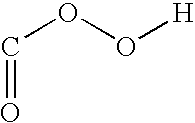
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Low ionic strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aqueous displacement fluid injection for enhancing oil recovery from an oil bearing formation
InactiveUS20110306525A1Reduce ionic strengthIncrease oil productionFlushingDrilling compositionLow ionic strengthUltimate tensile strength
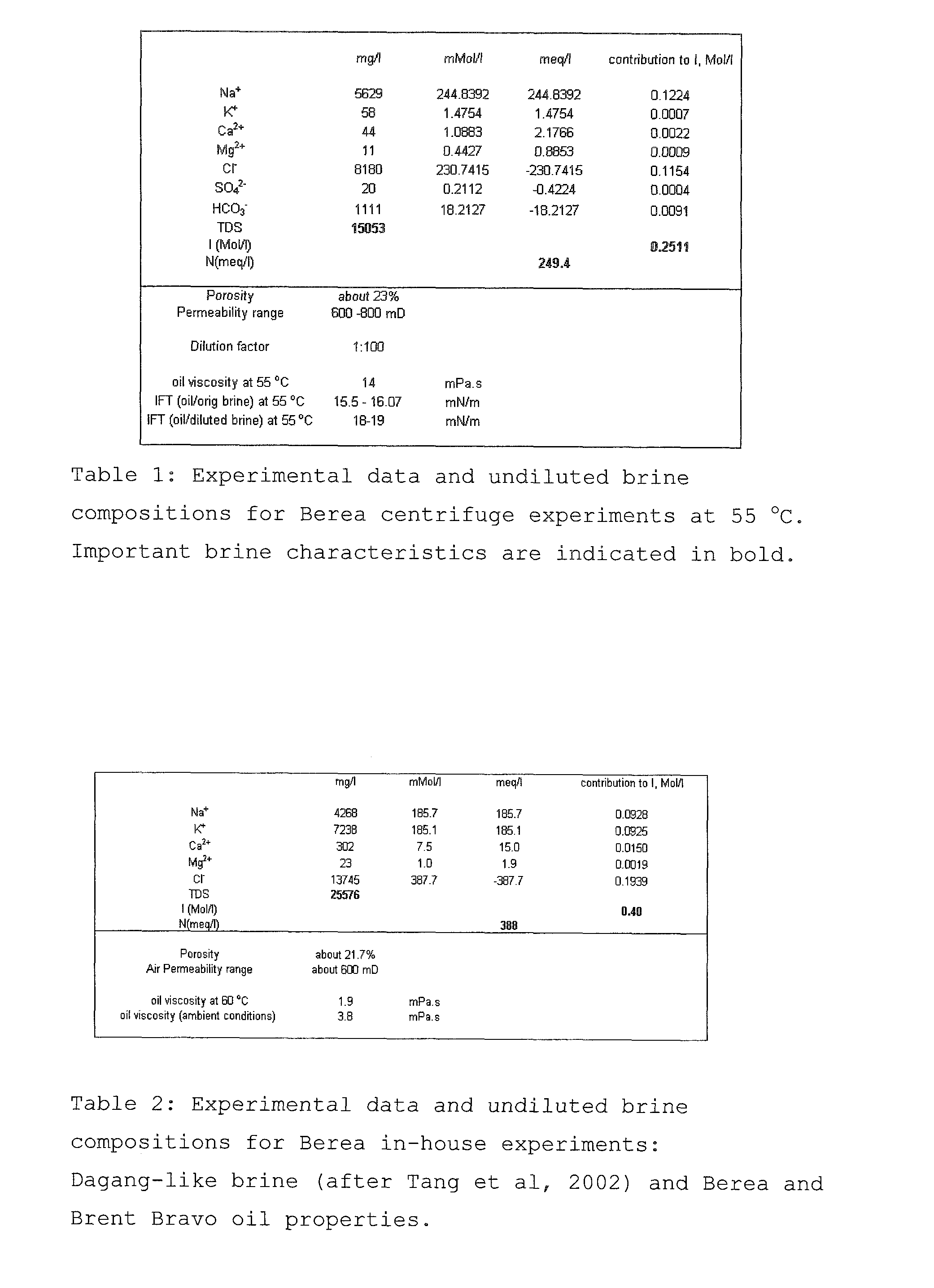
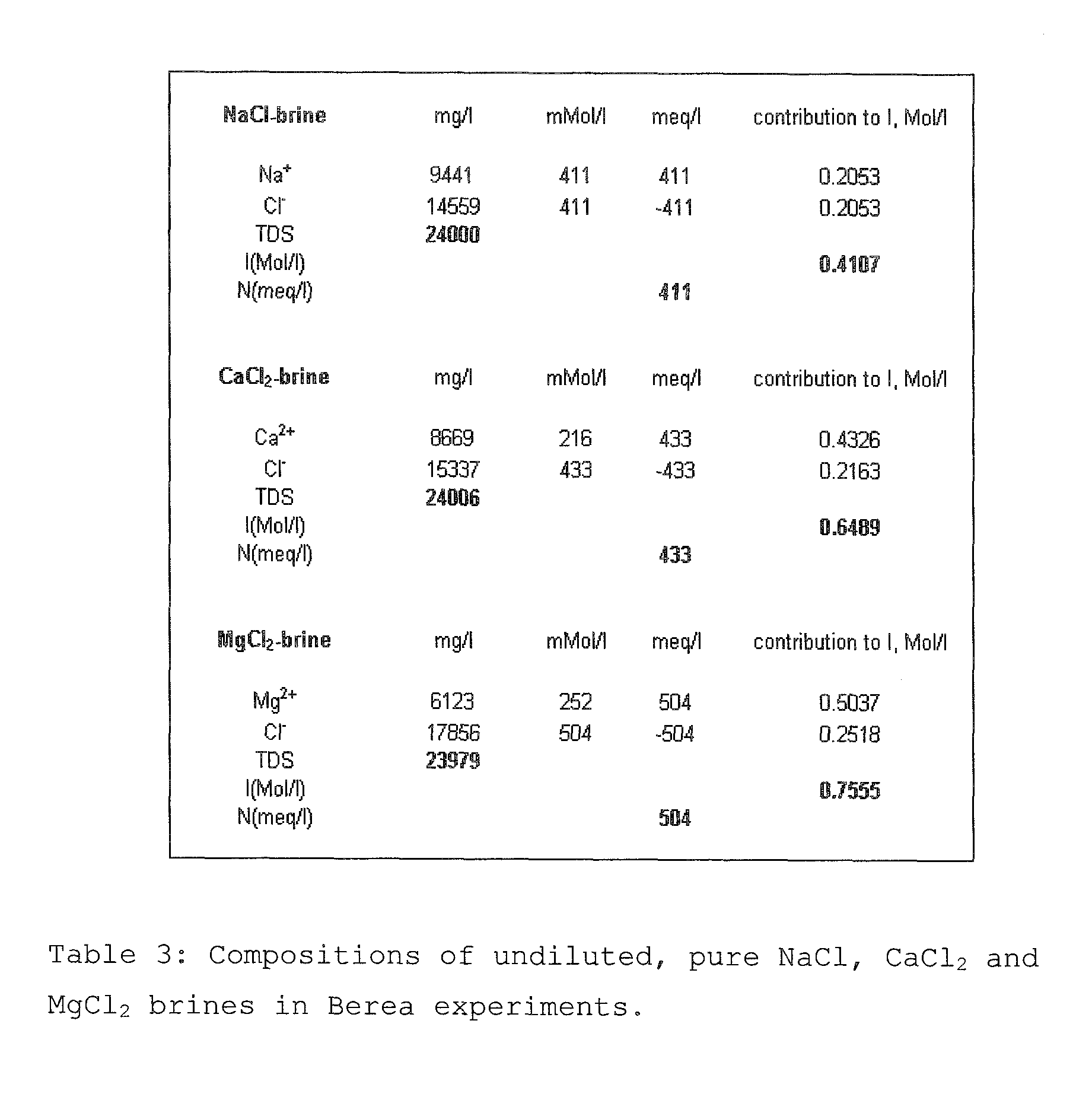
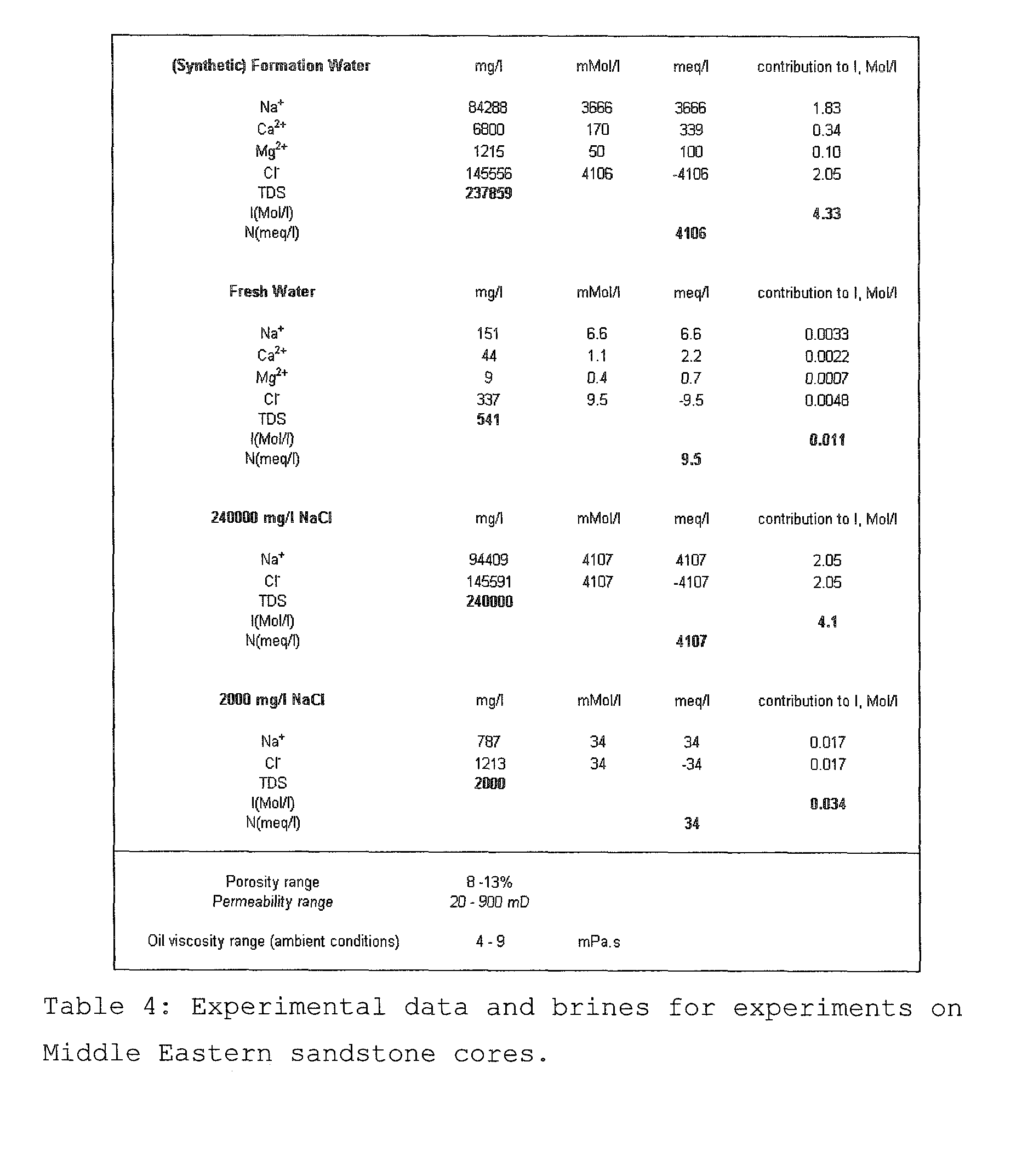
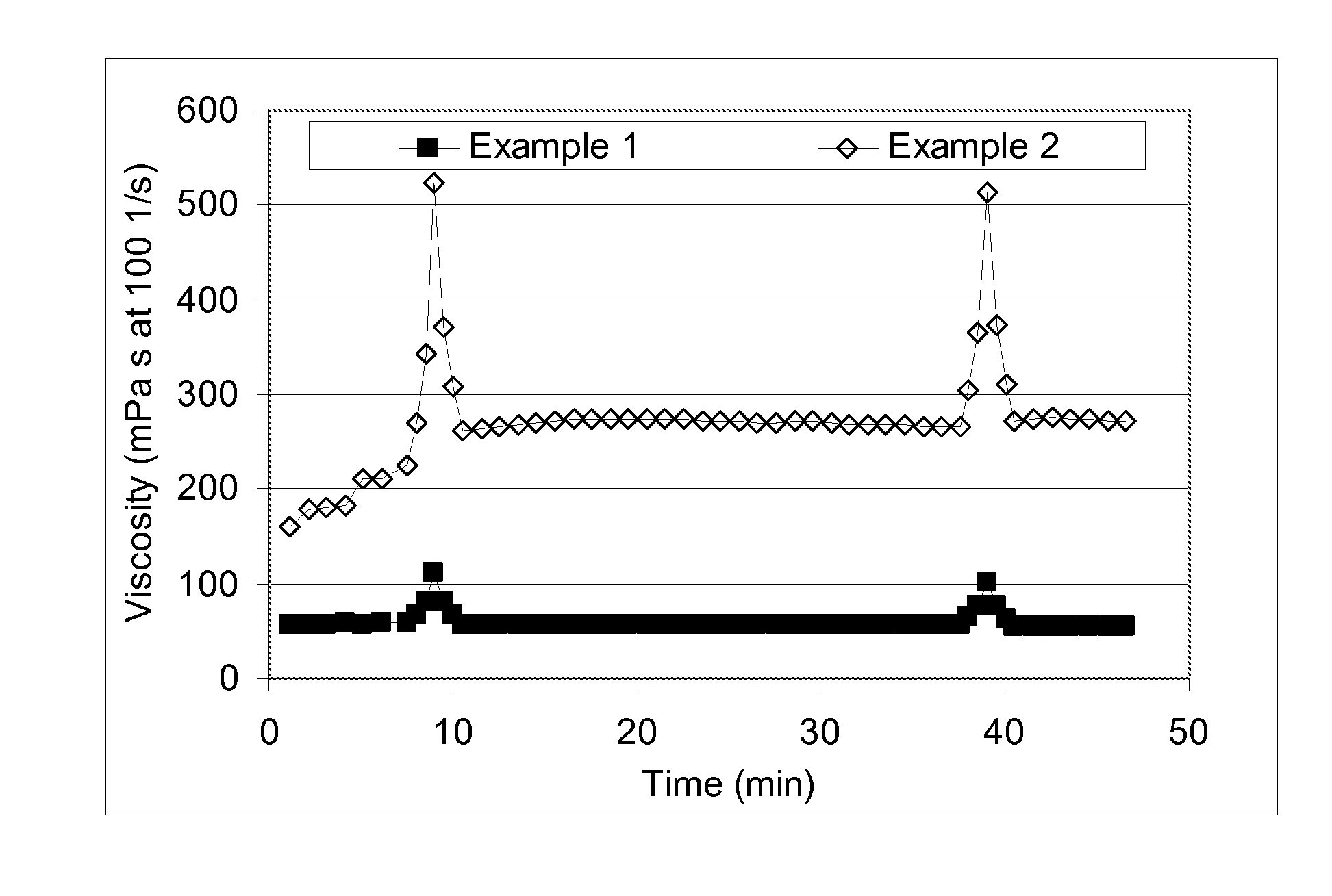
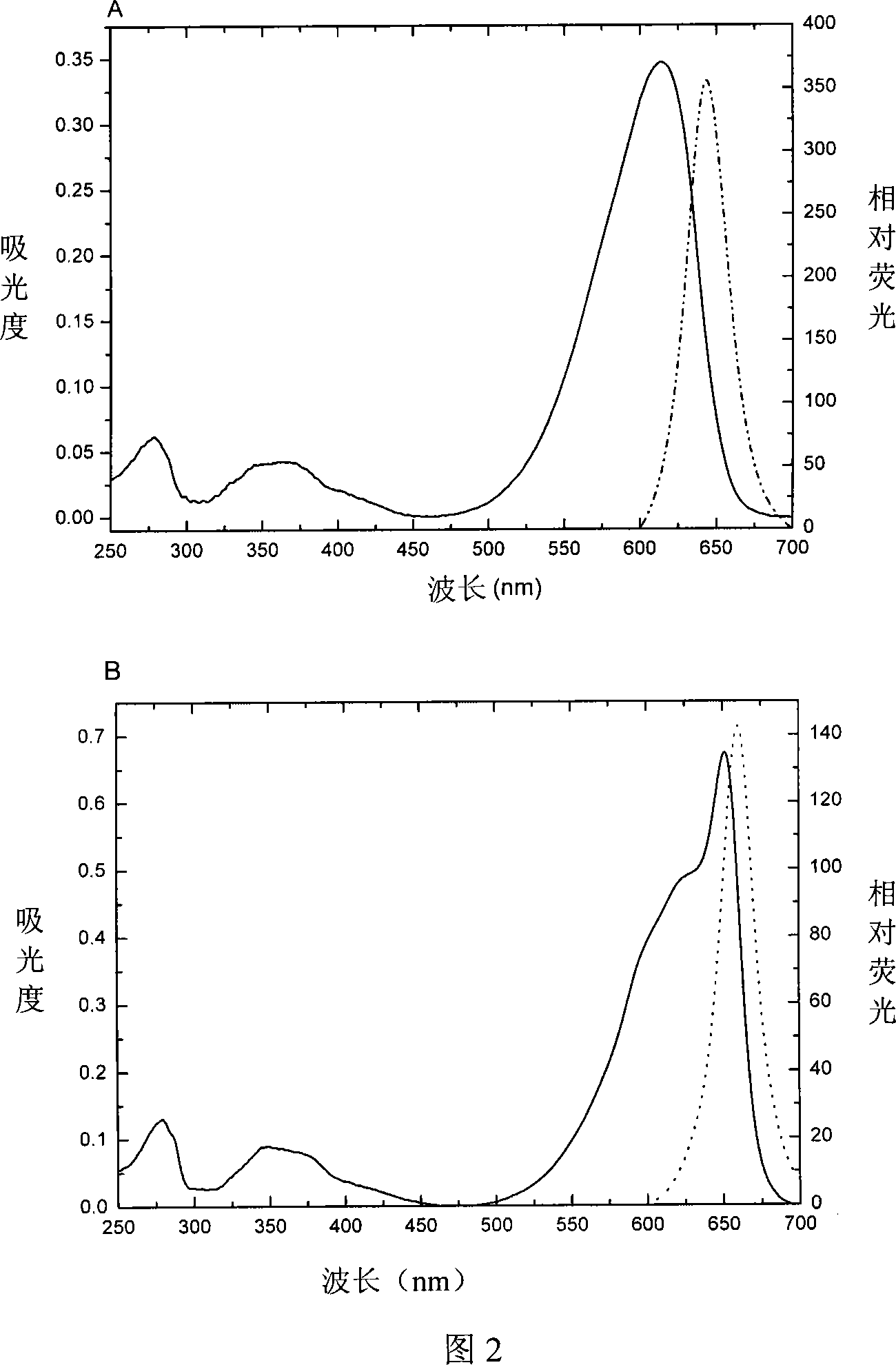
A method for enhancing recovery of crude oil from a porous subterranean formation of which the pore spaces contain crude oil and connate water comprises:—determining the Ionic Strength (Mol / l) of the connate water; and—injecting an aqueous displacement fluid having a lower Ionic Strength (Mol / l) than the connate water into the formation, which aqueous displacement fluid furthermore has an Ionic Strength below 0.15 Mol / l. FIGS. 13 and 16 and Table 4 demonstrate that injection of an aqueous displacement fluid with lower Ionic Strength than the connate water improves oil recovery (IOR).
