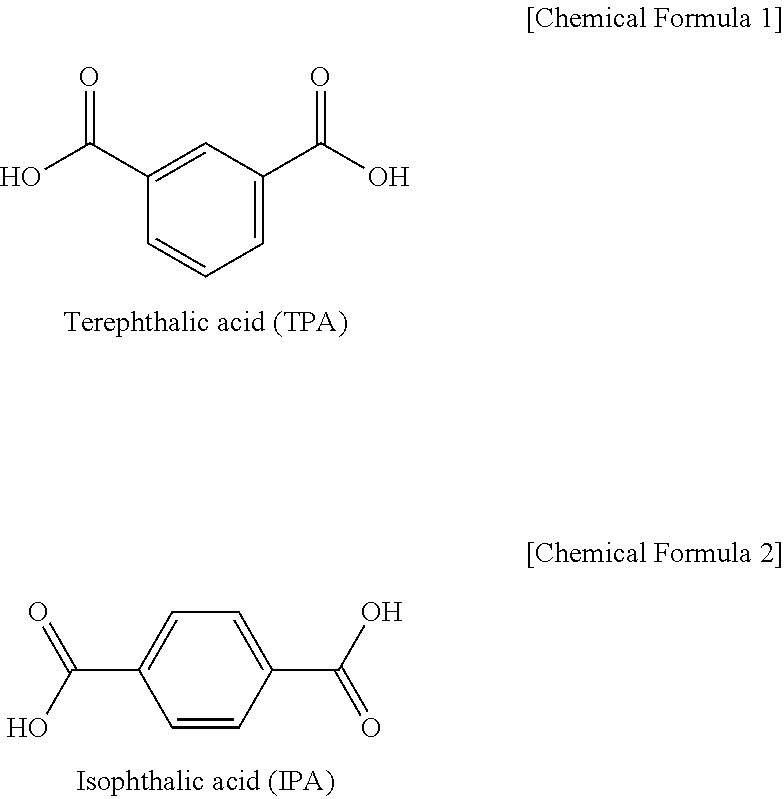
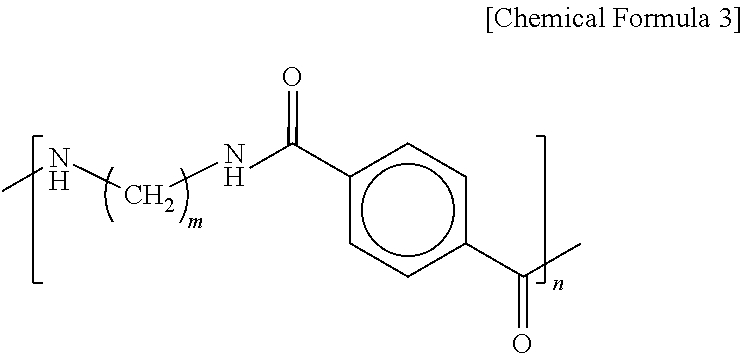
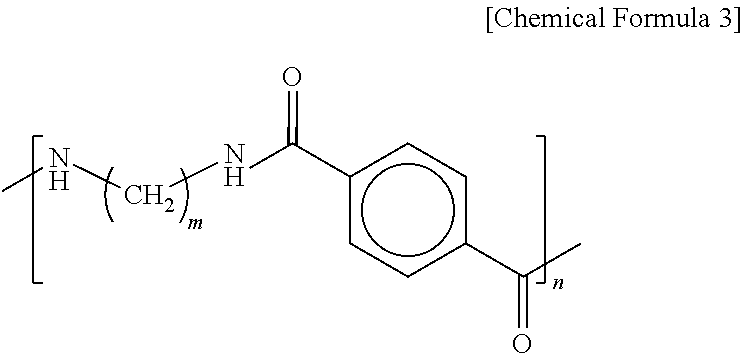
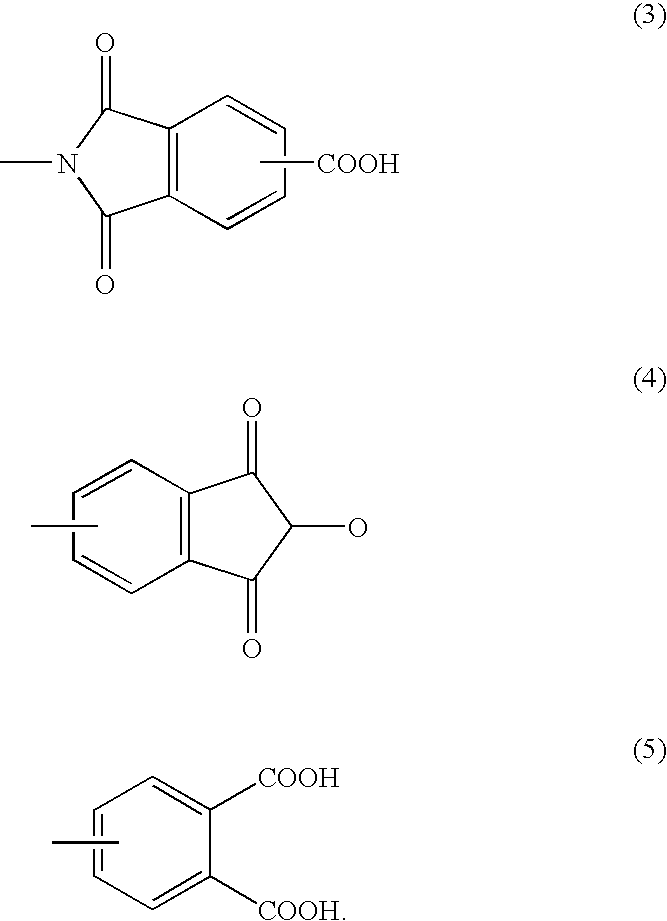
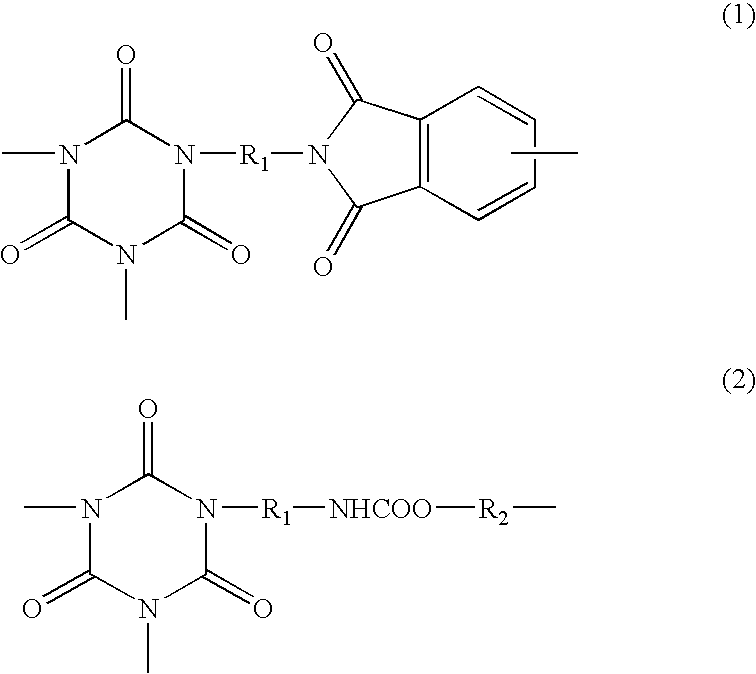
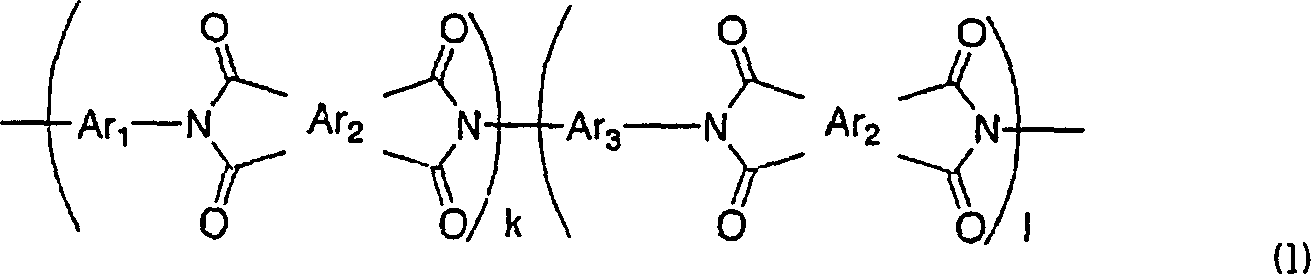
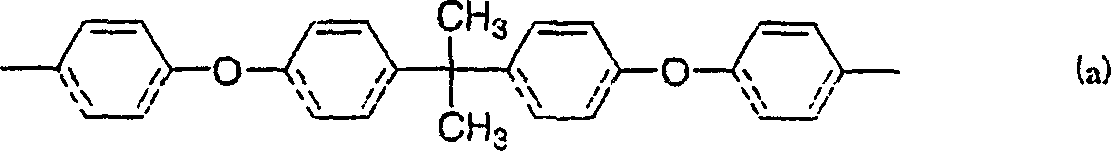
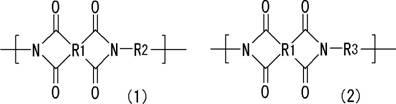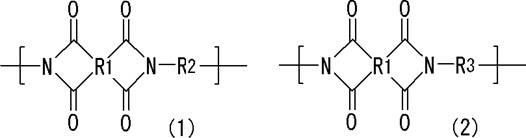Patents
Literature
157results about How to "Excellent heat-resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalyst and method for preparation thereof
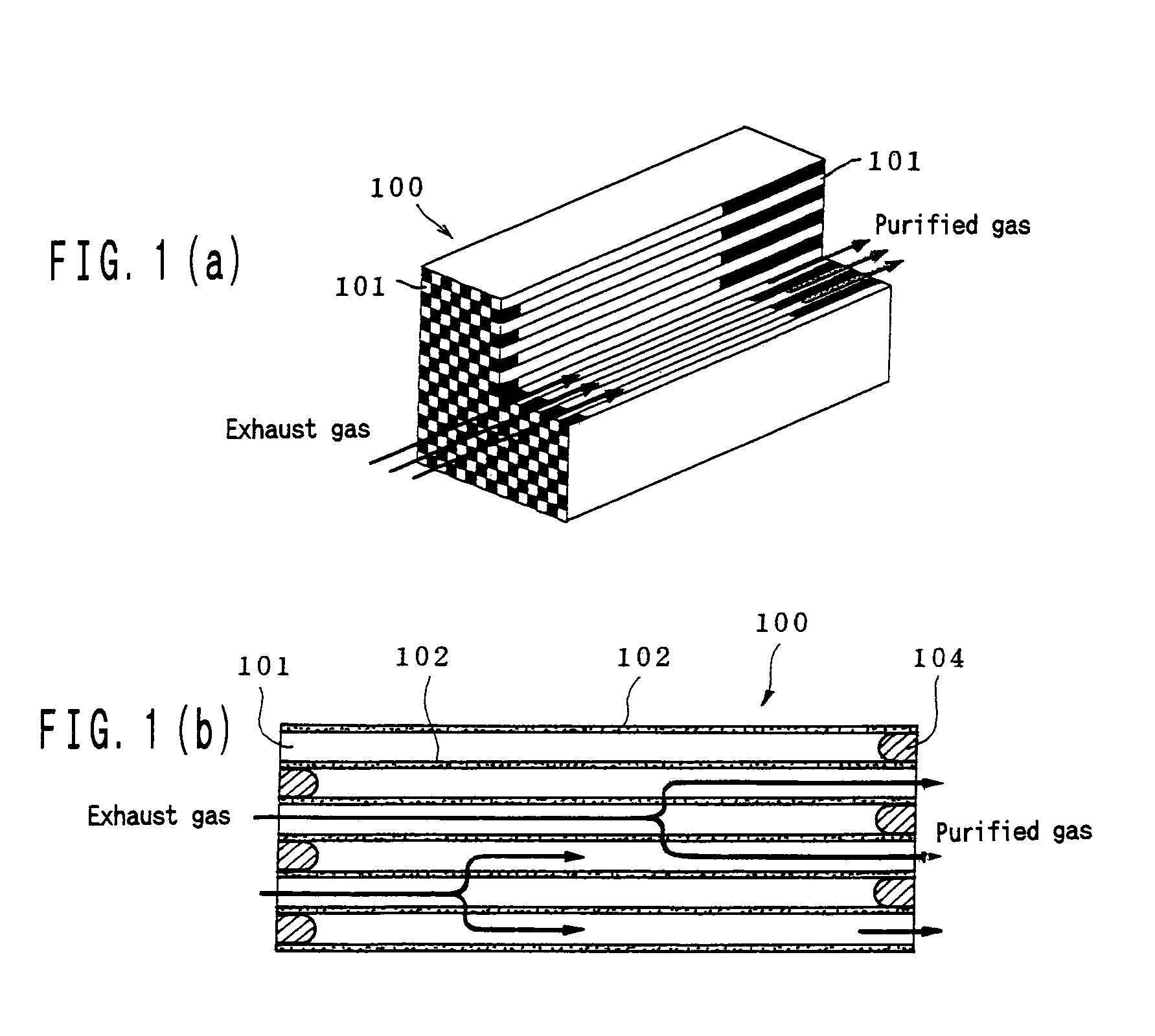
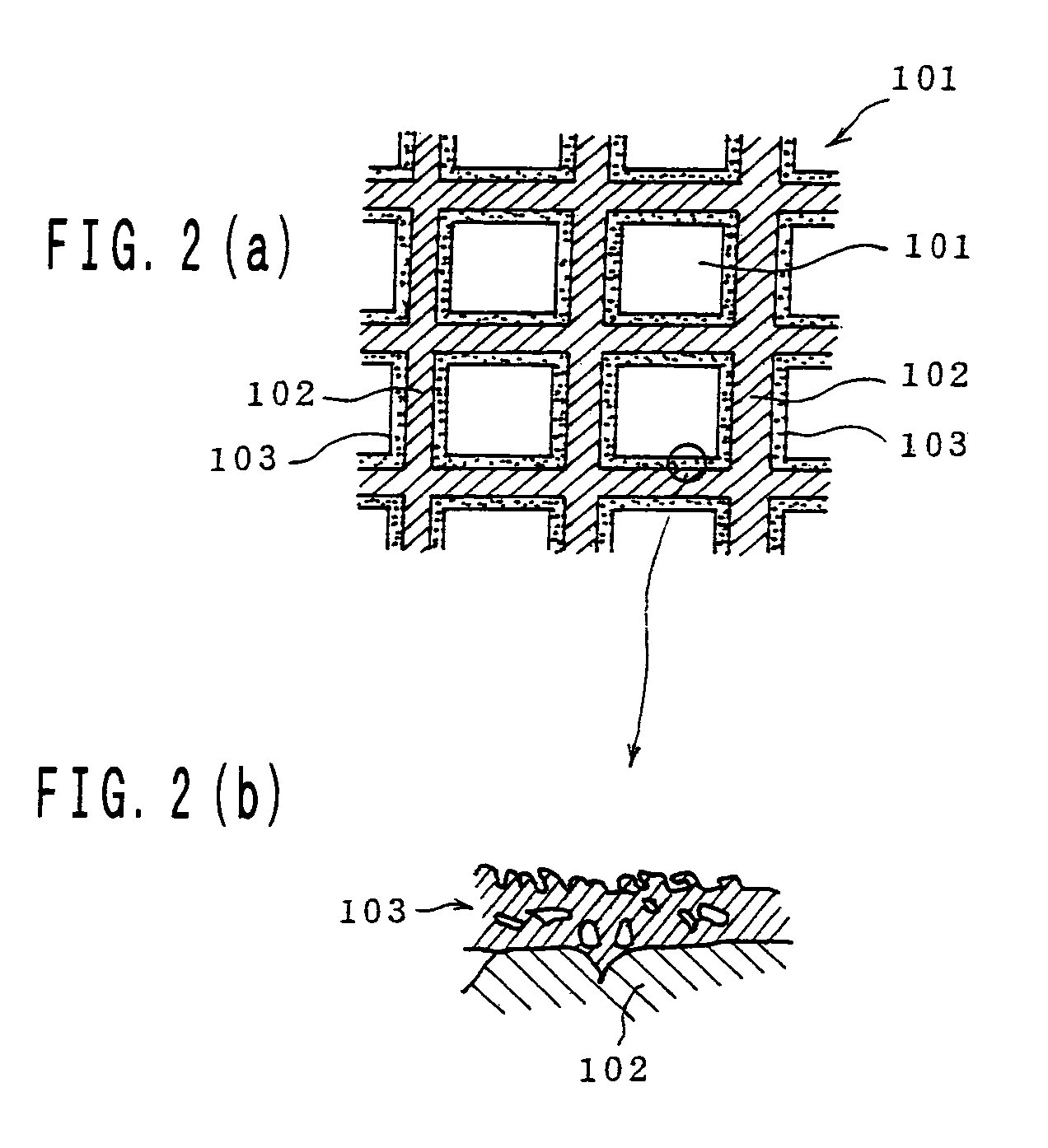
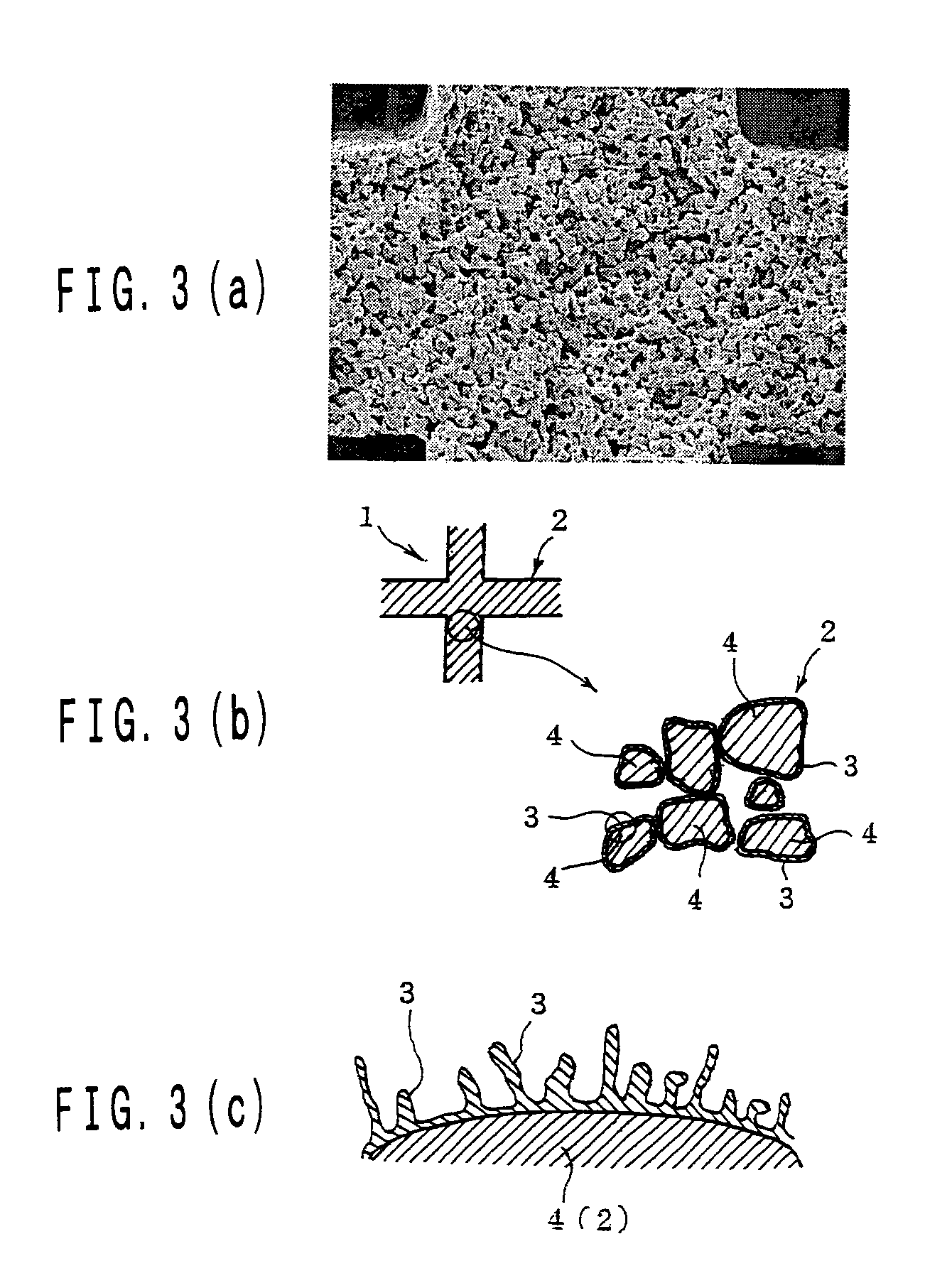
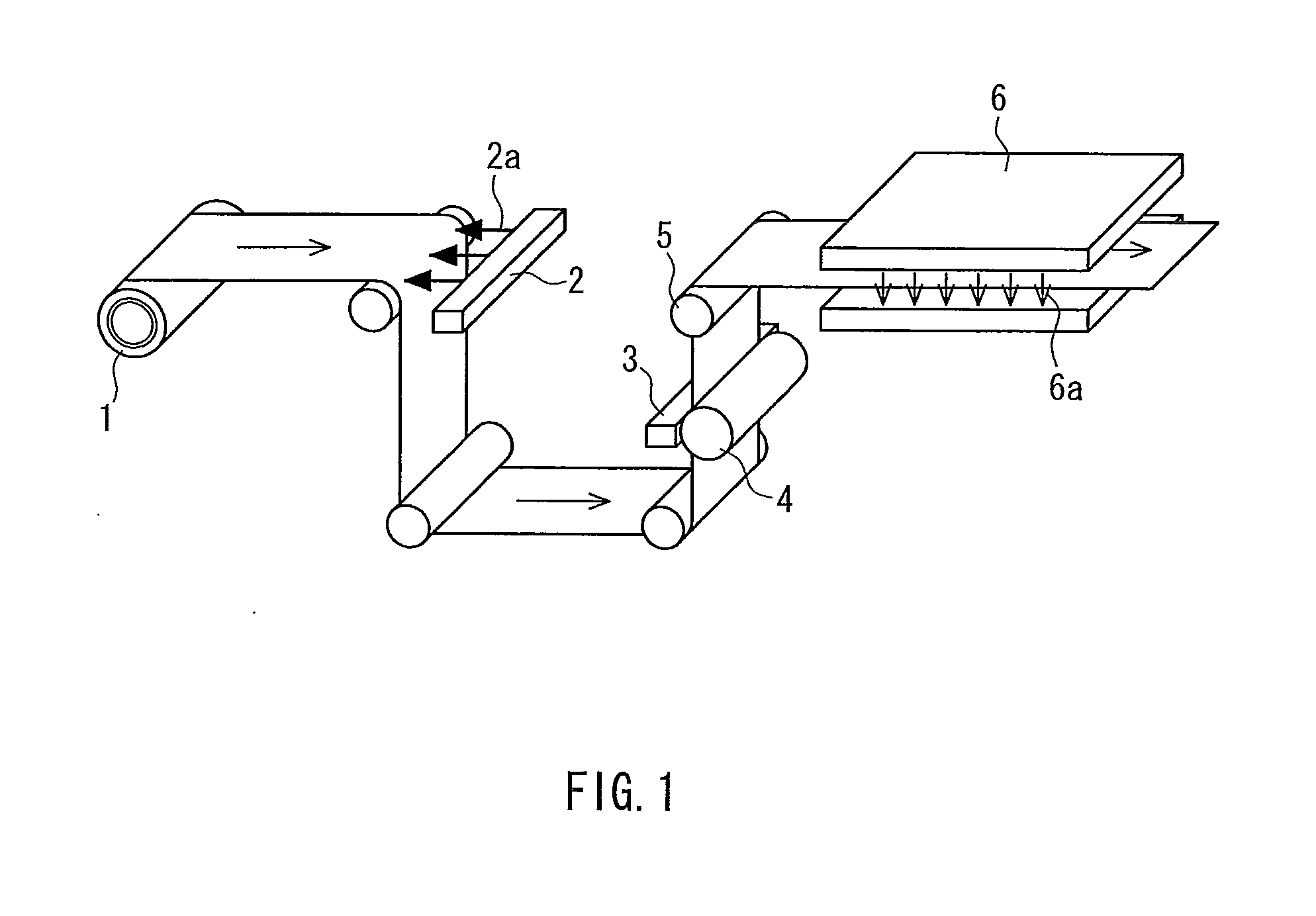
InactiveUS7250385B1Excellent hold propertyExcellent heat resistanceInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle separationThermal waterAluminium oxide
The invention is a catalyst formed by covering each surface of particles in a ceramic support with an alumina thin film and holding an active catalyst component with the surface of the thin film, which is large in the pore size and porosity and small in the pressure loss irrespectively of forming the alumina thin film on the surface and is produced, for example, by immersing the ceramic support in an aluminum-containing metallic compound, preliminarily firing, immersing in hot water, drying, firing and finally holding the active catalyst component on the alumina thin film on the surface of the support.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Slurry for forming insulating layer, separator for electrochemical device, method for producing the same, and electrochemical device
