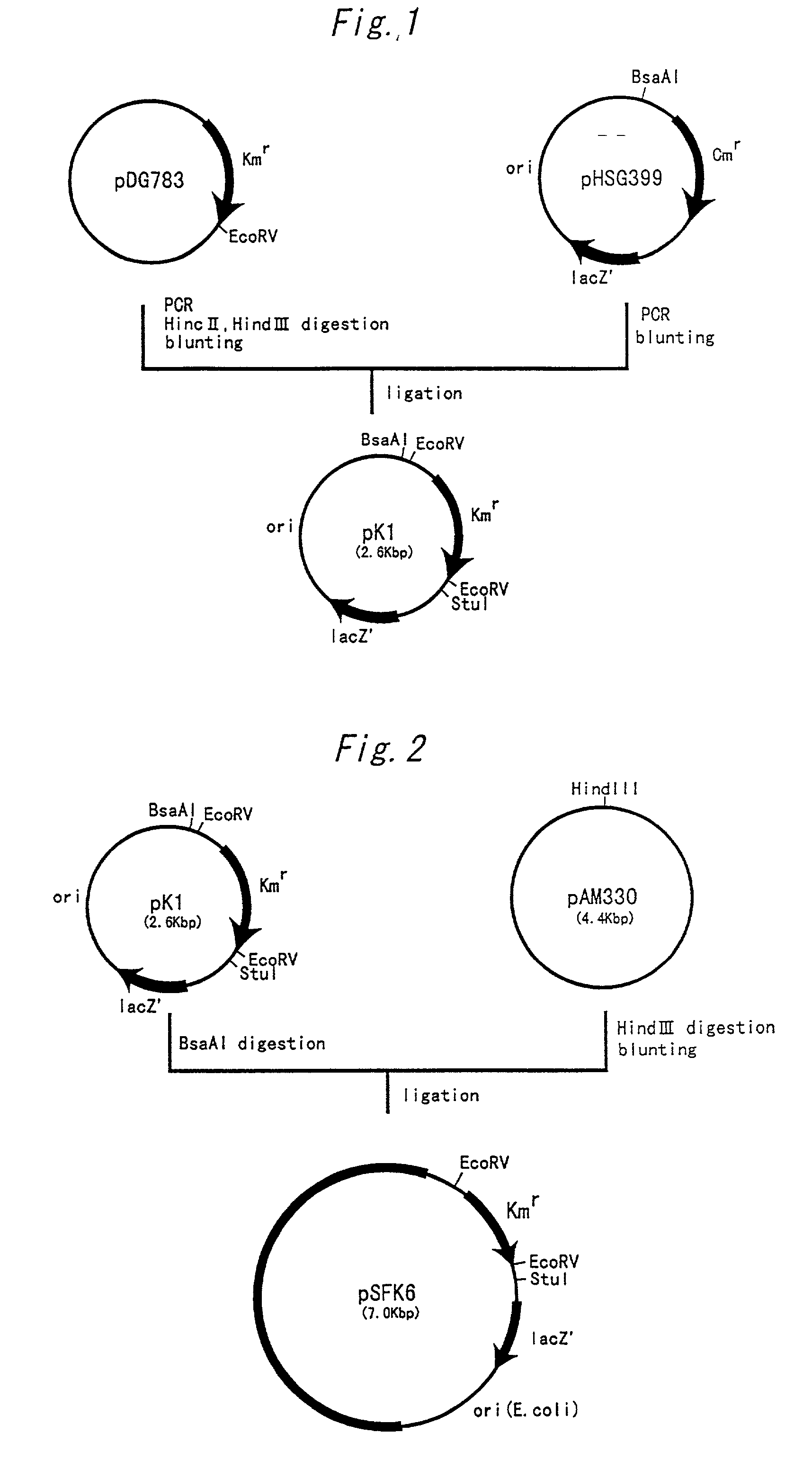
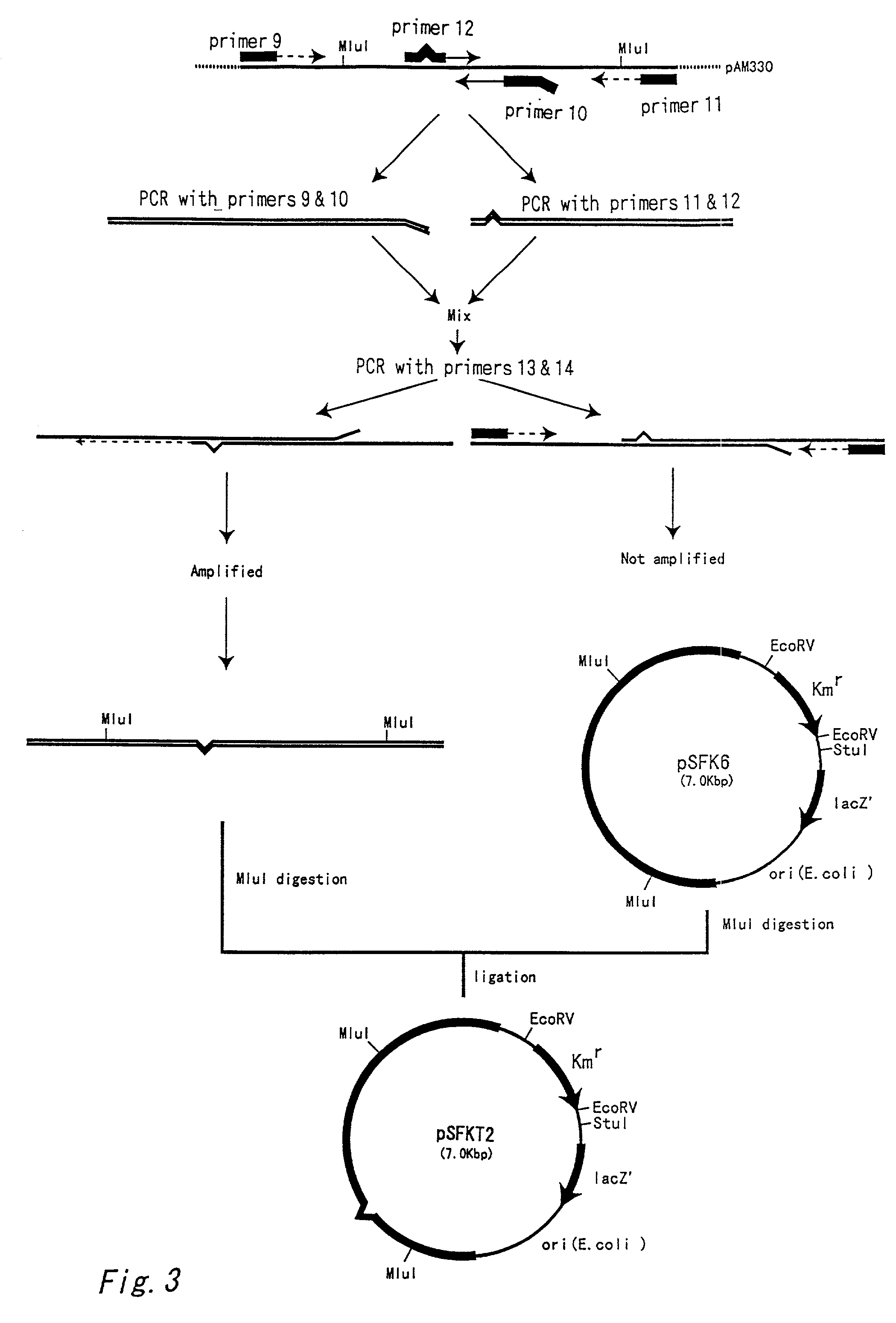
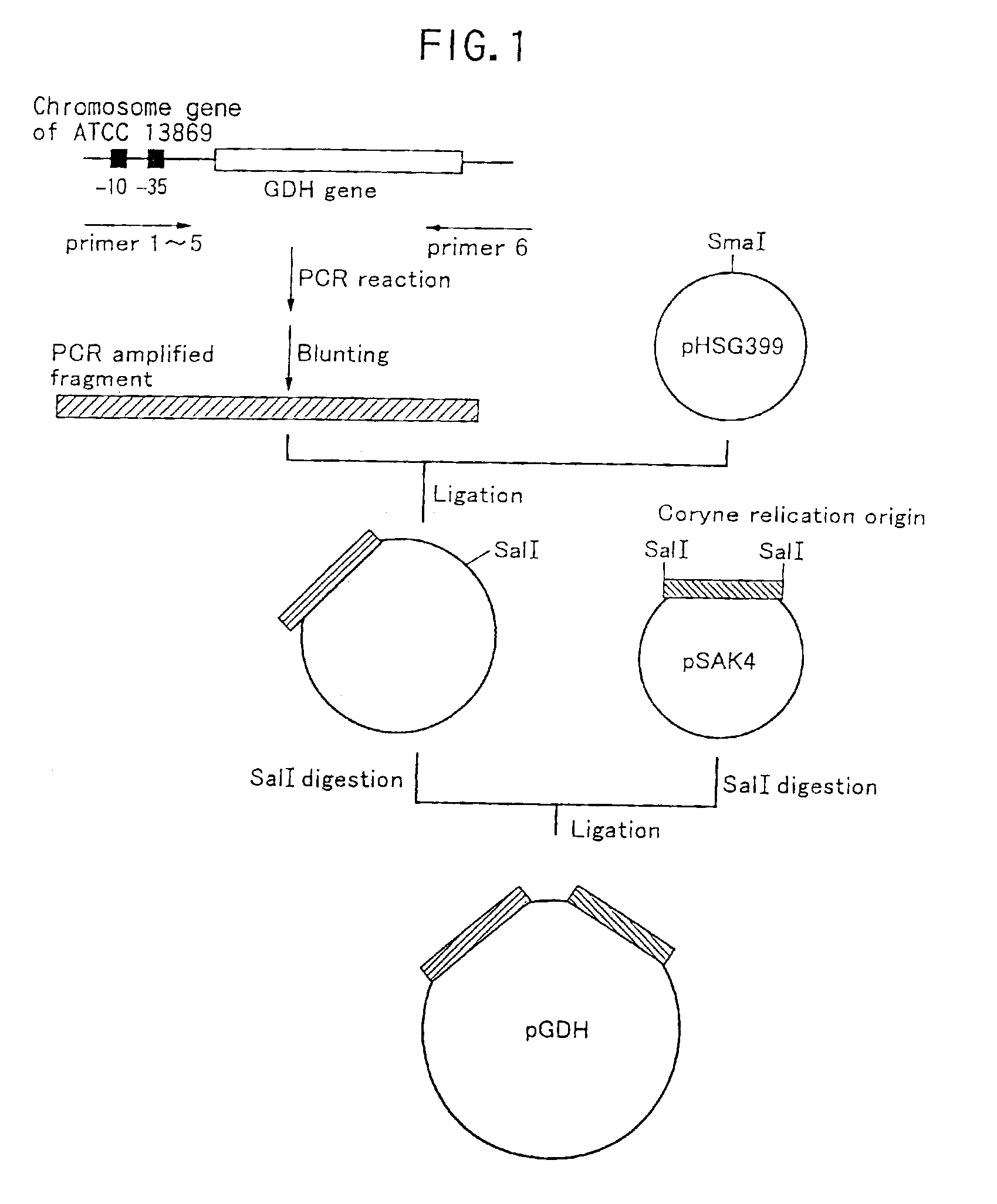
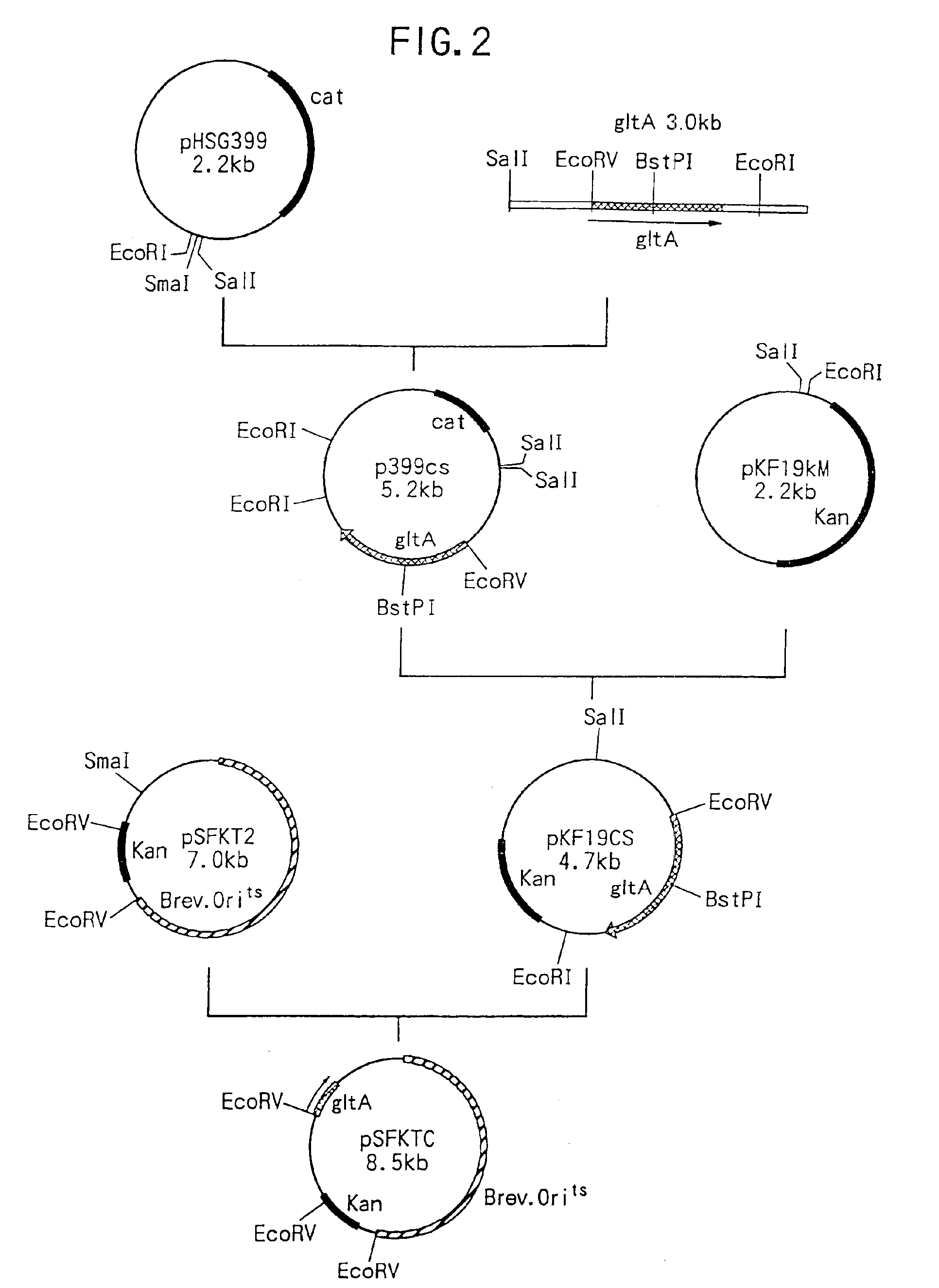
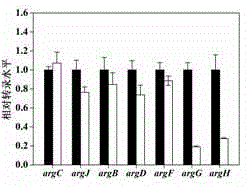
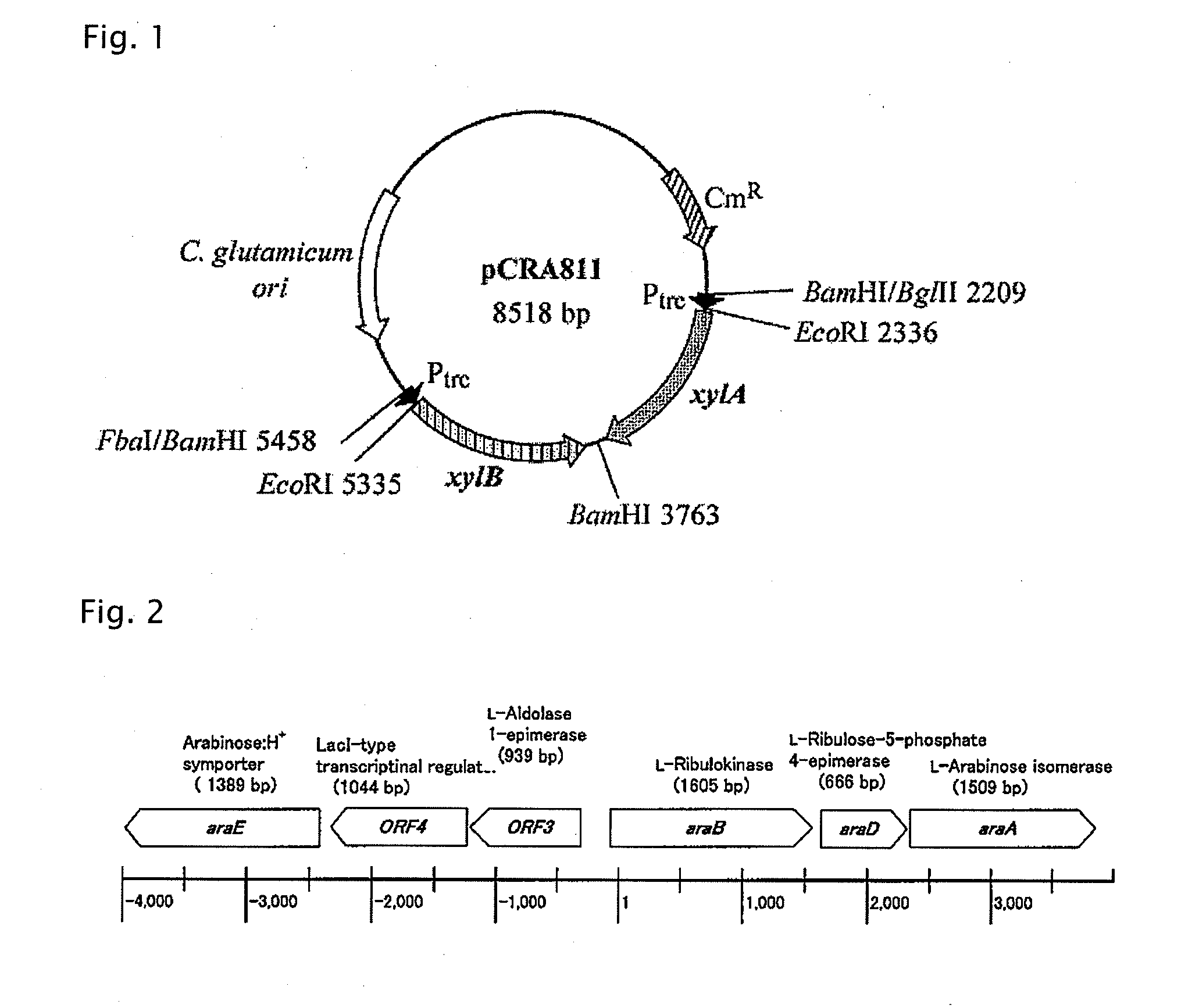
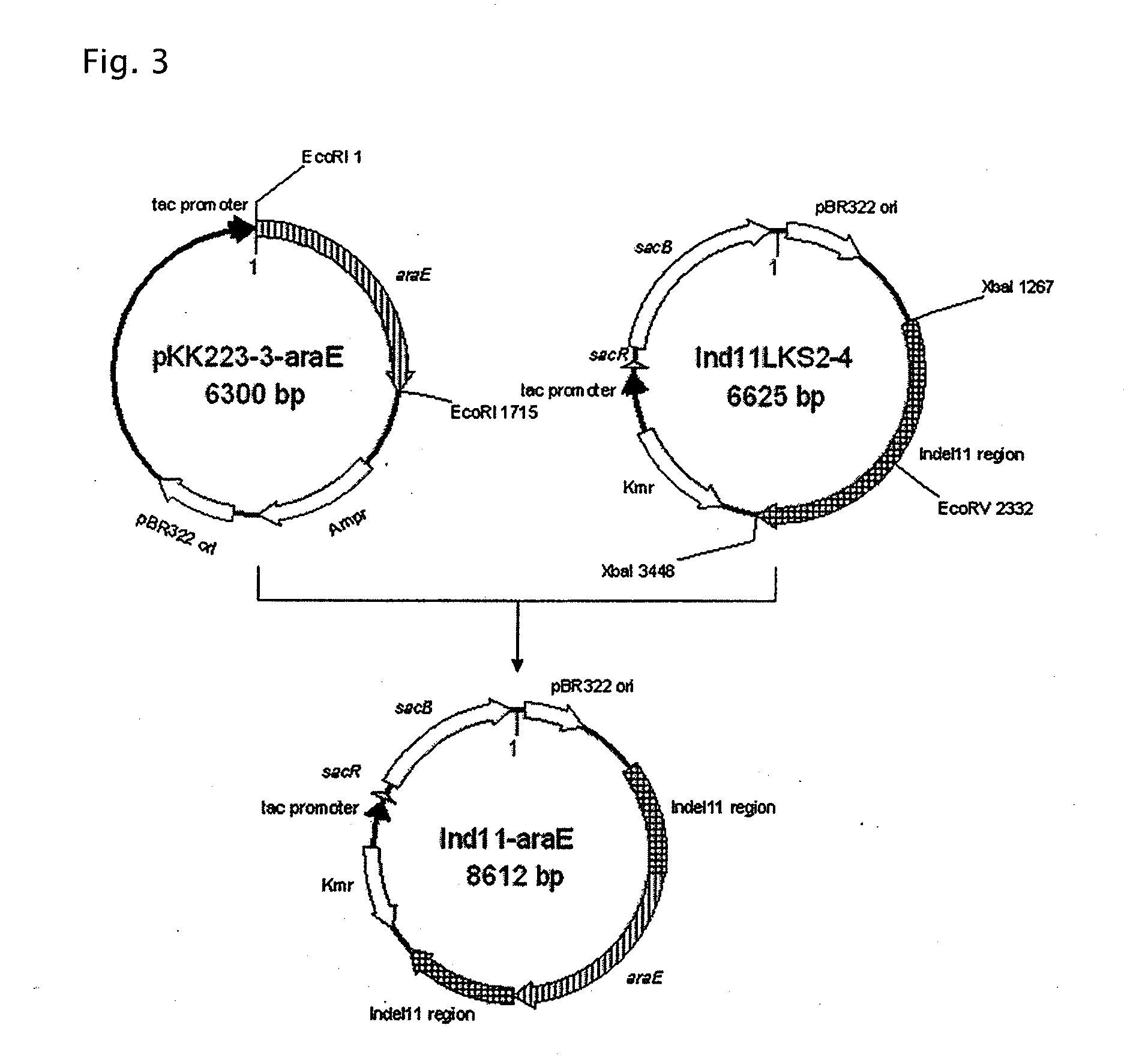
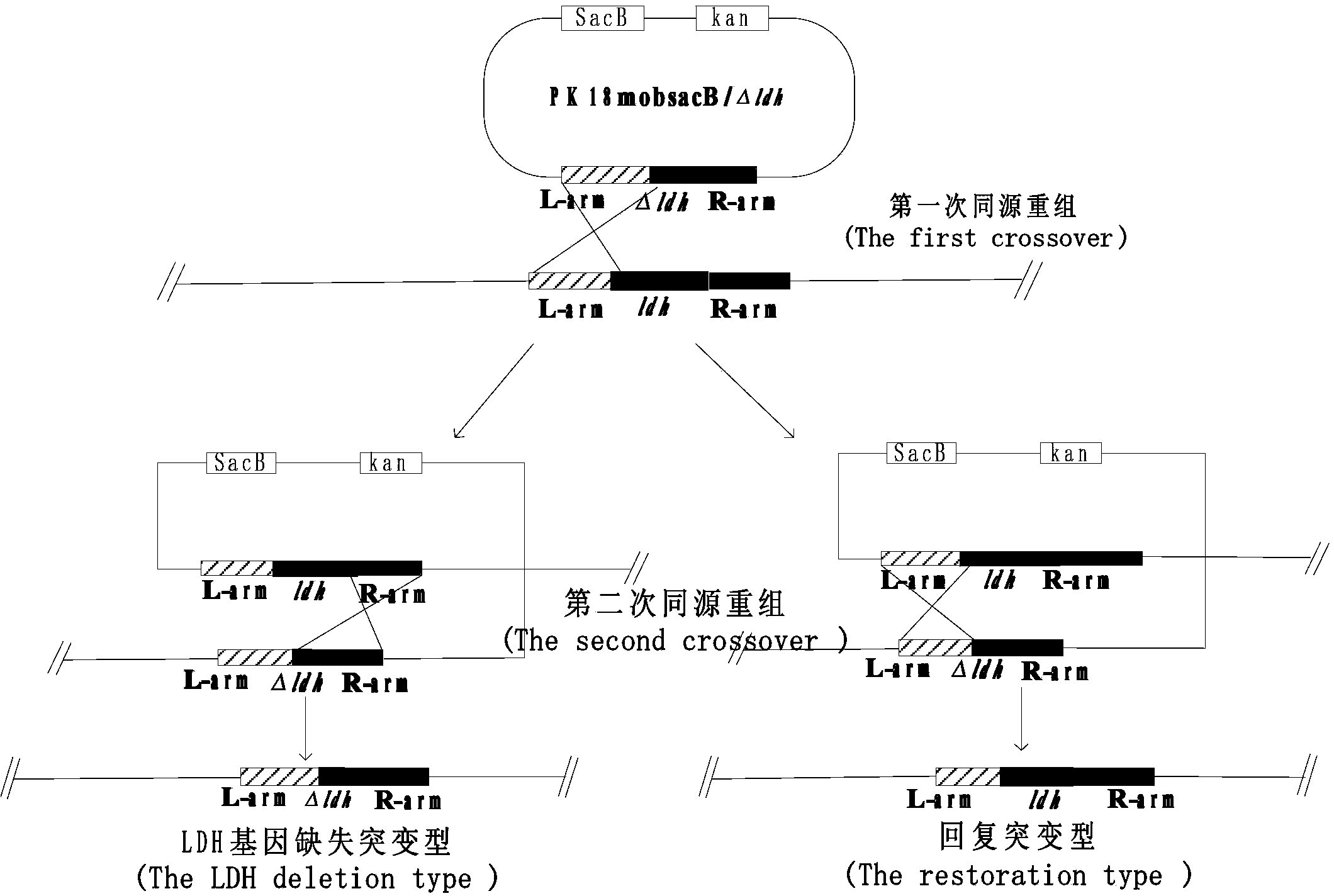
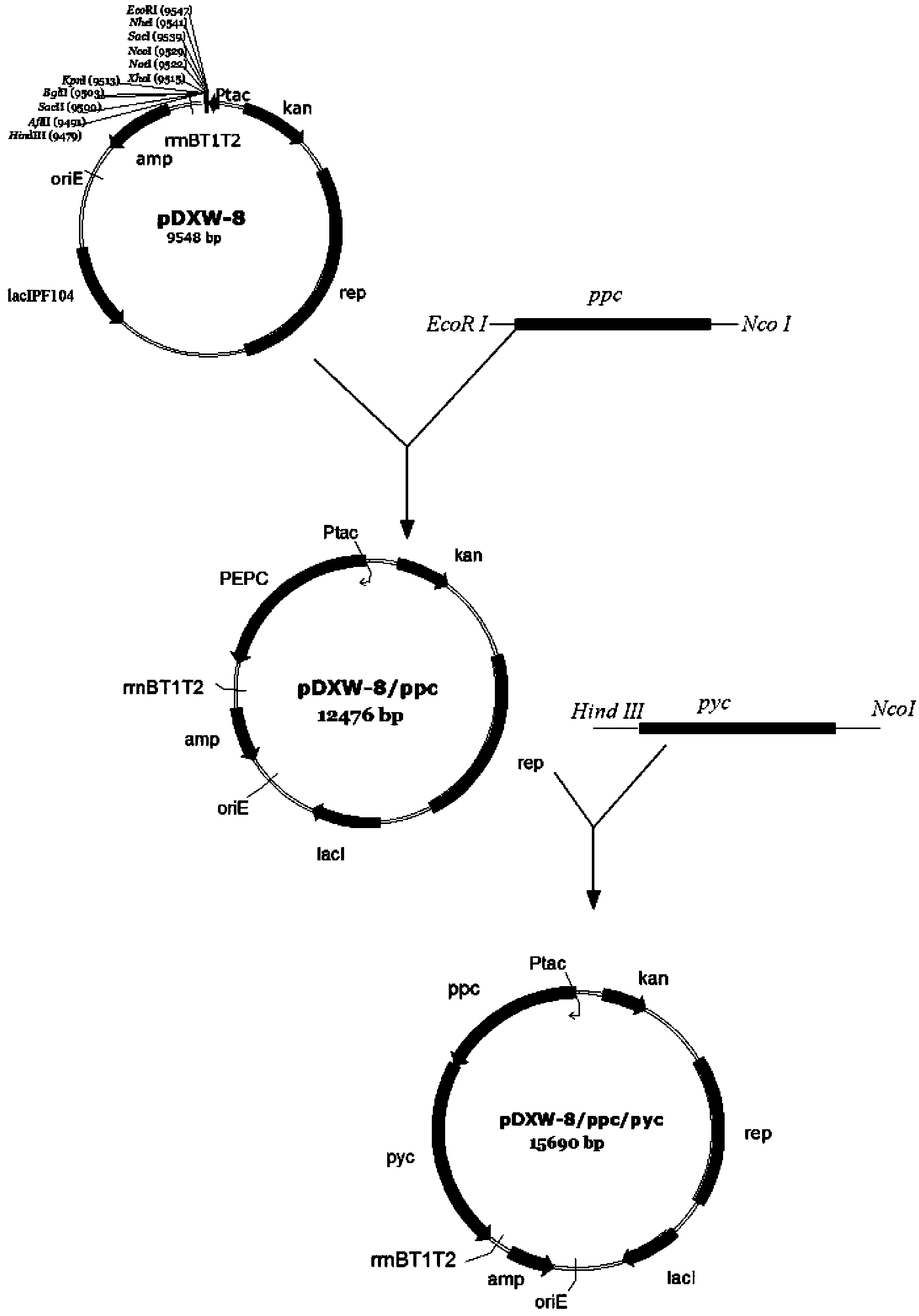
Patents
Literature
154 results about "Corynebacterium crenatum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Corynebacterium crenatum is a fast-growing, aerobic, gram-positive, non-sporulating coryneform bacterium. It is often used to produce large quantities of some long-chain amino acids such as leucine, isoleucine and arginine for industrial applications [25-27].
Arginine repressor deficient strain of coryneform bacterium and method for producing L-arginine
InactiveUS20020045223A1Produced in advanceSugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensMicrobiology
L-Arginine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium in which an arginine repressor involved in L-arginine biosynthesis is deleted by disrupting a gene coding for the repressor, and which has L-arginine producing ability in a medium to produce and accumulate L-arginine in the medium, and collecting the L-arginine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of constructing amino acid producing bacterial strains, and method of preparing amino acids by fermentation with the constructed amino acid producing bacterial strains
A method of producing coryneform bacteria having improved amino acid or nucleic acid productivity comprising the steps of introducing a mutation in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium to make it close to a consensus sequence, or introducing a change in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium by gene recombination to make it close to a consensus sequence, to obtain mutants of the coryneform amino acid- or nucleic acid-producing microorganism, culturing the mutants and selecting a mutant capable of producing the intended amino acid or nucleic acid in a large amount. This method allows the construction of a mutant capable of enriching or controlling the expression of an intended gene without using a plasmid and to promote production of amino acids in a high yield by recombination or mutation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutant of homoserine dehydrogenase from Corynebacterium and DNA encoding thereof