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Well Treatment with Ionic Polymer Gels
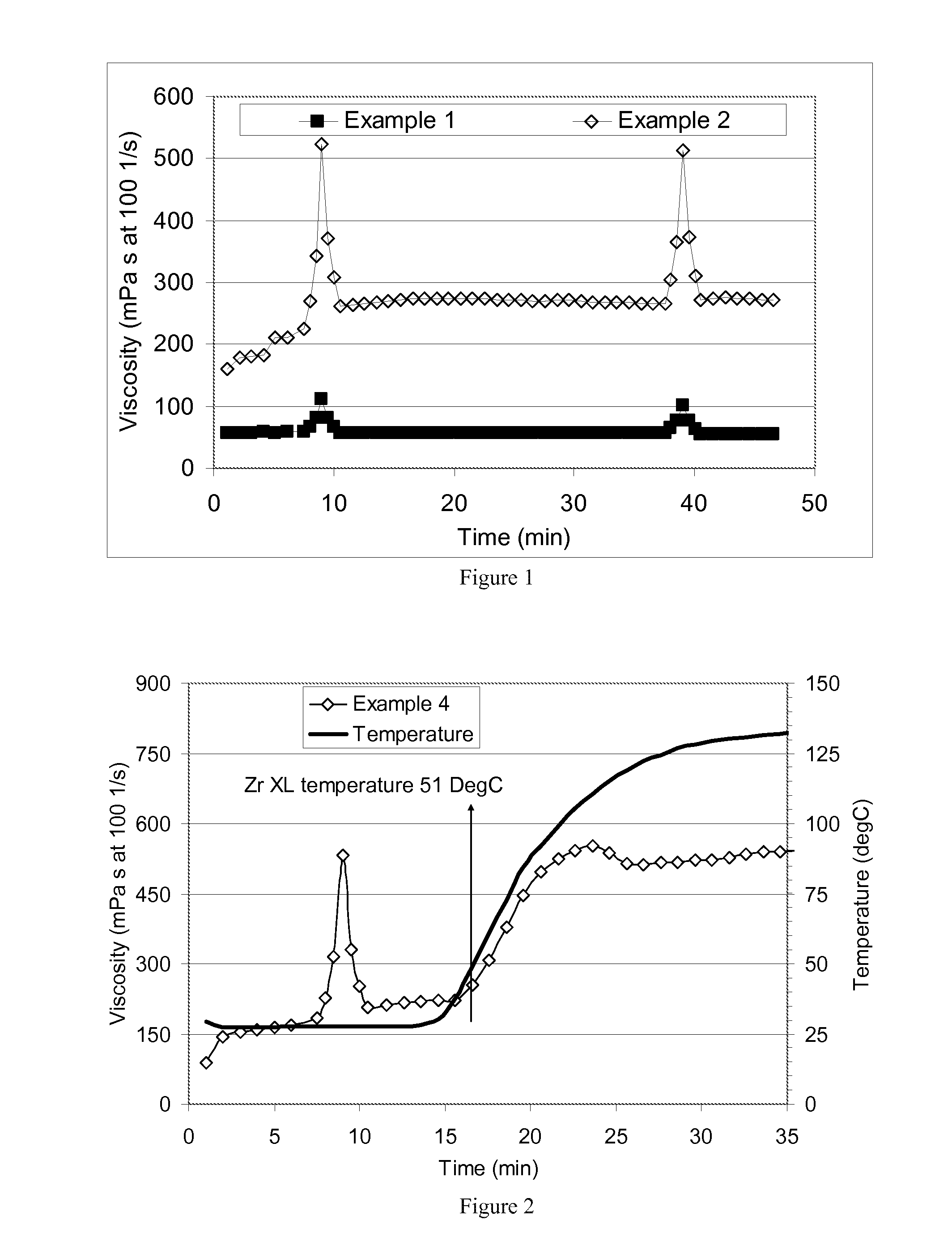
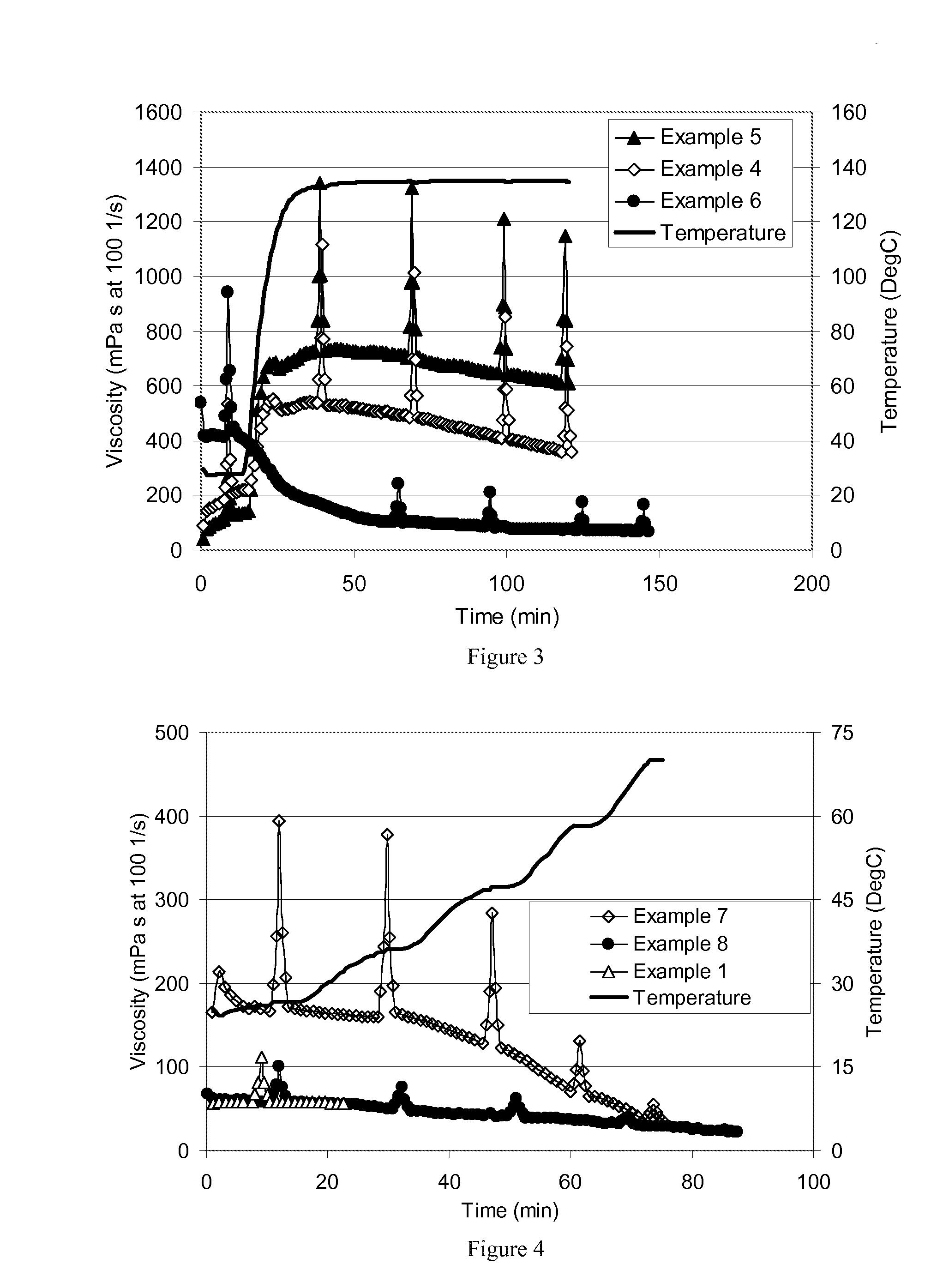
Methods comprising preparing an aqueous mixture of an anionic polymer, a charge screening surfactant, and a borate crosslinker, wherein the mixture has a conductivity less than 10 mS / cm, injecting the mixture down a wellbore, and gelling the mixture. An embodiment of the aqueous mixture can also include tetramethylammonium chloride as a clay stabilizer and a metal crosslinker such as a complex of zirconium and an amino acid ligand system. An embodiment can effectively provide borate crosslinking of an anionic polymer in a low-ionic-strength fluid system, without sacrificing ultimate gel strength or thermal persistence of the metal crosslinked polymer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
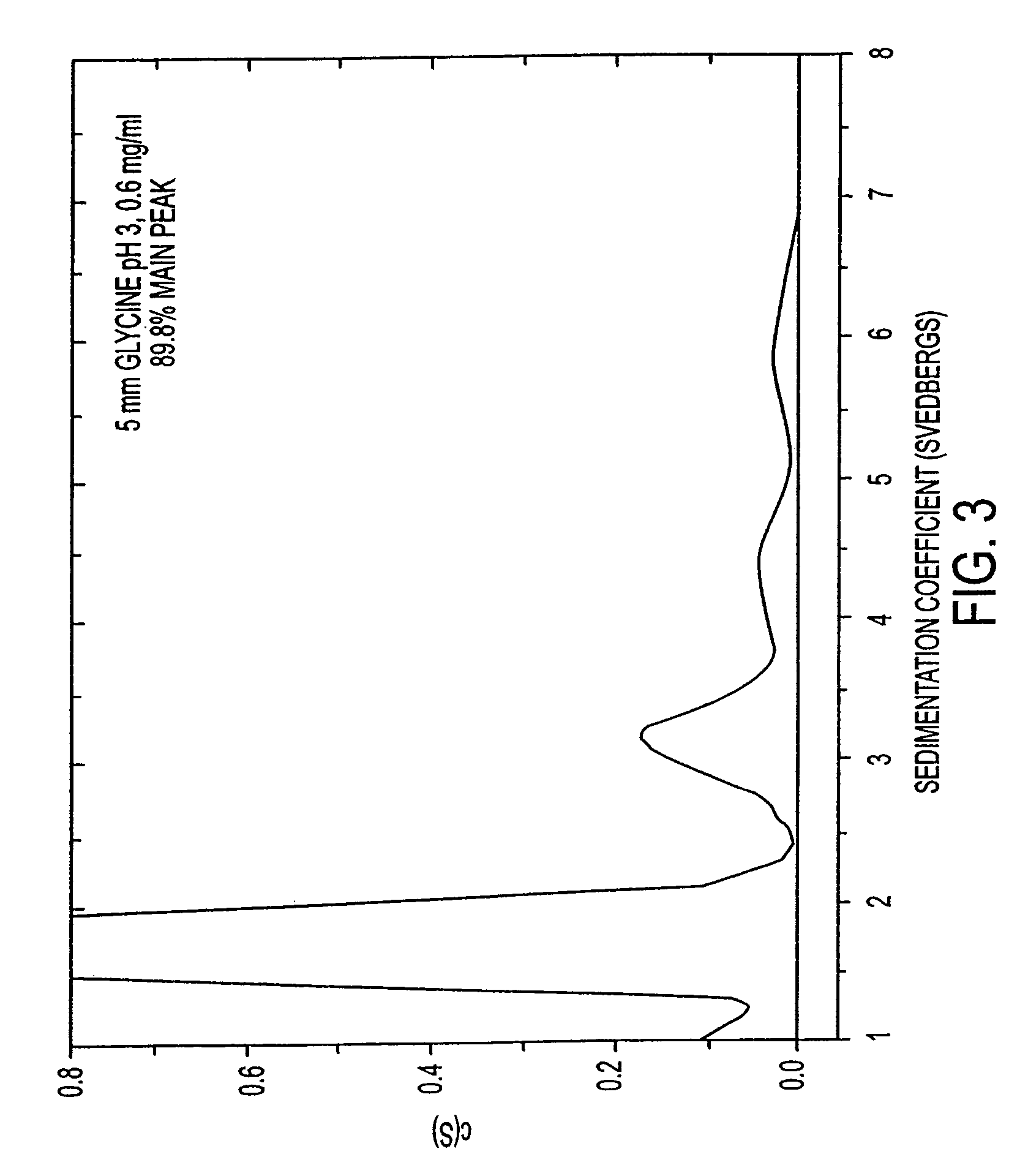
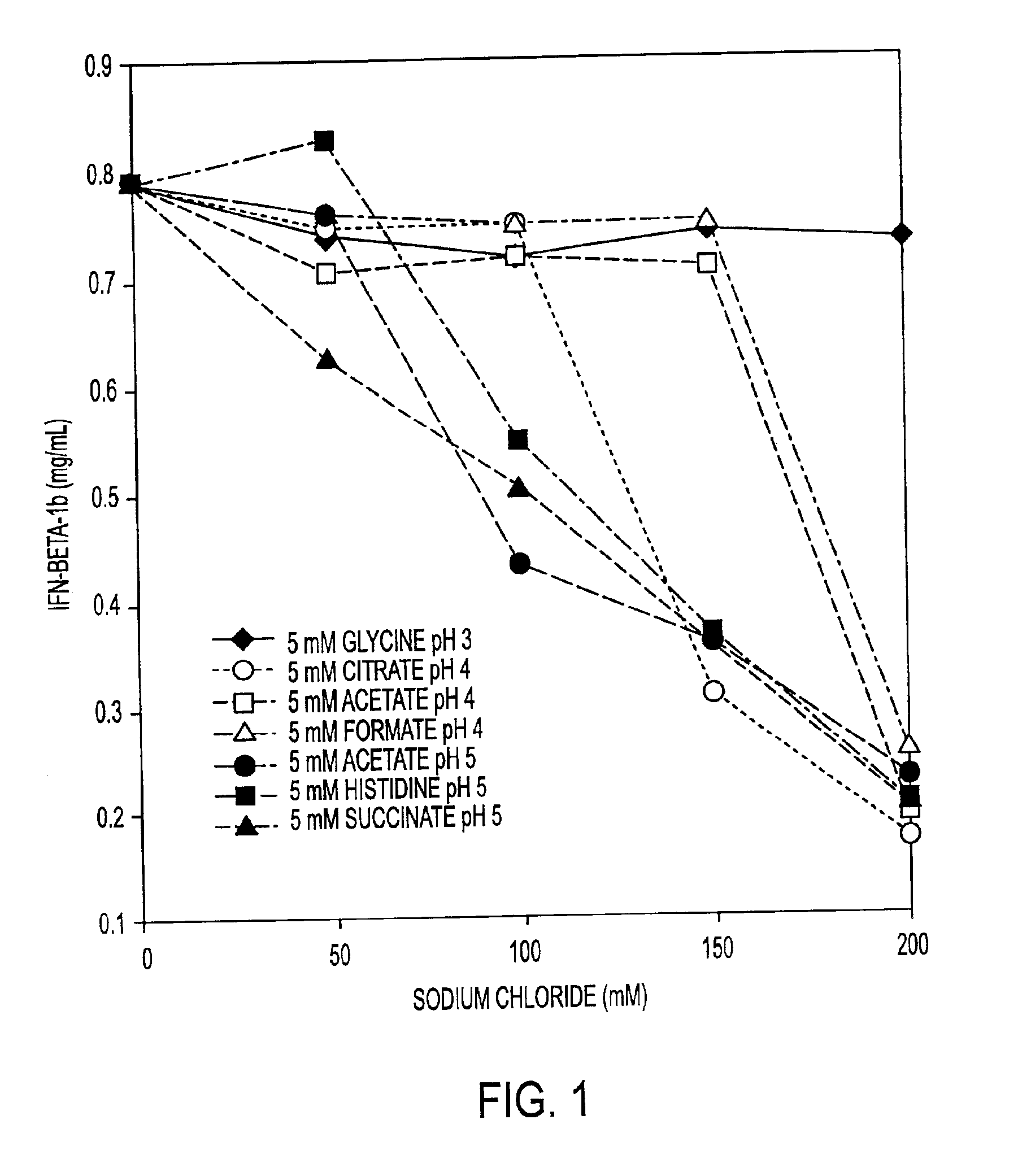
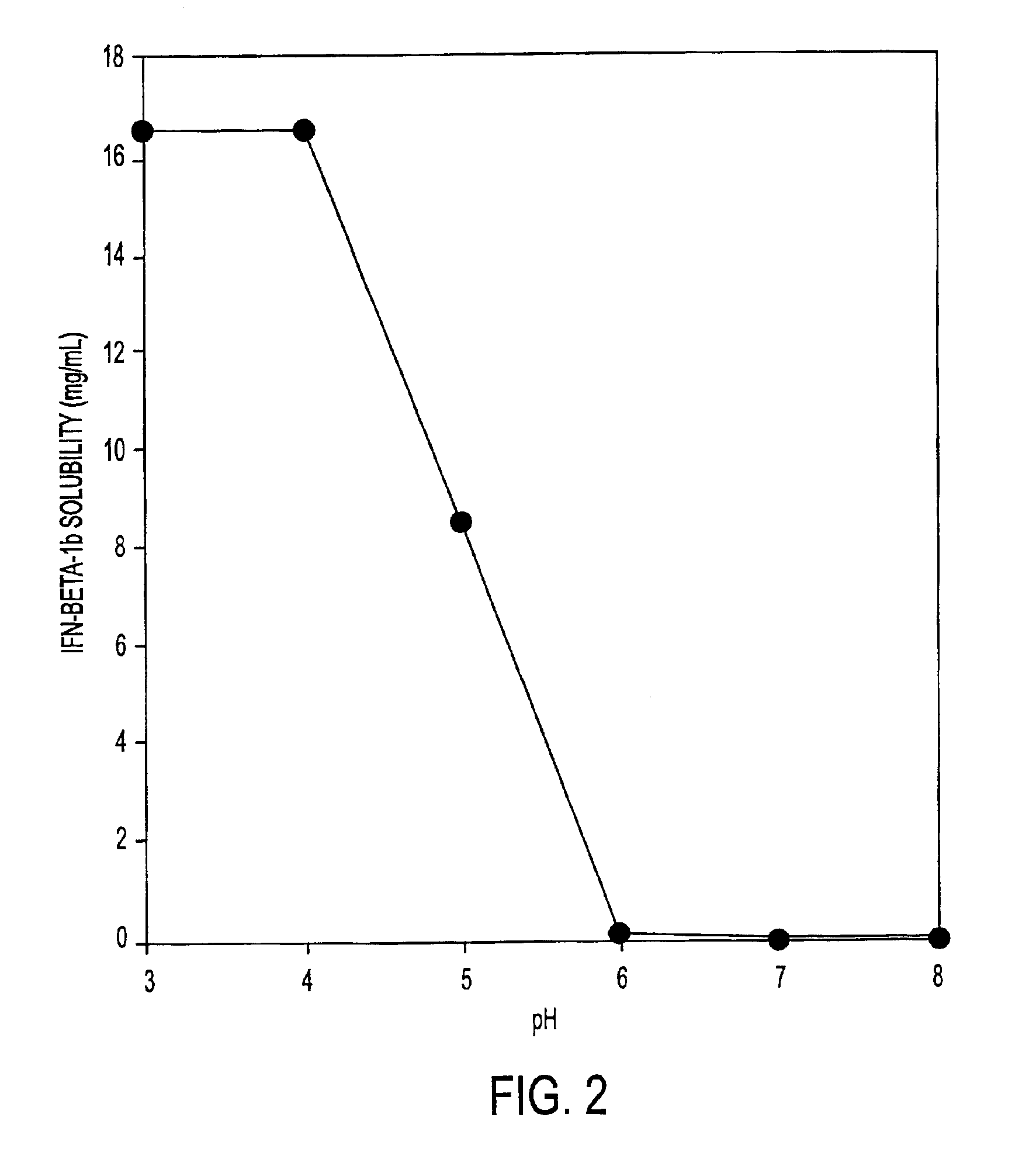
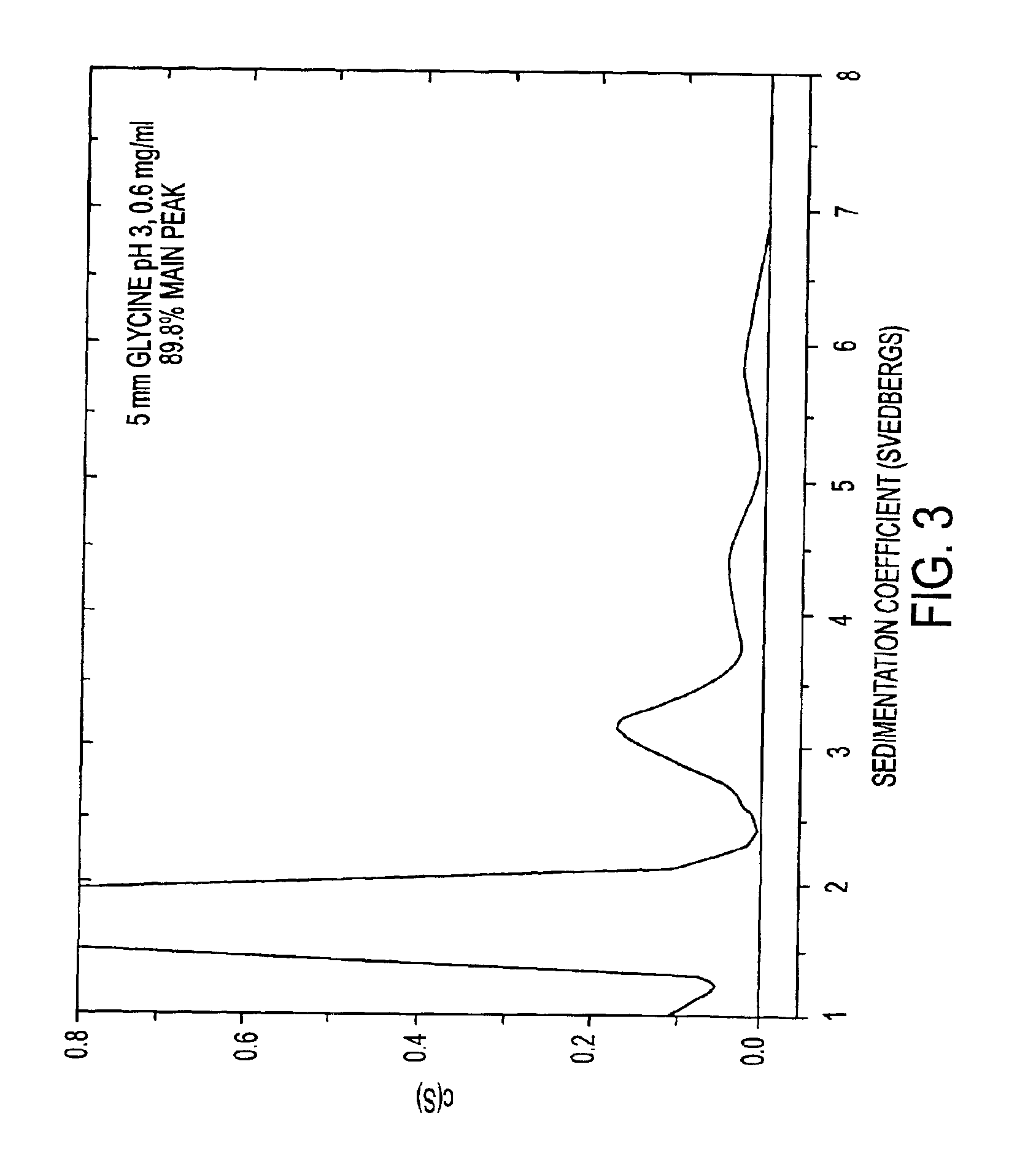
HSA-free formulations of interferon-beta
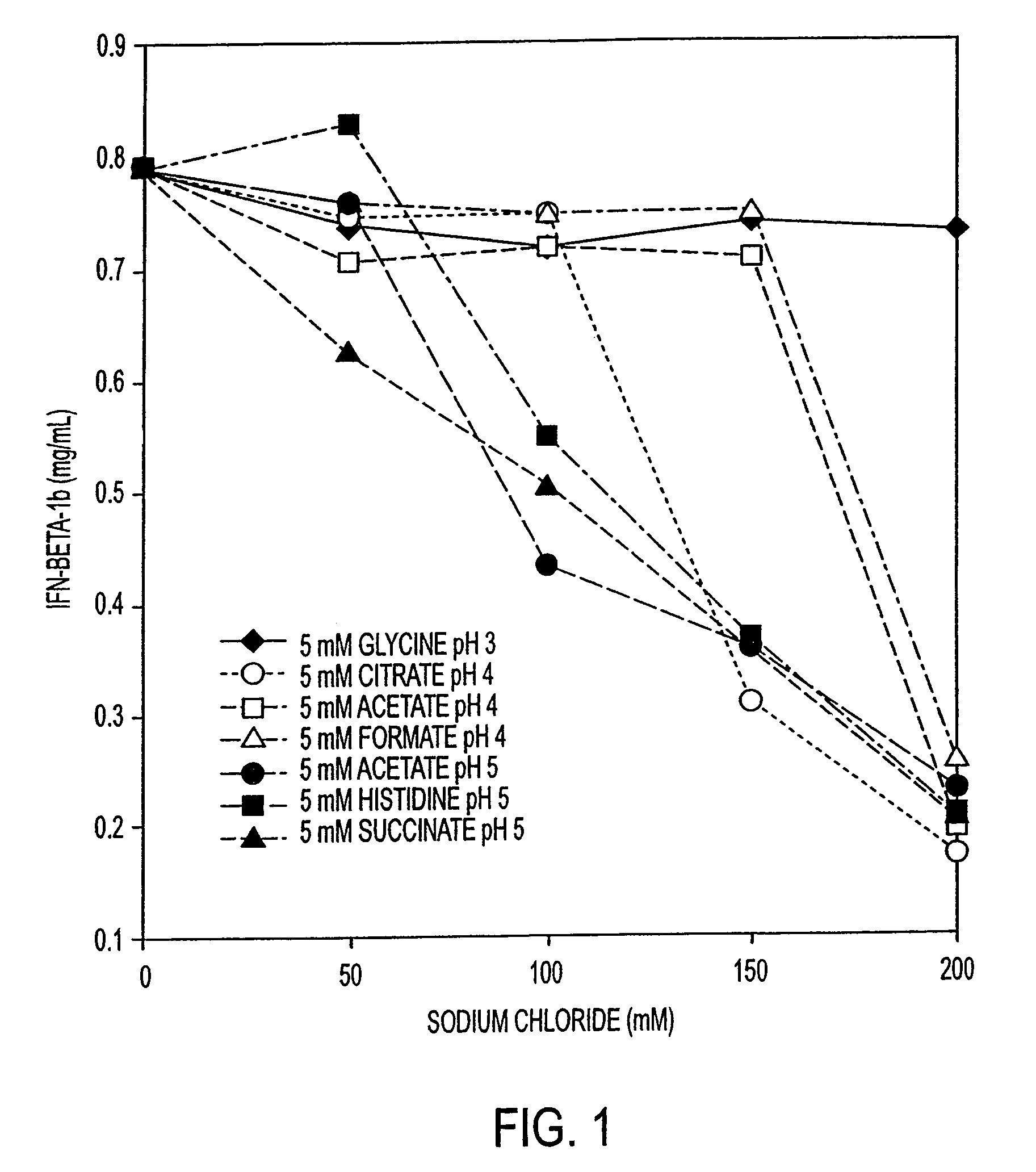
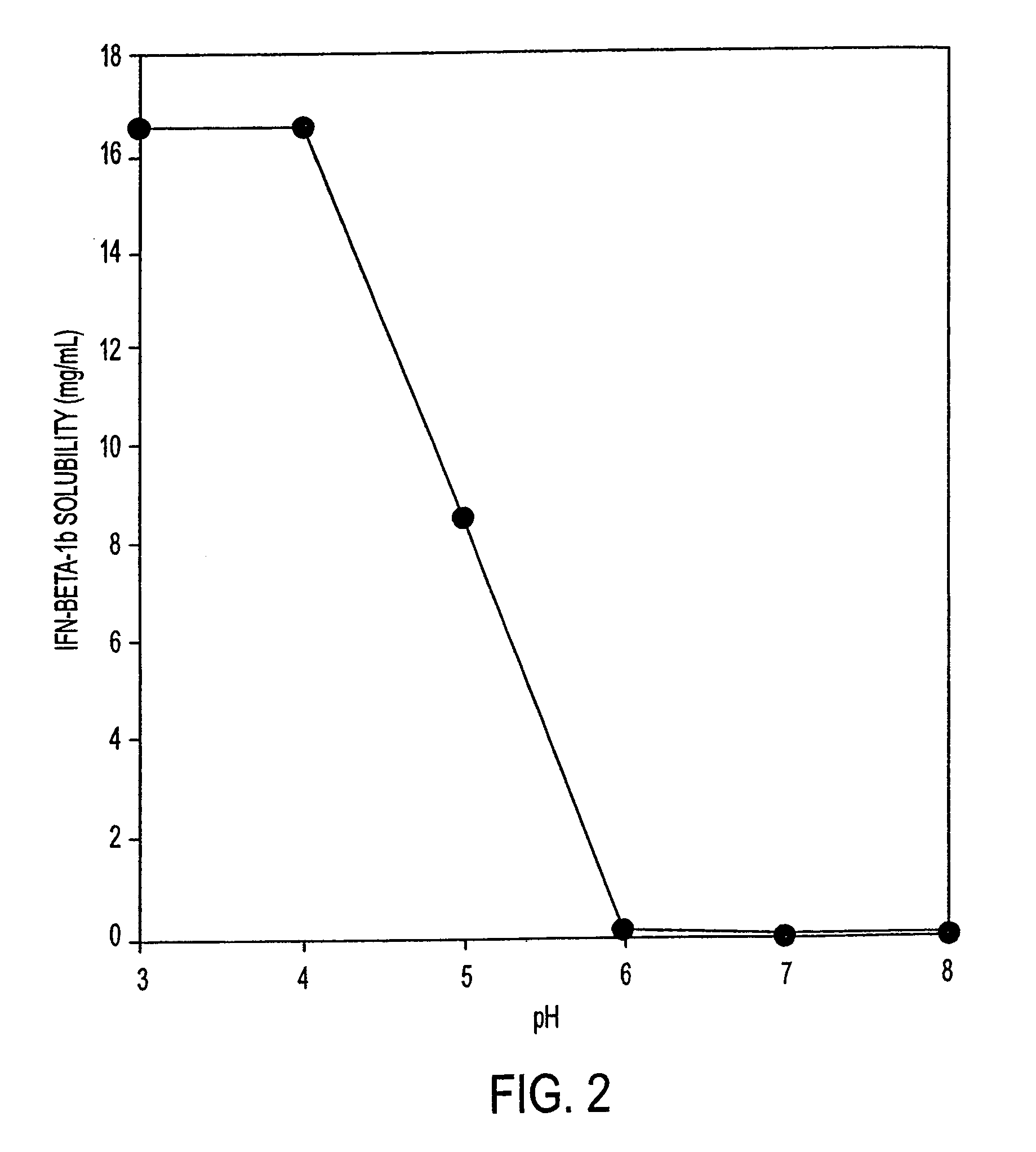
InactiveUS7371373B2Improve solubilityIncreasing the amount of monomeric IFN-βPowder deliveryNervous disorderSolubilityLow ionic strength
Stabilized pharmaceutical compositions comprising substantially monomeric interferon-beta (IFN-β) and methods useful in their preparation are provided. The compositions comprise the IFN-β solubilized in a low-ionic-strength formulation that maintains the composition at a pH of about 3.0 to about 5.0. Methods for preparing these compositions, and for increasing solubility of IFN-β in pharmaceutical compositions, are provided.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Water injection systems and methods
InactiveUS20120090833A1Promote recoveryReduce ionic strengthSurveyFluid removalLow ionic strengthUltimate tensile strength
There is disclosed a method for enhancing recovery of crude oil from a porous subterranean carbonate formation of which the pore spaces contain crude oil and connate water, the method comprising determining an ionic strength of the connate water; and injecting an aqueous displacement fluid having a lower ionic strength than the connate water into the formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
HSA-free formulations of interferon-beta
InactiveUS6887462B2Improve solubilityIncreasing the amount of monomeric IFN-βPowder deliveryNervous disorderSolubilityLow ionic strength
Stabilized pharmaceutical compositions comprising substantially monomeric interferon-beta (IFN-β) and methods useful in their preparation are provided. The compositions comprise the IFN-β solubilized in a low-ionic-strength formulation that maintains the composition at a pH of about 3.0 to about 5.0. Methods for preparing these compositions, and for increasing solubility of IFN-β in pharmaceutical compositions, are provided.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
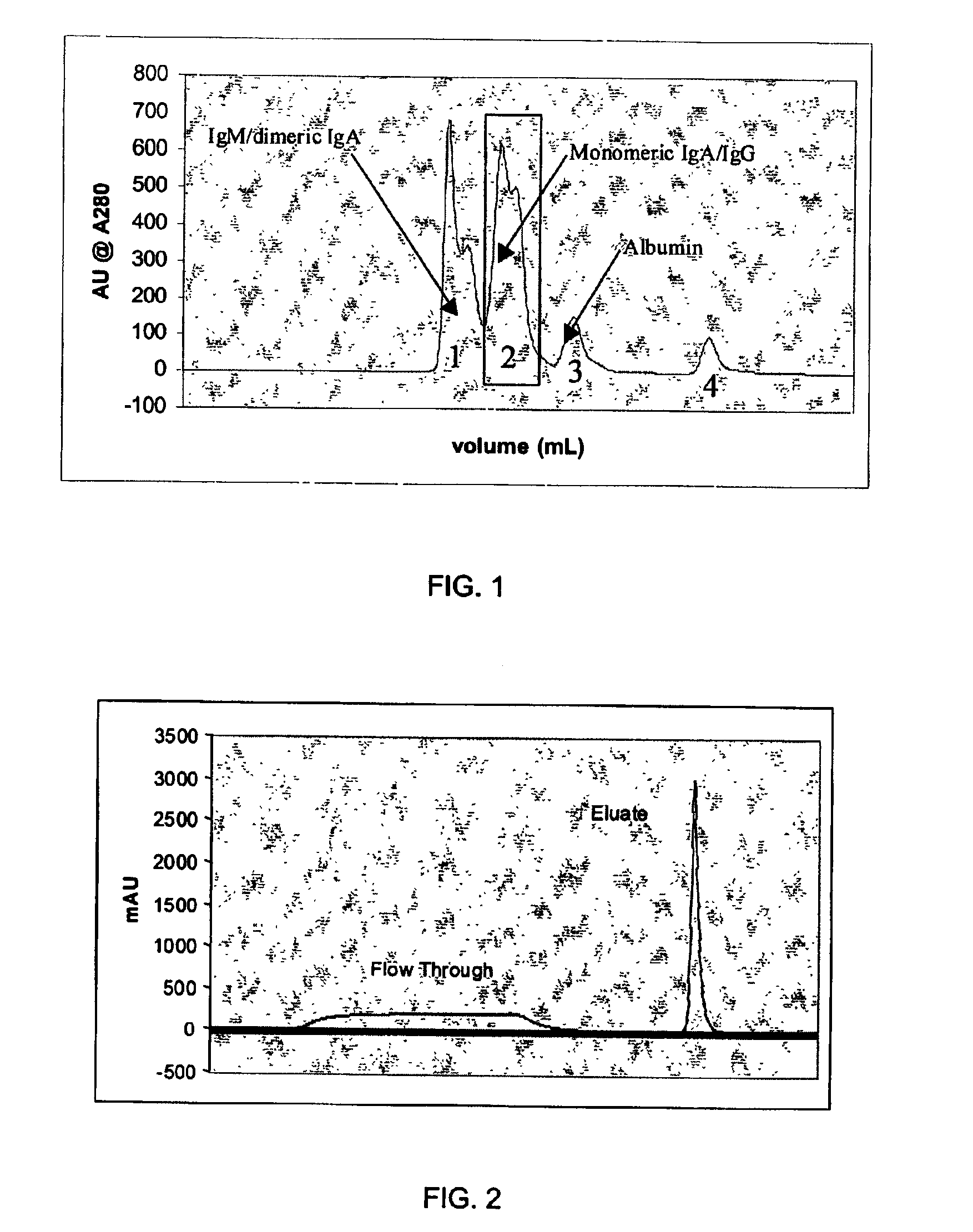
Chromatographic method for high yield purification and viral inactivation of antibodies