InactiveUS20100221965A1Excellent heat resistanceHigh reliabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsElectrochemistryMaterials science
A slurry for forming an insulating layer of the present invention includes heat-resistant insulating fine particles, a thickening agent, and a dispersion medium. The insulating fine particles are dispersed in the dispersion medium. The slurry for forming an insulating layer has a viscosity of 5 to 500 mPa·s. The proportion of particles with a particle size of 1 μm or less in the insulating fine particles is 30 vol % or more and the proportion of particles with a particles size of 3 μm or more in the insulating fine particles is 10 vol % or less. An electrochemical device of the present invention includes a separator for an electrochemical device of the present invention that is produced using the slurry for forming an electrochemical device of the present invention.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Polyamide Resin Composition with Excellent Reflectivity, Heat Resistance, and Water Resistance
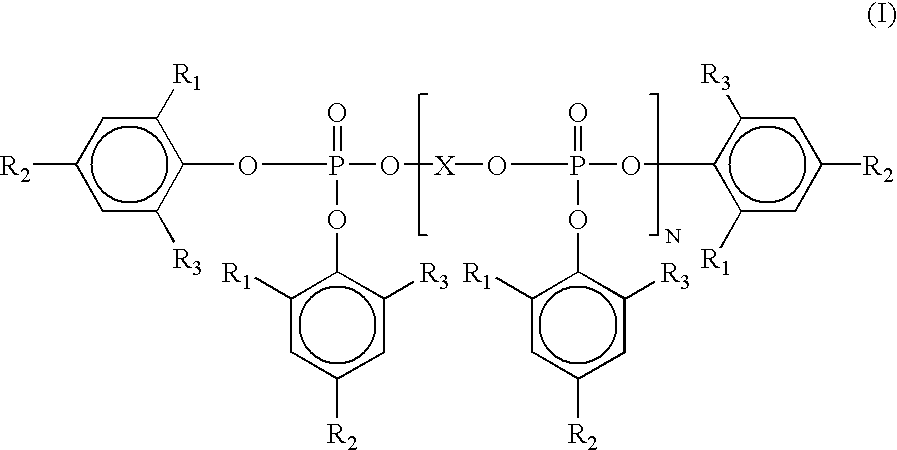
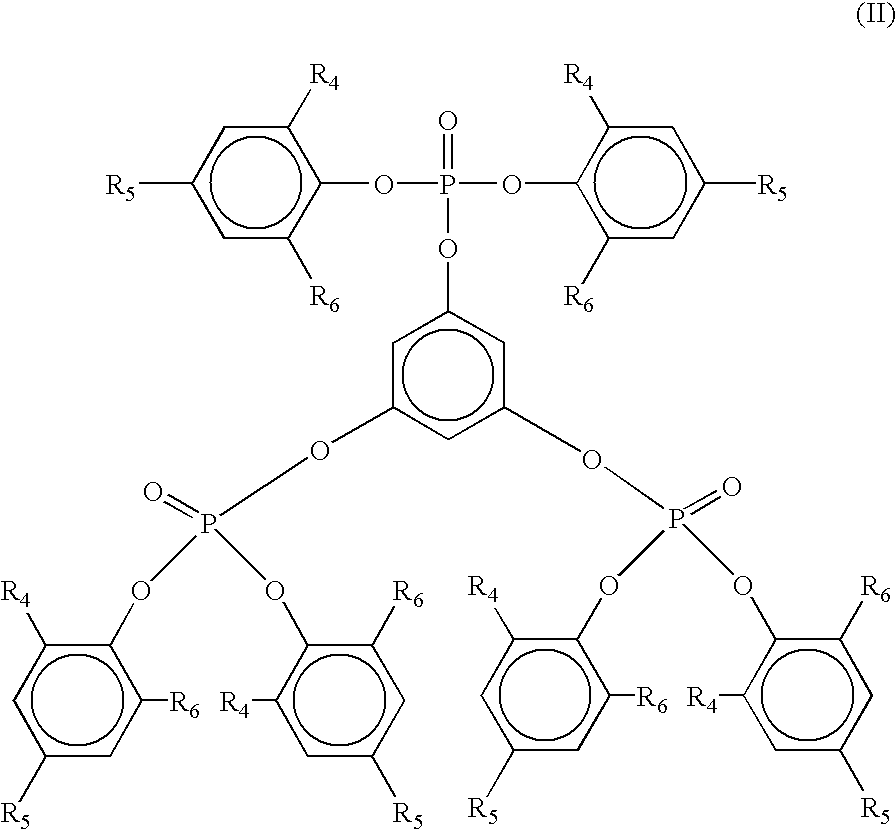
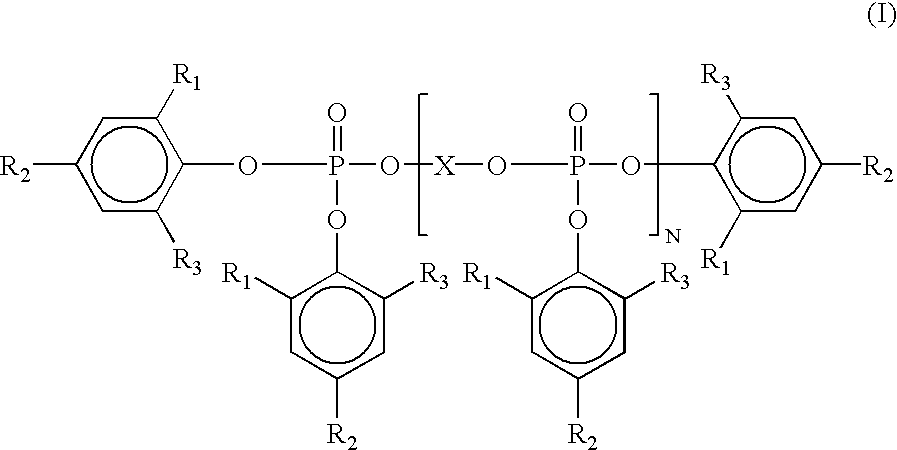
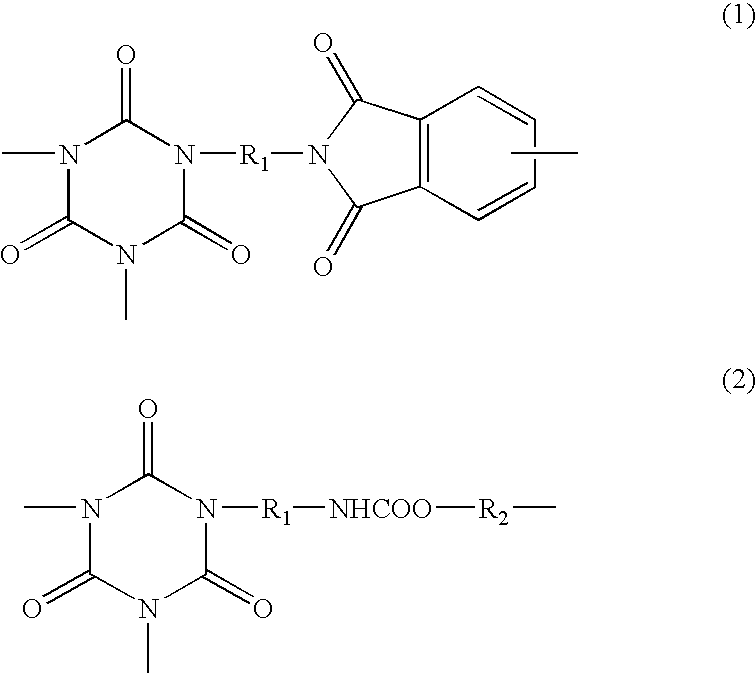
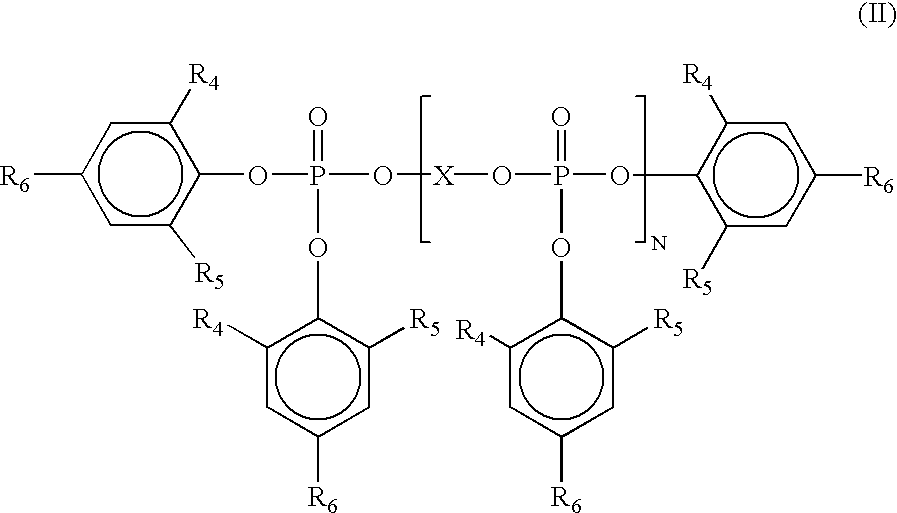
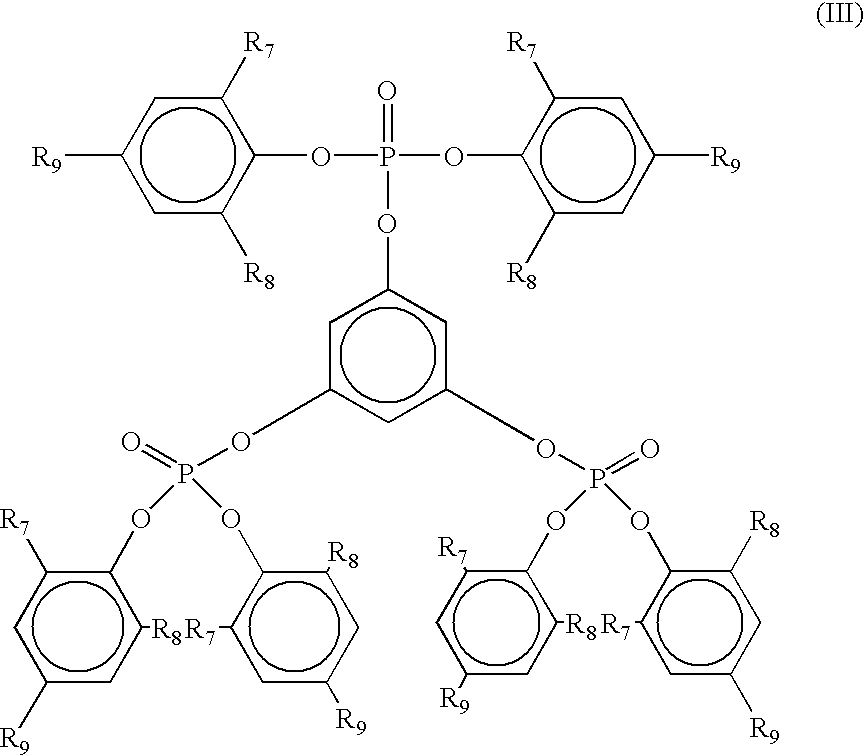
ActiveUS20130281587A1Excellent heat resistanceExcellent water resistanceOther chemical processesPhosphorus organic compoundsPolymer chemistryWater resistance
Owner:LOTTE ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Process for manufactruing superfine nano noble metal solution
