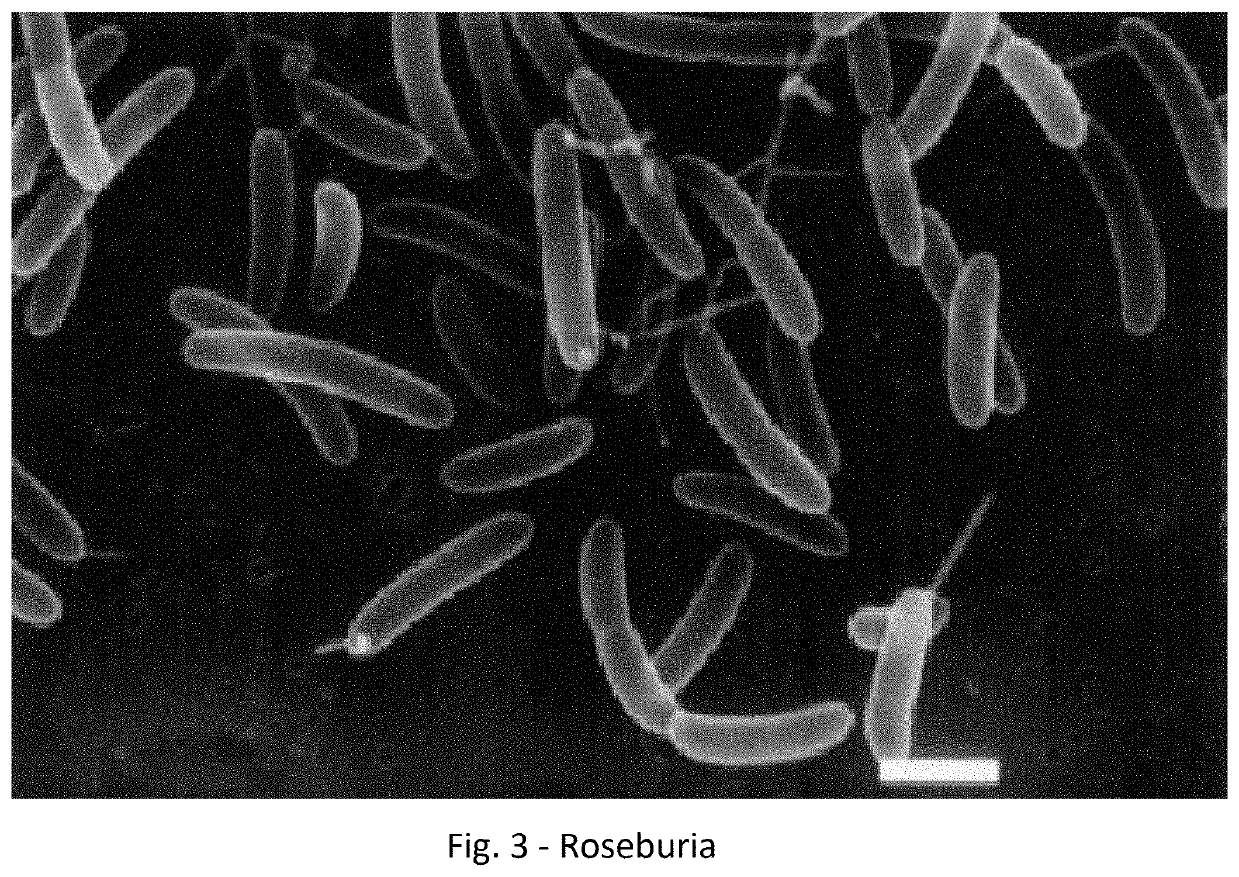
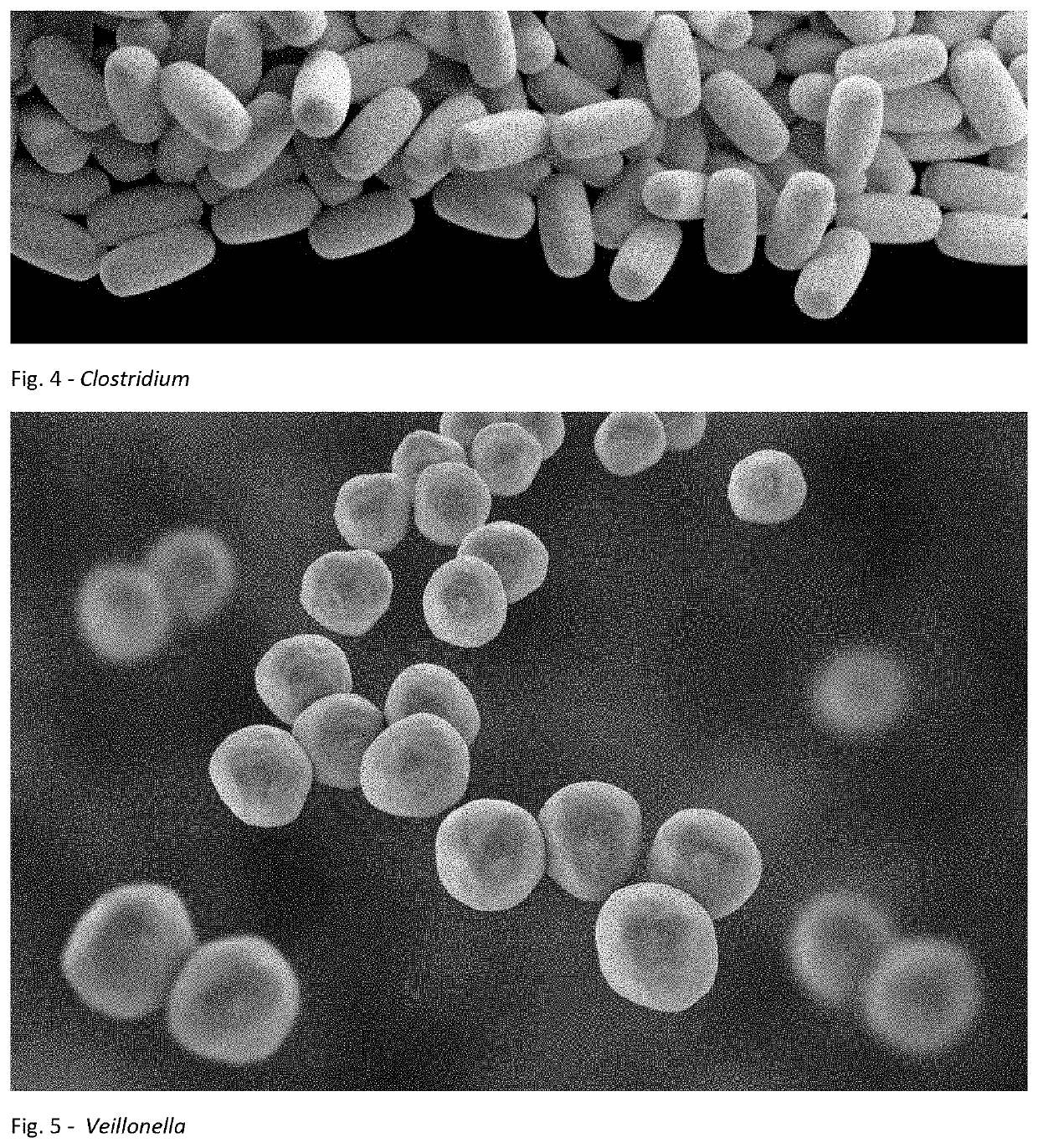
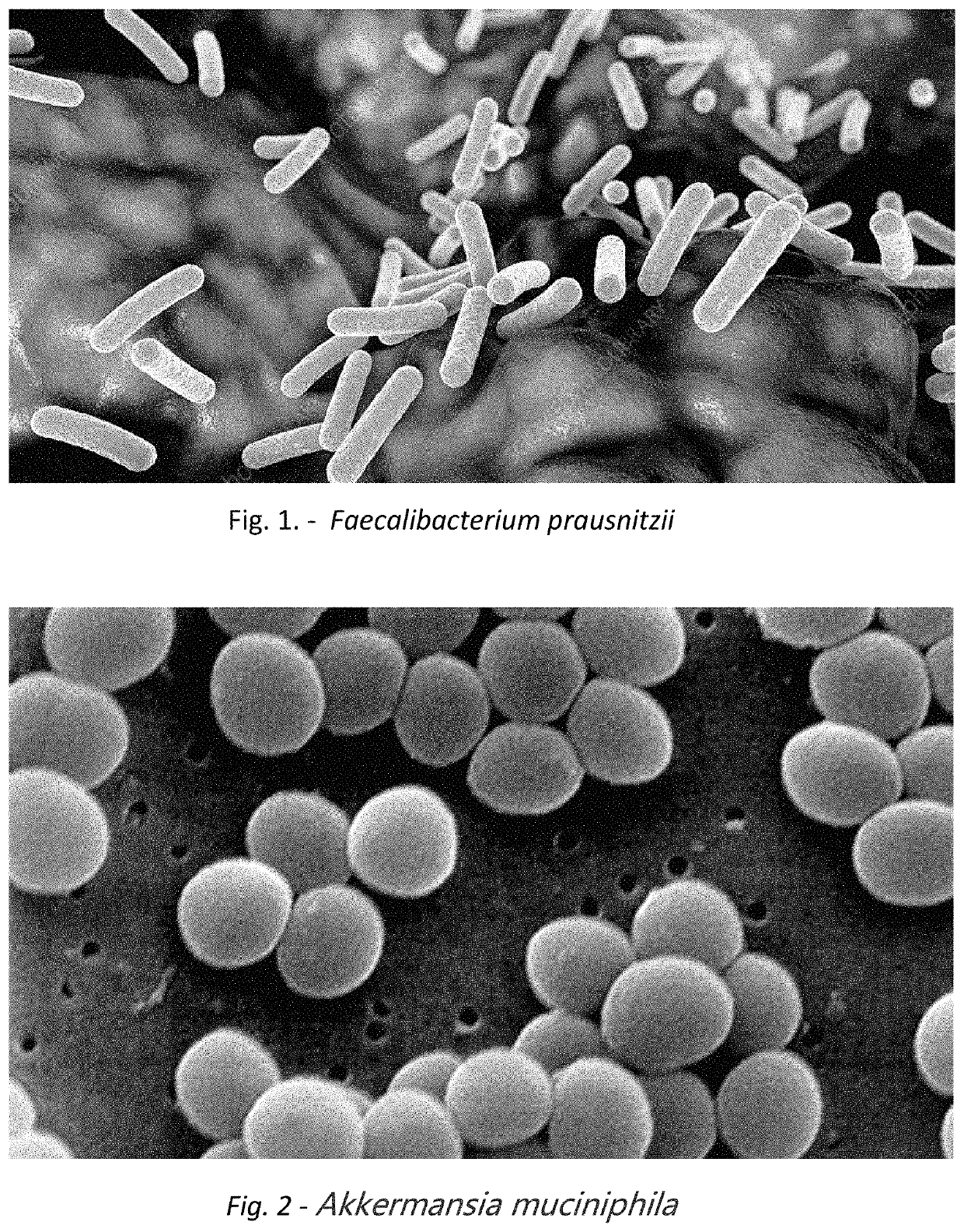
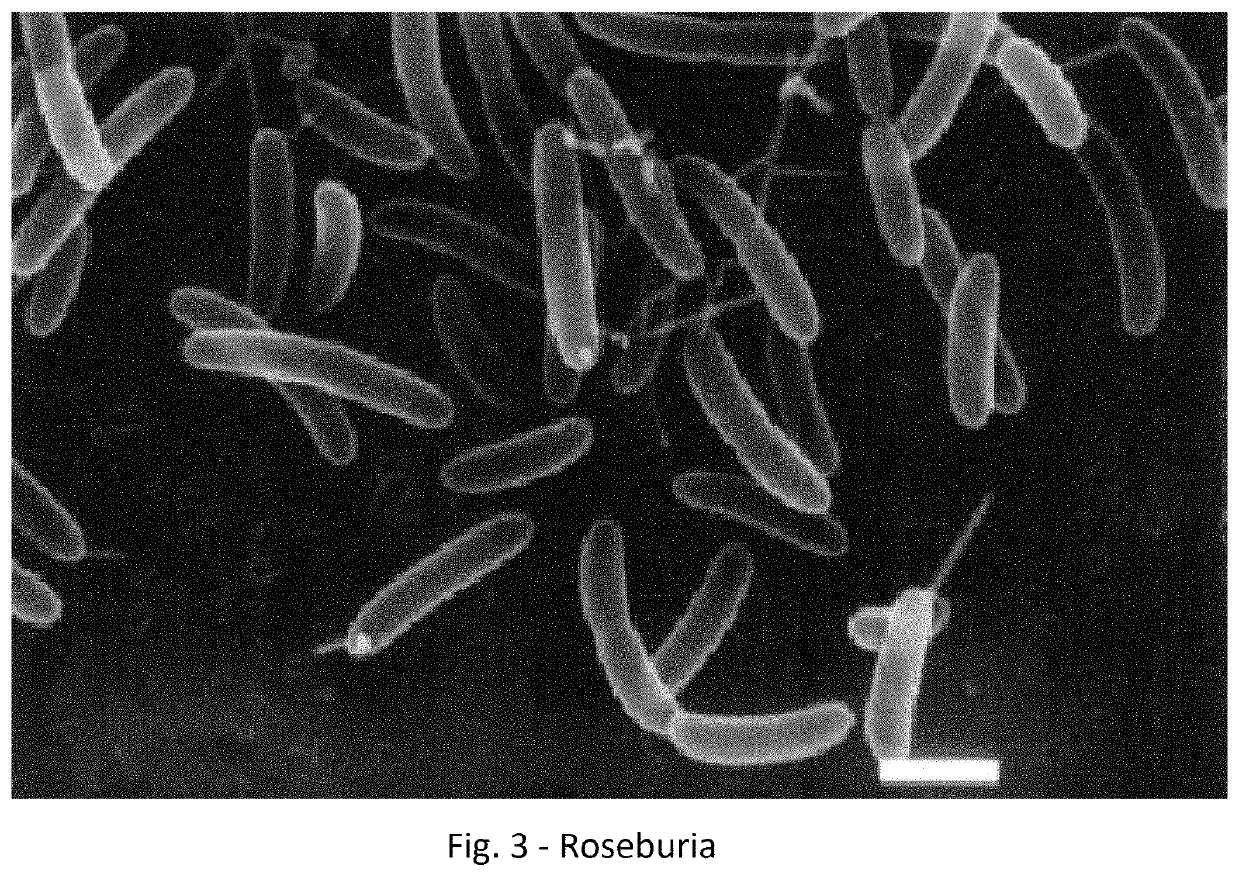
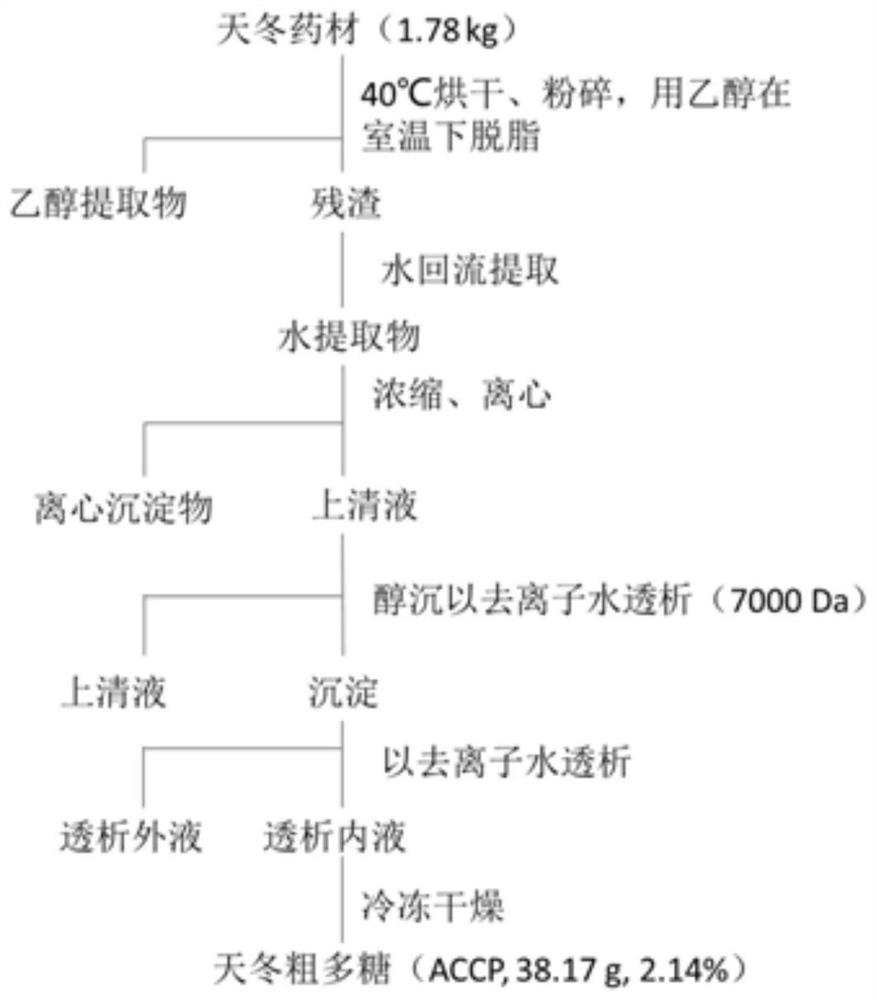
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Prevotella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
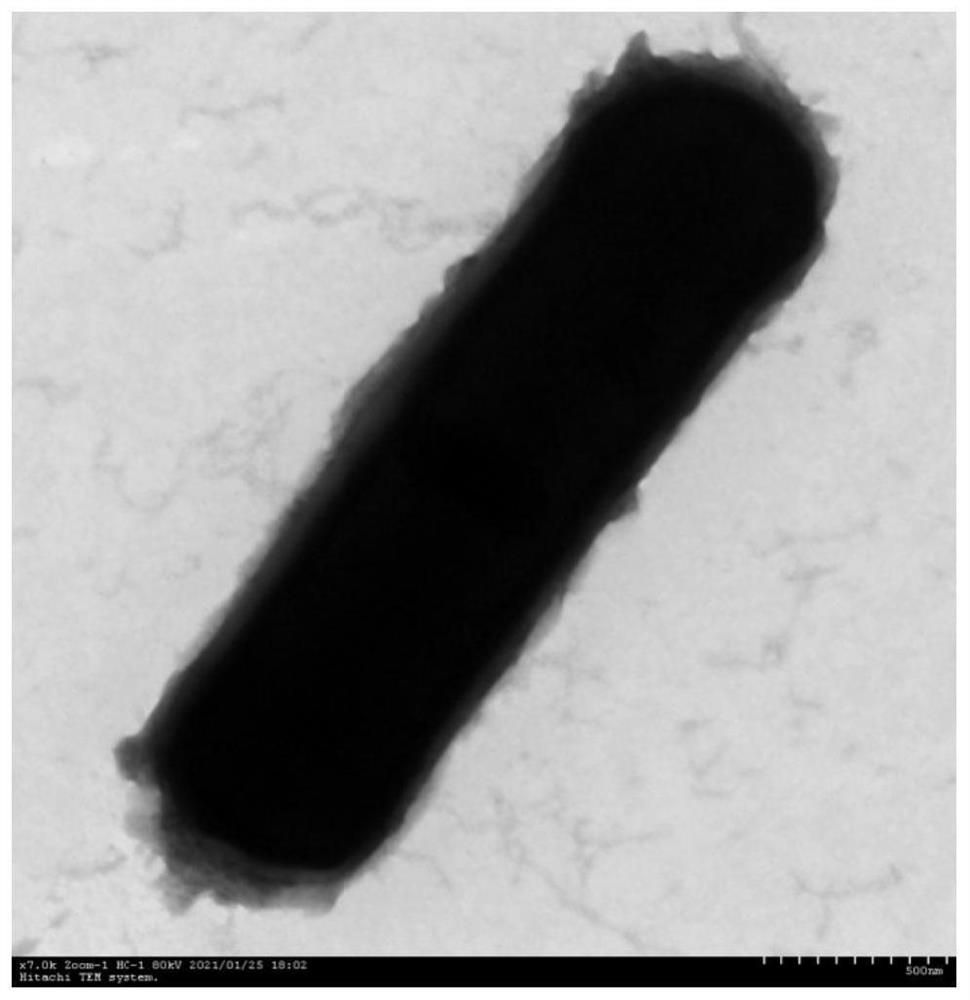
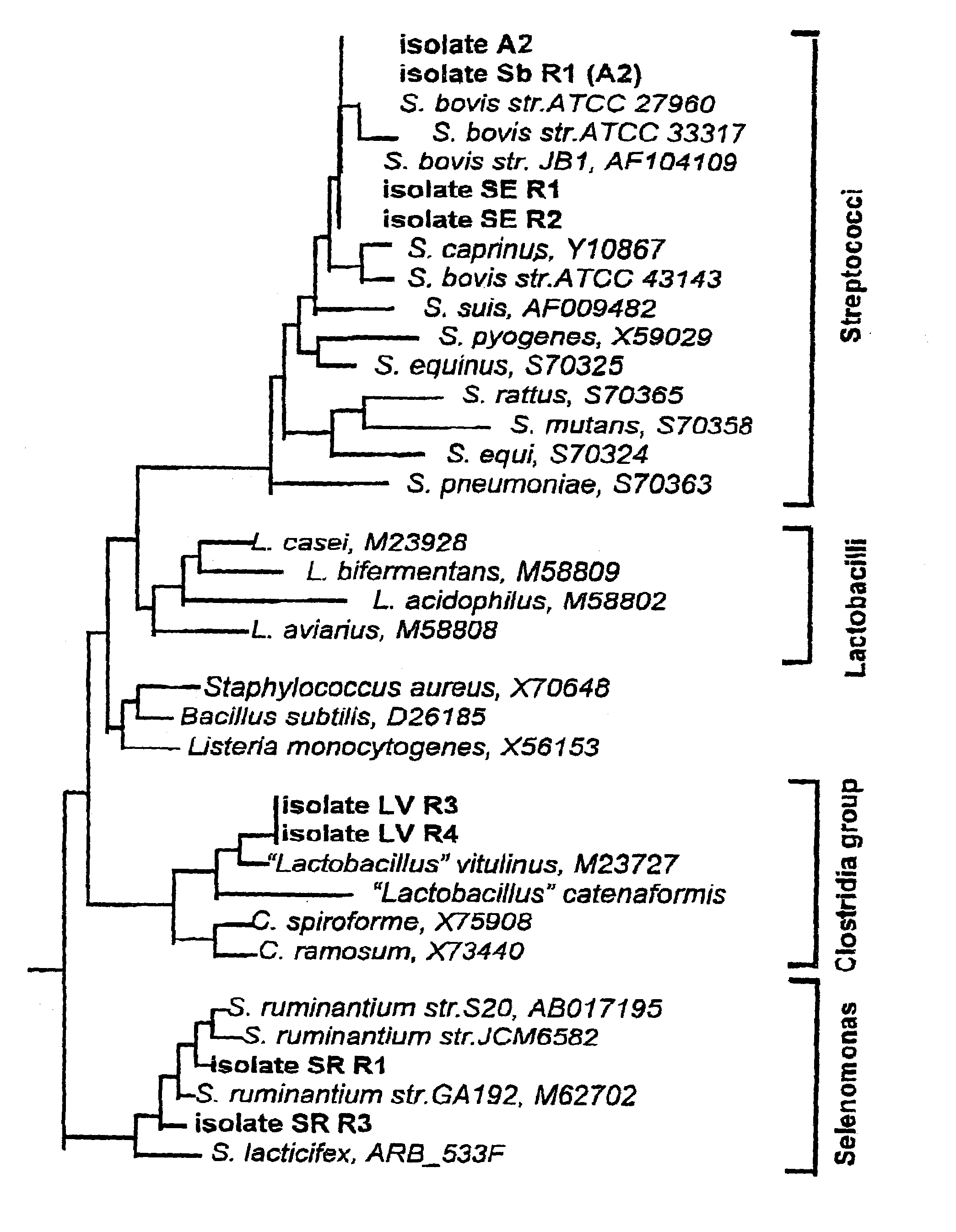
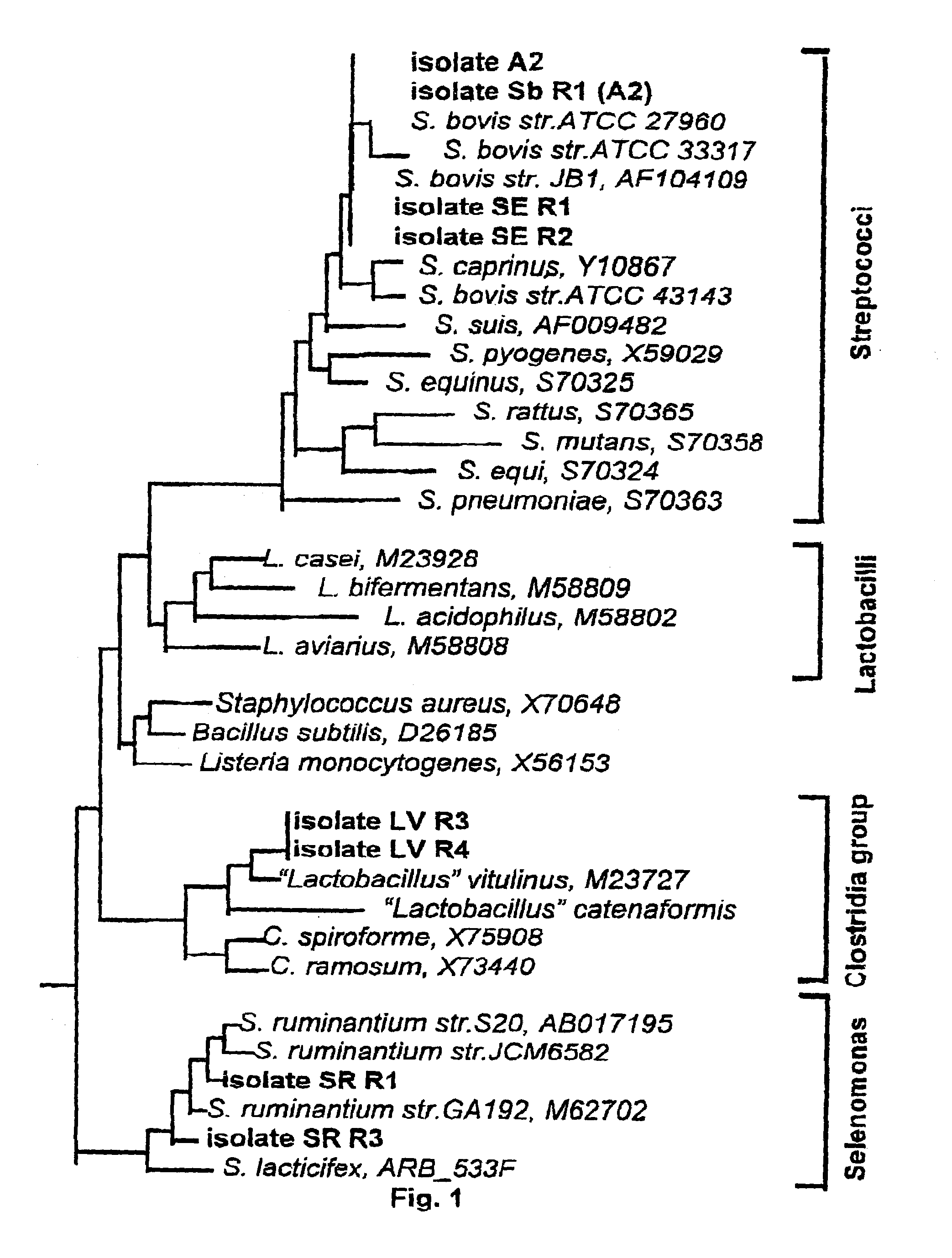
Prevotella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Prevotella spp. are members of the oral, vaginal, and gut microbiota and are often recovered from anaerobic infections of the respiratory tract. These infections include aspiration pneumonia, lung abscess, pulmonary empyema, and chronic otitis media and sinusitis. They have been isolated from abscesses and burns in the vicinity of the mouth, bites, paronychia, urinary tract infection, brain abscesses, osteomyelitis, and bacteremia associated with upper respiratory tract infections. Prevotella spp. predominate in periodontal disease and periodontal abscesses.
Control of acidosis
InactiveUS7011826B1Enhance immune responseBetter establishment of favourable starch utilising organismsOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention relates to a vaccine for the prevention of lactic acidosis in a vertebrate, said vaccine comprising at least one isolated microorganism, or fragment or fragments thereof, wherein said microorganism is capable of producing lactic acid within the gut of said vertebrate, and wherein said microorganism is selected from the group consisting of: Clostridium-like species, Prevotella-like species, Bacteroides-like species, Enterococcus-like species, Selenomonas species, non-dextran slime producing Streptococcus species and non-slime producing lactic acid bacterial isolates.
Owner:SPRUSON & FERGUSON +1
Mental disorder related intestinal tract microbial marker and application thereof
ActiveCN105603066AMonitoring the Effects of InterventionsMaster recoveryNervous disorderBacteriaBacteroidesAfter treatment
