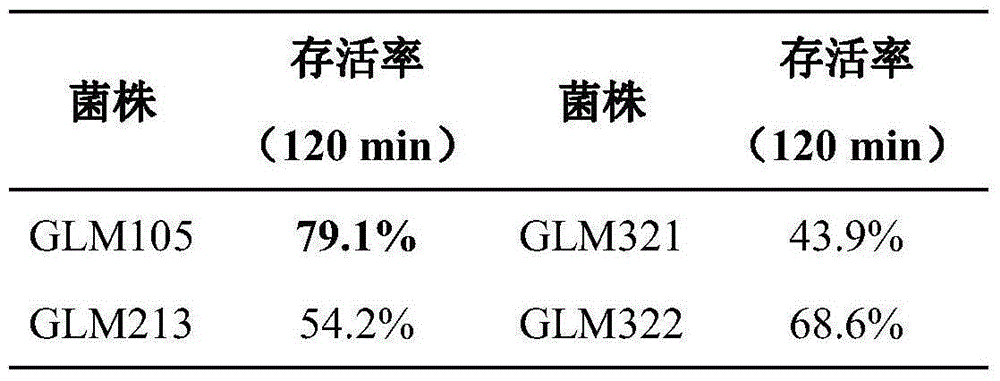
Patents
Literature
310 results about "Acid tolerance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nonionic waterborne polyurethane dispersoid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102690404AWide range of usesGood acid and alkali resistancePolyurethane dispersionPolymer science
The invention discloses a nonionic waterborne polyurethane dispersoid and a preparation method thereof. The dispersoid is mainly made from raw materials of A) diisocyanate, B) one or more than two polyols containing at least two hydroxy groups, wherein number average molecular weight of the polyols is 1000-4000, C) a small molecule chain extender and / or a small molecule cross-linking agent, D) methoxy polyethylene glycol with medium-low molecular weight, and E) one or more than one polyamines with number average molecular weight smaller than 500. According to the invention, the prepared dispersoid is with a small particle size, has long storage time and has great stabilities of acid tolerance, alkali tolerance and salt tolerance, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
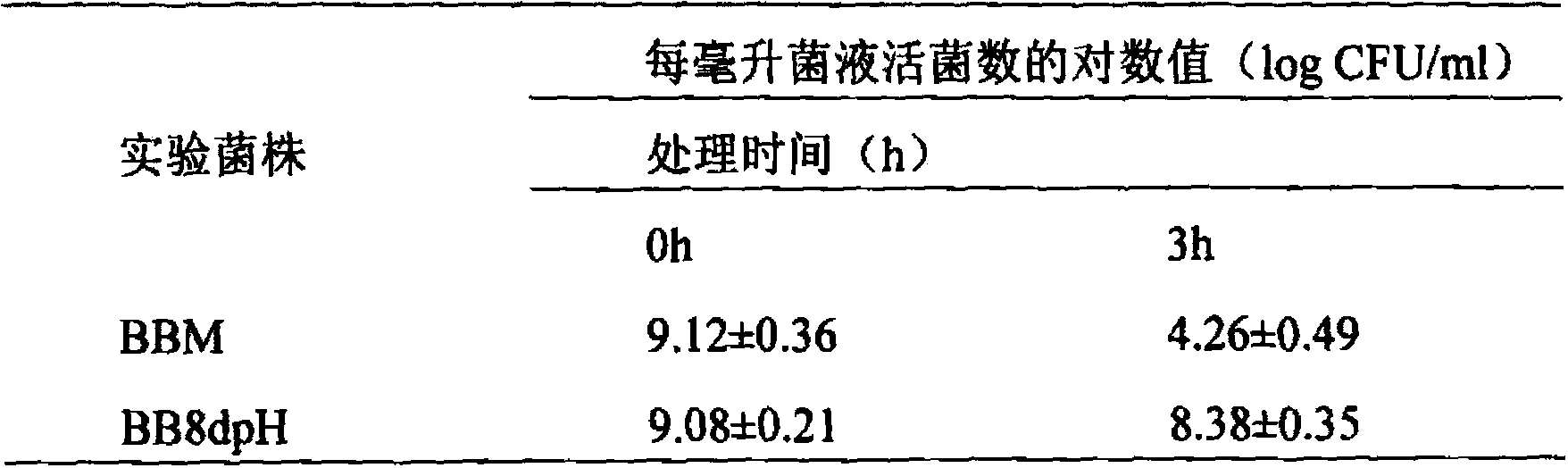
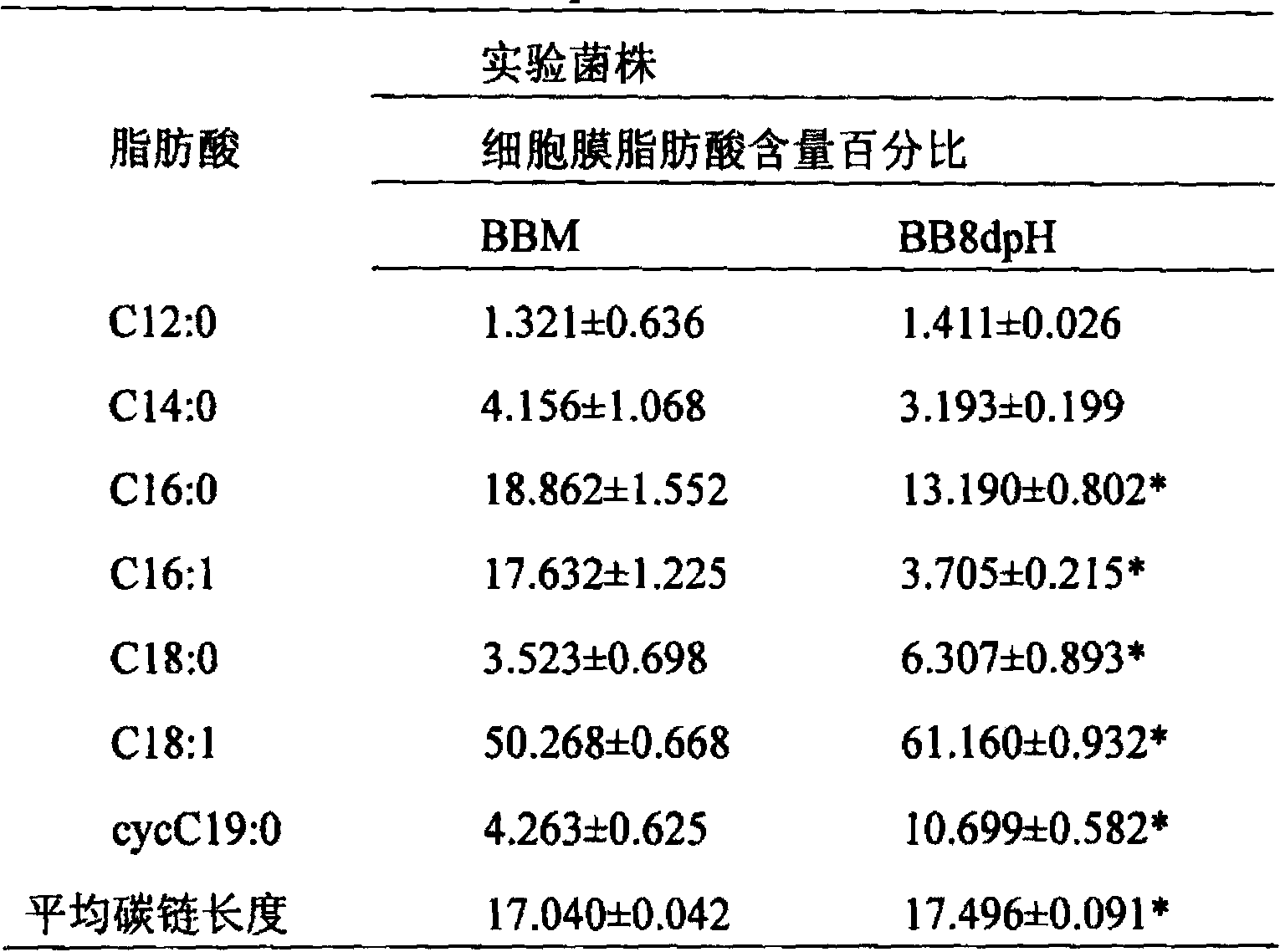
Acid-resistant bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH and application thereof
InactiveCN103849590AExcellent acid resistanceGenetically stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFecesCell membrane
The invention provides an acid-resistant bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the 16SrRNA gene part of the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and is stored with the preservation number of CGMCCNo.8370. The bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is a strain obtained by separating from the dejecta of healthy young people and further screening under the pH 3.2 acid condition. According to the fermentation and culturing process, anaerobic culture at 37 DEG C is carried out in a BL liquid substrate (containing 0.05% cysteine hydrochloride) for 24 hours. The bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH has remarkably better acid resistance than the common strains, and the acid resistance has genetic stability; the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH has different percent contents of cell membrane fatty acids from the common strains, the average carbon chain length of the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is remarkably longer than that of the common strains, and the cell membrane fluidity of the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is remarkably lower than that of the common strains; and the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is used in the production field of daily fermented food, health-care food and medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
