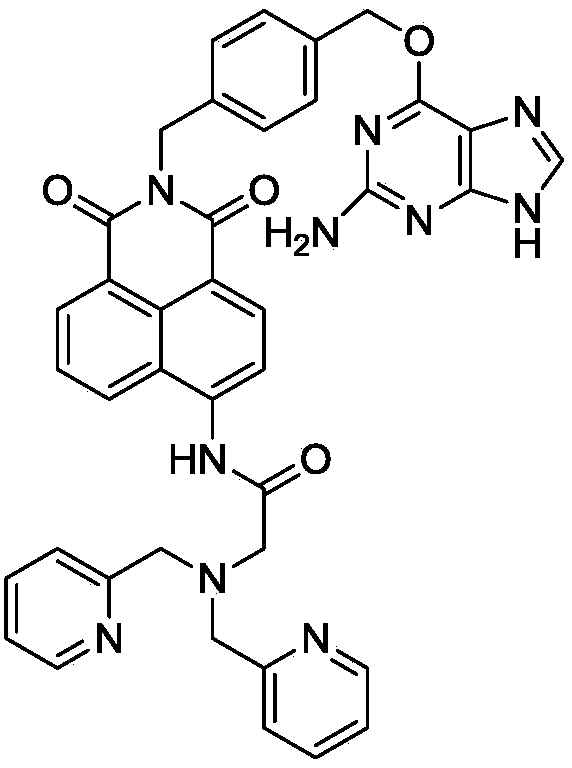
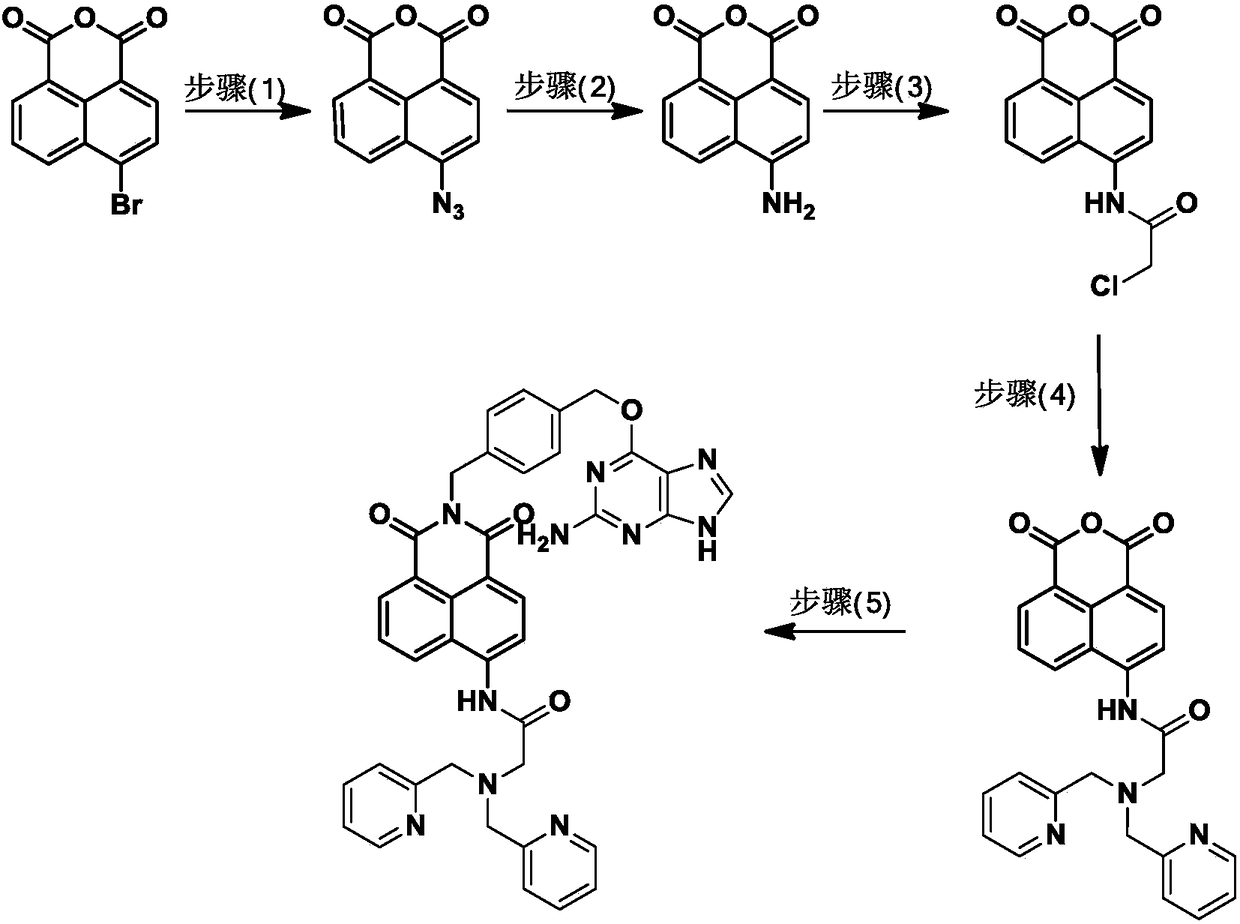
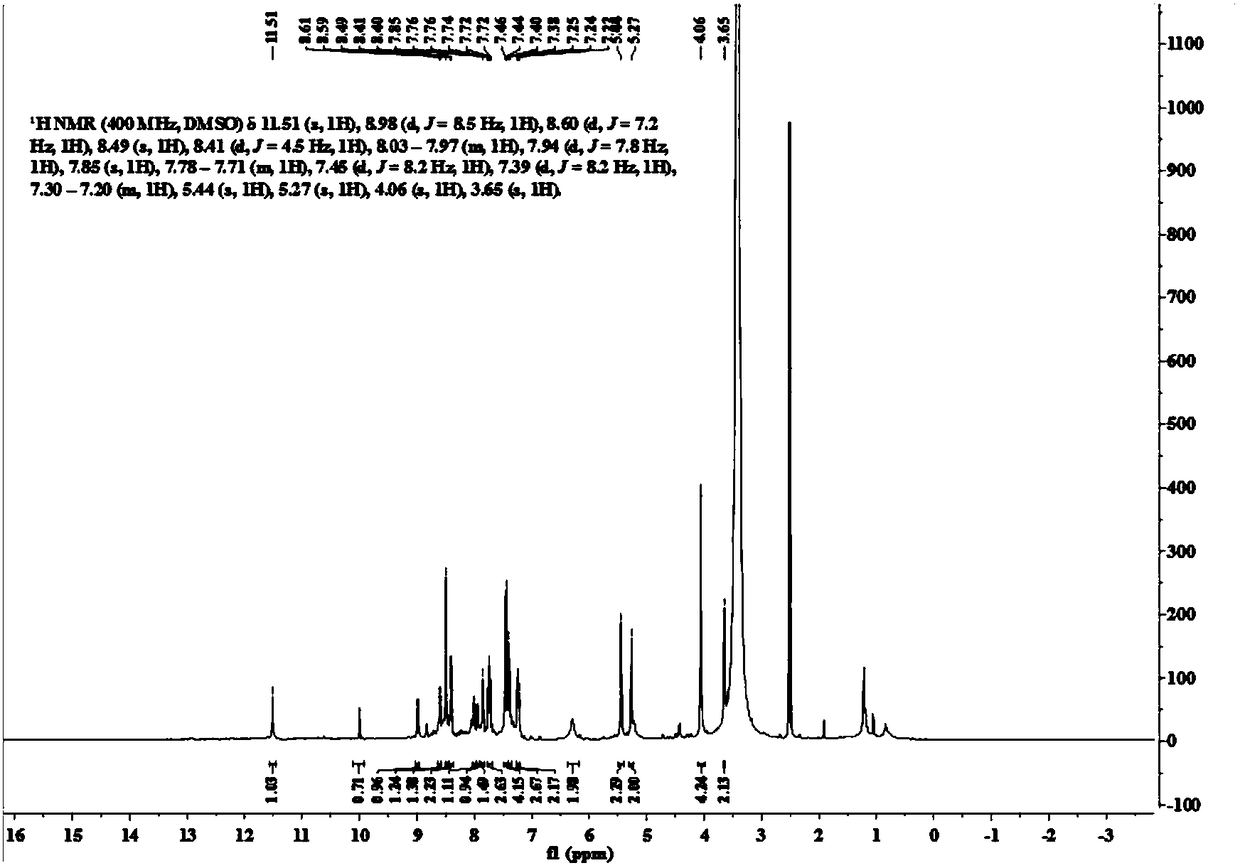
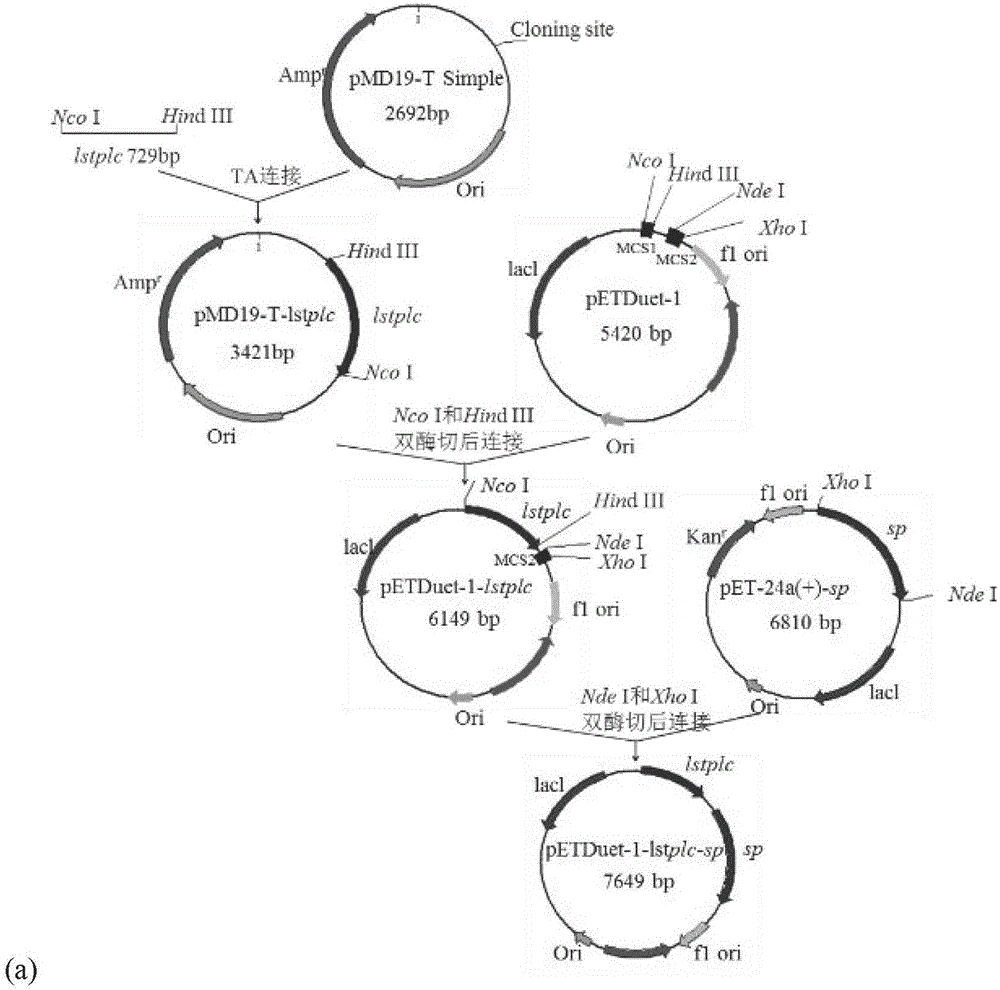
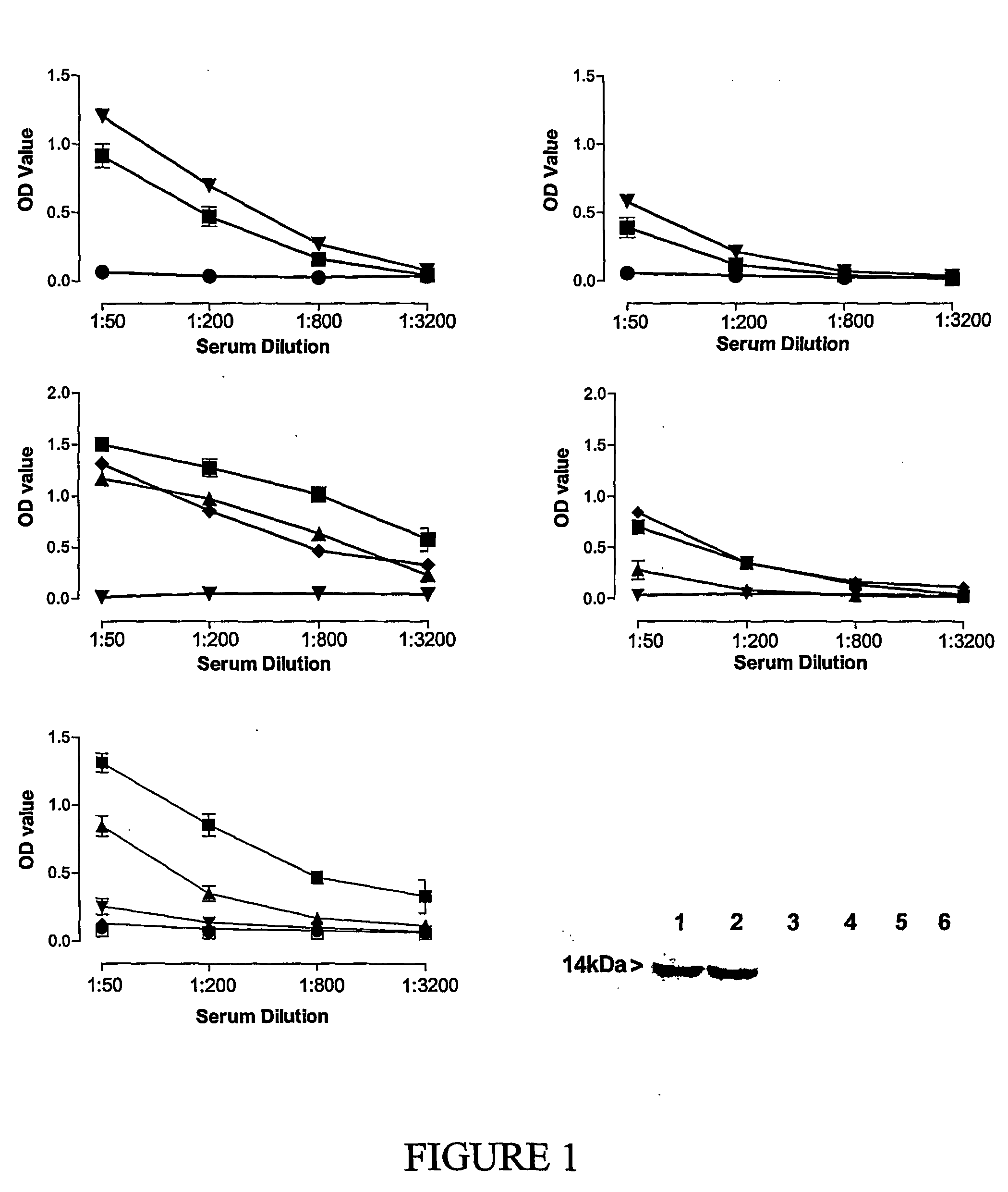
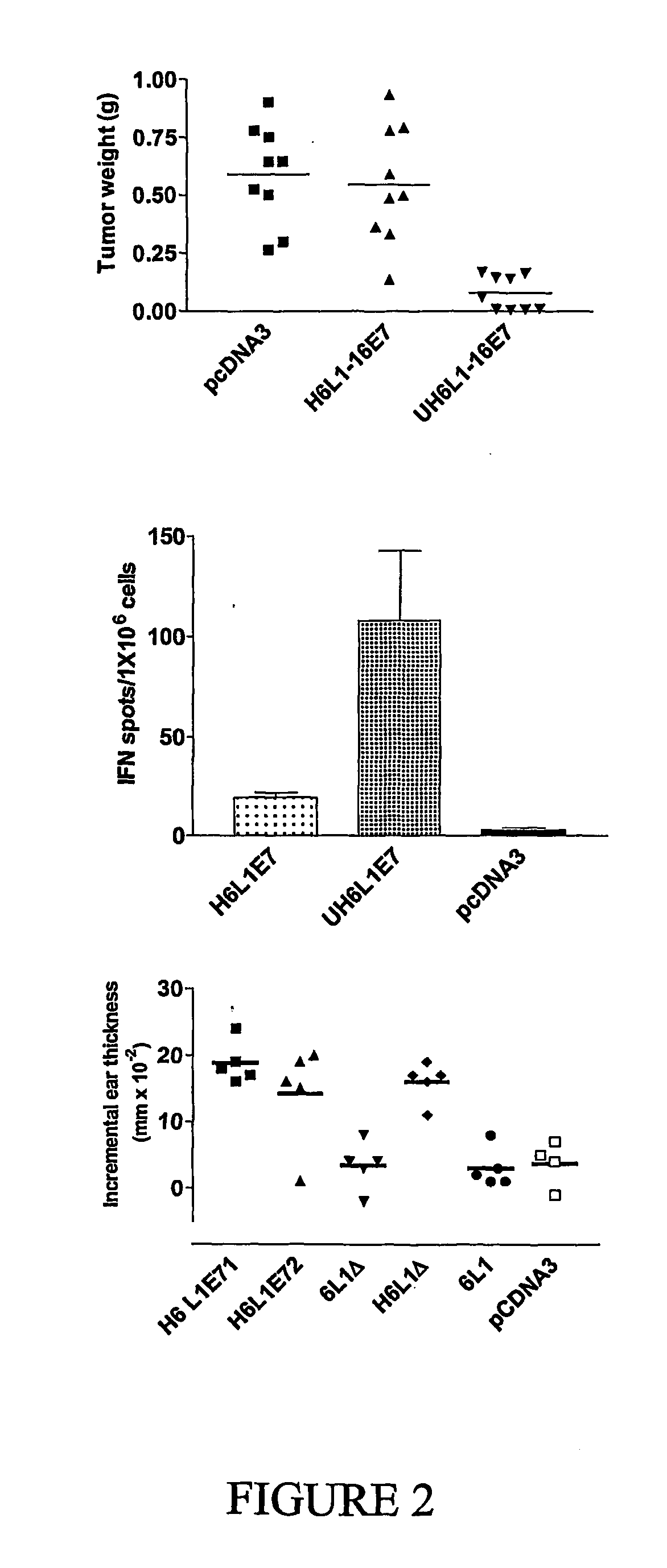
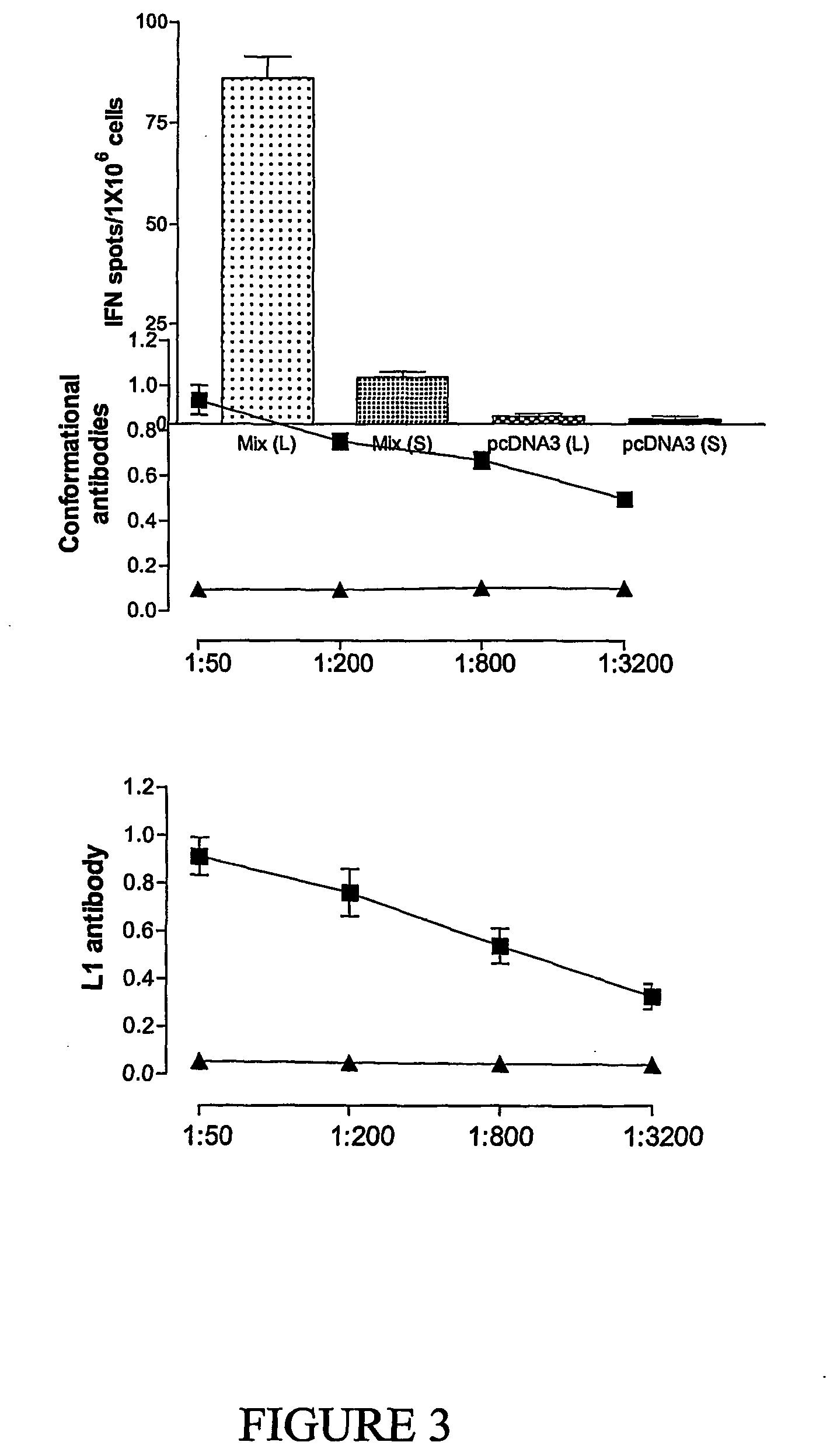
Patents
Literature
226 results about "Intracellular protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
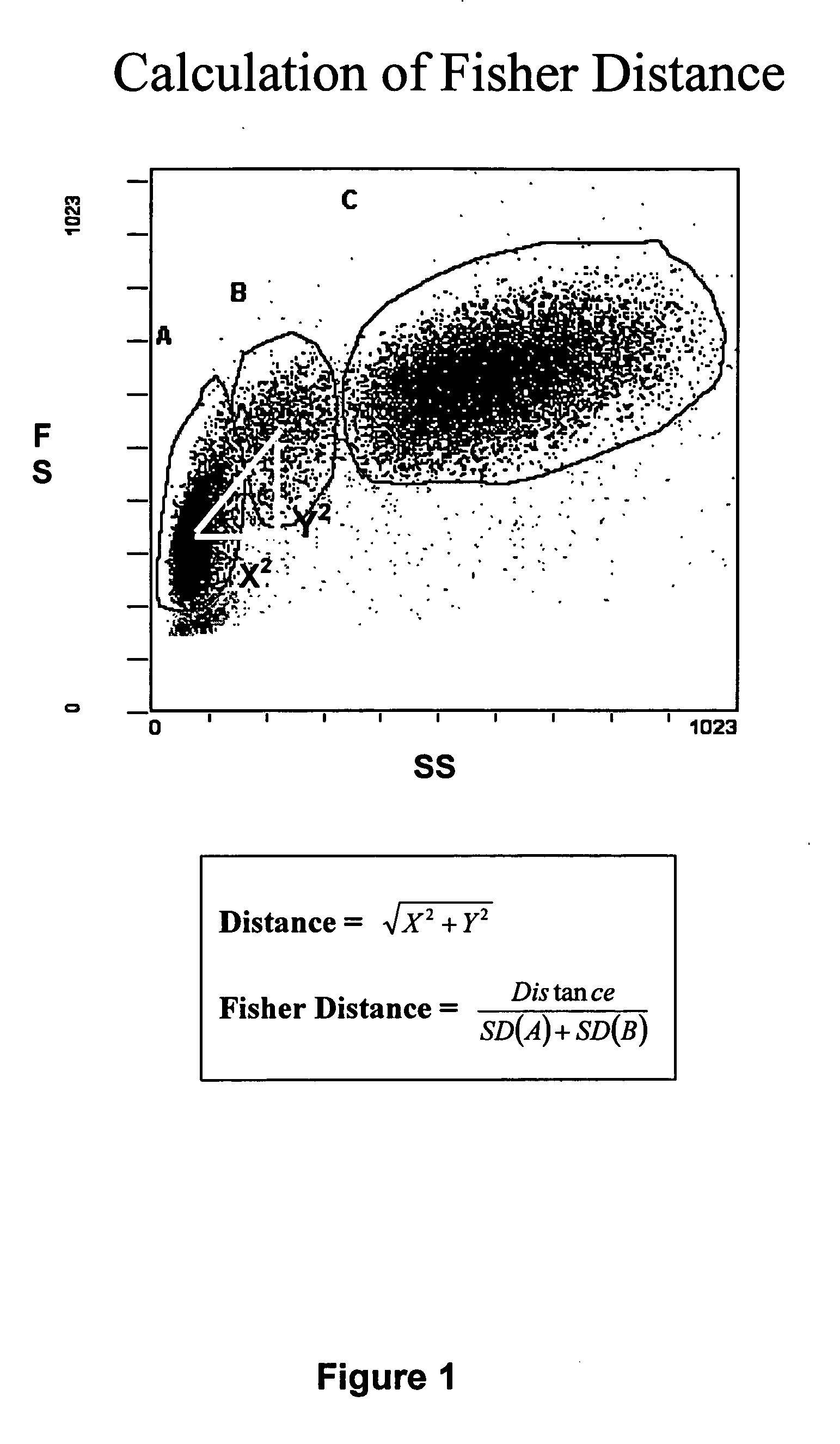
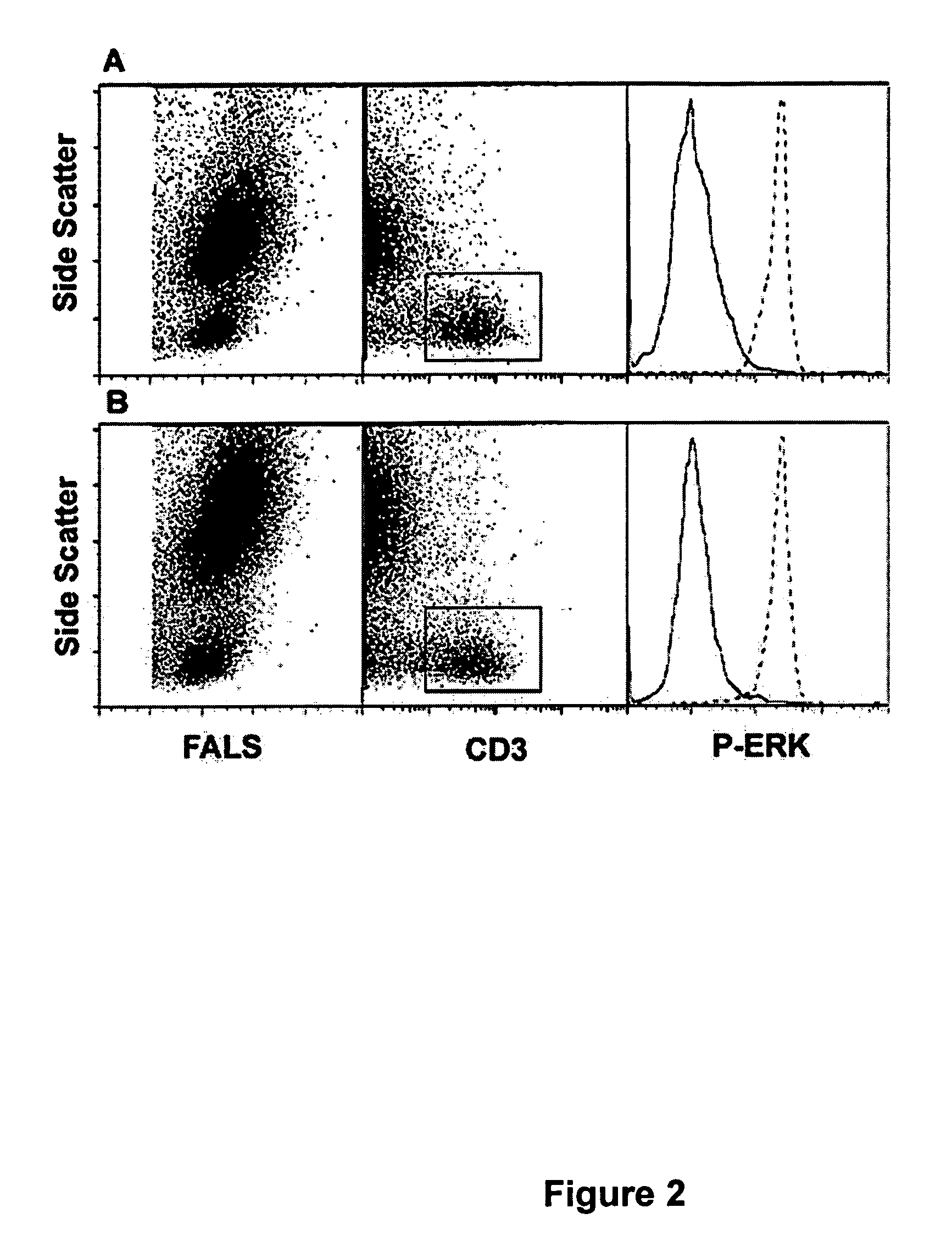
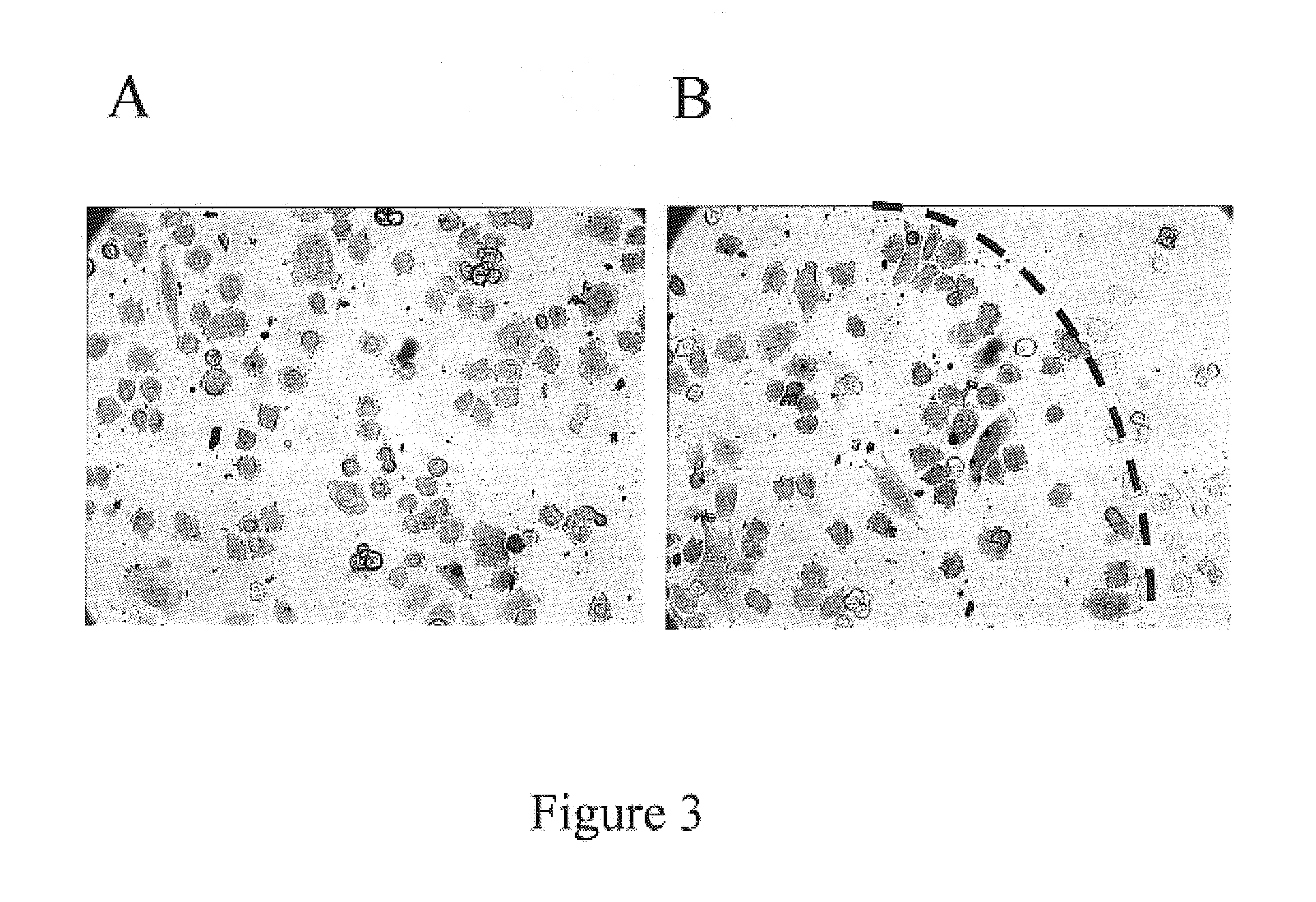
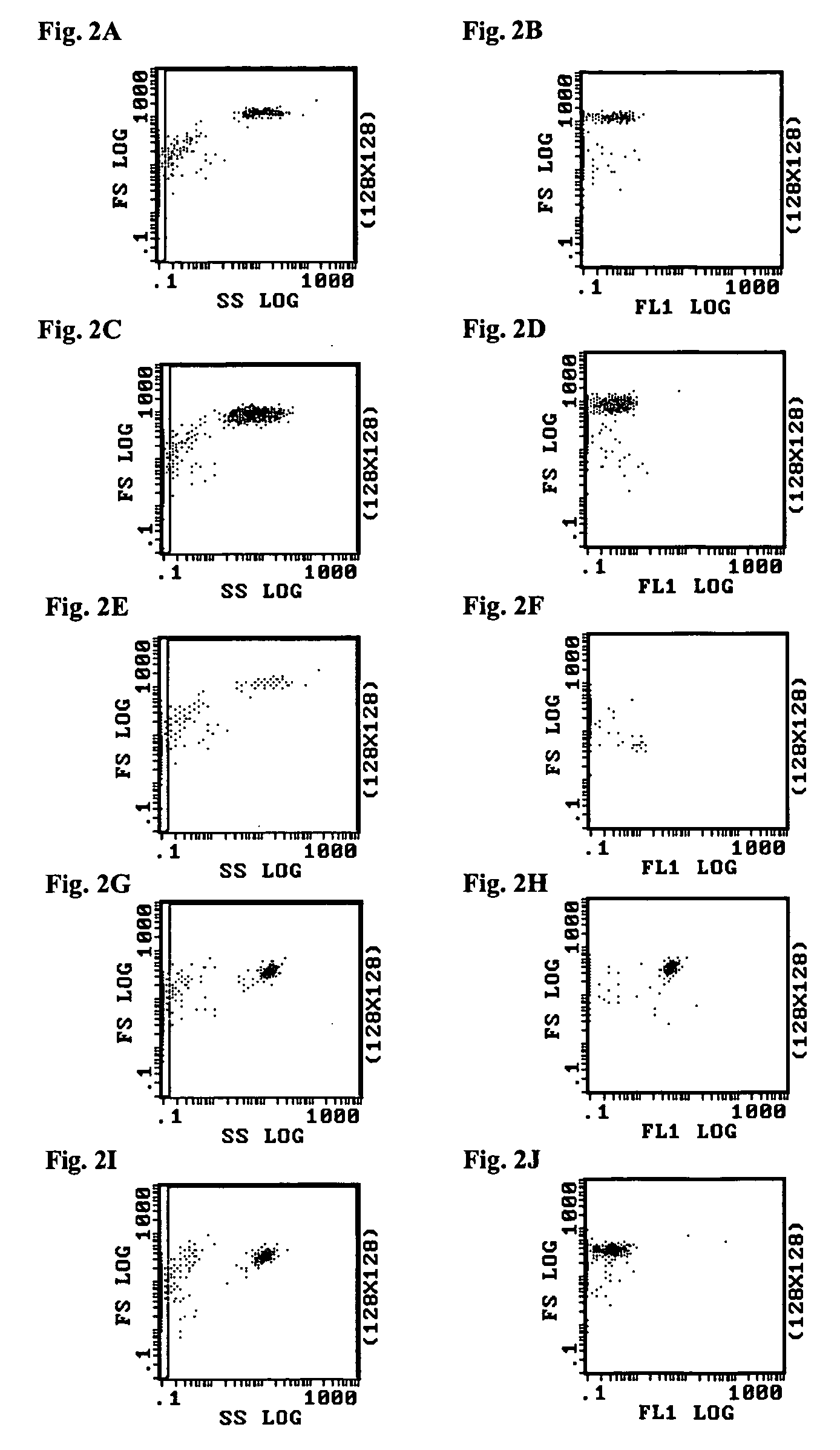
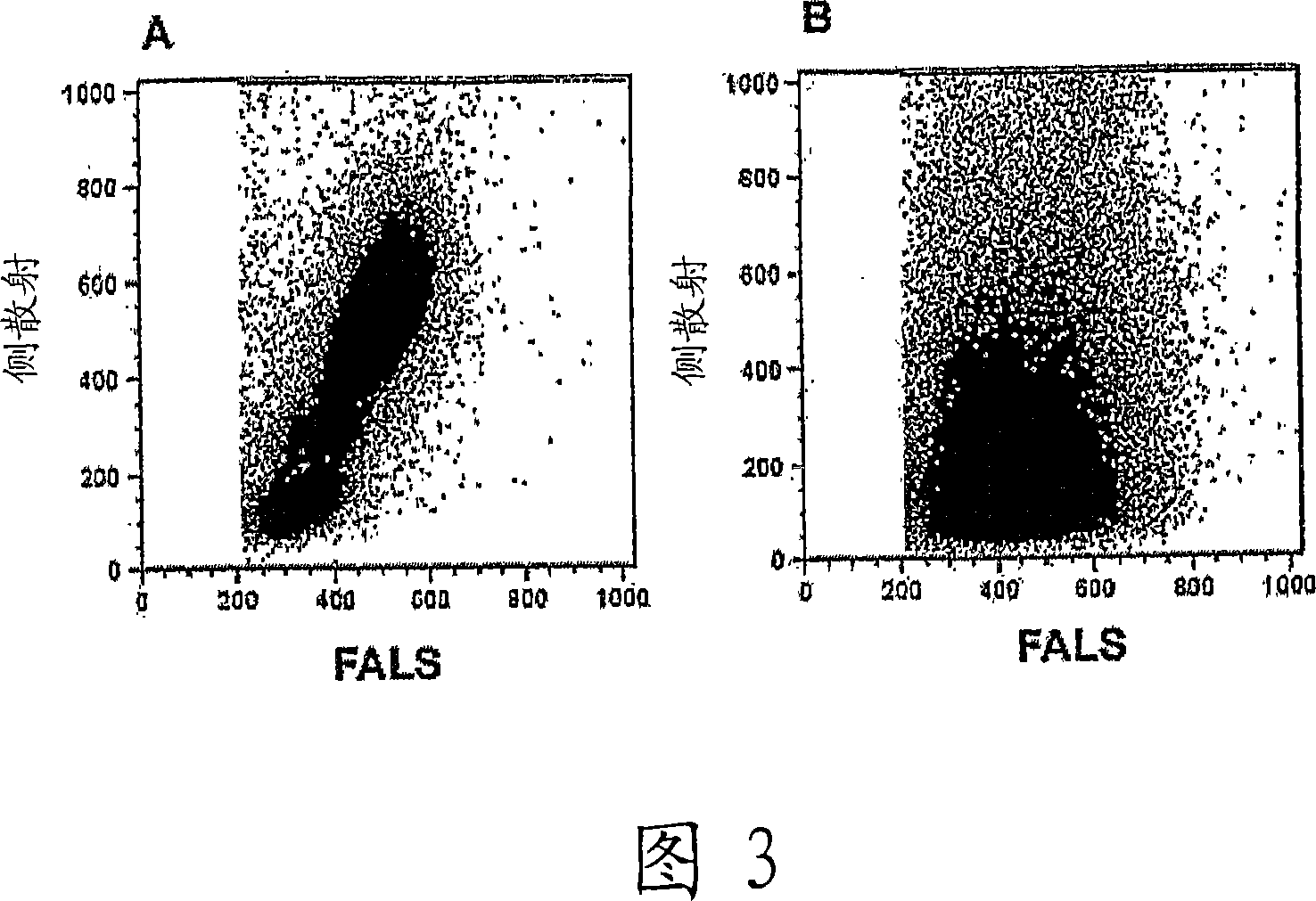
Whole blood preparation for cytometric analysis of cell signaling pathways
ActiveUS20060046272A1Quick fixWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCross-linkPeritoneal fluid
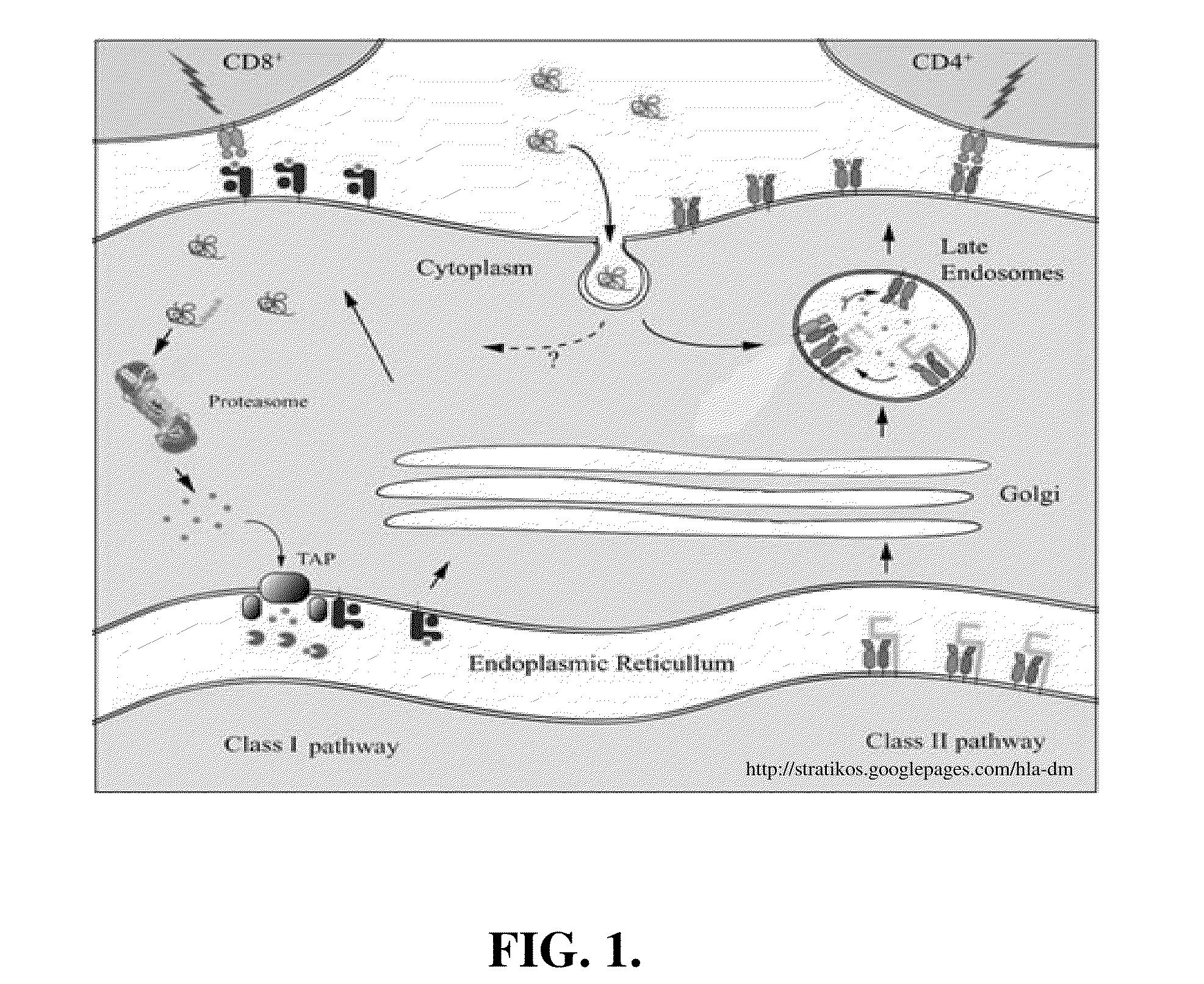
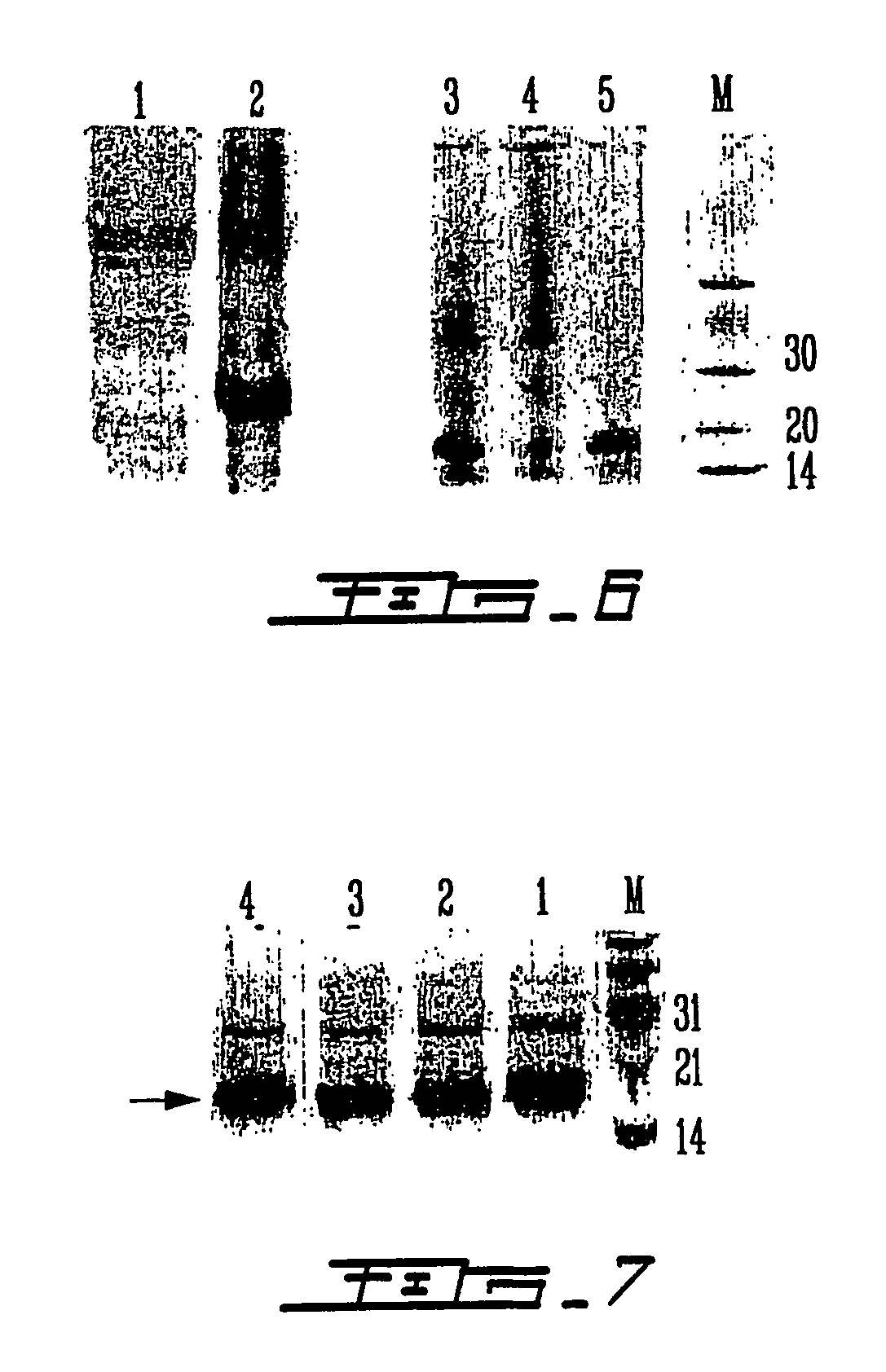
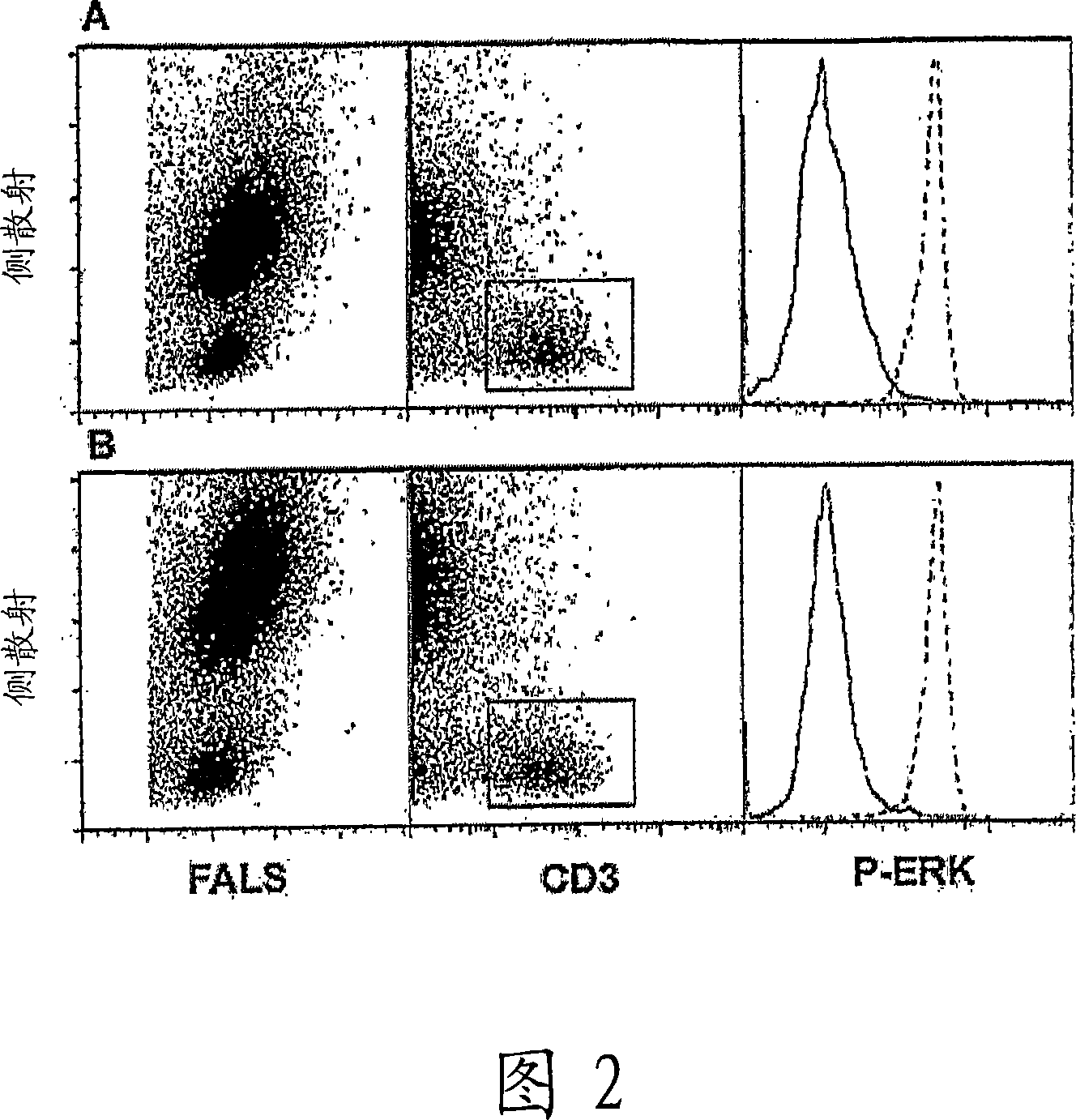
