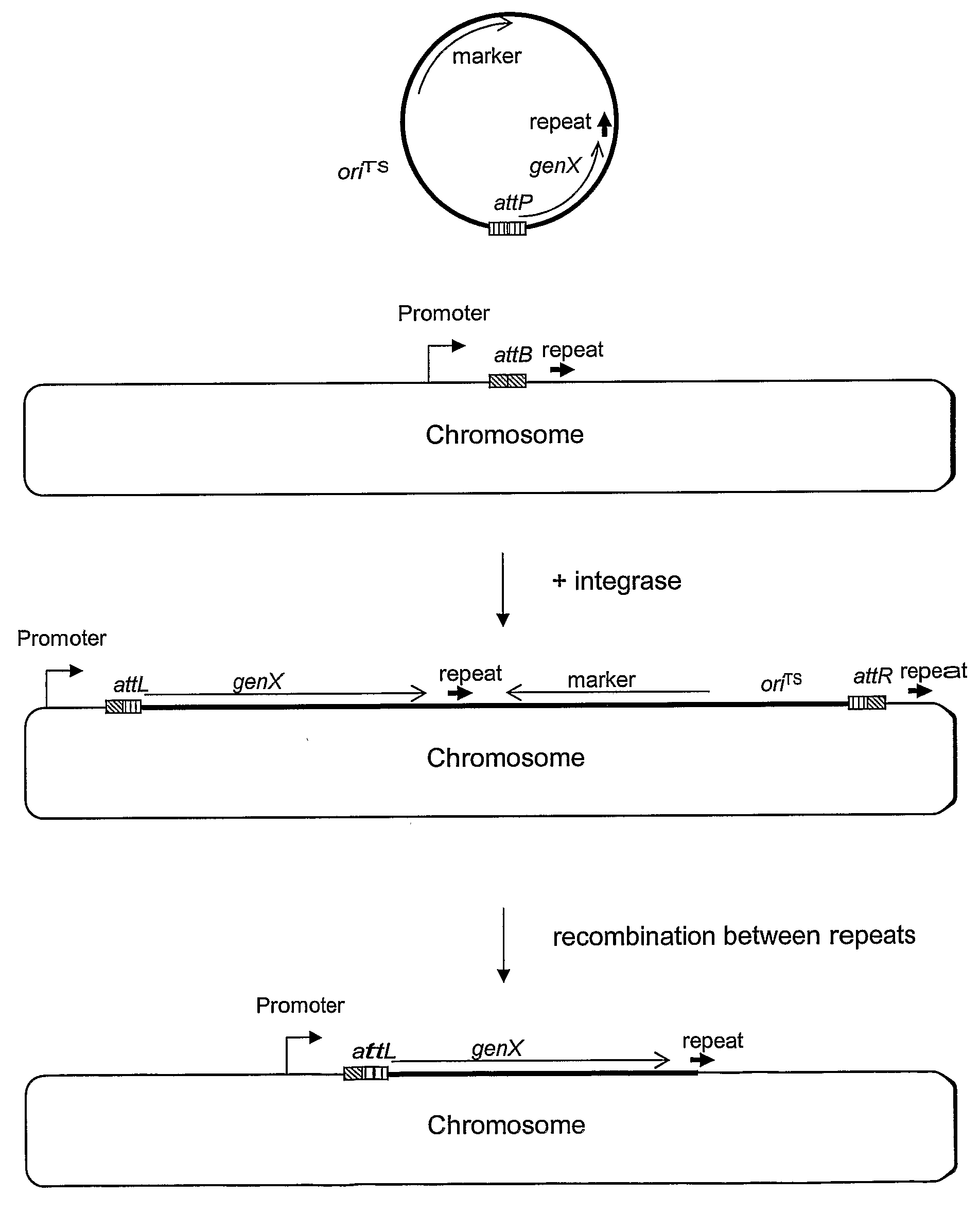
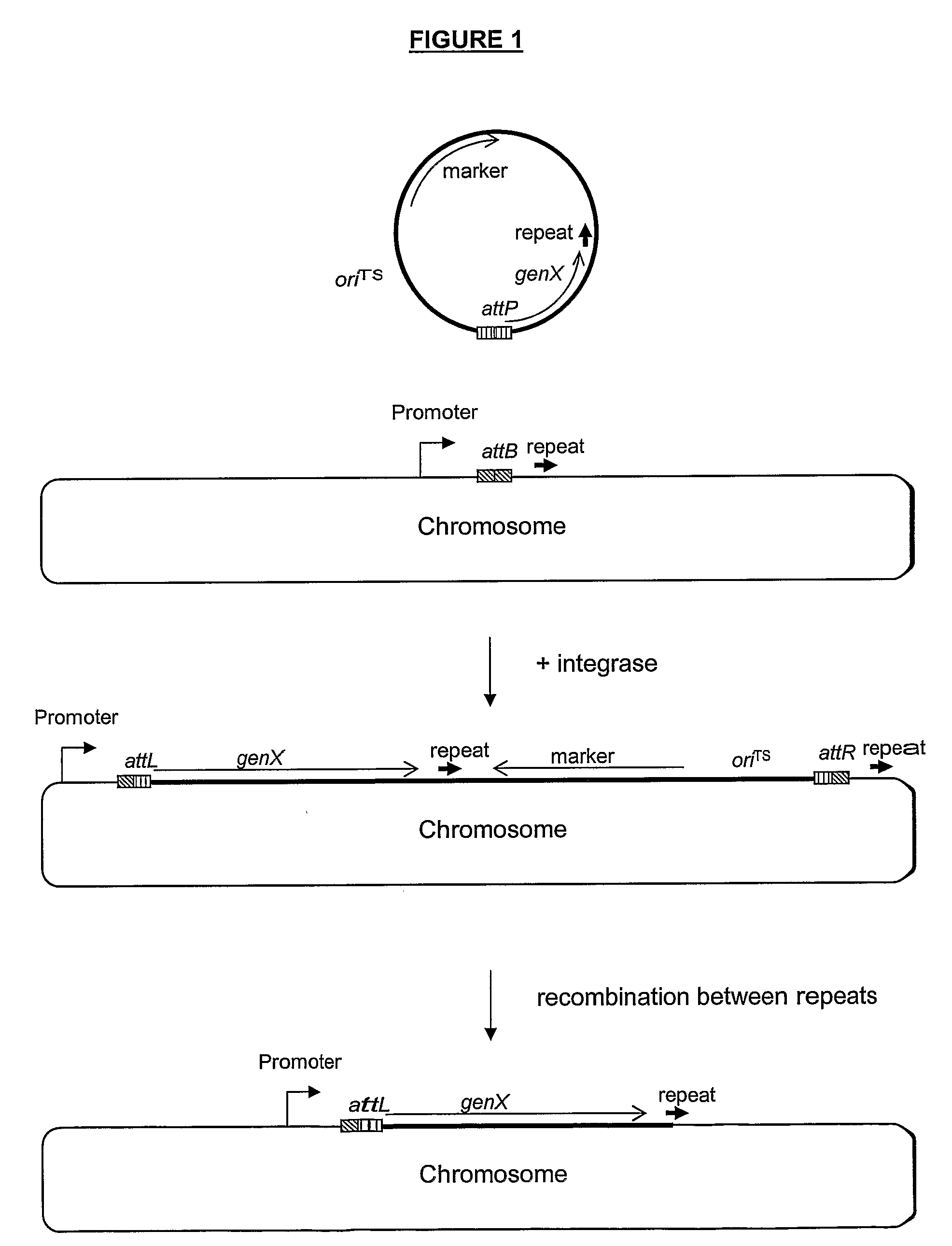
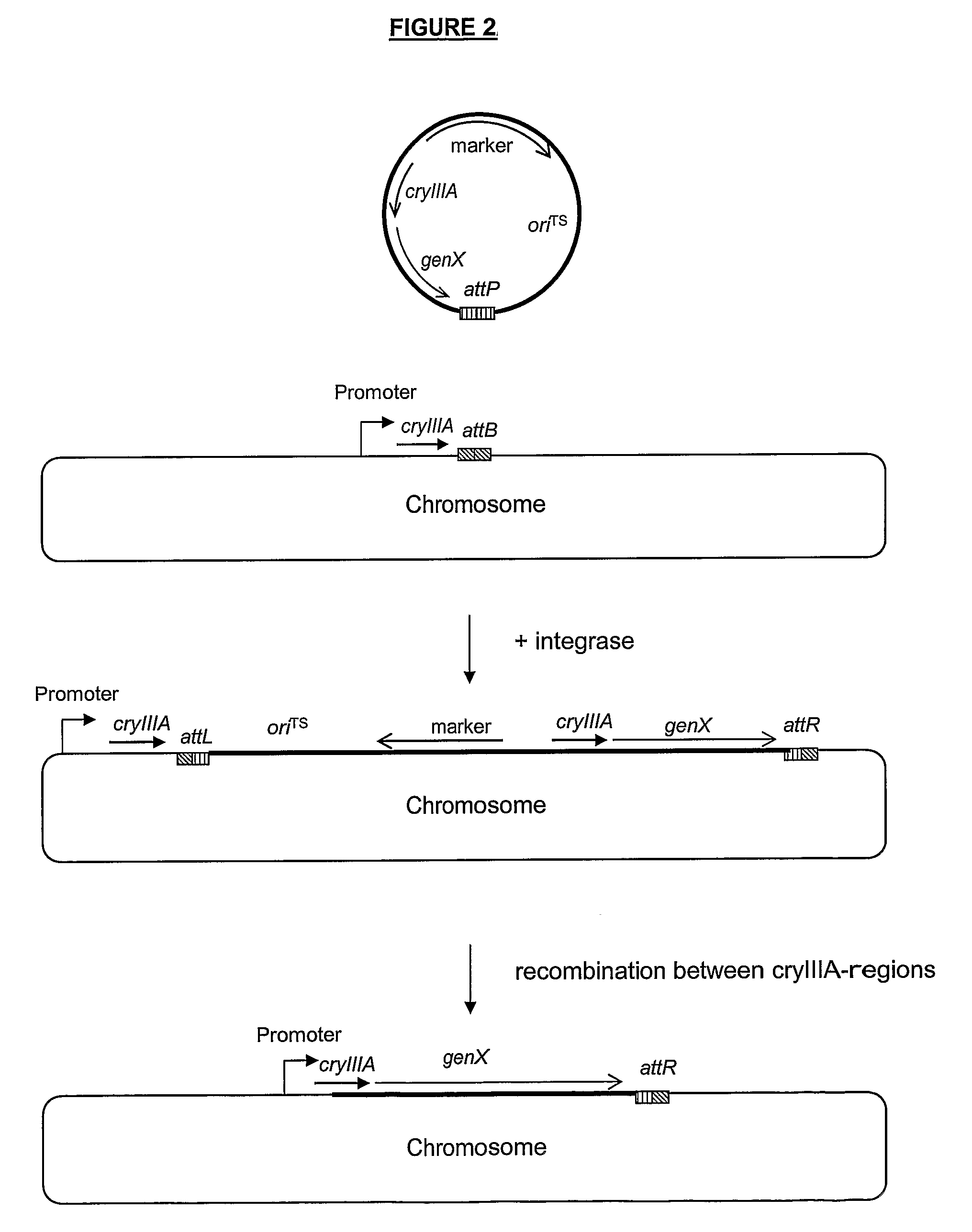
Stable Genomic Integration of Multiple Polynucleotide Copies
a technology of polynucleotide and genomic integration, which is applied in the field of stable genomic integration of multiple polynucleotide copies, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve proper chromosomal integration, and achieve the effect of increasing the number of polynucleotide copies and increasing the production of gene products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of a B. subtilis Strain with Two TP901-1 attB Sites in the Chromosome
[0162]As the first step, an 161 bp attB site (attB161, SEQ ID NO: 21) was integrated in the xyl locus in B. subtilis strain PL1801, resulting in the strain AEB43. Integration was obtained by double cross-over of a DNA fragment which contains attB161 adjacent to the cat gene, surrounded by an upstream and a downstream region of the xyl locus. The upstream and downstream xyl fragments were obtained with PCR on chromosomal DNA from B. subtilis using primers that are suitable for amplifying regions of sufficient size for an