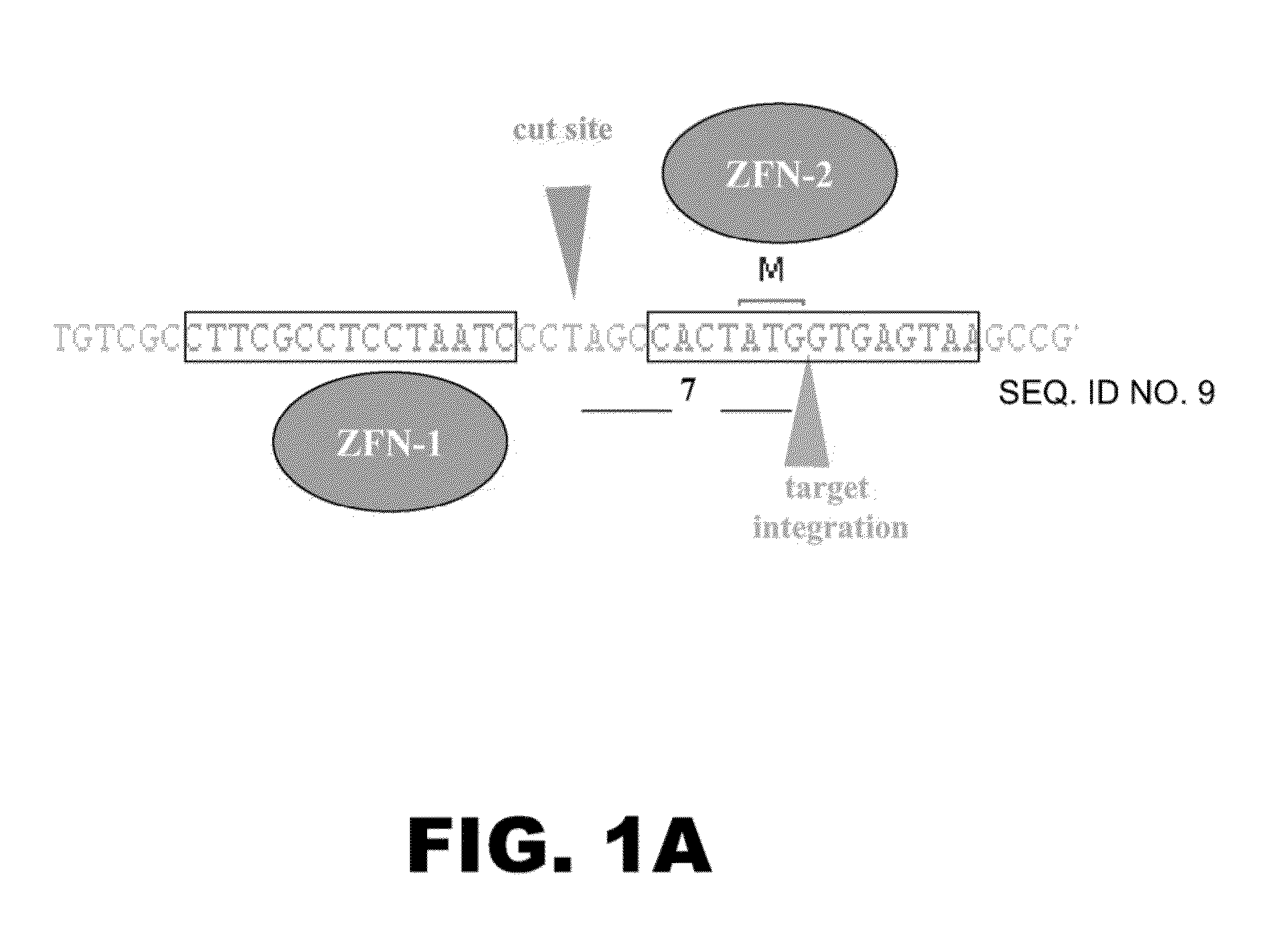
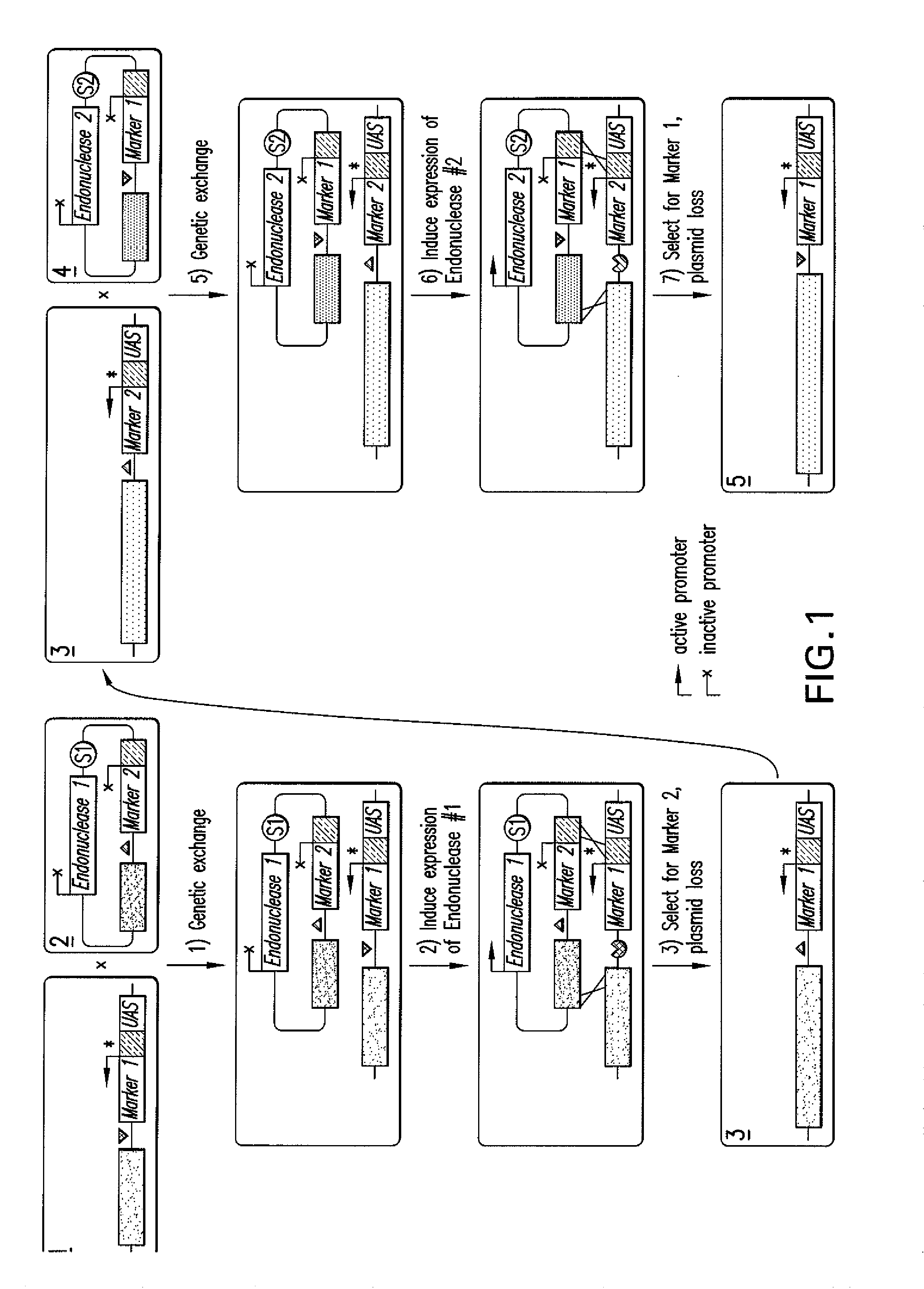
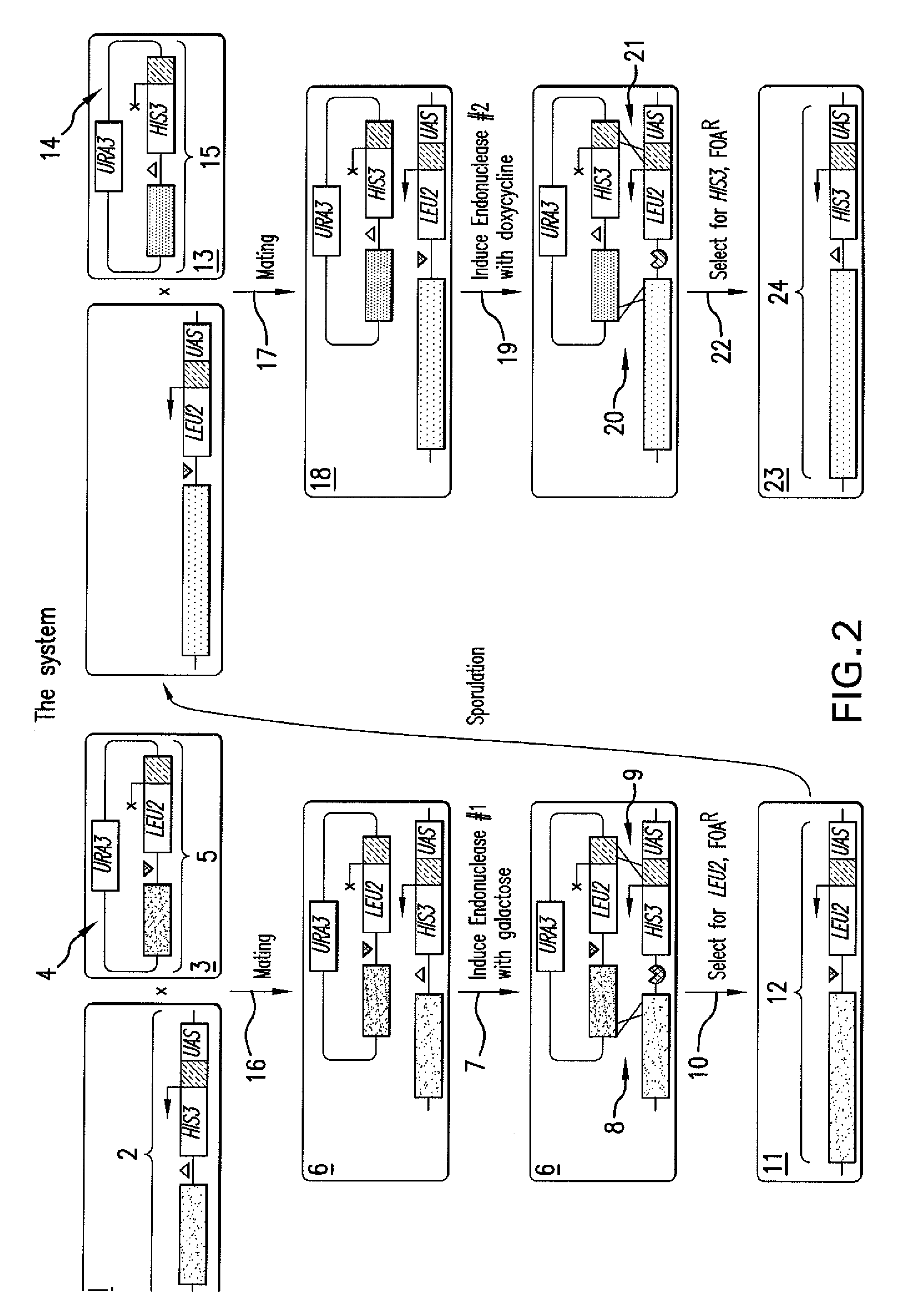
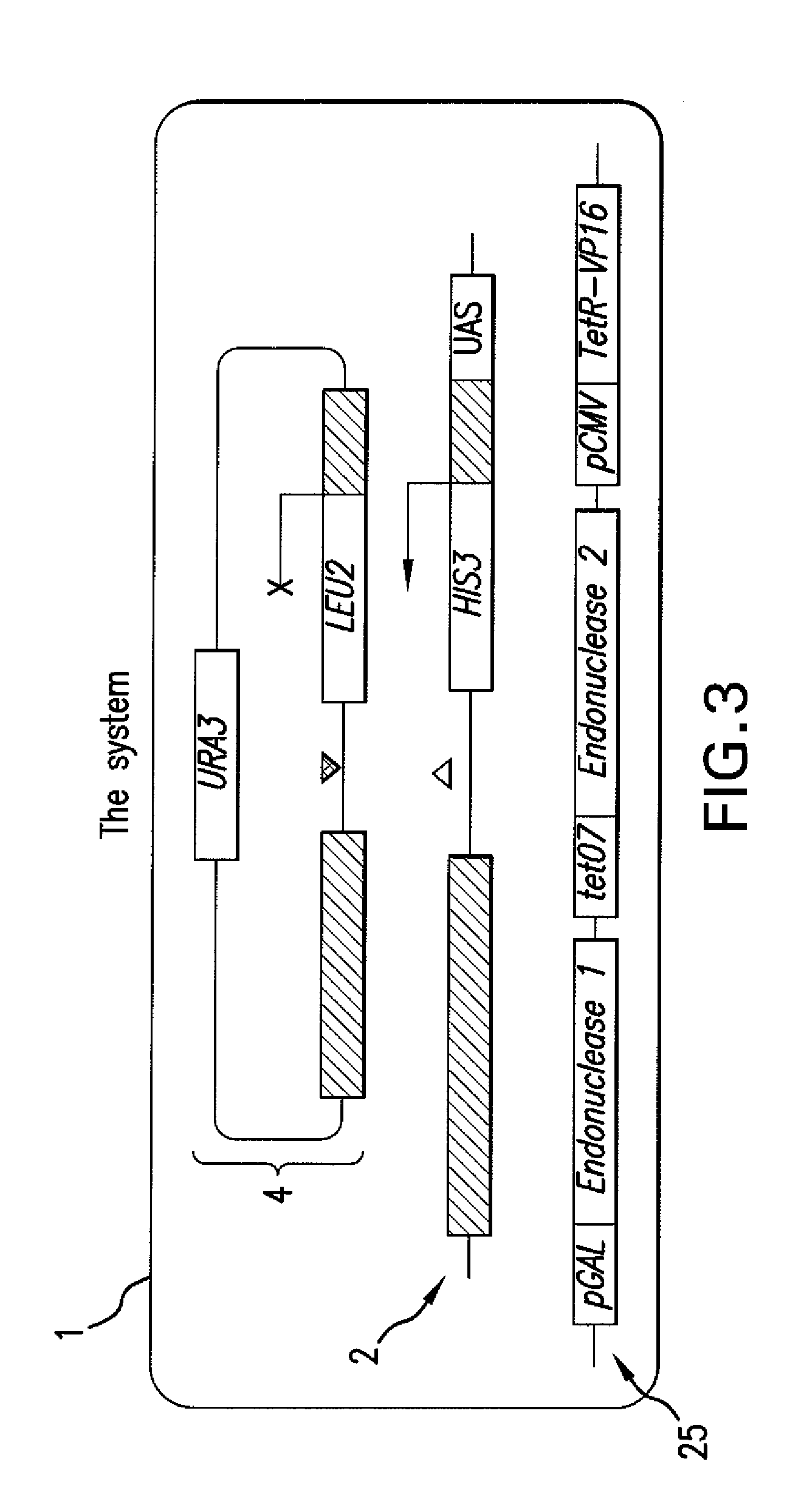
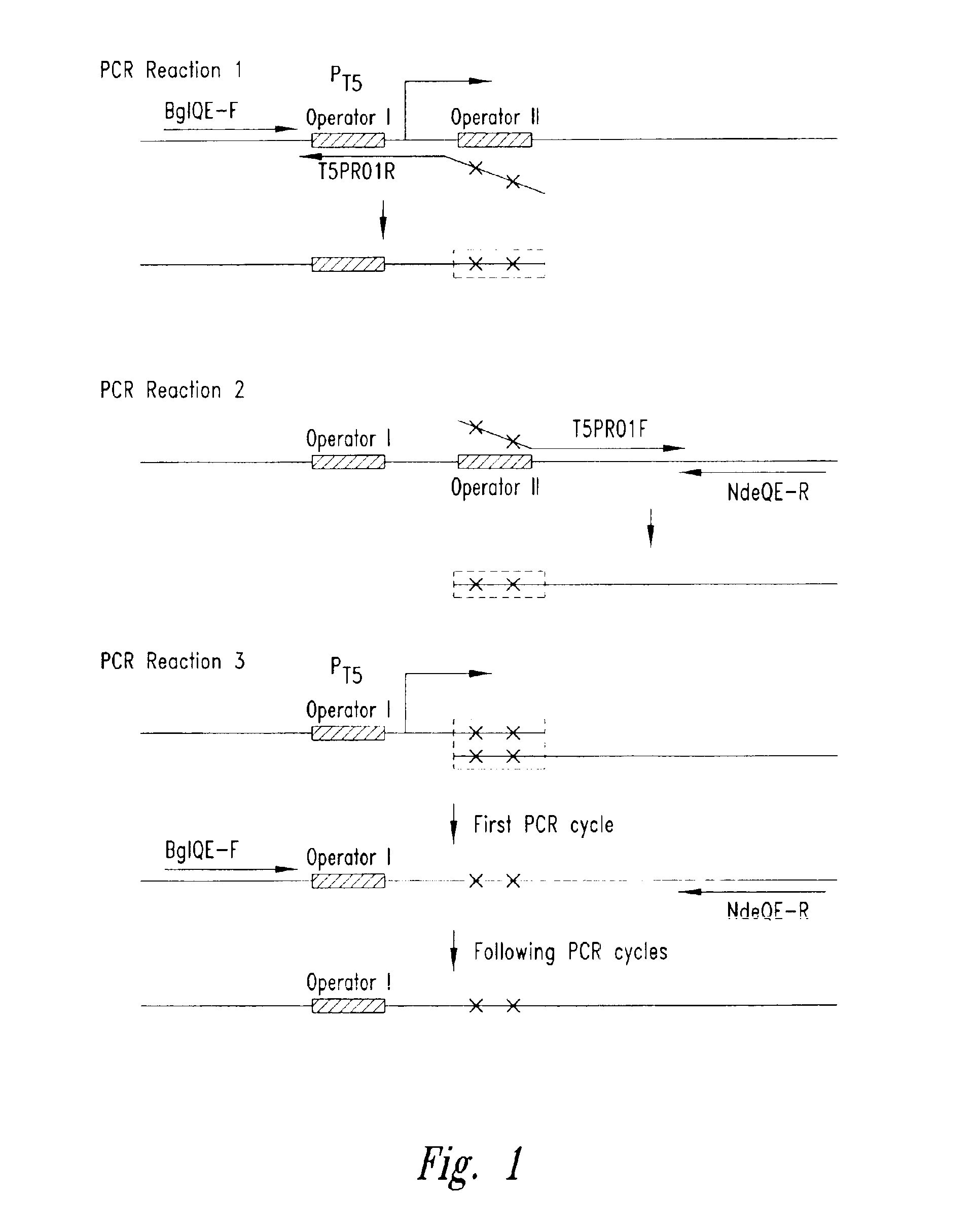
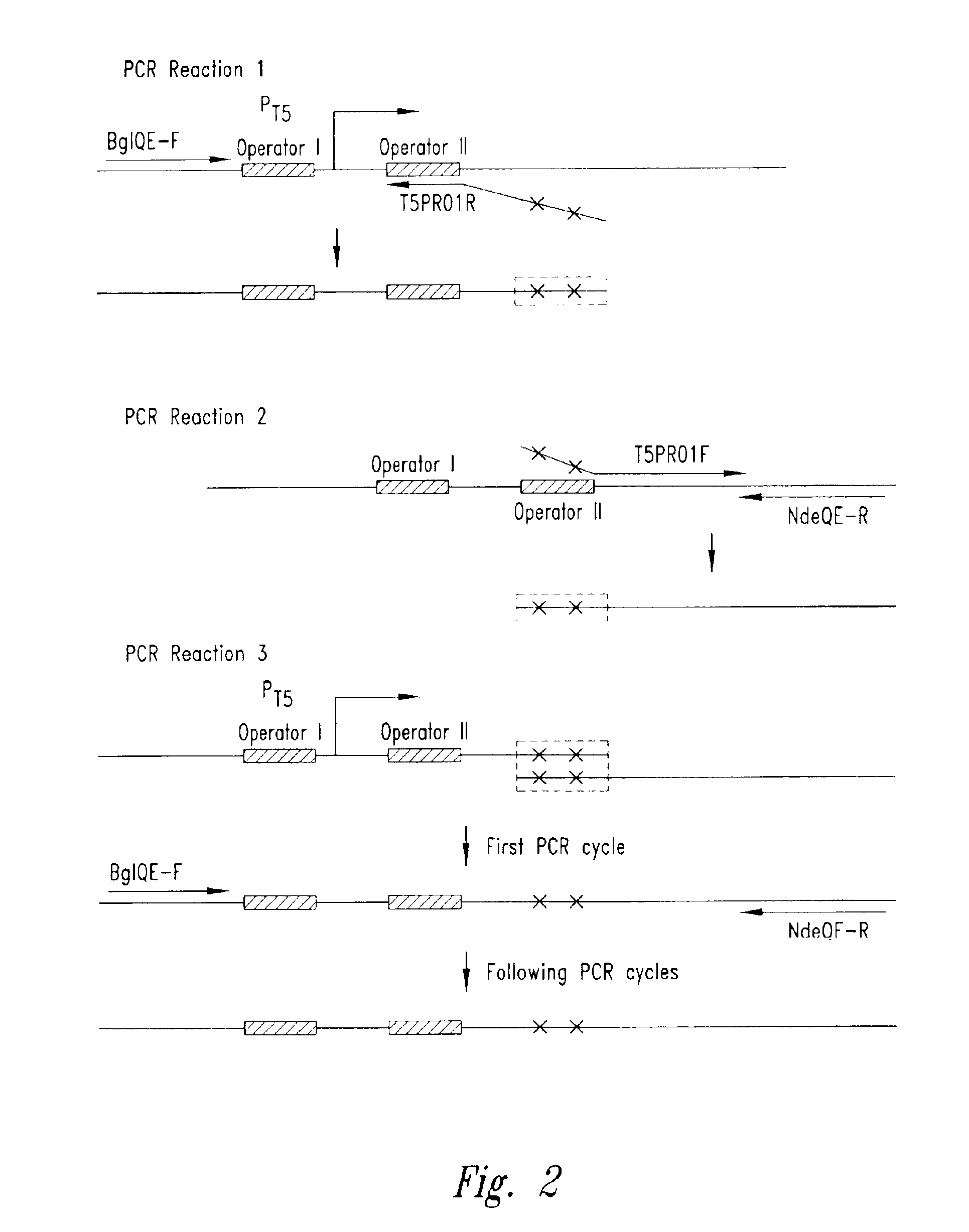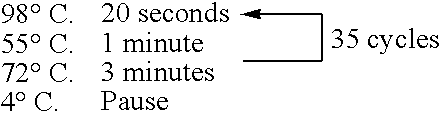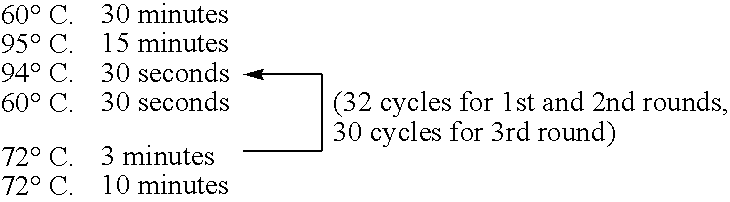Patents
Literature
121 results about "Transcription control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transcriptional control. (Science: molecular biology) control of gene expression by controlling the number of rNA transcripts of a region of dNA. A major regulatory mechanism for differential control of protein synthesis in both pro and eukaryotic cells.
