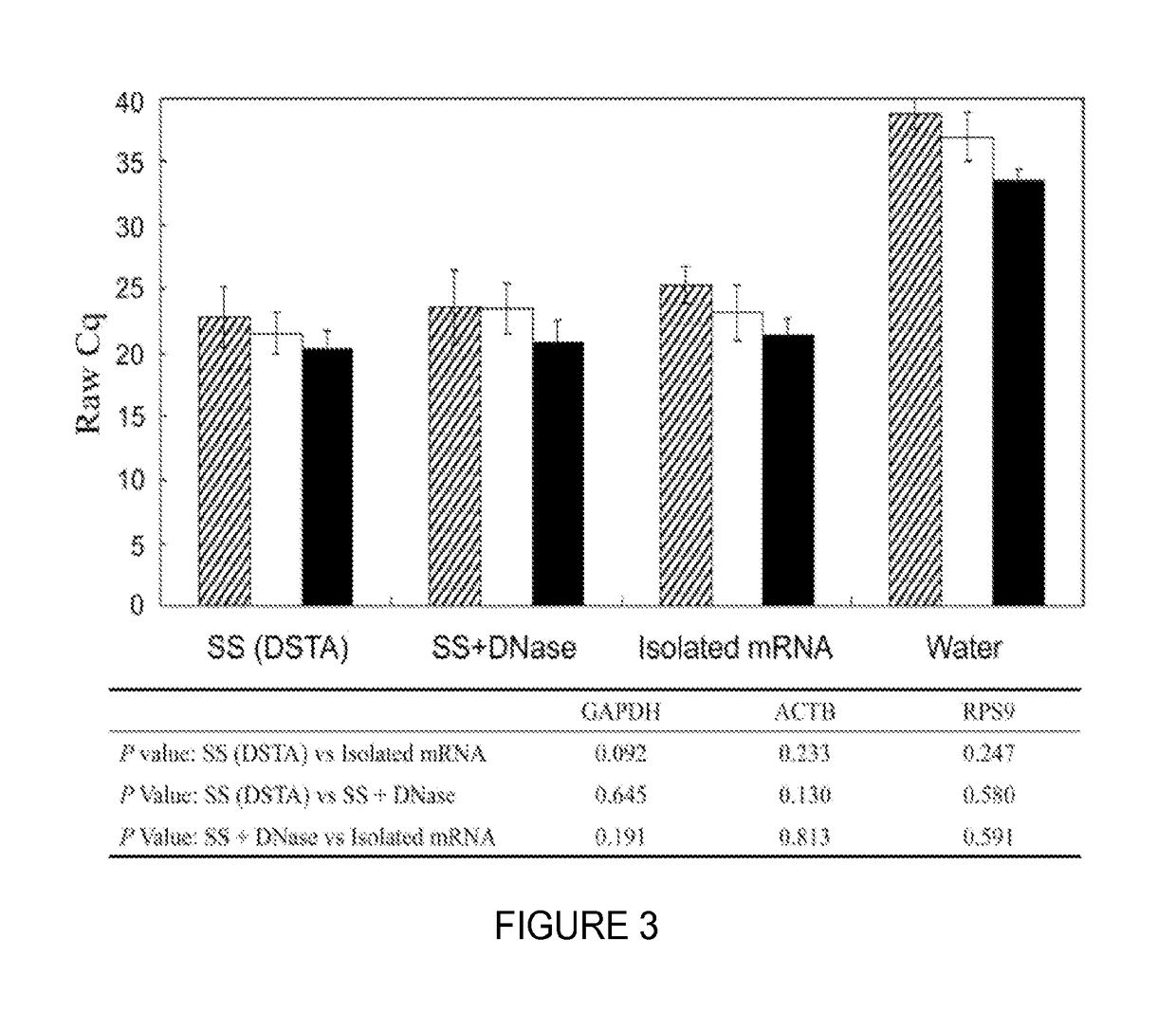
Fluorescent quantitative PCR method for simultaneous detection of streptococcus suis subtype 2 (SS2) extracellular protein factor and hemolysin gene
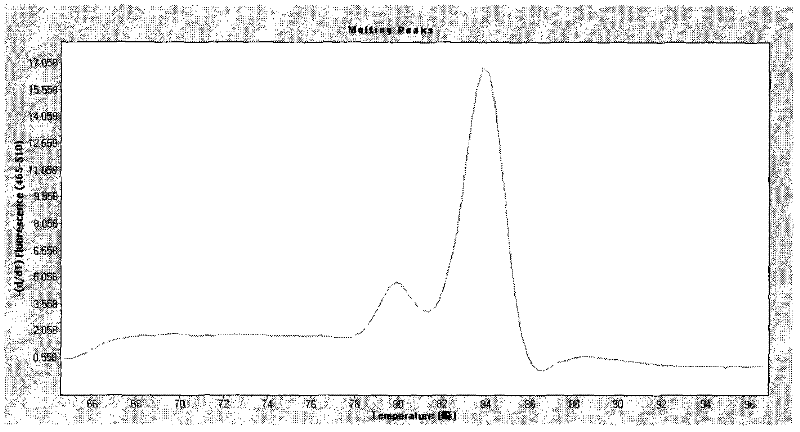
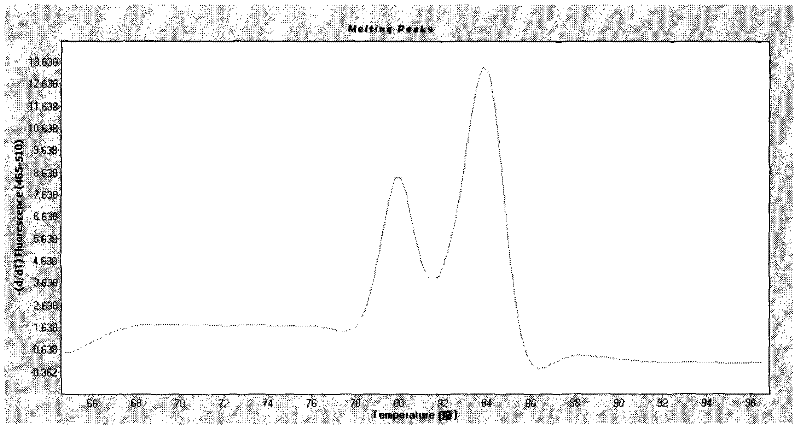
InactiveCN102229978AShort detection costReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSolubilityConserved sequence
The invention relates to a fluorescent quantitative PCR method for simultaneous detection of an extracellular protein factor EF and a hemolysin gene SLY of SS2 based on SYBR Green dye solubility curve method. According to the invention, two pairs of specific primers are designed and synthesized based on conserved sequences of the SS2 EF and SLY gene disclosed by GenBank, the PCR reaction system and reaction conditions are optimized, and the fluorescent quantitative PCR method for simultaneous detection of an EF and an SLY gene of SS2 based on SYBR Green dye method is established through analysis of an amplification curve and a solubility curve. On such bases, the mol ratio of EF primers and SLY primers are optimized and the amplification efficiency of