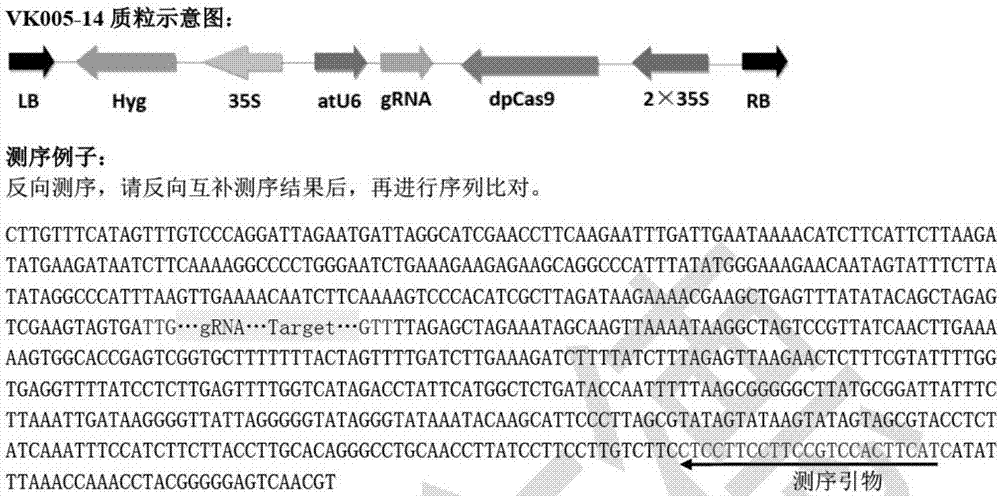
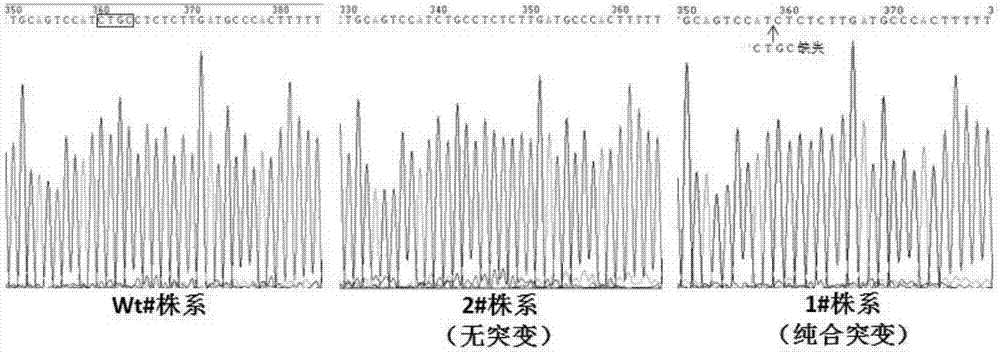
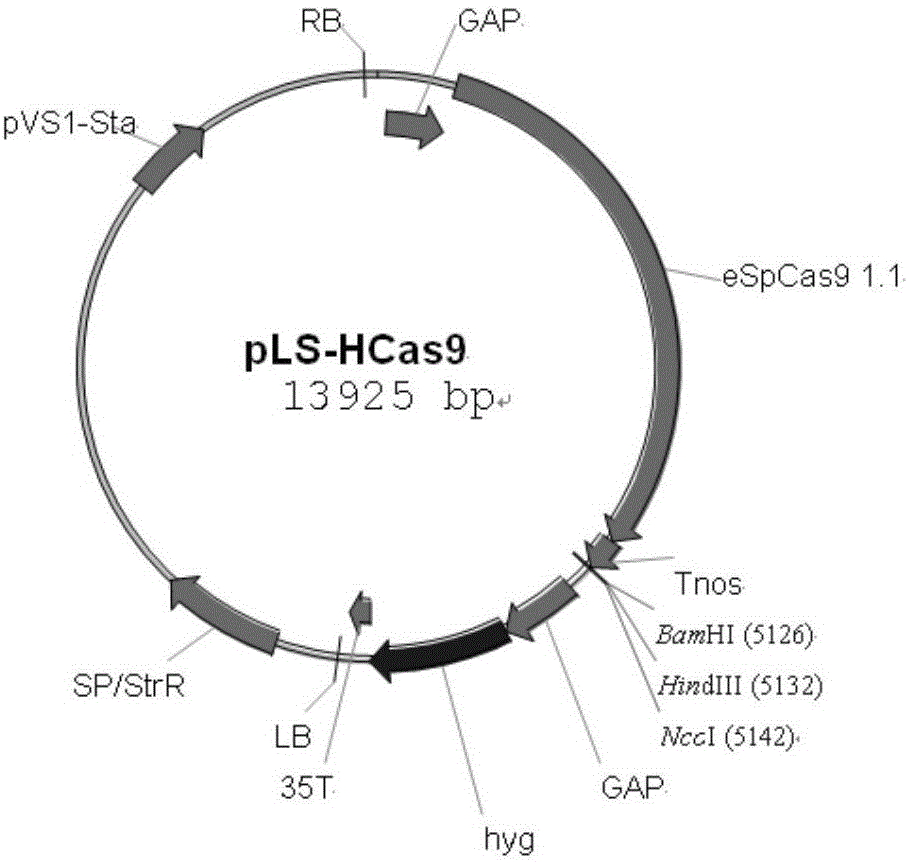
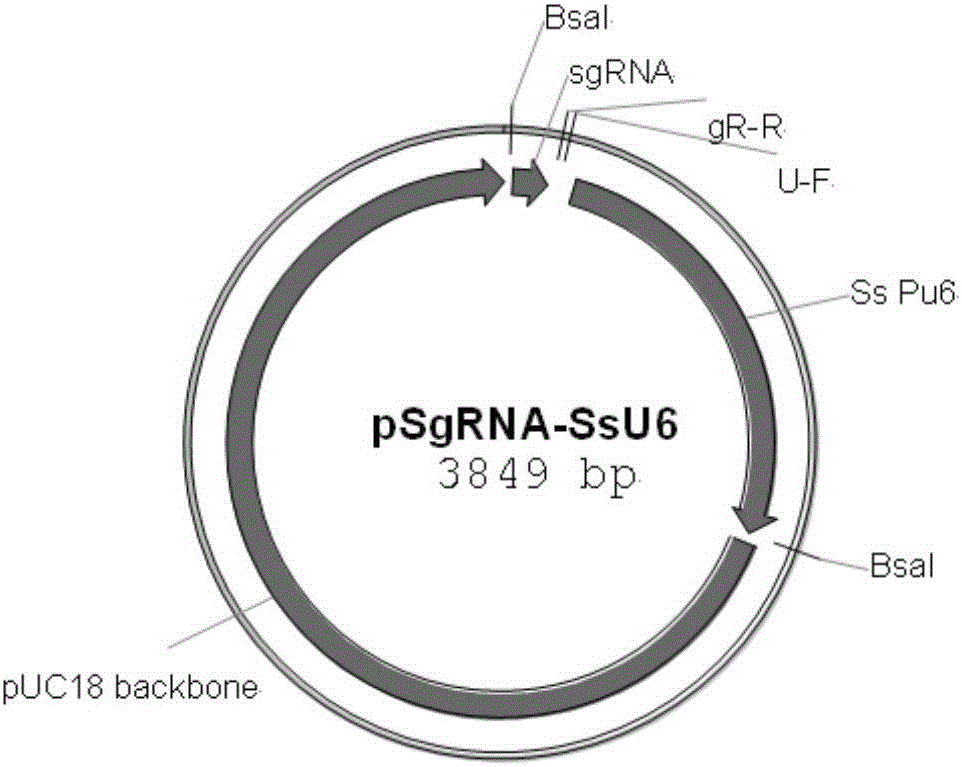
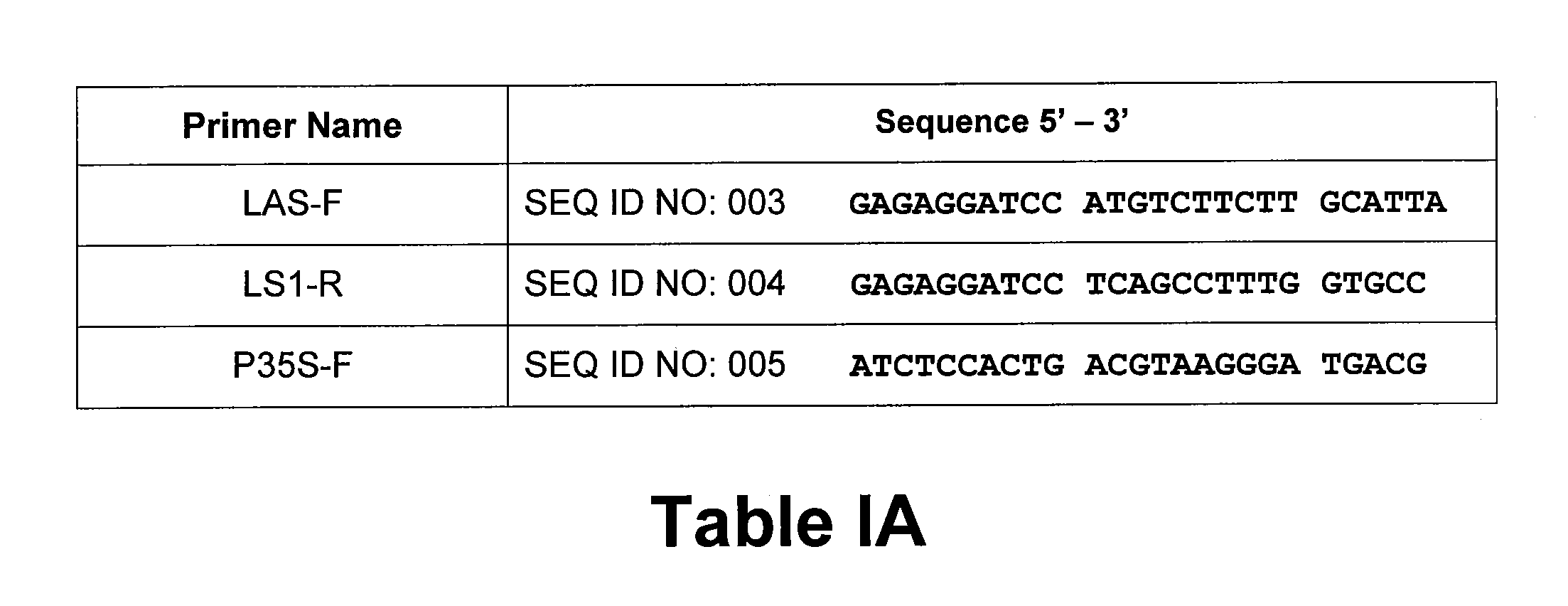
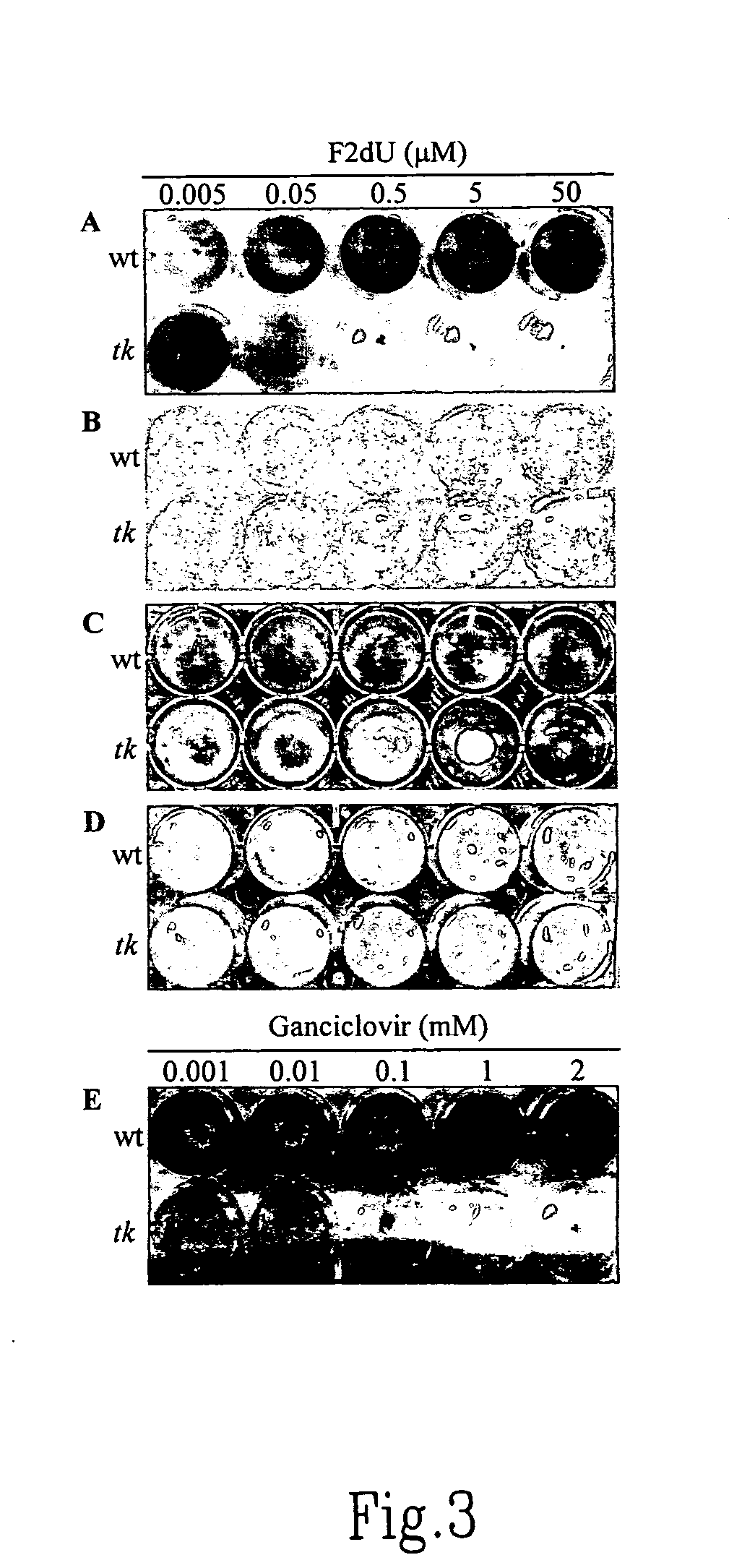
Patents
Literature
954 results about "Agrobacterium tumefaciens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agrobacterium tumefaciens (updated scientific name Rhizobium radiobacter, synonym Agrobacterium radiobacter) is the causal agent of crown gall disease (the formation of tumours) in over 140 species of eudicots. It is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative soil bacterium. Symptoms are caused by the insertion of a small segment of DNA (known as the T-DNA, for 'transfer DNA', not to be confused with tRNA that transfers amino acids during protein synthesis, confusingly also called transfer RNA), from a plasmid, into the plant cell, which is incorporated at a semi-random location into the plant genome.
Insect resistant plants
InactiveUS6943282B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacteroidesAureobasidium sp.