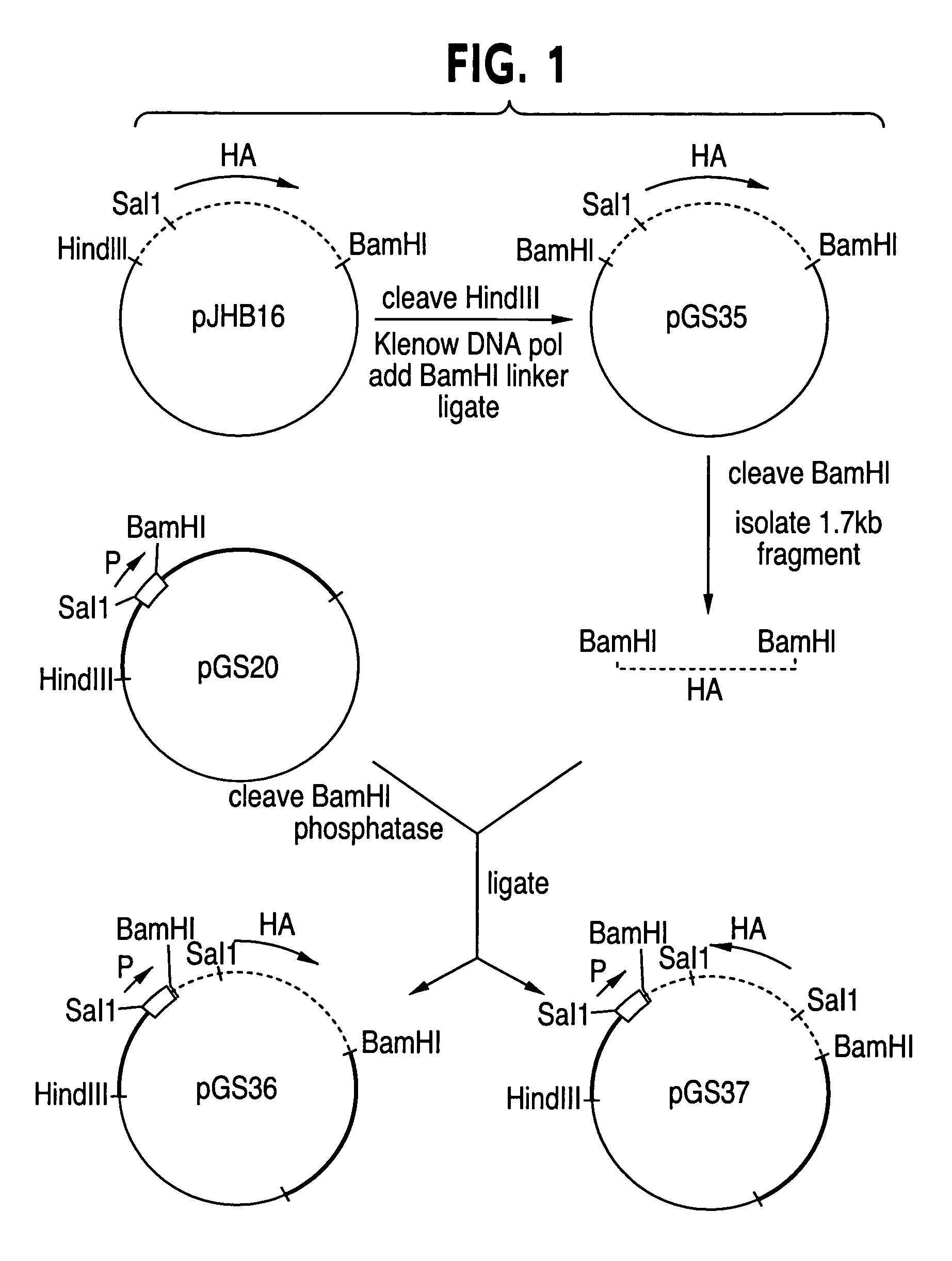
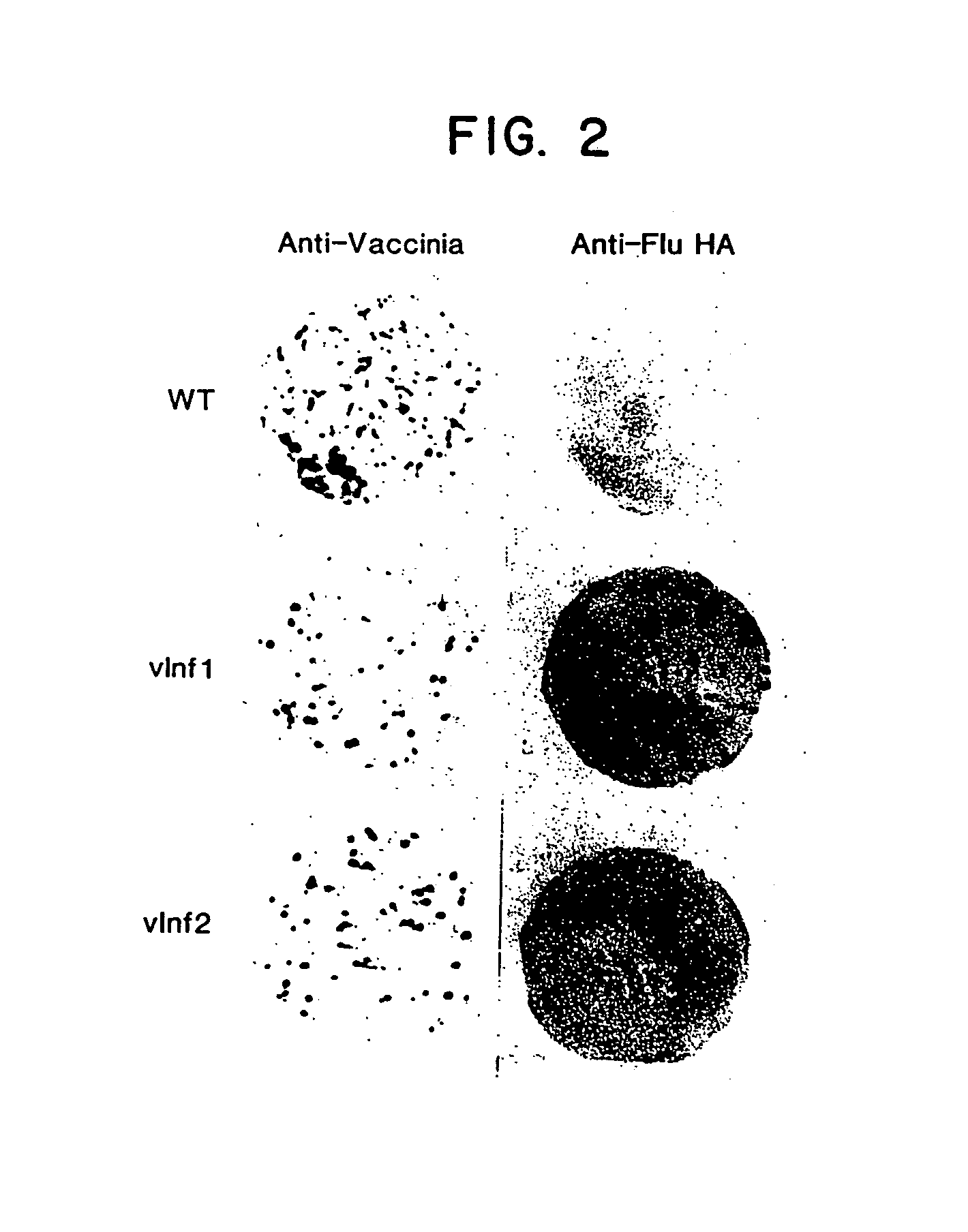
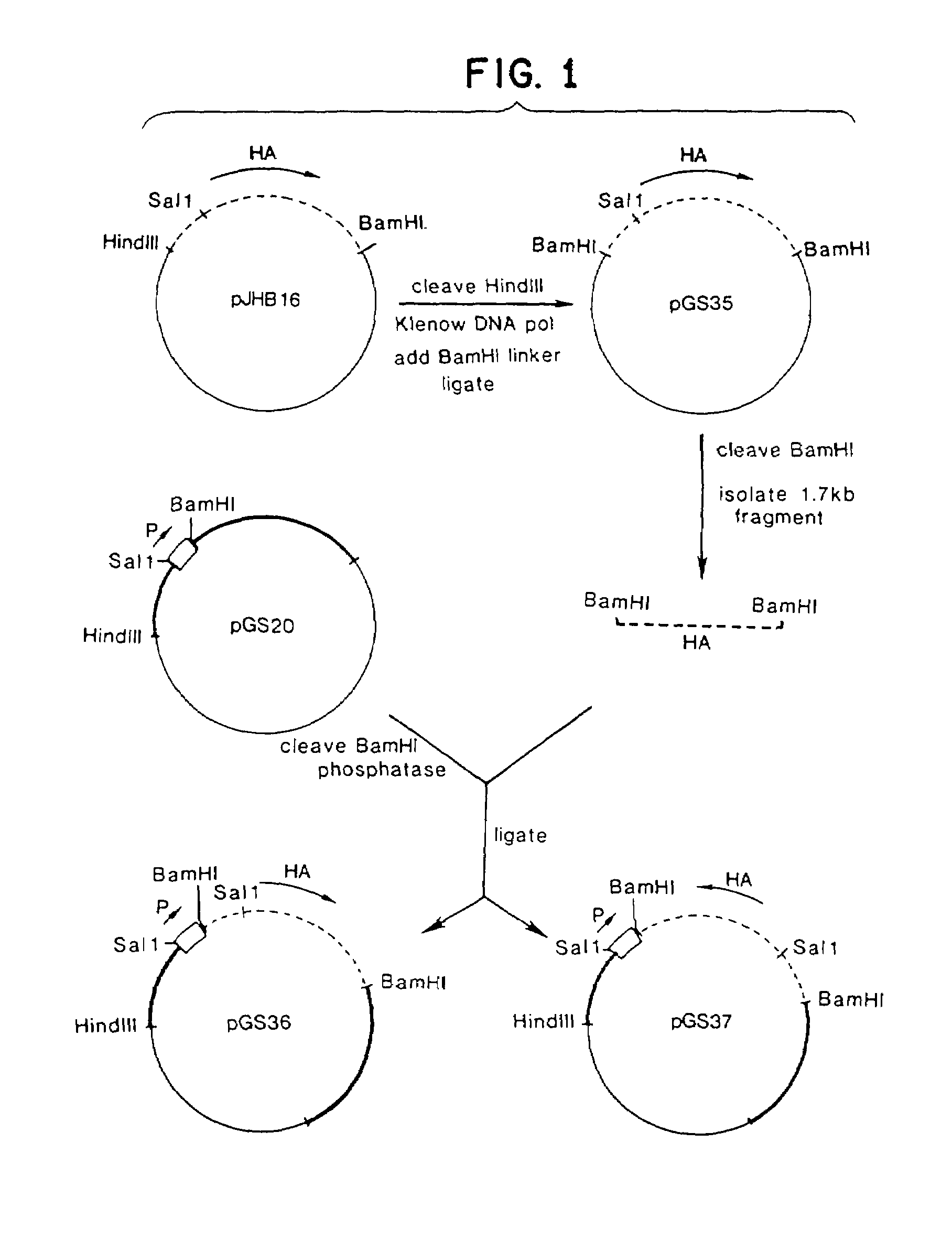
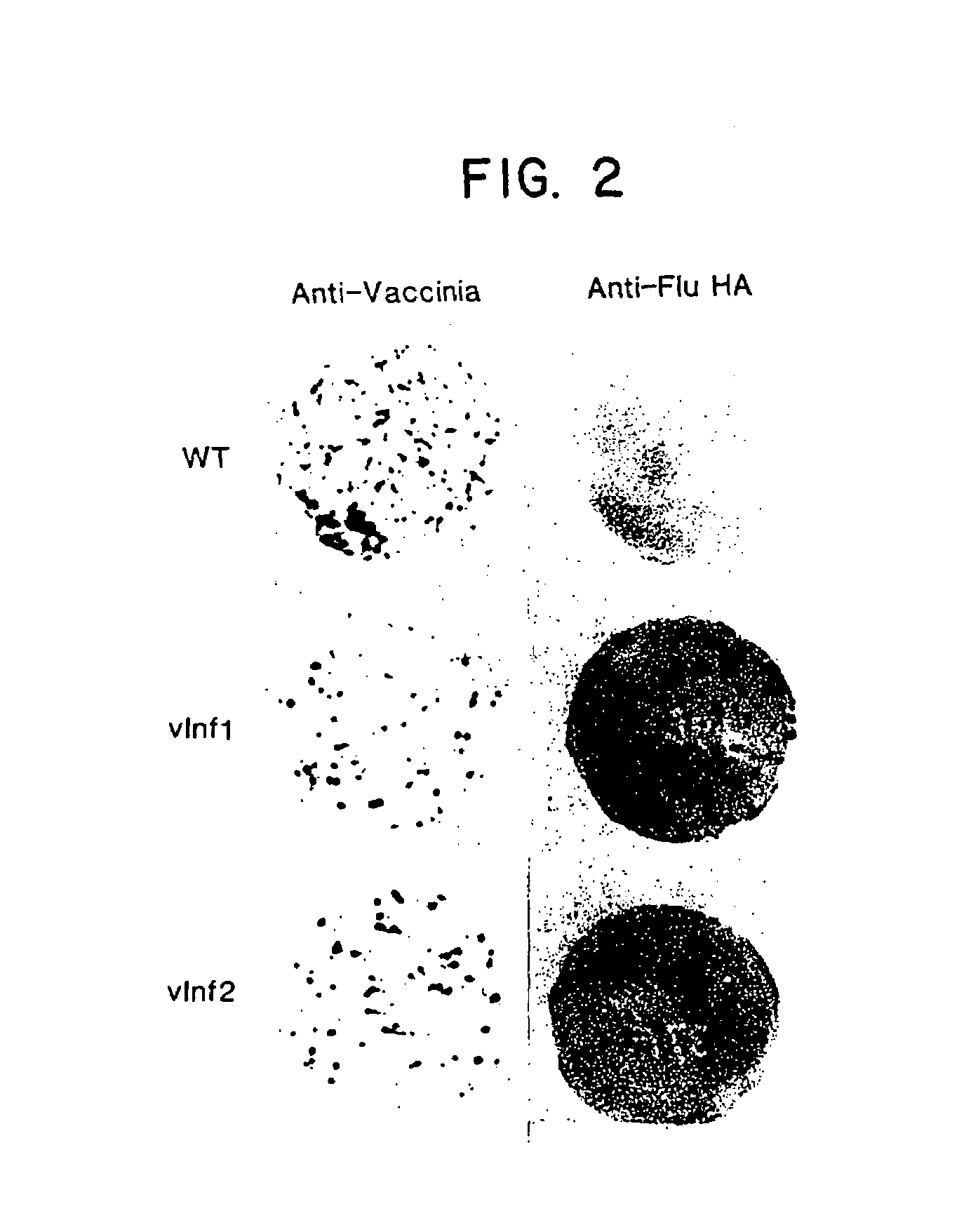
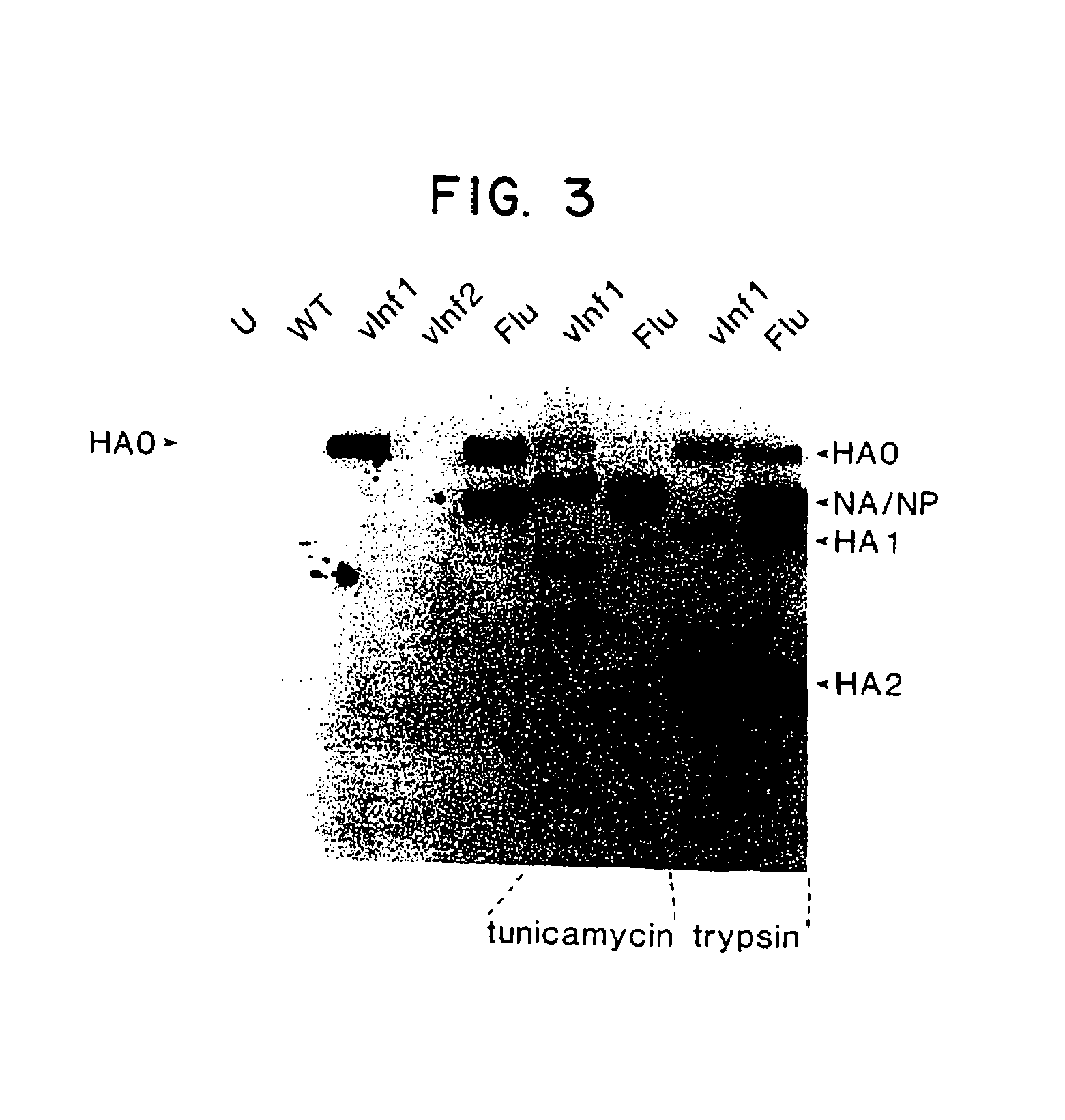
Recombinant poxviruses having foreign DNA expressed under the control of poxvirus regulatory sequences
InactiveUS6998252B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsTranscriptional regulationVaccinia
Recombinant poxviruses, such as vaccinia, are provided that comprises a segment comprised of (A) a first DNA sequence encoding a polypeptide that is foreign to poxvirus and (B) a poxvirus transcriptional regulatory sequence, wherein (i) said transcriptional regulatory sequence is adjacent to and exerts transcriptional control over said first DNA sequence and (ii) said segment is positioned within a nonessential genomic region of said recombinant poxvirus. Vaccines, carriers, cells, and media comprising recombinant poxviruses, and methods of immunization with recombinant poxviruses also are provided.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
Transcriptional regulatory elements of biological pathways tools, and methods
InactiveUS20090018031A1Determine effectNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningHuman DNA sequencingRegulation of gene expression
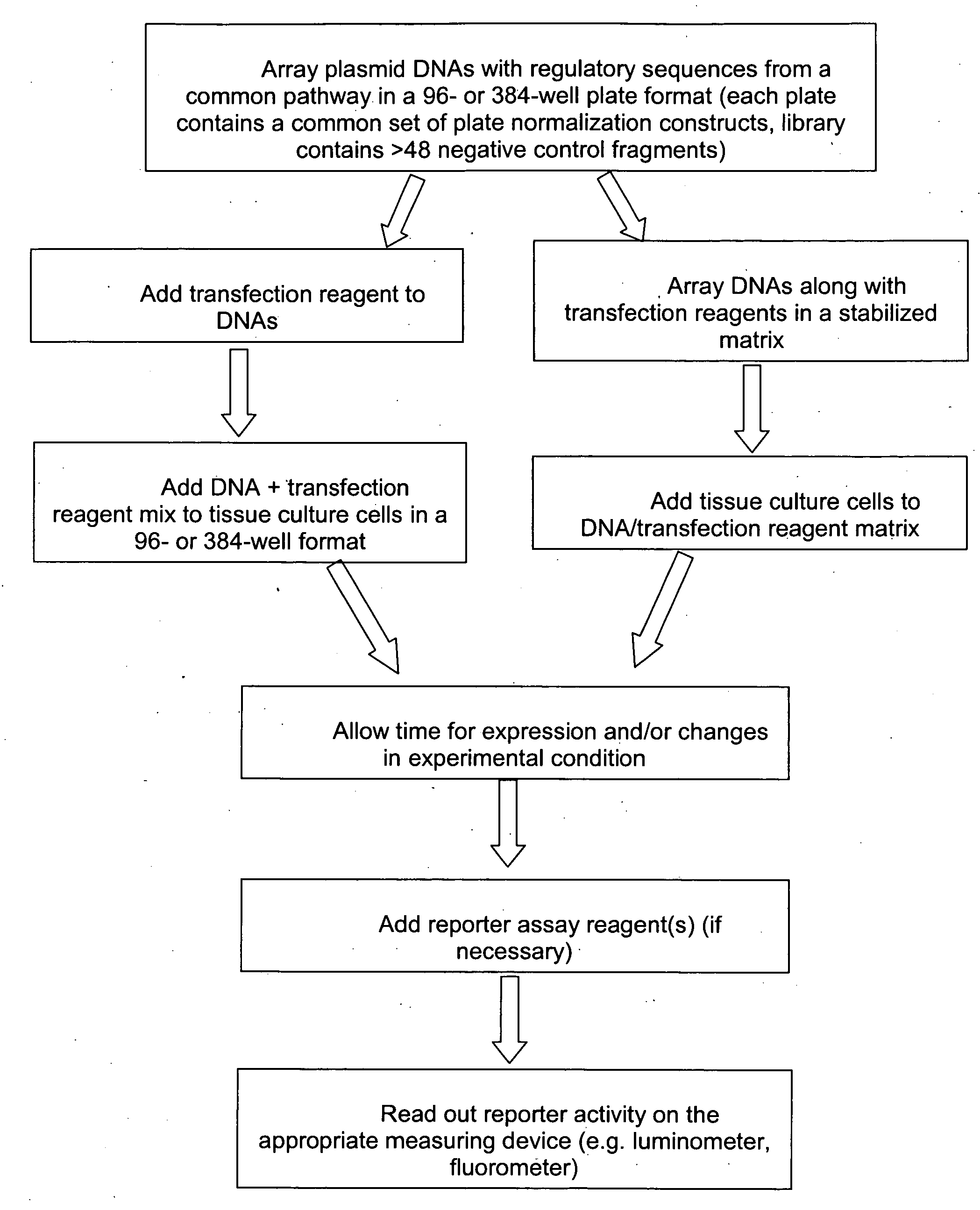
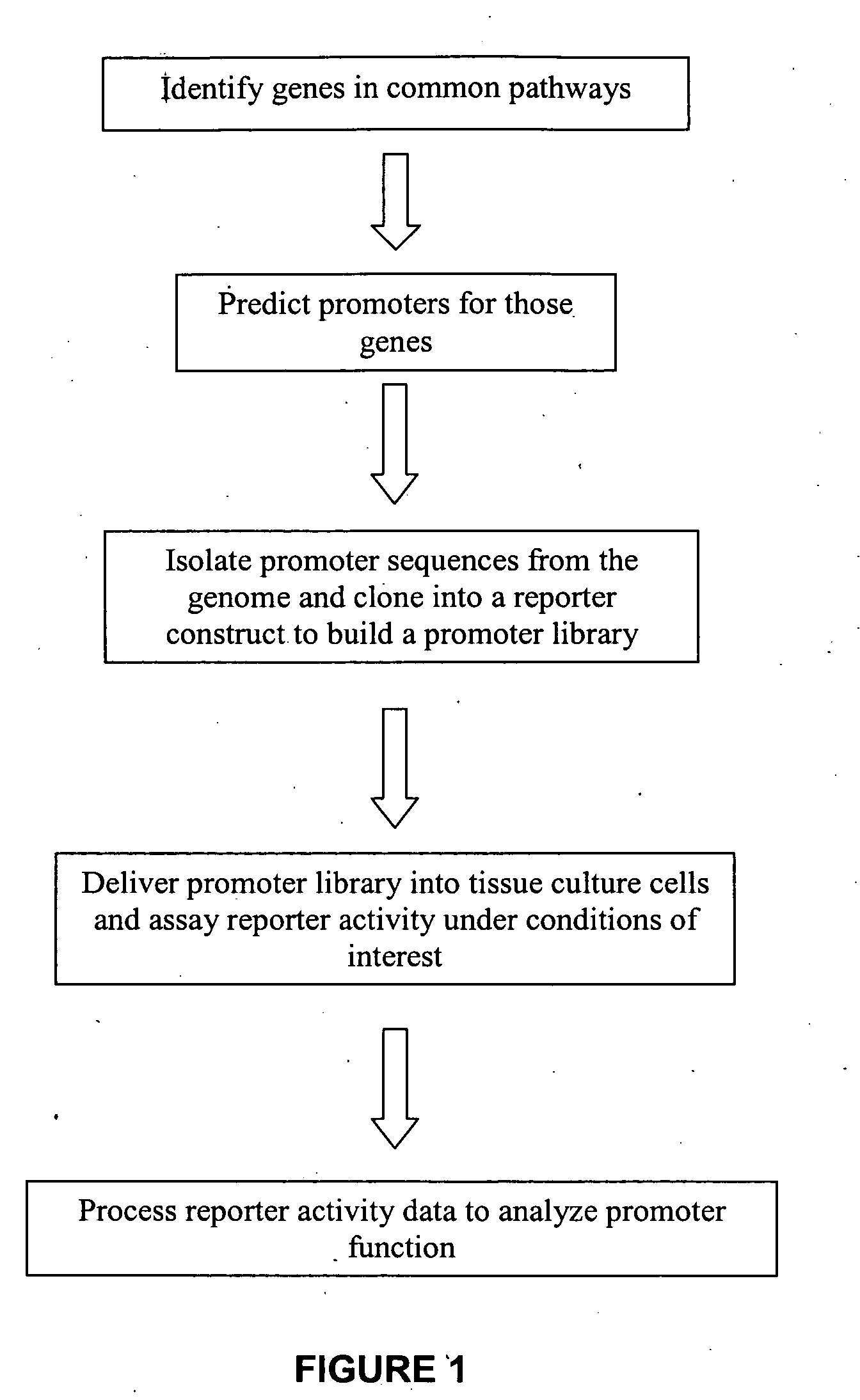
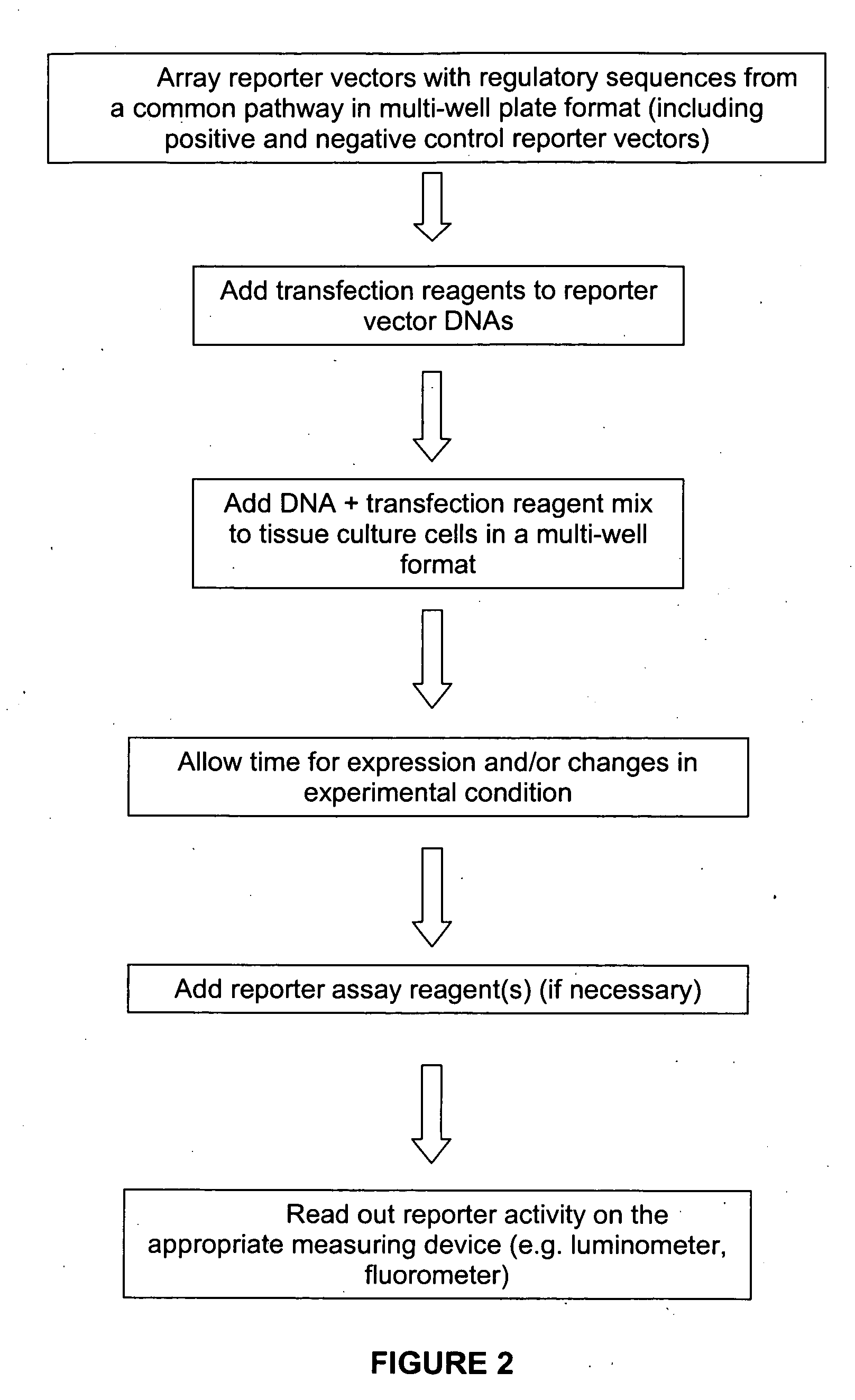
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome, that are part of a common pathway. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:SWITCHGEAR GENOMICS
Construction and application of mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector
ActiveCN103525868AReduced transcript levelsShorten the development cycleVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCloning SiteDeletion mutation
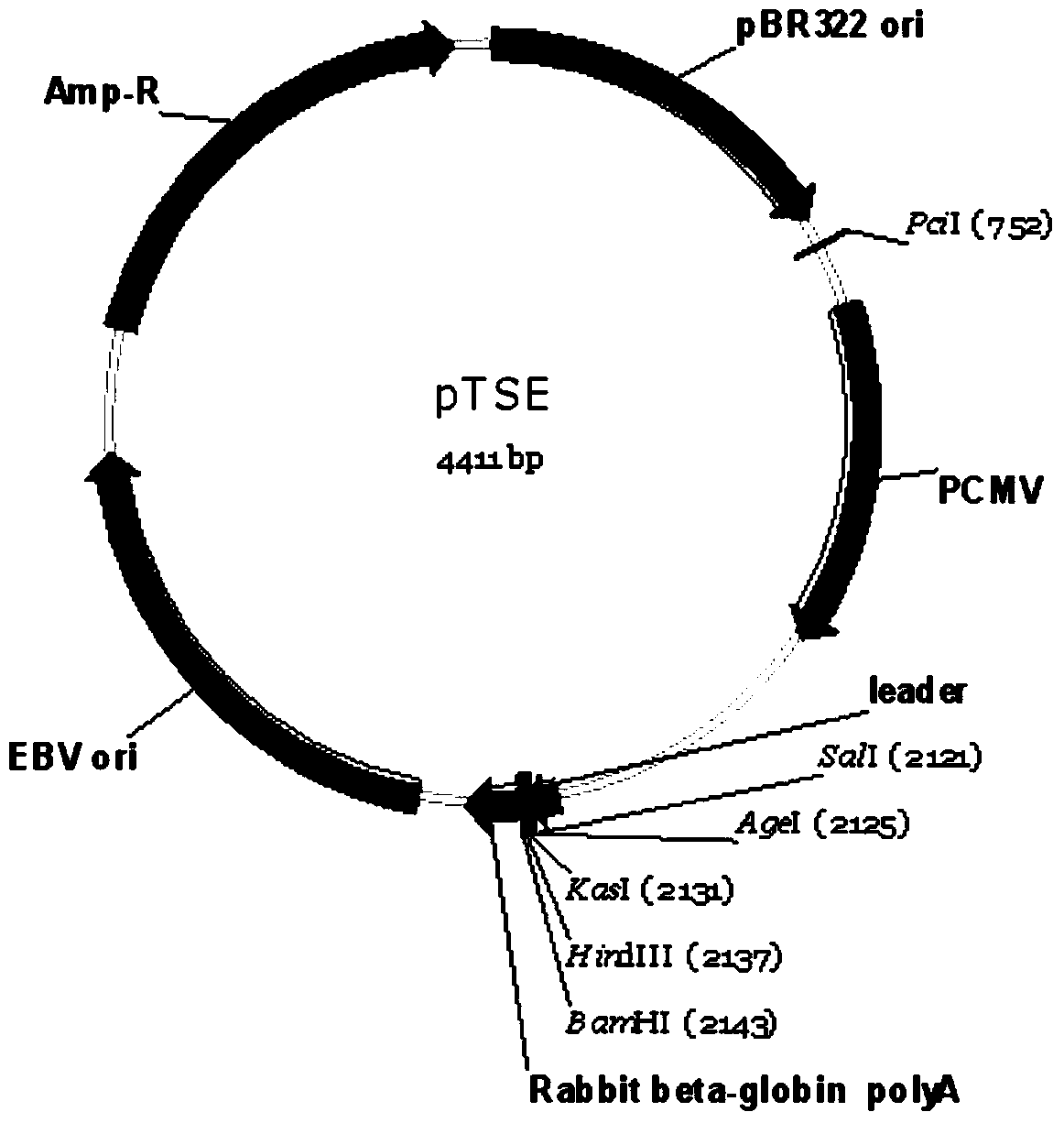
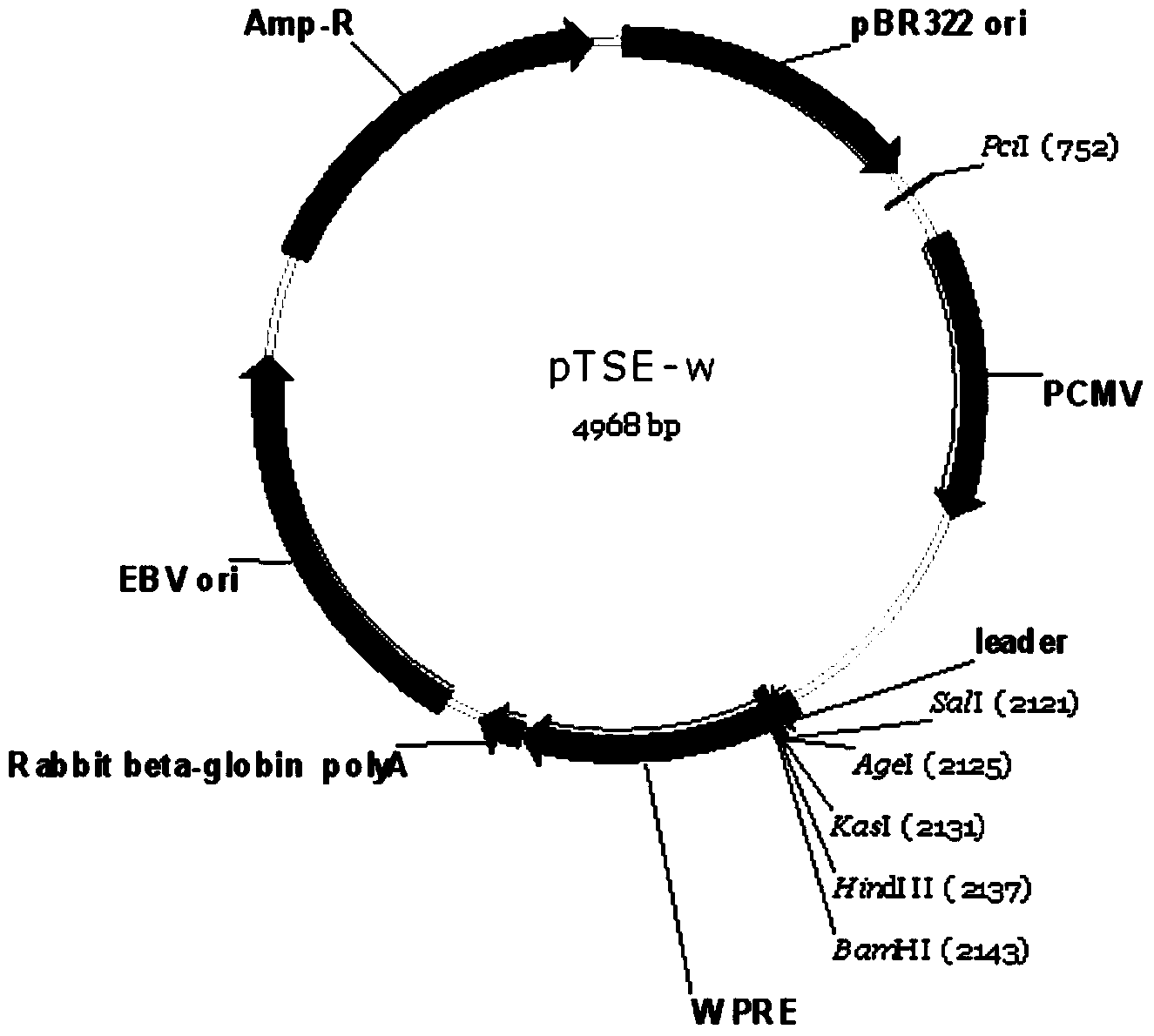