Novel polynucleotides derived from microorganisms belonging to coryneform bacteria and fragments thereof, polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides and fragments thereof, polynucleotide arrays comprising the polynucleotides and fragments thereof, recording media in which the nucleotide sequences of the polynucleotide and fragments thereof have been recorded which are readable in a computer, and use of them.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
L-arginine producing strain and its mutation method and usage in producing L-arginine
InactiveCN1441055AHigh genetic stabilityGood genetic stabilityBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyArginine
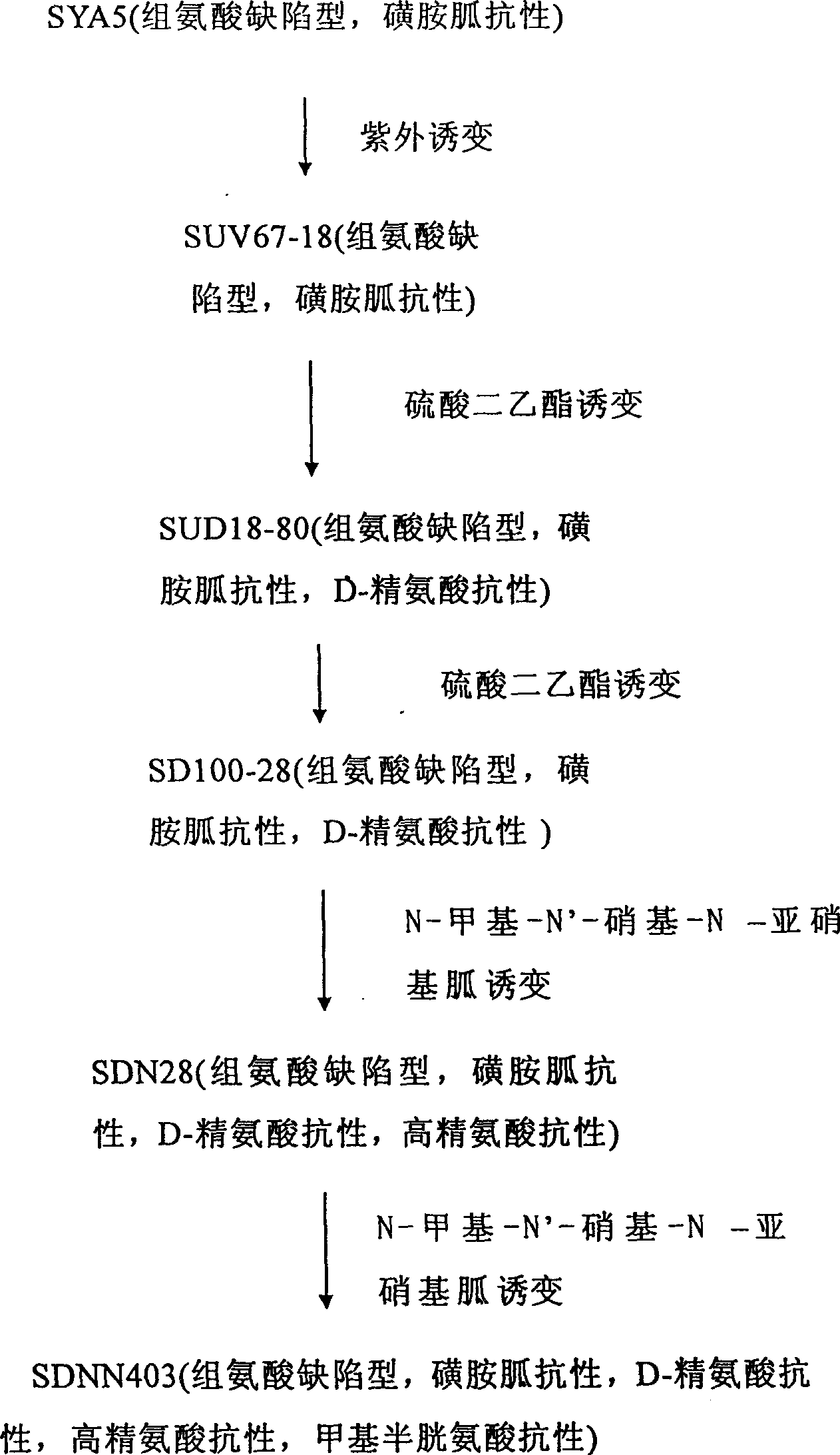
The present invention relates to the fermentation process of producing L-arginine. By using Corynebacterium crenatum SYA5 screened and preserved by the present lab as parent and through conventional physical and chemical mutation process and multiple structural analog resistance screening, mutant strain SDNN403 is obtained. Through culturing of the mutant strain under optimized condition, L-arginine is produced in the yield level of 30-35 g / L. The strain has high genetic stability, stable yield characteristic, high L-arginine yield level, less produced hetero acids and easy technological amplification, and is suitable four industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
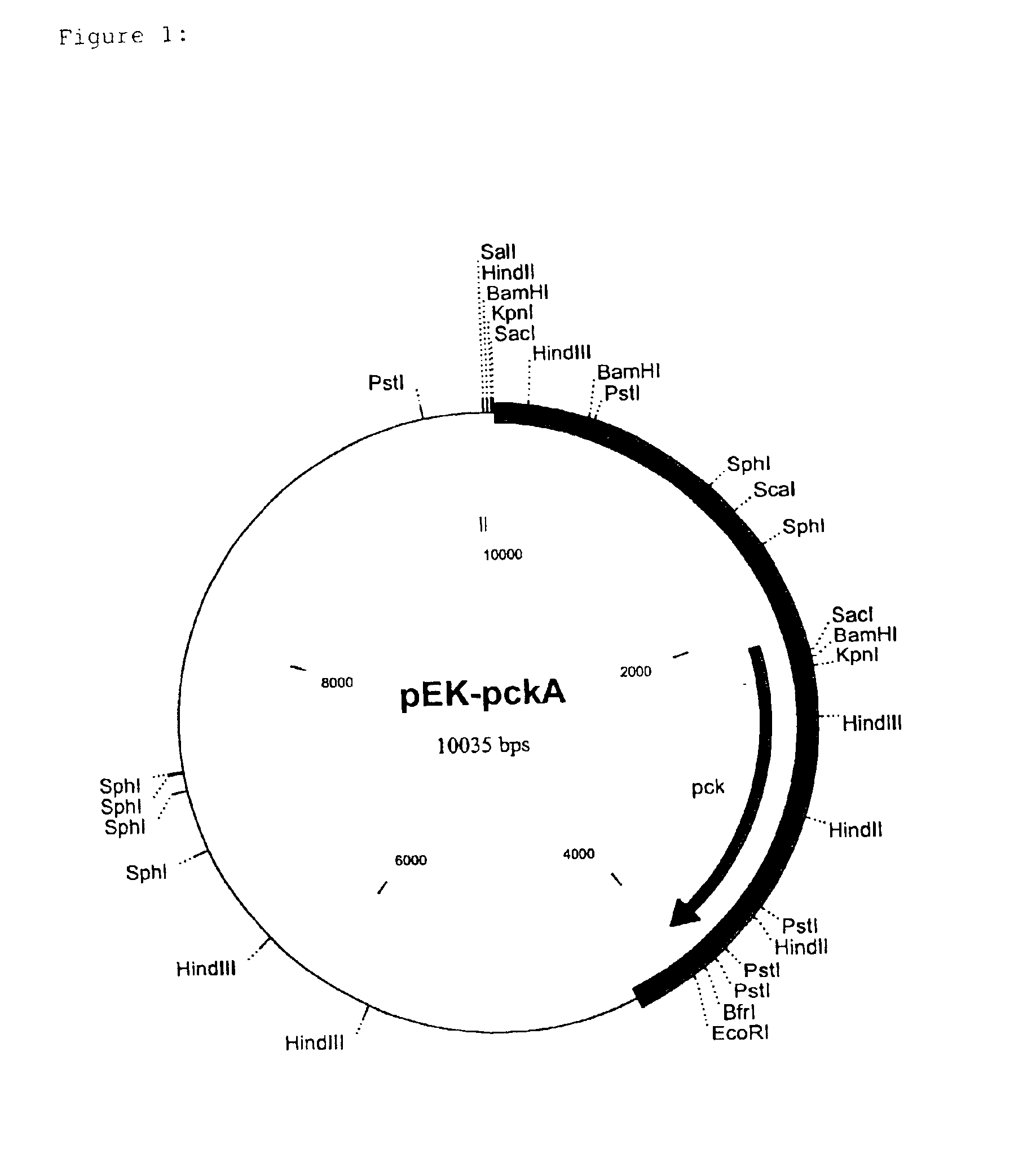
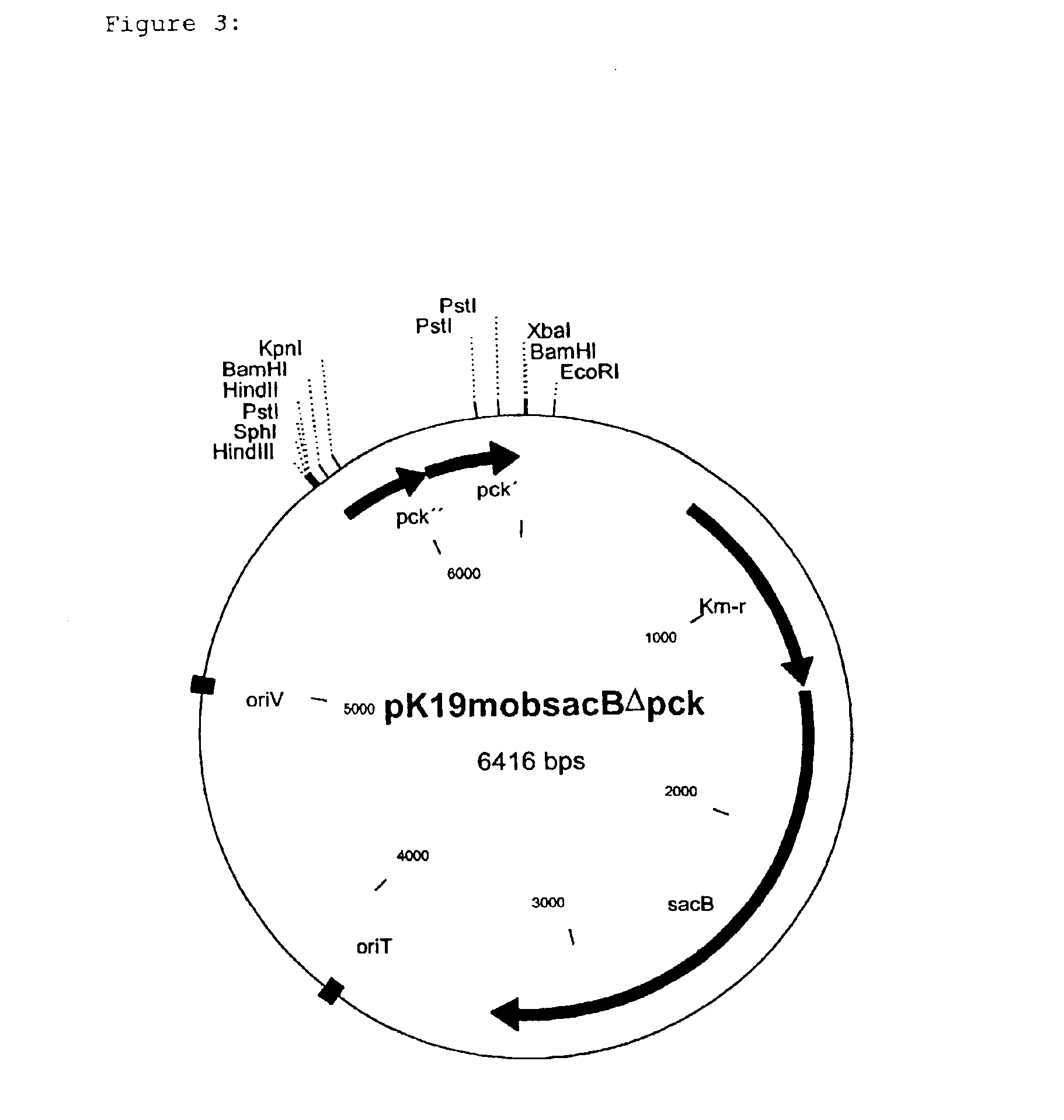
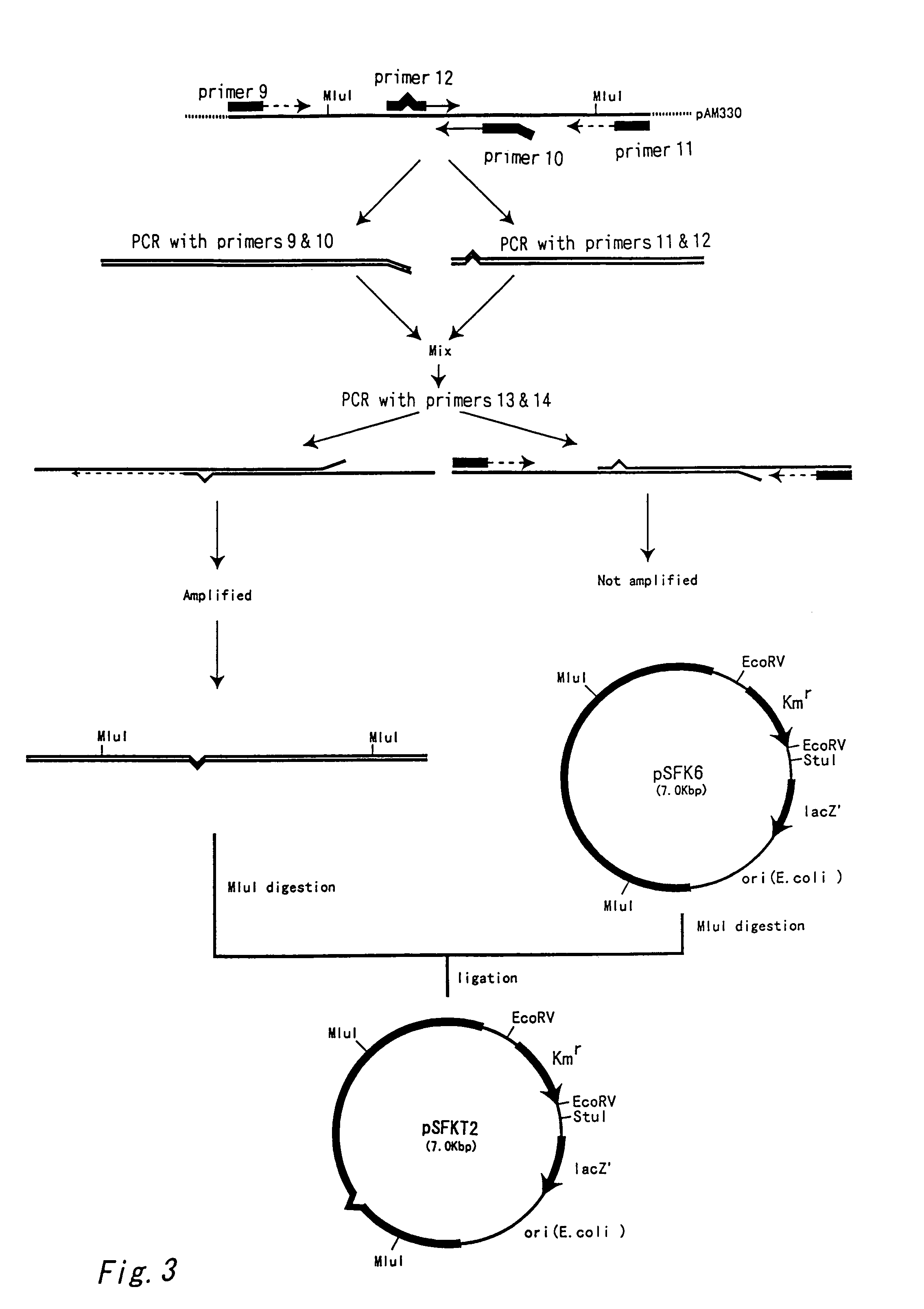
Nucleotide sequences which code for the pck gene
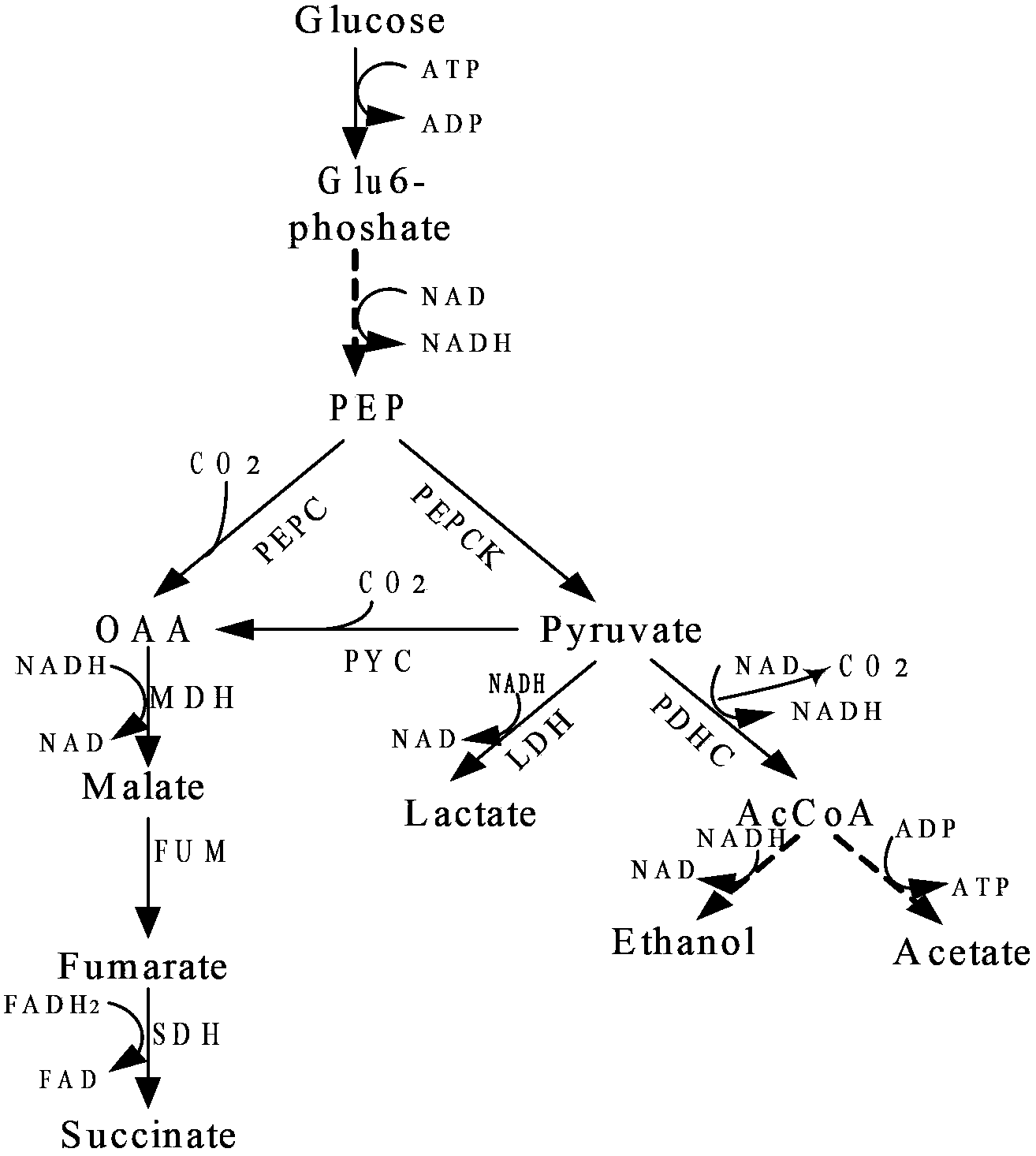
The invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences from Coryneform bacteria which code for the pck gene encoding the enzyme phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEP carboxykinase). The invention also relates a process for the fermentative preparation of L-amino acids, in particular L-lysine, L-threonine, and L-glutamate by attenuation of the pck gene.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