The invention discloses a mental disorder related intestinal tract microbial marker and application thereof. The intestinal tract microbial marker refers to one or more combinations of intestinal tract microbial florae of Prevotella and Bacteroides. The invention further discloses application of the mental disorder related intestinal tract microbial marker in preparing reagents for diagnosing mental disorders and methods for screening food, probiotics or drugs capable of intervening with mental disorders. Particularly, the methods include comparing proportion of microbial florae of Prevotella to microbial florae of Bacteroides before and after treatment or interference of the food, probiotics or drugs and / or comparing relative quantity of microbial florae of Prevotella and microbial florae of Bacteroides in feces specimens.
Owner:金锋 +1
Strain marker for assisting COVID-19 diagnosis and application thereof
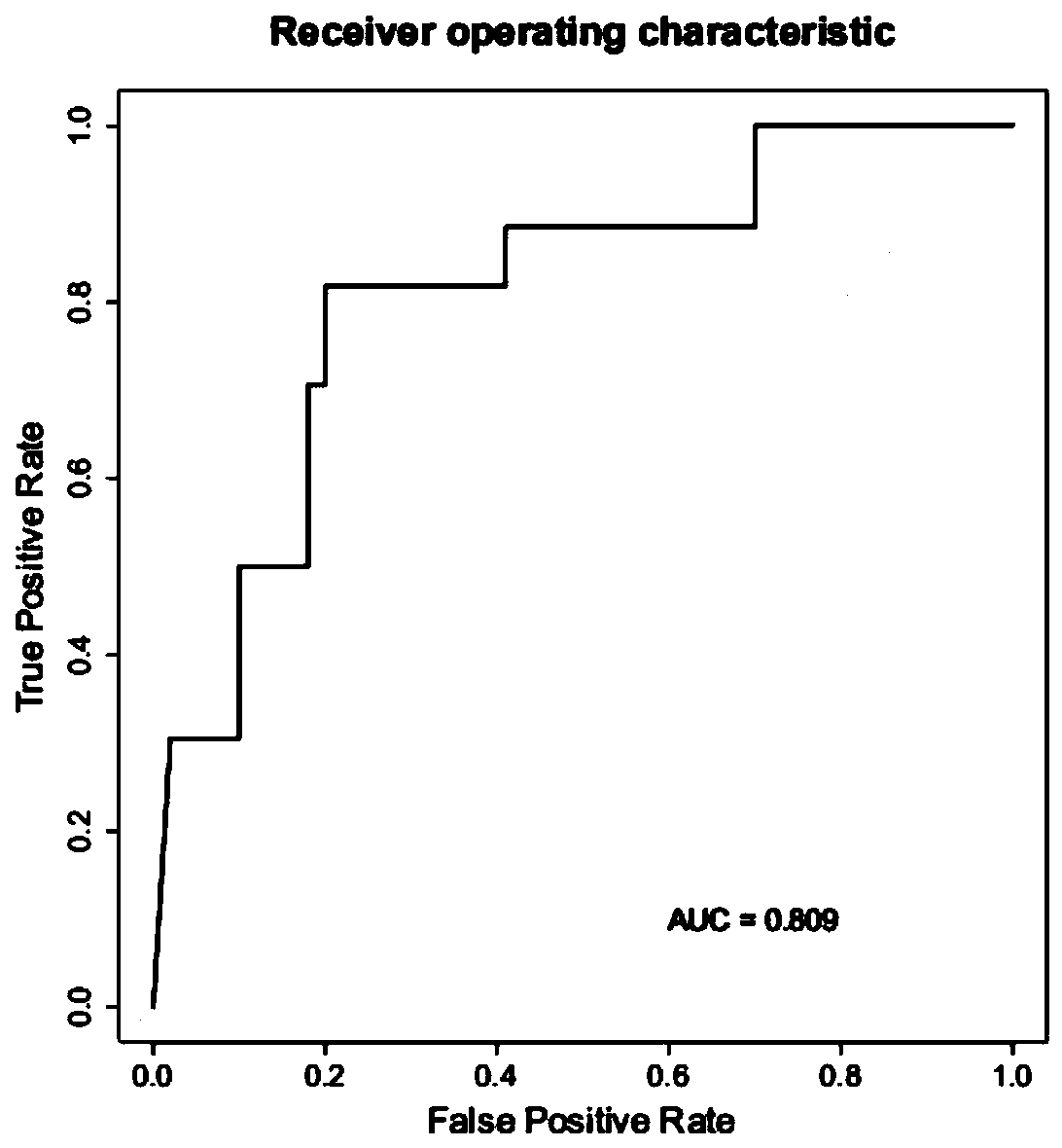
ActiveCN111378788AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesMake up for the defect of false negative testMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPrevotella nigrescensAggregatibacter
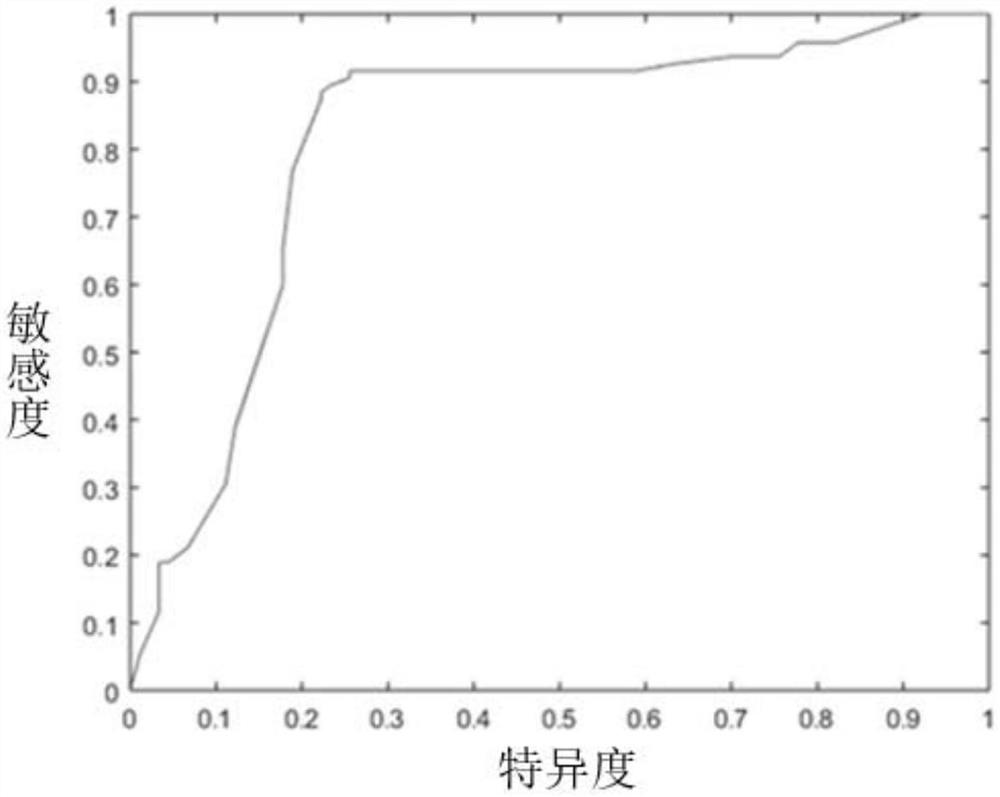
The invention relates to a strain marker for assisting COVID-19 diagnosis and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of pathogenic microorganism infection detection. The strain markercomprises at least one of haemophilus parainfluenzae, propionibacterium, veillonella atypica, aggregatibacter segnis, alloprevotellatannerae, campylobacter showae, fusobacteria, fusobacterium nucleatum, fusobacterium periodonticum, gemella sanguinis, haemophilus parahaemolyticus, haemophilus sputorum, porphyromonas gingivalis, prevotella intermedia, prevotella multifurmis, prevotella nanceiensis,prevotella nigrescens and prevotella timonensis. A prediction model ROC obtained by the strain marker has an AUC value being 0.910, and the strain marker can be used for assisting diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, so that the diagnosing performance on COVID-19 pneumonia can be improved, and the defect that viral nucleic acid detection is false negative can be overcome to a certain extent.
