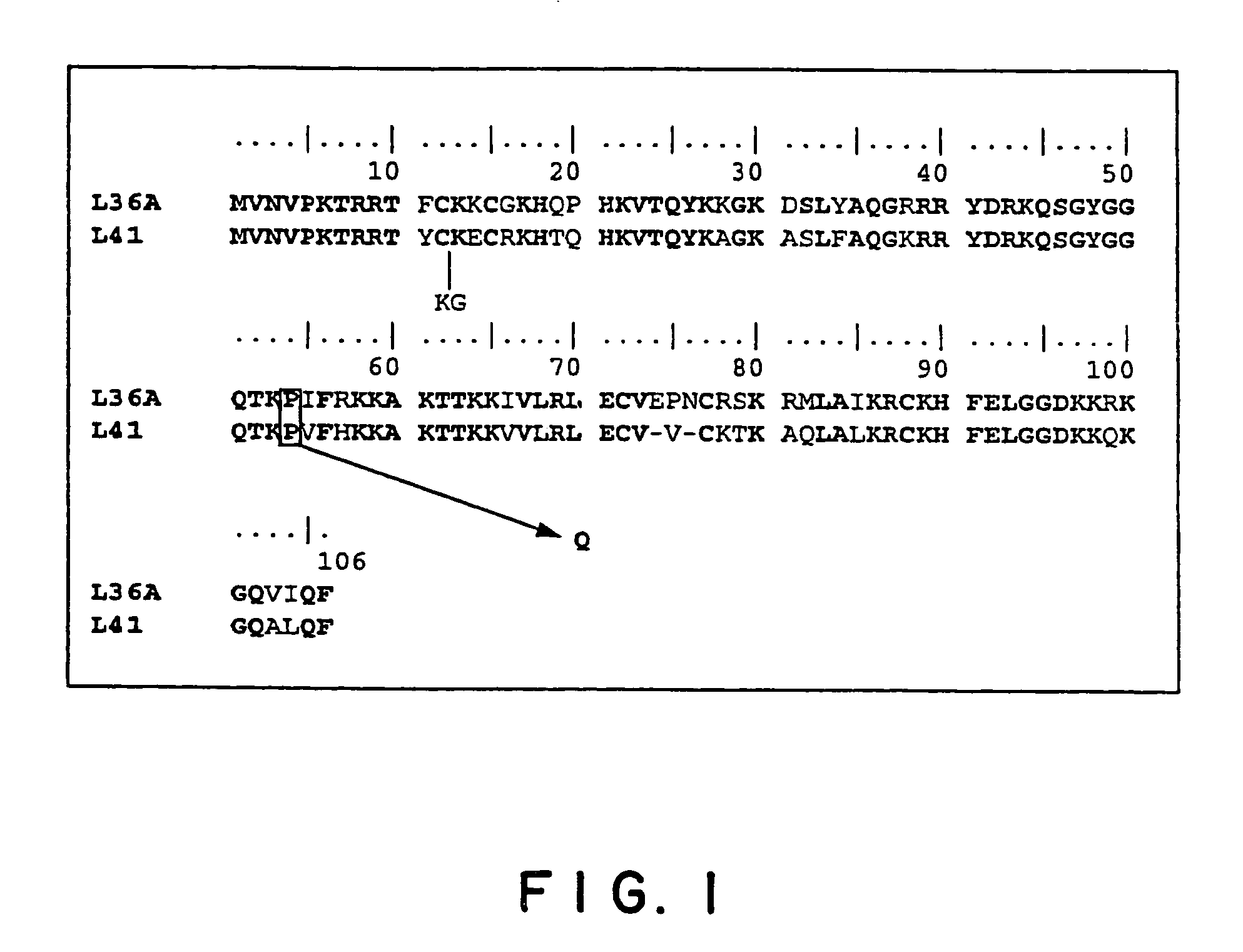
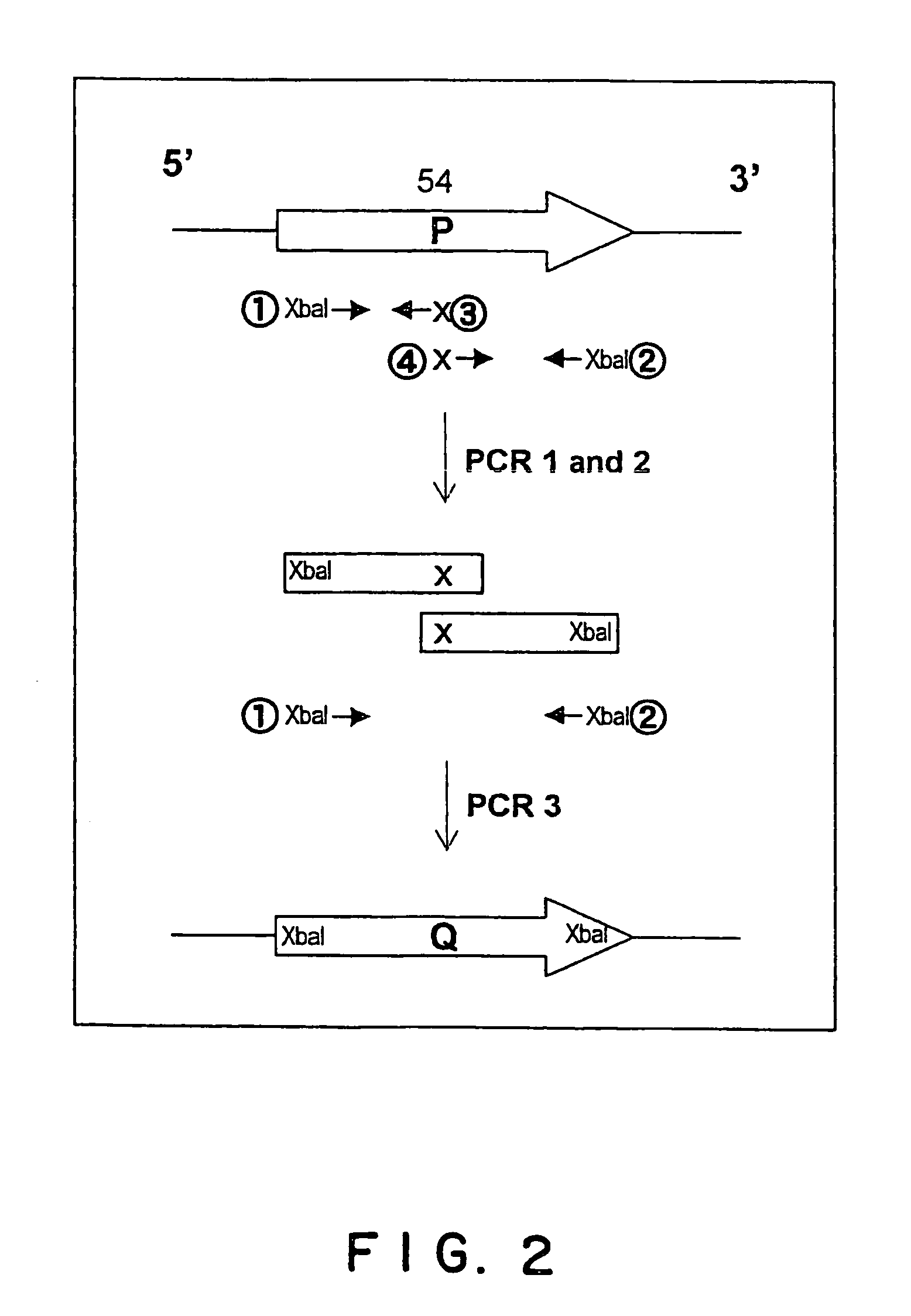
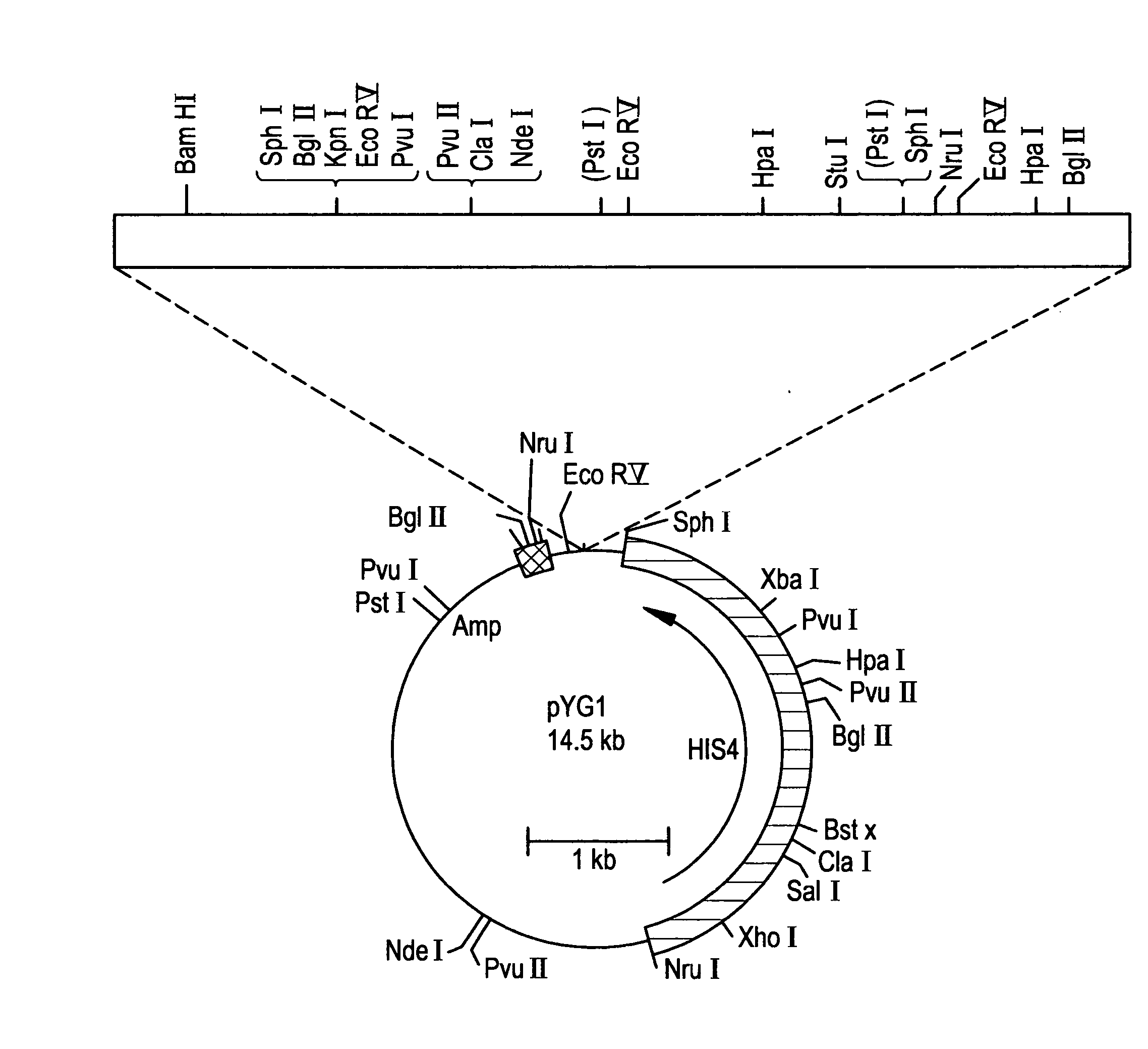
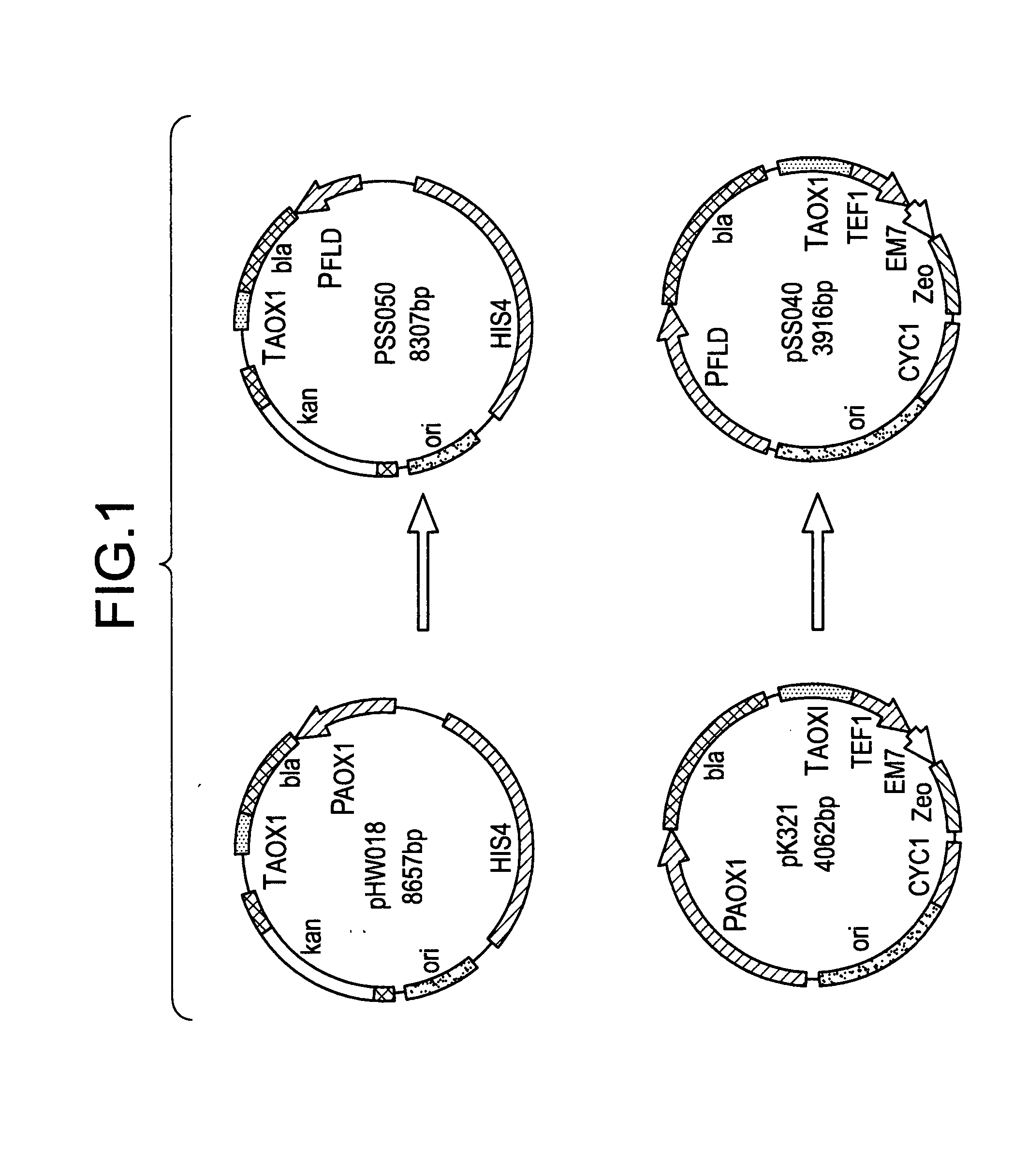
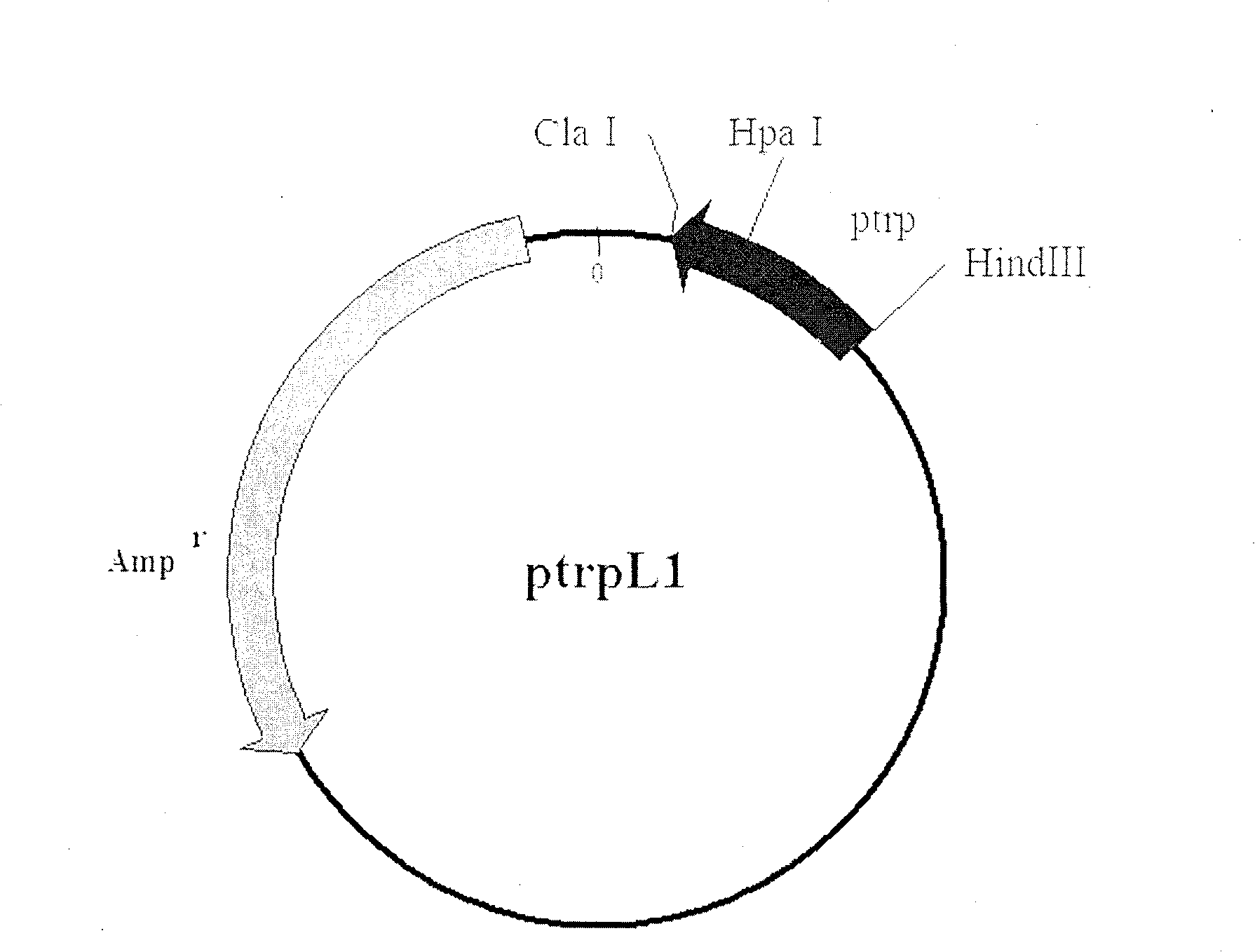Patents
Literature
225 results about "Structural gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A structural gene is a gene that codes for any RNA or protein product other than a regulatory factor (i.e. regulatory protein). A term derived from the lac operon, structural genes are typically viewed as those containing sequences of DNA corresponding to the amino acids of a protein that will be produced, as long as said protein does not function to regulate gene expression. Structural gene products include enzymes and structural proteins. Also encoded by structural genes are non-coding RNAs, such as rRNAs and tRNAs (but excluding any regulatory miRNAs and siRNAs).
Insect resistant plants
InactiveUS6943282B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacteroidesAureobasidium sp.