Alleles of the zwf gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the zwf gene of coryneform bacteria, which encode variants of the Zwf subunit of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC: 1.1.1.49), and to processes for preparing amino acids, in particular L-lysine and L-tryptophan, by using bacteria which harbor said alleles.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Methods for secretory production of proteins
The object of the present invention is to provide a method of producing a heterologous protein by making a coryneform bacterium to produce and efficiently extracellularly secrete (secreto-production) an industrially useful heterologous protein. According to the present invention, a genetic construct is used where a gene sequence encoding an intended protein which is ligated to the downstream of a sequence encoding the signal peptide derived from a coryneform bacterium, the gene construct is introduced into a mutant coryneform bacterium which has a capacity of secreting the heterologous protein at least 2-fold higher than the wild type Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13869, the mutant coryneform bacterium is cultured and the extracellularly released heterologous protein is recovered.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for improving yield of arginine by mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase
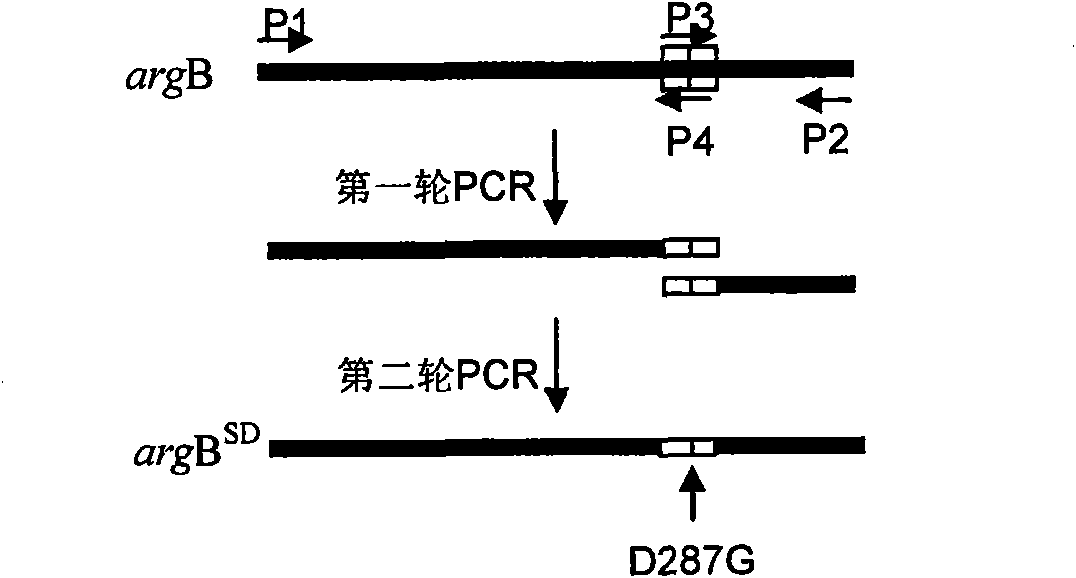
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of arginine by the mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase. L-arginine is one of semi-essential basic amino acids for a human body, and has various particular physiology and pharmacology functions. High-yield arginine mutant strain C. crenatum SYPA5-5 is compounded into the arginine through a circulating way, and N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the compounding way and is subject to the feedback inhibition of the product arginine. By using an overlapping PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, a GAT (glycerol phosphate acyl transferase) codon used for coding