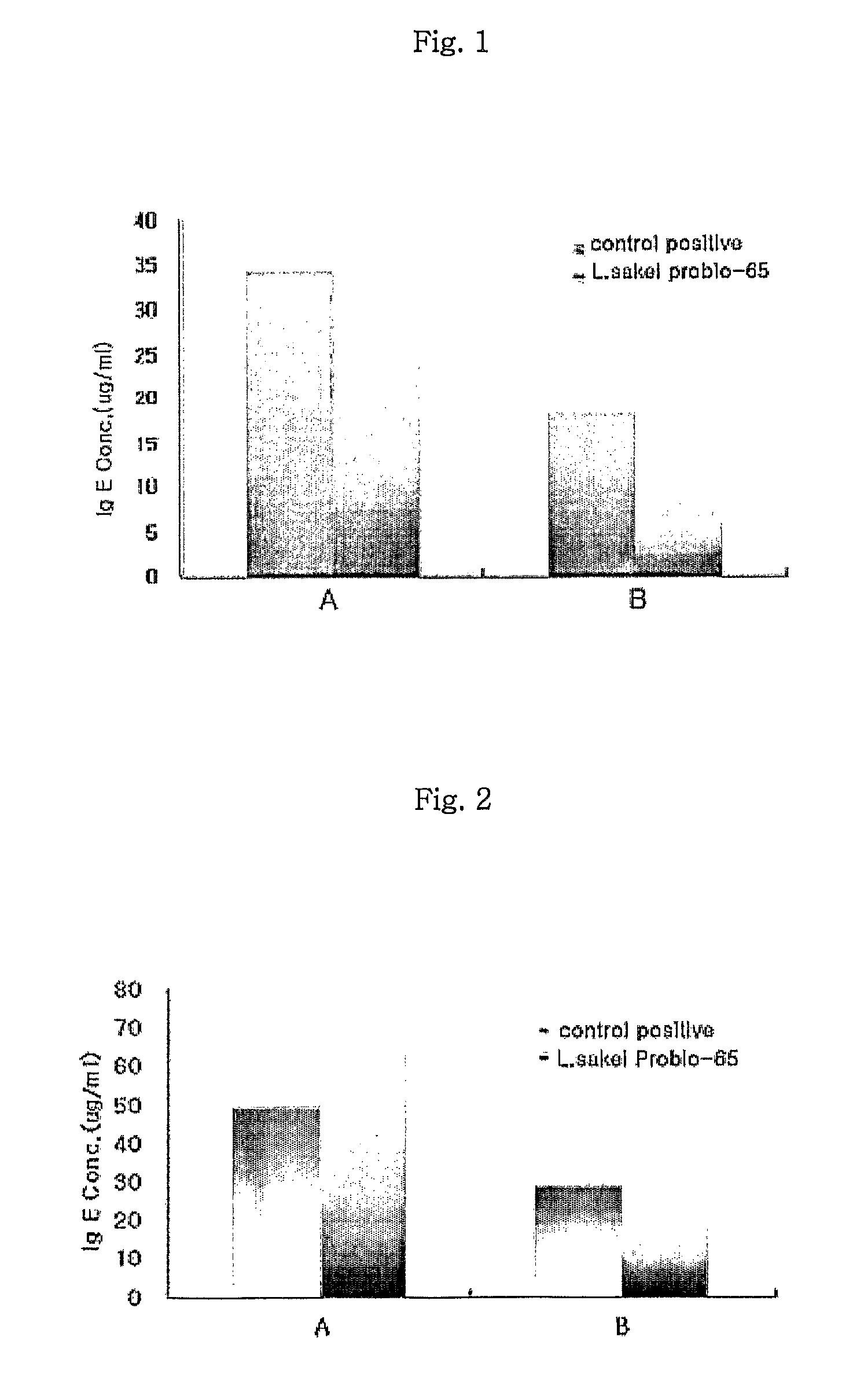
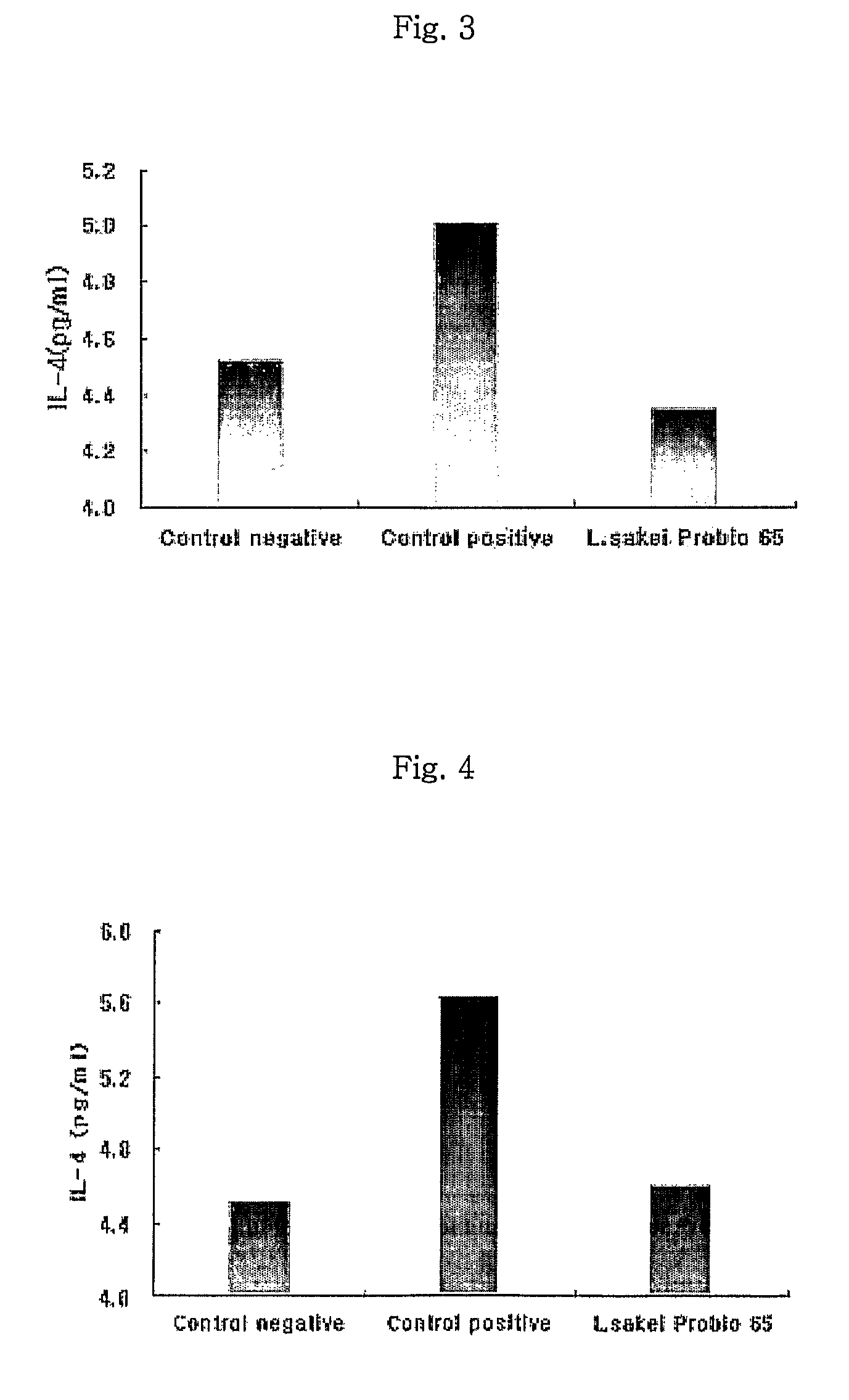
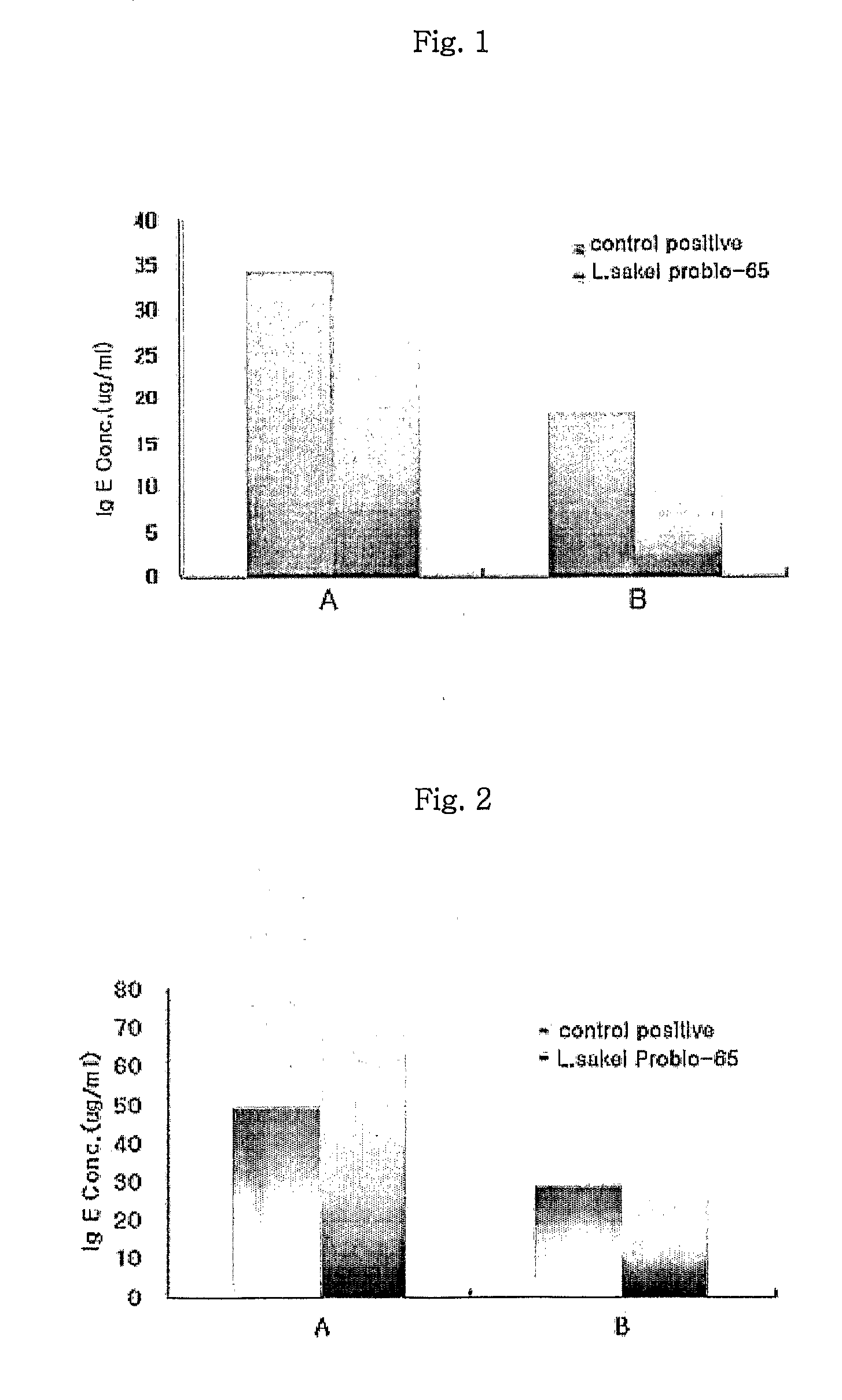
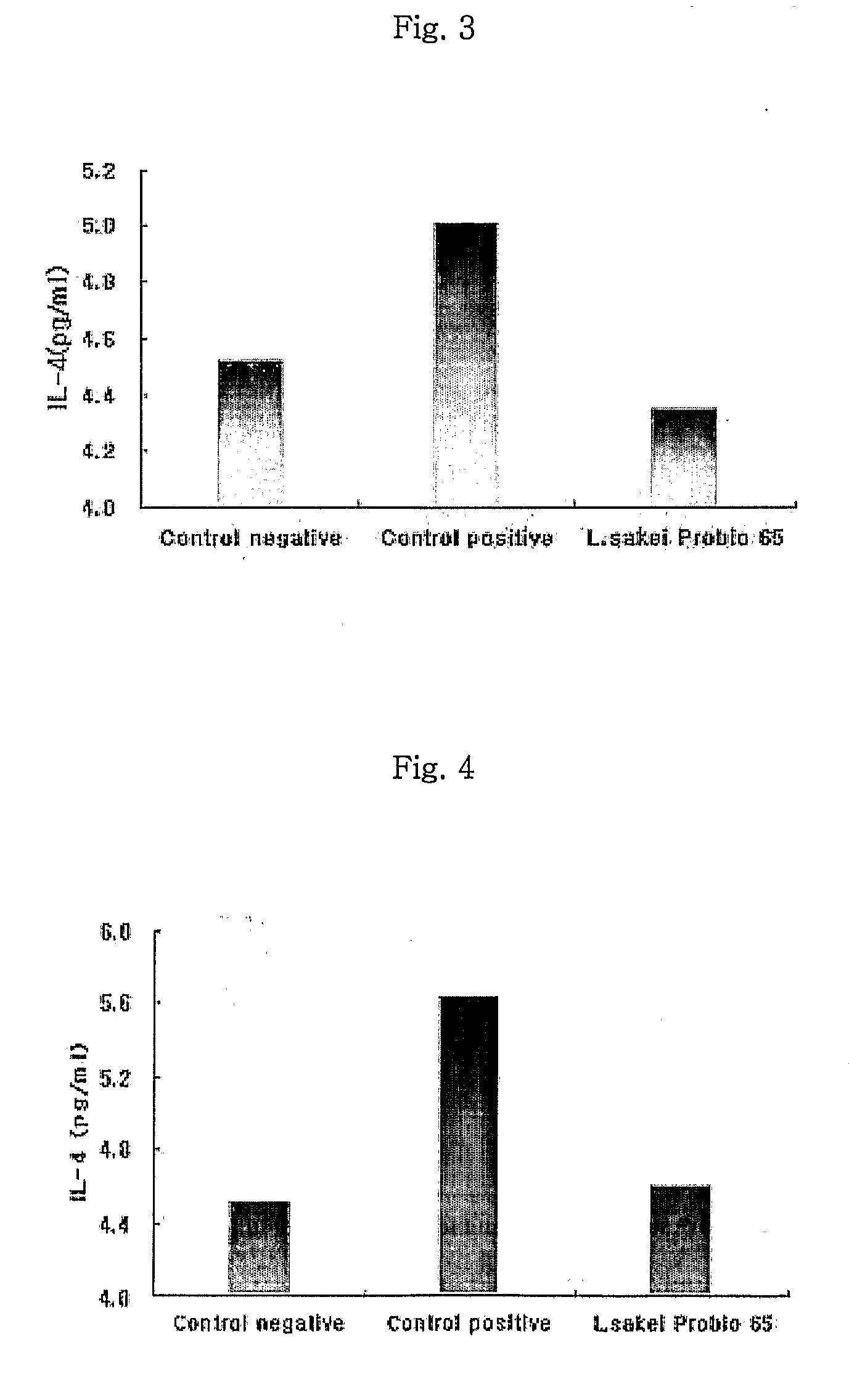
Acid tolerant Lactobacillus sakei probio-65 with the ability of growth suppression of pathogenic microorganisms and the anti-allergic effect
ActiveUS8034606B2Growth inhibitionEffectively inhibit harmful microorganismsBiocideCosmetic preparationsAcid-fastDisease
Disclosed are a novel tactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65, and the use thereof. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain has acid tolerance, bile acid tolerance and antibiotic resistance, inhibits the growth of harmful pathogenic microorganisms in the body and the intestine of animals, and has immunuenhancing activity. In particular, the novel strain inhibits the growth of Staphylocccus aureus, which is known to be a factor aggravating atopic dermatitis. Thus, the novel strain is useful for preventing or treating atopic dermatitis and allergy-related disorders. Also, the novel strain stabilizes intestinal microflors by inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain or a culture thereof is useful in pharmaceutical, feed, food, and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:PROBIONIC CO LTD
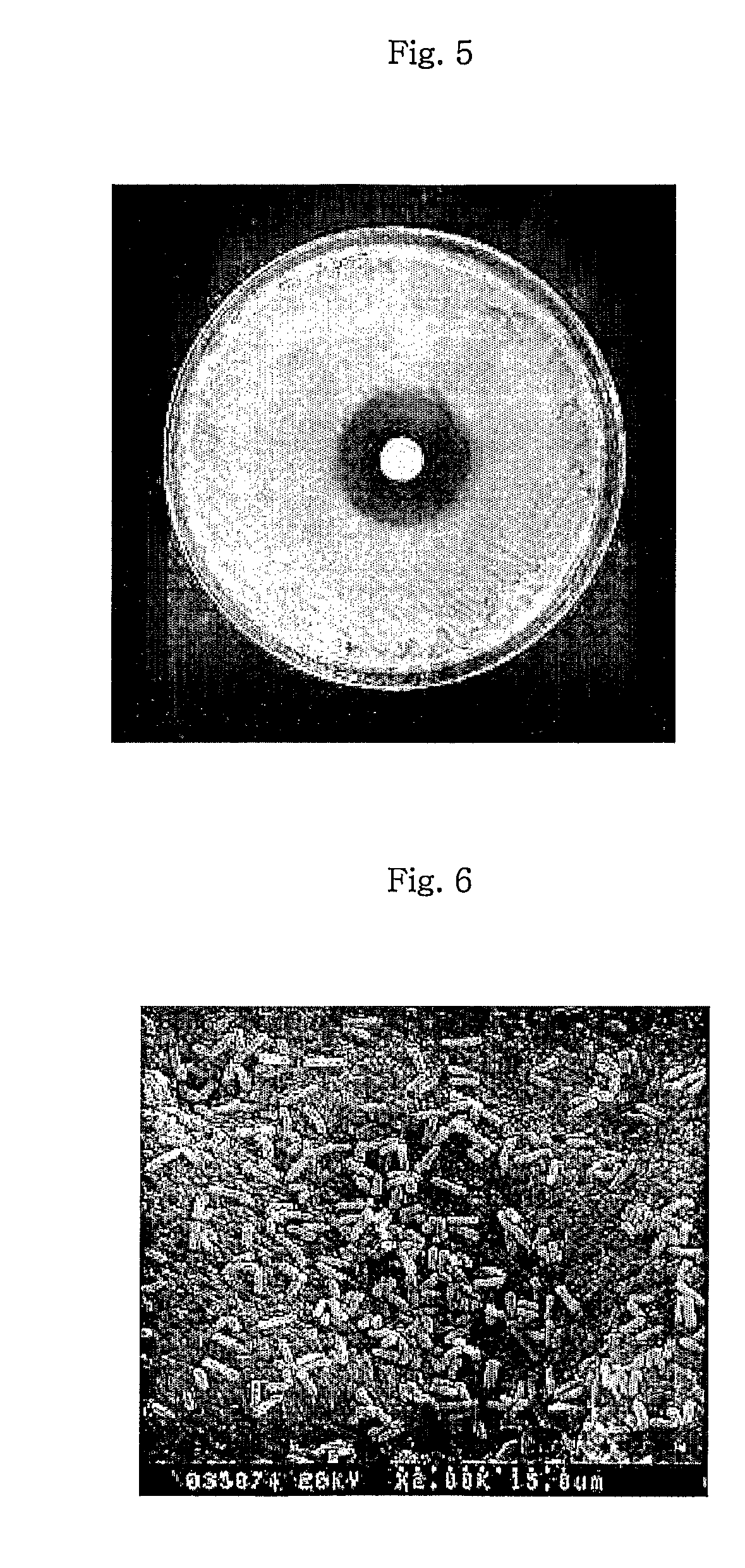
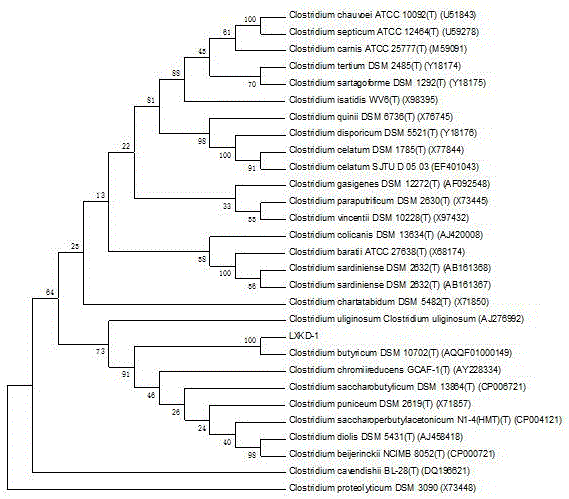
Preparation and application of Clostridium butyricum and live Clostridium butyricum preparation
ActiveCN106479924APromote growthPrevent diarrheaBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEggshell
The invention discloses preparation and application of Clostridium butyricum and a live Clostridium butyricum preparation; Clostridium butyricum LXKJ-1 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on 24 March, 2016 under CCTCC NO: M201613. A seed medium, fermentation medium formulation, culture conditions for Clostridium butyricum and a production of a preparation of live Clostridium butyricum are also disclosed. The Clostridium butyricum provided herein is tolerant to acids, bases and high temperature, is highly capable of producing butyric acid, can inhibit animal pathogens, such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Clostridium perfringens, and can prevent diarrhea in livestock and poultry due to Escherichia coli, Salmonella and Clostridium perfringens, improving intestinal flora balance, promoting the growth of livestock and poultry, relieving constipation in sows, improving egg weight for layers, improving eggshell quality for layers, and decreasing egg-feed ratio.