InactiveUS6955917B2Minimizes post virus treatment manipulationYield maximizationPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsLipid formationLow ionic strength
An improved process for the purification of antibodies from human plasma or other sources is disclosed. The process involves suspension of the antibodies at pH 3.8 to 4.5 followed by addition of caprylic acid and a pH shift to pH 5.0 to 5.2. A precipitate of contaminating proteins, lipids and caprylate forms and is removed, while the majority of the antibodies remain in solution. Sodium caprylate is again added to a final concentration of not less than about 15 mM. This solution is incubated for 1 hour at 25° C. to effect viral inactivation. A precipitate (mainly caprylate) is removed and the clear solution is diluted with purified water to reduce ionic strength. Anion exchange chromatography using two different resins is utilized to obtain an exceptionally pure IgG with subclass distribution similar to the starting distribution. The method maximizes yield and produces a gamma globulin with greater than 99% purity. The resin columns used to obtain a high yield of IgG retain IgM and IgA. IgA and IgM may be eluted from these resins in high yield and purity.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
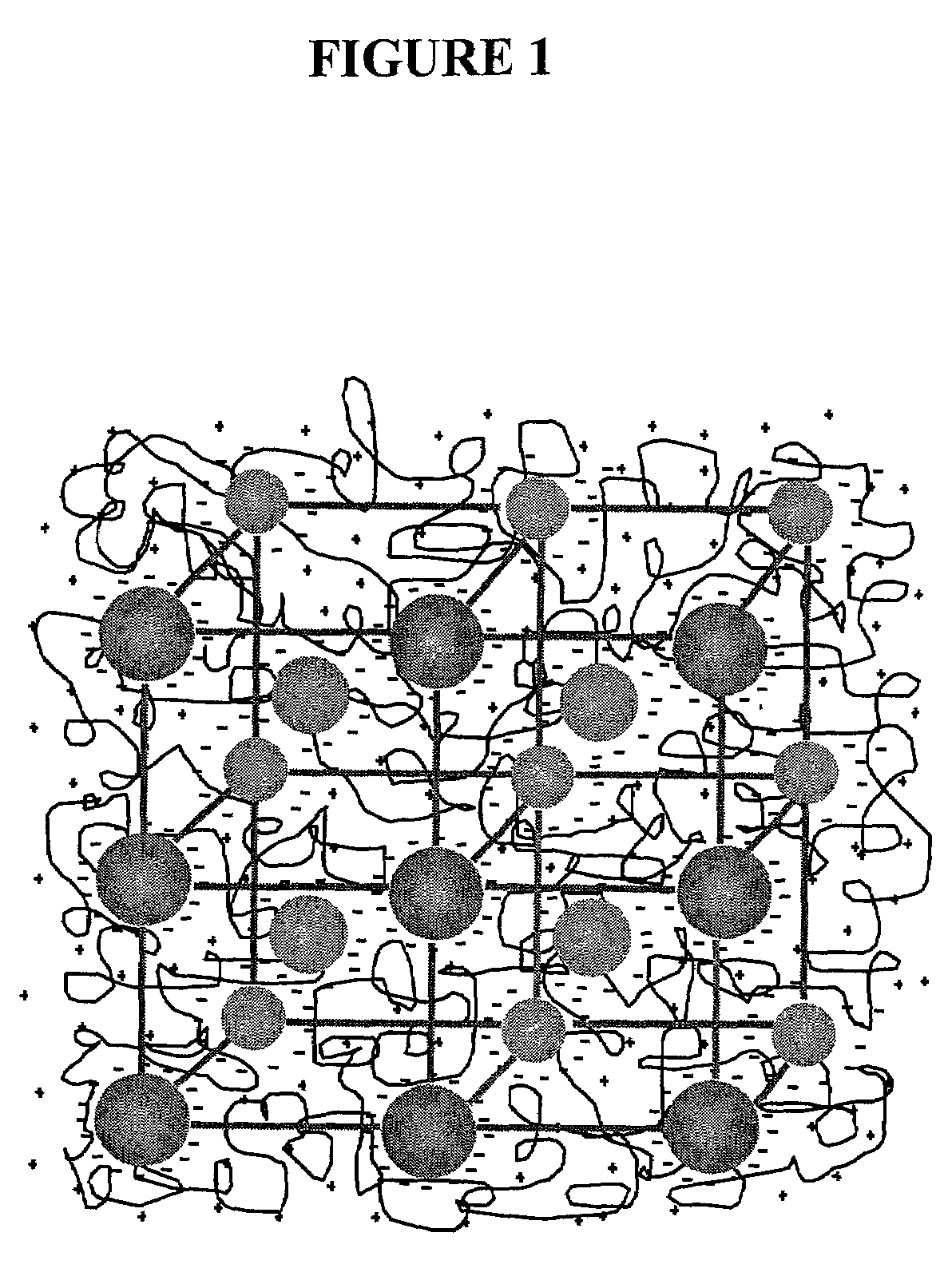
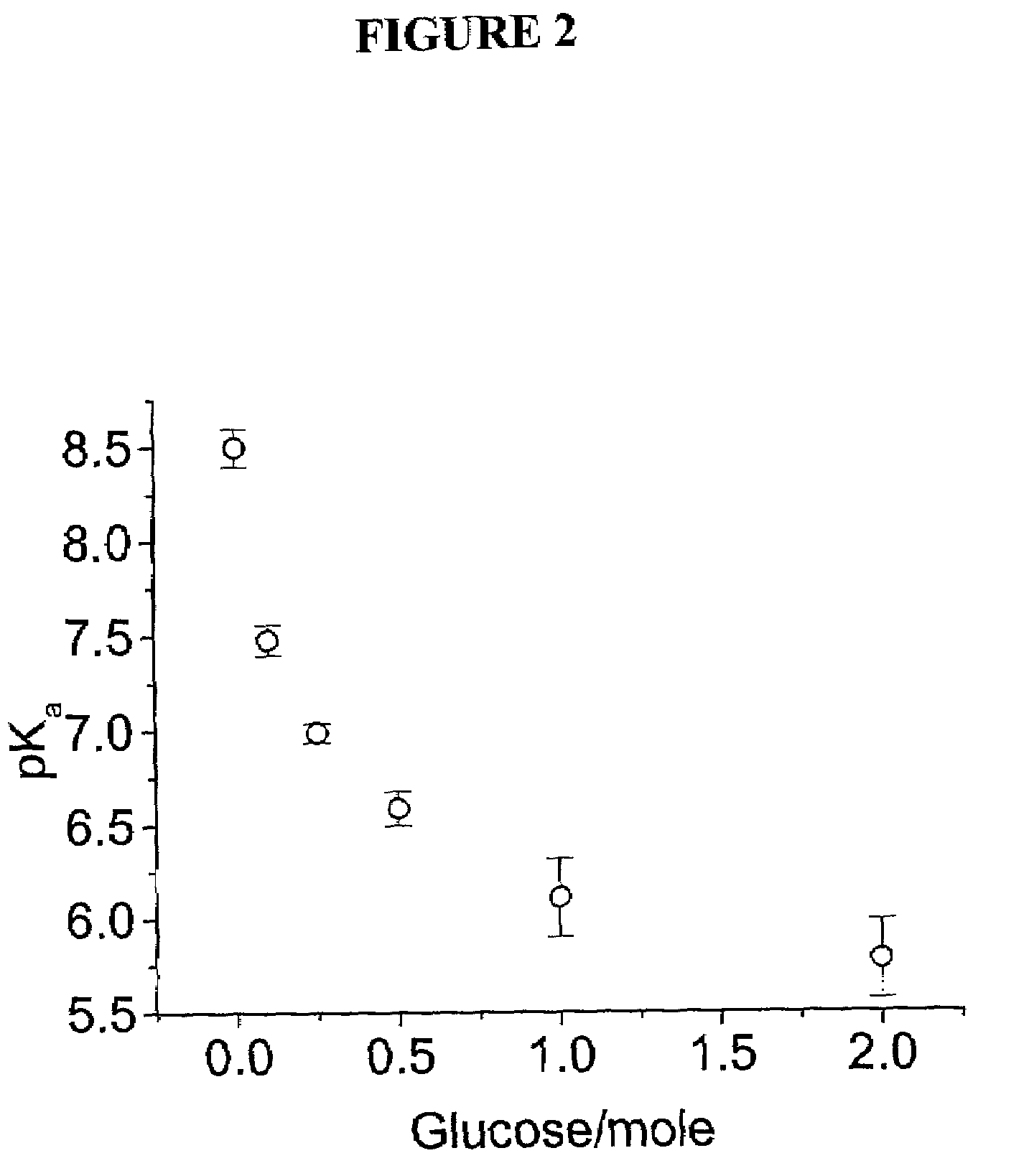
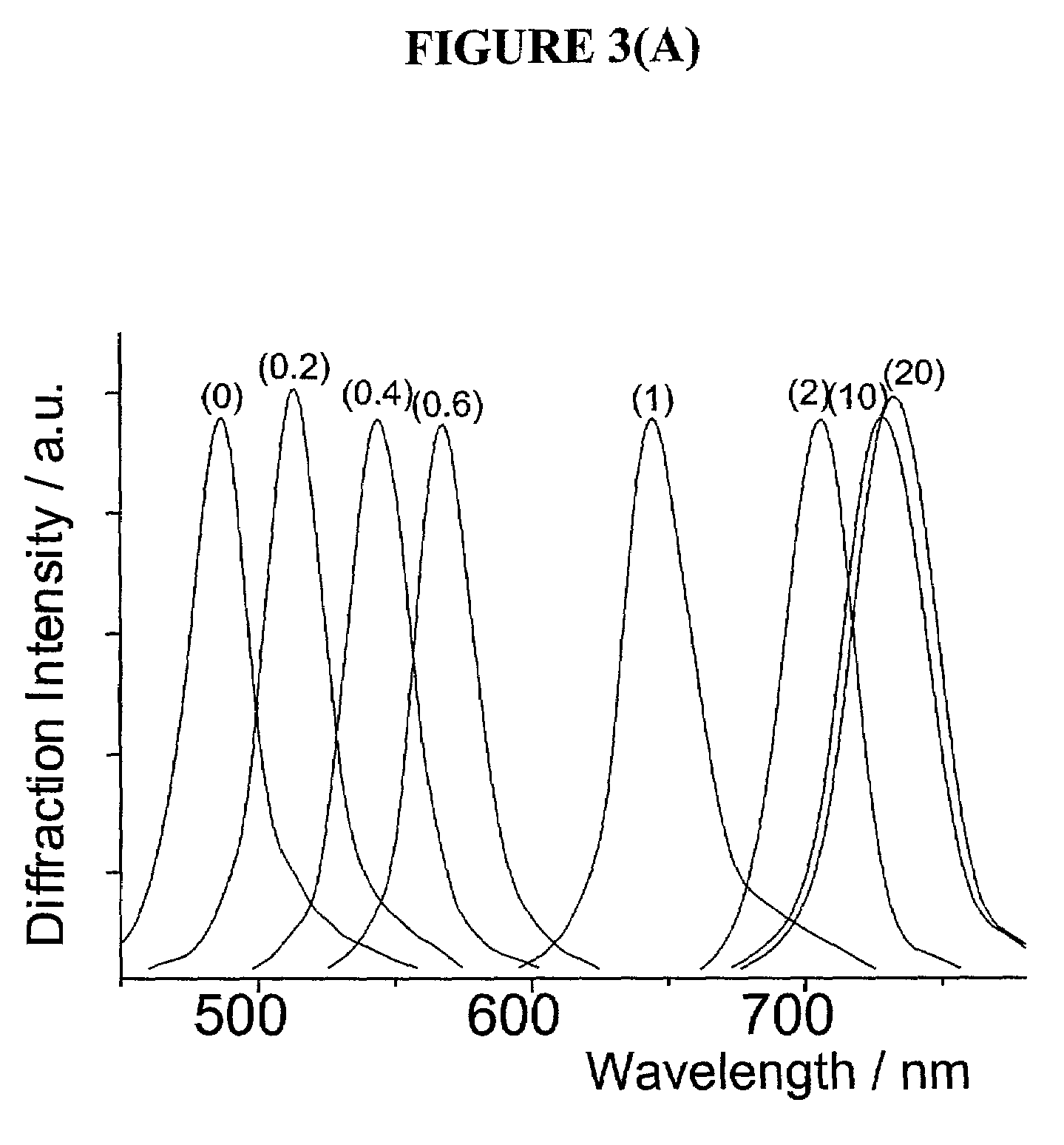
Intelligent polymerized crystalline colloidal array carbohydrate sensors
InactiveUS7105352B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
The present invention is related to glucose sensors that are capable of detecting the concentration or level of glucose in a solution or fluid having either low or high ionic strength. The glucose sensors of the present invention comprise a polymerized crystalline colloidal array (PCCA) and a molecular recognition component capable of responding to glucose. The molecular recognition component may be a boronic acid, such as a phenylboronic acid, glucose oxidase, a combination of phenylboronic acid and poly(ethylene)glycol or crown ether, or another component capable of detecting glucose in various fluids and solutions. The glucose sensors of the present invention may be useful in the development of noninvasive or minimally invasive in vivo glucose sensors for patients having diabetes mellitus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
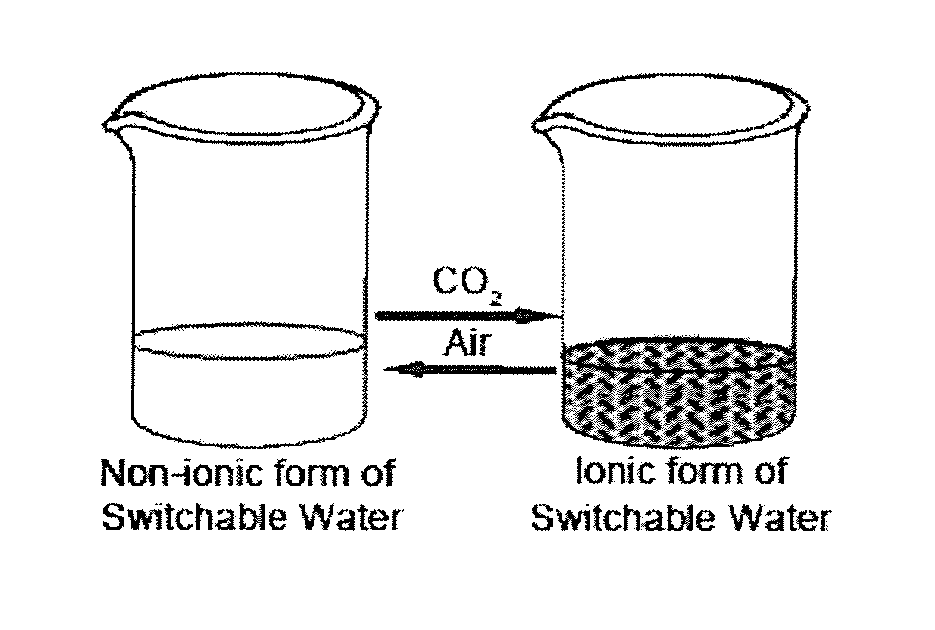
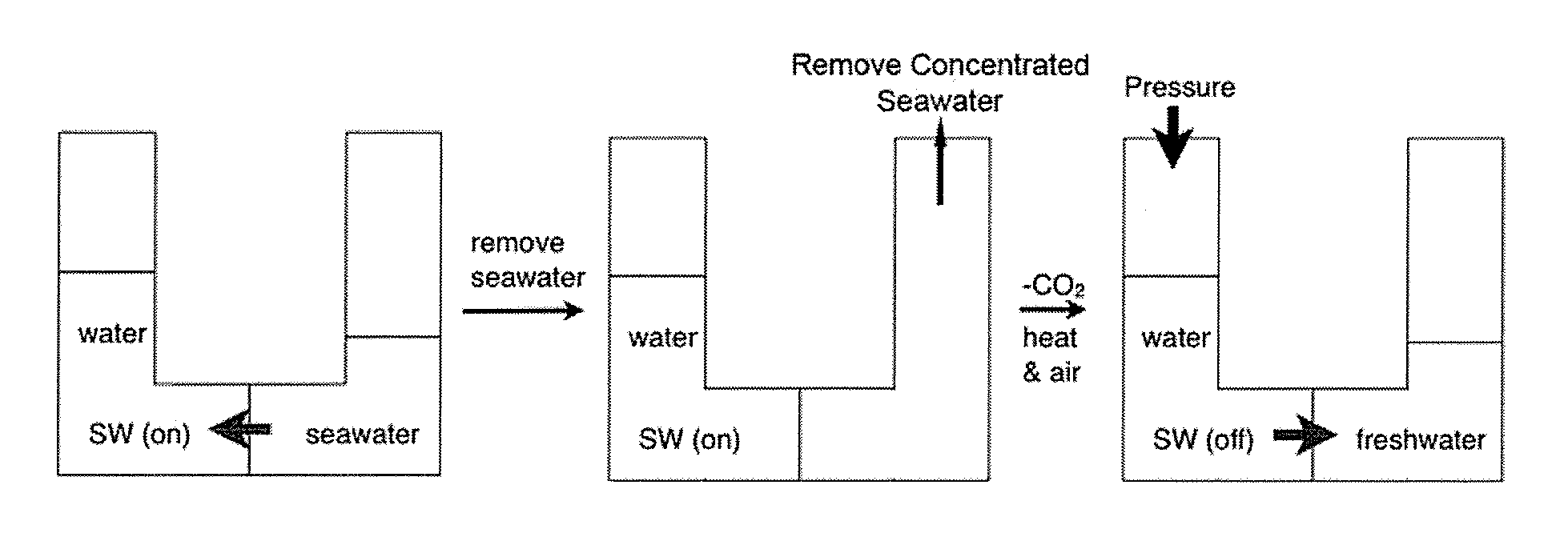
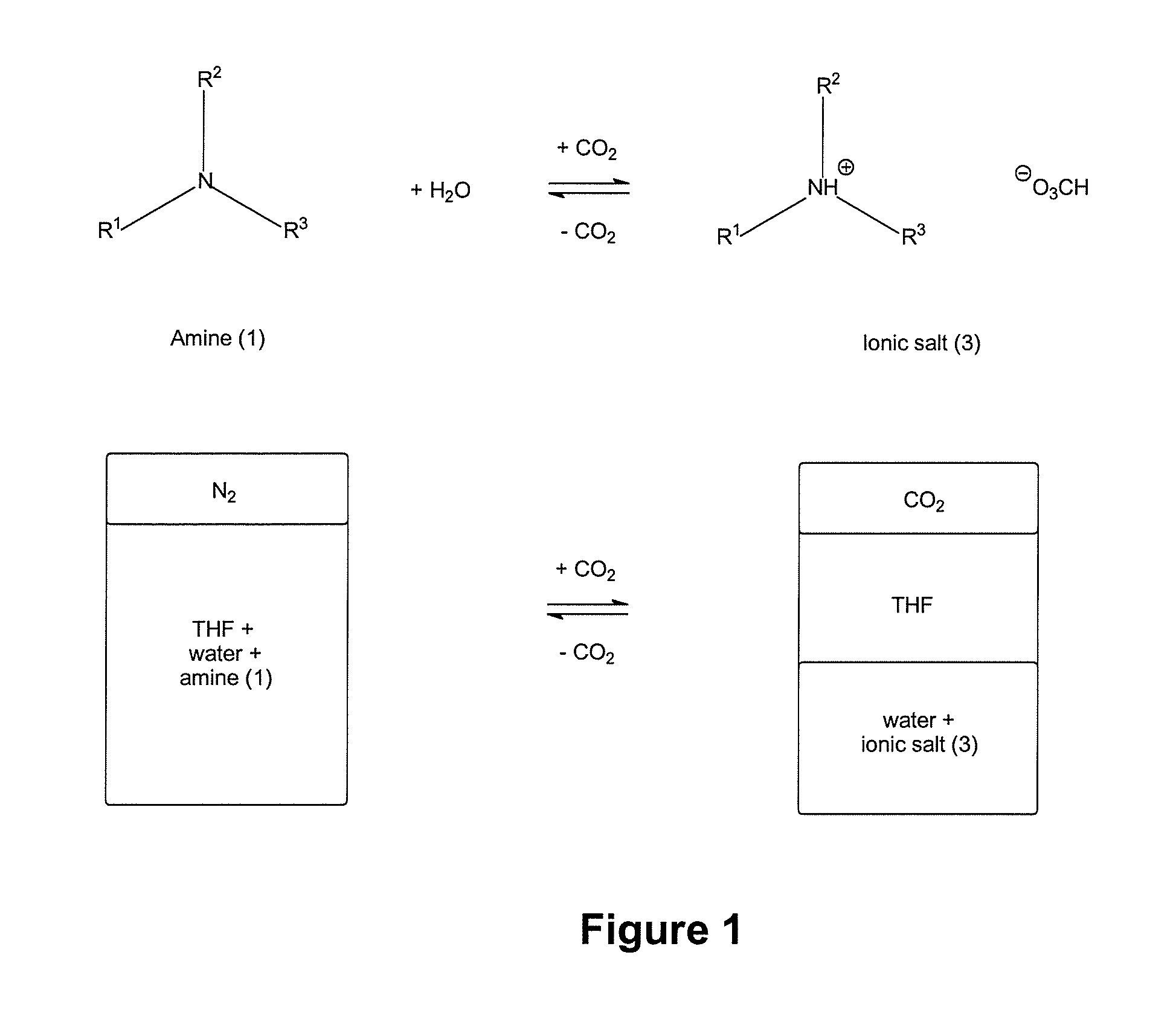
Systems and Methods for Use of Water with Switchable Ionic Strength
ActiveUS20140076810A1Increase ionic strengthChange viscosityWaste water treatment from quariesGeneral water supply conservationDistillationDesalination
