One-step method for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid by using recombinant corynebacterium crenatum and with glucose as substrate
A technology of Corynebacterium bluff and aminobutyric acid, which is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as lack of γ-aminobutyric acid synthesis pathway, and reduce production. Cost, improved safety, effect of simplified preparation steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Knockout Verification of the Corynebacterium blunt-toothed argB Gene
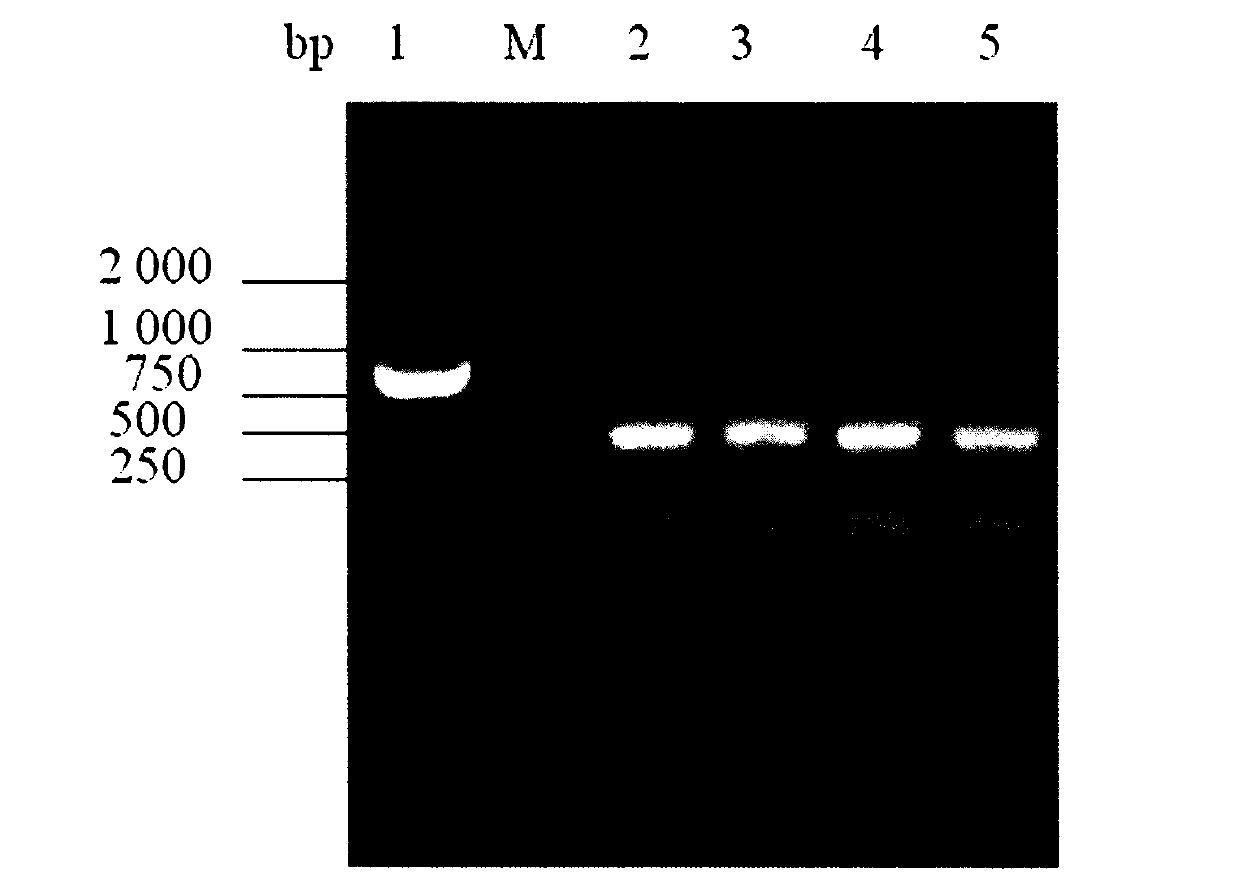
[0048] The identification of wild type / gene deletion type was carried out on the strains with the second homologous recombination. The chromosomes of transformants were extracted, and the upstream and downstream primers of the target gene argB were used for PCR identification. PCR identification results such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase in E.coli JM109