the two pairs of primers is adjusted,which enables the two product peaks in the solubility curve to be of similar size. Utilization of the established SYBR Green dye solubility curve method enables convenient and simultaneous detection of SS2 EFs and SLY genes.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
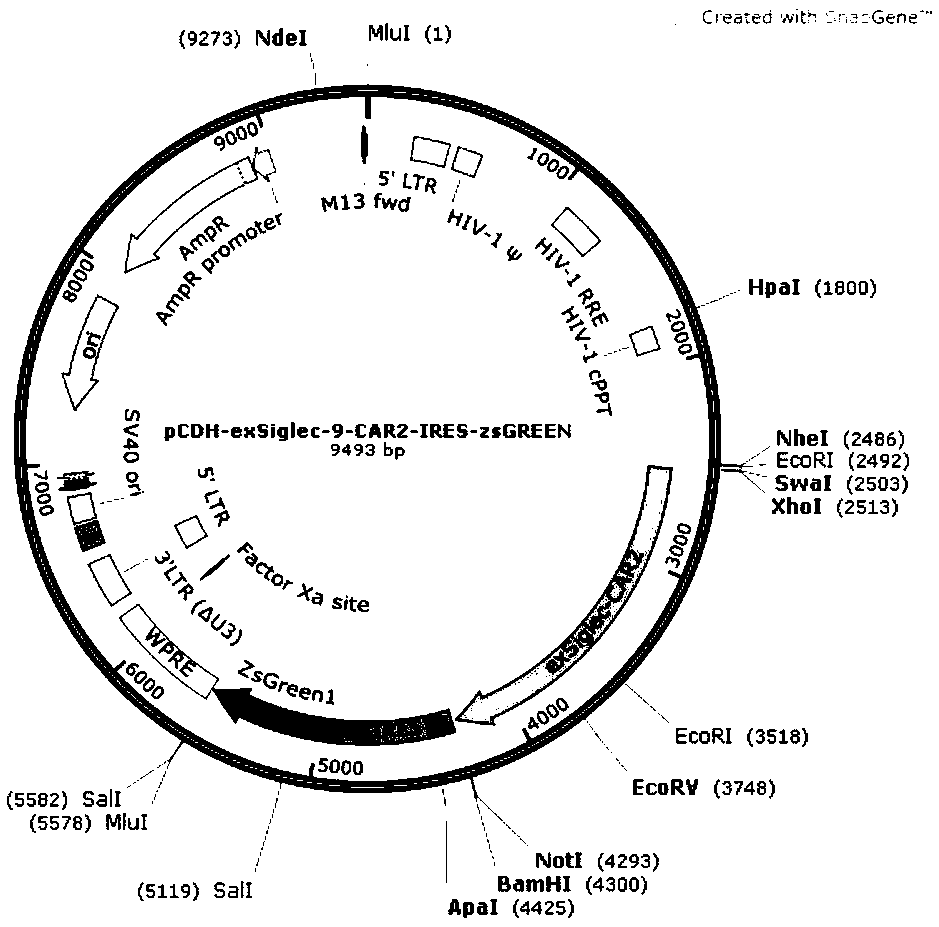
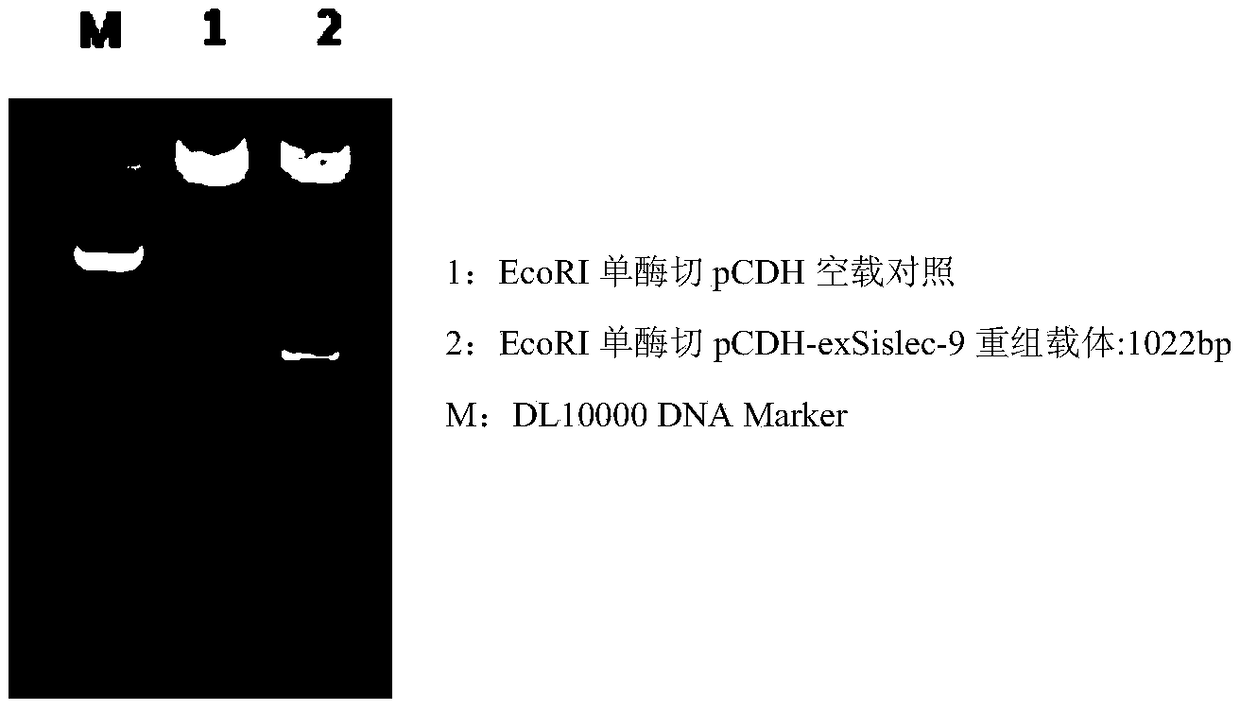
Siglec-9 targeted embedding antigen receptor T cell and purpose thereof
ActiveCN109320602APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorExtracellular proteins
The invention relates to a siglec-9 targeted embedding antigen receptor T cell and a purpose thereof. Concretely, the invention provides a Siglec-9 extracellular protein, a targeted MUC1 targeted CARand an engineering immune cell. The engineering immune cell can selectively kill tumor cells of malignant tumor from high-expression MUC1.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Saliva collection, processing, stabilization, and storage method
ActiveUS10023903B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSaliva sampleCell free