Owner:广州微远医疗器械有限公司 +4
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being
ActiveUS10086018B2Preventing cell entryReduce the amount requiredBacteria material medical ingredientsTetracycline active ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingIntestinal microorganisms
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being
ActiveUS10548761B2Reduce the possibilityEliminate symptomsOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
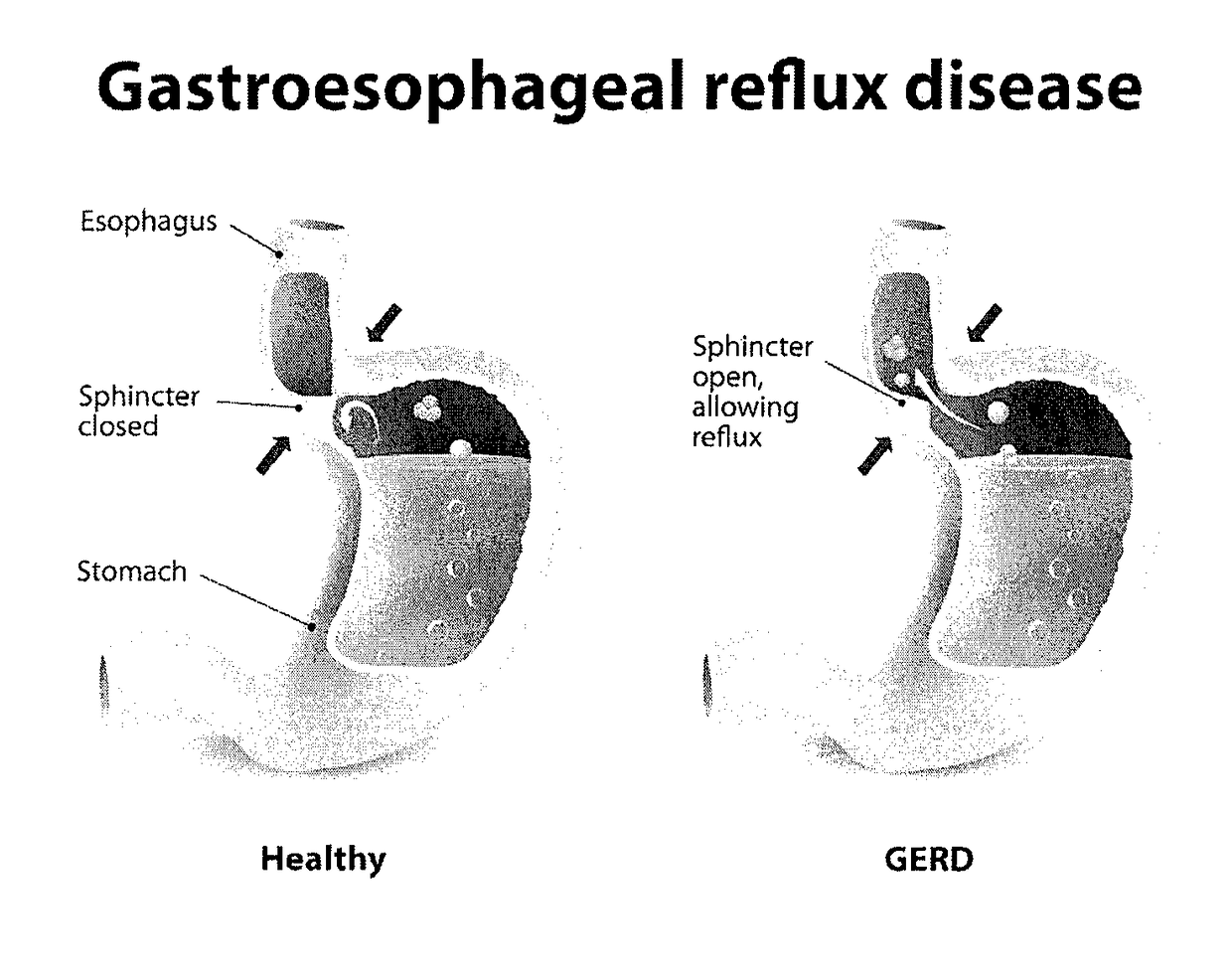
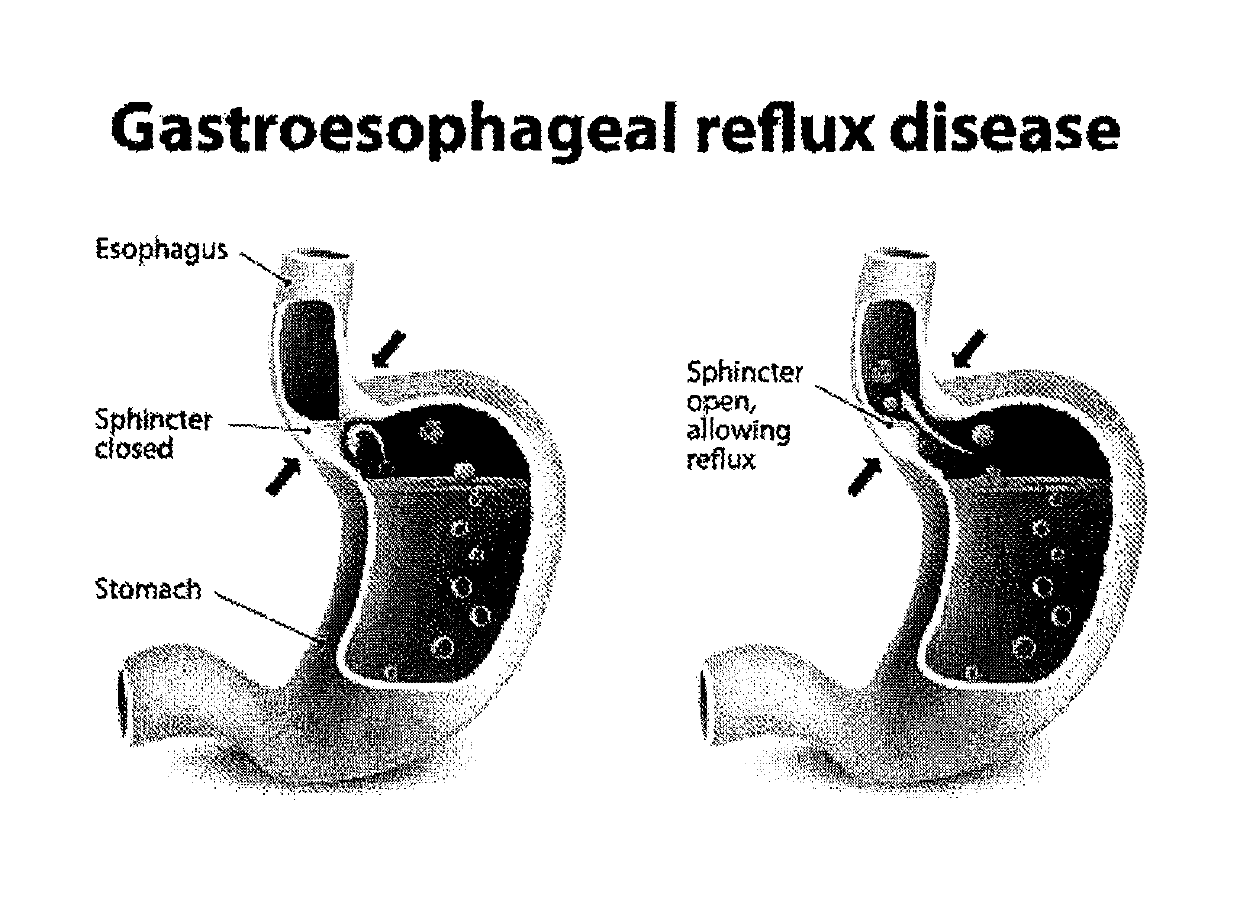
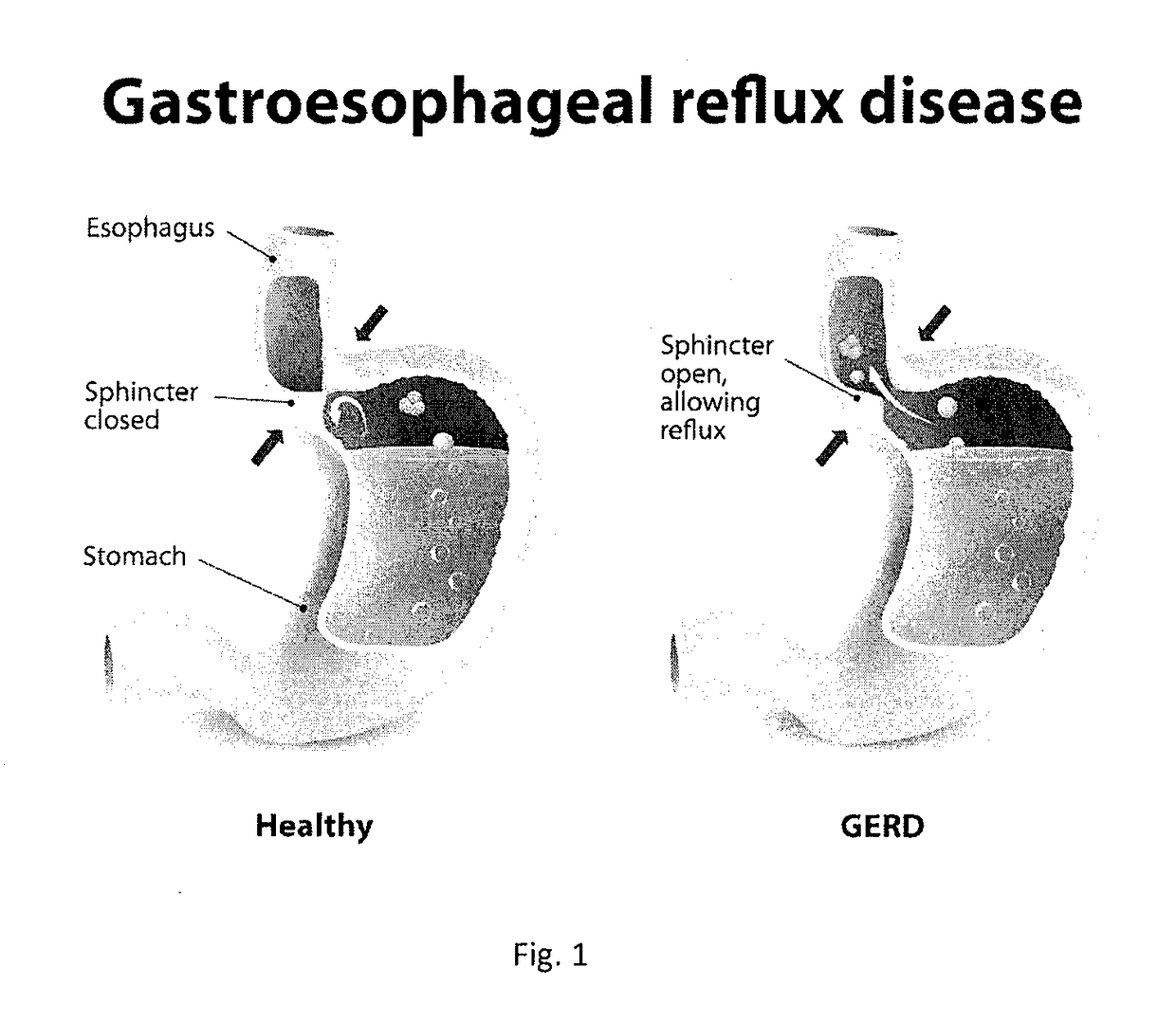
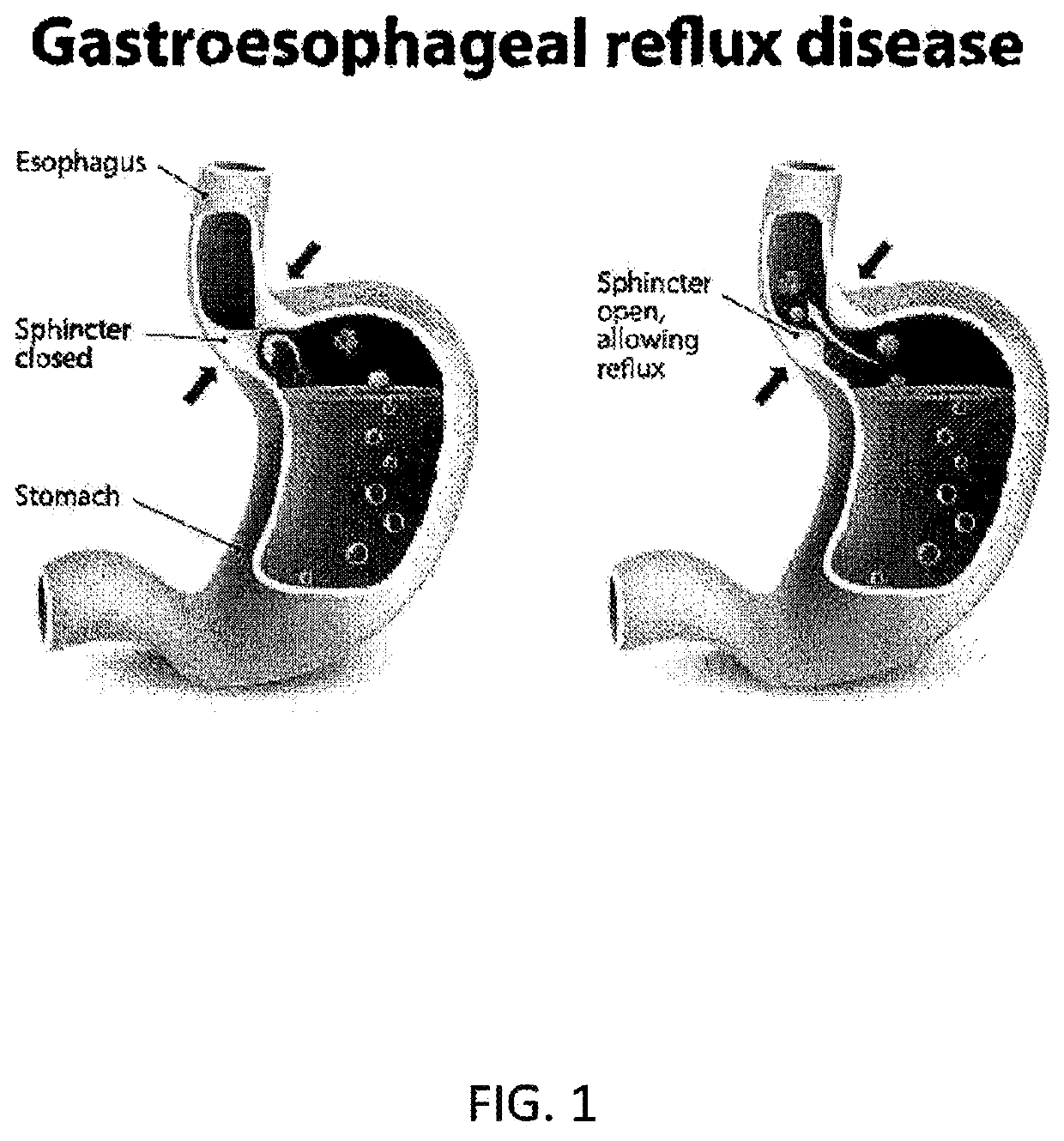
Method and System for Treating Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
ActiveUS20170106025A1Preventing cell entryReduce the amount requiredTetracycline active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsAntibiotic resistanceIntestinal microorganisms
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of GERD includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes in a manner that reduces, if not eliminates, the symptoms of GERD. Certain embodiments employ Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to render H. Pylori more susceptible to certain drugs, including antibiotics, thus addressing the antibiotic resistance otherwise experienced by treating H. Pylori with antibiotics.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Method for reducing the likelihood of developing bladder or colorectal cancer in an individual human being
ActiveUS11026982B2Treatment complicationsAvoiding undesiredAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPrevotellaMogibacterium diversum
A method for treating an individual suffering from one of bladder cancer and colorectal cancer employs a CRISPR system to selectively kill or reduce the numbers of pathogenic bacteria within the individual and the individual is then administered an immune checkpoint inhibitor. In particular embodiments, the pathogenic bacteria is one of E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella bacteria, and the checkpoint inhibitor is selected from the group consisting of nivolumab, pembrolizumab, pidilizumab, AMP-224, AMP-514, STI-A1110, TSR-042, RG-7446, BMS-936559, MEDI-4736, MSB-0020718C, AUR-012 and STI-A1010. Further embodiments include enhancing the growth of a second bacteria in the individual, such bacteria including Akkermansia, Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Enterococcus, Fusobacterium, Lactobacillus, Propionibacterium, Ruminococcus, Veillonella, Prevotella, Escherichia and Streptococcus. Still other embodiments include increasing the levels of Roseburia and / or Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, in the individual's gut microbiome.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Method for treating an individual suffering from a chronic infectious disease and cancer
ActiveUS11213552B2Treatment complicationsAvoiding undesiredAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPseudomonasPrevotella
A method for treating an individual suffering from a chronic infectious disease and who has cancer employs a CRISPR system to selectively kill or reduce the numbers of pathogenic bacteria within the individual and the individual is then administered an immune checkpoint inhibitor. In particular embodiments, the pathogenic bacteria is one of E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella bacteria, and the checkpoint inhibitor is selected from the group consisting of nivolumab, pembrolizumab, pidilizumab, AMP-224, AMP-514, STI-A1110, TSR-042, RG-7446, BMS-936559, MEDI-4736, MSB-0020718C, AUR-012 and STI-A1010. Further embodiments include enhancing the growth of a second bacteria in the individual, such bacteria including Akkermansia, Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Enterococcus, Fusobacterium, Coprococcus, Lactobacillus, Propionibacterium, Ruminococcus, Veillonella, Prevotella, Escherichia and Streptococcus. The CRISPR system may include Cas9, Cpf1 and Cas3, and may be delivered using a bacteriophage.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
