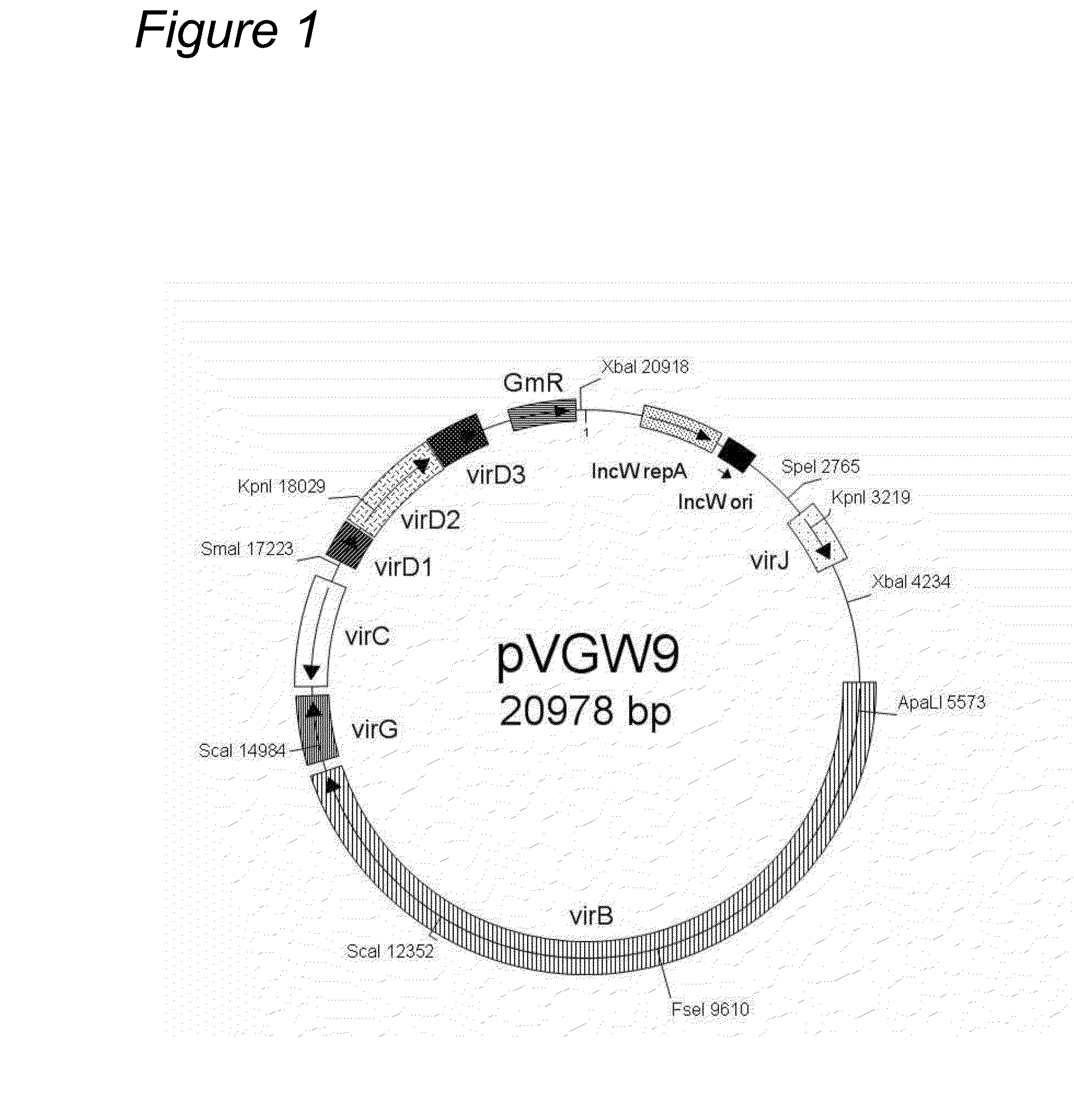
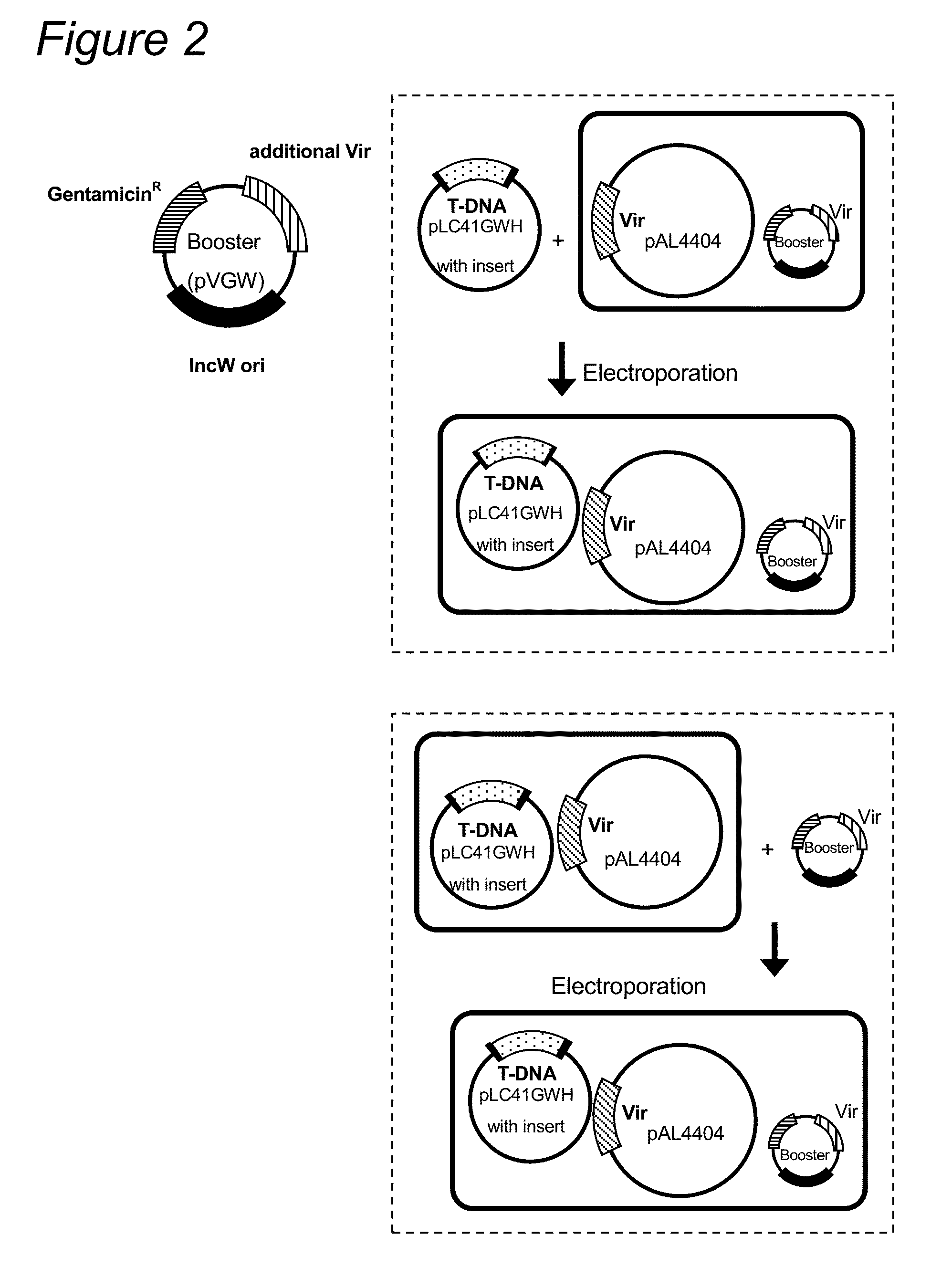
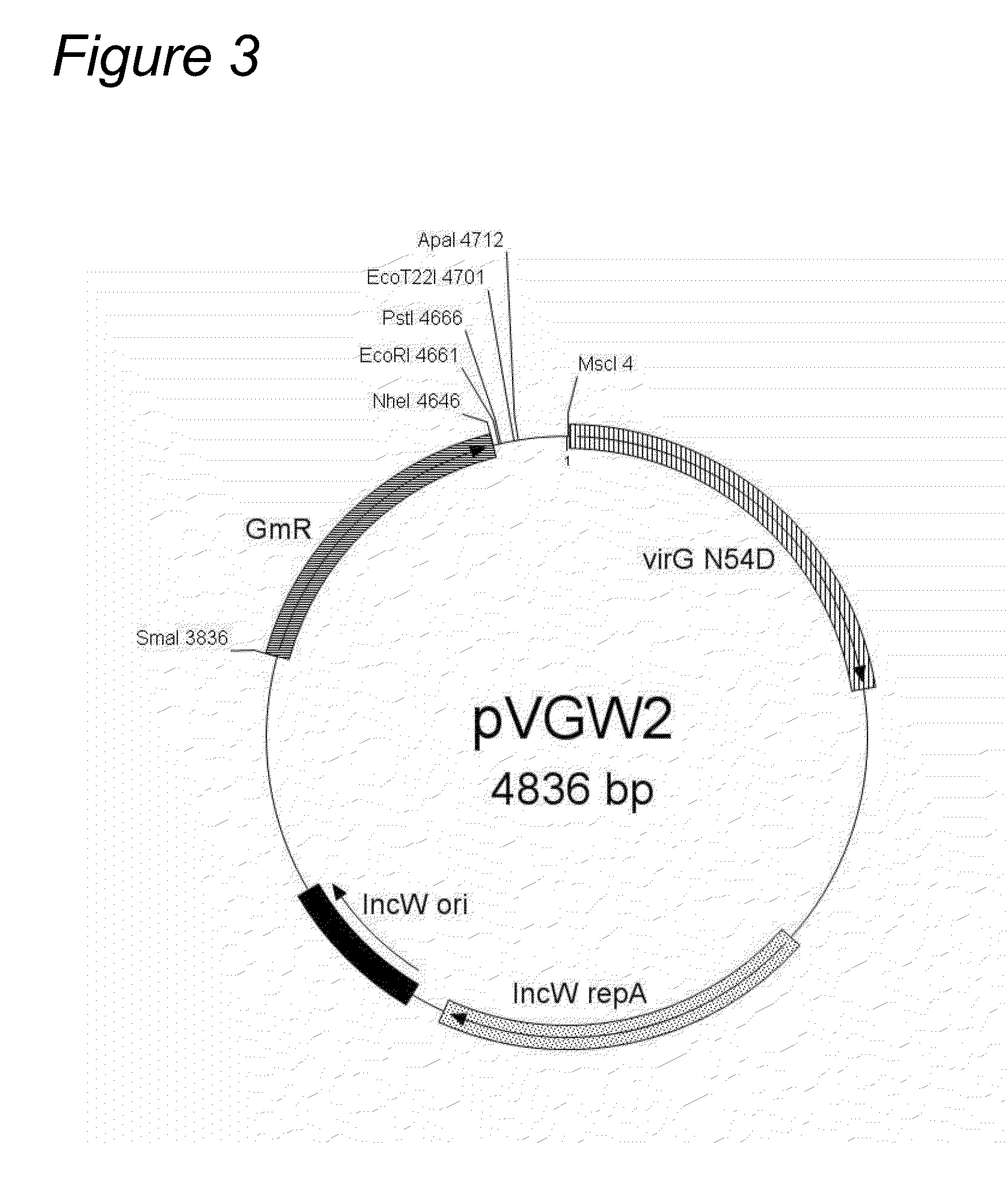
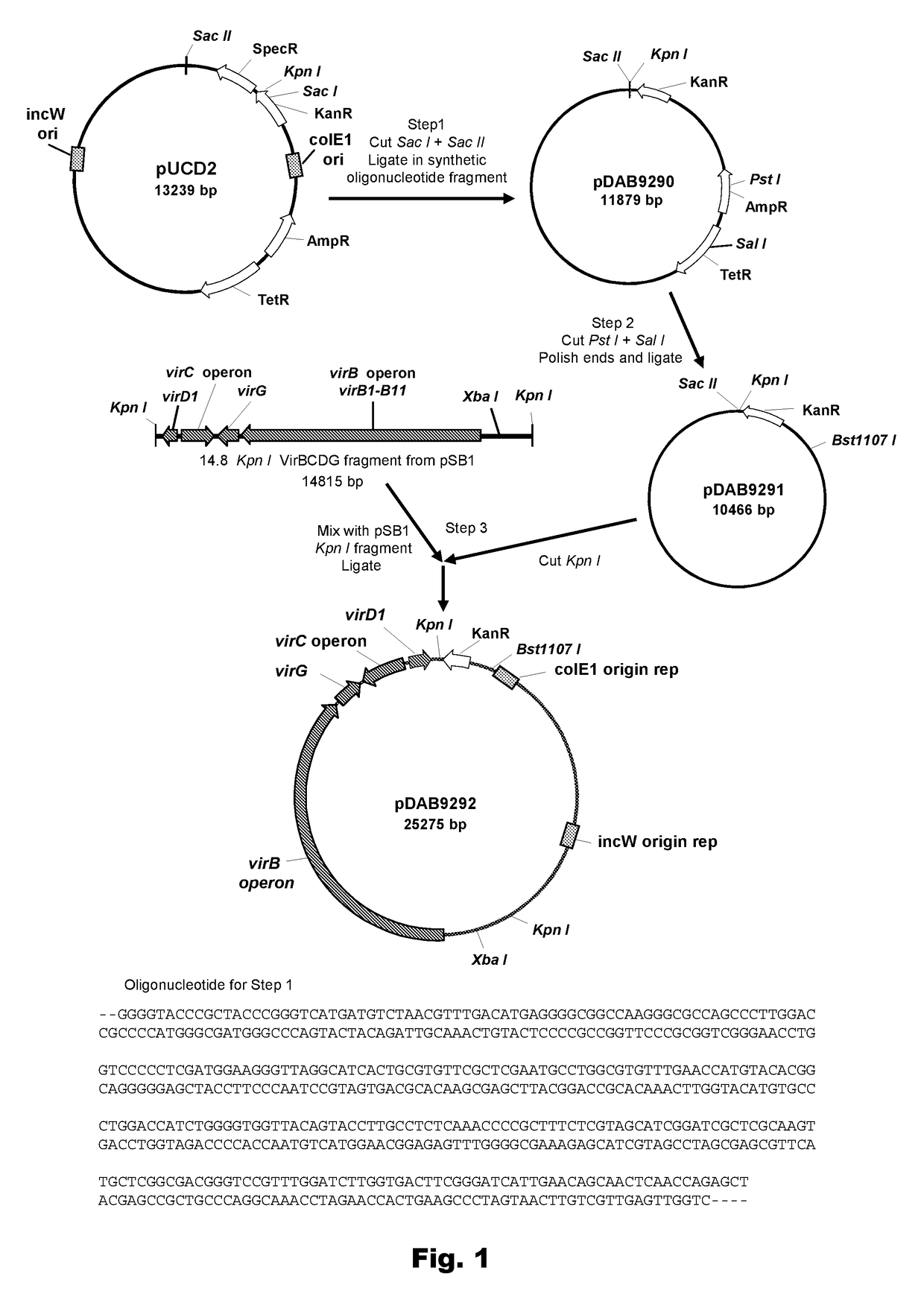
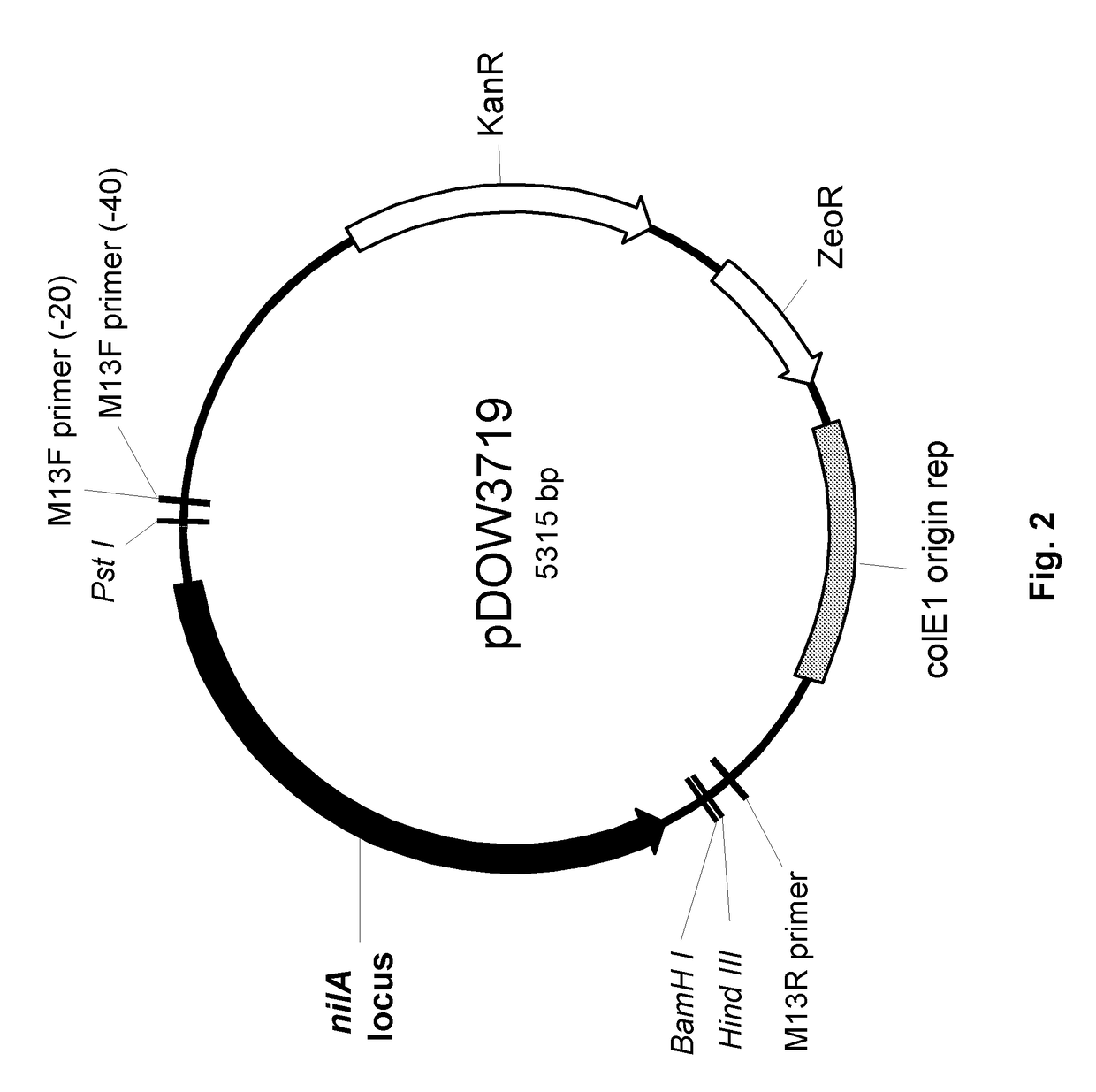
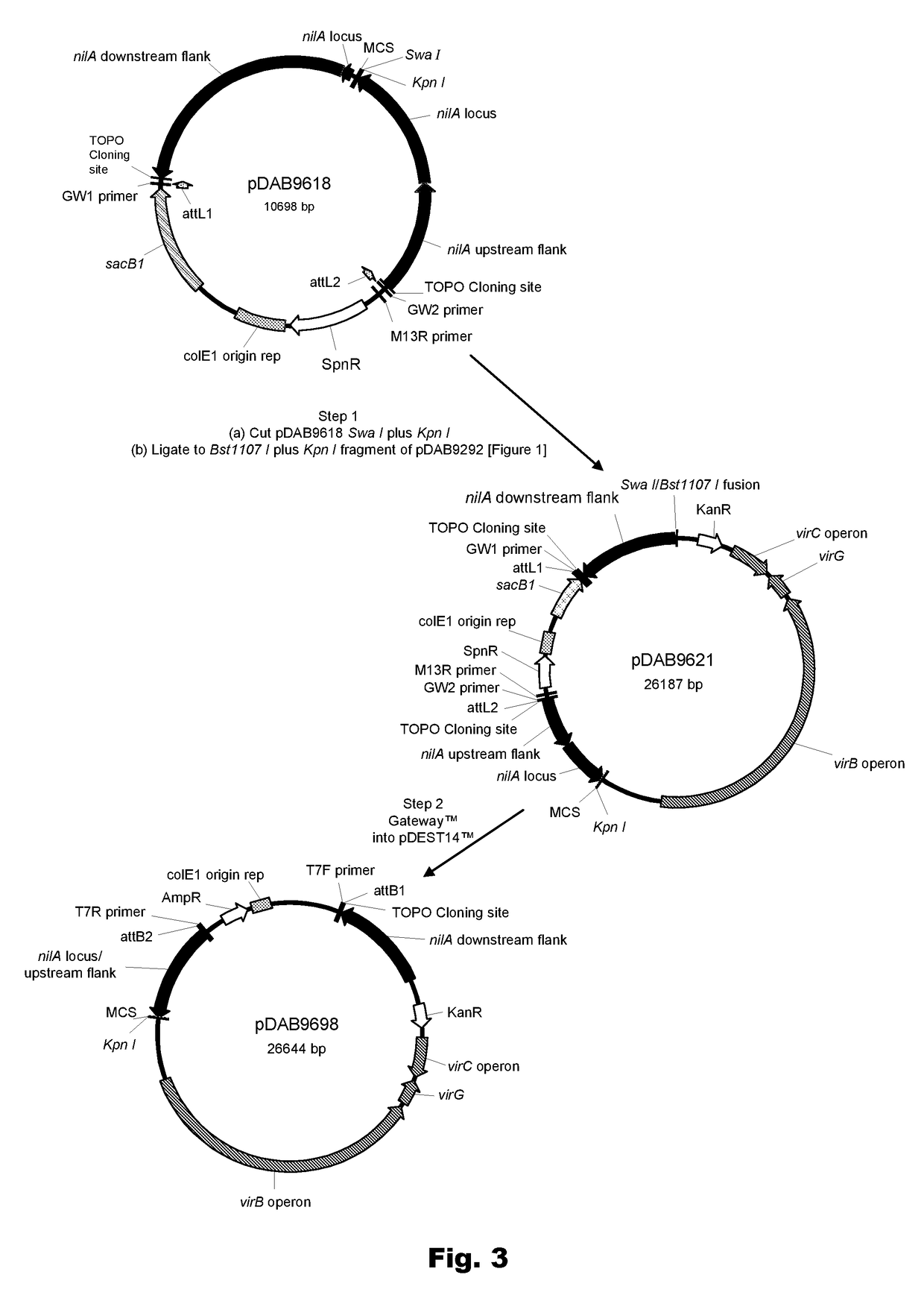
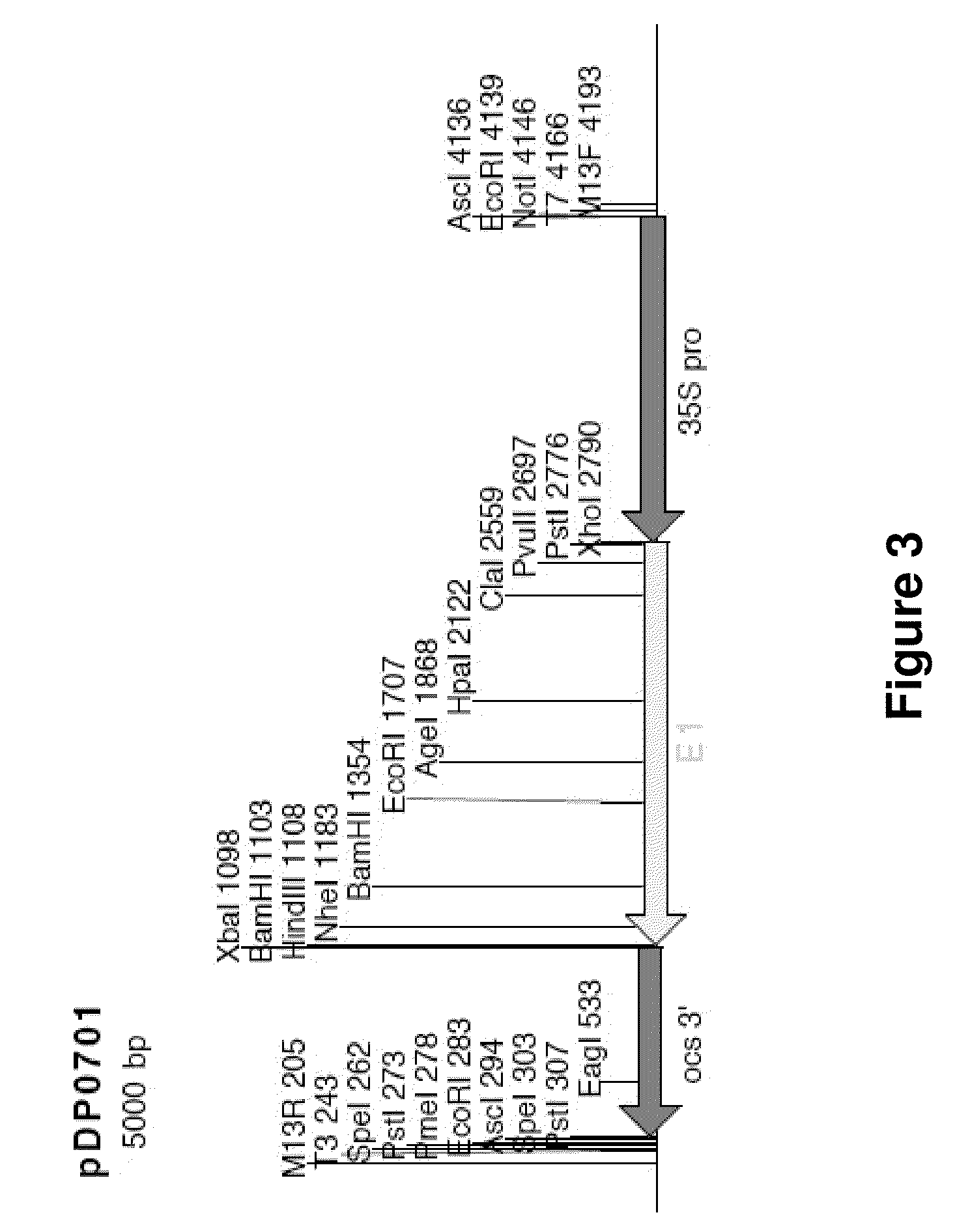
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Ti plasmid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
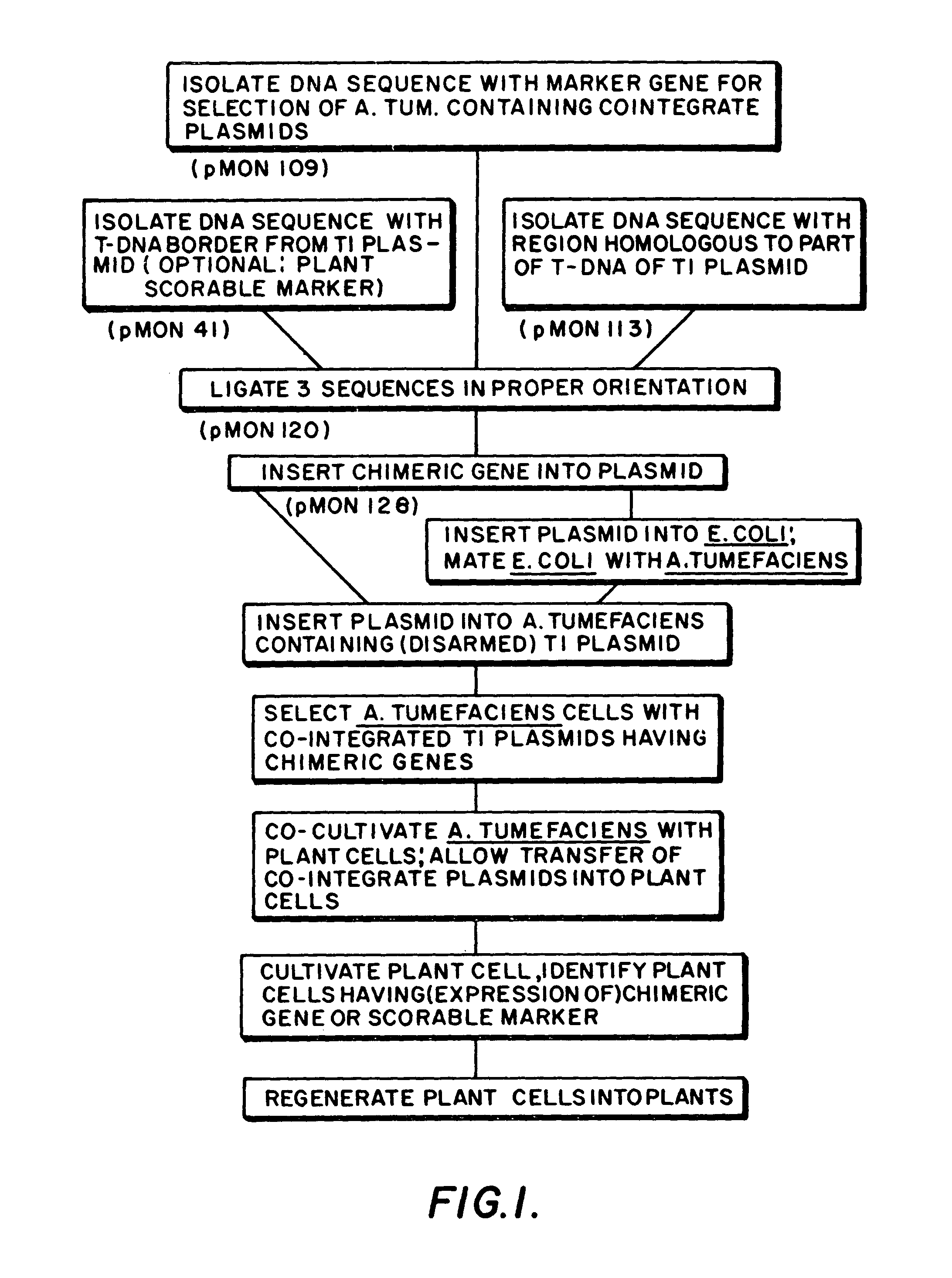
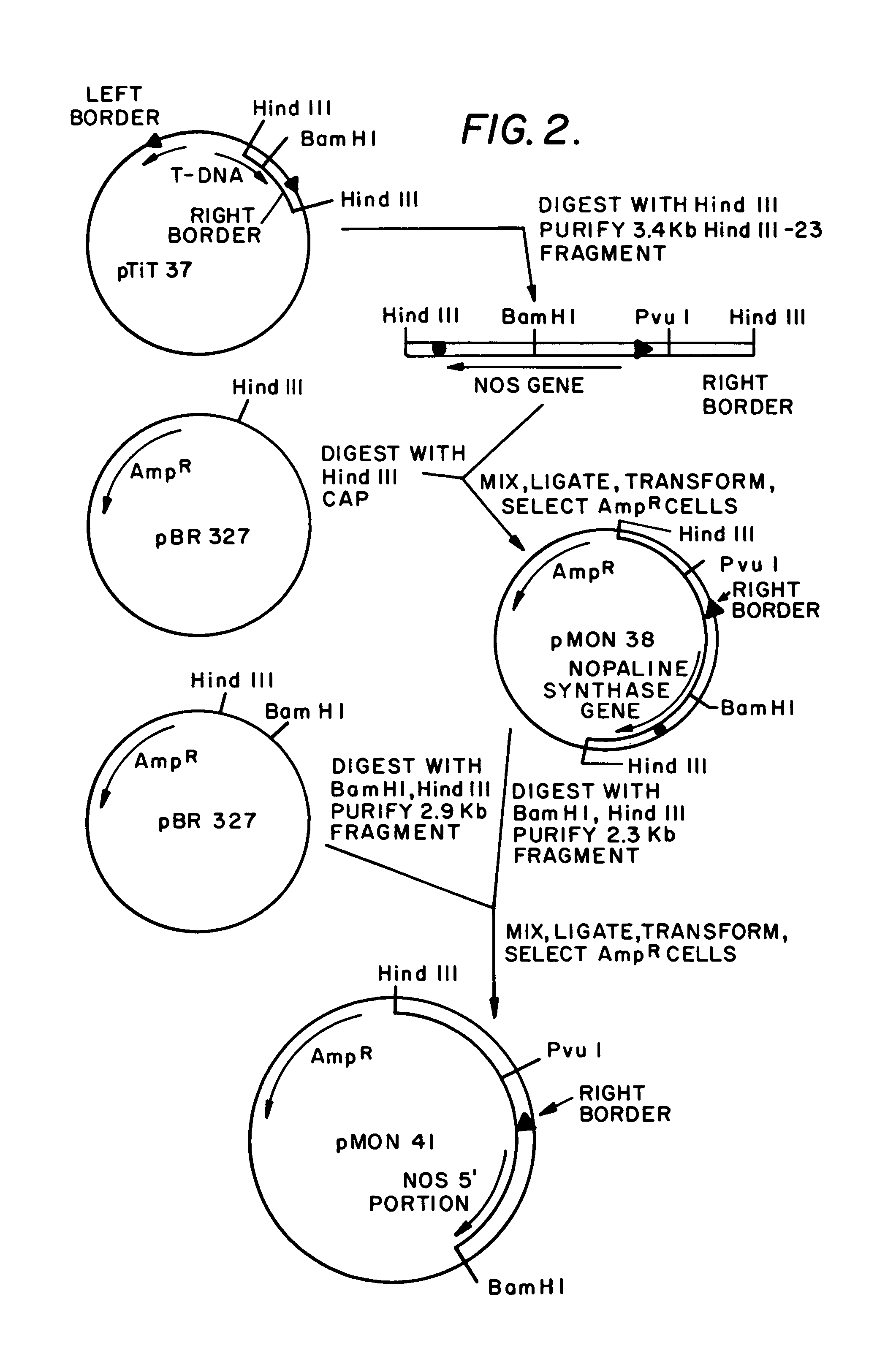
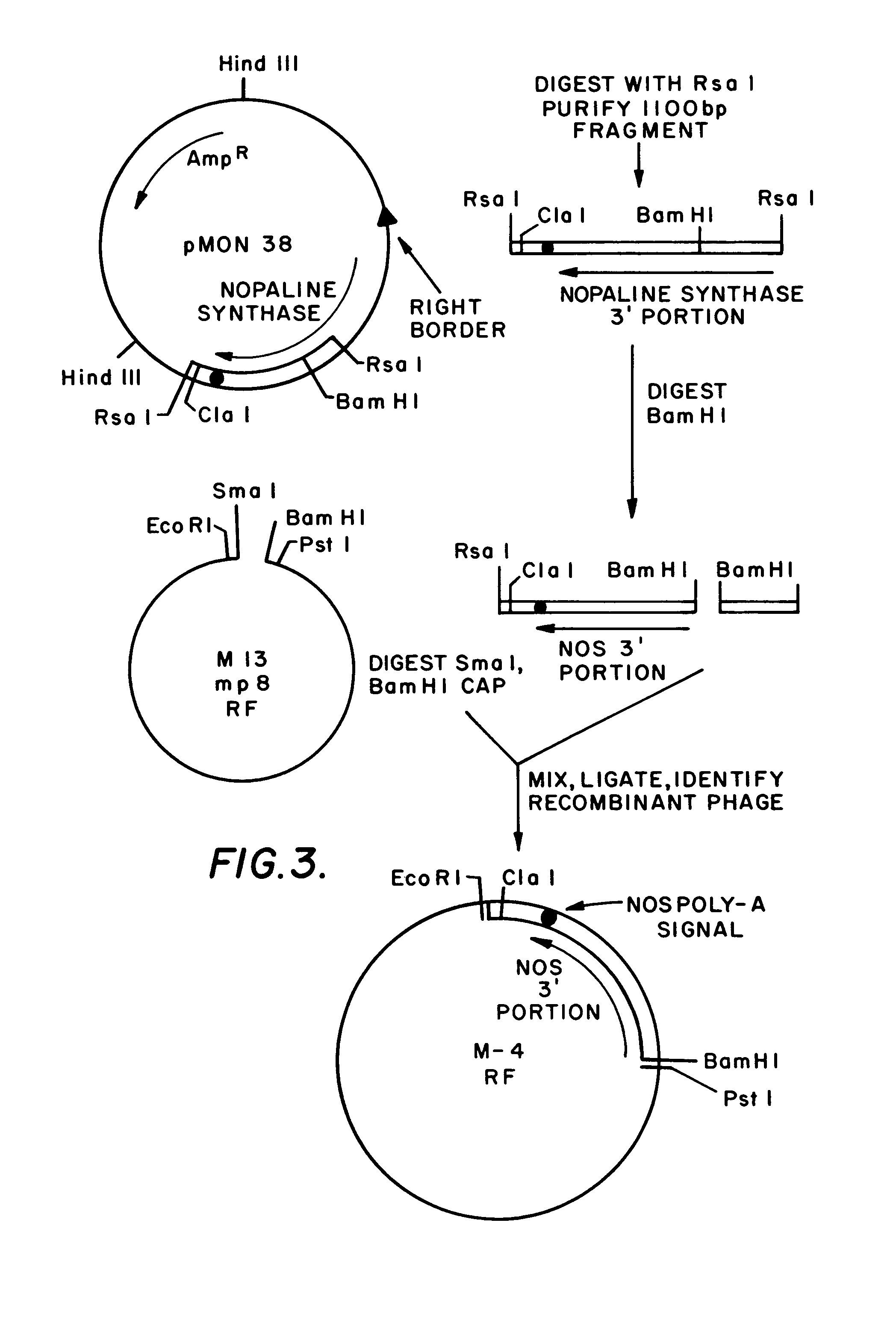
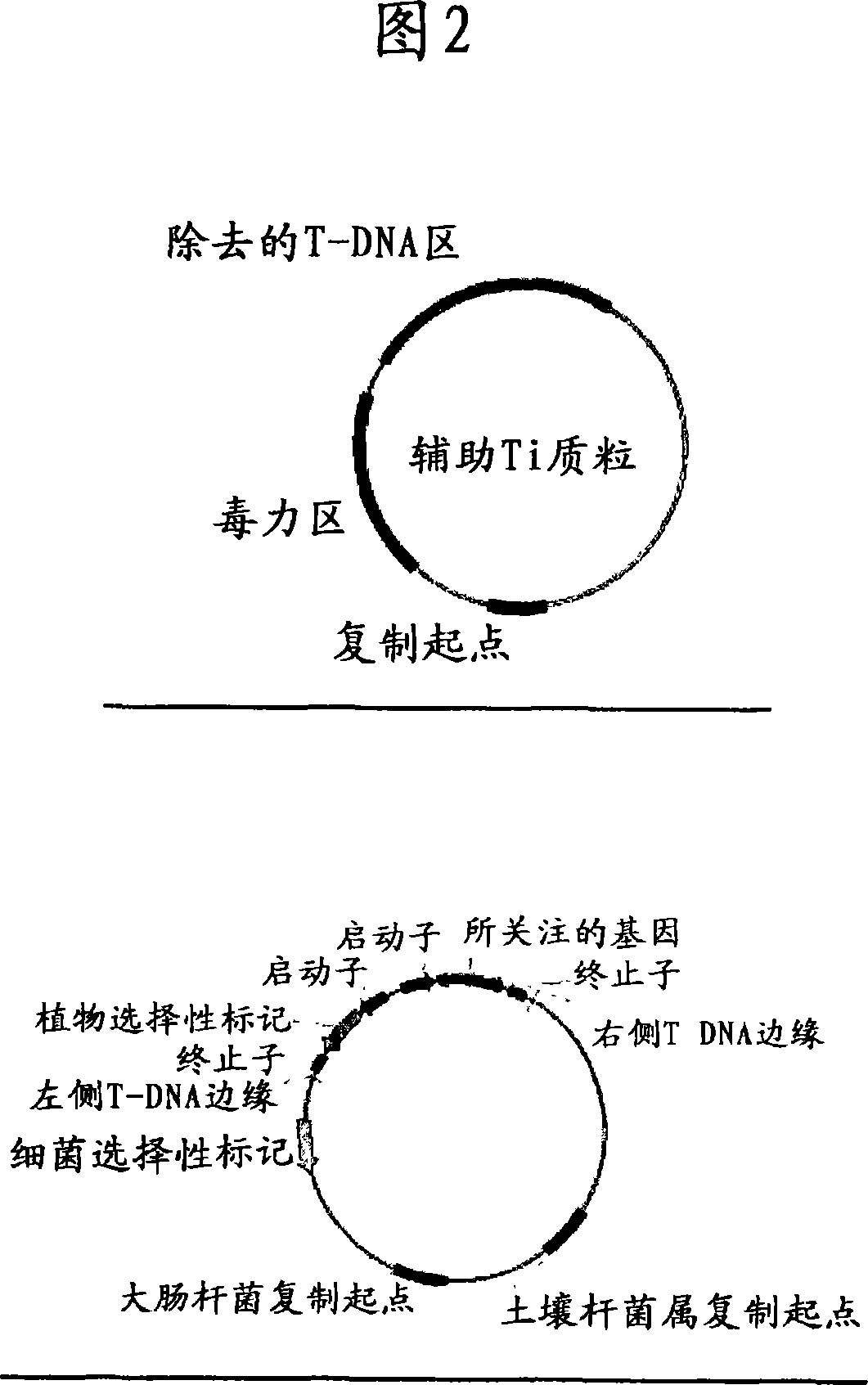
A Ti or tumour inducing plasmid is a plasmid that often, but not always, is a part of the genetic equipment that Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes use to transduce their genetic material to plants. The Ti plasmid is lost when Agrobacterium is grown above 28 °C. Such cured bacteria do not induce crown galls, i.e. they become avirulent. pTi and pRi share little sequence homology but are functionally rather similar. The Ti plasmids are classified into different types based on the type of opine produced by their genes. The different opines specified by pTi are octopine, nopaline, succinamopine and leucinopine.
Insect resistant plants
InactiveUS6943282B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacteroidesAureobasidium sp.
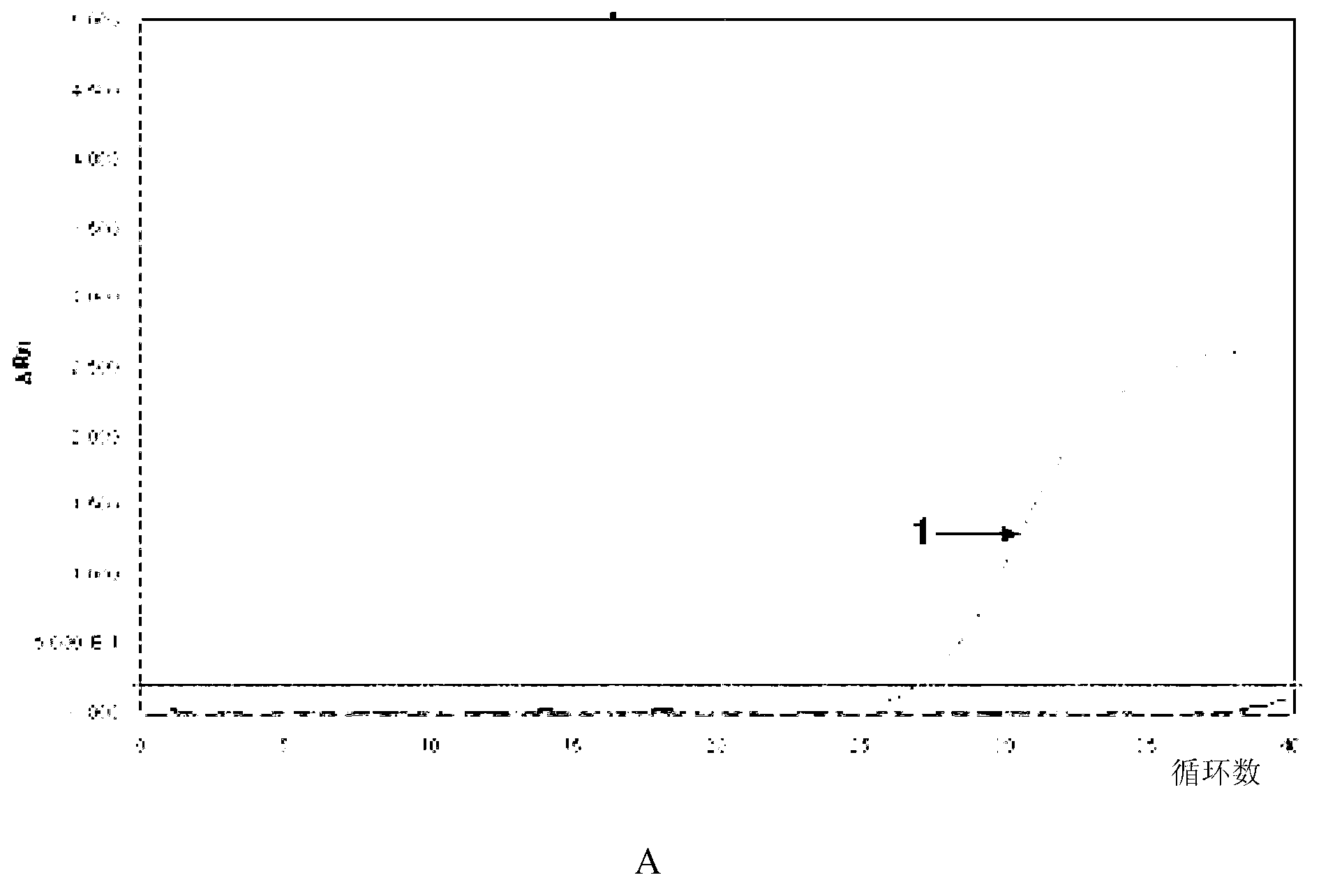
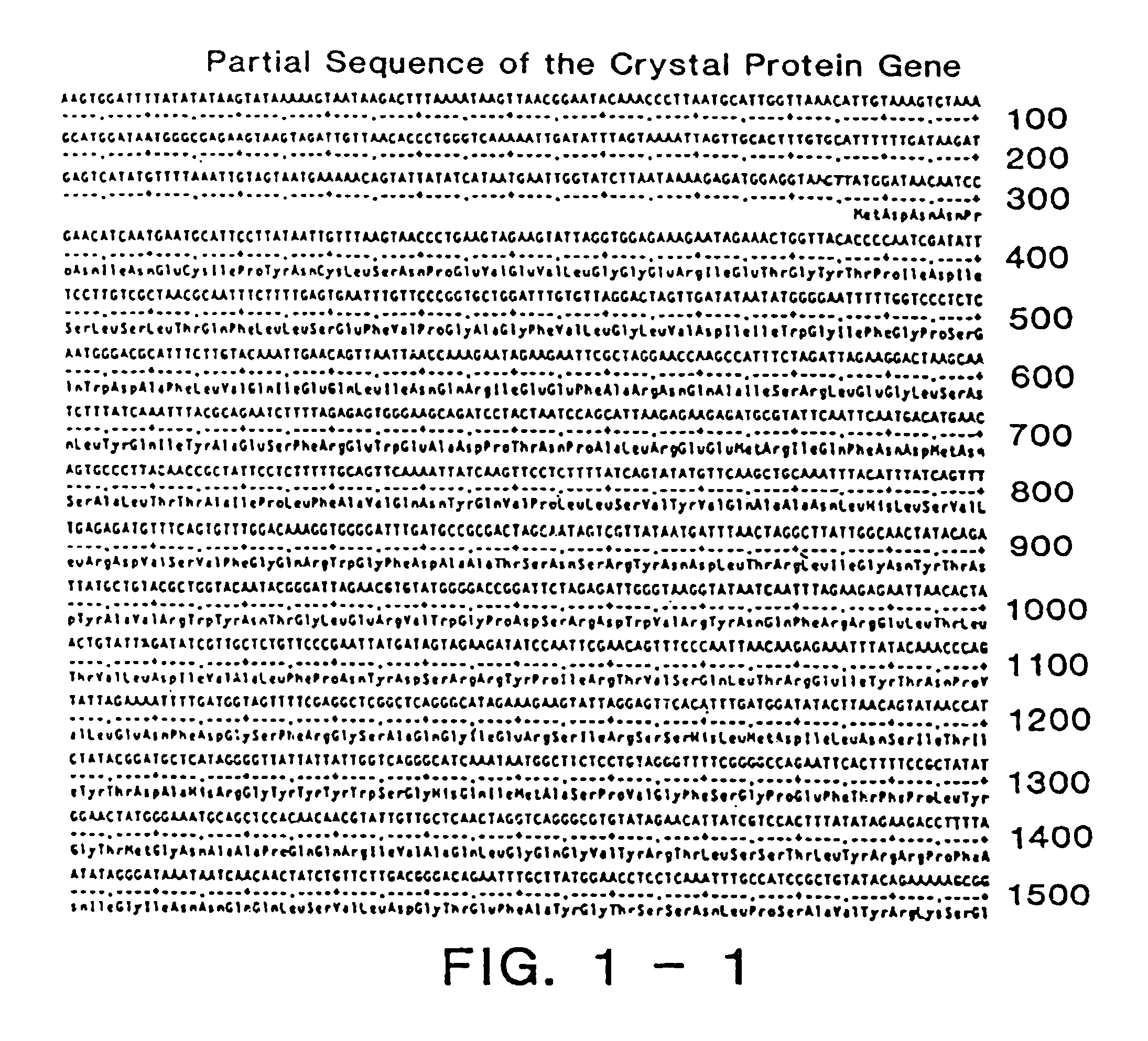
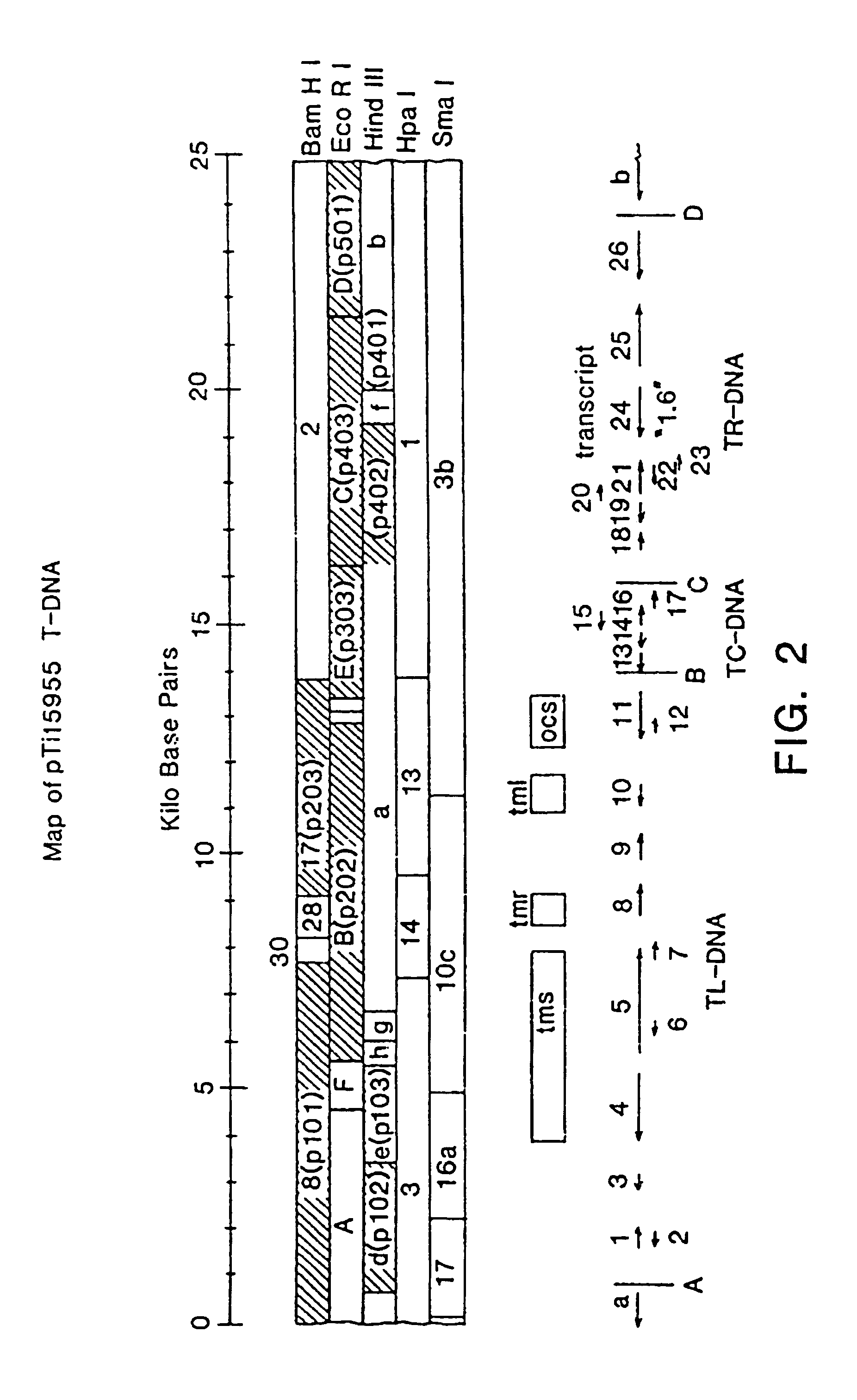
A method for expressing insecticidal protein structural genes in plant genomes is provided. In the preferred embodiments this invention comprises placing a structural gene for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein under control of a plant or a T-DNA promoter and ahead of a polyadenylation site followed by insertion of said promoter / structural gene combination into a plant genome by utilizing an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-based transformation system. The modified Ti plasmid is then used to transform recipient plant cells. Also provided are the plants and tissues produced by this method and bacterial strains, plasmids, and vectors useful for execution of this invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
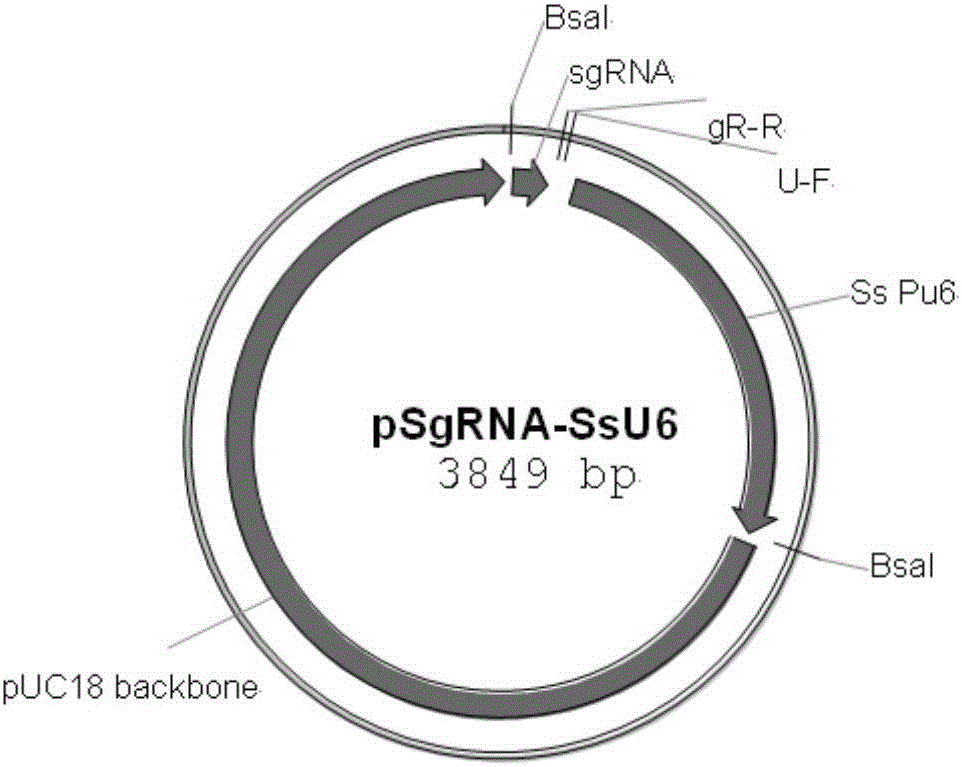
Site-specific insertional inactivation method and application mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR/Cas9
ActiveCN106434651ASpecify the direction of insertionRealize fixed-point insertionPeptidesNucleic acid vectorGenomicsMobile DNA
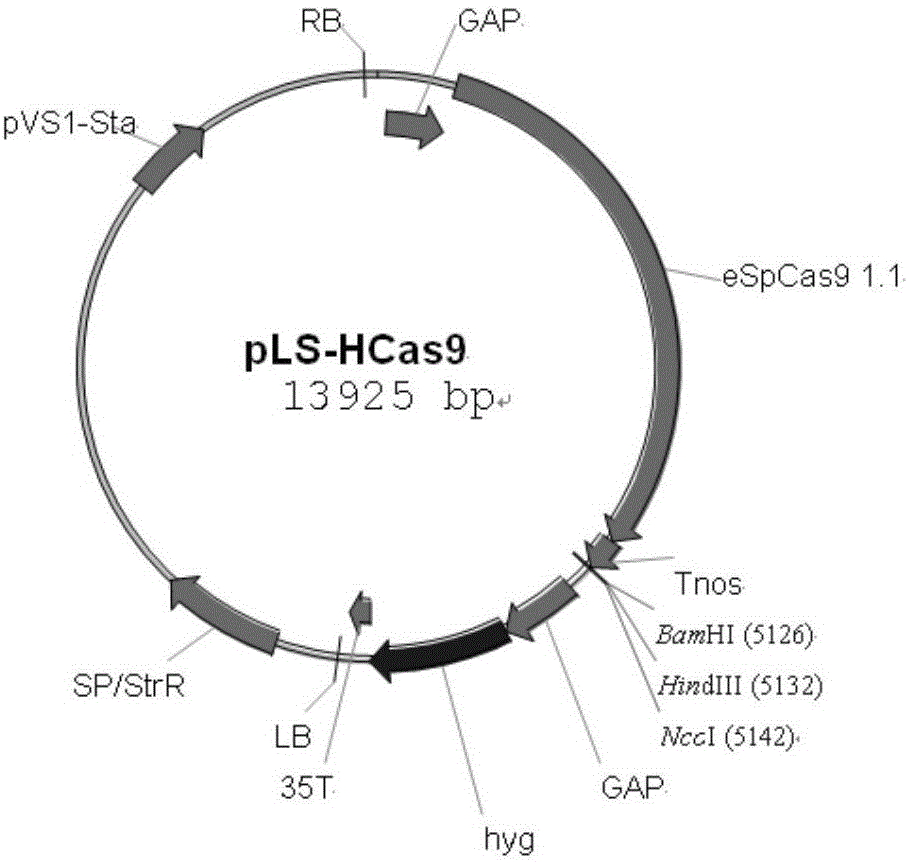
The invention discloses a site-specific insertional inactivation method mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR / Cas9. Endogenous snRNA promoter of Ustilago scitaminea (u6 promoter of Ustilago scitaminea) is used to drive sgRNA expression cassette. CRISPR / Cas9 system integrates with Ti plasmid of agrobacterium tumefaciens to construct the Ustilago scitaminea site-specific insertional inactivation system mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens with hygromycin as a selection marker. Specific sequence of the objective gene is cloned into sgRNA expression cassette for transformation of Ustilago scitaminea basidiospores, thus the mobile DNA fragment is exactly inserted into the objective gene sequence of Ustilago scitaminea, achieving the goal of damage to gene function. The invention provides an important tool for study of Ustilago scitaminea functional genomics. The system has the advantages of high efficiency and accuracy, and is convenient to use to conduct gene function researches in Ustilago scitaminea.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Biological gene transfer system for eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20050289672A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPlant cell