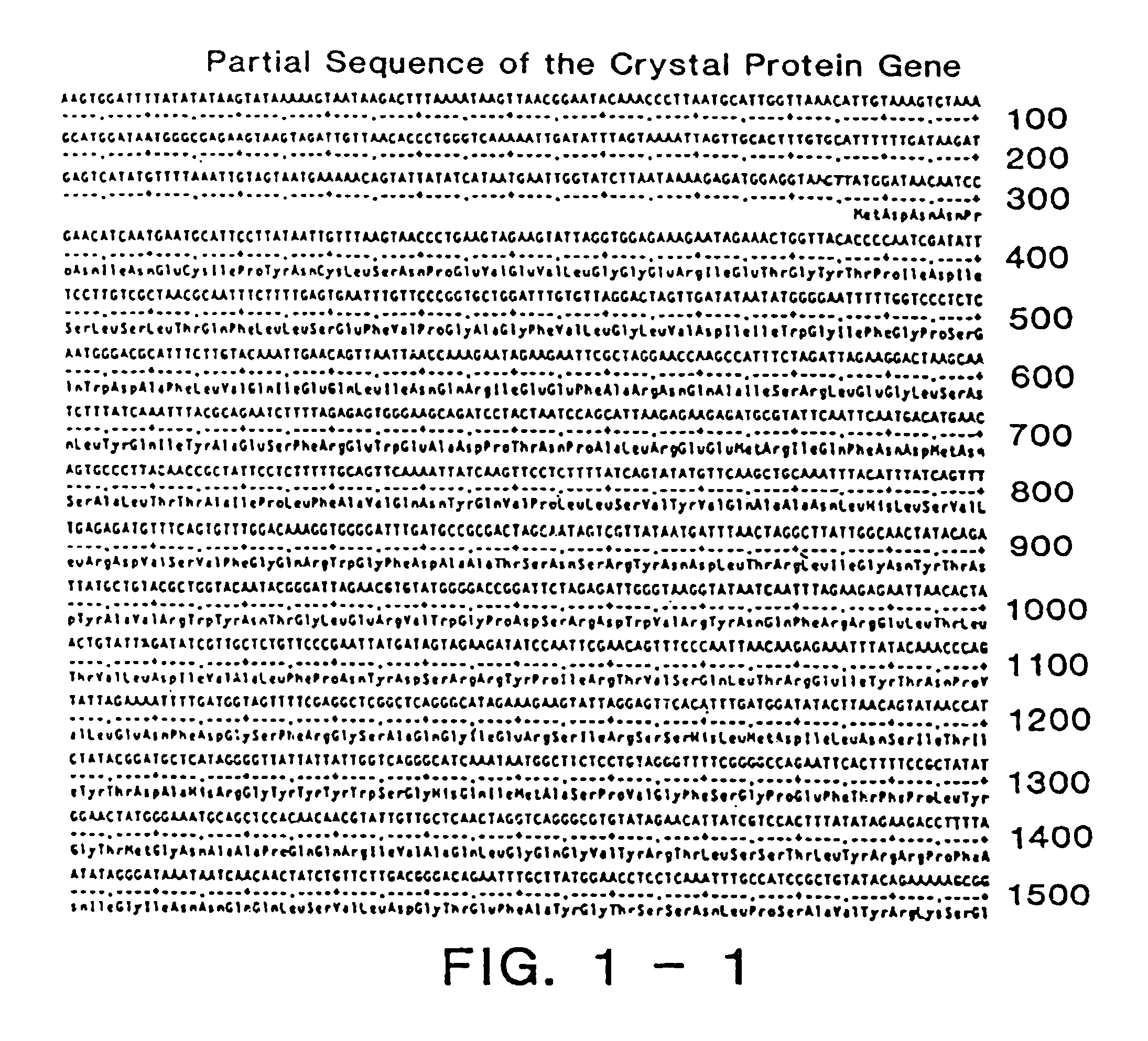
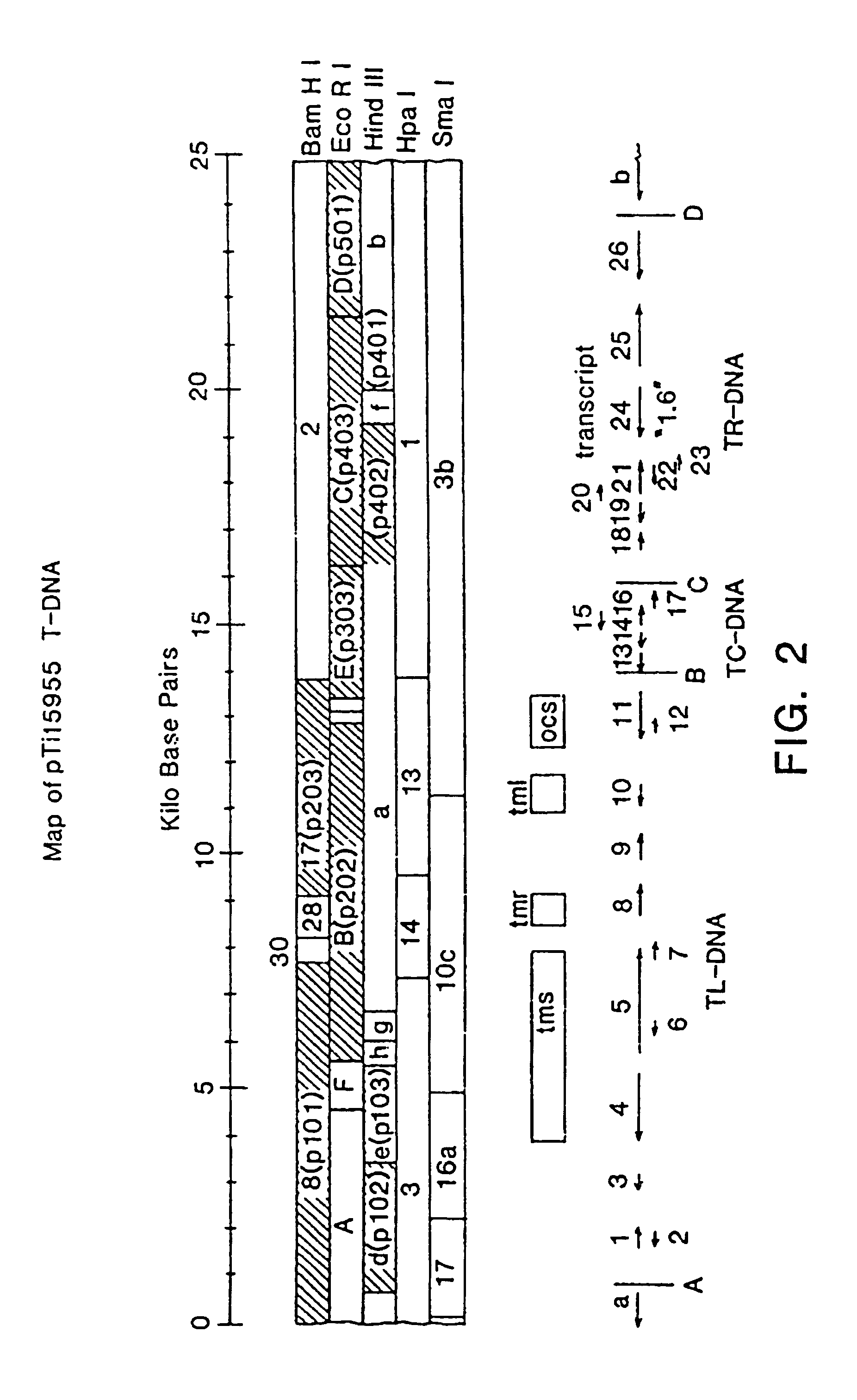
A method for expressing insecticidal protein structural genes in plant genomes is provided. In the preferred embodiments this invention comprises placing a structural gene for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein under control of a plant or a T-DNA promoter and ahead of a polyadenylation site followed by insertion of said promoter / structural gene combination into a plant genome by utilizing an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-based transformation system. The modified Ti plasmid is then used to transform recipient plant cells. Also provided are the plants and tissues produced by this method and bacterial strains, plasmids, and vectors useful for execution of this invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Soybean transformation and regeneration using half-seed explant
ActiveUS7473822B1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationTransgeneAgrobacterium tumefaciens
A method of transforming soybean comprising infecting half-seed explants of soybean with Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing a transgene, which method can further comprise regenerating the half-seed explants in vitro on selection medium.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
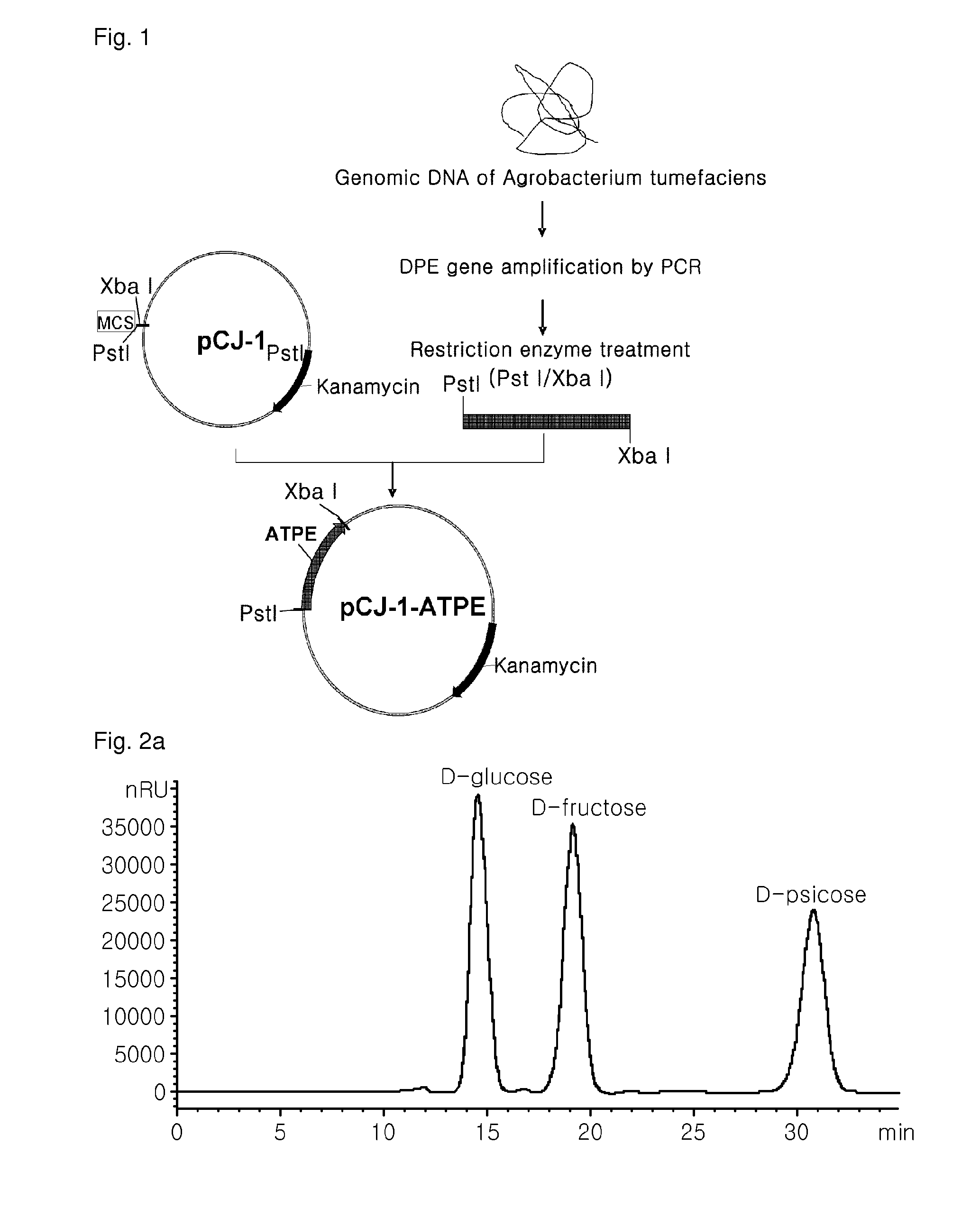
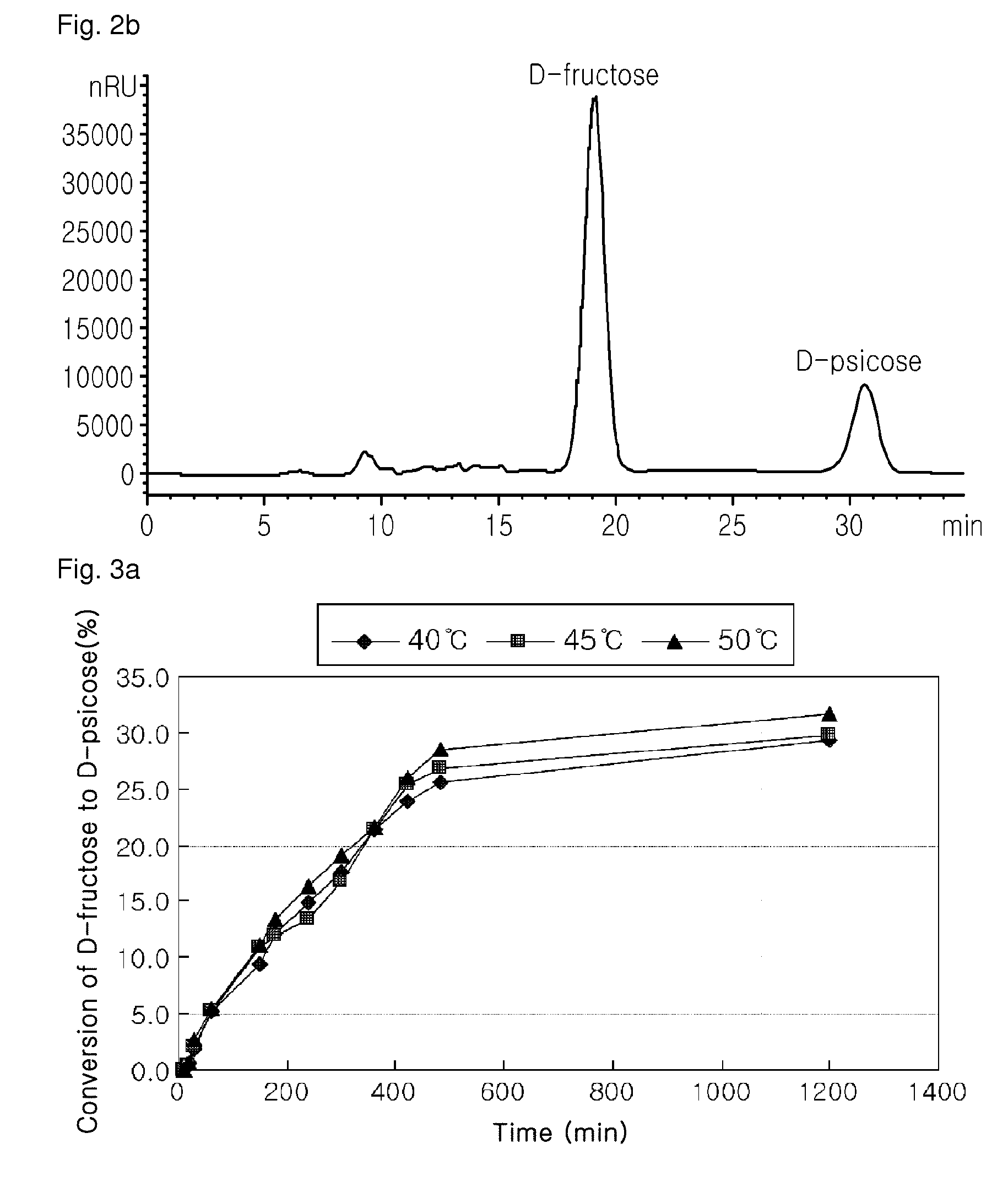
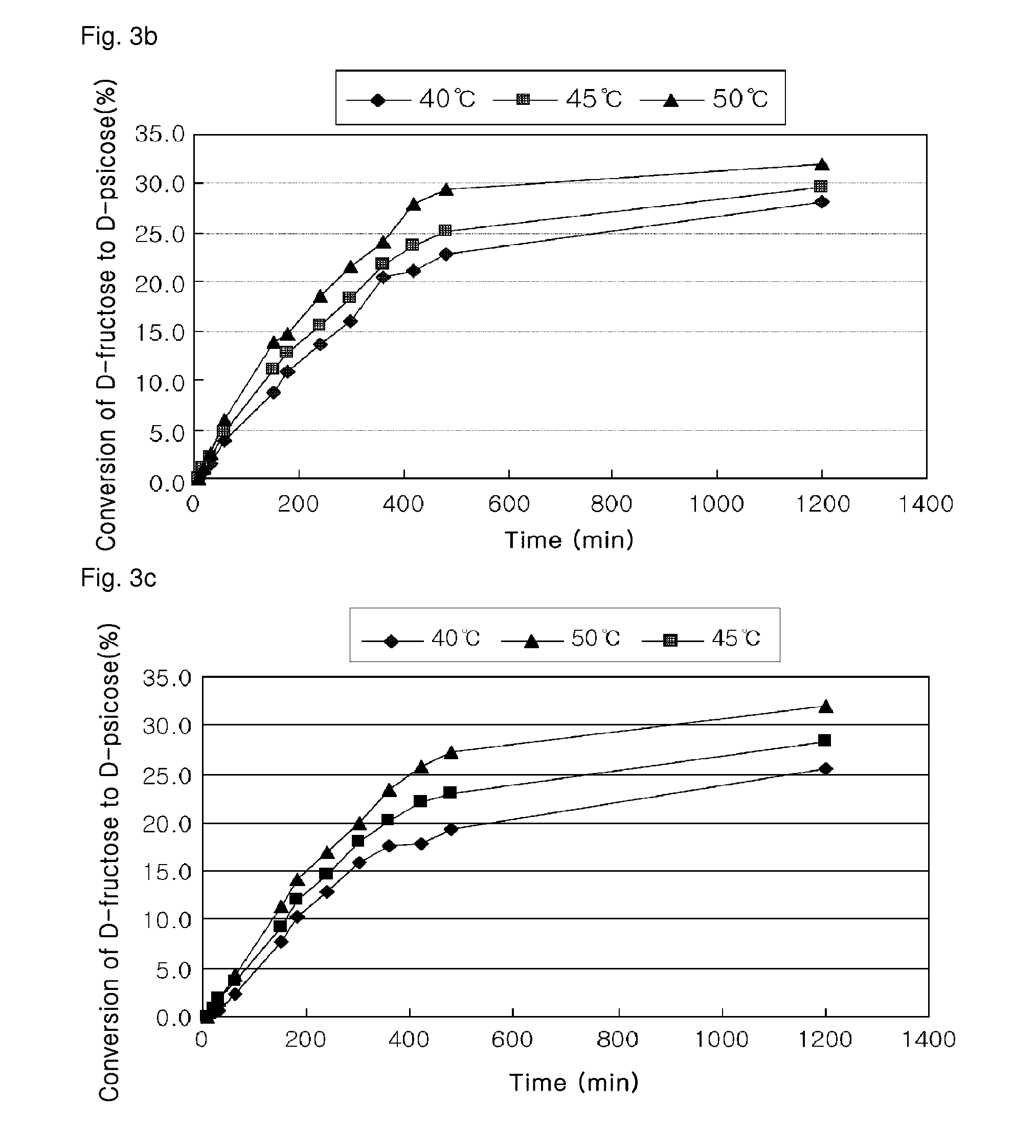
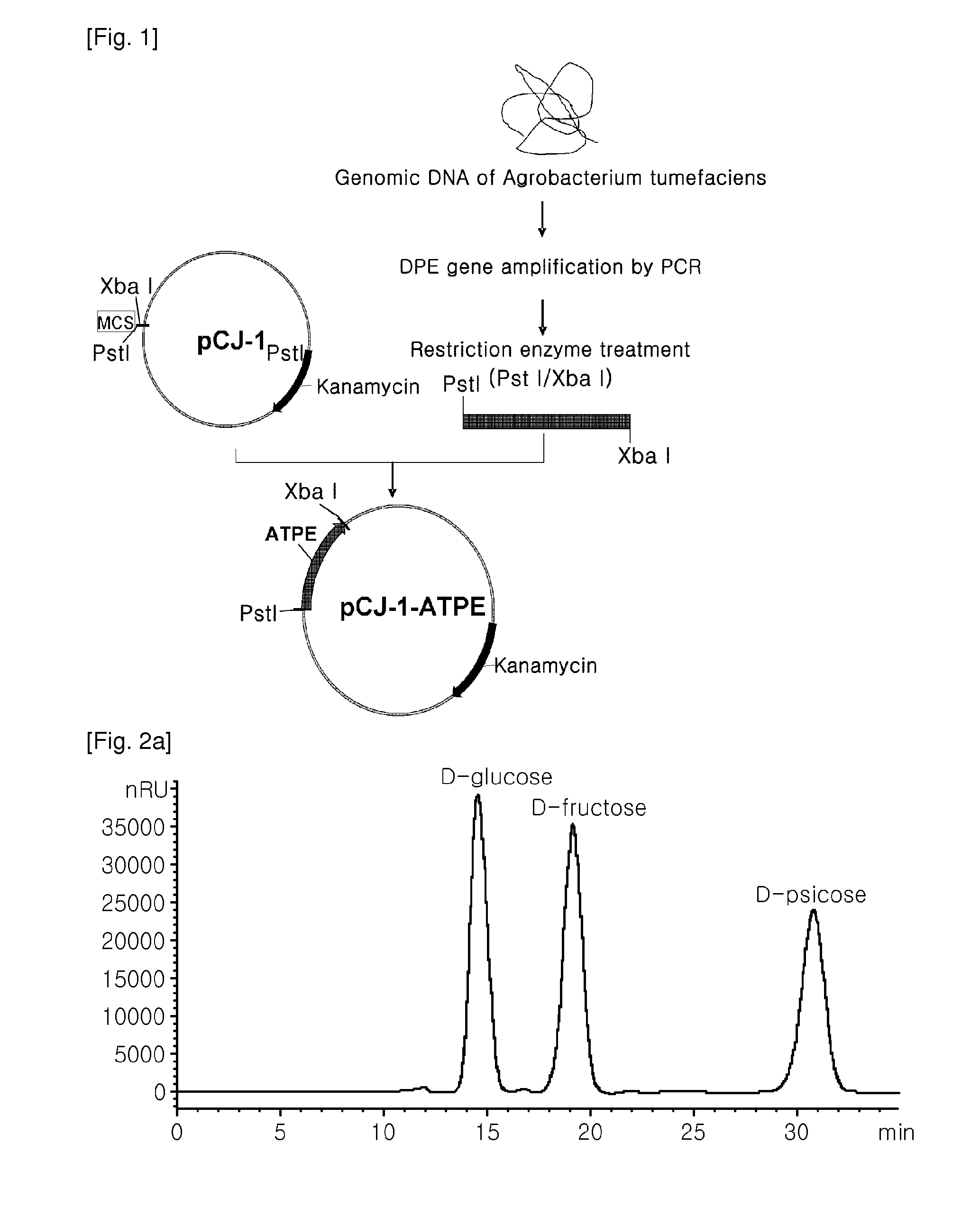
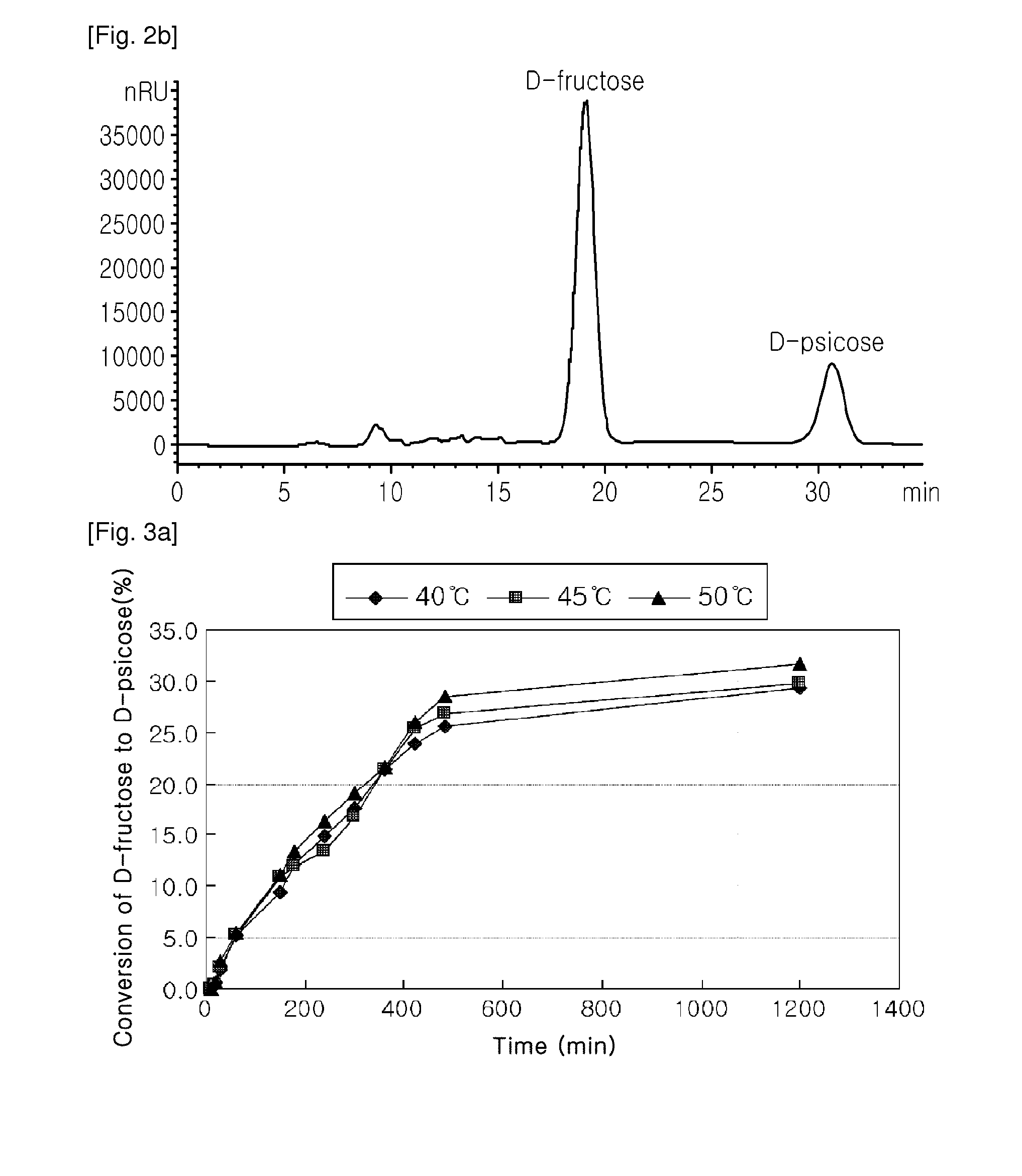
D-psicose production method by D-psicose epimerase
ActiveUS8030035B2Improve production yieldLow production costIsomerasesFermentationIsomerase activityEnzyme
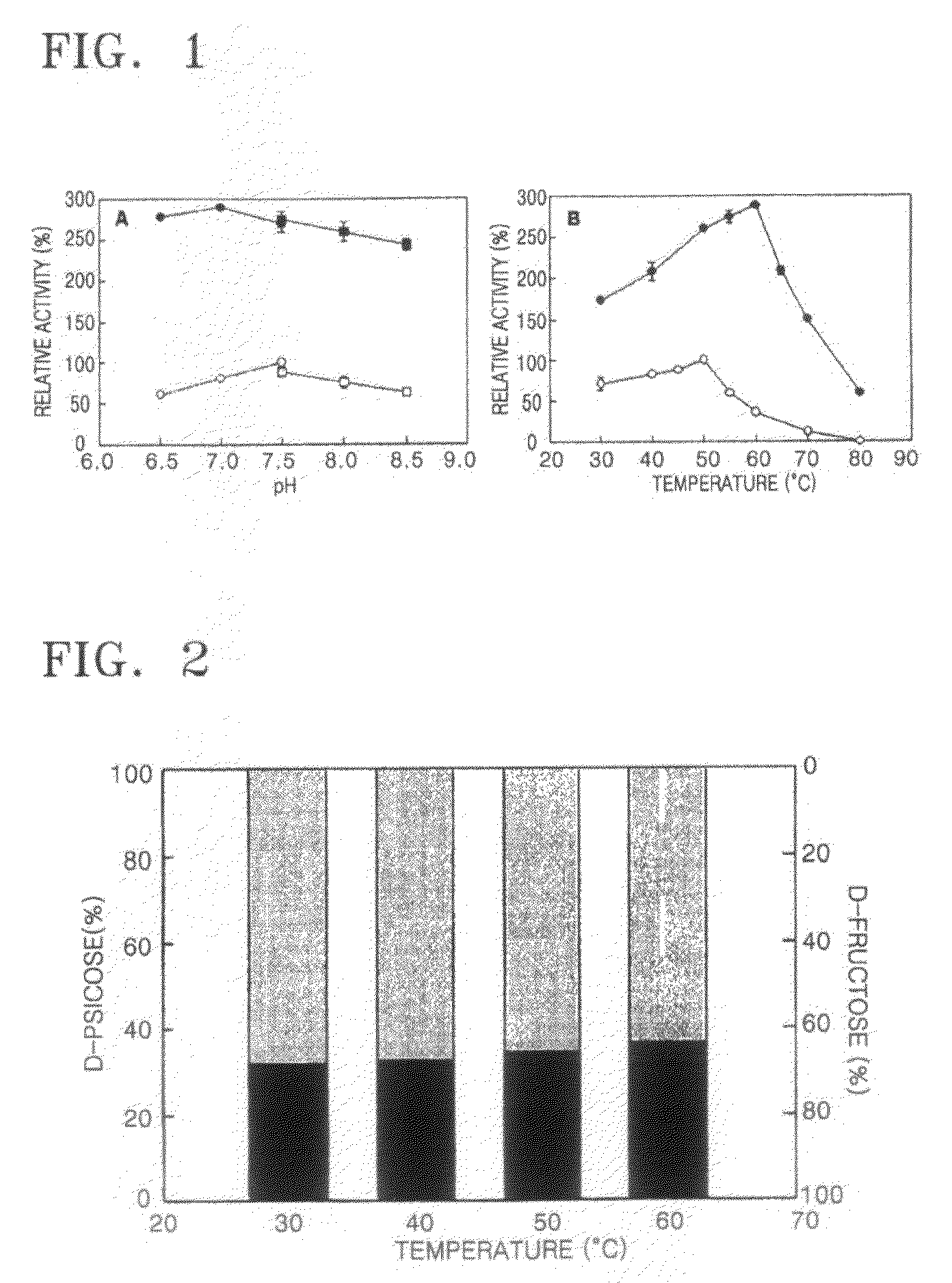
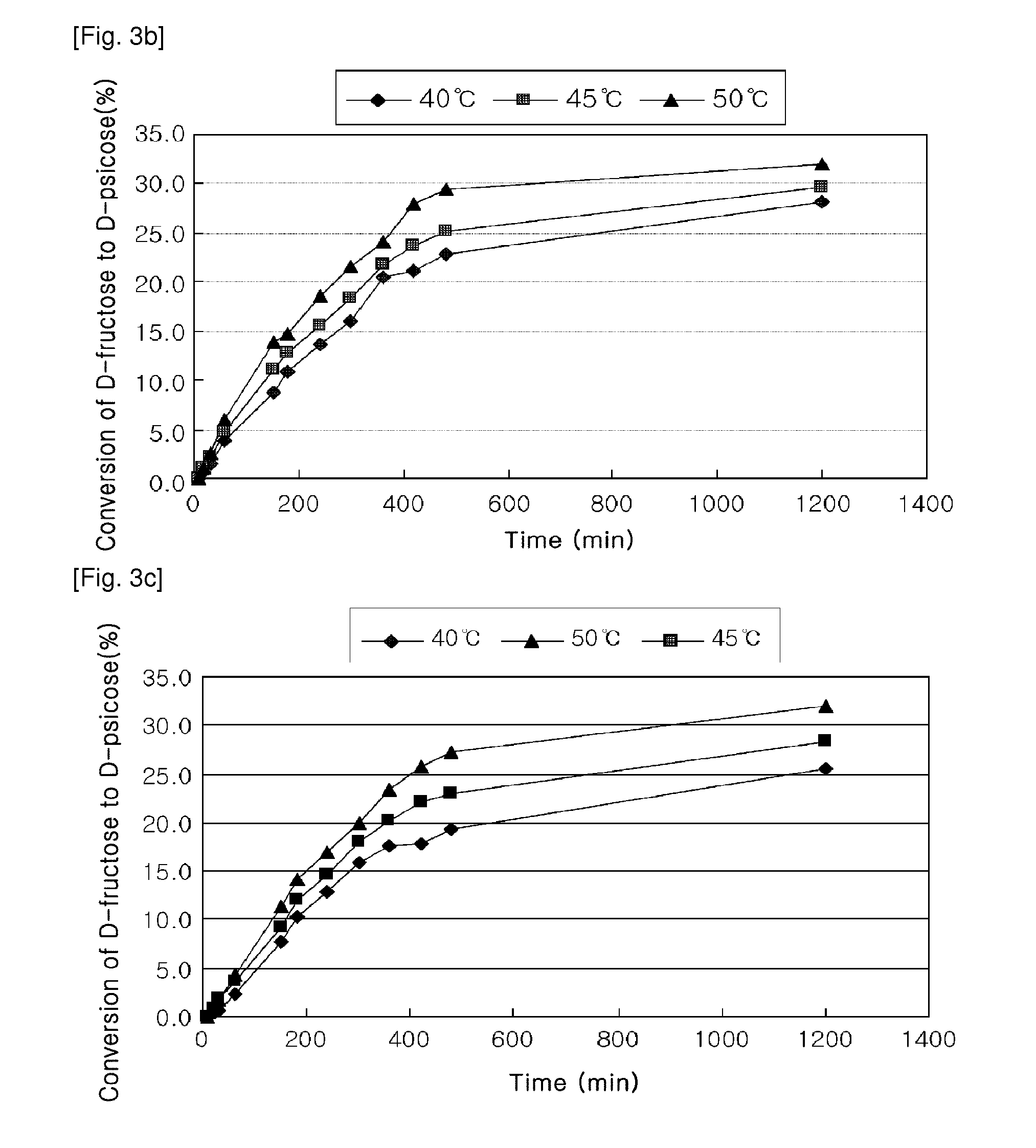
Provided is a method of producing D-psicose using a D-psicose epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Provided are a protein having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 and having a psicose 3-epimerase activity, a gene encoding the protein, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, and a method of producing D-psicose by reacting the protein produced on a mass scale with D-fructose. The method of producing D-psicose is an environmentally friendly method using a new enzyme, in which an inexpensive substrate is used, and the activity of the enzyme can be retained for a prolonged time period. Thus, the method can be efficiently used for the mass production of D-psicose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
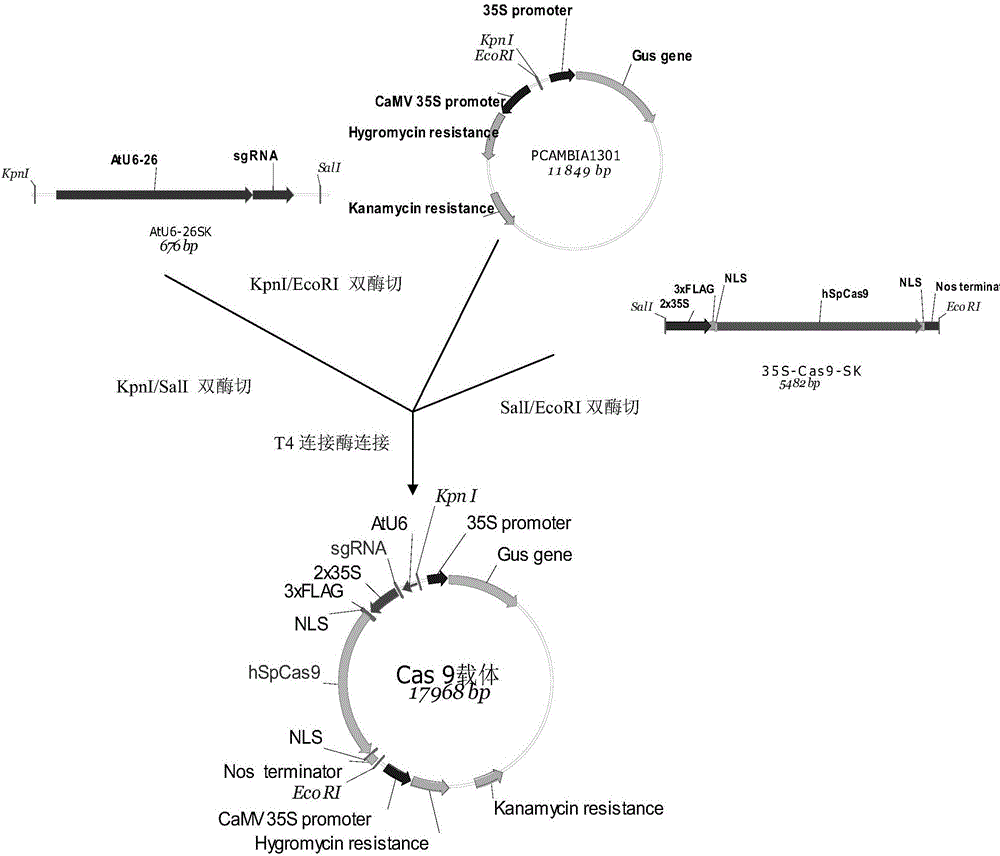
Gene editing method using CRISPR/Cas9 system to create pink fruit tomato
InactiveCN107312795AOvercoming the problem of being unable to knock out genes in a targeted mannerGenetic stabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEscherichia coliCompetent cell
The invention relates to construction of a tomato transgenic material, and aims to provide a gene editing method using a CRISPR / Cas9 system to mutate a tomato SlMYB12 gene in order to transform red fruit tomato into pink fruit tomato. The method includes the following steps: designing an oligo primer corresponding to the gRNA target site of the SlMYB12 gene, and recombining and connecting an oligo dimer with a Cas9 / gRNA vector; transforming Escherichia Coli competent cells, transforming a plasmid with a correct sequencing result into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and mediating and transforming tomato calluses to obtain a transgenic plant in order to obtain a transgenic positive strain; and carrying out gene sequencing and phenotype observation to determine a pure mutant strain which is an SlMYB12 function completely lost tomato mutant for pink fruits. The method can effectively knock out the transcriptional translation of the SlMYB12 gene, and is an ideal gene editing system for successfully transforming the tomato red fruits into the pink fruits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Site-specific insertional inactivation method and application mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR/Cas9