A method for expressing insecticidal protein structural genes in plant genomes is provided. In the preferred embodiments this invention comprises placing a structural gene for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein under control of a plant or a T-DNA promoter and ahead of a polyadenylation site followed by insertion of said promoter / structural gene combination into a plant genome by utilizing an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-based transformation system. The modified Ti plasmid is then used to transform recipient plant cells. Also provided are the plants and tissues produced by this method and bacterial strains, plasmids, and vectors useful for execution of this invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
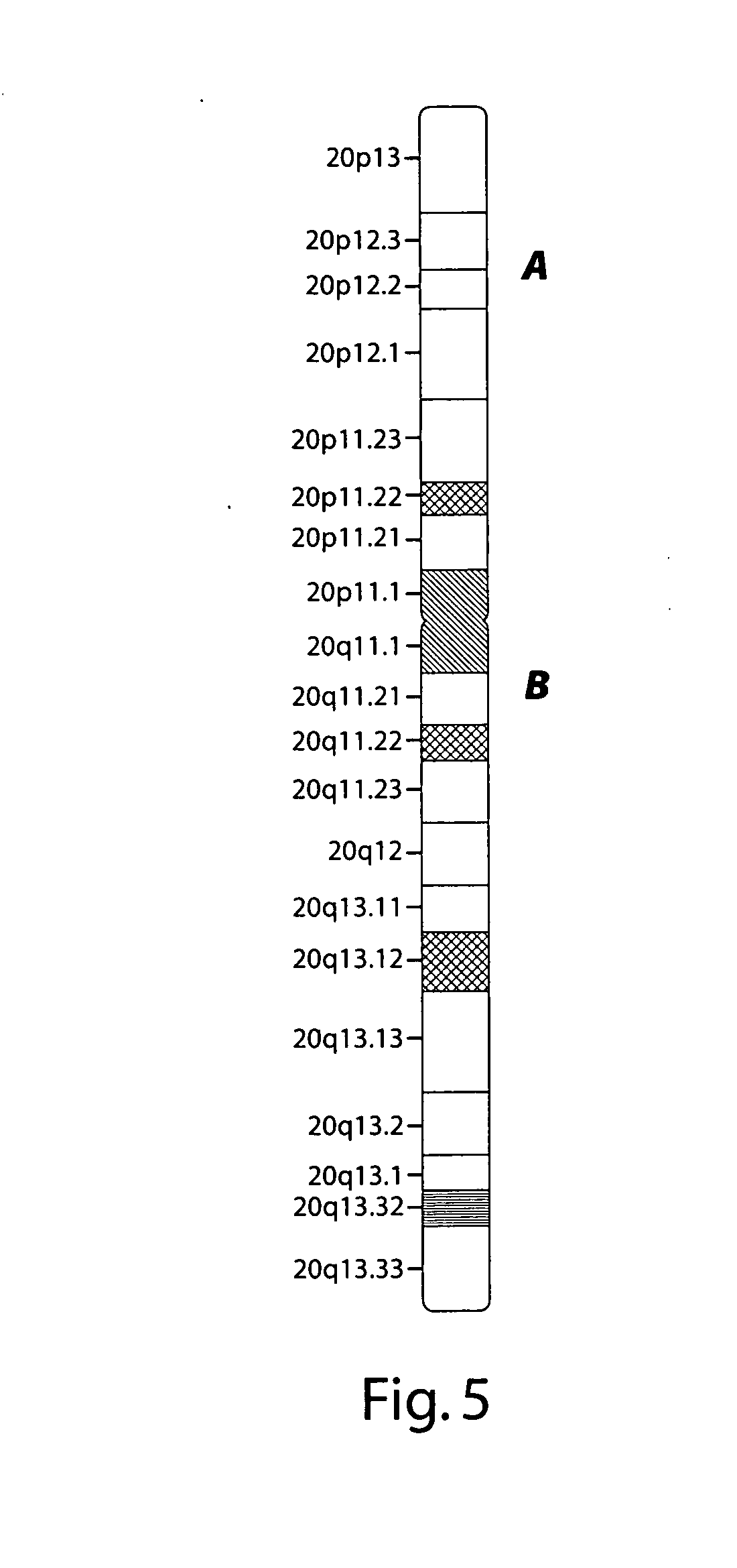
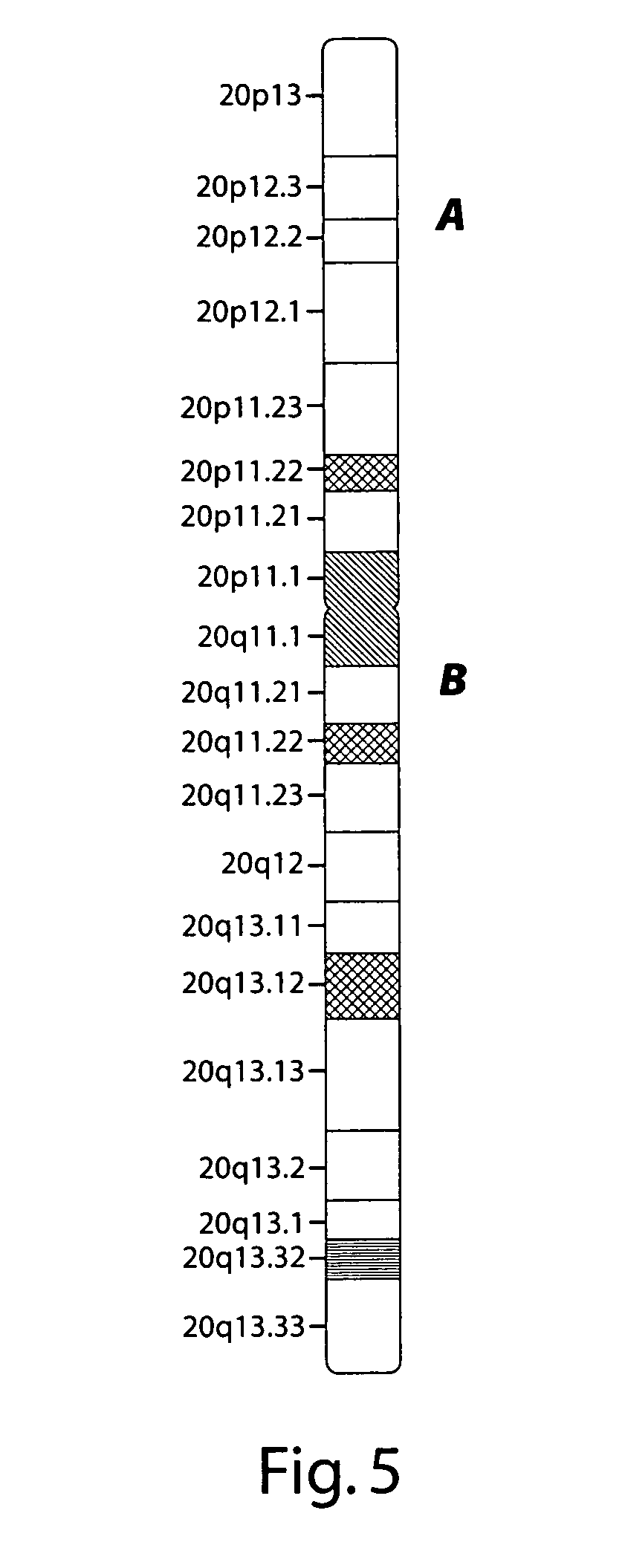
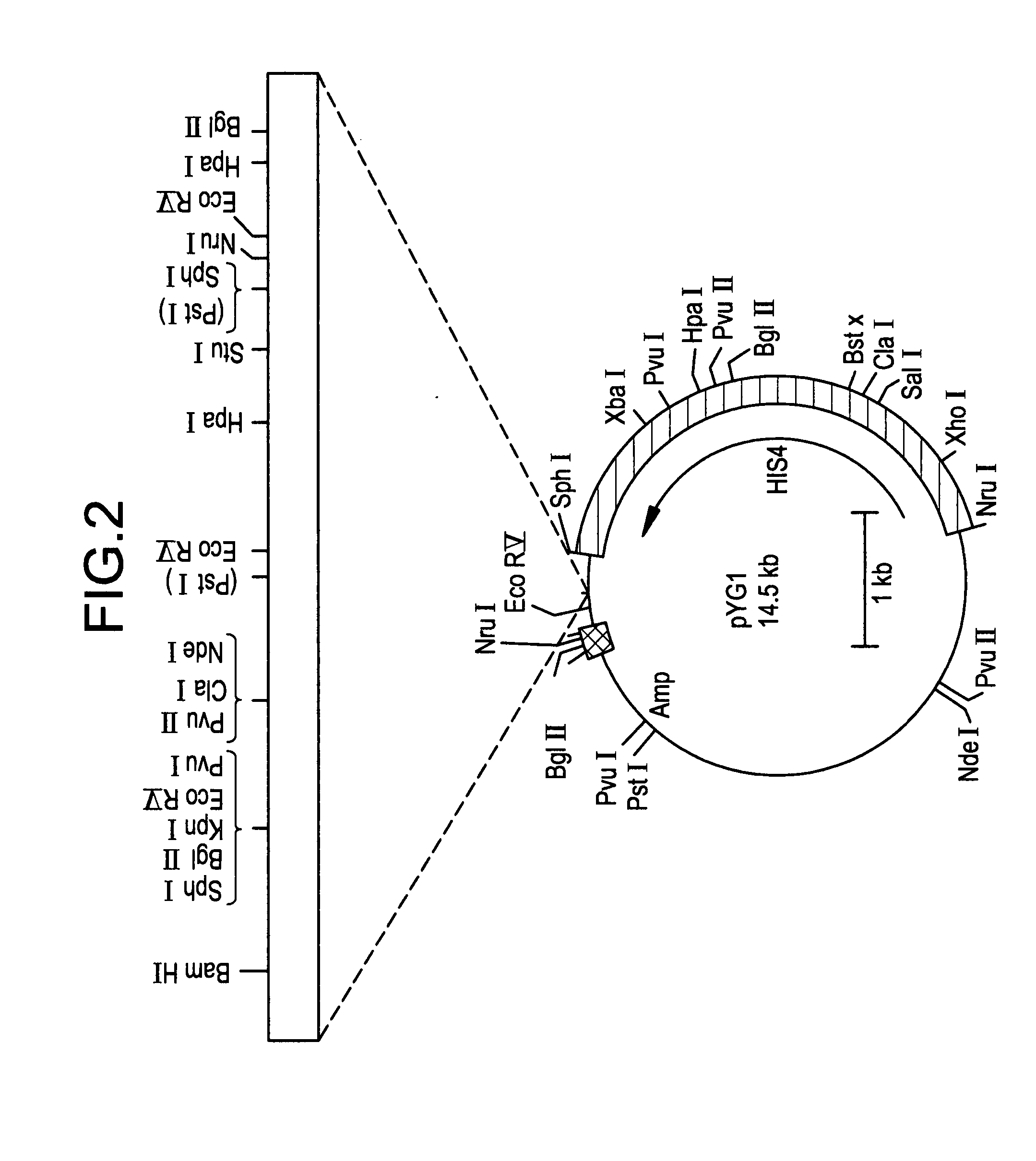
High resolution chromosomal mapping
ActiveUS20070238105A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural analysisGenome
The present invention generally relates to spatial and structural genomic analysis compositions, which can be used for the mapping of chromosomes and structural analyses of chromosomal rearrangements, including the entire chromosome, as well as specific portions or regions of interest of the chromosomes. In some embodiments, multiple portions of the genome can be distinguished, for instance, using a first detection entity and a second detection entity different from the first detection entity. The detection entities may be immobilized relative to oligonucleotides, which may be selected to bind to different locations within the chromosome. For instance, the oligonucleotides may be at least substantially complementary to the chromosome, e.g., substantially complementary to a specific location of the chromosome.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Packaging cell
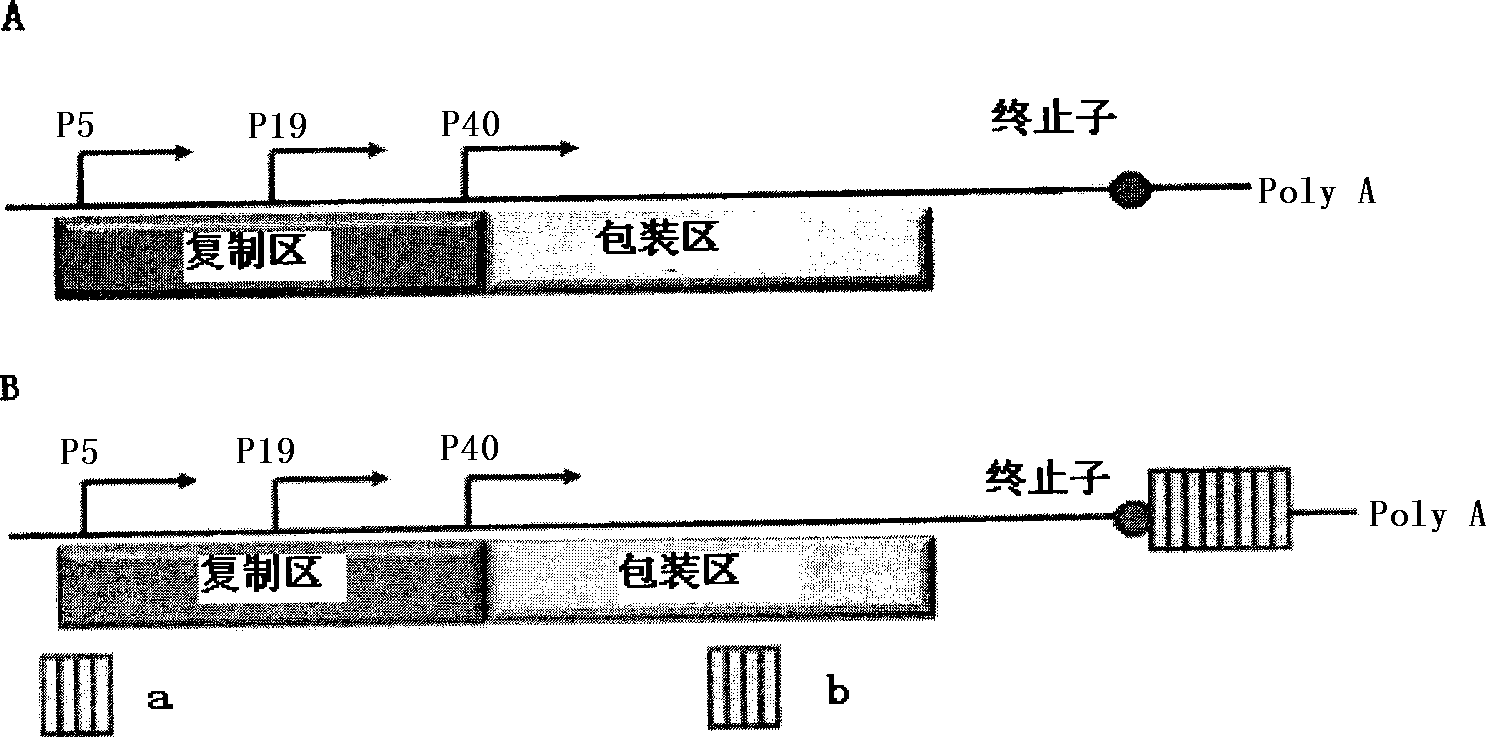
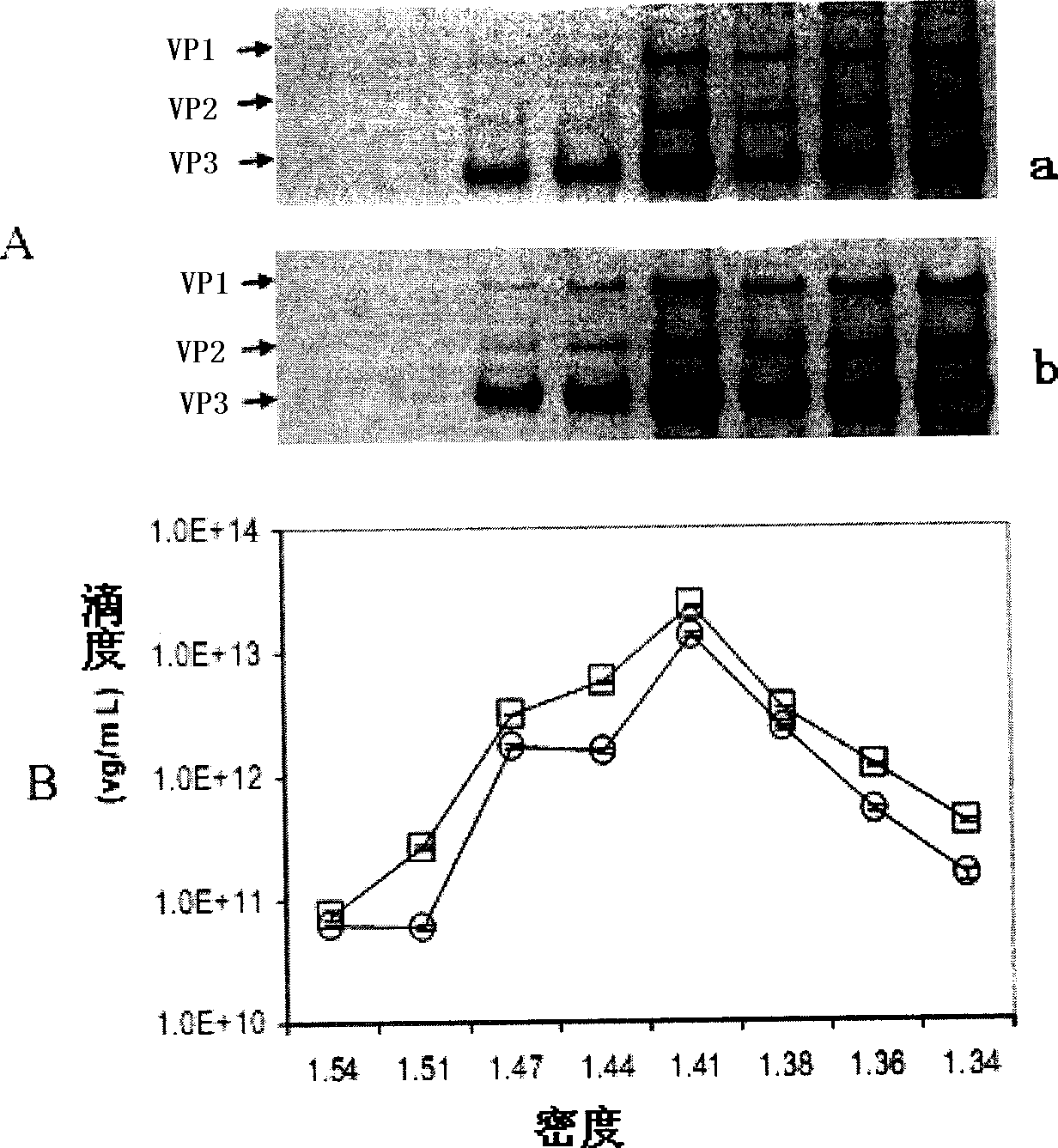
A virus-producing cell sustaining the ability to produce viruses at high titer is successfully constructed by expressing the virus structural gene under the regulation of EF1α promoter. In this virus-producing cell, the virus structural gene is ligated to a selection marker gene via IRES and domains other than the protein coding domain are eliminated from the DNA encoding virus structural proteins. Thus, reduction of the titer due to cell passages can be prevented and emergence of wild type viruses caused by unfavorable recombination of the virus genome can be inhibited.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
High resolution chromosomal mapping
ActiveUS8058055B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural analysisGenome
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
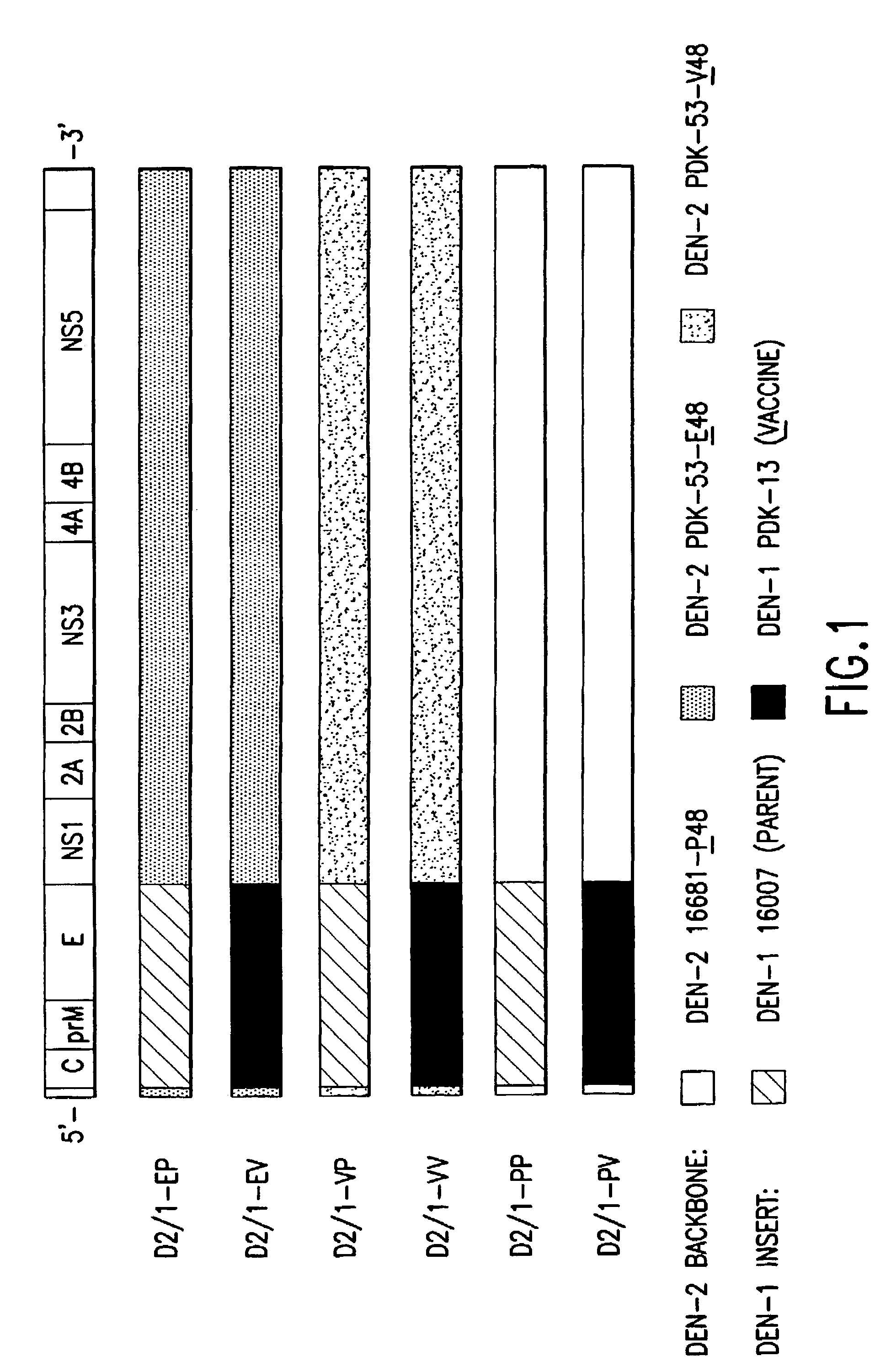
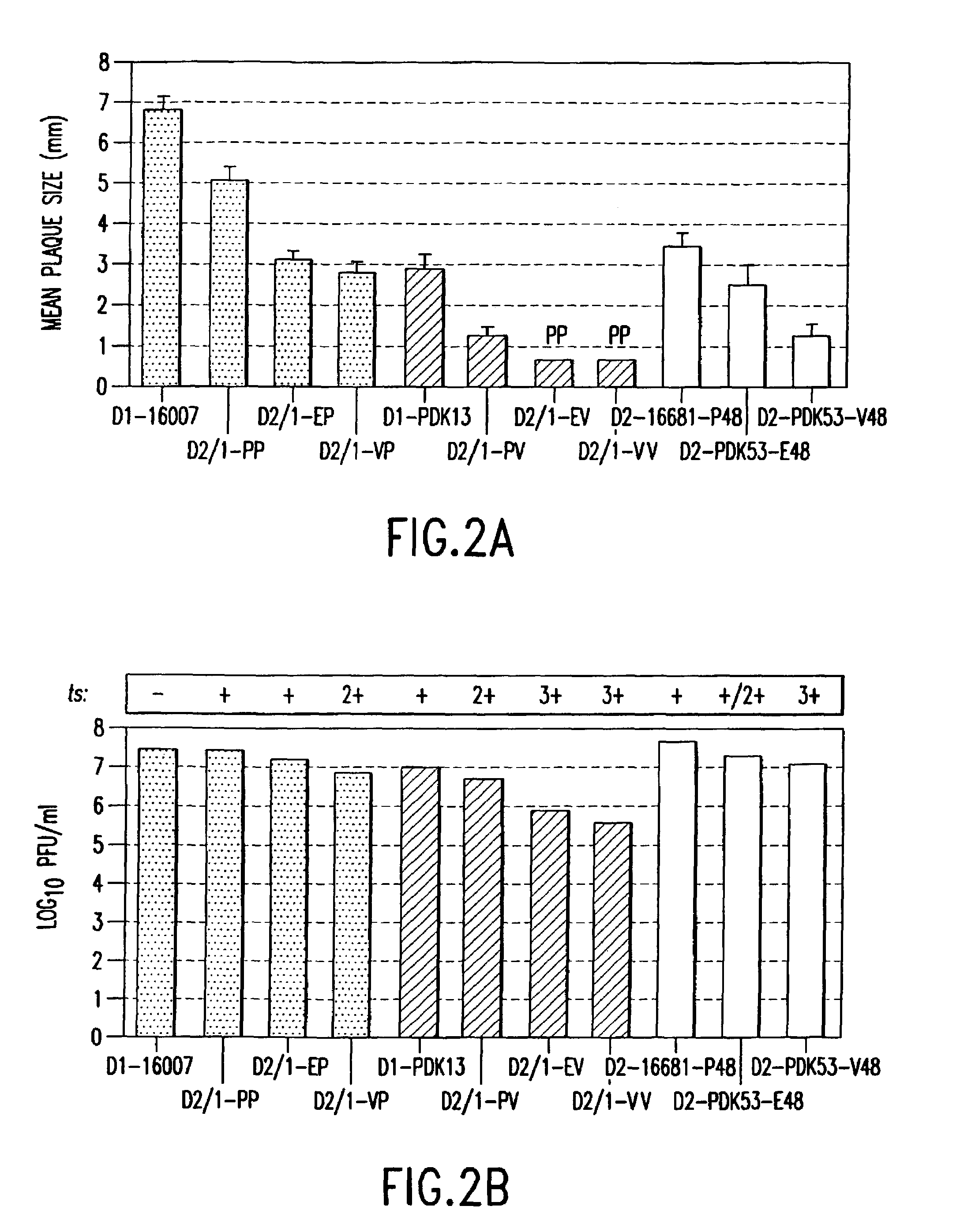
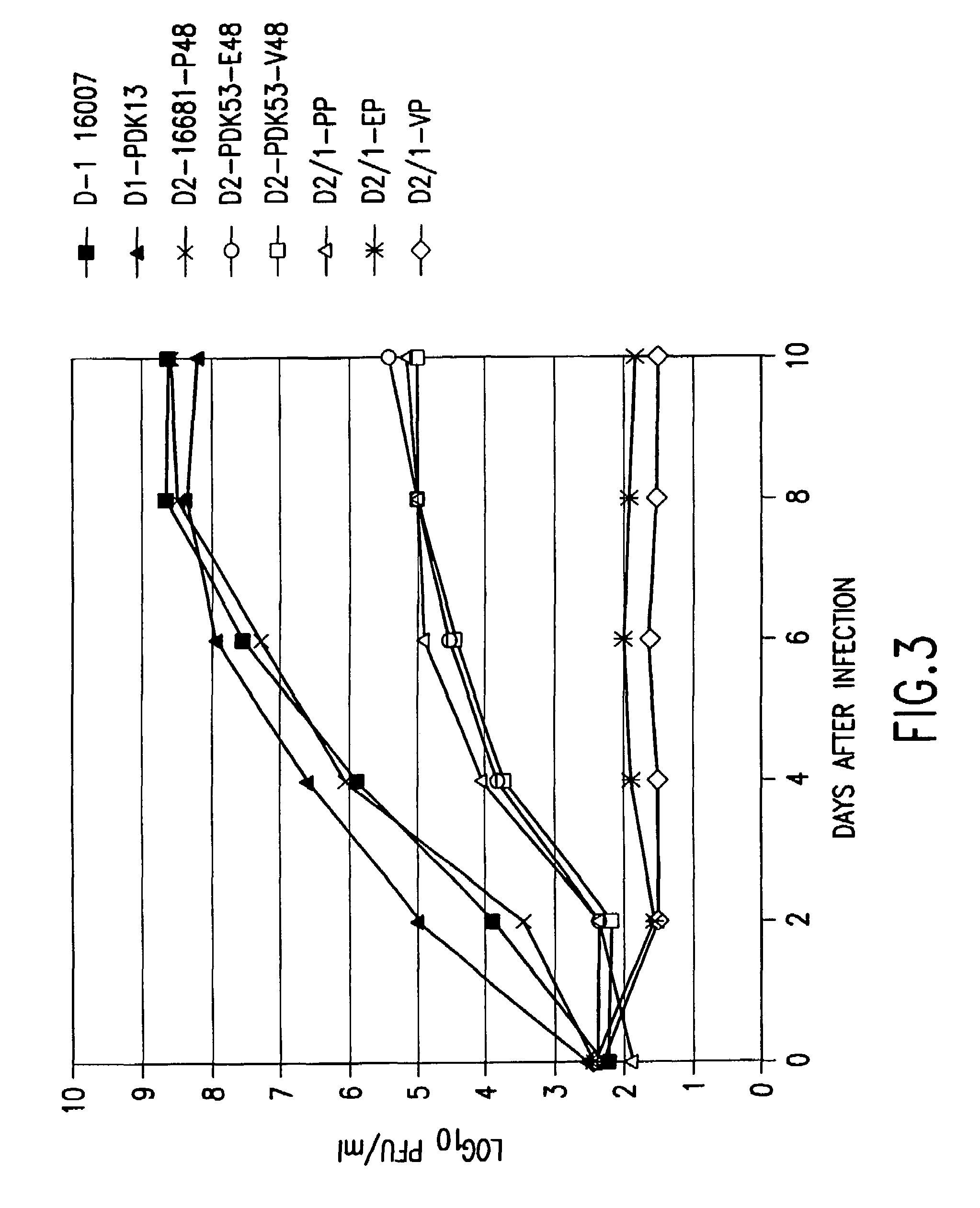
Avirulent, immunogenic flavivirus chimeras
InactiveUS7094411B2Minimize and inhibit infectionStable maintenanceOrganic active ingredientsVirusesViral diseaseAmino acid mutation
Chimeric flaviviruses that are avirulent and immunogenic are provided. The chimeric viruses are constructed to contain amino acid mutations in the nonstructural proteins of a flavivirus. Chimeric viruses containing the attenuation-mutated nonstructural genes of the virus are used as a backbone into which the structural protein genes of a second flavivirus strain are inserted. These chimeric viruses elicit pronounced immunogenicity yet lack the accompanying clinical symptoms of viral disease. The attenuated chimeric viruses are effective as immunogens or vaccines and may be combined in a pharmaceutical composition to confer simultaneous immunity against several strains of pathogenic flaviviruses.