The invention relates to a mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector pSNEO. The vector is constructed on the basis of neomycin resistance screening gene NEO by combined strategy of weakening screening gene expression and reinforcing target gene expression. The screening gene weakening comprises the following two sides: introducing deletion mutant into the promoter to implement transcription weakening of the screening gene, and introducing a hairpin structure sequence before the translation initial site of the screening gene to implement the translation weakening of the screening gene. The expression reinforcement of the target gene is implemented by adding a transcription control element WPRE sequence between polyclone site and polyA tail of the target gene expression frame. The pSNEO vector can conveniently and quickly complete the construction of the stable high-expression cell strain of the target gene, and provides a new tool for preparing the high-polymer recombinant protein.
Owner:BIOTECH PHARMA CO LTD
RNA respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6060308AFaster replicationImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideF proteinViral Vaccine
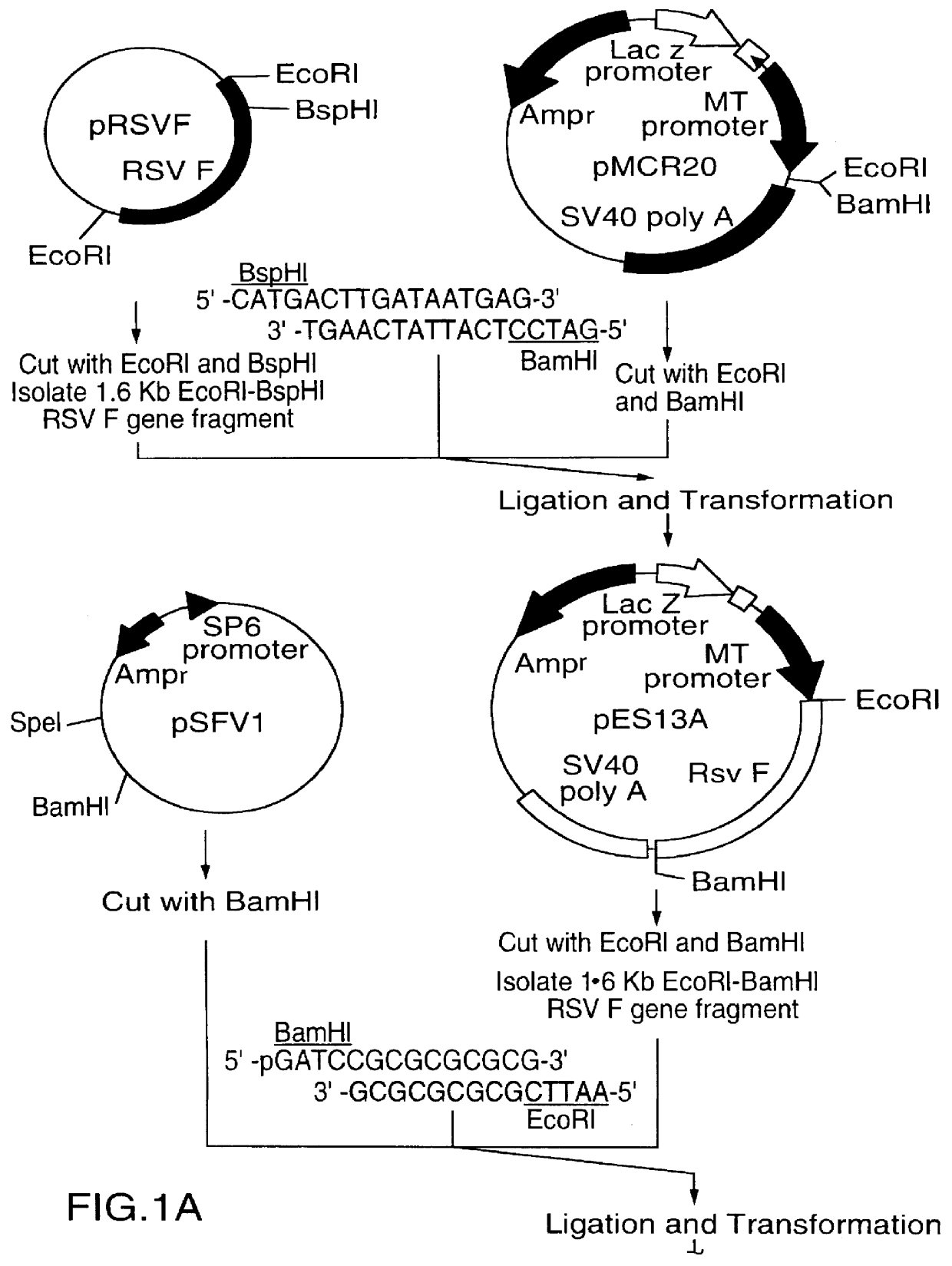
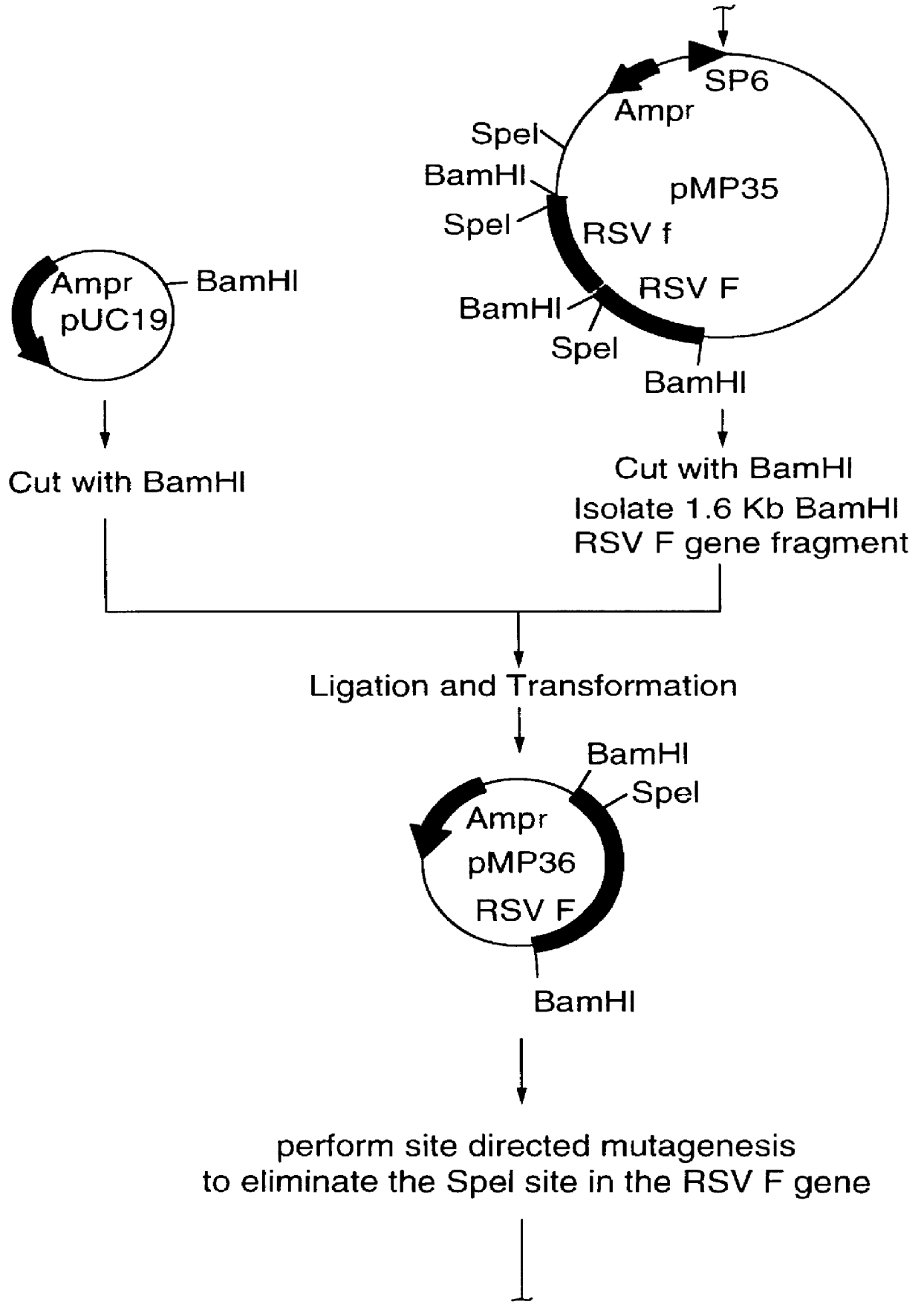
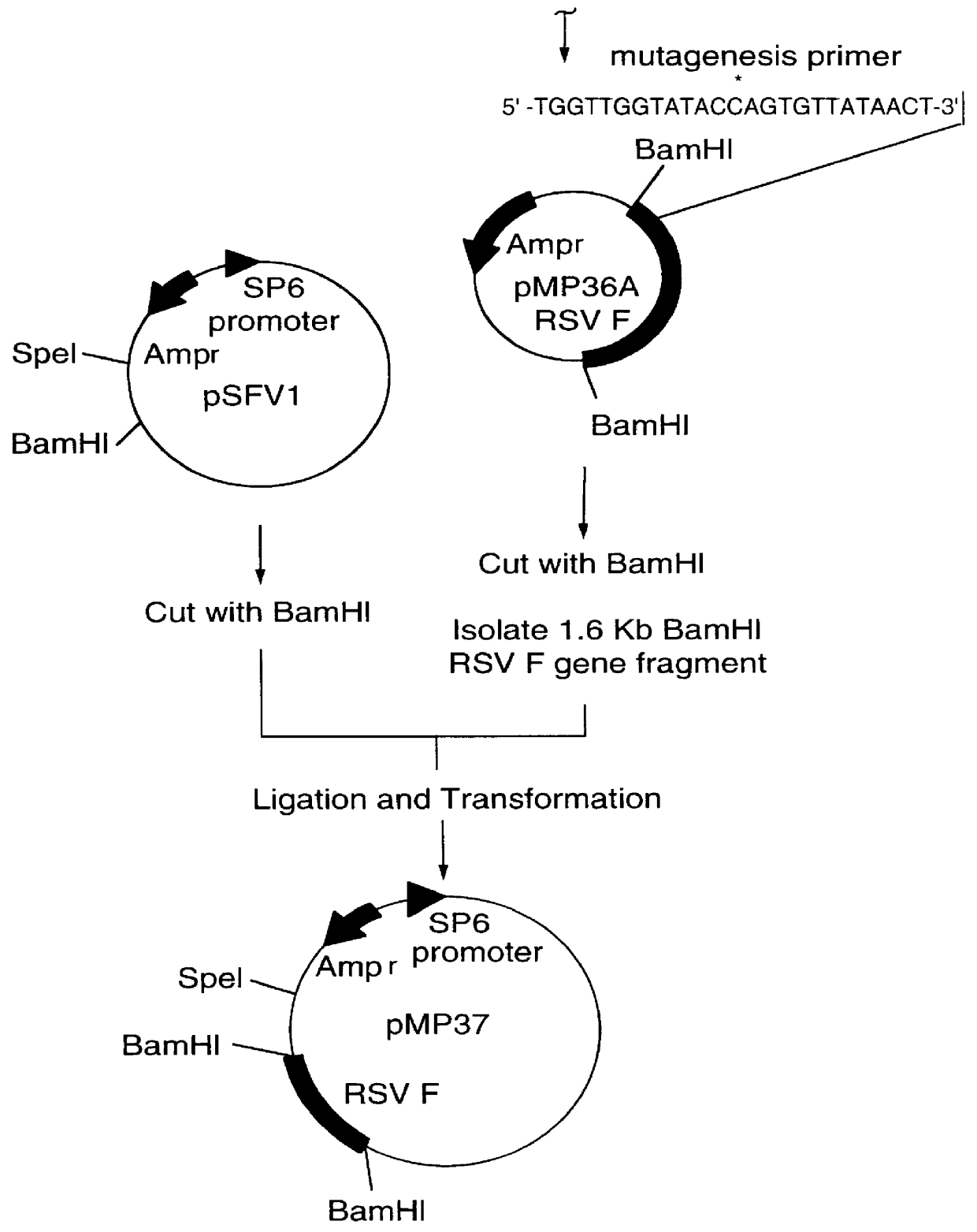
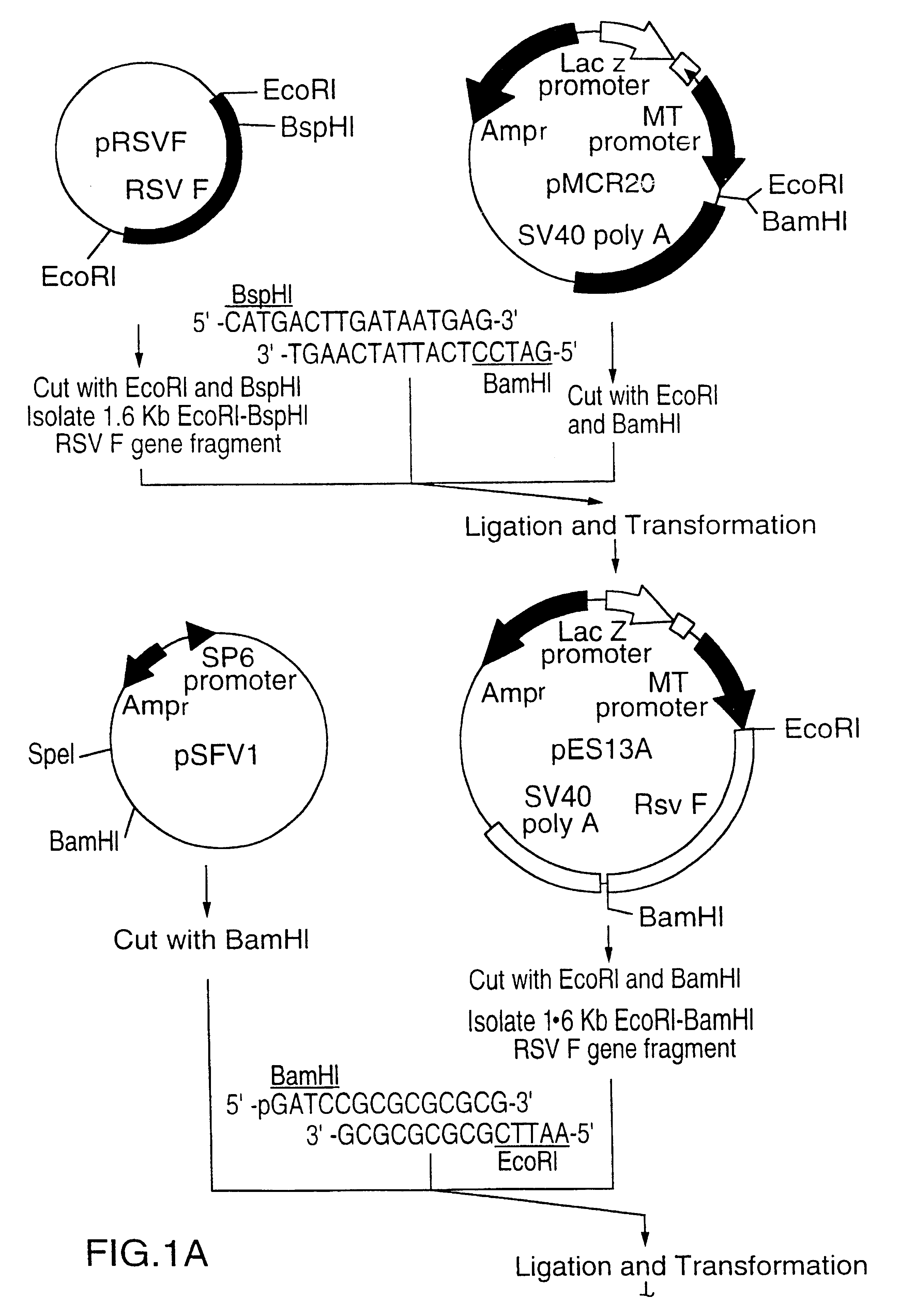
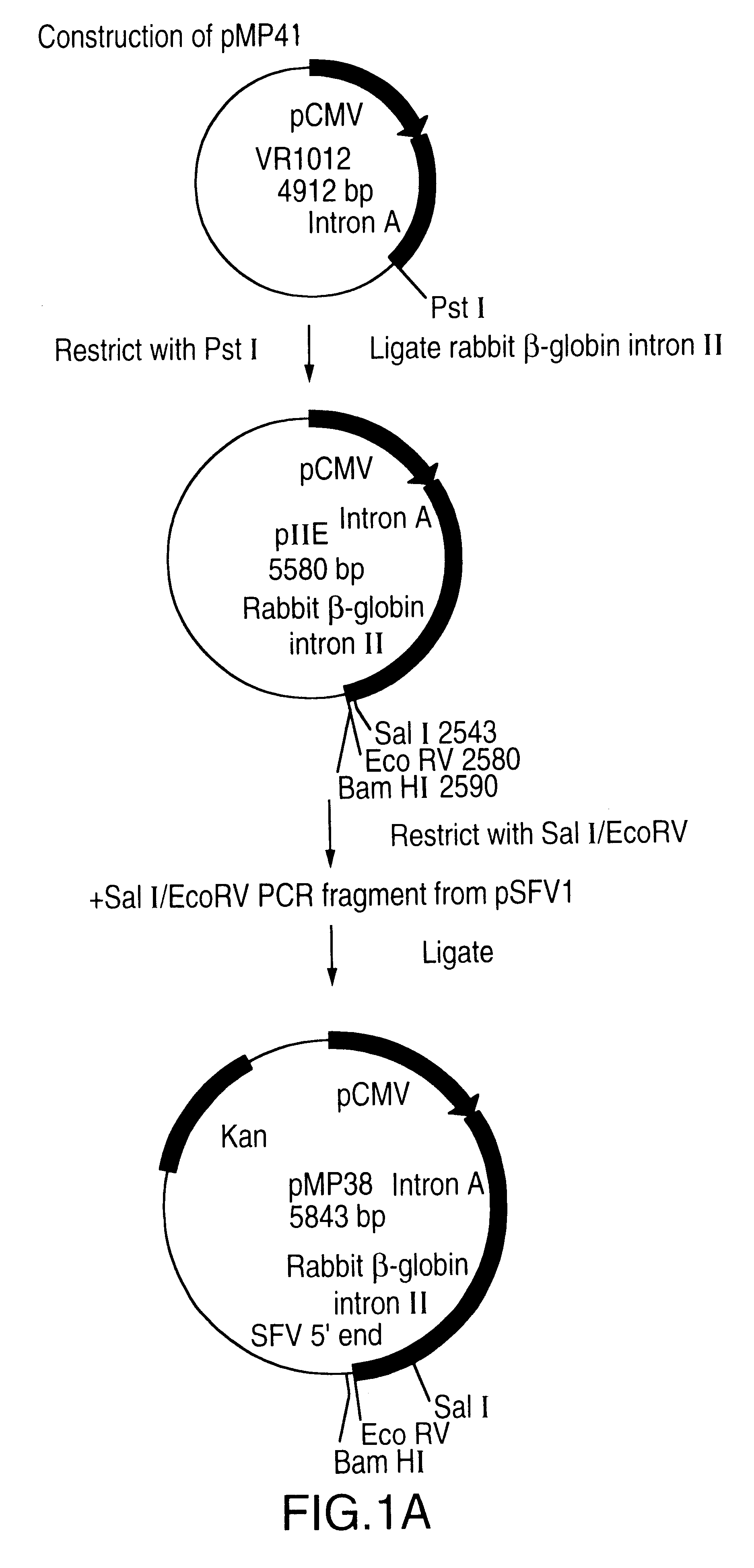
A vector comprising a first DNA sequence which is complementary to at least part of an alphavirus RNA genome and having the complement of complete alphavirus DNA genome replication regions, a second DNA sequence encoding a paramyxovirus protein, particularly a respiratory syncytial virus fusion (RSV F) protein or a RSV F protein fragment that generates antibodies that specifically react with RSV F protein, the first and second DNA sequences being under the transcriptional control of a promoter is described. Such vector may be used to produce an RNA transcript which may be used to immunize a host, including a human host, to protect the host against disease caused by paramyxovirus, particularly respiratory syncytial virus, by administration to the host.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Biologic device for regulation of gene expression and method therefor