Owner:湖北绿雪生物科技有限公司
Crystalline form of r)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin- 5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate
ActiveUS20100227839A1Reduce filter timeImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphateAntibacterial activity
A crystalline form of crystalline (R)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate, methods of making the crystalline form and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the crystalline form are useful antibiotics. Further, the derivatives of the present invention may exert potent antibacterial activity versus various human and animal pathogens, including Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococi, Enterococci and Streptococi, anaerobic microorganisms such as Bacteroides and Clostridia, and acid-resistant microorganisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Accordingly, the compositions comprising the crystalline form may be used in antibiotics.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Lactic acid bacterium with wide-spectrum bacteriostatic activity and application thereof
InactiveCN104611251AInhibit VibrioGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMicroorganismHemolysis
The invention belongs to the field of microbes, and concretely relates to a lactic acid bacterium with wide-spectrum bacteriostatic activity and application thereof. The lactic acid bacterium with wide-spectrum bacteriostatic activity is named lactobacillus salivarius GZPH2, is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) since 27th, November, 2014, and has the preservation number of CCTCC M 2014598. The provided lactic acid bacterium lactobacillus salivarius GZPH2 has good bacteriostatic effect on multiple pathogenic bacteria of human and aquaculture bionts, and possesses the characteristics of not generating histamine, no hemolysis, acid resistance, cholate resistance and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
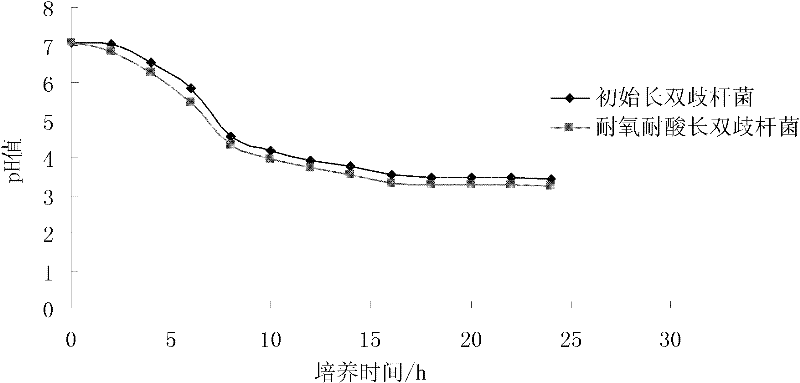
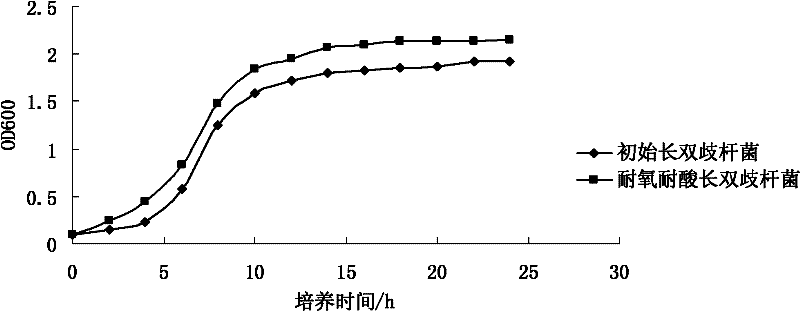
Oxygen-resistant acid-resistant Bifidobacterium longum
InactiveCN102206599AImprove physiological and biochemical performanceImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOxygenMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to oxygen-resistant acid-resistant Bifidobacterium longum, and is characterized in that: the name is CC-1, the category name is Bifidobacterium longum, the preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 4730, the preservation date is April 2, 2011, the preservation address is No.3, No.1 Court, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation institution is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. According to the invention, the physiological and biochemical properties of the bifidobacterium are effectively improved and the oxygen and acid tolerance of the bifidobacterium is increased; and oxygen-resistant acid-resistant Bifidobacterium longum is cultured in a PTYG (peptone-tryptone-yeast extract-glucose) liquid culture medium with a pH value of 4.0 in the presence of oxygen at the temperature of 37 DEG C, pour method viable count results show that the viable count of the cultured oxygen-resistant acid-resistant Bifidobacterium longum CC-1 can reach 4.7*10<7> CFU / ml, and the concentration has an important role in the research and application of bifidobacteria products.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bacillus licheniformis and applications thereof in kitchen waste
ActiveCN106190900AHigh activity proteaseHigh lipohydrolase activityBacteriaSolid waste disposalAcid-fastBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides bacillus licheniformis, wherein the classification name is bacillus licheniformis CY-1, the bacillus licheniformis CY-1 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the address is the Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences located in 3, Courtyard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the postal code is 100101, the accession number is CGMCC NO.12448, and the preservation date is May 13, 2016. The invention further provides applications of bacillus licheniformis in kitchen waste treatment. The bacillus licheniformis has the activities of high-activity protease, amylase and oil hydrolase, can degrade glucose for generating acid, and is a thermophilic bacterium with high salt tolerance and high acid tolerance, and through effective combination of the bacillus licheniformis with a carrier, the weight of the fed kitchen waste is rapidly and efficiently reduced by 85%.
Owner:BIOMAX ECOLOGICAL ENG
Rabeprazole sodium enterosoluble micro-particles and preparation method thereof
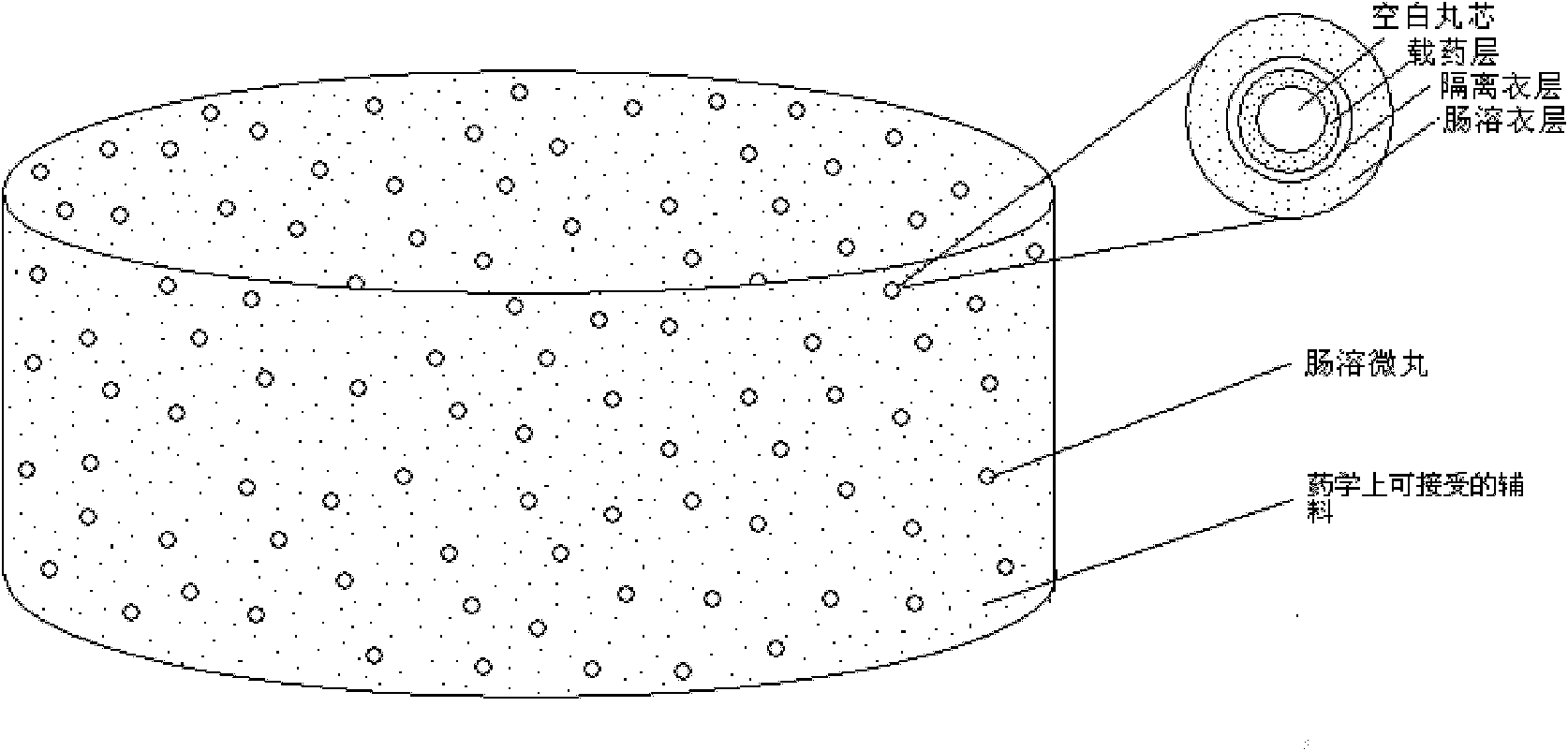
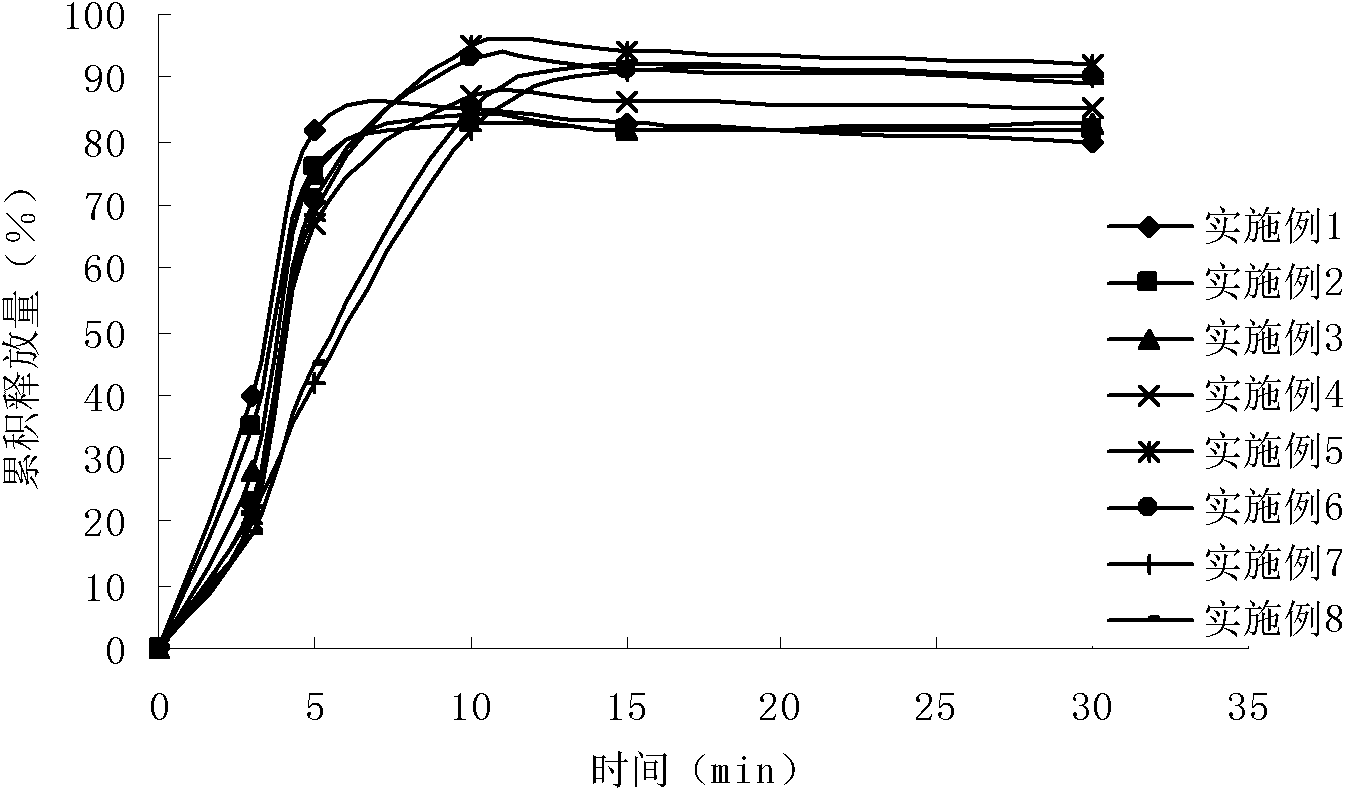
ActiveCN102652734AImprove complianceReduce adverse reactionsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsRefluxMedicine
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations, and particularly relates to novel rabeprazole sodium enterosoluble micro-particles with high stability in an acid medium, and a preparation method thereof. Each rabeprazole sodium enterosoluble micro-particle comprises a blank pill core (1), a medicine-carrying layer (2), an isolation coating layer (3) and an enteric coating layer (4) in sequence from inside to outside. A pH value regulator is used in the medicine-carrying layer, the isolation coating layer is added between the medicine-carrying layer and the enteric coating layer, and particularly, a retarding agent is added into an enteric coating layer combination, so that the acid tolerance of a medicament active ingredient namely rabeprazole sodium which is extremely unstable in acid is well improved. The rabeprazole sodium enterosoluble micro-particles and a preparation thereof can be used for treating diseases such as active duodenal ulcer, benign active gastric ulcer, rodent or ulcerative gastroesophageal reflux accompanied by clinical symptoms and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Acid composition comprising a phycocyanin
PendingUS20180271119A1Low pour pointImprove stabilityUnicellular algaeSkeletal disorderBiotechnologyPhycocyanin
The invention relates to an acid composition, particularly an acid food composition, comprising at least one phycocyanin resistant to pH acid.
Owner:FERMENTALG
Acid resistance and high temperature resistance saccharomyces cerevisiae and applications thereof
ActiveCN102936572AIncrease daily feed intakeIncrease daily weight gainFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDiarrhea
The present invention discloses a strain of acid resistance and high temperature resistance saccharomyces cerevisiae and applications thereof. The saccharomyces cerevisiae is Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sa-10, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and a preservation number is CGMCC No.6120. According to the present invention, after the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sa-10 is added to a basal diet of weaned piglets, daily feed intake and daily weight increase of weaned piglets can be significantly improved, and a diarrhea index can be reduced; and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sa-10 provides important significance and broad application prospects in the field of animal feed additive preparation or animal production performance improvement.