aspartic acid is used for substituting a GGA (General Gonadotropic activity) codon used for coding glycine at the site 287 in the coding NAGK albumen, and the NAGK which has high activity and arginine with obviously reduced by the feedback inhibition can be obtained after the mutation. An argBSD gene is brought into the Corynebacterium crenatum of the high-yield arginine through pJCl-tac, and the expression volume of the key enzyme is further improved. The final acid yield is increased to 36.3g / L from original 28g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 29.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Arginine repressor deficient strain of coryneform bacterium and method for producing L-arginine
InactiveUS7160705B2Improve L-arginine productivitySugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensMicrobiology
L-Arginine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium in which an arginine repressor involved in L-arginine biosynthesis is deleted by disrupting a gene coding for the repressor, and which has L-arginine producing ability in a medium to produce and accumulate L-arginine in the medium, and collecting the L-arginine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing xanthosine-5'-monophosphate by fermentation using mutant strains of Coryneform bacteria
InactiveUS20020098552A1Increase enzyme activitySuperior in pointBacteriaFermentationBacteroidesCorynebacterium efficiens
Xanthosine-5'-monophosphate is produced by cultivating the bacterium which has a resistance to growth inhibition by an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of inhibitors of cell membrane biosynthesis and / or functioning, phosphorylation inhibitors, uncoupling agents, RNA-polymerase inhibitors and methionine analogs, and has an ability to produce xanthosine-5'-monophosphate according to produce and accumulate xanthosine-5'-monophosphate in the culture, and recovering the xanthosine-5'-monophosphate therefrom.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
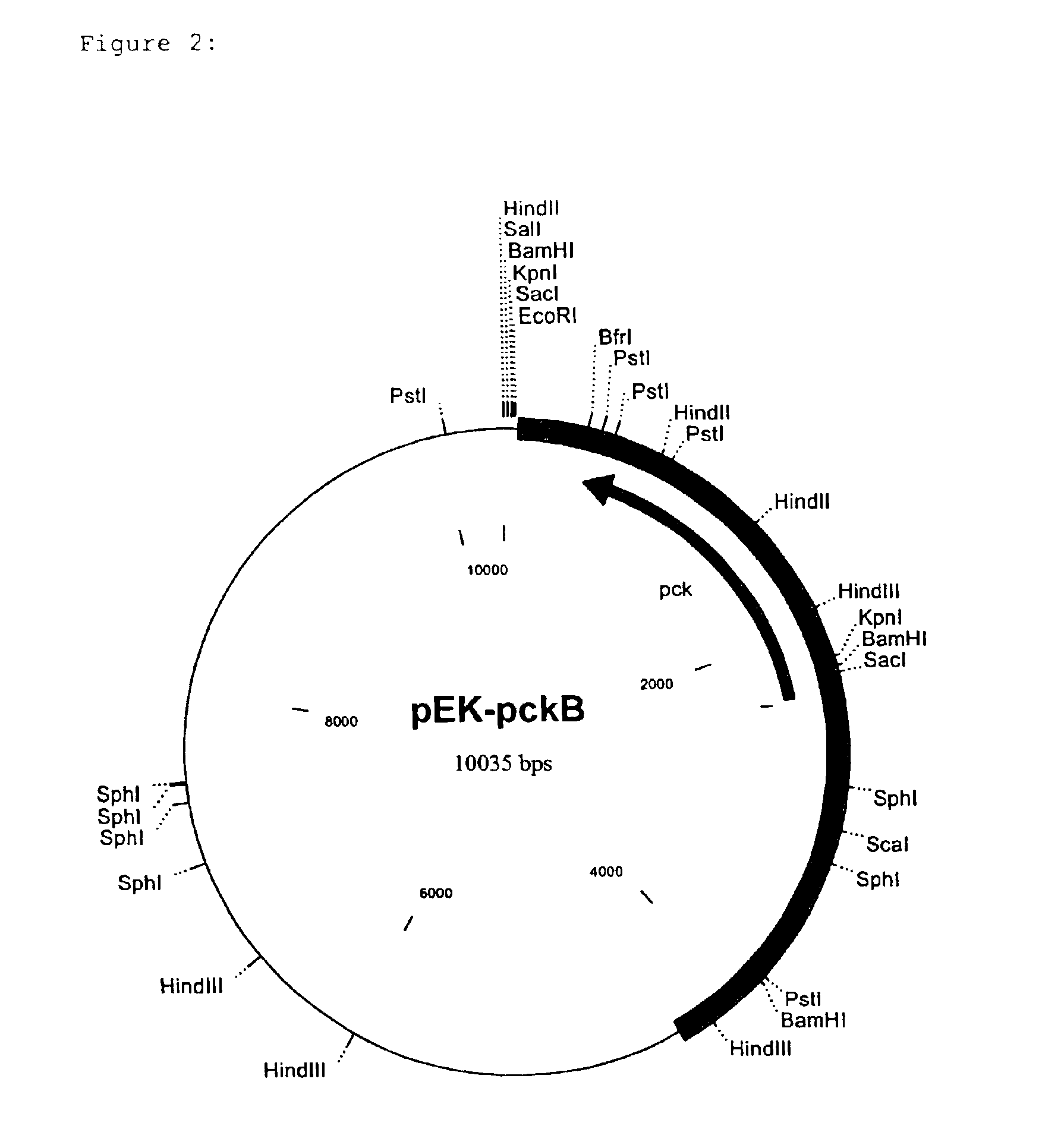
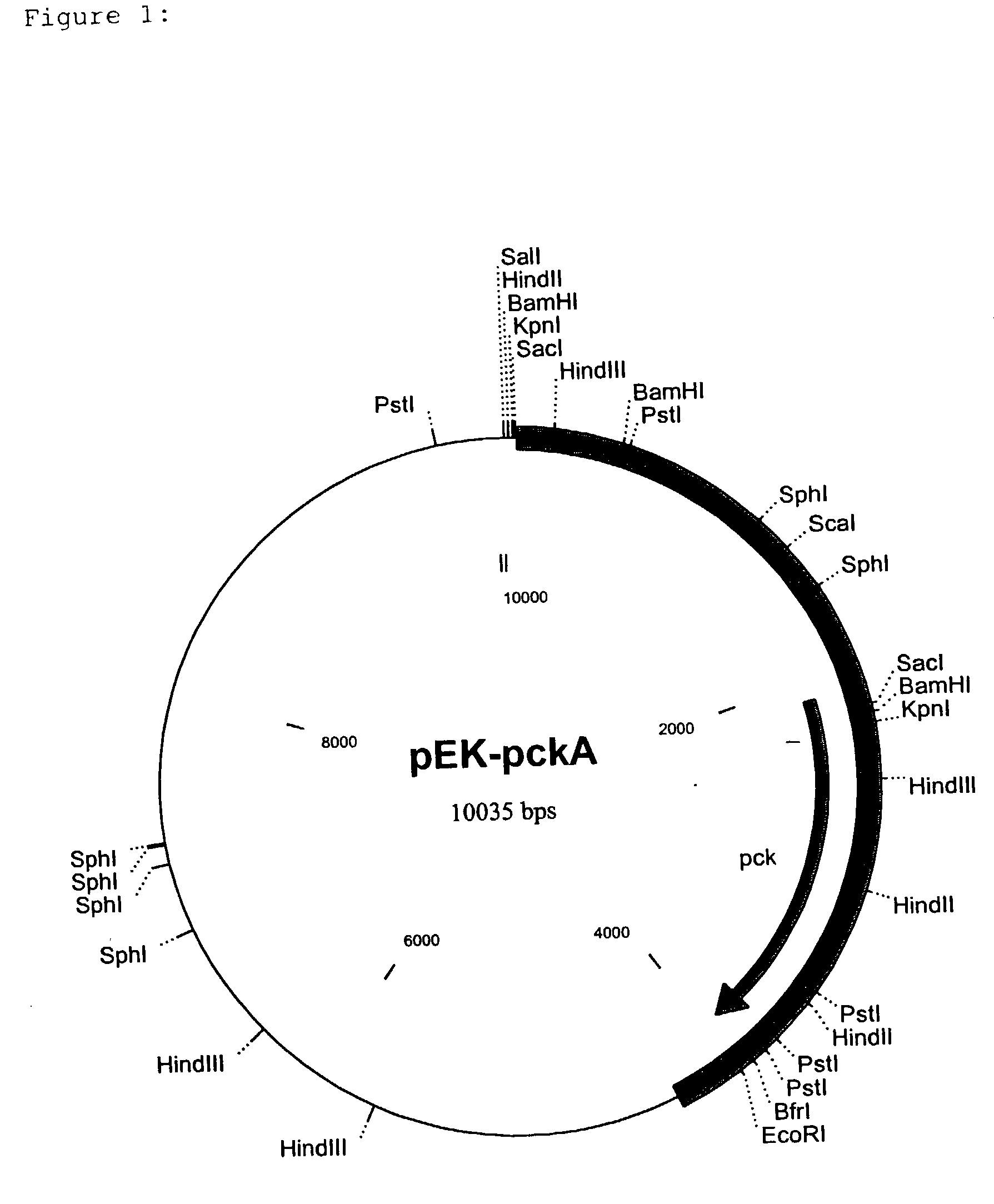
Nucleotide sequences which code for the pck gene
The invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences from Coryneform bacteria which code for the pck gene encoding the enzyme phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEP carboxykinase). The invention also relates a process for the fermentative preparation of L-amino acids, in particular L-lysine, L-threonine, and L-glutamate by attenuation of the pck gene.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
Recombinant strain, method for preparing recombinant strain and method for producing L-valine from recombinant strain
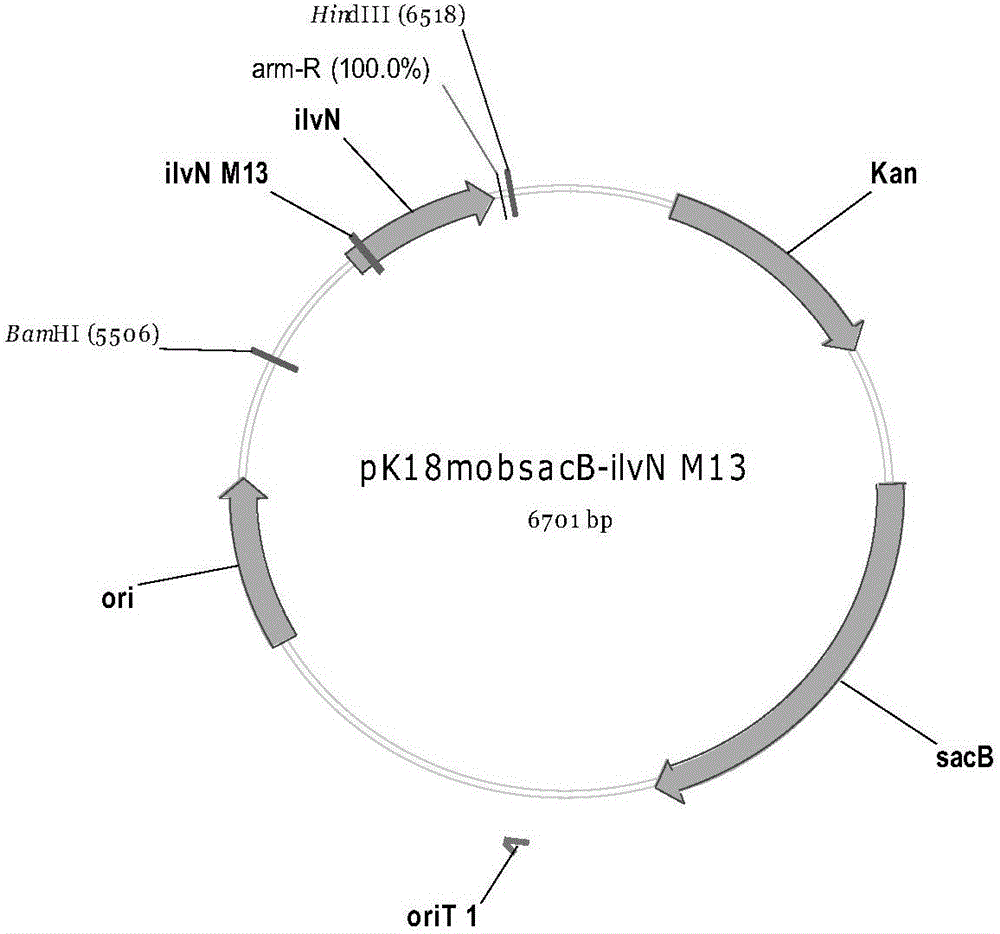
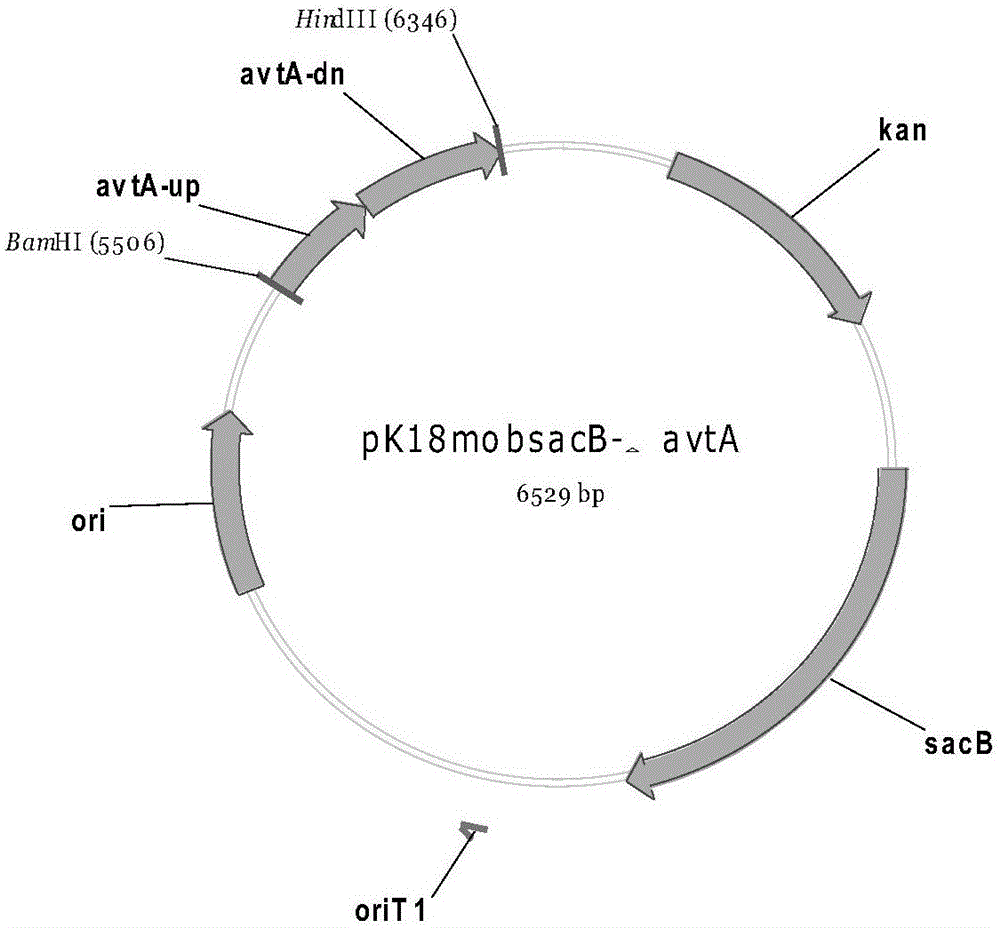
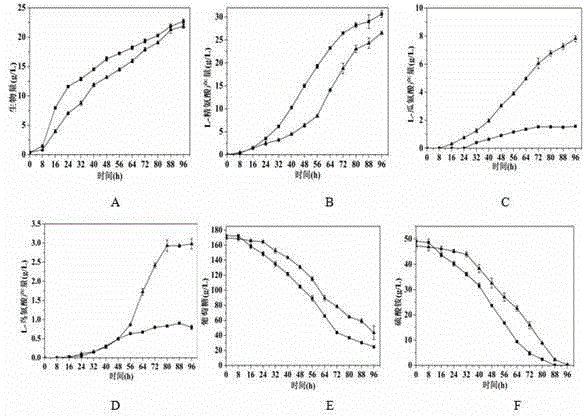
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology, in particular to a recombinant strain, a method for preparing the recombinant strain and a method for producing L-valine from the recombinant strain. According to the recombinant strain, corynebacterium serves as a starting strain for transformation, and the transformation process includes the steps of conducting point mutation on the ilvN gene and knocking out the avtA gene. The recombinant strain is obtained by conducting point mutation on the ilvN in a valine metabolism path and knocking out the avtA gene for transaminase coding; through fermentation culture, the yield of L-valine can reach 12.2 g / L, and generation of the by-product alanine is greatly reduced.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Metabolic transformation method for efficiently improving production capacity of corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 L-arginine
The invention provides a metabolic transformation strategy for efficiently improving production capacity of corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 L-arginine, and belongs to the biological technical field. Histidine at a site 268 in N-acetyl glutamatekinase, NAGK, argB of SYPA-5 is mutated into asparaginate, so that feedback inhibition effect of the L-arginine on NAGK can be effectively relived; a mutation site is precisely introduced to a corresponding position of SYPA5-5 genome, so that yield of the obtained feedback inhibition-preventing bacterial strain (H-7)L-arginine is lowered, and metabolic intermediate (L-ornithine and L-citrulline) is largely