InactiveUS20070036771A1Desirable effectAltered expressionBiocideInternal electrodesOpen reading frameRegulation of gene expression
A system and device are provided which include a gene regulatory system controlling expression of one or more expression cassettes present in or released by the device, by emitting one or more stimulations. An expression cassette includes a regulatable transcription control element that is responsive to the emitted stimulations linked to an open reading frame of interest. The system optionally includes a sensor to sense a parameter indicative of a need, a telemetry module to receive an external command, or a programmable device, for regulating gene expression of the open reading frame.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
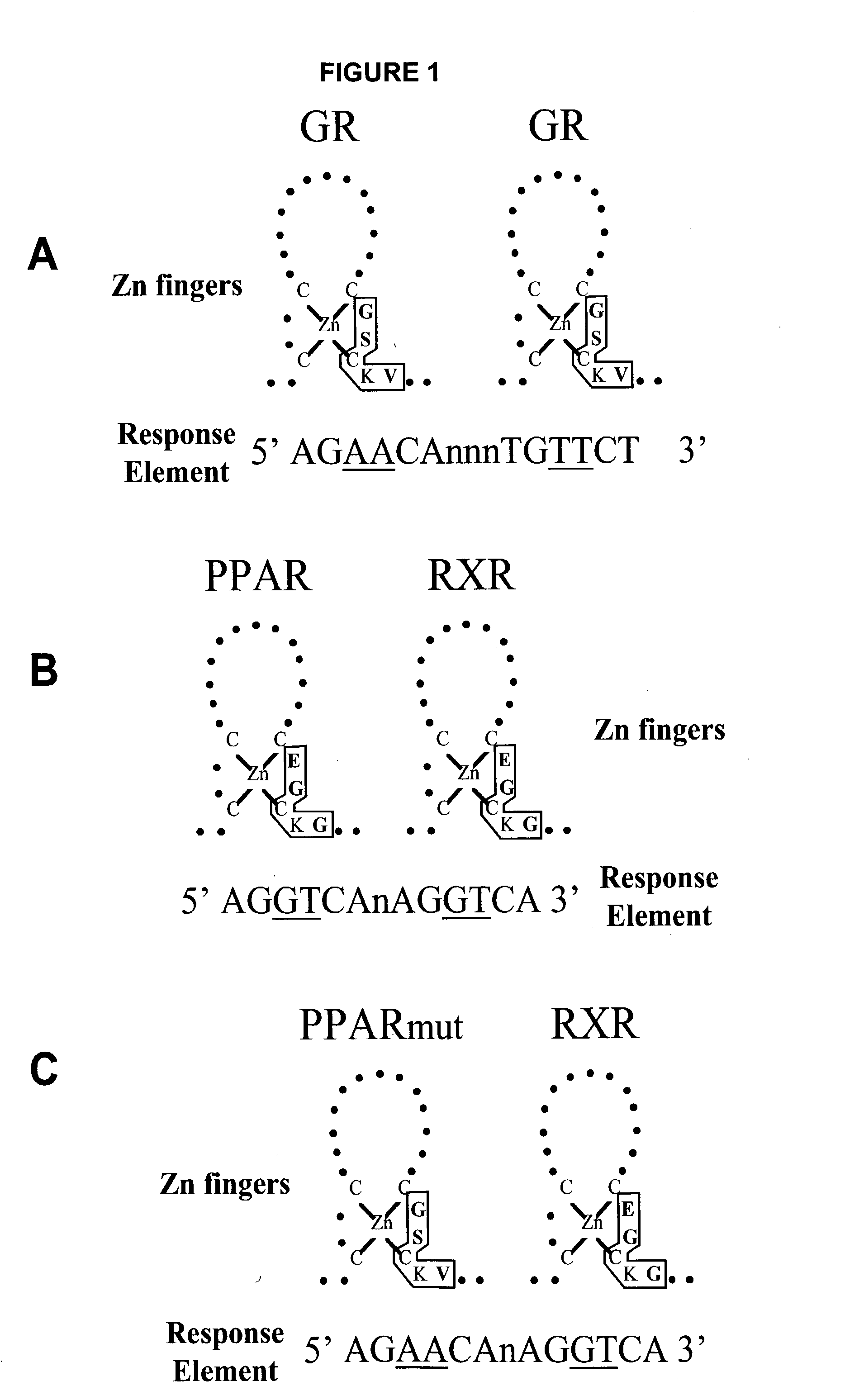
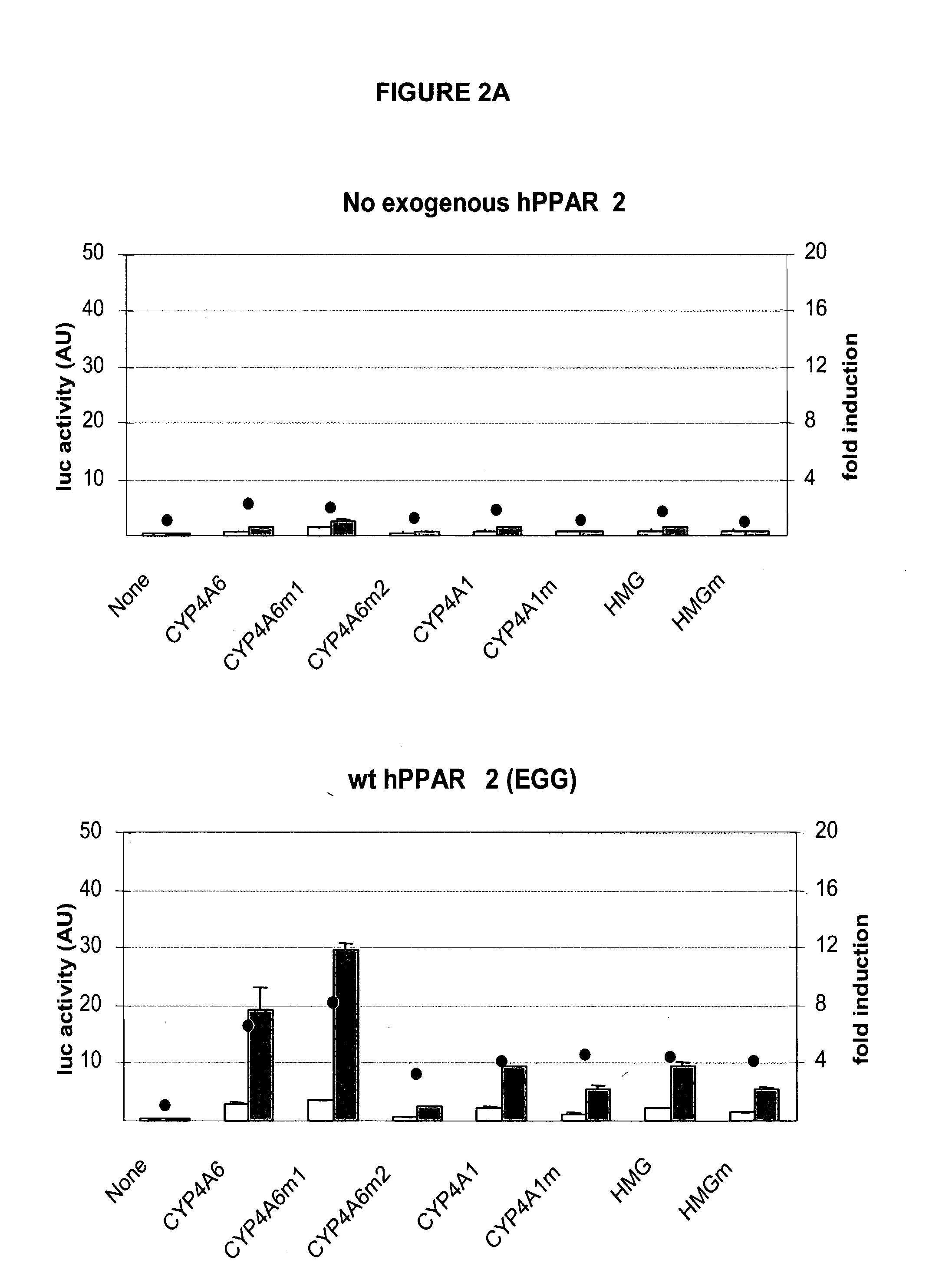
Inducible expression systems employing PPAR transcriptional activators
InactiveUS20040038249A1Increase specificity and safetyReduce riskVectorsSugar derivativesSide effectTranscription control
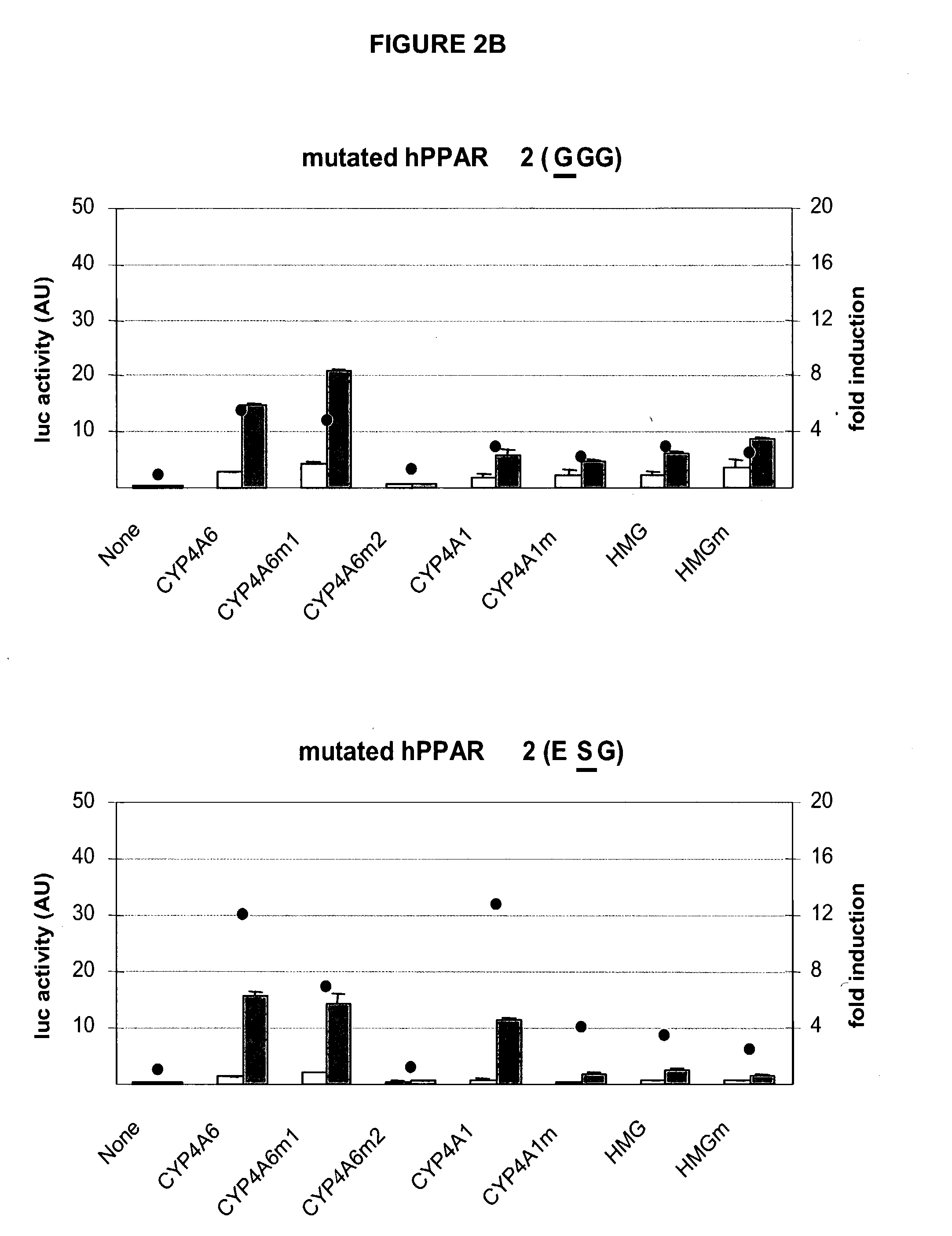
The invention relates to novel mammalian perixosome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) poplypeptides and their use. In a particular embodiment, PPAR polypeptides with mutations in the P-box domain possess advantageous properties as transcriptional activators for PPRE-bearing expression vectors and expression systems. The invention includes PPAR polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding them, expression systems, vectors, and methods for inducibly expressing a gene of interest. The methods and expression systems of the invetion provide improved dose-response or inducibility characteristics, improved and / or altered effects on cellular PPAR function, and / or improved transcriptional control. The selection of a homologous PPAR polypeptide to prepare the novel PPAR polypeptide of the invetion for a cell or tissue also improves the immune reaction side effect potential for particular uses.