Owner:MAHIDOL UNIV +2
DNA-based vaccine against the encephalitis alphaviruses
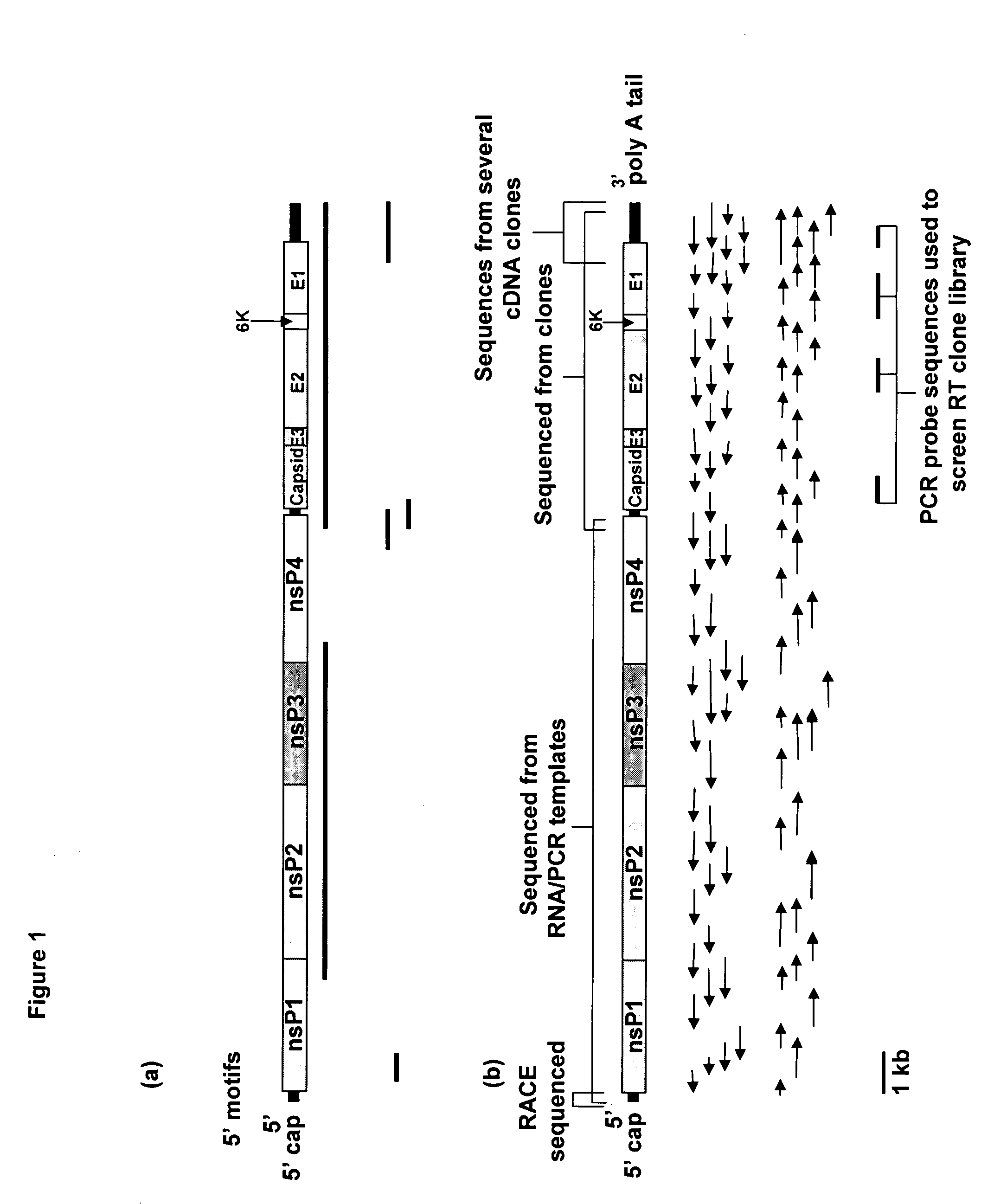
This invention relates to the development of a mammalian expression vector, under which expression of the structural genes of western equine encephalitis virus have been placed under the control of an eucaryotic promoter. When the recombinant vector is administered to mammalian cell culture or using a cell-free transcription / translation system, in vitro, authentic structural proteins of western equine encephalitis virus are produced as verified by reactivity with monoclonal antibodies developed to western equine encephalitis virus. When the recombinant DNA molecule is administered in vivo, a protective immune response is induced, thereby enhancing protection of the individual against subsequent infection by western equine encephalitis virus. In a similar manner, DNA vaccines to related alphaviruses (Venezuelan and eastern equine encephalitis viruses) could also be developed.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Avirulent, immunogenic flavivirus chimeras
InactiveUS20060062803A1Inhibition effectPreserve immunogenicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsViral diseaseFhit gene
Chimeric flaviviruses that are avirulent and immunogenic are provided. The chimeric viruses are constructed to contain amino acid mutations in the nonstructural proteins of a flavivirus. Chimeric viruses containing the attenuation-mutated nonstructural genes of the virus are used as a backbone into which the structural protein genes of a second flavivirus strain are inserted. These chimeric viruses elicit pronounced immunogenicity yet lack the accompanying clinical symptoms of viral disease. The attenuated chimeric viruses are effective as immunogens or vaccines and may be combined in a pharmaceutical composition to confer simultaneous immunity against several strains of pathogenic flaviviruses.
Owner:MAHIDOL UNIV +2
Novel vectors for animal cells and use thereof
InactiveUS20060078992A1Decrease productivityFold preciselyMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyForeign protein
Protein synthesis inhibitor resistance genes (typified by a cycloheximide resistance gene) are capable of imparting resistance to a protein synthesis inhibitor (typified by cycloheximide) to animal cells sensitive to the inhibitor. The genes have a sequence mutated by substitution in a gene encoding a ribosome-constituting protein derived from an animal. The genes may be placed in recombinant vectors, including expression vectors containing the gene together with a foreign protein structural gene.
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
New type cell special gene HAAVmir containing microRNA combined sequence for gene treating
InactiveCN101532024ADoes not affect appearanceDoes not affect productivityGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesMicroRNACell strain
Owner:许瑞安 +2
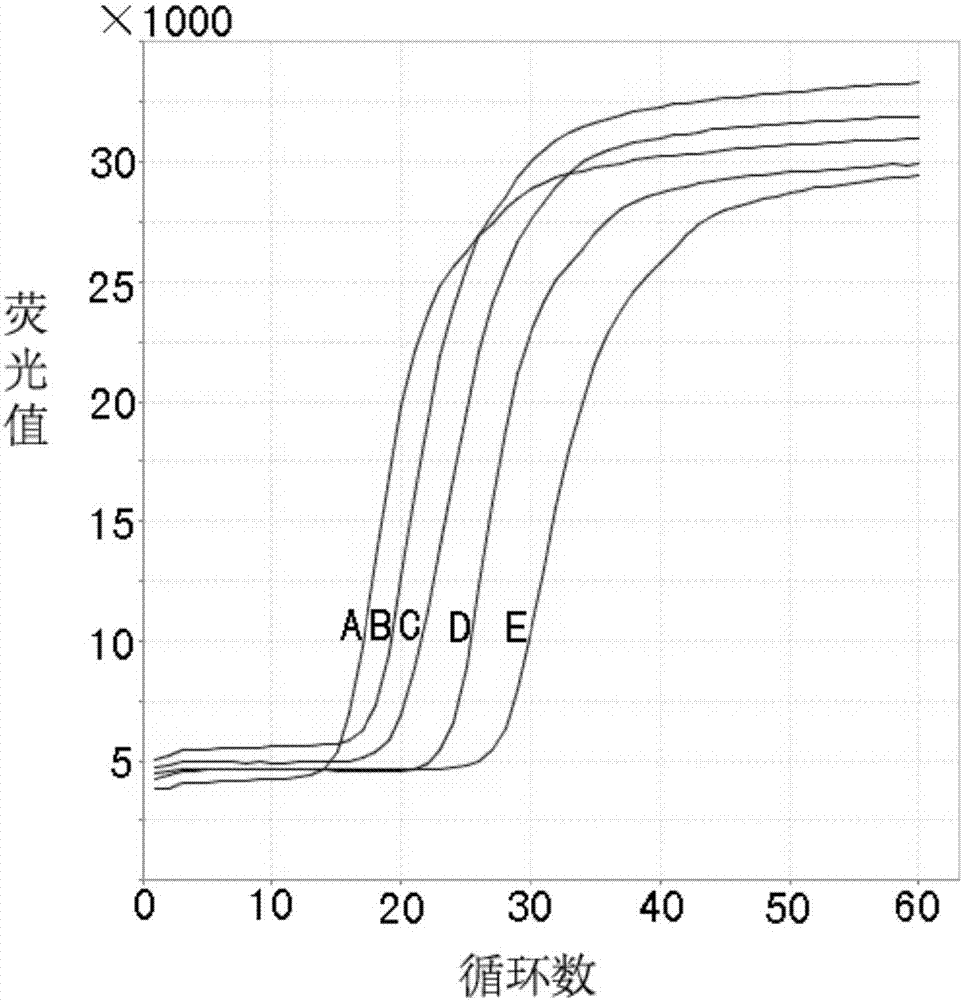
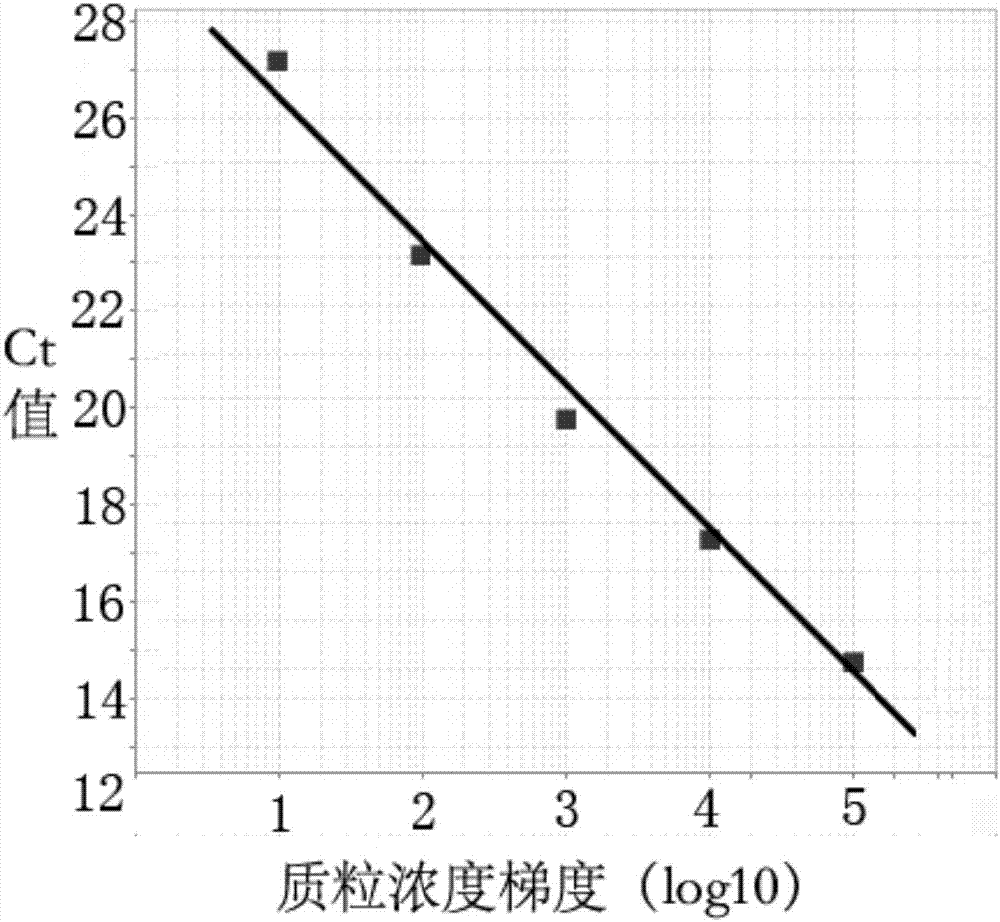
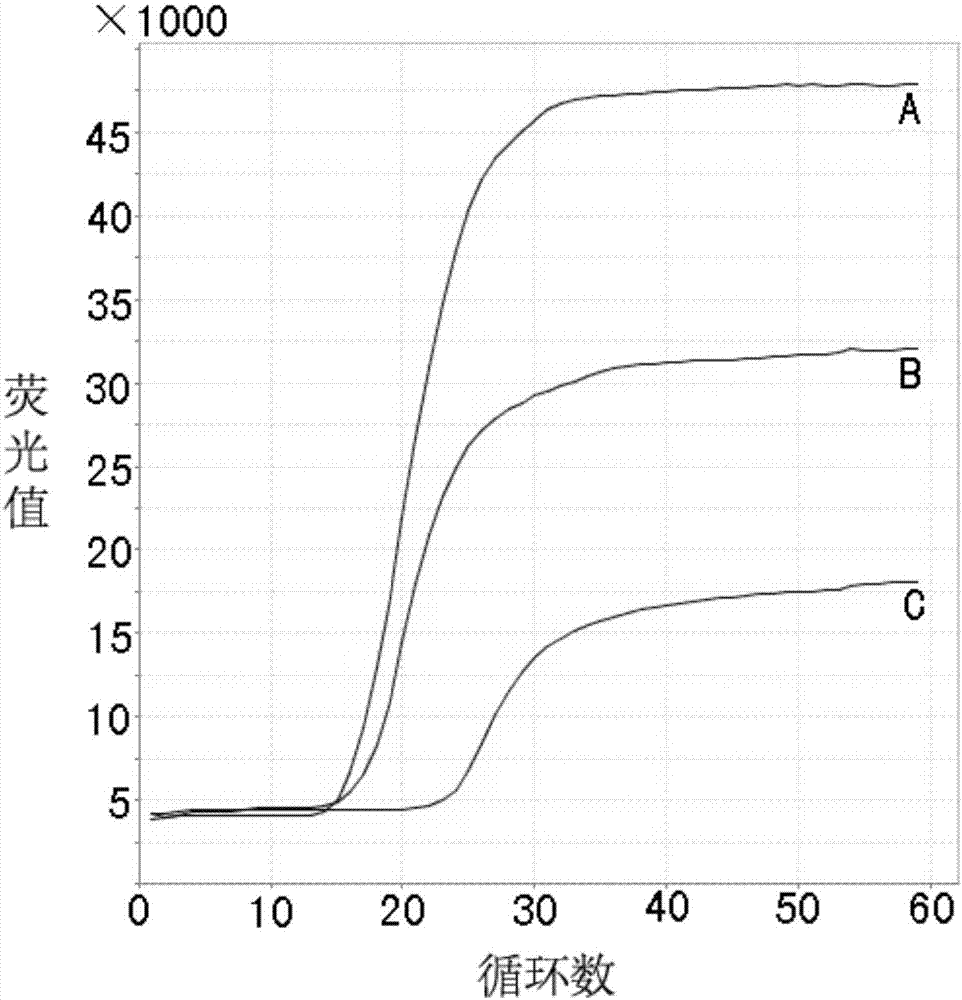
Real-time fluorescent LAMP detection primer group, kit and detection method of African swine fever virus non-structural gene
InactiveCN106947838ASensitiveImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGenotypeFluorescent pcr
The invention provides a real-time fluorescent LAMP detection primer group, a kit and a detection method of an African swine fever virus (ASFV) non-structural gene. The primer group is designed based on a non-structural DNA polymerase G1211R gene and comprises an FIP primer, a BIP primer, an F3 primer and a B3 primer. A detection result shows that a typical S-shaped nucleic acid amplification curve, and an amplification product has a specific melting curve. An ASFV70 strain virus nucleic acid is taken as a template, and LAMP detection is better than a fluorescent PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method in sensitivity. Intra-assay and inter-assay variable factors of repetitive testing LAMP detection are both smaller than 5 percent. An ASFVArm07 stain is used for preparing various clinic simulated samples, and detected positive rate is up to 17.31 percent. The detection method provided by the invention can provide a new technological means for preventing and controlling African swine fever virus, and detection on different genetic stains and quick screening for exit and entry are facilitated.
Owner:TECH CENT OF GUANGZHOU CUSTOMS
Method of forming ubiquinone-10
InactiveUS6103488AHigh purityInhibit productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicrobiologyRhodobacter species
The present invention relates to production of ubiquinone-10 in E. coli by isolating and sequencing a structural gene dds1 of decaprenyl diphosphate synthase derived from photosynthetic bacteria such as Rhodobacter capsulatus., and expressing it in E. coli.
