Inhibitors of extracellular proteases
a protease inhibitor and extracellular technology, applied in the field of protease inhibitors, can solve the problems that no one has used stress to improve or modify, and achieve the effect of reducing degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Preparation of Stressed and Non-stressed Plant Extracts
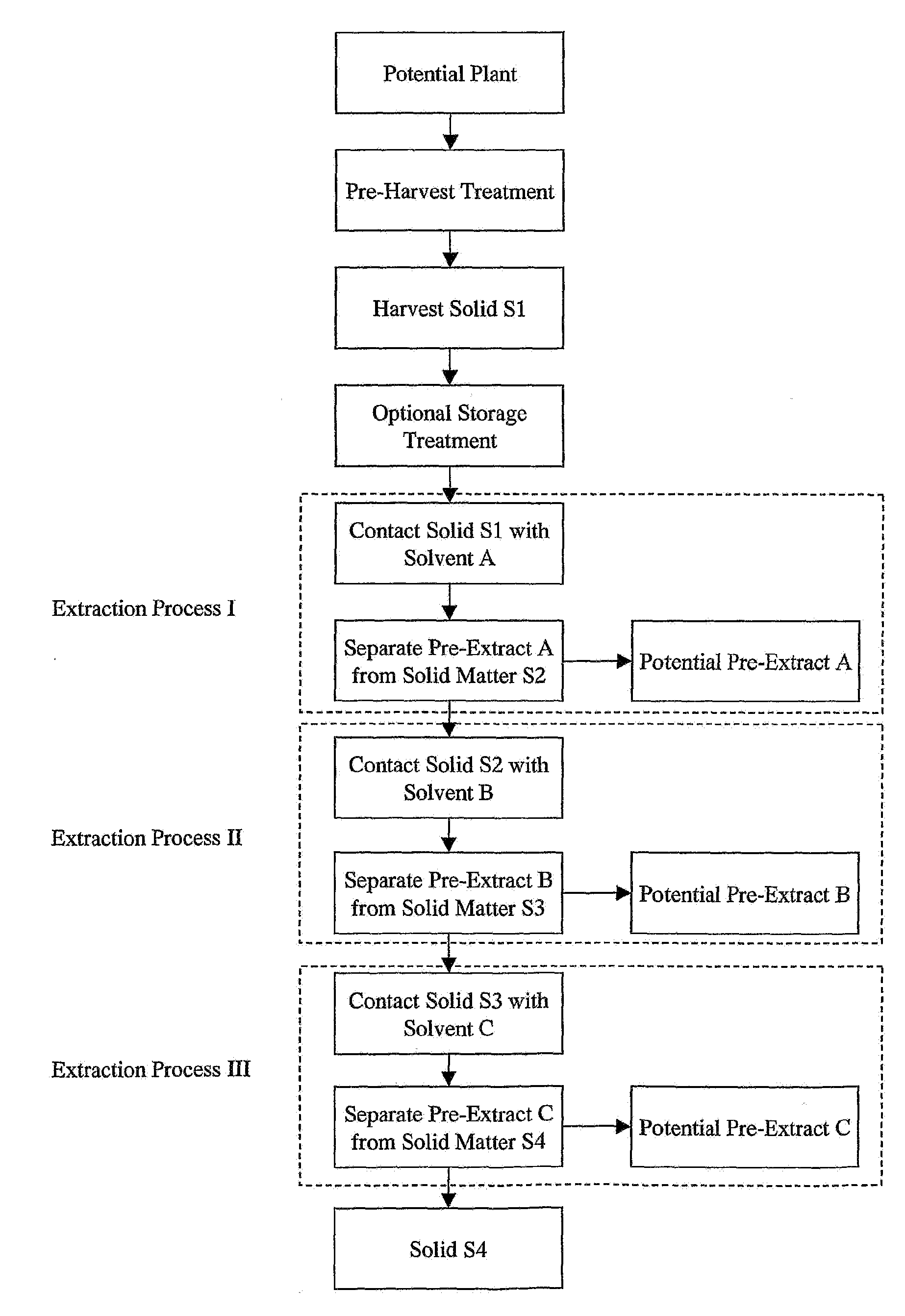
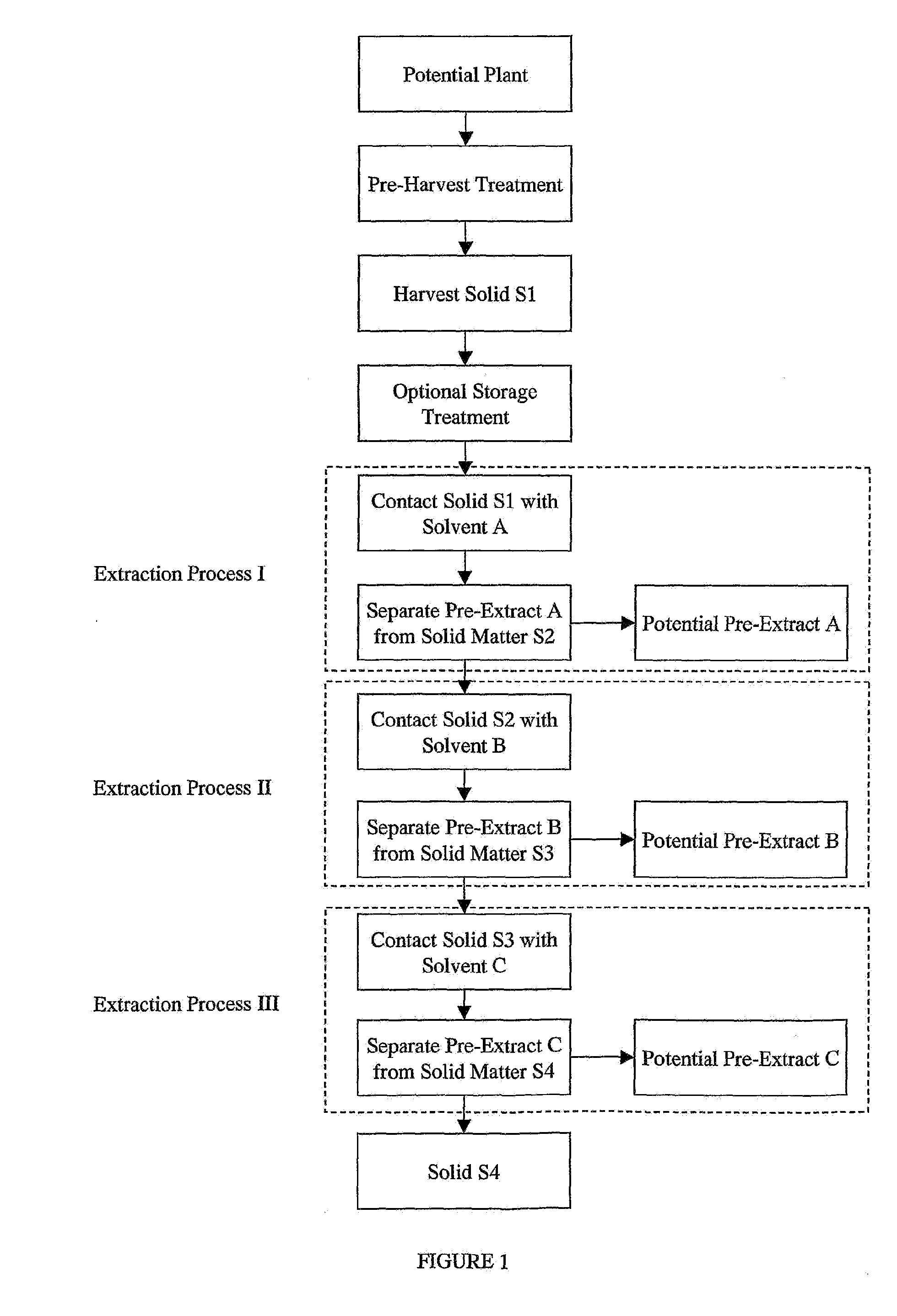
[0103]Pre-Harvest TreatmentAerian parts of a living plant are sprayed with an aqueous solution of gamma linolenic acid (6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid, Sigma L-2378) (stress G) or arachidonic acid (5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid, Sigma A-3925) (stress A) (400 μM in water with 0.125% (v / v) Triton X-100) to completely cover the leaves.
Harvest Solid SI and Optional Storage Treatment
[0104]Twenty to twenty-four hours after the stress, more than 4 grams of leaves, stems, fruit, flowers, seeds or other plant parts are harvested and frozen immediately in dry ice, then transferred as soon as possible to a −20° C. freezer until use. Plant materials may be stored at −20° C. for a long period of time, more than a year, without losing inhibitory activity. Temperature is monitored to ensure a constant condition.
[0105]Stressed and non-stressed plant specimens are collected as wet samples and stored at −20° C. for various periods of time, and ar...