ActiveCN106434651ASpecify the direction of insertionRealize fixed-point insertionPeptidesNucleic acid vectorGenomicsMobile DNA
The invention discloses a site-specific insertional inactivation method mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR / Cas9. Endogenous snRNA promoter of Ustilago scitaminea (u6 promoter of Ustilago scitaminea) is used to drive sgRNA expression cassette. CRISPR / Cas9 system integrates with Ti plasmid of agrobacterium tumefaciens to construct the Ustilago scitaminea site-specific insertional inactivation system mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens with hygromycin as a selection marker. Specific sequence of the objective gene is cloned into sgRNA expression cassette for transformation of Ustilago scitaminea basidiospores, thus the mobile DNA fragment is exactly inserted into the objective gene sequence of Ustilago scitaminea, achieving the goal of damage to gene function. The invention provides an important tool for study of Ustilago scitaminea functional genomics. The system has the advantages of high efficiency and accuracy, and is convenient to use to conduct gene function researches in Ustilago scitaminea.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
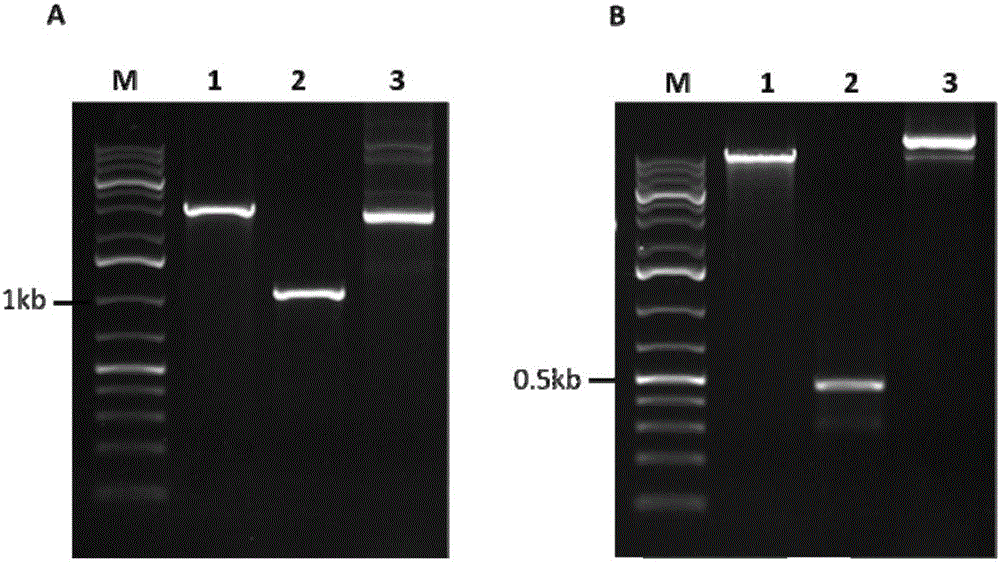
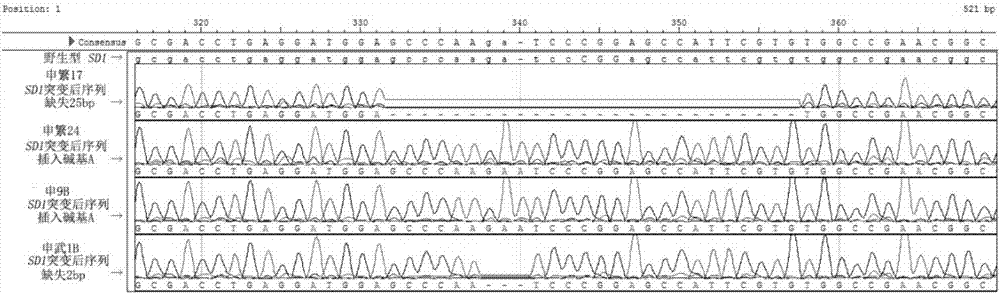
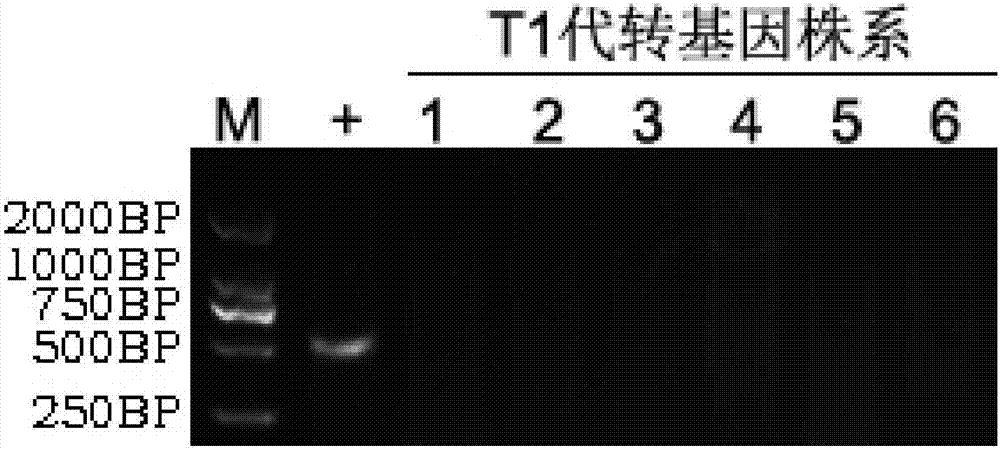
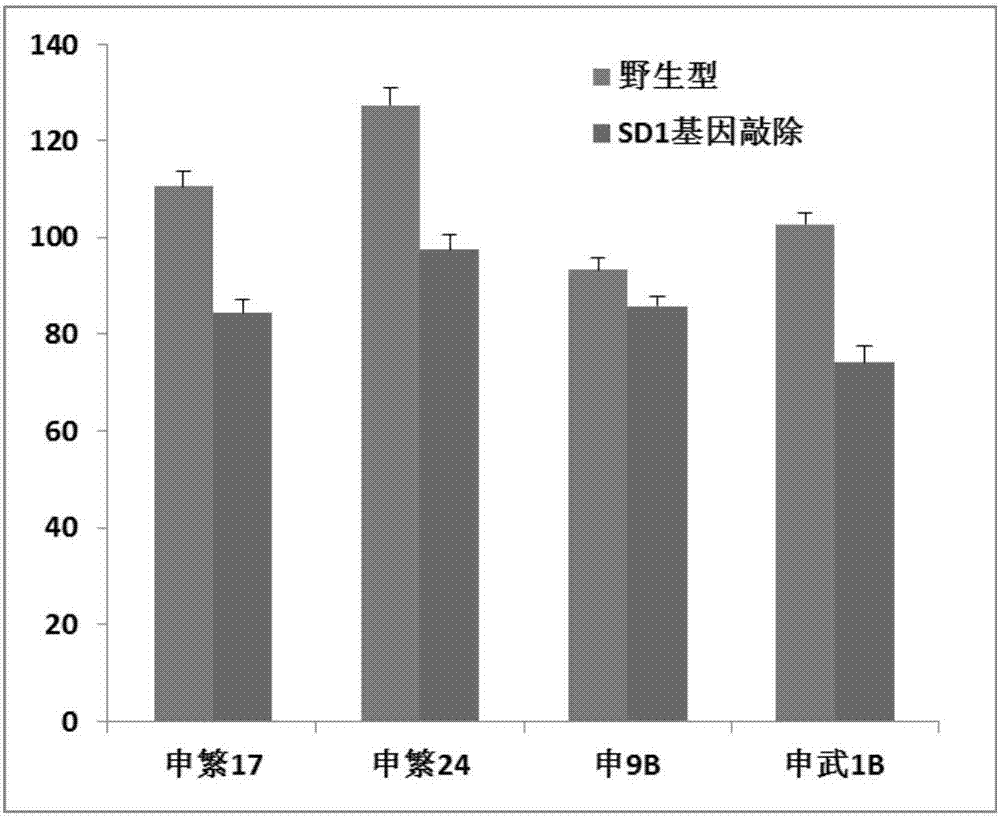
Method for performing target knockout on paddy rice dwarfing gene SD1 by using CRISPR/Cas9 technology
The invention discloses a method for performing target knockout on paddy rice dwarfing gene SD1 by using CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The method comprises the following steps: according to the design principle of CRISPR / Cas9, determining target sites, edited by a CRISPR / Cas9 system, in a paddy rice dwarfing gene SD1 encoding region, designing a primer according to the sequence of the target sites, constructing a CRISPR / Cas9 carrier, converting paddy rice callus tissues by using an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated method, and screening and identifying to finally obtain a SD1-mutated dwarfing paddy rice strain without transgenic DNA segments. The method is applied to breeding of the dwarfing paddy rice strain, so that the hybridization breeding work can be omitted, and the breeding period of the dwarfing paddy rice strain can be greatly shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
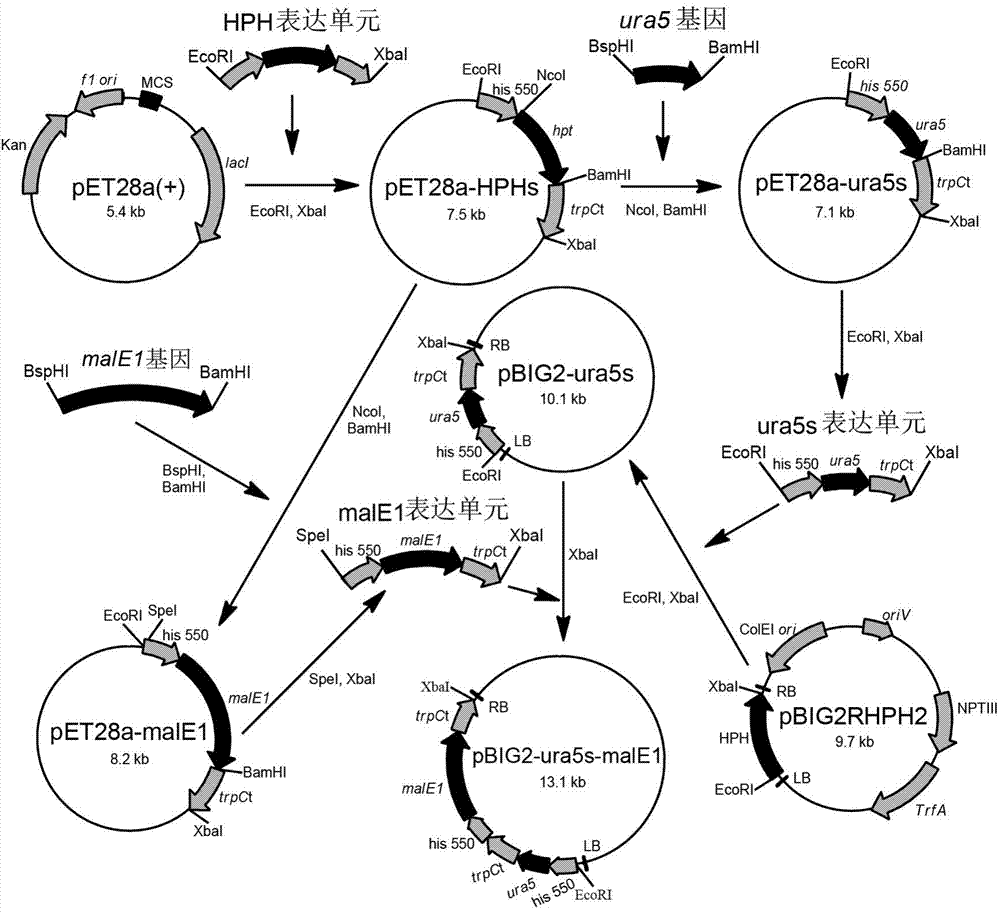
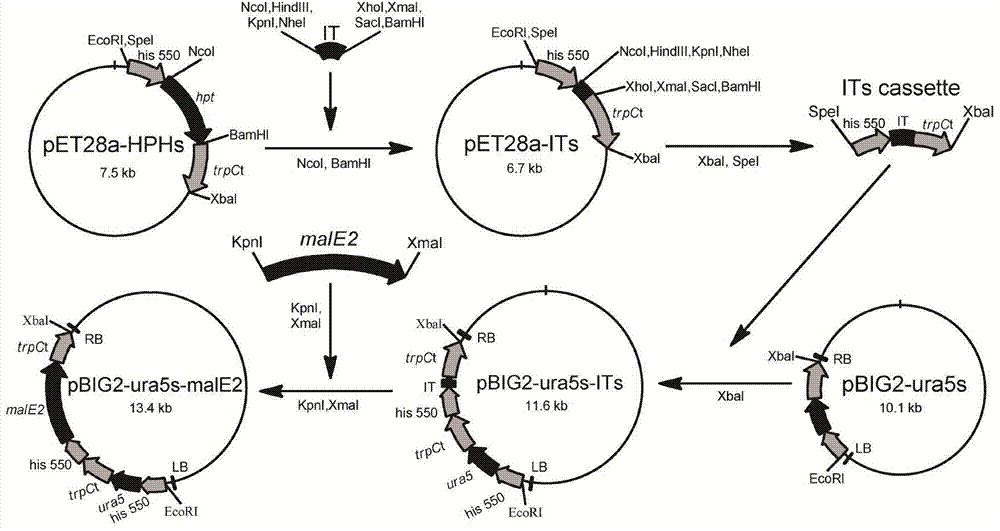
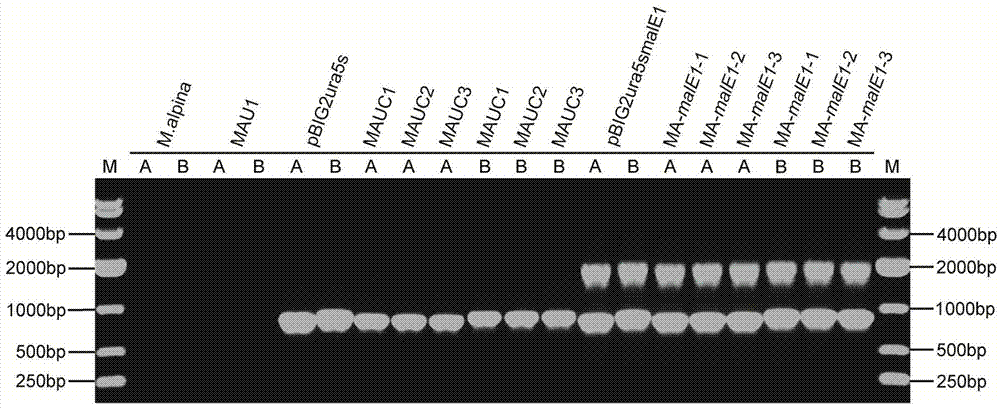
Recombination gene expression system of mortierella alpina and construction method and applications thereof