Owner:ALPHA FOODS CO LTD
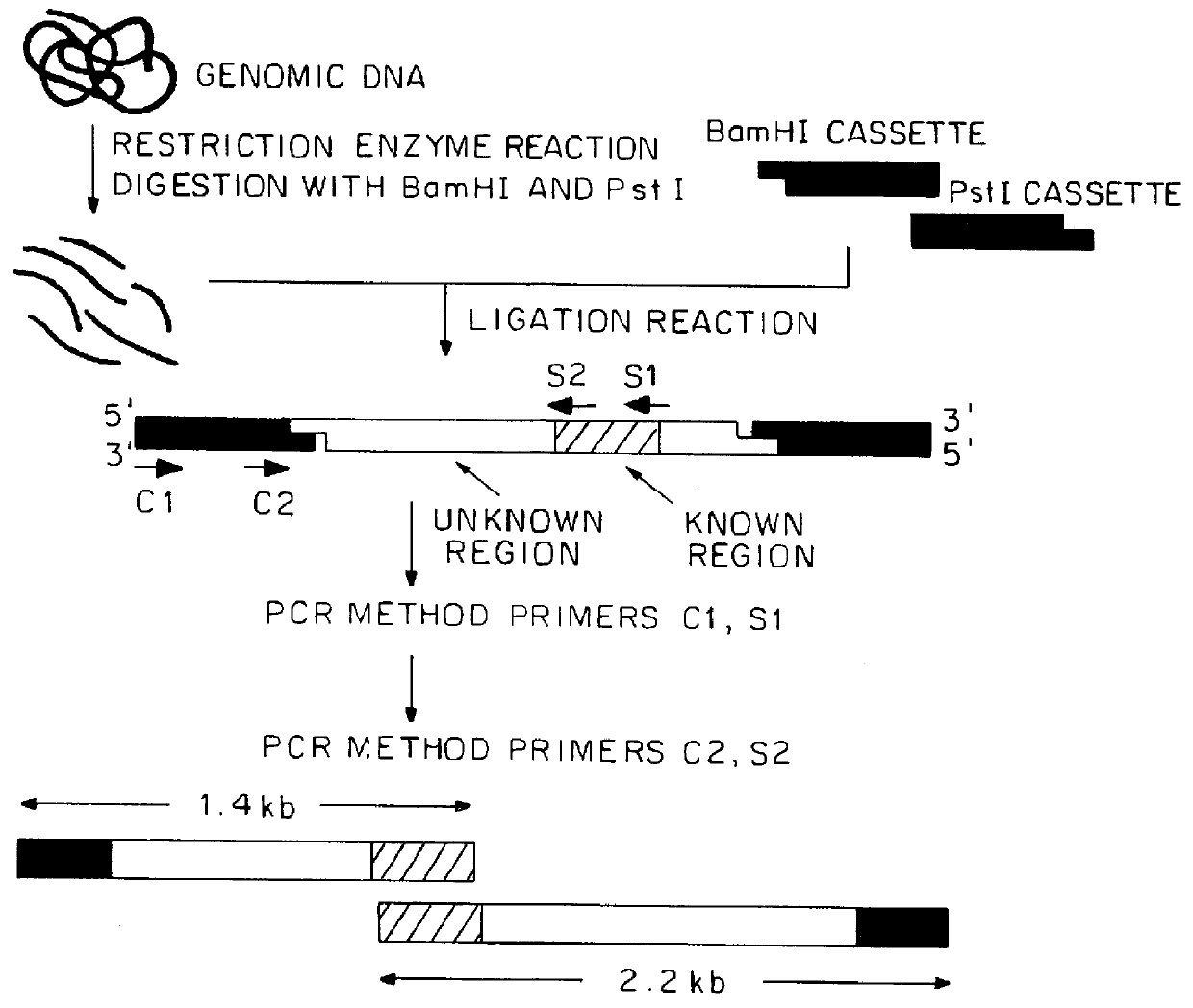
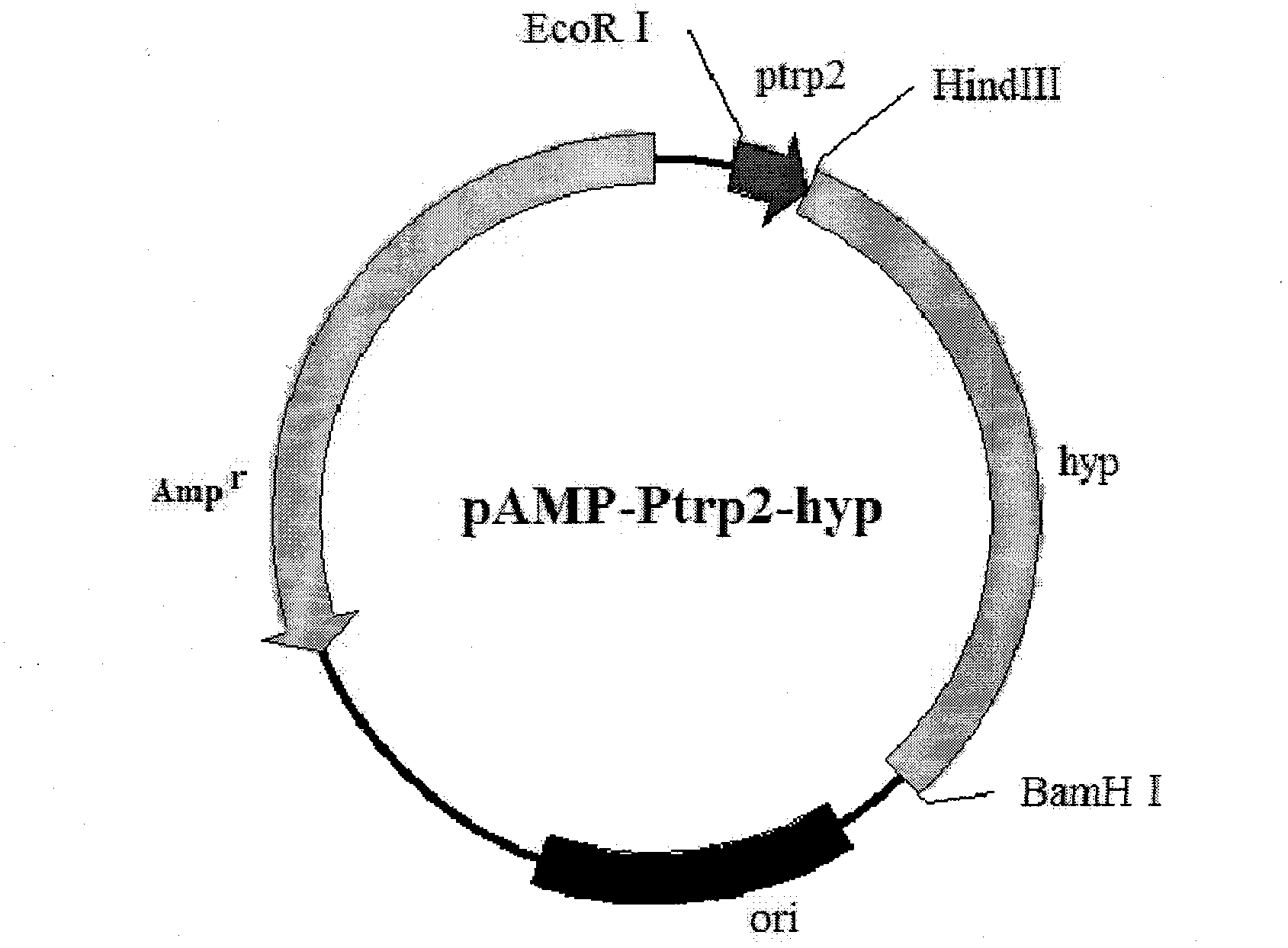
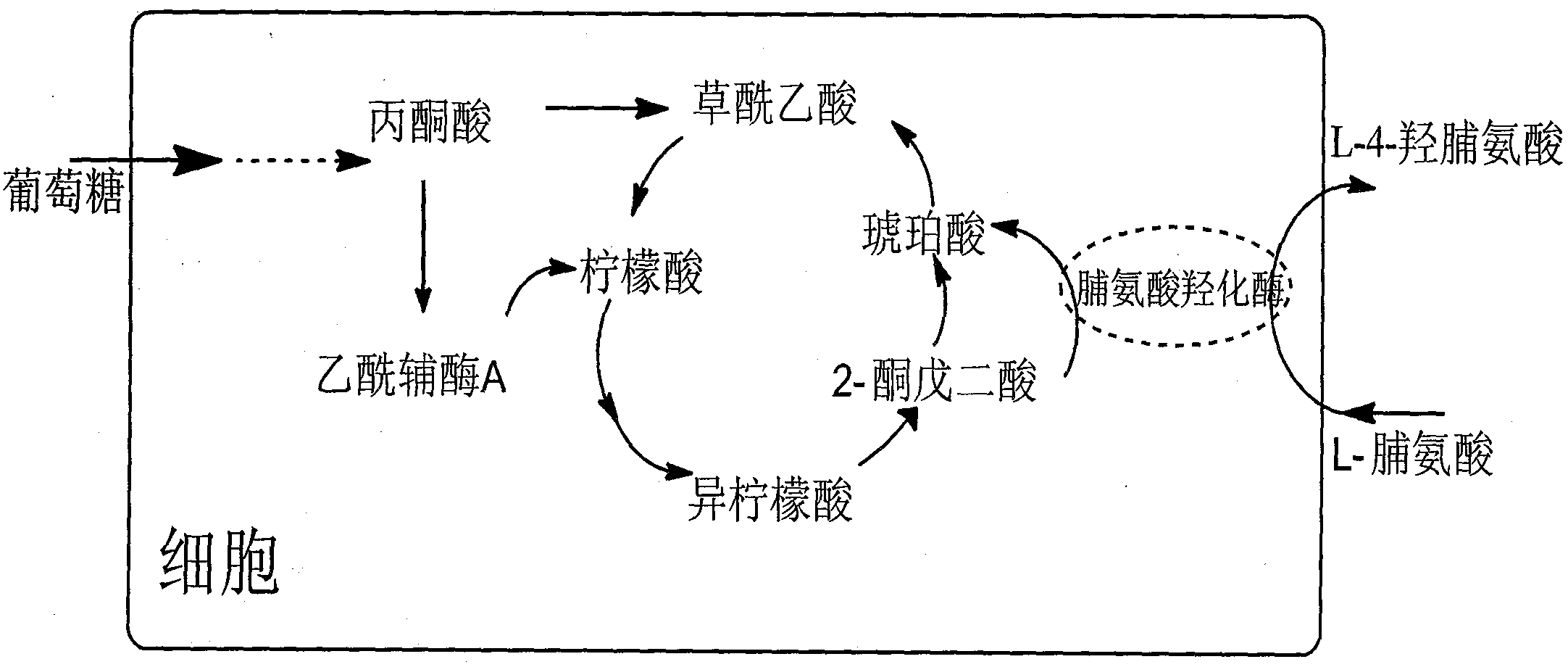
Method for production of L-4-hydroxyproline by using recombinant escherichia coli fermentation
InactiveCN103509813AImportant industrial application valueGood prospects for industrial developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxyproline
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses a method for production of L-4-hydroxyproline by using recombinant escherichia coli fermentation. Recombinant escherichia coli is constructed by the following method: according to a published proline-4-hydroxylase gene and tryptophan promoter sequence, first optimally designing a tryptophan tandem promoter and a proline-4-hydroxylase structure gene, then after the total gene synthesis of the tryptophan tandem gene promoter and the proline-4-hydroxylase structure gene, connecting the promoter and the structure gene to pAMP plasmid to construct recombinant plasmid pAMP-P2trp-Hyp for overexpression of proline-4-hydroxylase. The invention also discloses the application of the escherichia coli in the production of the 4-hydroxyproline, the shake flask fermentation results show that the 4-hydroxyproline prepared by the recombinant escherichia coli has a yield reached 0.31g / L, and suggest that the recombinant escherichia coli has good industrial development prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant cell strain for detecting dioxin compounds according to behaviour of leuciferinase gene
The present invention relates to one recombinant cell strain with foreign leuciferinase gene, and is especially one DNA segment of transfected mouse liver cancer cell strain Hepalcle7-M4P2 and Hepale7-MP and with dioxin reaction segment specific nucleotide sequence í‹cacgcíŒ and í‹gcgtgíŒ. The DNA segment is designed based on Mus musculus CYP1 A1 gene promoter area and partial fore end sequence of the structural gene. Therefore, the recombinant cell strain and the cultured descendant may be used in detecting dioxin compounds from the sample collected from natural environment by means of biological analysis process.
Owner:CHENG SHIU UNIVERSITY
Zinc finger protein derivatives and methods therefor
InactiveUS20050084885A1Modulate it functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainBiological activationTransgene
Zinc finger proteins of the Cys2His2 type represent a class of malleable DNA binding proteins which may be selected to bind diverse sequences. Typically, zinc finger proteins containing three zinc finger domains, like the murine transcription factor Zif268 and the human transcription factor Spl, bind nine contiguous base pairs (bp). To create a class of proteins which would be generally applicable to target unique sites within complex genomes, the present invention provides a polypeptide linker that fuses two three-finger proteins. Two six-fingered proteins were created and demonstrated to bind 18 contiguous bp of DNA in a sequence specific fashion. Expression of these proteins as fusions to activation or repression domains allows transcription to be specifically up or down modulated within cells. Polydactyl zinc finger proteins are broadly applicable as genome-specific transcriptional switches in gene therapy strategies and the development of novel transgenic plants and animals. Such proteins are useful for inhibiting, activating or enhancing gene expression from a zinc finger-nucleotide binding motif containing promoter or other transcriptional control element, as well as a structural gene or RNA sequence.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Methods of treating cancer using a heat shock factor activity inhibitor
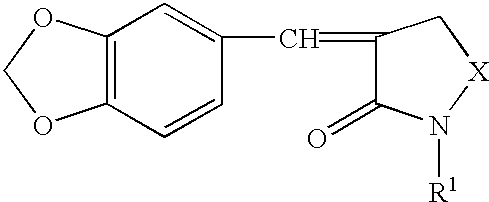
