Method for regulating and controlling expression level of saccharomyces cerevisiae genes by using terminators
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae, gene expression technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of limited production concentration of target products, limited regulatory elements, imbalanced metabolic flow, etc., to achieve efficient and balanced expression, flexible use, high-efficiency fine-tuning means Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
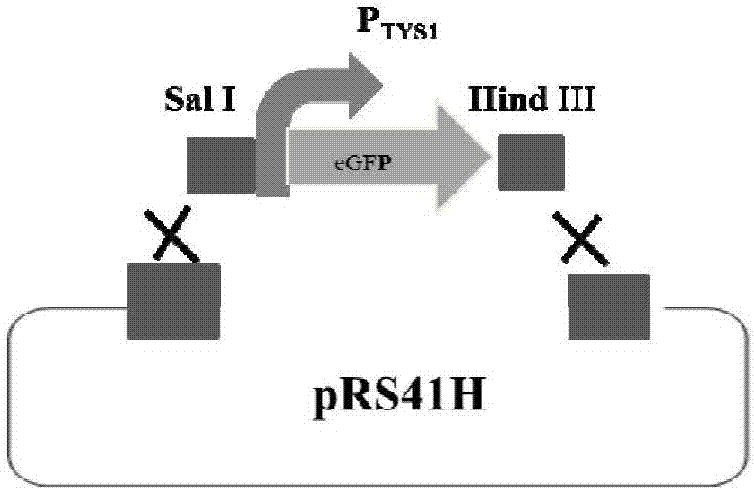
[0016] Embodiment 1: Construction of terminator verification vector
[0017] Step 1: Obtain the Saccharomyces cerevisiae constitutive promoter TYS1p gene sequence from the Genbank gene bank, extract the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome, and amplify to obtain the TYS1p gene fragment.
[0018] The primer sequences are:
[0019] Primer 1: 5'> ACGCGTCGAC TCCTTGCGCTTACTCGAATA<3', the underlined sequence is the overlapping sequence with the Sal I restriction site.
[0020] Primer 2: 5'> GGGACAACTCCAGTGAAAAGTTCTTCTCCCTTGCTCACCAT TGTTATCGTCAATTAGAG<3', the underlined sequence is the overlapping sequence with the reporter gene eGFP.
[0021] Step 2. Obtain the reporter gene eGFP fragment from the Genbank gene bank, and amplify the eGFP gene fragment after chemical synthesis.
[0022] The primer sequences are:
[0023] Primer 4: 5'> TCCATAACCGCATACTTCTAATTGACGATAACA ATGGTGAGCAAGGGAGAAGAACTTTTC<3', the underlined sequence is the overlapping sequence with the promoter TYS1p.
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: Construction of terminator library
[0028] Step 1: Query the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome sequence in the NCBI database, obtain the 3'-UTR terminator sequence information downstream of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae structural gene through bioinformatics analysis, design primers, and amplify to obtain the terminator. Taking the terminator TPS1t as an example, the 3'-UTR terminator gene sequence of the TPS1t structural gene was obtained from the NCBI database, and primers were designed to amplify the gene fragment of the terminator TPS1t.
[0029] The primer sequences are:
[0030] Primer 14: 5'> CCTGGGATTACACATGGCATGGATGAACTATACAAATAAATGAACCCGATGCAAATGAG <3', the underlined sequence is the overlapping sequence with the eGFP reporter gene.
[0031] Primer 15: 5'> GCTCCACCGCGGTGGCGGCCGCTCTAGAACTAGTGGATCTTTTTGTCTTTCTTCAAATTG <3', the underlined sequence is the overlapping sequence with the pRS41H plasmid.
[0032] Step 2: Pick a single colony of Esche...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: The regulatory effect of terminators on the expression intensity of fluorescent proteins
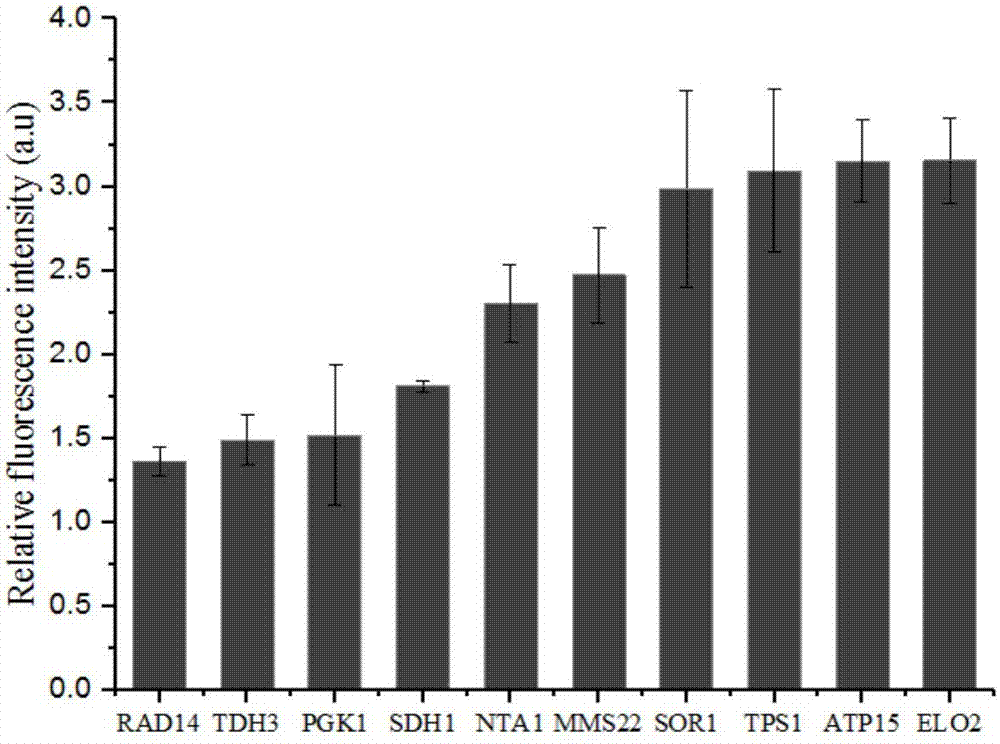
[0041] Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformants containing different terminator expression vectors were randomly selected from the terminator library, inoculated in 10 mL medium containing 2% glucose, 2% peptone and 1% yeast powder, and cultured with shaking at 30°C and 200rpm for 36 hours. The fluorescence intensity of intracellular eGFP was detected by flow cytometry, and the fluorescence intensity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C was used as a blank, and the fluorescence intensity of the terminator PGK1t was used as a reference. It was found that the terminator can effectively regulate yeast gene expression at the translation level (see attached figure 2 ), the order of fluorescent protein expression intensity as terminator RAD14t, TDH3t, SDH1t, NTA1t, MMS22t, SOR1t, TPS1t, ATP15t and ELO2t is:
[0042] RAD14t
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com