Patents
Literature
393 results about "Transcriptional regulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology and genetics, transcriptional regulation is the means by which a cell regulates the conversion of DNA to RNA (transcription), thereby orchestrating gene activity. A single gene can be regulated in a range of ways, from altering the number of copies of RNA that are transcribed, to the temporal control of when the gene is transcribed. This control allows the cell or organism to respond to a variety of intra- and extracellular signals and thus mount a response. Some examples of this include producing the mRNA that encode enzymes to adapt to a change in a food source, producing the gene products involved in cell cycle specific activities, and producing the gene products responsible for cellular differentiation in multicellular eukaryotes, as studied in evolutionary developmental biology.
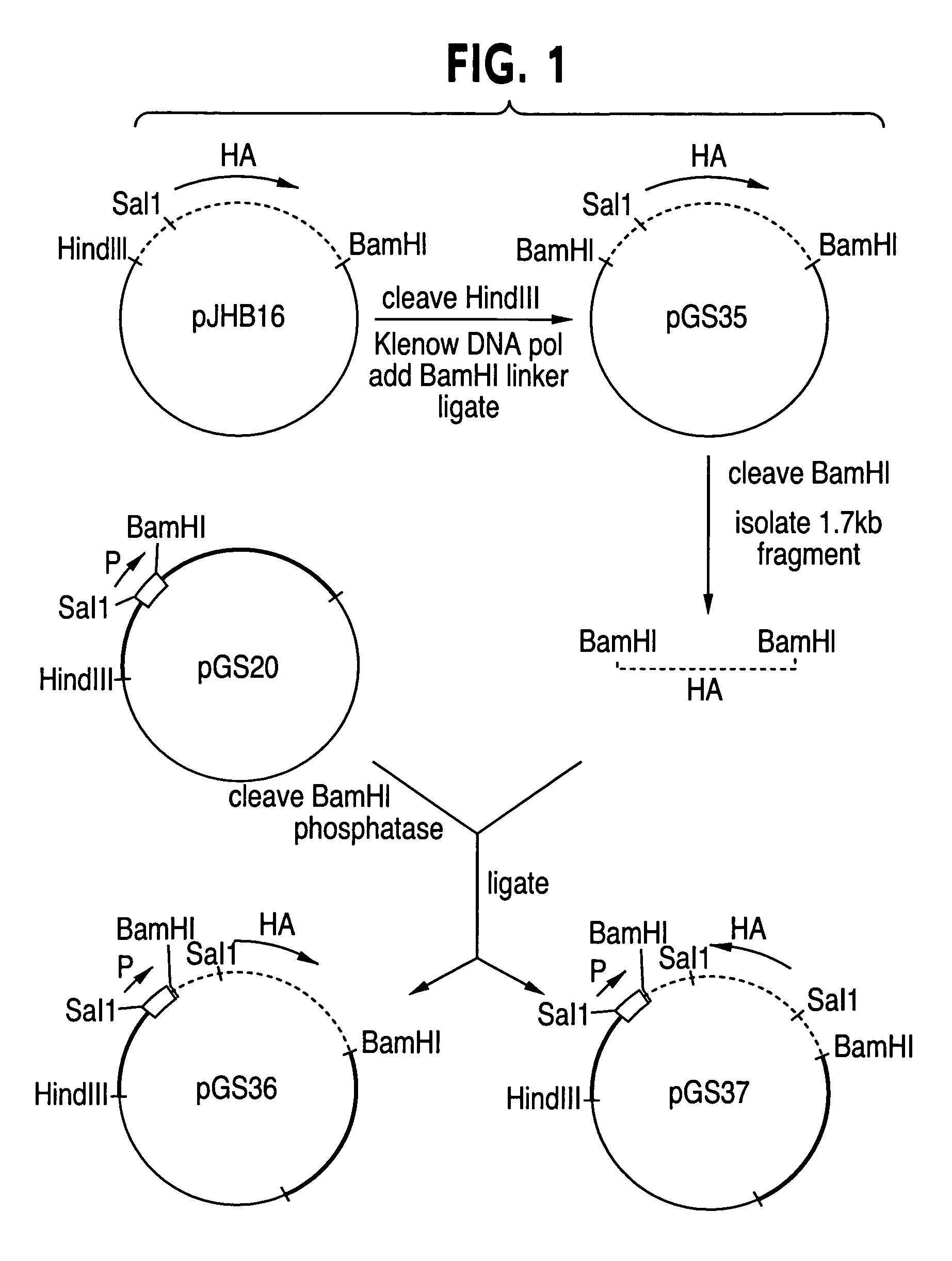
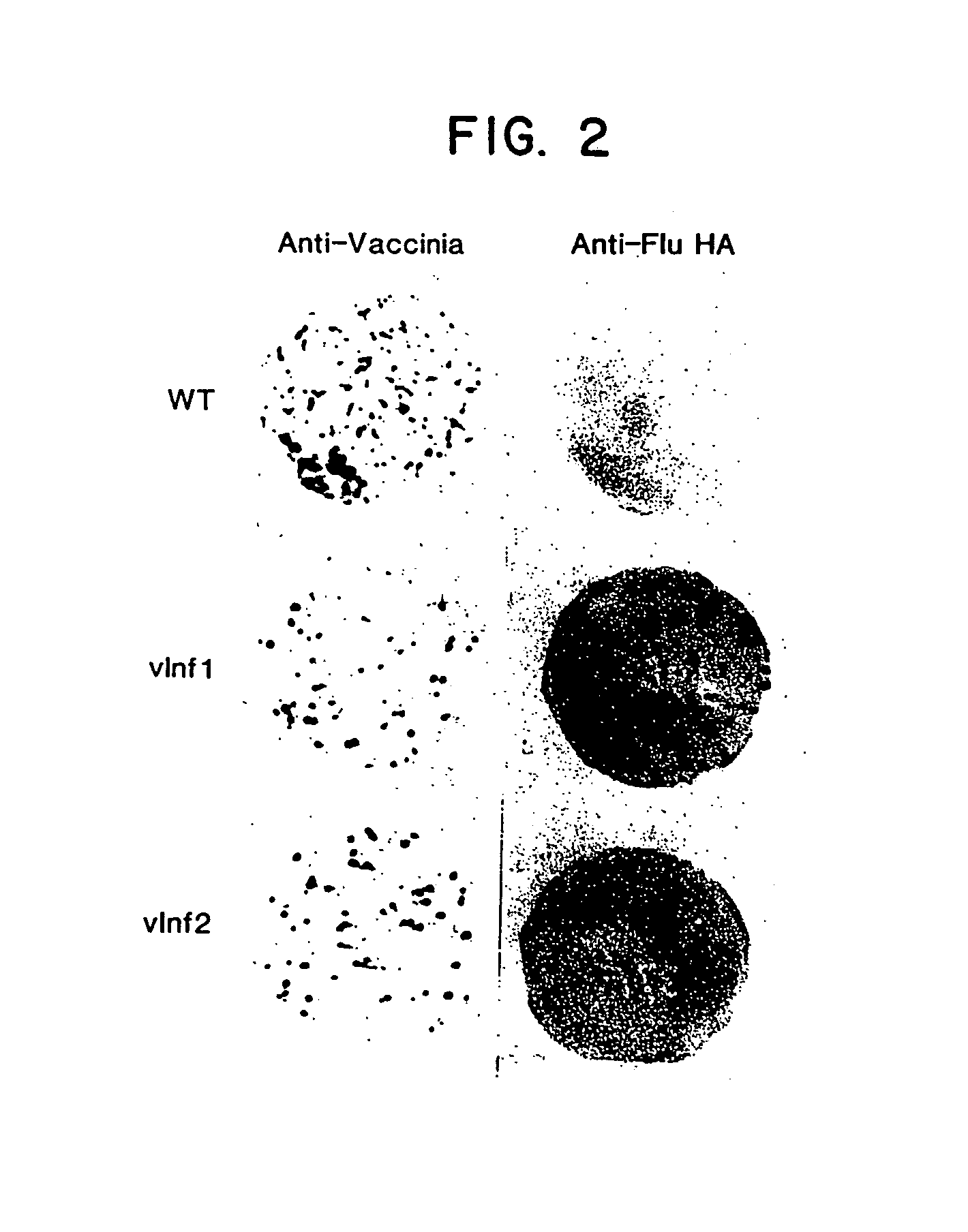
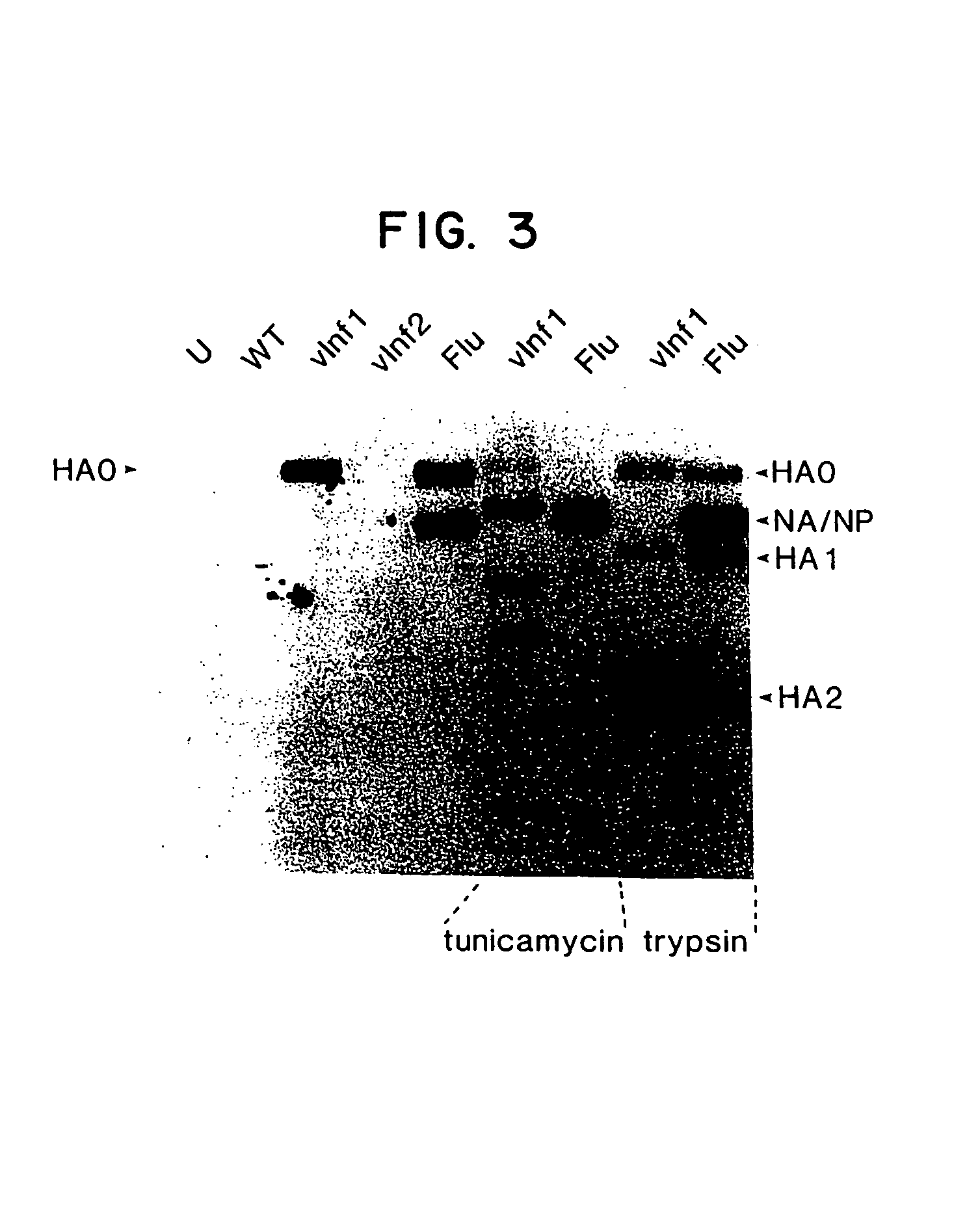
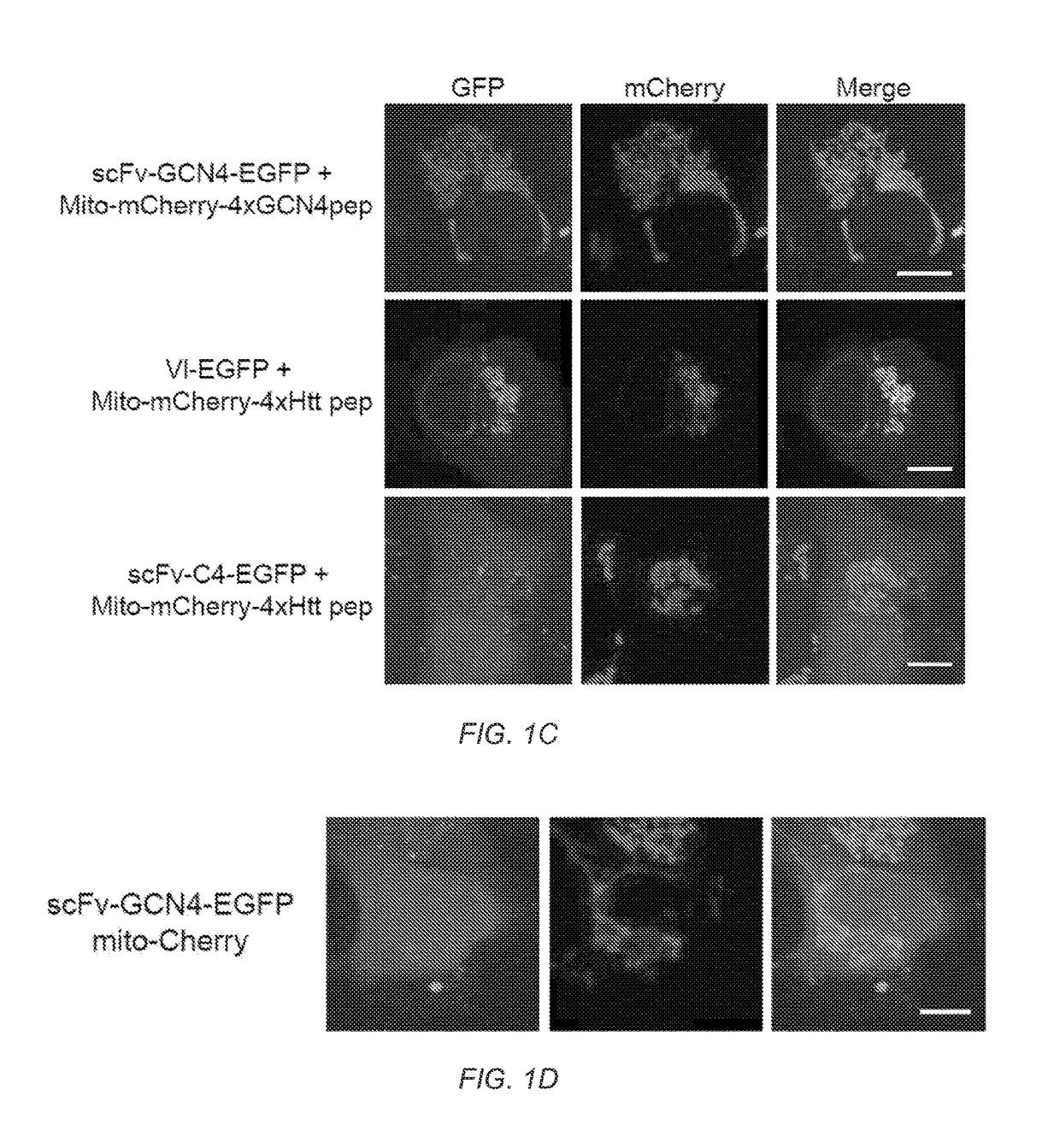
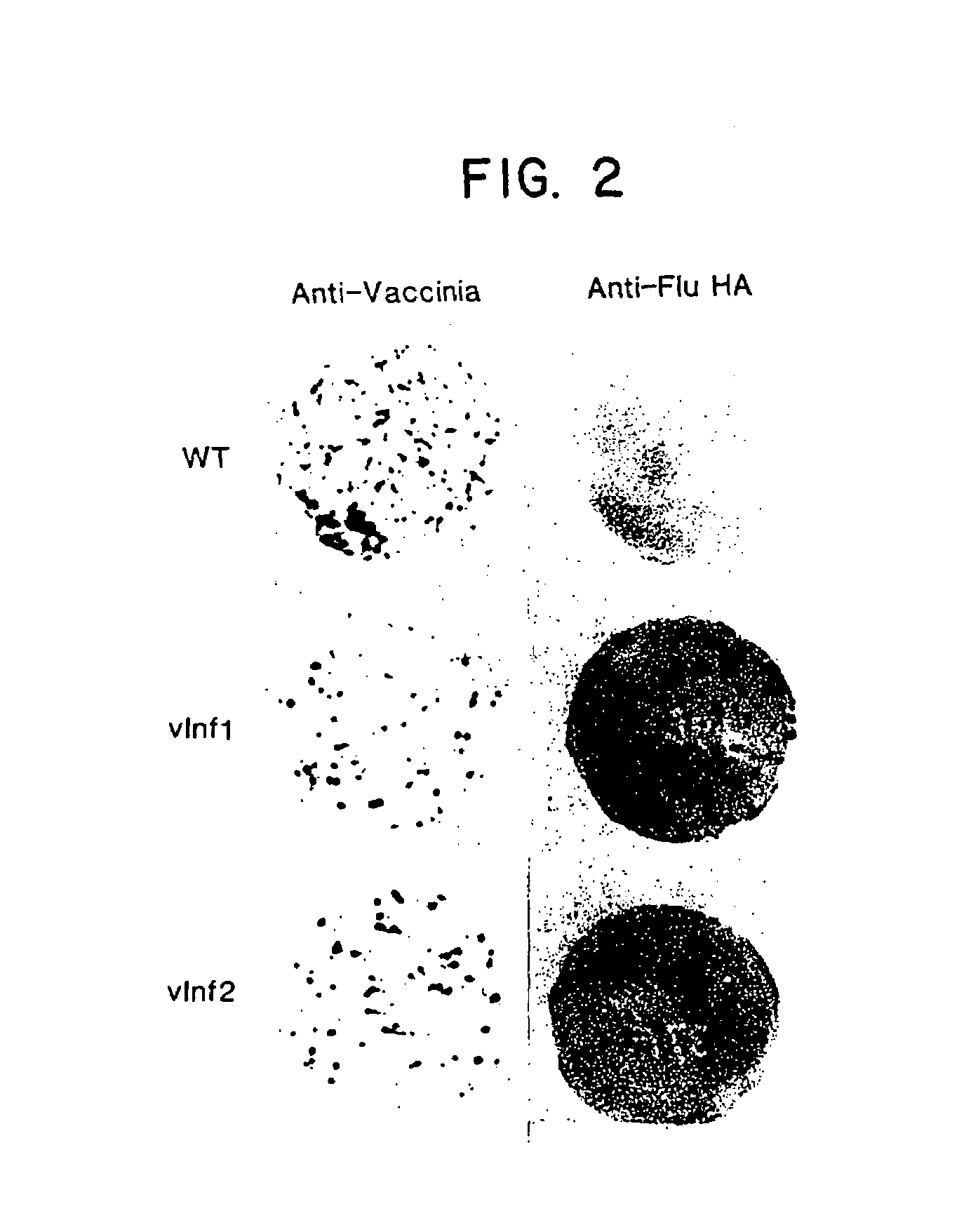
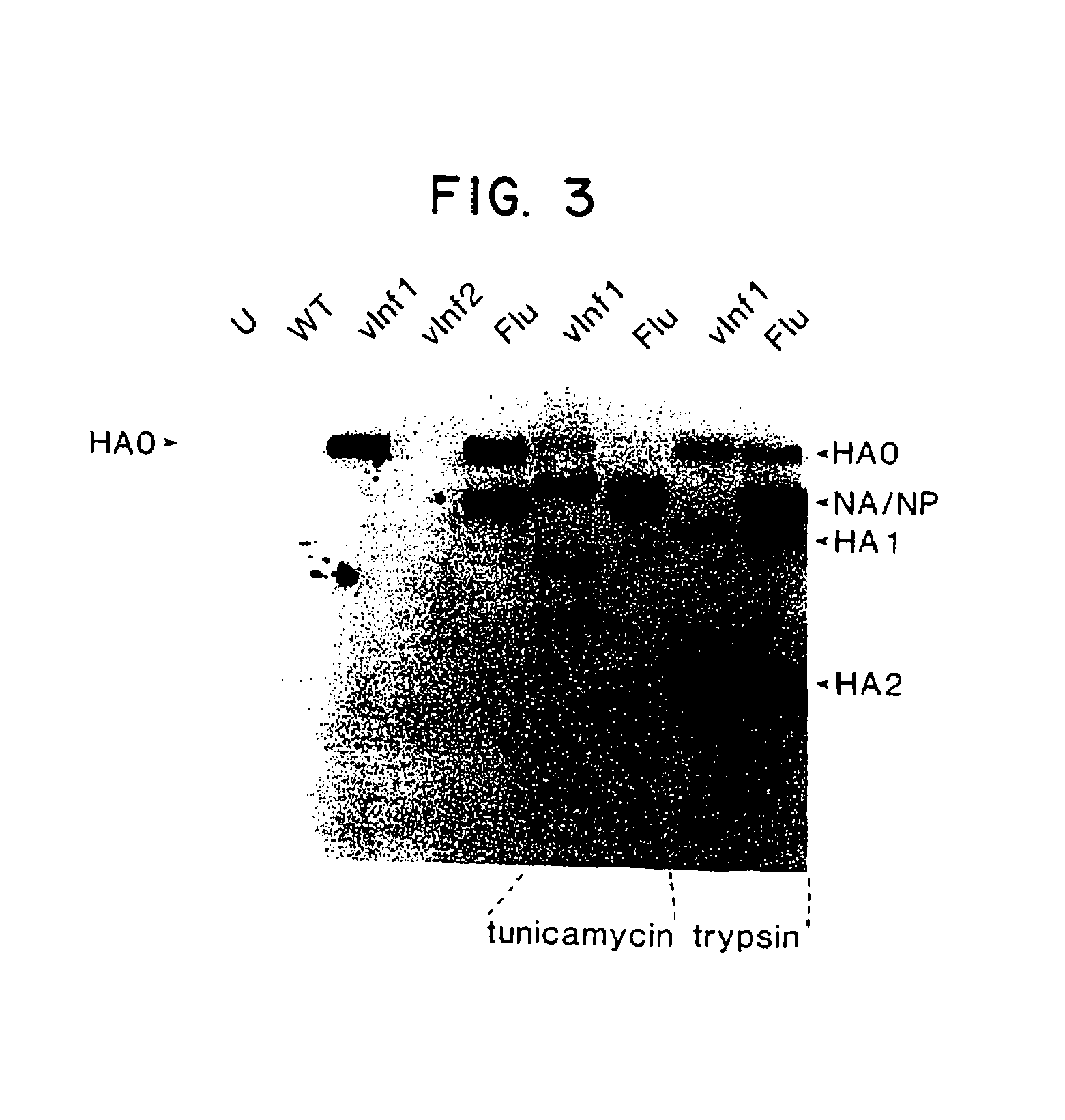
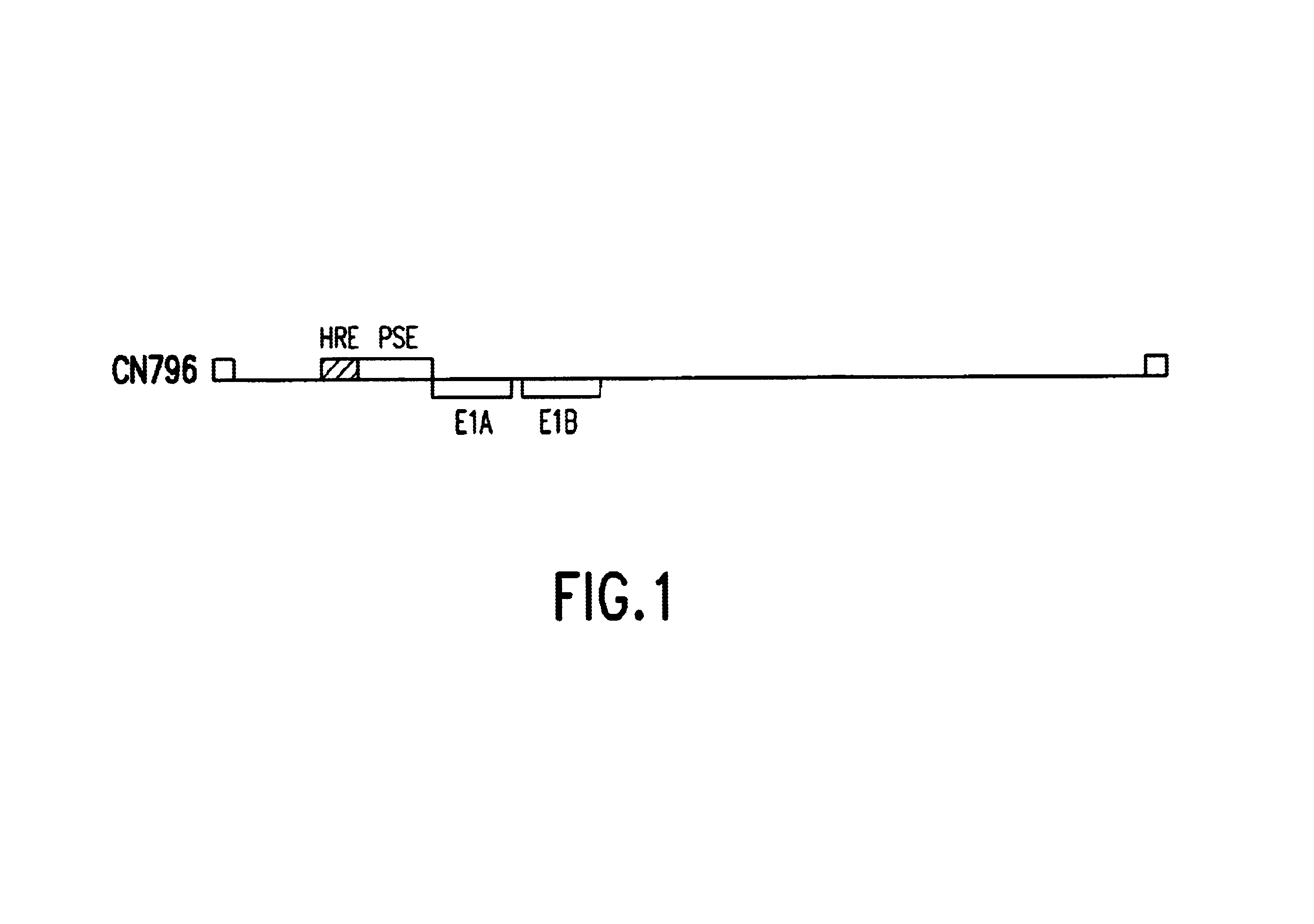
Recombinant poxviruses having foreign DNA expressed under the control of poxvirus regulatory sequences
InactiveUS6998252B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsTranscriptional regulationVaccinia
Recombinant poxviruses, such as vaccinia, are provided that comprises a segment comprised of (A) a first DNA sequence encoding a polypeptide that is foreign to poxvirus and (B) a poxvirus transcriptional regulatory sequence, wherein (i) said transcriptional regulatory sequence is adjacent to and exerts transcriptional control over said first DNA sequence and (ii) said segment is positioned within a nonessential genomic region of said recombinant poxvirus. Vaccines, carriers, cells, and media comprising recombinant poxviruses, and methods of immunization with recombinant poxviruses also are provided.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
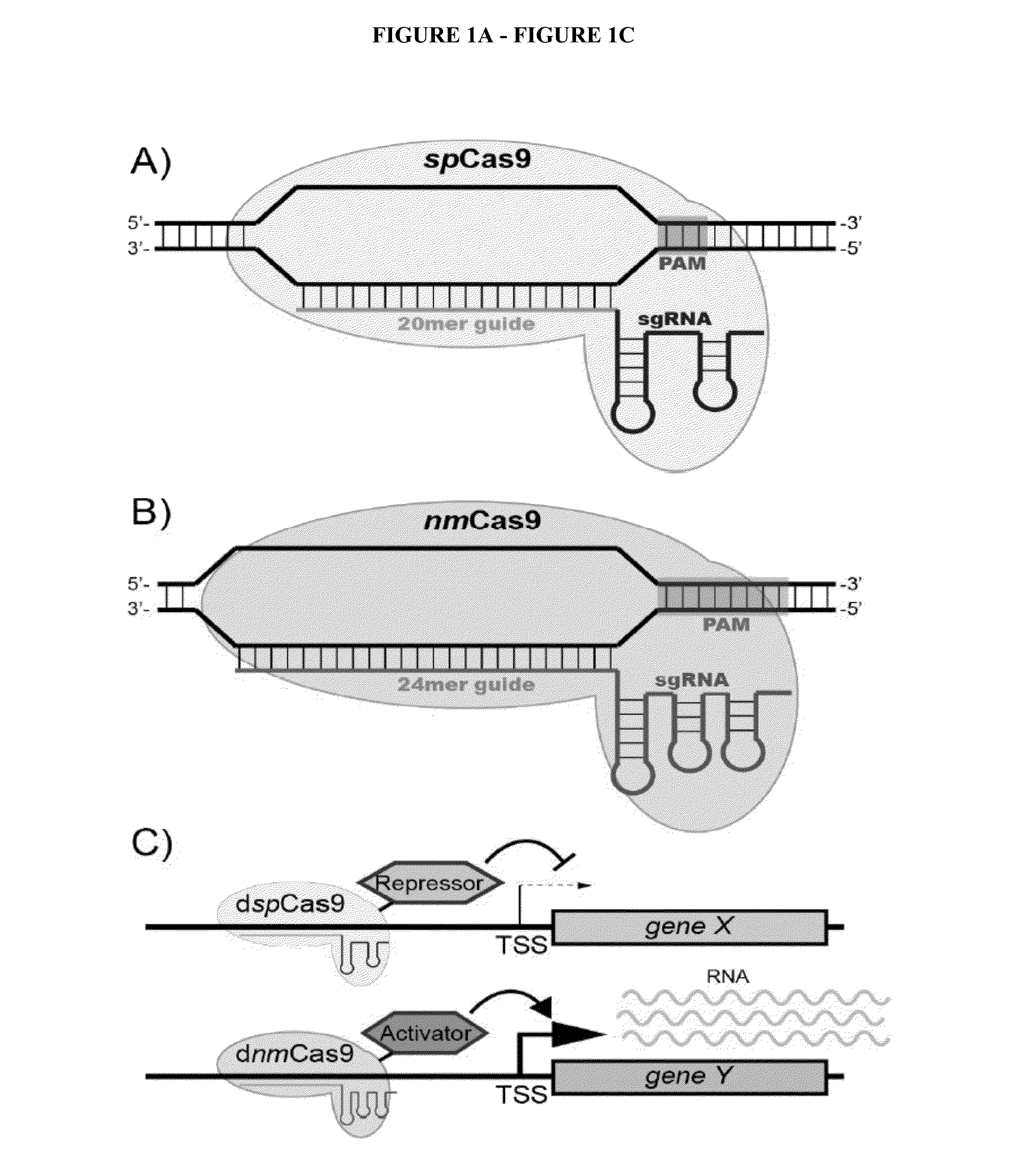
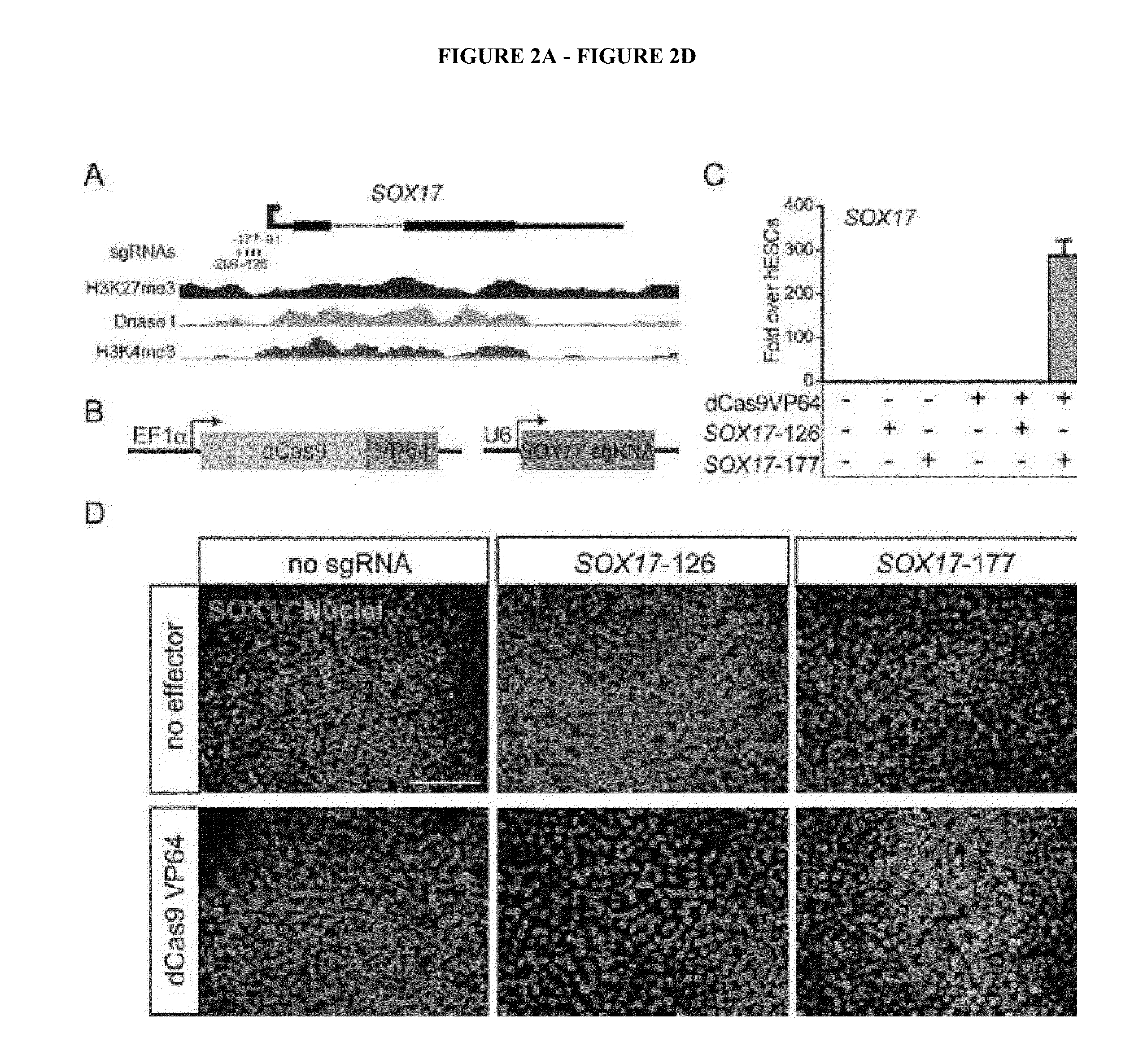
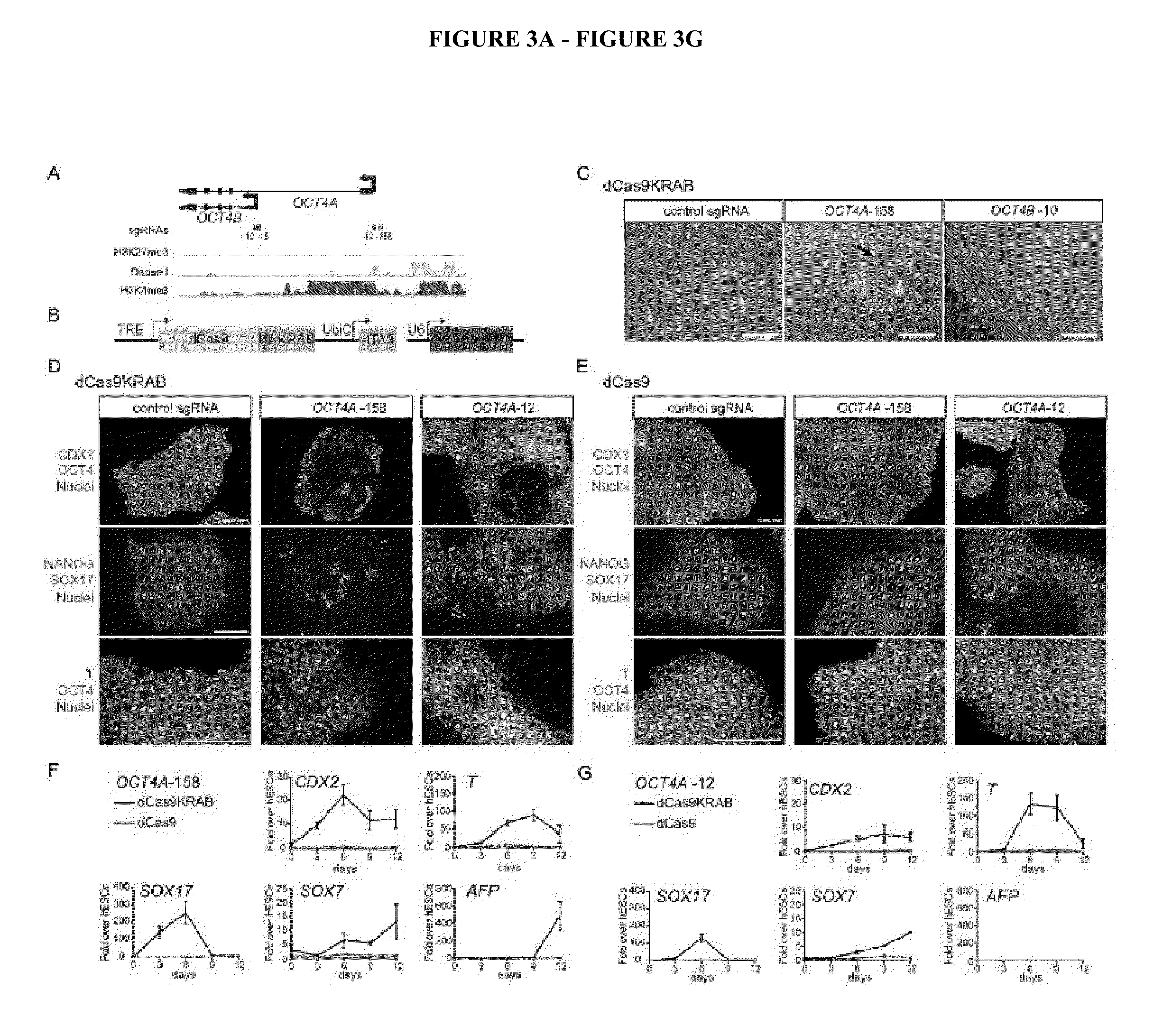
Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling
InactiveUS20150191744A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorReprogramming
The present disclosure relates to methods of and systems for modifying the transcriptional regulation of stem or progenitor cells to promote their differentiation or reprogramming of somatic cells. Further, the labeling and editing of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR / Cas9 components allow multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
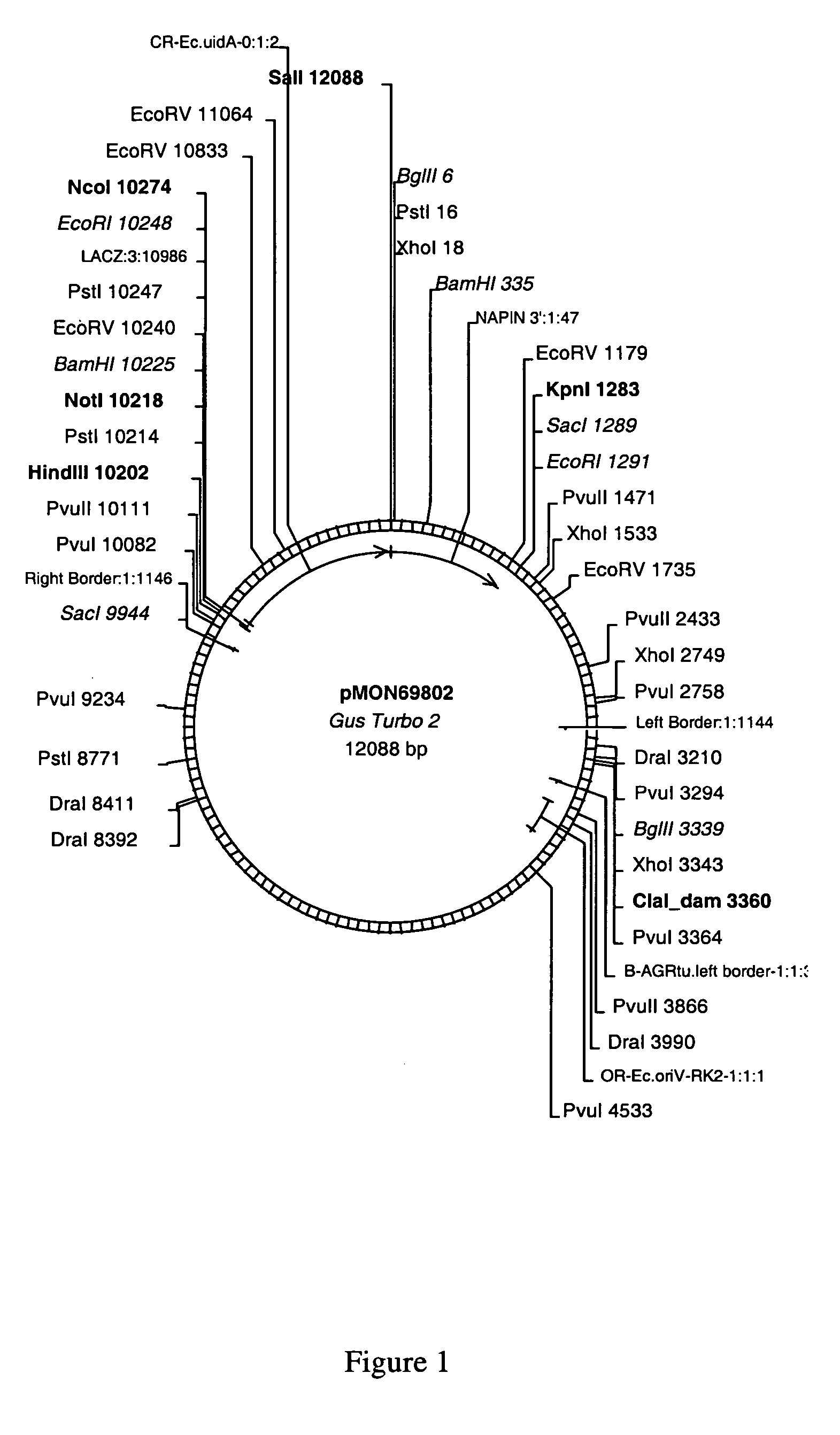
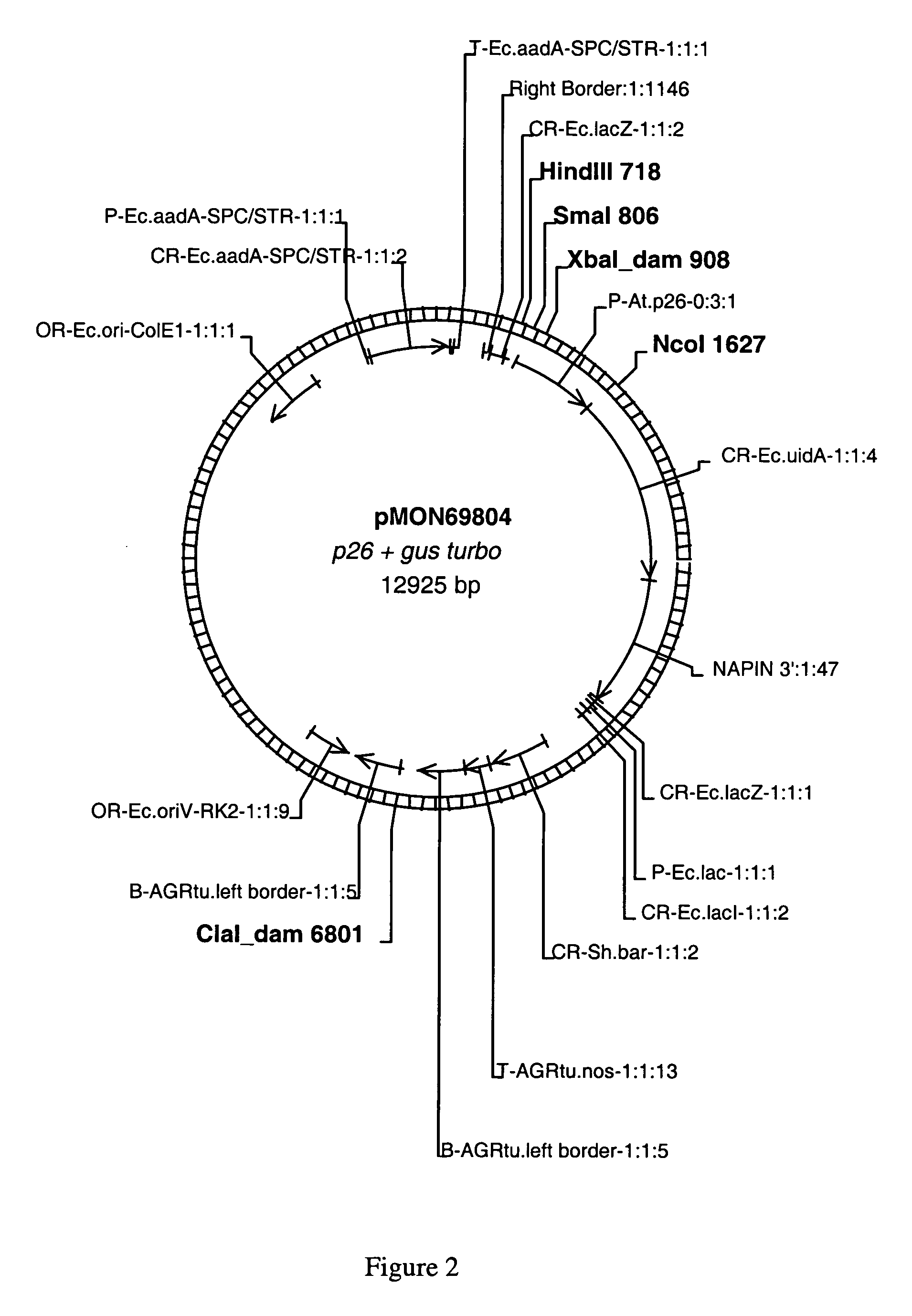
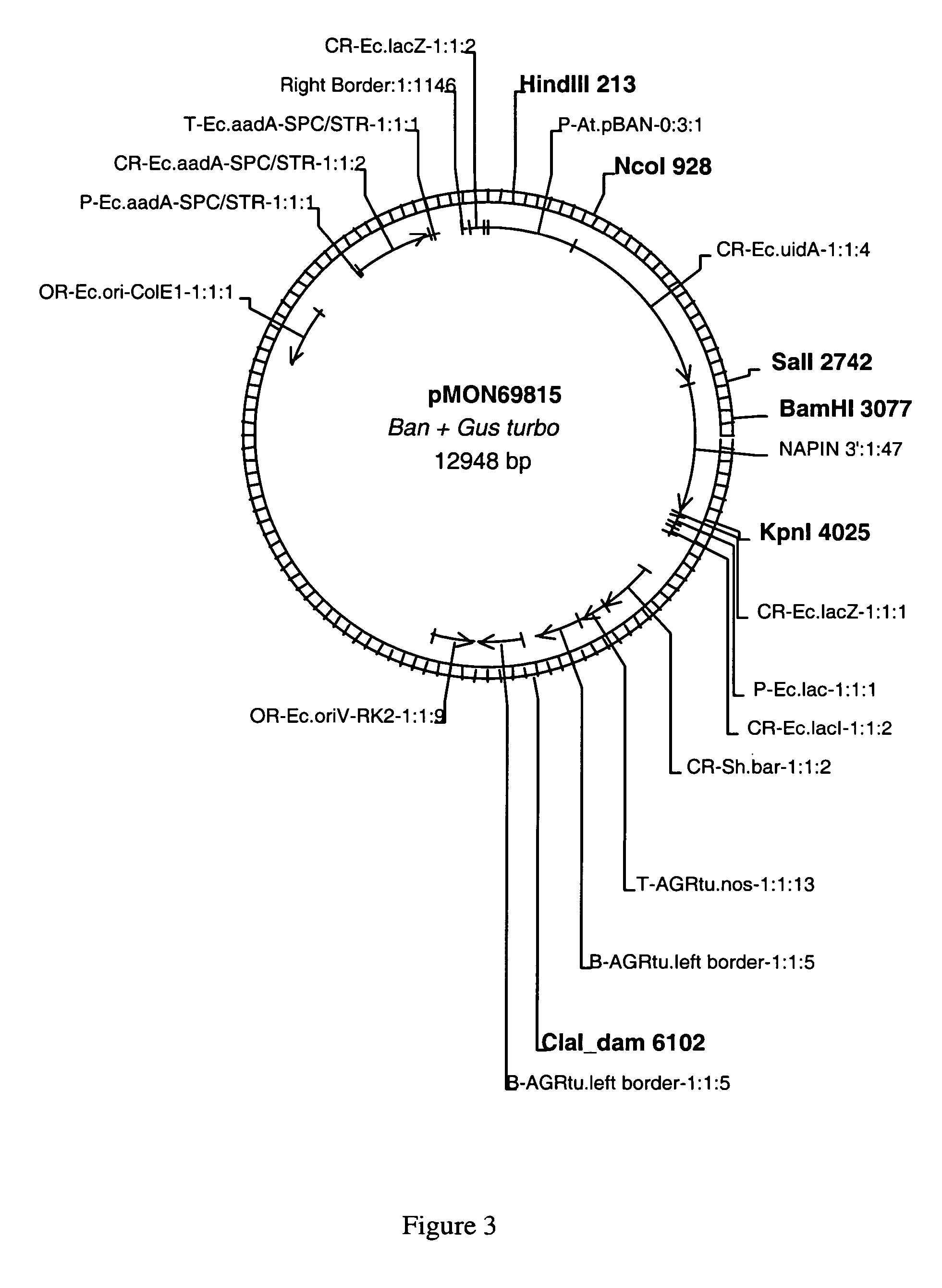
Plant promoters for use in early seed development
The present invention relates to DNA molecules that encode transcription regulatory regions. Furthermore, this present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding transcription regulatory regions that promote early seed enhanced or seed coat enhanced transcription of contiguous nucleotide sequences.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
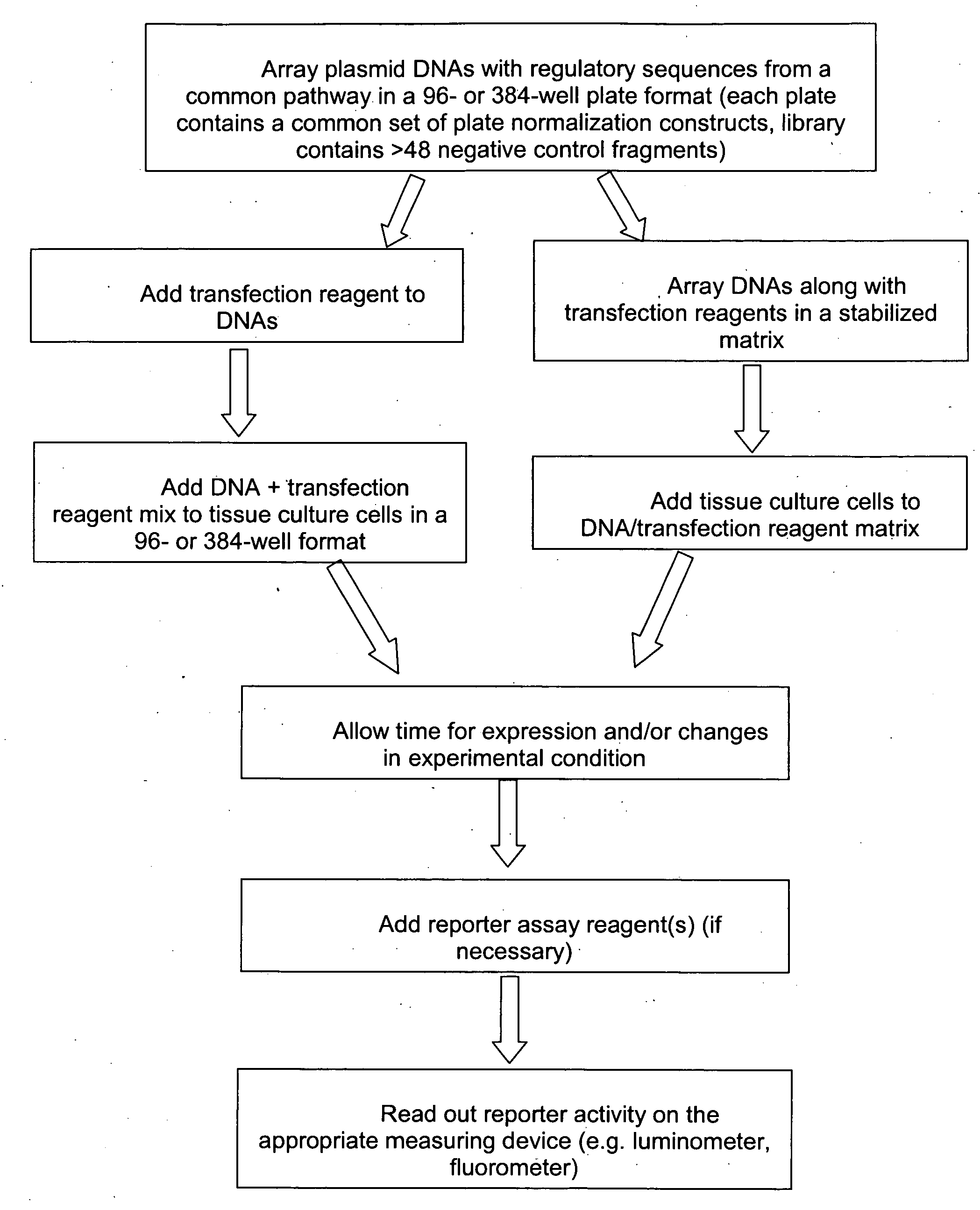
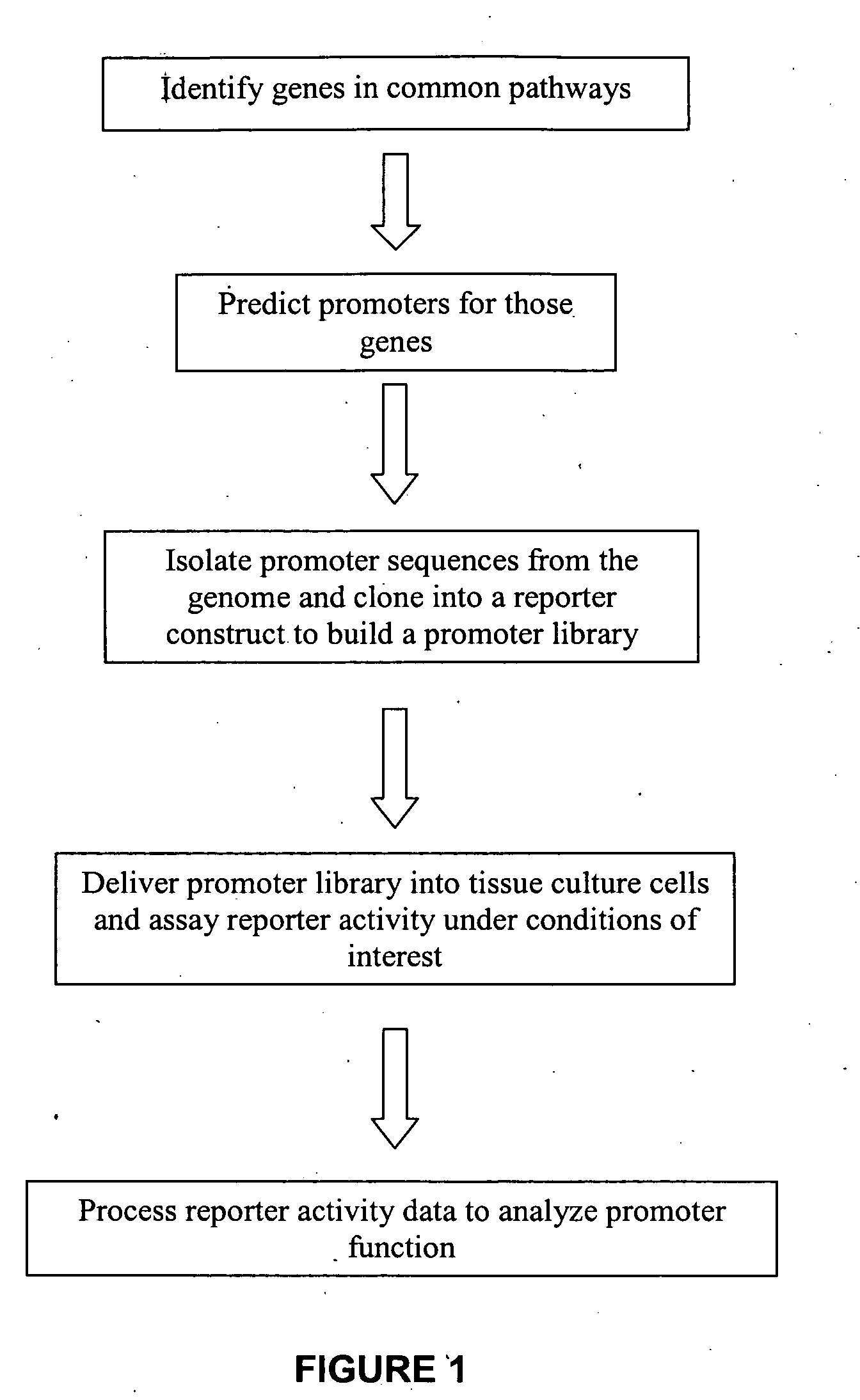
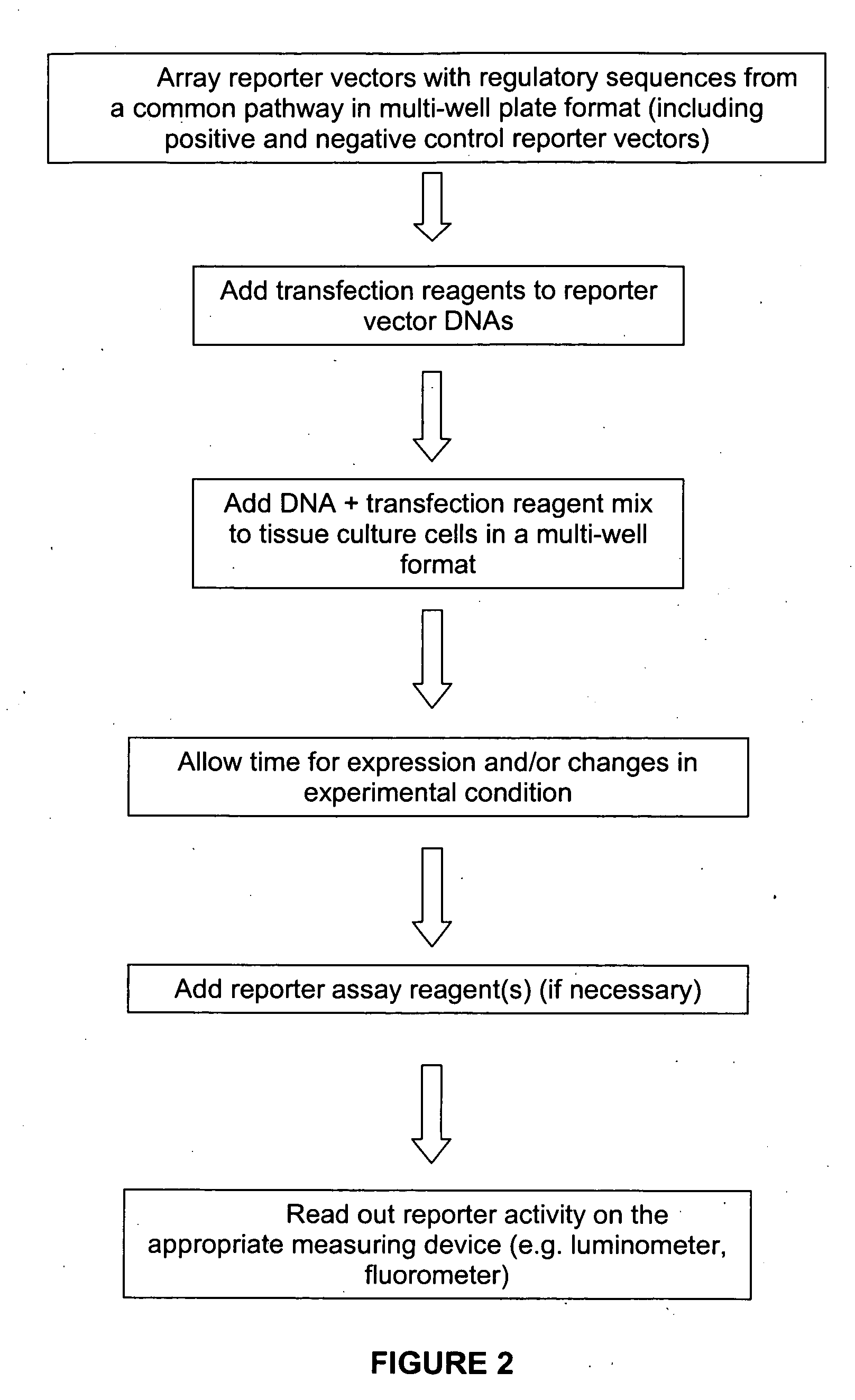
Transcriptional regulatory elements of biological pathways tools, and methods
InactiveUS20090018031A1Determine effectNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningHuman DNA sequencingRegulation of gene expression
