Control of acidosis
a technology of acidosis and acidosis, applied in the field of acidosis control, can solve the problems of reducing the risk of acidosis, reducing the risk of feed intake and weight gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Control of S. ruminantium, Clostridium-like vitulinus, S. bovis and S. equinus
Material and Methods
Isolation, Identification and characterisation of lactic acid producing bacteria
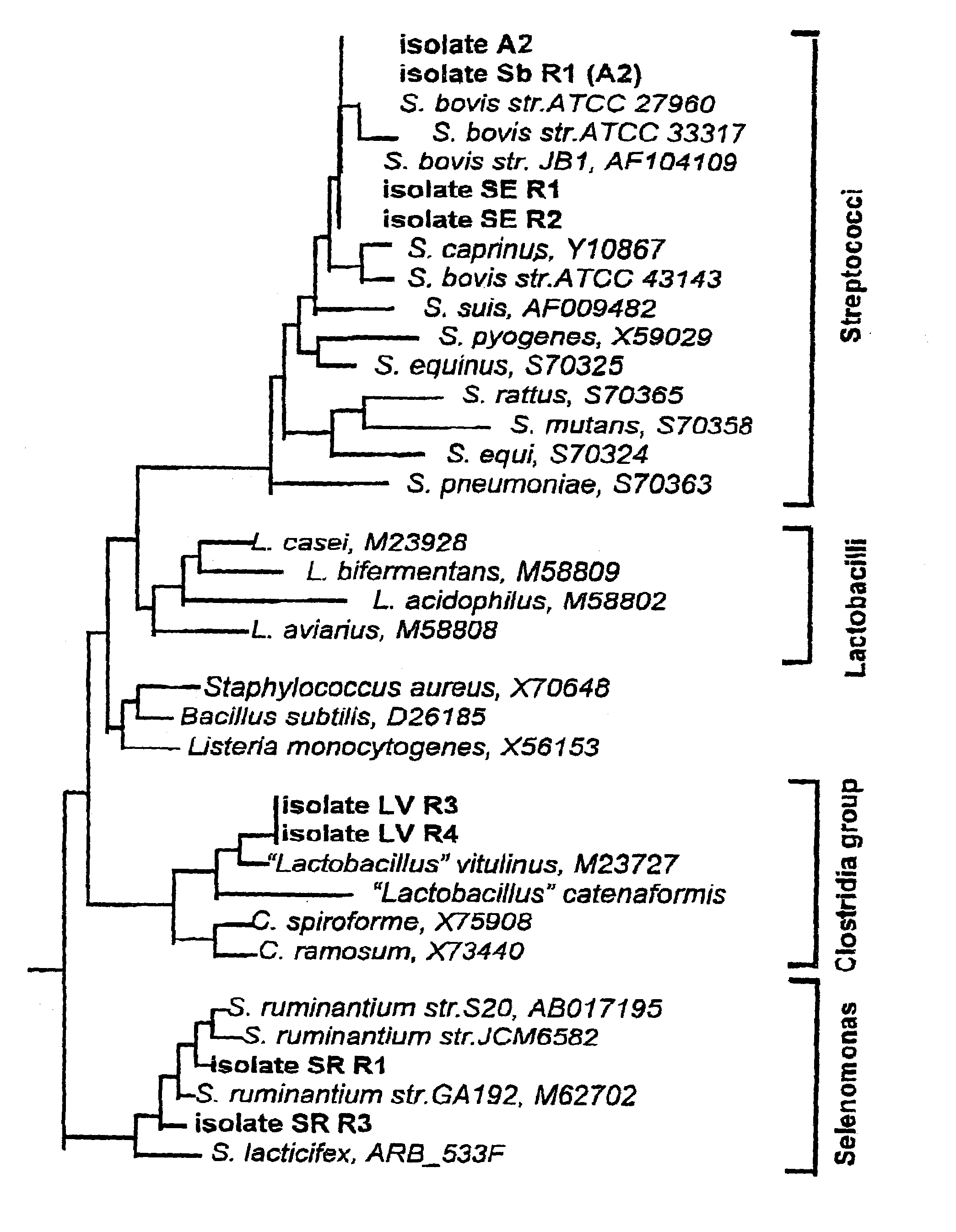
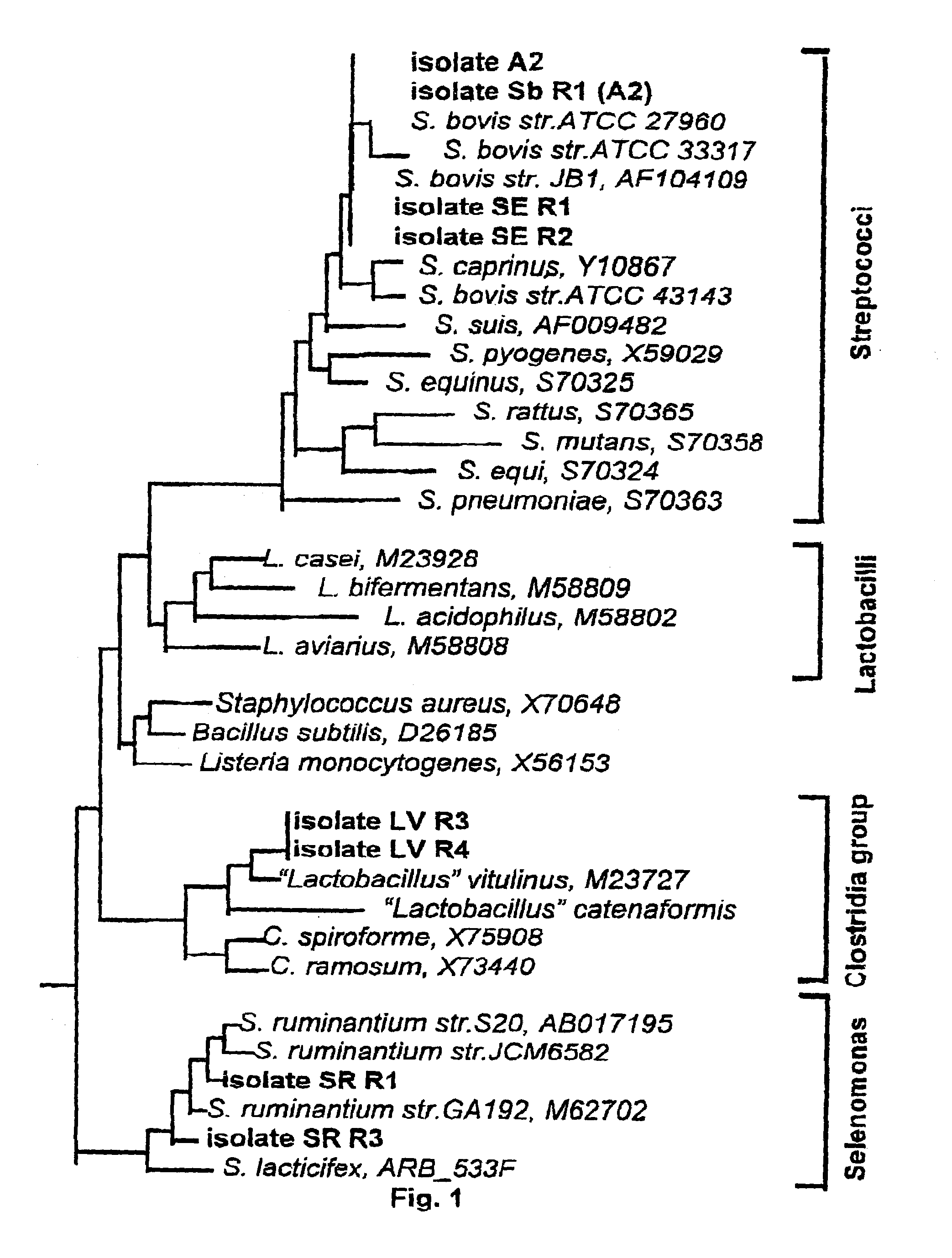
[0250]The following method was used to isolate the most numerous and most prolific acid-producing bacteria in the gut contents of ruminant and non-ruminant animals. Rumen fluid samples were obtained via stomach tube from sheep and via rumen fistula from cattle 24 h after regular grain feeding. Faecal samples were obtained directly from the rectum of sheep and cattle and from the freshly voided faeces from horses. Samples were processed for the enumeration of lactic acid bacteria following the method of Yanke and Cheng (1998) involving one-hour exposure prior to incubation. A semi-selective MRS-agar medium, Oxoid, England (De Man et al. 1960) was modified by adding a freshly prepared reducing solution (1 ml containing 0.02 g Cysteine, HCl and 0.026 g of Na2S.9H2S.9H2O per 100 ml of media) after boiling then ...
example 2
[0269]Samples of faceces were collected from 12 horses fed a mixture of chopped leucerne hay and different types of cereal grain (oats, barley, triticale and sorghum). The dominant lactic acid producing bacteria were isolated using the same method as described in Example 1. Two bacteria were isolated: Streptococcus bovis (SbR1) and Streptococcus equinus (SER1 and