Provided herein is an all-in-one saliva collection apparatus that collects saliva to allow for the filtration of saliva in order to separate saliva components, such as extracellular proteins and nucleic acids that are not present in intact cells, from the intact cells and debris remaining in the extracted sample. The filtered saliva samples can be aliquoted into two fractions for protein and / or nucleic acid analysis. The present invention further describes long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary nucleic acids, and long term storage at ambient temperatures of filtered salivary proteins added to an ethanol solution. The filtered cell-free saliva samples have diagnostic usefulness.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
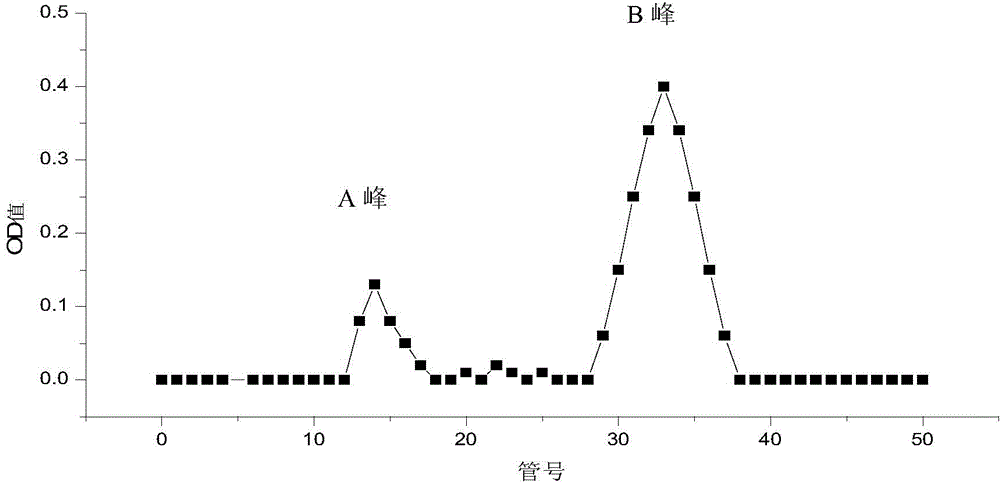
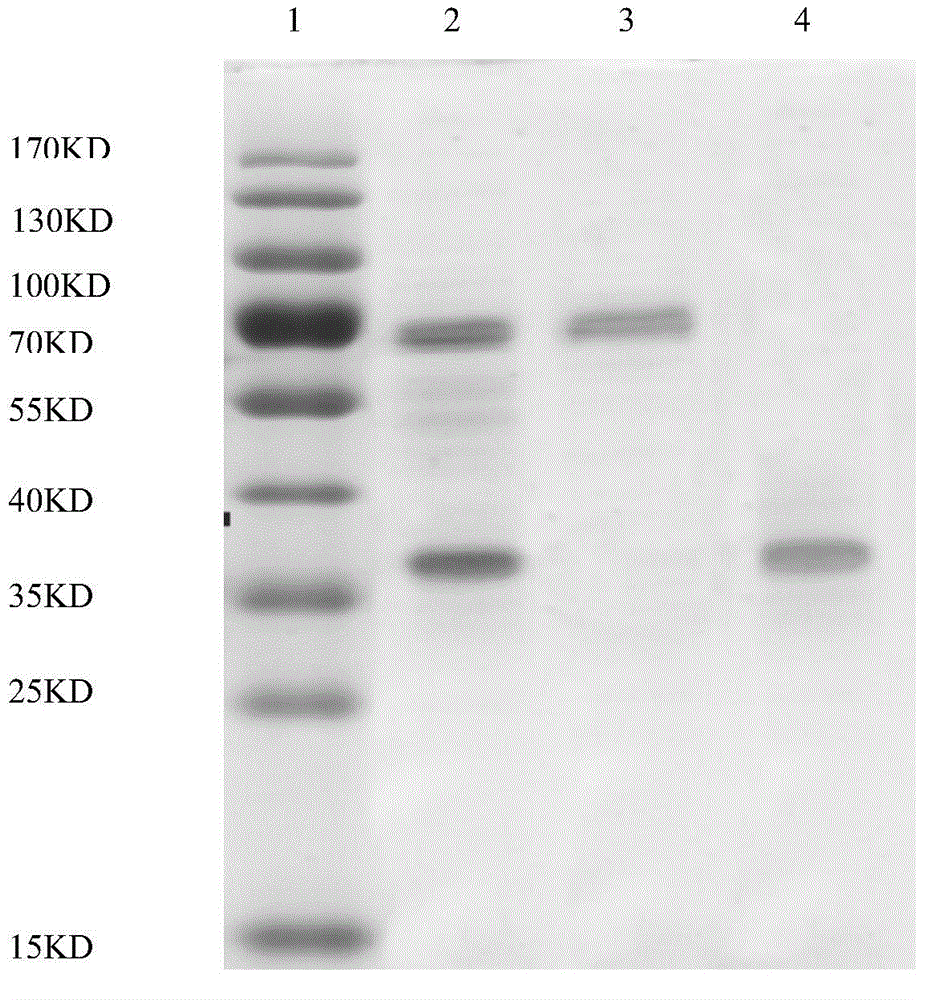
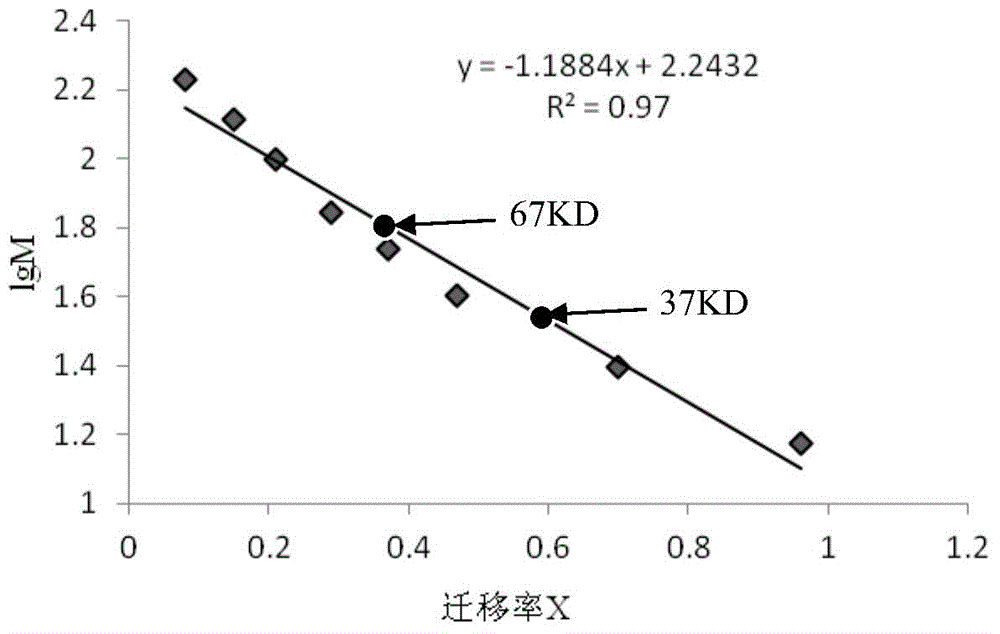
Extraction method and application of lactobacillus extracellular protein
InactiveCN104388503AGood for healthFacilitate the realization of large-scale preparation and productionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemPhosphateExtracellular proteins