The process of preparing nanometer noble metal solution is one chemical reduction process to reduce Cu, Ag or Au ion stabilized with different dispersant into nanometer Cu, Ag or Au particle while adding various kinds of protecting agent to inhibit the agglutination of nanometer particle. The process can prepare superfine nanometer noble metal solution of average granularity smaller than 5 nm and with high stability and greatly raised tolerance to acid, alkali, oxygen, light and heat, and the superfine nanometer noble metal solution has altered physical characteristic and expanded application range.
Owner:徐健宏
Organic compound, charge-transporting material, composition for charge-transporting material and organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20090284134A1Excellent heat resistanceExcellent amorphous natureOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceSinglet state
An organic compound having excellent heat resistance, an excellent amorphous nature, an excellent ability to transport charges, highly excited singlet and triplet states, and excellent solubility in an organic solvent is an organic compound represented by Formula (I):wherein Ar1 represents an optionally-substituted aromatic hydrocarbon group, an optionally-substituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or an optionally-substituted alkyl group; Ar2 represents an optionally-substituted aromatic hydrocarbon group or an optionally-substituted aromatic heterocyclic group; R1 and R2 each represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, and R1 and R2 may be bonded to each other to form a ring; and Q is represented by Formula (I-1) or (I-2):wherein Ar3 to Ar5 each represent an optionally-substituted aromatic hydrocarbon group or an optionally-substituted aromatic heterocyclic group, and Ar3 and Ar4 may be bonded to each other to form a ring.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
