Patents
Literature
320 results about "Transcriptional activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transcriptional activity refers to the binding and processive activity of RNA polymerase. There are different ways to measure this experimentally, but with a microarray you are measuring the amount of actual transcripts relative to the control array.
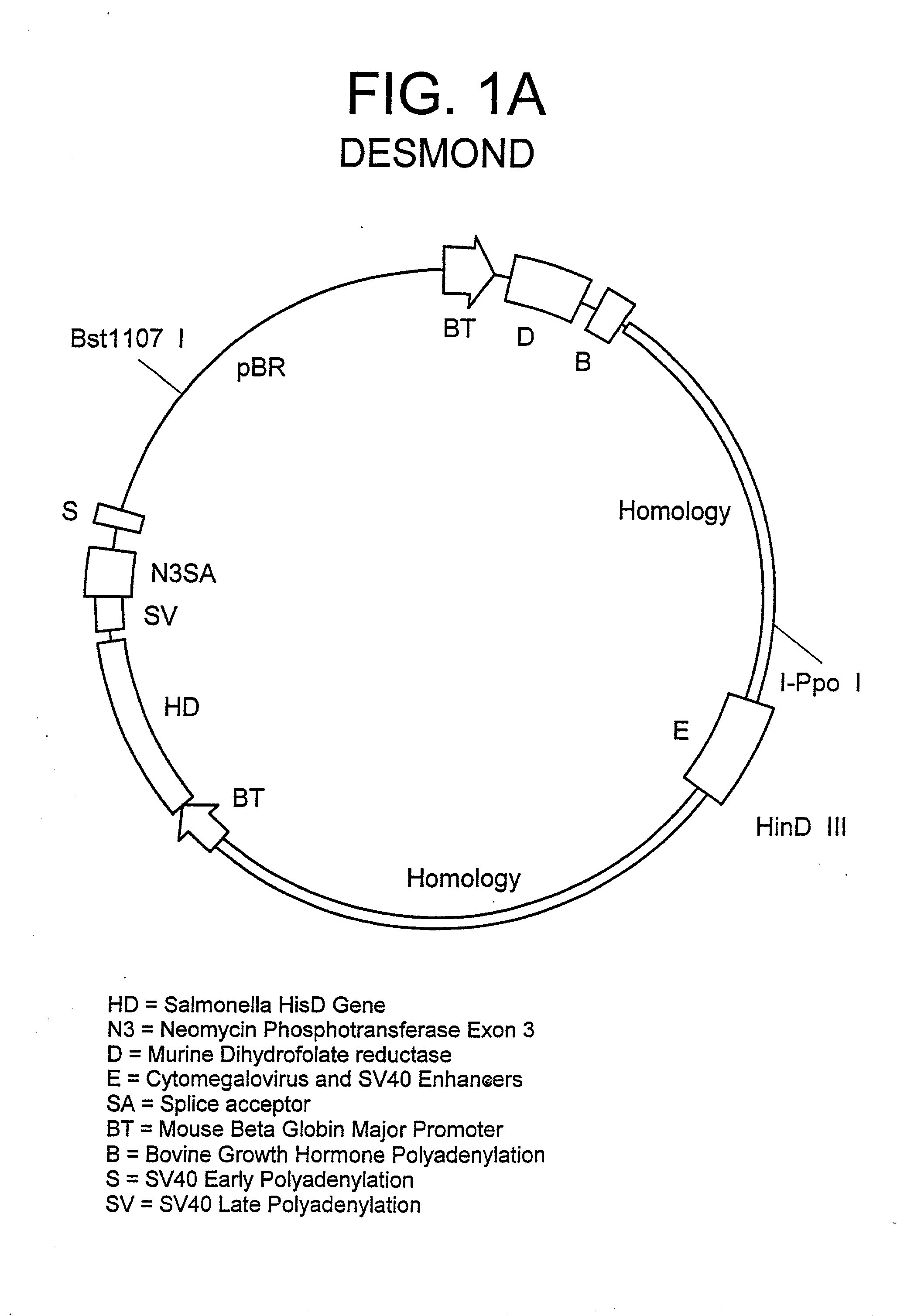
Method for integrating genes at specific sites in mammalian cells via homologous recombination and vectors for accomplishing the same
InactiveUS6413777B1Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalReactive site
A method for achieving site specific integration of a desired DNA at a target site in a mammalian cell via homologous recombination