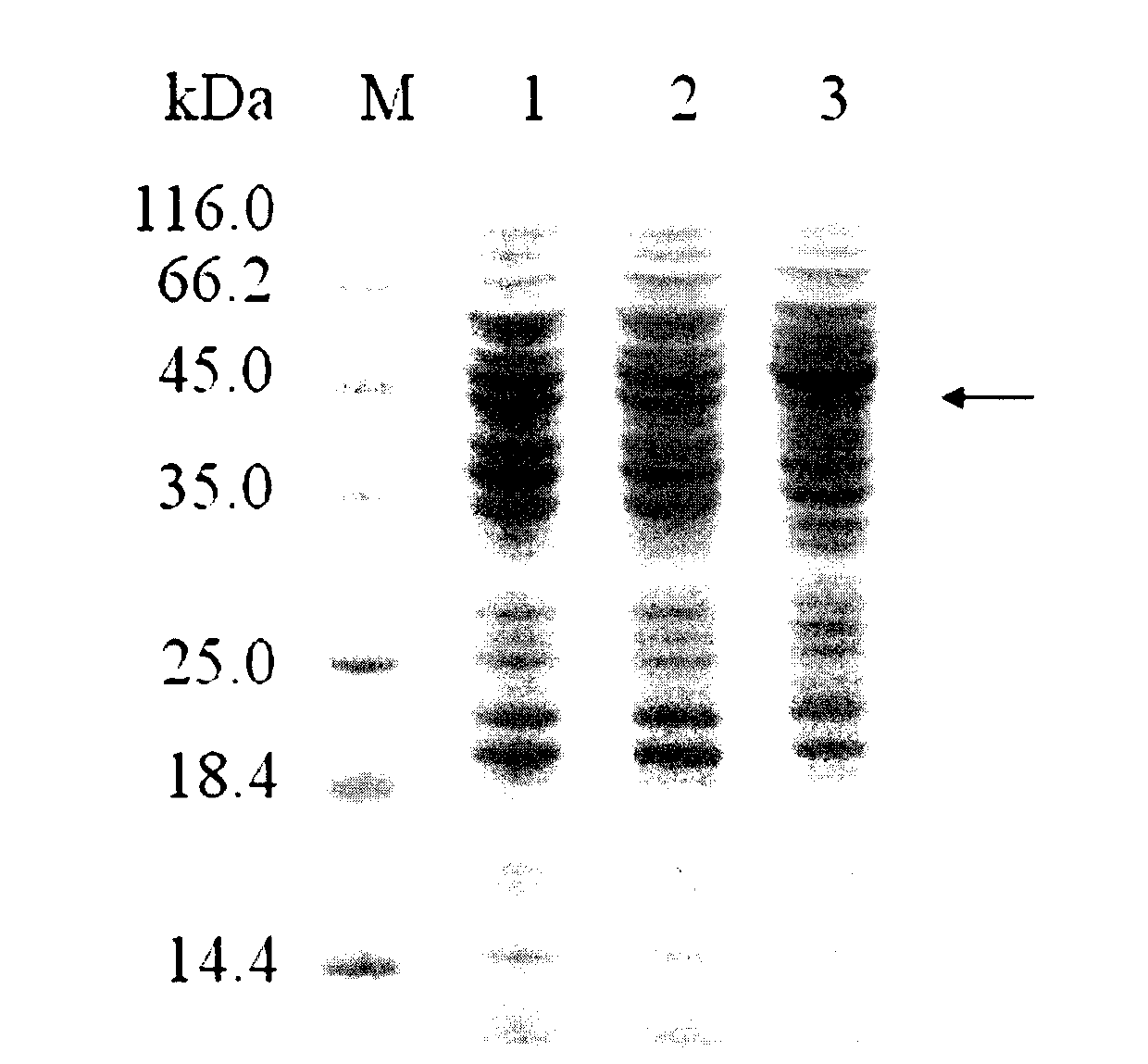
[0050] The recombinant plasmid pGAD was transferred into E.coli JM109, and the positive transformant was picked on the kanamycin-resistant LB plate to liquid LB. After IPTG induction, the bacteria were collected and crushed by ultrasonic waves. The supernatant was detected by SDS-PAGE. A specific band with a molecular weight of about 53kDa ( figure 2 ), consistent with the reported size of the target protein, but neither the control strain E.coli JM109 / pJC-tac nor the uninduced E.coli JM109 / pGAD had this band. It shows that the recombinant plasmid pGAD is correctly expressed in Escherichia coli, so the constructed recombinant plasmid pGAD can be transformed into Corynebacterium bacillus to detect whether glutamic acid decarboxylase can be effectively expressed.