The invention relates to a recombination gene expression system of mortierella alpina (Mortierella alpina ATCC 32222) and applications thereof. According to the invention, by taking mortierella alpina ATCC 32222 uracil auxotroph strains as materials, a set of recombination gene expression system of mortierella alpina is constructed through carrying out genetic manipulation by using an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated genetic manipulation technique; and an operation is operated by using the system, so that multiple high-yield polyunsaturated fatty acid mortierella alpina strains are obtained, therefore, the recombination gene expression system of mortierella alpina and construction method and applications thereof disclosed by the invention are of great importance in the basic theory study and product development of oil-producing fungi mortierella alpina ATCC 32222.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cas9 mediated carnation gene editing carrier and application
The invention relates to a Cas9 mediated carnation gene editing carrier and application. The application comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a CRISPR-Cas9 system of carnation-containing target gene sites, introducing the Cas9 expression carrier into an agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 strain, putting roots of carnation leaves into a pre-culture medium, culturing with light for 3-4 days at 22+ / -2 DEG C, activating agrobacterium containing the Cas 9 expression carrier, dipping the pre-cultured explant into the activated agrobacterium solution for 20-30 minutes, completely absorbing the agrobacterium solution, transferring into a co-culture medium, performing dark culture for 3-4 days at 22+ / -2 DEG C, further transferring into a screening culture medium to culture, performing light culture at 22+ / -2 DEG C so as to differentiate regeneration buds, further transferring the regeneration buds into a multiplication medium for multiplication screening culture, detecting positive transgenosis regeneration plants, sequencing target sites, and detecting mutation strain systems of carnation target gene sites.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of non-transgenic CRISPR mutant
InactiveCN108611364AReduce frequencyImprove accuracyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodSexual reproduction
The invention provides a preparation method of a non-transgenic mutant based on a CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Specifically, the preparation method comprises a construction method and a screening method. The construction method is characterized in that CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA are preassembled and are located at T-DNA of agrobacterium tumefaciens; site-directed change of a target gene of a target plant can be realized by infection of the target plant by the agrobacterium tumefaciens and coculture without integrating the sequences of the CRISPR-Cas9 and the sgRNA into a genome of the target plant, so that an obtained site-directed mutant material of the target gene does not need the processes of sexual reproduction, segregation posterity, population screening and the like or does not contain any exogenous gene sequence. The obtained regeneration seedlings are screened by a high-throughput sequencing and high-resolution melting curve technology provided by the invention; mutant plants of which target genes are mutated can be obtained by identifying the regeneration seedlings efficiently and quickly at the current generation of transgene, even if low-proportion mutants of which the proportionis 1 / 100 of a mixed population can be screened. The screening method provided by the invention still can ensure excellent accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Establishment and application of plant multi-gene knockout vector
ActiveCN105112435AQuick cullingVector-based foreign material introductionTransgenic technologyMutant
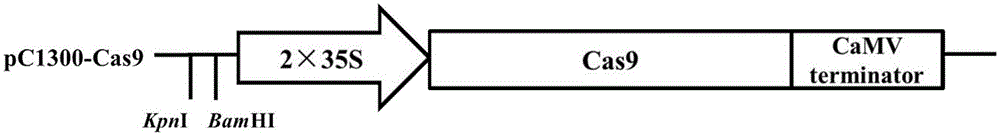
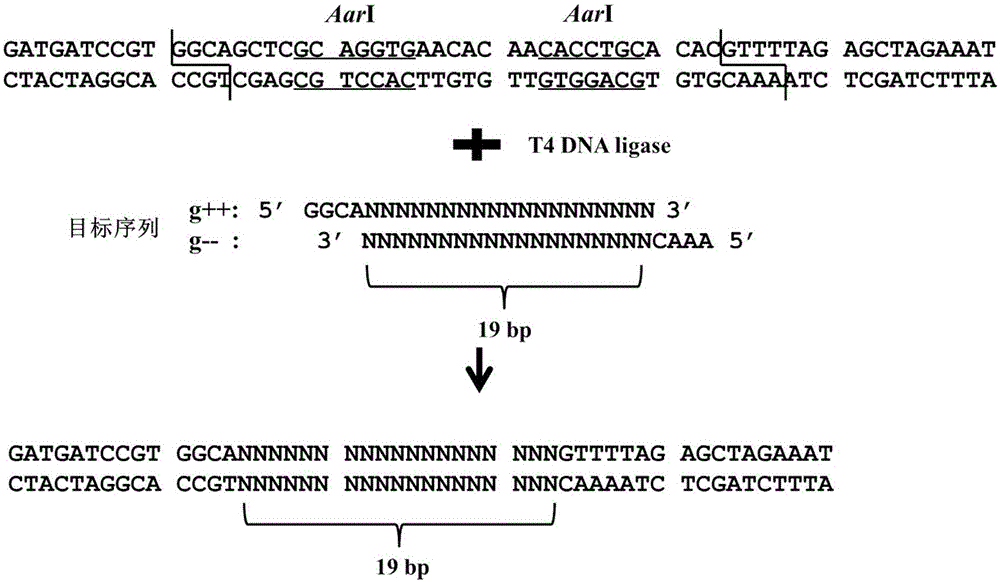