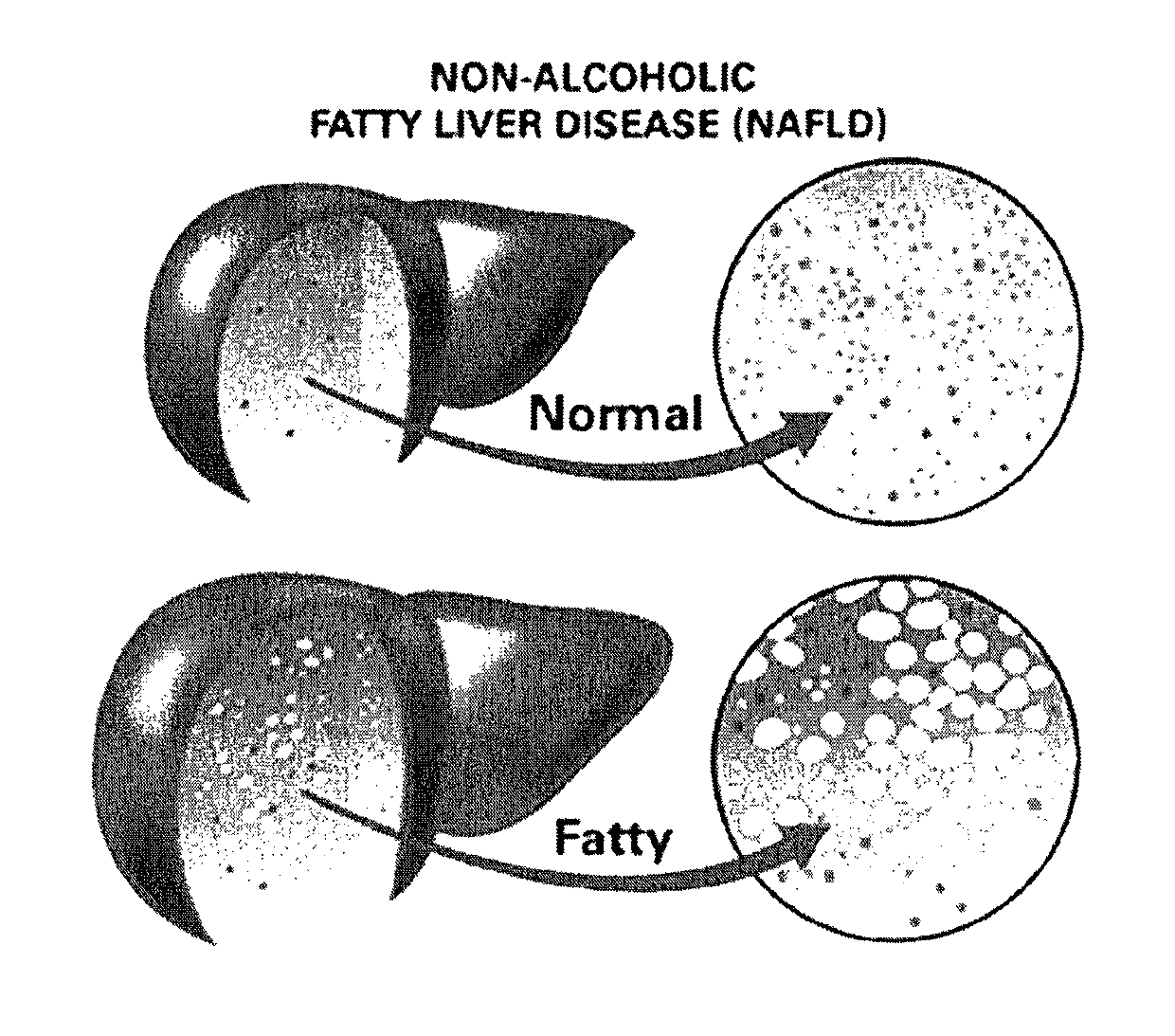
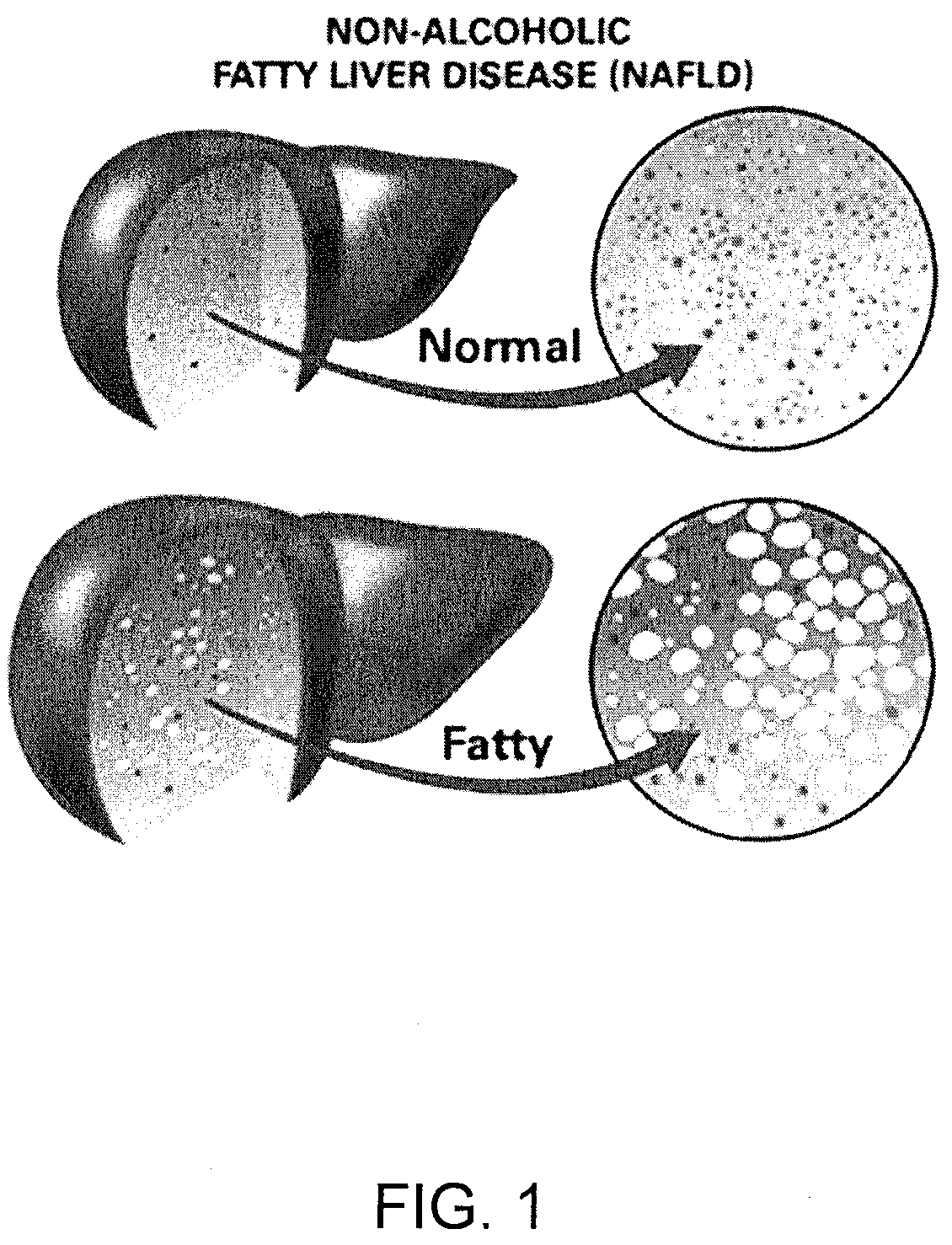
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of developing NASH in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ActiveUS10245288B2Improvements in intestinal dysbiosisReduce intestinal permeabilityUnknown materialsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDiseaseOxidized low density lipoprotein
A method for reducing the likelihood of developing liver cancer in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease that involves providing an individual with an effective amount of a composition of bacteria modified using a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system so that the bacteria is able to produce a therapeutically effective amount of anti-bodies to oxidized low density lipoprotein, with the modified bacteria preferably being from the Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Streptococcus species; and most preferably including L. reuteri bacteria modified using CRISPR-Cas and / or Cpf1 systems so that it is able to survive the conditions in the duodenum and jejunum of the small intestine of a human.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Application of enteric microorganism as marker of bronchial pulmonary dysplasia of premature infant
ActiveCN112831579AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFecesIntestinal microorganisms
The invention discloses an application of an enteric microorganism as a marker of bronchial pulmonary dysplasia of a premature infant. The enteric microorganism is one or more of Klebsiella, Prevotella and Streptococcus. The application comprises the following steps: sequencing a separated intestinal flora nucleic acid sample to obtain a sequencing result, detecting the relative abundance of the intestinal microorganisms in the intestinal flora according to the sequencing result to obtain a relative abundance value, and comparing the obtained relative abundance value of the intestinal microorganisms with a set value, and taking the obtained result as intermediate information to assist in diagnosing the premature bronchial pulmonary dysplasia. The premature infant excrement sample 16SrDNA gene is sequenced through a high-throughput sequencing technology, the relationship between intestinal flora and premature infant BPD occurrence is discussed for the first time, and a reliable basis is provided for prevention and treatment of BPD.
Owner:SOOCHOW UNIV AFFILIATED CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
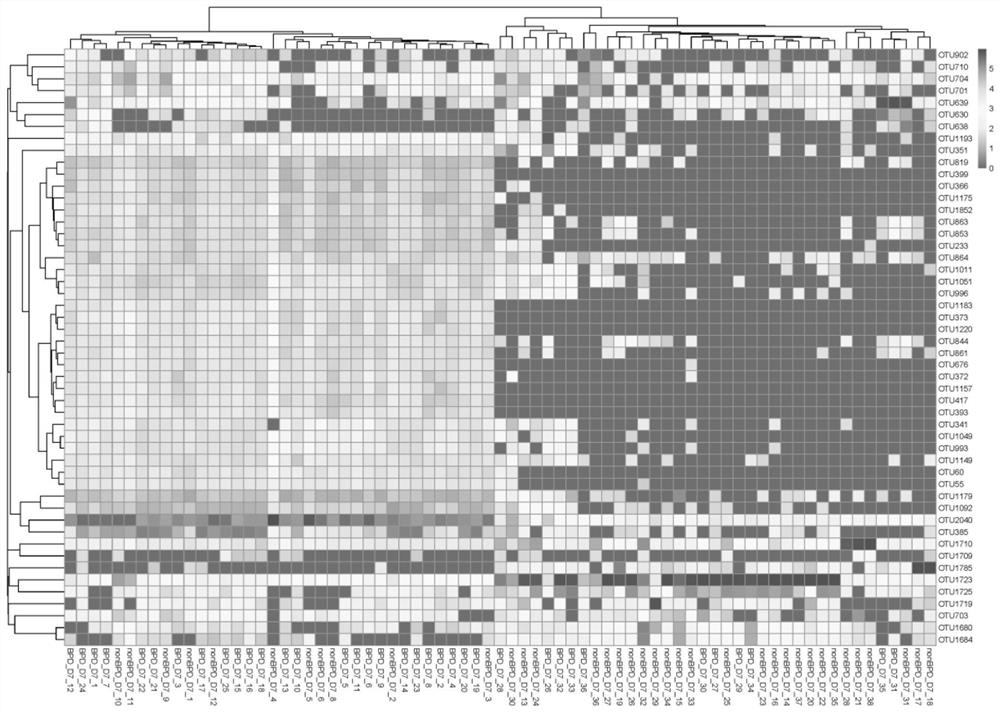
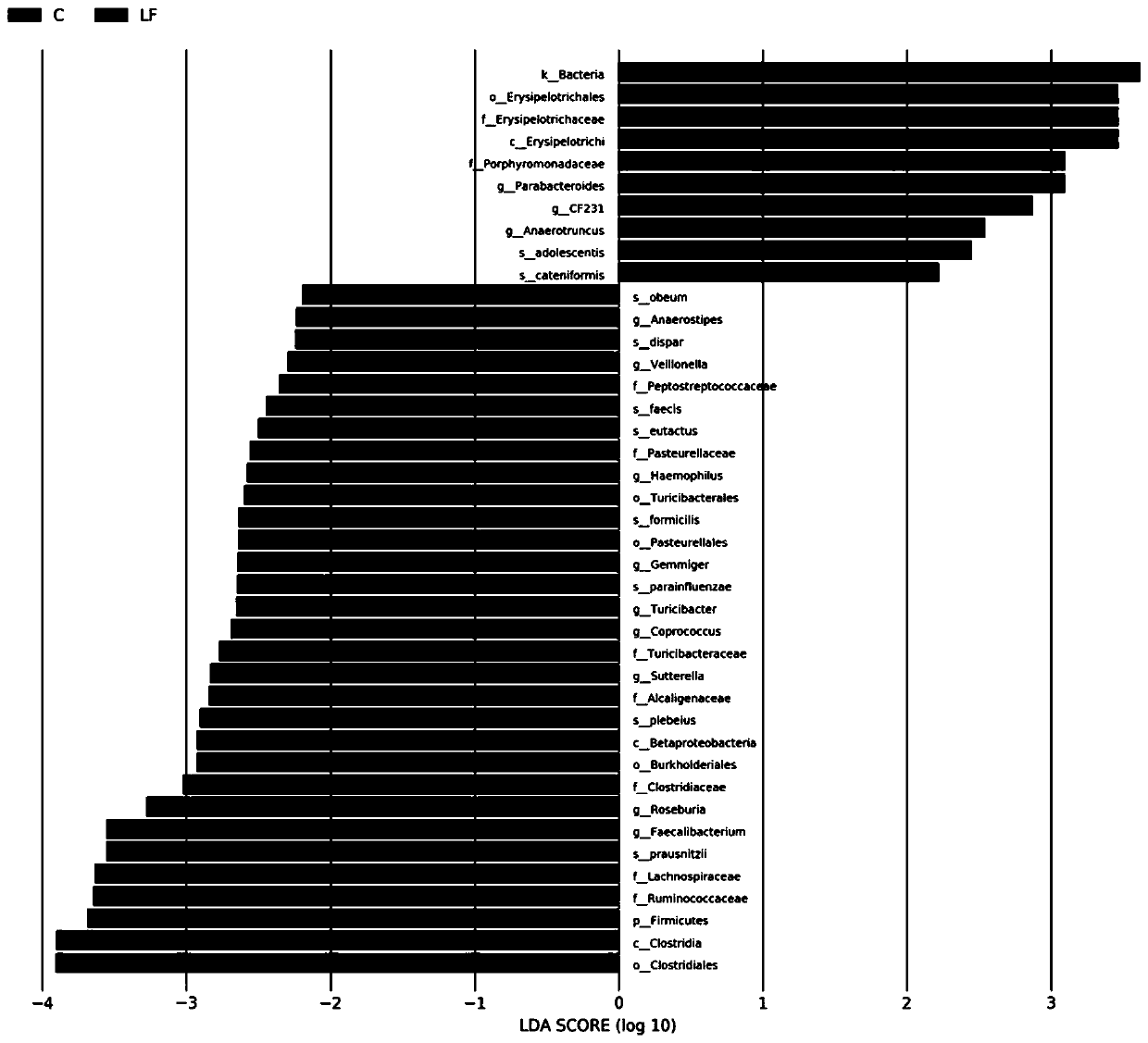
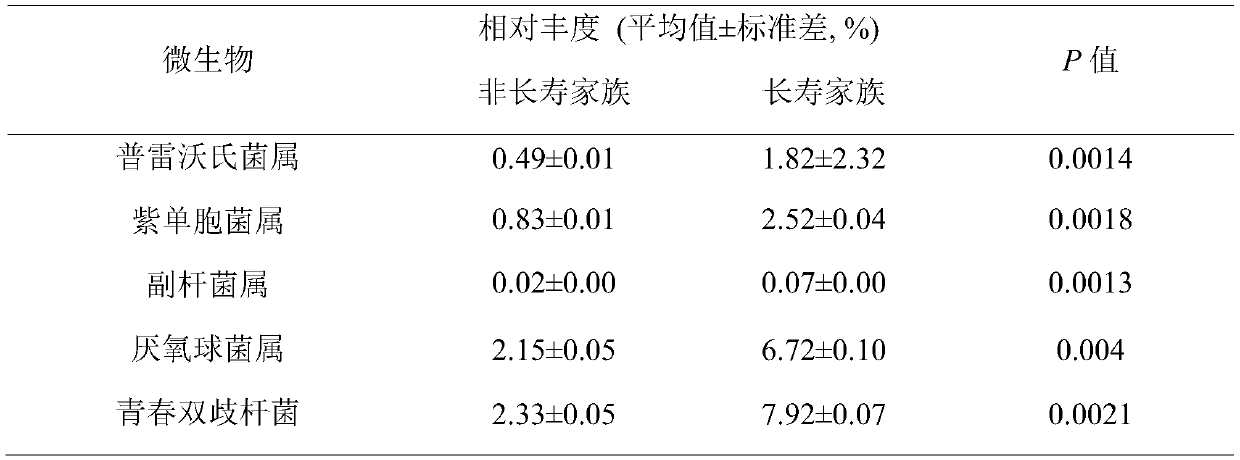
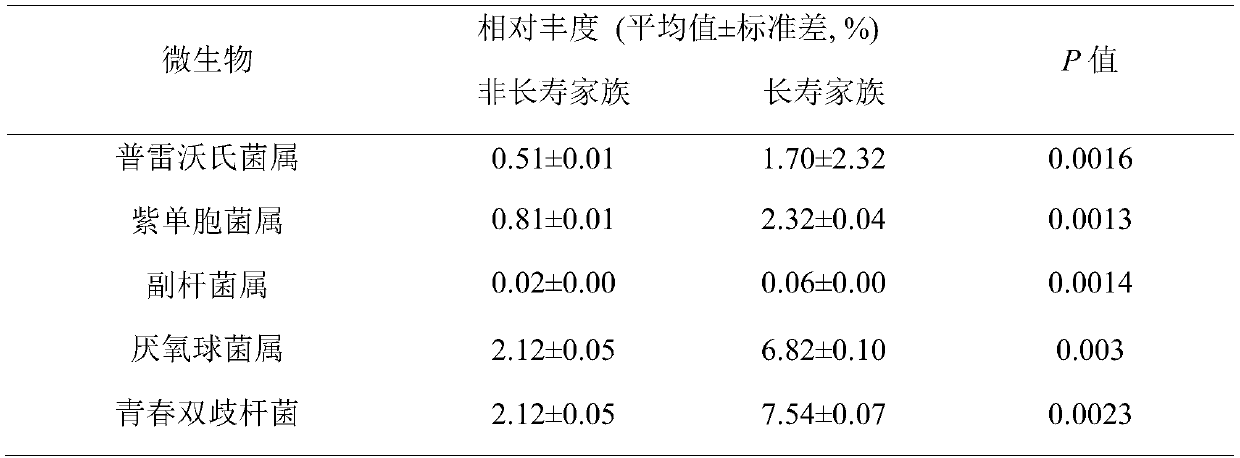
Intestinal tract micro-ecological map of longevity family and application of intestinal tract micro-ecological map in field of aging health
PendingCN111455016AThe mechanism of treatment is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention discloses establishment of an intestinal tract micro-ecological map of a longevity family and an application of the intestinal tract micro-ecological map in the field of aging health. Itis discovered that the following microorganisms including at least one of bacteroides-prevotella, porphyromonadaceae, parabacillus, anaerobic cocci and bifidobacterium adolescentis can be used to more comprehensively observe the flora distribution of the intestinal tracts of longevity crowds, a new marker is provided for diagnosing the health condition of the body and predicting the life of the human body, and more reasonable diet and nutrition suggestions are provided for the healthy life of people. Meanwhile, a new method and thought are provided for research on a mechanism of interaction between metabolites of intestinal microorganisms of the longevity crowds and the bodies, an anti-aging treatment mechanism is clearer, and a solid theoretical basis is provided for research on novel conditioning products including microecological preparations, viable bacterial drugs, fecal microbiota transplantation, nutrient products and the like.