efficient integration by homologous recombination (0.5 kb or more). By PCR, these fragments were joined with the attB161 fragment (obtained from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris 3-107) and with the cat gene, yielding chloramphenicol (Cm) resistance.
[0163]This xylup-attB-cat-xyldown fragment was introduced into PL1801 by transformation and the transformants were plated on Cm containing...
example 2
Construction of an Integrase-Donor Plasmid
[0166]The TP901-1 integrase is needed to perform the recombination between the attB and attP sites. The expression of the integrase can be placed under the control of a constitutive or an inducible promoter. In plasmid pAEB146 expression of the integrase is under the control of the Pxyl-promoter, which is induced from a low to a high level of activity upon the addition of xylose. pAEB146 has a temperature sensitive replicon functional in Bacillus and the oriT region from plasmid pUB 110 which enables conjugation, and thus can be used in both B. subtilis and B. lichenformis. Alternatively, the integrase can be expressed from a plasmid which has a different kind of replicon, or it could be integrated into the chromosome.
example 3
Construction of an attP Plasmid
[0167]pAEB153 contains the minimal attP site of TP901-1 (SEQ ID NO: 23) determined in Brøndsted and Hammer (1999) App. Environ. Microbiol. 65 752-758, but a larger attP region can also be used, or a smaller, if it is still active in recombination. Replication of pAEB153 is dependent on donation of replication protein from another plasmid with the pE194 replicon such as pAEB146. Alternatively the attP site can be cloned on a different plasmid vector, e.g. one with an origin which is not dependent on other plasmids for replication, and / or a thermosensitive origin. The attP site can also be included on the plasmid from which integrase is expressed.
[0168]The plasmid containing attP can be used as a vector for cloning genes in such a way, that integration of the plasmid in attB in the chromosome will lead to expression of the gene from a promoter present in the chromosome next to the attB site. We therefore included the mRNA-stabilizing cryIIIA region in pA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| stability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polarity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com