This invention relates generally to technologies for the transfer of nucleic acids molecules to eukaryotic cells. In particular non-pathogenic species of bacteria that interact with plant cells are used to transfer nucleic acid sequences. The bacteria for transforming plants usually contain binary vectors, such as a plasmid with a vir region of a Ti plasmid and a plasmid with a T region containing a DNA sequence of interest.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Biological gene transfer system for eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20050289667A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPlant cell
This invention relates generally to technologies for the transfer of nucleic acids molecules to eukaryotic cells. In particular non-pathogenic species of bacteria that interact with plant cells are used to transfer nucleic acid sequences. The bacteria for transforming plants usually contain binary vectors, such as a plasmid with a vir region of a Ti plasmid and a plasmid with a T region containing a DNA sequence of interest.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance
InactiveCN103205459APerfect genetic transformation systemIncreased genetic transformation rateGenetic engineeringFermentationTi plasmidBiological activation
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses an agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method includes: (1) induction and multiplication of embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (2) activation and cultivation on agrobacterium tumefaciens with target genes, (3) agrobacterium infestation with vacuum infiltration assistance on embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (4) resistant material screening and germination, and (5) resistant material verification. With the agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method, the agrobacterium can pass through the gaps among callus cells and enter deep cells on vacuum, and tiny wounds can be generated on the surfaces of the cells, so that phenolic substances are secreted by plants to activate shear and transfer of T-DNA (transferred deoxyribonucleic acid) in Ti plasmids. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation system is perfected. Genetic transformation rate of sugarcane is remarkably improved as compared with that of the prior art.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST
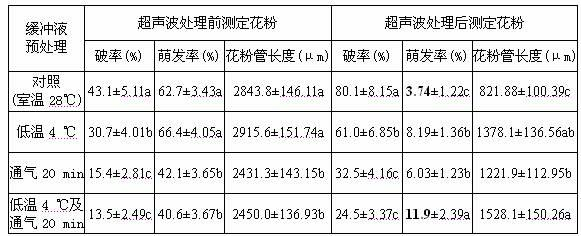
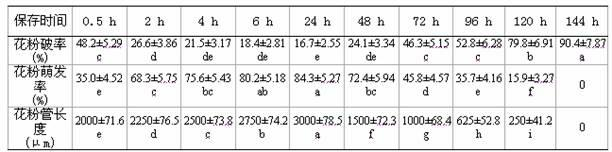
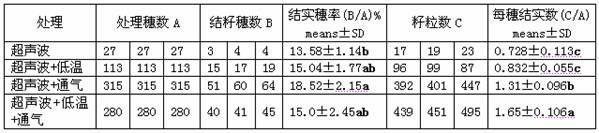
Ultrasonic-assisted pollen mediated plant genetic transformation method
InactiveCN102127567AImprove seed setting rateAvoid the cultivation processVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliSaccharum
The invention relates to an improved ultrasonic-assisted pollen mediated plant genetic transformation method, and aims to obviously increase the setting percentage of the plant fertilized by pollen subjected to ultrasonic treatment, thereby increasing the number of transformants obtained for each treatment. The method comprises the following steps: by using an agrobacterium Ti plasmid carrying an exogenous gene segment, colibacillus plasmid or any other DNA vector as a genetic donor and using plant pollen as a receptor, mixing the pollen and exogenous DNA in a 5-50% sucrose solution subjected to aeration and low-temperature treatment, and transferring