Methods and systems for use of switchable water, which is capable of reversibly switching between an initial ionic strength and an increased ionic strength, is described. The disclosed methods and systems can be used, for example, in distillation-free removal of water from solvents, solutes, or solutions, desalination, clay settling, viscosity switching, etc. Switching from lower to higher ionic strength is readily achieved using low energy methods such as bubbling with C02, CS2 or COS or treatment with Bronsted acids. Switching from higher to lower ionic strength is readily achieved using low energy methods such as bubbling with air, inert gas, heating, agitating, introducing a vacuum or partial vacuum, or any combination or thereof.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON +1
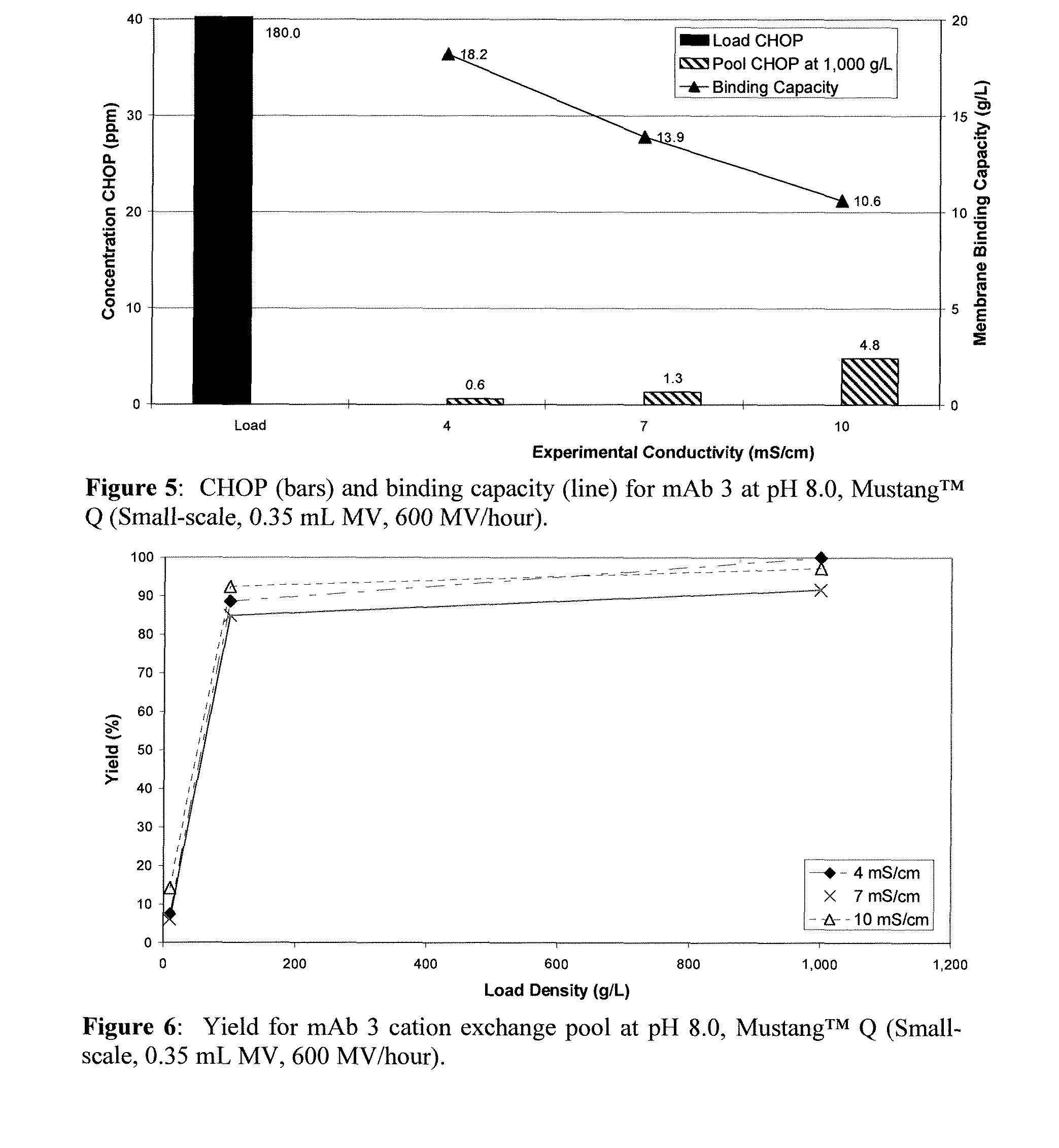
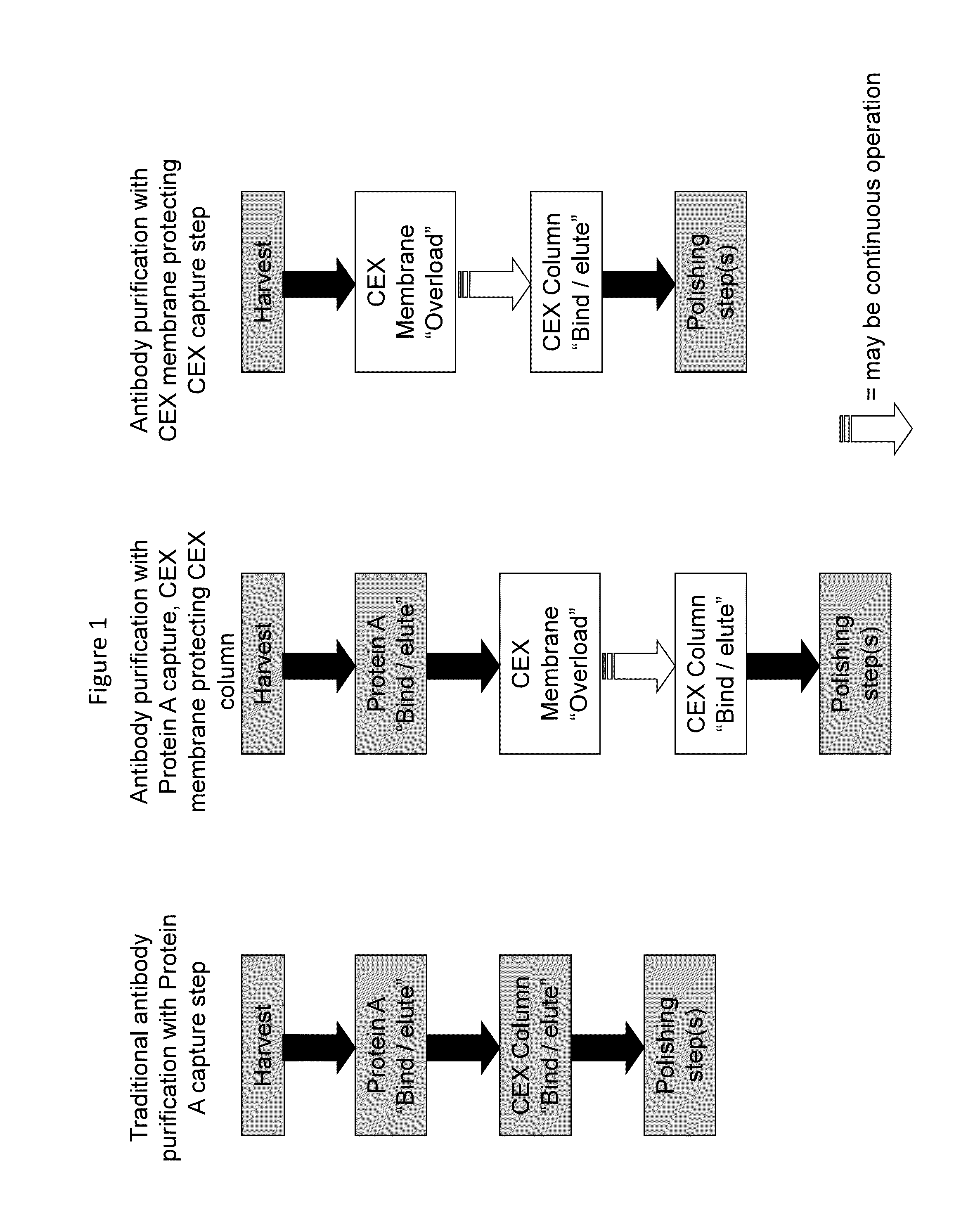
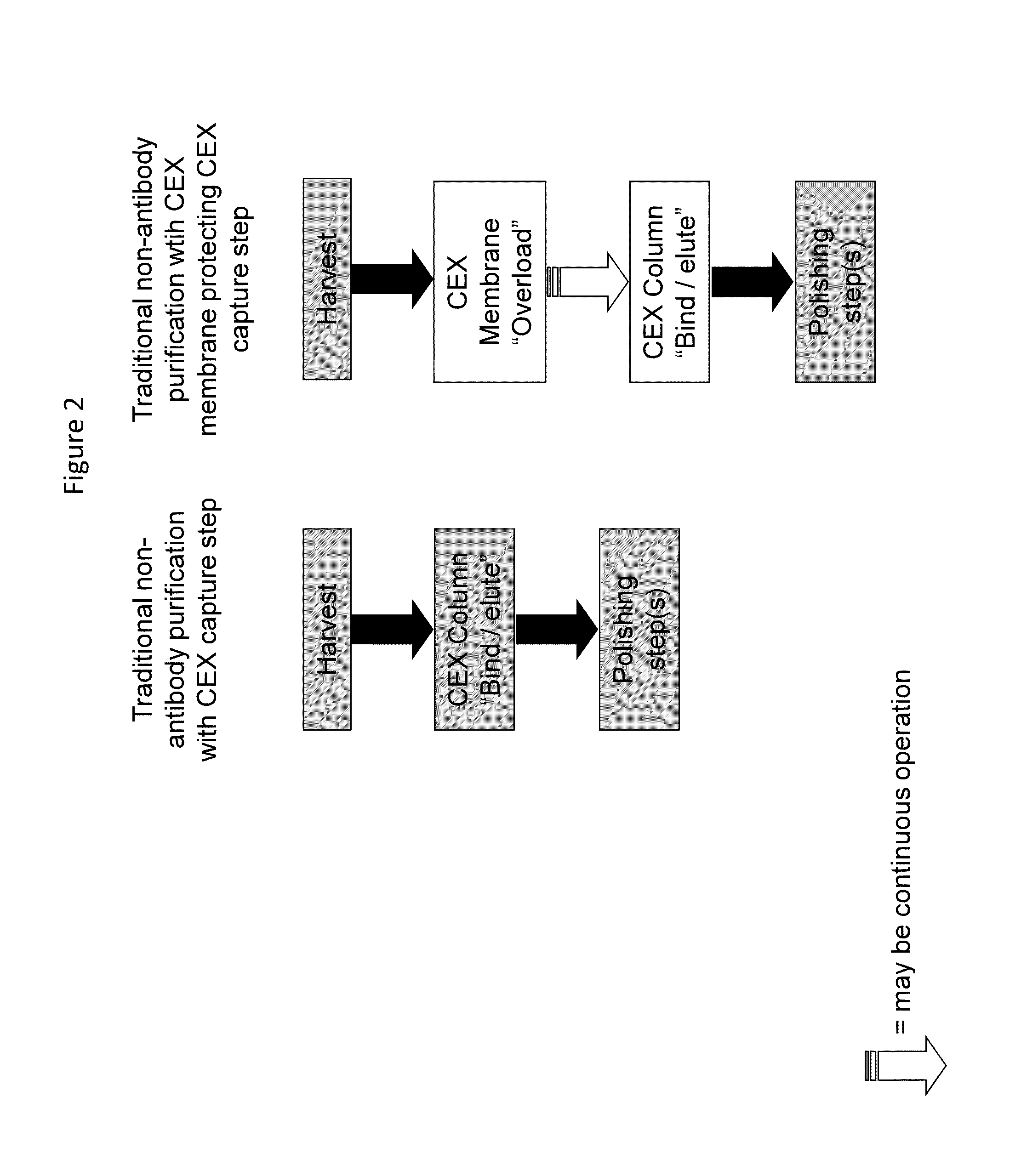
Methods for removing a contaminant using indigenous protein displacement ion exchange membrane chromatography
ActiveUS20120122759A1Increase costAvoid blockingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsLow ionic strengthIon-exchange membranes
Methods for purifying a polypeptide from a composition comprising the polypeptide and at least one contaminant are described, which methods comprise the sequential steps of: (a) passing the composition through an ion exchange membrane, where the polypeptide and the membrane have opposite charge, at operating conditions comprised of a buffer having a pH sufficiently distinct from the pI of the polypeptide to enhance the charge of the polypeptide and a low ionic strength effective to prevent the shielding of charges by buffer ions, which cause the membrane to bind the polypeptide and the at least one contaminant, and (b) recovering the purified polypeptide from the effluent.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
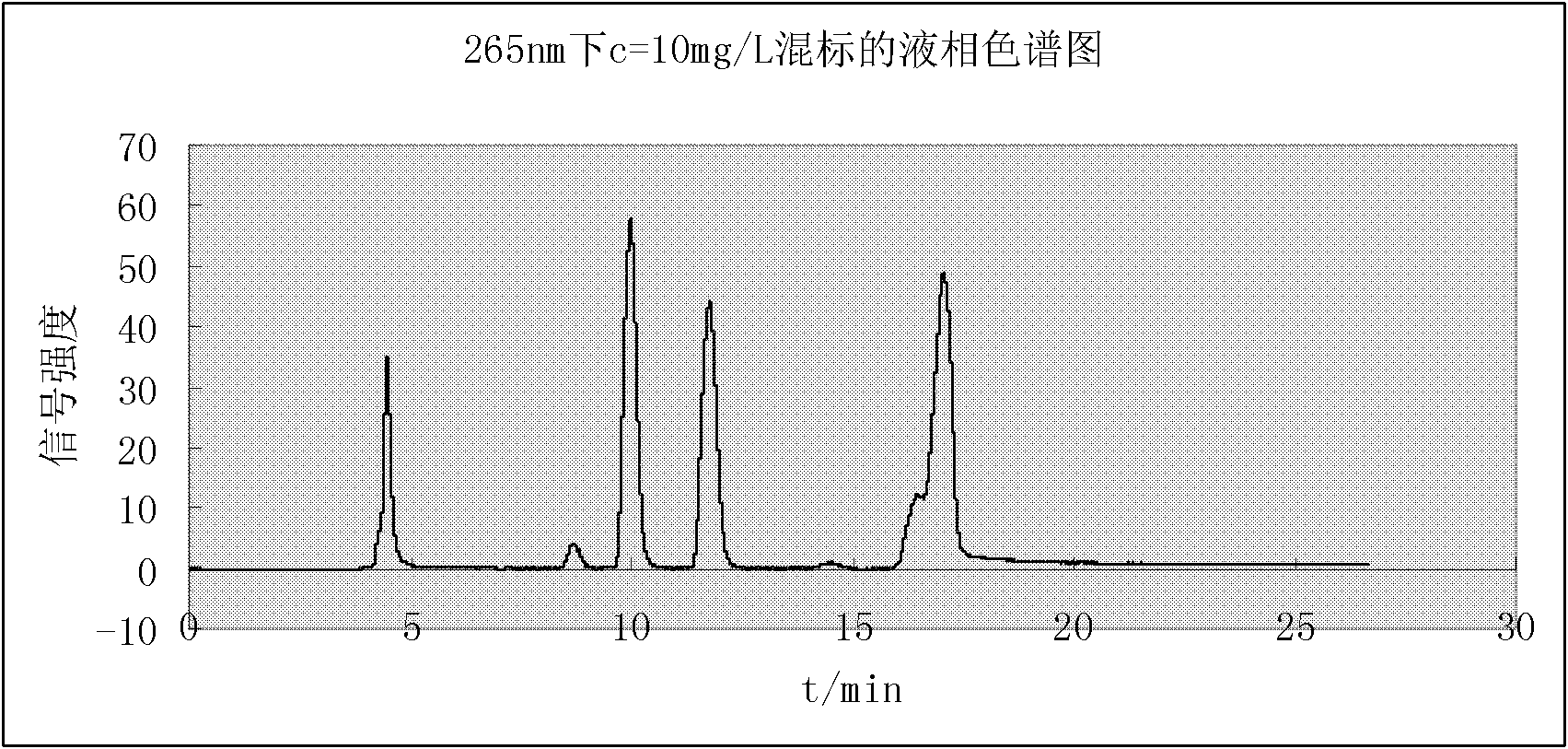
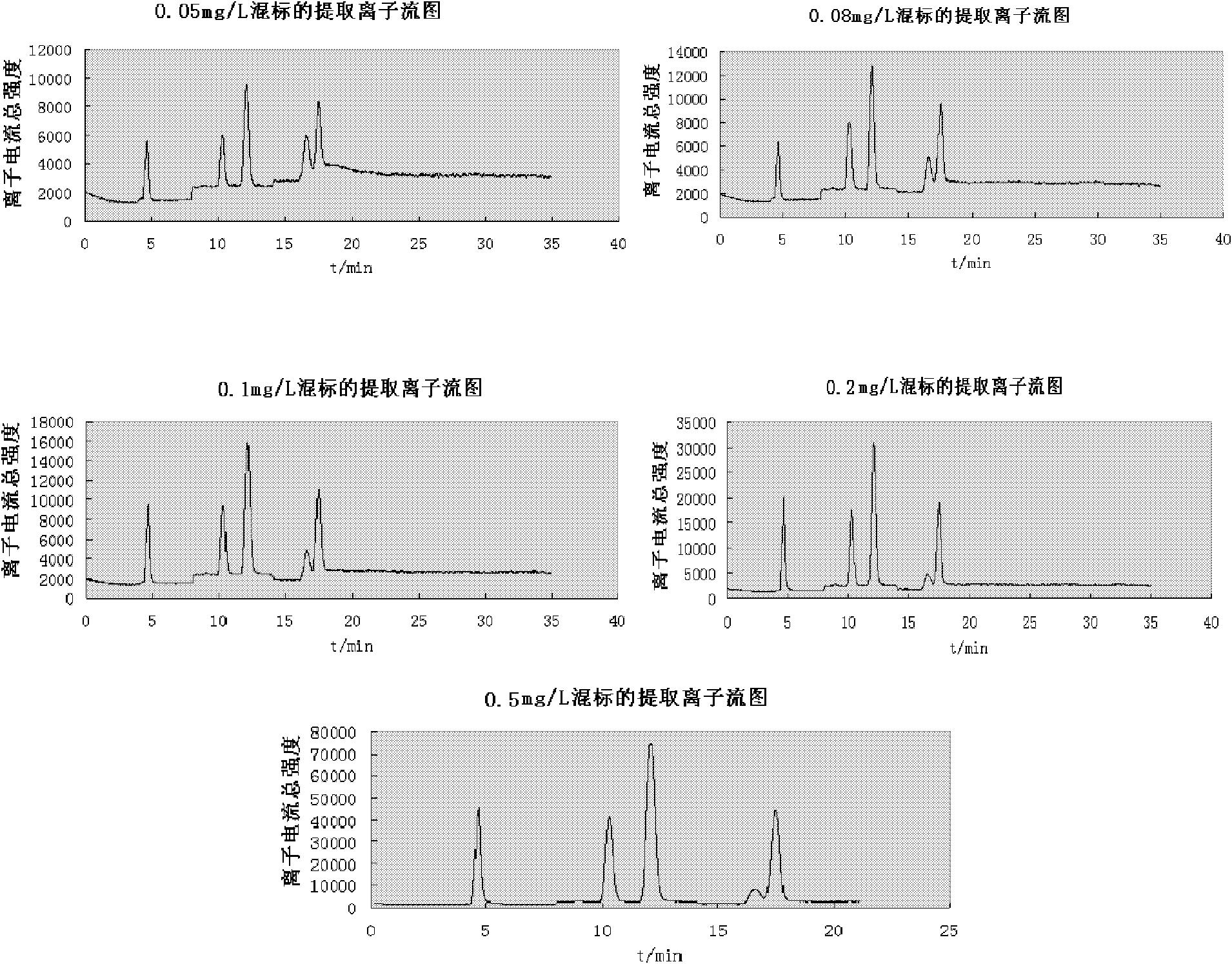
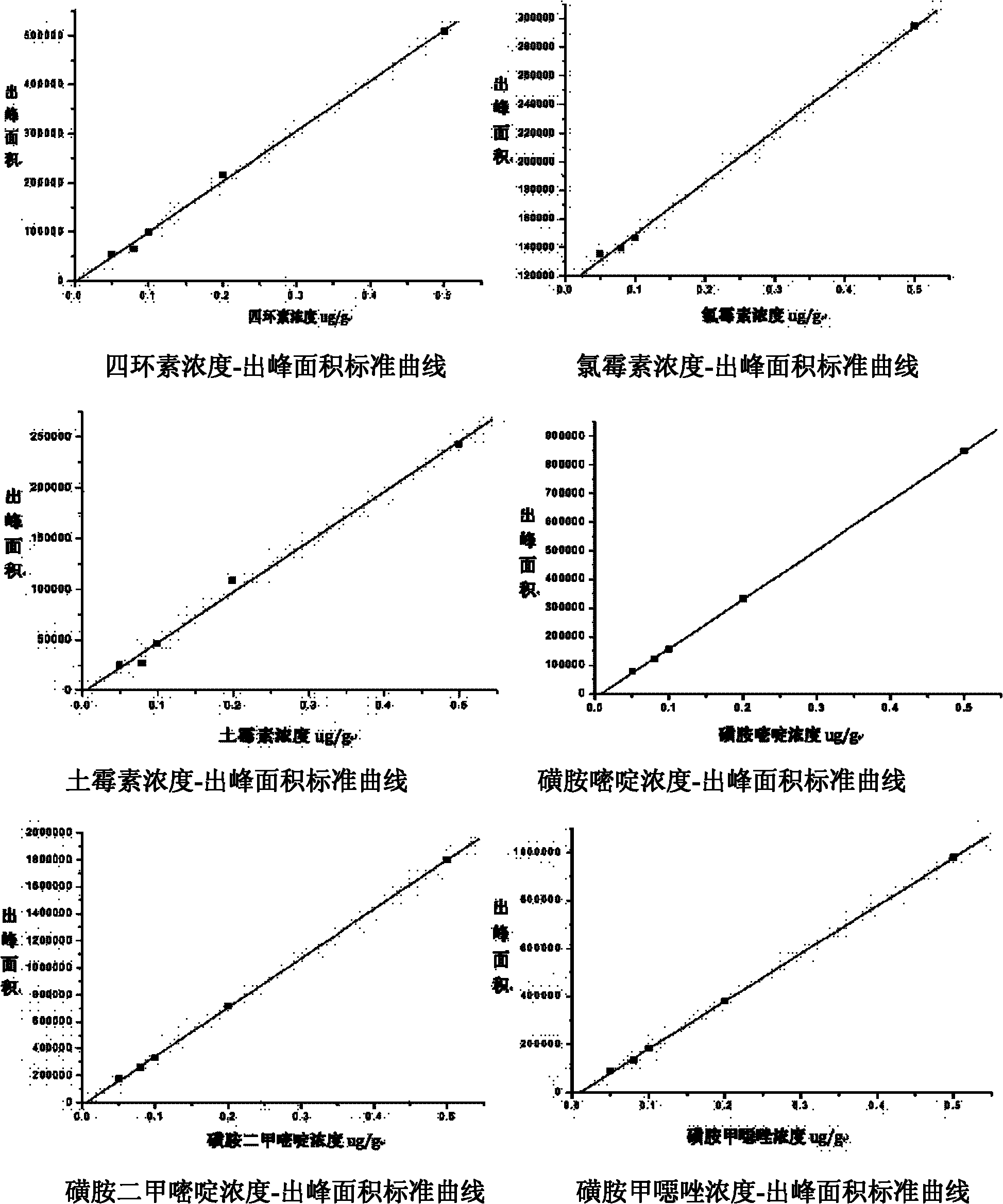
Simultaneous Quantitative Determination of Multiple Antibiotics at One Time
InactiveCN102269747ASolve the problem of difficult separation of peaks with similar peak timesAvoid errorsComponent separationAnalysis dataLow ionic strength
The present invention relates to a method for one-time simultaneous quantitative determination of multiple antibiotics, comprising: (1) preparing a sample filtrate; (2) setting liquid chromatography conditions and mass spectrometry conditions; (3) using the above liquid chromatography conditions and mass spectrometry conditions to determine For the sample filtrate prepared in step (1), analyze the data to determine the type and content of antibiotics in the analyzed sample. The present invention can simultaneously detect multiple antibiotics in one experiment and quantify the detected antibiotics at the same time. The combination of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry not only solves the problem of difficult separation of peaks with similar peak times in liquid chromatography, but also overcomes the The error caused by the inconspicuous peak of low ion current intensity in the mass spectrum is eliminated; the invention can be widely used in the detection and quantitative analysis of antibiotics in various samples such as feces, soil, water, food, and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Methods for synthesizing precipitated silica and use thereof