accumulated. Transcriptional analysis is carried out on an arg gene cluster of h-7 to find that arg GH transcriptional level is lowered. Arg GH reinforced expression is carried out in H-7, and production capacity of the obtained recombinant bacterial strain H-7-GH, L-arginine is improved by 99.0% in comparison with SYPA5-5. Preliminary optimization is carried out on a fermentation culture medium of H-7-GH, so that yield of the L-arginine is 45.1g / L, which is improved by 49.8% in comparison with that before optimization, and improved by 1.13 times in comparison with SYPA5-5. Feedback inhibition of the L-arginine on NAGK is relieved, and metabolic transformation strategy of the arg GH gene is expressed in a strengthened manner at the same time, so that production capacity of the L-arginine of the SYPA 5-5 is effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
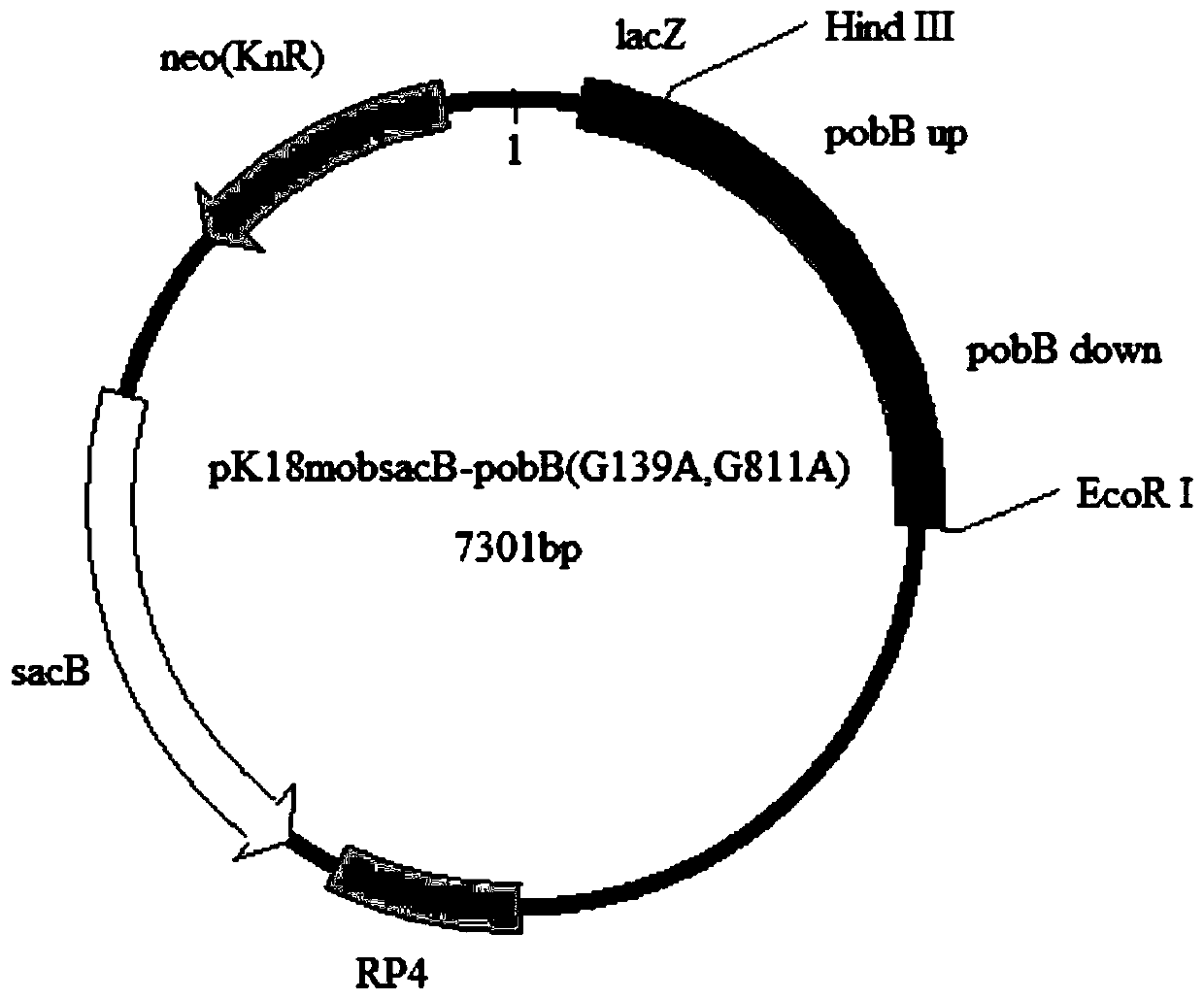
Recombinant bacterial strain for high-yield production of L-lysine, and construction method and application of recombinant bacterial strain
ActiveCN110607313AImprove stabilityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCorynebacterium efficiensOpen reading frame
The invention provides a recombinant bacterial strain for high-yield production of L-lysine, and a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterial strain. A polynucleotide sequence comprises a modified pobB gene coding polynucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and the invention provides a recombinant protein coded by the polynucleotide sequence, the recombinant bacterial strain containing the polynucleotide sequence, a construction method of the recombinant bacterial strain, and an application of the recombinant bacterial strain in fermentation production of L-lysine. According to the recombinant strain disclosed by the invention, point mutation is carried out on the nucleotide sequence of an open reading frame coding region of the pobB gene in wild-type corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain the recombinant strain modified by the coding region of the pobB gene, and the yield of L-lysine is realized compared with the yield of L-lysine by using wild bacterial strains.