SER2). Based on these results it is important that any vaccine, diagnosis or other treatment to prevent or control acidosis should be effective against both S. bovis and S. equinus. Under some conditions it will also be necessary for these diagnostic tools and methods of treatment to be effective against S. ruminantium, Clostridium-like vitulinus as well as S. bovis and S. equinus.
[0270]In certain conditions it is likely that Selenomonas ruminantium and Clostridium-like vitulinus bacteria may be present and in this case animals should be vaccinated against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative lactic acid producing bacteria...
example 3
[0271]Following calving, cows grazing lush green pasture are exposed to high levels of soluble carbohydrate in the form of fructans in grasses and sugars and starch in clovers. In addition to fermentable carbohydrates in the pasture, concentrate feed supplements, based on cereal grain, are fed twice daily during milking. The fructants in pastures and the starch in legumes and concentrate are rapidly fermented in either the rumen or the hind gut to form a range of volatile fatty acids and lactic acid. The accumulation of acids in the gut contribute to the metabolic acid load of the animal, can cause inflammation of the gut wall leading to stimulation of the immune system and can lead to increased pathogenicity in the populations of bacteria and parasites within the gut. The adverse effects of acid accumulation in the gut result in reduced productivity and an increased incidences of disease including lameness, respiratory conditions and mastitis.
[0272]Acid accumulation in the gut unde...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com