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome, that are part of a common pathway. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:SWITCHGEAR GENOMICS
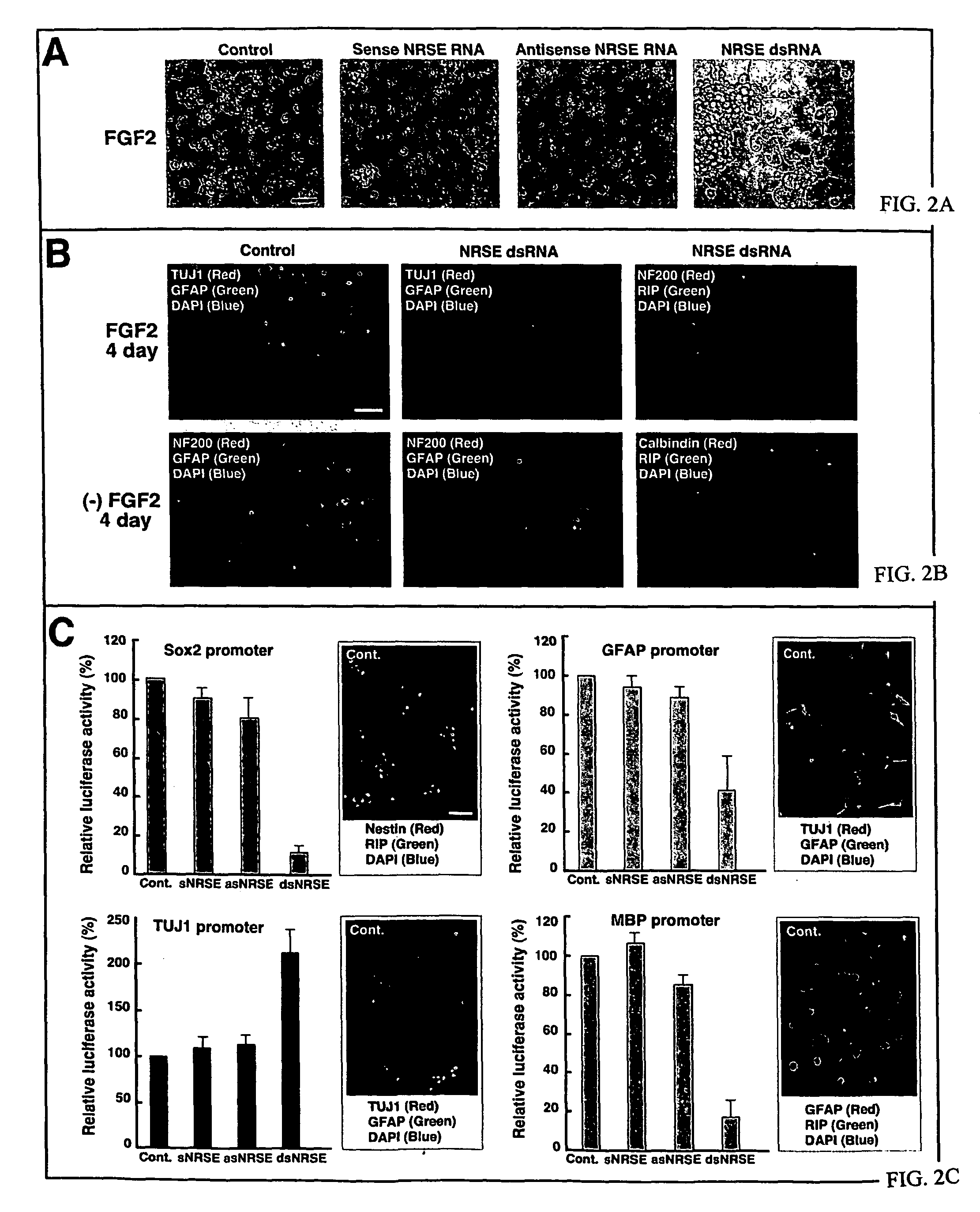
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression by small double-stranded modulatory RNA
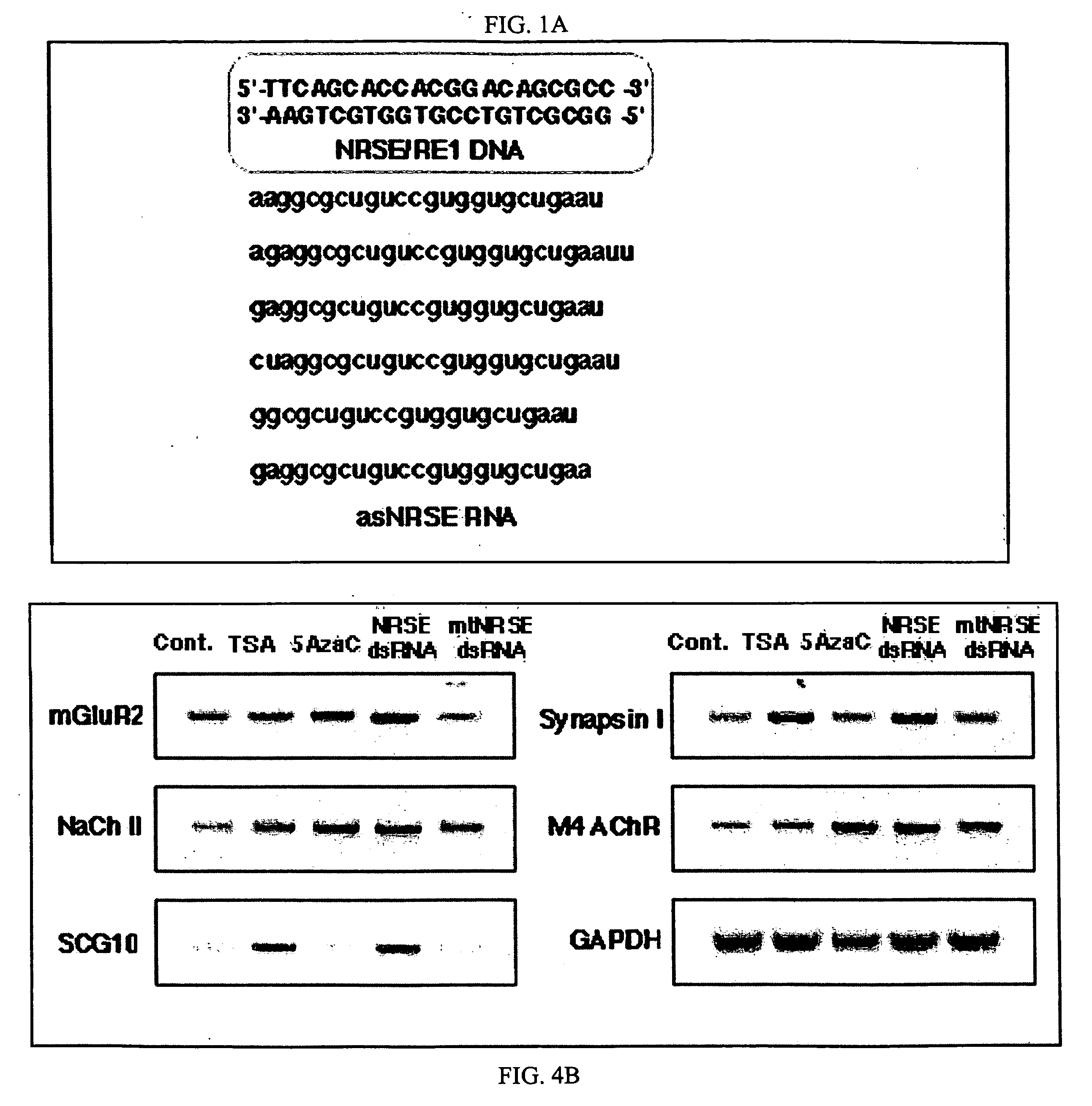
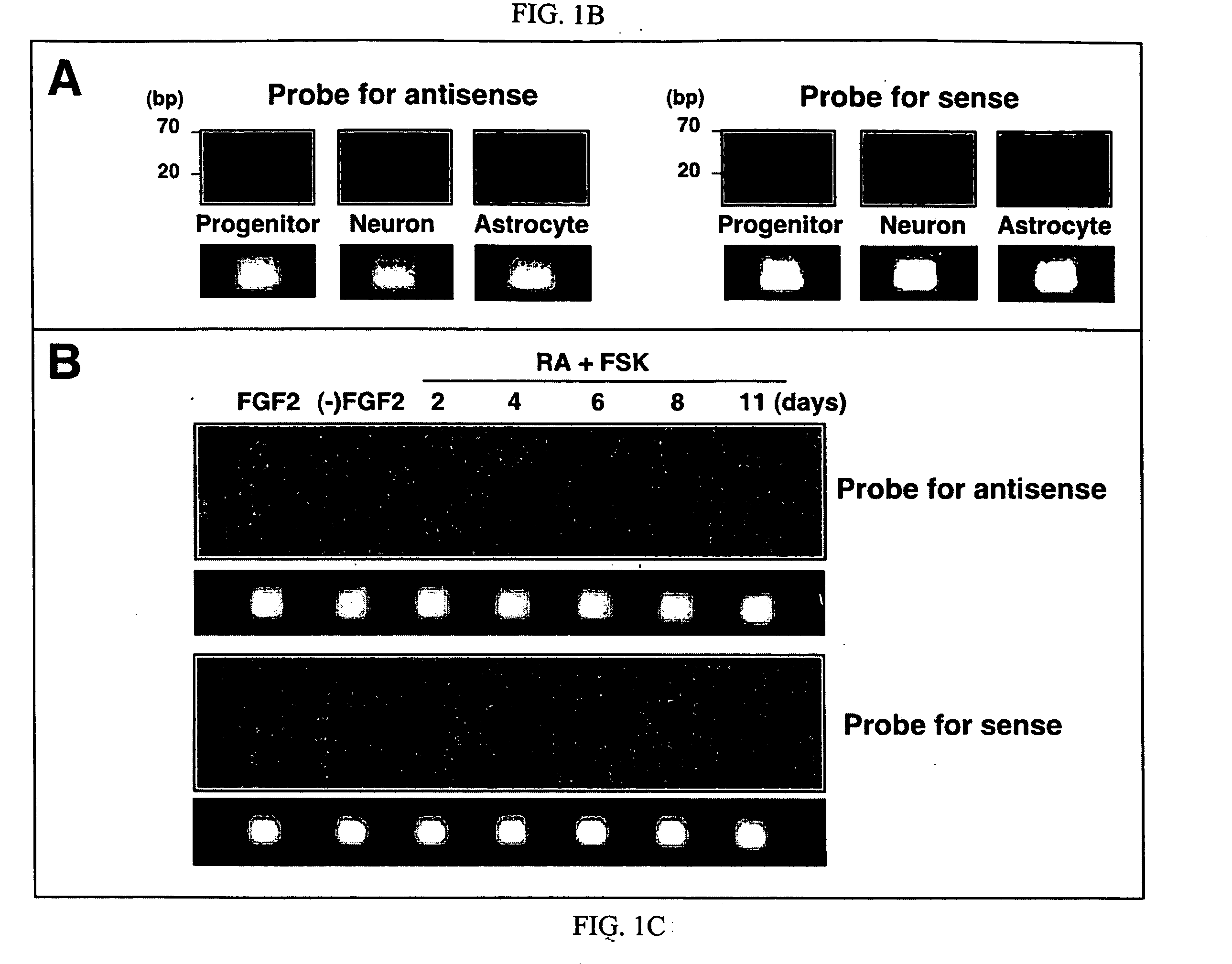
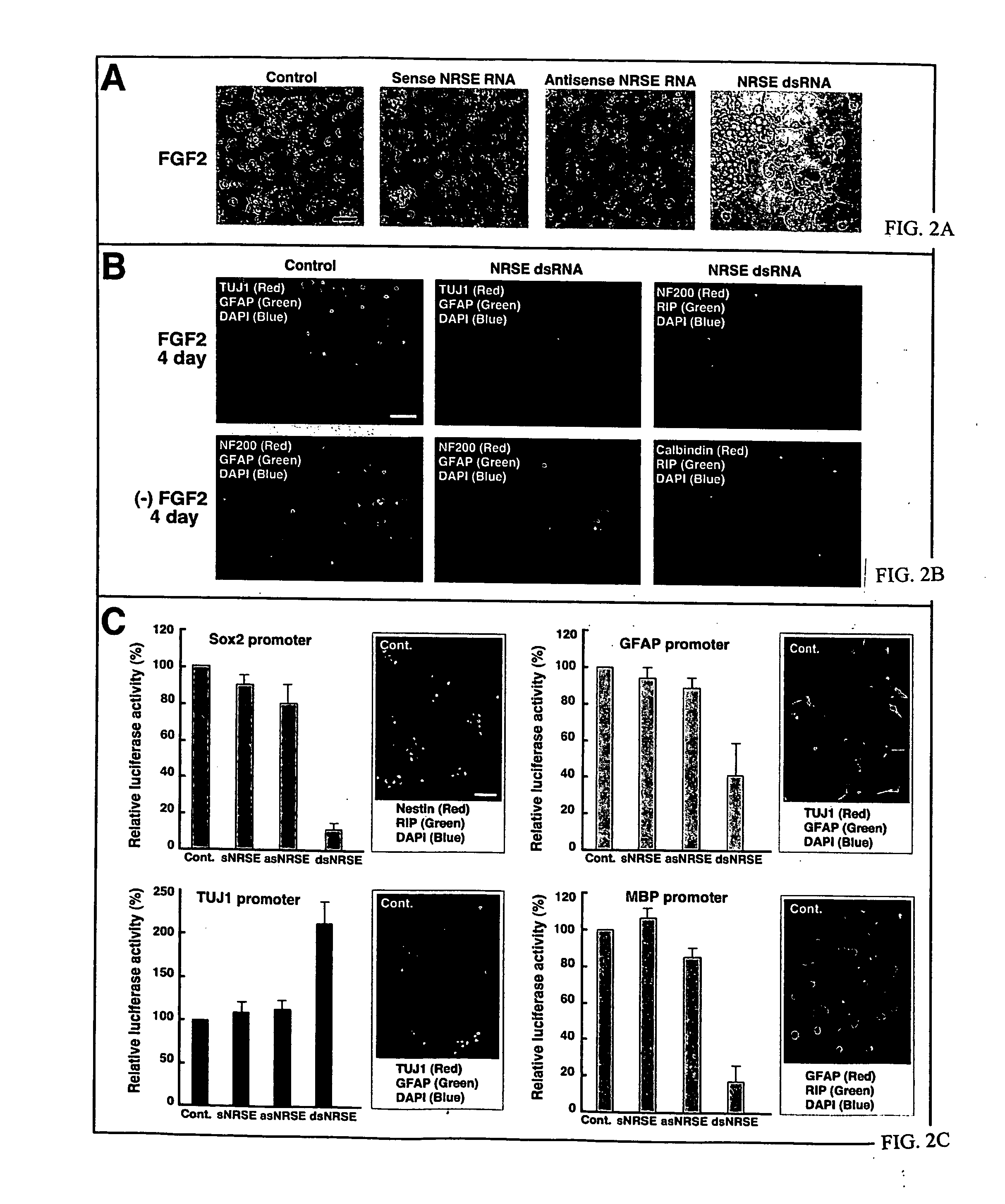
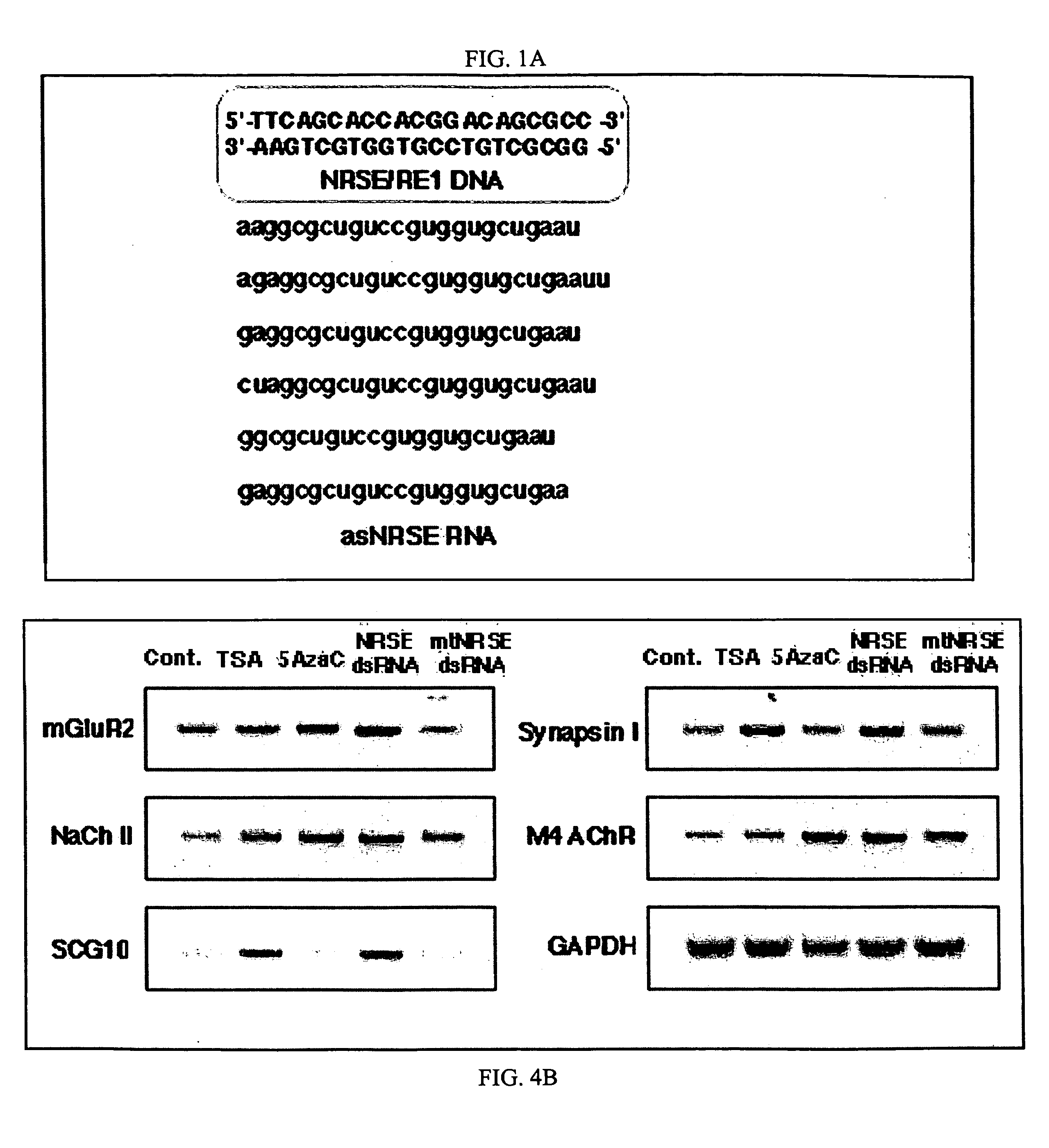
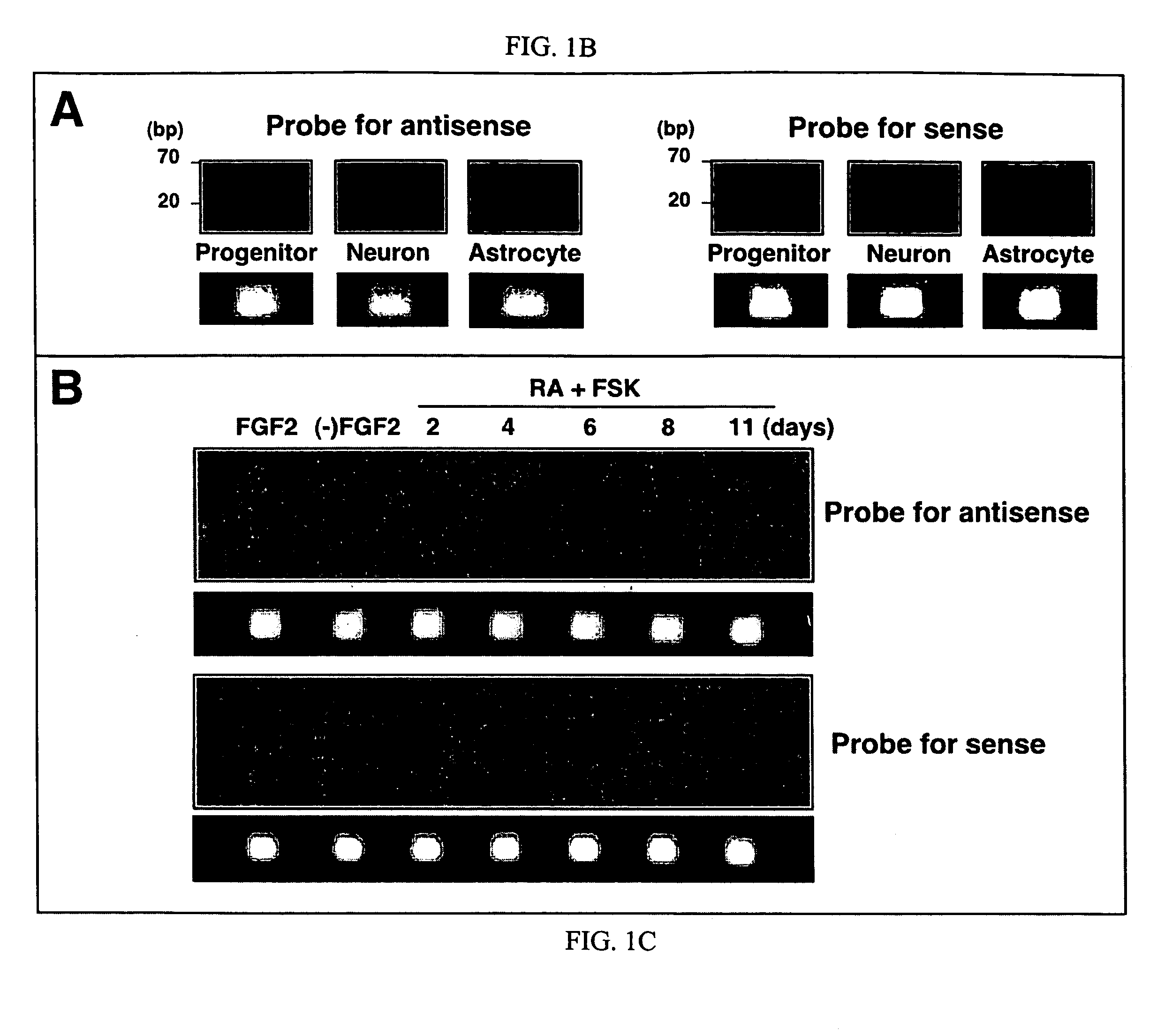
The invention provides a method for modulating gene expression by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes, wherein the association results in altered expression of the one or more genes. The invention is further directed to method for directing the differentiation of neuronal stem cells into neurons by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes involved in neuronal differentiation and directing the transcription of the one or more genes. In related embodiments, the invention provides particular compositions of double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules as well as therapeutic and screening applications of the invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Transcriptional regulation of plant biomass and abiotic stress tolerance
InactiveUS20050097638A1Increase biomassImprove toleranceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesWild typeTranscriptional regulation
The invention relates to plant transcription factor polypeptides, polynucleotides that encode them, homologs from a variety of plant species, and methods of using the polynucleotides and polypeptides to produce transgenic plants having advantageous properties, including increased biomass or improved cold or other osmotic stress tolerance, as compared to wild-type or reference plants. The invention also pertains to expression systems that may be used to regulate these transcription factor polynucleotides, providing constitutive, transient, inducible and tissue-specific regulation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
Method for the determination of cellular transcriptional regulation
InactiveUS20060134639A1Rapidly and reliably detectingRapidly and reliably and quantifyingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal onTranscriptional regulation
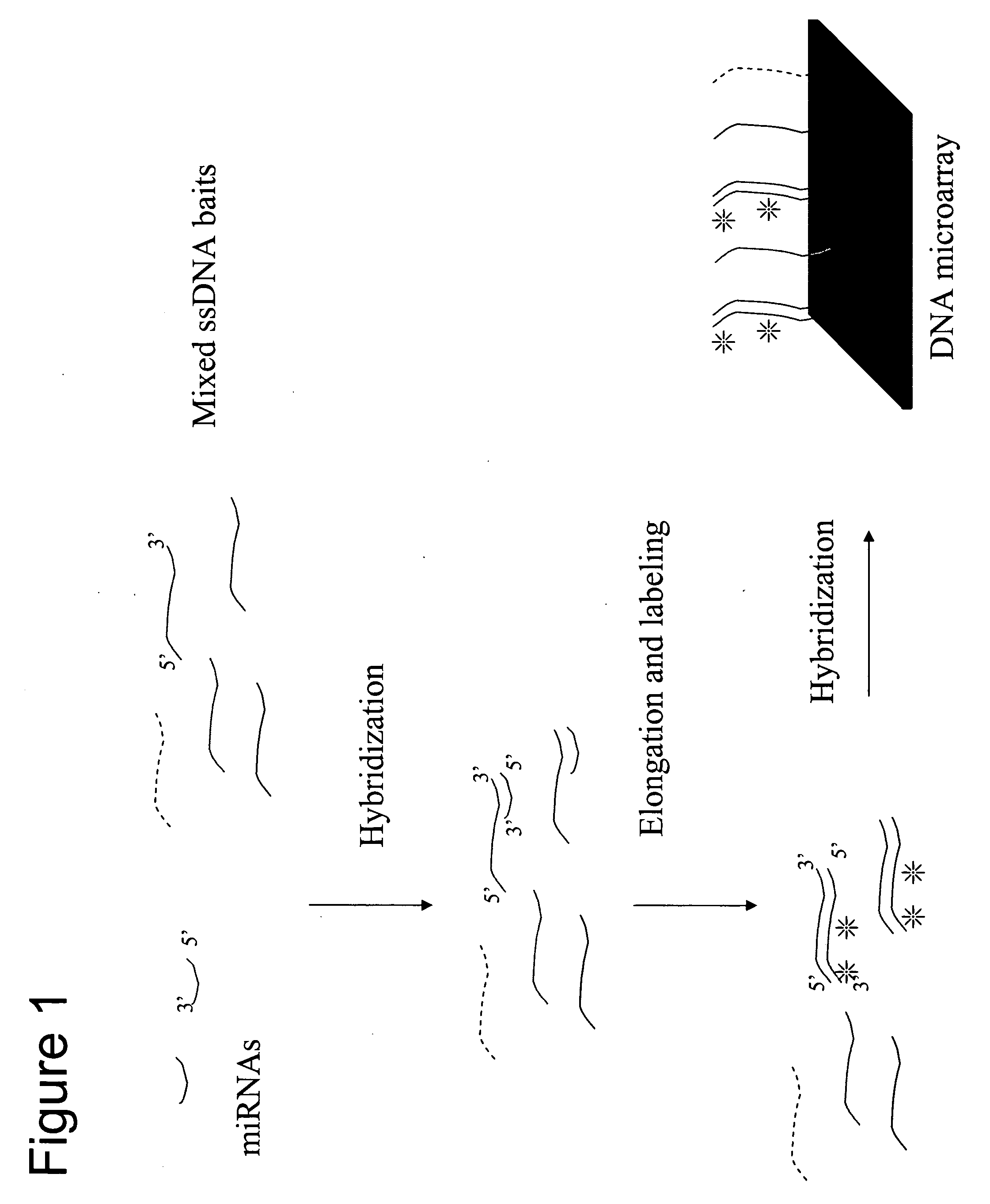
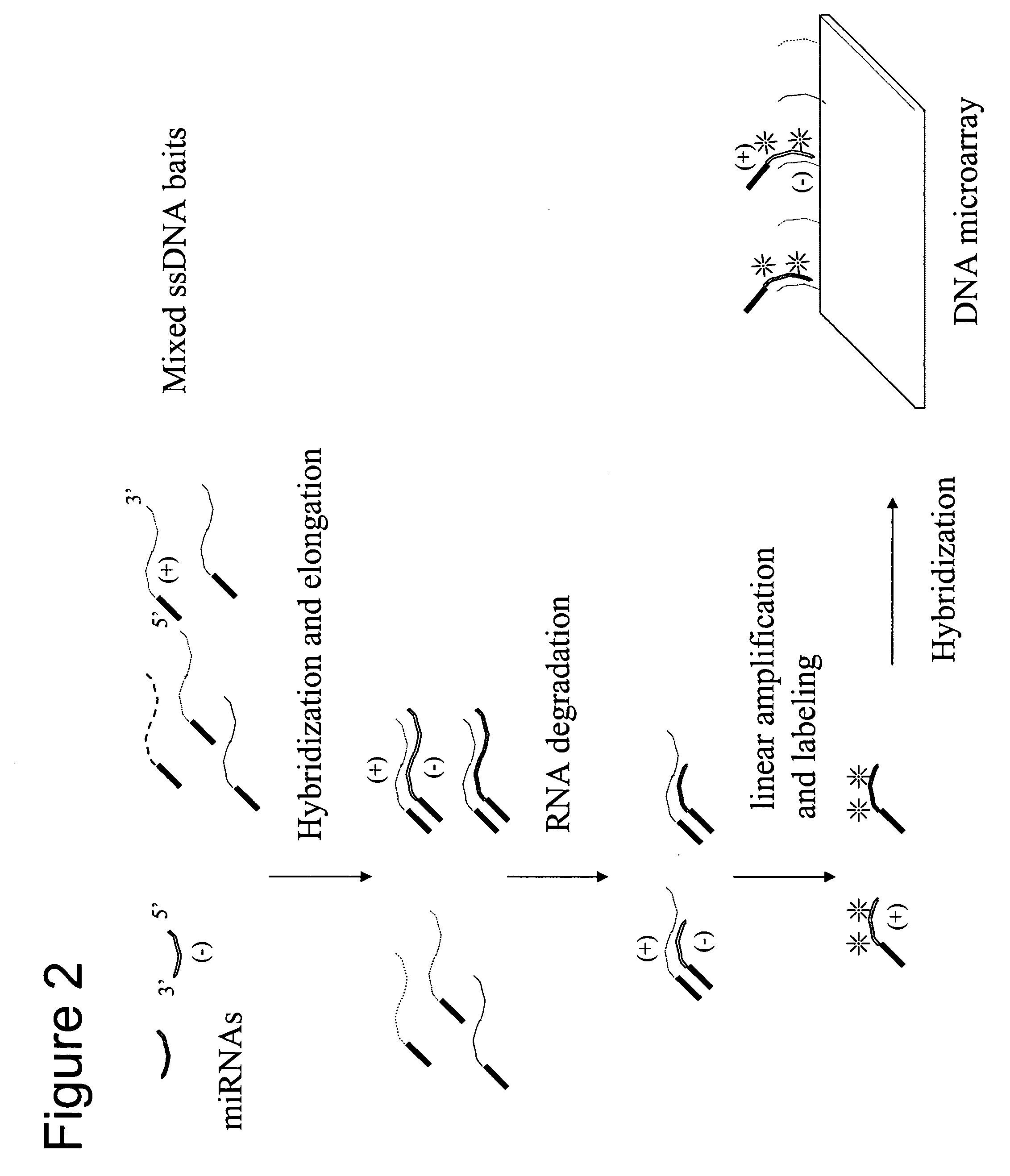
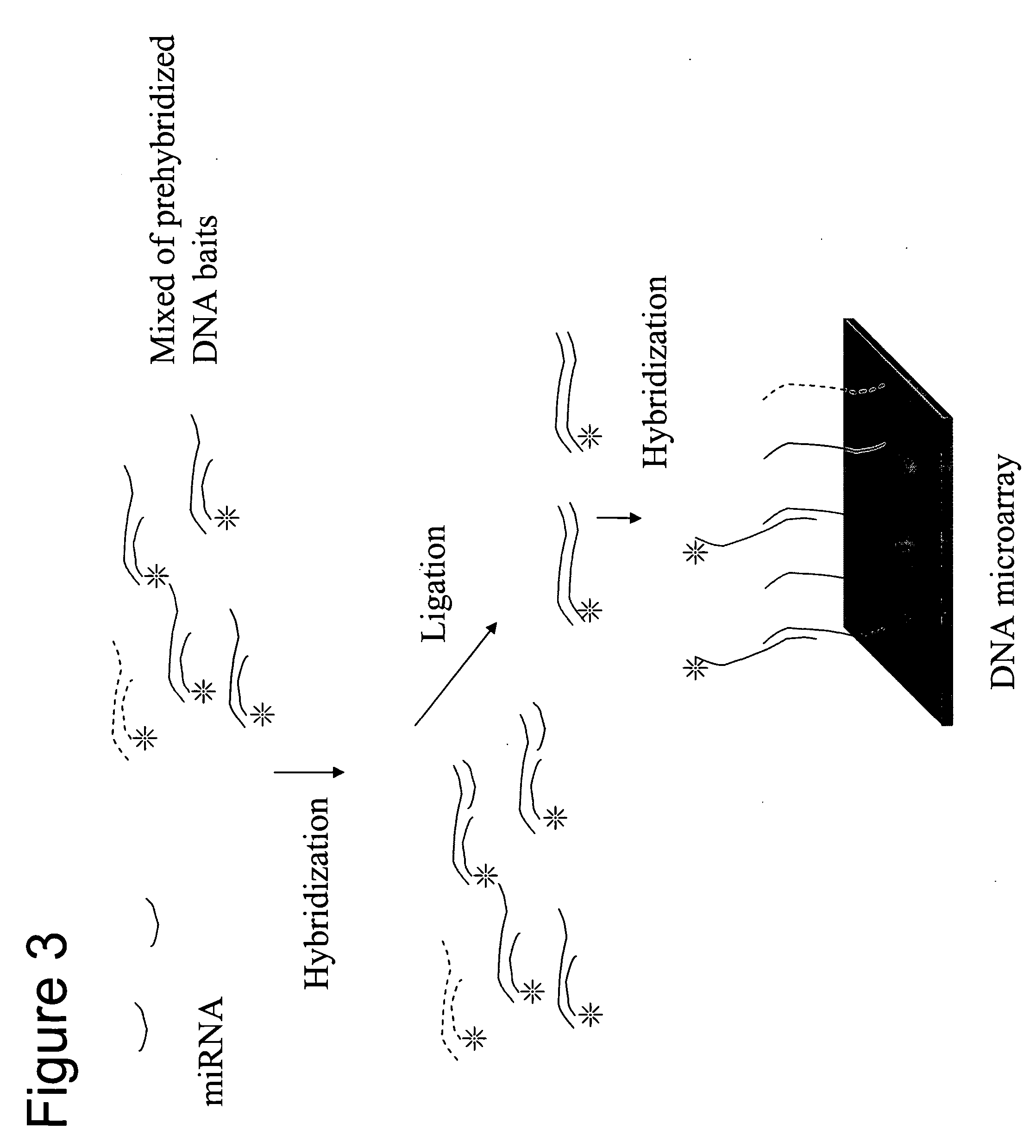
The present invention relates to a new method for determining the RNAi mediated transcriptional regulation of a cell by the determination of a pattern of at least 3 miRNA detected simultaneously and quantified in the same cell extract. The determination of a pattern of miRNA comprises the steps of: (i) providing an array onto which are fixed capture probes, said capture probes being arranged on pre-determined locations and reflecting the genomic or transcriptional matter of a cell; (ii) isolating a miRNA pool potentially present from a cell; (iii) elongating or ligating said miRNAs into labeled capture probes, (iv) contacting said labeled polynucleotides with the array under conditions allowing hybridization of the labeled polynucleotides to complementary capture probes present on the array; (v) detecting and quantifying a signal present on the specific locations of the array, wherein the detection of a pattern of at least 3 signals on the array reflects the pattern of miRNAs being involved in the RNAi mediated cellular transcriptional regulation.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