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: Identification of recombinant bacteria C.crenatum E01 / pGAD
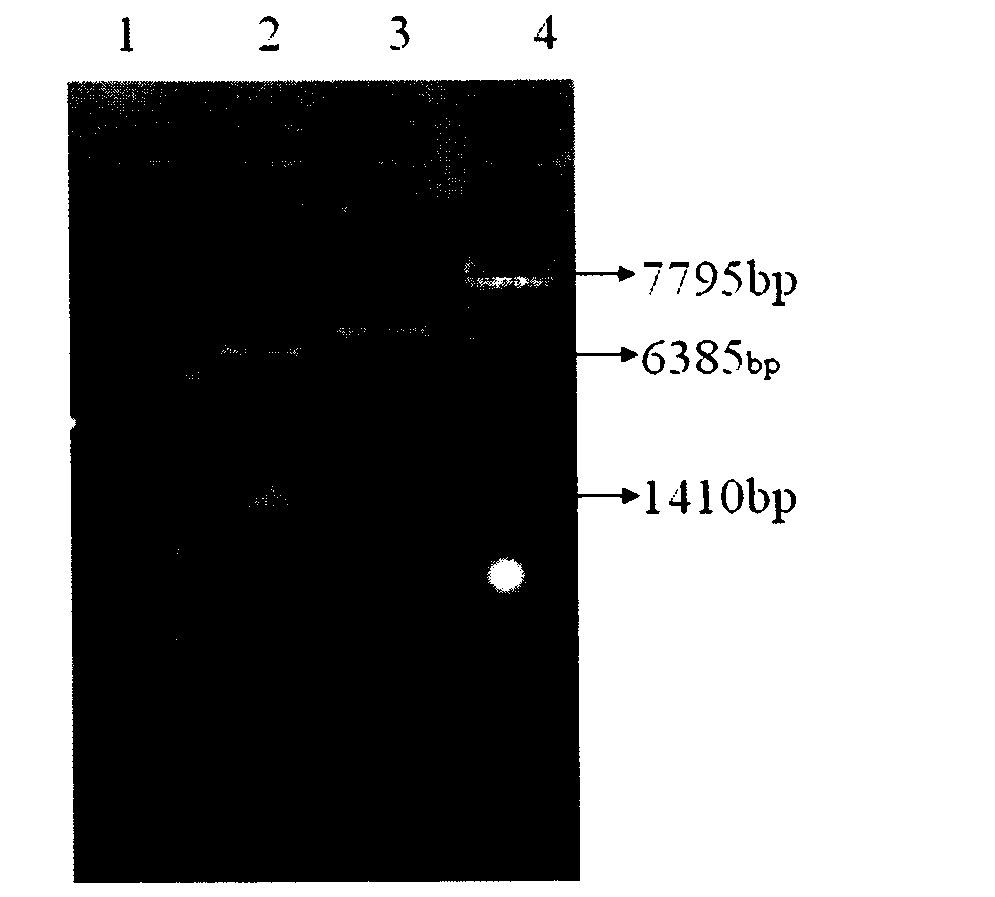
[0052] The recombinant plasmid pGAD was electroporated to transform C.crenatum E01, and after the transformant grew out, it was transferred to LBG liquid medium containing kanamycin, and the plasmid was extracted from the bacterial solution for PCR verification and enzyme digestion verification. The PCR products all showed a size of 1410bp The target band, after verification by Sal I / BamH I enzyme digestion, the result is as follows image 3 , indicating that the recombinant strain C.crenatum E01 / pGAD was constructed successfully.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com