Owner:广州市华永睿健生物科技有限公司
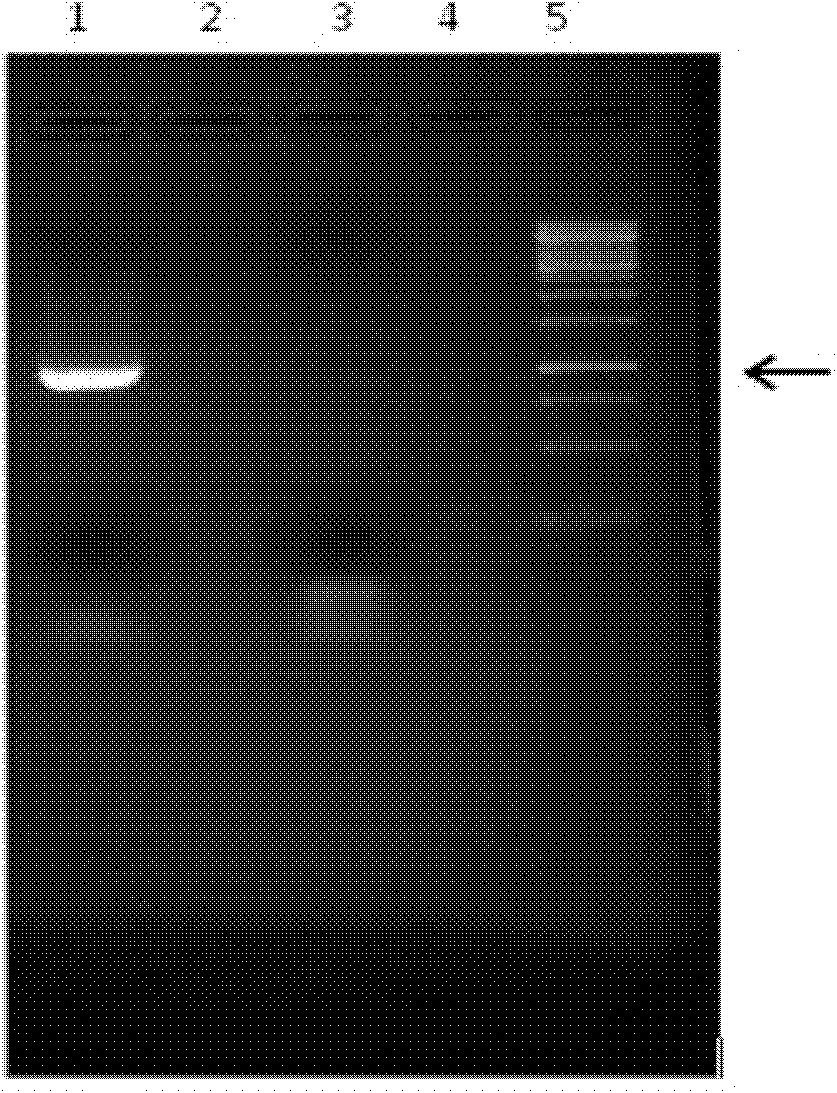
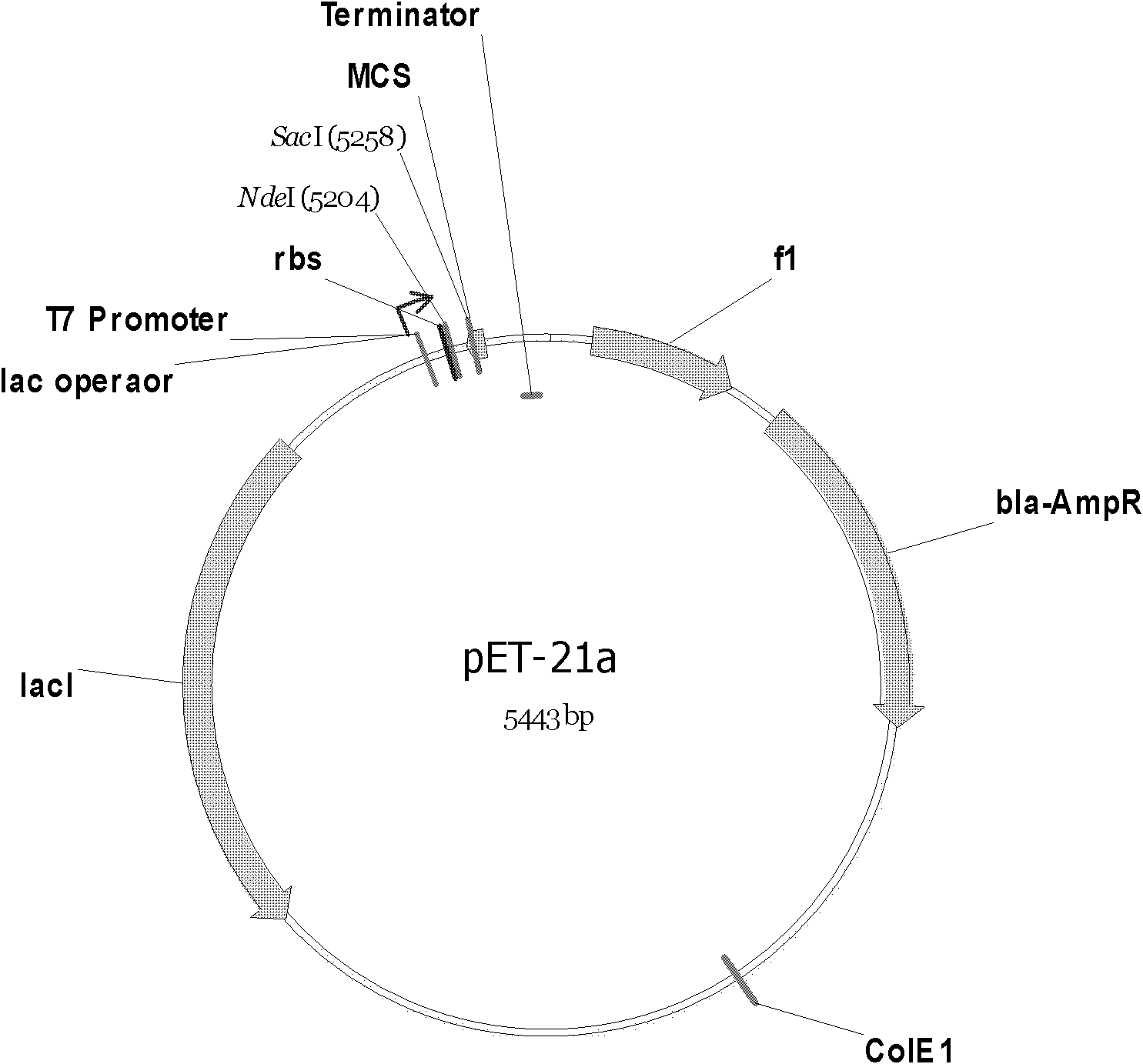
A method for preparing a recombinant Prevotella asparaginase
InactiveCN102851302AReduce process stepsProduct quality is easy to controlHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention relates to the biomedical field and the field of gene recombination, more specifically, to a preparation method of a recombinant Prevotella asparaginase, which includes the steps of amplifying full length or fragment DNA of asparaginase from the genomic DNA of Prevotella using PCR technique, performing ligation of the obtained DNA and a cloning plasmid with ligase, cutting out the full length or fragment DNA of the asparaginase from the cloning plasmid and then inserting into an eukaryotic expression vector, transforming into Escherichia coli, culturing transformed Escherichia coli in a selective medium containing antibiotic to amplify the expression vector containing the full length or fragment DNA of asparaginase, collecting transformed bacteria, and centrifugating to separate the bacteria; disrupting the bacteria, and releasing the recombinant asparaginase; and performing two-step column chromatography to purify the recombinant Prevotella asparaginase. The inventive method has the advantages of few process steps, controllable quality and large production quantity.
Owner:范铭琦
Method and System for Reducing the Likelihood of Colorectal Cancer in a Human Being
ActiveUS20200163796A1Reduce the possibilityEliminate symptomsOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of developing liver cancer in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ActiveUS20200121743A1Inhibit progressEarly detectionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseIntestinal microorganisms
A method for reducing the likelihood of developing liver cancer in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease involves providing in the gut of an individual a population of beneficial bacteria selected from the group consisting of Lactobacillus species, and administering fiber to the individual to maintain a therapeutically effective amount of the beneficial bacteria in the gut of the individual. In certain embodiments, monoacylglycerolacyltransferase-3 (MGAT3) synthesis is inhibited to lower triacylglycerol (TAG) production, while in others, expression of diacylglycerolacyltransferase-2 (DGAT-2) is inhibited. The beneficial bacteria are preferably modified to produce increased amounts of butyrate and may also be encapsulated in a frangible enclosure. Levels of Roseburia are preferably increased while the levels of Akkermansia spp. in the individual's gut microbiome are reduced. In other embodiments, a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is administered, or a composition comprising modified L. reuteri bacteria having the ability to survive conditions in the duodenum or jejunum of the individual's small intestine. Other embodiments include the administration of a bacterial formulation comprising at least one of Coprococcus, Veillonella, Roseburia, Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Prevotella.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Application of prevotella in preparation of medicine for treating cholestatic diseases
PendingCN113509494AReduce sedimentationImprove fibrosisBacteria material medical ingredientsDigestive systemEnterohepatic circulationBile Juice
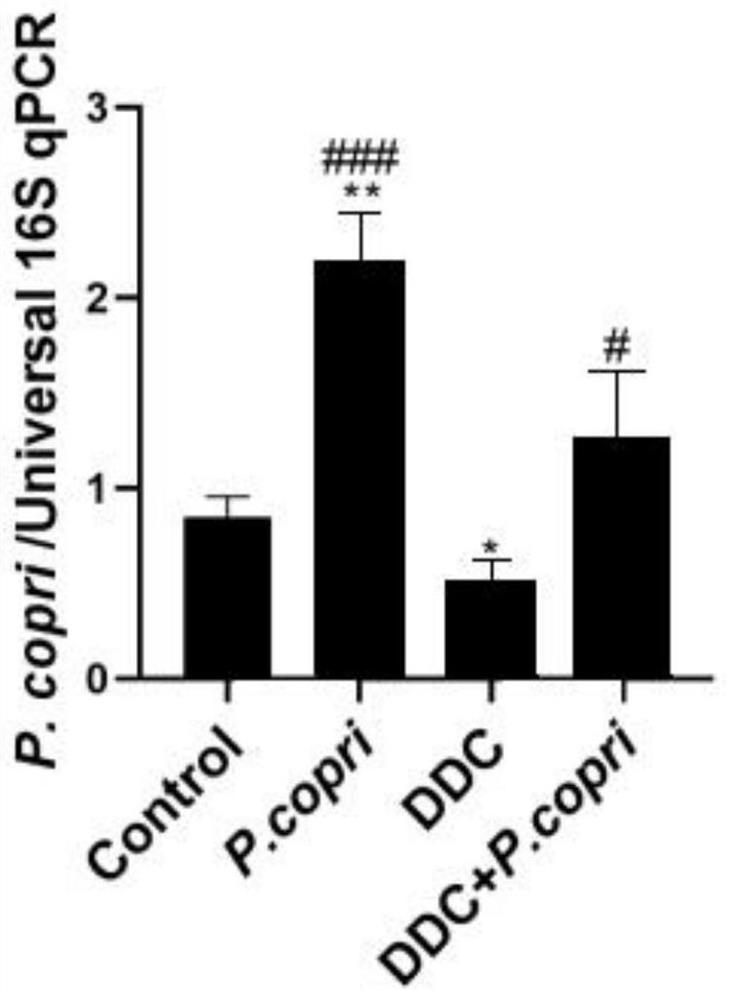
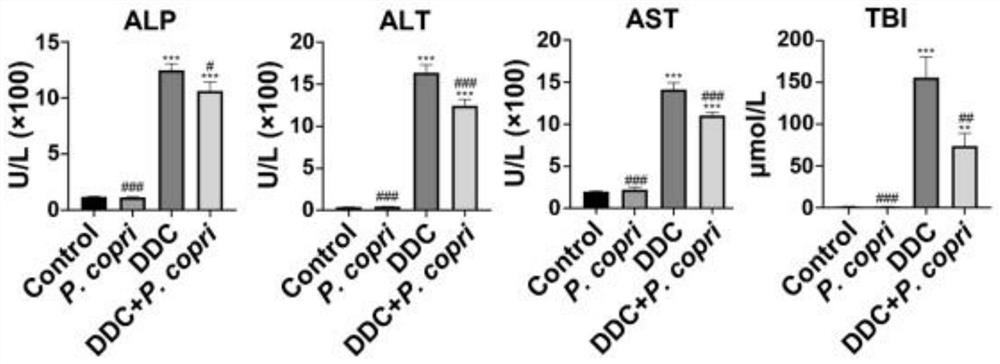
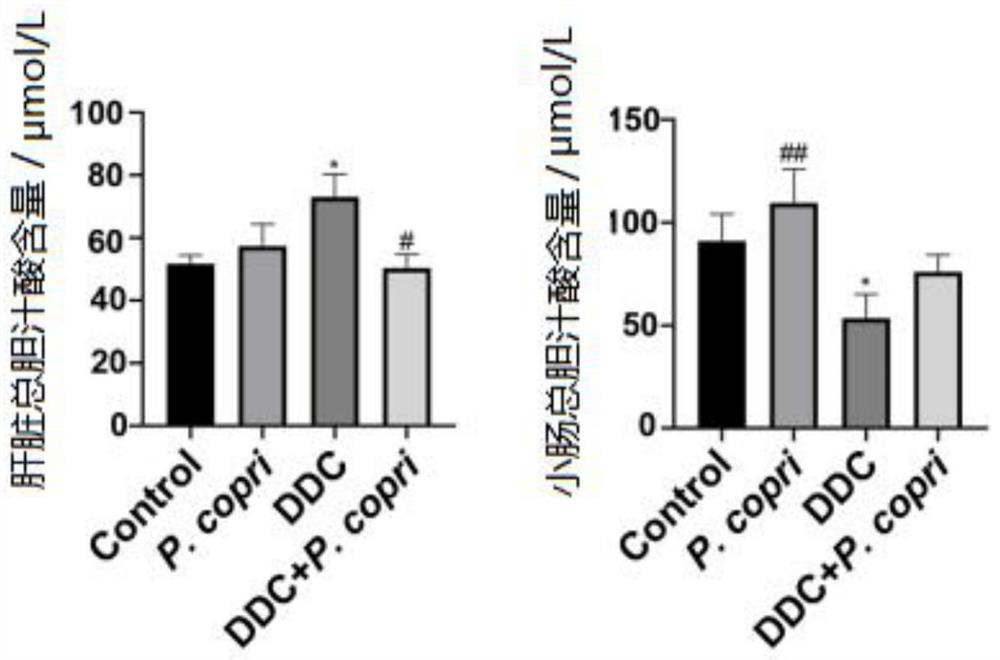
