Method for preparing high-activity recombination lipoidase
A technology of lipase and specific activity, which is applied in the field of preparation of recombinant lipase, can solve problems such as difficulty in soluble expression and difficulty in large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] One of the keys of the preparation method of the highly active recombinant lipase of the present invention lies in lipase inclusion body denaturation-renaturation technology, which mainly includes suitable denaturation conditions and optimized renaturation conditions for inclusion bodies.
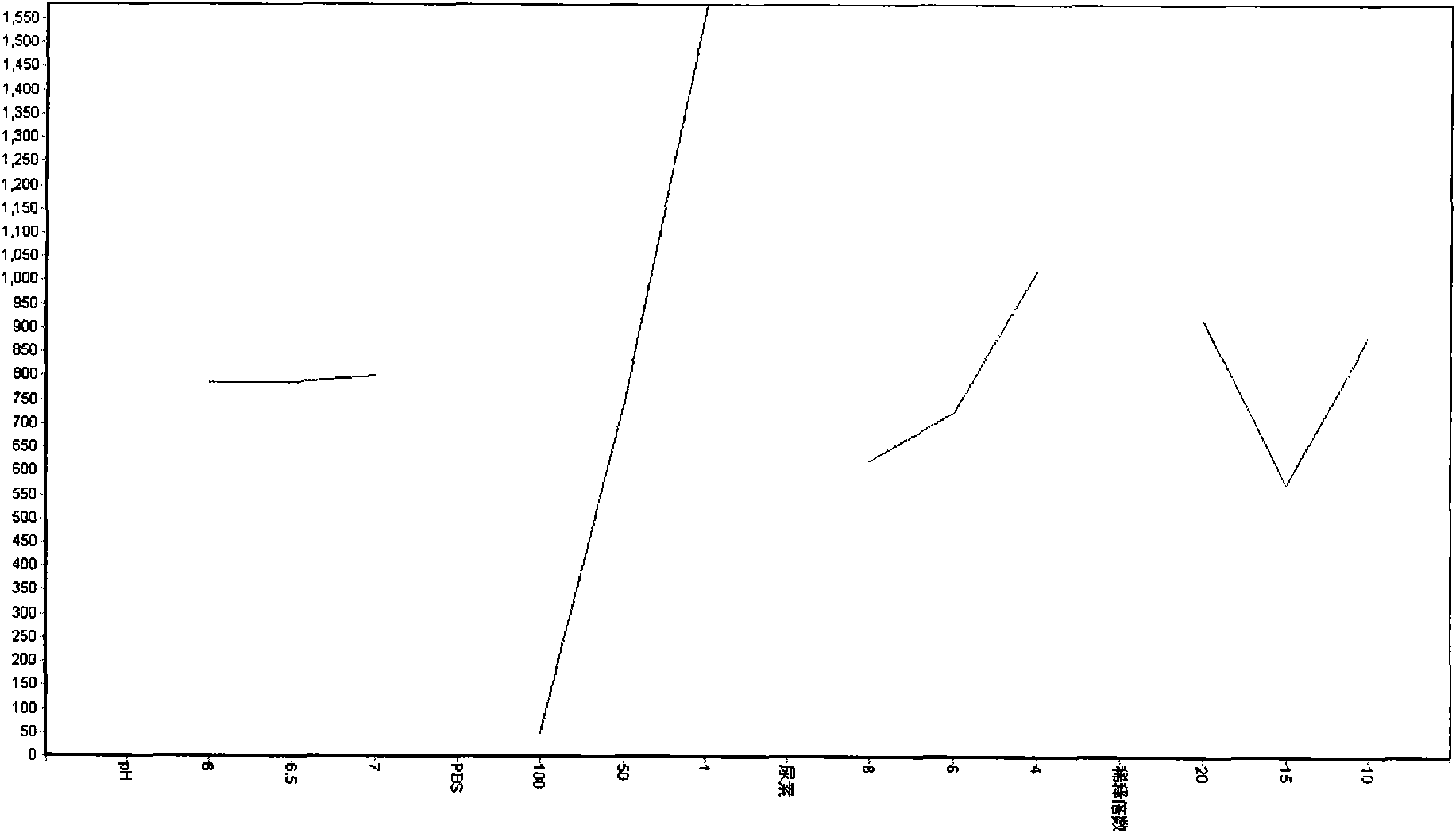
[0040] In a preferred embodiment, the denaturation condition is preferably 8M urea rather than 6M guanidine hydrochloride; the refolding method is preferably a dilution refolding method; the composition of the refolding solution includes a redox pair: 0.5mM GSSG+1mM GSH; pH5.0-pH9 .0 buffer system; the buffer pair is preferably Tris-HCl and phosphate buffer; the refolding temperature is preferably low temperature, such as 4°C; the refolding time is preferably 20h-60h.