InactiveUS20050228106A1Affects ionic strengthReduce ionic strengthMaterial nanotechnologySilicaLow ionic strengthColloid
The synthesis of precipitated silica having improved chemical and physical properties of use as a reinforcing filler in polymeric matrices is described. Improvements in the properties result from the synthesis of the silica al a reduced ionic strength. In particular, the use of silicia acid during synthesis, provides a solution of reduced ionic strength, which favors the formation of improved colloidal structure via increased aggregation and reduced agglomeration. In addition, the surface of the silica precipitate formed may be modified by the addition of surface modifying agents, during synthesis to further enhance the desired reinforcing properties of the precipitated silica. The invention also embodies polymeric compositions of improved tensile and elongation strengths, with the compositions including precipitated silica, synthesized at reduced ionic strengths and having modified surfaces, in combination with a polymeric compound.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use
ActiveUS20060178294A1Improve breathabilityProcess stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLow ionic strengthSulfate
A cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use are disclosed. The reagent contains a N-acyl sarcosine or a salt thereof, a pH adjusting agent to adjust pH of the reagent in a range from about 4 to about 6; and an aqueous medium; the reagent having a low ionic strength defined by a conductivity of less than 9.0 mS / cm. The reagent further contains bovine serum albumin and glycerol. The reagent may further include an alkyl sulfate surfactant. Upon incubating the cells with the reagent, the reagent permeates the cellular membrane to allow penetration of an intracellular marker, causes intracellular protein aggregation within the cellular membrane, while preserves a cellular constituent for binding with a cellular marker for subsequent analysis by flow cytometry.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of laundry washing
InactiveUS7476258B2Other washing machinesDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesLow ionic strengthPulp and paper industry
The invention provides a method of washing a laundry fabric in a wash liquor in a washing machine, wherein during a single wash cycle no more than 10% by weight of the wash liquor is drained from the washing machine, wherein the method comprises the step of varying the ionic strength of the wash liquor over at least 10% of the duration of the wash cycle by addition of one or more ionic ingredients to the wash liquor, and wherein the lowest ionic strength of the wash liquor is from 0.001 to 0.06 M and the highest ionic strength of the wash liquor is from 0.01 to 0.5 M.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Method for extracting fibrillin from chicken
InactiveCN101161671AHigh purityHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesMyofibrilForeign protein