Owner:NINGXIA EPPEN BIOTECH
Method for increasing yield of L-arginine synthesized from corynebacterium crenatum
ActiveCN109370975AIncrease productionOptimizing Fermentation ConditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidArginine
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of L-arginine synthesized from corynebacterium crenatum, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. By means of the method, recombinant corynebacterium crenatum of which a nitrogen transcriptional regulation factor AmtR is knocked out and ammonium transport protein is over-expressed is successfully constructed. By adopting a strategy of batch fermentation by a 5-L fermentation tank and optimizing fermentation conditions, finally the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum Cc5-5 / pXMJ19-amtB is fermented for 96 h, the L-arginine yield of the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum reaches 60.9+ / -1.31 g / L, the yield is increased by 30.56% compared with an original strain of corynebacterium crenatum original strain SYPA5-5, the production intensity reaches 0.634 g / L.h, and the saccharic acid conversion rate is 0.36+ / -0.018 g / g, so that high yield of the L-arginine is realized. Meanwhile, utilization of NH4+ is increased in therecombinant corynebacterium crenatum, so that it is shown that knockout of the nitrogen transcriptional regulation factor and overexpression of the ammonium transport protein have a remarkable effecton the yield of the L-arginine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing L-glutamine by fermentation and L-glutamine producing bacterium
InactiveUS7262035B2Avoid by-productsImprove abilitiesSugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensBacteroides
L-Glutamine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium which has L-glutamine producing ability and has been modified so that its intracellular glutamine synthetase activity should be enhanced, preferably which has been further modified so that its intracellular glutamate dehydrogenase activity should be enhanced, in a medium to produce and accumulate L-glutamine in the medium and collecting the L-glutamine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Coryneform Bacterium Transformant and Process for Producing Valine Using the Same
A transformant obtainable by introducing one or more of the following DNAs (a), (b), and (c) into a coryneform bacterium as a host.(a) A DNA which encodes acetohydroxy acid synthase derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum and which has a mutation changing the glycine at position 156 to glutamic acid (G156E) in an amino acid sequence encoded by the DNA, or an analog thereof.(b) A DNA which encodes acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum and which has mutations changing the serine at position 34 to glycine (S34G), the leucine at position 48 to glutamic acid (L48E), and the arginine at position 49 to phenylalanine (R49F) in an amino acid sequence encoded by the DNA, or an analog thereof.(c) A DNA which encodes leucine dehydrogenase derived from Lysinibacillus sphaericus, or an analog thereof.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Method for producing L-amino acid using methylotroph
InactiveUS7439038B2Improve productivityAbundantly and inexpensively availableSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesMethylotroph
A DNA encoding for a mutant of LysE protein, or a homologous protein thereof, of a coryneform bacterium, wherein the mutant, when introduced into a methanol-assimilating bacterium imparts resistance to L-lysine analogue. The DNA encoding for a mutant of LysE protein, or a homologous protein thereof, is introduced into a methanol-assimilating bacterium to improve L-lysine and L-arginine productivity of the methanol-assimilating bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Improvement of L-arginine yield of corynebacterium crenatum by enhancement of transport protein LysE expression
InactiveCN102747025AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainArginine transport
Endocellular secretion of L-arginine to the exterior of cells depends on transport protein LysE. According to the invention, corynebacterium crenatum is used as a research bacterial strain for the first time; a shuttle expression plasmid pJC-tac-lysE carrying a lysE gene of its own is constructed and is electrically transferred to the corynebacterium crenatum so as to obtain a recombinant corynebacterium crenatum with enhanced lysE gene expression. The original bacterium and the recombinant bacterium are qualitatively detected through plate color development and are cultured by a basal medium so as to examine the L-arginine transport status; over expression of the L-arginine transport protein LysE in the corynebacterium crenatum is verified, which indicates that the enhancement of transport protein LysE expression can reduce the intracellular L-arginine concentration to a certain extent and improve the L-arginine yield. The original bacterium and the recombinant bacterium are subject to a fermentation experiment in a 250-mL shake flask, and results show that the L-arginine yield of the recombinant bacterium is increased by about 12%; the maximal yield is increased by 11.1%; and the fermentation period is shortened.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Signal peptide and application thereof in synthesis of l-arginine from conjac powder and value enhancement of conjac powder
ActiveUS20180258385A1Promote cell growthEfficient productionBacteriaPeptidesΒ mannanaseL-ornithine L-aspartate
The present invention relates to application of a novel signal peptide in L-arginine and its derivatives production from konjac powder, which belongs to the field of gene engineering, enzyme engineering and metabolism engineering. The present invention fused the signal peptide set forth in SEQ ID NO.1 with the β-mannanase of Bacillus subtilis CCTCC M 209200, and expressed the fused gene in the strain with high L-arginine yield. The recombinant strain Corynebacterium crenatum CGMCC 0890 / p MSPman had advantages on utilizing cheaper konjac powder as substrate, and after fermenting for 96 hours in a 5 L bioreactor, the L-arginine yield reached 45 g / L. Another two recombinant strains were constructed based on Corynebacterium crenatum CGMCC 0890 / pMSPman, and after fermenting for 96 hours in a 5 L bioreactor, the L-ornithine yield and L-citrulline reached 23.5 g / L and 26.3 g / L respectively.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
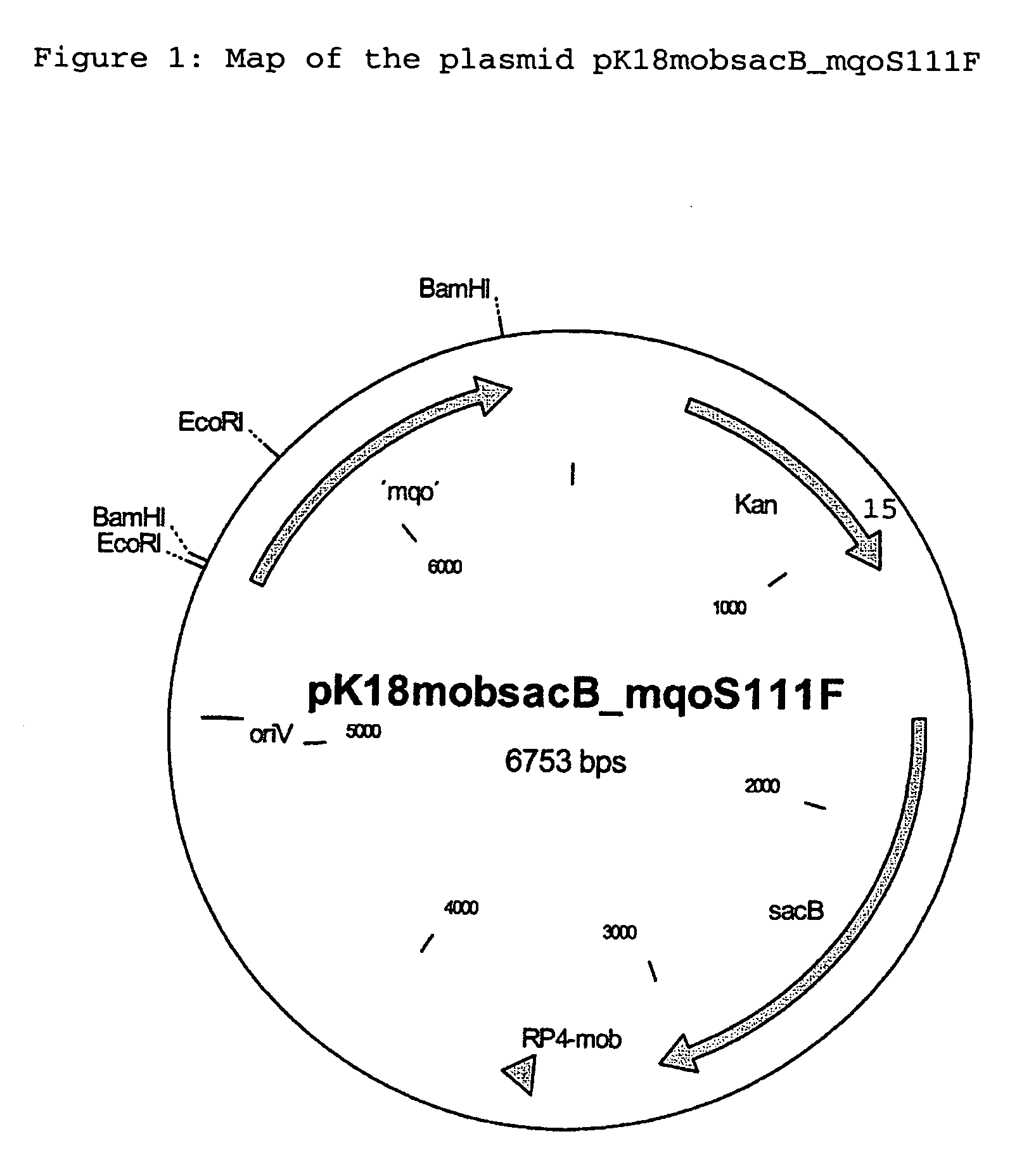
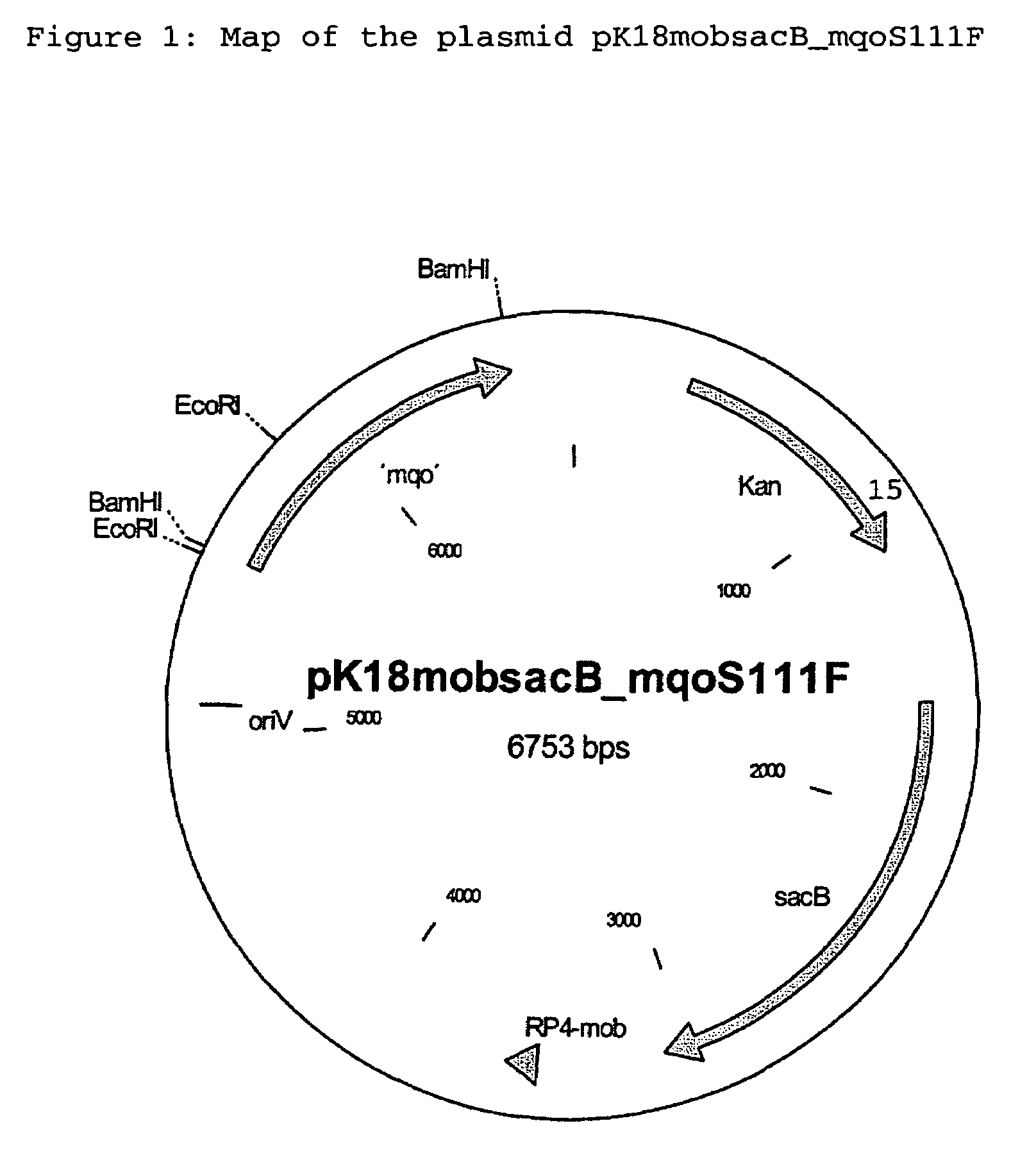
Alleles of the mqo gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the coryneform bacterium mqo gene which encodes malate quinone oxidoreductases which contain any amino acid apart from L-serine at position 111, or a comparable position, in the amino acid sequence, and to processes for fermentatively preparing amino acids, preferably L-lysine, L-tryptophan and L-proline, using bacteria which comprise these alleles.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
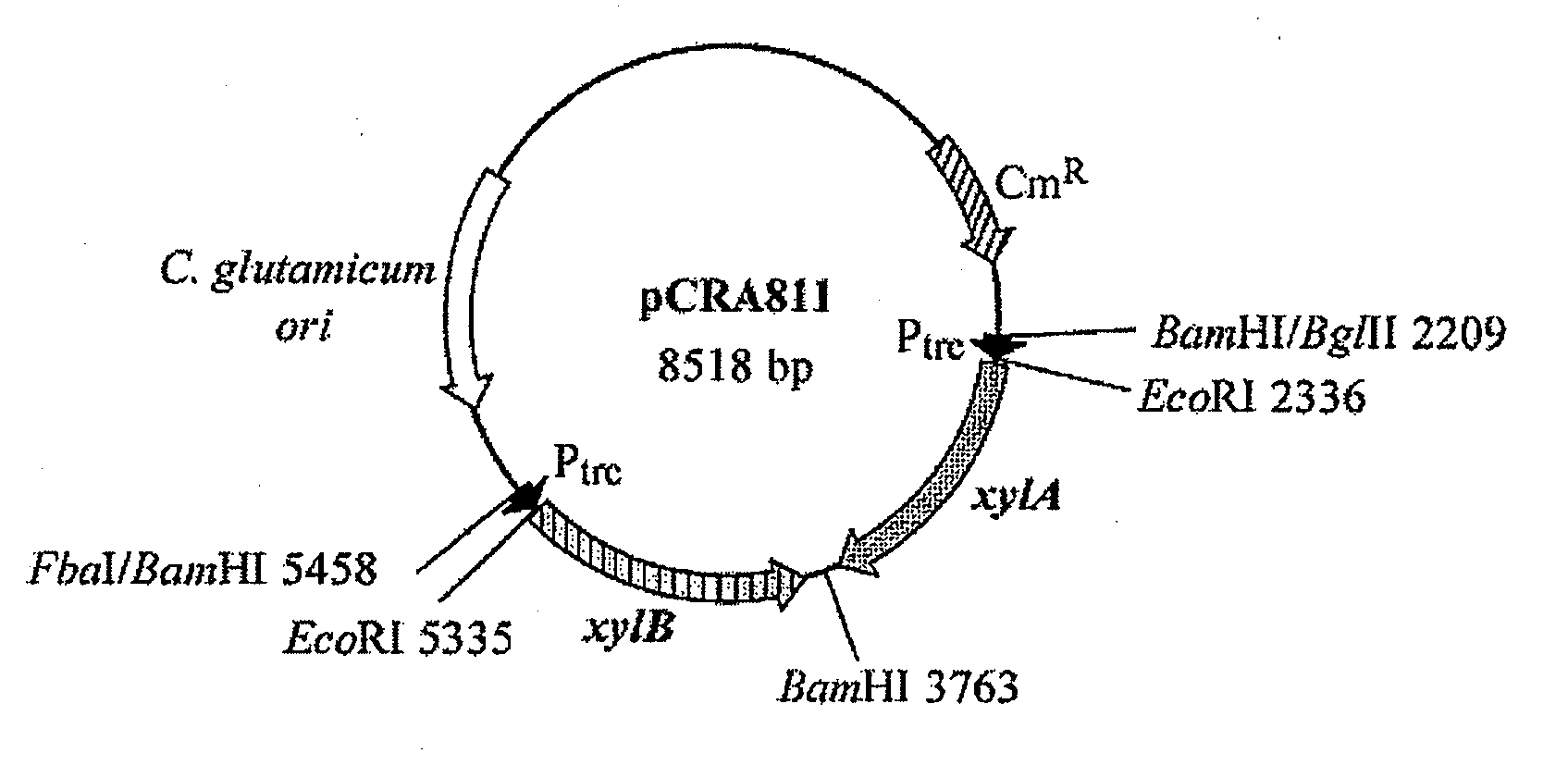
Coryneform bacterium transformant having improved d-xylose-utilizing ability
ActiveUS20110117612A1Effective utilization of D-xyloseEffective resourcesBacteriaBiofuelsCorynebacterium efficiensMicrobiology
A coryneform bacterium transformant prepared by transferring an exogenous gene which encodes a protein having a sugar transporter function into a coryneform bacterium capable of utilizing D-xylose.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