Owner:北京英惠尔生物技术有限公司
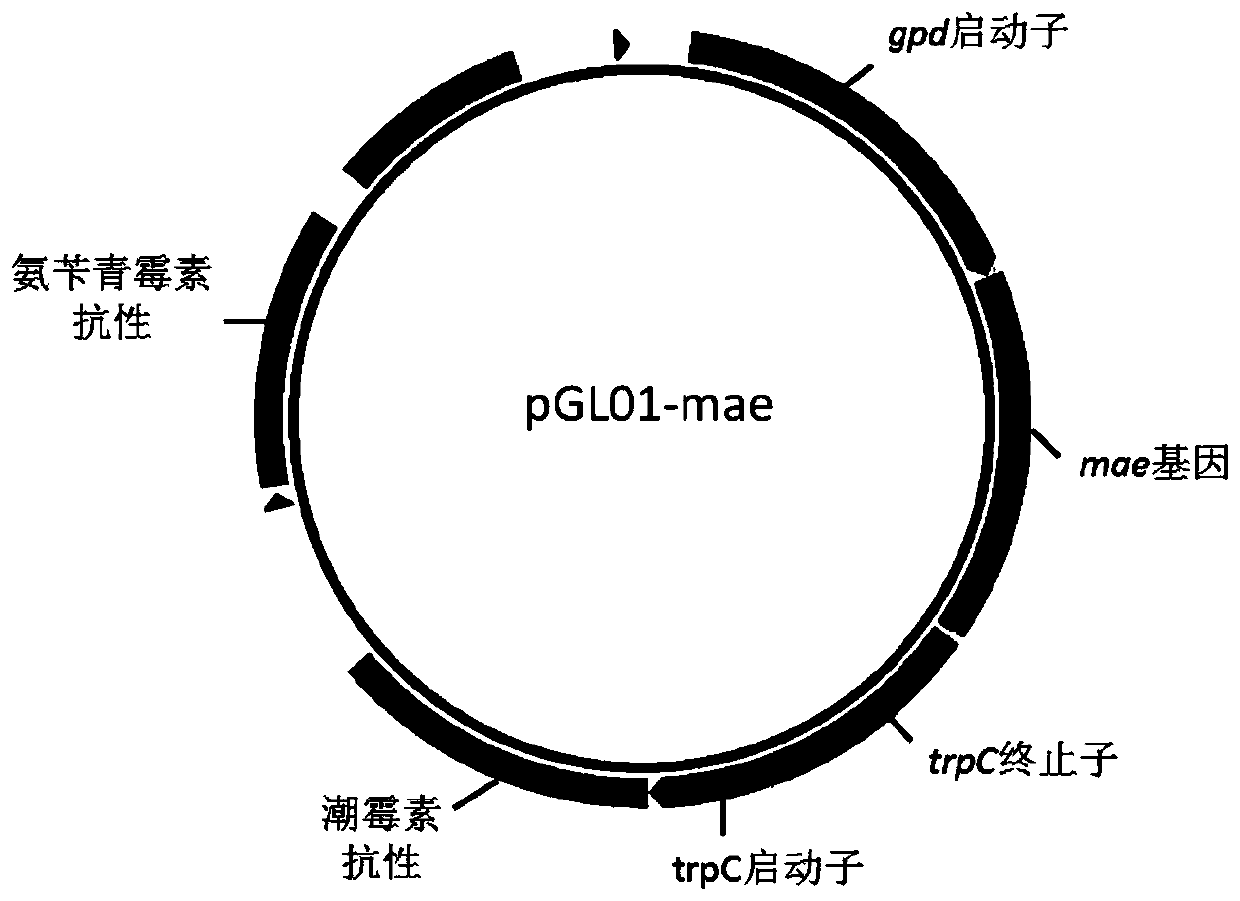
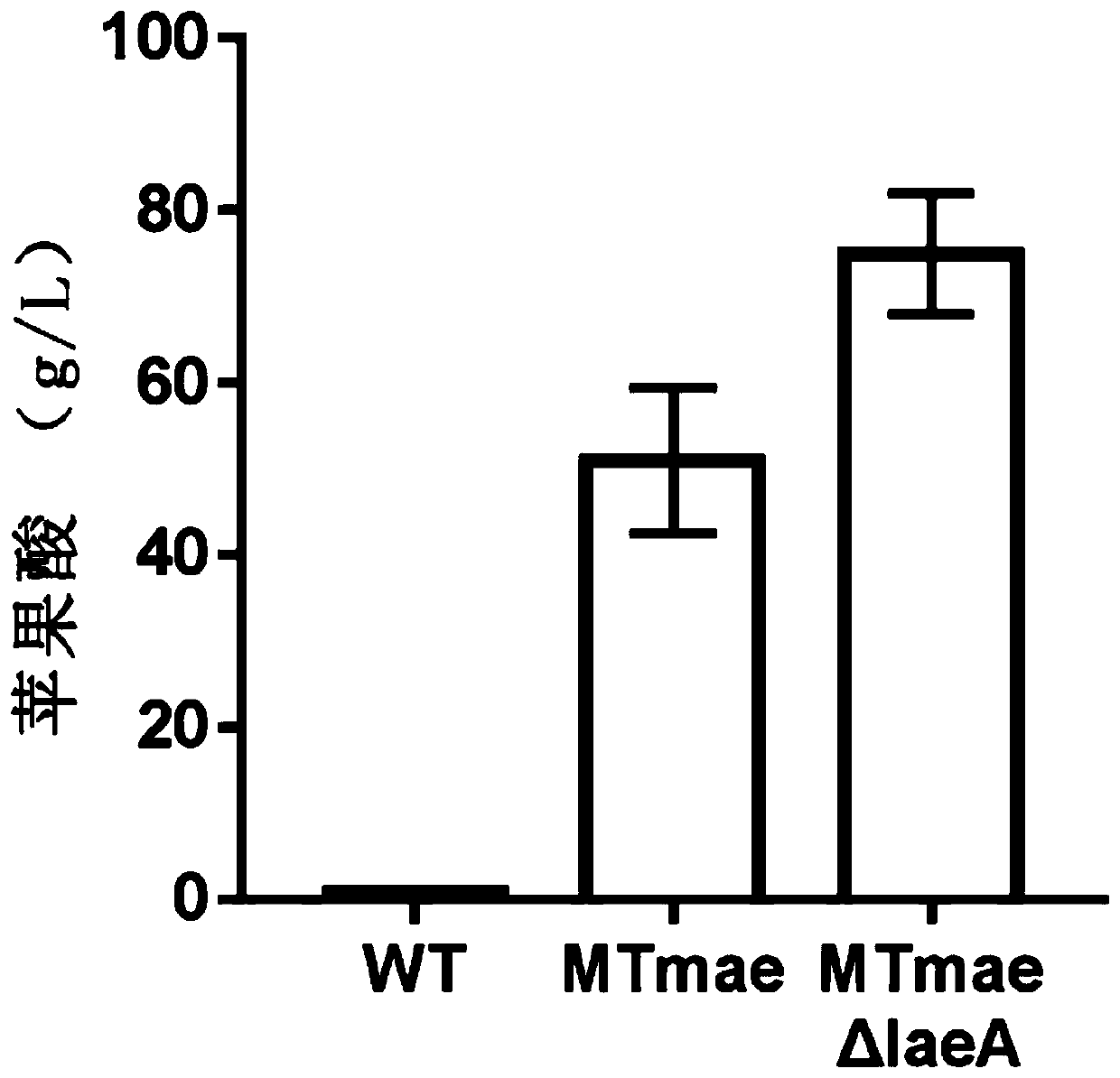
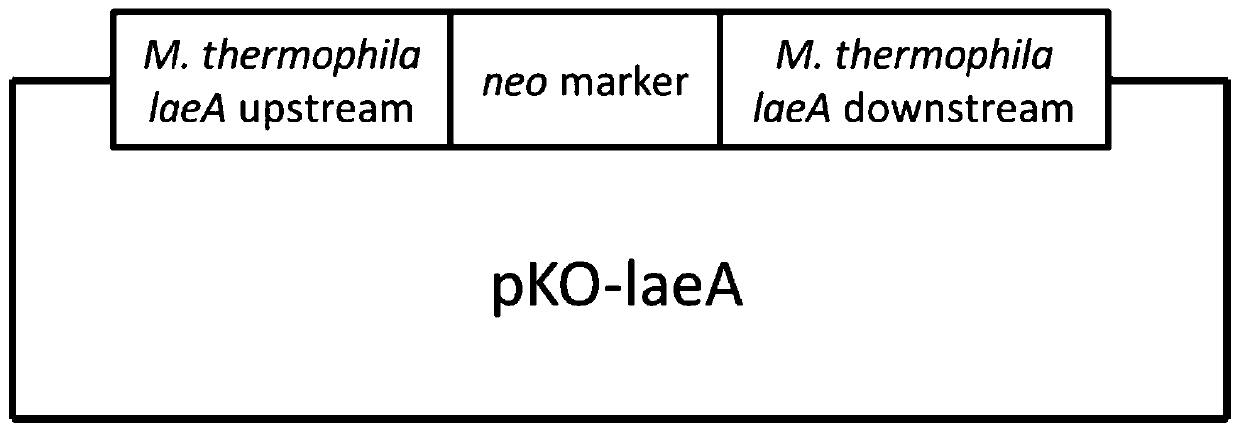
Genetically engineered bacterium producing malic acid and method for producing malic acid
ActiveCN109797111AIncrease productionHas acid resistanceFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyGenetically engineered
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium producing malic acid and a method for producing the malic acid. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by increasing the expressionor activity of diacid transporter in the recipient bacterium and decreasing the expression or activity of methyltransferase laeA in the recipient bacterium. By the arrangement, the yield of the malicacid is effectively increased, furthermore, use of a neutralizer is effectively avoided by introducing the acid-resistant engineered bacterium.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGGENG CHEM TECH CO LTD
Lactobacillus reuteri and application thereof
ActiveCN110373342AGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationMicroorganismStrong acids
The invention provides lactobacillus reuteri. The lactobacillus reuteri was deposited at the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection and Management Committee on December 14, 2017 with the deposition number of CGMCC No. 15062. The lactobacillus reuteri has broad-spectrum bacteriostatic effect, good adhesion property and strong acid resistance and bile salt resistance, is obviously superior to an existing commercial strain, and is a newly isolated and discovered active bacterium with a good probiotic function.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司 +1
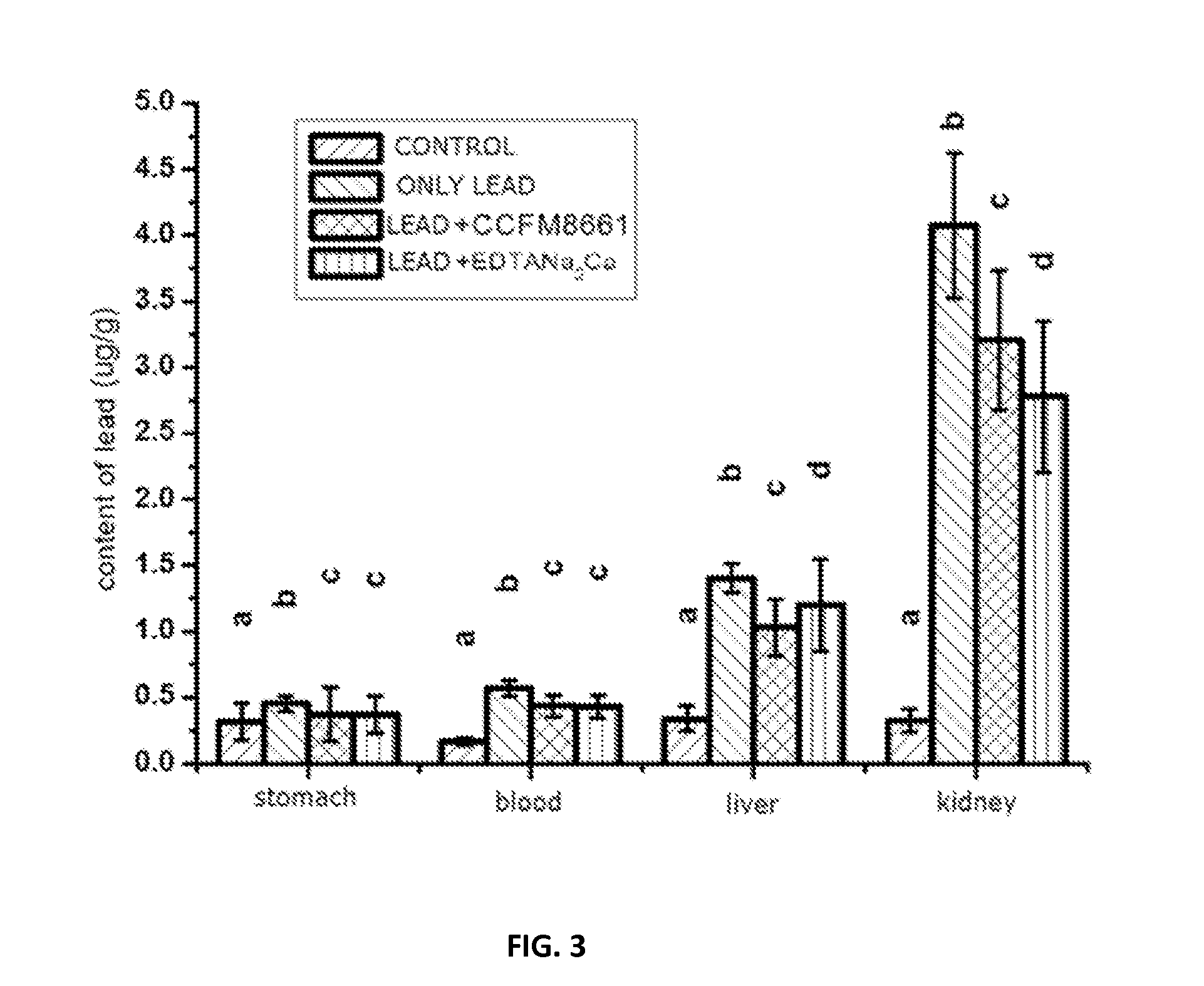
protective effects and application of a Lactobacillus plantarum on the alleviation of lead toxicity
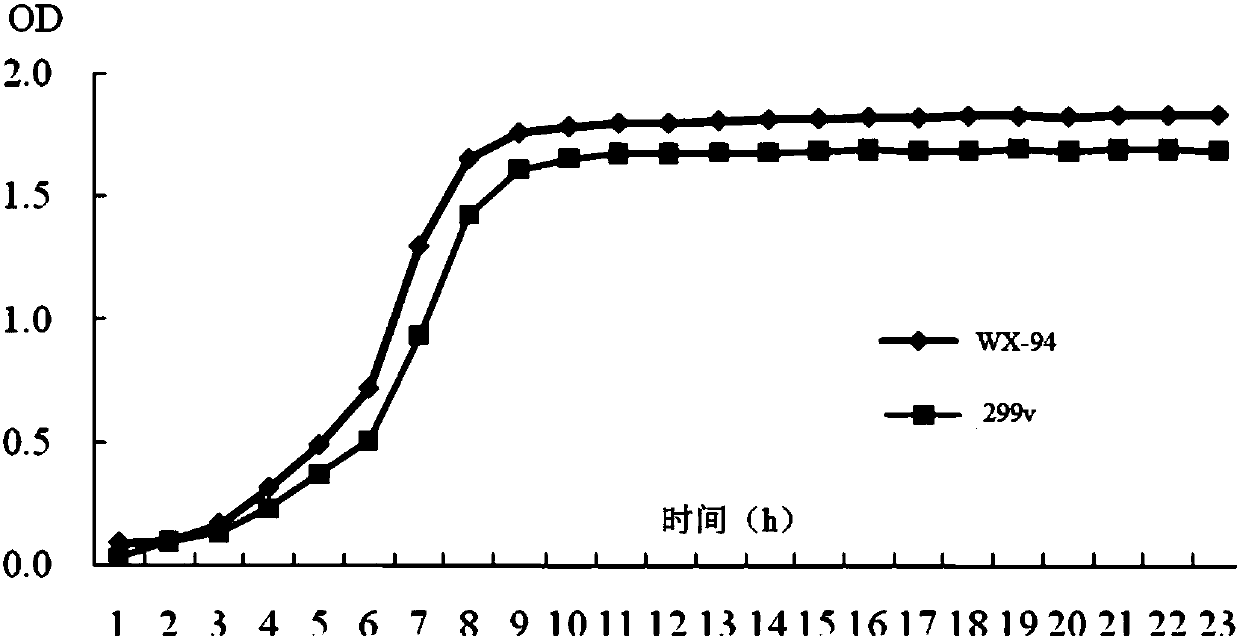
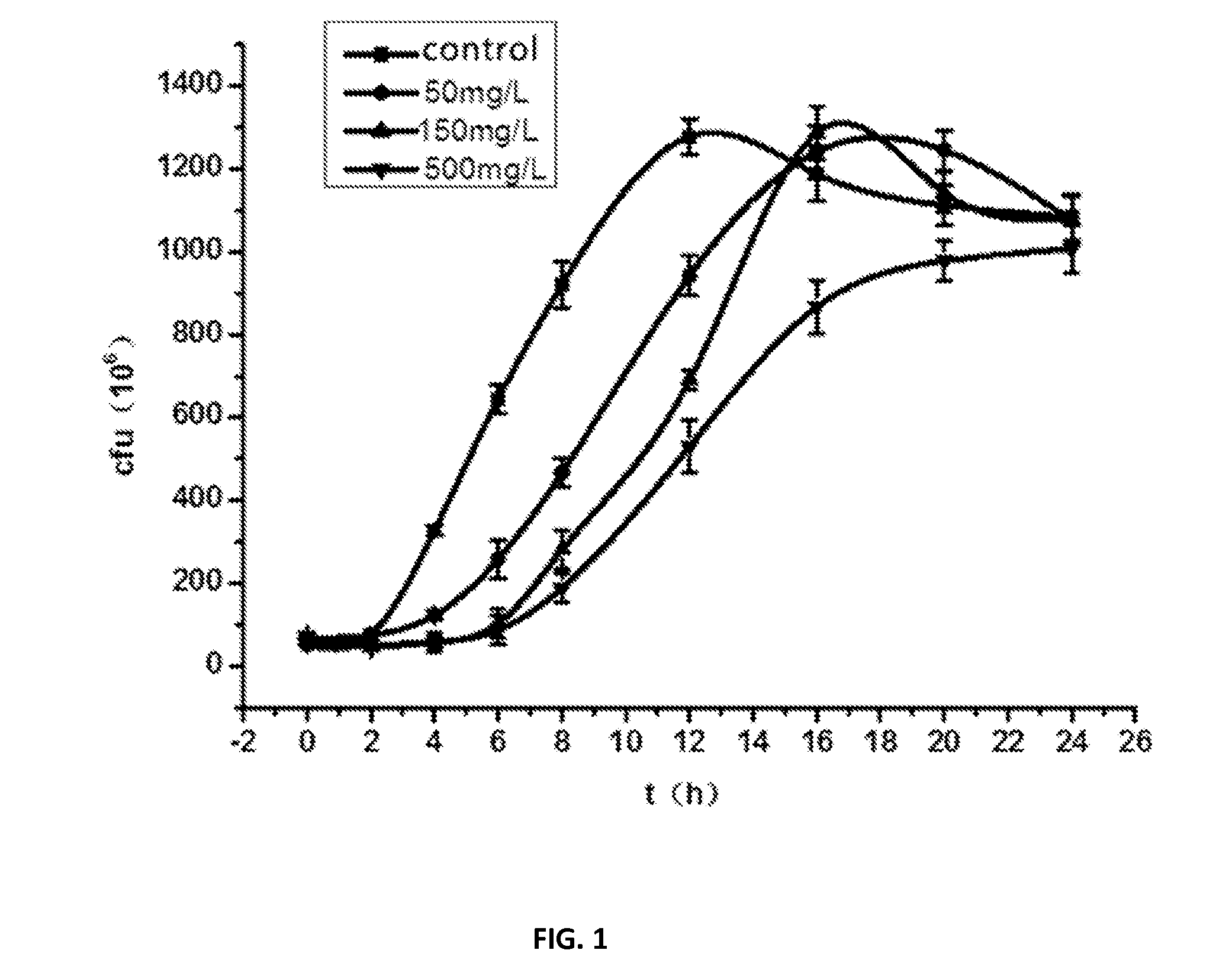
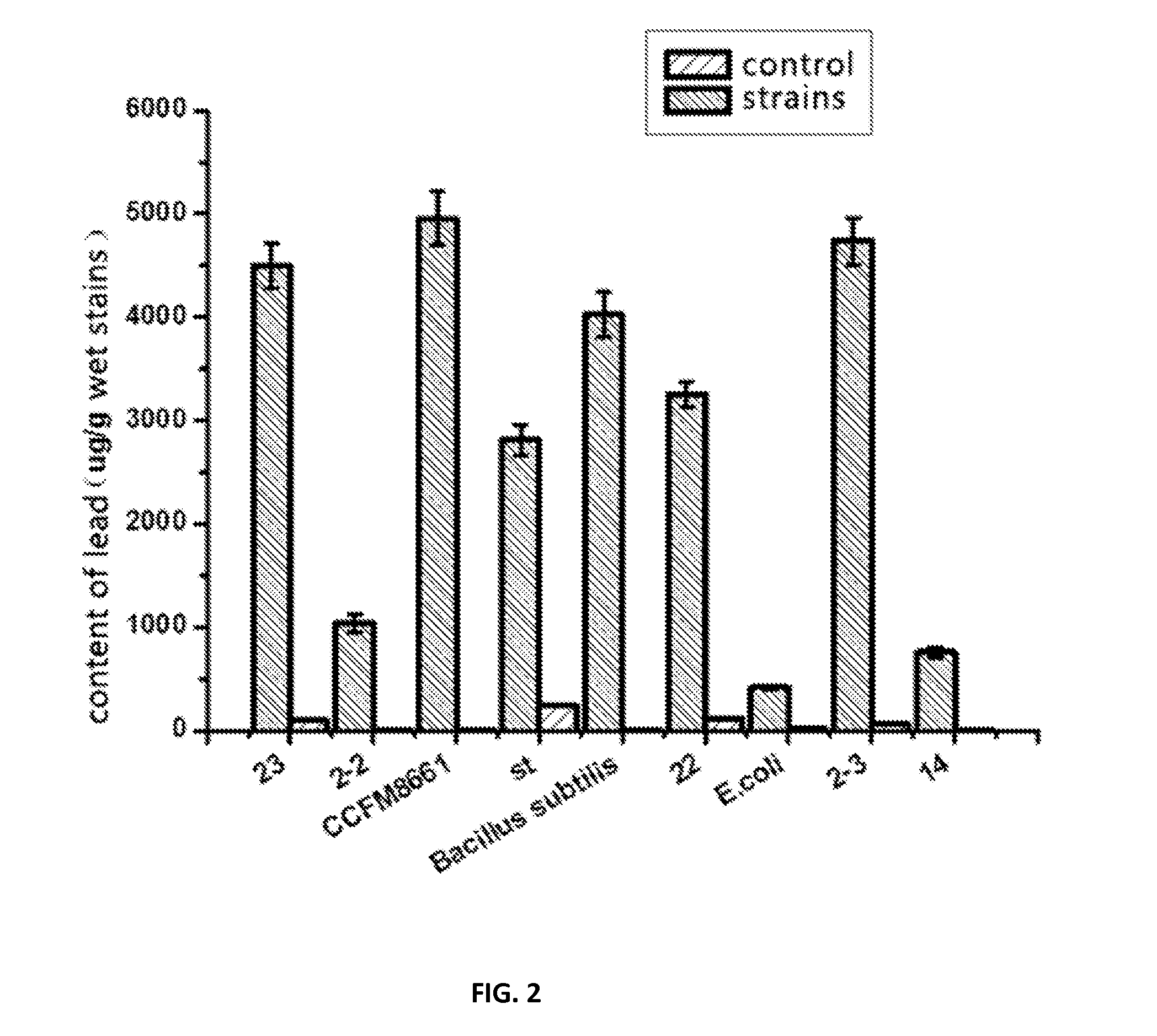
The Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8661 is tolerant to acid and lead ions in vitro which can tolerate lead ions solution with the initial concentration of 150 mg / L, and has a strong capability of binding lead ions, which can reduce the lead level in mice blood, liver, kidney and stomach, significantly improve antioxidant indicators and alleviate pathological symptoms of lead exposed mice.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Acid-proof and high-temperature resistant alpha-amylase and production thereof
A fire-resistant and acid-proof alpha-amylase and its production are disclosed. The process is carried out by separating precursor-alpha-amylase gene from lichenized bacillosporin, mutating for L134 and S320 amino acid residues and high-efficient expressing alpha-amylase mutant in bacterium. It achieves better safety, expression and acid stability, and more yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Highly efficient and low-cost microbiological feed proteins based on vinegar residue and miscellaneous meal
InactiveCN102696860ALow priceImprove qualityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffRapeseedAnimal product
The invention relates to the field of producing highly efficient and low-cost microbiological feed proteins based on the three-stage fermentation of vinegar residue and miscellaneous meal by using probiotics. The vinegar residue used as a main carbon source and the cottonseed meal used as a main nitrogen source as well as a partial carbon source are subjected to the first-stage fermentation pretreatment by using food-grade mould, the product is subjected to the second-stage fermentation by using bacillus and yeast as zymocytes and adding partial cottonseeds, and finally the product is added with partial soybean meal and rapeseed meal used as a nitrogen source as well as a partial carbon source, inoculated with lactobacillus and acid-resisting bifidobacterium and uniformly mixed, and then the product is subpackaged in one-way membrane bio-bags for sealed storage, namely the finished products are obtained by the three-stage fermentation. The microbiological feed proteins are extremely low in production cost and can be used as a feed component, and the adding amount reaches 5 to 40 percent. Because the finished products do not need drying treatment, the finished products have more viable bacteria as well as enzymes, few other bacteria and an obvious feeding effect; moreover, the microbiological feed proteins also have the advantages of greatly improving the utilization rate of livestock and poultry feed, increasing yield, improving intestinal environment, improving immunity and resistance, replacing antibiotics and improving quality of animal products.