A disease treatment is provided by controlling the expression of a protein induced by a heat shock factor.The novel compound benzo-1,3-dioxole provides an inhibitor of HSF activity or an inhibitor of inducing the production of a protein regulated by HSF, which inhibits the activity of a heat shock factor, a transcriptional regulatory factor, thereby in turn inhibiting transcription of a structural gene having a heat shock element sequenc in the gene region for transcriptional regulation into RNA, and thus inhibiting translation of the gene into a protein, and resulting in inhibition of inducing production of RNA or protein encoded by the gene. It also provides a drug for treating or preventing cancer through thermotherapy and a drug for treating or preventing stress diseases such as depression.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
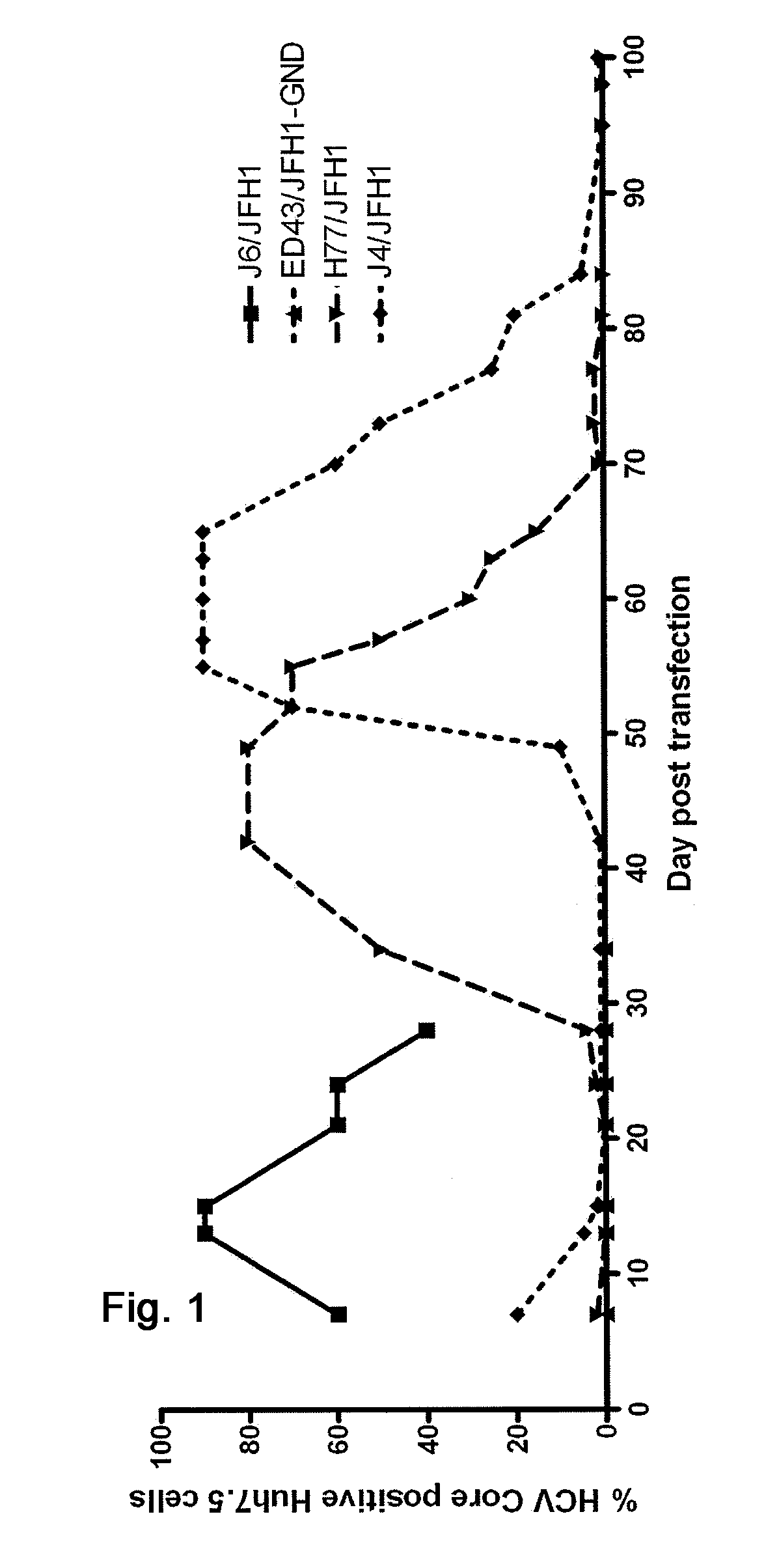
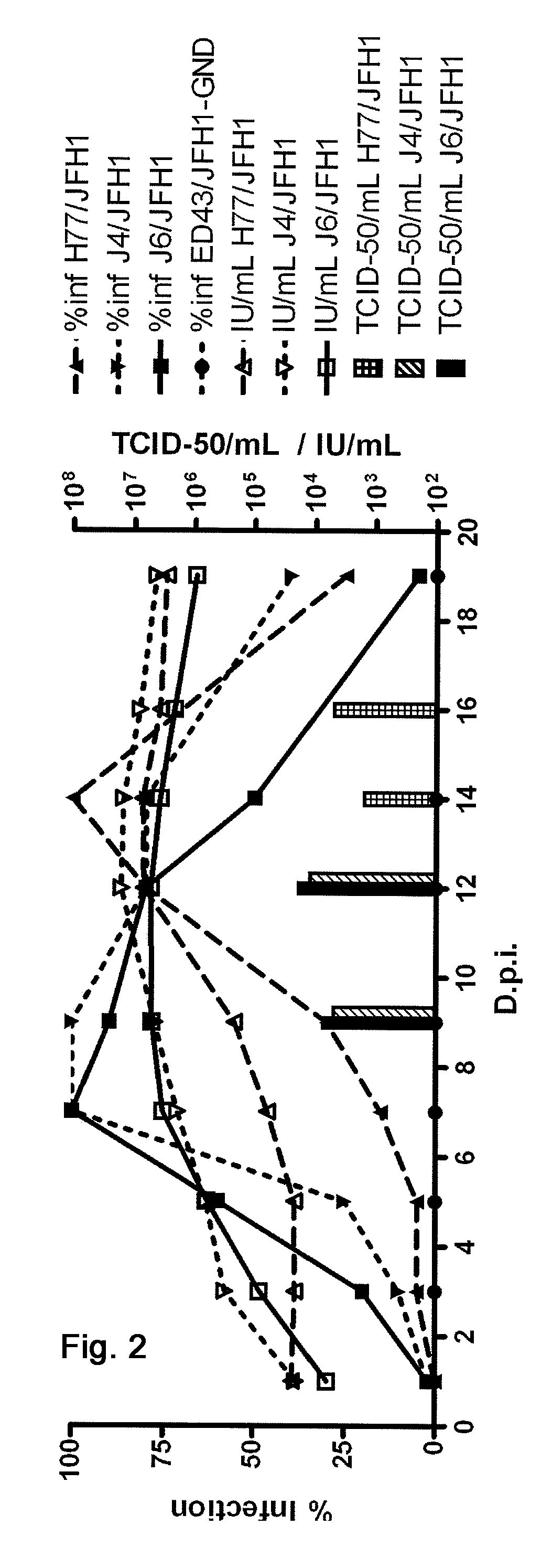
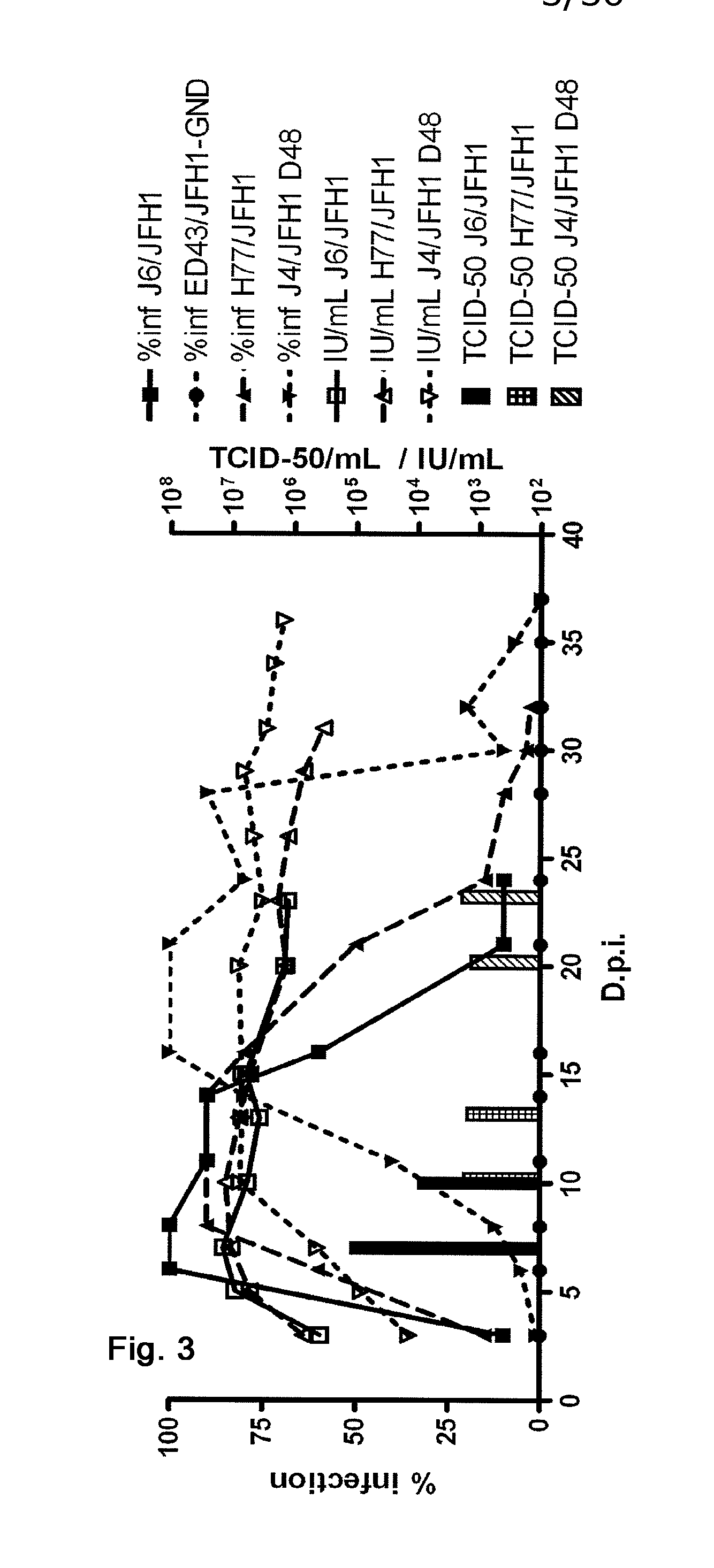
Efficient cell culture system for hepatitis C virus genotype 5A
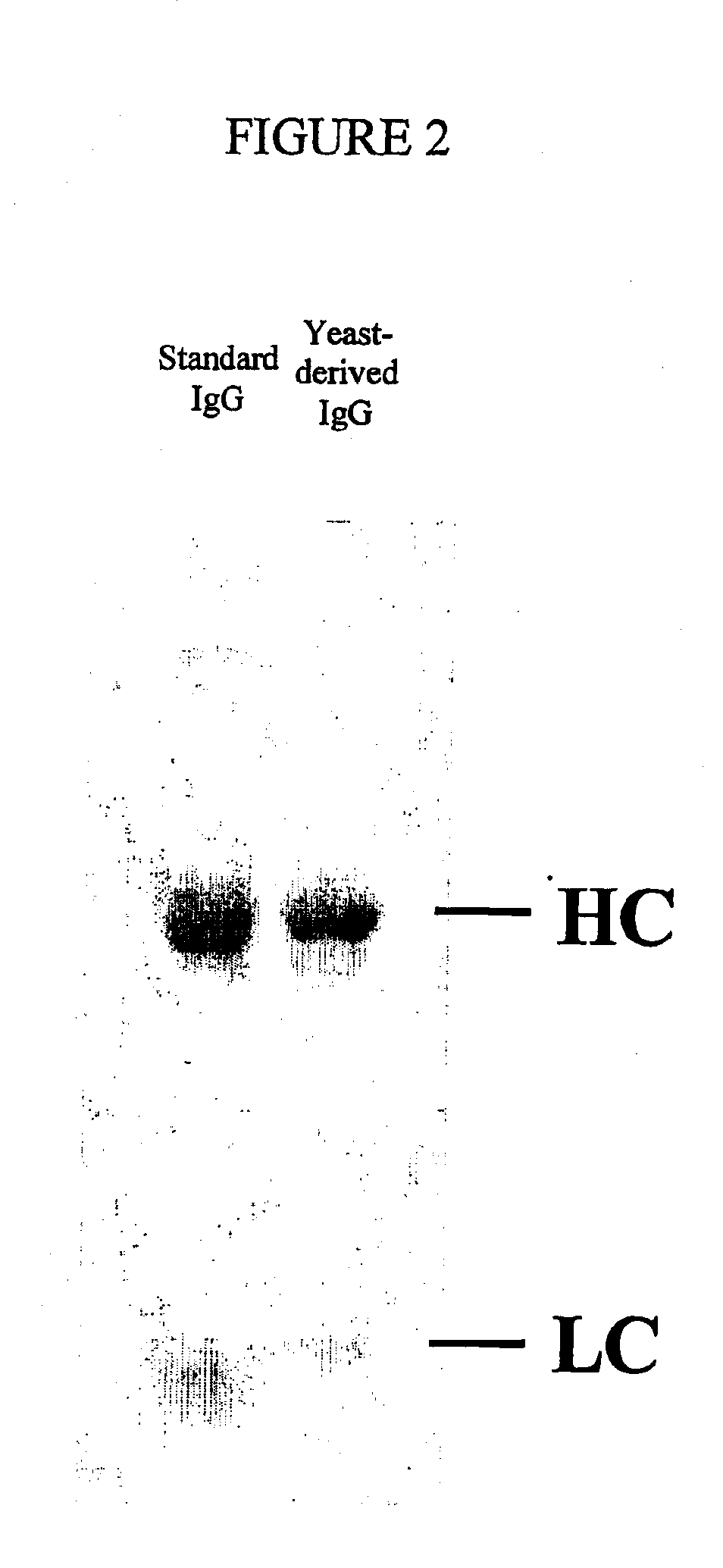
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
Vectors for animal cells and utilization thereof
InactiveUS7064194B2Decrease productivityFold preciselyOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismsBiotechnologyForeign protein
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
Formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes from methylotrophic yeasts
InactiveUS20070298500A1Microbiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesMethyl groupAmmonium sulfate
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
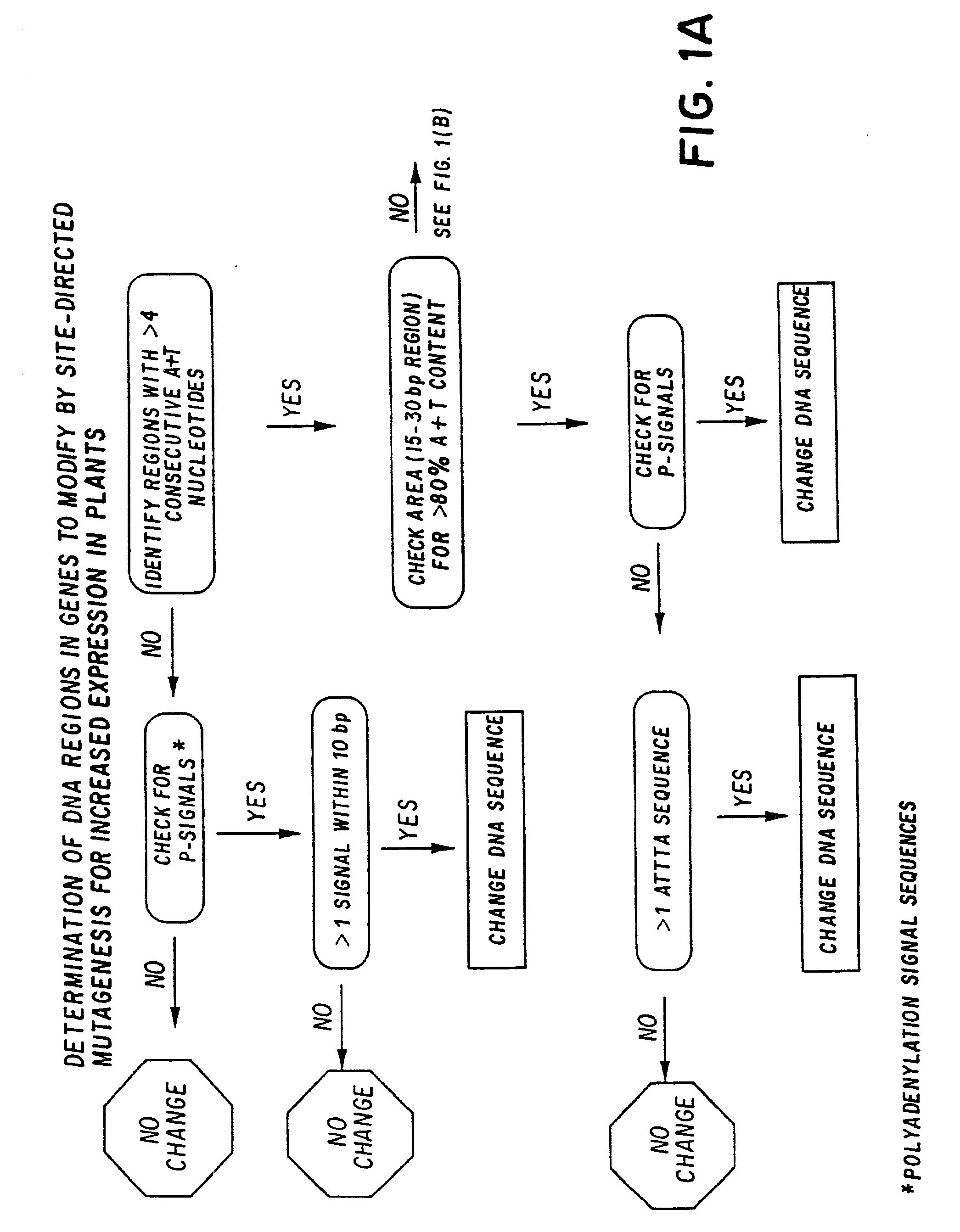
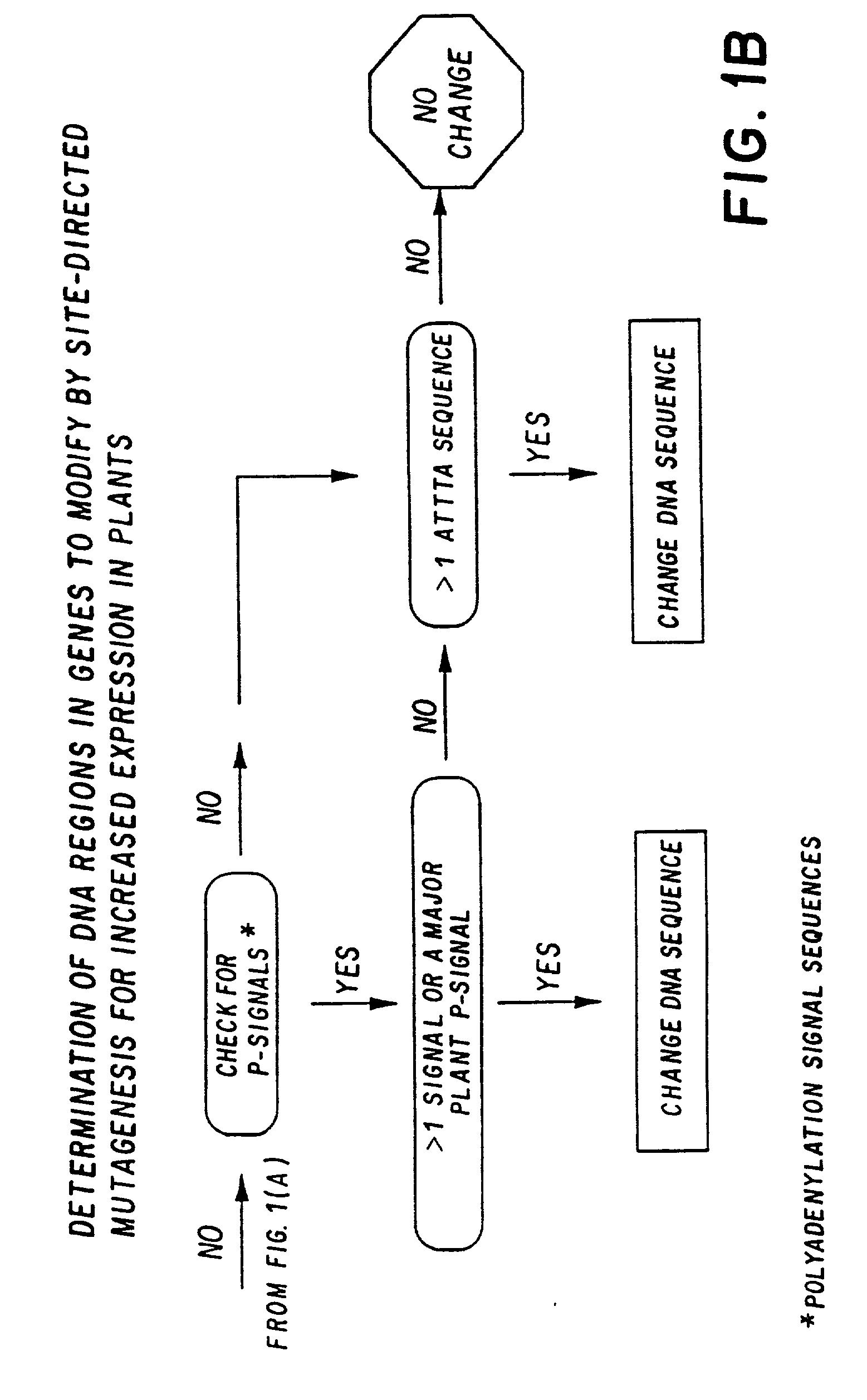
Synthetic plant genes and method for preparation
InactiveUS20030192078A1Raise the possibilityReduce the possibilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPotato leaf roll virusBiotechnology
A method for modifying structural gene sequences to enhance the expression of the protein product is disclosed. Also disclosed are novel structural genes which encode insecticidal proteins of B.t.k. HD-1, B.t.k. HD-73, B.t. tenebrionis, B.t. entomocidus, 2 protein of B.t.k. HD-1, and the coat protein of potato leaf roll virus.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
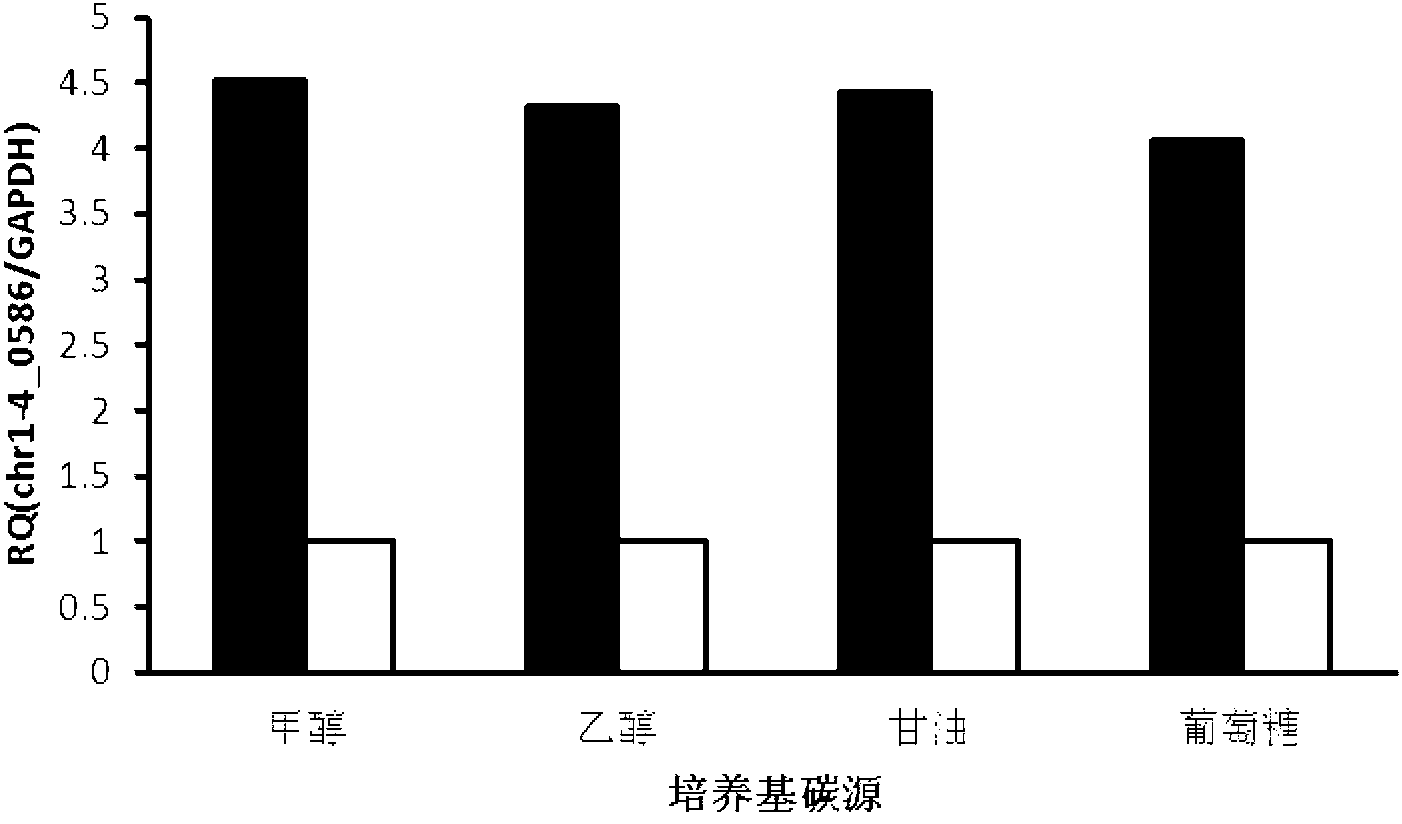
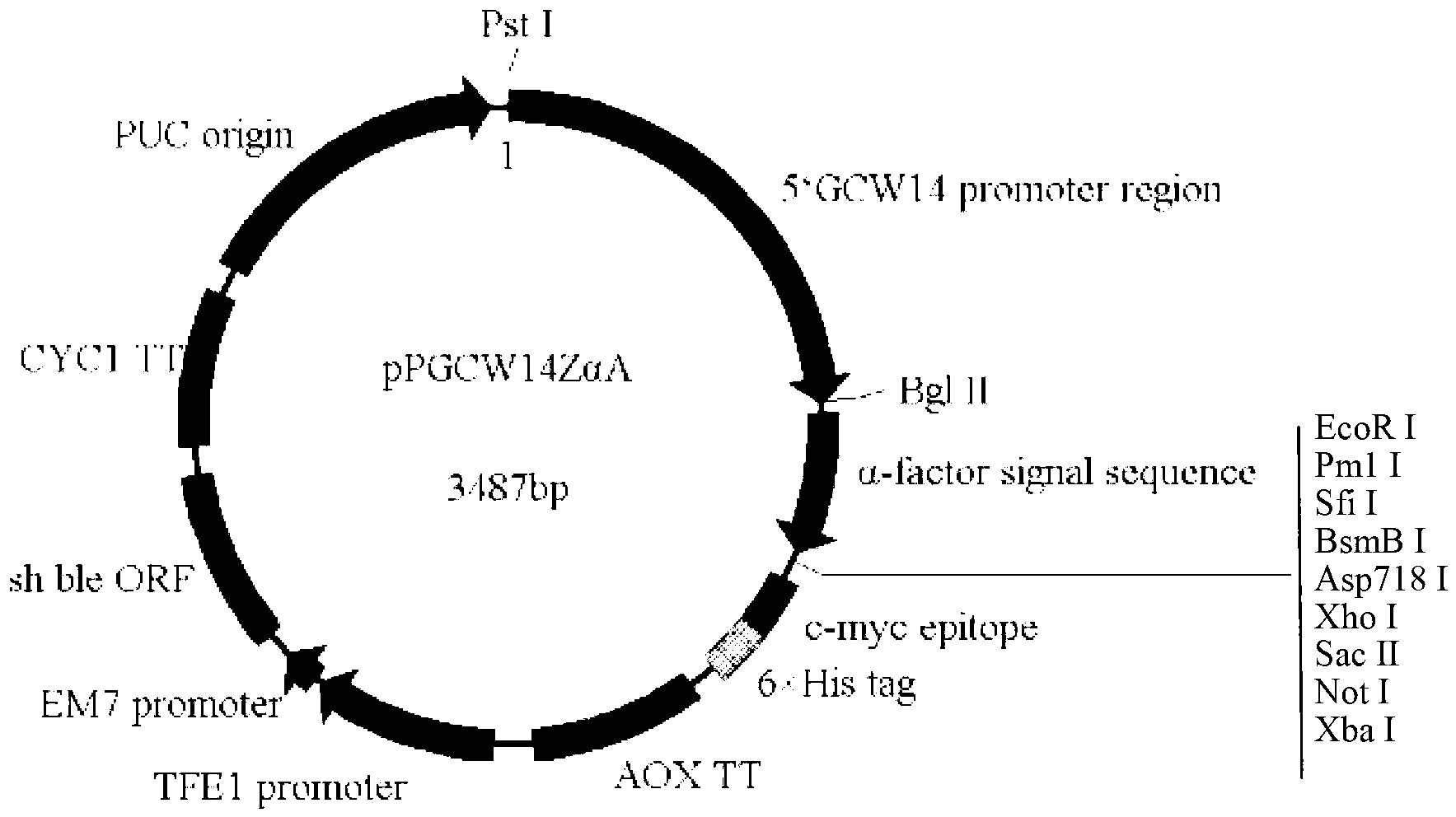
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) with constitutive promoter activity, application of DNA and pichia pastoris expression vector
ActiveCN102994501ALittle change in transcriptional activityIncrease transcriptional activityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisBase J
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) with constitutive promoter activity, application of the DNA and a pichia pastoris expression vector. The DNA has a base sequence as shown in SEQ No.1 (Sequence Number); and the application of the DNA relates to the application of the DNA in construction of the pichia pastoris (Pinchia Pastoris) expression vector. The DNA disclosed by the invention has the constitutive promoter activity, and can activate the transcription of a downstream structural gene without an inductor; the transcriptional activity shows little change in four different culture mediums, namely, ethanol, methanol, glucose and glycerol; the promoter activity is efficient, and the efficiency of the initiation transcription is four times more than the pichia pastoris GAPDH (Reduced Glyceraldehyde-phosphate Dehydrogenase) promoter. The pichia pastoris expression vector, constructed by the DNA disclosed by the invention, can efficiently express the extrinsic protein without methanol induction, and the efficiency of expressing the extrinsic protein (Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein) is about 6 to 8 times that of the expression system of the GAPDH promoter and 1.5 to 2 times that of the expression system of a TEF1 (Transcription Enhancer Factor 1) promoter.