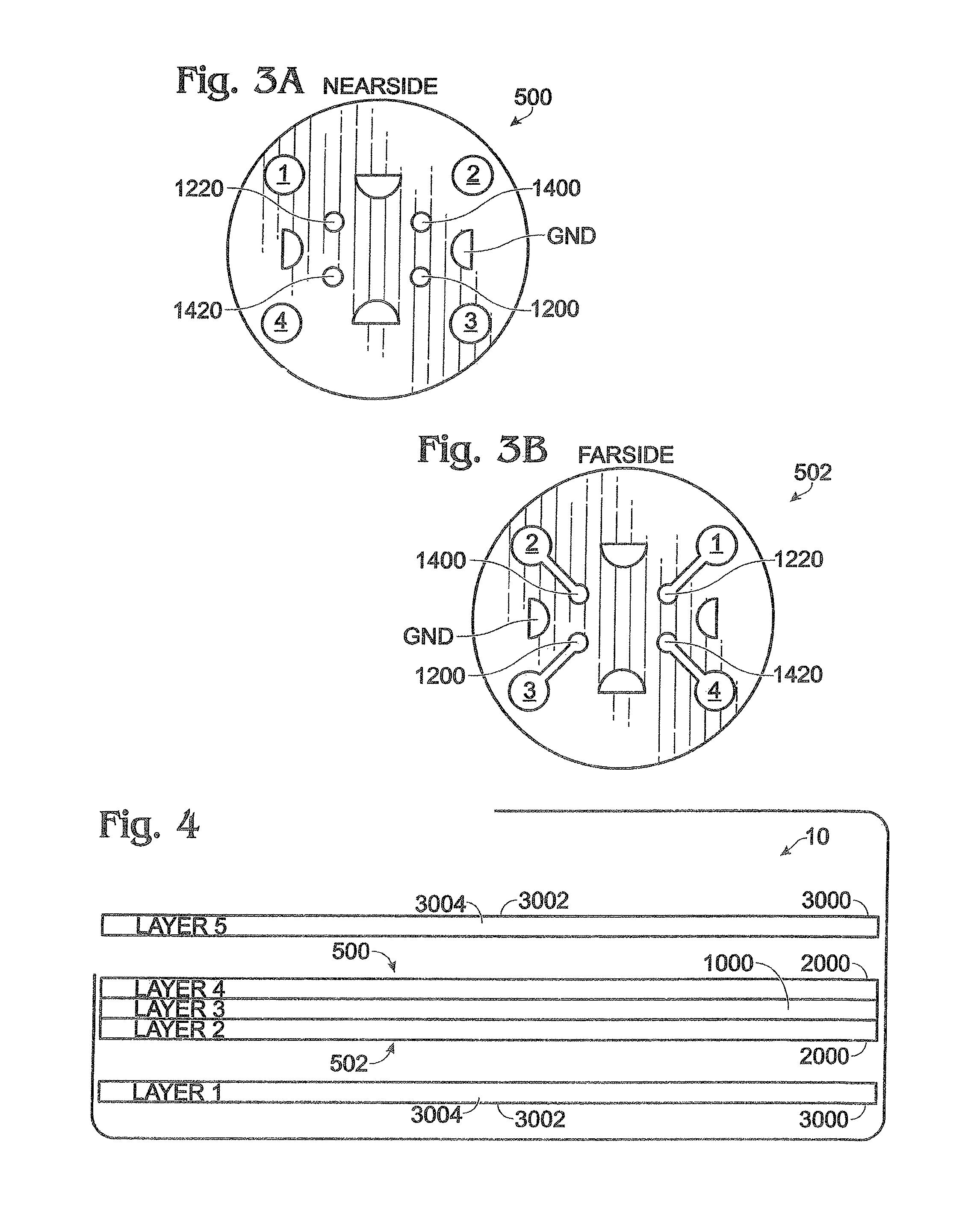
Coupler device
ActiveUS8044749B1Reduce thicknessExcellent heat resistanceMultiple-port networksWaveguidesDielectric substrateGround plane
The present invention is directed to a coupler that includes a coupler structure including at least one first transmission line disposed on a first major surface of a coupler dielectric substrate and at least one second transmission line disposed on a second major surface of the coupler dielectric substrate. The coupler structure includes four symmetric ports such that each port of the four symmetric ports is characterized by substantially identical impedance characteristics. A first ground plane structure is coupled to the coupler structure and including a first outer dielectric material and a first conductive exterior layer disposed substantially parallel to the first major surface. A second ground plane structure is coupled to the coupler structure and including a second outer dielectric material and a second conductive exterior layer disposed substantially parallel to the second major surface. A thermal path is disposed between the coupler structure and at least one of the first conductive exterior layer or second conductive exterior layer. The thermal path is characterized by a thermal resistance substantially within a range between 15 W / mK and 50 W / mK, such that the coupler has a power handling capability of more than 800 W per square inch of heat sink interface.