the exogenous gene into the receptor pollen under the assisting action of ultrasonic; fertilizing the treated pollen onto the stigma of the plant, and harvesting when the grains become ripe; and in the subsequent growth season, sowing the harvested seeds which are obtained after the fertilization of the transformed pollen, screening the germinated seeds and seedlings, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and Southern hybridization on the DNA of a seedling sample, and further determining the transformant. The method provided by the invention does not need tissue culture, does not have species or genotype dependency, and can shorten the genetic transformation breeding time and save the manpower and material resources.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
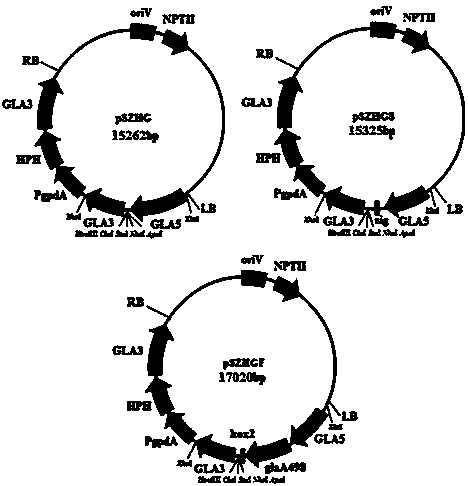
Ti plasmid aspergillus niger gene replacement expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN103409458AEliminate position effectEliminate competition effectsFungiMicroorganism based processesPosition effectTi plasmid
The invention provides a Ti plasmid aspergillus niger gene replacement expression vector and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The T-DNA (Triple helix Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) region elements of the Ti plasmid aspergillus niger gene replacement expression vector are arranged in the following sequence: an aspergillus niger target gene promoter, a multiple cloning site, an aspergillus niger target gene terminator, an aspergillus nidulans 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase gene promoter PgpdA, an aspergillus niger selection marker gene and an aspergillus niger target gene terminator. According to the invention, a target gene is integrated at the site of the aspergillus niger target gene through homologous recombination, and the target gene is regulated and controlled by a target gene promotor of high expression; therefore, the position effect of transgenosis is eliminated and the expression level is improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
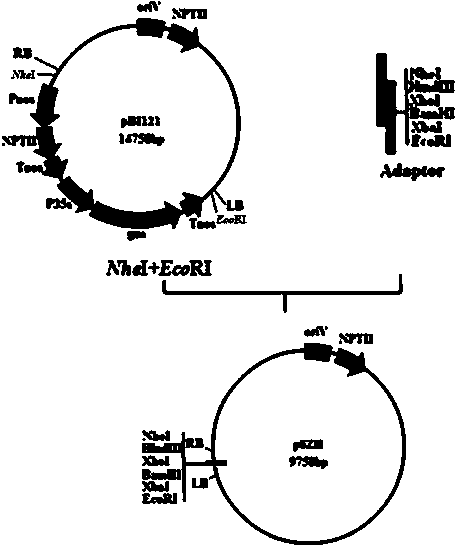
Plasmids for transforming plant cells
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Conversion for Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated plasmid to parietal sporamycin
InactiveCN1778913AHigh industrial valueImprove conversion rateBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismMycelium
The invention is about the Cephalosporium acremonium transformation leaded by the plasmid Ti of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Compared to the 1-4 transformants it can get above 100 transformants from the 107 receptor cells. So the transforming efficient has improved greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
Application method of stress tolerance related gene ZmHDZIV14 in regulation and control of plant stress resistance
InactiveCN105524156AImprove stress resistanceMicroinjection basedPlant peptidesPlant virusNucleotide
The invention relates to a plant stress resistance enhancement related protein named as ZmHDZIV14. The protein is derived from a maize (Zea mays L.) inbred line B73, the amino acid sequence of the protein is represented as a sequence table SEQ ID NO:2, and an encoding gene sequence of the protein is a nucleotide sequence represented as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention further provides an application method of an encoding gene of the plant stress resistance enhancement related protein. According to the application method of the encoding gene of the plant