Owner:GENCELL SA
Compositions containing recombinant poxviruses having foreign DNA expressed under the control of poxvirus regulatory sequences
InactiveUS7015024B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsTranscriptional regulationVaccinia
Recombinant poxviruses, such as vaccinia, are provided that comprises a segment comprised of (A) a first DNA sequence encoding a polypeptide that is foreign to poxvirus and (B) a poxvirus transcriptional regulatory sequence, wherein (i) said transcriptional regulatory sequence is adjacent to and exerts transcriptional control over said first DNA sequence and (ii) said segment is positioned within a nonessential genomic region of said recombinant poxvirus. Vaccines, carriers, cells, and media comprising recombinant poxviruses, and methods of immunization with recombinant poxviruses, also are provided.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE
Composition and method for stimulating immune response to pathogen using complex adenoviral vector
InactiveUS6964762B2Improving immunogenicityStrong immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsHeterologousProgenitor
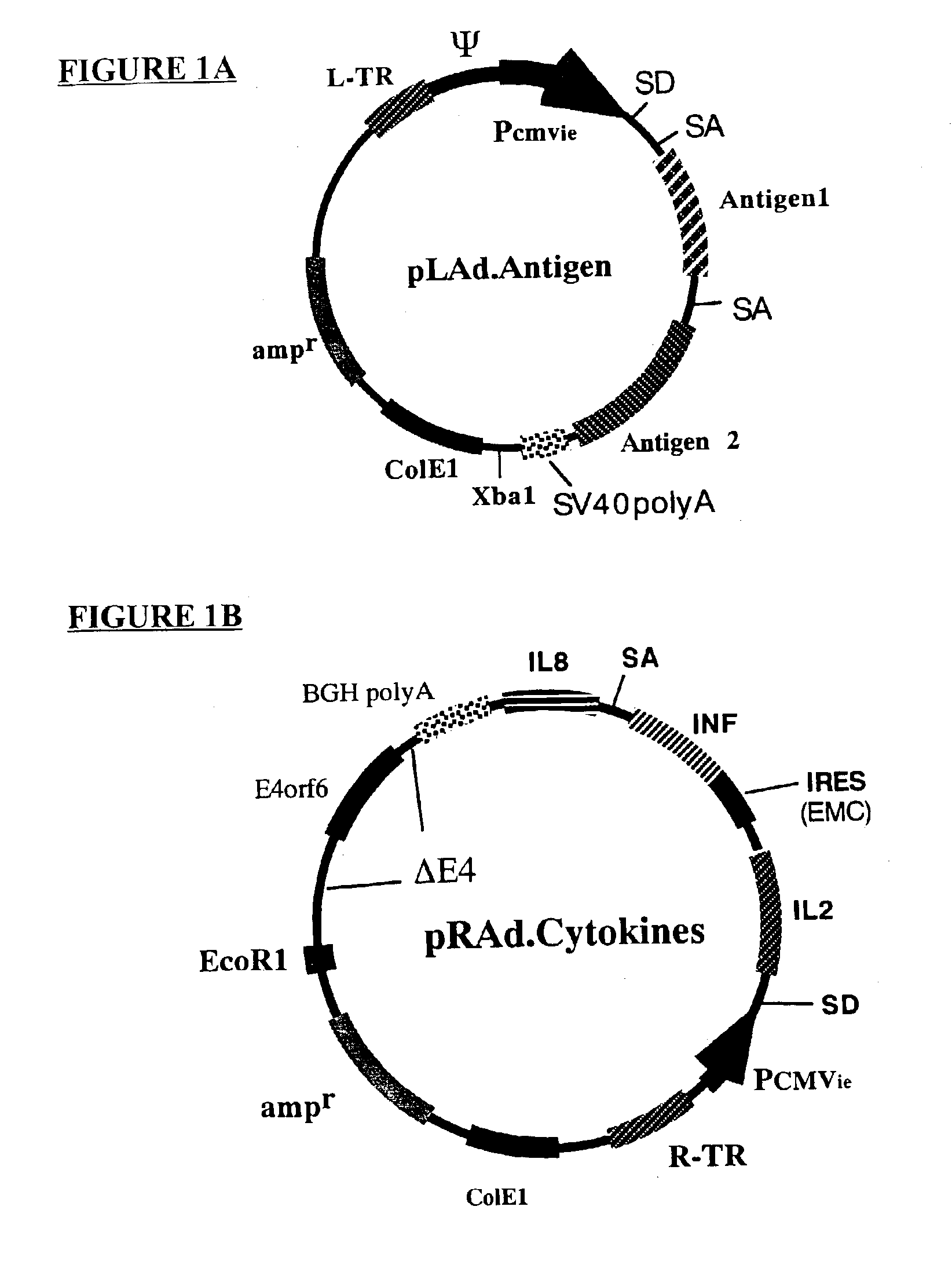
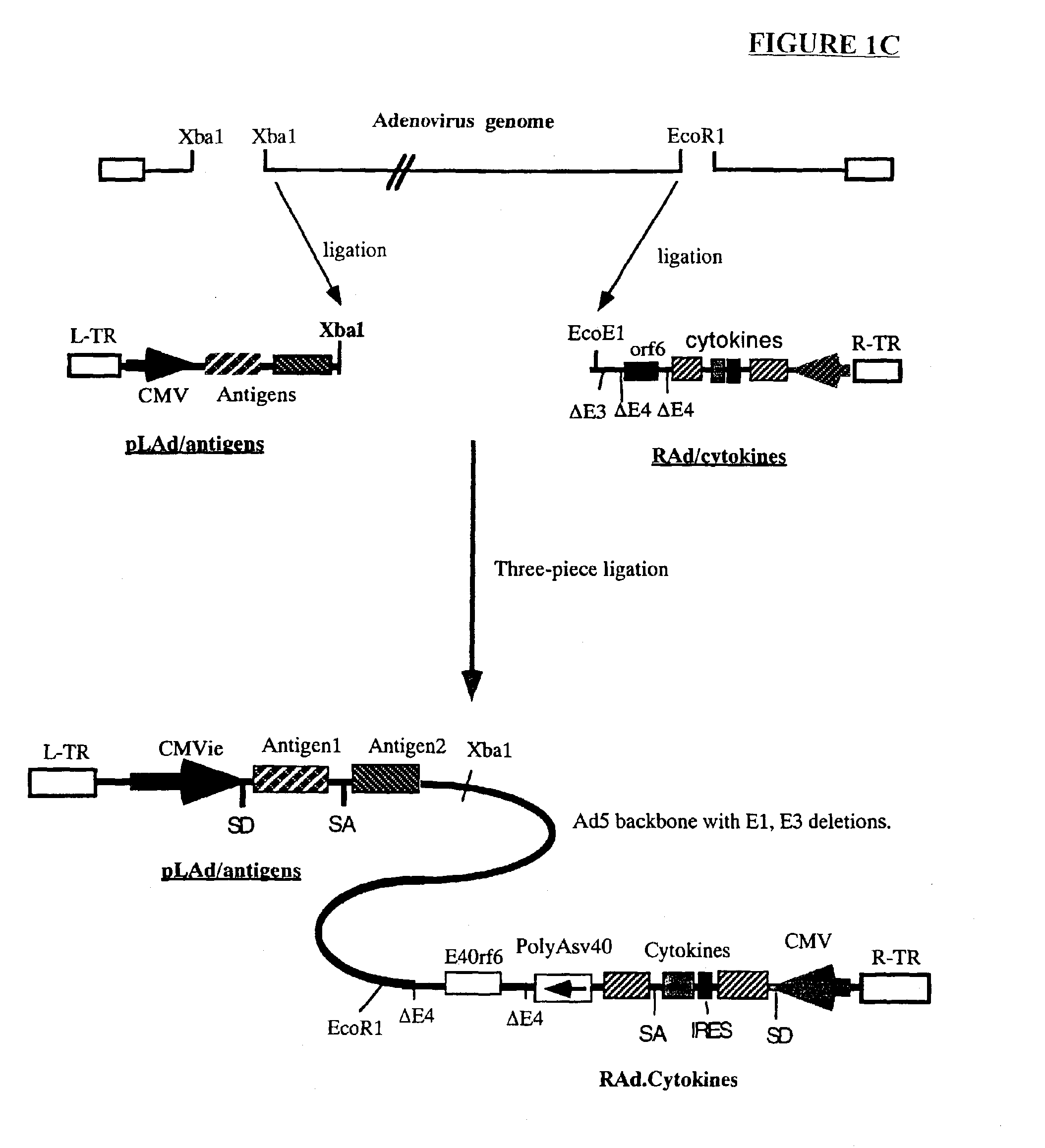
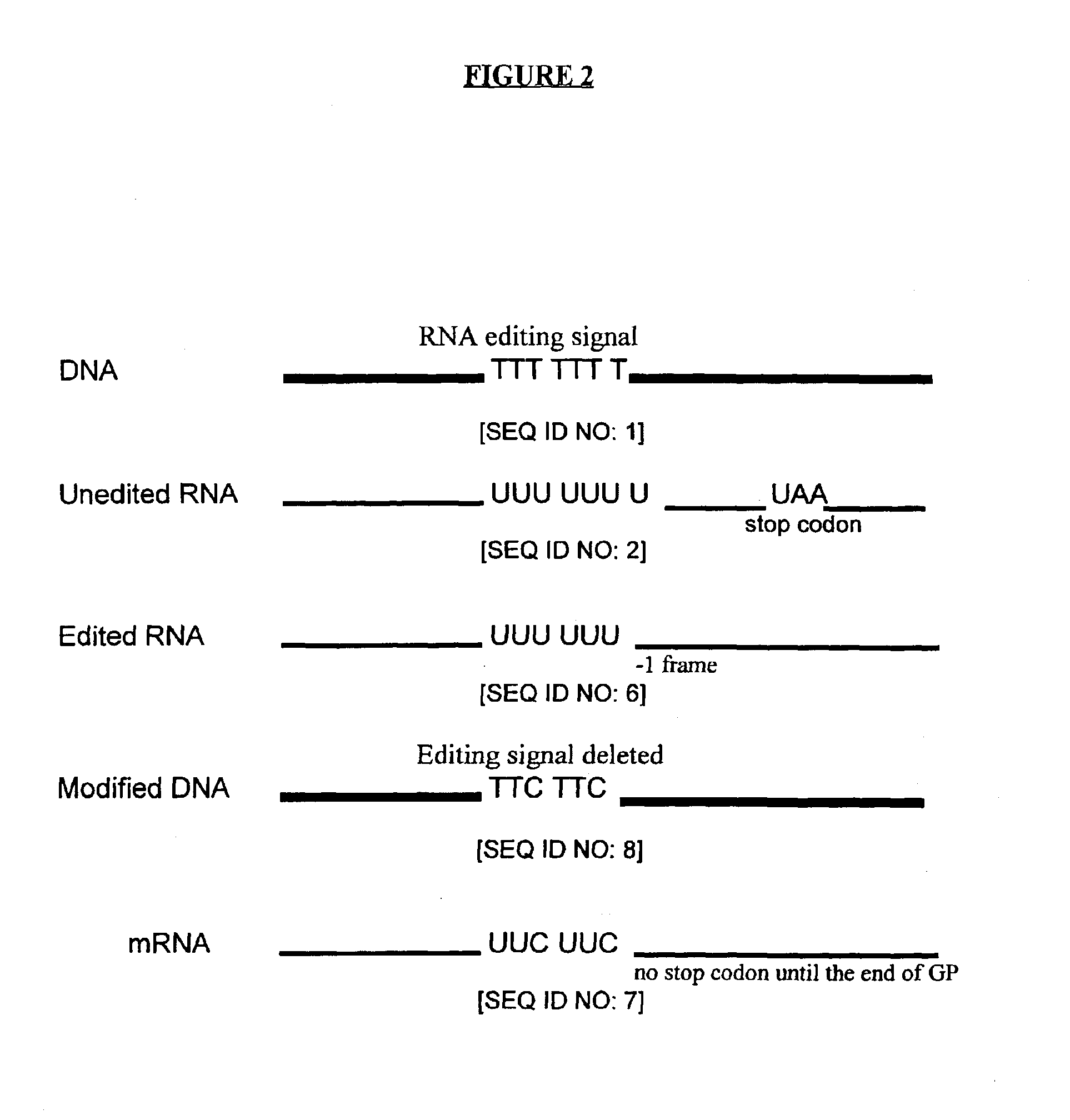
Genetic vaccines and methods are provided for enhancing the immunity of a host such as a human to one or more pathogens. In one aspect, a method of enhancing the immunity of a host to a pathogen is provided. The method comprises administering to the host a recombinant virus comprising an antigen sequence that is heterologous to a native progenitor of the recombinant adenovirus and encodes a viral antigen from a pathogenic virus, expression of which is under the transcriptional control of a first promoter; and a cytokine sequence that is heterologous to the native progenitor of the recombinant adenovirus and encodes a cytokine, expression of which is under the transcriptional control of a second promoter. Expression of the antigen and cytokine sequences elicits an immune response directed against the viral antigen upon infection of the host by the recombinant virus. The method can be used for immunizing a host against a wide variety of pathogen viruses, such as HIV, Ebola virus, Marburg virus, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, influenza virus, human simplex virus, human papilloma virus and respiratory syncytial virus.
Owner:GENPHAR INC
Systems and devices for photoablation
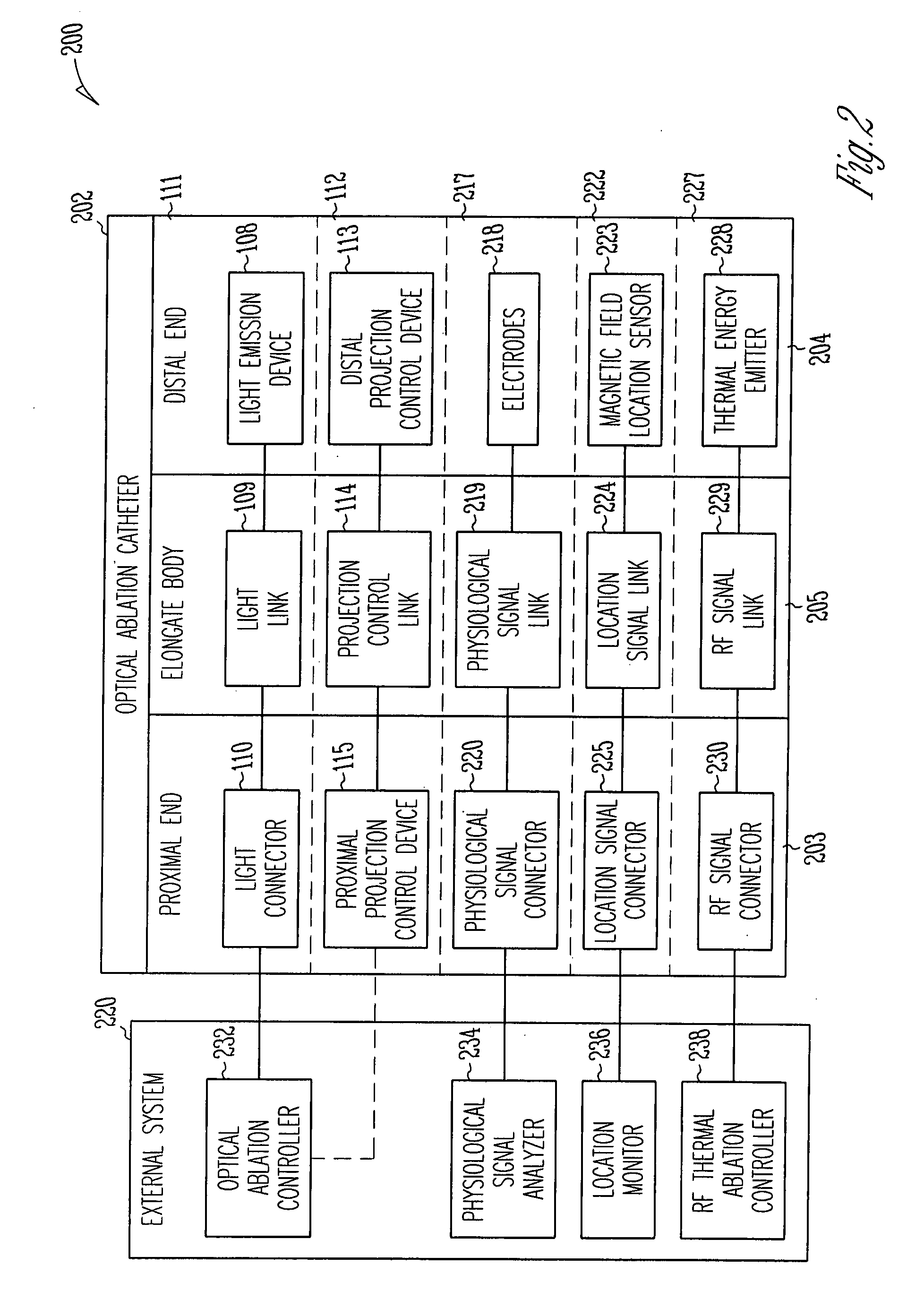
ActiveUS8480662B2Reduce the risk of blood clotsPrevent, inhibit or treat cardiac arrhythmiasSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyPhotoablationLight emission
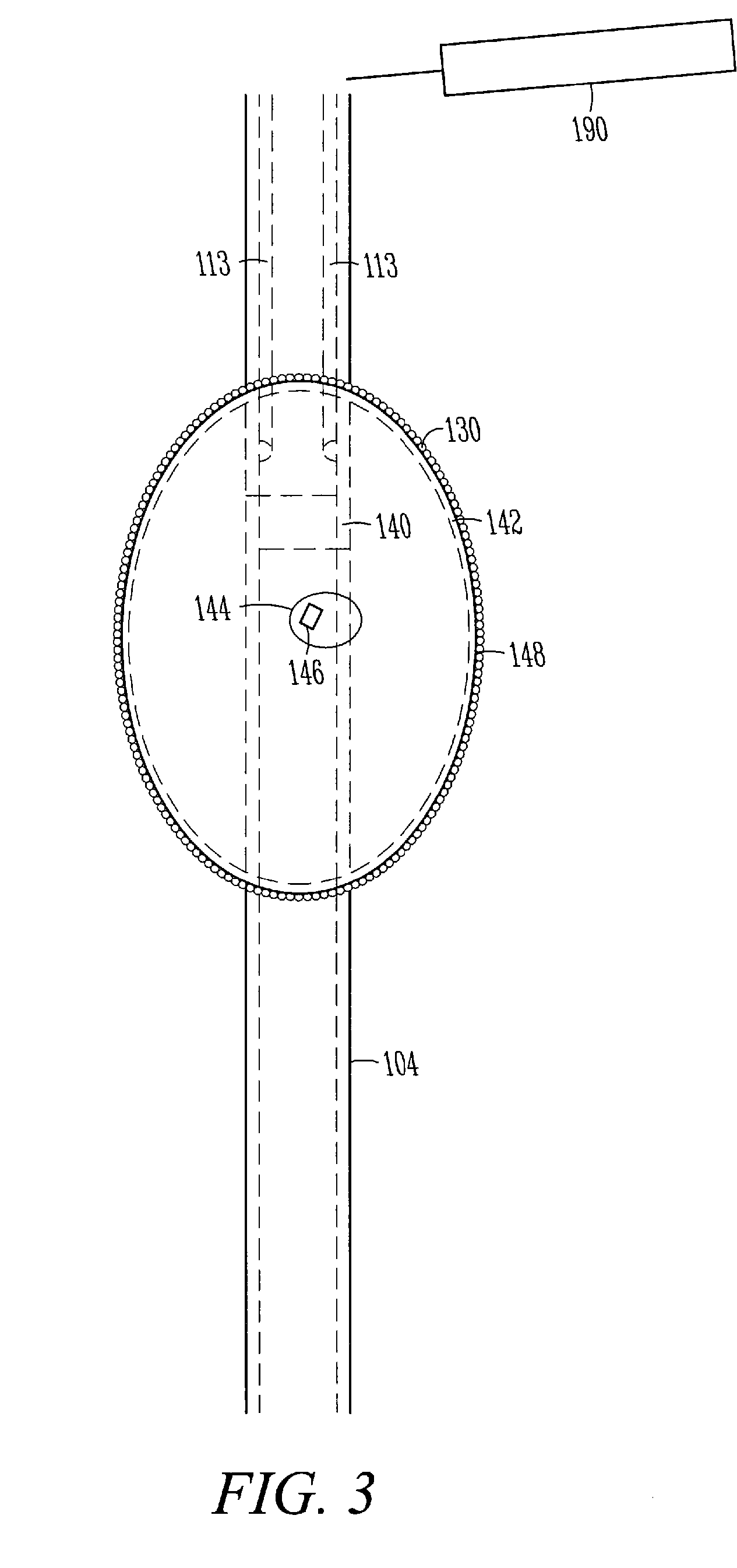
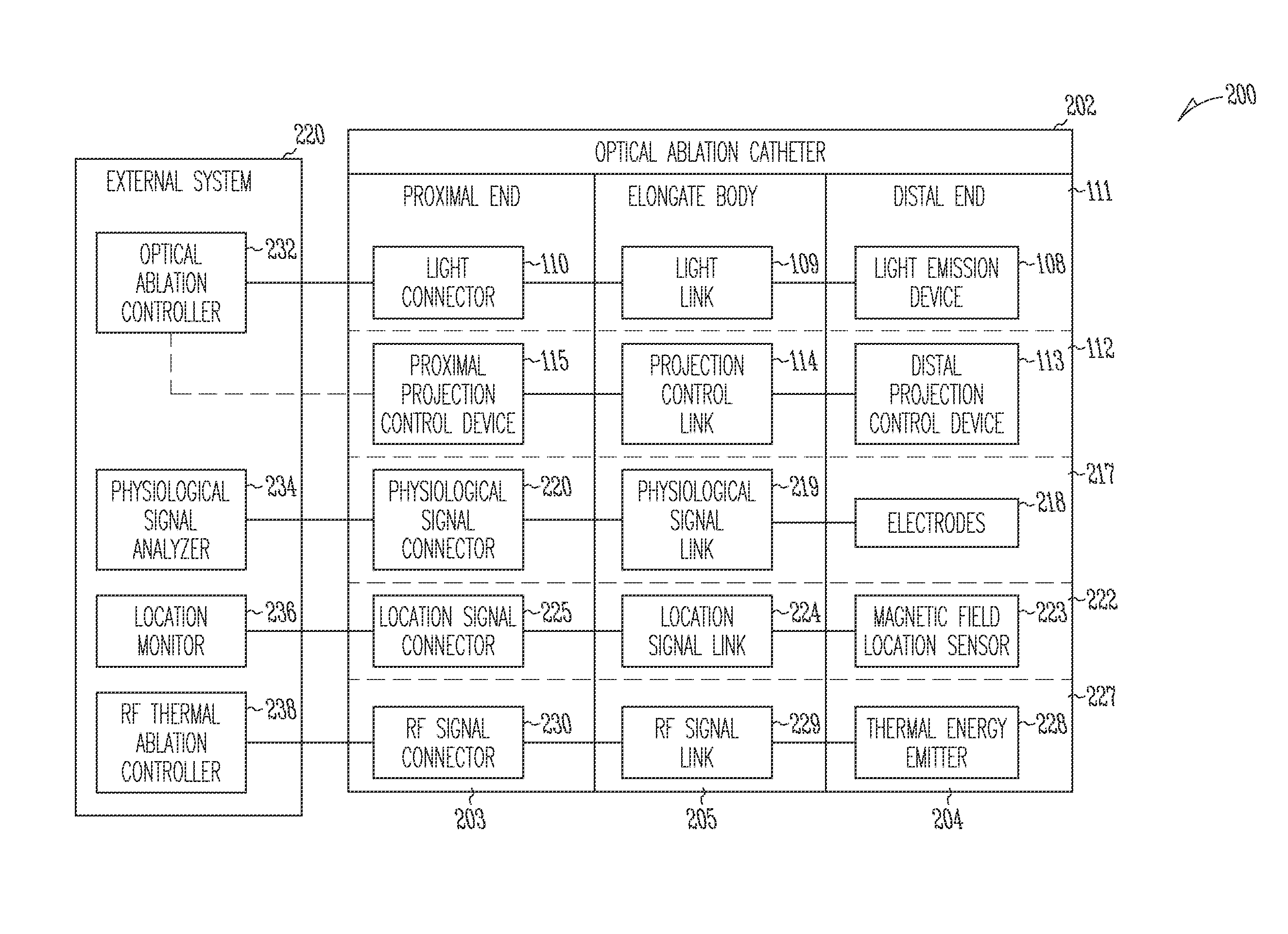
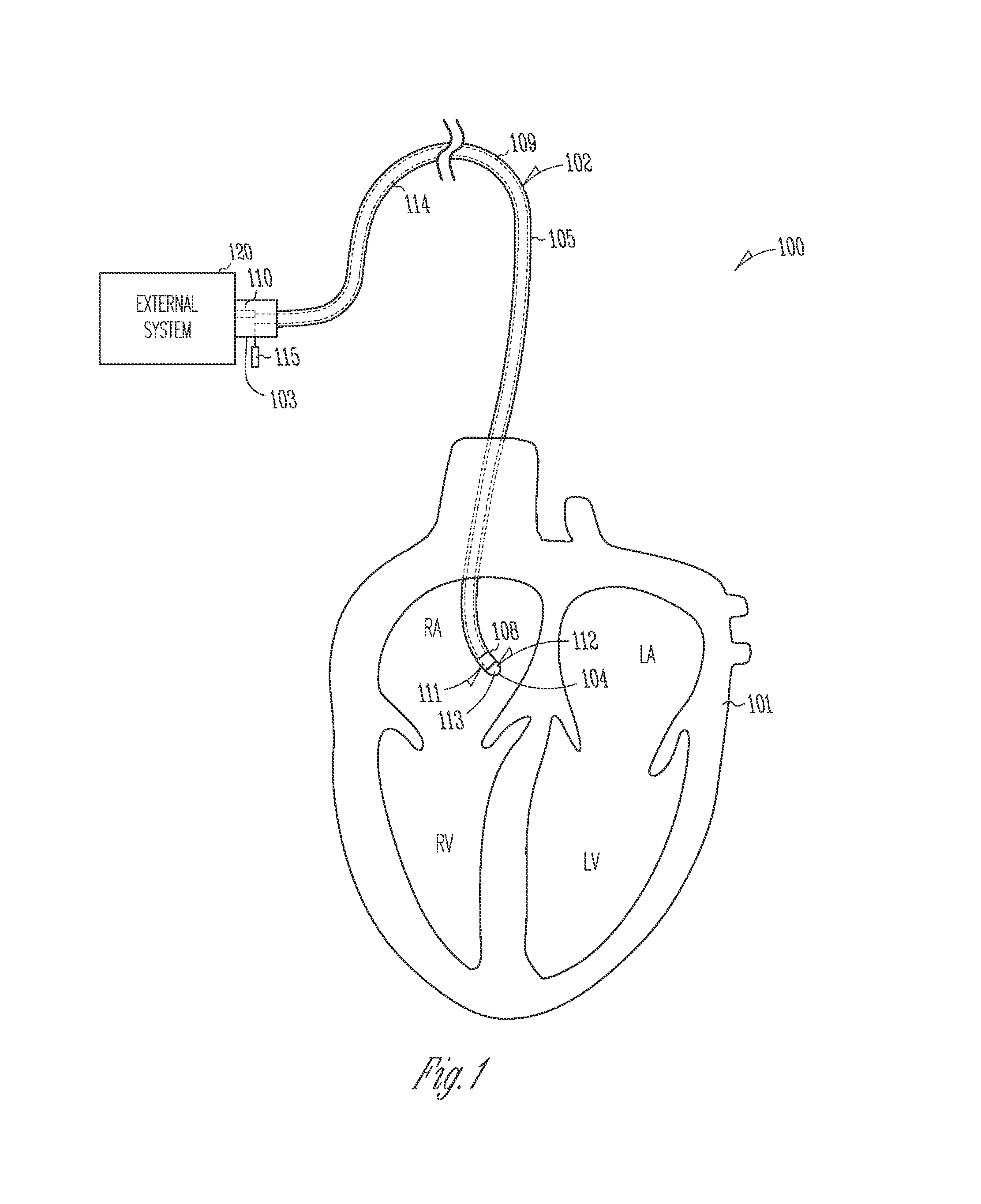
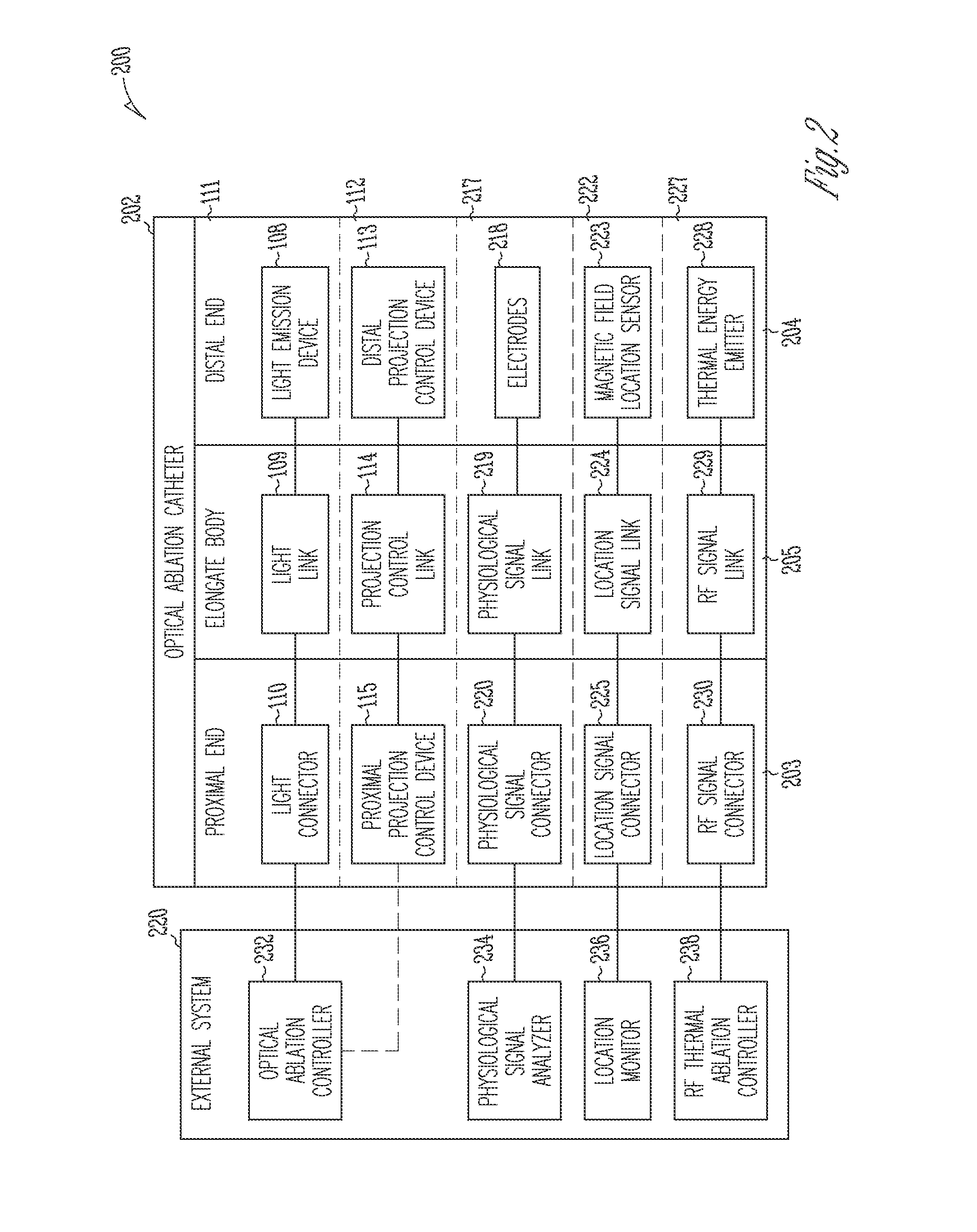
The invention provides a catheter for optical ablation of tissue in a living body, the catheter including: a distal end; a proximal end; an elongate catheter body coupled between the distal end and the proximal end; a light emission device at the distal end and configured to emit an ablation light having characteristics selected to regulate an optically regulatable transcription control element operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence for a gene product, the expression of which gene product in cells directly or indirectly kills cells; and a projection control mechanism coupled to the light emission device and configured to control an effectively illuminated area where the optically regulatable transcription control element is effectively regulatable by the ablation light projected from the light emission device. Also provided is a system which includes the catheter, and methods to prevent, inhibit or treat AF which employ an expression cassette and / or one or more selected wavelengths of light.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Enhancement of adenoviral oncolytic activity by modification of the E1A gene product
ActiveUS7662795B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTranscriptional Regulatory ElementsCytotoxicity
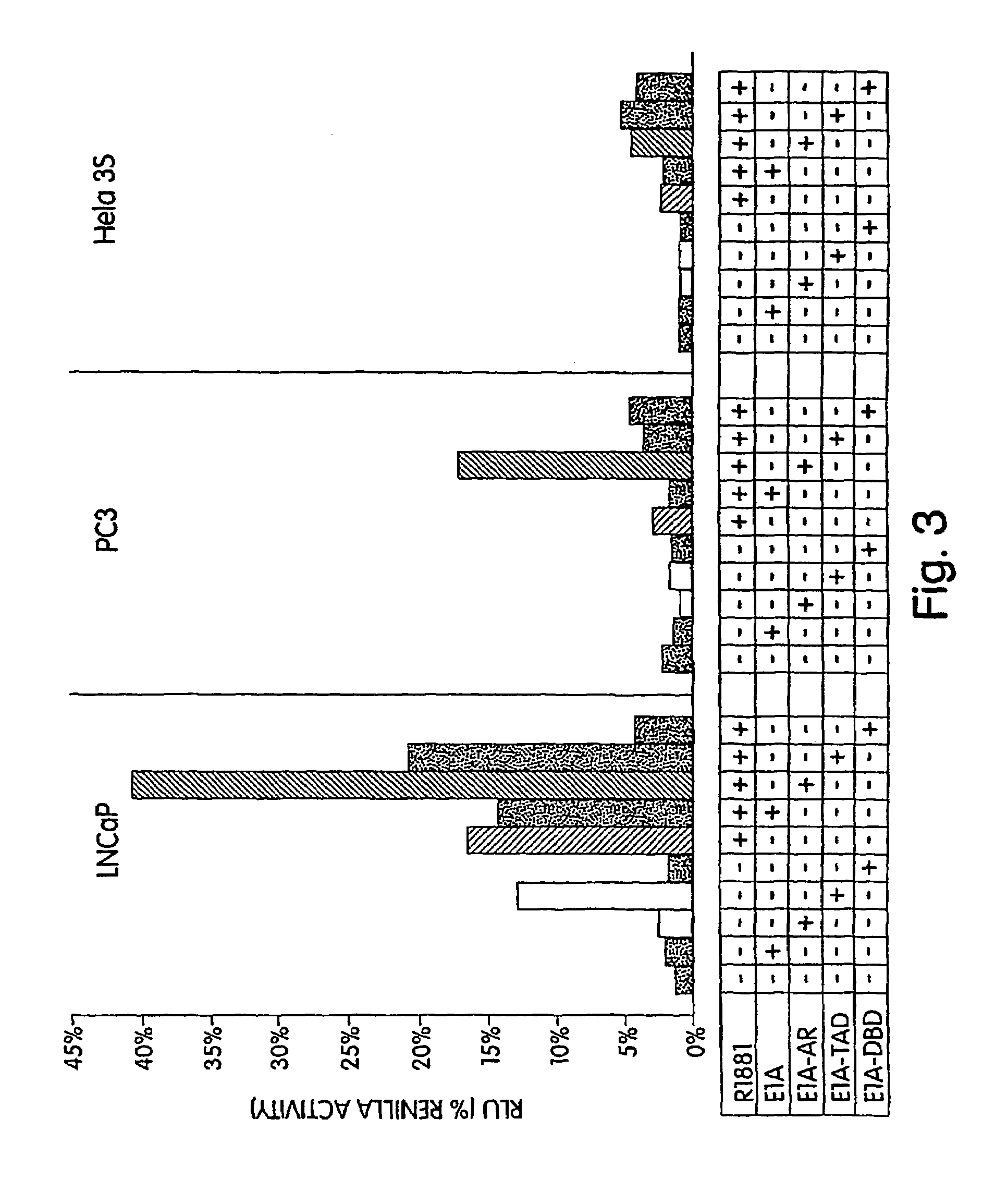
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for enhancing the oncolytic activity of replication-competent, target cell-specific adenovirus vectors by modification of the E1A gene product. The target cell-specific replication-competent adenovirus vectors comprise a chimera of an adenovirus gene essential for replication, preferably an early gene, and the Androgen receptor (or a portion thereof) under the transcriptional control of a cell type-specific transcriptional regulatory element (TRE). By providing for cell type-specific transcription through the use of one or more cell type-specific TREs, the adenovirus vectors effect prostate-specific cytotoxicity due to selective replication.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Selective antibody targeting of undifferentiated stem cells
This invention provides a system for producing differentiated cells from a stem cell population for use wherever a relatively homogenous cell population is desirable. The cells contain an effector gene under control of a transcriptional control element (such as the TERT promoter) that causes the gene to be expressed in relatively undifferentiated cells in the population. Expression of the effector gene results in expression of a cell-surface antigen that can be used to deplete the undifferentiated cells. Model effector sequences encode glycosyl transferases that synthesize carbohydrate xenoantigen or alloantigen, which can be used for immunoseparation or as a target for complement-mediated lysis. The differentiated cell populations produced are suitable for use in tissue regeneration and non-therapeutic applications such as drug screening.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC +1