This invention is directed to a method for preparation of a biological sample for measurement of protein epitopes that allows for the preservation of intracellular protein epitopes and detection of signal transduction pathways based on the ability to capture transient activation states of the epitopes. The method provided by the invention allows for the rapid fixation of biological samples containing red blood cells, to ensure that epitopes of signal transduction molecules and other intracellular protein epitopes are preserved in the active state. The method of the invention further allows for lysis of red blood cells, thereby making it a useful method for cytometric analysis of biological samples, including, for example, whole blood, bone marrow aspirates, peritoneal fluids, and other red blood cell containing samples. The invention also provides a method to recover or “unmask” epitopes on intracellular antigens that have been made inaccessible by the cross linking fixative necessary to fix the sample. Significantly, the methods of the invention allow preservation and analysis of phospho-epitope levels in biological samples taken directly from patients to determine disease-specific characteristics.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
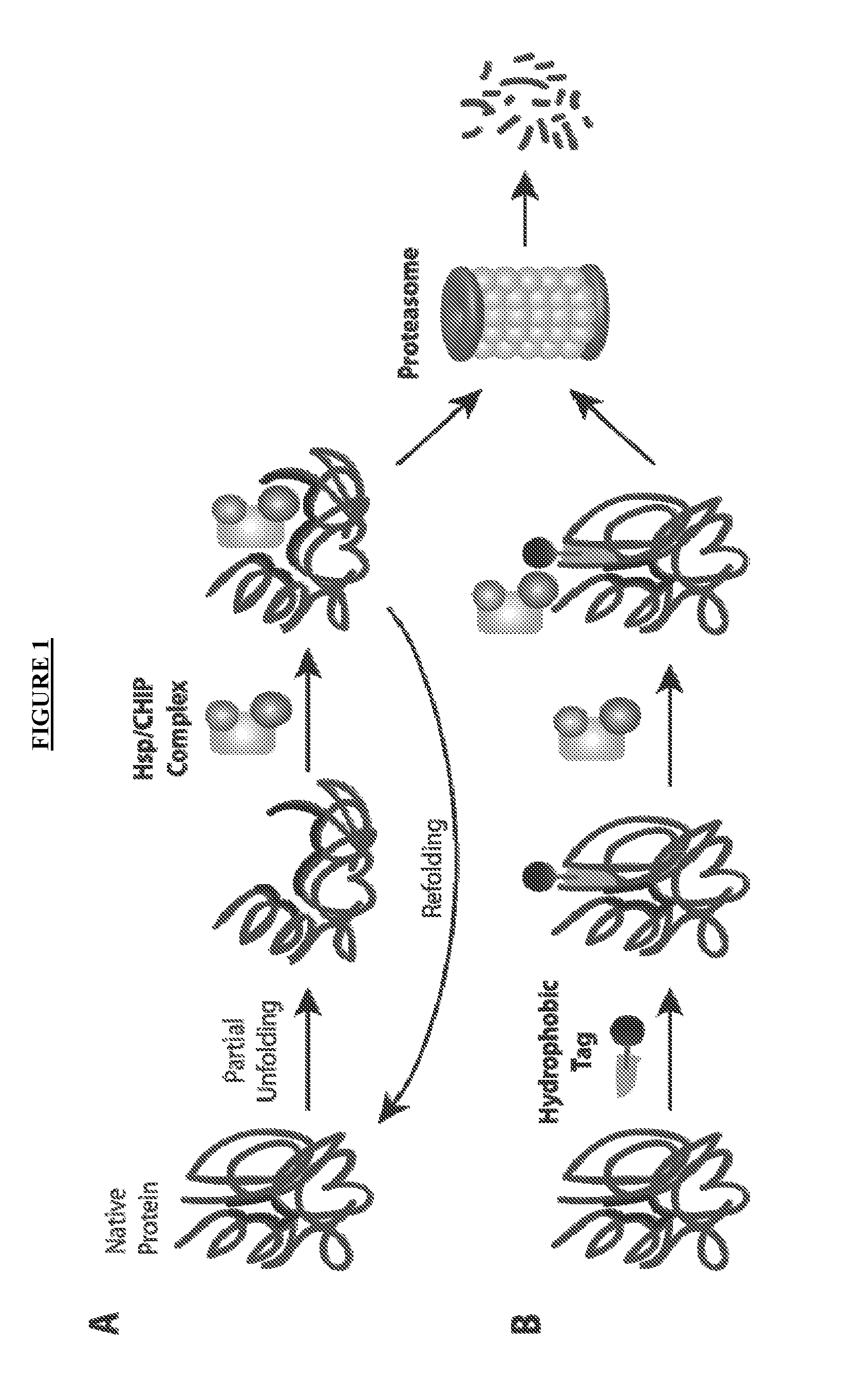
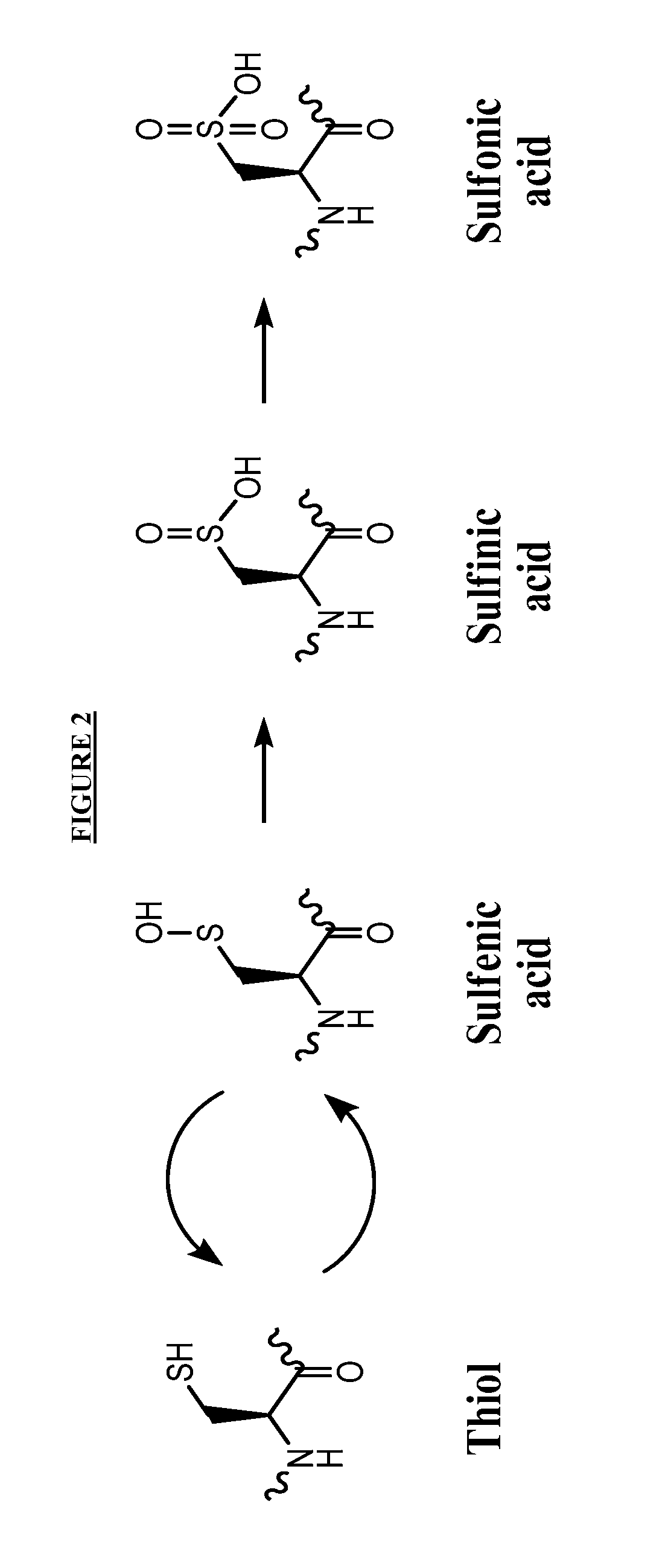
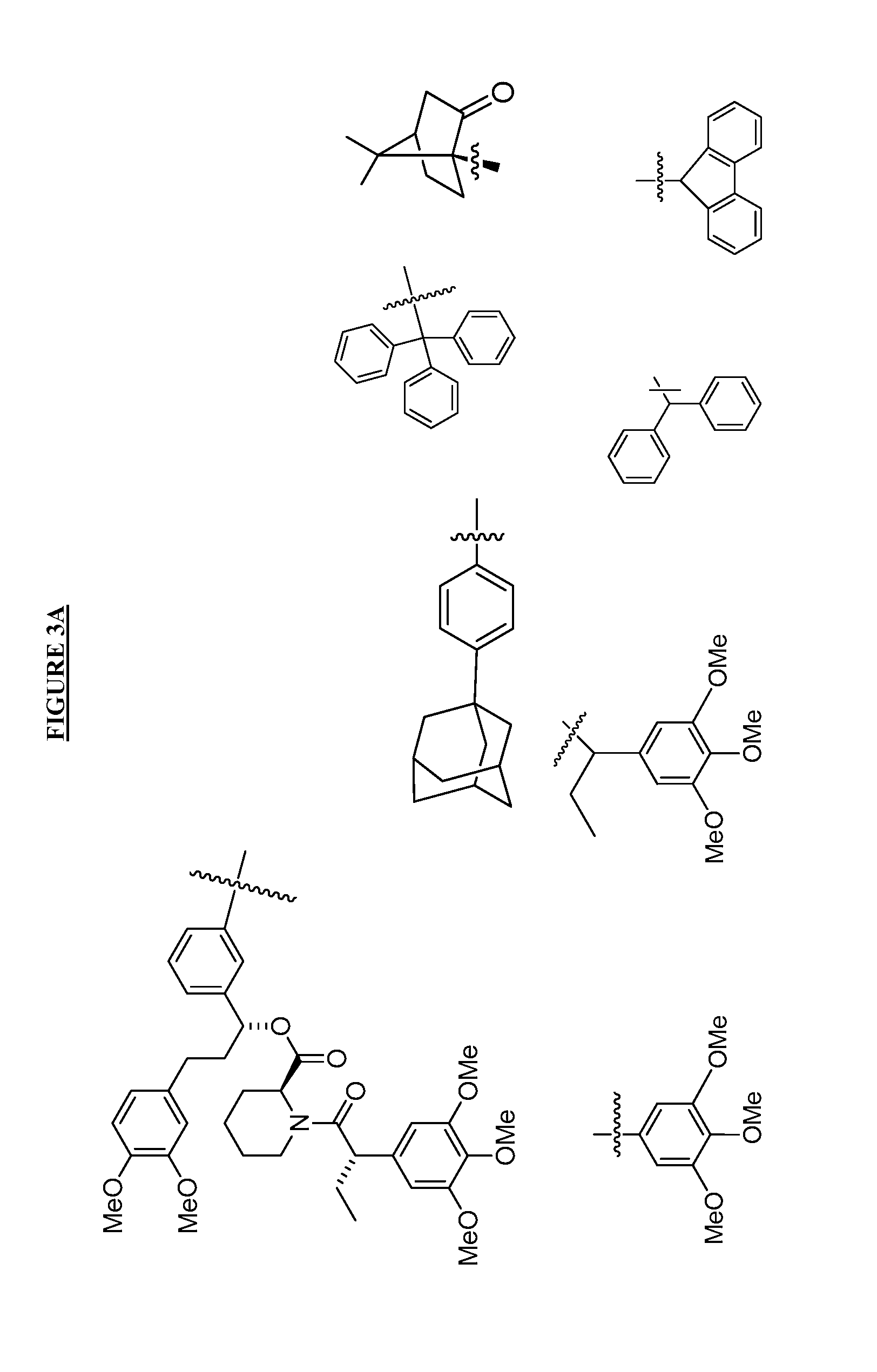
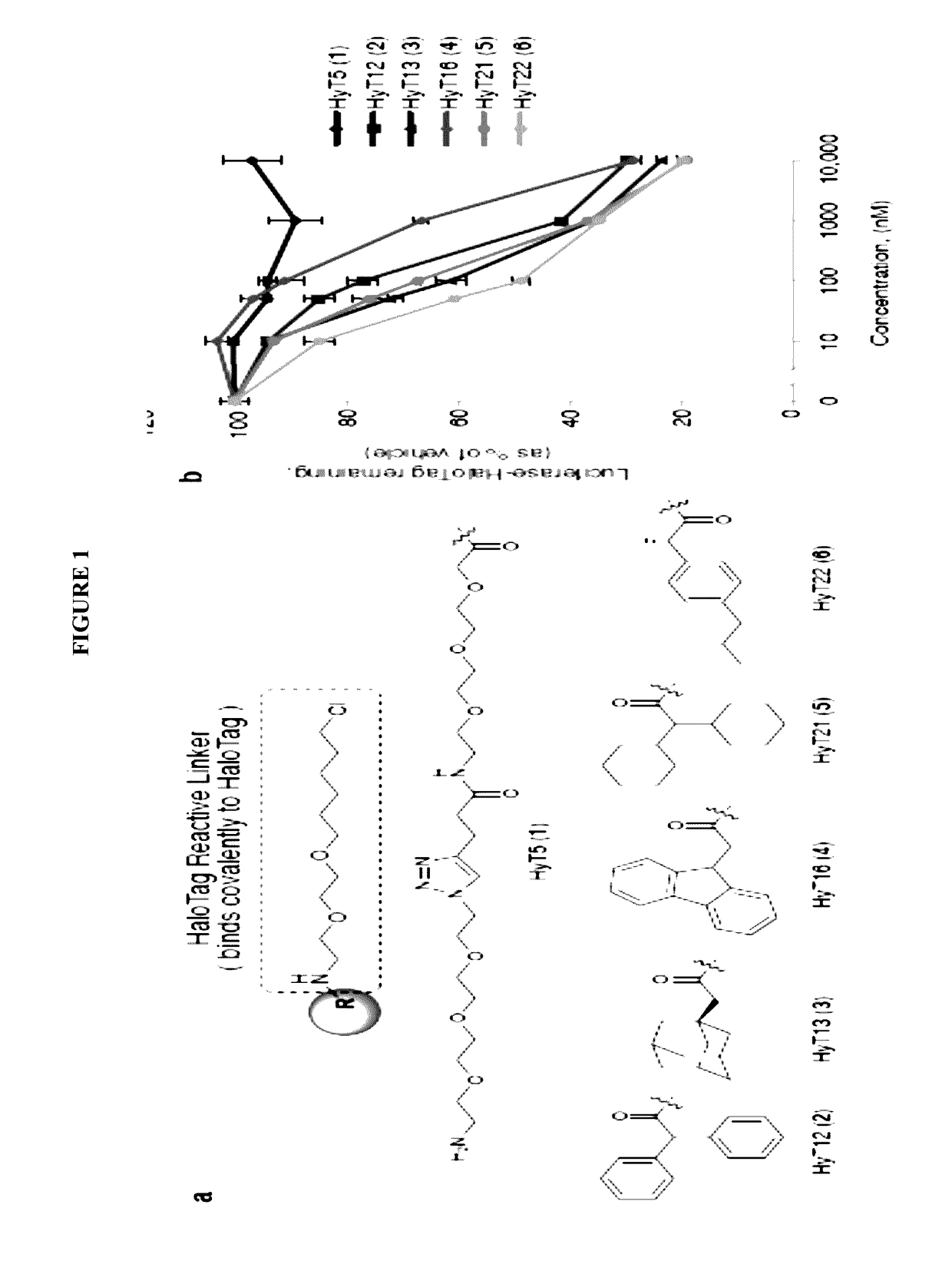
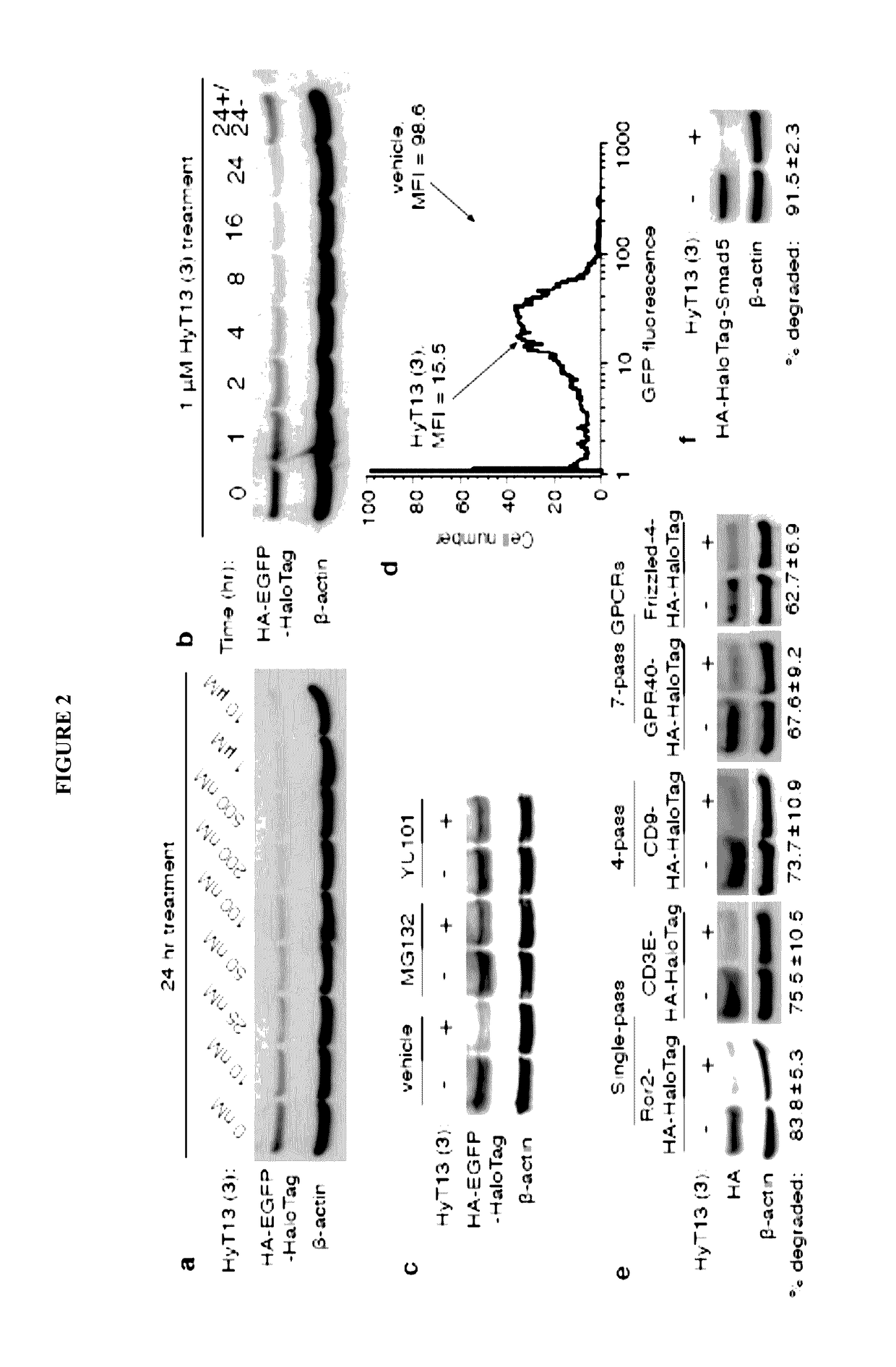
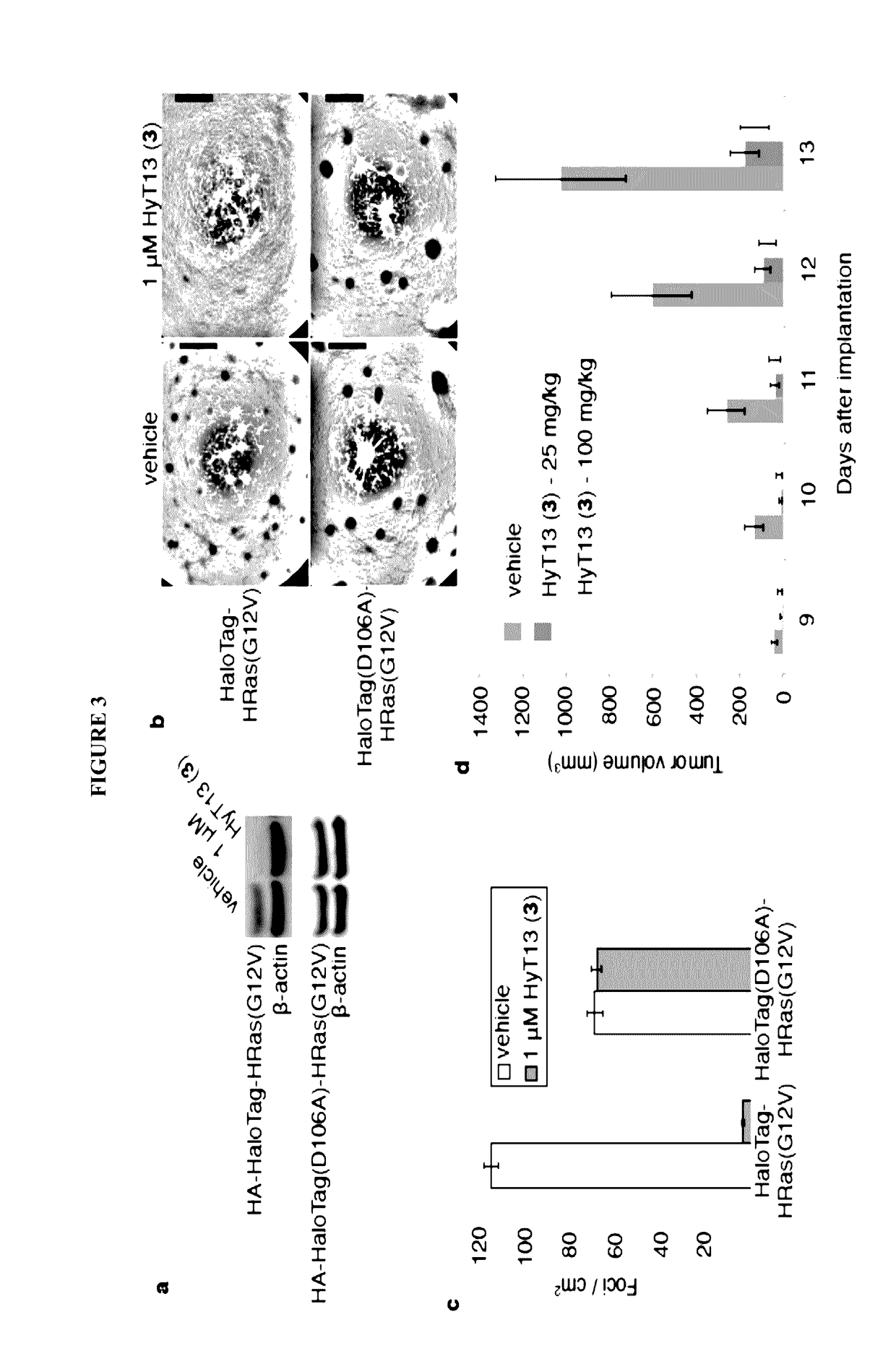
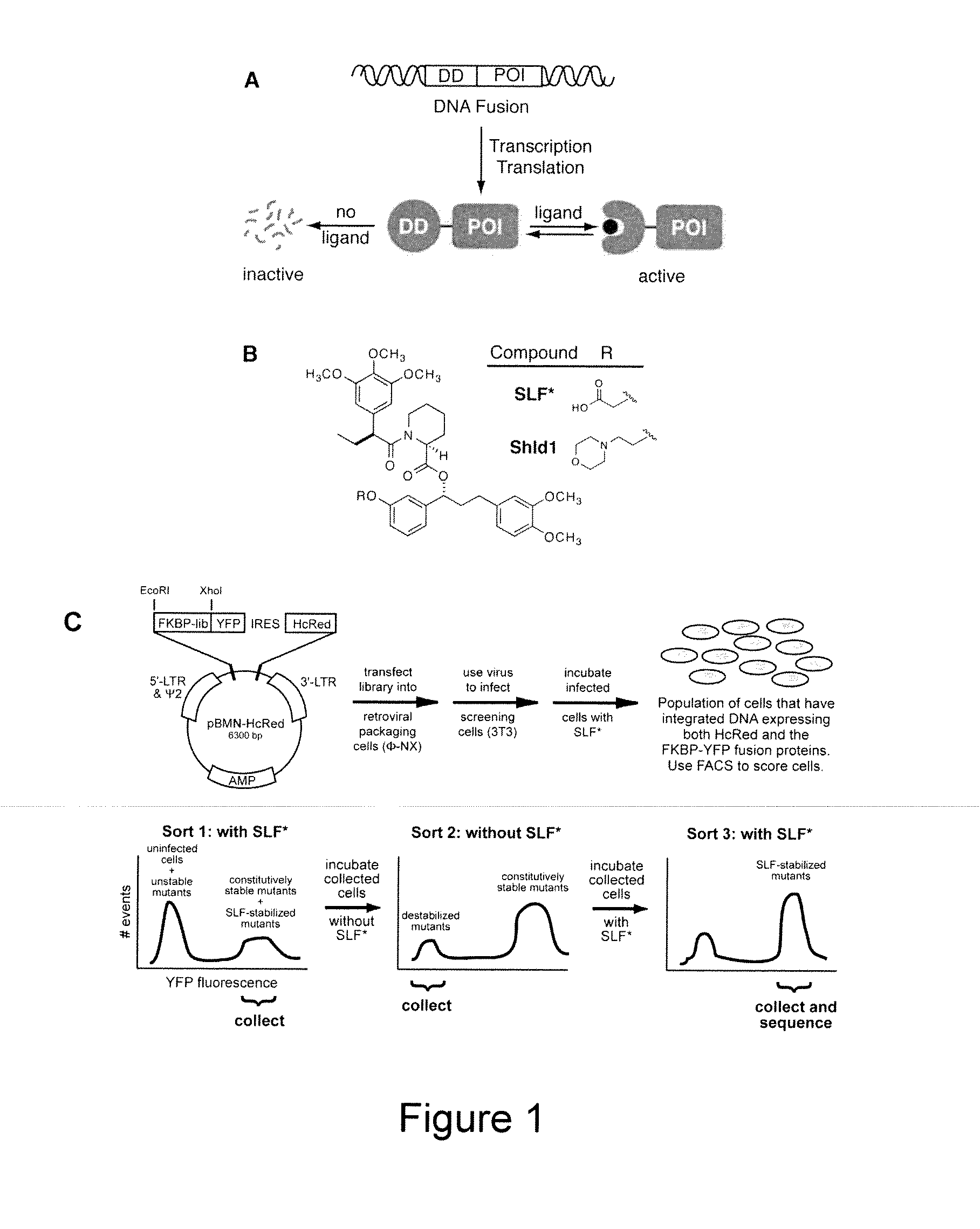
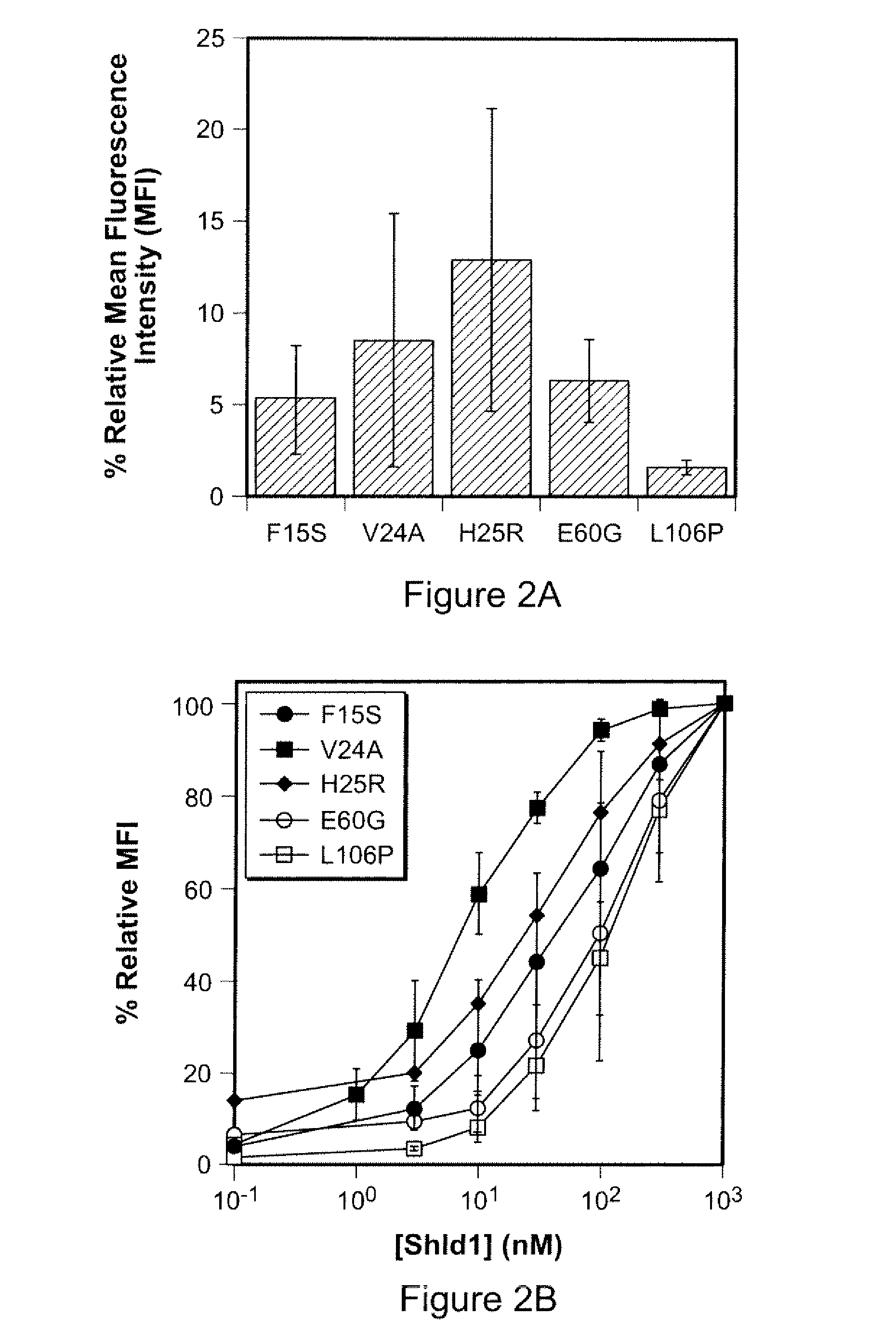
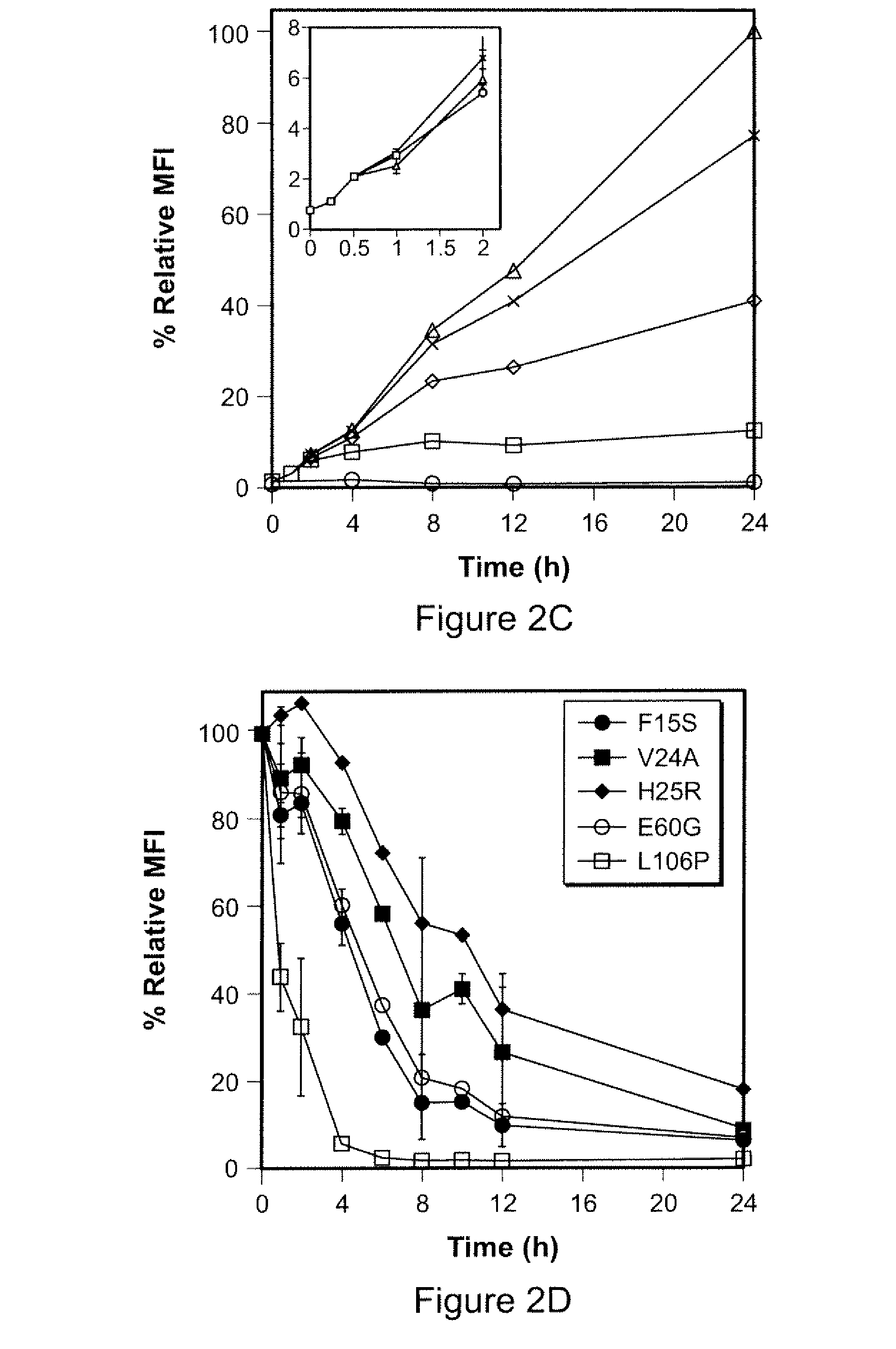
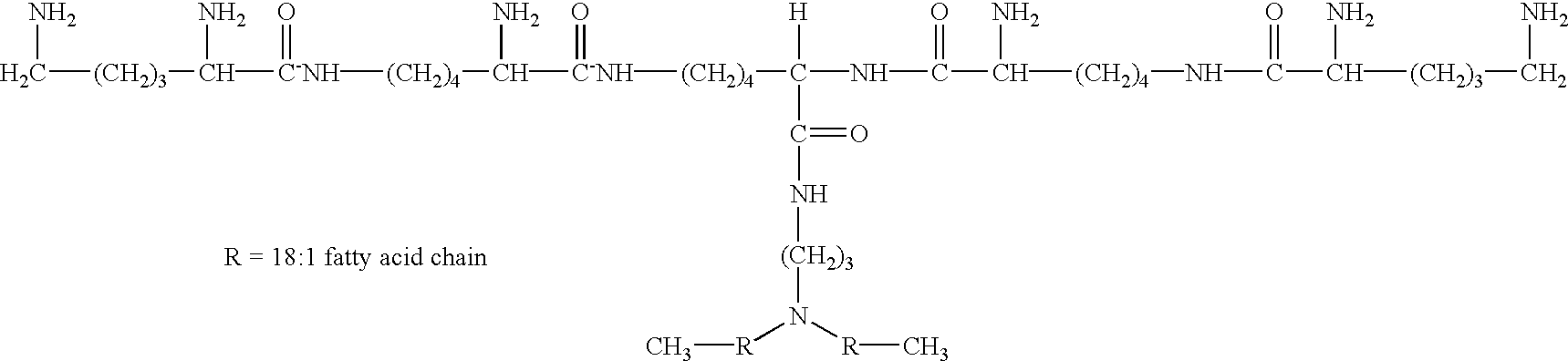
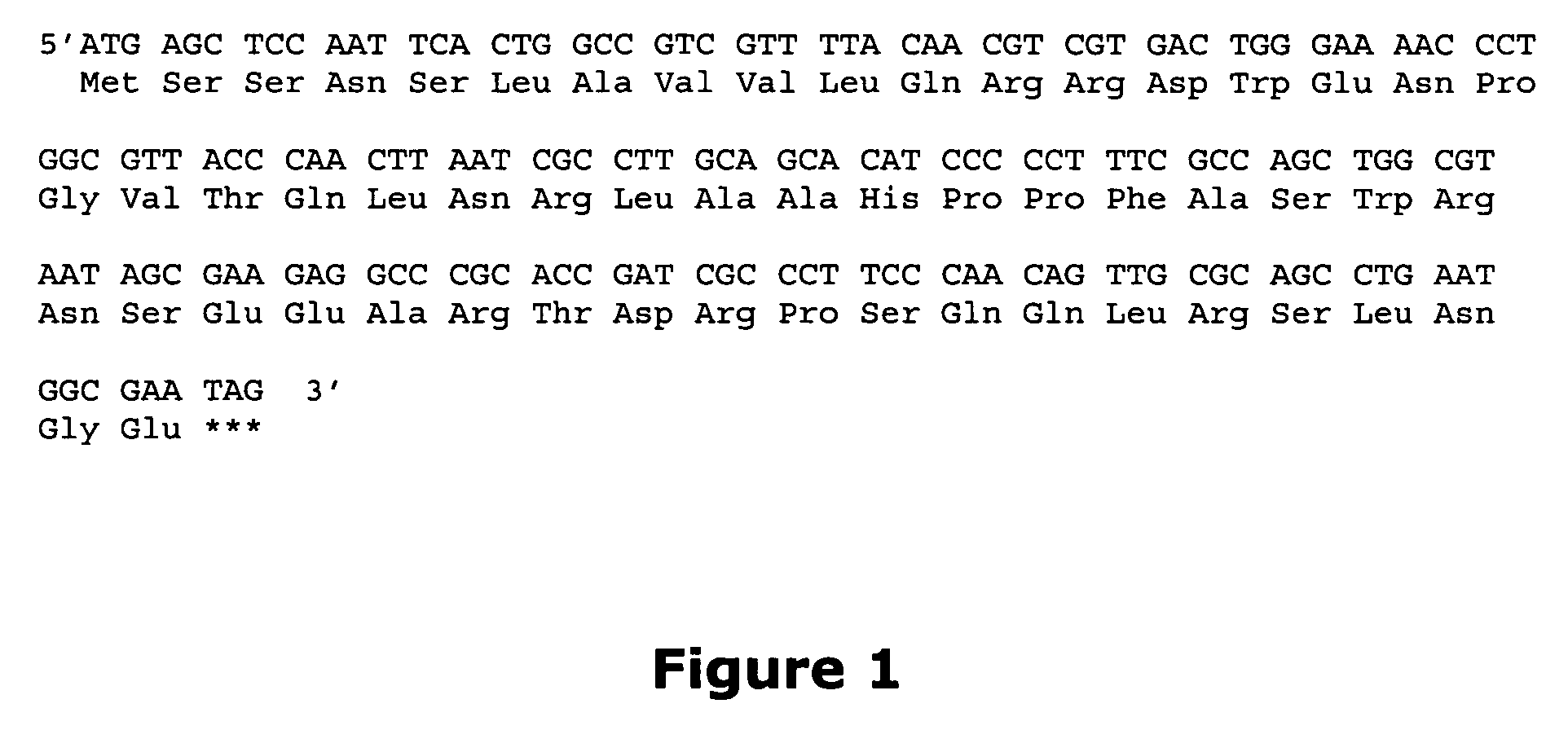
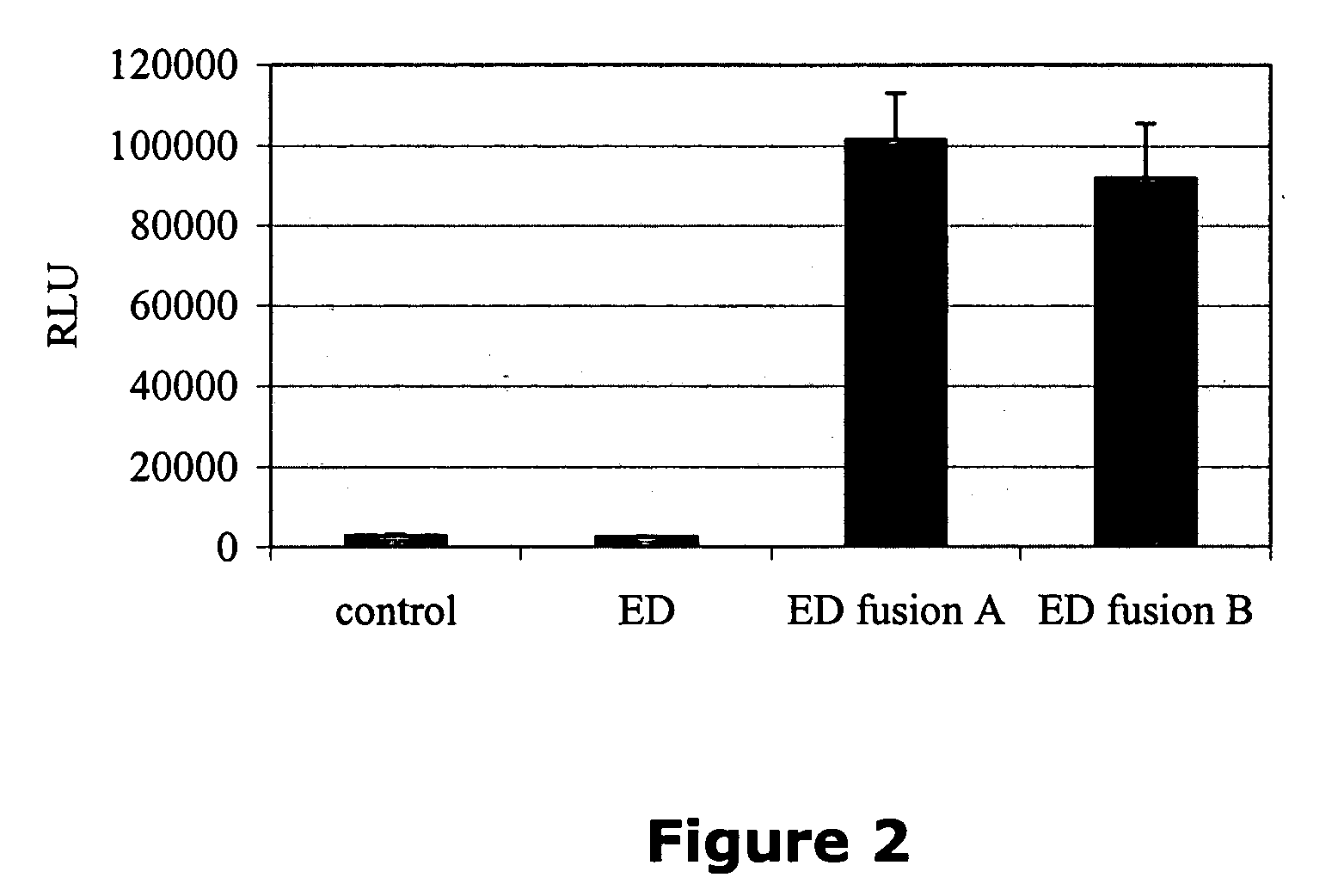
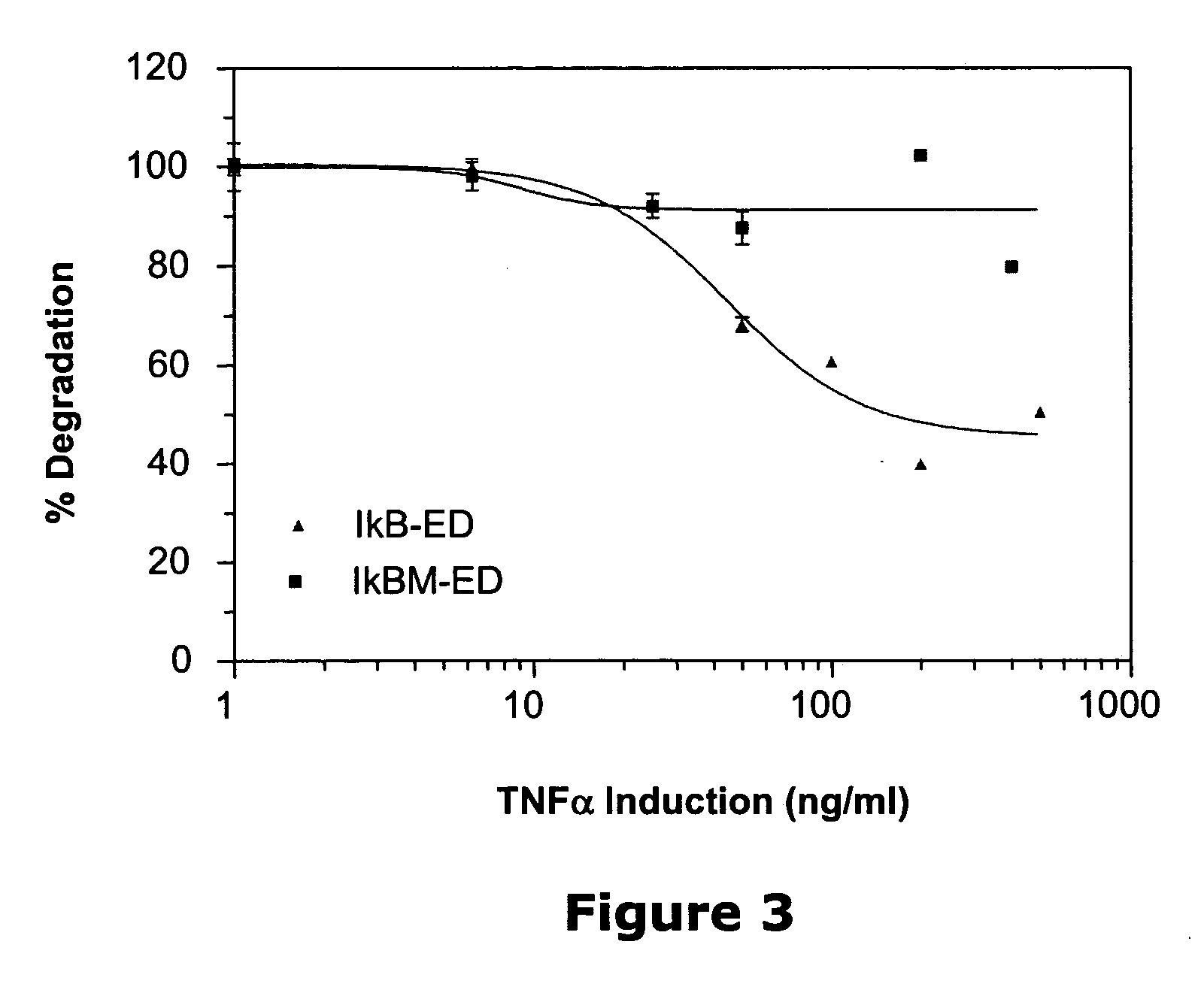
Small-molecule hydrophobic tagging of fusion proteins and induced degradation of same
The present invention includes compounds that are useful in perturbing or disrupting the function of a transmembrane or intracellular protein, whereby binding of the compounds to the transmembrane or intracellular protein induces proteasomal degradation of the transmembrane or intracellular protein. The present invention further includes a method of inducing proteasomal degradation of a transmembrane or intracellular protein. The present invention further includes a method of identifying or validating a protein of interest as a therapeutic target for treatment of a disease state or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
System for detecting protease
InactiveUS7109293B2Suppress viral proliferationDecreased crop yieldCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProteinase activityProtease
Disclosed is a system for detecting a protease inside a cell. In one embodiment, the system includes a chimeric protein that comprises as covalently linked components: 1) at least one optionally masked signal protein; 2) at least one protease-specific cleavage site; and 3) at least one detectable amino acid sequence. The invention has a wide spectrum of applications including use in the detection of novel protease inhibitors inside cells and tissue.