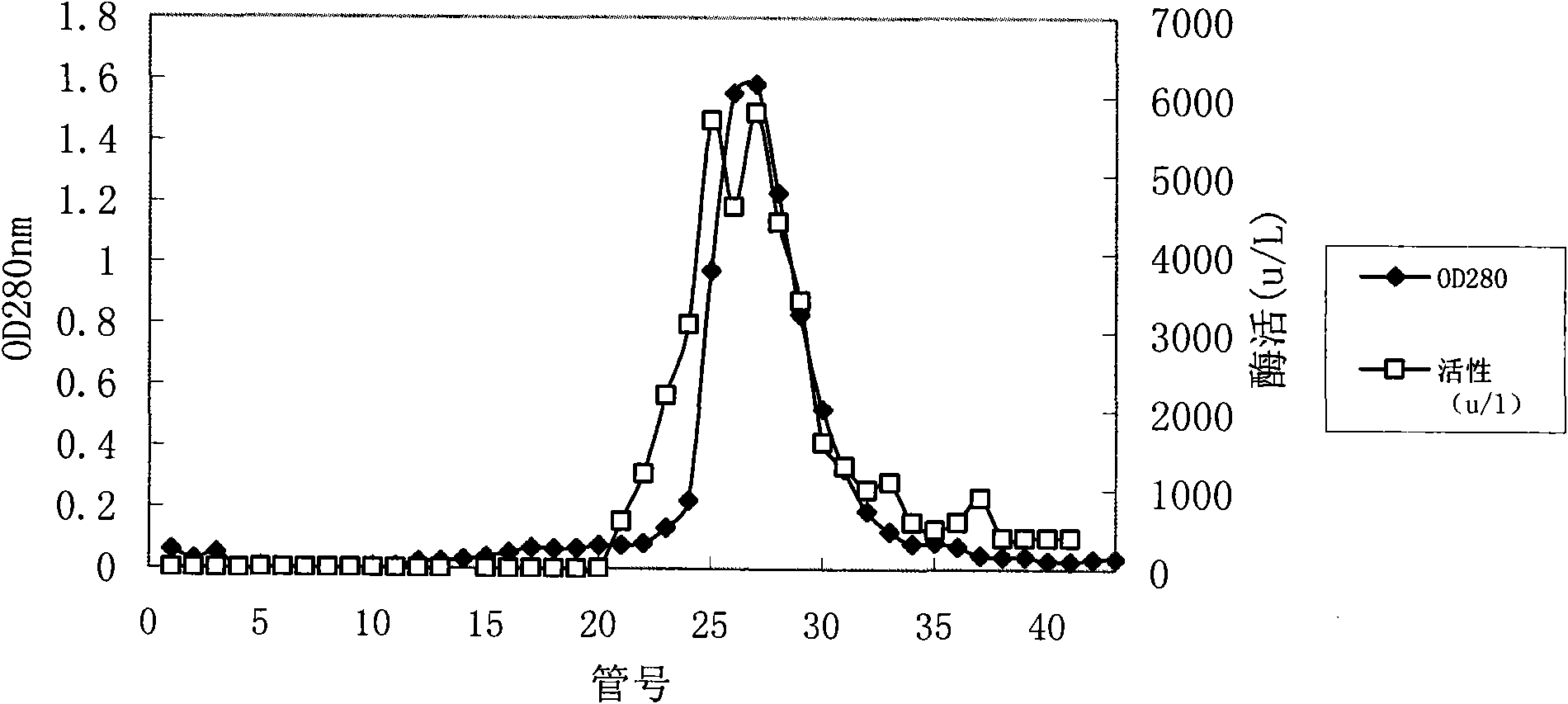
[0041]Concentration and / or purification can also be carried out for the recombinant lipase obtained after renaturation.