Owner:TTM TECH INC
Toner and full-color image forming method
InactiveUS20020051924A1High transparencyExcellent low temperature fixabilityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternWaxAbsorption curve
A toner, particularly a color toner suitable for full-color image formation through a substantially oil-less heat-pressure fixing device, is formed from at least a binder resin, a colorant and a wax. The toner has viscoelasticity including: a storage modulus at 80° C. (G'80) in a range of 1x106-1x1010 dN / m2, storage moduli at temperatures of 120-180 ° C. (G'120-180) in a range of 5x103-1x106 dN / m2, and loss tangents (tan delta=G'' / G' as a ratio between G'' (loss modulus) and G' (storage molecules)) including a loss tangent at 180° C. (tan delta180) and a minimum of loss tangents over a temperature range of 120-180 ° C. (tan deltamin) satisfying 1<=tan delta180 / tan deltamin. The toner further exhibits a thermal behavior providing a heat-absorption curve according to differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showing a maximum heat-absorption peak temperature in a range of 50-110 ° C. in a temperature range of 30-200° C.
Owner:CANON KK
Sealing composition and seals made by using the same
InactiveUS20050054753A1Excellent heat resistanceImprove heat resistanceEngine sealsOther chemical processesCompression setPolyimide
The invention relates to a sealing composition which comprises a crosslinkable fluoroelastomer, a crosslinking agent for this elastomer and a reinforcing polyimide resin powder; and seals such as O-rings, made by molding the composition into a prescribed shape and crosslinking the molded article. According to the invention, seals free from metals and sulfur can be made from a fluoroelastomer suitable for the production unit for semiconductor devices without a scatter of physical properties within one seal or among seals, and the obtained seals are lowered in the compression set determined ate the same hardness level to cause little permanent set by compression in use, thus having a prolonged service life.
Owner:JTEKT CORP +1
Epoxy resin composition for use in a carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material, prepreg, and carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveUS20130005855A1Excellent in tensile strength and compressive strengthExcellent heat resistanceBuilding materialCarbon fiber reinforced composite
Disclosed is a carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material that is suitable for use as a construction material and exhibits high mechanical strength in harsh usage environments such as low-temperature environments and high-temperature moisture-absorbing environments. Also disclosed are an epoxy resin composition for producing the aforementioned carbon-fiber-rein-forced composite material and a prepreg obtained through the use of said epoxy resin composition. Said epoxy resin composition comprises at least the following constituents, by mass with respect to the total mass of the composition: (A) between 20% and 80% of an epoxy resin having the structure represented by formula (1); and (B) between 10% and 50% of an epoxy resin that has at least two ring structures with four or more members each and also has one amine glycidyl or ether glycidyl directly connected to a ring structure.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Non-yellowing alkali weight reduction wet-process dyed polyurethane resin for superfine fiber synthetic leather and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102276783AImprove hydrolysis resistanceExcellent acid and alkali resistanceTextiles and paperPolyurethane elastomerAlcohol
The invention belongs to a polyurethane elastomer material and a preparation method thereof and in particular relates to non-yellowing alkali deweighting wet method dyeing polyurethane resin for superfine fiber synthetic leather and a preparation method thereof. The invention adopts the following technical scheme that: the non-yellowing alkali deweighting wet method dyeing polyurethane resin for the superfine fiber synthetic leather is characterized by mainly comprising the following components based on the total mass of the polyurethane resin: 16 to 20 percent of macromolecular dihydric alcohol compound, 2.5 to 4 percent of chain extender, 7.5 to 10.5 percent of diisocyanate and 68 to 72 percent of solvent, wherein the chain extender consists of dihydric alcohol, diamine and an alcohol amine compound. According to the above scheme, the invention provides the non-yellowing alkali deweighting wet method dyeing polyurethane resin for the superfine fiber synthetic leather and the preparation method thereof so as to solve the problems at present.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAFON SYNTHETIC RESIN
Special modified rosin resin for road marking paint and preparation method of special modified rosin resin
InactiveCN103360952AStrong absorption capacityImprove thermal stabilityRosin coatingsNatural resin chemical modificationLacquerAntioxidant
The invention discloses a special modified rosin resin for road marking paint and a preparation method of the special modified rosin resin. The modified rosin resin comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 67.4%-84.8% of gum rosin, 10%-18% of glycerol, 2%-8% of fumaric acid, 3%-6% of lauric acid, 0.1% - 0.3% of antioxidant and 0.1% - 0.3% of ultraviolet light absorber. The preparation method of the special modified rosin resin comprises the following steps of: adding the gum rosin to a reaction kettle, introducing nitrogen, heating so as to dissolve rosin, adding the fumaric acid, the antioxidant, the glycerol and the lauric acid so as to carry out polymerization esterification reaction, then adding the ultraviolet light absorber, uniformly stirring, and cooling to a room temperature, thus obtaining the product. The modified rosin resin produced by the method can be used for ensuring the strong adhesive force of coatings and has good flexibility and the advantages of cost conversation and environmental protection.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHONGCHANG RESIN
Moldings of flame-retardant aromatic polycarbonate resin compositions
InactiveUS20050159518A1Excellent heat resistanceExcellent flame retardancySpecial tyresCeramic shaping apparatusPolycarbonateBisphenol-A-polycarbonate
A molded article produced by injection-molding a molten form of a flame-retardant aromatic polycarbonate resin composition comprising: 100 parts by weight of an aromatic polycarbonate (A) (Mw: 17,000 to 35,000), 0.01 to 3 parts by weight of inorganic compound particles (B) (average diameter: 10 nm to 10 μm), 0.001 to 0.5 part by weight of an alkali metal salt (C) of an organic sulfonic acid, and 0.01 to 0.5 part by weight of a fluoropolymer (D), wherein the largest FL / t ratio of the molded article is 50 or more, wherein FL is a flow length of the composition in a mold and t is a thickness of the molded article, the FL / t ratios being obtained by measuring the thicknesses of the molded article at portions corresponding to flow paths (L) (from a gate to points at which the flow of the composition stops) of the composition in the mold during the molding, and calculating an integral of (dL / T′) along each (L) (dL: length of a segment of (L), t′: thickness of the molded article at a portion corresponding to the segment), wherein the calculated integrals are defined as the FL / t ratios.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Resin composition for printed wiring board