is described. This method provides for the reproducible selection of cell lines wherein a desired DNA is integrated at a predetermined transcriptionally active site previously marked with a marker plasmid. The method is particularly suitable for the production of mammalian cell lines which secrete mammalian proteins at high levels, in particular immunoglobulins. Novel vectors and vector combinations for use in the subject cloning method are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
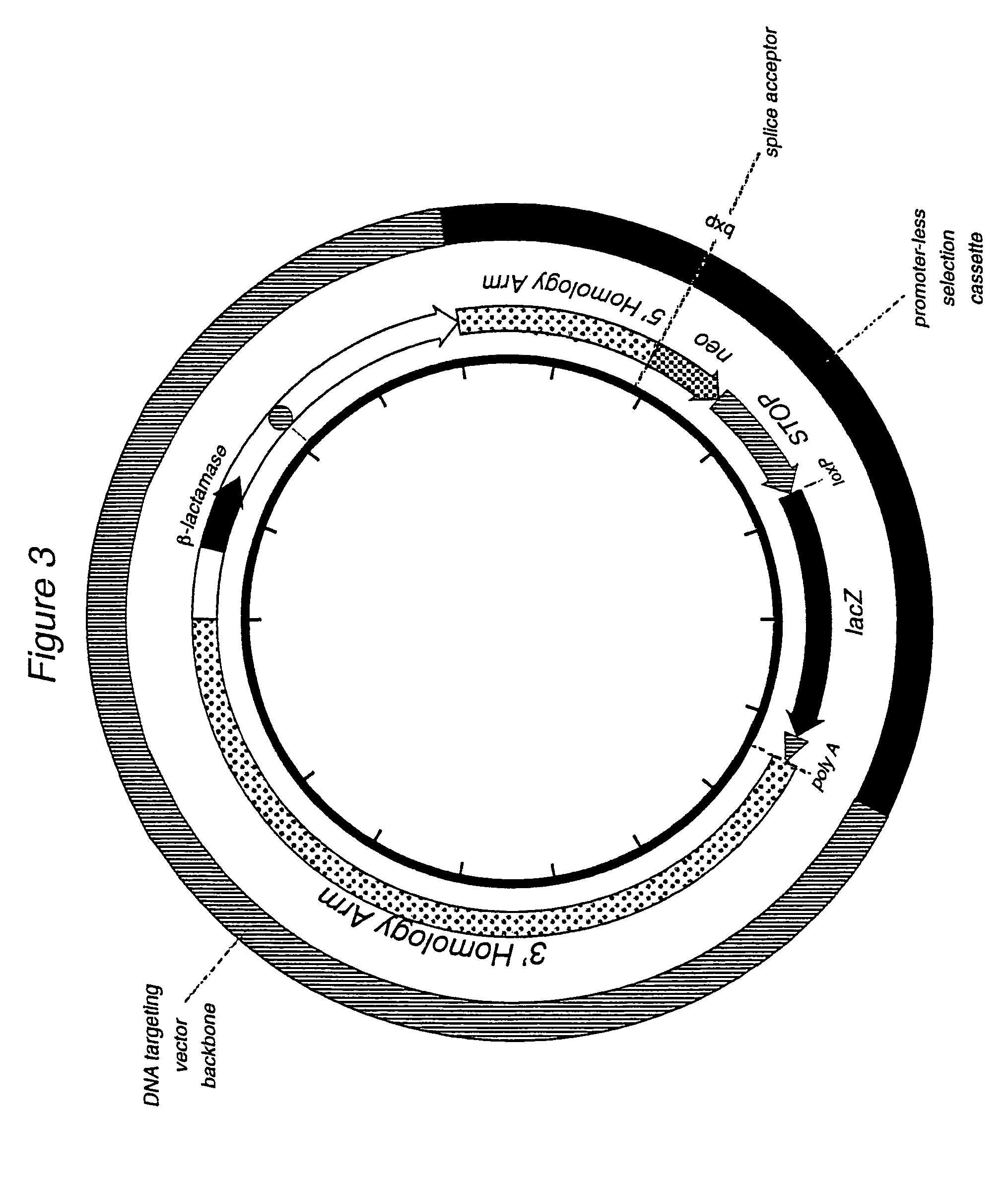
Method for targeting transcriptionally active loci
The present invention provides a method of achieving very high targeting efficiency by utilizing targeting vectors that utilize promoter-less selection cassettes