Owner:林影 +1
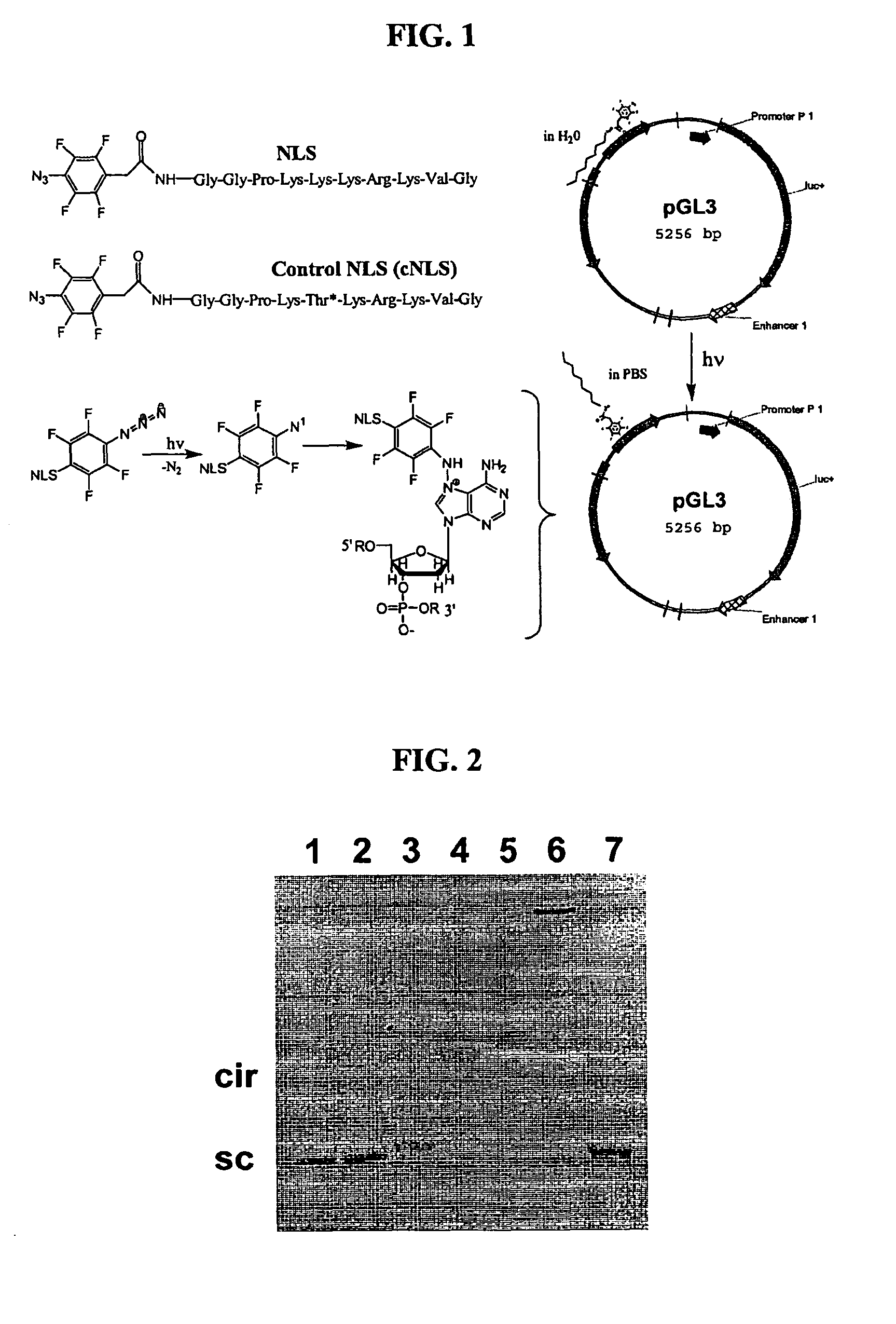
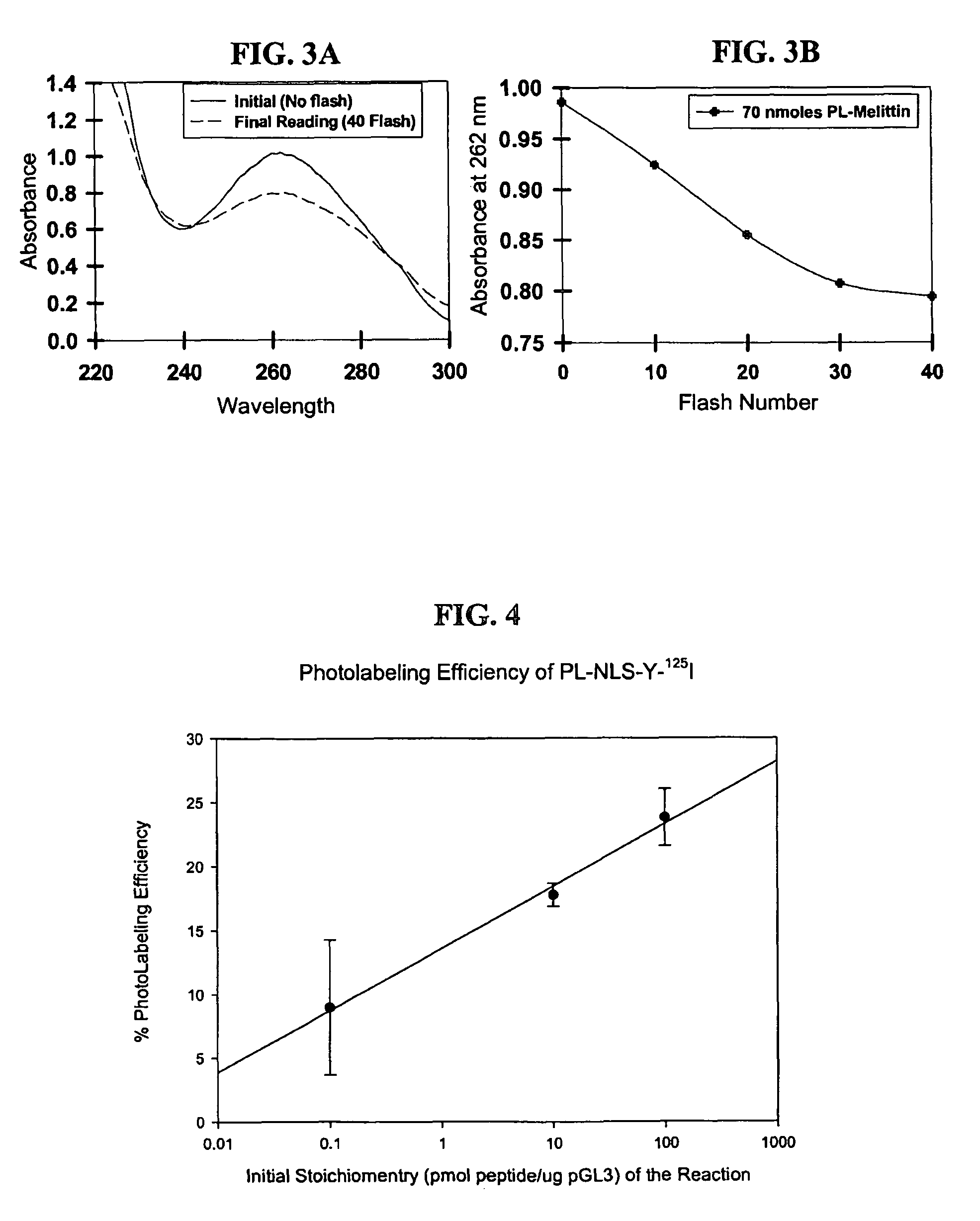
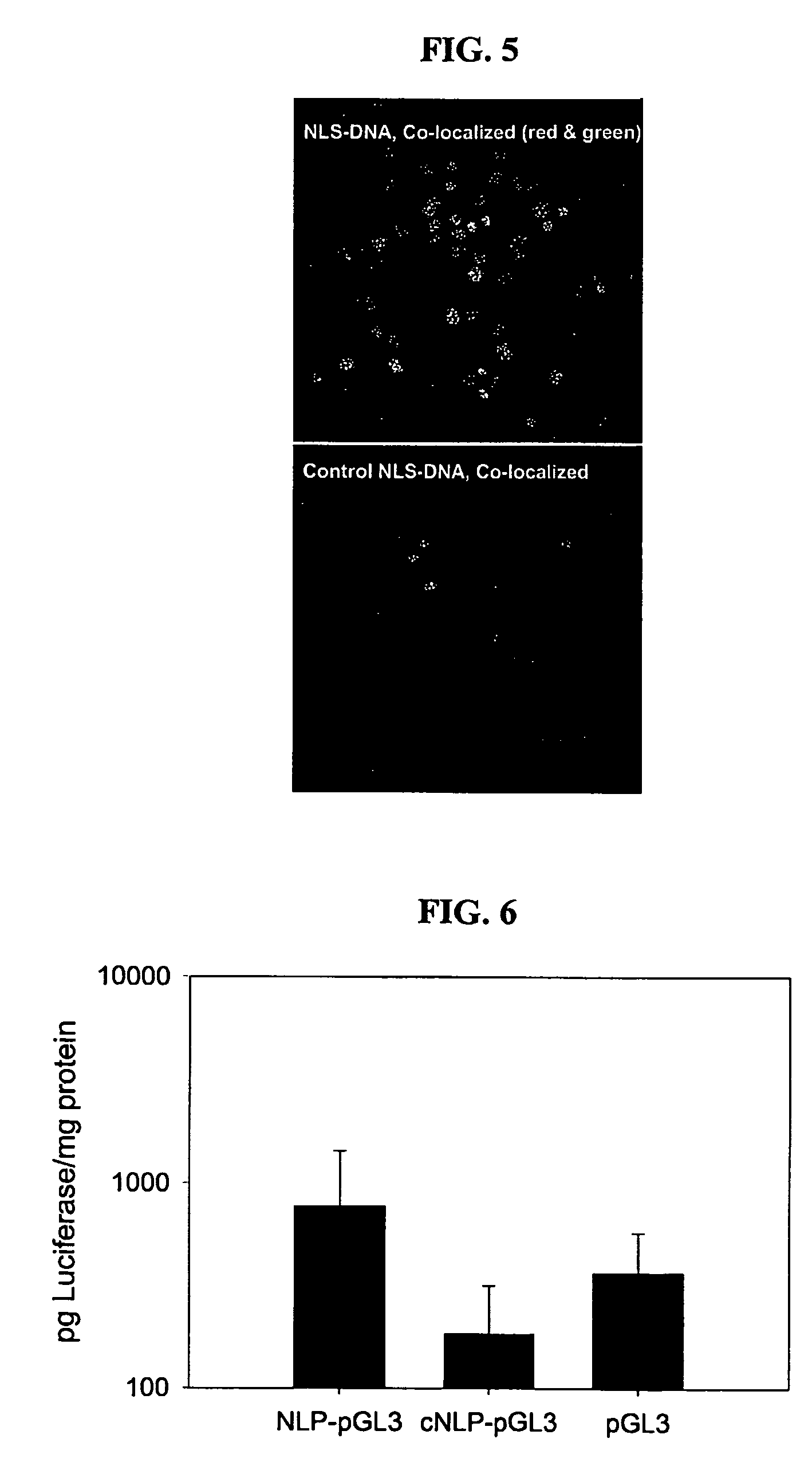
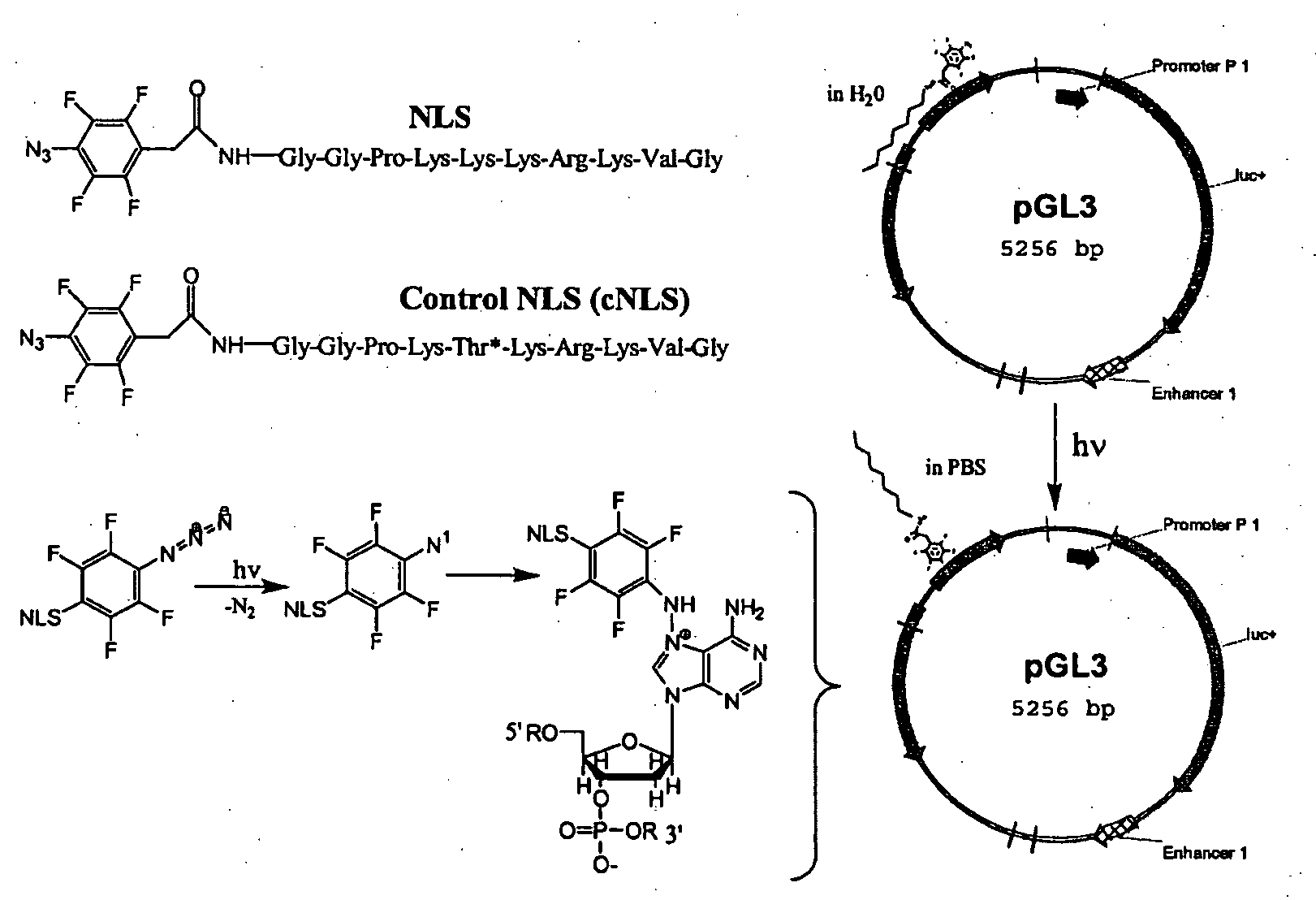
Compositions and methods for nucleic acid delivery
ActiveUS7795380B2Reduce deliveryIncrease gene expressionGenetic material ingredientsPeptide sourcesNucleotideViral nucleic acid
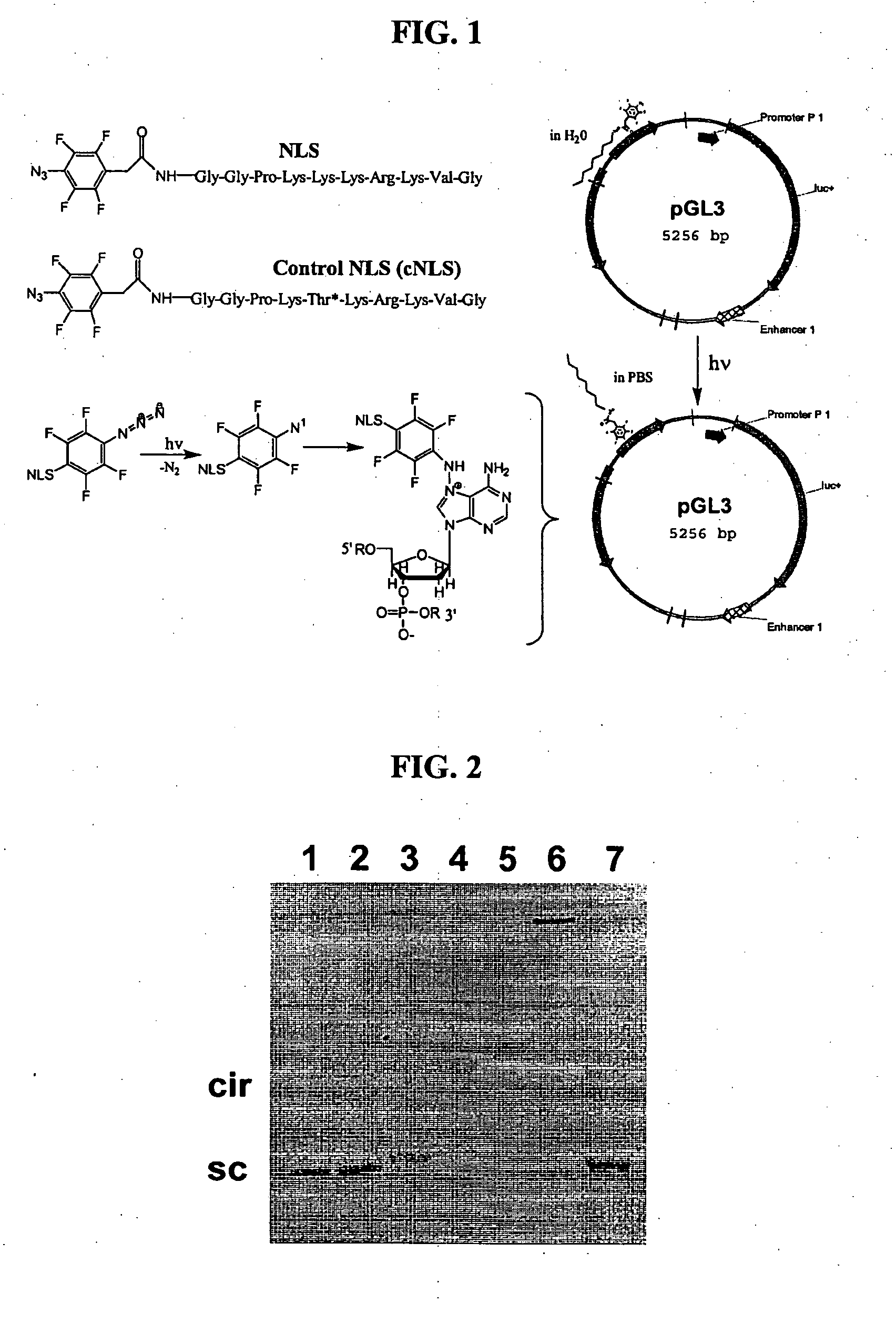
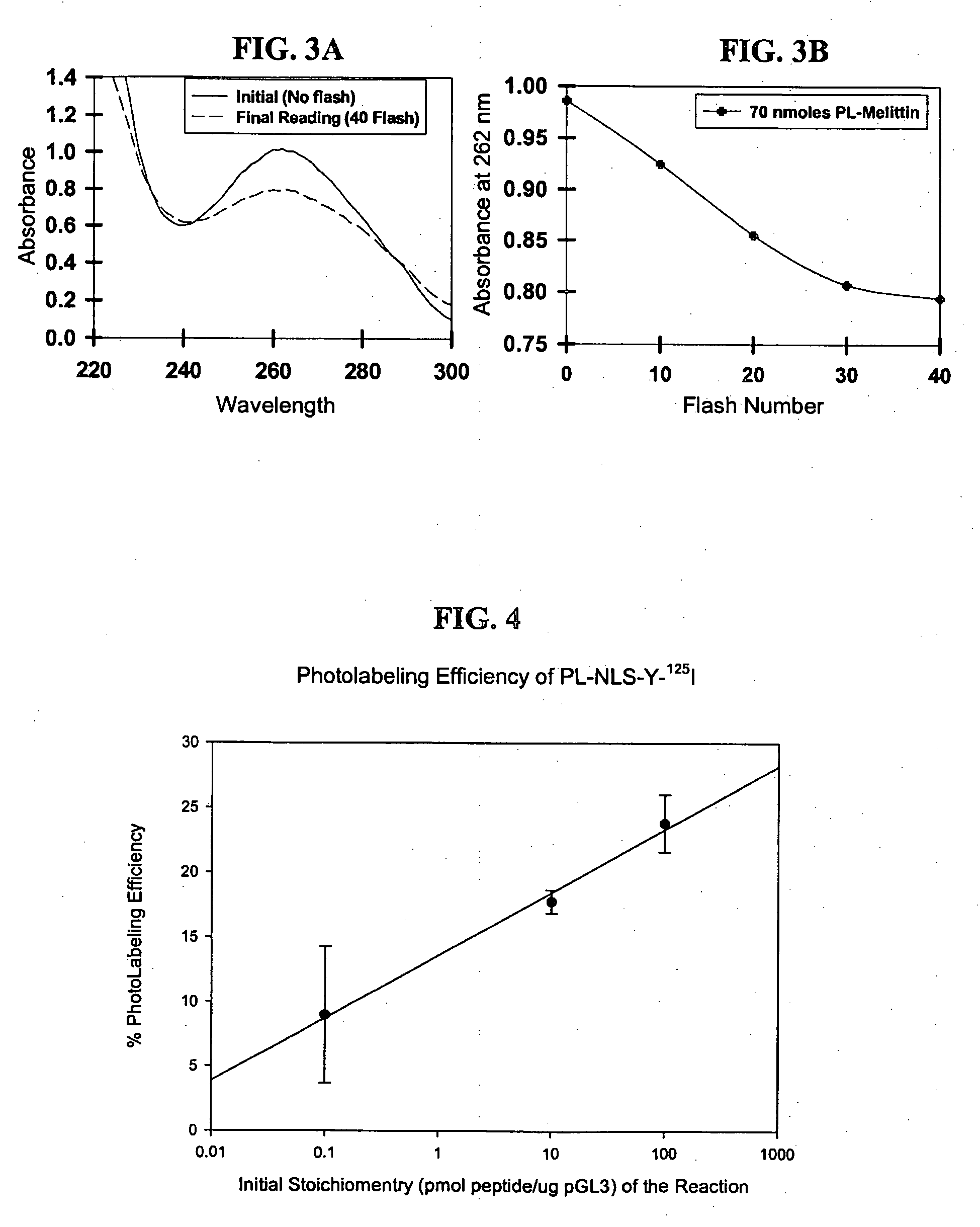
Compositions and methods are described for non-viral nucleic acid delivery. A targeting peptide capable of mediating targeting to a cell or subcellular compartment is derivatized with a photoaffinity label. Following an ionic interaction with a polynucleotide, such as DNA, and photolysis, the bioactive peptide becomes covalently attached to the DNA. Upon contact with a cell, the peptide facilities uptake of the peptide-polynucleotide conjugate into the cell or subcellular compartment. Methods for using this system for delivery of structural genes, including reporter genes, and detection of expression using bioluminescence are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Novel DNA-based vaccine against the encephalitis alphaviruses
InactiveUS20050118251A1BiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseCell freeEastern equine encephalitis virus
This invention relates to the development of a mammalian expression vector, under which expression of the structural genes of western equine encephalitis virus have been placed under the control of an eucaryotic promoter. When the recombinant vector is administered to mammalian cell culture or using a cell-free transcription / translation system, in vitro, authentic structural proteins of western equine encephalitis virus are produced as verified by reactivity with monoclonal antibodies developed to western equine encephalitis virus. When the recombinant DNA molecule is administered in vivo, a protective immune response is induced, thereby enhancing protection of the individual against subsequent infection by western equine encephalitis virus. In a similar manner, DNA vaccines to related alphaviruses (Venezuelan and eastern equine encephalitis viruses) could also be developed.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Cell culture system of a hepatitis c genotype 3a and 2a chimera
InactiveUS20100093841A1Efficient and sustainable growthDifferential efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenomic sequencingNS5A
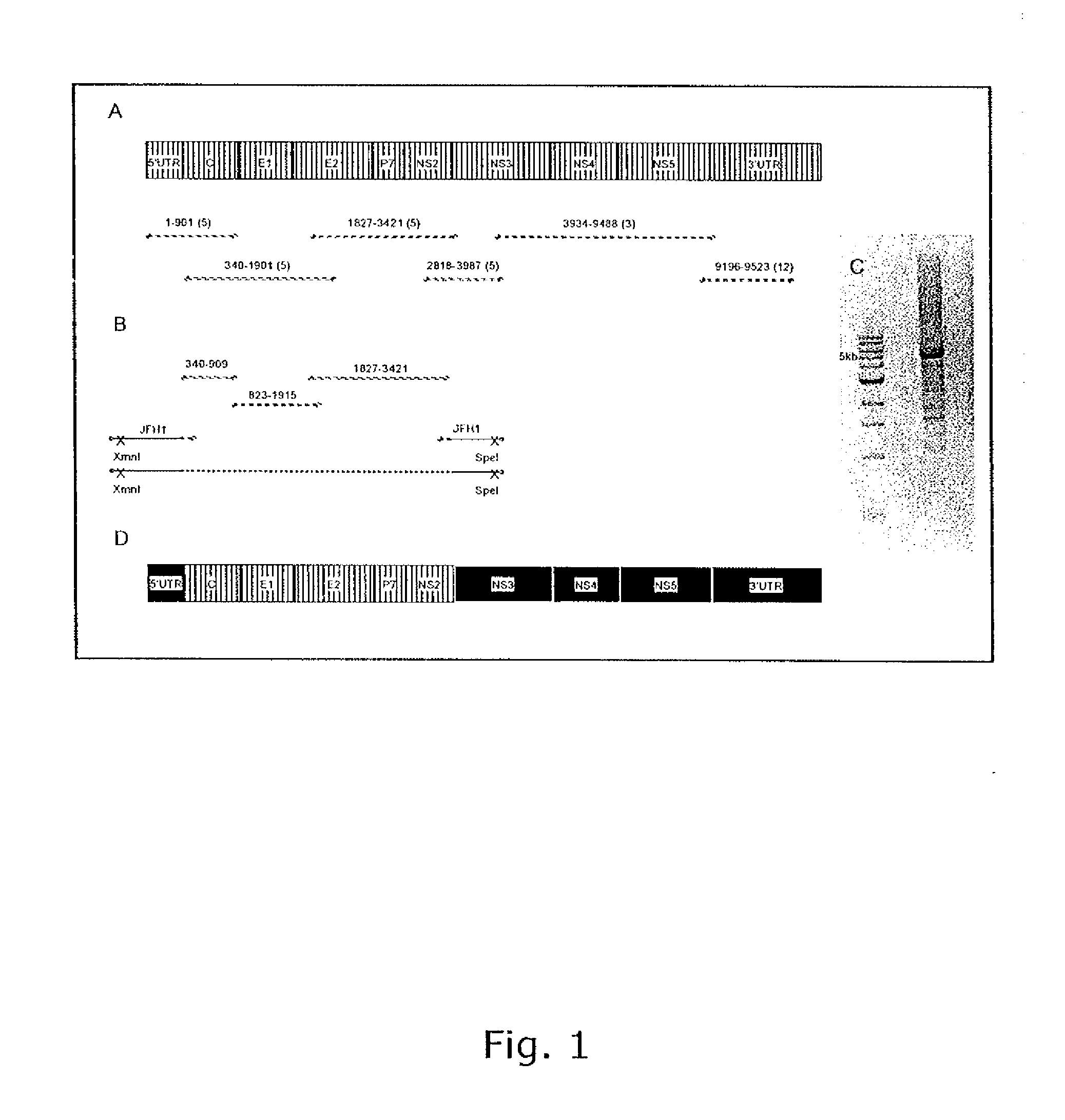
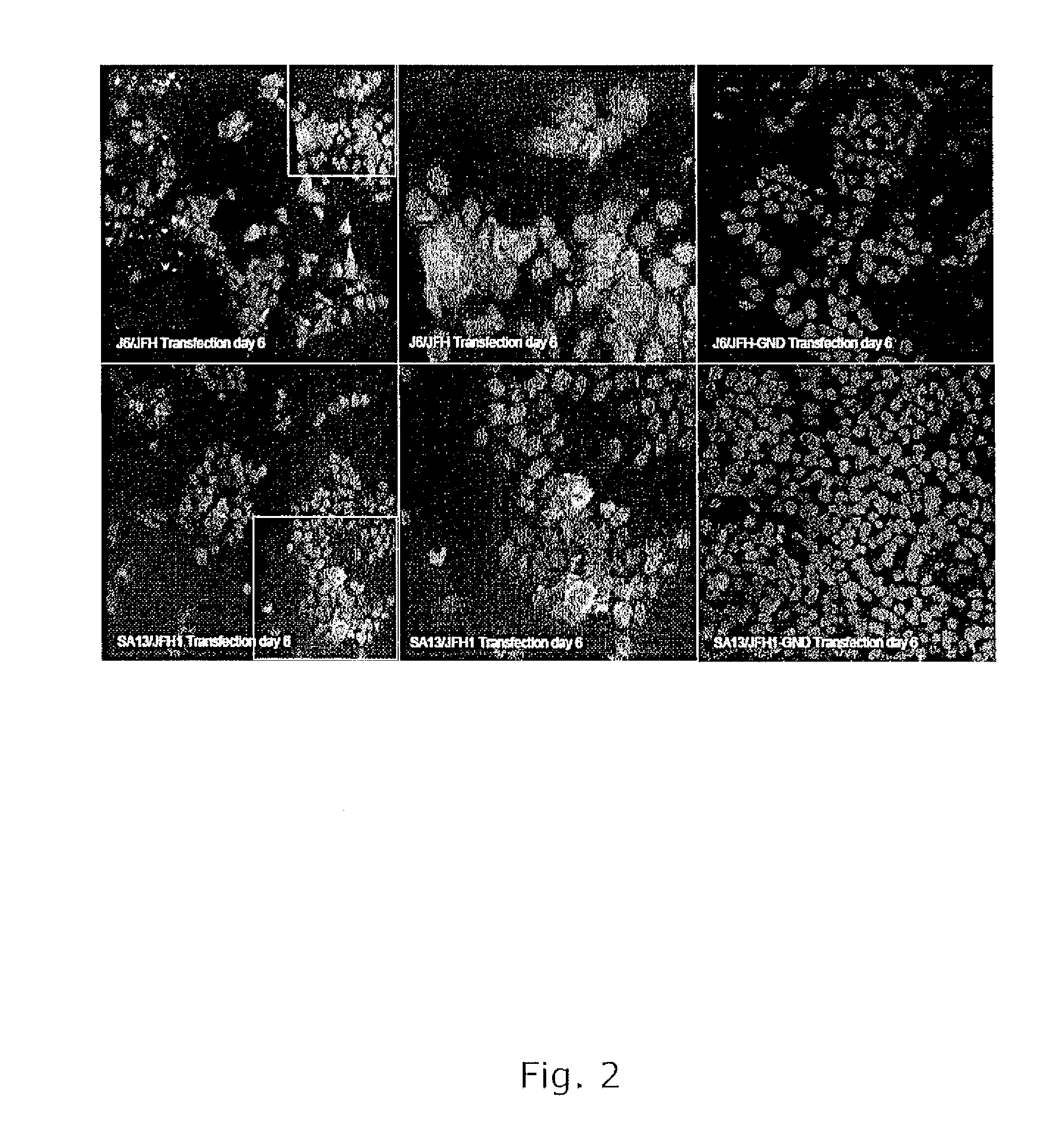
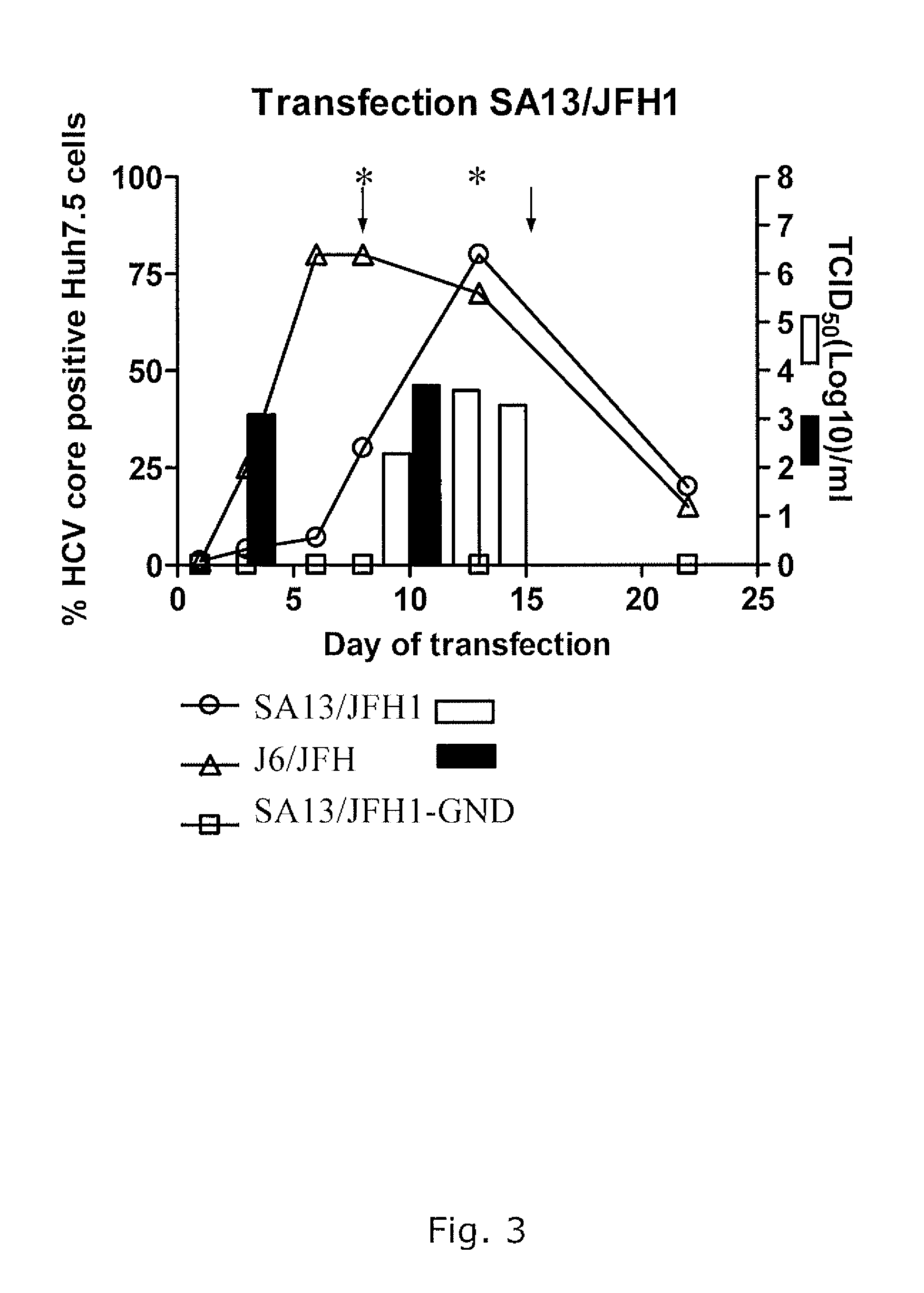
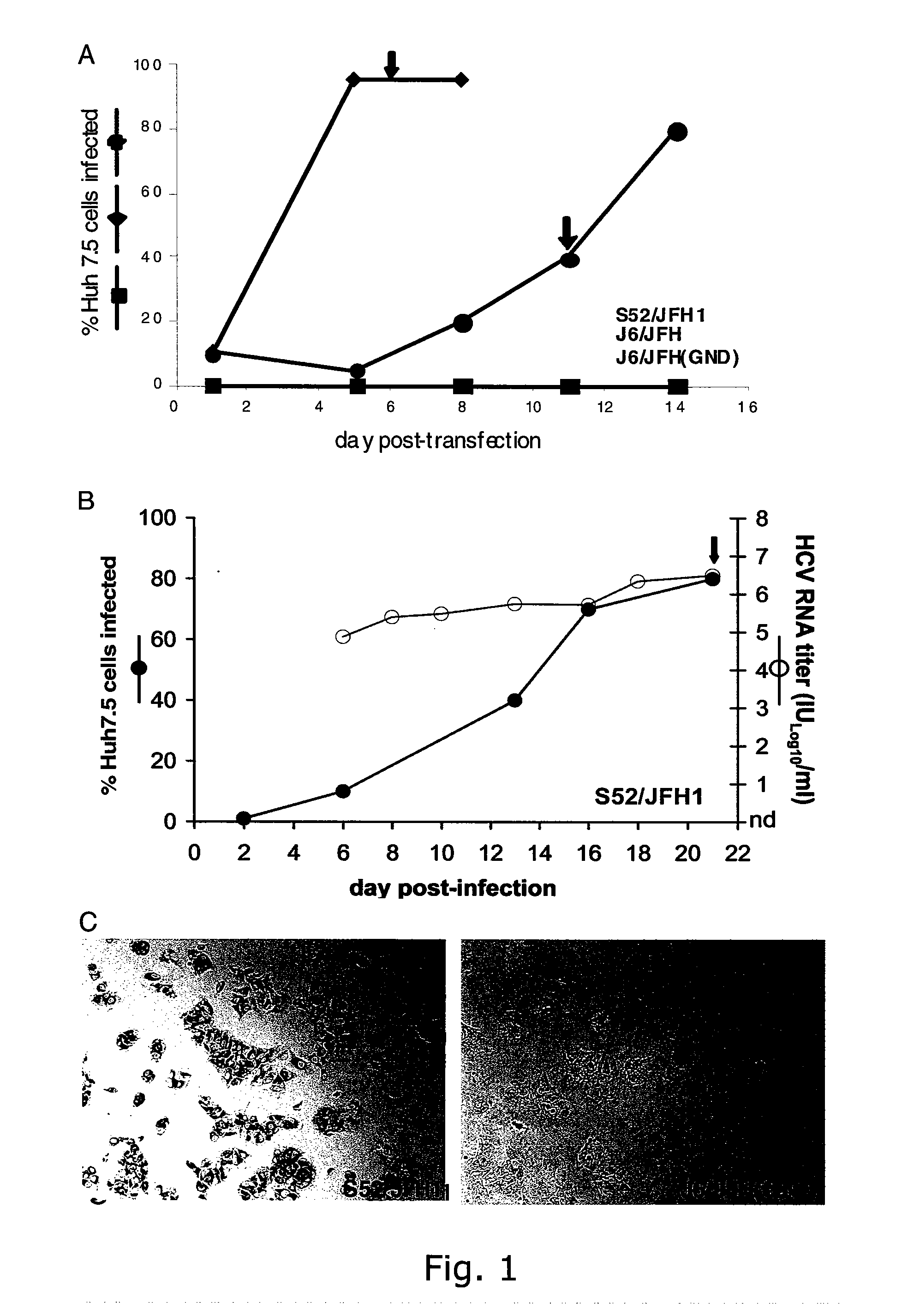
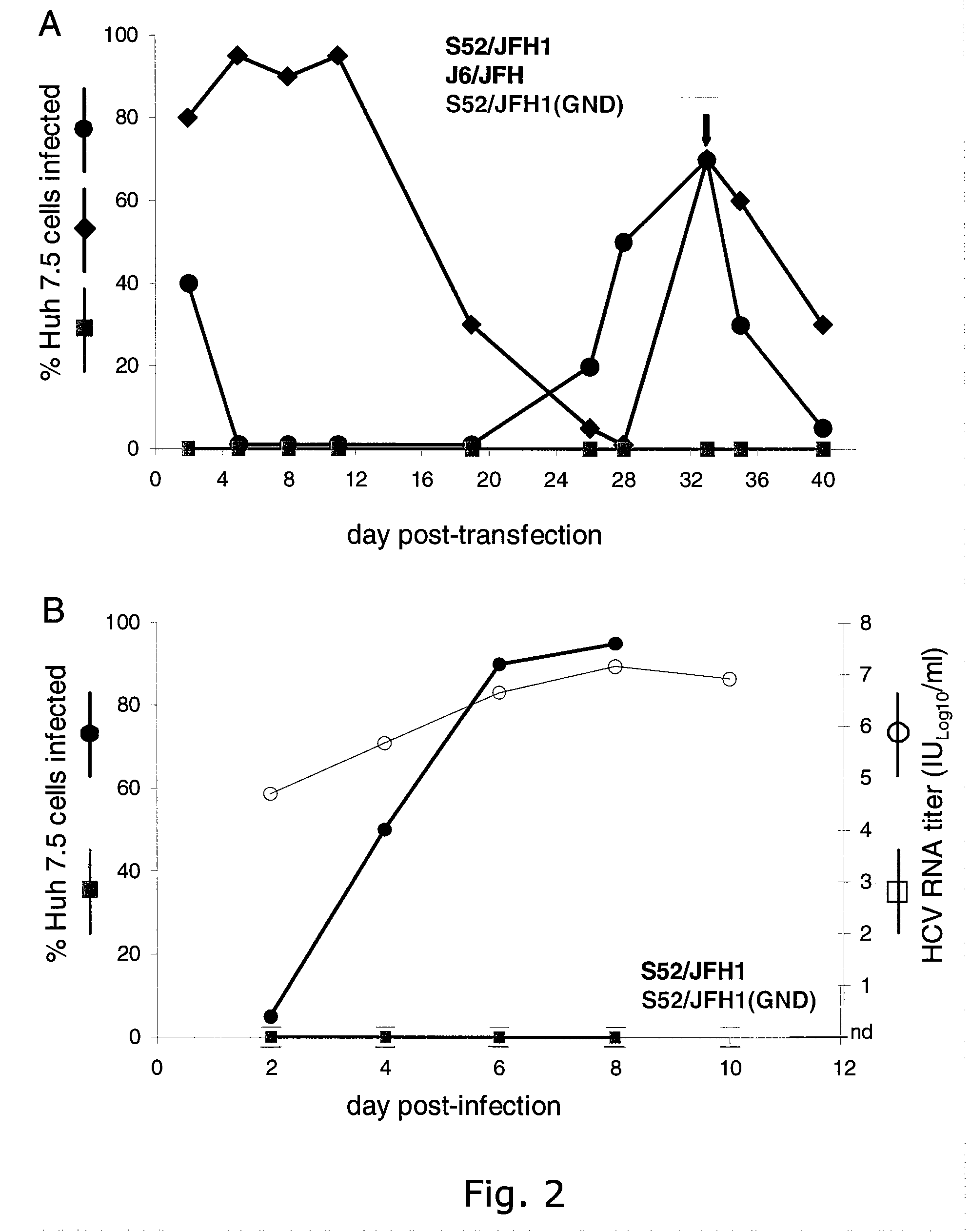
The present inventors have developed a culture system for genotype 3a, which has a high prevalence worldwide. Since intergenotypic recombinant genomes exploiting the replication characteristics of JFH1 will be a valuable tool for the genotype specific study of the replaced genes and related therapeutics, the present inventors constructed a genotype 3a / 2a (S52 / JFH1) recombinant containing the structural genes (Core, E1, E2), p7 and NS2 of strain S52 and characterized it in Huh7.5 cells. S52 / JFH1 and J6 / JFH viruses passaged in cell culture had comparable growth kinetics and yielded similar peak HCV RNA titers and infectivity titers. Direct genome sequencing of cell culture derived S52 / JFH1 viruses identified putative adaptive mutations in Core, E2, p7, NS3 and NS5A; clonal analysis revealed, that all genomes analyzed exhibited different combinations of these mutations. Finally, viruses resulting from transfection with RNA transcripts of five S52 / JFH1 recombinant containing these combinations of putative adaptive mutations performed as efficiently as J6 / JFH viruses in Huh7.5 15 cells and were all genetically stable after viral passage. In conclusion, the present inventors have developed a robust and genetically stable cell culture system for HCV genotype 3a.