Owner:泉州华惠生物科技有限公司
Lactobacillus johnsonii, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102839136AImprove Gut HealthIncrease production capacityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMicroorganismFeces
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus johnsonii, and a preparation and application thereof, and discloses an optimal culture medium for the strain and a preparation method of a freeze-dried preparation of the strain. The microbial preservation number of the Lactobacillus johnsonii ZLJ010 is CGMCC No.5762. The strain is definite in hereditary basis, and has the characteristics of good growth performance and high acid production, acid resistance, heat resistance and bacterium inhibition capabilities. When being used as a feed additive for sows, the freeze-dried preparation of the strain can improve the intestinal tract health of the sows, reduce the number of harmful bacteria in feces, enhance the body immunity and increase the production performance of the sows.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
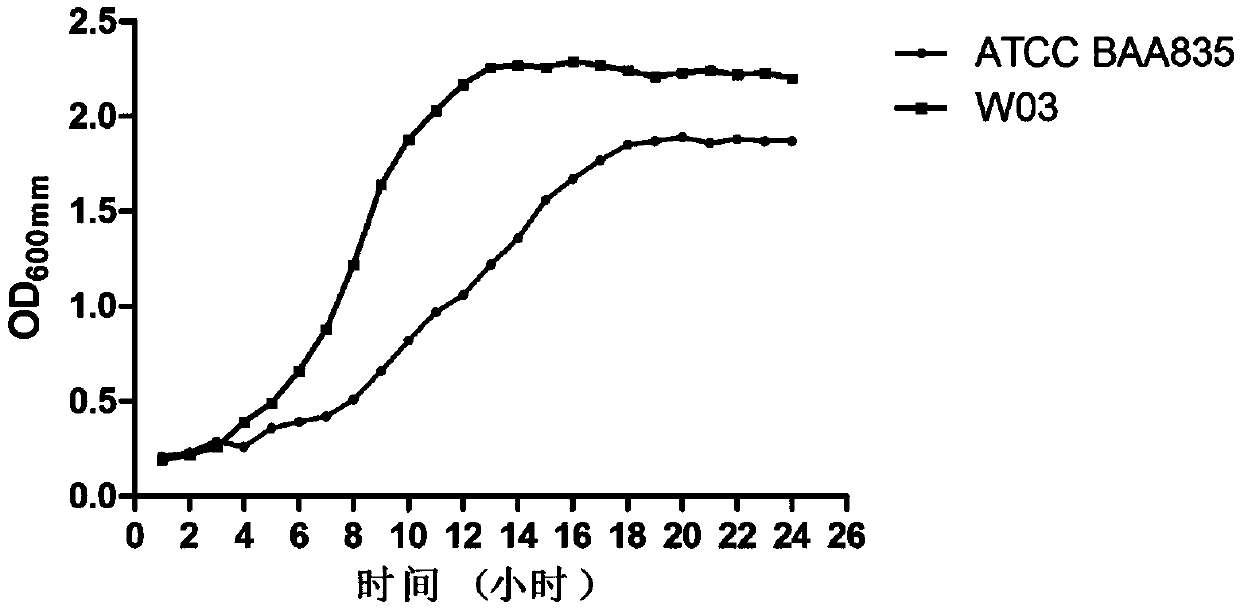
Strain for preventing and treating metabolic diseases and application for strain
ActiveCN110964650AImprove fermentation performanceGood storage stabilityBacteriaMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyDisease
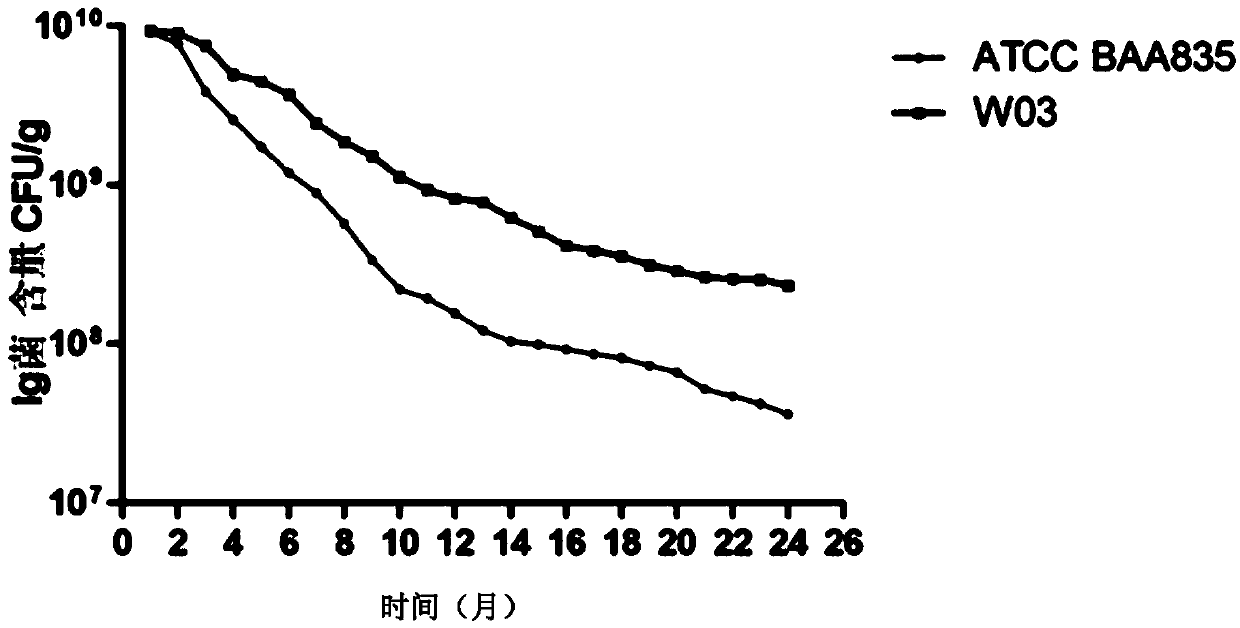
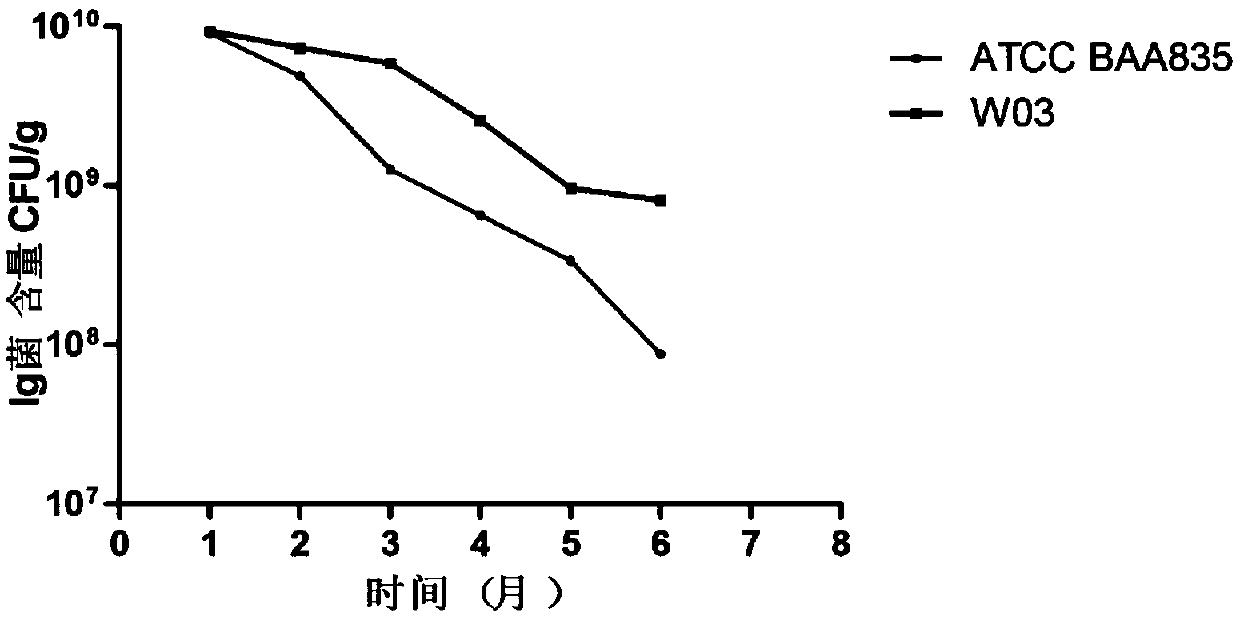
The invention discloses a strain for preventing and treating metabolic diseases and application for the strain. The strain is Akkermansia muiniphila strain which is named Akkermansia muciniphila SSYD-3 and has the preservation number being CGMCC No.14764. Compared with the existing Ackermann muiniphila strain ATCC BAA 835, the Akkermansia muiniphila strain provided by the invention is more ideal in fermentation performance, storage stability, acid resistance, bile salt tolerance and the effect of treating the metabolic diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINE PHARMA LAB +1
Novel Acid Tolerant Lactobacillus Sakei Probio-65 with the Ability of Growth Suppression of Pathogenic Microorganisms and the Anti-Allergic Effect
ActiveUS20090214497A1Prevent proliferationGrowth inhibitionBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseIntestinal structure
Disclosed are a novel tactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65, and the use thereof. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain has acid tolerance, bile acid tolerance and antibiotic resistance, inhibits the growth of harmful pathogenic microorganisms in the body and the intestine of animals, and has immunuenhancing activity. In particular, the novel strain inhibits the growth of Staphylocccus aureus, which is known to be a factor aggravating atopic dermatitis. Thus, the novel strain is useful for preventing or treating atopic dermatitis and allergy-related disorders. Also, the novel strain stabilizes intestinal microflors by inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain or a culture thereof is useful in pharmaceutical, feed, food, and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:PROBIONIC CO LTD
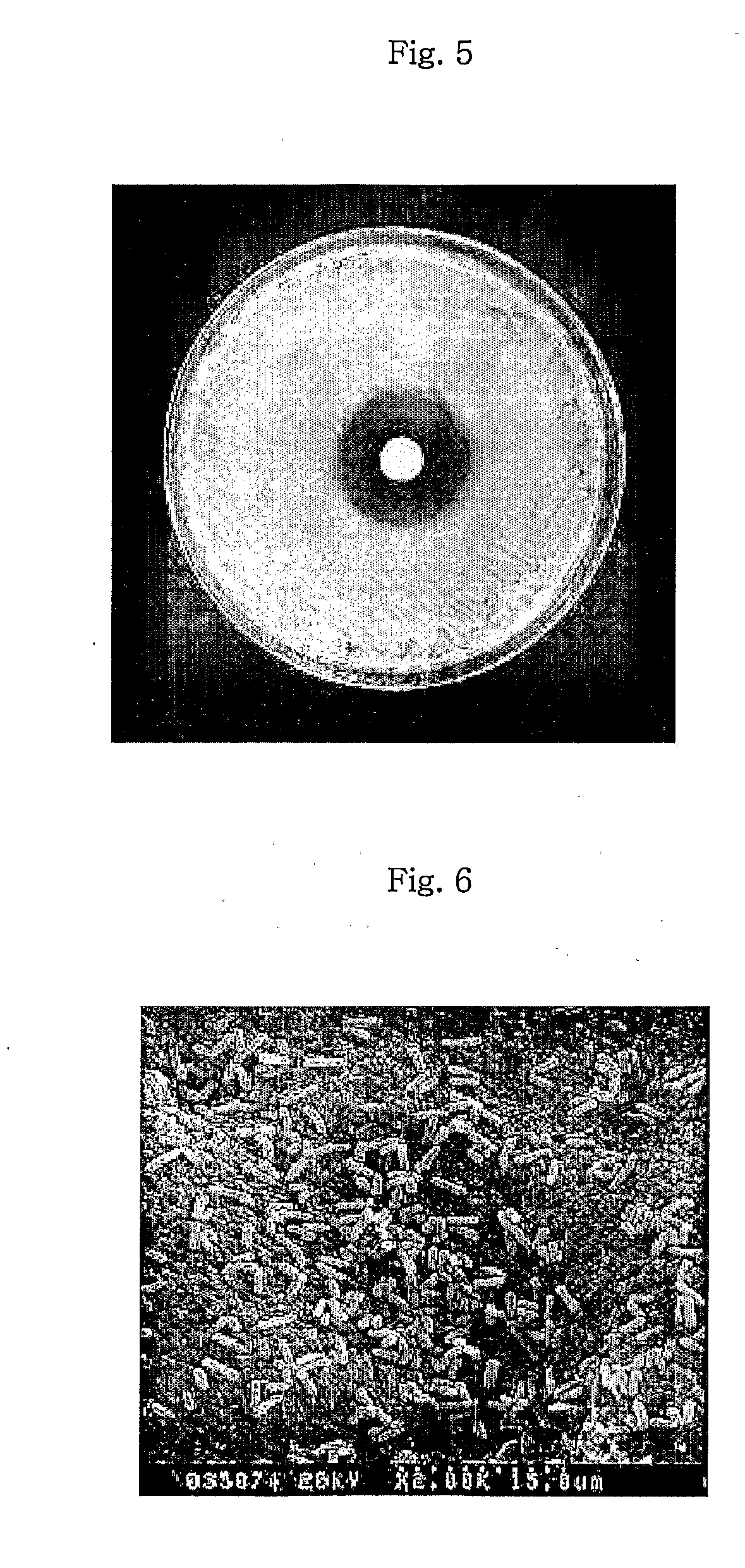
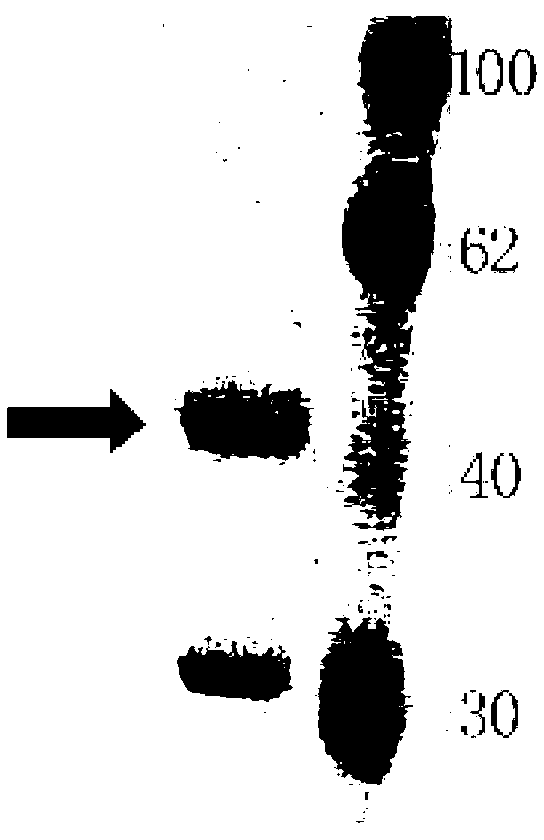
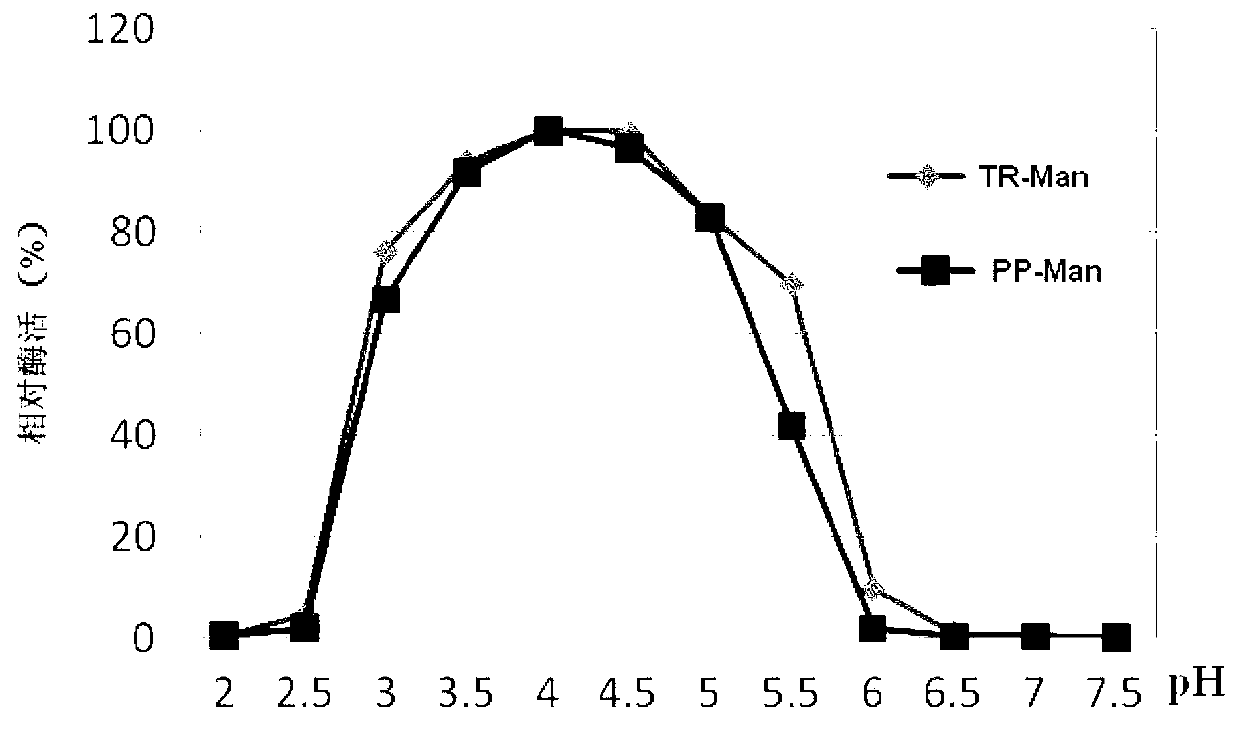
Mannose
The invention relates to a novel mannose, an amino acid sequence of which is SEQ ID NO: 1. The mannose is respectively transferred to trichoderma reesei and pichia pastoris to form a recombined expression engineering strain. The invention provides a novel mannose gene, and respectively constructs pichia pastoris engineering bacteria and trichoderma reesei engineering bacteria for recombining and expressing the gene. The optimal action pH for generating the mannose by the pichia pastoris engineering bacteria and trichoderma reesei engineering bacteria is 4.5, and the optimal action temperature is 60 DEG C. The mannose provided by the invention is acid-resistant, heat-resistant, can be extensively used as a feed additive, and can effectively improve the utilization rate of the feed, so that the usage amount of feed in breeding is reduced, the gain resources and breeding cost are saved, and the productivity effect is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