Isolation and identification of mouse and human transcription control elements associated with cytochrome expression
The present invention relates to transcription control elements derived from mouse and human genes associated with cytochrome expression, e.g., Cyp3A11 and CYP3A4, respectively. Isolated polynucleotides, expression cassettes, vectors, recombinant cells, and transgenic animals, may comprise such transcription control elements as described herein.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
Recombinant cells that highly express chromosomally-integrated heterologous gene
InactiveUS7192772B1Impairs succinate productionReduce productionSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliHeterologous
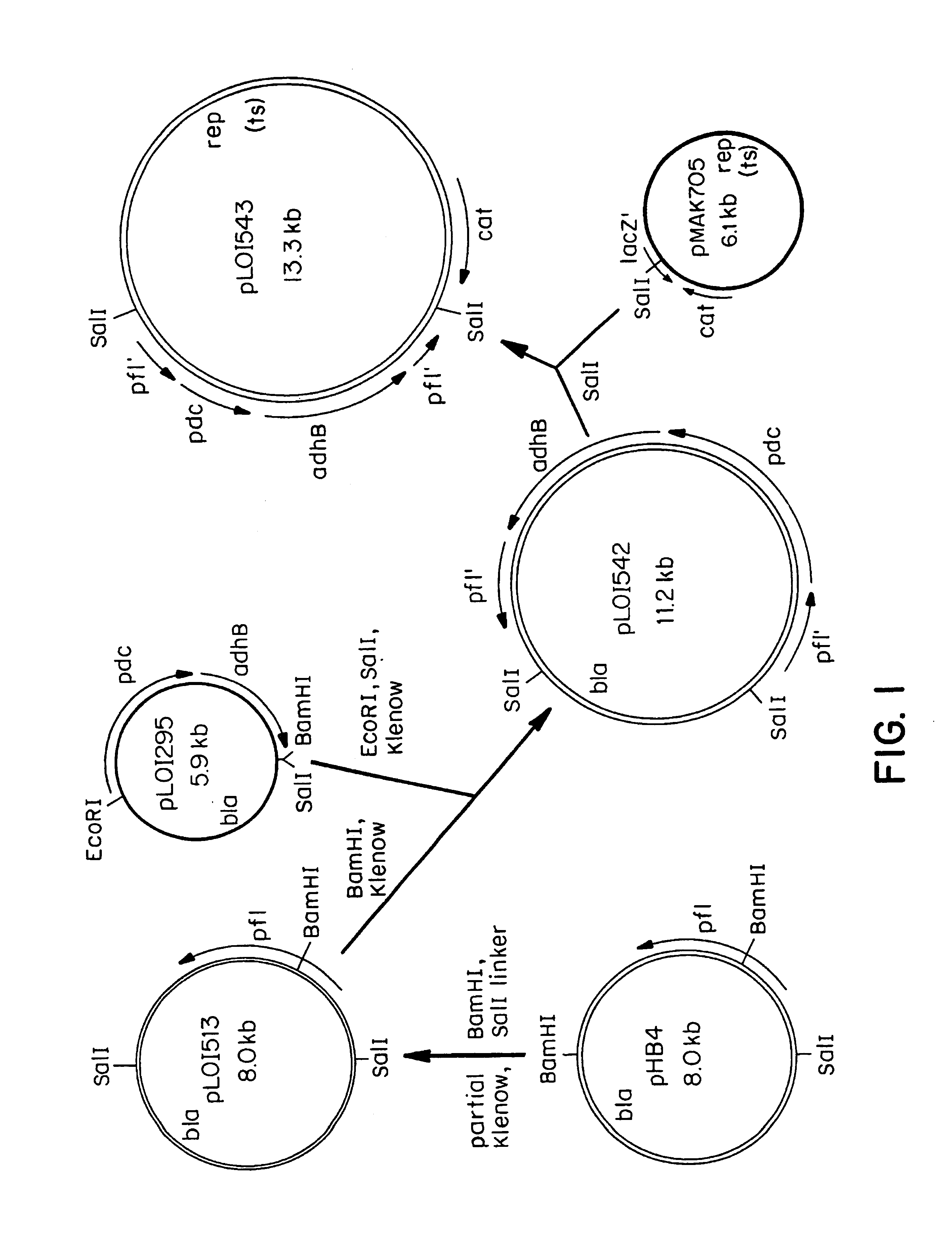
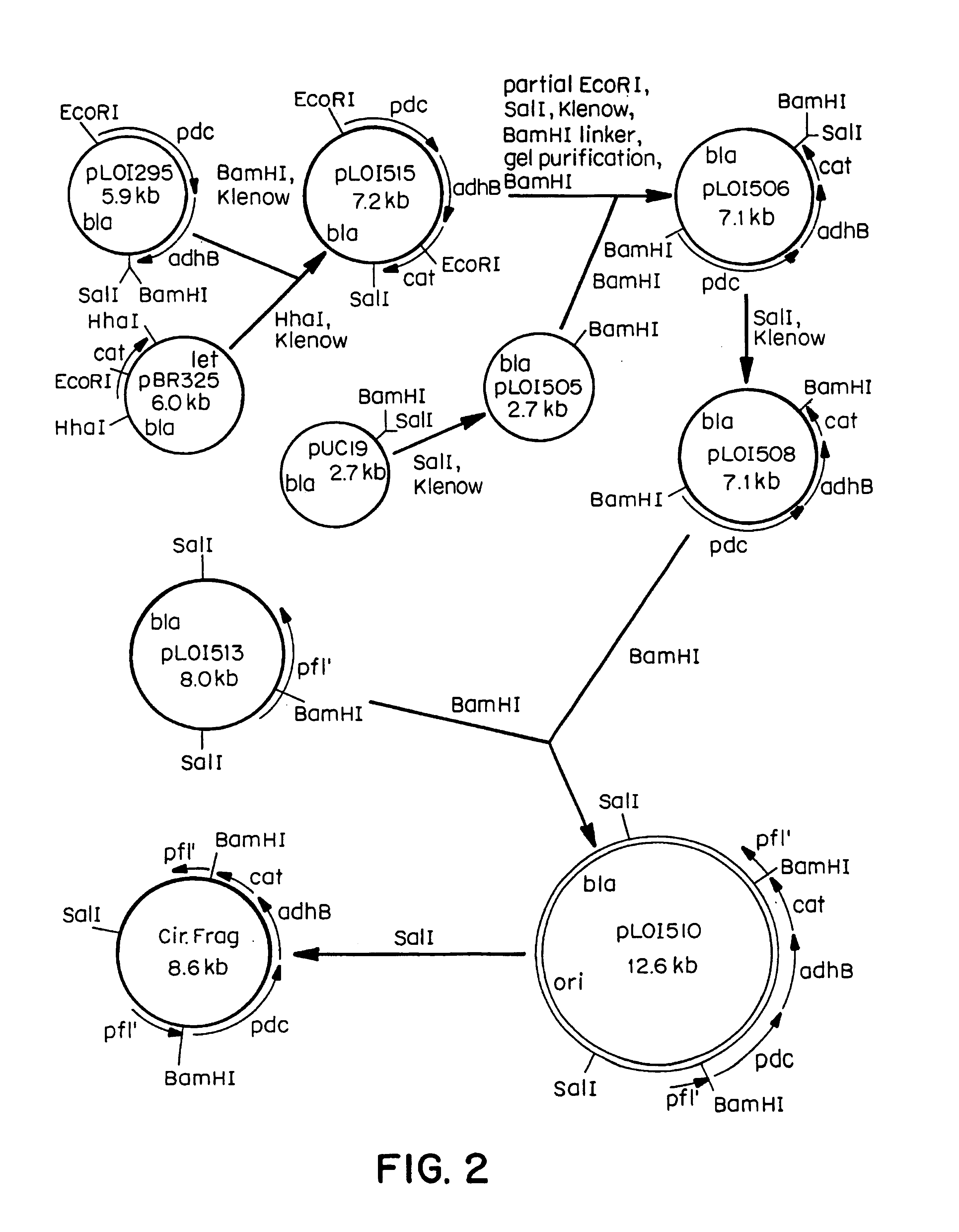
Recombinant host cells are obtained that comprise (A) a heterologous, polypeptide-encoding polynucleotide segment, stably integrated into a chromosome, which is under transcriptional control of an endogenous promoter and (B) a mutation that effects increased expression of the heterologous segment, resulting in enhanced production by the host cells of each polypeptide encoded by that segment, relative to production of each polypeptide by the host cells in the absence of the mutation. The increased expression thus achieved is retained in the absence of conditions that select for cells displaying such increased expression. When the integrated segment comprises, for example, ethanol-production genes from an efficient ethanol producer like Zymomonas mobilis, recombinant Escherichia coli and other enteric bacterial cells within the present invention are capable of converting a wide range of biomass-derived sugars efficiently to ethanol.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods of Producing Adenovirus Vectors and Viral Preparations Generated Thereby
InactiveUS20130052165A1Reducing angiogenesisReducing angiogenesis in the subjectBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousTarget expression
The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to methods of producing adenoviruses such as pro- and anti-angiogenic adenovirus vectors and preparations generated thereby. Particularly, in some embodiments, the viral vectors comprise a heterologous pro- or anti-angiogenic gene under the transcriptional control of the murine pre-proendothelin promoter (e.g. PPE-1-3X), for targeted expression of in angiogenic endothelium.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
Systems and devices for photoablation
ActiveUS20090054883A1Avoid photolysisReduce the risk of blood clotsSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyPhotoablationLight emission
The invention provides a catheter for optical ablation of tissue in a living body, the catheter including: a distal end; a proximal end; an elongate catheter body coupled between the distal end and the proximal end; a light emission device at the distal end and configured to emit an ablation light having characteristics selected to regulate an optically regulatable transcription control element operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence for a gene product, the expression of which gene product in cells directly or indirectly kills cells; and a projection control mechanism coupled to the light emission device and configured to control an effectively illuminated area where the optically regulatable transcription control element is effectively regulatable by the ablation light projected from the light emission device. Also provided is a system which includes the catheter, and methods to prevent, inhibit or treat AF which employ an expression cassette and / or one or more selected wavelengths of light.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Recombinant hosts suitable for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
The invention provides recombinant host cells containing at least one heterologous polynucleotide encoding a polysaccharase under the transcriptional control of a surrogate promoter capable of increasing the expression of the polysaccharase. In addition, the invention further provides such hosts with genes encoding secretory protein / s to facilitate the secretion of the expressed polysaccharase. Preferred hosts of the invention are ethanologenic and capable of carrying out simultaneous saccharification fermentation resulting in the production of ethanol from complex cellulose substrates.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Construction method of genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN102304539AReduce the content of intermediate productsIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme GeneTryptophan
The invention discloses a construction method of a genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing an escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out; 2, constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 containing key enzyme genes aroGFBR, aroE, aroB, aroD, tktA and ppsA in the metabolic pathway of the shikimic acid, so that the genes are subjected to transcriptional control of a tryptophan promoter Ptrp; and 3, transferring the recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 into the escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out to obtain a production strain for expressing the shikimic acid. In the method, the aim of interrupting the metabolism of the shikimic acid is fulfilled by the knock-out of the single gene aroA, a small number of genes are knocked out, the operating difficulty is low, and the expression of the genes is in the state of starting and stopping automatically and is started automatically in the middle and late period without the induction of inducers, so the possibility of adding toxic substances into a culture medium is reduced, and the shikimic acid has high yield.