Crispr/cas transcriptional modulation
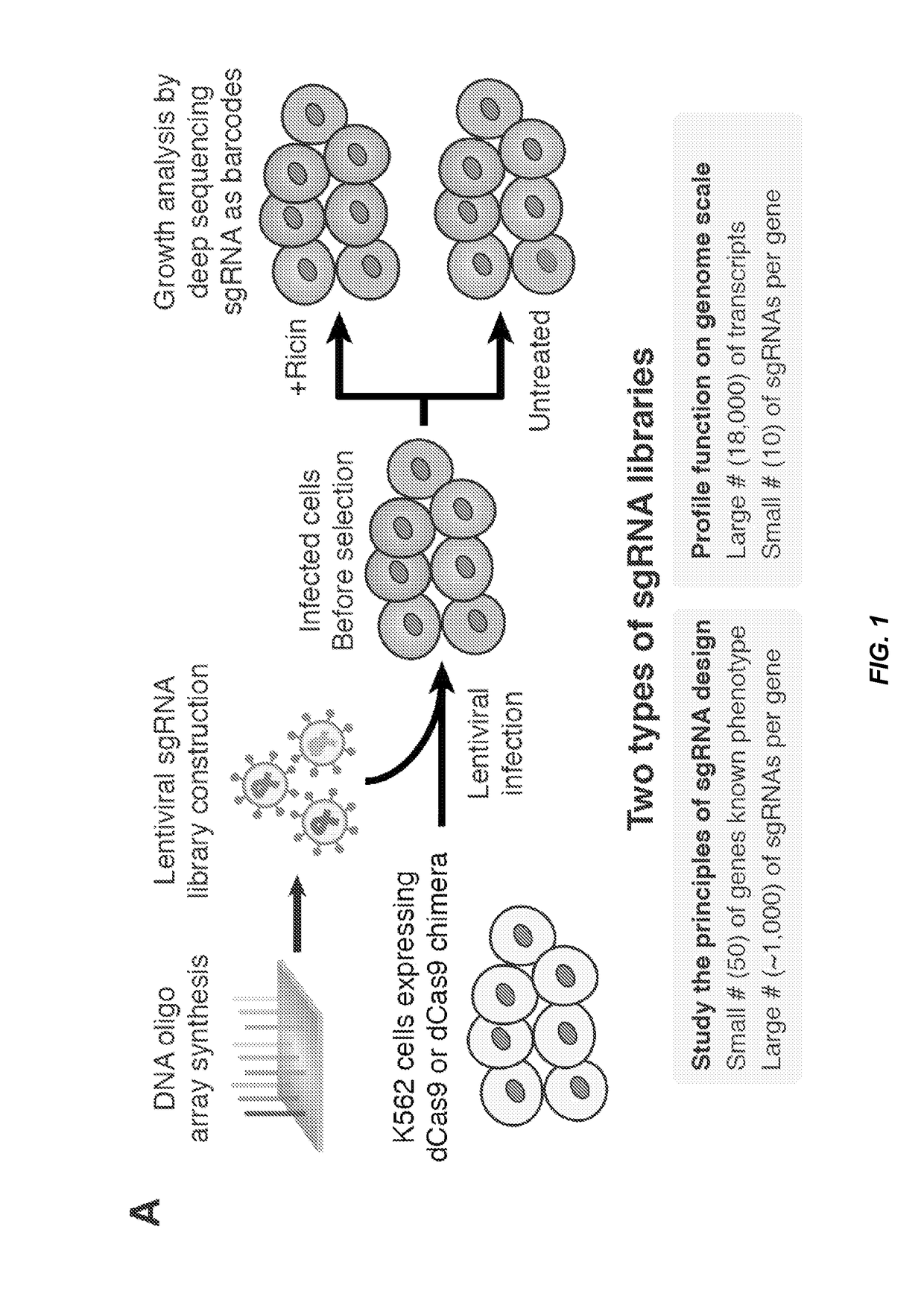
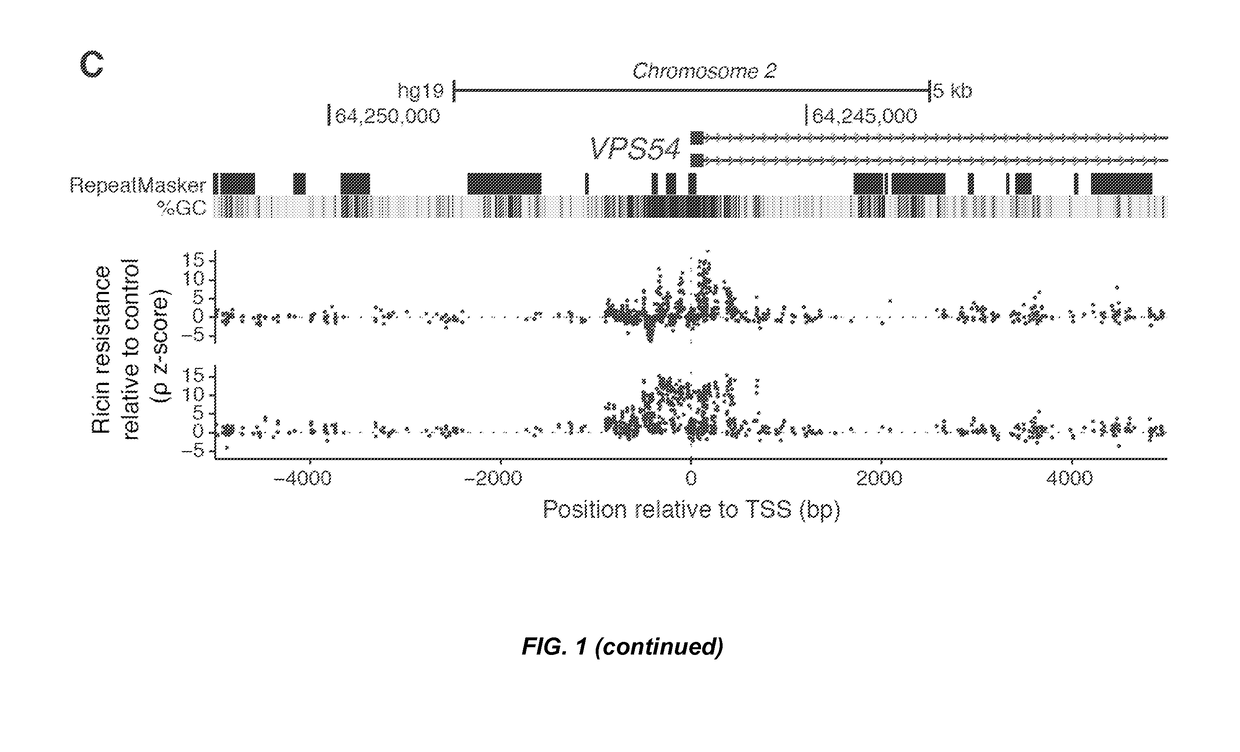
ActiveUS20170204407A1Increased stability and activityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionTranscriptional regulationBioinformatics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
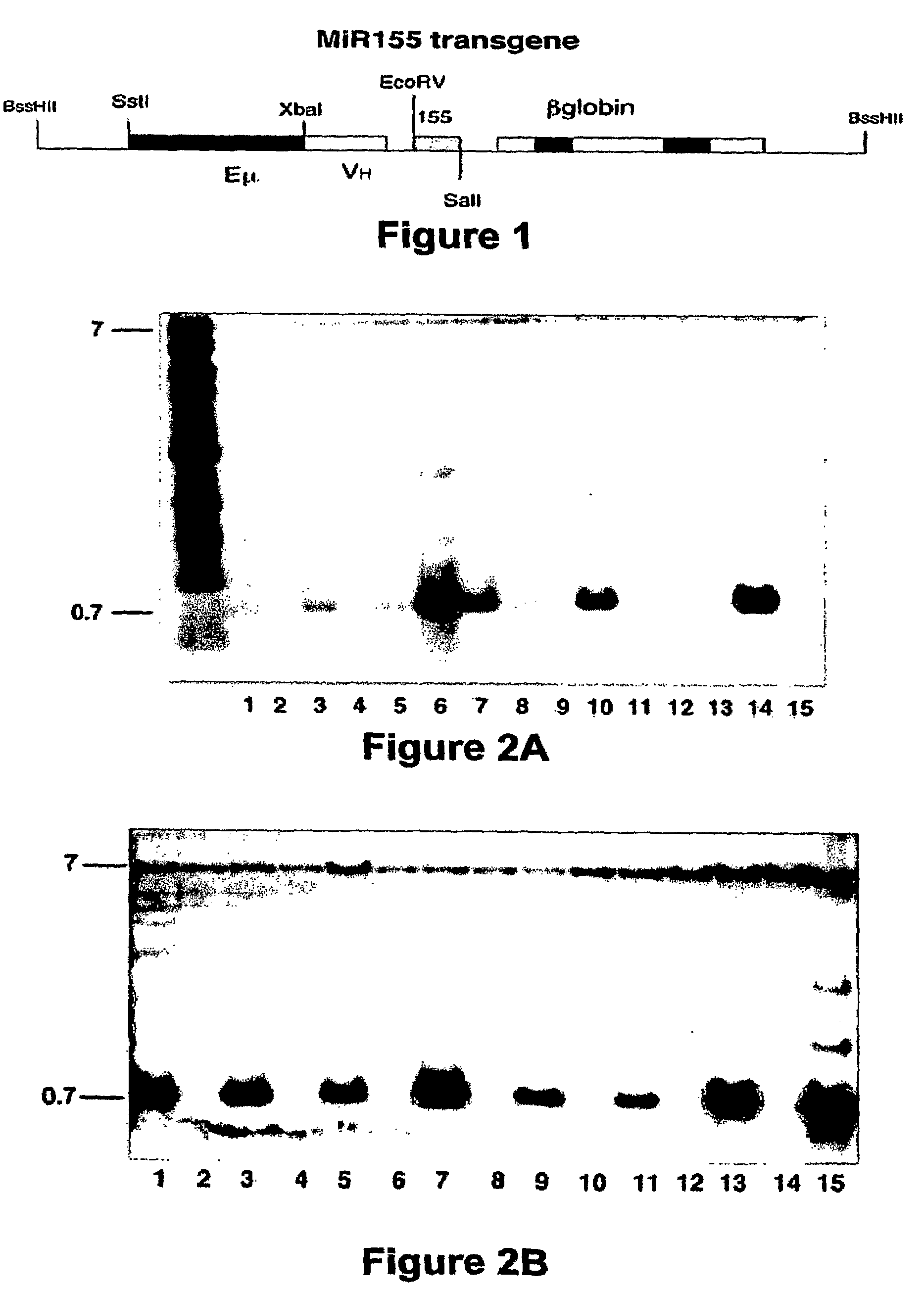
Transgenic mouse model of B cell malignancy
A transgenic non-human animal, such as a mouse, has a genome that include a nucleic acid construct having at least one transcriptional regulatory sequence capable of directing expression in B cells of the animal, wherein the transcriptional regulatory sequence is operably linked to a nucleic acid encoding a miR155 gene product. A method of testing the therapeutic efficacy of an agent in treating or preventing a lymphoproliferative condition includes assessing the effect(s) of the agent on a transgenic non-human animal.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
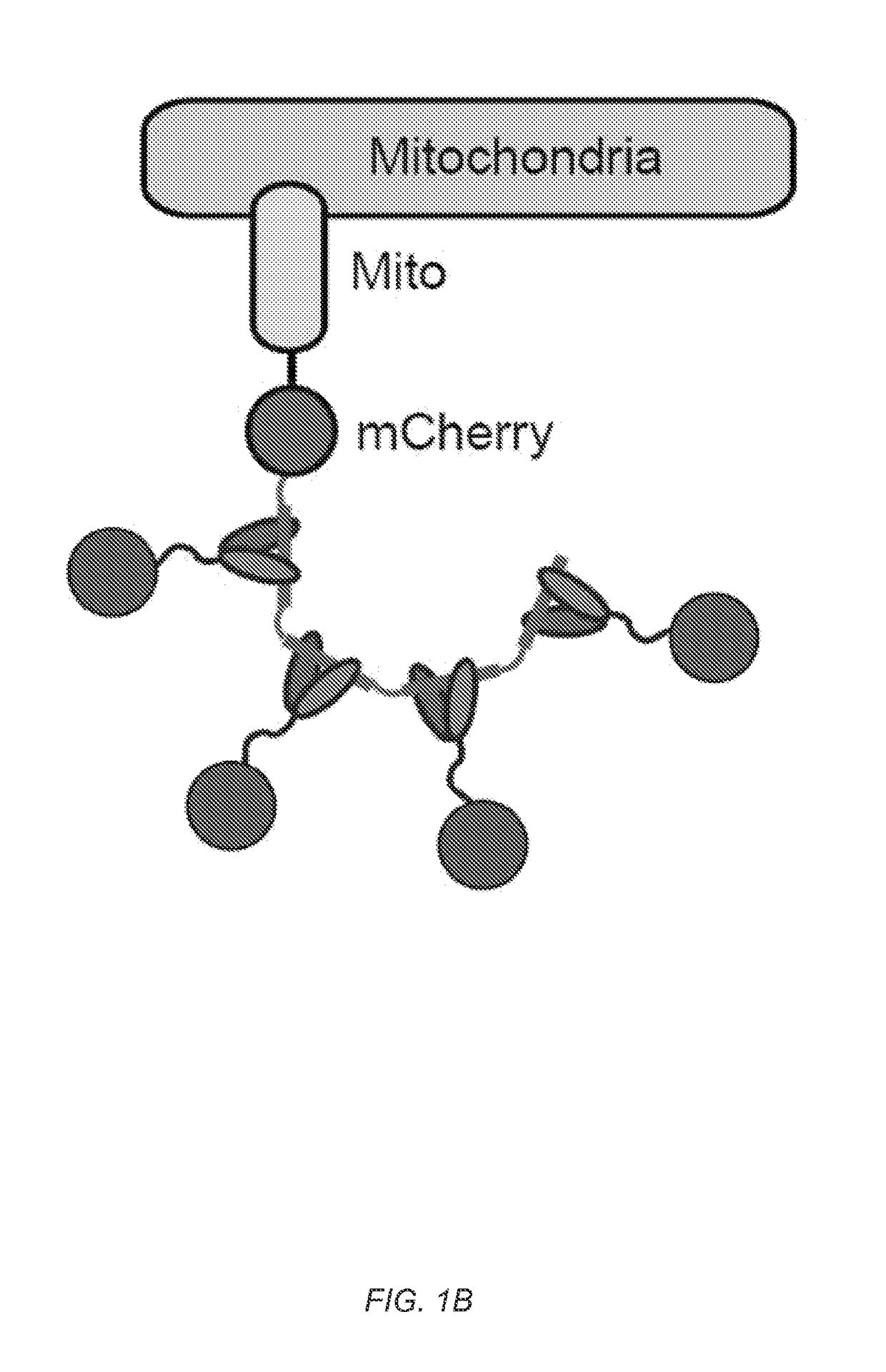
A protein tagging system for in vivo single molecule imaging and control of gene transcription
InactiveUS20170219596A1HydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTranscriptional regulationGenetic element
Methods, compositions, and kits are provided for imaging a polypeptide of interest. Methods, compositions, and kits are also provided for site-specific transcriptional regulation of one or more genetic elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions containing recombinant poxviruses having foreign DNA expressed under the control of poxvirus regulatory sequences
InactiveUS7015024B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsTranscriptional regulationVaccinia
Recombinant poxviruses, such as vaccinia, are provided that comprises a segment comprised of (A) a first DNA sequence encoding a polypeptide that is foreign to poxvirus and (B) a poxvirus transcriptional regulatory sequence, wherein (i) said transcriptional regulatory sequence is adjacent to and exerts transcriptional control over said first DNA sequence and (ii) said segment is positioned within a nonessential genomic region of said recombinant poxvirus. Vaccines, carriers, cells, and media comprising recombinant poxviruses, and methods of immunization with recombinant poxviruses, also are provided.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE
Cis/trans riboregulators
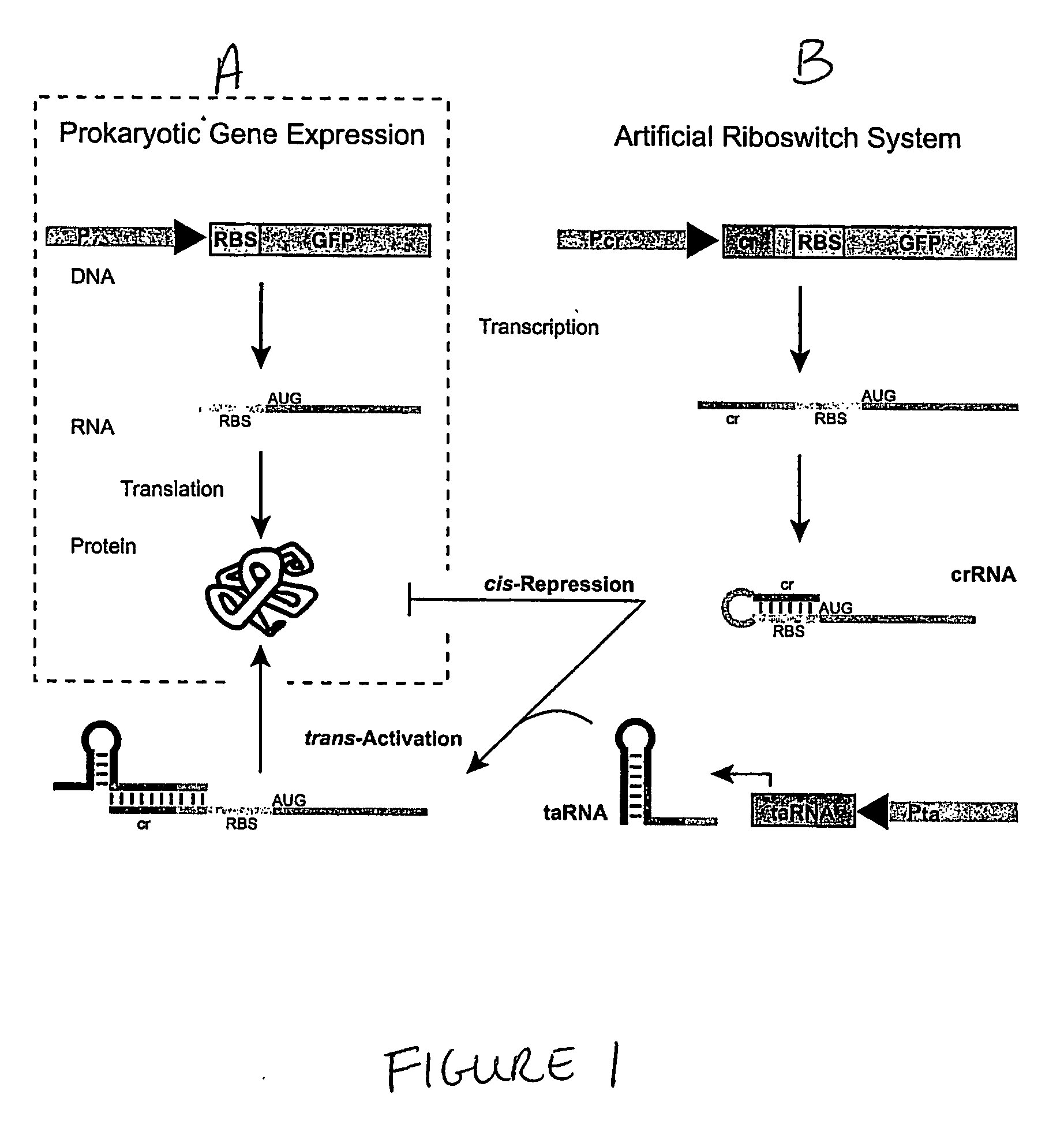
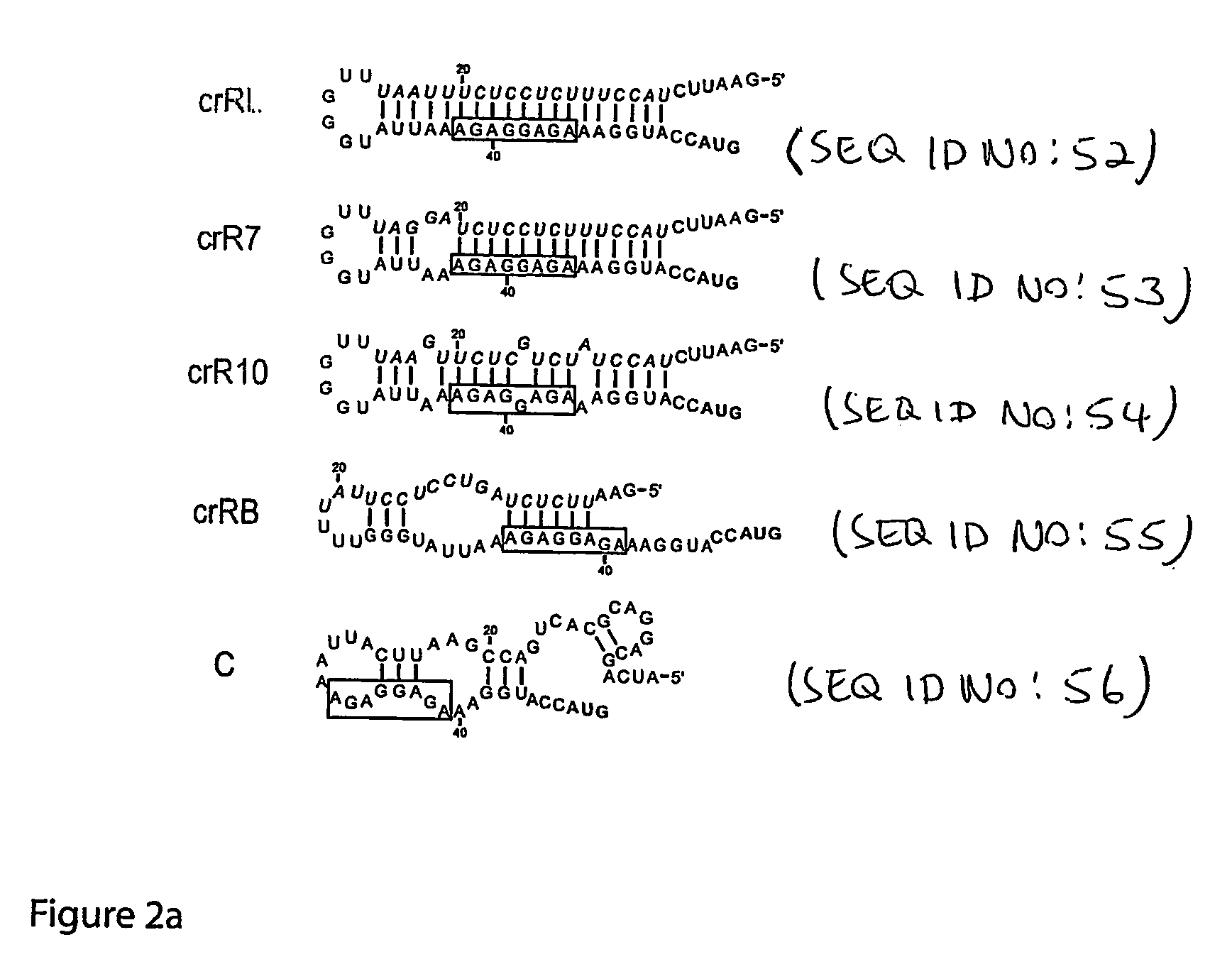
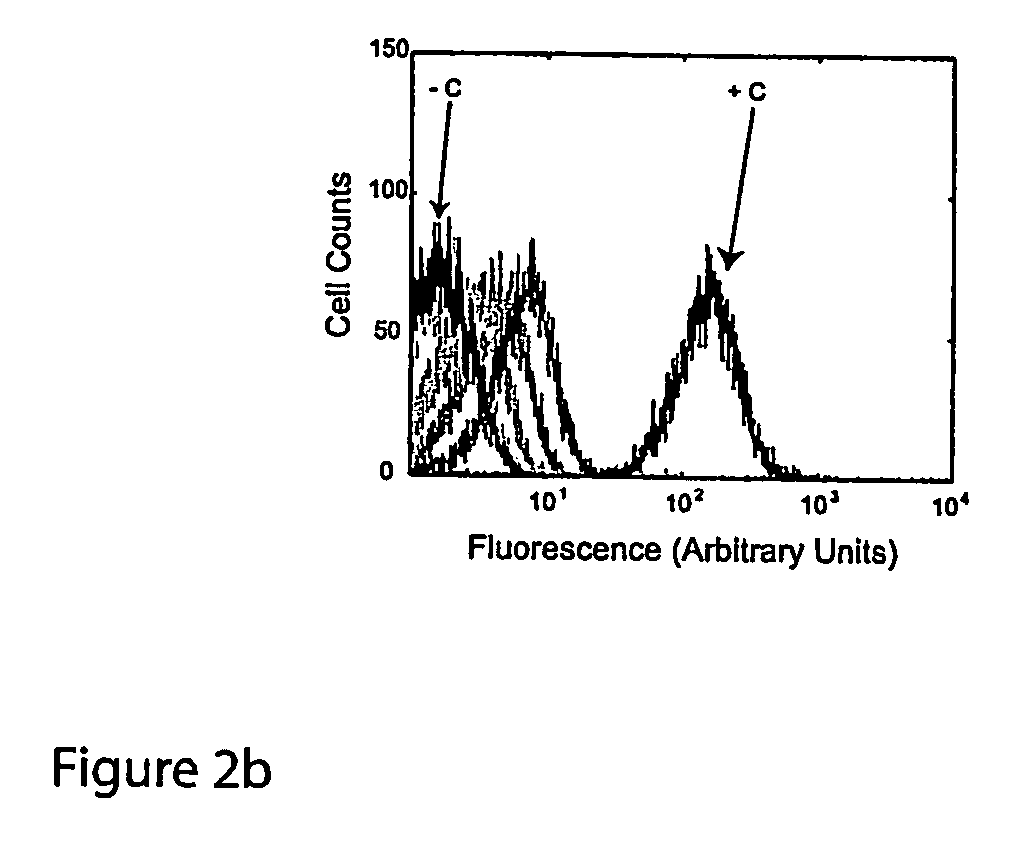
ActiveUS20070136827A1Easy to controlInhibition of translationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameBinding site
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules, DNA constructs, plasmids, and methods for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression using RNA molecules to both repress and activate translation of an open reading frame. Repression of gene expression is achieved through the presence of a regulatory nucleic acid element (the cis-repressive RNA or crRNA) within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) of an mRNA molecule. The nucleic acid element forms a hairpin (stem / loop) structure through complementary base pairing. The hairpin blocks access to the mRNA transcript by the ribosome, thereby preventing translation. In particular, in embodiments of the invention designed to operate in prokaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin secondary structure sequesters the ribosome binding site (RBS). In embodiments of the invention designed to operate in eukaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin is positioned upstream of the start codon, anywhere within the 5′ UTR of an mRNA. A small RNA (trans-activating RNA, or taRNA), expressed in trans, interacts with the crRNA and alters the hairpin structure. This alteration allows the ribosome to gain access to the region of the transcript upstream of the start codon, thereby activating transcription from its previously repressed state.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