stress resistance enhancement related protein, an expression vector carrying the ZmHDZIV14 gene is used for converting plant cells or tissue by the aid of conventional biological methods including application of Ti plasmids, Ri plasmids and plant virus vectors, direct DNA transformation, microinjection, electric conduction, agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation and the like, a plant is cultured from the converted plant through tissue culture, and the plant with improved drought resistance and stress resistance is obtained. The expression vector carrying the ZmHDZIV14 gene is used for converting the plant cells or tissue by the aid of the conventional biological methods including application of Ti plasmids, Ri plasmids and plant virus vectors, direct DNA transformation, microinjection, electric conduction, agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation and the like, the plant is cultured from the converted plant through tissue culture, and the plant with the improved stress resistance is obtained.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
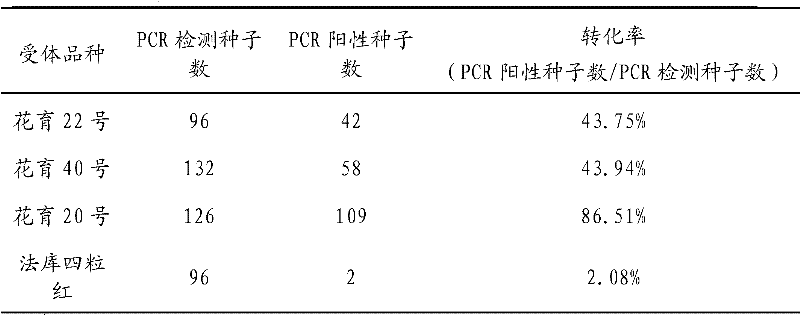
Standard molecule for specifically detecting transgenic rice strain Kefeng No.6 and application thereof
ActiveCN103160533AHigh sensitivityWide linear rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
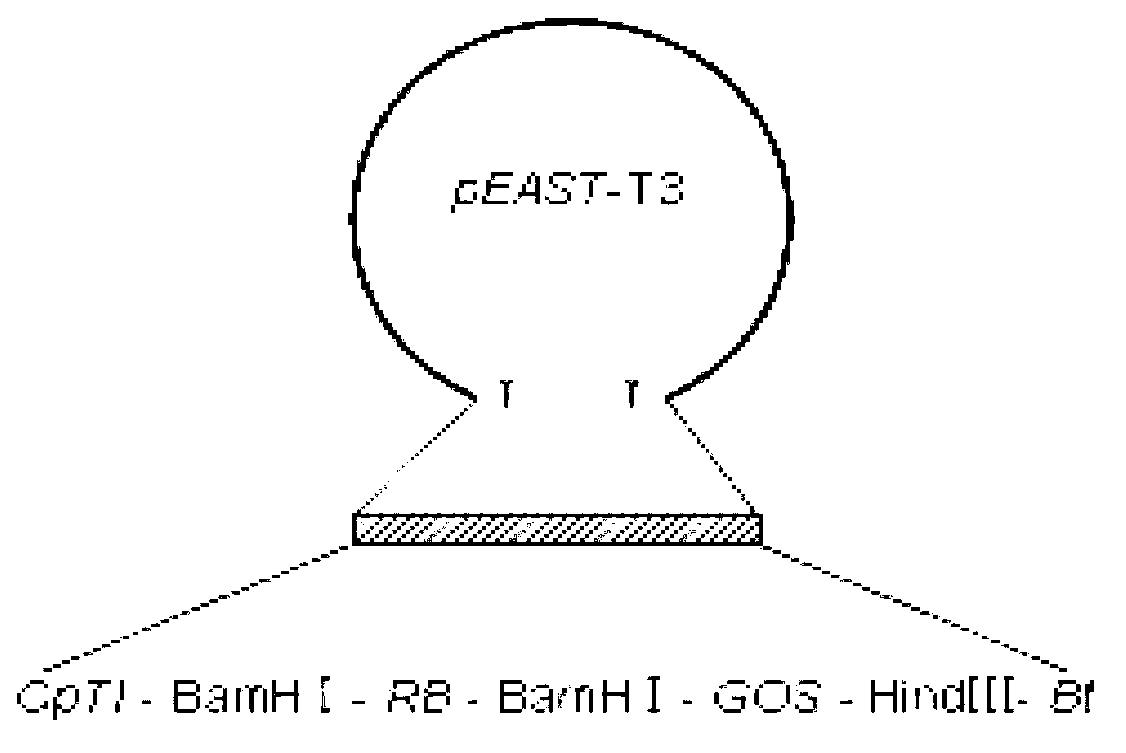
The invention discloses a standard molecular for specifically detecting a transgenic rice strain Kefeng No.6 and an application thereof. The standard molecule disclosed by the invention is an annular carrier which comprises a cowpea trypsin inhibitor coding gene segment shown by the 10th-101st sites of a sequence 1, a bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein coding gene segment shown by the 256th-336th sites of the sequence 1, a rice endogenous gene GOS segment shown by the 191th-258th sites of the sequence 1 and a border sequence segment of Ti plasmid T-DNA shown by the 108th-184th sites of the sequence 1. Experiments prove that the standard molecule disclosed by the invention has high sensitivity, wide linear range, good uniformity and strong stability, and is of important significance to the qualitative and quantitative detection of the transgenic rice strain Kefeng No.6; and the lowest detection line of the standard molecule can reach 2 copies.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Ultrasonic-assisted agrobacterium-mediated plant germination seed gene transformation method
InactiveCN102212553AThe conversion method is simpleFast conversion methodFermentationGenetic engineeringUltrasonic assistedTi plasmid
The invention discloses an ultrasonic-assisted agrobacterium-mediated plant germination seed gene transformation method. Plant germination seeds are directly used as agrobacterium infection receptors, and tissue culture and plant regeneration processes are not needed. The method comprises the following steps of: performing scratch and ultrasonic treatment on growing point parts of receptor plant germination seeds in the seed germination process by using the plant germination seeds as the receptors and using agrobacterium Ti plasmids carrying exogenous gene fragments as gene vectors, and then culturing the seeds and the agrobacterium together, transferring exogenous genes to a receptor genome, and further determining the transformed plants by direct screening of the seeds or seedlings and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and Southern hybridization of the plant leaf DNA.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