Owner:河南孟成生物药业股份有限公司
Use of endogenous promoters to express heterologous proteins
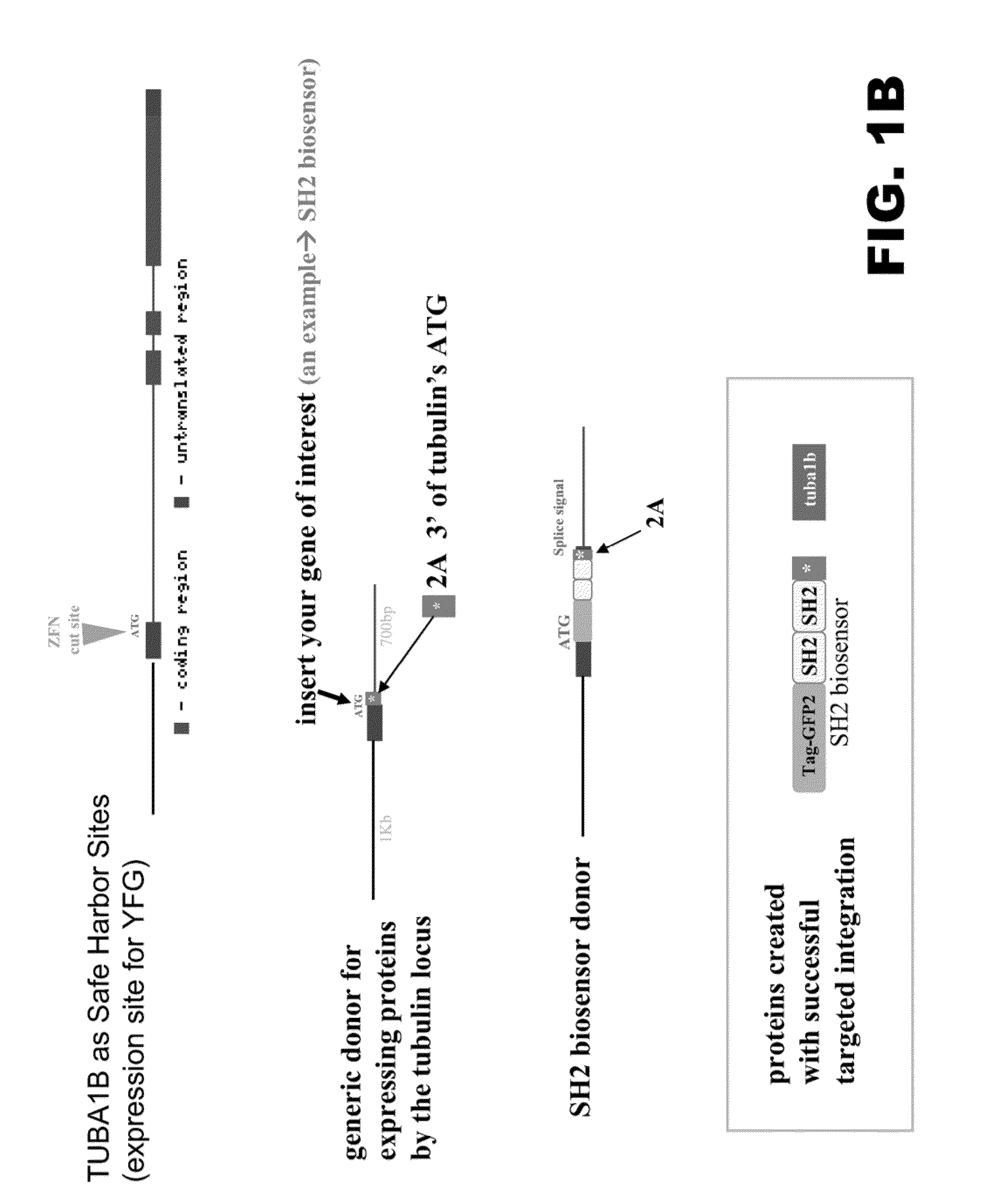
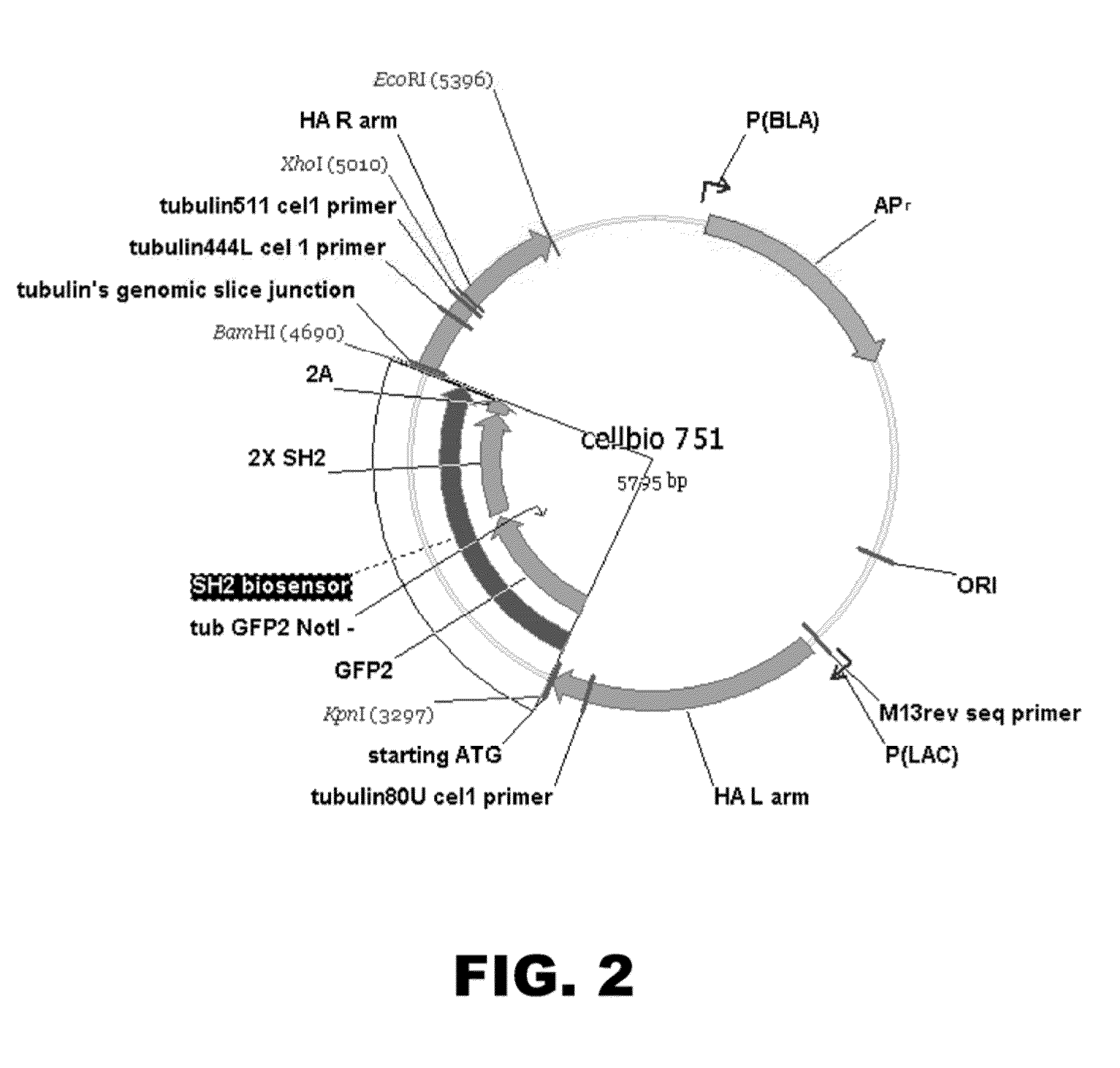
The present invention provides methods for using endogenous transcriptional control systems to regulate the expression of heterologous protein(s). In particular, targeted genome editing is used to integrate a sequence encoding the heterologous protein(s) in-frame with an endogenous coding sequence such that the expression of the heterologous and endogenous sequences is regulated by the endogenous control system.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Stable Genomic Integration of Multiple Polynucleotide Copies
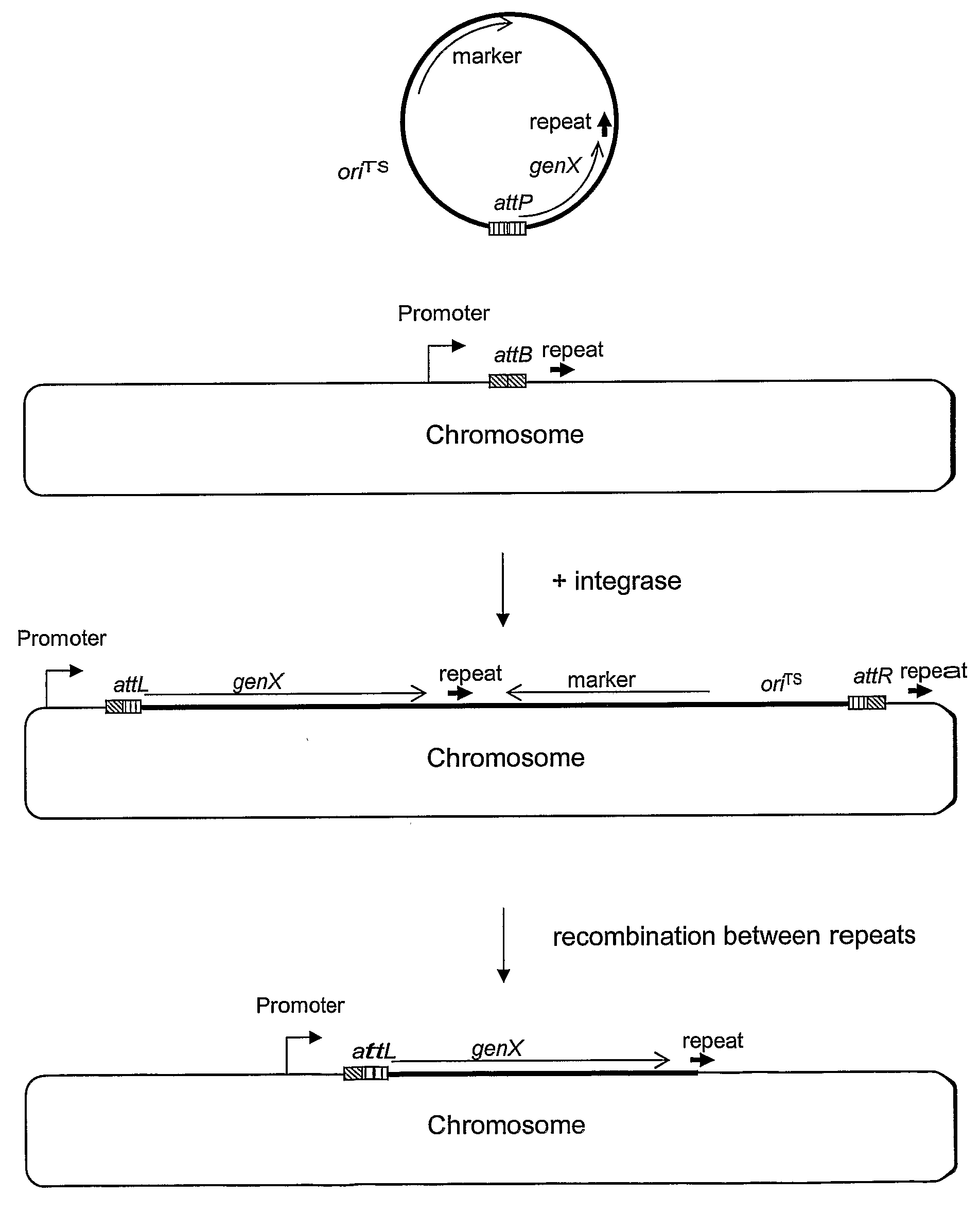
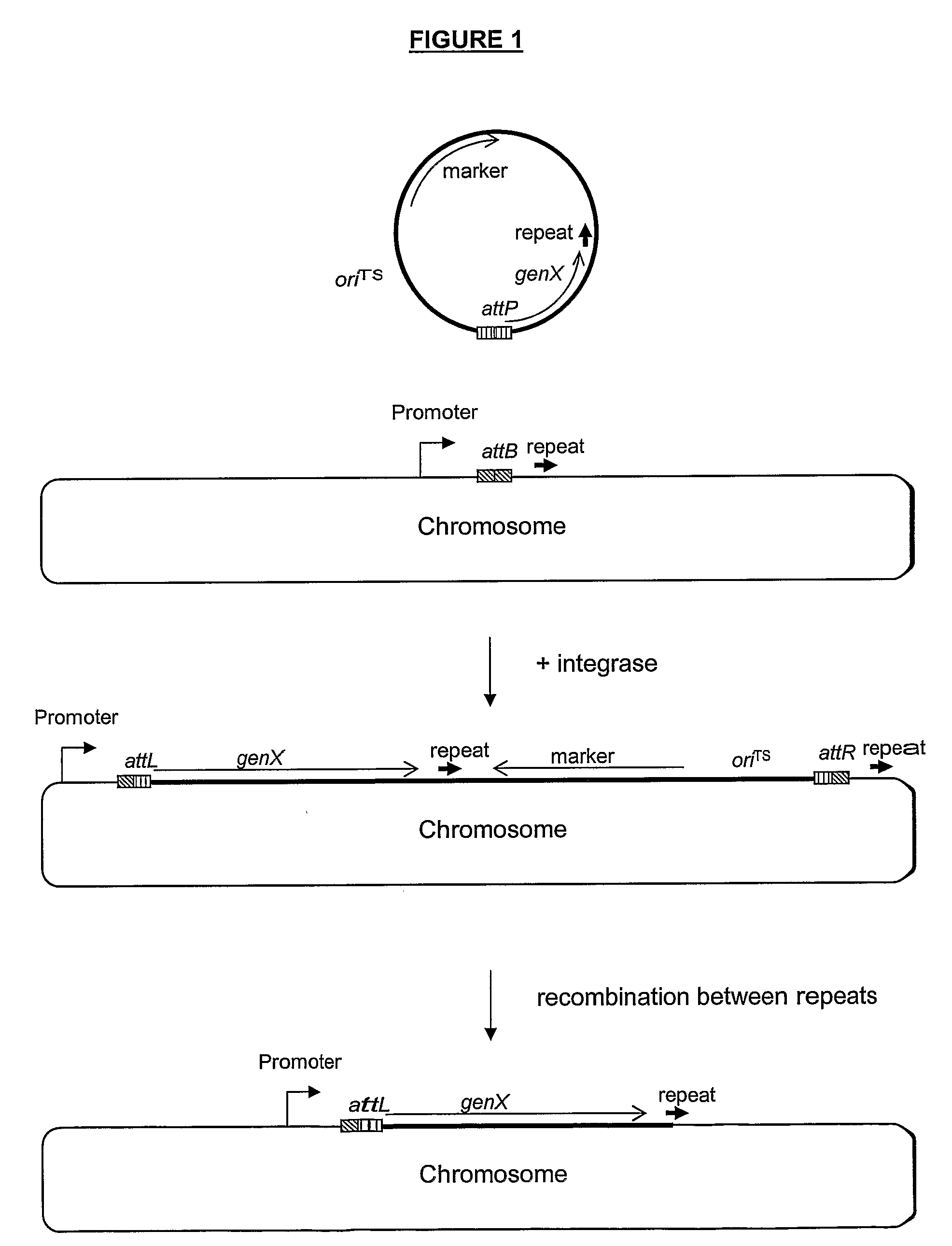
Methods of constructing a cell comprising in its chromosome one or more copies of an open reading frame (ORF) or operon encoding at least one polypeptide of interest, each copy being under the transcriptional control of a heterologous promoter using a site specific recombinase and in vivo integration by recombination; means for Promoter carrying out the methods, resulting cells, and methods for producing a polypeptide of interest using the resulting cells.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Methods of Producing Adenovirus Vectors and Viral Preparations Generated Thereby
InactiveUS20130295053A1Reducing angiogenesisReducing angiogenesis in the subjectBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousTarget expression
The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates to methods of producing adenoviruses such as pro- and anti-angiogenic adenovirus vectors and preparations generated there by. Particularly, in some embodiments, the viral vectors comprise a heterologous pro- or anti-angiogenic gene under the transcriptional control of the murine pre-proendothelin promoter (e.g. PPE-1-3X), for targeted expression of in angiogenic endothelium.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
In vivo assembly of DNA via homologous recombination
InactiveUS20120202251A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPromoter activityDNA construct
According to the present invention, a DNA construct of interest is assembled from overlapping subfragments via an acceptor module which comprises the distal end of the construct at a position downstream from a promoter. The construct is assembled distal to proximal via homologous recombination events occurring in the span between that distal end of the construct and the upstream end of the promoter. These recombination events occur iteratively between the acceptor module and alternative donor modules. Successful recombination places one of at least two marker genes under the transcriptional control of an active form of the promoter. As a result of alternating use of two varieties of donor modules, as few as two selection markers may be used to produce a complex DNA construct.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Efficient protein expression system
InactiveUS6939959B2Alters transcriptional activityNot alter transcriptional activityAntibacterial agentsFungiEukaryotic plasmidsTranscription control
Nucleic acid expression control sequence cassettes and vectors containing the same are provided for use in making abundant quantities of recombinant polypeptides of interest. The modified transcriptional control sequences, which include a T5 promoter sequence, are highly stable and can be used in a variety of vectors, such as plasmids.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL CORP OF WASHINGTON
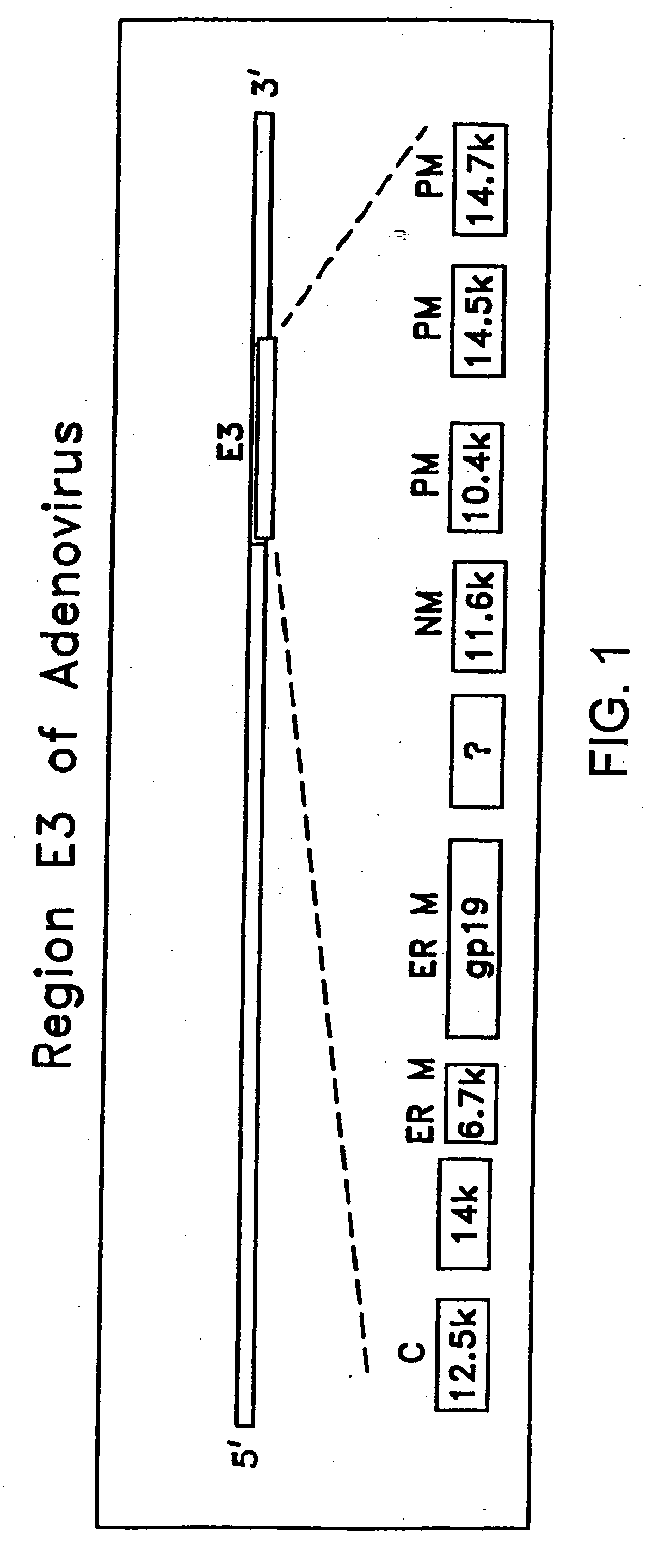
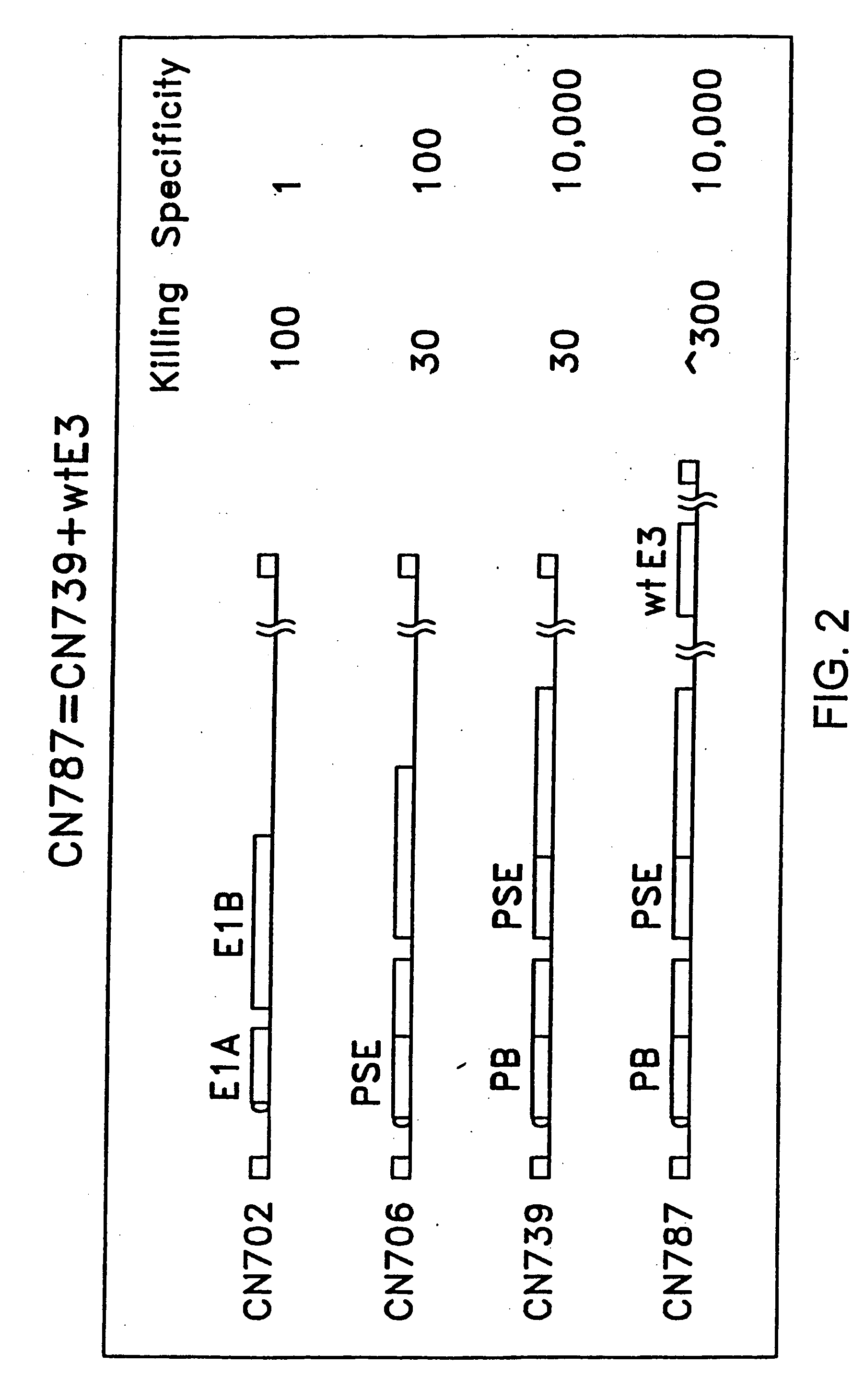
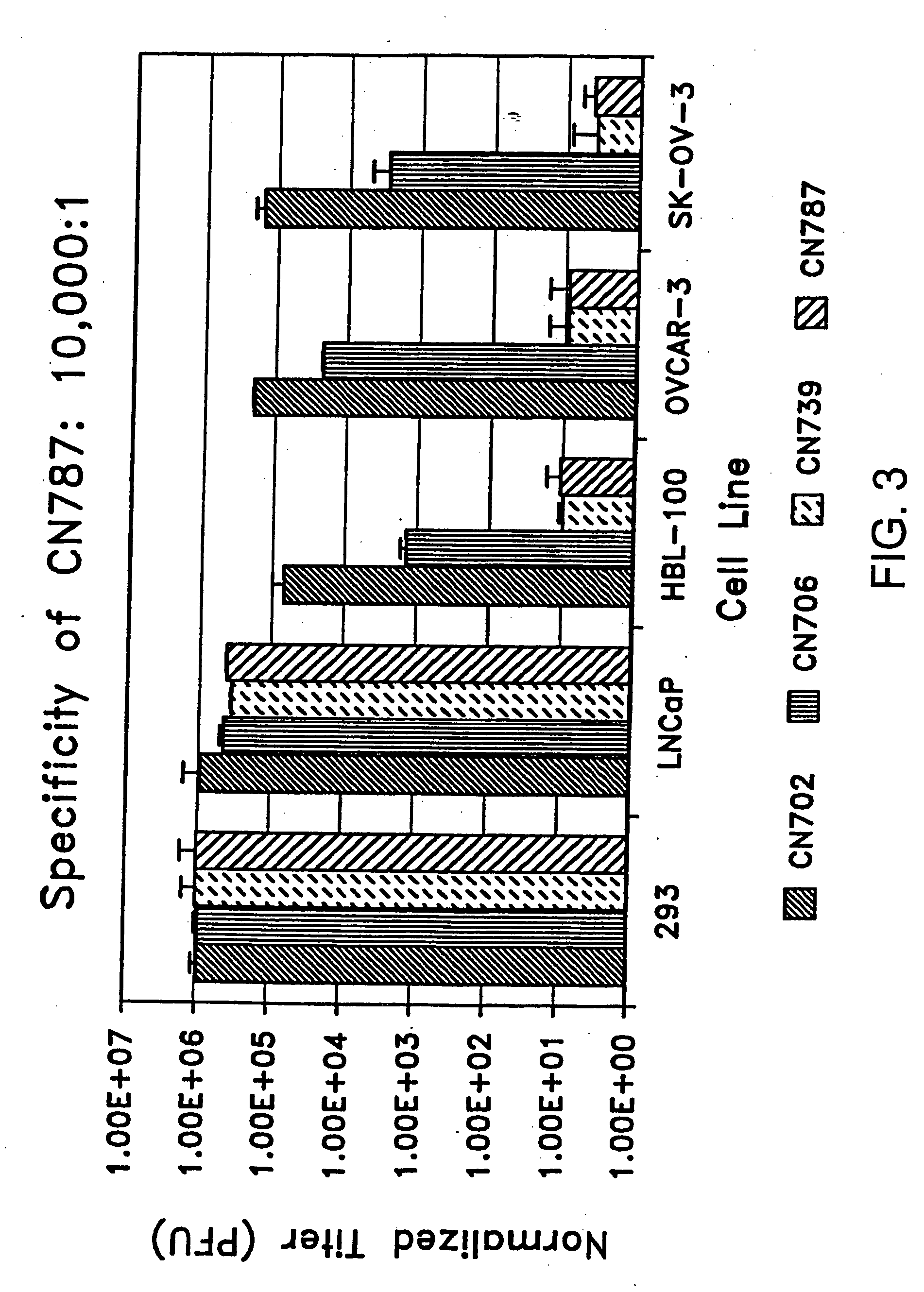
Target cell-specific adenoviral vectors containing E3 and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060024273A1Strong cytotoxicityEnhanced adenoviral productionBiocideVectorsCell specificCytotoxicity
The invention provides adenoviral vectors (preferably replication competent) comprising both an E3 sequence and at least one adenoviral gene under transcriptional control of a target cell-specific transcriptional response element. These vectors display significantly improved cytotoxicity, which is especially useful in the cancer context, in which selective destruction of target cells is desirable. The invention further provides host cells comprising the vectors. The invention further provides methods of using the adenoviral vectors.
Owner:HENDERSON DANIEL +1
RNA respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6428324B1Faster replicationImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsF proteinRestriction site
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Alphavirus vectors for paramyxovirus vaccines
InactiveUS6475780B1Reduce doseLess timeSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseF protein
A DNA vector comprises a first DNA sequence which is complementary to at least part of an alphavirus RNA genome and having the complement of complete alphavirus DNA genome replication regions, and a second DNA sequence encoding a paramyxovirus protein, particularly a respiratory syncytial virus fusion (RSV F) protein or a RSV F protein fragment that generates antibodies that specifically react with RSV F protein, the first and second DNA sequences being under the transcriptional control of a promoter, preferably a cytomegalovirus promoter, which may include Intron A. Such vectors also contain a further nucleotide sequence located between the promoter sequence and the alphavirus sequence to enhance the immunoprotective ability of the RSV F protein when expressed in vivo. Such DNA vectors may be used to immunize a host against disease caused by infection with RSV or other paramyxovirus, including a human host, by administration thereto, and may be formulated as immunogenic compositions with pharmaceutically-acceptable carriers for such purposes. Such vectors also may be used to produce antibodies for detection of RSV or other paramyxovirus infection in a sample.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
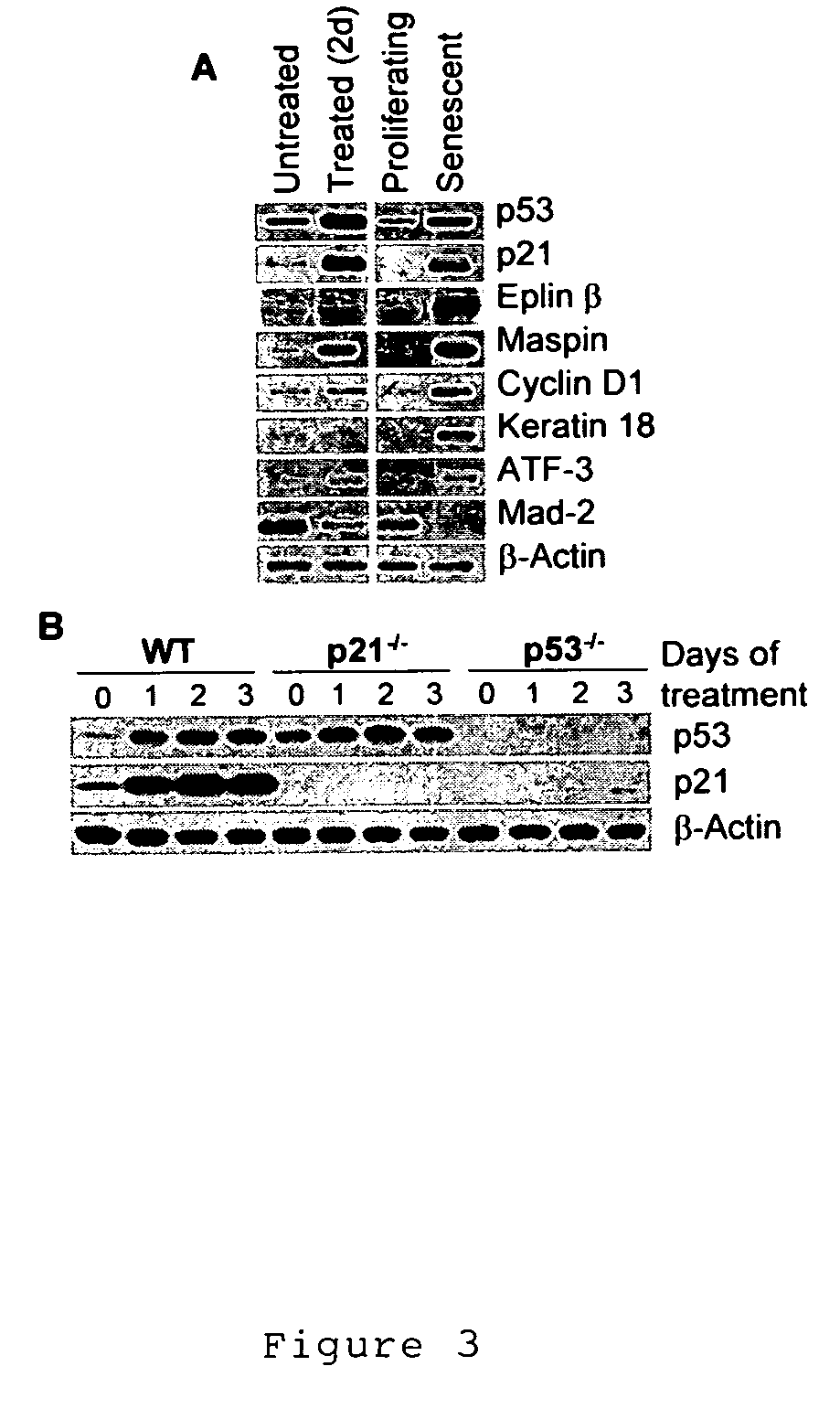
Reagents and methods for identifying and modulating expression of tumor senescence genes
InactiveUS20090208935A1Minimal cytotoxicityGuaranteed long-term growthMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthMammal
This invention identifies tumor senescence genes induced by treatment with cytotoxic agents. The invention provides reagents and methods for identifying compounds that induce expression of these cellular genes and produce cellular senescence, particularly senescence in tumor cells. The invention also provides reagents that are recombinant mammalian cells containing recombinant expression constructs that express a reporter gene under the transcriptional control of a promoter for a gene the expression of which is modulated in senescent cells, and methods for using such cells to identify compounds that modulate expression of these cellular genes.