The invention discloses establishment and application of a plant multi-gene knockout vector. A method of the establishment of the plant multi-gene knockout vector comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a binary expression vector pC1300-Cas9; (2) establishing an intermediate vector SK-9RNA; (3) establishing single objective gRNA; and (4) serially connected a plurality of pieces of gRNA and establishing a final binary expression vector. A plurality of gRNA sequences are connected to the binary expression vector of an existing Cas9 sequence by an isocaudamer connecting method, and multiple plant mutants can be obtained by an agrobacterium tumefaciens infected transgenic technology. By an isocaudamer connecting establishment strategy, pieces of gRNA can be combined, and multiple plant mutants can be obtained by transgenosis once, so that an efficient and convenient multiple plant mutants preparing method is established.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Transformed embryogenic microspores for the generation of fertile homozygous plants
InactiveUS6316694B1Increase the number ofImprove conversion efficiencyBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryogenesisRegulatory control
The invention relates to transformed, embryogenic microspores and progeny thereof characterized by being transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, capable of leading to non-chimeric transformed haploid or doubled haploid embryos that develop into fertile homozygous plants within one generation and containing stably integrated into their genome a foreign DNA, said DNA being characterized in that it comprises at least one gene of interest and at least base pairs within the right border sequence of Agrobacterium T-DNA. The invention furthermore relates to a method for the incorporation of foreign DNA into chromosomes of microspores comprising the following steps: a) infecting of embryogenic microspores with Agrobacteria, which contain plasmid carrying a gene of interest under regulatory control of initiation and termination regions bordered by at least one T-DNA border, b) Washing out and killing the Agrobacteria after co-cultivation.
Owner:AGREVO CANADA
Immobilization of psicose-epimerase and a method of producing D-psicose using the same
The present invention relates to a method of successively producing D-psicose from D-fructose or D-glucose by using a psicose-epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens which is expressed in a food safety form.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
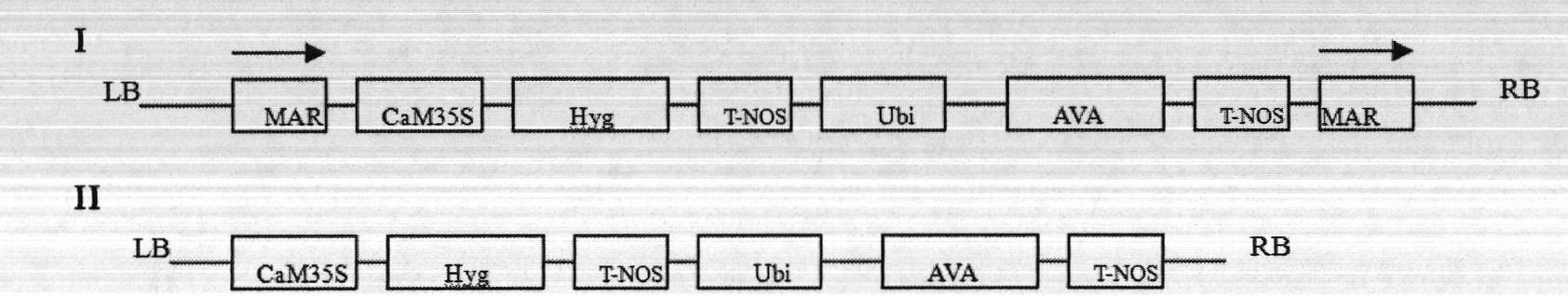
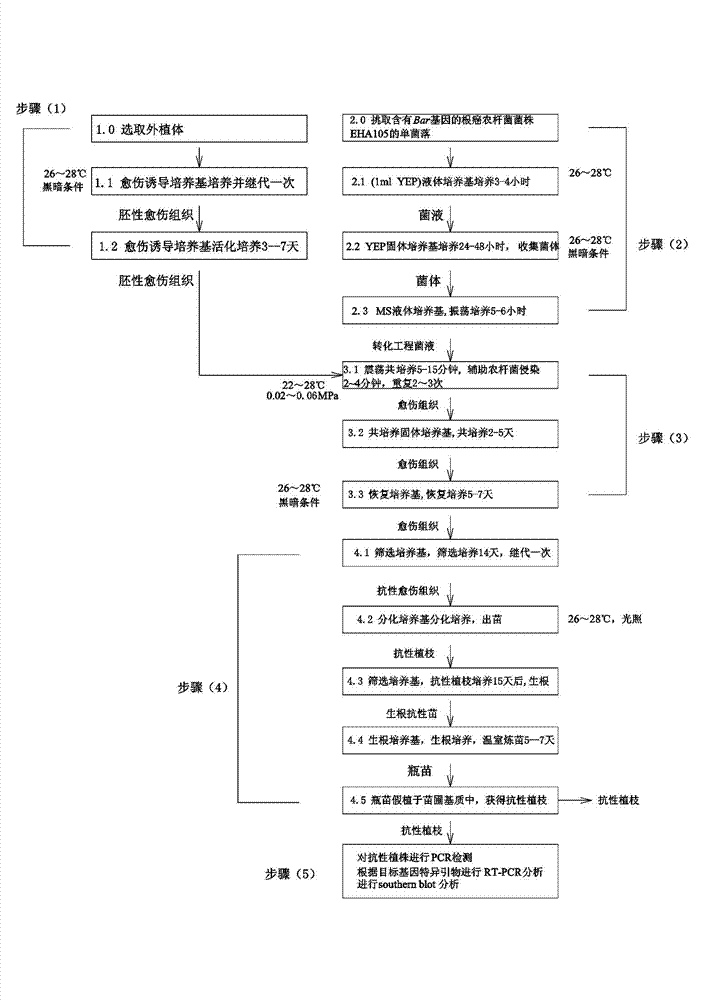
Method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane
InactiveCN102154364AOvercome serious shortfalls in conversionAddress serious deficienciesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMetal ArtifactTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane. The method comprises the steps: leading agrobacterium tumefaciens liquor carrying plant expression vectors to infect embryogenic callus of the sugarcane; and selecting and proliferating resistant calli to induce the resistant calli to obtain the resistant buds of the sugarcane, wherein matrix attachment region sequences are connected at two sides of a gene expression box of the plant expression vector. According to the method, MARs (metal artifact reduction) sequences are built at two sides of the gene expression box of the plant expression vector, thus greatly improving the exogenous gene transformation efficiency and seedling rate of the sugarcane, and being simple in process flow and low in cost.