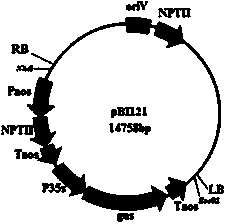
Plasmid system for constructing plant multi-gene expression vector and application of plasmid system
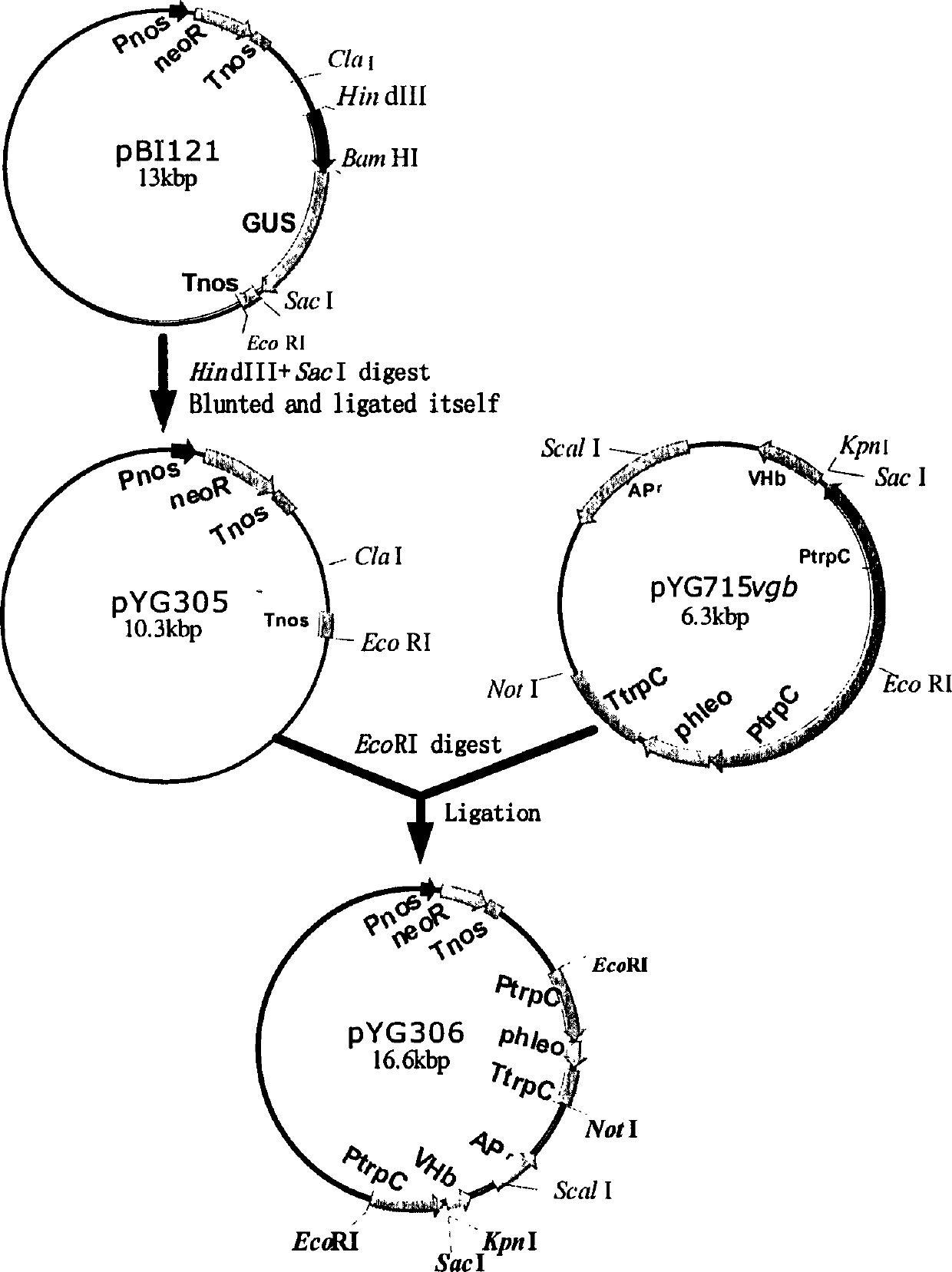
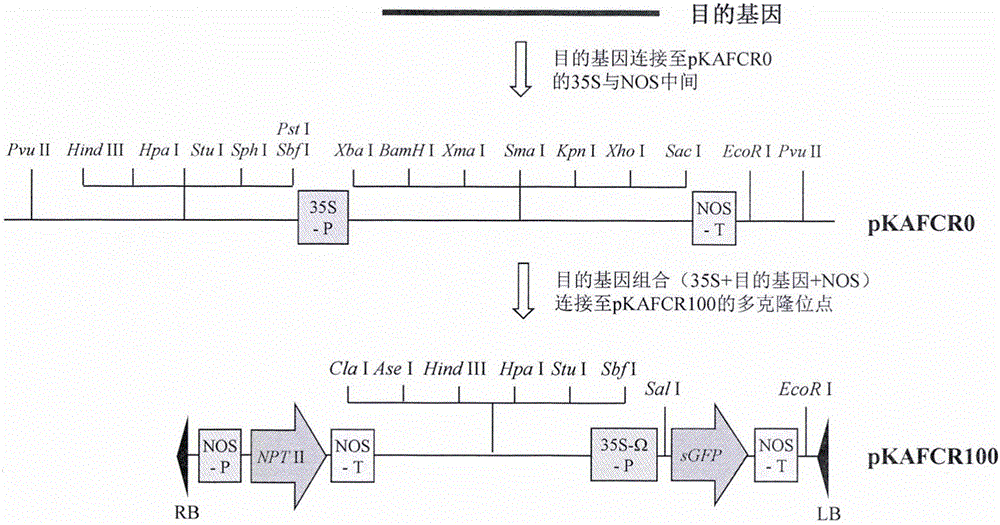
ActiveCN106244624AFirmly connectedImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsEscherichia coliKanamycin
The invention discloses a plasmid system for constructing a plant multi-gene expression vector and an application of the plasmid system. By transforming an escherichia coli plasmid vector pUC18 and a dual-core agrobacterium Ti plasmid pBI121, recombinant plasmids pKAFCR0 and pKAFCR100 are formed. The pKAFCR0 has a 35S promoter and an NOS terminator which are the most common in plant gene expression, a plurality of cloning restriction sites are introduced to the upstream side, the middle side and the downstream side of the pKAFCR0, and a gene segment, which is obtained by conducting cloning by virtue of such methods as PCR and the like, can be linked to the middle part of the 35S and the NOS of the pKAFCR0 by virtue of a plurality of modes; and the pKAFCR100 has a kanamycin NPT II tolerance gene and an sGFP green fluorescent protein reporter gene, as well as multiple-cloning restriction sites in middle. By using the pKAFCR0 and pKAFCR100 plasmids in a matched mode, one or more plant gene expression vector can be conveniently constructed.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Sonication-assisted pollen-mediated plant transformation method
InactiveUS20130232639A1Improve conversion efficiencyDemanding technical operationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationEscherichia coliUltrasound - action
A transformation method, including the following steps: preparing an Agrobacterium Ti-plasmid, Escherichia coli plasmid, or other DNA vectors carrying exogenous genetic fragments as a genetic donor; collecting a male gamete (pollen) of the plant as a recipient; preparing a 5-50% sucrose solution after aeration and low temperature pretreatment; mixing the pollen with the exogenous genetic fragments in the 5-50% sucrose solution; transferring the exogenous genetic fragments into the pollen in the presence of ultrasonication; pollinating a pistil stigma of the plant with the treated pollen; harvesting seeds at maturity; sowing the seeds in a subsequent growing season; screening a germinating seed and a seedling; and performing PCR amplification and Southern hybridization using DNA samples of plants to further determine transformants.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
Dual-elemental Ti plasmid with bidirectional promoter trapping and plasmid rescuing functions and construction method of dual-elemental Ti plasmid
InactiveCN103525861AIncrease success rateConvenient and accurate accessFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionOpen reading frameTrapping
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Agrobacterium bacterium to be used in plant transformation method
ActiveUS20160083737A1Improve transformation efficiencyBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesOrigin of replicationBacteroides
This invention relates to the Agrobacterium bacterium to be used in plant transformation method comprising three types of plasmids. The Agrobacterium bacterium of this invention comprises plasmids of (1) to (3) shown below:(1) a plasmid comprising the following components:(i) the virB gene, the virC gene, the virD1 gene, the virD2 gene, the virD3 gene, the virG gene and the virJ gene of pTiBo542, and(ii) an origin of replication;(2) a disarmed Ti plasmid or a disarmed Ri plasmid of Agrobacterium bacterium; and(3) a plasmid having a T-DNA region consisting of a desired DNA;wherein each of the plasmids of (1) to (3) has a replication mechanism that enables a mutual coexistence with each other.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for improving transgenosis efficiency of cotton