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST
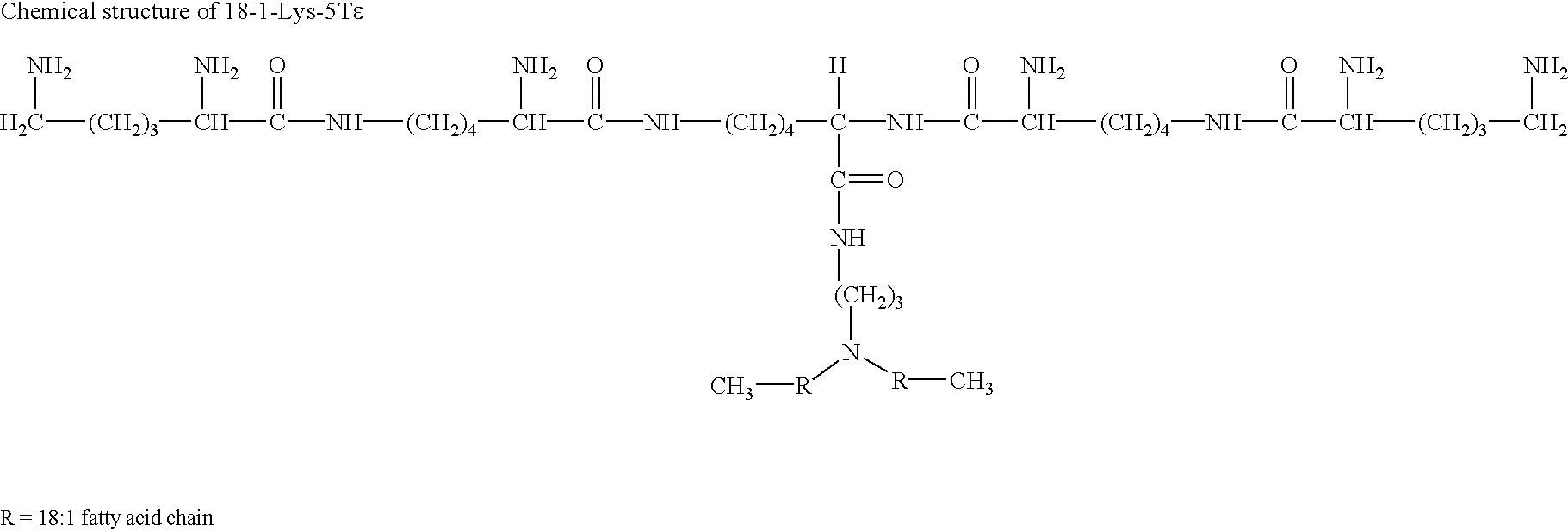
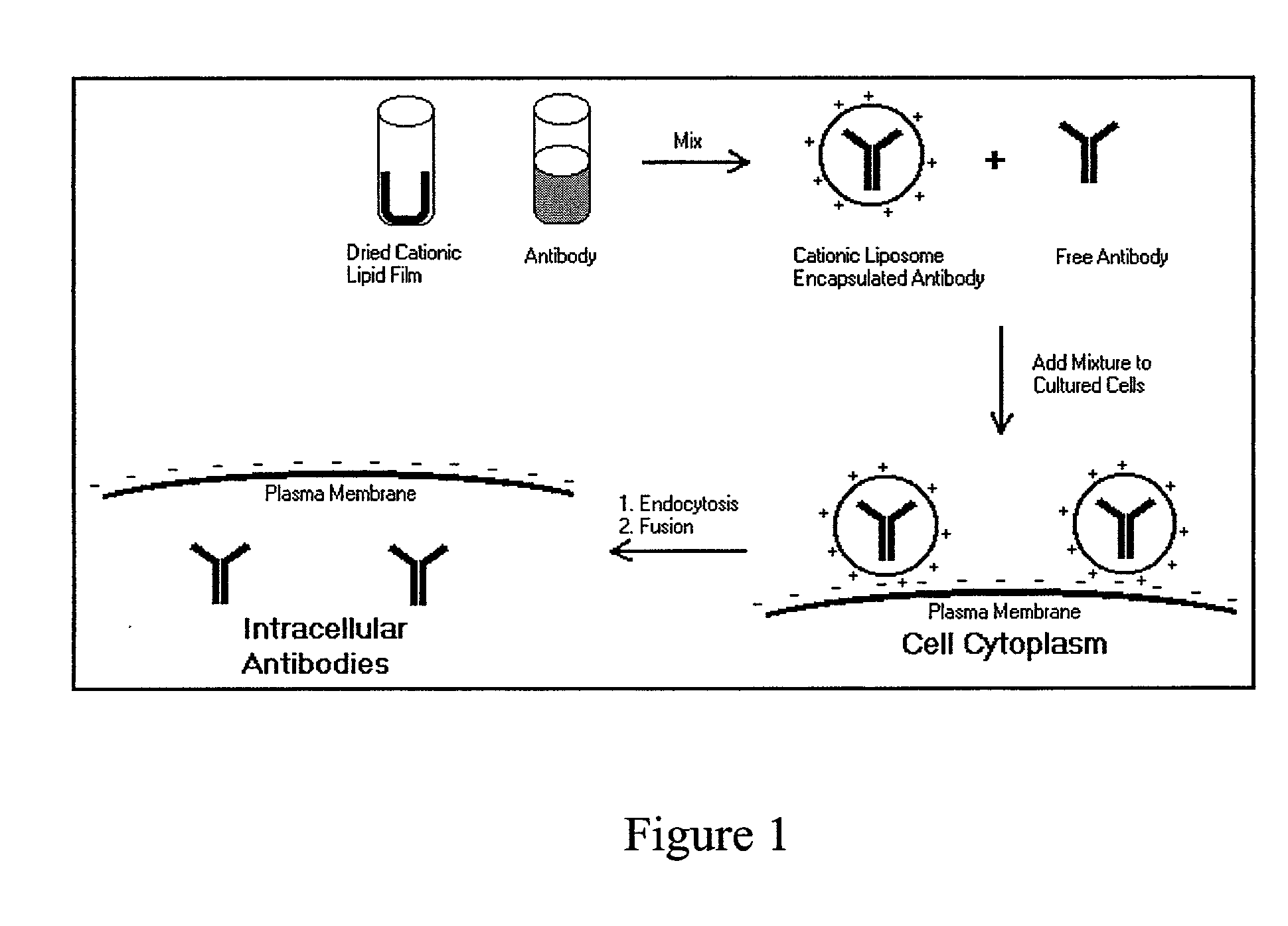
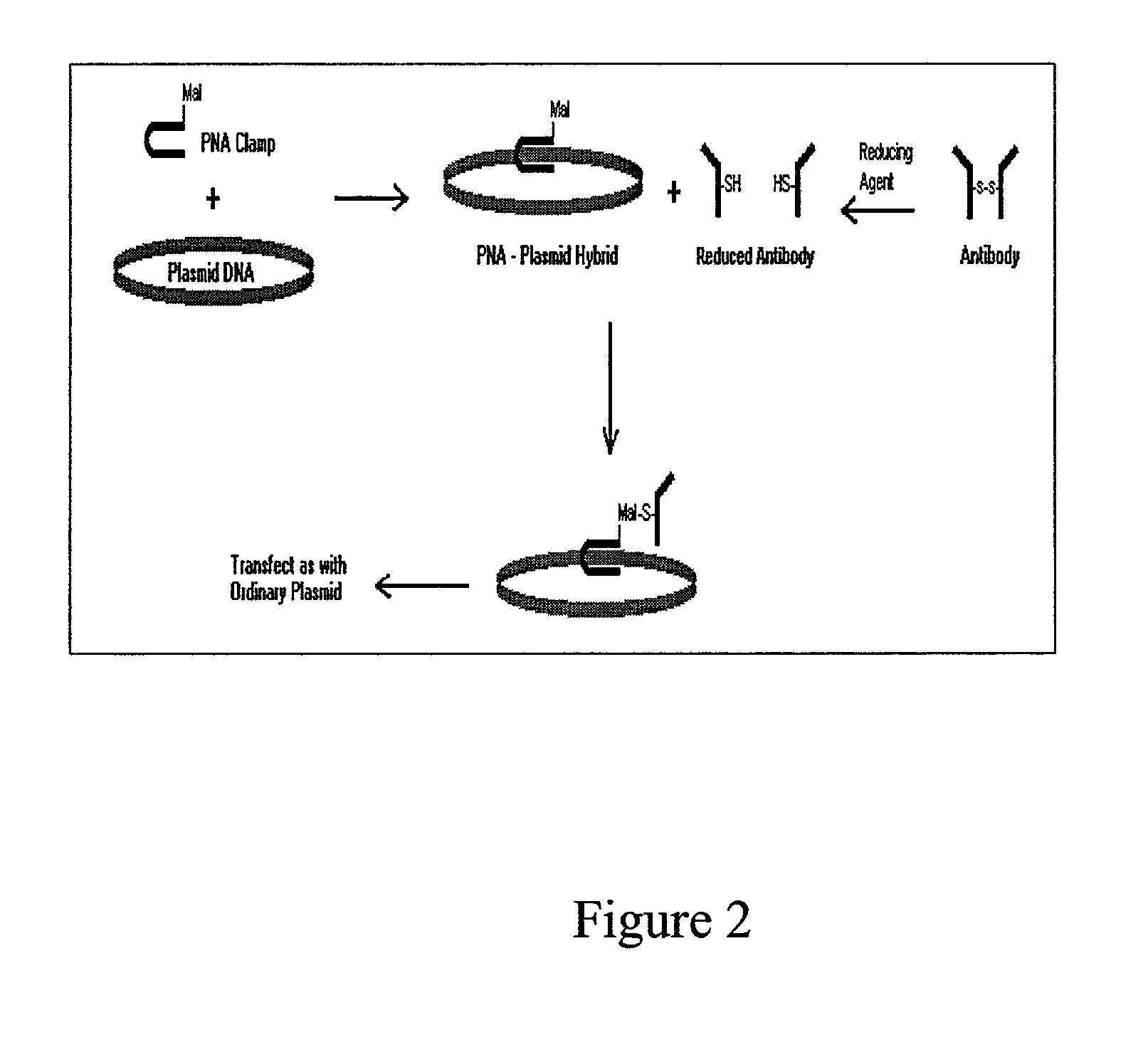
Intracellular protein delivery compositions and methods of use
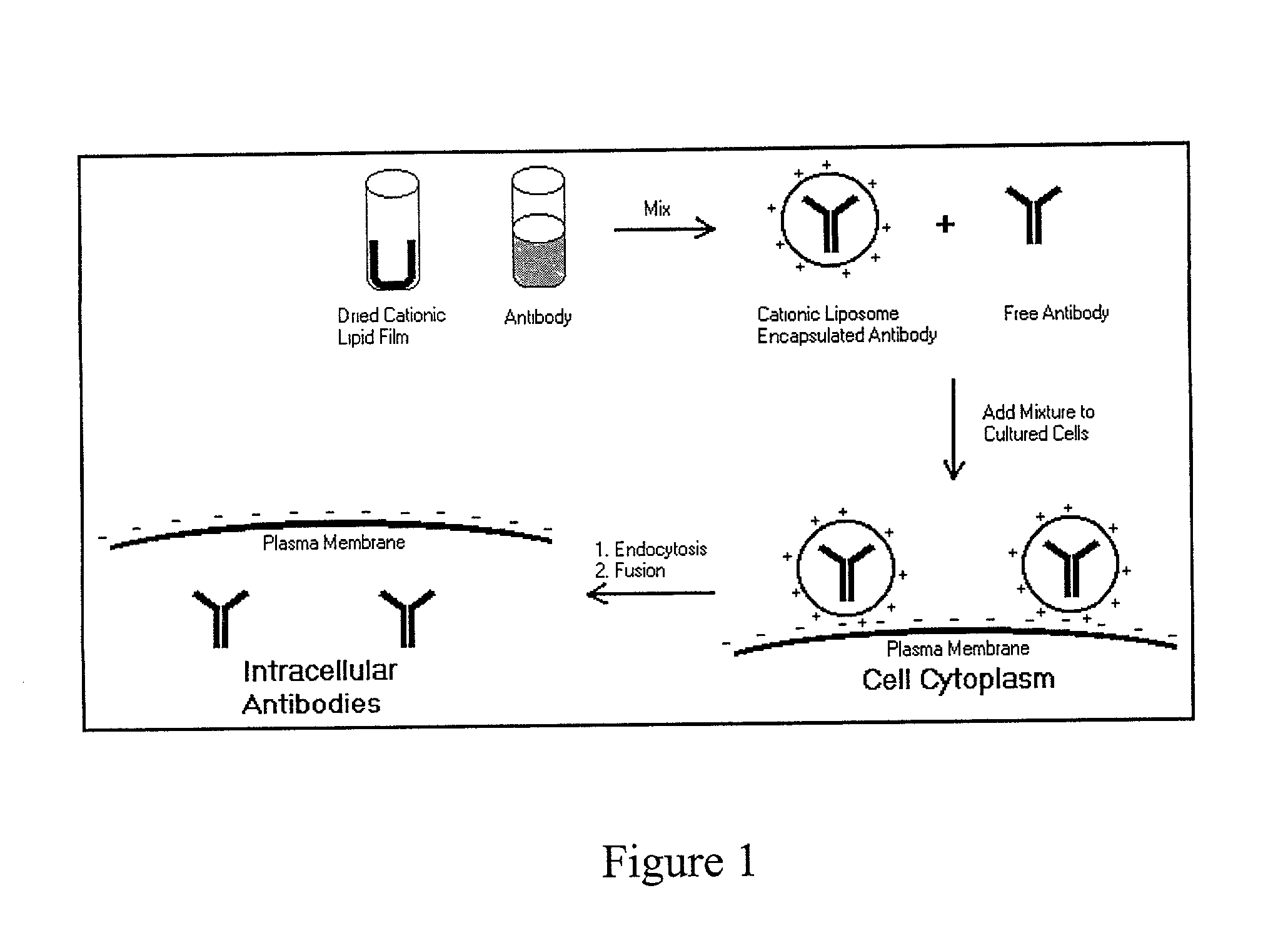
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for intracellular protein delivery. The compositions include a protein operatively associated with a cationic lipid in such a way as to facilitate intracellular delivery of the protein by the cationic lipid, such as by associating directly with a cationic lipid, encapsulating it in a cationic liposome, associating the protein with a lipoplex comprising cationic lipid and nucleic acid, or associating the protein with an anionic polymer that is in association with a cationic lipid. These compositions are useful in delivering antibodies to intracellular proteins to neutralize their activity, and to introduce therapeutically useful proteins, peptides or small molecules.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST
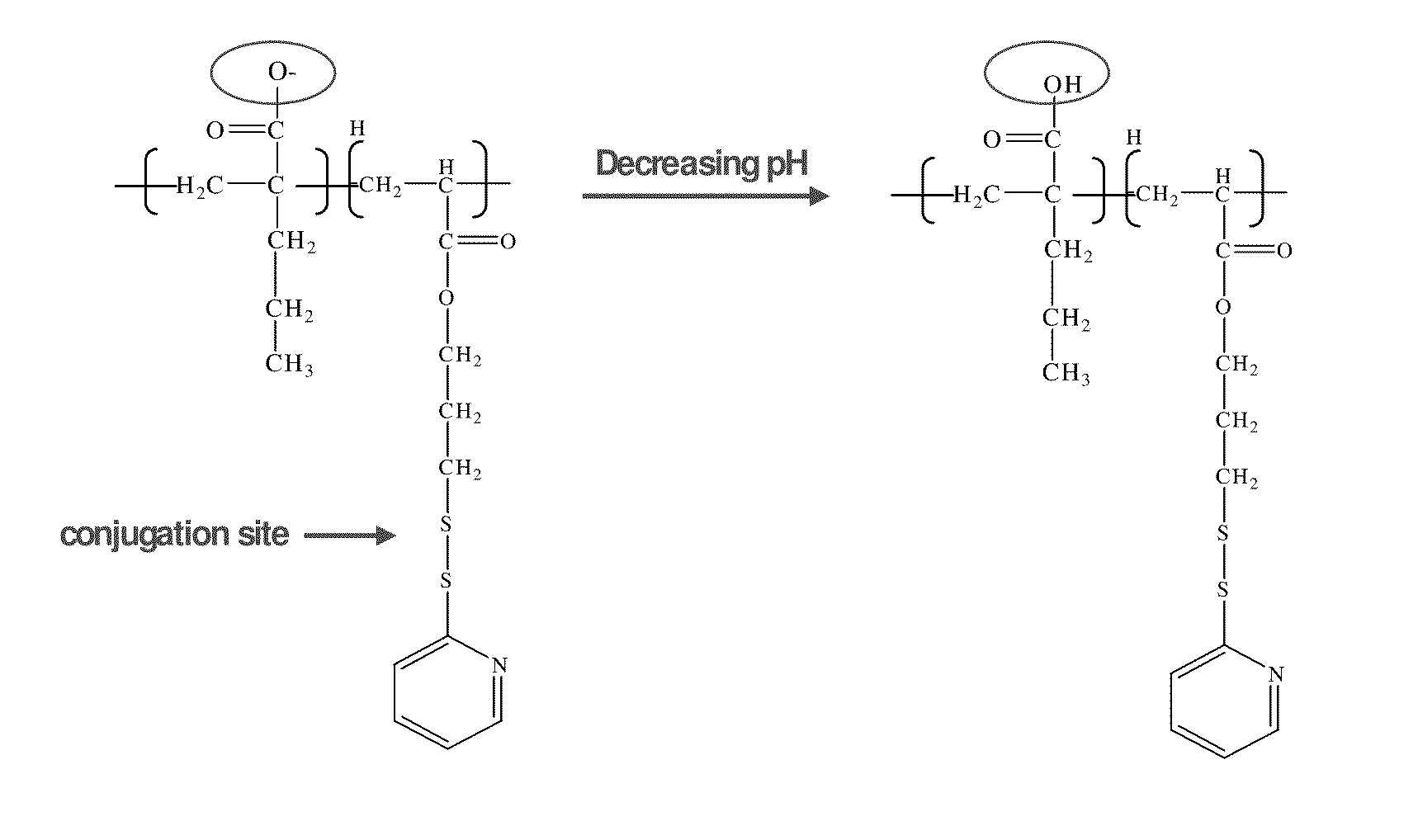
pH-RESPONSIVE POLYMER CARRIER COMPOSITIONS FOR CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN DELIVERY
InactiveUS20100150952A1Amount of remainedIncrease volumeCancer antigen ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsAntigen deliveryLymphocyte
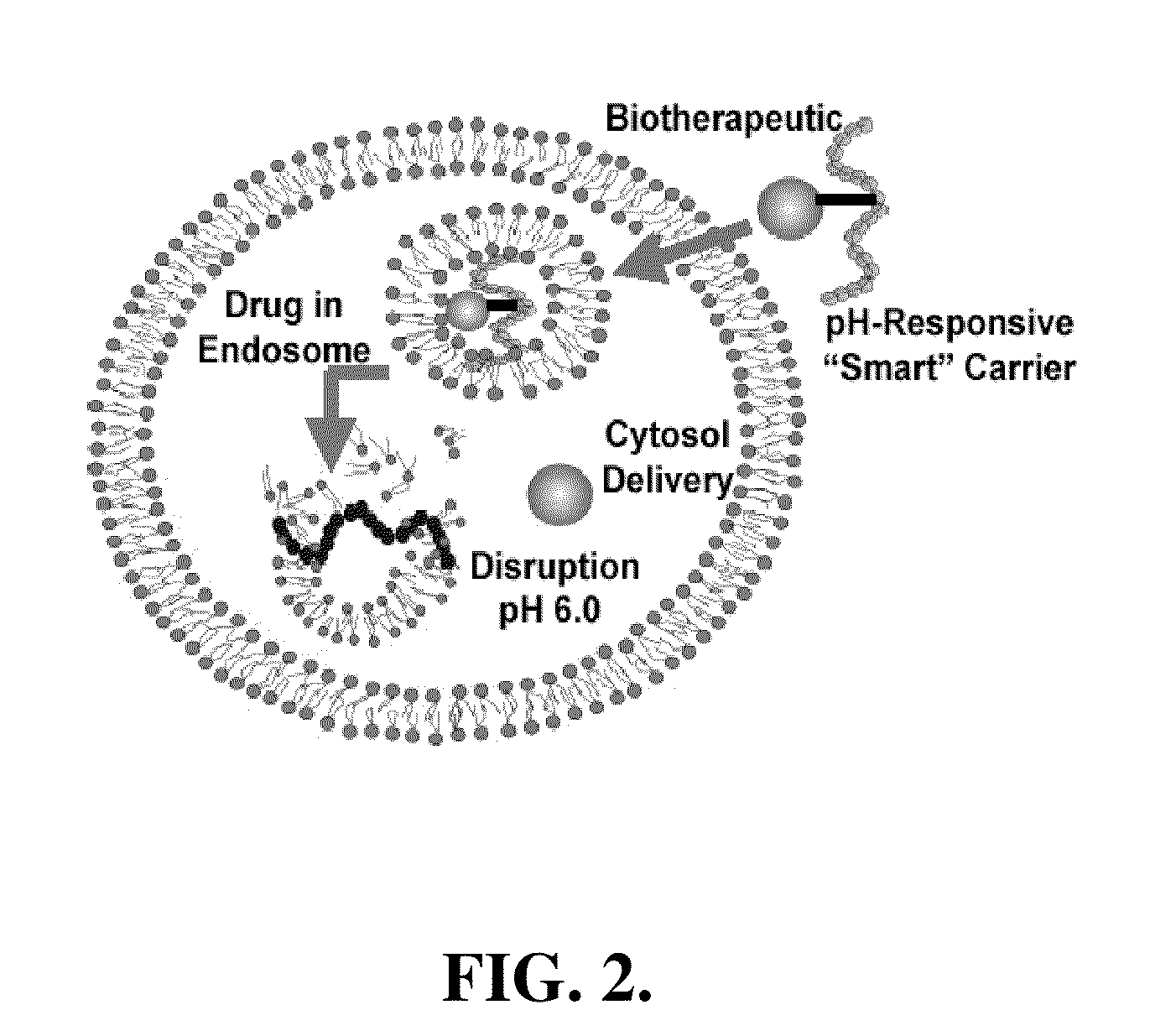
pH-Responsive polymer-based protein delivery carriers and compositions, methods for making the carriers and compositions, and methods for using the carriers and compositions for intracellular protein antigen delivery, inducing a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response, introducing a tumor-specific protein antigen to an antigen presenting cell to induce an immune response, and providing tumor protection to a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method and device for protein delivery into cells
InactiveUS7105347B2Reduce deliveryImprove delivery efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVolumetric Mass DensityCell cluster
Owner:CORNING INC
Microbial strains and processes for the manufacture of biomaterials
InactiveUS20090226962A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCell culture media
DNA constructs and genetically engineered microbial strains constructed using these DNA constructs, which produce a nuclease enzyme with specificity for DNA and / or RNA, are provided. These strains secrete nuclease into the periplasm or growth medium in an amount effective to enhance productivity and / or recovery of polymer, and are particularly suited for use in high cell density fermentation processes. These constructs are useful for modifying microbial strains to improve production and recovery processes for polymers such as intracellular proteins, such as enzymes, growth factors, and cytokines; for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates; and for producing extracellular polysaccharides, such as xanthan gum, alginates, gellan gum, zooglan, hyaluronic acid and microbial cellulose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Use of apotosis inhibiting compounds in degenerative neurological disorders
The invention provides methods and compositions for localized delivery of a vector comprising a therapeutic agent to a specific region of the brain associated with a neurodegenerative diseases that is characterized by an excess buildup of buildup of intracellular protein aggregates. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions used to deliver an adeno-associated virus vector (AAV) comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding an inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) to cells in the region.
Owner:MEIRAGTX UK II LTD
Analytical method for researching protein structure or protein-protein interaction
ActiveCN107525842ARich varietySimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein containing complexHydrolysate
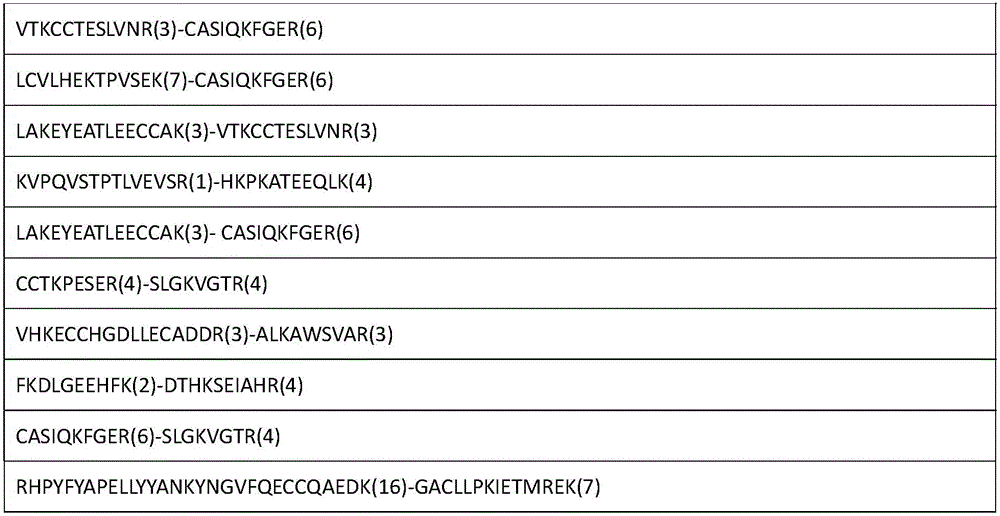
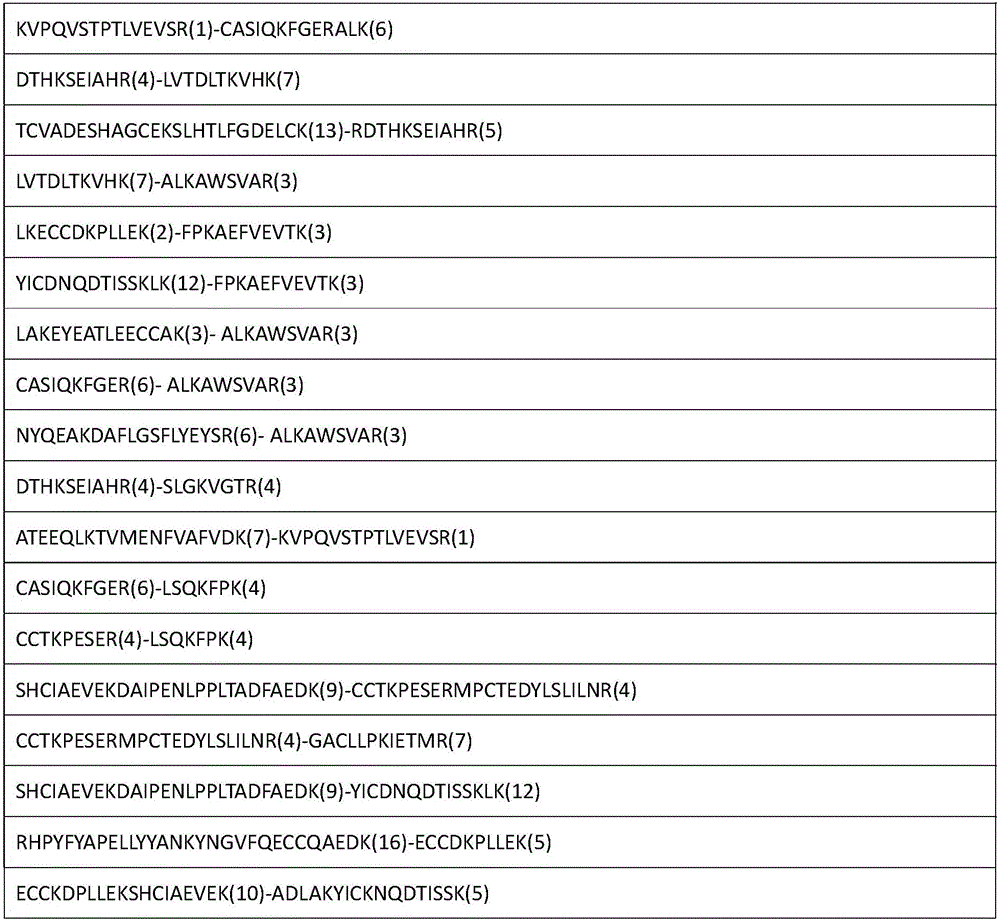
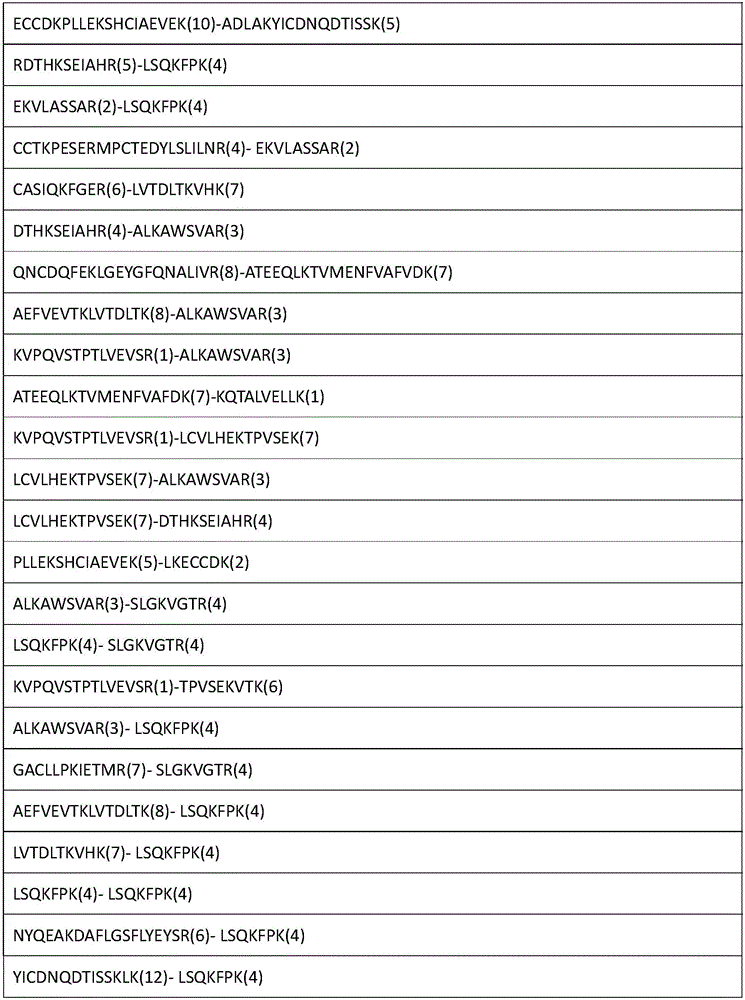
The invention relates to an analytical method for researching protein structure or protein-protein interaction. The method comprises the following steps: performing crosslinking and enzymolysis on a protein composite in a cell by using a crosslinking agent with reactive groups on two sides and a breakable group, and taking a part of the enzymatic hydrolysate for a derivatization reaction for mass spectrometry; after breaking the crosslinking agent by means of a chemical method for the other part of the enzymatic hydrolysate, enriching peptide sections with an enriching material, and performing mass spectrometry on the enzymatic hydrolysate without the enriched peptide sections; determining the crosslinked peptide sections according to a library searching result so as to establish a peptide section library; finding out a candidate peptide section from the peptide section library according to N-terminal amino acid information of the crosslinked peptide section determined in the mass spectrogram of the crosslinked peptide section; and determining the crosslinked peptide section sequence by combining the mass spectrogram m / z of the crosslinked peptide section and the characteristic ions of the peptide section so as to obtain the protein structure and protein-protein interaction information. The method has the advantage of being simple to operate, and is applied to structural analysis of proteins and analysis of protein-protein composite interaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
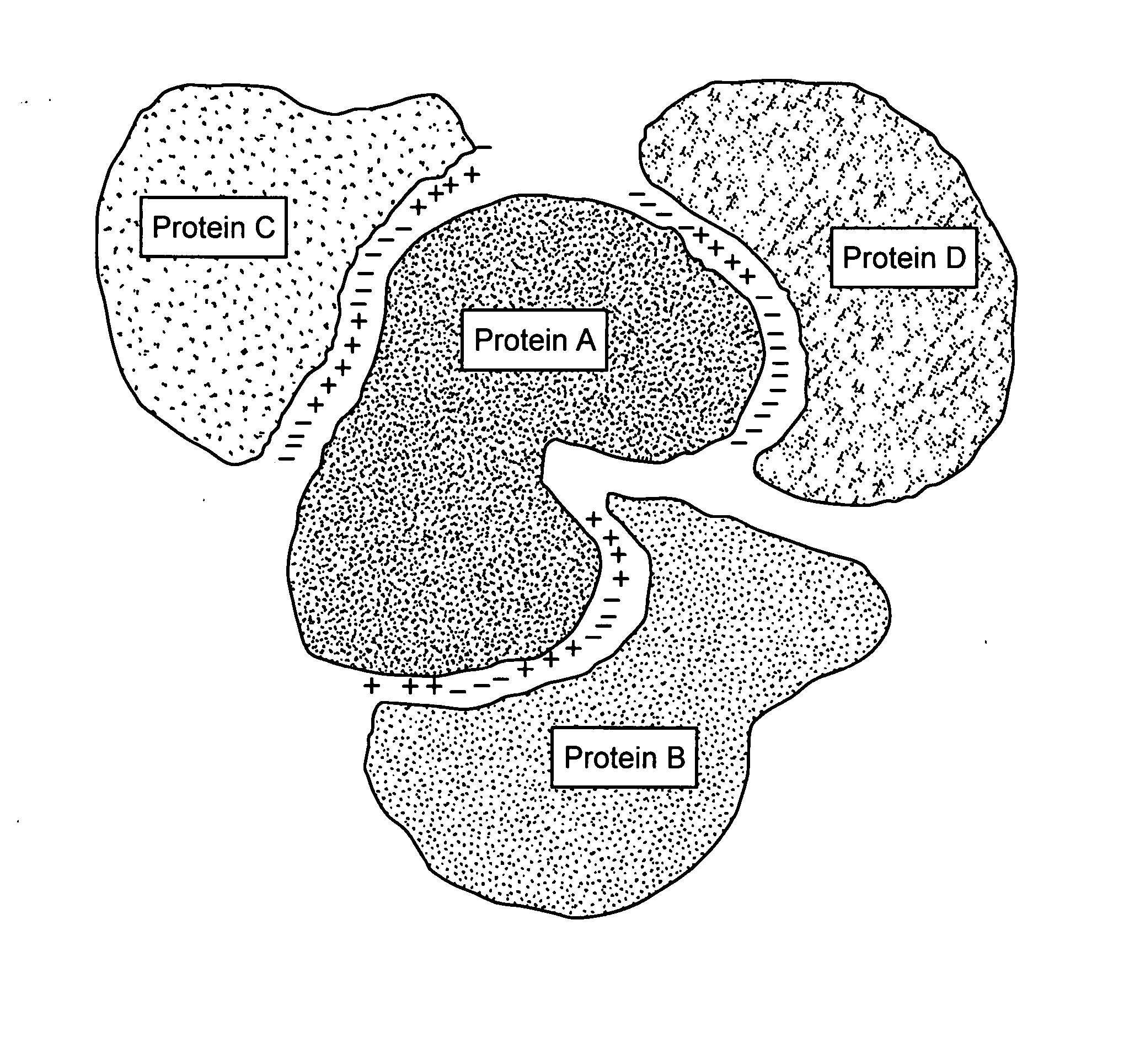
Protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction
InactiveUS20080009068A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLibrary screeningBiologyHigh affinity binding