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
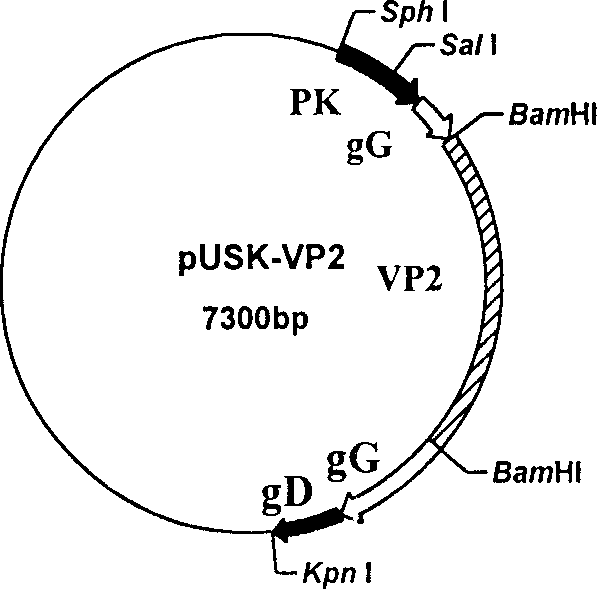
Recombinant pseudo-rabies virus expressing swine parvovirus VP2 gene and vacine and its preparation method
The present invention relates to main structure gene VP2 of artificial constructed pseudorabies virus, PrV and porcine parvovirus, PPV. In the pseudorabies virus genome in which the main toxicity gene (TK) and virus generation nonessential gene (gG) are deleted the VP2 gene of porcine parvovirus can be site-specifically inserted to make it be positioned in strong late promoter downstream of pseudorabies virus, and the inserted exogenous gene coded protein has good immunogenicity, and can stimulate swine to produce protective immune reaction for resisting two virulent challenges of porcine parvovirus and pseudorabies virus. Said invention also includes recombinant pseudorabies virus, Hzau AVL-PRppvV-VP2, vaccine prepared by using it and its preparation method.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
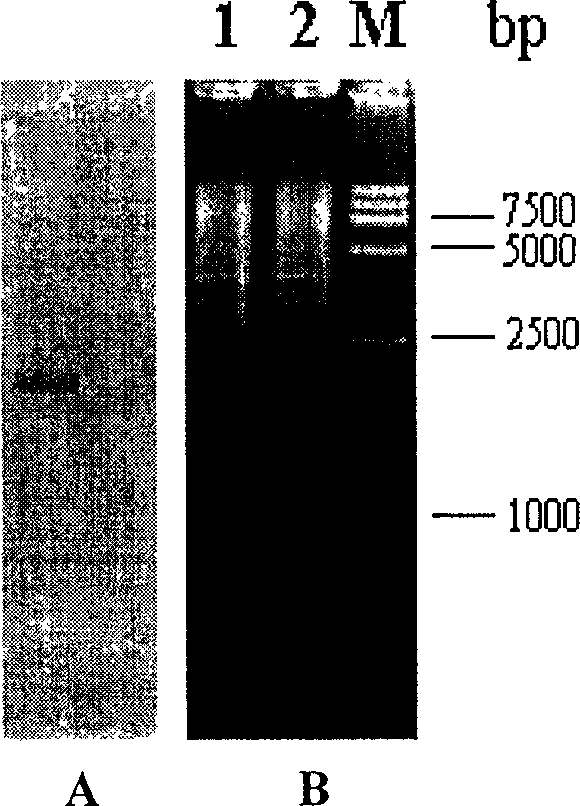
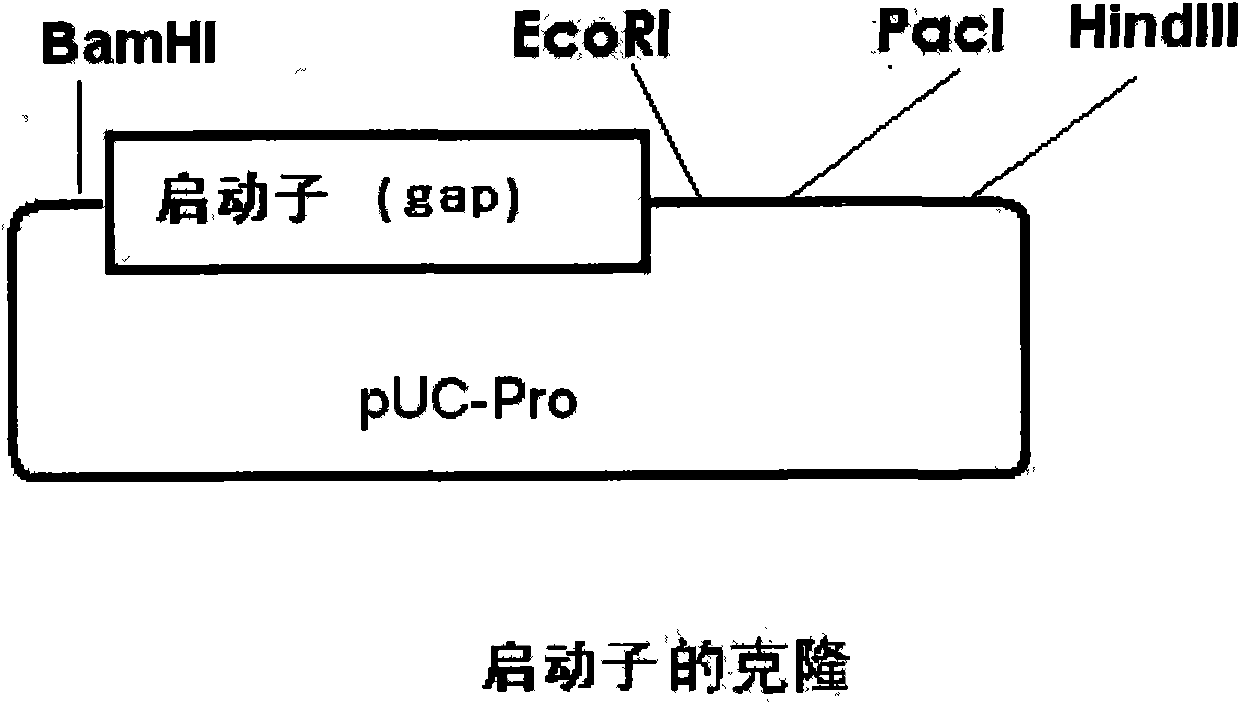
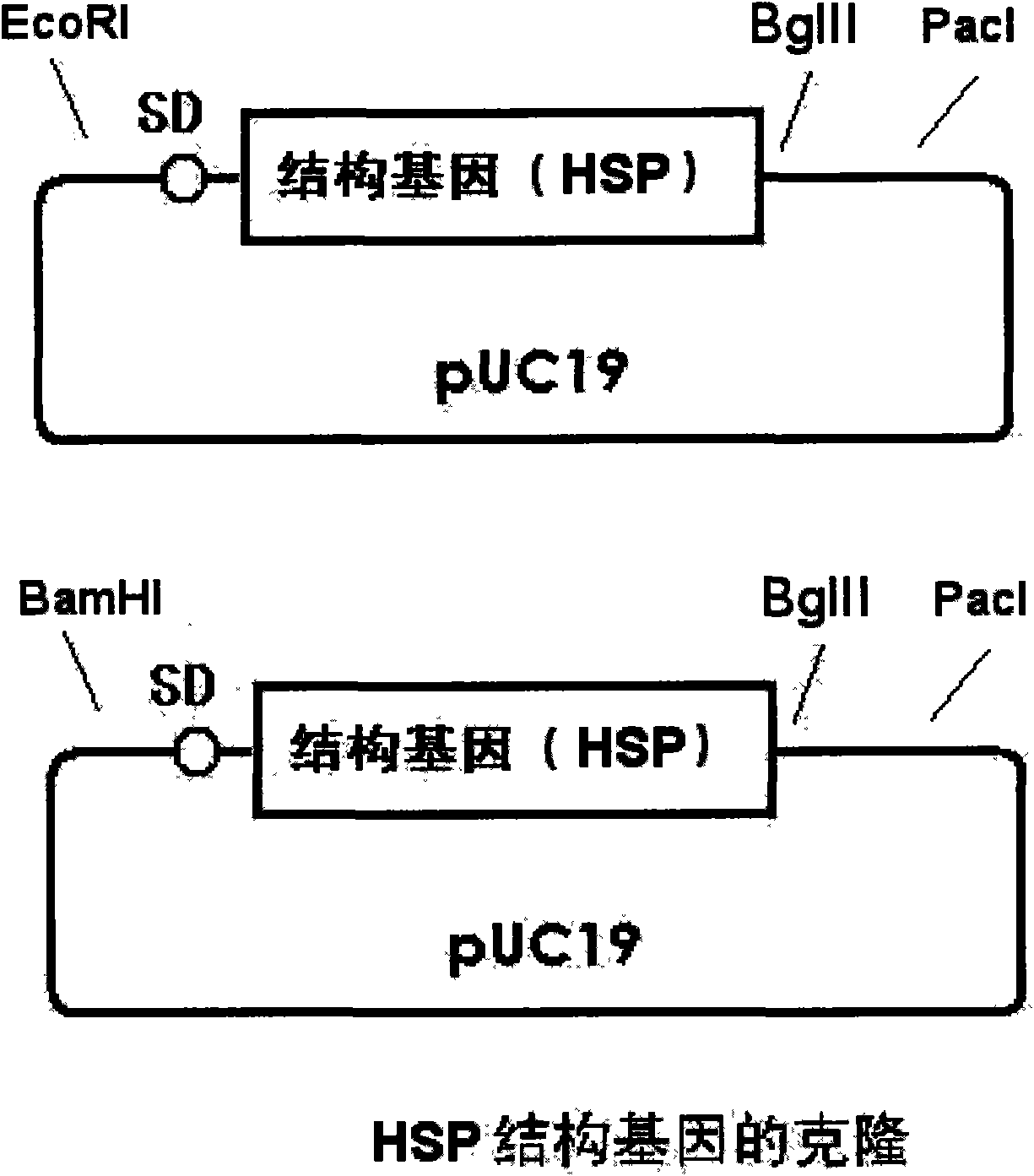
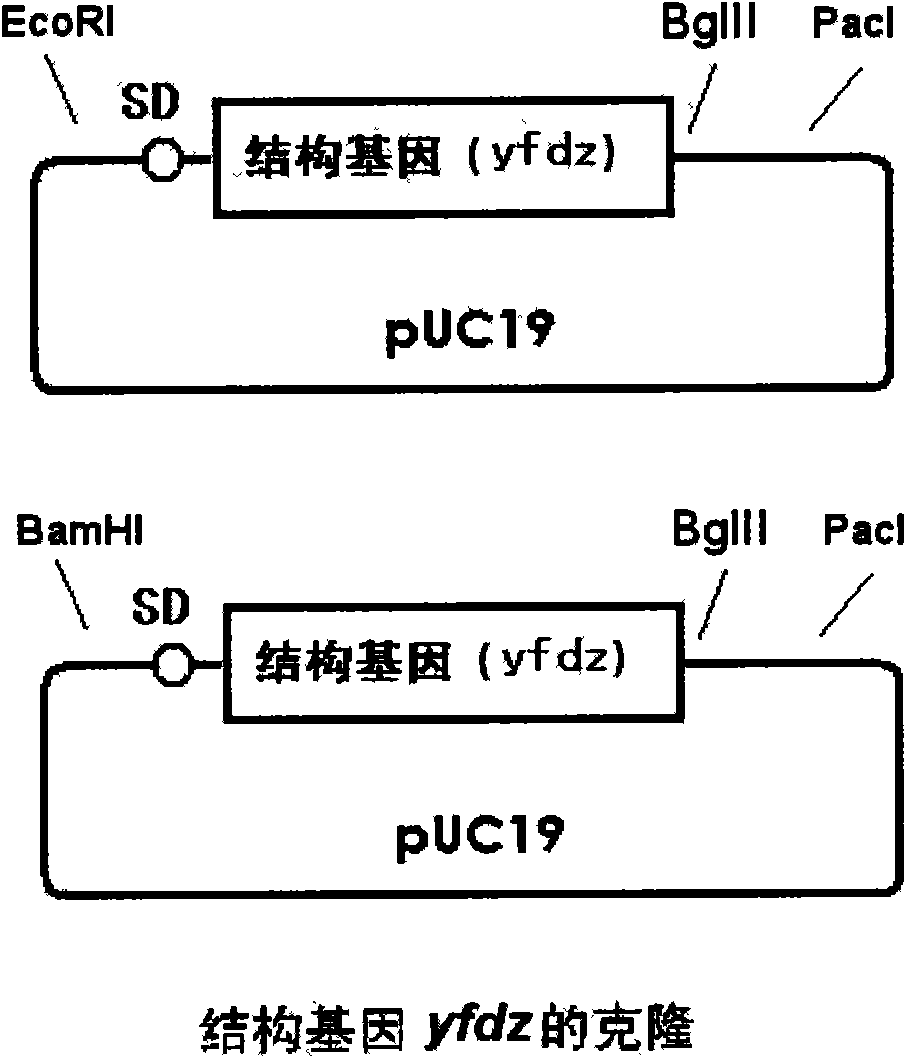
Establishment of gene recombination mobile fermentation monad applied to alcoholic fermentation
The invention relates to a method for applying establishment of gene recombination mobile fermentation monad to alcoholic fermentation. The microorganism is obtained by leading an operon capable of expressing in the mobile fermentation monad, wherein the operon consists of a sequence for coding a promoter and a sequence for coding a structure gene and comprises a sequence coding at least one promoter, and the sequence of the promoter can be identified by the mobile fermentation monad and regulates expression of at least more than one structural gene. The operon comprises a sequence for coding at least one heat shock protein HSP and is used for enhancing the survivability of the mobile fermentation monad in an adverse environment and increasing the temperature of alcoholic fermentation; the operon comprises a sequence for coding at least one lysine anabolism enzyme yfdz so that the mobile fermentation monad can automatically synthesize lysine; the operon comprises a sequence for coding at least one methionine anabolism enzyme metB so that the mobile fermentation monad can automatically synthesize methionine used for lowering the nutrition requirement of the mobile fermentation monad for cultures; and the operon also comprises a sequence for coding a structural gene, which ensures that the mobile fermentation monad can utilize at least one pentaose to generate. The operon enters the mobile fermentation monad in a plasmid transforming way or integrated with the genome of the mobile fermentation monad to obtain a transporton recombinant in a transporton way. The mobile fermentation monad obtained by gene engineering enhances the survivability in an adverse environment, can be fermented to generate the alcohol under higher temperature, obviously lowers the nutrition requirement for the cultures, can utilize the pentaoses to generate the alcohol and still stably retains the characteristics after transfer of culture for 200 times.