InactiveCN105002209AAvoid degradationIntegration avoidanceVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction enzyme digestionTi plasmid
The invention discloses a method for improving the transgenosis efficiency of cotton. The method comprises the following steps: after mixing restriction enzyme digestion DNA with a plasmid DNA protective agent, introducing a target gene into cotton through the pollen tube pathway method by using lipidosome packaging to carry toxic protein genes on Ti plasmids. The method can effectively improve the transgenosis efficiency.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated peanut efficient transgenic method
The invention relates to a plant transgenic technology and in particular relates to an Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated peanut transgenic method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adopting the conventional method to deliver the constructed Ti plasmid vector carrying the target gene into Agrobacterium tumefaciens; (2) using the transformed bacteria to perform shake culture in YEP culture medium; (3) taking 2-6mu l of weight drop bacterial solution to inject in a peanut plant in the suitable period of the growth of peanut to ensure the infection and convertion of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in the peanut plant; (4) taking the sheets of the peanut cotyledon tissue after harvesting seeds, rapidly extracting the DNA of the sample to be tested to use the DNA as the PCR template; and(5) using a specific primer designed according to the target gene sequence to perform PCR identification, and performing electrophoresis detection. In the method, an Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transgenic technology is utilized, thus viable offspring can be obtained conveniently and rapidly and the single tissue culture regeneration stage is not required.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
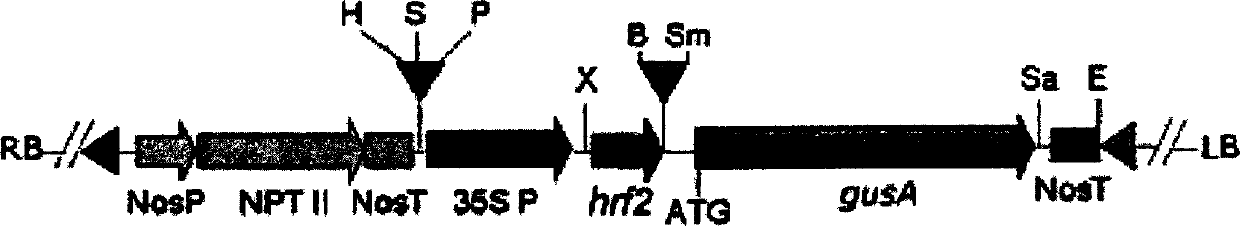
Rice flavamonocell hrf2 gene, recombinant vector and method for transgenic breeding plant therefor
InactiveCN1219059CImprove disease resistancePlant type dwarfSugar derivativesFused cellsDiseaseAgricultural science
An hrf 2 gene of rice Xanthomonas is disclosed. It can be used as the target gene to be constructed on the Ti-plasmid dual-element vector pBI121 expressed in plant, so obtaining its recombinant vector pBI121:hrt2. Said recombinant vector is transferred to EHA105 to transform plant cells. The transformed regenerative plant (To generation) is screened in the culture medium and detected. The resultant transgenic plant has the improved broad-spectrum power to resist diseases and pests, and the improved other productive characteristics.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
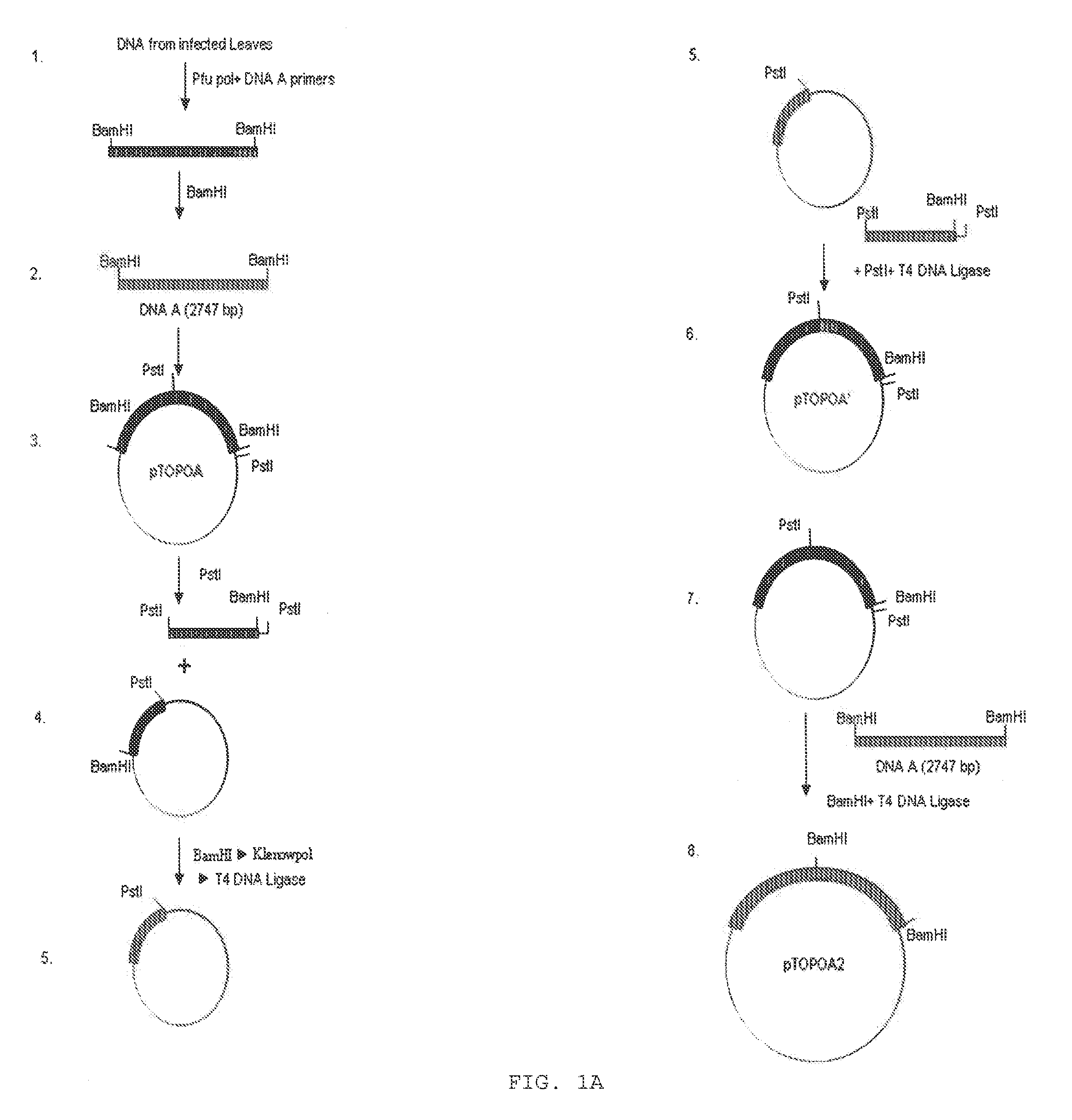
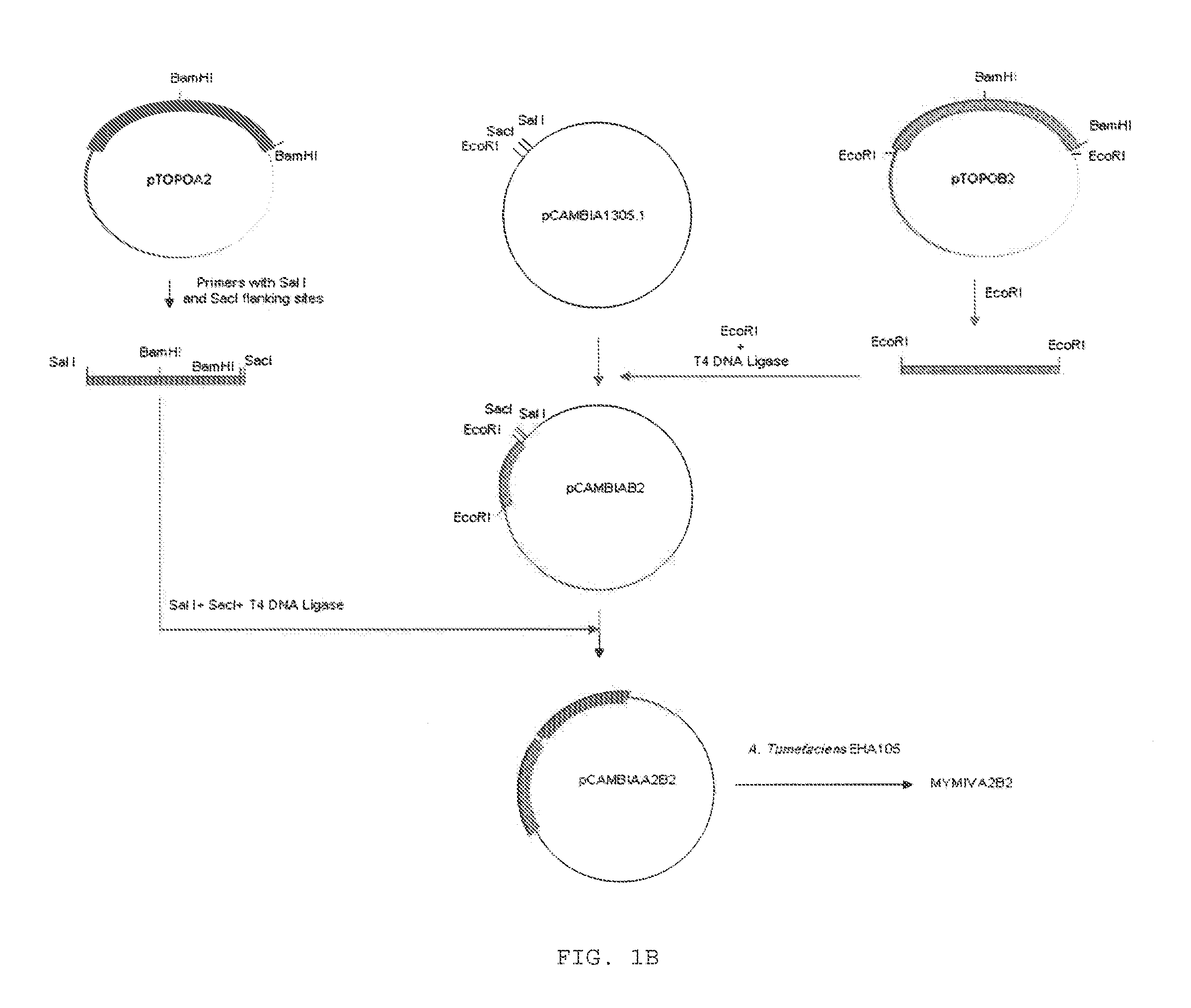
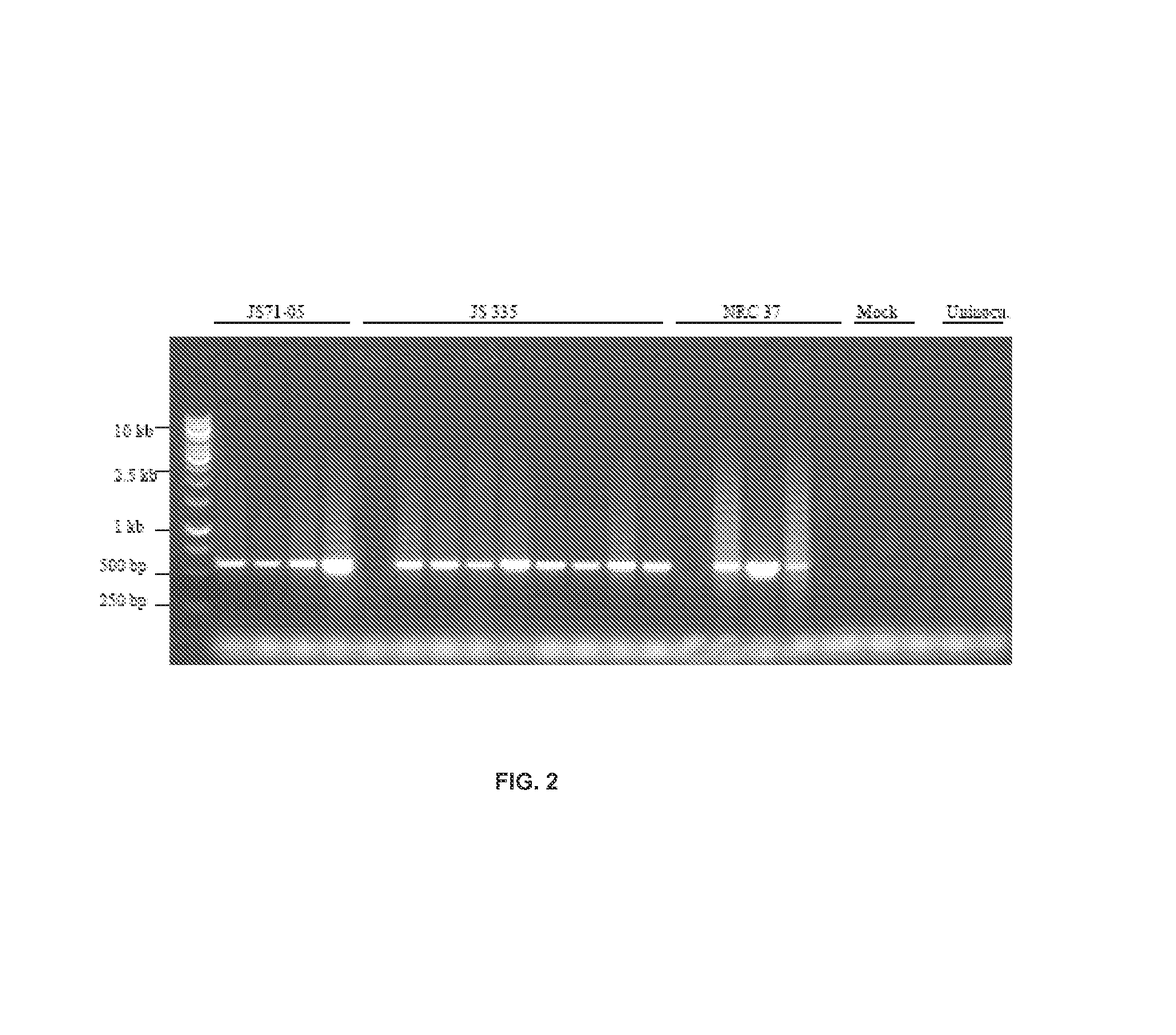
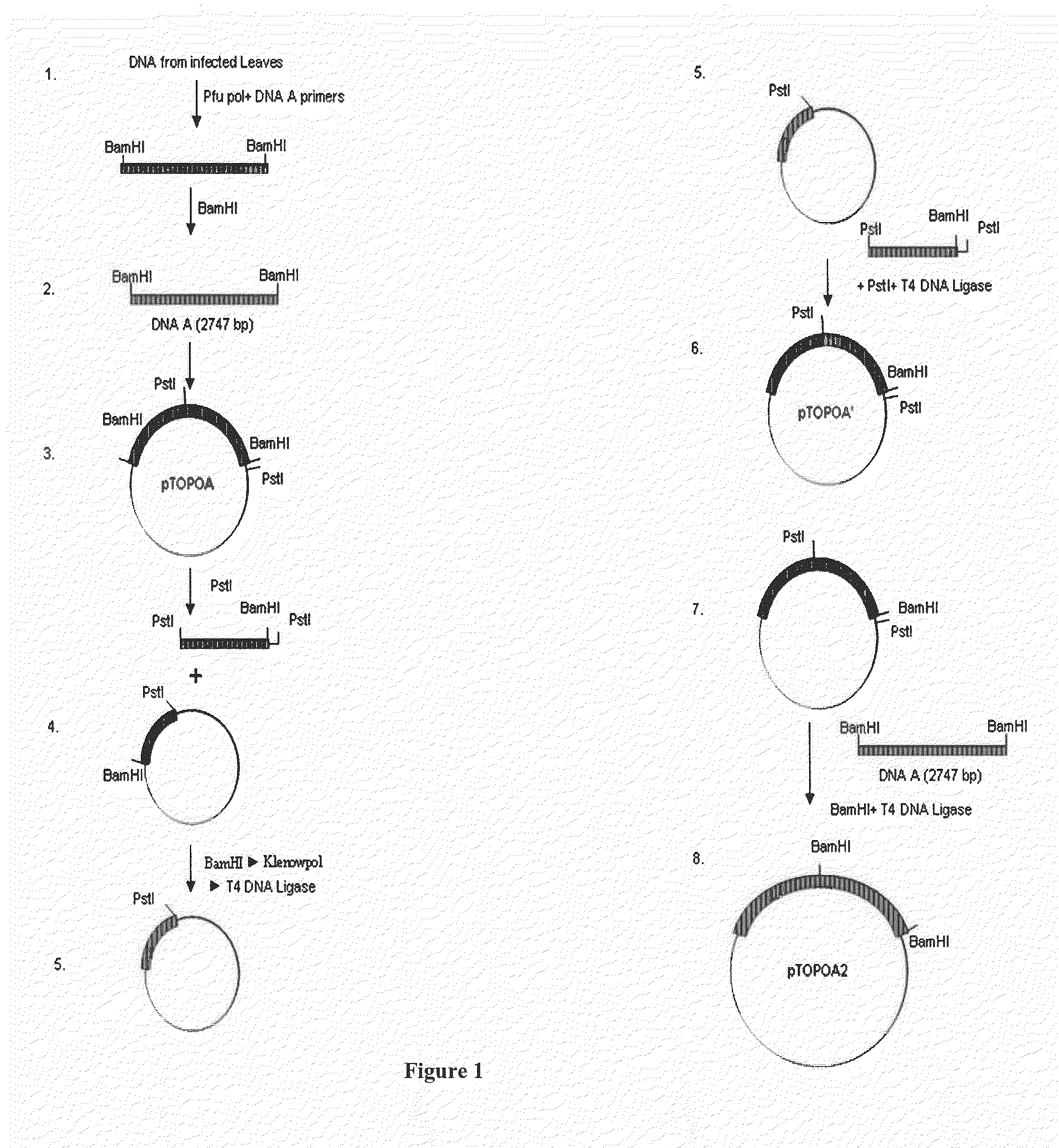
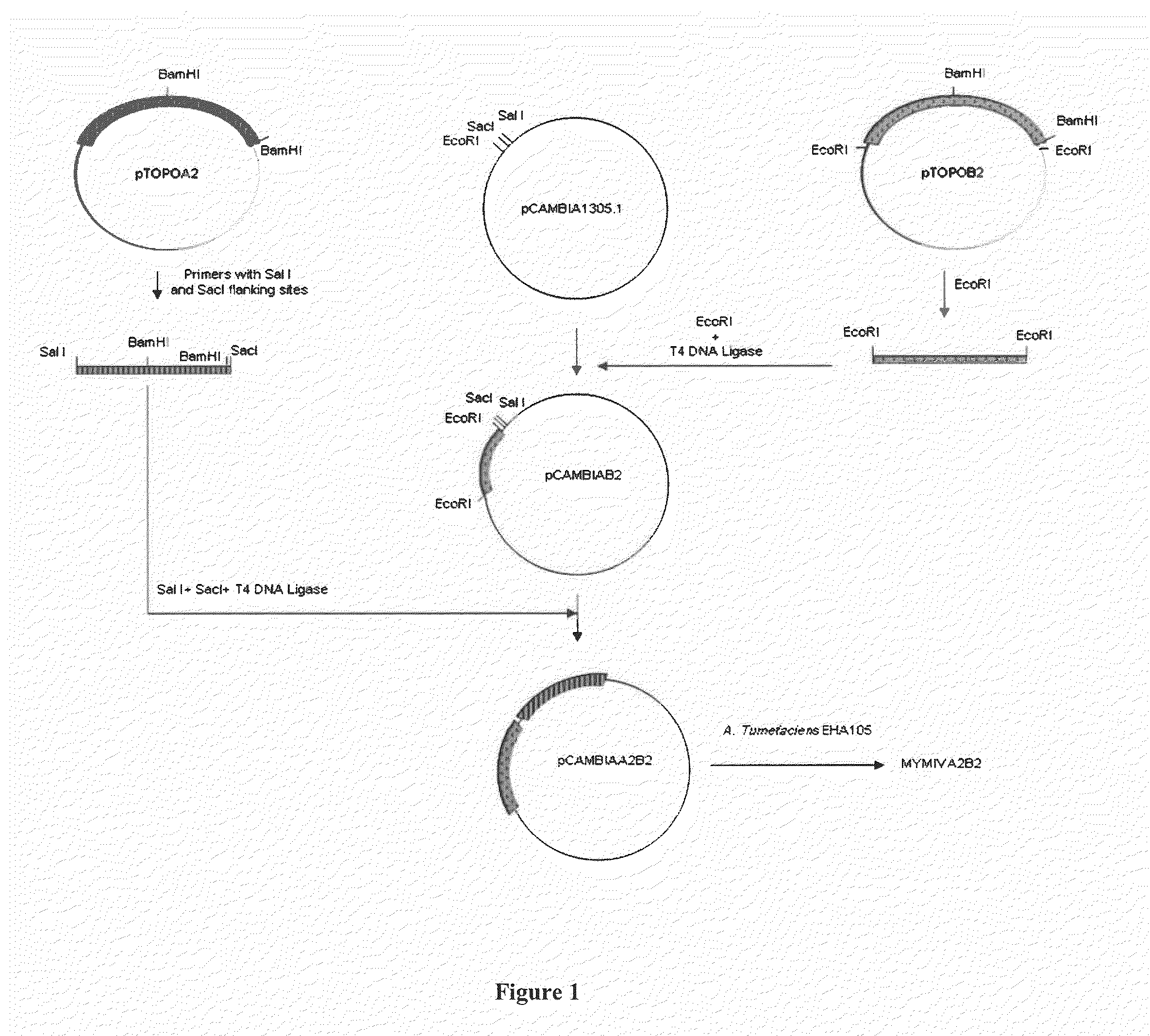
Chimeric construct of mungbean yellow mosaic india virus (MYMIV) and its uses thereof
A recombinant DNA construct, recombinant vectors and host cells comprising the dimers of DNA A and DNA B of Mungbean Yellow Mosaic India Virus (MYMIV) in a single Ti plasmid are provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF PLANT GENOME RES