Owner:广西作物遗传改良生物技术重点开放实验室
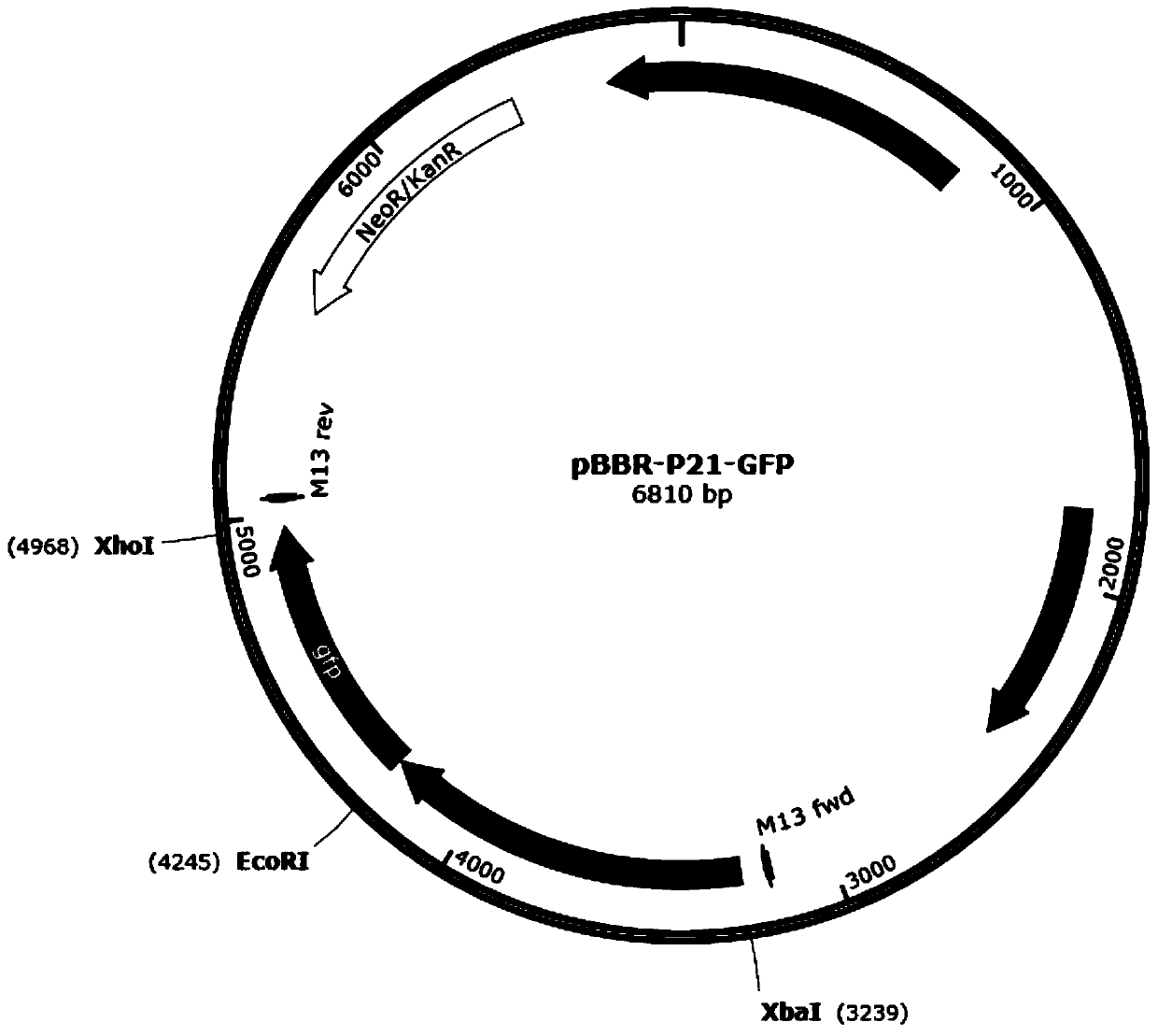
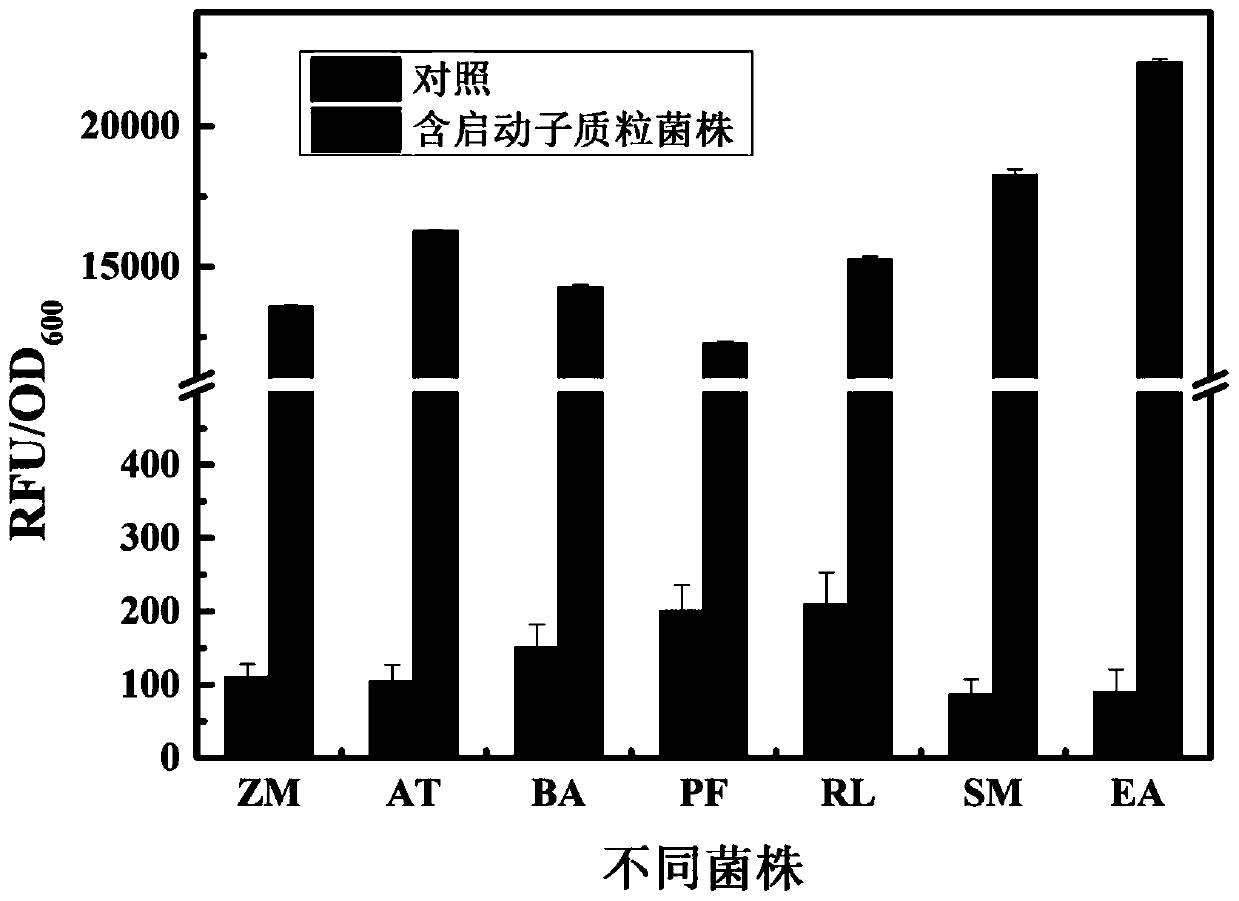
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for generating resistance against citrus diseases caused by insects, fungi, oomycetes, bacteria or nematodes
ActiveUS20110119788A1Reduce accumulationAchieve resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNematodeWhole body
The invention consists in modifying the levels of accumulation and emission of monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes in citrus as a mechanism to achieve systemic resistance against pathogens or repellency against pests. The alteration of the content of d-limonene and other terpenes is achieved by genetic transformation via the introduction of a gene that encodes an enzyme with d-limonene synthase activity, from a citrus fruit or plant or from another living organism, in antisense or RNAi (RNA interference) configuration. Genetic modification is achieved either by Agrobacterium tumefaciens or any other method of genetic transformation of plants from protoplasts or explants. The construction is incorporated in citrus genotypes or related genera of the family Rutaceae in order to reduce the levels of accumulation and emission of the monoterpene and precursor compounds and / or derivatives, either of leaves or flowers and / or fruit.
Owner:INST VALENCIANO DE INVESTIGACIONES AGRARIAS IVIA
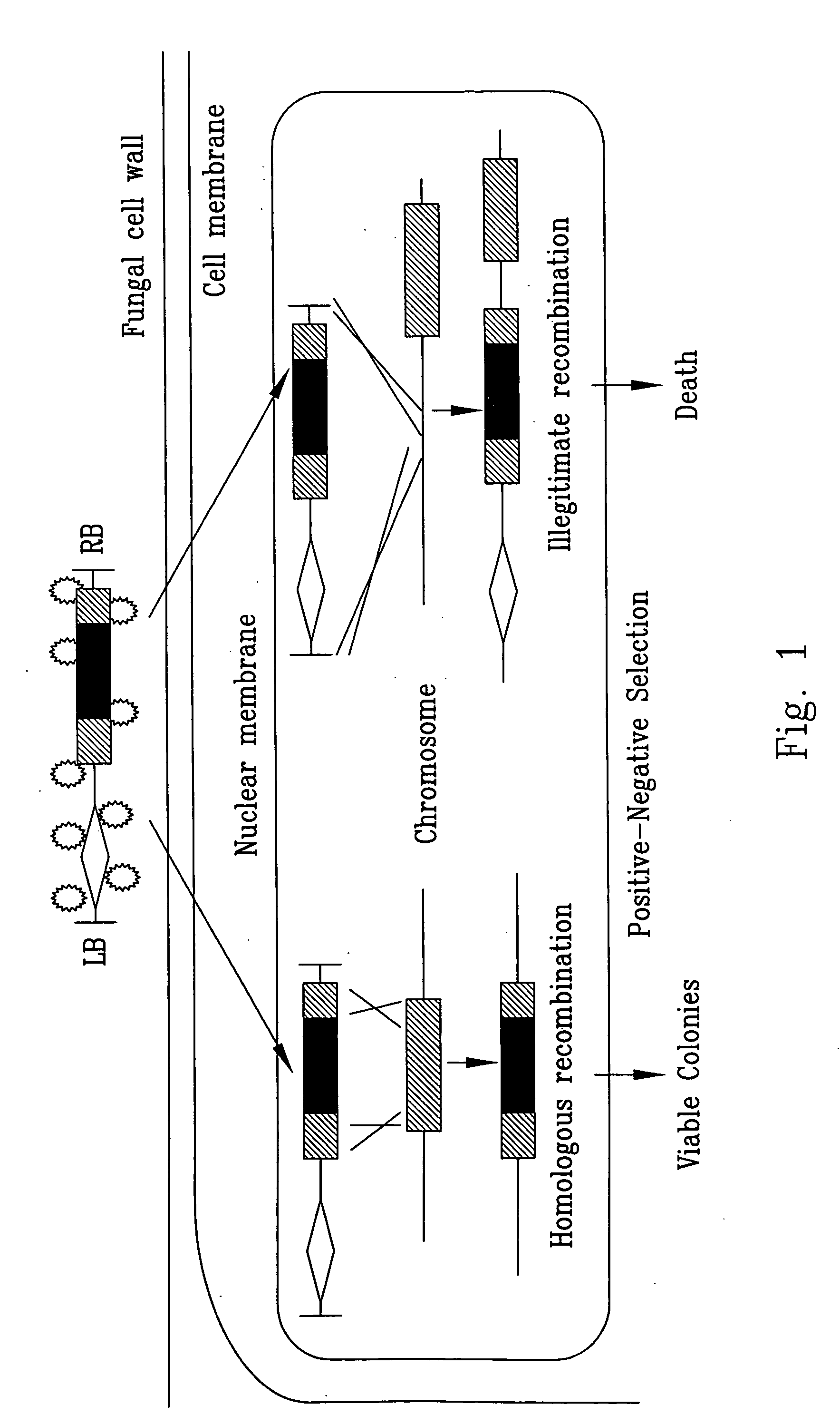
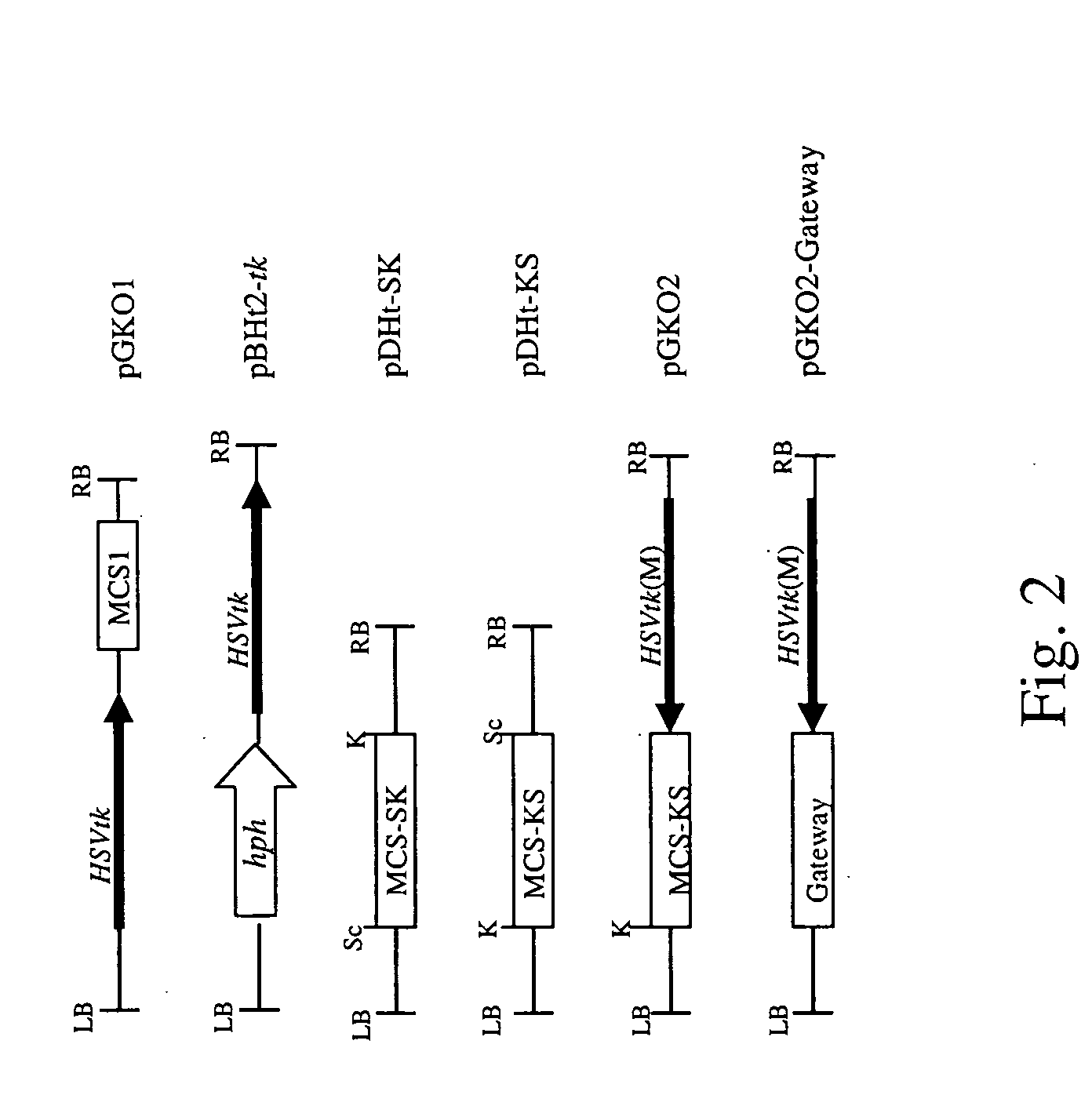
Dual selection based, targeted gene disruption method for fungi and fungus-like organisms
InactiveUS20050181509A1Improve efficiencyReduce frequencyFungiFermentationBiotechnologyBiological body
The invention disclosed herein is useful as an efficient targeted gene manipulation tool that can be applied, with minimal modifications, to targeted genes in a broad spectrum of fungi and fungus-like organisms. The invention is based on Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation followed by a subsequent positive-negative selection scheme to isolate target mutants.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Soybean transformation for efficient and high-throughput transgenic event production
A method is disclosed for the Agrobacterium-mediated germline transformation of soybean, comprising infecting split soybean seeds, with a portion of the embryonic axis, with Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing a transgene. The method can further comprise regenerating the explants produced from the transformation of the split soybean seeds comprising a portion of embryonic axis in vitro on selection medium.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance
InactiveCN103205459APerfect genetic transformation systemIncreased genetic transformation rateGenetic engineeringFermentationTi plasmidBiological activation
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses an agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method includes: (1) induction and multiplication of embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (2) activation and cultivation on agrobacterium tumefaciens with target genes, (3) agrobacterium infestation with vacuum infiltration assistance on embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (4) resistant material screening and germination, and (5) resistant material verification. With the agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method, the agrobacterium can pass through the gaps among callus cells and enter deep cells on vacuum, and tiny wounds can be generated on the surfaces of the cells, so that phenolic substances are secreted by plants to activate shear and transfer of T-DNA (transferred deoxyribonucleic acid) in Ti plasmids. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation system is perfected. Genetic transformation rate of sugarcane is remarkably improved as compared with that of the prior art.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST
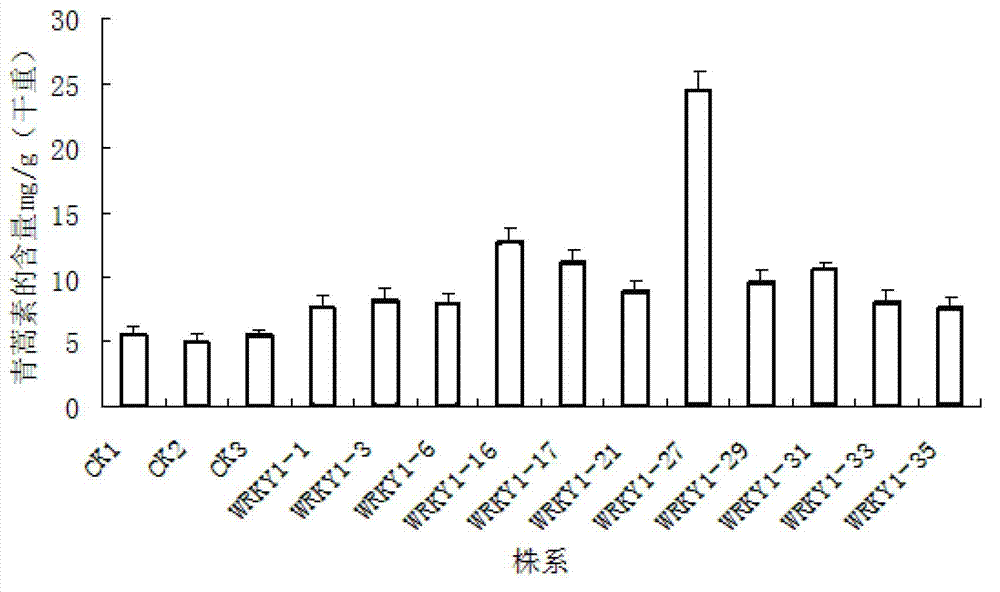
Method for increasing artemisinin content of sweet wormwood by transferring AaWRKY1 gene
InactiveCN102776225AIncrease artemisinin contentIncrease contentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein ArtemisBiology
The invention discloses a method for increasing artemisinin content of sweet wormwood by transferring AaWRKY1 gene. The method includes the steps of cloning WRKY type transcription factor AaWRKY1 gene in sweet wormwood; constructing a plant expression vector containing the AaWRKY1; introducing the AaWRKY1 gene into the sweet wormwood to regrow a plant under mediation of Agrobacterium Tumefaciens; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to detect integration status of the foreign target gene AaWRKY1; measuring the content of artemisinin in the transgenic sweet wormwood by efficient liquid chromatography and an evaporative light scattering detector, and screening to obtain the plants of sweet wormwood with artemisinin content increased. The content of artemisinin in the transgenic sweet wormwood with the AaWRKY1 gene is increased to 24.59mg / g DW by the method and is 4.44 times of that of the non-transgenic sweet wormwood. The method provides new high-yield and stable drug sources for large-scale production of artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Modified glyphosate-resistant gene and glyphosate-resistant rice cultivation method