The invention discloses application of prevotella in preparation of a medicine for treating cholestatic diseases. The cholestatic diseases include, but is not limited to, primary sclerosing cholangitis. After the inventor constructs a PSC animal model, it is determined that the abundance of P.copri in mice is consistently reduced in the same population, then intervention effects of P.copri on inflammation, fibrosis, cholestasis and the like of the PSC model are observed and evaluated through intragastric administration for one week and daily supplementation of 1*10<8> CFU of P.copri bacterial liquid, bile acid metabolism changes are determined through total bile acid determination and targeted bile acid detection analysis, and the action mechanism is analyzed. Experiments prove that the P.copri can obviously relieve cholestasis in hepatointestinal circulation of PSC mice and obviously improve liver fibrosis, which is of great significance to prevention or treatment of cholestatic diseases.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
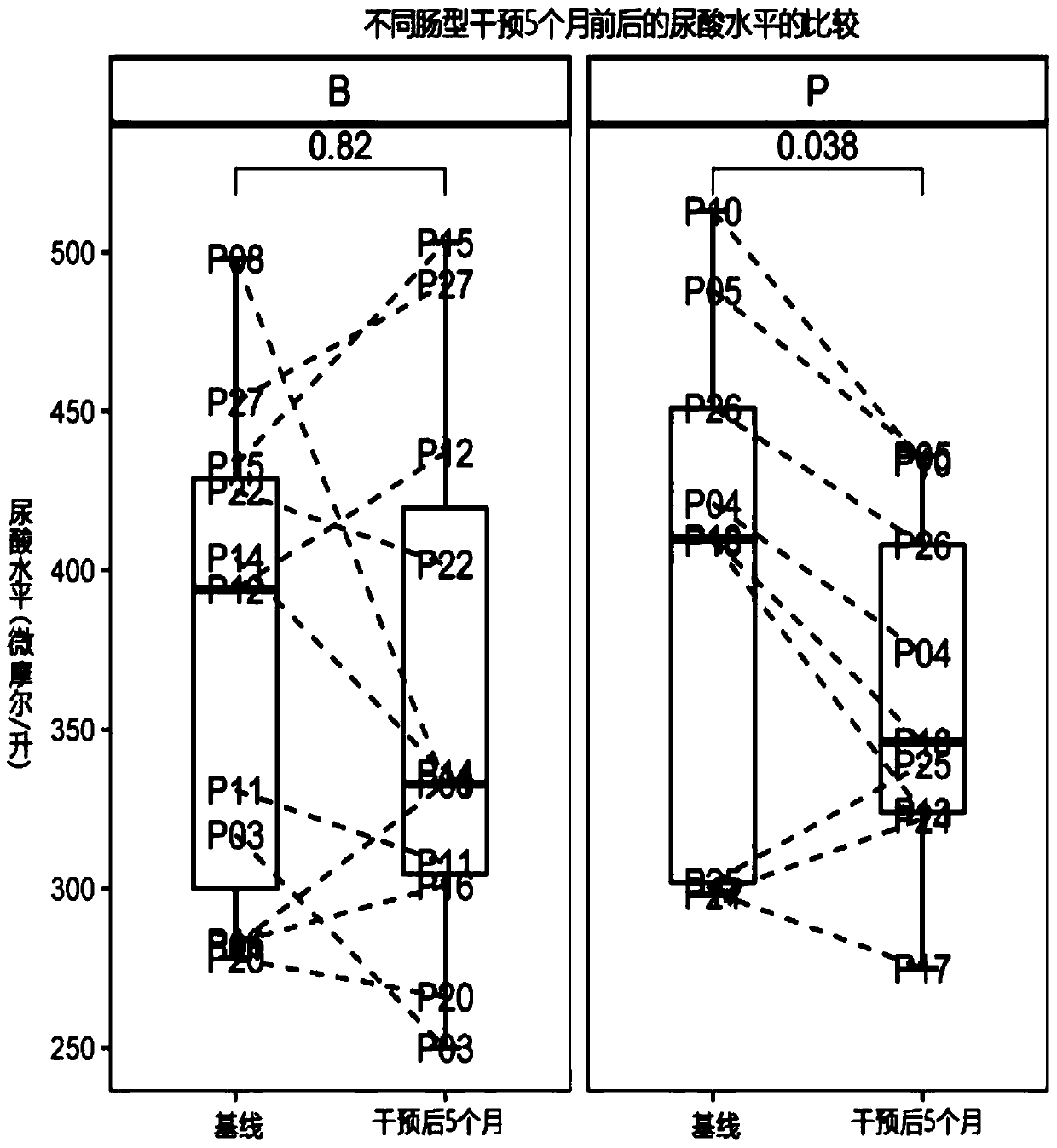
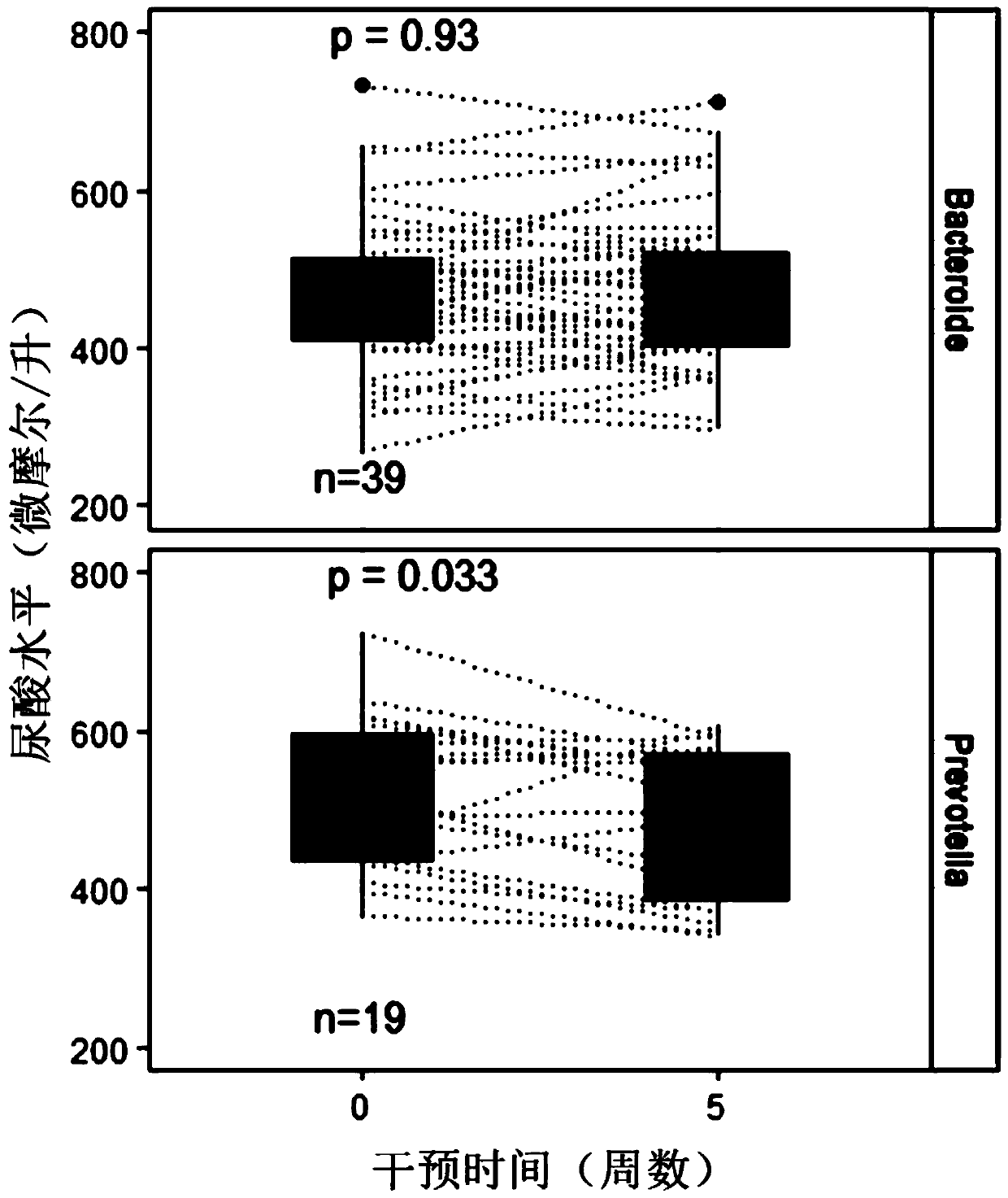
Application of plant polysaccharide in preparing medicines for intestinal type-related hyperuricemia
PendingCN111134329AImprove guidanceOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderBiotechnologyBacteroides
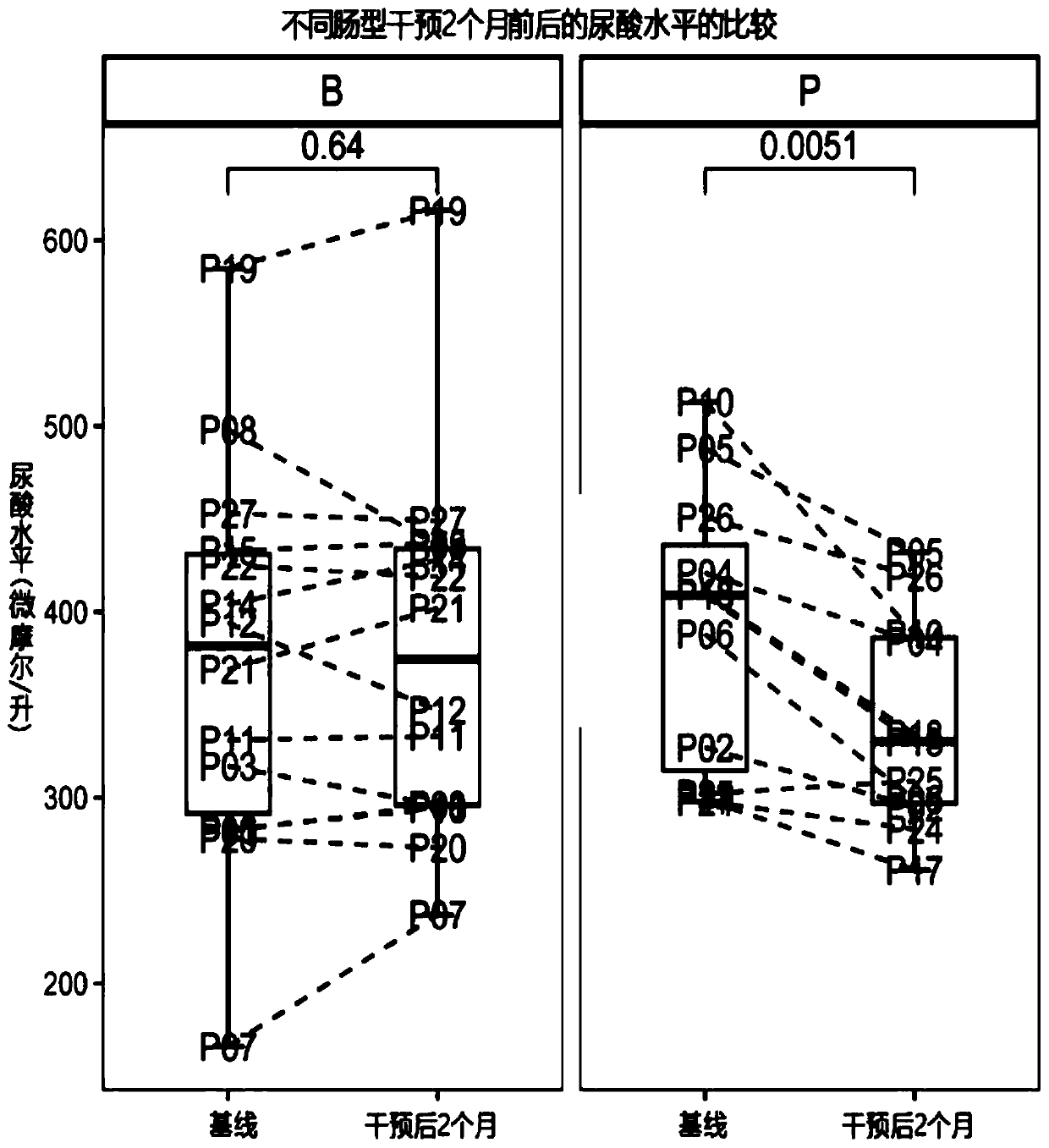
The invention discloses an application of plant polysaccharide in preparing medicine, food, health care product or food additive for intestinal type-related hyperuricemia, wherein the plant polysaccharide is inulin and / or psyllium seed husk, and the intestinal type-related hyperuricemia is prevotella intestinal type hyperuricemia and / or bacteroides intestinal type hyperuricemia. The invention provides the new application for two vegetable polysaccharides comprising inulin and psyllium seed husks, namely, the application in treating or preventing intestinal type-related hyperuricemia, in particular to prevotella intestinal type hyperuricemia and / or bacteroides intestinal type hyperuricemia. Discovery of the new application has a good guiding effect on implementation of individualized diagnosis and treatment, and has important significance on clinical application and deep research of vegetable polysaccharides.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Methods and compositions for treating cancer
PendingCN113645981ABacteria material medical ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrevotellaBacteroides salyersiae
Described herein are methods and compositions for treating cancer and for predicting a subjects' response to combination checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Aspects of the disclosure relate to a method of treating cancer and / or reducing toxicity to a therapy in a subject comprising administering to the subject a composition comprising at least one isolated or purified population of bacteria belonging to one or more of the genera Flavonifractor, Dielma, Akkermansia, Alistipes, Bacteroides, Butyricimonas, Vampirovibrio, Tyzzerella, Parabacteroides distasonis, Fournierella, Fournierella massiliensis, Eisenbergiella tayi, Tissierellales, Hungateiclostridium thermocellum, Dorea formicigenerans, Caloramator coolhaasi, Muricomes, Geosporobacter, Prevotella paludivivens, Lactobacillus secaliphilus, Bacteroides fmegoldii, Lactobacillus johnsonii, Parapedobacter composti, and Anaerotignum lactatifermentans and wherein the method further comprises treating the subject with a combination of (i) a PD-1, PDL1, or PDL2 inhibitor and (ii) a CTLA-4, B7-1, or B7-2 inhibitor.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
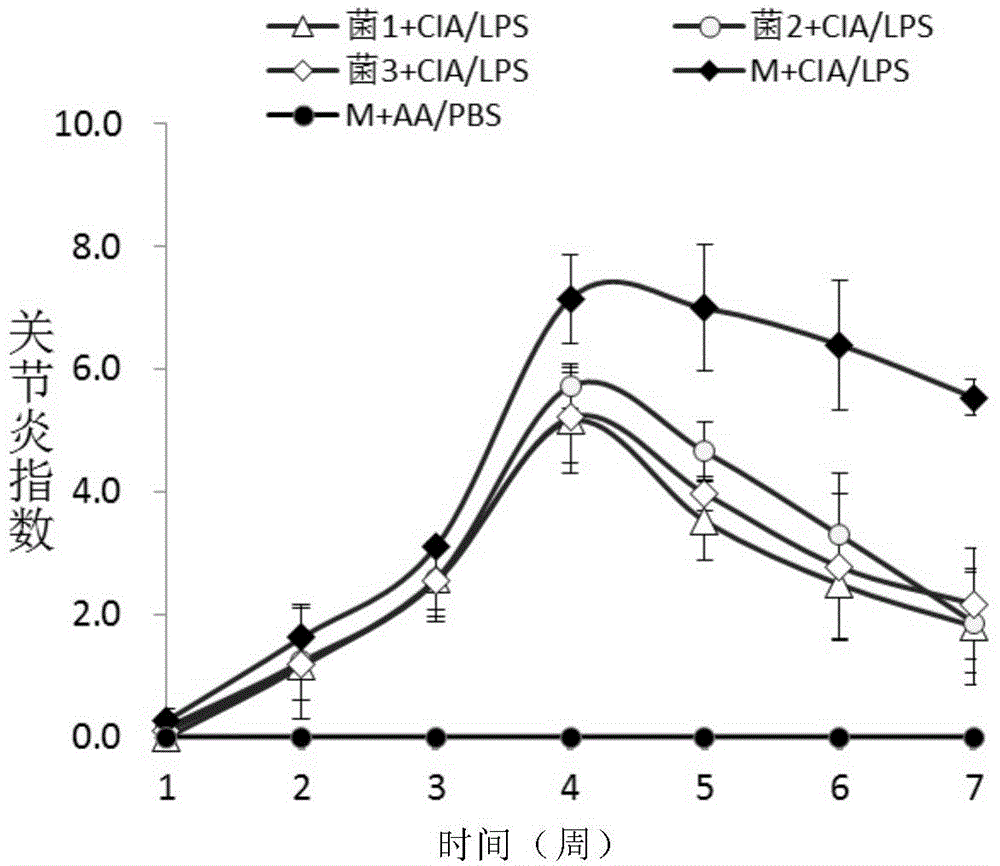
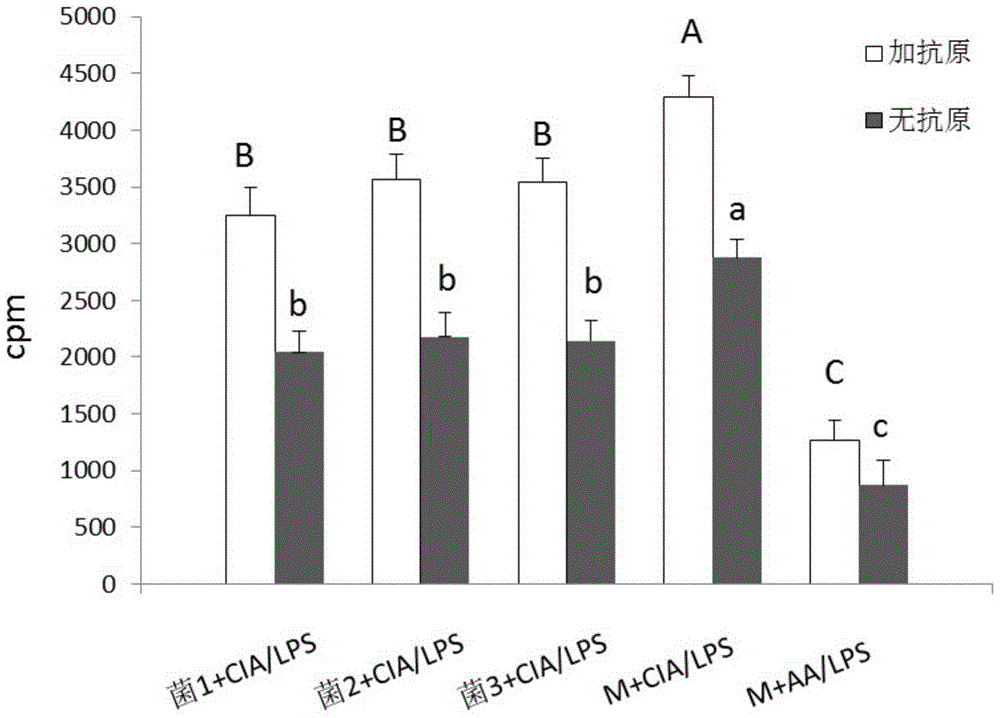
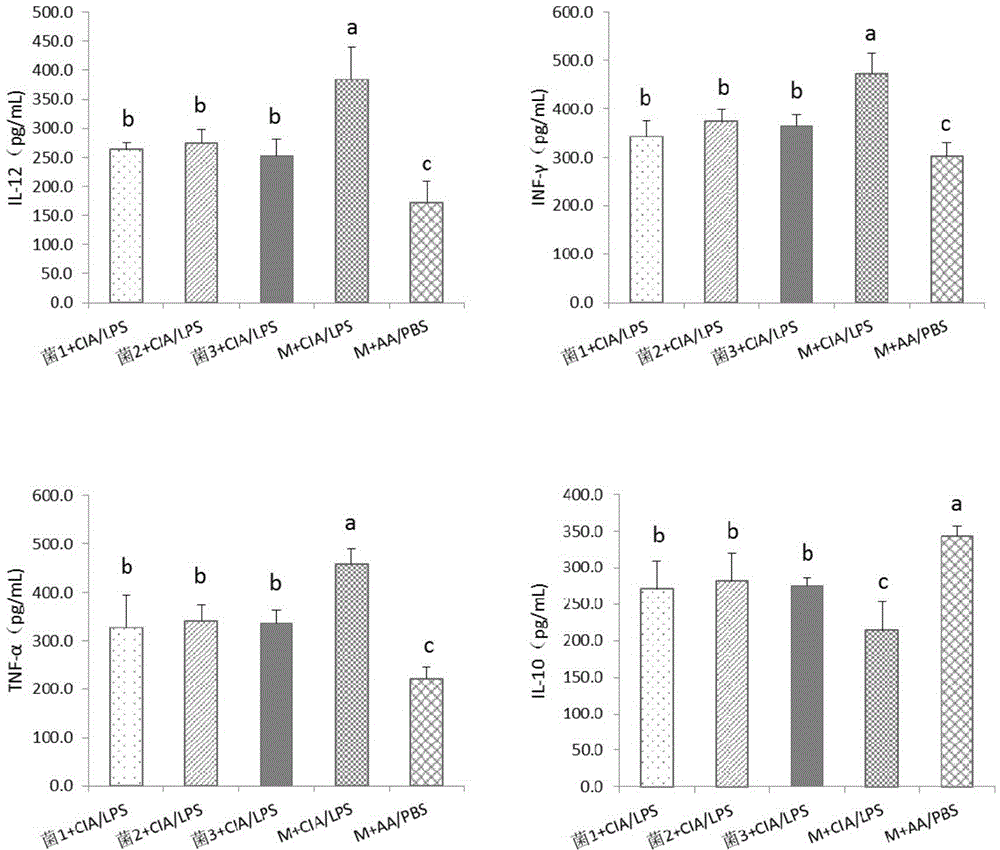
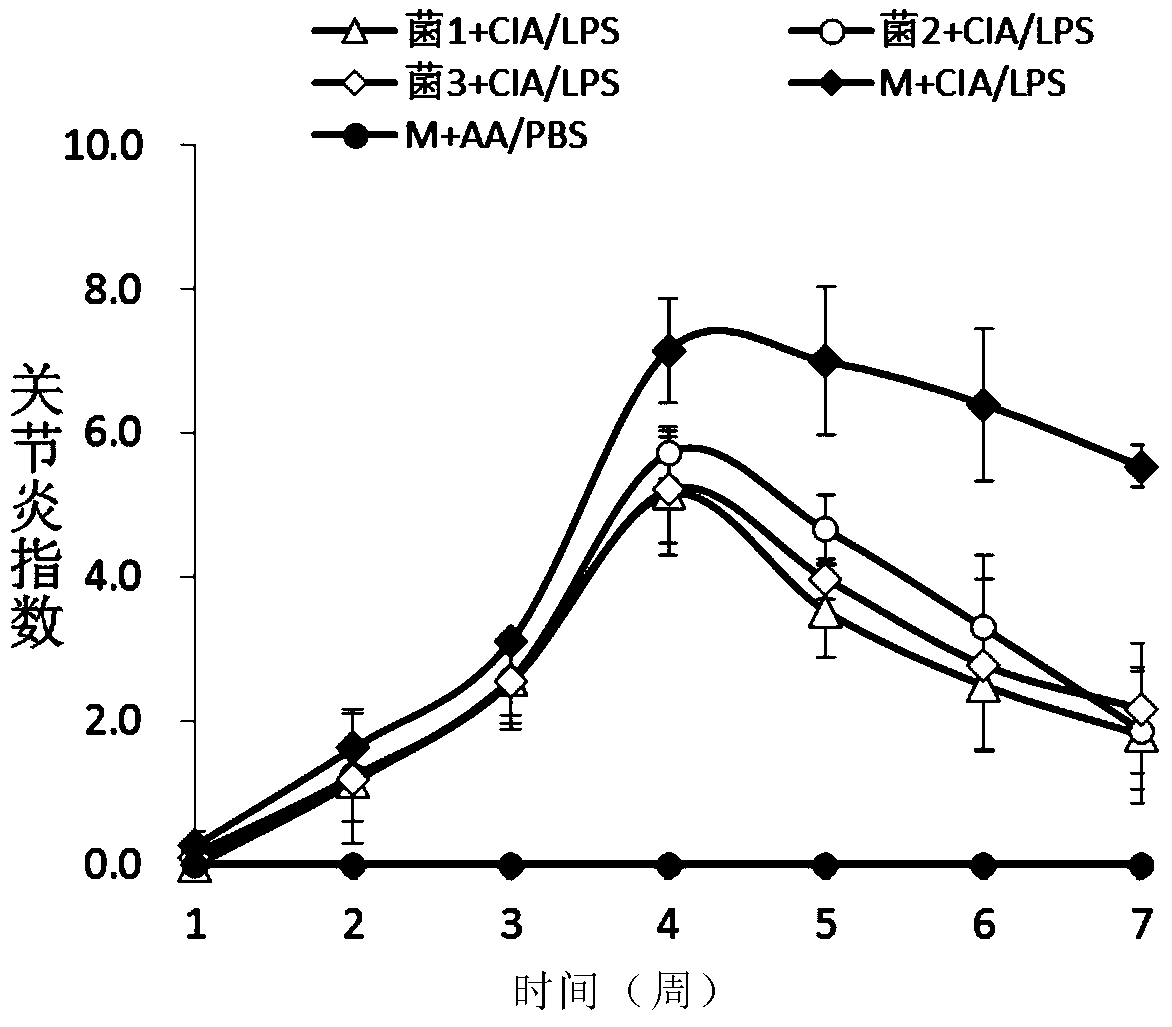
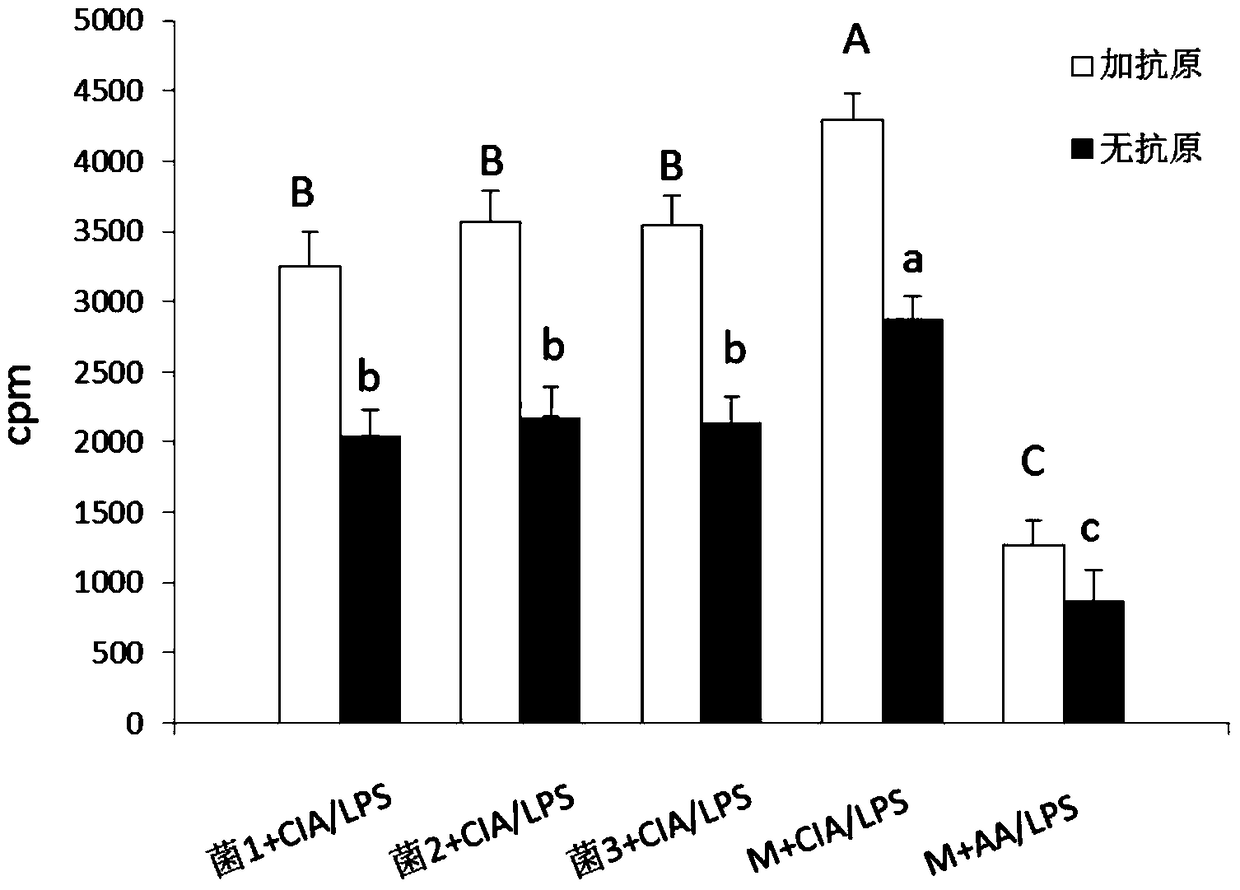
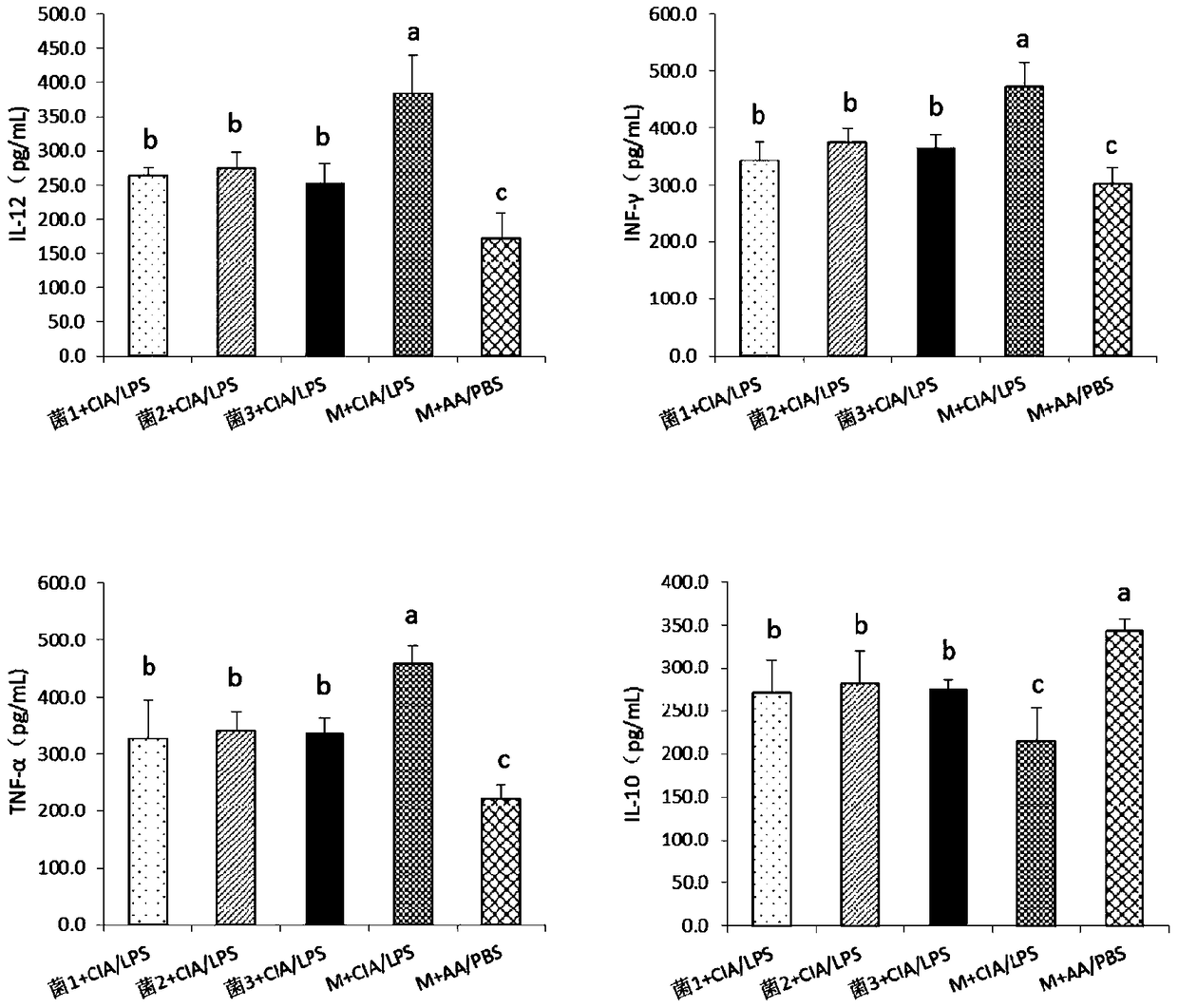
Application of speckled prevotella in treatment or prevention of rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof
ActiveCN104546936AAntipyreticBacteria material medical ingredientsPrevotellaEarly rheumatoid arthritis
The invention provides an application of speckled prevotella in treatment or prevention of rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof, and also provides speckled prevotella containing pharmaceutical compositions, medicaments, foods and feeds. By providing speckled prevotella for animals, an anti-inflammatory effect can be effectively played, the symptoms such as redness and swelling of joints are effectively improved, the symptoms of arthritis are obviously relieved, and therefore, the speckled prevotella can be effectively used for treating or preventing rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
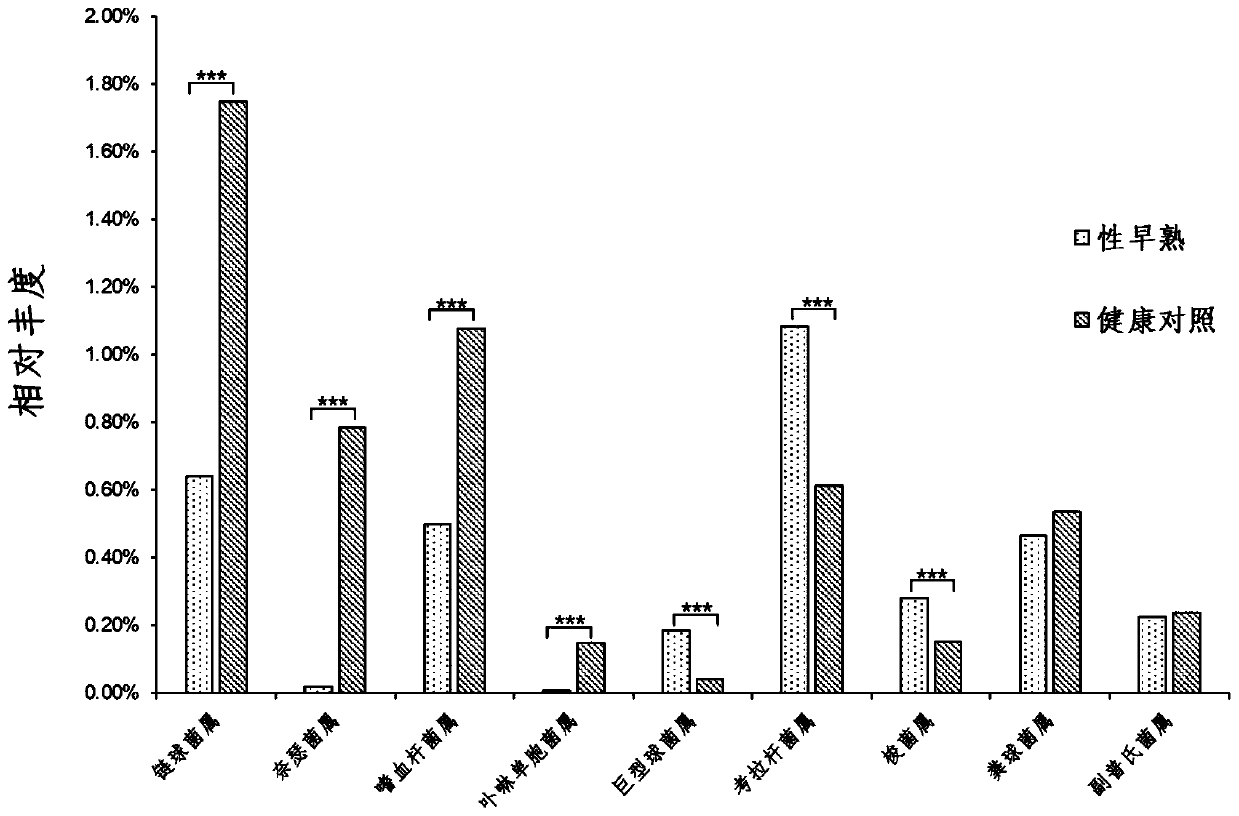
Intestinal flora microorganisms for evaluating sexual precocity of children
PendingCN111269973AReduce abundanceIncrease abundanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenus Porphyromonas
The invention provides intestinal flora microorganisms for evaluating sexual precocity of children. The method comprises the following steps of: comparing intestinal flora data of an object with intestinal flora data of healthy children; and mainly analyzing the relative abundance of streptococcus, neisseria, haemophilus, porphyromonsginglivlis, megacoccus, phascolarctobacterium, clostridium, coprococcus and prevotella, wherein the relative abundance of the streptococcus, the neisseria, the haemophilus and the porphyromonsginglivlis is reduced, and the relative abundance of the megacoccus, thephascolarctobacterium and the clostridium is increased. Therefore, the streptococcus, the neisseria, the haemophilus, the porphyromonsginglivlis, the megacoccus, the phascolarctobacterium and the clostridium have higher specificity and sensitivity. Therefore, the streptococcus, the neisseria, the haemophilus, the porphyromonsginglivlis, the megacoccus, the phascolarctobacteriumand the clostridiumhave higher specificity and sensitivity. In the process of evaluating the sexual precocity of children, detection and research results are compared to evaluate the level change of intestinal flora microorganisms of children, and whether the risk of the sexual precocity exists or not is judged according to the level change of the intestinal flora microorganisms.
Owner:QILU CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
Upper gastrointestinal flora-improving agent
The problem is solved by an upper gastrointestinal flora-improving agent, the agent containing lactobacilli as an active ingredient, to be used in persons positive and negative for Helicobacter pylori. Lactobacilli of the genus Lactobacillus are preferably used as the lactobacilli, more preferably Lactobacillus gasseri OLL 2716 (FERM BP-6999). Improvement of the upper gastrointestinal flora is, for example, a reduction in upper gastrointestinal bifidobacteria and / or an increase in upper gastrointestinal Prevotella bacteria.
Owner:MEIJI CO LTD +1
Upper gastrointestinal flora-improving agent
InactiveUS20190151381A1Preventing or improving functional gastrointestinal disordersMilk preparationDigestive systemBifidobacteriumAdditive ingredient
The problem is solved by an upper gastrointestinal flora-improving agent, the agent containing lactic acid bacteria as an effective ingredient, to be used in persons positive and negative for Helicobacter pylori. Lactic acid bacteria of the genus Lactobacillus is preferably used as the lactic acid bacteria, more preferably Lactobacillus gasseri OLL2716 (FERM BP-6999). Improvement of the upper gastrointestinal flora is, for example, a reduction in upper gastrointestinal Bifidobacterium and / or an increase in upper gastrointestinal Prevotella.