Chimeric construct of mungbean yellow mosaic india virus (MYMIV) and its uses thereof
A recombinant DNA construct, recombinant vectors and host cells comprising the dimers of DNA A and DNA B of Mungbean Yellow Mosaic India Virus (MYMIV) in a single Ti plasmid are provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF PLANT GENOME RES
Biological gene transfer system for eukaryotic cells
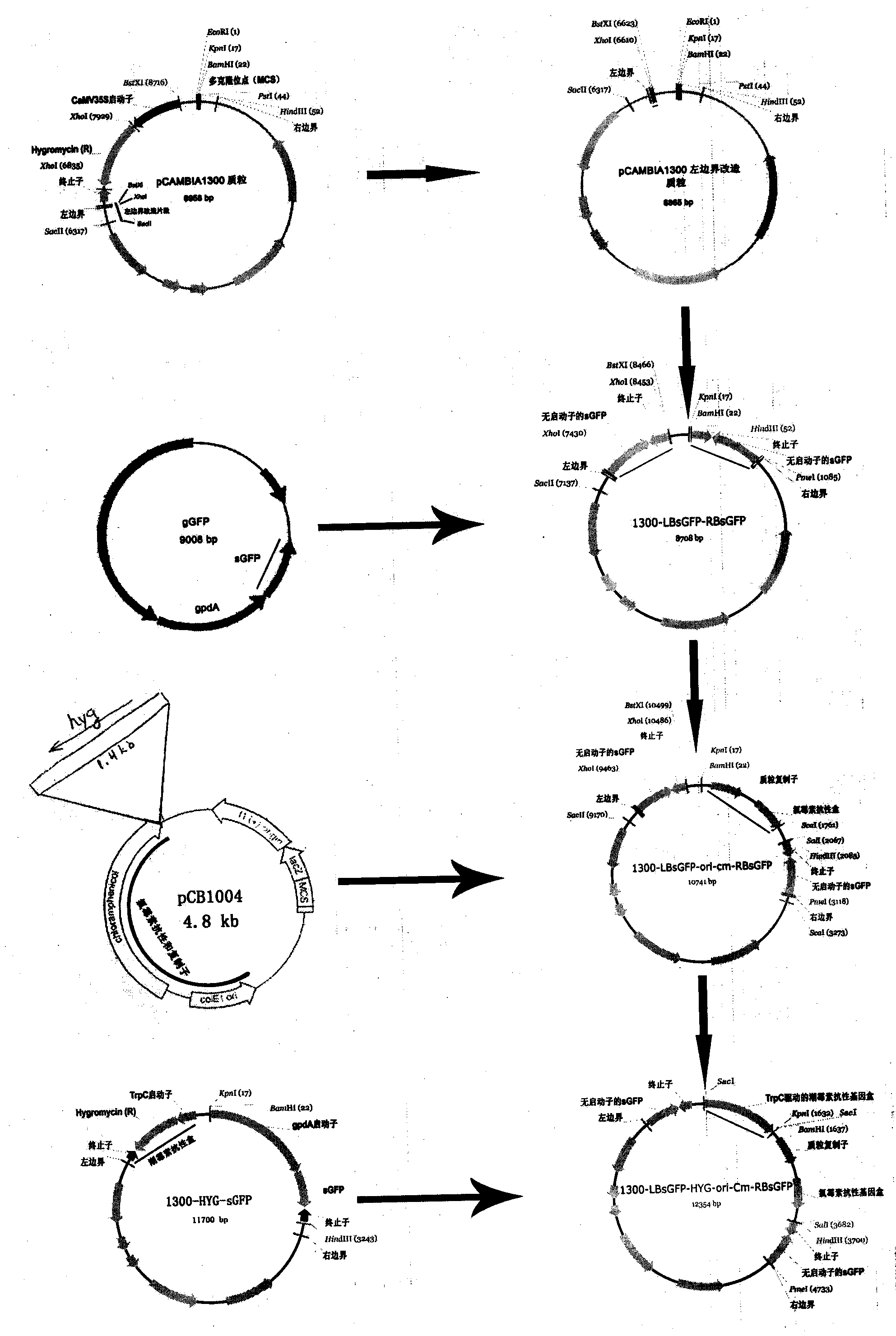
InactiveCN101123869AVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyPlant cell
Owner:卡姆比亚公司
Application method of stress resistance-related gene ZmHDZIV13 in regulation of plant stress resistance
The invention relates to a gene for enhancing plant drought resistance, and provides a related protein for enhancing plant stress resistance. The gene has a is named as ZmHDZIV13, and derived from maize (Zea maysL.) inbred line B73, and has an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence table SEQIDNO:2. A coding gene sequence of the protein is shown in SEQIDNO:1. The invention also relates to an application method of the encoding protein of the related protein for enhancing plant stress resistance. The method is as below: transforming an expression vector carrying the ZmHDZIV13 gene into plant cells or tissues through conventional biological methods including Ti plasmid, Ri plasmid, a plant virus vector, direct DNA conversion, micro injection, conductance and Agrobacterium mediation, and culturing the transformed tissue into plants to obtain plants with improved drought resistance. The ZmHDZIV13 gene can be constructed into the existing plant expression vector by the method used in the prior art, and the encoding gene of the related protein for enhancing plant stress resistance can be converted into other plants by conventional methods to enhance the drought resistance of plants.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
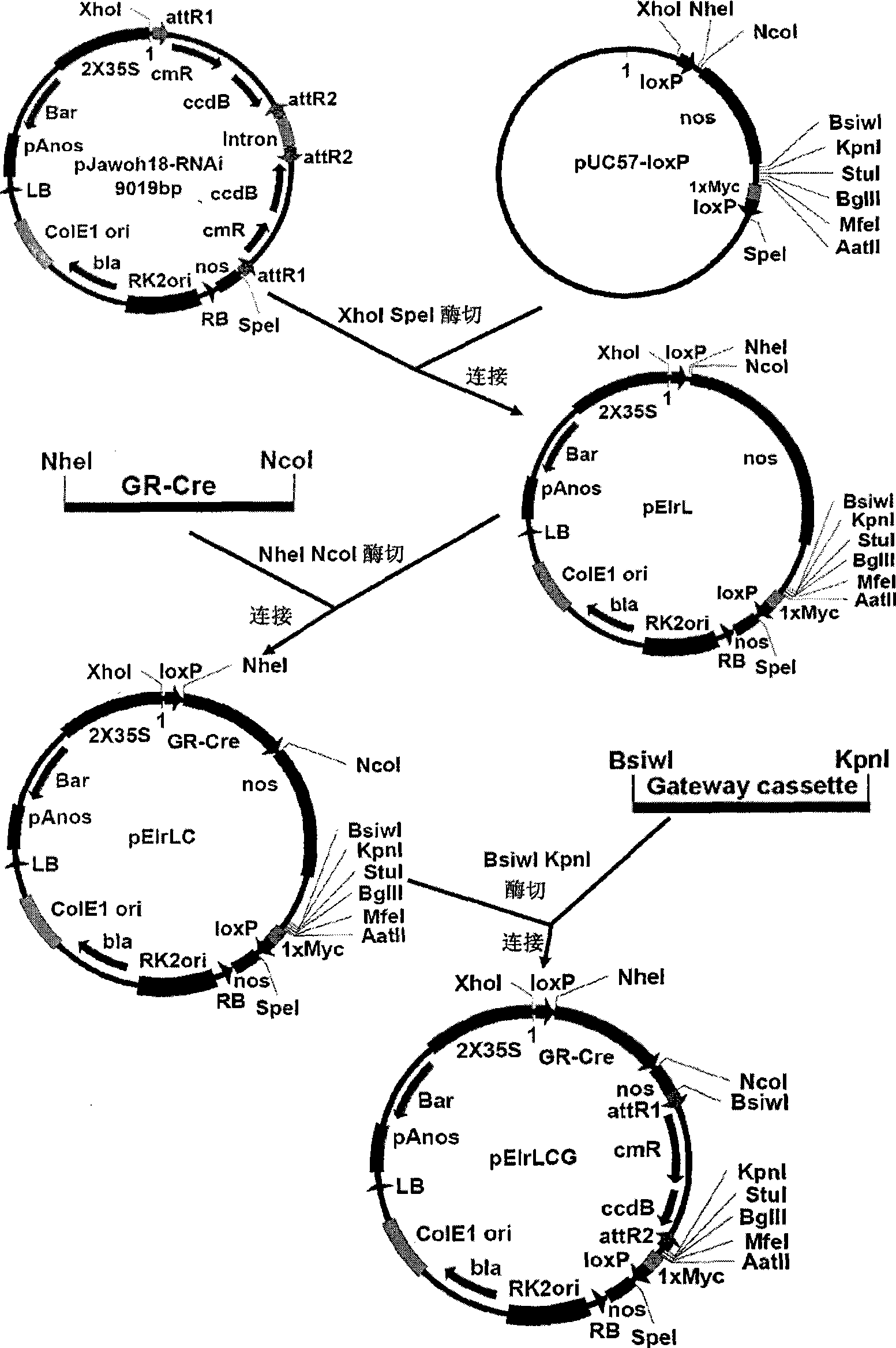
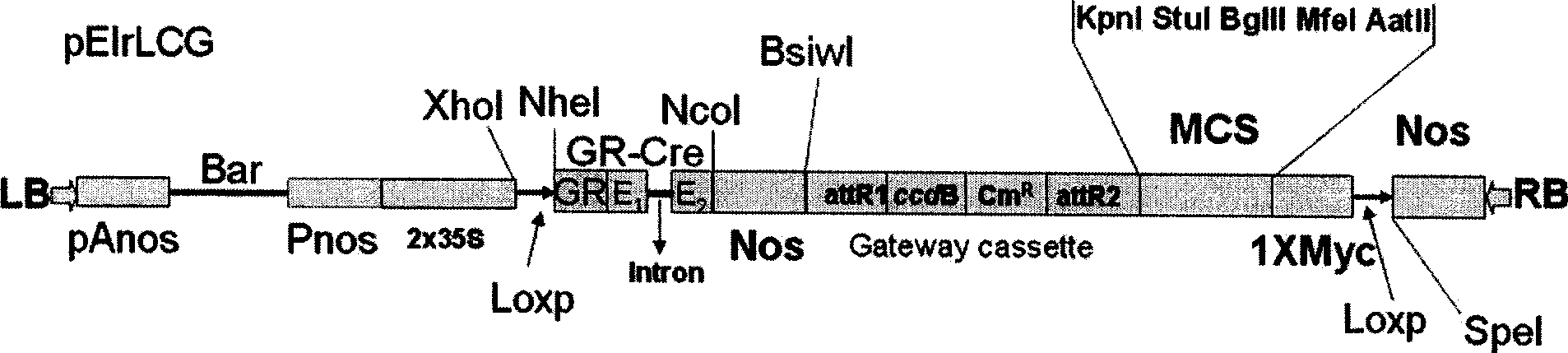
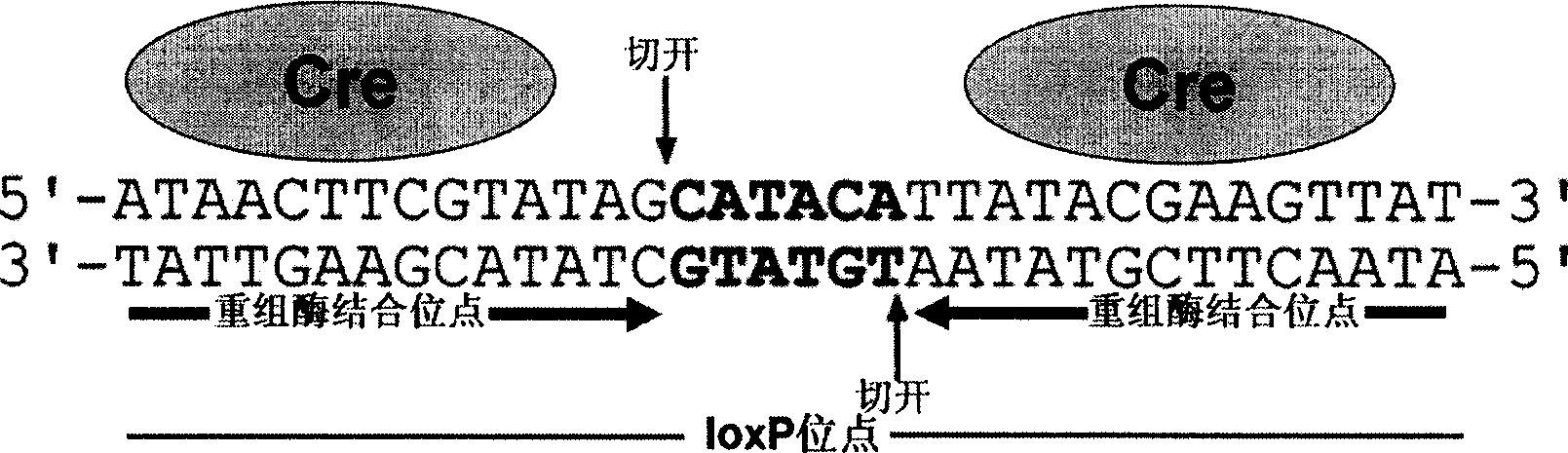
Novel Ti plasmid pElrLCG for saving plant embryos from lethal mutation and its preparation method
InactiveCN101544989ADevelop special biological traitsConvenient timeGenetic engineeringFermentationPlasmid VectorTi plasmid
The present invention discloses a novel Ti plasmid pElrLCG for saving embryos from lethal mutation and a preparation method of the Ti plasmid pElrLCG. Connect 5.211kb long bearer fragment recovered from enzyme cutting of original bearer pJawoh18 with synthesized XhoI-loxP-NheI-NcoI-Nos-BsiwI-KpnI-StuI-BgIII-MFeI-AatII-1xMyc-loxP-SpeI fragment, and then insert Gr-Cre, Gateway Cassettee fragment between two loxP loca, to construct a new plasmid vector pElrLCG. The plasmid vector can be used to obtain homozygote of embryonic lethal mutant or study the development of homozygote of embryonic lethal mutant in late stage, and therefore is of great significance for study on lethal mutations of embryos, hybridization breeding, and special biologic behaviors of lethal mutants of embryos.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Plant-Based Production of Heterologous Proteins
ActiveUS20120045818A1Low production costImprove energy balanceFermentationGenetic engineeringHeterologousBiotechnology
Described herein are viral amplicon-based protein expression systems and methods useful for producing heterologous proteins, such as enzymes, by agroinfiltration. The methods involve producing an Agrobacterium with a Ti plasmid encoding a heterologous protein, infecting plant cells with the Agrobacterium, allowing expression of the heterologous protein, and recovering the heterologous protein from the plant cells. In one embodiment, the protein produced is an endoglucanase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