InactiveCN107129993AIncrease resistanceAgronomic traits do not changeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to a modified glyphosate-resistant gene and a glyphosate-resistant rice cultivation method and comprises modification of glyphosate genes, building of plant expression vectors of the glyphosate-resistant gene and a glyphosate-resistant transgenosis rice cultivation method. Artificially-synthesized modified glyphosate-resistant gene serves as a target gene, the sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the target gene is led into rice receptors by an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation method to obtain high glyphosate-resistant transgenosis rice GT28. the glyphosate-resistant gene of GT28 is recombined by the aid of sexual hybridization and somatic hybridization technique to obtain new rice germplasm, and new glyphosate-resistant varieties (strains) of rice are cultivated.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
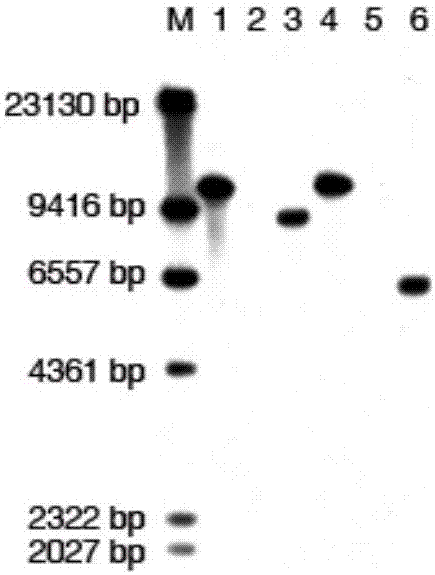
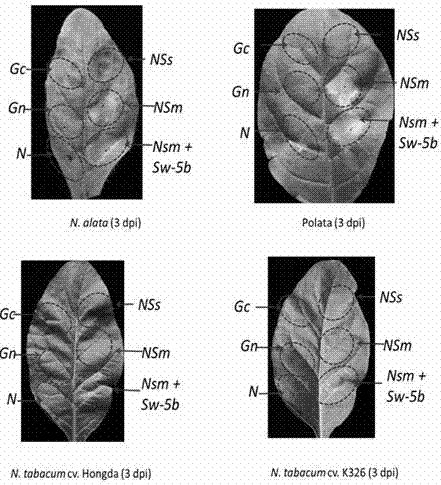
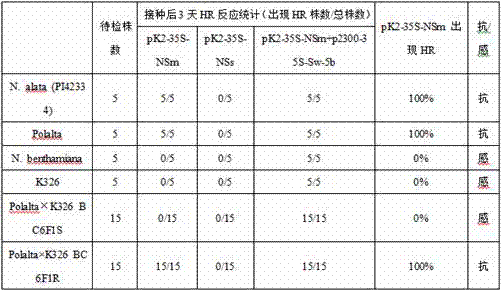
Method for identifying tobacco resistance by use of tomato spotted wilt virus NSm gene
ActiveCN107400674AEasy to identifySpeed up breedingSsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention relates to a method for identifying tobacco resistance by use of a tomato spotted wilt virus NSm gene and belongs to the technical field of plant protection. The NSm gene contains a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1. The NSm gene is an avirulence gene which stimulates tobacco containing a resistant locus RTSW to produce disease resistance response. An agrobacterium tumefaciens transient expression system is adopted for transient expression of the NSm gene in tobacco leaves, and whether test tobacco contains the resistant locus RTSW is judged by detecting whether the test tobacco shows an allergic reaction. The resistance of the tobacco to the tomato spotted wilt virus disease can be rapidly and accurately identified with the method, and the method can be applied to disease-resistant breeding as well as positioning and cloning of disease-resistant genes.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
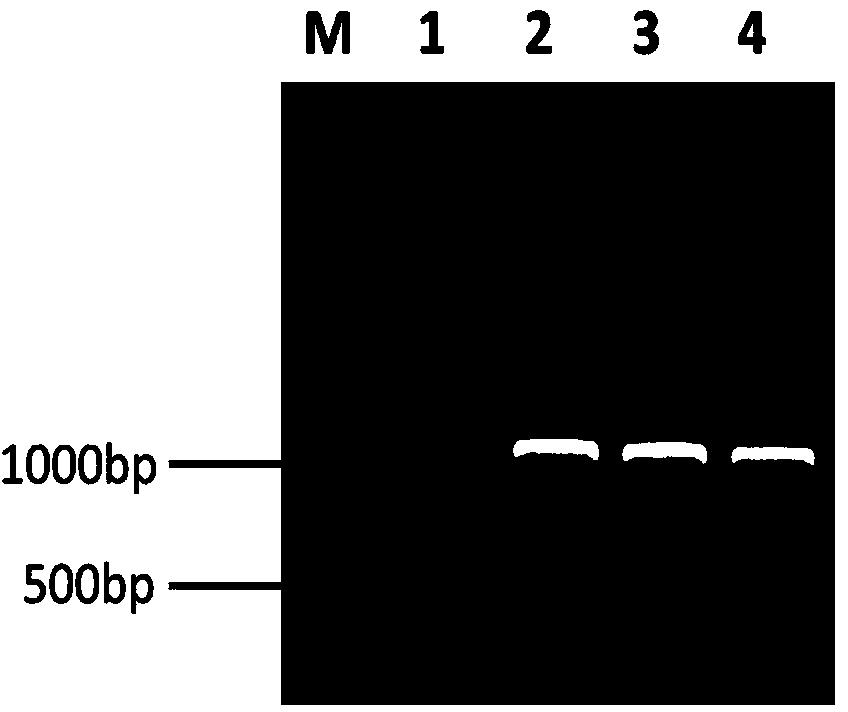
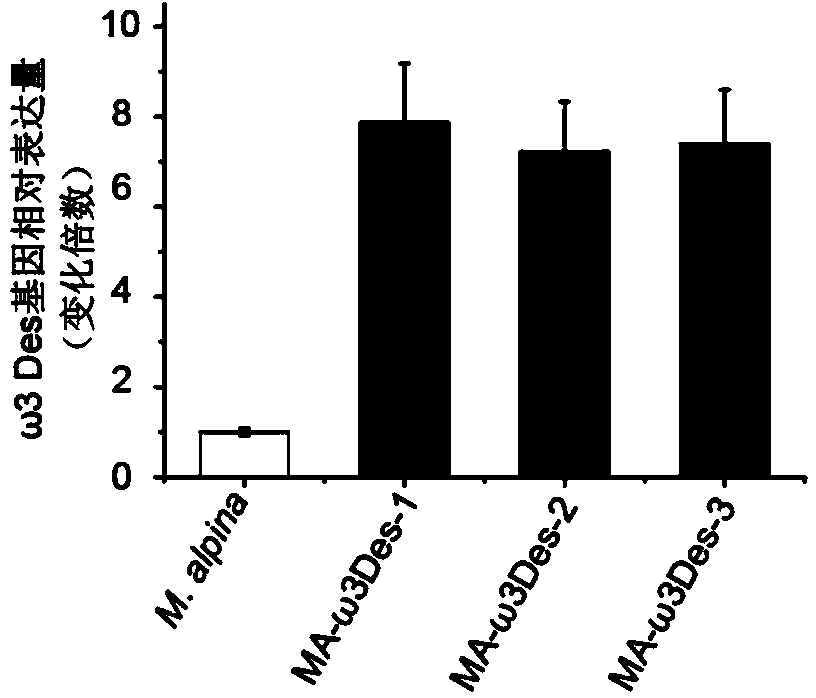
Mortierella alpina, M. alpina genetic engineering strain of overexpression omega 3 desaturase gene and construction method of strain
The invention relates to a mortierella alpina, M. alpina genetic engineering strain of an overexpression omega 3 desaturase gene (FADS15) and a construction method of the strain. According to the invention, a mortierella alpina, M. alpina uracil nutritional-deficient strain MAU1 (CCFM501) is taken as a material, an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic manipulation technology is applied to obtain an omega 3 desaturase (omega 3Des) overexpression strain of high-yield EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and the strain and the construction method have important significance on basic theoretical research and product development of mortierella alpina, M. alpine as an oil-producing fungus.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
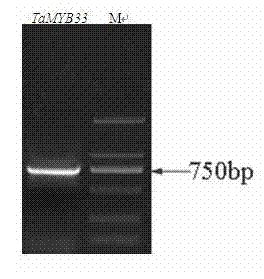
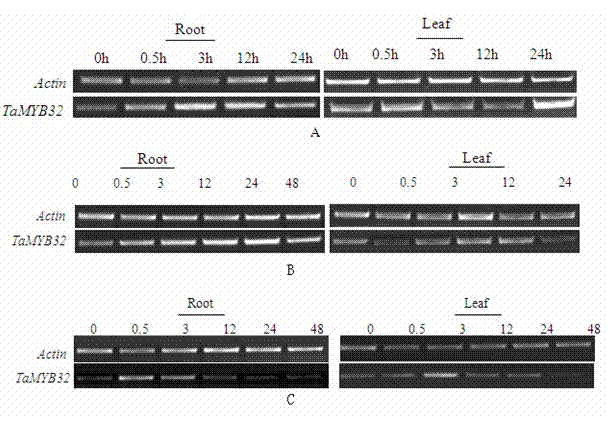
Salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat and coding protein as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102234653AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention particularly relates to a salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat and coding protein as well as application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological gene engineering. The salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat is a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table. The invention has the beneficial effects that an MYB transcription factor gene TaMYB33 of wheat is obtained by cloning for the first time, and a mediation method of agrobacterium tumefaciens is used for transferring the gene into arabidopsis. The comparative analysis proves that compared with a wild arabidopsis plant, the salt tolerance and drought resistance of a transgenic arabidopsis plant containing the gene TaMYB33 provided by the invention are obviously improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN +1
Immobilization of psicose-epimerase and a method of producing d-psicose using the same
The present invention relates to a method of successively producing D-psicose from D-fructose or D-glucose by using a psicose-epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens which is expressed in a food safety form.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Soybean transformation for efficient and high-throughput transgenic event production
A method is disclosed for the Agrobacterium-mediated germline transformation of soybean, comprising infecting split soybean seeds, with a portion of the embryonic axis, with Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing a transgene. The method can further comprise regenerating the explants produced from the transformation of the split soybean seeds comprising a portion of embryonic axis in vitro on selection medium.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Infectious clone vector of pepper mild mottle virus, agrobacterium tumefaciens strain, method for preparing same and application of infectious clone vector
InactiveCN105219800AInvasive cloneEfficient infectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant virusTobacco mosaic virus
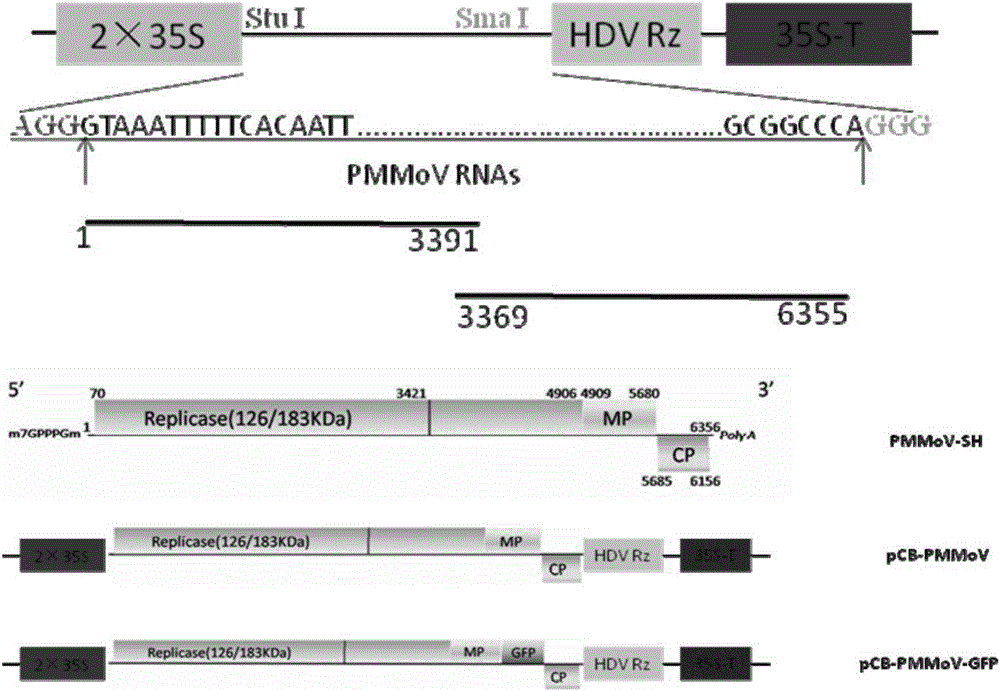