[0042] A preferred concentration method is anion resin adsorption; preferred anion resins inclu...
Embodiment 1
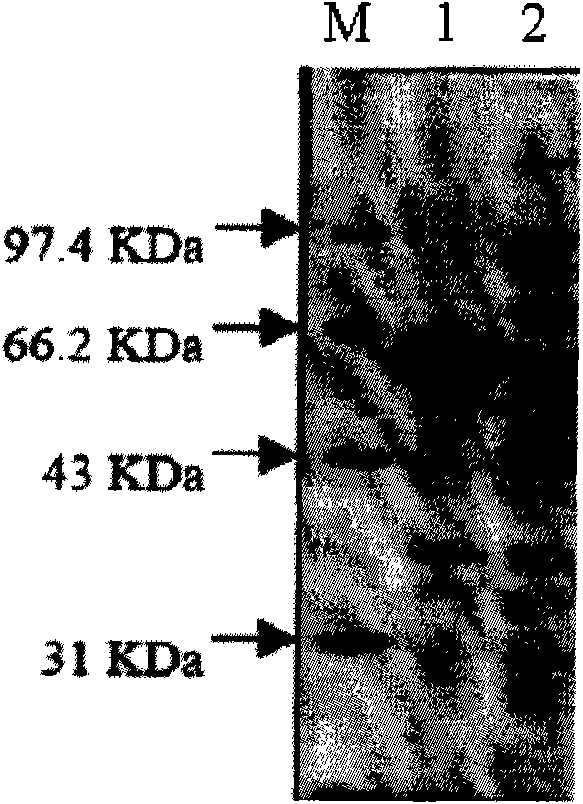
[0053] Induced Expression of Recombinant Bacteria Producing Lipase and SDS-PAGE Protein Electrophoresis Identification
[0054] I. Engineering bacteria
[0055] Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (purchased from East China University of Science and Technology; see Jian-He Xu et al., Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic 47 (2007) 105-110) with the expression plasmid of the recombinant lipase gene was inoculated in the Ampicillin (100 μg / ml) solid LB medium growth. The engineered bacterium expresses lipase in the form of inclusion body, and the lipase comes from Serratia marcescens ECU1010 with the preservation number CGMCC 1219 (patent application 200410067046.1).
[0056] II. Fermentation expression
[0057] Pick a single colony of engineering bacteria and put it in 5ml LB (containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin) liquid medium, shake the bacteria overnight at 37°C; Bacteria to OD600nm 0.3-0.5, induced by IPTG, 3-5 hours after induction, centrifuged to collect the bacteria.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Washing and denaturation of inclusion bodies
[0063] I. Denaturation and washing of inclusion bodies: Escherichia coli expressing lipase inclusion bodies was lysed, centrifuged, and the precipitate was collected. The identification by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis showed that the precipitate was the expression part of lipase inclusion body. The inclusion bodies were collected, suspended with 0.5% Triton-X 100, washed, centrifuged, and fully washed with Tris-HCl buffer without Triton-X 100.
[0064] II. After centrifuging the inclusion bodies thoroughly washed with 0.5% Triton-X 100, dissolve the lipase inclusion bodies separately in 8M, 6M or 4M urea according to the ratio of 20mg / ml (wet inclusion body / denatured solution), 6M or 3M guanidine hydrochloride, or 1% or 0.25% SDS; the results are shown in Table 1.
[0065] Table 1 Solubility of lipase inclusion bodies under different denaturing conditions
[0066]
[0067] After fully dissolving, centrifuge and take the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com