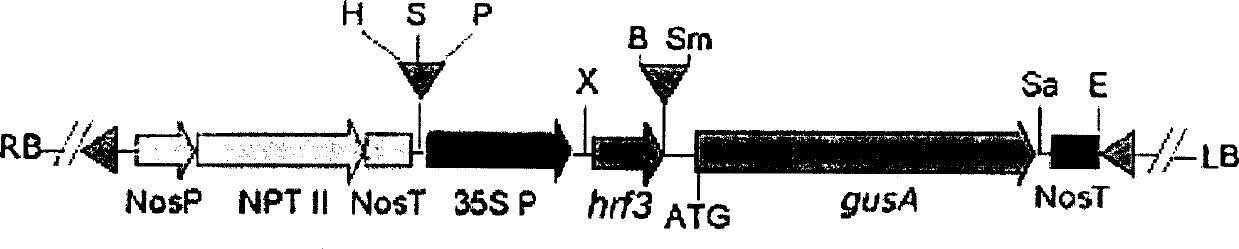
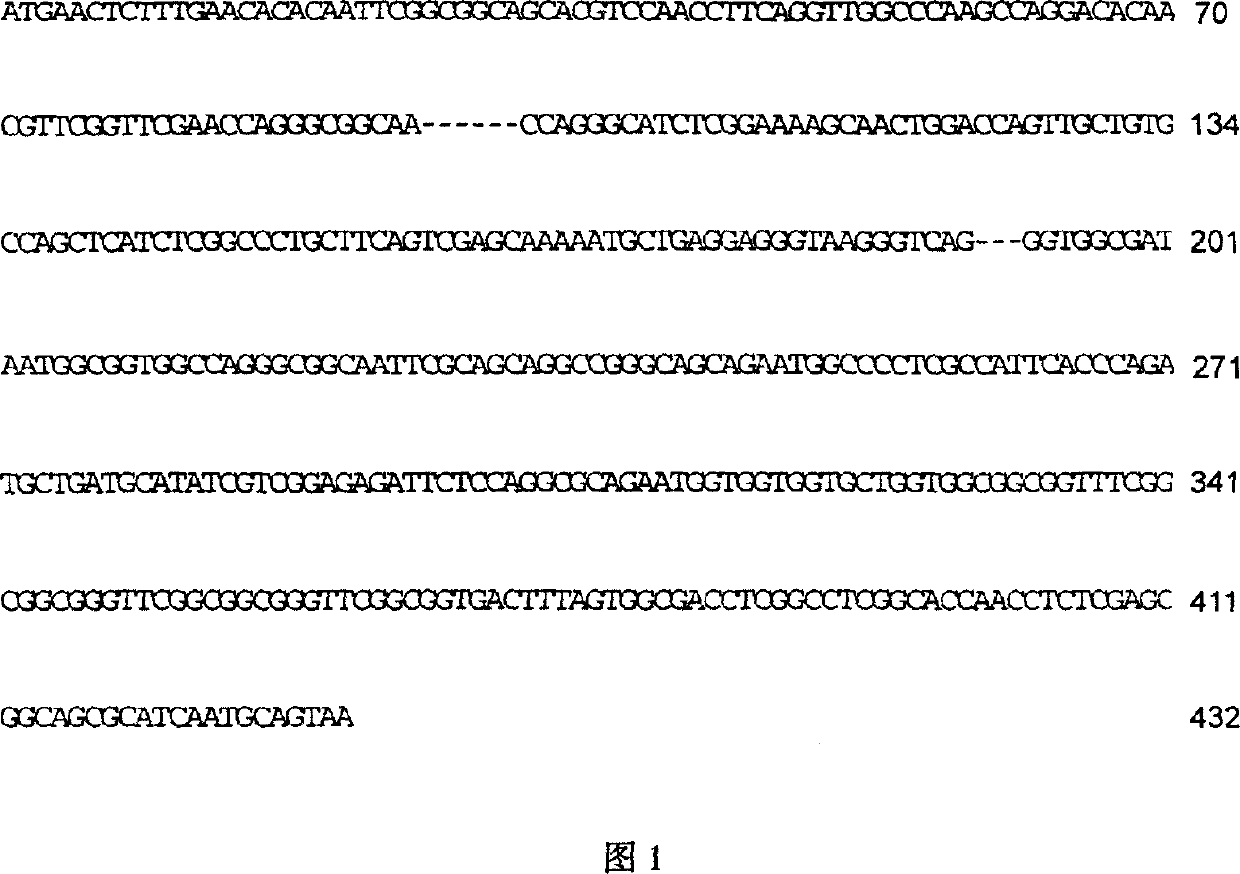
Rice flavamonocell hrf3 gene, recombinant vector and breeding method for plant transgene
InactiveCN1225559CImprove disease resistancePlant type dwarfMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseBiotechnology
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Insect resistant cotton plants
ActiveUS7345229B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationAureobasidium sp.Bacillus thuringiensis
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Construction method and application of agrobacterium Ti plasmid vector PCHF1302
PendingCN109929874AFirmly connectedHigh selectivityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a construction method and application of an agrobacterium Ti plasmid vector PCHF1302 and belongs to the technical field of plant genes. Double enzyme digestion is simultaneously conducted on enzyme digestion sites ECORI and HindIII on an agrobacterium Ti plasmid Pcambia 1302, wherein the PCHF3300 comprises a 35S promoter, a NOS terminator and a complete gene expression frame of MCS, a homologous arm is added through PCR, an expression frame started by the 35S promoter is successfully connected to the plasmid Pcambia 1302, and the PCHF1302 is constructed; the target genecloned by PCR and other methods can be conveniently connected to a plurality of cloning enzyme digestion sites (MCS), so that the target gene can be stably expressed in plants; a TDNA region containing hygromycin resistance gene and mGFP5 green fluorescent protein reporter gene can significantly improve the screening effect of transgenic plants.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method of increasing plant transformation frequency using modified strains of Agrobacteria
Agrobacterium strains that harbor transformation-enhancing genes on a plasmid capable of replication independently of the Agrobacterium chromosome, the Ti plasmid, and plant transformation binary vectors, and uses for these Agrobacterium strains are provided. Additionally, Agrobacterium strains that are deficient in DNA recombination functions that result in instability or rearrangement of plant transformation binary vectors, and that harbor transformation-enhancing genes on a plasmid capable of replication independently of the Agrobacterium chromosome, the Ti plasmid, and plant transformation binary vectors, and uses for these strains, are also provided. Further included are Agrobacterium strains that harbor transformation-enhancing genes integrated into the Agrobacterium chromosome at a locus that does not interfere with or otherwise compromise the normal growth and plant transformation ability of the Agrobacterium cells, and uses for these Agrobacterium strains. Plants made using these Agrobacterium strains are also described.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Production of cellulase enzymes in plant hosts using transient agroinfiltration
Described herein are methods useful for producing proteins, such as enzymes, by agrofiltration. The methods involve producing an Agrobacterium with a Ti plasmid encoding a cellulase, infecting plant cells with the Agrobacterium, allowing expression of the cellulase, and recovering the cellulase from the plant cells. In one embodiment, the protein produced is an endoglucanase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com