The present invention discloses a method to extract myofibril protein from chicken, aiming to provide a method to extract myofibril protein with high purity, simplicity and low cost. The procedures are as follows: chicken under room temperature is cut into pieces, added with a low-ionic-strength extract with the pH of 6.0-7.0 to dissolve the dissolvable under the condition of low ionic acid strength, the solution undergoes even centrifuge to obtain a deposit containing myofibril protein, which is added with a high-ionic-strength extract with the pH of 6.0-7.0, the solution undergoes even centrifuge, and the separated myofibril protein deposit undergoes cycles of extraction with the high-ionic-strength extract, each of which is followed by centrifuges to eliminate the foreign proteins and the other impurities from the chicken, the deposit obtained from centrifuged suspension is the myofibril protein, which is added with the high-ionic-strength extract to prepare a solution, which is dialyzed under room temperature, frozen and dried to obtain the intended product of myofibril protein.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Water with Switchable Ionic Strength
InactiveUS20130105377A1Ionic strengthReduce ionic strengthWaste water treatment from quariesGeneral water supply conservationSalting outDistillation
A method and system for reversibly converting water between an initial ionic strength and an increased ionic strength, using a switchable additive, is described. The disclosed method and system can be used, for example, in distillation-free removal of water from solvents, solutes, or solutions. Following extraction of a solute from a medium by dissolving it in water, the solute can then be isolated from the aqueous solution or “salted-out” by converting the water to a solution having an increased ionic strength. The solute then separates from the increased ionic strength solution as a separate phase. Once the solute is, for example, decanted off, the increased ionic strength aqueous solution can be converted back to water having its original ionic strength and reused. Switching from lower to higher ionic strength is readily achieved using low energy methods such as bubbling with CO2, CS2 or COS. Switching from higher to lower ionic strength is readily achieved using low energy methods such as bubbling with air, heating, agitating, introducing a vacuum or partial vacuum, or any combination or thereof.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Method for fast separating and purifying R-phycoerythrin, R-phycocyanin
InactiveCN101240009AChromatography is slowLoad lessPeptide preparation methodsLow ionic strengthPhycoerythrin
A rapid separation method of purified R-phycoerythrin and R-phycocyanin, which pertains to separation and purification of red algae technical field. The invention uses red algae as raw material, extracts R-phycoerythrin and R-phycocyanin by freeze dissolving and intensified swelling with low ions, carries out primary purification after precipitation with ammonia sulfate, then absorb and enrich R-phycoerythrin and R-phycocyanin by anion exchange chromatography, and further elutes highly purified R-phycoerythrin and R-phycocyanin from anion exchange chromatography step by step. The method eliminates conventional complex separation and purification step which uses multiple chromatography combining molecular sieve chromatography with hydroxyapatite chromatography, solves the problem of extensive and rapid preparation. The method is easy in operation, time and energy saving, with little requirements to apparatus, and high in yield.