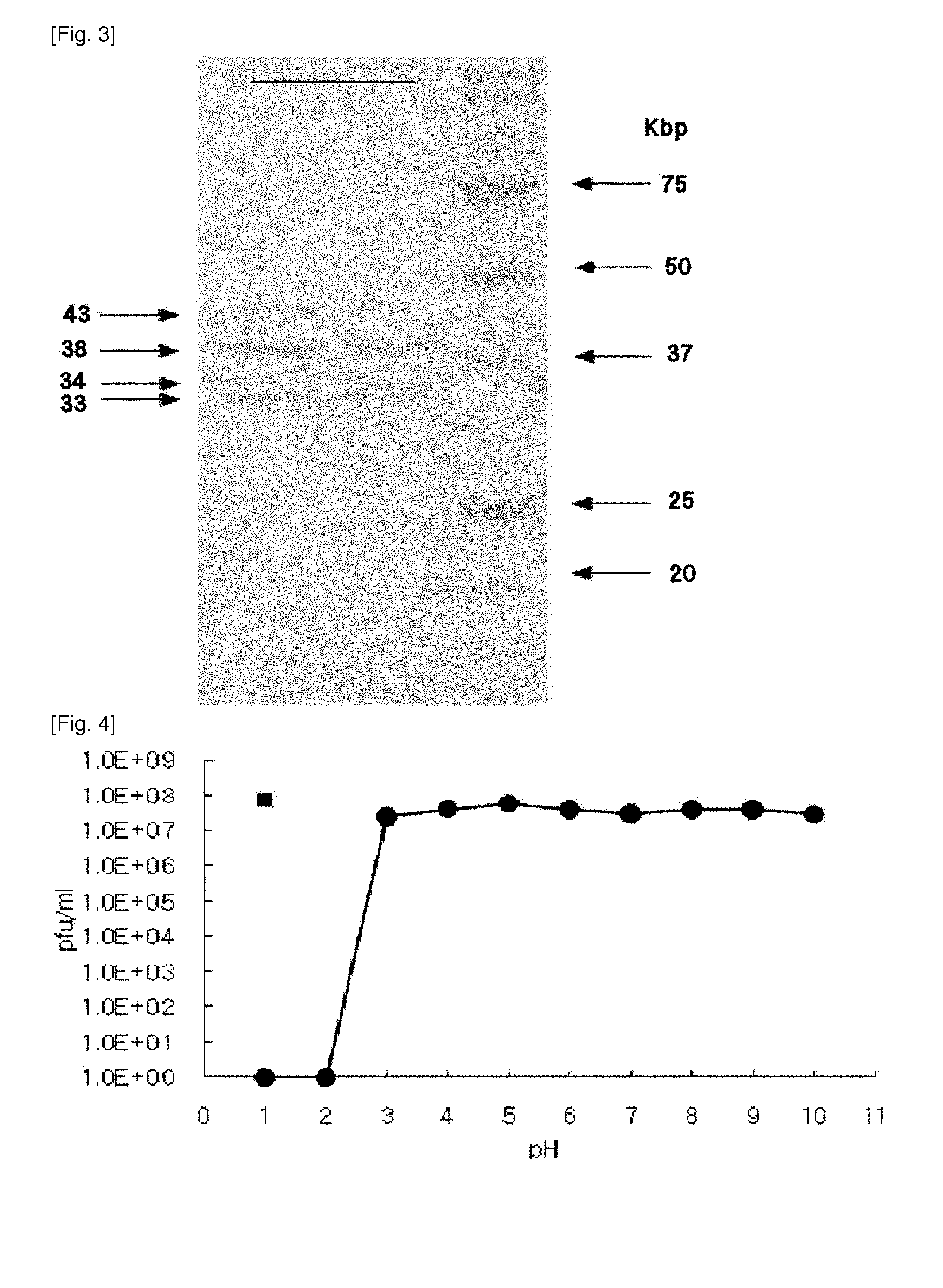
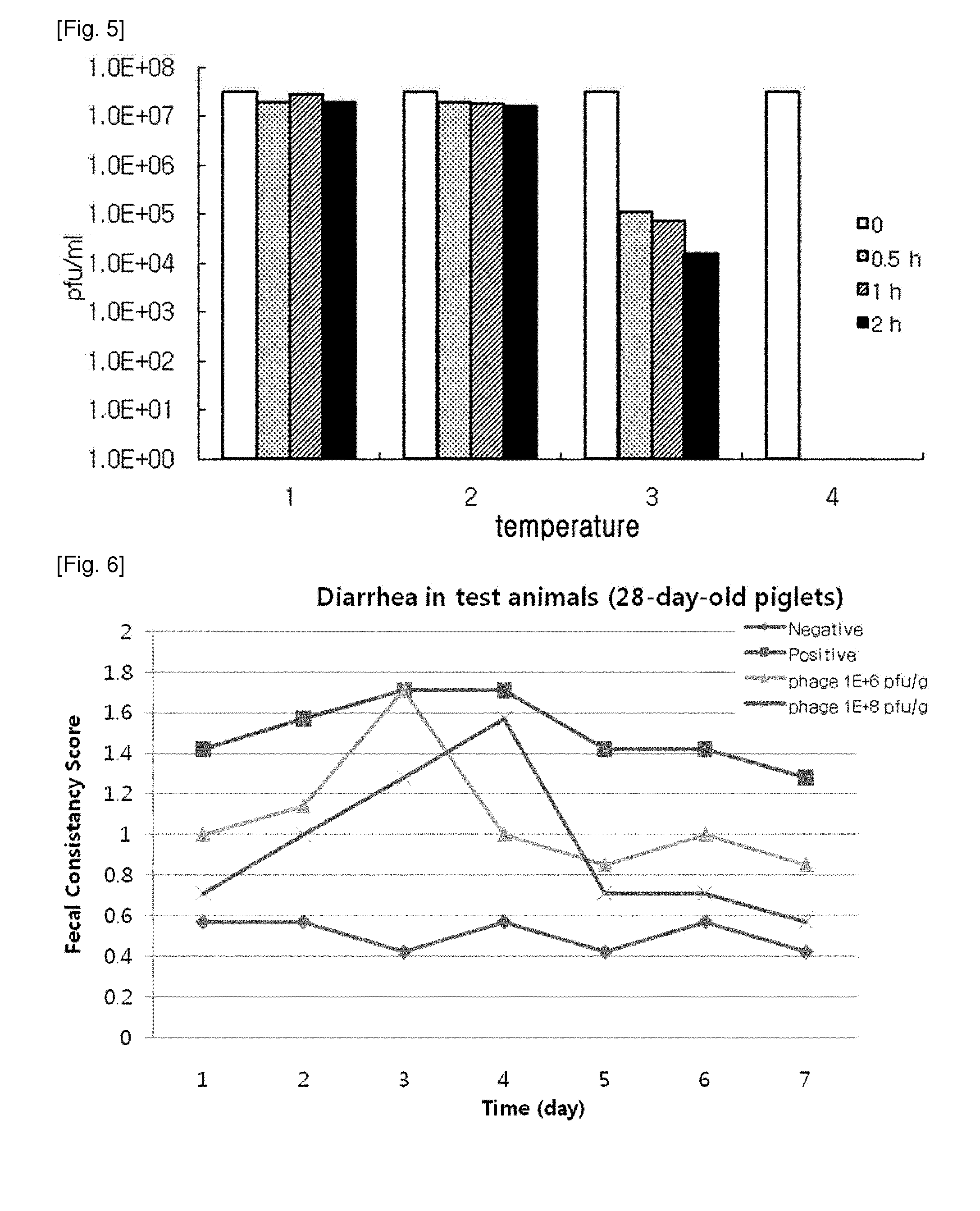
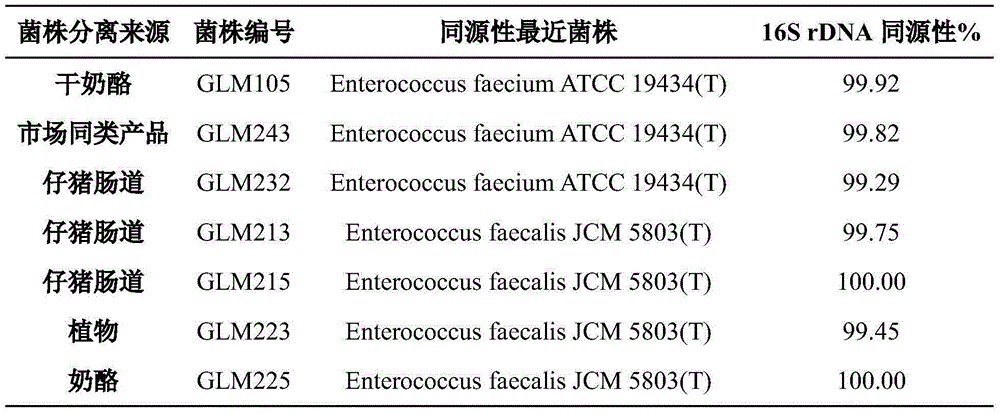
Novel isolated bacteriophage having e. coli-specific bactericidal activity and antibacterial composition comprising the same
ActiveUS20140356330A1Good acidExcellent heat-resistanceAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliPhage therapy
The present invention relates to a novel bacteriophage having an E.-coli-specific bactericidal activity, a composition for the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases caused by Enterotoxigenic E.-coli comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, an antibiotic comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, a feed additive composition comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, a sanitizer or cleaner comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, and a method for treating colibacillosis using the bacteriophage. The novel bacteriophage of the present invention has a specific bactericidal activity against pathogenic E. coli, and excellent acid- and heat-resistance. Therefore, the novel bacteriophage can be used for the prevention or treatment of swine colibacillosis, which is an infectious disease caused by pathogenic E.-coli, and can also be widely used in animal feed additive compositions, sanitizers, and cleaners.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Enterococcus faecium, culture medium thereof for high-density solid-state fermentation, and high-density solid-state fermentation method
ActiveCN105132321AExtended shelf lifeHigh concentration of live bacteriaBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyFeed conversion ratio
The invention discloses enterococcus faecium, a culture medium thereof for high-density solid-state fermentation, and a high-density solid-state fermentation method, wherein the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No.11155. Enterococcus faecium has the excellent performances of inhibiting bacteria, resisting acid and cholate, and the like, is tolerant to low moisture, and has relatively long shelf life under solid state fermentation condition. The culture medium contains wheat bran, bean pulp, cane molasses, activated carbon, calcium carbonate and beta- cyclodextrine. In the preparation technology, lactobacillus is inoculated into the culture medium for fermentation, and then drying is carried out at 45-65 DEG C, and thus obtaining a fermentation product. Compared with the like enterococcus faecium strains, the strain and the fermentation product provided by the invention have the advantages of high concentration of viable organisms, long shelf life and the like. The solid-state fermentation product of the strain provided by the invention can significantly improve the daily gain, the survival rate and the feed conversion ratio of nursery pigs, is obvious in economic benefit, and can be taken as a feed additive.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GLAM BIOTECH
Method for preparing high-viscosity sodium carboxymethylcellulose with apple residue
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is a cellulose ether product which currently enjoys the most attention, has a wide application range and can be conveniently used. The sodium carboxymethyl cellulose can form high-viscosity gel and solution and has properties such as adherence, thickening, flowing, emulsification and dispersion, shaping, water holding, colloid protection, film shaping, acid tolerance, salt tolerance and suspending, so the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is widely applicable in the production of fields such as food, medicines, daily chemicals, petroleum, paper making, textiles and buildings. For a long time, the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is prepared with cotton linter as material, so the cost is high. If apple pomace can substitute cotton to prepare the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, the cost of the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose can be reduced. The present invention uses the apple pomace as material to prepare the high-viscosity sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, so, not only is the cost reduced, but also waste can be utilized, so that the value of the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose can be increased.
Owner:吴茂玉 +2