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to preparation of an infectious clone vector of a Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) of RNA (ribonucleic acid) plant viruses and tobacco mosaic viruses, pathogenesis analysis on an infectiously cloned agrobacterium tumefaciens strain with the pepper mild mottle virus and exogenous proteins infectiously cloned and expressed by the aid of the PMMoV. The preparation, the pathogenesis analysis and exogenous proteins have the advantages that genomes of Shanghai bay isolate of the pepper mild mottle virus are constructed onto efficient plant expression vectors pCB301-CH by the aid of a genetic recombination process, the recombinant vectors are transferred into the agrobacterium tumefaciens strain by means of electroporation, and accordingly the virus vector with infection ability can be obtained; the plant expression vectors can be constructed by means of infectious cloning, and the exogenous proteins can be efficiently and stably expressed in host plants; mature systems can be provided for studying structures and functions of the virus genomes and studying interaction between the virus and hosts.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Process for transformation of mature trees of Eucalyptus plants
InactiveUS6563024B1Efficient conversionImprove abilitiesHybrid cell preparationOther foreign material introduction processesShootINDUCTION TREATMENT
The present invention discloses a process for transforming mature trees of Eucalyptus plants comprising: induction adventitious shoots from segments of the explant obtained from an adult tree of a Eucalyptus plant, preculturing the adventitious shoots in infection induction medium, infecting the adventitious shoots subjected to infection induction treatment with infection medium containing Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and rotary-culturing the infected explant segments in sterilization medium containing antibiotic; whereby sterilizing and forming transgenic calli, which regenerate transgenic plants by way of formation of shoot primordia by rotary-culturing under illumination.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Agrobacterium tumefaciens gene transformation method of hybrid poplar
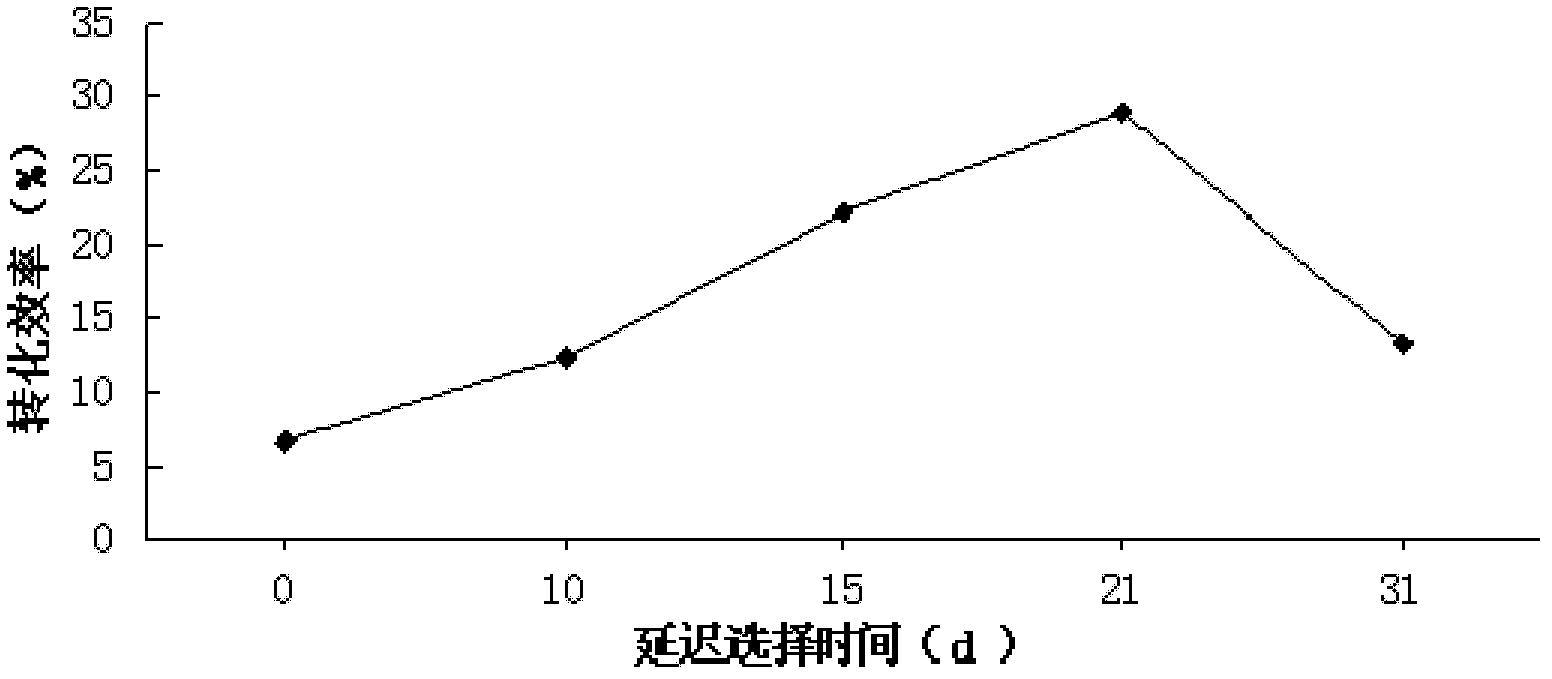
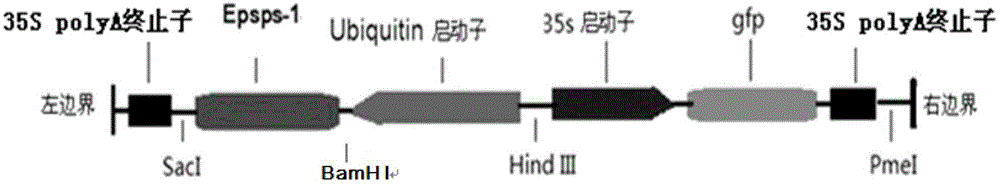
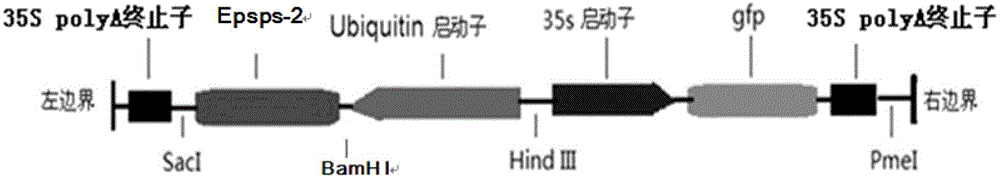
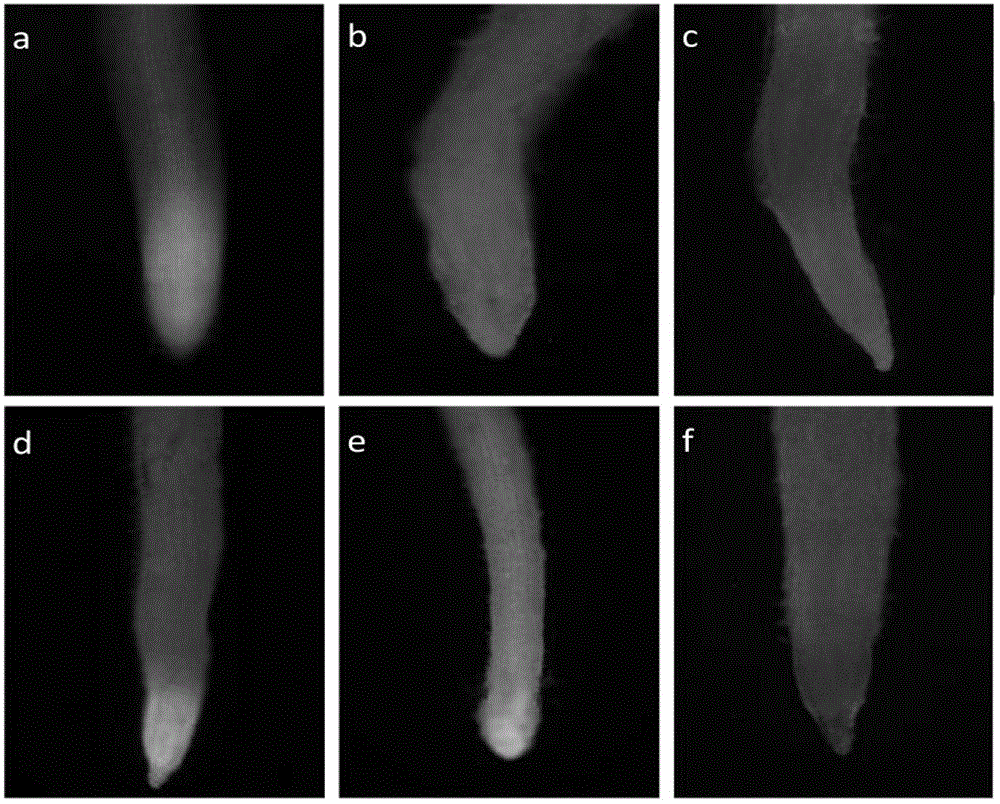
InactiveCN102634541AImprove conversion efficiencyShort cycleHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureTransformation efficiencyBiological activation
The invention discloses an agrobacterium tumefaciens gene transformation method of hybrid poplar. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pre-culture; (2) strain activation and culture; (3) infection; (4) co-culture; (5) delayed selection; (5) adventitious bud induction; (7) extension culture; and (8) root induction and detection. In the method provided by the invention, NAA and 2ip act together to induce the agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated stem section or leaf stalk to generate callus; under the effect of cytokinin TDZ, the callus redifferentiation is promoted to form adventitious buds; the bud in a vitrified state extends under the induction of BAP (Benzo A Pyrene), and the form gradually becomes normal; and the resistant regenerated poplar roots in a 1 / 2MS (Murashige and Skoog) culture medium containing antibiotic hygromycin. The resistant genetically-modified poplar obtained by the method has the advantages of short period and high transformation efficiency, thereby laying firm foundation and theoretical support for the practical breeding of the genetically-modified poplar.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Procedure for the genetic transformation of adult plants of woody species
InactiveUS6103955AShorten the time periodLow costTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesWoody plantShoot
The procedure is based on the use, as vegetable starting material for the transformation, of the first shoots from the graft of buds of adult trees onto stock, the genetic transformation of explants from the adult shoots by mean of co cultivation with Agrobacterium tumefaciens in mother plaques, and the obtaining of complete adult woody plants by means of in vitro micrografting of the transgenic buds, apices or shoots, regenerated by means of the explants, by means of in vitro micrograft onto stock cultivated in vitro. This procedure makes it possible to avoid the juvenile period and the high heterozygosis which affects most woody species, blossoming and fruiting of the transgenic plants are brought forward, and it permits the direct genetic transformation of commercially interesting varieties. It has argicultural applications.
Owner:INST NAT DE INVESTIGACION Y TECH AGRARIA Y ALIMENTARIA INIA +1
Preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice
InactiveCN104004781AReduce the number of copiesShort processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMolecular identificationGenetically modified rice
The invention provides a preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. The method comprises the following steps: converting an expression vector containing glyphosate resistant gene into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, invading rice calluses by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens, transferring the calluses to a selective aluminum containing glyphosate for screening, choosing resistant calluses, differentiating, rooting, hardening-seedling, and transplanting to obtain glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. A molecular identification result shows that an exogenous gene is stably expressed. The obtained glyphosate resistant transgenic rice contains glyphosate herbicide resistant gene, contains no other screening marker genes, and can be used as a commercial herbicide resistant rice kind to reduce the reduce the later process and accelerate the breeding pace. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low copy number of transgenic plants, stable heredity properties, and good market application prospect.
Owner:CHINA NAT SEED GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com