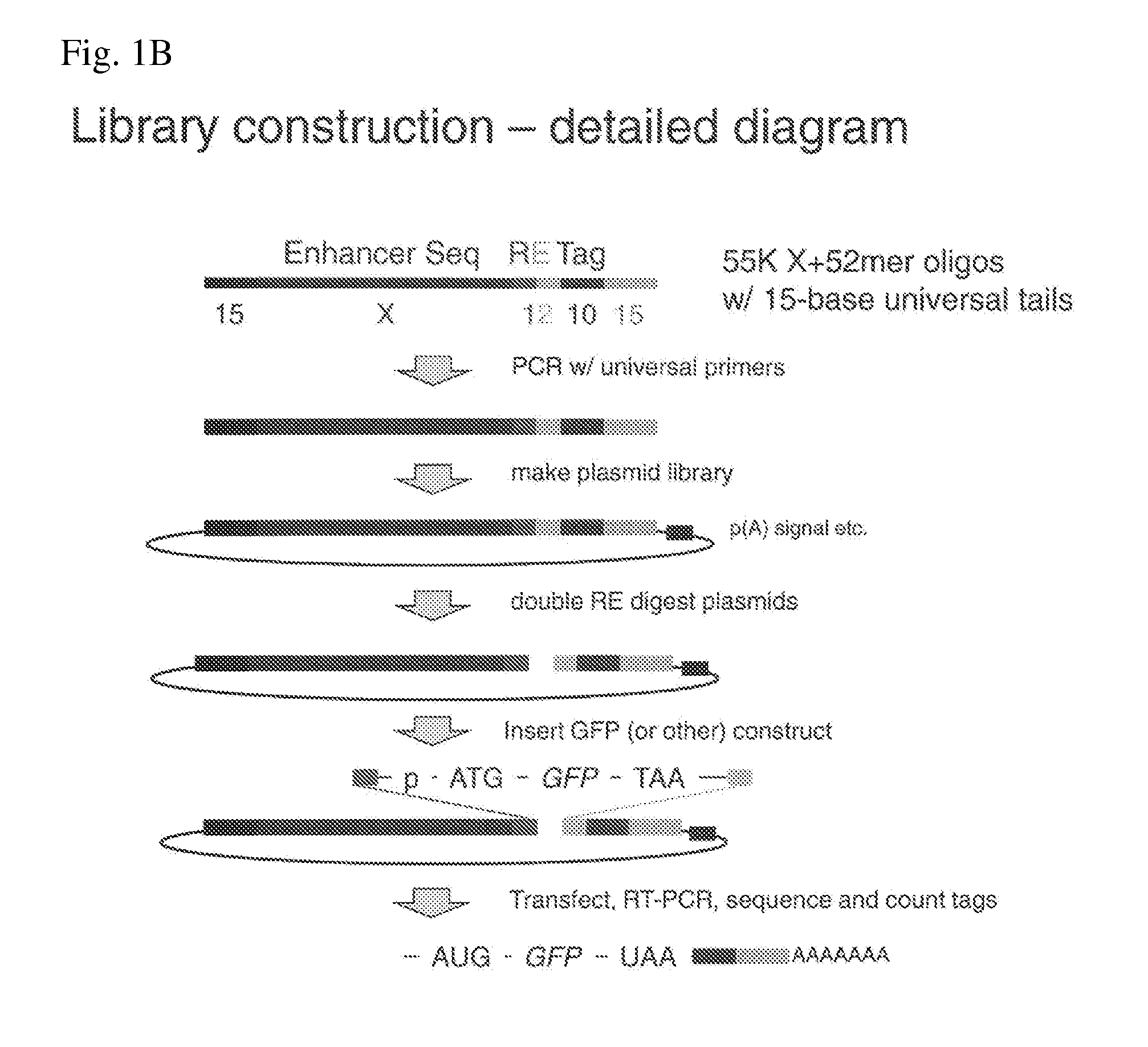
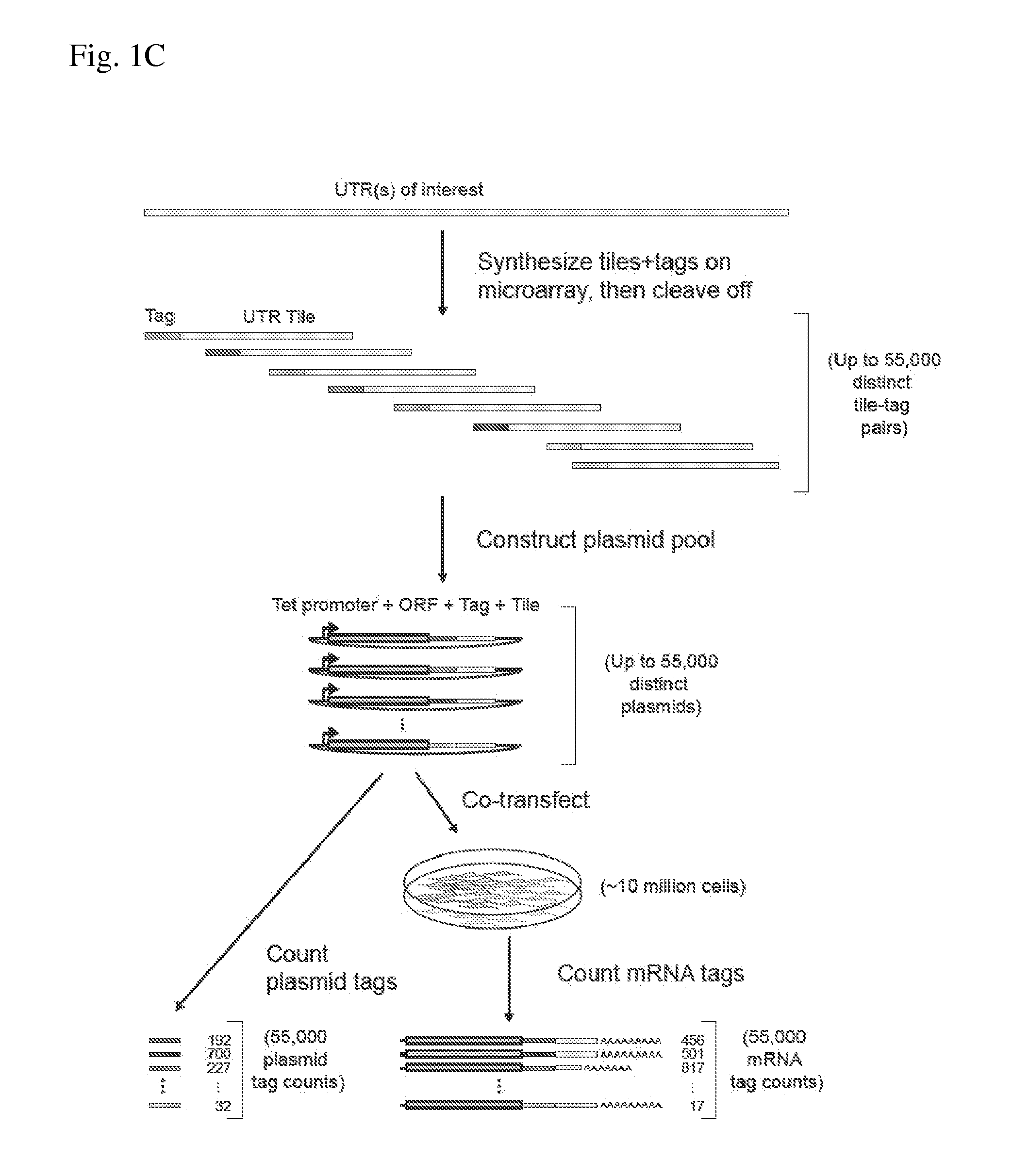
Multiplexed genetic reporter assays and compositions
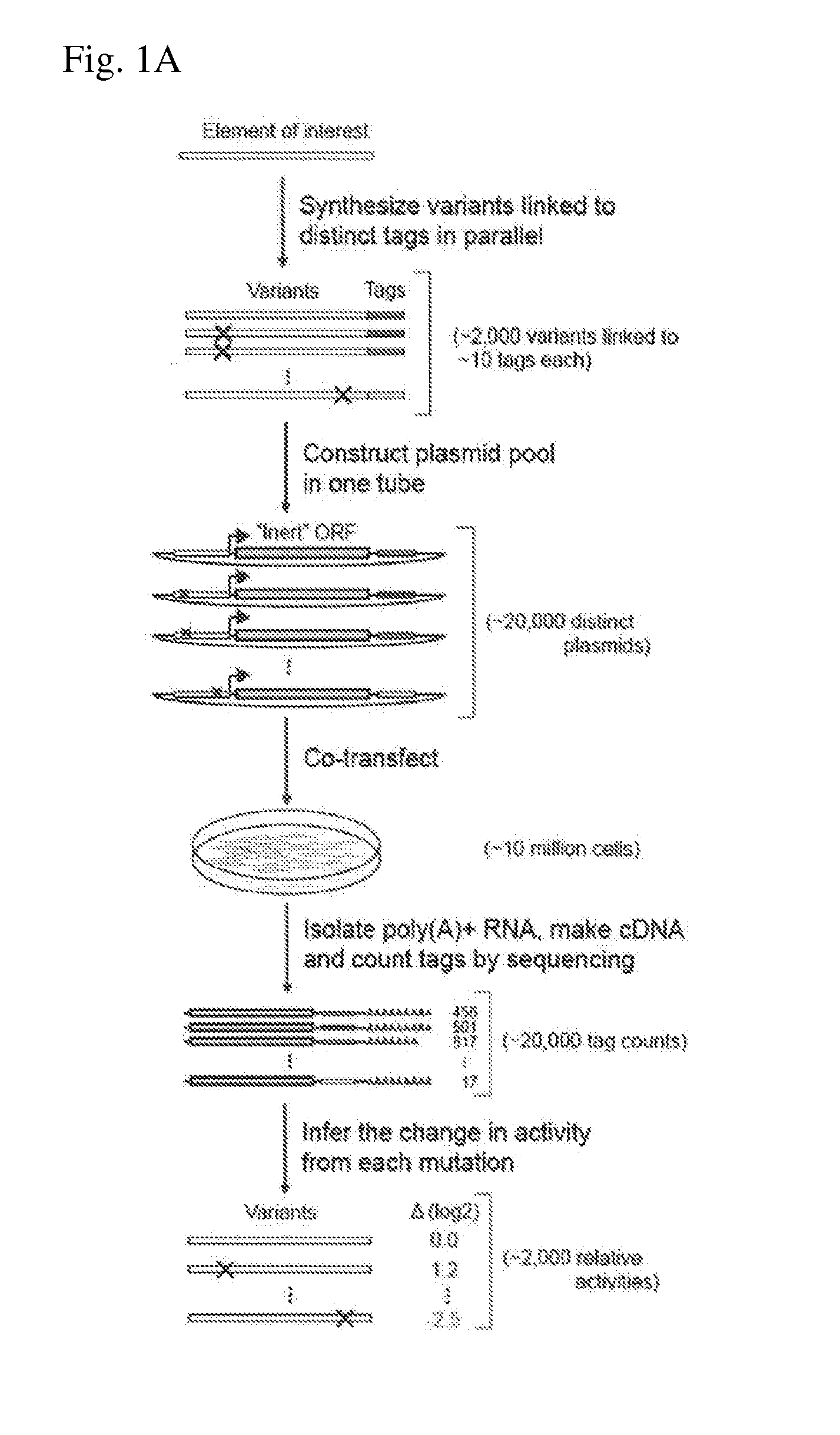
ActiveUS20140200163A1Easy to optimizeHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAssayTranscriptional regulation
The invention provides methods for determining the activity of a plurality of nucleic acid regulatory elements. These methods may facilitate, e.g., the systematic reverse engineering, and optimization of mammalian cis-regulatory elements at high resolution and at a large scale. The method may include integration of multiplexed DNA synthesis and sequencing technologies to generate and quantify the transcriptional regulatory activity of e.g., thousands of arbitrary DNA sequences in parallel in cell-based as says (e.g., mammalian cell based assays).
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC
Adenovirus vectors containing cell status-specific response elements and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides adenoviral vectors comprising cell status-specific transcriptional regulatory elements which confer cell status-specific transcriptional regulation on an adenoviral gene. A “cell status” is generally a reversible physiological and / or environmental state. The invention further provides compositions and host cells comprising the vectors, as well as methods of using the vectors.
Owner:CG ONCOLOGY INC
Transcriptional modulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) of dermal fibroblasts
The present invention includes peptides, compositions as well as their use for the prevention or treatment of various age related or pathological conditions of skin or other tissues including skin wrinkles, wounds, different types of fibrosis and methods of reconstructing different tissues such as techniques used in regenerative medicine. The invention further includes peptide mimetics and methods of use including interfering with transcriptional complexes characteristic of fibroblasts of aged skin and stimulating synthesis of structural components of extracellular matrix.
Owner:FIBROTX OU
MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation
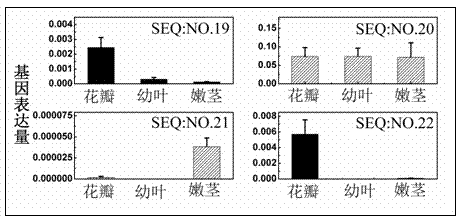
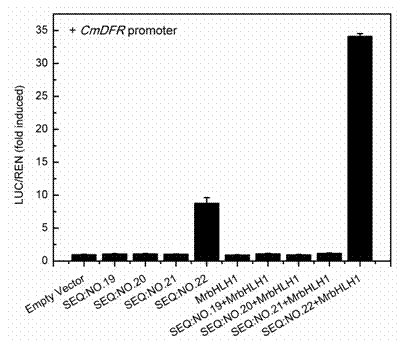
The invention provides an MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 implicated in chrysanthemum petal anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The coding region sequence of the MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 contains 765 nucleotides. A CmMYB6 amino acid sequence contains a conserved R2R3 MYB domain, a [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif and an ANDV motif exist in the R3 domain, the [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif can interact with bHLH, and the ANDV motif is the characteristic motif of the MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The gene expression of CmMYB6 rises in the petal growth process and is significantly and positively correlated with anthocyanin synthesis the CmMYB6 can induce the activity of synthesis of a key gene CmDFR promoter from anthocyanin, and the CmMYB6 has substantially enhanced induction usefulness and can strongly induce accumulation of tobacco leaf anthocyanin during cooperative expression of the CmMYB6 and MrbHLH1. The MYB transcription factor can be used in transcription regulation of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and plant color modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression by small double-stranded modulatory RNA