Acid resistant medium temperature alpha-amylase and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses acidproof medium-temperature alpha-amylase and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: A1, amplifying a precursor alpha-amylase gene; A2, performing site-directed mutagenesis on the precursor alpha-amylase; A3, constructing a mutant alpha-amylase expression vector; and A4, transforming bacillus subtilis by using the expression vector. A recombinant strain obtained by the method can be used for industrialized production of an acidproof alpha-amylase mutant. The required acidproof alpha-amylase mutant can be obtained by the following steps of: culturing recombinant cells in a liquid culture medium with selection pressure without induced expression, precipitating supernatant by using ammonium sulfate, dialyzing a precipitate, desalting, adding an allyl dextran S300 gel column, and eluting by using eluent.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
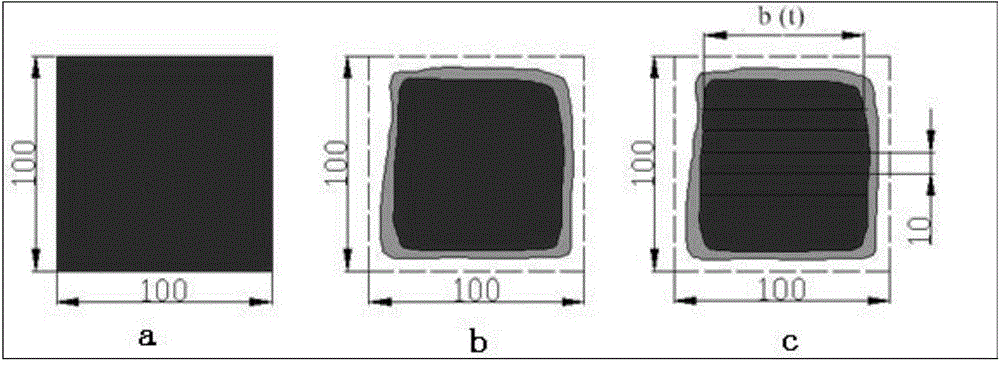
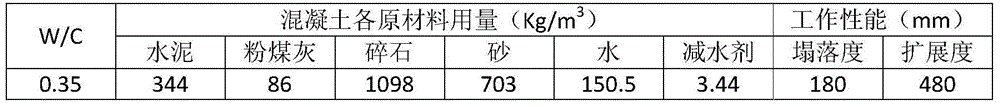
Method for evaluating acid tolerance of concrete
InactiveCN104897562ARapid evaluation of acid durabilityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAcid corrosionCompressive strength
The invention relates to a method for evaluating acid tolerance of concrete. The method includes: 1), preparing concrete strength testing pieces and acidization depth testing pieces; 2), maintaining the testing pieces in a standard maintaining chamber for 26d, dry-maintaining the testing pieces for 2d, disposing the testing pieces into mixed acid liquid for soaking, taking out the testing pieces for drying for 2d after being soaked for 5d each time, measuring compressive strength X (t) of a group of the concrete strength testing pieces and width b (t) of un-corroded parts of a group of the acidization depth testing pieces after four circulating periods of soaking-drying; 3), calculating concrete acid-corrosion-resistant coefficient Q according to the obtained compressive strength X (t); 4), calculating concrete acidization depth d according to the width b (t) of the un-corroded parts; 5), dividing concrete corrosion-resistant grades into I, II, III and IV according to data conditions of Q and d, and evaluating acid-corrosion-resistant grade, acid resistance and suitable environment acting grade of concrete according to the concrete corrosion-resistant grades.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Screening method for anaerobe capable of degrading chlorophenol
InactiveCN1827765AObservation and trainingObserve the growthBacteriaTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSludgeAnaerobic bacteria
The method uses the anaerobic glove case and many modified culture medium to screen the anaerobic bacteria which possesses the highly effective character of degrading chlorophenol and acid resistance. The method comprises the following steps: A. screening the anaerobic particle sludge; B. segregation and purifying bacteria; C. primary screening the anaerobic bacteria degrading chlorophenol; D. second screening: segregation and purifying with the solid-liquid culture medium, until the cell shape being the single thallus. The operation is simple, and the theory meaning and economic value are important. The method provides the theory basis for anaerobic biological treatment process of chlorophenol waste water. The method can be used to separate, screen and culture the chlorophenol degradation bacterium, and provide the good screening method for researching chlorophenol degradation rule and interaction between function bacteria.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
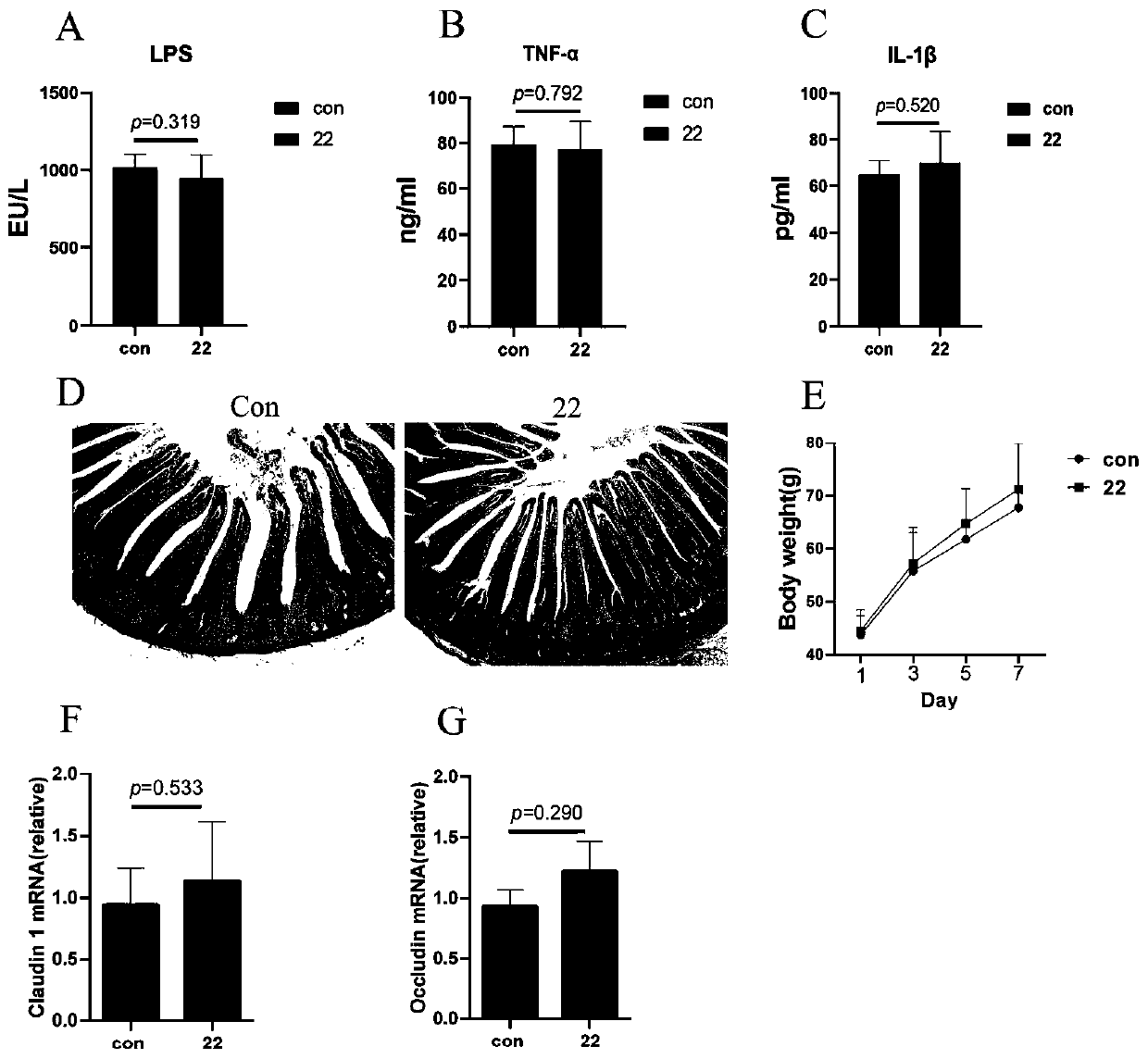
Lactobacillus reuteri 22 and application thereof
ActiveCN110540950AGrowth inhibitionImprove adhesionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInflammatory factorsBiotechnology