One-step method for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant corynebacterium crenatum and with glucose as substrate
ActiveCN103215198AReduce manufacturing costSimple preparation stepsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseCorynebacterium crenatum
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and relates to a one-step method for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant corynebacterium crenatum (C.crenatum) and with glucose as a substrate. According to the method, a genetic engineering method is adopted, C.crenatum SYPA5-5 gene argB is knocked out, such that a safe strain C.crenatum E01 which can accumulate glutamic acid is obtained; a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene is cloned from L.Plantarum GB01-21 and is expressed in the C.crenatum E01, such that recombinant C.crenatum E01 / pGAD used for directly synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid with glucose as a substrate is obtained. A recombinant strain fermentation broth gamma-aminobutyric acid accumulation reaches 13.98g / L. According to the invention, glutamic acid and gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolic pathways are successfully integrated, such that one-step production from glucose to gamma-aminobutyric acid is realized. Therefore, preparation method is simplified, cost is reduced, safety is improved, and novel idea is provided for high-efficiency and low-cost amino acid preparation.
Owner:南宁汉和生物科技股份有限公司
Method for producing L-arginine or L-lysine by fermentation
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombined Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing L-Phe and constructing method and application thereof
InactiveCN104531597AIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesCorynebacterium efficiensEscherichia coli
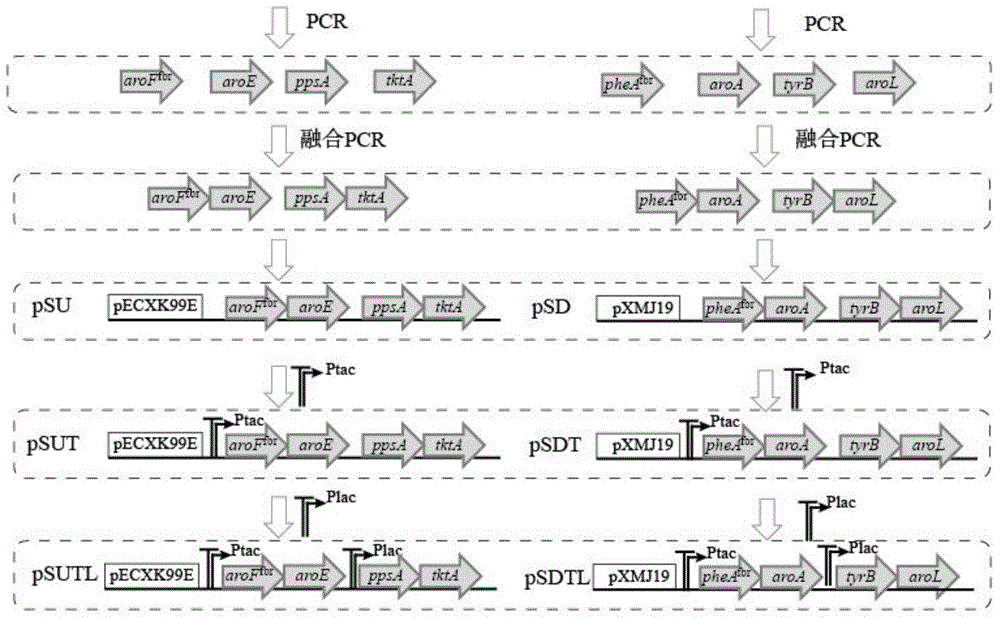
The invention discloses a recombined Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing L-Phe and a constructing method and the application thereof, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. In Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, two shuttle expression vectors pEC-XK99E and pXMJ19 of the Corynebacterium glutamicum and escherichia coli are used for expressing eight key enzyme genes comprising aroF<fbr>, tktA, ppsA, aroL, pheA<fbr>, aroE, aroA and tyrB in a L-Phe synthetic route, two promoters Ptac and Plac of different intensities are used for carrying out combinational expression on the eight genes to improve the L-Phe yield, the L-Phe yield can reach as high as 5.59+ / -0.11 g / l, and accumulated shikimic acid is 0.31+ / -0.11 g / L. According to the method, over expression is achieved for the L-Phe shikimic acid key enzyme genes, and the yield of L-Phe produced by the Corynebacterium glutamicum in a fermentation mode is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Construction and application method for L-ornithine synthesis bacteria
The invention relates to construction and an application method for L-ornithine synthesis bacteria. An argF gene coding ornithine carbamoyltransferase (OTC) in corynebacterium crenatum SYPA5-5 is knocked out, and research on fermenting on an obtained recombination bacterial strain for producing L-ornithine is performed, and the technical scheme belongs to the technical field of biology. Firstly, an argF gene deletion segment (delta argF) is constructed and linked to pK18mobsacB for obtaining a recombinant plasmid pK18mobsacB delta argF, the recombinant plasmid pK18mobsacB delta argF is electrically transferred into SYPA5-5, two times of homologous recombination and screening are performed, so that a recombination strain SYPA5-5 delta argF is obtained. Secondly, influences of different nutrition conditions on growth of the recombination strain and accumulation of L-ornithine are investigated, addition of 0.3 g / L of L-arginine is capable of satisfying requirements on growth of SYPA5-5 delta argF and accumulation of L-ornithine; by utilizing a saccharic raw material as a raw material and fermenting for 96 h, the output of L-ornithine reaches 21.5 g / L, the saccharic acid conversion efficiency is 0.17 g (L-ornithine) / g (glucose).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
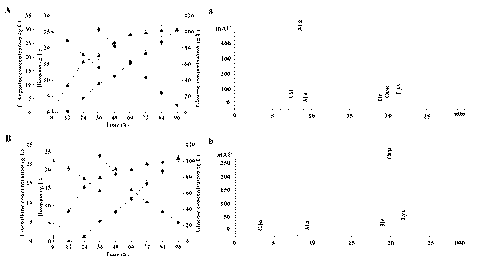
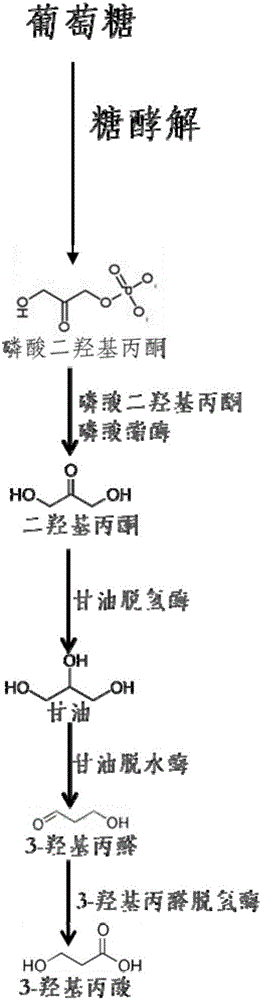
3-hydracrylic-acid-producing recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105950529ASolving Tolerance IssuesAddress biosecurityBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidGlycerol
The invention relates to a 3-hydracrylic-acid-producing recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, and a construction method and application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain comprises the following steps: in a Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, overexpressing an endogenous dihydroxyacetone phosphate phosphatase gene hdpA, and overexpressing a glyceroldehydrogenase gene gldA, a glycerol anhydrase and activating factor gene pduCDEGH and a 3-hydroxypropylaldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH. When the recombinant strain is used for producing 3-hydracrylic acid by fermentation, the Corynebacterium glutamicum strain can perform fermentation by using different cheap raw materials, thereby further lowering the raw material cost. The 3-hydracrylic-acid-producing recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum strain solves the problems of biosafety and acid tolerance. The strain in the fermentation process can be used in a feed additive as a product. The method can generate fewer byproducts, so that the separation process of the end product 3-hydracrylic acid is simplified.
Owner:GUANGDONG TSINGDA SMART BIOTECH CO LTD
Optimized high-yield technique for producing L-arginine Corynebacterium crenatum by batch fermentation
ActiveCN103981231APromote growthFinal bacterial concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationMinor elementArginine
The laboratory systemically researches the induced mutation breeding and strain metabolism engineering modification for producing L-arginine by Corynebacterium crenatum fermentation, and 4 national patents of invention have been authorized to related achievements. On the basis of early research, the invention provides an optimized high-yield technique for producing L-arginine Corynebacterium crenatum by batch fermentation, which is an improvement on the basis of the previous technique for producing L-arginine by Corynebacterium crenatum fermentation; and the improvement of the seed culture and fermentation technique is mainly utilized to enhance the L-arginine yield. In the seed culture process, the seed growth speed is high, and the final bacterium concentration is high. In the fermentation process, the fermentation culture medium is simple in components and does not need vitamins, amino acids or other minor elements, the technique is easy to control, the fermenting property of the strain is stable, and the L-arginine yield is up to 56.3g / L and is one of the maximum yield in China at present; and the sugar acid conversion rate is up to 32%, and is the highest level in China at present.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Alleles of the mqo gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the coryneform bacterium mqo gene which encodes malate quinone oxidoreductases which contain any amino acid apart from L-serine at position 111, or a comparable position, in the amino acid sequence, and to processes for fermentatively preparing amino acids, preferably L-lysine, L-tryptophan and L-proline, using bacteria which comprise these alleles.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com