The invention relates to protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction. Using overlapping hexapeptides that encode for the entire amino acid sequences of the linker domains of human P-glycoprotein gene 1 and 3 (HP-gp1 and HP-gp3), a direct and specific binding between HP-gp1 and 3 linker domains and intracellular proteins was demonstrated. Three different stretches (617EKGIYFKLVTM627, (SEQ ID NO: 1) 658SRSSLIRKRSTRRSVRGSQA677 (SEQ ID NO: 2) and 694PVSFWRIMKLNLT706 (SEQ ID NO: 3) for HP-gp1 and 618LMKKEGVYFKLVNM631 (SEQ ID NO: 4), 648KAATRMAPNGWKSRLFRHSTQKNLKNS674 (SEQ ID NO: 5), and 695PVSFLKVLKLNKT707 (SEQ ID NO: 6) for HP-gp3) in linker domains bound to proteins with apparent molecular masses of ˜80 kDa, 57 kDa and 30 kDa. The binding of the 57 kDa protein was further characterized. Purification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequencing of the 57 kDa protein showed that it encodes the N-terminal amino acids of alpha and beta-tubulins. The method of the present invention was further validated with Annexin. The present invention thus demonstrates a novel concept whereby the interactions between two proteins are mediated by strings of few amino acids with high and repulsive binding energies, enabling the identification of high affinity binding sites between any interacting proteins.
Owner:GEORGES ELIAS
Microfluidic chip and single cell protein quantitative detection device and method
InactiveCN107064091ARealize high-throughput quantitative detectionAvoid the impact of test resultsLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingFluorescenceSingle-cell protein
The invention provides a microfluidic chip and a single cell protein quantitative detection device and method. The chip is composed of a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) layer and a quartz layer; a microfluidic chip technology is combined with a liquid drop formation technology, a fluorescence antibody preparation technology and a fluorescence detection technology and then high-throughput quantitative detection of proteins in single cells is realized; reliable device and method are provided for characterization of cell biological characteristics. By designing and manufacturing a fluorescence antibody pair and setting an optical filter, the detection precision can be effectively improved and detection errors are reduced. Equipment including an inverted fluorescent microscope, a photomultiplier and the like can be used in a traditional biological laboratory, so that the device and the method have strong adaptability and high portability and are convenient to realize.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Pharmacokinetics of protease inhibitors and other drugs
A method for modulating at least one pharmacokinetic property of a protease inhibitor upon administration to a host is provided. One administers to the host an effective amount of a bifunctional compound of less than about 5000 daltons comprising the protease inhibitor or an active derivative thereof and a pharmacokinetic modulating moiety. The pharmacokinetic modulating moiety binds to at least one intracellular protein. The bifunctional compound has at least one modulated pharmacokinetic property upon administration to the host as compared to a free drug control that comprises the protease inhibitor.
Owner:AMPLYX PHARMA INC
Method for Regulating Protein Function in Cells In Vivo Using Synthetic Small Molecules
ActiveUS20100034777A1Improve survivalInhibit tumor growthBiocideOrganic active ingredientsIn vivoProtein function
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Intracellular protein delivery compositions and methods of use
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for intracellular protein delivery. The compositions include a protein operatively associated with a cationic lipid in such a way as to facilitate intracellular delivery of the protein by the cationic lipid, such as by associating directly with a cationic lipid, encapsulating it in a cationic liposome, associating the protein with a lipoplex comprising cationic lipid and nucleic acid, or associating the protein with an anionic polymer that is in association with a cationic lipid. These compositions are useful in delivering antibodies to intracellular proteins to neutralize their activity, and to introduce therapeutically useful proteins, peptides or small molecules.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST
Cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use
ActiveUS20060178294A1Improve breathabilityProcess stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLow ionic strengthSulfate
A cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use are disclosed. The reagent contains a N-acyl sarcosine or a salt thereof, a pH adjusting agent to adjust pH of the reagent in a range from about 4 to about 6; and an aqueous medium; the reagent having a low ionic strength defined by a conductivity of less than 9.0 mS / cm. The reagent further contains bovine serum albumin and glycerol. The reagent may further include an alkyl sulfate surfactant. Upon incubating the cells with the reagent, the reagent permeates the cellular membrane to allow penetration of an intracellular marker, causes intracellular protein aggregation within the cellular membrane, while preserves a cellular constituent for binding with a cellular marker for subsequent analysis by flow cytometry.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Monitoring intracellular proteins
InactiveUS20040137480A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein insertionBeta-galactosidase activity
Methods and compositions are provided for analyzing intracellular events employing fusion proteins comprising the small beta-galactosidase fragment fused to a protein of interest or fragment thereof. By expressing the fusion protein in a cellular host, one can determine the effect of various agents on the activity of the fusion protein, adding the large beta-galactosidase fragment to the fusion protein, either intracellularly or in a lysate and determining the activity of the formed beta-galactosidase using a substrate that forms a detectable product. In this manner, degradation, complex formation, RNAi inhibition or other situation that affects beta-galactosidase activity can be determined.