Owner:MEIJI CO LTD +1
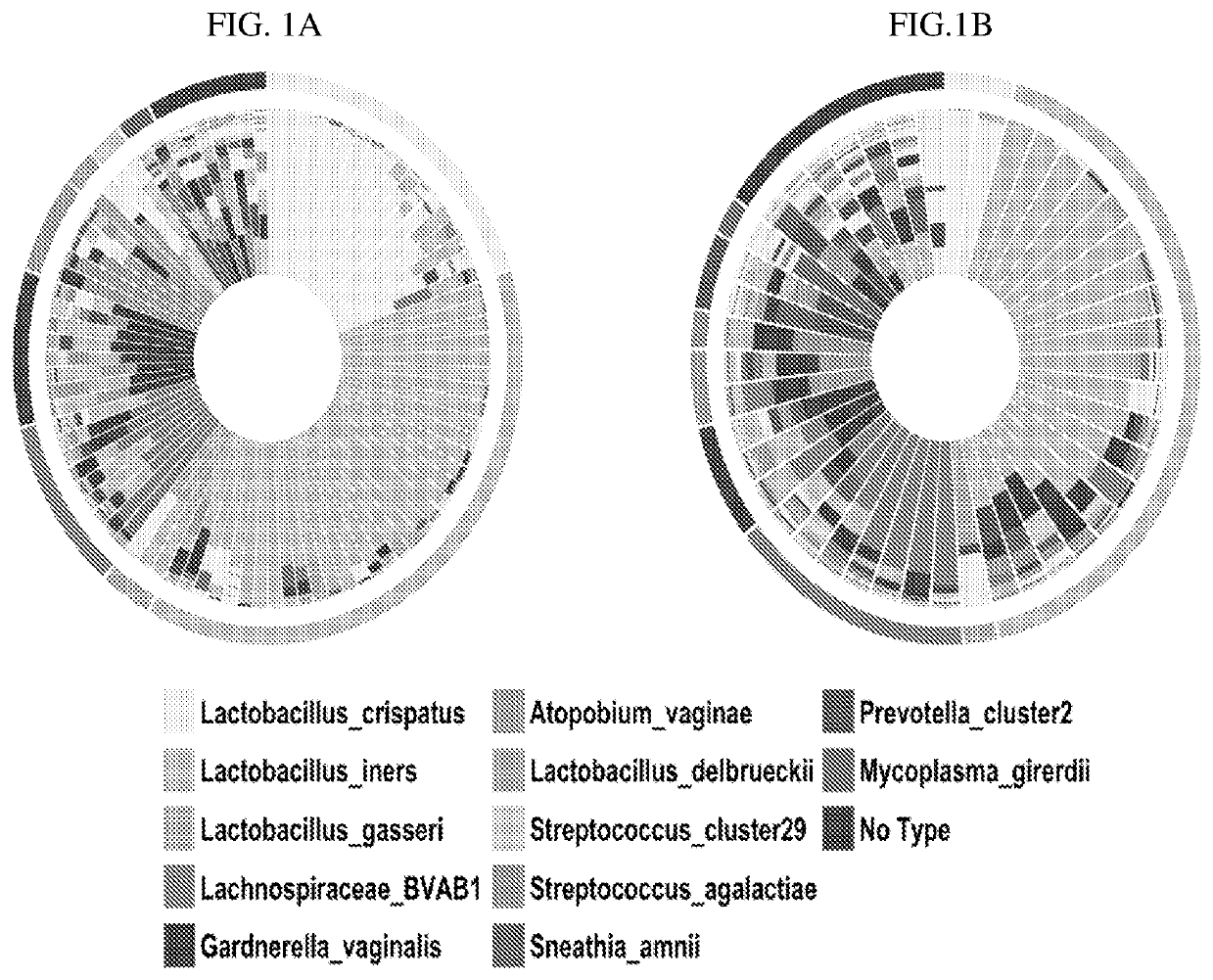
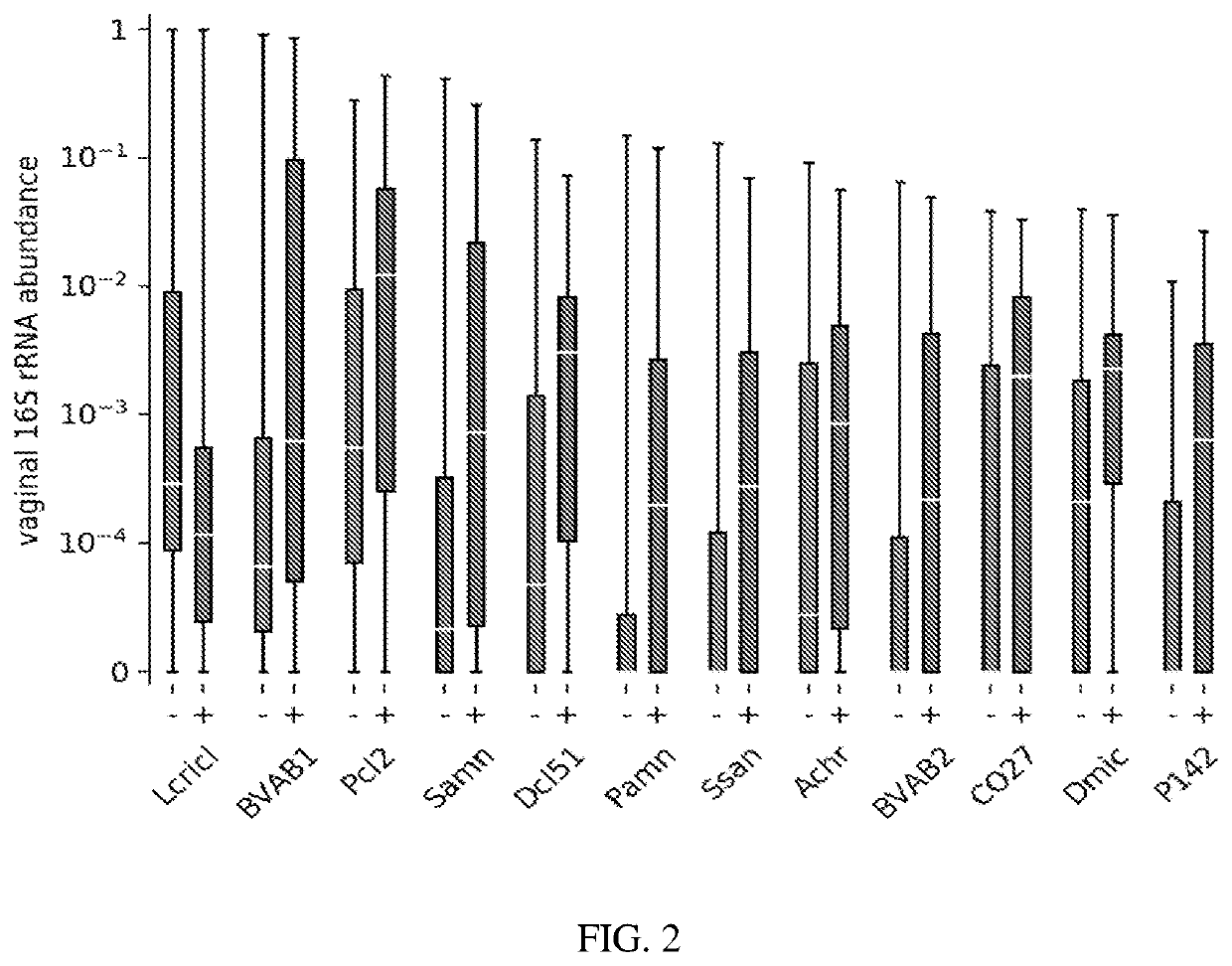
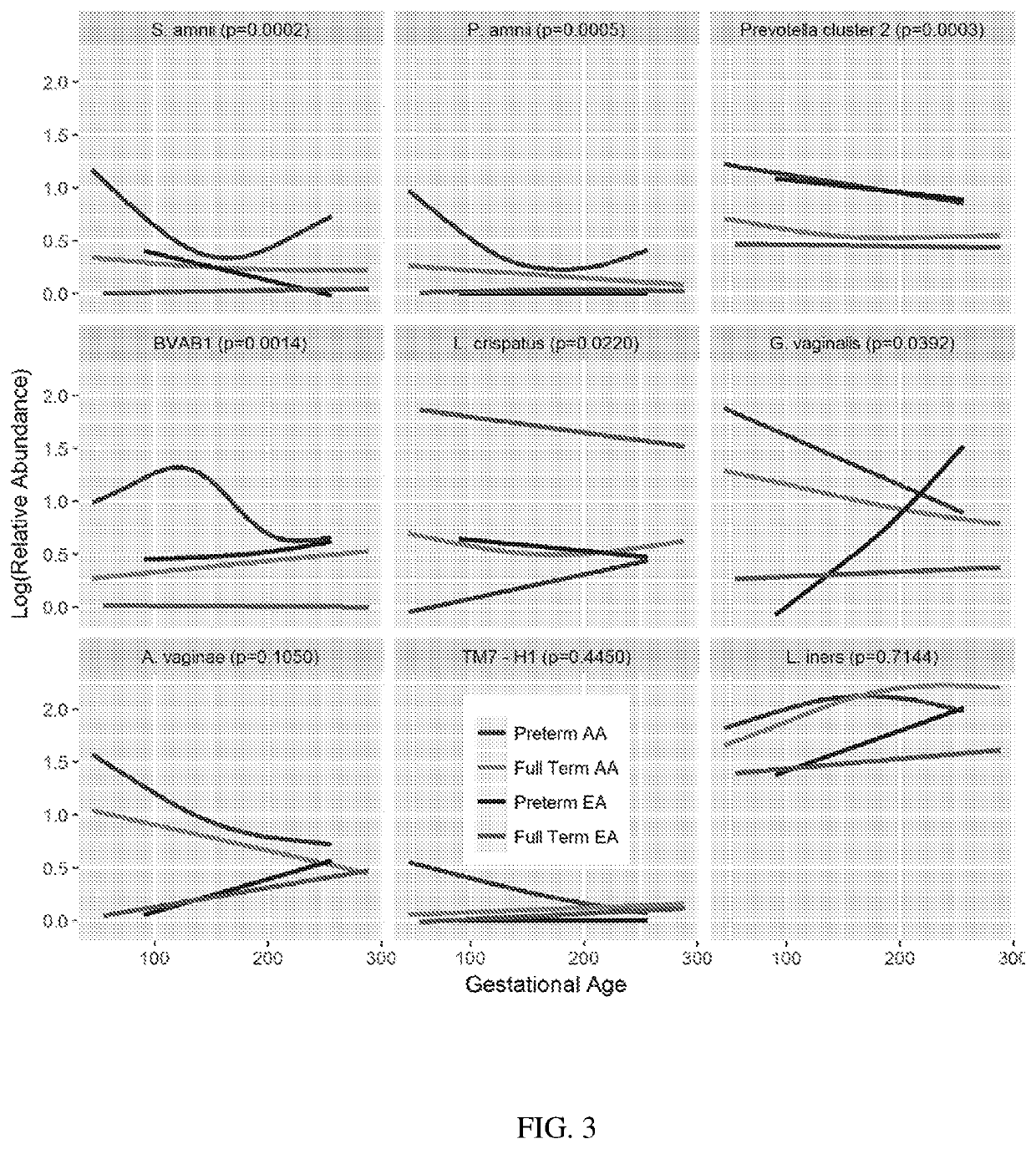
Vaginal microbiome markers for prediction of prevention of preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes
PendingUS20220243247A1High degree of sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisVaginal microbiomeObstetrics
A method for determining the risk of an adverse pregnancy outcome for a woman is provided comprising the steps of measuring a level of TM7-H1 and optionally one or more of BVAB1, Sneathia amnii, and Prevotella cluster 2 in a vaginal sample obtained from the woman, and identifying the woman as having an increased risk for an adverse pregnancy outcome, or other adverse pregnancy outcomes, if the levels are increased compared to corresponding standard control levels. Methods for the prophylactic treatment of subjects identified as being at increased risk for an adverse pregnancy outcome are also provided.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Lactobacillus crispatus and its application in the production of products that improve the human vaginal environment
ActiveCN113278548BIncrease acidityRealize industrial applicationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsBiotechnologyGardnerella
The present application discloses a bacterial strain, which is a strain of Lactobacillus crispatus (Lc-17217), and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 21221. Compared with other Lactobacillus crispatus of the same species, the strains of the present application have stronger acid production capacity, hydrogen peroxide production capacity and value-added capacity. The strains of the present application can inhibit the growth of various pathogenic bacteria and can inhibit vaginal Gardnerella, Micrococcus flavum, and Prevotella have broad market prospects.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV +1
Gut microbial markers of mental disorders and their application
ActiveCN105603066BMonitoring the Effects of InterventionsMaster recoveryNervous disorderBacteriaBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention discloses a mental disorder related intestinal tract microbial marker and application thereof. The intestinal tract microbial marker refers to one or more combinations of intestinal tract microbial florae of Prevotella and Bacteroides. The invention further discloses application of the mental disorder related intestinal tract microbial marker in preparing reagents for diagnosing mental disorders and methods for screening food, probiotics or drugs capable of intervening with mental disorders. Particularly, the methods include comparing proportion of microbial florae of Prevotella to microbial florae of Bacteroides before and after treatment or interference of the food, probiotics or drugs and / or comparing relative quantity of microbial florae of Prevotella and microbial florae of Bacteroides in feces specimens.
Owner:金锋 +1
Application of asparagus polysaccharide in the regulation of intestinal flora
ActiveCN111808207BPromote productionLower ratioOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemBacteroidesMegamonas
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Salivary biomarkers for detection of epidermoid cancer of head and neck
PendingCN114008458AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFretibacteriumPrevotella
Present invention relates to the in vitro use of the level or concentration in a salivary or breath sample of bacteria belonging to the Alloprevotella, Prevotella, Campylobacter, Rothia, Catonella, Porphyromona, Fretibacterium genus, or any combination thereof, for the diagnosis of carcinomas or epidermoid cancers, especially epidermoid cancer of the head and neck, in a patient, or to obtain useful data that allow such a diagnosis.
Owner:ビオノウリサーチエセエレ
Stable coronary heart disease onset risk assessment marker and application thereof
ActiveCN114360726AImprove forecast accuracyMedical simulationHealth-index calculationK pneumoniaeMegamonas
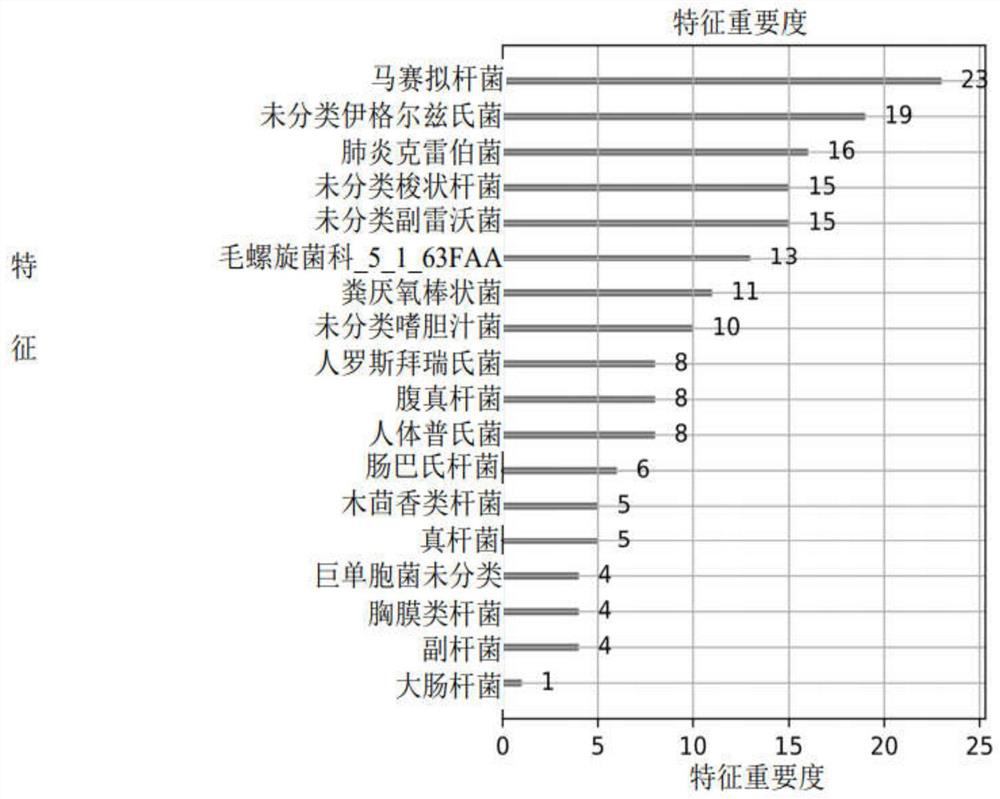
The invention discloses a stable coronary heart disease onset risk assessment marker and application thereof. The markers comprise bacteroides martensii, unclassified Eagle's bacilli, klebsiella pneumoniae, unclassified clostridium, unclassified pararevovirus, helicobacter sp. 5163FAA, anaerobic corynebacterium faecalis, unclassified biliphilic bacteria, human rosiberia, Eubacterium abdominalis, human body prevotella, pasteurella gut, wood anise bacilli, Eubacterium and unclassified megamonas. , bacillus pleurati, parabacterium and escherichia coli. According to the method, the onset risk of the stable coronary heart disease is predicted, and the prediction accuracy can be improved.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
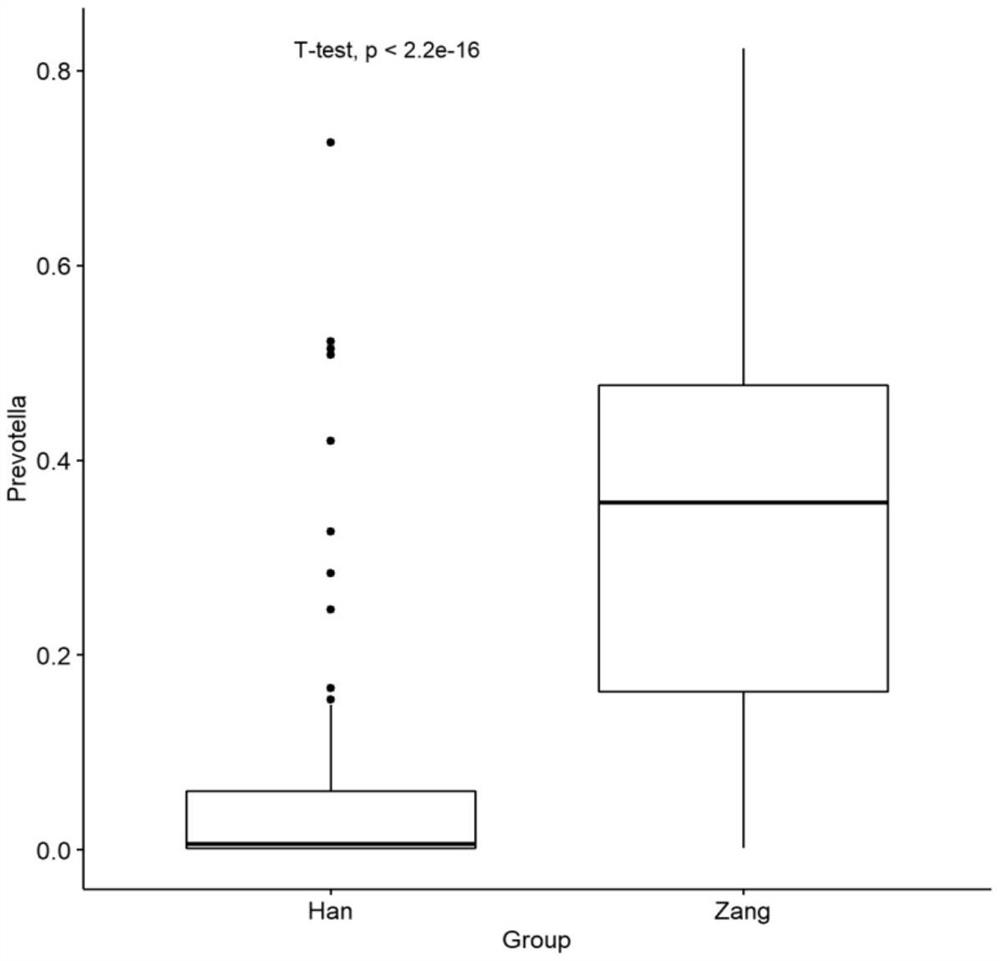
Use of Prevotella spp. in identifying and/or differentiating individuals of different ethnic groups
ActiveCN109913524BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present invention provides an application of a microbial marker in identifying and / or distinguishing individuals of different nationalities, and the microbial marker is Prevotella genus.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method and System for Reducing the Likelihood of Colorectal Cancer in a Human Being
ActiveUS20190029871A1Preventing cell entryReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingIntestinal microorganisms
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Application of Prevotella minor spotted in the treatment or prevention of rheumatoid arthritis
The invention provides an application of speckled prevotella in treatment or prevention of rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof, and also provides speckled prevotella containing pharmaceutical compositions, medicaments, foods and feeds. By providing speckled prevotella for animals, an anti-inflammatory effect can be effectively played, the symptoms such as redness and swelling of joints are effectively improved, the symptoms of arthritis are obviously relieved, and therefore, the speckled prevotella can be effectively used for treating or preventing rheumatoid arthritis or related diseases thereof.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com