InactiveCN102209754AImprove heat resistanceGood solvent resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSynthetic resin layered productsHeat resistanceSolvent
Disclosed is a resin composition for printed wiring boards that comprises (A) a polyimide resin that has hexafluoroisopropanol groups and a siloxane structure and (B) a heat curable resin. The resin composition has excellent solvent resistance and excellent heat resistance with little temperature variation in the modulus of elasticity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Thermal conductive sheet
InactiveUS20130200298A1Excellent formabilityExcellent heat resistanceSolid-state devicesHeat-exchange elementsChemistryBoron nitride
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
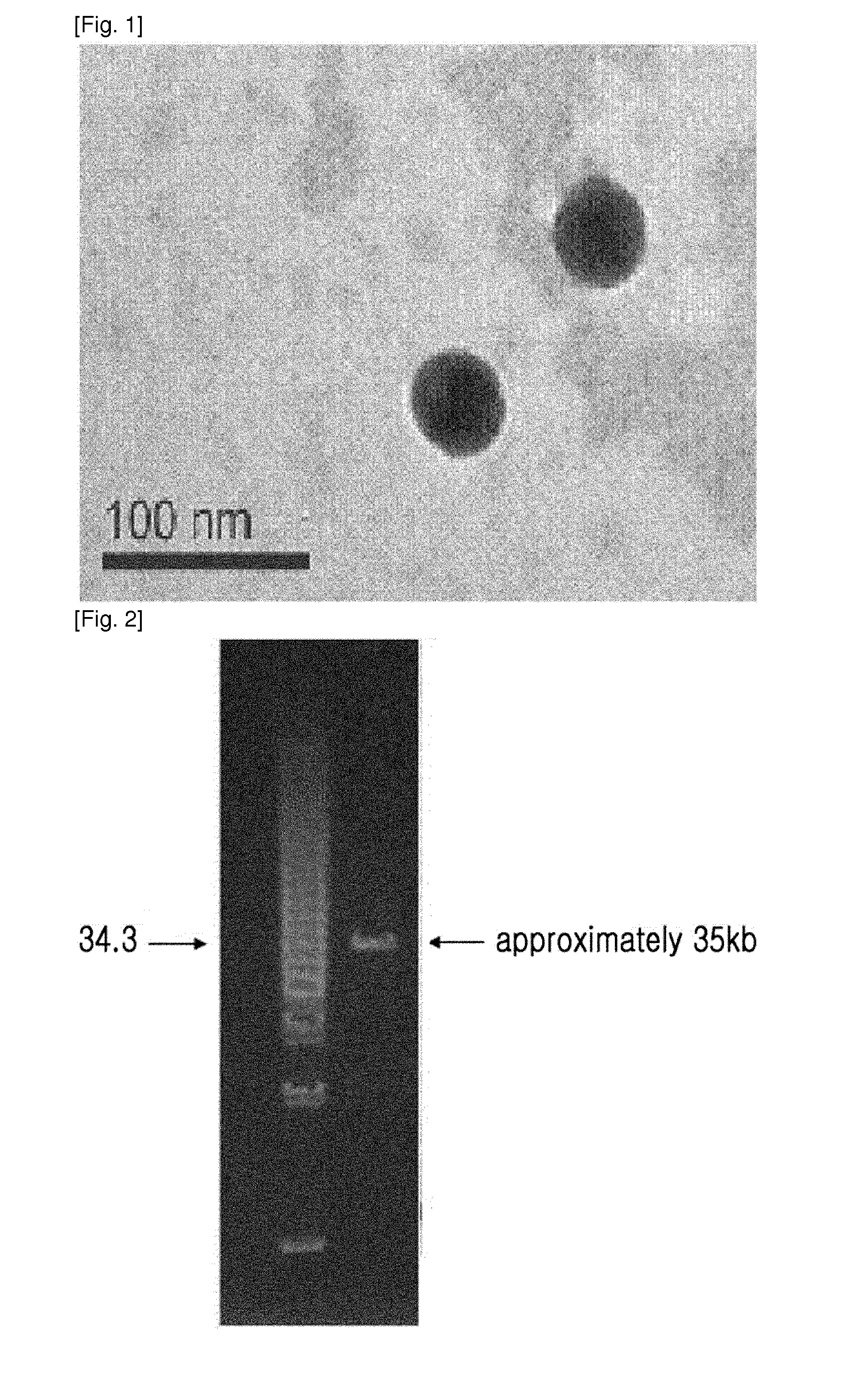
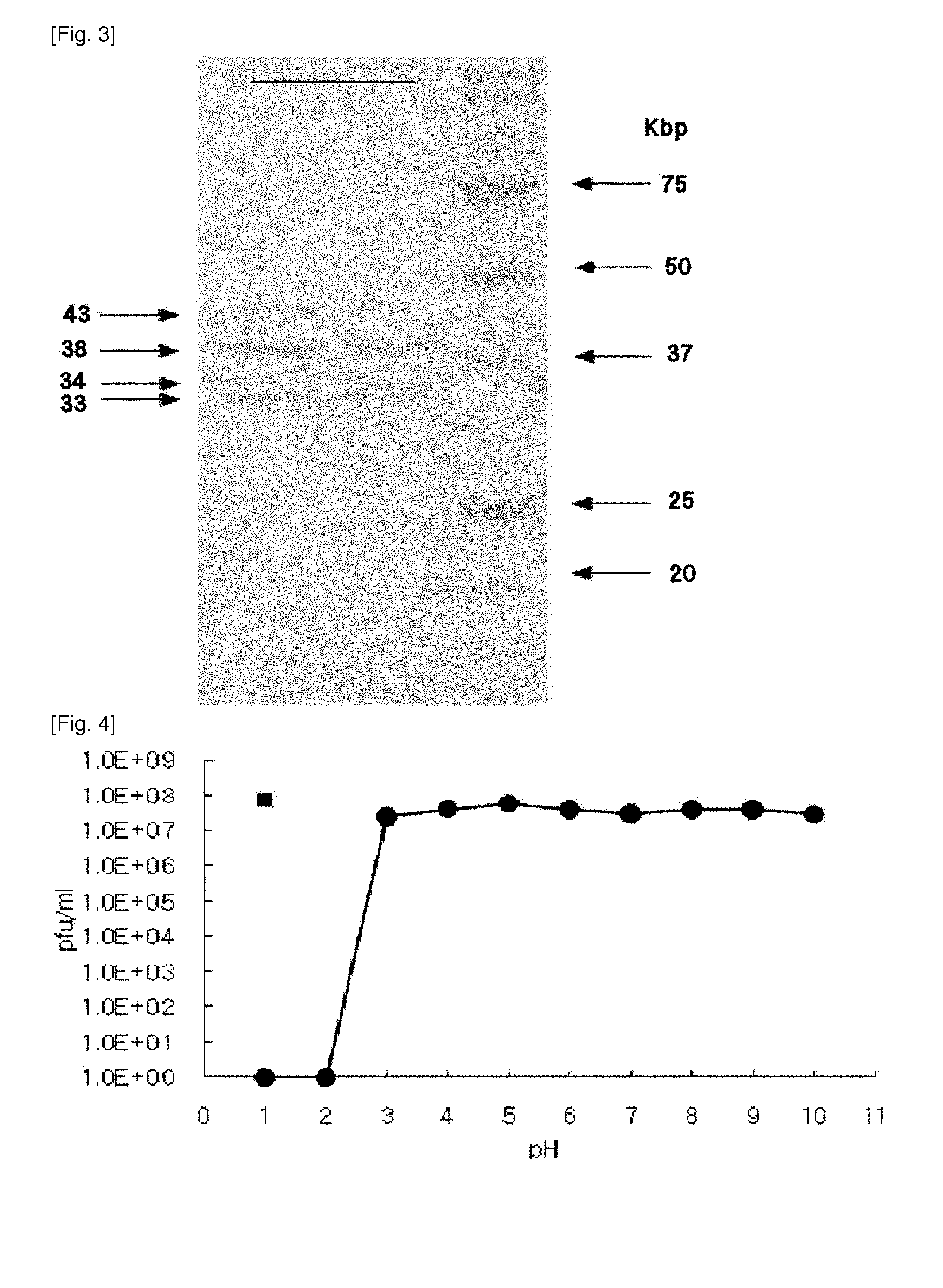
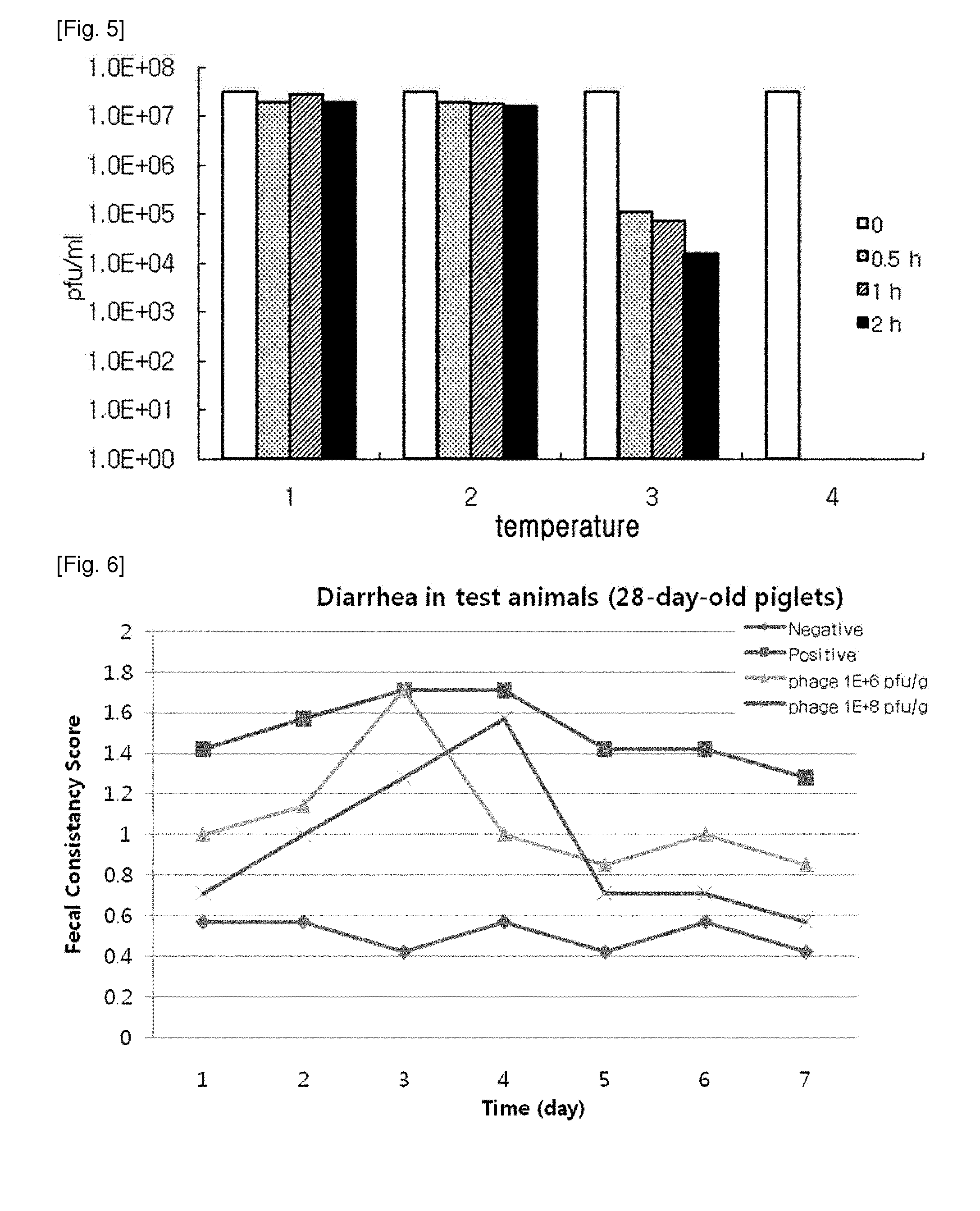
Novel isolated bacteriophage having e. coli-specific bactericidal activity and antibacterial composition comprising the same
ActiveUS20140356330A1Good acidExcellent heat-resistanceAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliPhage therapy
The present invention relates to a novel bacteriophage having an E.-coli-specific bactericidal activity, a composition for the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases caused by Enterotoxigenic E.-coli comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, an antibiotic comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, a feed additive composition comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, a sanitizer or cleaner comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, and a method for treating colibacillosis using the bacteriophage. The novel bacteriophage of the present invention has a specific bactericidal activity against pathogenic E. coli, and excellent acid- and heat-resistance. Therefore, the novel bacteriophage can be used for the prevention or treatment of swine colibacillosis, which is an infectious disease caused by pathogenic E.-coli, and can also be widely used in animal feed additive compositions, sanitizers, and cleaners.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Binder Fiber and Separator for Alkaline Cell Using Same
InactiveUS20070232175A1Excellent workabilityExcellent heat resistanceMonocomponent copolyamides artificial filamentSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperPolyamideAlkane
A binder fiber comprising a polyamide component in at least part of a surface thereof is prepared. The polyamide component contains a semi-aromatic polyamide at least having an aromatic ring unit and a C3-7 alkane unit which may have a branched CA 1-3 alkyl chain. In the binder fiber, the polyamide component may be (a) a semi-aromatic copolyamide having an aromatic ring unit, a C3-7 alkane unit which may have a branched C1-3 alkyl chain, and a C8-12 alkane unit which may have a branched C1-3 alkyl chain. The polyamide component may be (d) a combination of (b) a semi-aromatic polyamide and (c) a semi-aromatic polyamide, wherein the polyamide (b) has an aromatic ring unit and a C3-7 alkane unit which may have a branched C1-3 alkyl chain, and the polyamide (c) has an aromatic ring unit and a C8-12 alkane unit which may have a branched C1-3 alkyl chain.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Thermoplastic flameproof resin composition
InactiveUS20020065343A1Improve flame retardant performanceExcellent heat resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPhosphorus organic compoundsPhosphoric Acid EstersPolymer science
A flameproof thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention comprises (A) a base resin comprising 40 to 95% by weight of a rubber modified styrene-containing resin (a1) composed of 20 to 100% by weight of a styrene-containing graft copolymer resin (a11) and 0 to 80% by weight of a styrene-containing copolymer resin (a12), and 60 to 5% by weight of polyphenylene ether resin (a2); (B) 2 to 40 parts by weight of a styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer containing 5 to 18% by weight of acrylonitrile per 100 parts by weight of the base resin; (C) 5 to 30 parts by weight of an aromatic phosphoric acid ester compound having a melting point of more than 90° C. per 100 parts by weight of the base resin; and (D) 3 to 30 parts by weight of a phenolic resin per 100 parts by weight of the base resin. The flameproof thermoplastic resin composition may further comprise 0 to 30 parts by weight of an anti-dripping agent, an impact modifier, a plasticizer, a heat stabilizer, an oxidation inhibitor, a light stabilizer, a compatibilizer, pigments, dyes and / or inorganic fillers on the basis of 100 parts by weight of the base resin.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Thermosetting polyimide resin composition process for producing polyimide resin, and polyimide resin
InactiveUS6887967B2Easily produceExcellent heat resistancePrinted circuit manufactureCircuit susbtrate materialsPrepolymerDielectric loss
A thermosetting polyimide resin composition is provided which comprises a polyimide resin and an epoxy resin, which has excellent heat resistance, low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss tangent and also yields a cured article having good mechanical properties such as tensile strength and tensile elongation. Also, a process for producing a polyimide resin used in the polyimide resin composition is provided. The thermosetting polyimide resin composition comprises a polyimide resin (X), which has a carboxyl group and a linear hydrocarbon structure having a number-average molecular weight of 300 to 6,000, and an epoxy resin (Y). The polyimide resin is obtained by reacting a prepolymer (A) having an isocyanate group at the end, which is obtained by reacting a polyisocyanate compound (a1) with a polyol compound (a2) having a linear hydrocarbon structure in which a number-average molecular weight of a linear hydrocarbon structure is from 300 to 6,000, with an anhydride (B) of polycarboxylic acid having three or more carboxyl groups in an organic solvent.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Battery separator, and battery separator manufacturing method
ActiveUS20140349169A1Excellent adhesionExcellent heat resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsLi-accumulatorsPorous membranePolypropylene
A battery separator includes a porous membrane A with a thickness of less than 10 μm including a polypropylene resin, and a porous membrane B laminated thereon including a heat resistant resin and inorganic particles or cross-linked polymer particles, wherein the porous membrane A satisfies a specific range of thickness, average pore size, and porosity, and the entire battery separator satisfies a specific range of thickness, peeling strength at the interface between the porous membrane A and the porous membrane B, and difference in air resistance between the entire battery separator and the porous membrane A.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Battery separator, and battery separator manufacturing method
ActiveUS20150228949A1Excellent adhesionExcellent heat resistanceCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufacturePorous membraneElectrical battery
A battery separator includes a porous membrane A including a polyethylene resin, and a porous membrane B laminated thereon including a heat resistant resin and inorganic particles or cross-linked polymer particles, wherein the porous membrane A satisfies expressions (a) to (c), and the entire battery separator satisfies expressions (d) to (f).