Owner:DISCOVERX INC
Fluorescent probe for intracellular protein labelling as well as synthesis method and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN108069967ASimple stepsEasy to purifyOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceSynthesis methods
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for intracellular protein labelling as well as a synthesis method and an application of the fluorescent probe. The provided probe is synthesized in simple steps and has good light stability. Compared with existing fluorescent probes for cell labeling, the probe can be specifically bound with SNAP labels in a complicated system and label any protein in cells. The probe can be applied to detection of copper ions in the cells, fluorescence gradually disappears with increase of the concentration of the copper ions, and the copper ion detection function isrealized. The probe realizes labeling of any protein and detection of the copper ions in the complicated environment and has very important application value in the biological and medical fields.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein
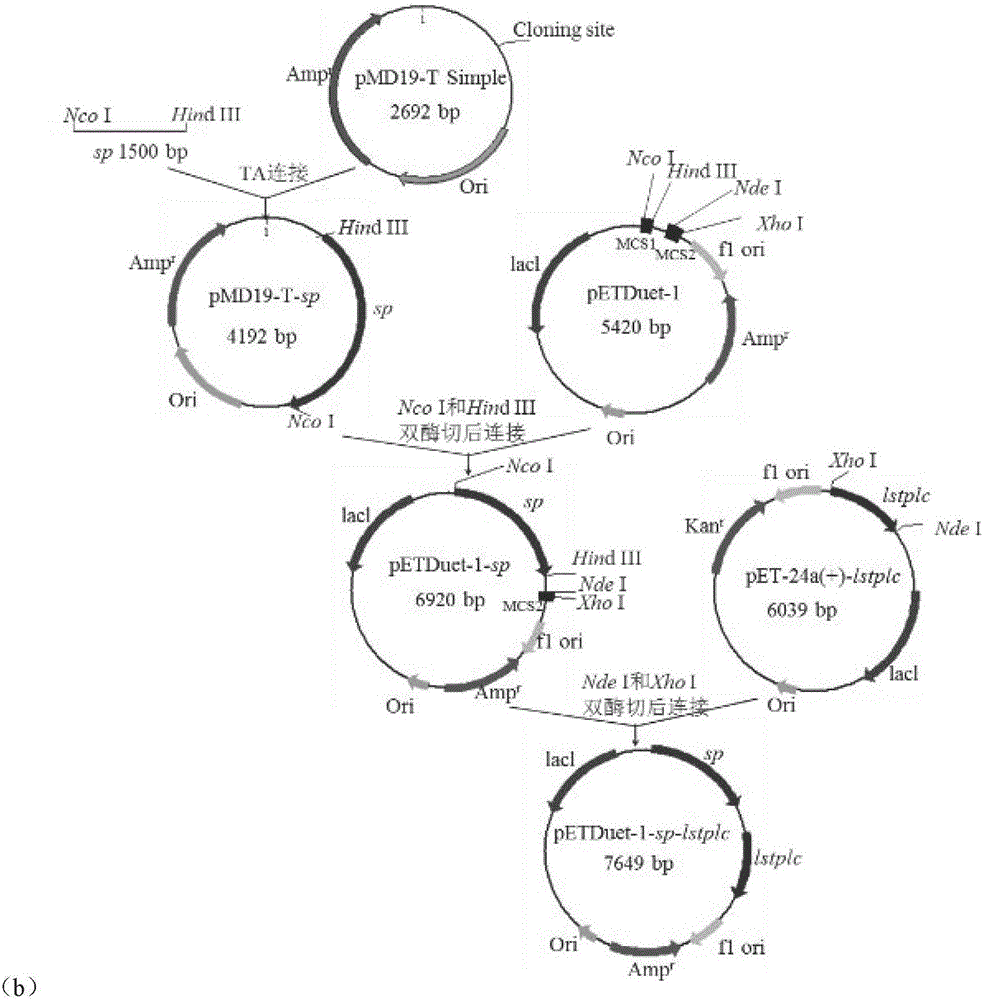
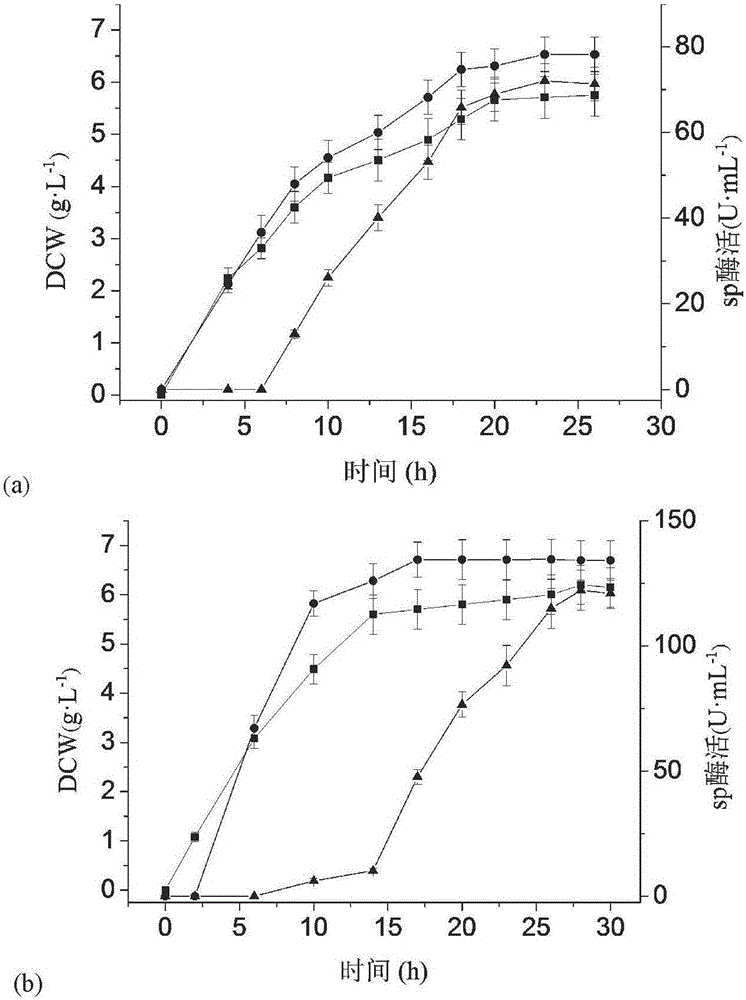
PendingCN106754601ALarge domestic and foreign market demandImprove permeabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellularProtein target
The invention discloses a method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Through co-expression phospholipase C, intracellular positioning protein is released to the outsides of cells by means of nonspecific leaking, and high-performance phospholipase C and co-expression recombinant bacteria high in target protein extracellular enzyme activity are obtained by screening. Enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular sucrose phosporylase co-expressing sucrose phosphorylase and phospholipase C is 1445.1U mL-1, and enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular trehalase co-expressing trehalase and phospholipase C is 322.3U mL-1. The method can realize extracellular expression of intracellular positioning protein, improve production efficiency and simplify post-extraction process, has wide application value in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industry and has great demand in market at home and abroad.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Identifying inhibitors of intracellular protein fibrillization
Methods for identifying and characterizing inhibitors of protein filament formation are provided. These methods are particularly useful for identifying those agents which inhibit or prevent protein filament formation within neurons of mammalian subjects, particularly human subjects, such as the formation of tau filaments in Alzheimer's patients, and α-synuclein filaments in Parkinson's patients. According to the methods, protein monomers which are associated with formation of intra- or extra-cellular aggregates are combined under physiological conditions with a fibrillization inducer and the formation of protein aggregates is assessed in the absence and the presence of a test agent. The absence or a reduction in the size or stability of proteinaceous polymeric filaments as compared to a control indicates that the test agent is an inhibitor of proteinaceous polymeric filament formation.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Hydrophobically tagged janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170044112A1Improve biological activityReduces avoids symptom causeOrganic chemistryAutoimmune diseaseKinase inhibition
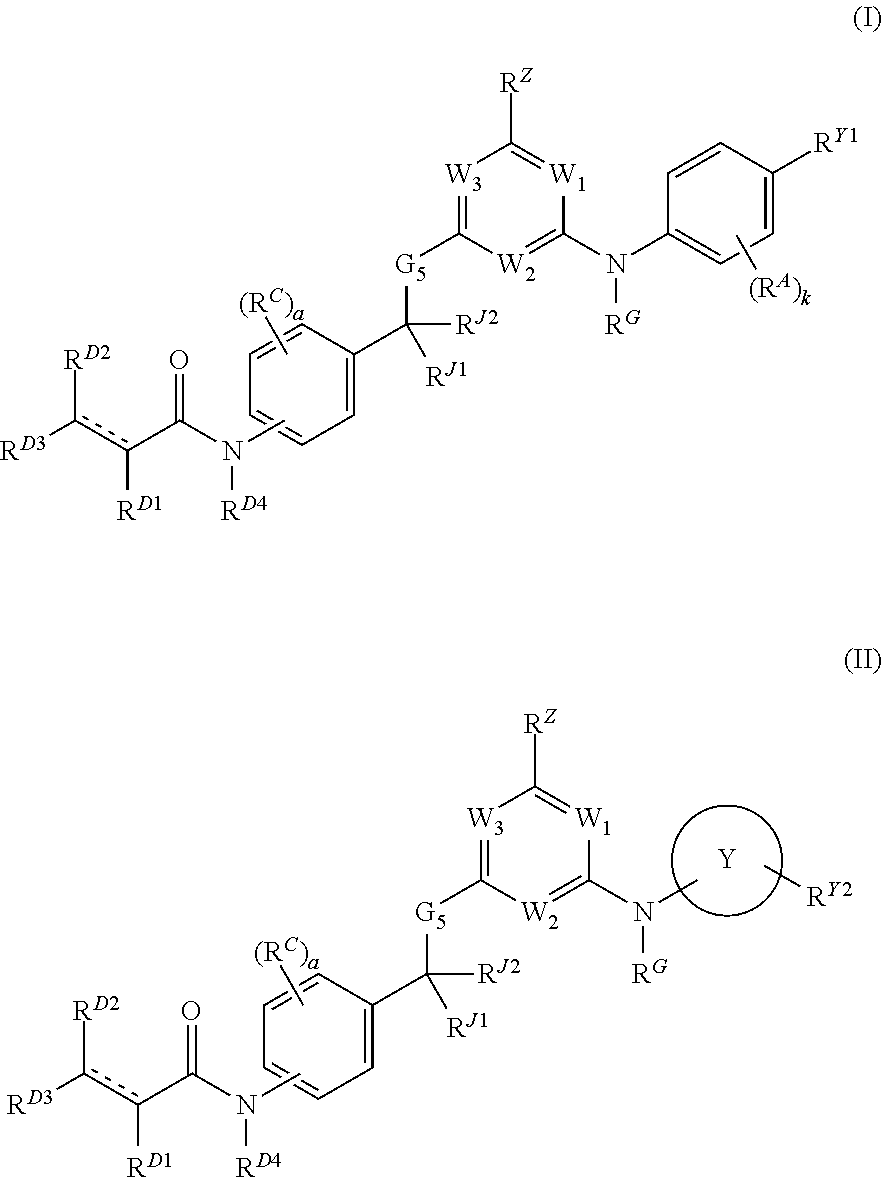
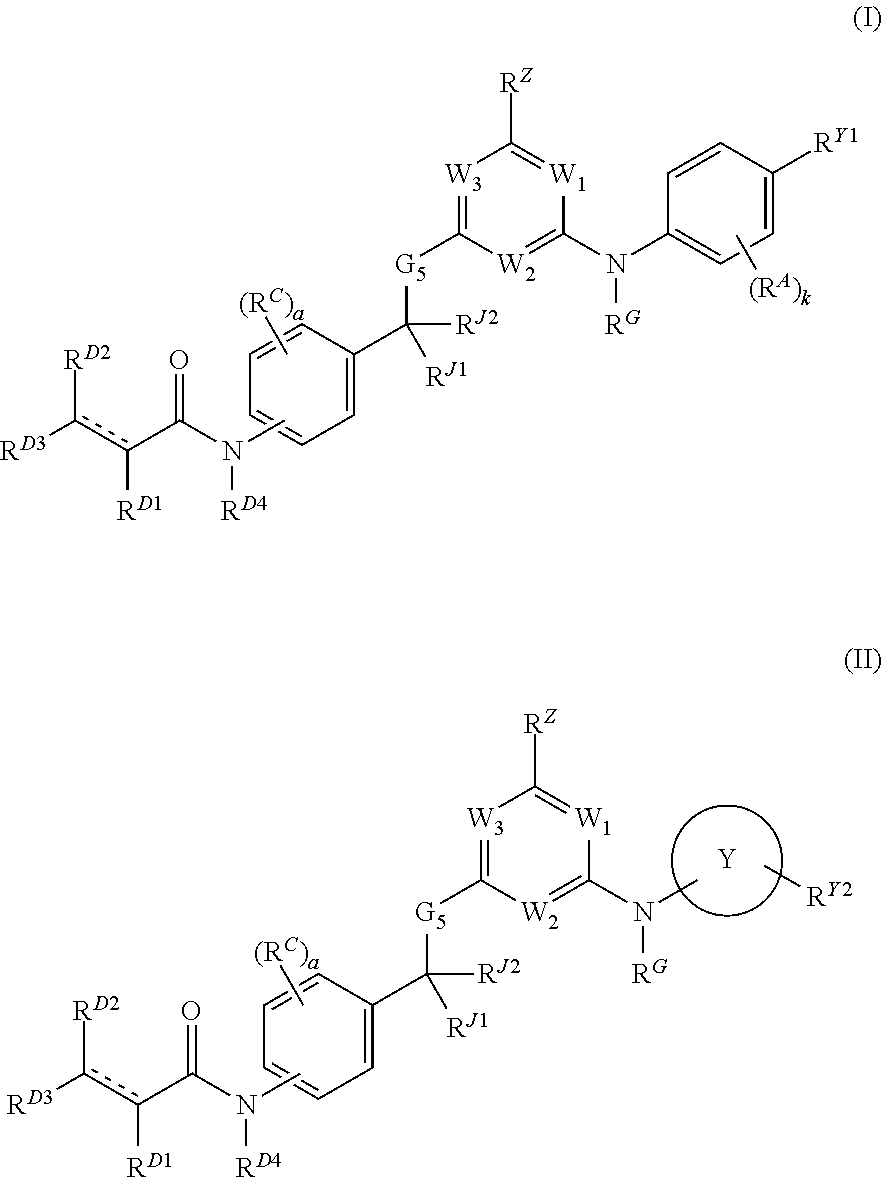
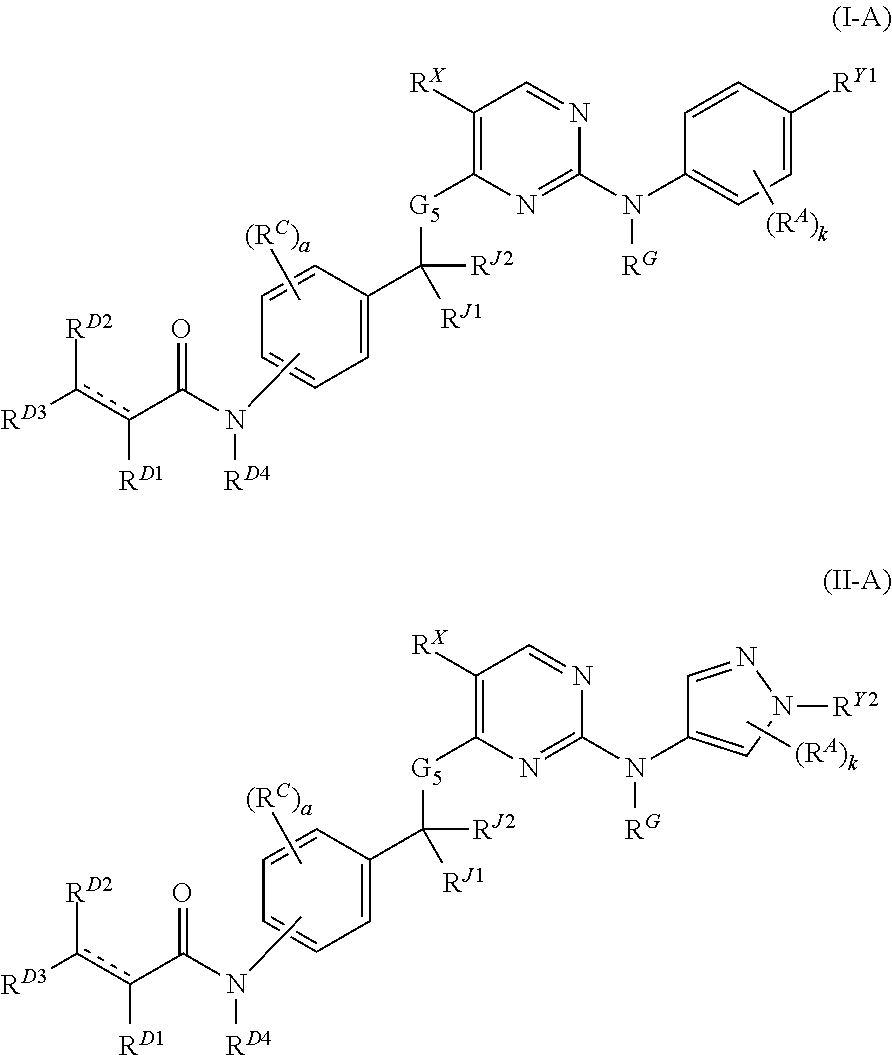
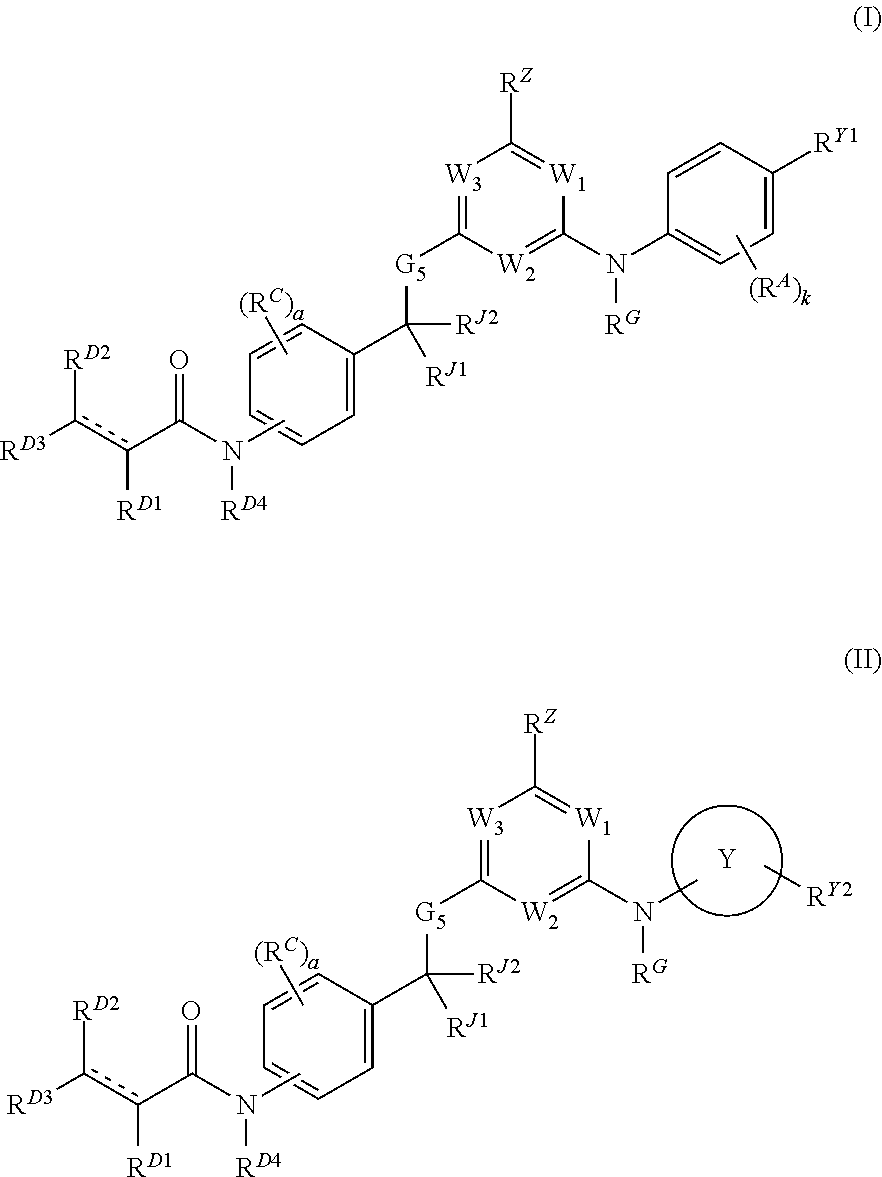
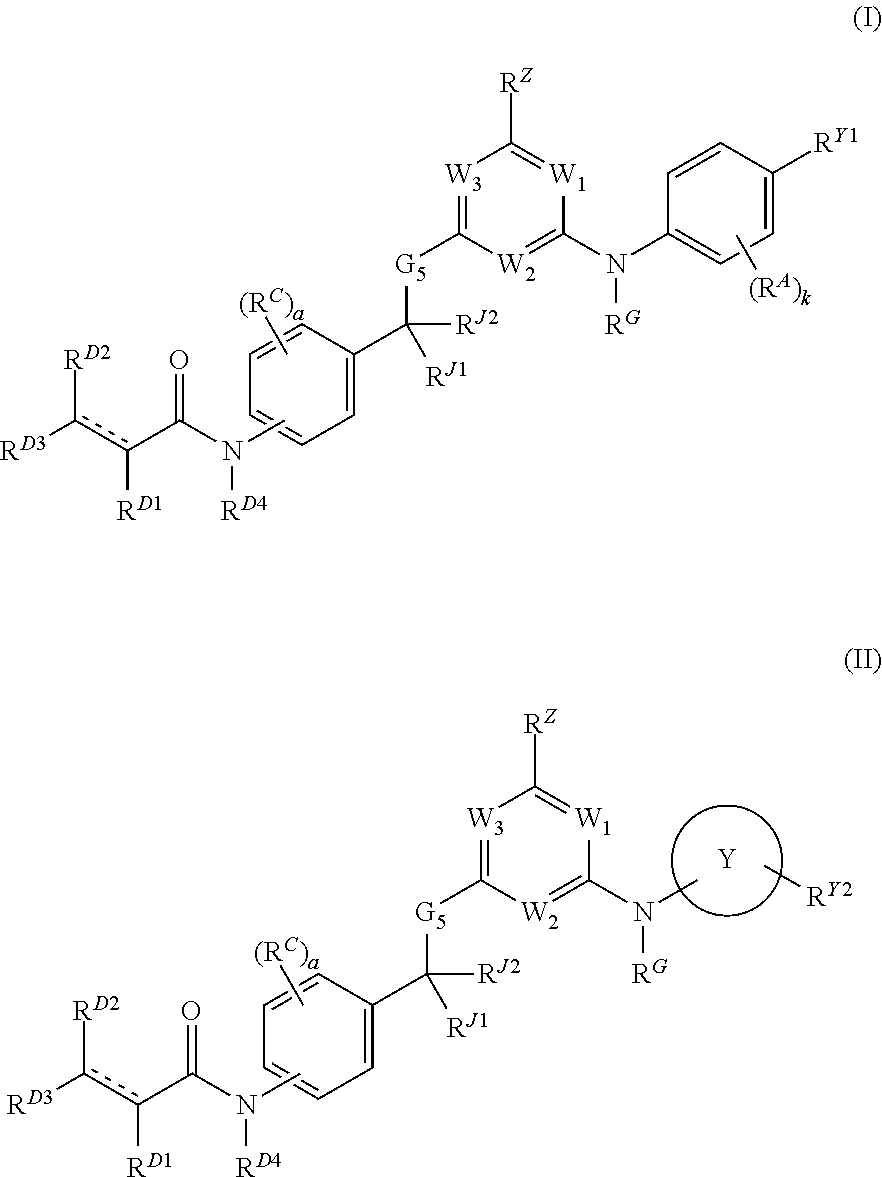
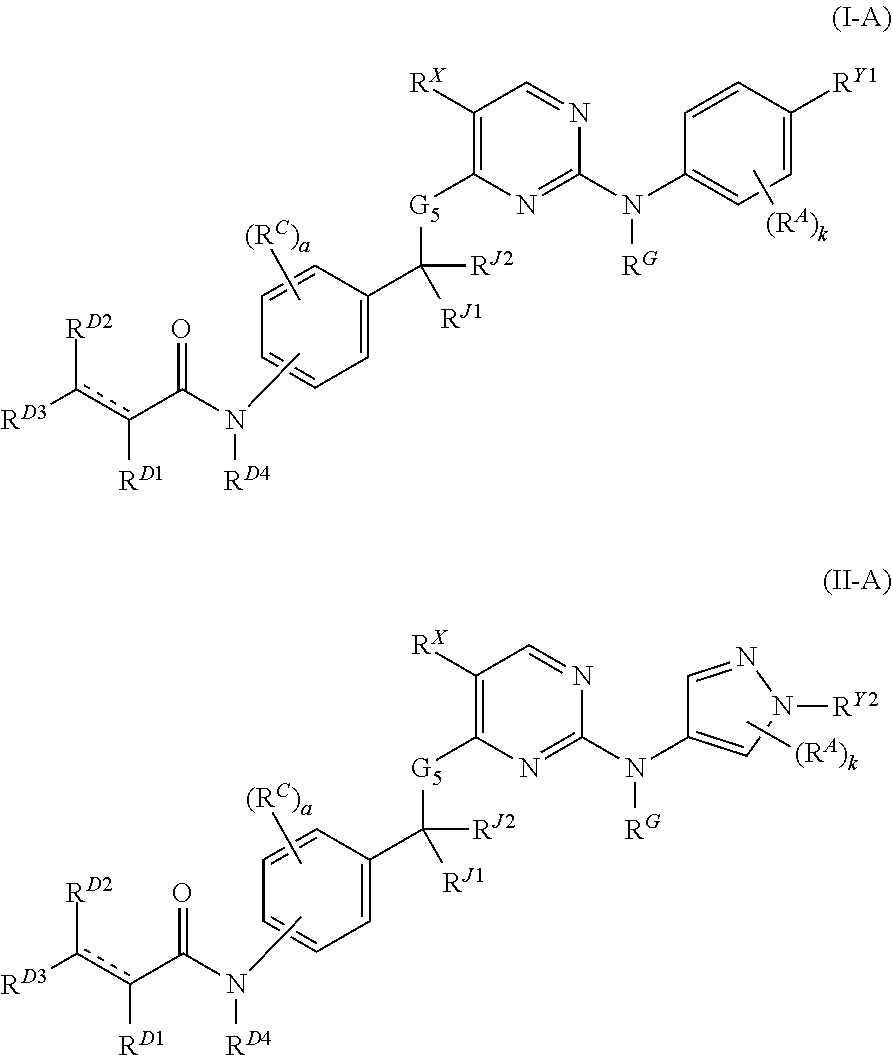
The present invention provides Janus kinase inhibitors, such as compounds of Formula (I) and Formula (II) wherein RY1 and RY2 comprise a tagged hydrophobic moiety RH. The compounds may covalently or non-covalently bind a kinase (e.g., Janus kinase 3 (JAK3)). The hydrophobic moiety RH may signal to the intracellular protein homeostasis machinery to induce degradation of the targeted kinase. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits, methods, and uses that involve the compounds for reducing the activity of a kinase and / or treating and / or preventing a condition associated with aberrant activity of a kinase (e.g., a proliferative disease, inflammatory disorder, autoimmune disorder, painful condition, and / or viral infection).