The invention provides a method for modulating gene expression by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes, wherein the association results in altered expression of the one or more genes. The invention is further directed to method for directing the differentiation of neuronal stem cells into neurons by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes involved in neuronal differentiation and directing the transcription of the one or more genes. In related embodiments, the invention provides particular compositions of double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules as well as therapeutic and screening applications of the invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
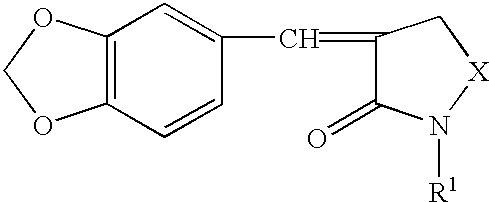
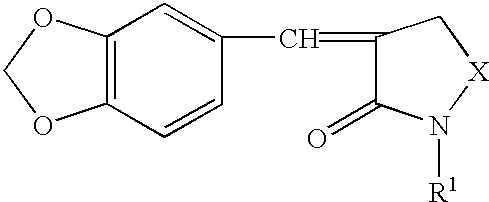
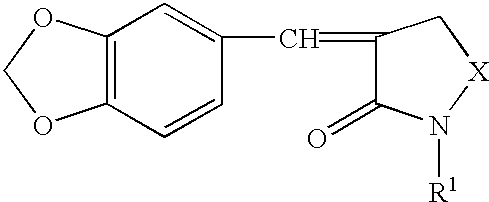
Methods of treating cancer using a heat shock factor activity inhibitor
A disease treatment is provided by controlling the expression of a protein induced by a heat shock factor.The novel compound benzo-1,3-dioxole provides an inhibitor of HSF activity or an inhibitor of inducing the production of a protein regulated by HSF, which inhibits the activity of a heat shock factor, a transcriptional regulatory factor, thereby in turn inhibiting transcription of a structural gene having a heat shock element sequenc in the gene region for transcriptional regulation into RNA, and thus inhibiting translation of the gene into a protein, and resulting in inhibition of inducing production of RNA or protein encoded by the gene. It also provides a drug for treating or preventing cancer through thermotherapy and a drug for treating or preventing stress diseases such as depression.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
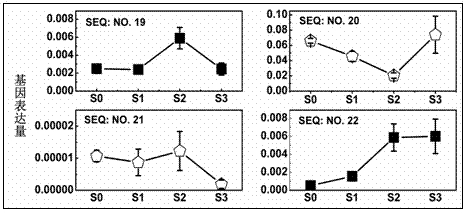
Nanometer antibody, encoding sequence and application of H2A.Z variant
InactiveCN103497253ABacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEscherichia coliComplementarity determining region
The invention discloses a nanometer antibody, an encoding sequence and an application of H2A.Z variant, and meanwhile, discloses a gene sequence encoding the nanometer antibody, a method for preparing the nanometer antibody and a host cell for expressing or capable of expressing the nanometer antibody. A nanometer antibody VHH chain of the histone H2A.Z variant comprises framework regions and a complementary determining region, wherein four framework regions are arranged and are respectively FR1-FR4; the complementary determining region is amino acid sequences of CDR1-CDR3, wherein CDR1 refers to amino acid sequences as shown in SEQNO.16-SEQNO.18; CDR2 refers to amino acid sequences as shown in SEQNO.19-SEQNO.21; CDR3 refers to amino acid sequences as shown in SEQNO.22-SEQNO.24. The nanometer antibody can be efficiently expressed in Escherichia coli and can be applied in research on high expression of cancer associated protein and related transcription regulation mechanism.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
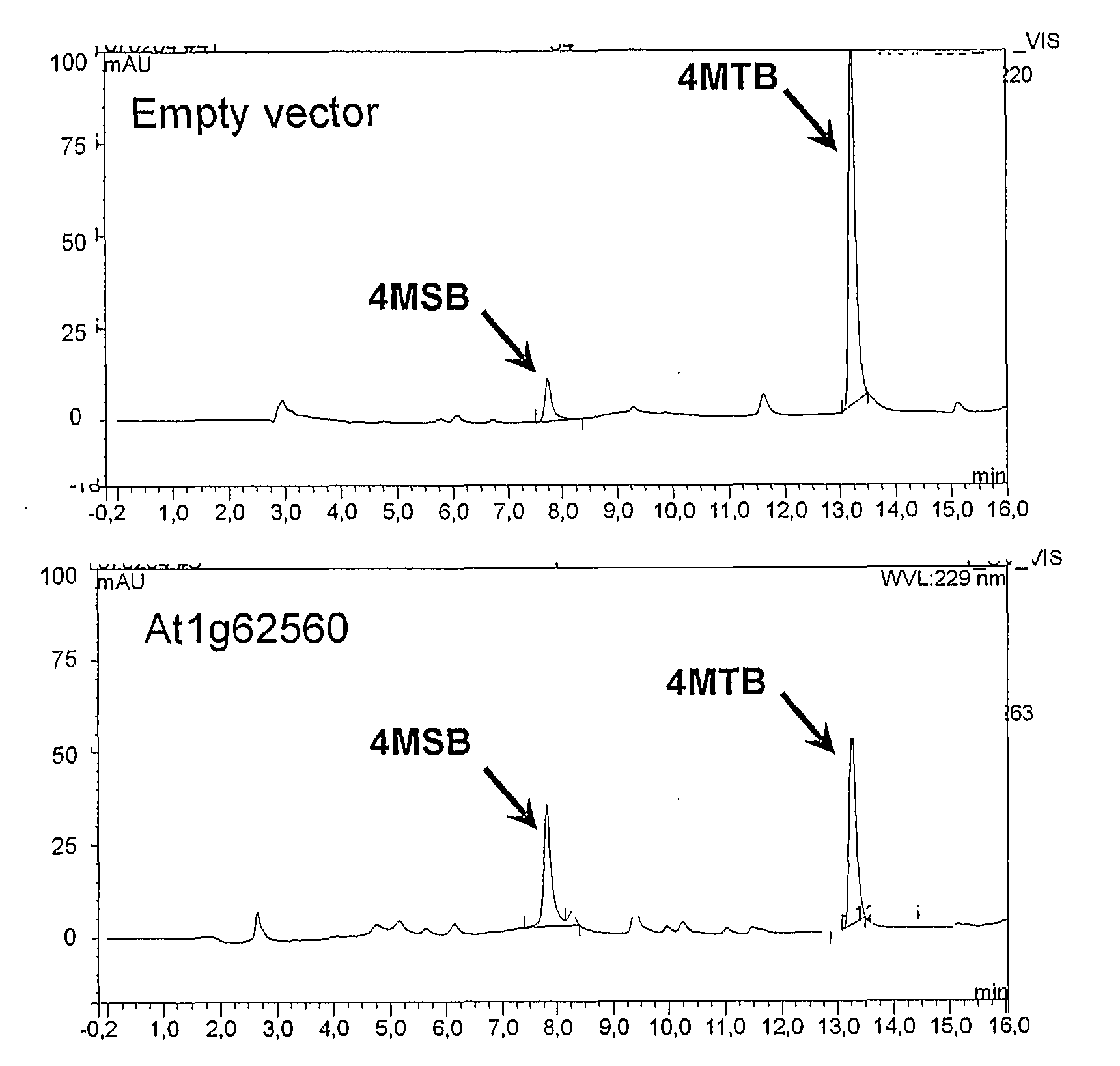
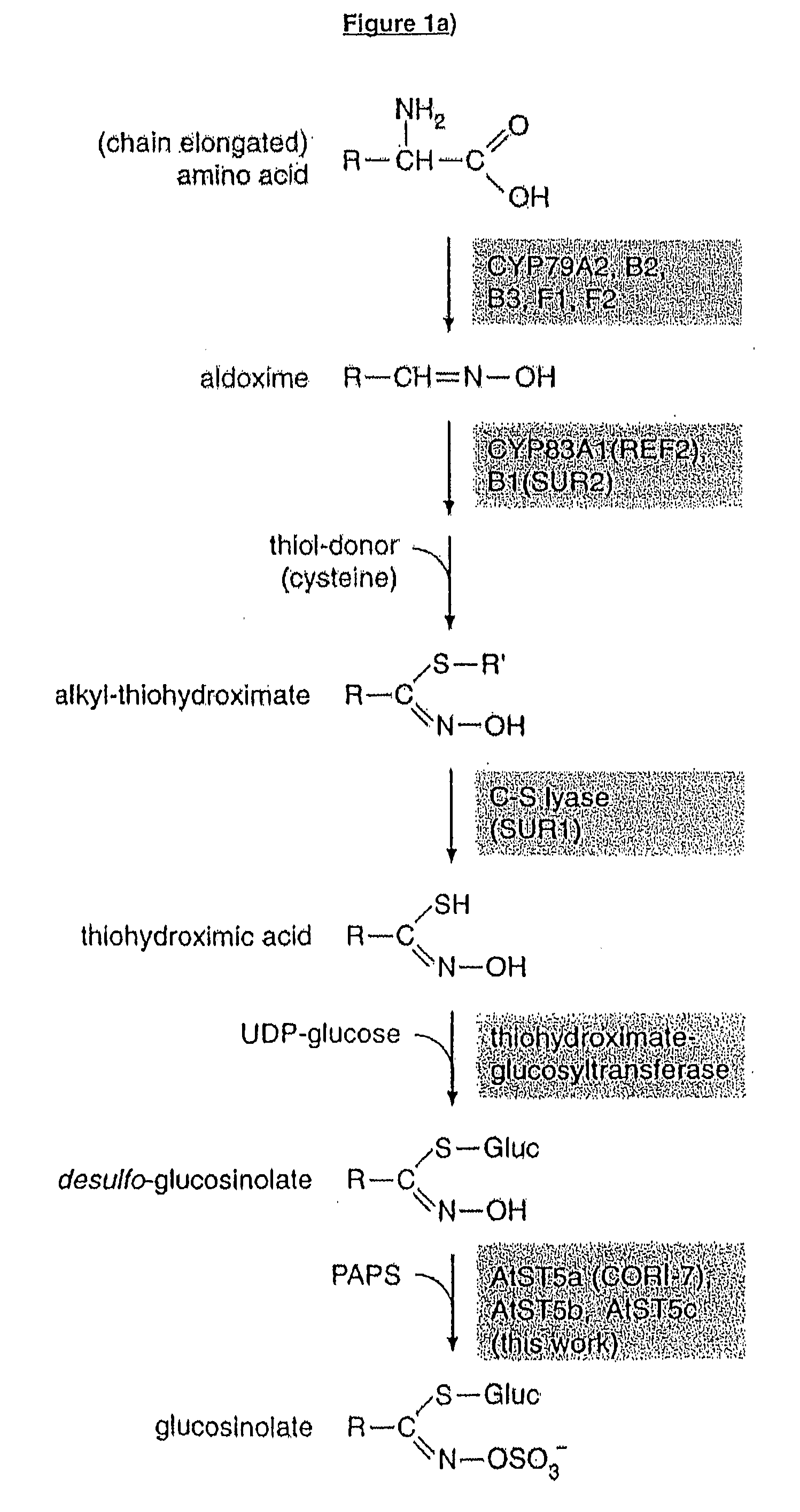