and which are engineered to targeted into transcriptionally active loci. In particular, the invention provides a method for targeting promoter-less selection cassettes into transcriptionally active loci in stem cells or other eukaryotic cells with much greater efficiency than previously observed with other methods, thus reducing the number of drug-resistant clones to be screened or eliminating the need to screen for targeted cells altogether. The invention also encompasses the DNA targeting vectors, the targeted cells, as well as non-human organisms, especially mice, created from the targeted cells.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
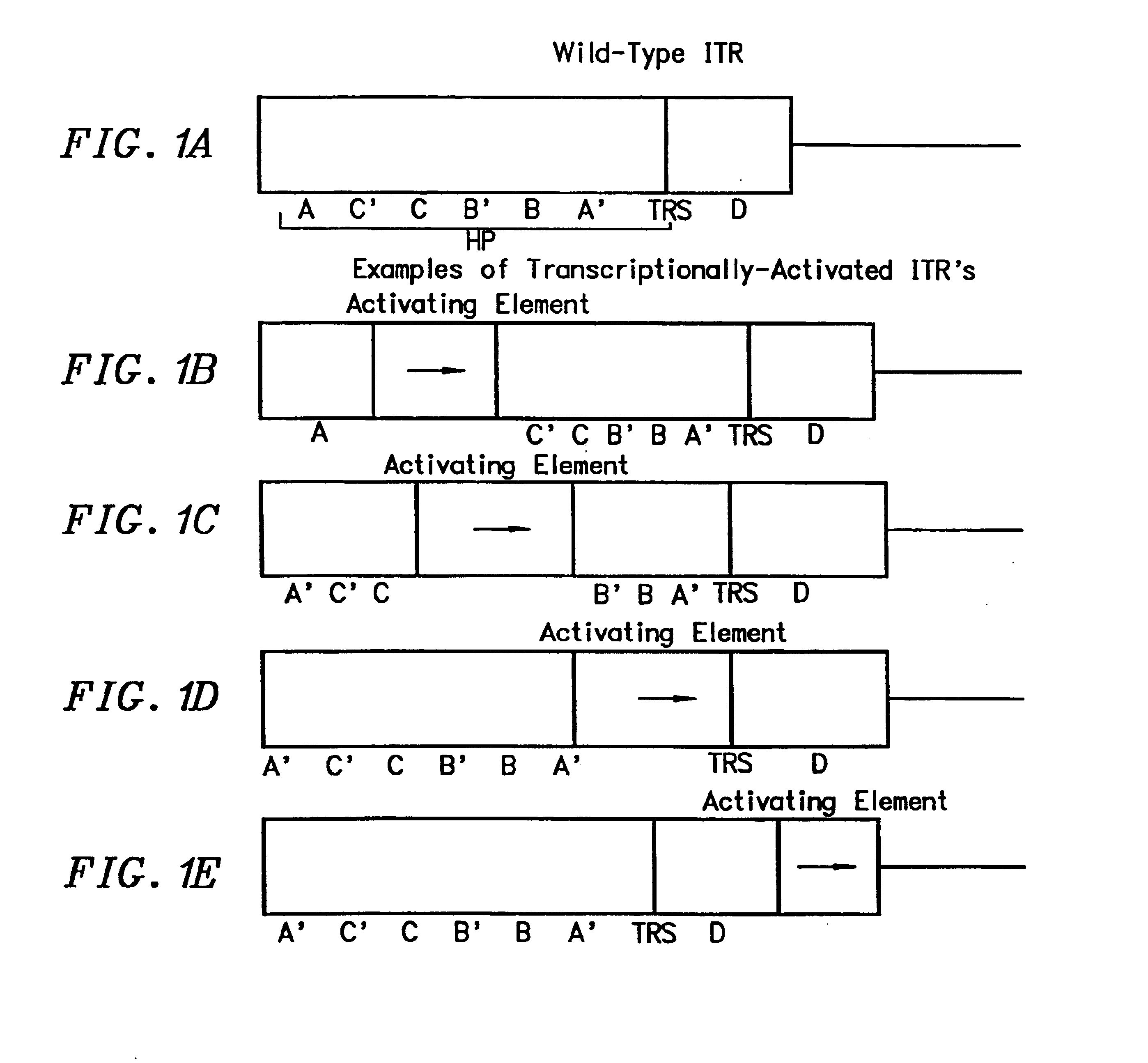
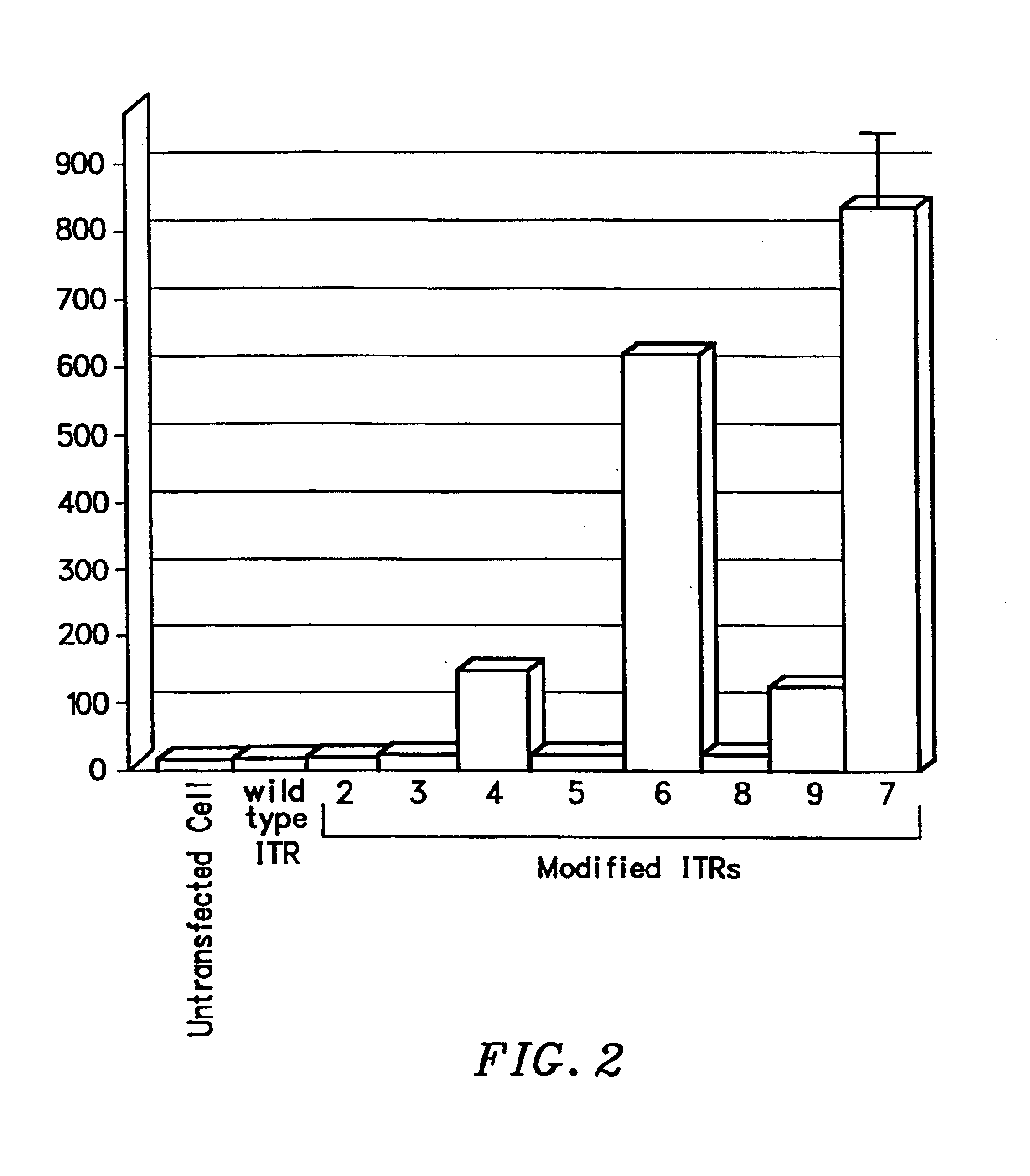