example ii
In vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assays
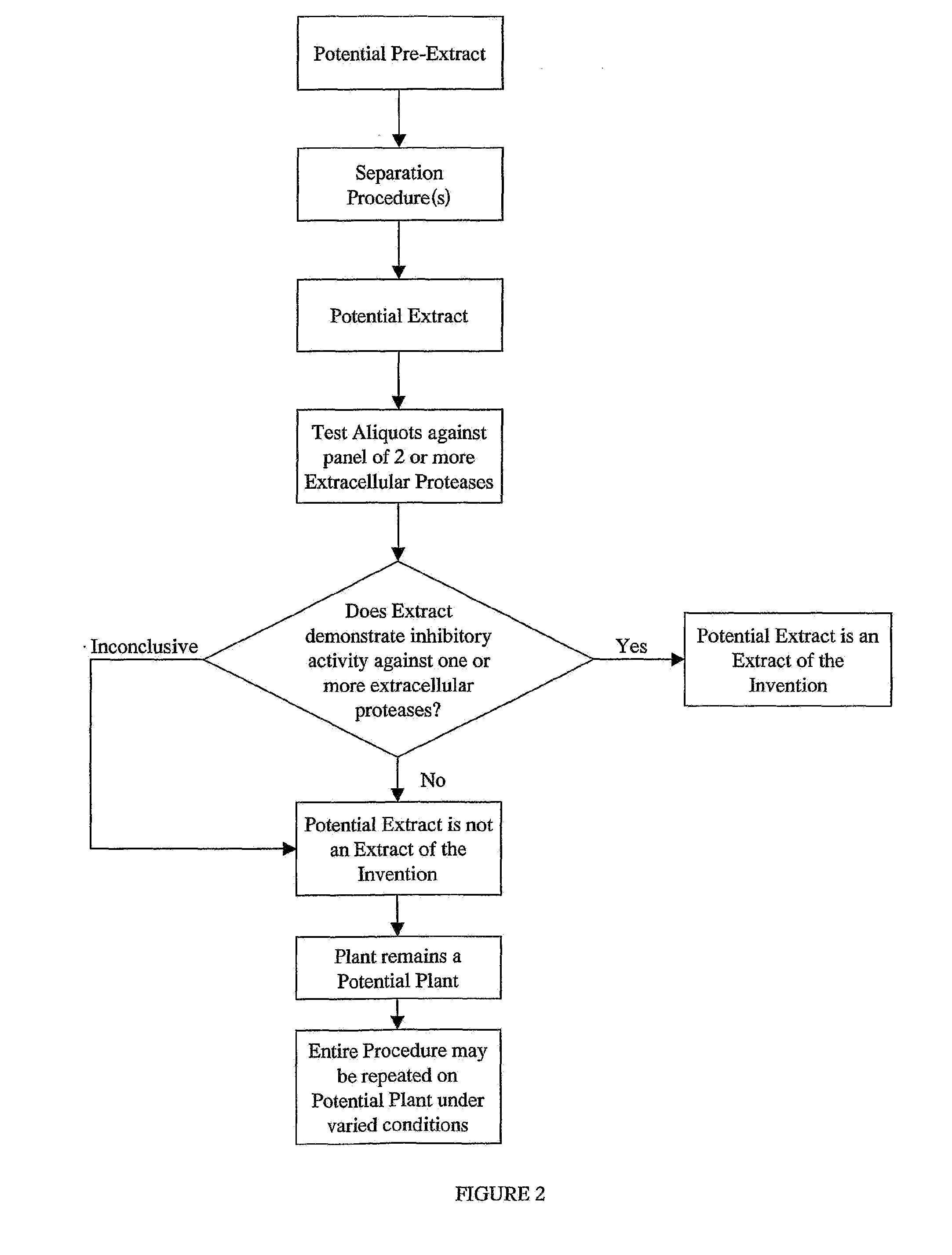
[0113]The inhibitory activity of sample compositions towards human MMP-1, human MMP-2, human MMP-3, human MMP-9, human cathepsin-B, human cathepsin-D, human cathepsin-G, human cathepsin-L, human cathepsin-K, human leukocyte elastase (HLE), bacteria clostripain and bacteria subtilisin can be determined using either fluorogenic substrates or the FASC assay.
Measurement of Human MMP-1, -2, -3 and -9 Activity with Fluorogenic Peptidic Substrates
[0114]MMP-1, -2, -9 are purified from natural sources (human immortalized cell lines: 8505C (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen and Zellkulturen GmbH) for MMP-1, HT-1080 (ATCC, Manassas, Va.) for MMP-2 and THP-1 (ATCC, Manassas, Va.) for MMP-9) as described in literature and based on protocols found in I. M. Clark: Matrix metalloproteinases protocol>>, Humana Press (2001). Recombinant human MMP-3 is overexpressed in E. Coli and purified according to Windsor L J, Steele D L (2001), Methods Mol Biol 151:191-205. P...
example iii
Examplary Purification of Inhibitory Activityfound in an Extract
[0124]Extracts were separated by HPLC on an Agilent 1100 system (San Fernando, Calif.). Briefly, 100 μl of a crude extract prepared as described in Example I was applied on a C18 reverse-phase column (Purospher RP-18 5 μm, 4.0×125 mm (HP), Agilent, San Fernando, Calif.). Elution of compounds was achieved with a linear gradient of 10-85% acetonitrile. Fractions were collected, evaporated, resuspended in aqueous buffer and then reanalysed for their inhibition activity on specific enzymes as already described. Fractions of interest (demonstrating a biological activity) where then reisolated at a larger scale for further analysis and characterization.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| latitude | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com