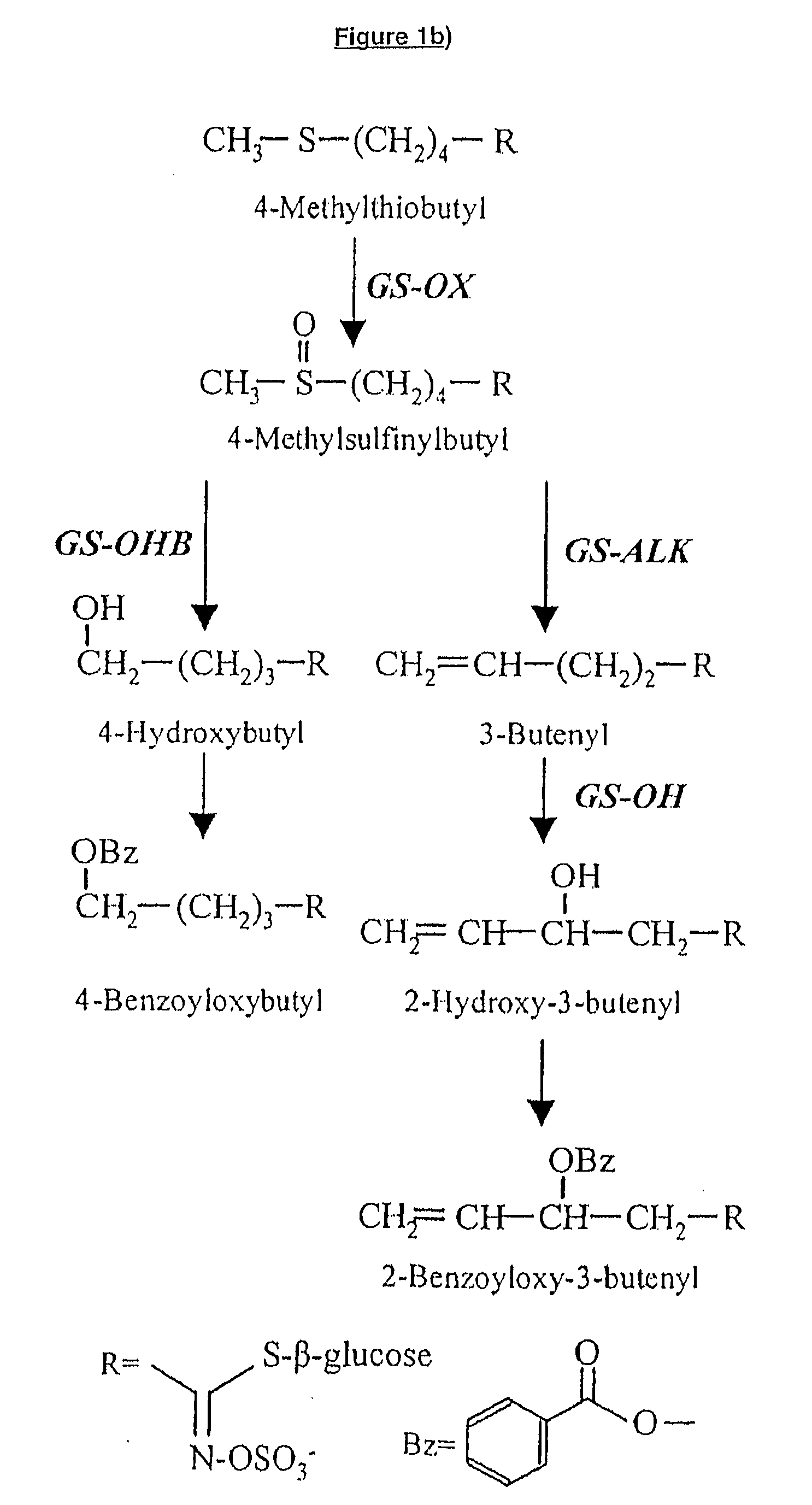
Flavin monooxygenases and transcription factors involved in glucosinolate biosynthesis
InactiveUS20100011462A1Add flavorImprove seed qualitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesTranscriptional regulation
The invention provides methods and materials relating generally to plant derived flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMOs) capable of catalysing oxidation of a thio- to a sulphinyl-group during glucosinolate biosynthesis. It further relates to plant derived MYB factors capable of transcriptional regulation of biosynthetic genes. These have utility in the modification of glucosinolate biosynthesis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
Transgenic Plant Having Enhanced Drought Tolerance
InactiveUS20110209247A1Improve drought toleranceImprove disease resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellGMO Plants
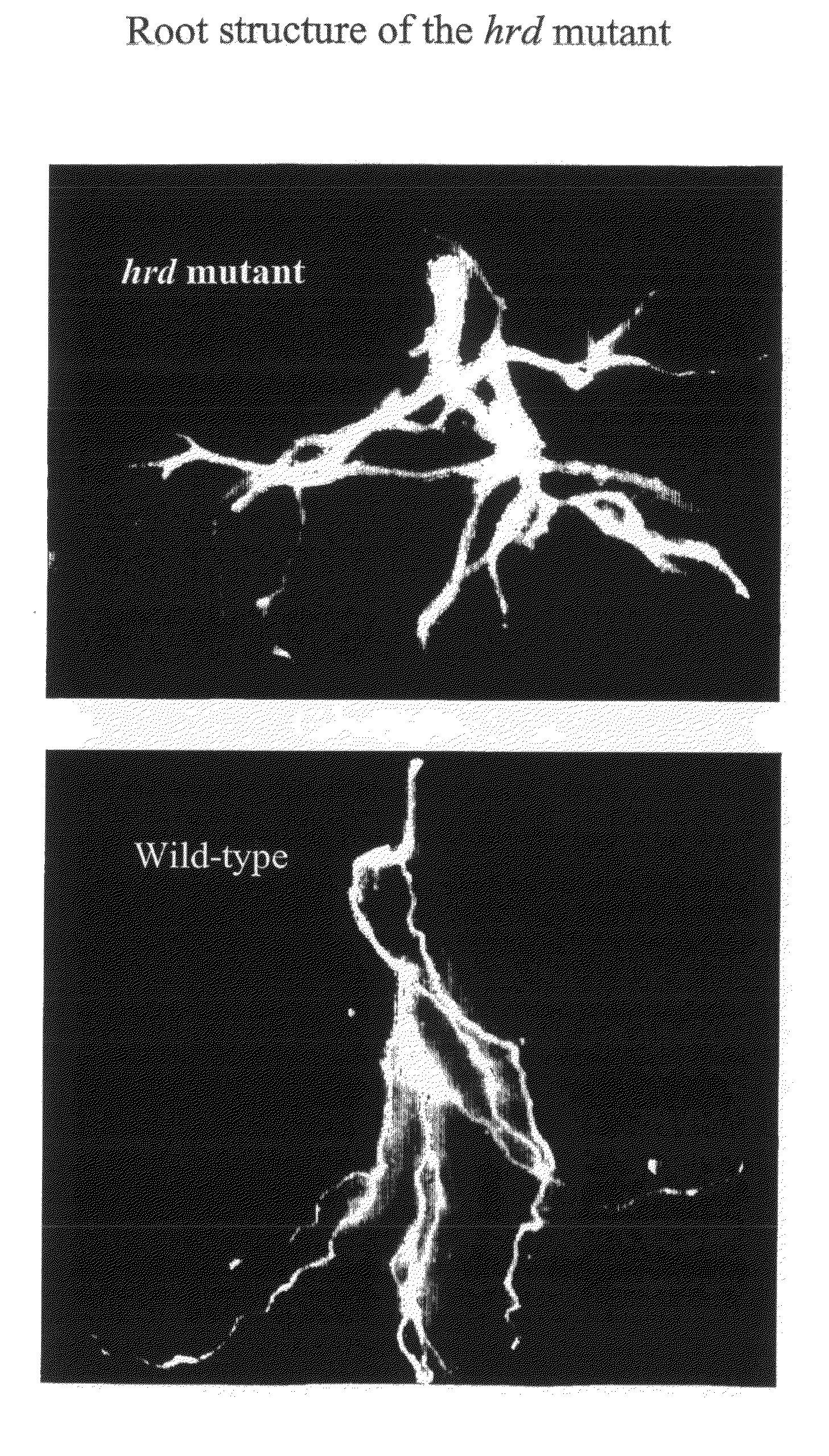
The present invention relates to the field of transgenic plants with novel phenotypes, especially plants with enhanced drought and pathogen resistance. Provided are transgenic crop plants comprising integrated in their genome a chimeric gene, characterized by said chimeric gene comprising a transcription regulatory sequence active in plant cells operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a protein having the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 or a protein at least 70% identical to SEQ ID NO: 3, or an ortholog protein or a functional fragment thereof. In addition to enhanced drought tolerance the transgenic plants may show enhanced disease resistance and enhanced root structure.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES
Artificial transcription factor induced pluripotent stem cells
The invention relates to an artificial factor and application thereof in reprogramming somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells and other cell lineages, in particular to a fusion protein containing a protein coded by a cell totipotency related gene and a transcriptional regulation structure domain, a coding sequence and an expression vector thereof, and a composition thereof. The invention also relates to a method for reprogramming somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells and other cell lineages, and cells containing the fusion protein and the coding sequence.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
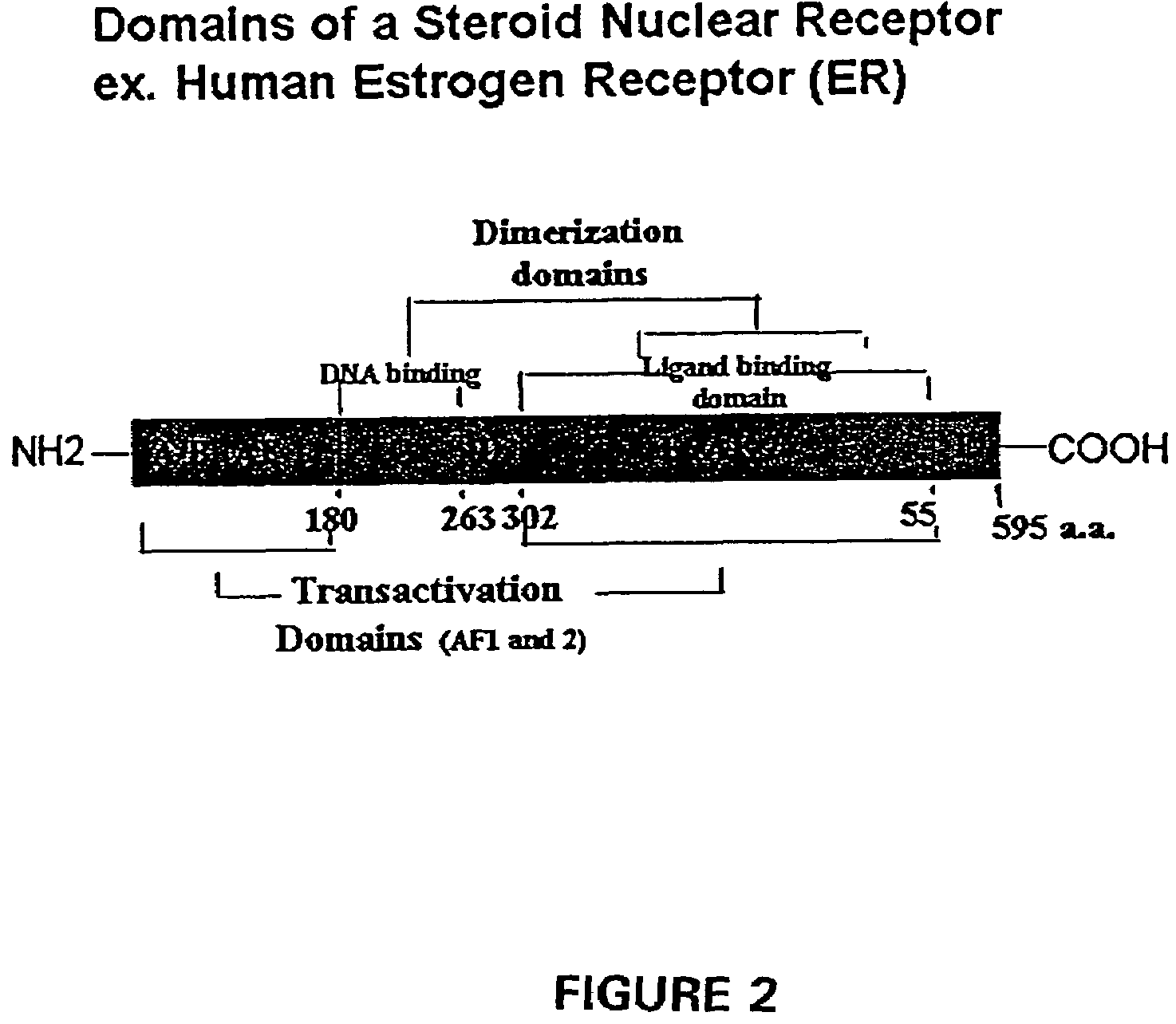
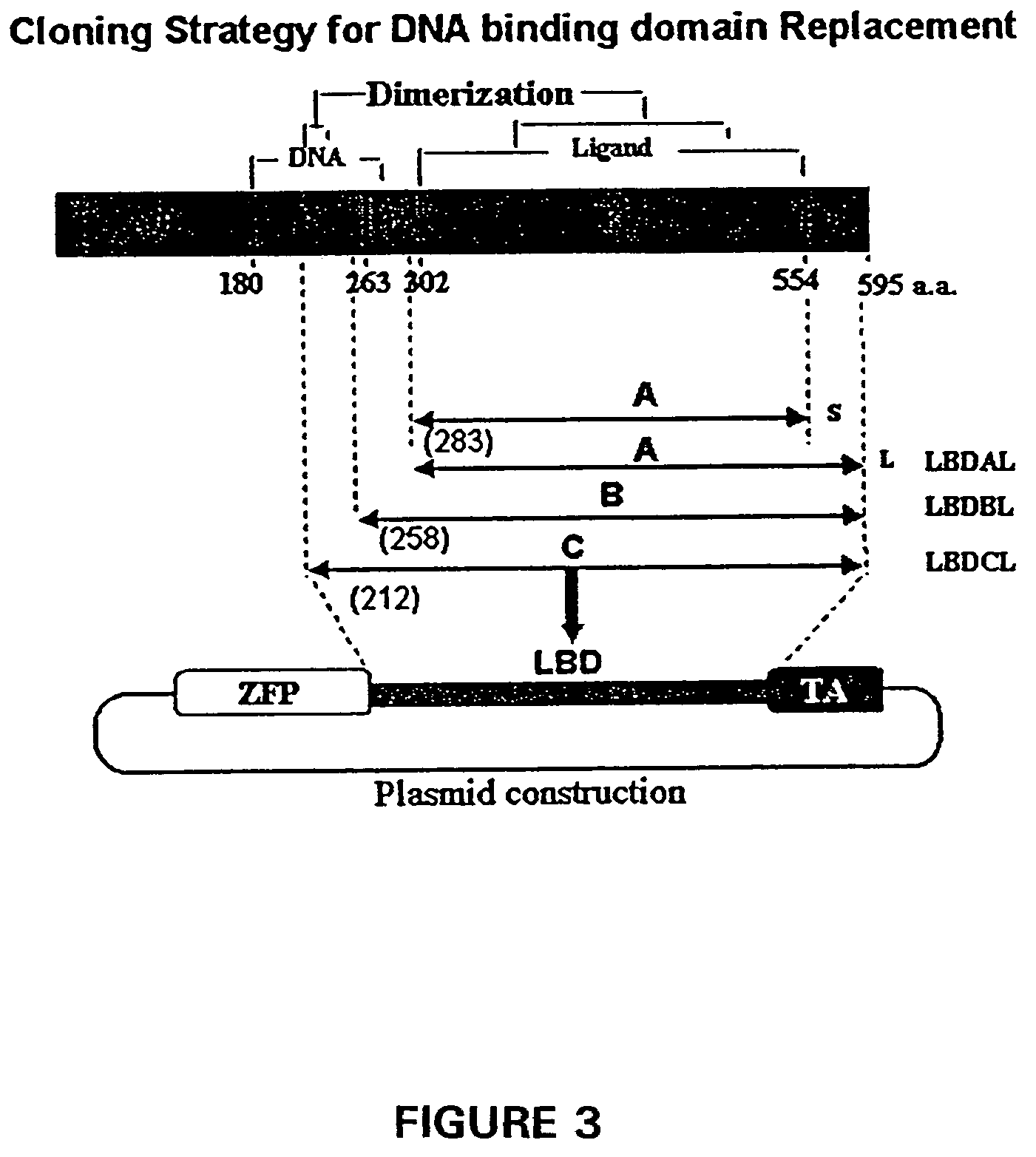
Ligand activated transcriptional regulator proteins
InactiveUS7329728B1Avoid undesirable immunological responseFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideBinding domain
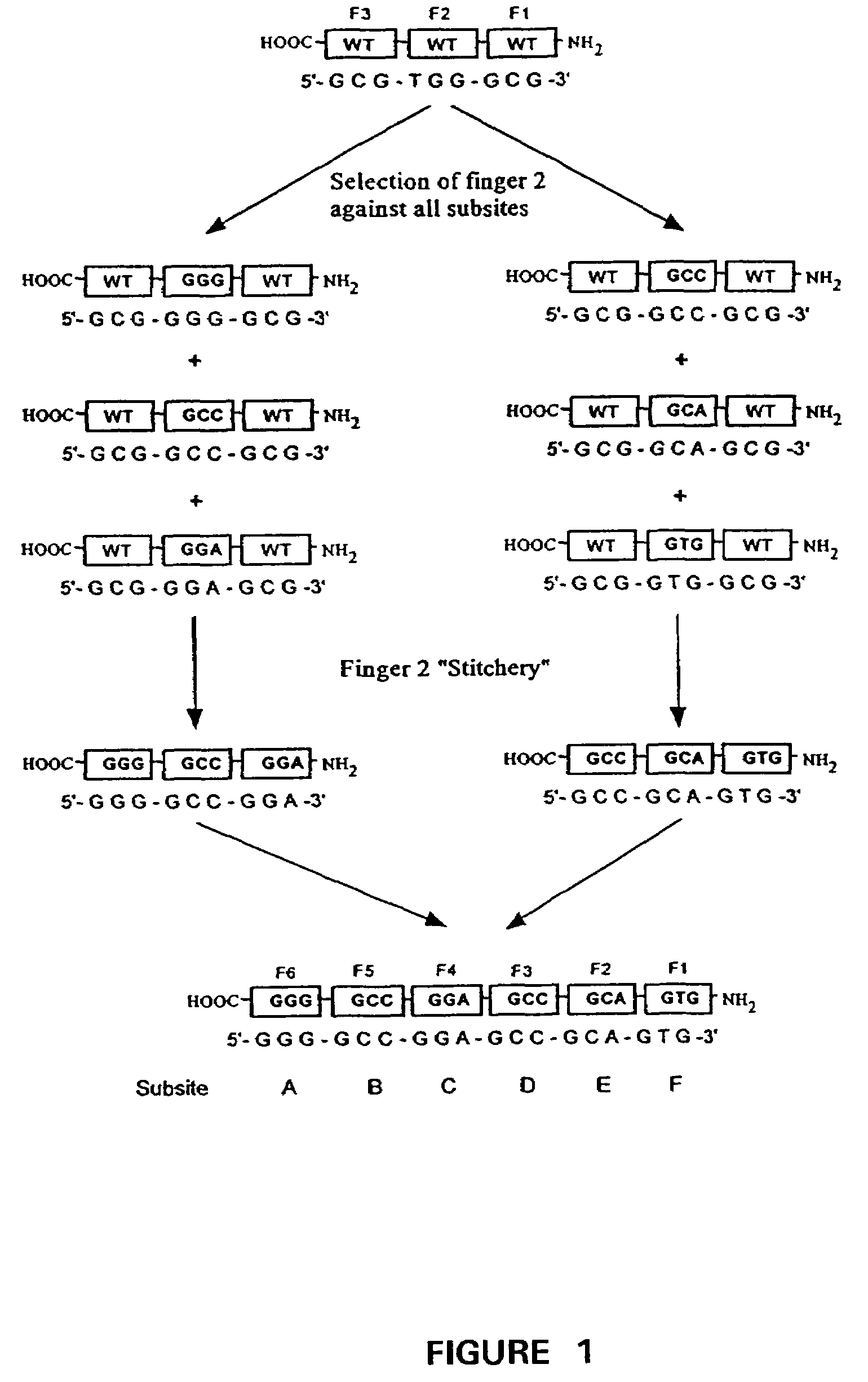
Fusion proteins for use as ligand-dependent transcriptional regulators are provided. The fusion proteins include a nucleotide binding domain operatively linked to a ligand-binding domain. They also can include a transcription regulating domain. The nucleotide binding domain is a zinc-finger peptide that binds to a targeted contiguous nucleotide sequence of from 3 to about 18 nucleotides are provided. The fusion proteins are used for gene therapy. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding the fusion proteins, expression vectors, and transfected cells.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
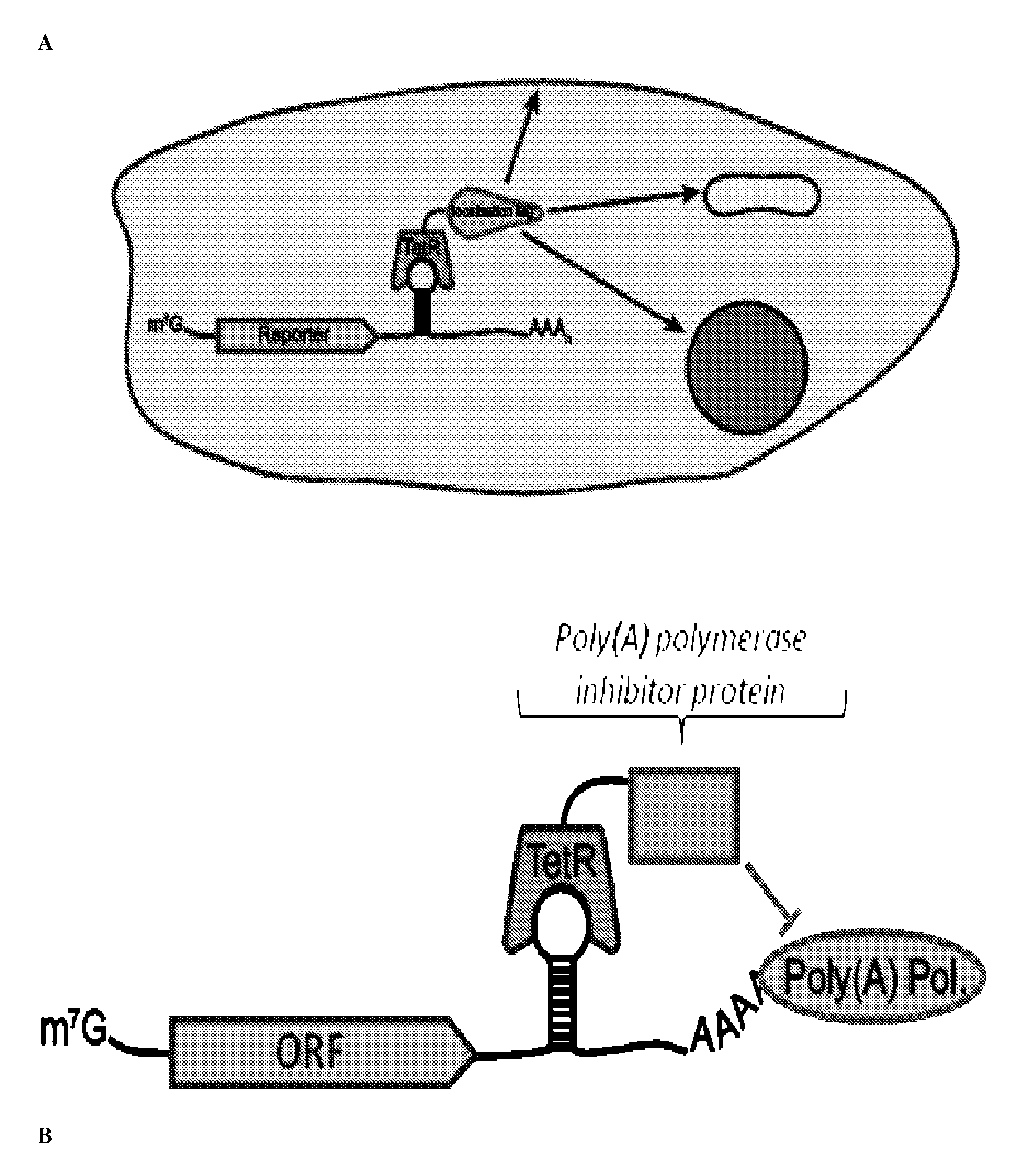
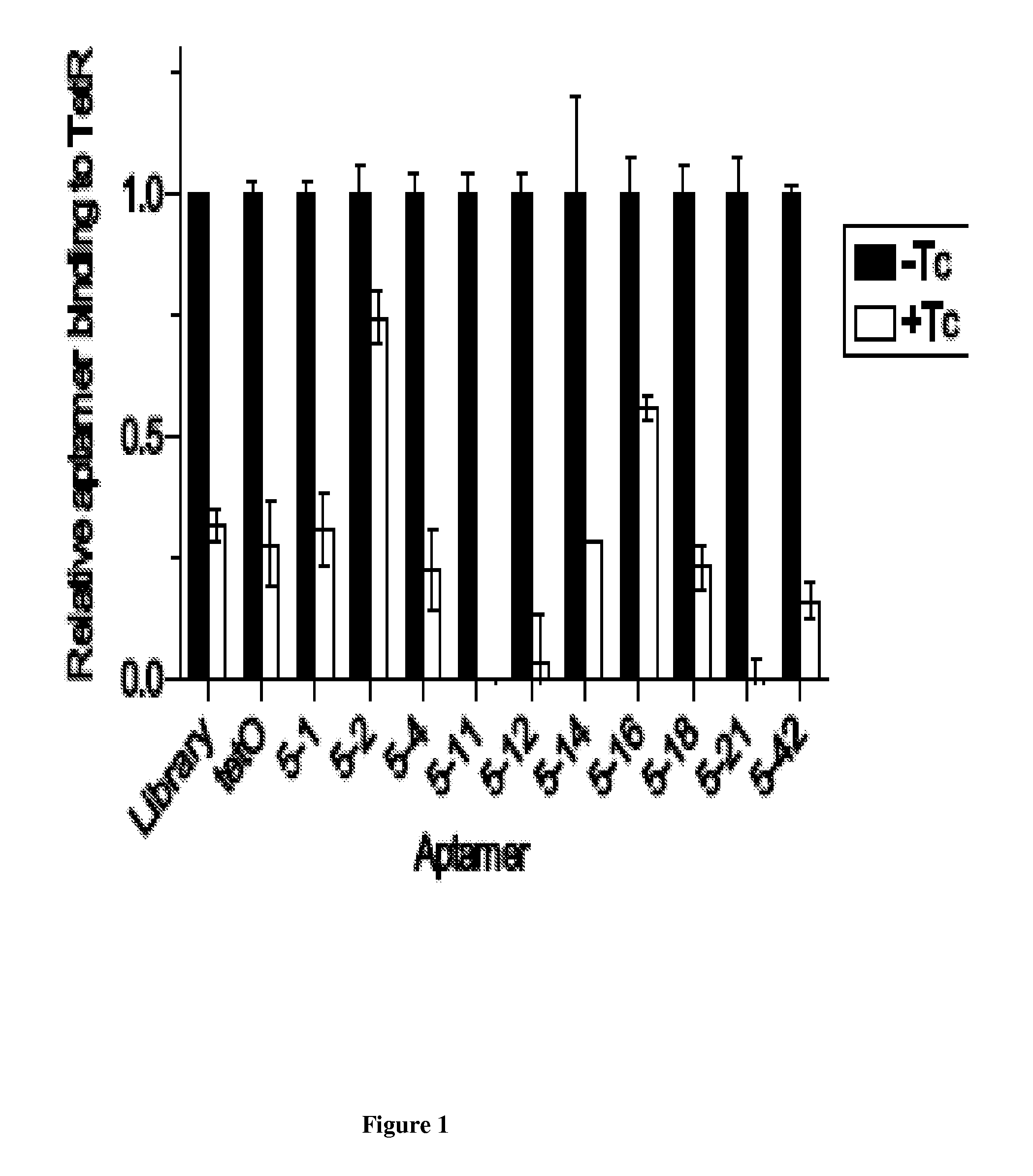
Post-Transcriptional Regulation Of RNA-Related Processes Using Encoded Protein-Binding RNA Aptamers