The invention discloses an extraction method and an application of lactobacillus extracellular protein. The method can be used for obtaining extracellular protein secreted by lactobacillus at a relatively high level and is simple in a preparation process, low in cost and applicable to large-scale production. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating the lactobacillus in an improved tomato juice culture medium and culturing at the temperature of 37 DEG C under an anaerobic condition; scraping off cultured lactobacillus lawn, transferring to a phosphate buffer solution of which the pH value is 7.2-7.4, re-suspending, afterwards shaking, centrifuging to remove thallus and collecting liquid supernatant; desalting by means of dialysis and concentrating to obtain a crude extract solution of the lactobacillus extracellular protein; performing SephadexG-100 dextran gel chromatography on the crude extract solution of the lactobacillus extracellular protein, and collecting a protein solution having a protein peak to obtain purified lactobacillus extracellular protein. Identification on molecular weight of the lactobacillus extracellular protein shows that the molecular weight is 67KD and 37KD. Application tests of two types of lactobacillus acidophilus extracellular protein show that the 67KD and 37KD extracellular protein has different inhibition effects on growth of HT-29 cells.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Functional enhancement of microorganisms to minimize acrylamide production
The present disclosure provides yeast transformed with a nucleic acid molecule (GAT1) to reduce nitrogen catabolite inhibition of asparagine transport / degradation under food preparation / processing conditions and / or to overexpress enzymes encoding proteins involved in asparagine degradation Genes for cell wall or extracellular proteins (ASP1 or ASP3) and / or genes encoding proteins involved in asparagine transport (AGP1 or GNP1 or GAP1). The genetically modified yeast has an enhanced ability to reduce the concentration of acrylamide in foods prepared by heating. Also provided are methods and uses of the transgenic yeast for reducing the concentration of allylamine in foods and foods with reduced allylamine content prepared using the transgenic yeast.
Owner:复兴生物科技公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com