Owner:SENEX BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
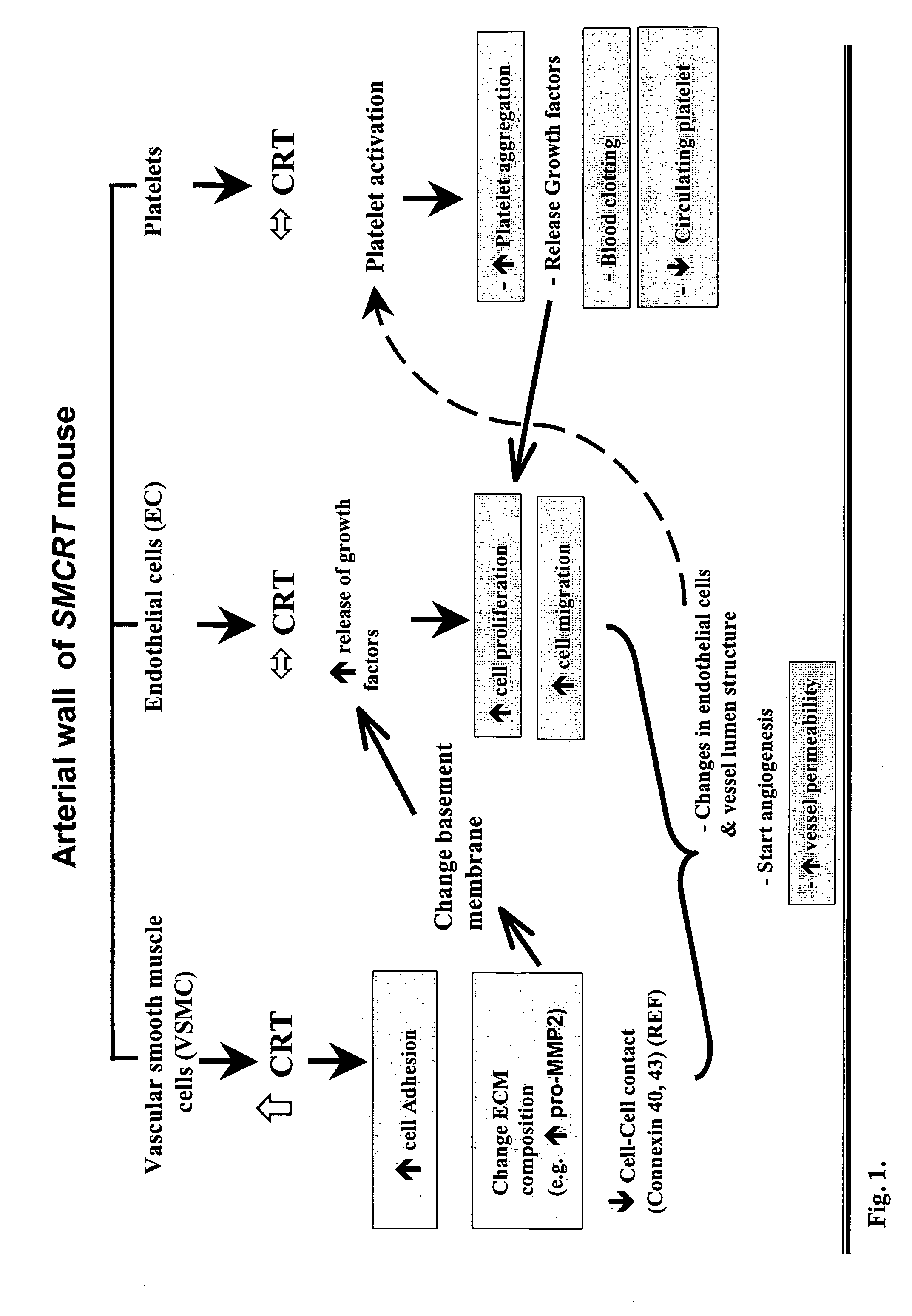
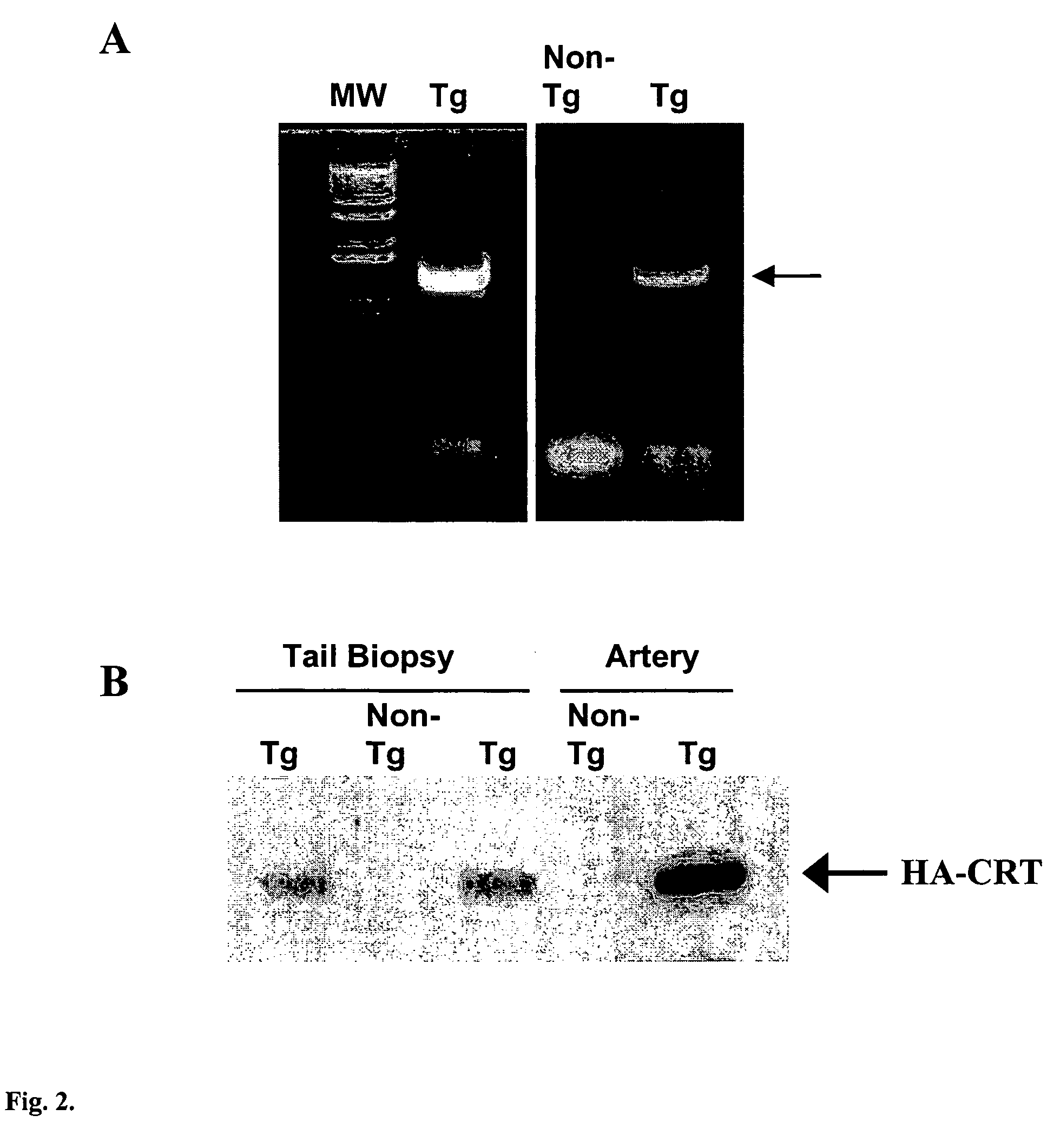
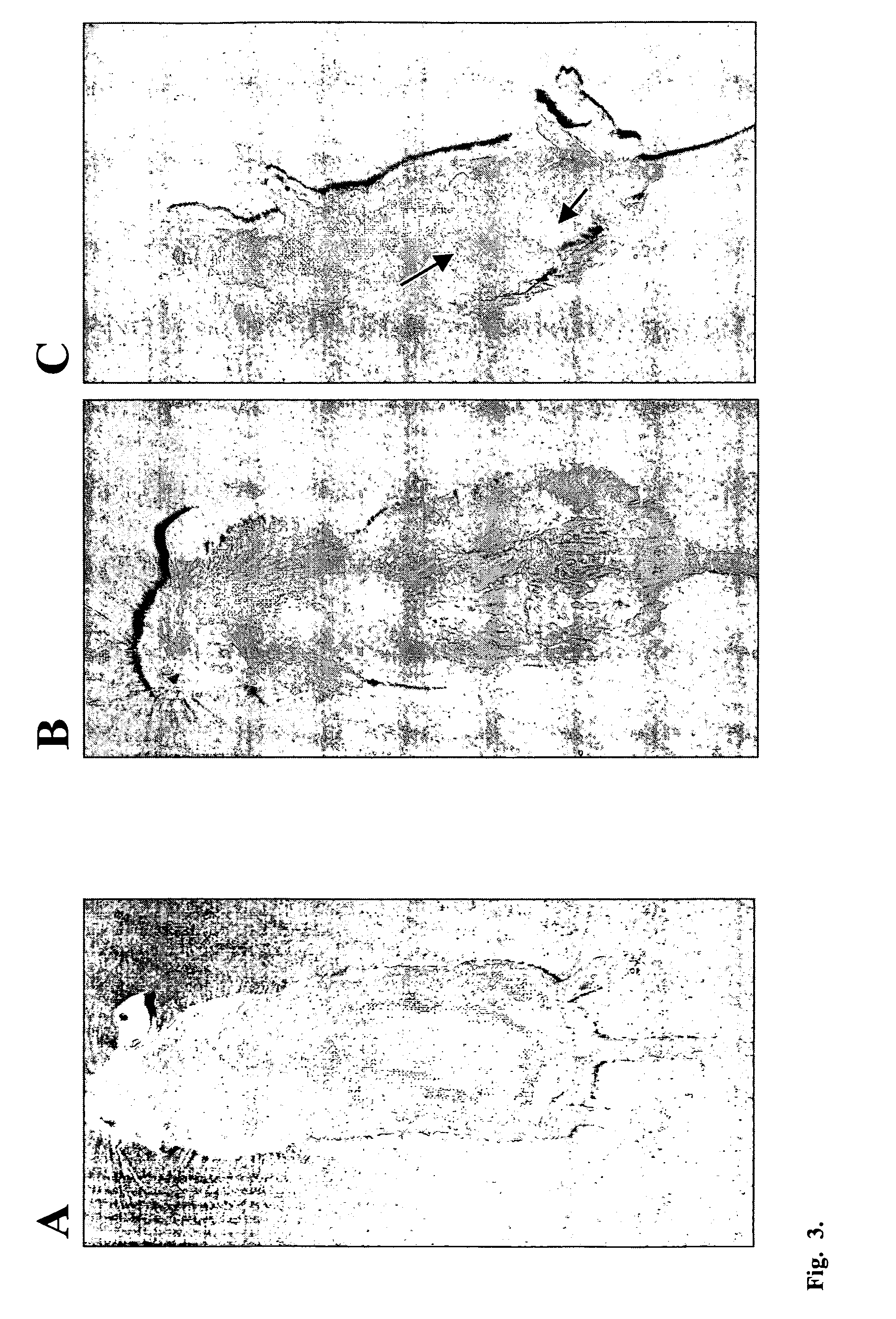
Transgenic mouse over-expressing calreticulin (CRT) in vascular smooth muscle cells
InactiveUS7186882B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce expressionVectorsSugar derivativesCalreticulinTranscription control
A transgenic mouse whose genome comprises a transcriptional control region operably linked to a cDNA encoding calreticulin (CRT) is described.
Owner:MESAELI NASRIN
Hepodxilin analog enantiomers
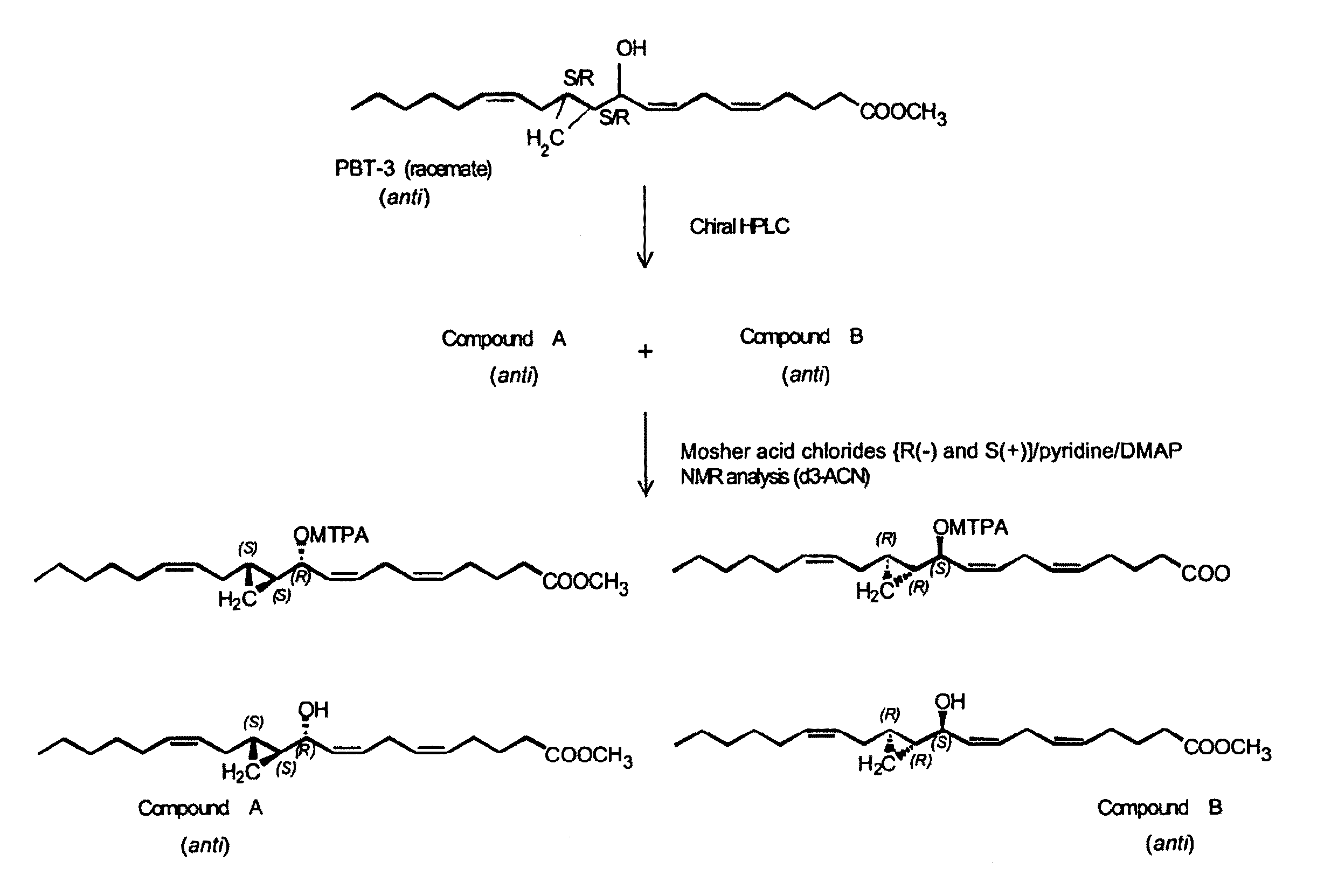
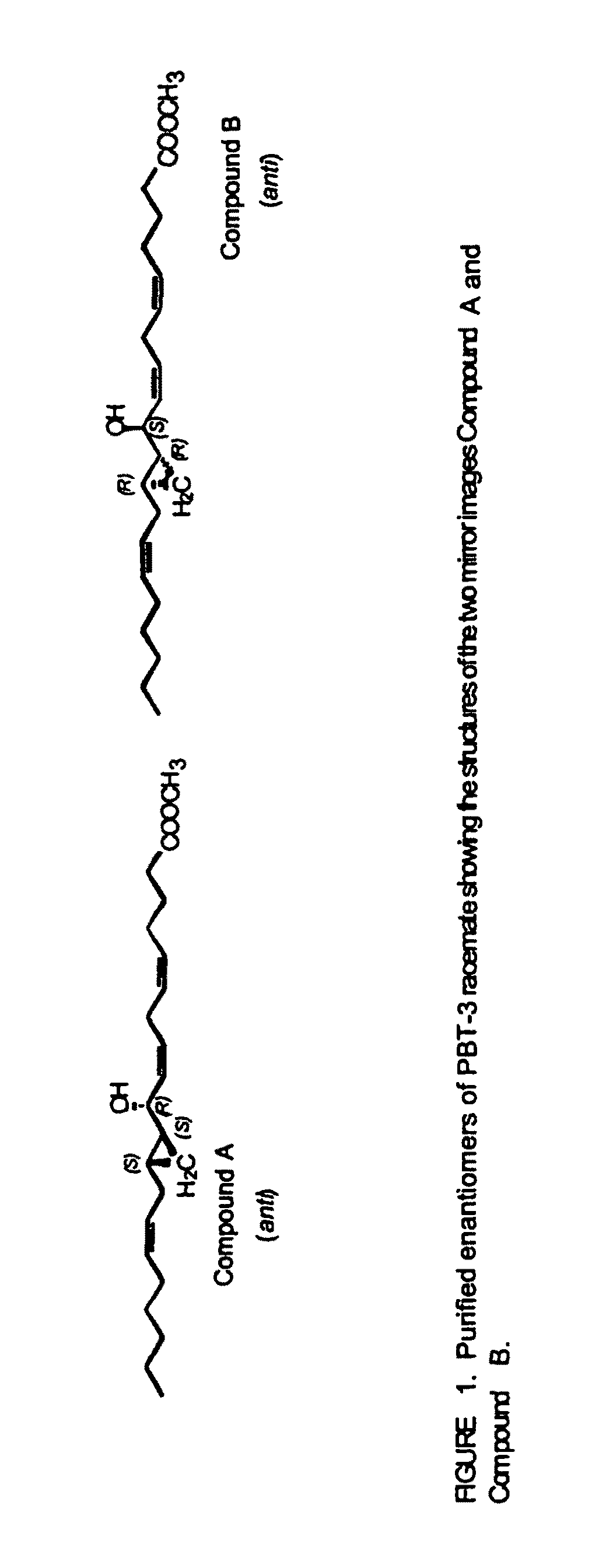
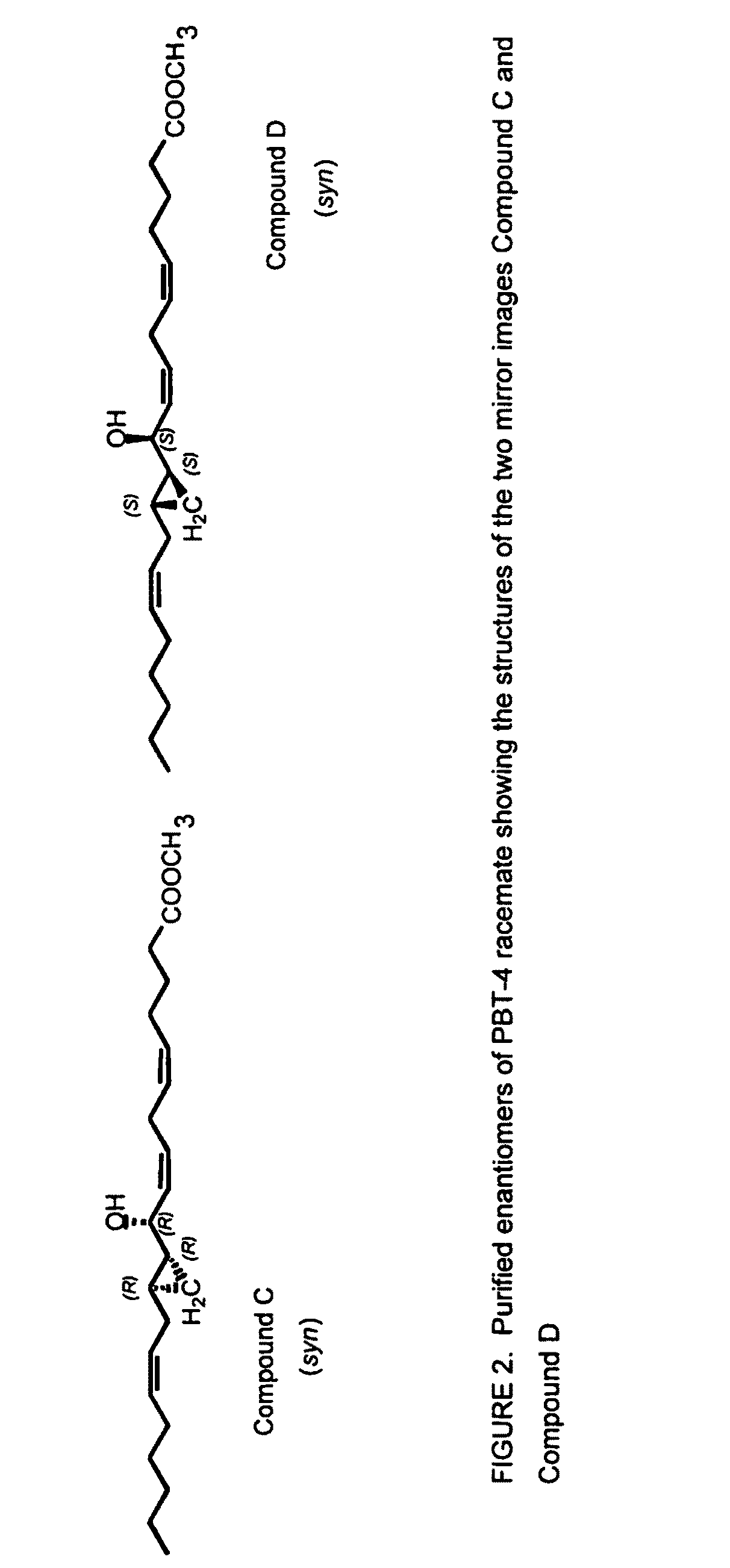
The present invention relates to enantiomeric forms of hepoxilin analogs of Formula I-VIII, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, a method for the separation of said enantiomeric forms of hepoxilin analogs comprising applying said hepoxilin to a chiral phase HPLC column and eluting said hepoxilin with an alkane and alcohol solvent mixture. Said enantiomeric forms of hepoxilin analogs of Formula I-VIII were found to be useful in controlling the biological effects of PPAR mediated transcriptional control for the treatment of diseases such as cancer, thromboxane-mediated diseases and for modulating intracellular calcium concentration.
Owner:CECIL PACE ASCIAK +1
Protein forming complex with c-fos protein, nucleic acid encoding the same and method of using the same
Proteins that interact with c-Fos, nucleic acids encoding them and inhibitors utilizing them as well as methods for detecting an interaction and screening methods utilizing a protein that interacts with c-Fos are provided. Comprehensive analysis of transcription control factor complexes in a mouse brain cDNA library with c-Fos as a bait by using the cotranslation selection and screening of in vitro virus (IVV) and the C-terminal labeling method are conducted, thereby to analyze proteins unknown so far, proteins known so far, but unknown to form a complex with the c-Fos protein, and so forth.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Regulatable promoter
A method of producing a protein of interest (POI) by culturing a recombinant eukaryotic cell line comprising an expression construct comprising a regulatable promoter and a nucleic acid molecule encoding a POI under the transcriptional control of said promoter, comprising the steps a) cultivating the cell line with a basal carbon source repressing the promoter, b) cultivating the cell line with a limited amount of a supplemental carbon source de-repressing the promoter to induce production of the POI at a transcription rate or at least 15% as compared to the native pGAP promoter, and c) producing and recovering the POI; and further an isolated regulatable promoter and a respective expression system.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com