The invention discloses a lactobacillus reuteri 22 and application thereof. The lactobacillus reuteri 22 disclosed by the invention is separated from healthy chicken flocks, is classified and named aslactobacillus reuteri, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.17932. By detecting the performance of probiotics, the invention finds that the lactobacillus reuteri 22 has good acid resistance, cholate resistance and adhesion performance, and can inhibit growth of pathogenic bacteria. Through Animal assays, in a healthy physiological state, the lactobacillus reuteri 22 does not influence the level of inflammatory factors, but can increase the number of goblet cells and promote the increase of expression levels of related genes such as compact protein, defensin and lysozyme, can increase thelength of intestinal villi and the depth of crypt, and has the potential of maintaining intestinal mucosa barriers. Therefore, the strain is expected to be developed into probiotics for maintaining achicken intestinal mucosa barrier and guaranteeing green and healthy chicken breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Composite biopolysaccharide magnetic microsphere preparation method
InactiveCN1763126AStrong acid and alkali resistanceSmall swelling coefficientCross-linkSulfanilic acid
The present invention relates to the preparation process of magnetic microballoon of composite polysaccharide. The magnetic microballoon with certain magnetic response property is prepared with tamarind gelatin or sweet wormwood gelatin and chitosan as material, ferroferric iron as magnetofluid, glutaraldehyde as cross-linking agent and o-aminobenzene sulfonic acid as aminating agent. The magnetic microballoon has surface functional radical of -OSO2(C6H4)N-C(CH2)3CHO. The magnetic microballoon of composite polysaccharide has less volume swelling, high acid tolerance and low cost.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
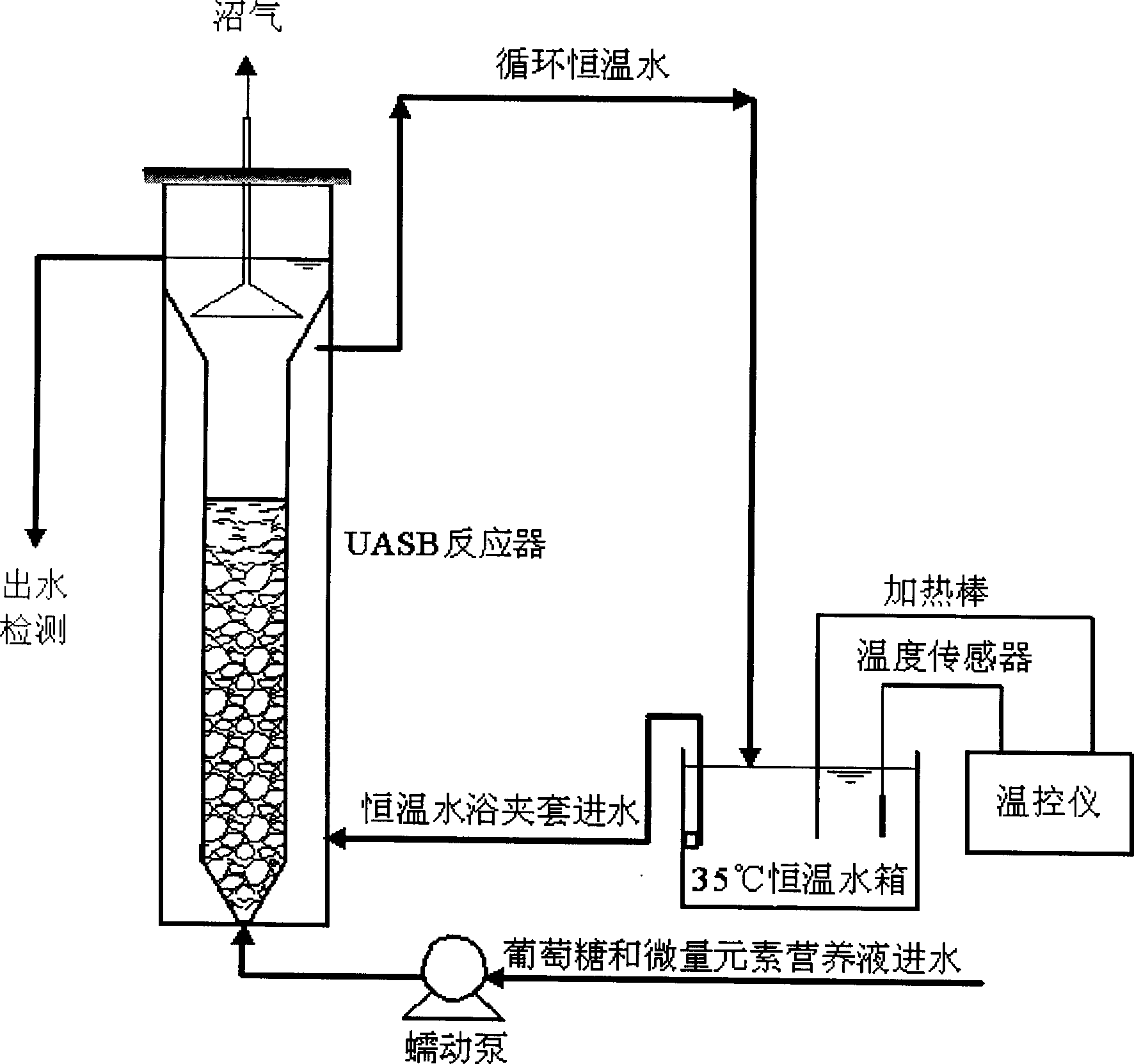
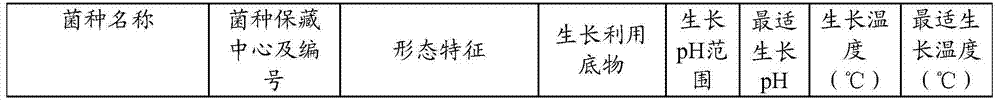
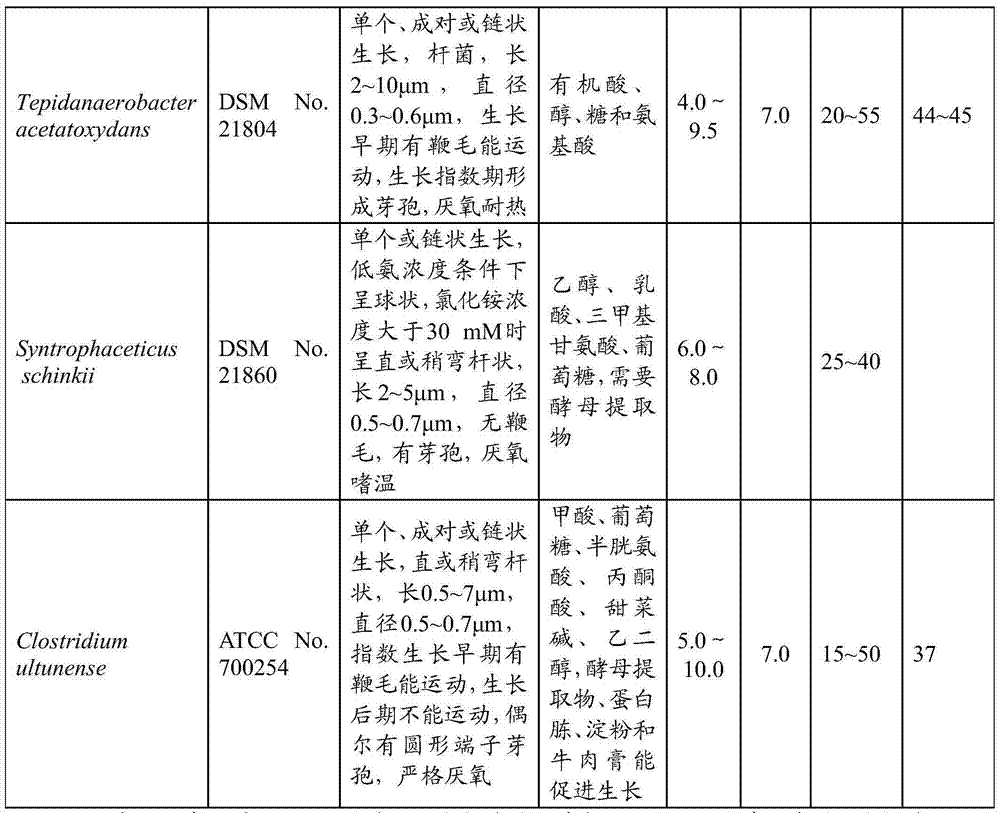
Compound biological agent for enabling acidified marsh gas fermentation system to restore gas production and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103667101AContinuous and stable gas productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMinor elementAcetic acid
The invention relates to a compound biological agent for enabling an acidified marsh gas fermentation system to restore gas production and a preparation method thereof. The compound biological agent contains acidophilus acid-resistant methane-producing bacteria, syntrophic acetic acid oxidation bacteria and minor elements. The compound biological agent enables an acidified marsh gas fermentation system to quickly restore normal gas production without adding alkaline substances or performing massive material discharging or changing, thus ensuring continuous stable gas production of the marsh gas fermentation system. The invention also provides a preparation method of the compound biological agent, which comprises the following steps: under anaerobic conditions, mixing a mixed bacterium solution of acidophilus acid-resistant methane-producing bacteria and a mixed bacterium solution of syntrophic acetic acid oxidation bacteria to obtain a compound bacterium solution, concentrating until the total concentration of cells of the acidophilus acid-resistant methane-producing bacteria and the syntrophic acetic acid oxidation bacteria is at least 1*10<9> / mL, and then adding the minor elements; and packaging, preserving at low temperature, and preparing into the liquid compound biological agent for enabling an acidified marsh gas fermentation system to restore gas production. A solid agent can be further prepared by stirring and mixing with auxiliary materials and then performing anaerobic drying.
Owner:深圳克格瑞环保生物科技有限公司
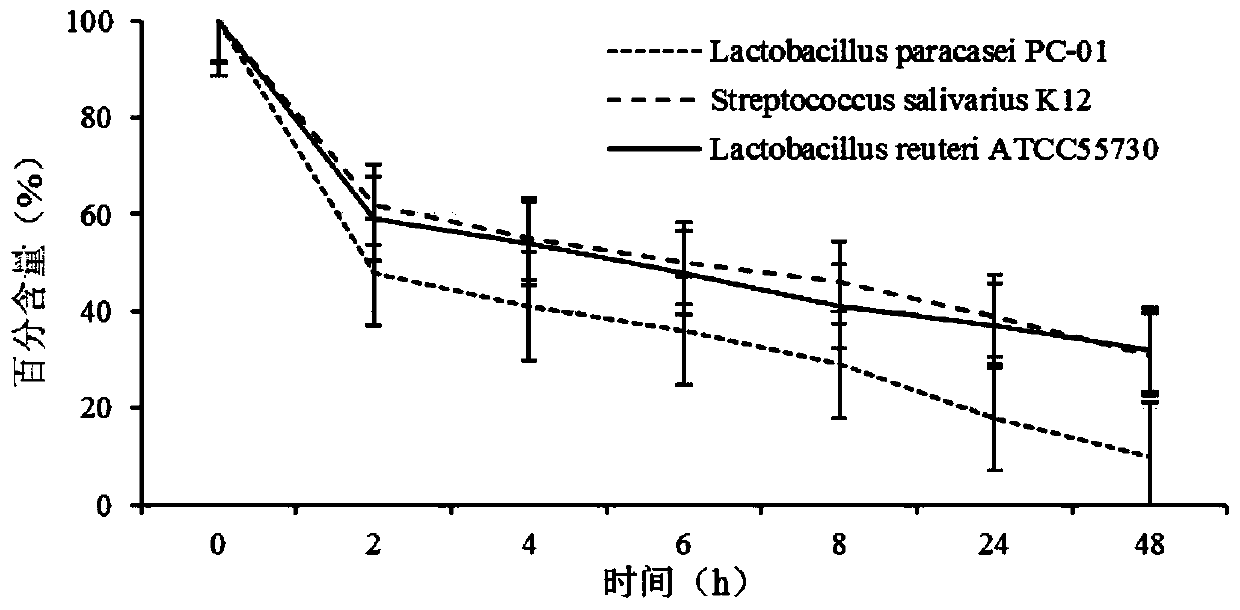
Isolated Lactobacillus paracasei PC-01 for promoting oral health and application of Lactobacillus paracasei PC-01
ActiveCN110257297AImprove imbalanceGood acid toleranceAntibacterial agentsBacteriaOral health promotionTreponema denticola
The application provides a lactobacillus paracasei PC-01 isolated from sour yak milk in Longren Township, Dangxiong County, Lhasa, Tibet, wherein the microbial preservation number of the lactobacillus paracasei PC-01 is CGMCC No.17537. The Lactobacillus paracasei PC-01 can improve oral health flora imbalance, has probiotics with better acid tolerance and bile salt tolerance, has probiotic characteristics, can be directly taken as a preparation for improving oral microecological environment, or as a raw material to prepare a microbial antagonist for pathological states in oral cavity, wherein the pathological state microorganisms comprise at least one of streptococcus mutans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, Genus Prevotella and Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MENGNIU DAIRY IND (GRP) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com