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Flexible laminose plate and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN1733473AExcellent adhesionExcellent heat resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationMetal foilEngineering
To provide a flexible laminated board coping with mounting conditions under high temperature and high pressure while retaining characteristics possessed by the flexible laminated board. In the flexible laminated board having a metal foil on one surface or both surfaces of an insulating resin layer, the insulating resin layer comprises a plurality of layers of a polyimide resin provided with at least one high elastic modulus resin layer in contact with the metal foil of a polyimide resin with >=1*10<8>Pa storage elastic modulus at 350[deg.]C, and at least one low thermal expansion resin layer of <=20*10<-6> / K linear expansion coefficient, where the rate of thickness of the high elastic modulus layer in the insulating resin layer is in the range of 3-45%.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICALL &MATERIAL CO LTD
Ultraviolet-cured acrylic ester hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107201180ASolve the dangerSolve the smell problemNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer scienceUltraviolet
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ultraviolet-cured acrylic ester hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesive. The ultraviolet-cured acrylic ester hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesive for an adhesive tape is in the form of a non-solvent 100-percent hot melt adhesive, is mainly prepared from an acrylic ester series polymer, a photo-initiator component binding to a main chain of the polymer, and a tackifying resin which is adopted as required, can be cured rapidly under the radiation of ultraviolet C (the wavelength is 190 to 280 nanometers), has high heat resistance characteristic at the temperature of 120 to 140 DEG C, can be applied to industrial adhesive tapes, can be taken as a bonding agent for automobile heating components, has the characteristics of nontoxicity, safety, skin affinity and adjustable glass transition temperature, and can be applied in the field of sanitary and medical products. The ultraviolet-cured acrylic ester hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesive can be coated under a high gram weight and at a high speed on the aspect of coating implementation; the problems of solvent explosion danger, solvent discharge and odor in the solvent type acrylic acid series pressure-sensitive adhesive are solved.
Owner:WUXI WANLI ADHESION MATERIALS
Flameproof thermoplastic resin composition
InactiveUS6451889B1Maintain good propertiesExcellent heat resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPhosphorus organic compoundsThermoplasticPhosphoric Acid Esters
A flameproof thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention comprises (A) 100 parts by weight of a rubber modified styrene-containing base resin composed of 20~100% by weight of a styrene-containing graft copolymer resin and 0~80% by weight of a styrene-containing copolymer resin; (B) 5~40 parts by weight of a phenolic resin; (C) 3~40 parts by weight of a PPE resin having a hindered phenolic structure; and (D) 5~30 parts by weight of an aromatic phosphoric acid ester having a hindered phenolic structure. Said flameproof thermoplastic resin composition may further comprise 0.01~2.0 parts by weight of a fluorine resin to 100 parts by weight of said rubber modified styrene-containing base resin.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
LED fluorescent glue and packaging method for improving luminescence uniformity, and LED
InactiveCN105845812AGood dispersionLarge specific surface areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesFluorescenceWavelength
The invention discloses an LED fluorescent glue that improves the uniformity of light emission. In parts by weight, the fluorescent glue consists of 1 part of packaging glue, 0.01-1 part of fluorescent powder, 0.01-0.1 part of silica-based inorganic nanoparticles, 0.01 part of ‑1 part silicone granules. Inorganic nanomaterials and silicone particles are mixed in the encapsulation glue, which reduces the sedimentation rate of the phosphor in the encapsulation glue, improves the uniformity of the phosphor distribution in the colloid, makes the white light spot more uniform, and improves the light diffusivity and transmittance. The light rate is maximized, and by changing the propagation path of the light, the light of various wavelengths is more fully mixed, and the spatial color uniformity of the light is further improved. It also provides an LED packaging method and LED that improve the uniformity of light emission, which improves the consistency of products, reduces the probability of uneven color distribution in space due to uneven distribution of phosphor powder, and improves product yield and product production. efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN JUFEI OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
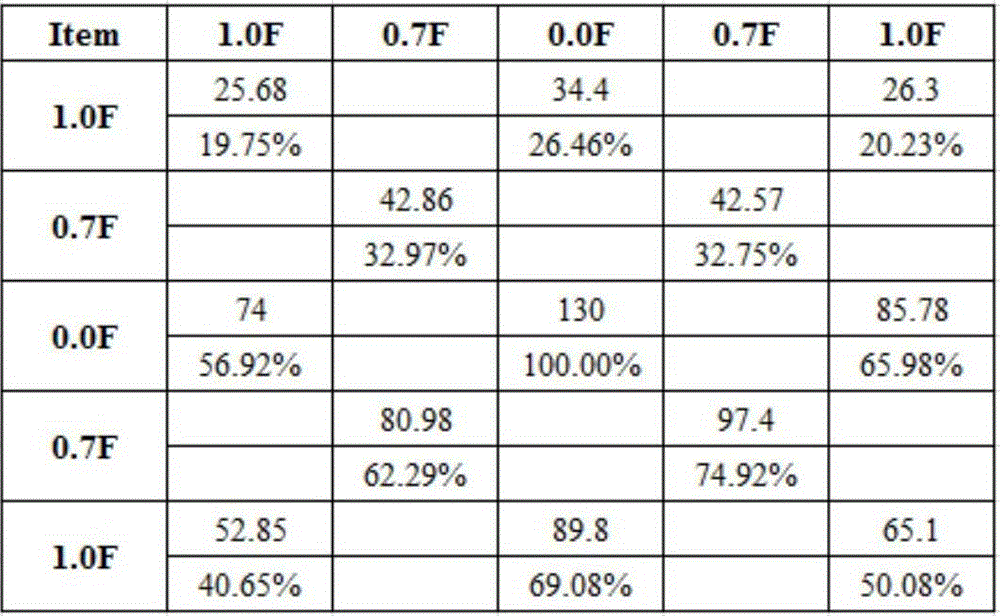
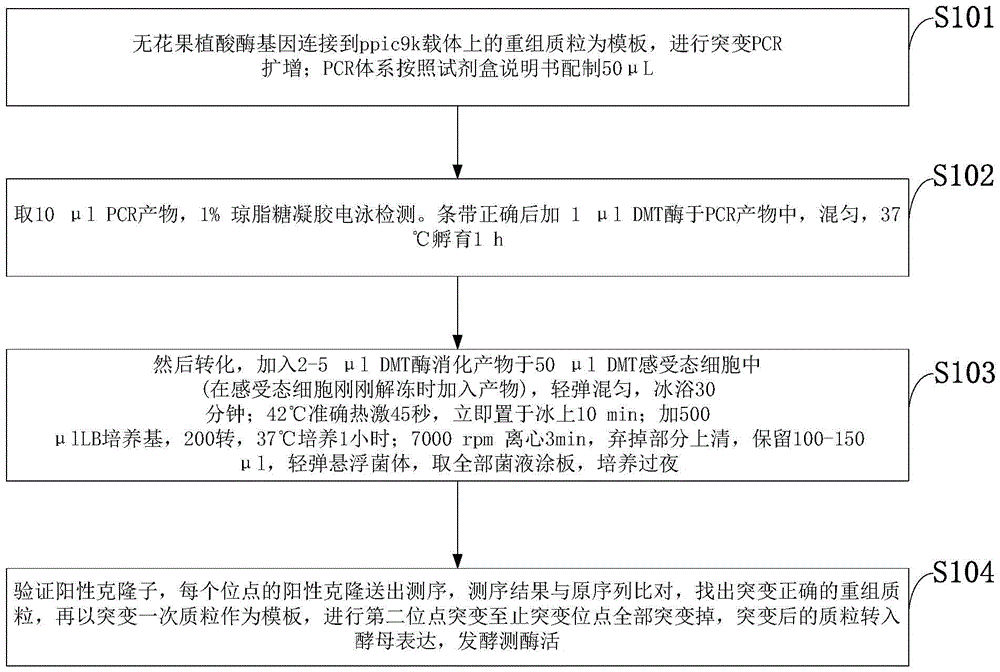
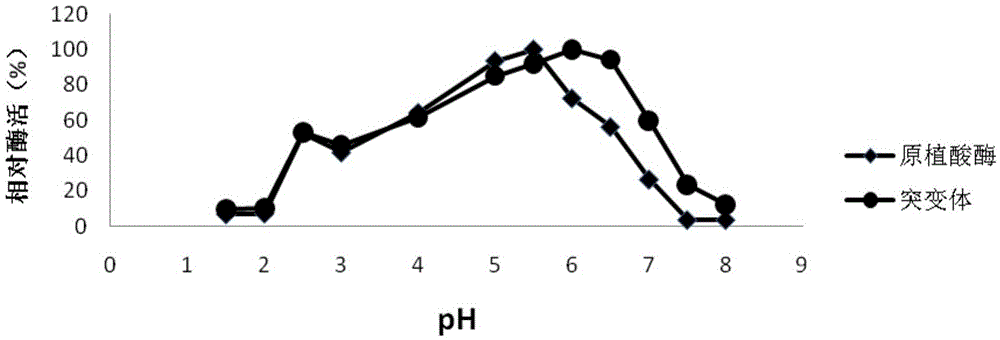
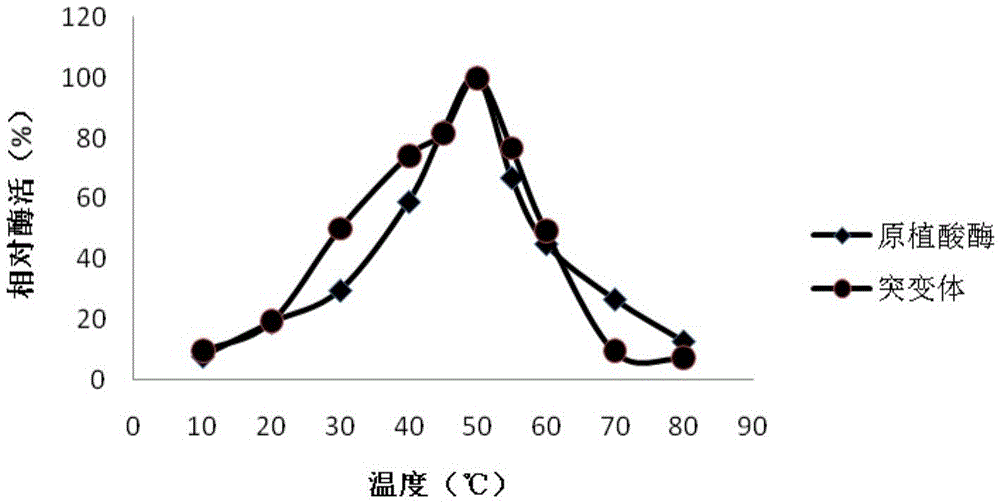
Phytase mutant and applications thereof
InactiveCN105567656AImprove heat resistanceExcellent heat resistanceFungiHydrolasesFeed additiveAmino acid
The invention discloses a phytase mutant and applications thereof. The sequence of the phytase mutant is represented by SEQ ID No.1. The mutant is obtained through the following mutations of amino acid that encodes the amino acid sequence (SEQ ID No.3) of fig aspergillus phytase: A39E, N40D, S42L, V43S, I44V, P46S, R167G, Q169T, P170N, G171R, Q172A, T252R, S253T, T254S, V255D, D256A, T257S, and K258Q. The phytase mutant can be used in feed additive. A mutant (SEQ ID No.2) of novel phytase gene is obtained. The mutant is effective in a wide pH range, has an ideal heatproof characteristic, is suitable for high temperature granulation, and meets the requirements of feed industry.