In vitro SELEX has been used to discover high affinity RNA aptamers interacting with the tetracycline repressor protein in a tetracycline-dependent manner. Using in silico RNA folding predictions to guide the design of both aptamer truncations and mutants, minimized tetracycline repressor protein high affinity binding aptamers have been defined. Using one such aptamer, inducible post-transcriptional regulation in vivo has been demonstrated that is predicated on a direct interaction between a tetracycline repressor protein and a RNA aptamer element. These aptamer components can be integrated in any organism to inducibly regulate RNA translation of a gene of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
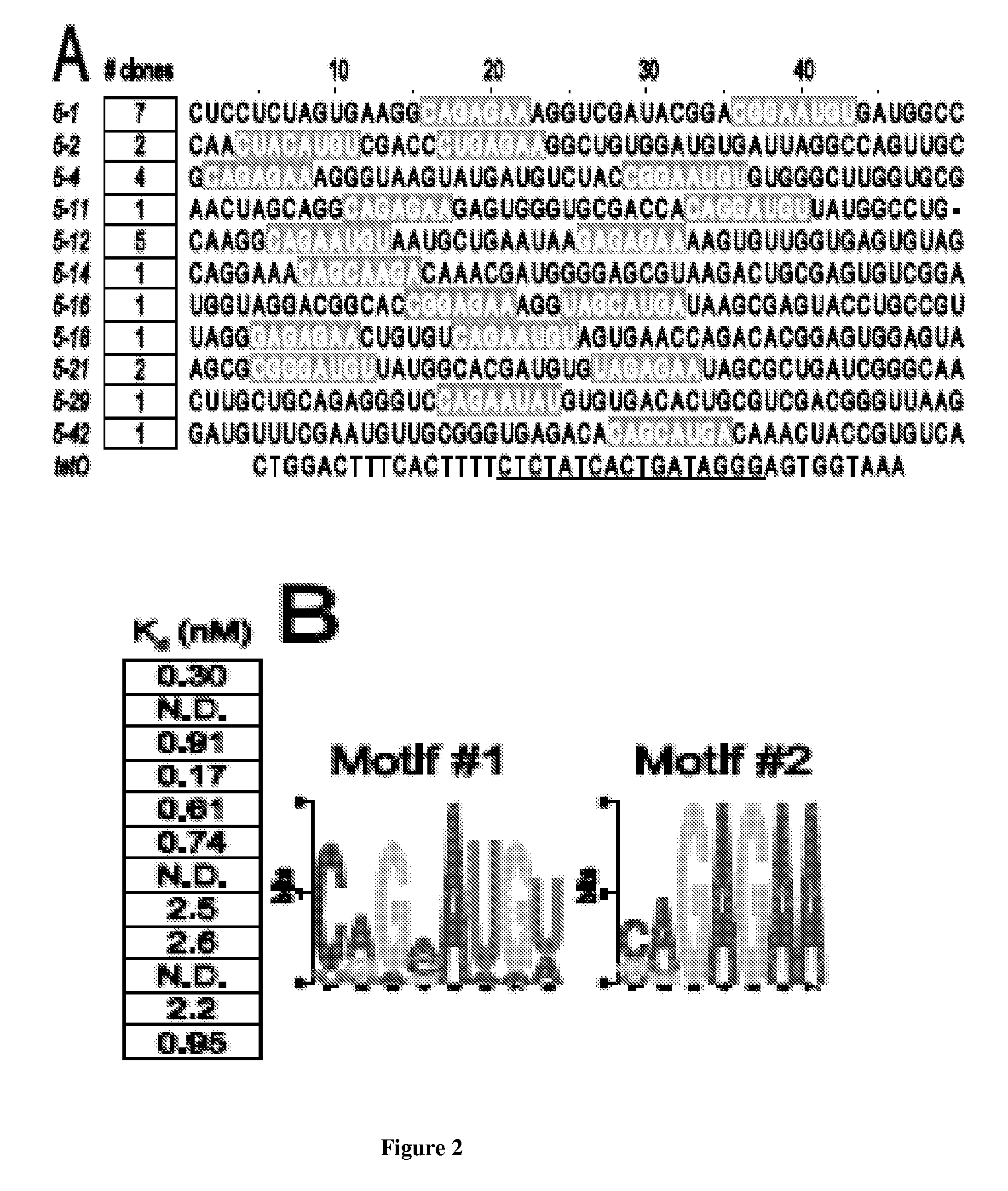
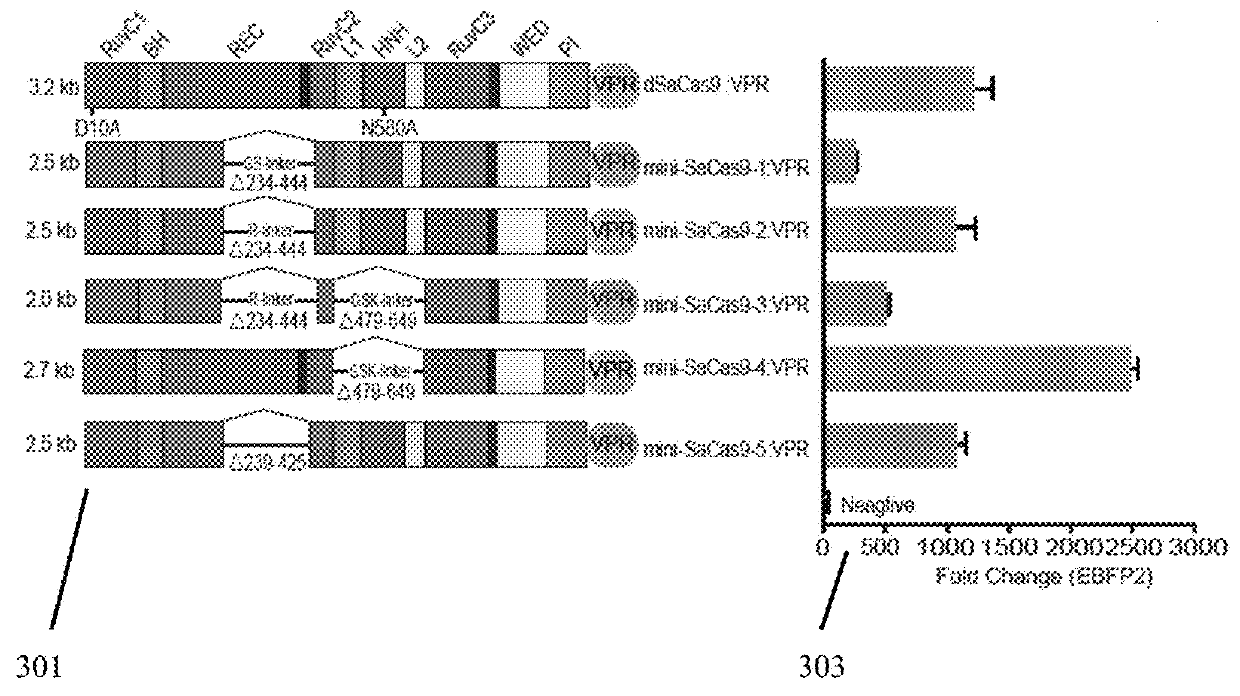
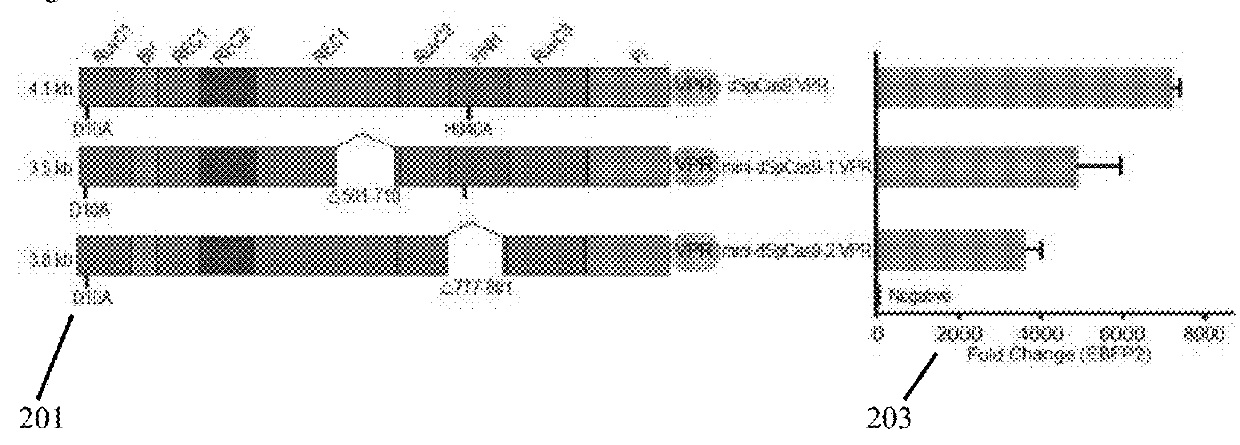
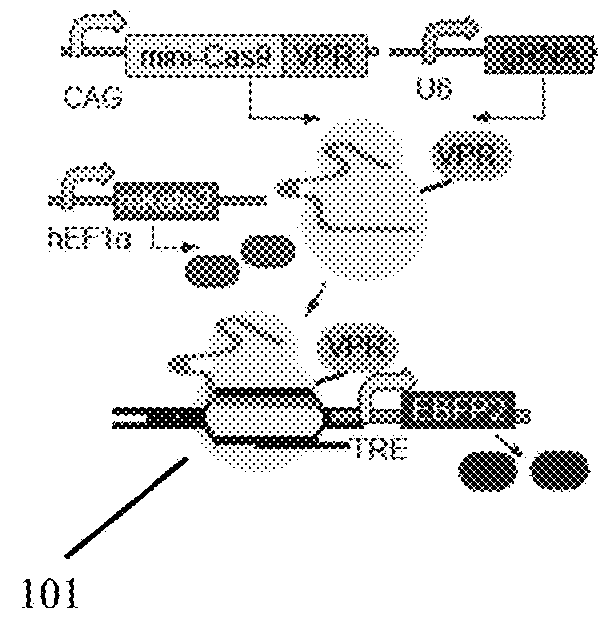
Engineering of a minimal SaCas9 CRISPR/Cas system for gene editing and transcriptional regulation optimized by enhanced guide RNA
The presently claimed invention offers programmable and precise regulation of Cas9 functions by utilizing a set of compact Cas9 derivatives created by deleting conserved HNH and / or REC-C domains based on the structural information across variant class 2 CRISPR effectors. In addition, a novel strategy for engineering the dimeric gRNA-guided nuclease by splitting the mini-dSaCas9 and fusing the FokI domain right after the split point is claimed to increase the on-target DNA cleavage efficiency and potentially reduce the off-target effect because of a closer proximity of dimeric FokI nuclease to the target sequence. By combining the optimized and compact gRNA expression cassette and the downsized SaCas9 derivatives, the entire CRISPR / Cas system with different effector domains for transactivation, DNA cleavage and base editing is loaded into a single AAV virus. Such an all-in-one AAV-CRISPR / Cas9 system will be particularly appealing in biomedical applications that require safe and efficient delivery in vivo.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
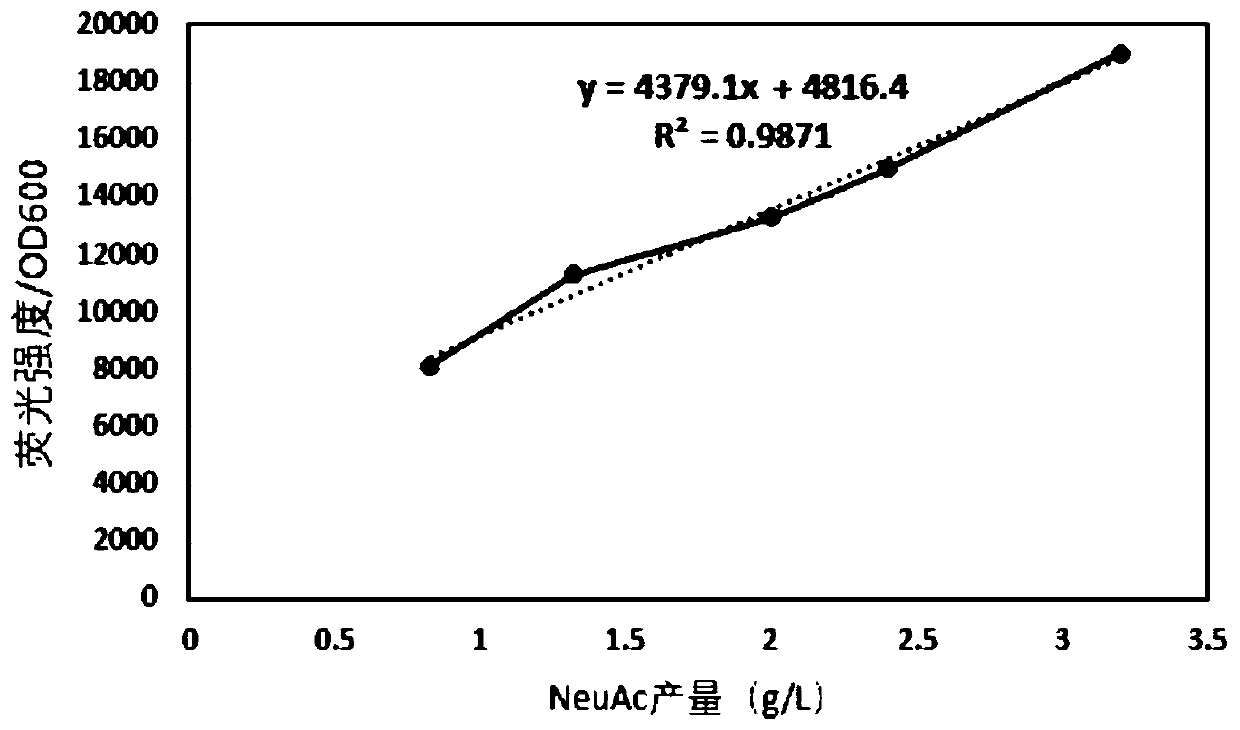
N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor and application thereof
The invention discloses an N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor is constructed with transcriptional regulation factor NanR and GFP (green fluorescent protein) gene, from Escherichia coli K12, acting as reporter genes; an effective relationship between N-acetylneuraminic acid and fluorescence intensity is established. The N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor has an important application prospect in screening microorganisms which produce target metabolites.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Synthetic nucleic acids from aquatic species
InactiveUS20090191622A1Enhanced levelReduce in quantityFungiSugar derivativesAquatic speciesFluorescence
A synthetic nucleic acid molecule is provided that includes nucleotides of a coding region for a fluorescent polypeptide having a codon composition differing at more than 25% of the codons from a parent nucleic acid sequence encoding a fluorescent polypeptide. The synthetic nucleic acid molecule has at least 3-fold fewer transcription regulatory sequences relative to the average number of such sequences in the parent nucleic acid sequence. The polypeptide encoded by the synthetic nucleic acid molecule preferably has at least 85% sequence identity to the polypeptide encoded by the parent nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:PROMEGA
Method for increasing yield of L-arginine synthesized from corynebacterium crenatum