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Methods, compositions, and kits for analysis of enzyme activity in cells
InactiveUS20050244907A1Facilitates intracellular deliveryHigh yieldCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLight signalLiposome
In one aspect, the present disclosure relates to methods for detecting an activity of an enzyme in a cell. In some embodiments, the methods include contacting a cell with a liposome containing at least one substrate thereby facilitating introduction of the substrate into the cell. The substrate is capable of producing a detectable light signal when acted on by the enzyme, and the signal is detected. The methods can be used in screening agents that can inhibit or activate an enzyme activity. The methods can also be used in various downstream assays such the detection of interactions between intracellular proteins, screening for variants of an enzyme, and detection of various diseases. Compositions and kits for carrying out the various methods are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Reference Control for Cell by Cell Analysis
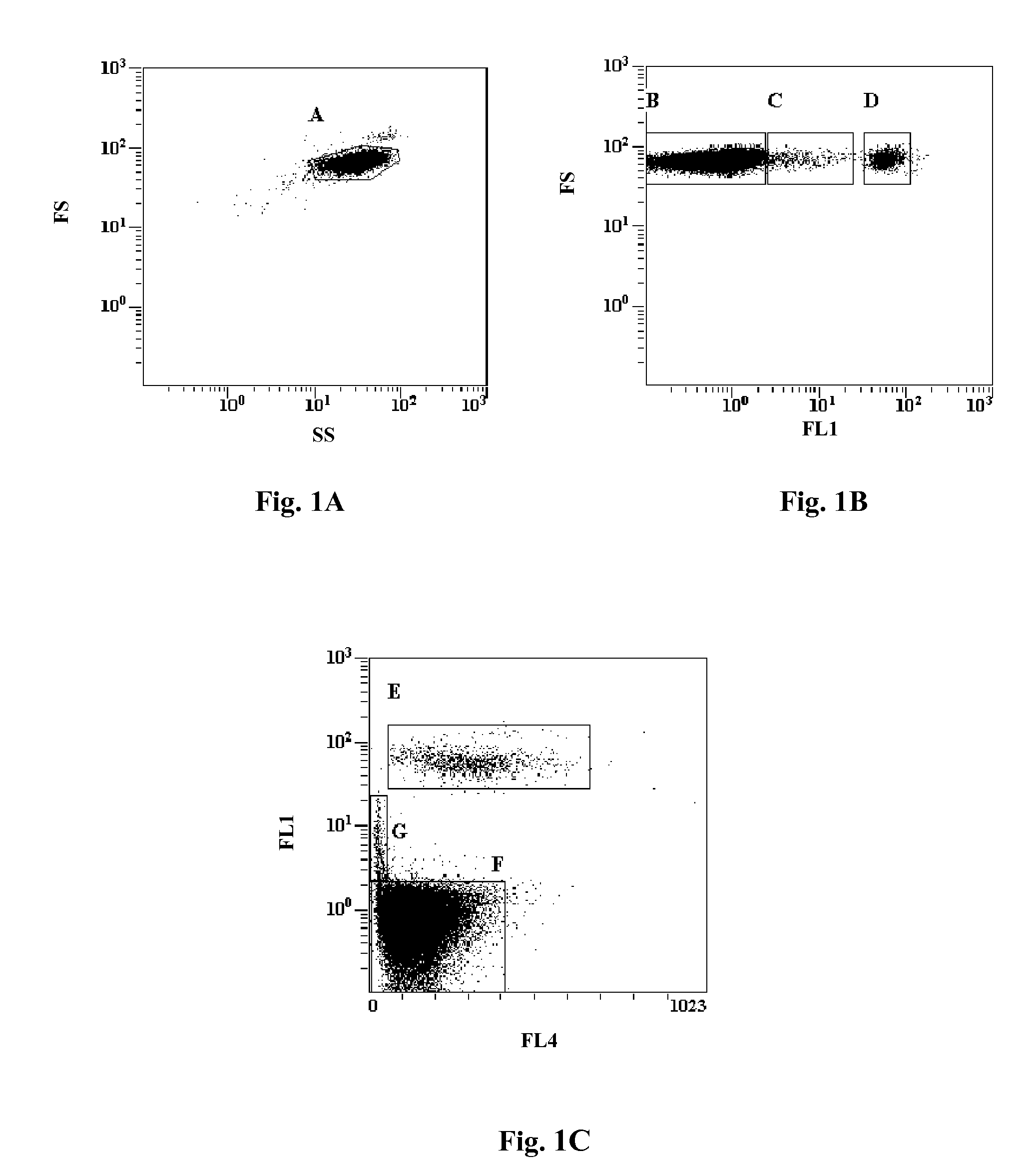
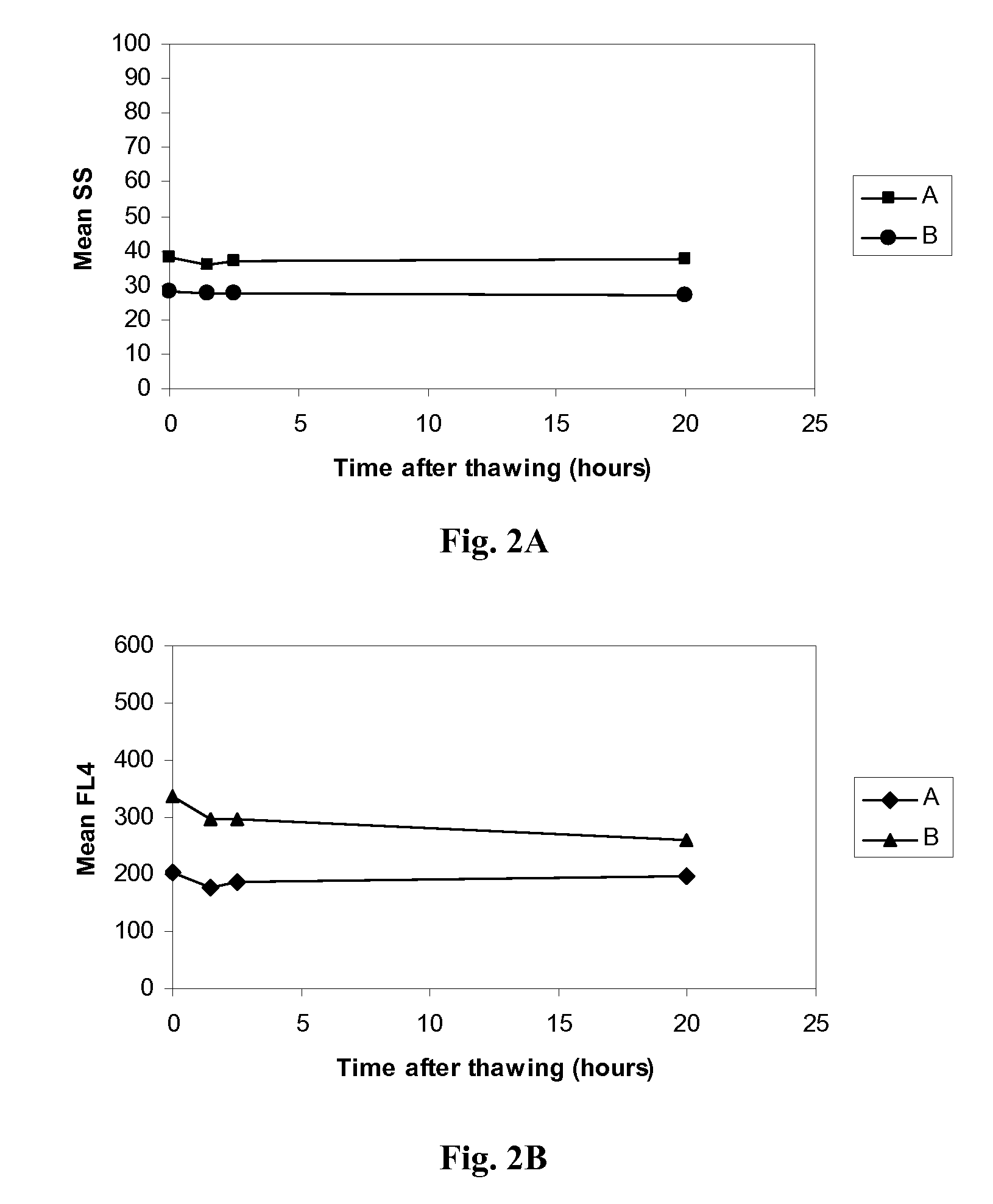
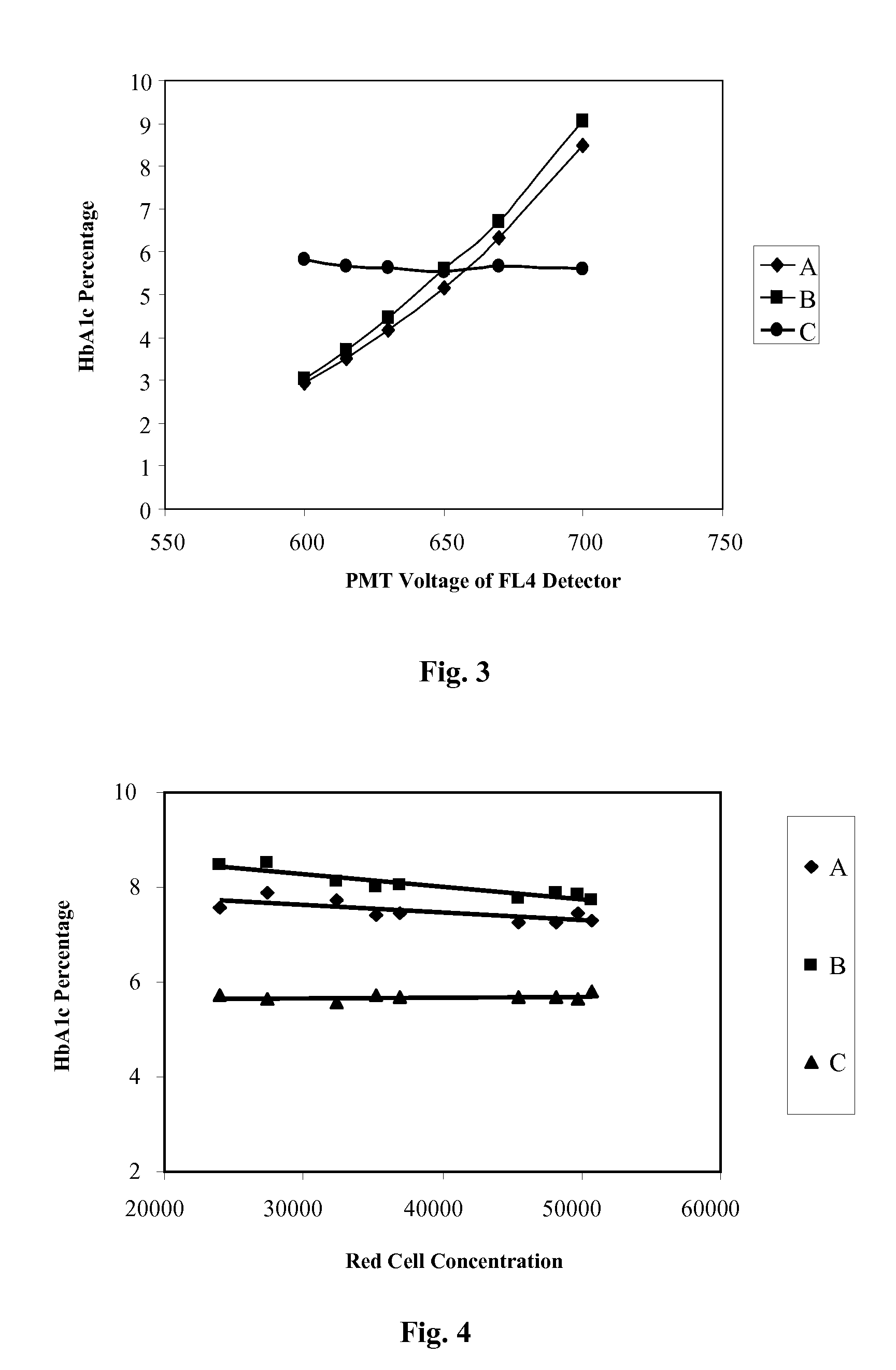
ActiveUS20100041011A1Avoid reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationFluorescenceCell membrane
A reference control for cell by cell analysis on flow cytometric analyzers contains cellular analogs made of permeated blood cells containing therein aggregated intracellular proteins and preserved antigenic sites thereof, having cellular membrane permeable to antibodies and a suspension medium. The reference control is frozen after being prepared and thawed prior to use. The cellular analogs further contain a fluorescence marker therein. Further disclosed are a method of making the reference control and a method using the reference control, as an internal or stand-alone control, for measurements of cellular hemoglobin and cellular hemoglobin variant of a blood sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Hydrophobically tagged janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS9862688B2Reduces avoids symptom causeGood curative effectOrganic chemistryAutoimmune diseaseKinase inhibition
The present invention provides Janus kinase inhibitors, such as compounds of Formula (I) and Formula (II) wherein RY1 and RY2 comprise a tagged hydrophobic moiety RH. The compounds may covalently or non-covalently bind a kinase (e.g., Janus kinase 3 (JAK3)). The hydrophobic moiety RH may signal to the intracellular protein homeostasis machinery to induce degradation of the targeted kinase. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits, methods, and uses that involve the compounds for reducing the activity of a kinase and / or treating and / or preventing a condition associated with aberrant activity of a kinase (e.g., a proliferative disease, inflammatory disorder, autoimmune disorder, painful condition, and / or viral infection).
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Staphylococcal nuclease fusion proteins for the production of recombinant peptides
InactiveUS7390639B2Easy to disassembleNot complicate subsequent stepSugar derivativesBacteriaInclusion bodiesHplc method
Peptides are produced as fusions with a suitable carrier protein. The carrier protein disclosed herein are adapted from the N-terminal domain of staphylococcus nuclease. This novel carrier protein acts to promote the over-expression of the peptide-protein fusion in the form of inclusion bodies, which minimizes in-cell proteolysis of desired peptides. The fusion protein is readily purified by conventional procedures or His-tag affinity chromatography when His-tag is inserted into the fusion protein. The target peptide is released from the purified fusion protein by a simple cleavage step and separated from the librated carrier protein by use of a reverse-phase HPLC process or by repeating the same affinity purification method. A particular advantage of the disclosed method, in addition to the obvious advantage of high yields, is its use for producing isotopically labeled peptides for NMR characterization of bioactive peptides and their interactions with target proteins.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Analysis method of microalgae proteome
ActiveCN102707001AComponent separationColor/spectral properties measurementsQuantitative ResultAnalysis method
The invention discloses an analysis method of microalgae proteome. The analysis method comprises the steps of collecting microalgae cells; extracting intracellular protein; and identifying the differentially expressed proteins. The inventtion provides an approach for analyzing microalgae proteome. The approach involves cell collection, protein extraction and protein analysis, thereby obtaining protein qualitative and quantitative results of microalgae under different cultivation conditions, so as to provide the analysis method of microalgae proteome. The method has significance for promoting microalgae proteome research.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Whole blood preparation for cytometric analysis of cell signaling pathways
This invention is directed to a method for preparation of a biological sample for measurement of protein epitopes that allows for the preservation of intracellular protein epitopes and detection of signal transduction pathways based on the ability to capture transient activation states of the epitopes. The method provided by the invention allows for the rapid fixation of biological samples containing red blood cells, to ensure that epitopes of signal transduction molecules and other intracellular protein epitopes are preserved in the active state. The method of the invention further allows for lysis of red blood cells, thereby making it a useful method for cytometric analysis of biological samples, including, for example, whole blood, bone marrow aspirates, peritoneal fluids, and other red blood cell containing samples. The invention also provides a method to recover or ''unmask'' epitopes on intracellular antigens that have been made inaccessible by the cross linking fixative necessary to fix the sample. Significantly, the methods of the invention allow preservation and analysis of phospho-epitope levels in biological samples taken directly from patients to determine disease-specific characteristics.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC +1
Method of herding and collection of oil spilled at the aquatic surface
ActiveUS20120074067A1General water supply conservationSolid sorbent liquid separationSAA proteinStress Proteins
Disclosed are methods of removing oil from an aqueous surface, comprising: surrounding an oil spot on the aqueous surface with an oil-absorbing material; and introducing a solution comprising a surfactant to the oil spot. Also disclosed are the above methods where the oil is not mechanically directed towards the oil-absorbing material, or where the oil-absorbing material is not mechanically directed towards the oil. Also disclosed are the above methods further comprising introducing a solution comprising a protein / surfactant complex to the oil spot, where the protein / surfactant complex comprises a protein component obtained from the fermentation of yeast, comprising a mixture of multiple intracellular proteins, at least a portion of the mixture including yeast polypeptides obtained from fermenting yeast and yeast stress proteins resulting from subjecting a mixture obtained from the yeast fermentation to stress.
Owner:ADVANCED BIOCATALYTICS
Novel compositions and uses therefor
ActiveUS20040241177A1Increase ratingsMore responsiveViral antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsLong latencyProtection sex
The invention is directed to the use of (i) a first antigen corresponding to a target antigen of interest, together with (ii) a second antigen, corresponding to a modified form of the target antigen, whose rate of intracellular proteolytic degradation is increased, enhanced or otherwise elevated relative to the first antigen, in compositions and methods for inducing both humoral and cellular immunity in an individual. The ability to provide compositions, which are capable of inducing both host-protective antibody and cell-mediated immune responses, facilitates the generation of immunogenic compositions capable of combating, inter alia, conditions that have long latency periods and, therefore, benefit from the dual approach of prophylaxis and therapy in one delivery.
Owner:JINGANG MEDICINE AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Soil protein extraction and intracellular protein separation method
InactiveCN101531708AHigh extraction rateImprove electrophoresisMicroorganismsDepsipeptidesBüchner funnelExtracellular proteins
The invention provides a high-efficiency soil protein extraction method, comprising the following steps: adding soil in a pre-cooling soil protein extraction buffer solution and blending and oscillating the mixture in a 4 DEG C shaking table over night; performing drawing and filtering of the shaken mixture in a buchner funnel using a crude filter paper; processing the drawing and filtering liquid by macroporous resin (D101), filtering the processed liquid through a 0.22 Mum microporous membrane, the filtered liquid being the extracellular protein mother liquid; processing the cells on the filter membrane by cleaning, crushing, centrifugalizing and vacuum drying to obtain the dried powder, namely intracellular soil protein sediment. The extracellular protein mother liquid is processed by centrifuging, separating and vacuum drying to obtain the intracellular soil protein dried powder; degrading the intracellular soil protein dried powder until the degraded intracellular soil protein dried powder is clearly separated on 10% polyacrylamide gel SDS-PAG electrophoresis, the method has high separation efficiency, microbial yield is 37.5%, which is higher than the yield of the traditional method 0.1-1%, simple operation flow, good SDS-PAGE resolution and good mass spectrum identification effect.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com