Owner:WUHAN CNZYME BIOTECH
Efficient cell culture system for hepatitis c virus genotype 1a and 1b
The present inventors developed hepatitis C virus 1a / 2a and 1b / 2a intergenotypic recombinants in which the JFH1 structural genes (Core, E1 and E2), p7 and NS2 were replaced by the corresponding genes of the genotype Ia reference strain H77C or TN or the corresponding genes of the genotype Ib reference strain J4. Sequence analysis of recovered 1a / 2a and 1b / 2a recombinants from 2 serial passages and subsequent reverse genetic studies revealed adaptive mutations in e.g. p7, NS2 and / or NS3. In addition, the inventors demonstrate the possibility of using adaptive mutations identified for one HCV isolate in generating efficient cell culture systems for other isolates by transfer of mutations across isolates, subtypes or major genotypes. Furthermore neutralization studies showed that viruses of e.g. genotype 1 were efficiently neutralized by genotype Ia, 4a and 5a serum, an effect that could be utilized e.g. in vaccine development and immunological prophylaxis. The inventors in addition demonstrate the use of the developed systems for screening of antiviral substances in vitro and functional studies of the virus, e.g. identification of receptors required for HCV entry
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
Compositions and methods for nucleic acid delivery
ActiveUS20080213898A1Reduce deliveryIncrease gene expressionGenetic material ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsNucleotideViral nucleic acid
Compositions and methods are described for non-viral nucleic acid delivery. A targeting peptide capable of mediating targeting to a cell or subcellular compartment is derivatized with a photoaffinity label. Following an ionic interaction with a polynucleotide, such as DNA, and photolysis, the bioactive peptide becomes covalently attached to the DNA. Upon contact with a cell, the peptide facilities uptake of the peptide-polynucleotide conjugate into the cell or subcellular compartment. Methods for using this system for delivery of structural genes, including reporter genes, and detection of expression using bioluminescence are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Novel p. pastoris pastoris promoters, and the use thereof to direct expression of proteins in yeast, preferably using a haploid mating strategy
Novel promoters which are derived from P. pastoris pastoris which are inducible or repressible under specific growth conditions are provided. These promoters are useful for regulating the expression of a desired structural gene, e.g., a mammalian polypeptide. Particularly preferred is the use of these novel promoters to regulate gene expression in polyploidal yeast such as diploidal P. pastoris produced by mating or spheroplast fusion.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Efficient cell culture system for hepatitis c virus genotype 6a
InactiveUS20110059512A1Raise the potentialSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesSequence analysisHCV Genotyping
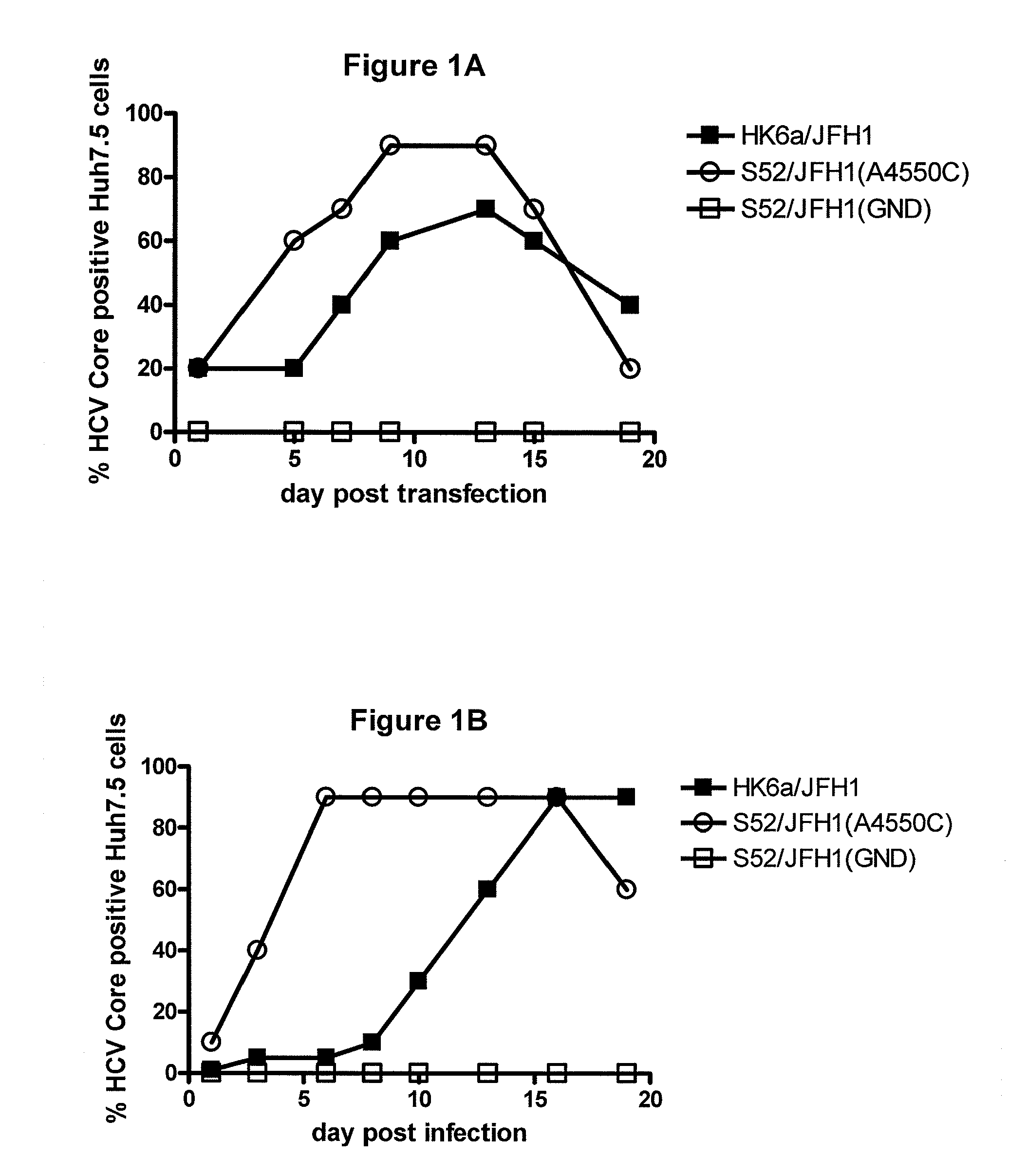
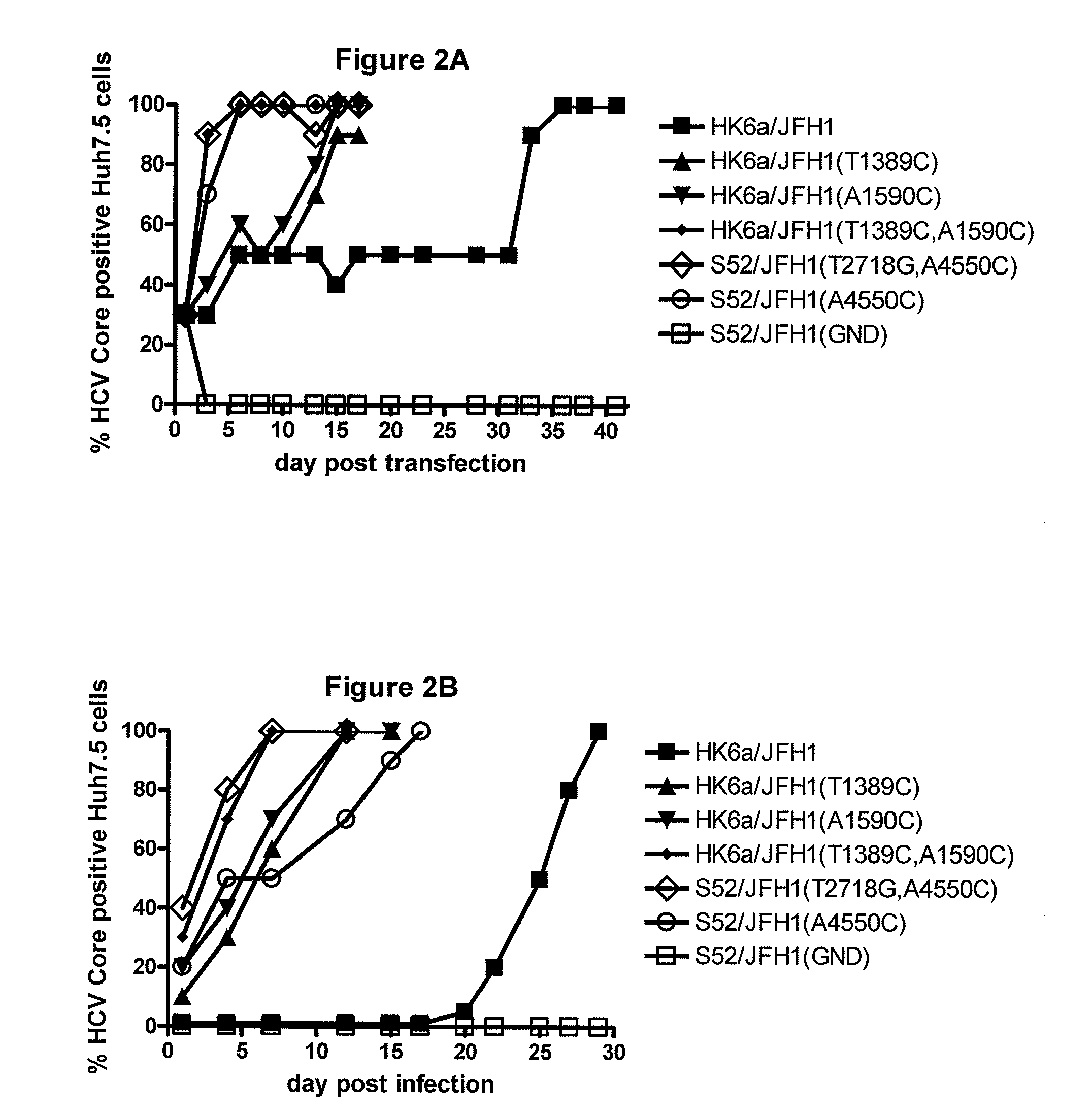
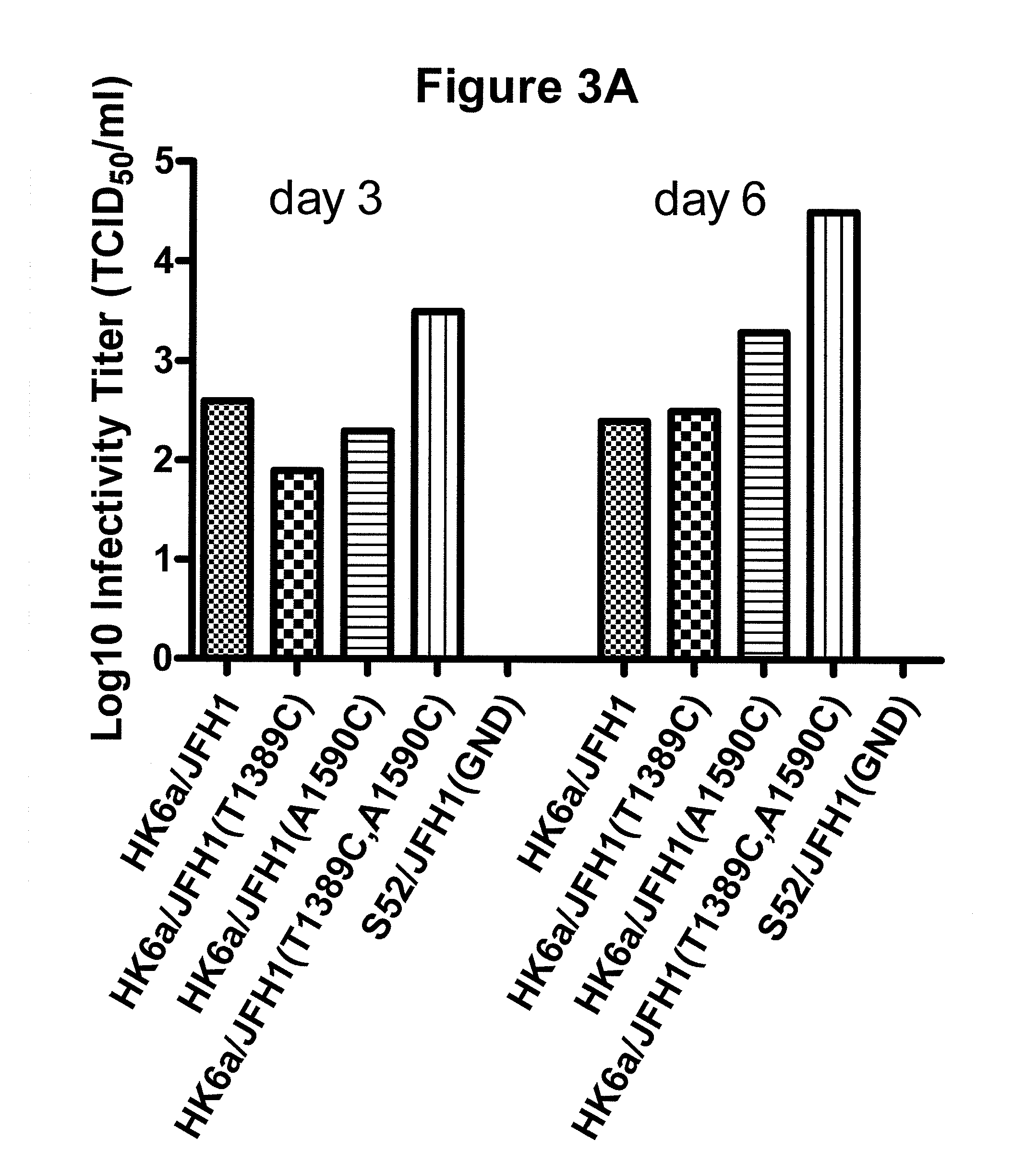
The present inventors developed hepatitis C virus 6a / 2a intergenotypic recombinants in which the JFH1 structural genes (Core, E1 and E2), p7 and the complete NS2 were replaced by the corresponding genes of the genotype 6a reference strain HK6a. Sequence analysis of recovered 6a / 2a recombinants from 2 transfection experiments and subsequent reverse genetic studies revealed adaptive mutations in E1 and E2. Conclusion: The developed 6a / 2a viruses provide a robust in vitro tool for research in HCV genotype 6, including vaccine studies and functional analyses.
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
Method for regulating and controlling expression level of saccharomyces cerevisiae genes by using terminators
InactiveCN107326041ARegulated expression strengthEasy to operateVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionMetabolic pathwayComputational biology
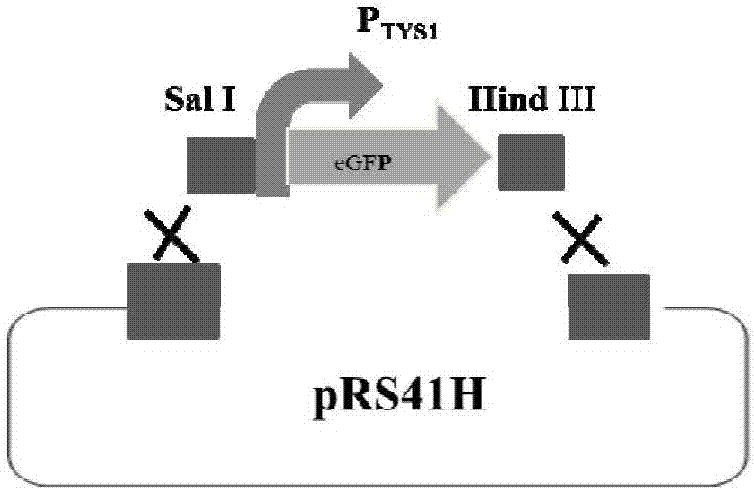
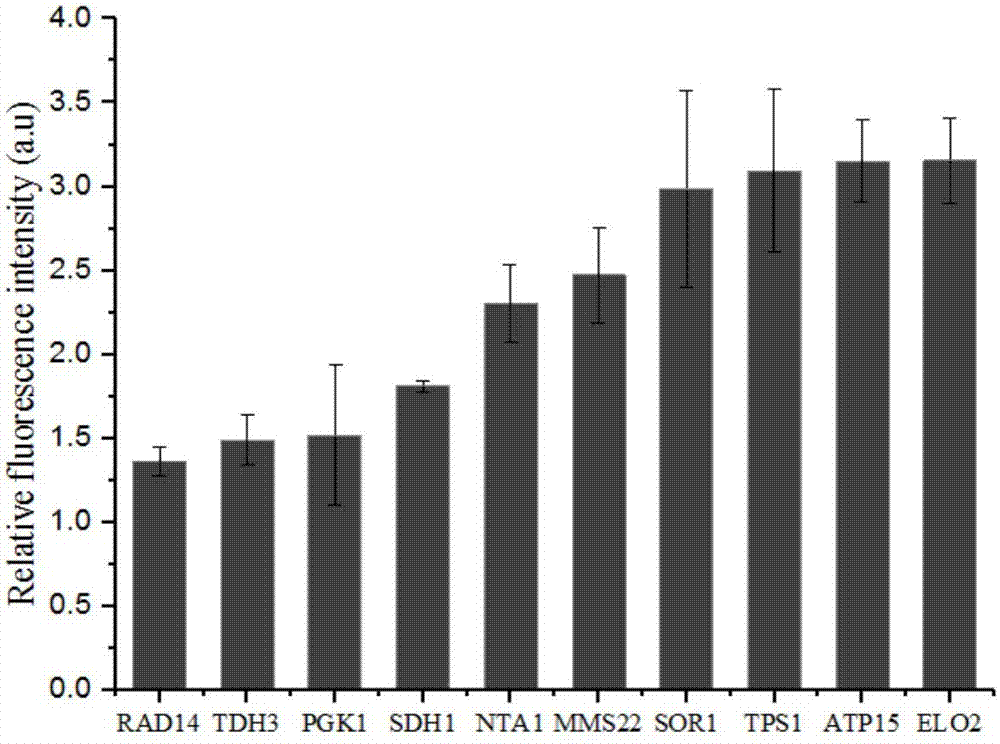
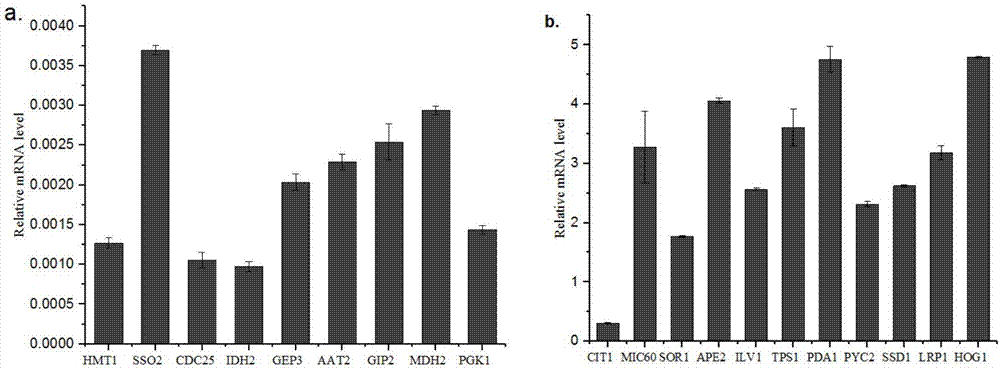
The application discloses a method for regulating and controlling the expression level of saccharomyces cerevisiae genes by using terminators and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a terminator verification carrier containing a promoter and a reporter gene; analyzing sequence information of 3'-UTR (Untranslated Region) terminators on the downstreams of saccharomyces cerevisiae structural genes by bioinformatics, amplifying the terminators and connecting the amplified terminator with the terminator verification carrier to form a terminator library. By replacing or changing the terminators in a gene expression cassette, regulation and control of the expression level of target genes or pathways can be realized from the transcription and translation levels; the method provides an efficient fine regulation and control means for optimizing a metabolic pathway of yeast, and facilitates efficient and balanced expression of exogenous genes or pathways in yeast cells.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com