ActiveCN109370975AIncrease productionOptimizing Fermentation ConditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidArginine
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of L-arginine synthesized from corynebacterium crenatum, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. By means of the method, recombinant corynebacterium crenatum of which a nitrogen transcriptional regulation factor AmtR is knocked out and ammonium transport protein is over-expressed is successfully constructed. By adopting a strategy of batch fermentation by a 5-L fermentation tank and optimizing fermentation conditions, finally the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum Cc5-5 / pXMJ19-amtB is fermented for 96 h, the L-arginine yield of the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum reaches 60.9+ / -1.31 g / L, the yield is increased by 30.56% compared with an original strain of corynebacterium crenatum original strain SYPA5-5, the production intensity reaches 0.634 g / L.h, and the saccharic acid conversion rate is 0.36+ / -0.018 g / g, so that high yield of the L-arginine is realized. Meanwhile, utilization of NH4+ is increased in therecombinant corynebacterium crenatum, so that it is shown that knockout of the nitrogen transcriptional regulation factor and overexpression of the ammonium transport protein have a remarkable effecton the yield of the L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
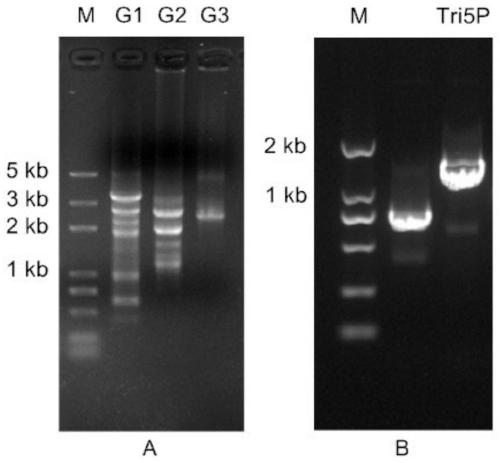
Myrothecium roridum A553 trichothecene synthase gene Tri5 promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN109735537AImprove expression levelIncrease transcriptional activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a myrothecium roridum A553 trichothecene synthase gene Tri5 promoter and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of a promoter is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. According to the promoter, through a chromosome walking technology, the upstream promoter sequence of the Tri5 gene is obtained, the core region of the promoter is predicted, and the myrothecium roridum A553 trichothecene synthase gene Tri5 promoter Tri5P is obtained. By means of the promoter, expression of a hygromycin resistance gene can be efficiently started, the starting efficiency is close to that of a constitutive promoter TEF1, and a molecular biology basis is laid for increasing the yield of trichothecene toxin and obtaining more novel trichothecene toxin with high activities through transcriptional regulation and heterologous expression in the later period.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
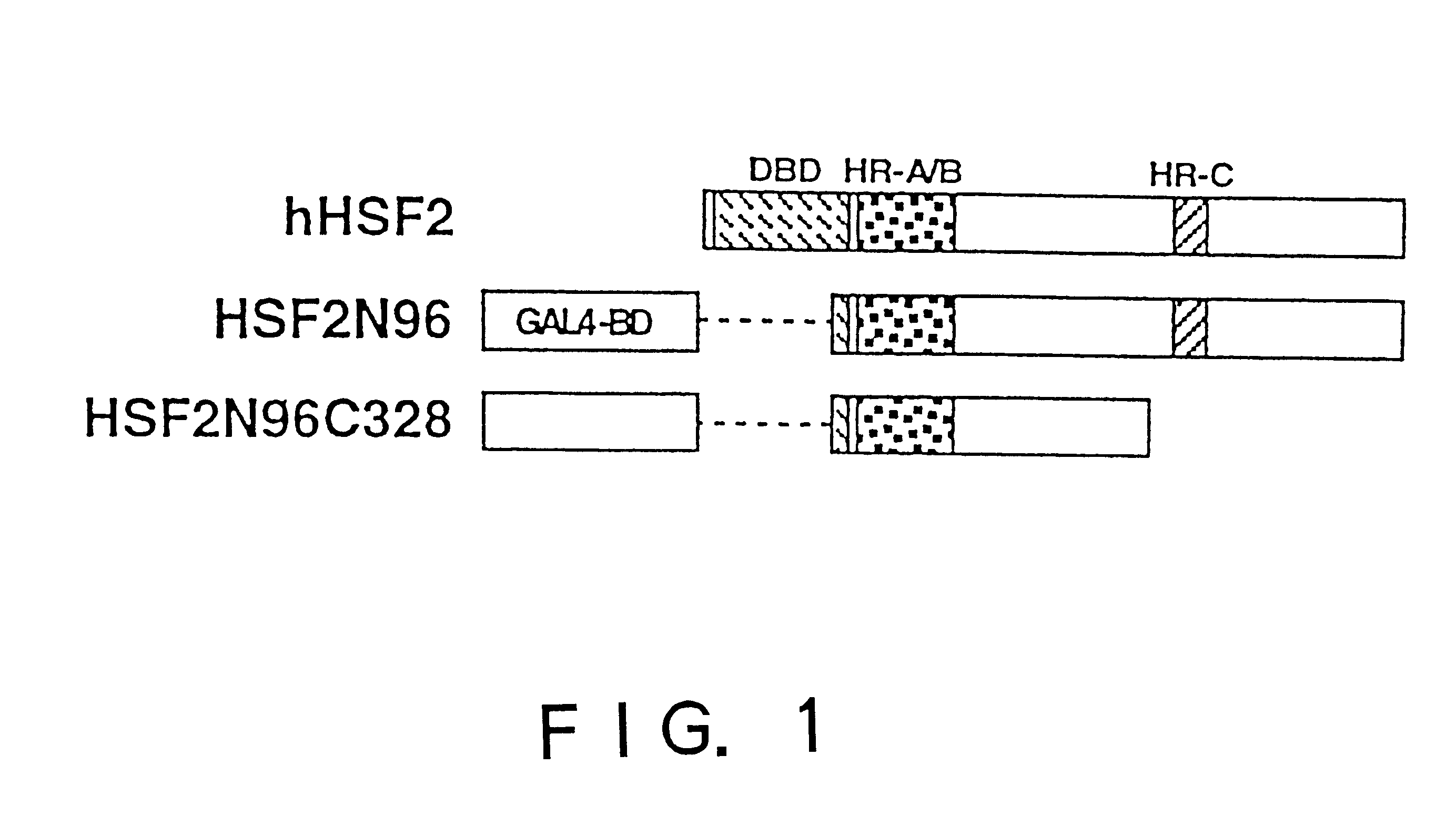
Heat shock transcription factor-binding protein
InactiveUS6485936B1Rule out the possibilityImprove purification effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesA-DNAHsp70
To provide a heat shock transcription factor (HSF) 2 binding factor, which can be involved in the transcriptional regulation of HSP70.2 playing an essential role in spermatogenesis; a DNA encoding the binding factor; an expression vector carrying the DNA; a transformant harboring the expression vector; a process for preparing a recombinant protein comprising the step of culturing the transformant; an antibody or a fragment thereof capable of specifically binding to the binding factor; an antisense DNA or antisense RNA complementary to the DNA; and an oligonudeotide probe or primer capable of specifically hybridizing to the DNA.
Owner:HSP RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com