Owner:KUNMING QACTIVE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Epoxy resin adhesive for potting PVDF hollow fiber membrane and preparation method of epoxy resin adhesive
InactiveCN104371626AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove aging resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesHydrophobic silicaSilicon oxide
The invention provides an epoxy resin adhesive for potting a PVDF hollow fiber membrane. The epoxy resin adhesive comprises a component A and a component B at a mass ratio of 100 to (15-35), wherein the component A comprises 50-70 parts of epoxy resin, 5-15 parts of a toughening agent and 1-5 parts of a defoaming agent, the component B comprise an amine curing agent, the epoxy resin comprises bisphenol A diglycidyl ether; the toughening agent is a low-molecular polyurethane or polyol glycidyl ether; and the defoaming agent is one or more selected from organic phosphonic acid, polysiloxane, fatty alcohol, fatty acid ester and hydrophobic silicon oxide. The epoxy resin adhesive provided by the invention has the advantages of excellent mechanical property, aging resistance, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, good flexibility and the like, especially, the flexibility is enhanced and the problems of breakage and soaking of a membrane fiber during the potting of the epoxy resin adhesive are solved.
Owner:HUNAN OVAY TECH CO LTD
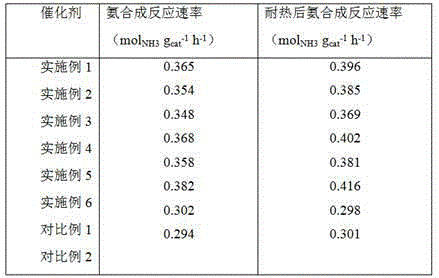
Preparation method of carbon material-supported ruthenium metal catalyst containing barium auxiliary agent
InactiveCN105413683AHigh activityExcellent heat resistanceHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBarium nitrateHydrogen atmosphere
The invention provides a preparation method of a carbon material-supported ruthenium metal catalyst containing a barium auxiliary agent and relates to a preparation method of a catalyst taking a carbon material as a carrier, ruthenium metal as an active component and barium as an auxiliary agent. The preparation method particularly comprises the following steps: firstly, impregnating a ruthenium metal loaded carbon material into a barium nitrate water solution and carrying out reduction treatment under a certain temperature; treating the sample at a certain temperature range under the condition that carbon-containing gas exists; finally, reducing in a hydrogen atmosphere or nitrogen-hydrogen mixed gas to obtain the carbon material-supported ruthenium catalyst containing the barium auxiliary agent. Compared with the carbon material-supported ruthenium metal catalyst containing the barium auxiliary agent, which is prepared by an existing method, the catalyst provided by the invention has relatively high ammonia synthesis activity and heat stability and a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIVERSITY
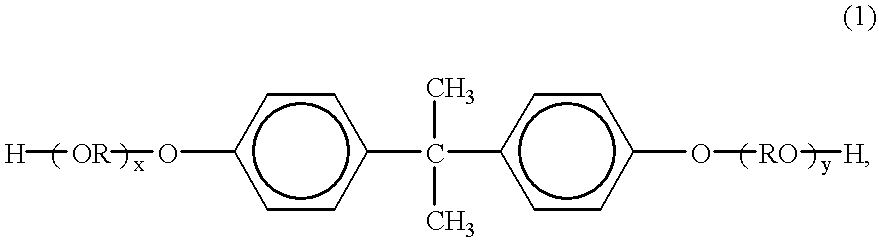
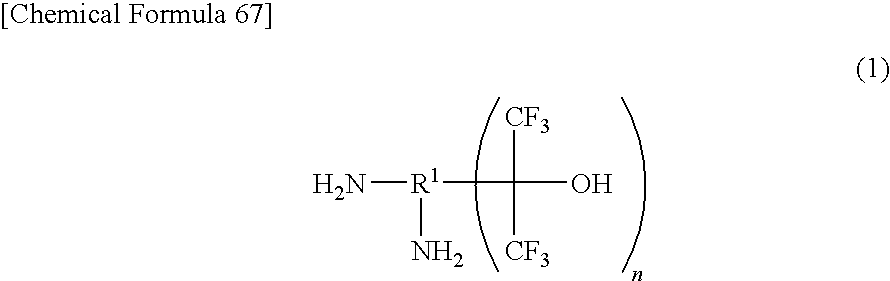
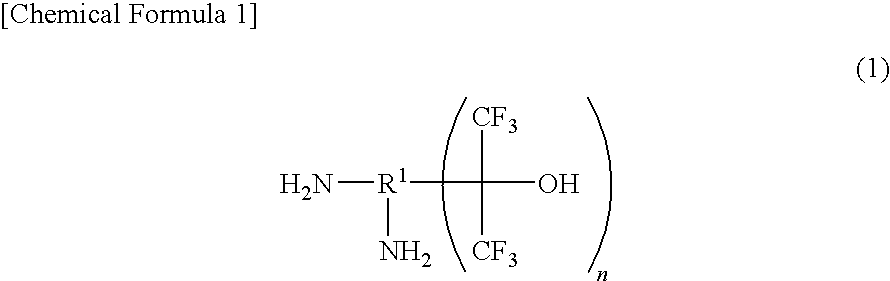
Fluorinated Diamine and Polymer Formed Therefrom
InactiveUS20100029895A1Heat resistance characteristic been improvedImprove rigidityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationThermal expansionAromatic hydrocarbon
There is provided a fluorine-containing diamine represented by formula (1).In this formula, R1 represents a condensed polycyclic type aromatic hydrocarbon group, and at least one —C(CF3)2OH group and at least one —NH2 group are in a relation such that they are attached to adjacent carbons of carbon atoms constituting the condensed polycyclic type aromatic hydrocarbon group. Polymer compounds derived from this fluorine-containing diamine have superior low dielectric property and low water-absorbing property, and, in addition to that, shows low thermal expansion property and high glass transition temperature.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Al alloy film for use in display device
InactiveUS20120301732A1Excellent heat resistanceHigh heat resistanceCellsVacuum evaporation coatingRare-earth elementCorrosion
Disclosed is an Al alloy film for use in a display device, which does not undergo the formation of hillocks even when exposed to high temperatures of about 450° C. to 600° C., and has excellent high-temperature heat resistance, low electrical resistance (wiring resistance) and excellent corrosion resistance under alkaline environments. Specifically disclosed is an Al alloy film for use in a display device, which comprises at least one element selected from a group X consisting of Ta, Nb, Re, Zr, W, Mo, V, Hf and Ti and at least one rare earth element, and which meets the following requirement (1) when heated at 450° C. to 600° C. (1) Precipitates each having an equivalent circle diameter of 20 nm or more are present at a density of 500,000 particles / mm2 or more in a first precipitation product containing at least one element selected from Al and the elements included in the group X and at least one rare earth element.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Exothermic enamel glaze, and exothermic container coated with same
InactiveCN102548920AImprove heating characteristicsGentrificationThin material handlingThermal energyVitrification
The present invention relates to an exothermic container to be used in a microwave oven which cooks foods using a magnetron. The exothermic container absorbs a portion of the microwaves generated by the magnetron and generates heat to cook foods in the cooking chamber of the microwave oven. The exothermic container to be used in the microwave oven is produced by the steps of providing an exothermic enamel glaze, coating a metal container to be produced into an enameled container (low carbon steel plate, aluminum, and stainless steel to be produced into an enameled container) with the exothermic enamel glaze provided in the previous step, drying the resulting structure, firing the resulting structure to vitrify same, and cooling the resulting structure, to thereby achieve improved resistance against hot temperatures, improved exothermic performance,; and higher quality as compared to conventional exothermic container products (silicon rubber and ferrite). A method for producing the exothermic enamel glaze involves mixing or adding (MnZn-based, MgCuZn-based, NiZn-based) ferrite, having high magnetic permeability, and alloy powders of (Fe-Si-based, Fe-Si-Al-based, Fe-Si-B-based, Fe-Si-B-Co-based, Fe-Ni-based, etc.) soft magnetic metal materials to the glaze (glass frit) commonly used in enameling, to thereby provide the glaze with exothermic properties for absorbing microwaves (2.45GHz) and for converting the absorbed microwaves into thermal energy in a microwave oven.
Owner:YOU&I TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com