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use
ActiveUS7678578B2Improve breathabilityStabilize surfactantBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCellular componentLow ionic strength
A cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use are disclosed. The reagent contains a N-acyl sarcosine or a salt thereof, a pH adjusting agent to adjust pH of the reagent in a range from about 4 to about 6; and an aqueous medium; the reagent having a low ionic strength defined by a conductivity of less than 9.0 mS / cm. The reagent further contains bovine serum albumin and glycerol. The reagent may further include an alkyl sulfate surfactant. Upon incubating the cells with the reagent, the reagent permeates the cellular membrane to allow penetration of an intracellular marker, causes intracellular protein aggregation within the cellular membrane, while preserves a cellular constituent for binding with a cellular marker for subsequent analysis by flow cytometry.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
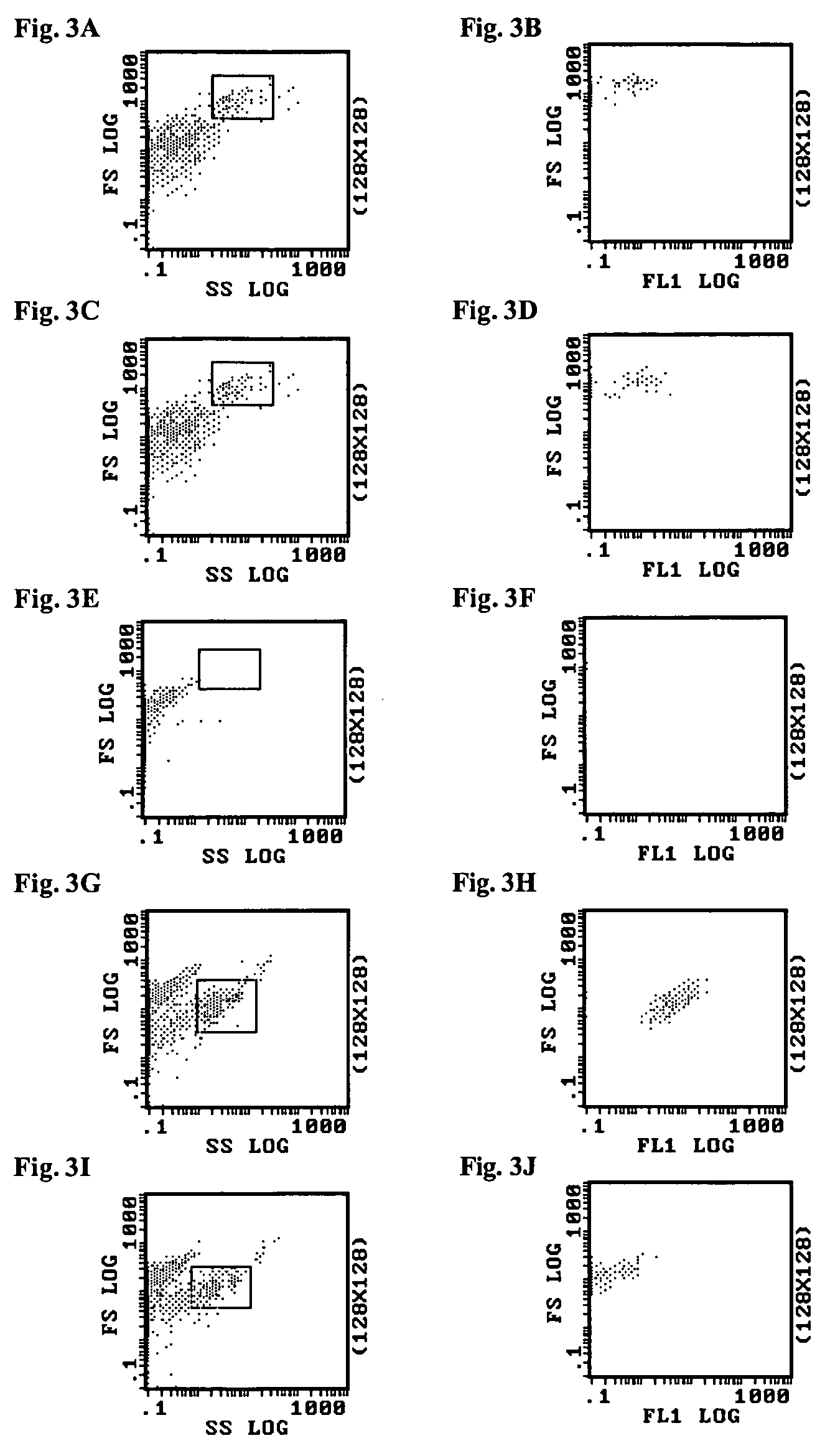
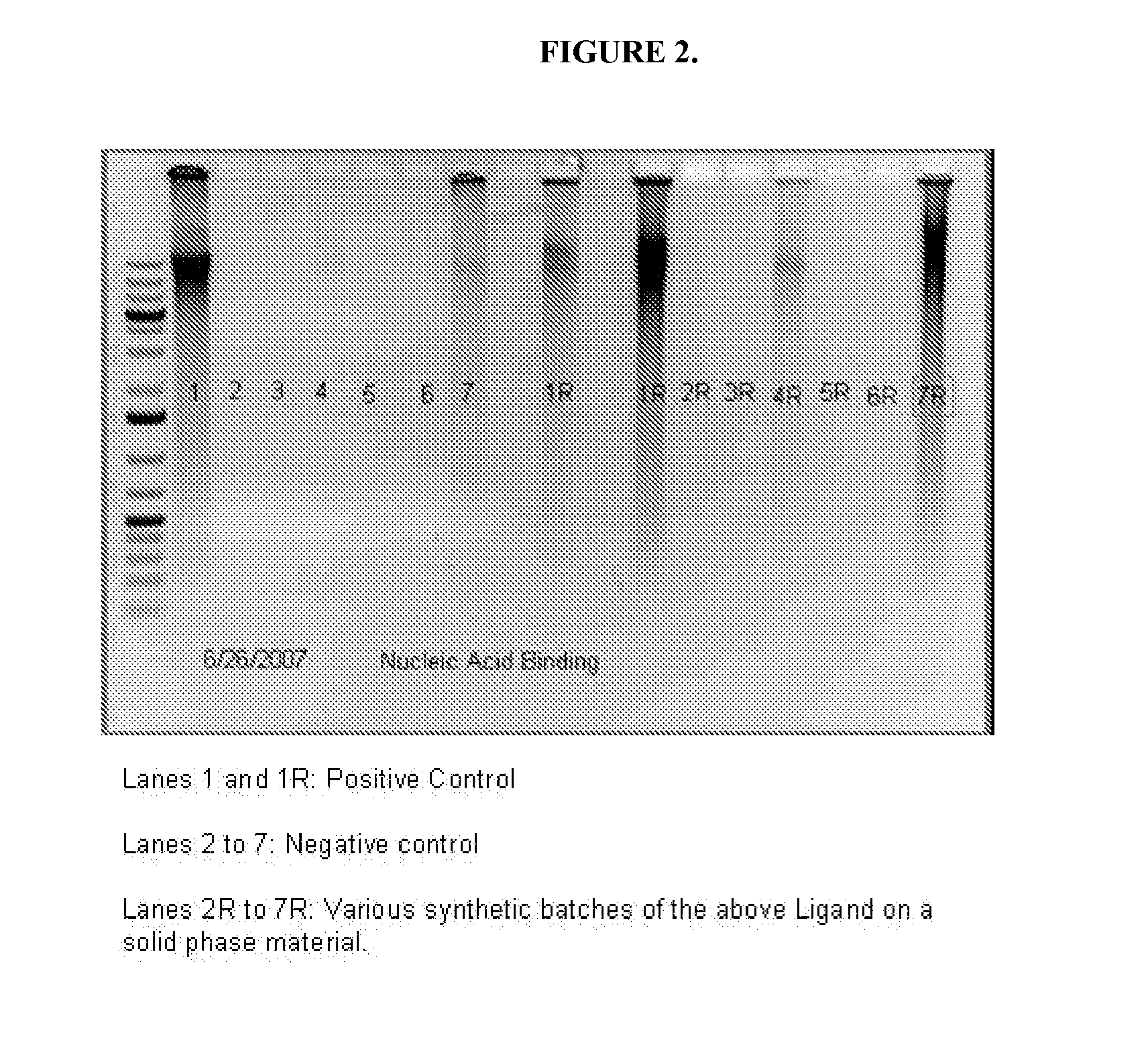
Method for nucleic acids isolation
ActiveUS20110118457A1Sugar derivativesSolid sorbent liquid separationPresent methodLow ionic strength
The present invention provides a method for isolating nucleic acids. The method comprises: contacting a sample containing nucleic acids with a solid phase in a first aqueous solution to provide a loaded solid phase; washing the loaded solid phase with a second aqueous solution to provide a washed solid phase; and eluting the washed solid phase with a low ionic strength liquid to obtain the isolated nucleic acids. The present invention also provides a kit for practicing the present method.
Owner:PROGENTECH +1
Systems and methods for intravenous drug management using immittance spectroscopy
InactiveCN103501839AReduce ionic strengthData processing applicationsMedical devicesLow ionic strengthMedicine
Described herein are devices, systems, and methods for determining the composition of liquids, including the identity of one or more drugs in the liquid, the concentration of the drug, and the type of diluent using immittance spectroscopy. These devices, systems and methods are particularly useful for describing the identity and, in some variations, concentration of one or more components of a medical liquid such as intravenous fluid. In particular, described herein are devices, systems and methods that may operate in low ionic strength diluents. Also described are methods of recognizing complex immittance spectrograph patterns to determine the composition of a liquid by pattern recognition.
