Lactobacillus helveticus bacterium having high capability of producing tripentide, fermented milk product, and preparing process thereof
A technology for dairy products and Lactobacillus, applied in the field of new lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus helveticus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] (Selection of strains capable of producing fermented milk with high ACE inhibitory activity)
[0103] 36 strains of Lactobacillus helveticus isolated from different milk products were screened. The ACE inhibitory activity in the fermented milk of each strain was determined according to the following method. Each Lactobacillus helveticus was cultured at 37° C. for 24 hours in a 9% (weight percent) non-fat milk solids medium. The cultivated medium was added to the same type of fresh medium, and the new medium contained 3% (weight percentage) of the cultivated medium. It was further fermented at 37°C for 24 hours. After the fermentation, the acidity of lactic acid (weight percent), peptide content in whey (μg / mL), cell number and ACE inhibitory activity (U / mL) were measured. The results are shown in Table 1. Among the 36 strains, 7 strains had extremely weak fermentation ability. The acidity of lactic acid in the fermented milk produced by 15 strains is not lower than 1...
Embodiment 2
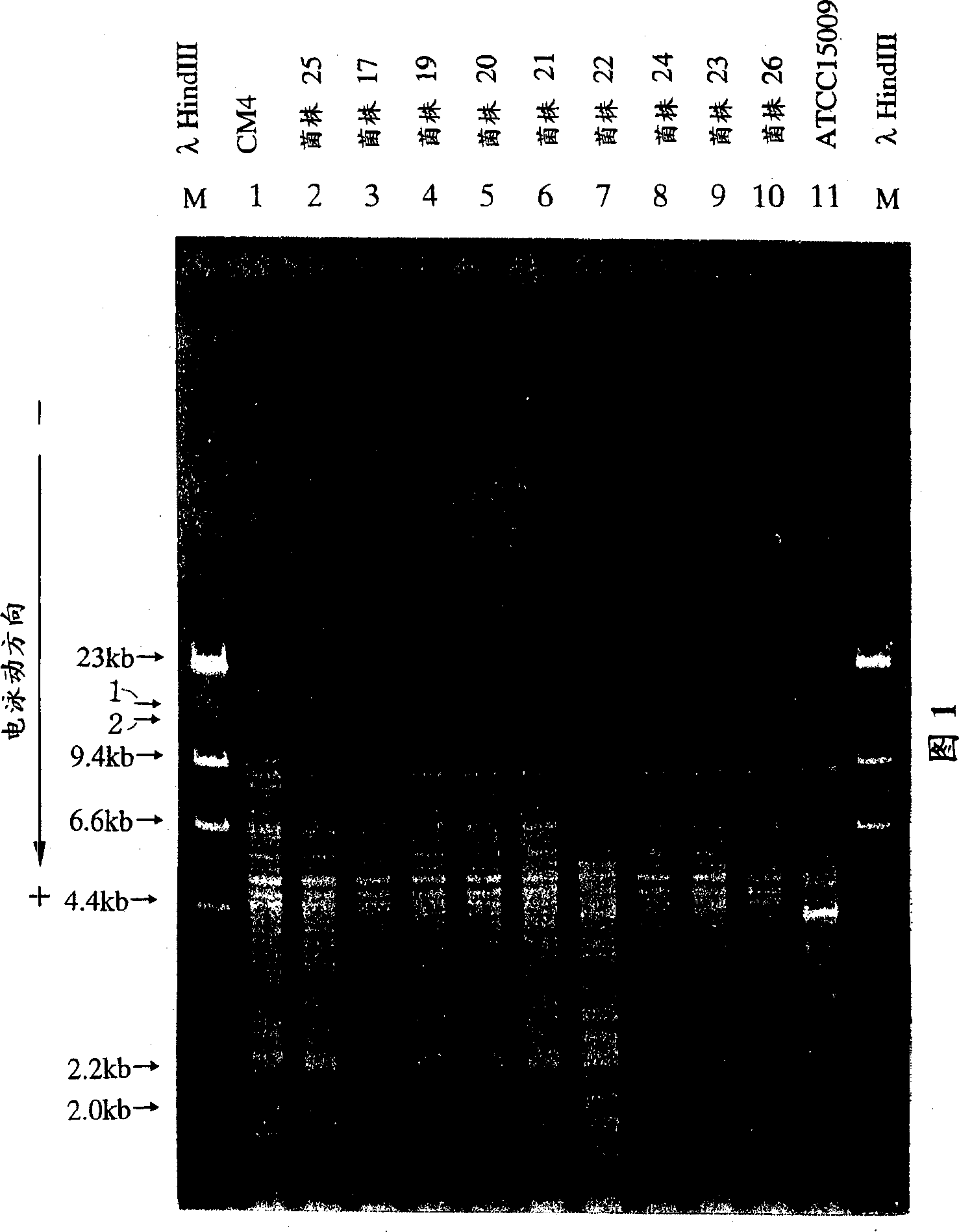
[0129] Select 11 strains from the 36 strains of Lactobacillus helveticus in Example 1, extract chromosomal DNA with reference to methods such as Leenhouts (Leenhouts K (1990) Applied Environmental Microbiology 56: 2726), digest with several restriction enzymes, at 0.8 Electrophoresis band patterns were analyzed on % agarose gel electrophoresis.
[0130] As a result, characteristic DNA fragments could be observed in the chromosomal DNA fragments of CM4 strain digested with EcoRI and PsII (see arrow 1 in Figure 1). It was not observed in the chromosomal fragments of the remaining strains, but a fragment shorter than the characteristic fragment of CM4 could be observed in most strains (see arrow 2 in Figure 1). The digested product of lambda bacteriophage DNA HindⅢ was used as the molecular size marker (23.1kb, 9.4kb, 6.6kb, 4.4kb, 2.3kb, 2.0kb, and the mobility was accelerated in turn) to compare the electrophoresis results, and the characteristic fragments The molecular weight...
Embodiment 3
[0132] Produce fermented milk with Lactobacillus helveticus CM4 selected in Example 1. The CM4 strain was cultured in 100 g of 9% (weight percent) skim milk at 37° C. for 12 hours, then mixed with 3 kg of fresh medium and continued to culture at 37° C. for 12 hours. After fermentation, all fermented milk (CM4 cell number 6.3×10 8 / mL) as 100kg of 9% (weight percent) skim milk starter and cultivated at 32°C for 20 hours. After the fermentation, the fermented milk contained 74.8 μg / mL lactotripeptide, and the lactic acid content was 1.9% (percentage by weight).
[0133] Take 43kg of fermented milk which has been prepared, homogenate with 4kg of granular sucrose, 3kg of water and 0.15kg of high methoxy pectin to prepare 50kg of yogurt drink. The yogurt beverage has a good taste, pH 3.6, and the number of live CM4 cells is 4.6×10 8 / mL.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com