Owner:S E A MEDICAL SYST
Method for fast separating and purifying C-phycocyanin and isophycocyanin from blue algae
InactiveCN101240010AReduce manufacturing costHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsDEAE-SepharoseLow ionic strength
A rapid separation and purification process of C-phycocyanin and allophycocyanin from blue algae, which pertains to separation and purification of phycocyanin technical field. The invention extracts C-phycocyanin and allophycocyanin by freeze dissolving and intensified swelling with low ions, finally carries out primary purification after precipitation with ammonia sulfate, elutes buffer liquid with constant ionic strength and pH gradient by DEAE Sepharose Fast Flow ionexchange chromatography, so that C-phycocyanin and allophycocyanin with high purity is obtained by one step. The process is easy in operation, time and energy saving, with little requirements to apparatus, high in yield. The process also dramatically lower preparation cost of CPC and APC, thus lays a foundation for CPC and APC application in ultrasensitive detection in biomedical.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Convergent detection type erythrocyte blood type irregular antibody detection kit based on solid-phase agglutination technology and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110174519AImprove coating efficiencyReduce testing costsBiological testingAgainst vector-borne diseasesLow ionic strengthMonoclonal antibody
The invention relates to a convergent detection type erythrocyte blood type irregular antibody detection kit based on a solid-phase agglutination technology and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of kit preparation. The kit comprises (1) a convergent detection type solid-phase agglutination reaction micro-plate; (2) a low-ion-strength solution; (3) an indication system; (4) negative control serum; and (5) positive control serum. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) preparing the convergent detection type solid-phase agglutination reaction micro-plate; (2) preparing the low-ion-strength solution; (3) preparing the indication system; (4) preparing the negative control serum; and (5) preparing the positive control serum; and through innovative utilization of high specificity adsorption of the erythrocyte by virtue of a monoclonal antibody, a freeze-drying preservation technology and a high-sensitivity two-step method indication system,the problems of low sensitivity, difficulty in storing the erythrocyte, easiness in leak detection and the like in an existing clinically irregular antibody detection method are practically solved, and the high-cost-performance detection kit is provided for the clinical front-line detection work.
Owner:广州血液中心
Electrochemical sensor
InactiveUS20130256133A1Improve reaction speedLower activation energyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectrochemical gas sensorReaction rate
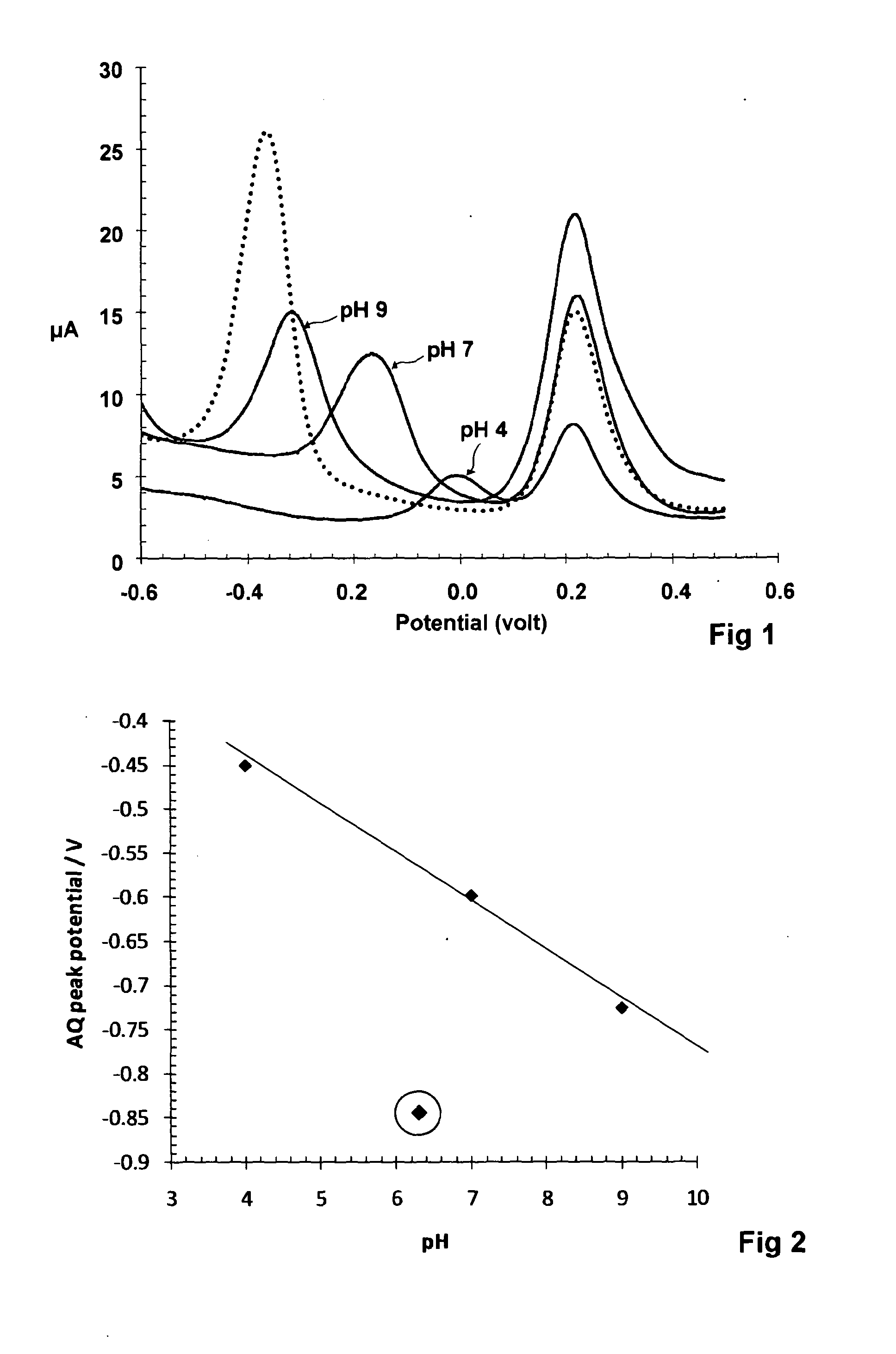
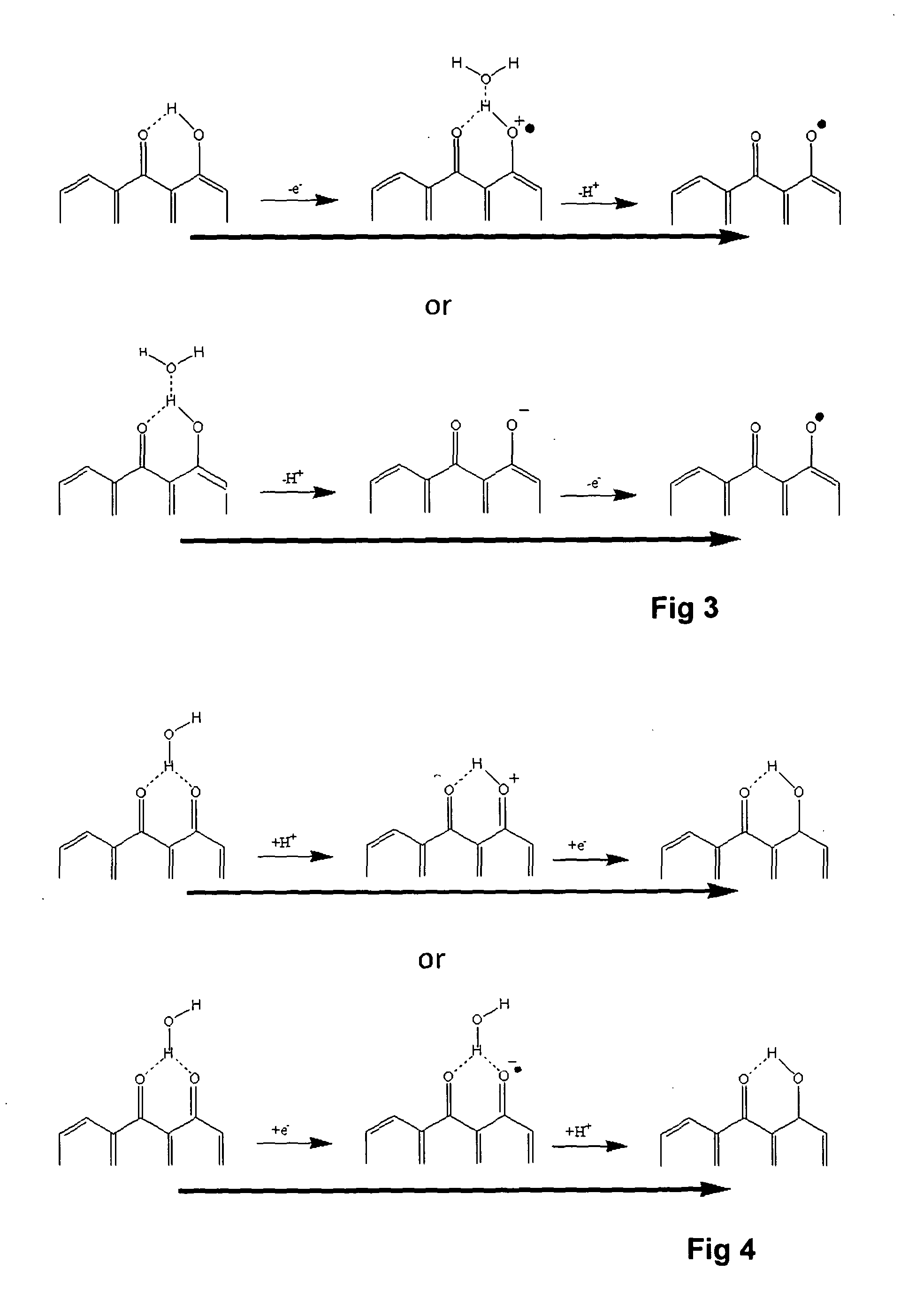
A voltammetric pH sensor, especially for characterising wellbore fluids, comprises a plurality of electrodes with a redox active organic compound attached to an electrode and having at least one functional group convertible electrochemically between reduced and oxidized forms with transfer of at least one proton between the compound and surrounding aqueous phase, wherein the compound has at least one substituent group which promotes hydrogen bonding at a said functional group and thereby increases the reaction rate of proton transfer. The substituent group may form an internal hydrogen bond with a redox-convertible group or may enhance polarity to promote electrostatic interaction with water molecules and reduce activation energy. Typical examples include alizarin or 1,2-dihydroxy-anthraquinone (RH=72-48-0), quinizarin or 1,4-dihydroxy-anthraquinone (RN=81-64-1), 2-acetoxy-benzoquinone (RN=1125-55-9), chloranil or 2,3,4,5-tetrachloro-benzoquinone (RN=118-75-2) and 1,4-diamino-2,3-dichloro-anthraquinone (RN=81-42-5) deposited on a glassy carbon electrode. In this way, anomalous measurements at low ionic strength and low concentrations of pH buffering species can be overcome.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Fritillariae cirrhosae bulbus polysaccharide extraction, separation and purification technology
ActiveCN106397622AOvercoming the low extraction rateOvercome purityBulk chemical productionDEAE SephadexPyridinium
The invention discloses a fritillariae cirrhosae bulbus polysaccharide extraction, separation and purification technology. As a novel supercritical CO2 extraction technology is utilized, the defects that a general method is low in extraction rate and not high in purity are overcome; quaternary ammonium salt cetyl pyridinium chloride monohydrate and fritillariae cirrhosae bulbus polysaccharide can precipitate in water solution with low ionic strength; when the ionic strength is high, precipitate can be dissolved, dissociated and released, and the purification effect is good; DEAE-Sephadex ionic exchange column chromatography is utilized to further remove neutral impurities and impurities with positive charges, and the separation and purification effect is better.
Owner:CHONGQING THREE GORGES MEDICAL COLLEGE
Well treatment with ionic polymer gels
Methods comprising preparing an aqueous mixture of an anionic polymer, a charge screening surfactant, and a borate crosslinker, wherein the mixture has a conductivity less than 10 mS / cm, injecting the mixture down a wellbore, and gelling the mixture. An embodiment of the aqueous mixture can also include tetramethylammonium chloride as a clay stabilizer and a metal crosslinker such as a complex of zirconium and an amino acid ligand system. An embodiment can effectively provide borate crosslinking of an anionic polymer in a low-ionic-strength fluid system, without sacrificing ultimate gel strength or thermal persistence of the metal crosslinked polymer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for preparing high-activity recombination lipoidase
InactiveCN101684460AEfficiently obtainedSimple preparation processHydrolasesInclusion bodiesLow ionic strength
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-activity recombination lipoidase. The method comprises the following steps: (a) mixing lipase inclusion body and 3-10M urea aqueous solution so as to dissolve the inclusion body to obtain modified solution containing modified lipase; (b) diluting and renaturing the modified solution of the step (a) in renaturation solution with low ionic strength to obtain the renaturation solution containing active lipase; and (c) separating and purifying the renaturation solution of the step (b) to obtain lipase with specific activity being more than or equal to 10000U / g, or concentrating the renaturation solution of the step (b) to obtain concentration solution of the lipase with the specific activity being more than or equal to 10000U / g. The method of the invention can effectively obtain high-activity and high-purity recombination lipoidase.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-chamber hypochlorous acid dispenser
ActiveUS20180179059A1Simple preparation processMeet the blocking requirementsBiocideSingle-unit apparatusAcetic acidLow ionic strength
The invention provides a skin disinfectant for treating skin with eczema, preventing bacterial proliferation, and removing biofilm. Compositions of the invention include hypochlorous acid, acetic acid, water, and one or more additives or excipients. The formulation process removes metal ions, reduces ionic strength, controls pH, and reduces exposure to air, thus improving stability and lengthening shelf-life.
Owner:WIAB WATER INNOVATION
Method of laundry washing
InactiveUS20050148482A1Surface-active detergent compositionsOther washing machinesLow ionic strengthAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a method of washing a laundry fabric in a wash liquor in a washing machine, wherein during a single wash cycle no more than 10% by weight of the wash liquor is drained from the washing machine, wherein said method comprises the step of varying the ionic strength of the wash liquor over at least 10% of the duration of the wash cycle by addition of one or more ionic ingredients to the wash liquor, and wherein the lowest ionic strength of the wash liquor is from 0.001 to 0.06 M and the highest ionic strength of the wash liquor is from 0.01 to 0.5 M.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Extraction, separation and purification process of brasenia schreberi polysaccharide
ActiveCN106146685AOvercome the disadvantage of low extraction rateThere is no safety problem in the use of strong alkaliBulk chemical productionAlkaline proteaseLow ionic strength
The invention discloses an extraction, separation and purification process of brasenia schreberi polysaccharide. According to the process, the supercritical CO2 extraction technology is utilized, the defect that the extraction rate is low through a hot water extraction method and a NaOH extraction method is overcome, and the safety problem appearing in the situation that strong base needs to be used in NaOH extraction does not exist. When a crude product of the brasenia schreberi polysaccharide is purified, alkaline protease is adopted for treating and removing protein; cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and the brasenia schreberi polysaccharide can form quaternary amine complexes, the complexes do not dissolve in an aqueous solution with a low ionic strength and can dissociate and dissolve when the ionic strength is high, and the separation and purification effect is better; by using 312 weak-acid anionic exchange resin chromatography, some positively-charged impurities can be removed, and the separation and purification effect is better.
Owner:CHONGQING THREE GORGES MEDICAL COLLEGE
Cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use
InactiveCN101115388AReduce ionic strengthReduce conductivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLow ionic strengthGlycerol
A cell permeabilization and stabilization reagent and method of use are disclosed. The reagent contains a N-acyl sarcosine or a salt thereof, a pH adjusting agent to adjust pH of the reagent in a range from about 4 to about 6; and an aqueous medium; the reagent having a low ionic strength defined by a conductivity of less than 9.0 mS / cm. The reagent further contains bovine serum albumin and glycerol. The reagent may further include an alkyl sulfate surfactant. Upon incubating the cells with the reagent, the reagent permeates the cellular membrane to allow penetration of an intracellular marker, causes intracellular protein aggregation within the cellular membrane, while preserves a cellular constituent for binding with a cellular marker for subsequent analysis by flow cytometry.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Ion exchange membrane chromatography
ActiveUS20140348845A1Increase costEnhancing efficiency of downstream chromatography stepsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsLow ionic strengthIon-exchange membranes
Methods of enhancing efficiency of downstream chromatography steps for purification of proteins comprising: (a) passing a composition comprising a polypeptide of interest and various contaminants through an ion exchange membrane, wherein the polypeptide and the membrane have opposite charge, at operating conditions comprised of a buffer having a pH sufficiently distinct from the pi of the polypeptide to enhance the charge of the polypeptide and a low ionic strength effective to prevent the shielding of charges by buffer ions, which cause the membrane to bind the polypeptide and at least one contaminant, (b) overloading the ion exchange membrane such that at least one contaminant remains bound to the membrane while the polypeptide of interest is primarily in the effluent; (c) collecting the effluent from the ion exchange membrane comprising the polypeptide of interest; (d) subjecting the membrane effluent comprising the polypeptide of interest to a purification step of similar charge as the previous membrane, and (e) recovering the purified polypeptide from the effluent of the charged ion exchange chromatography purification step.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com