Transcriptionally-activated AAV inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) for use with recombinant AAV vectors
InactiveUS6936466B2Increase transcriptional activityGenetic material ingredientsFermentationLong terminal repeatGenetics
This invention provides transcriptionally-activated AAV ITRs (inverted terminal repeats) which are small and transcriptionally active and uses thereof to optimize the expression of relatively large transgenes packaged in recombinant AAV vectors.
Owner:TARGETED GENETICS CORPORTION
Berbamine derivative and application of salt thereof
InactiveCN101273989AHigh antagonistic activityStrong against leukemiaOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseSide effect
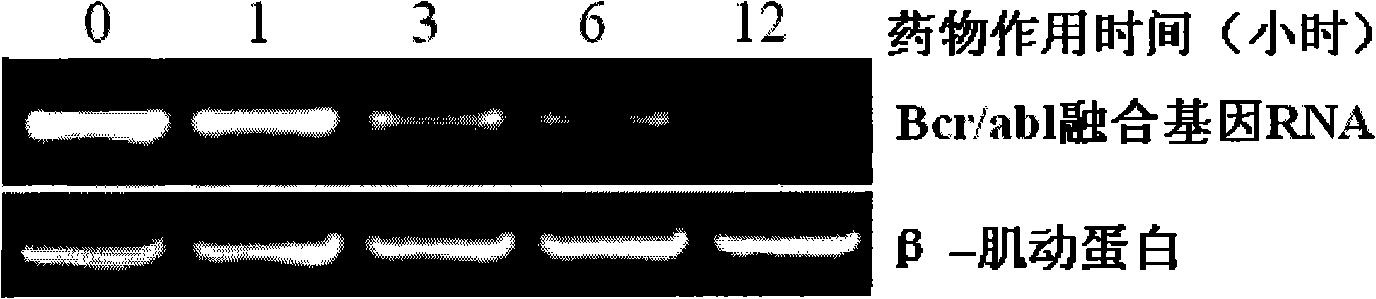
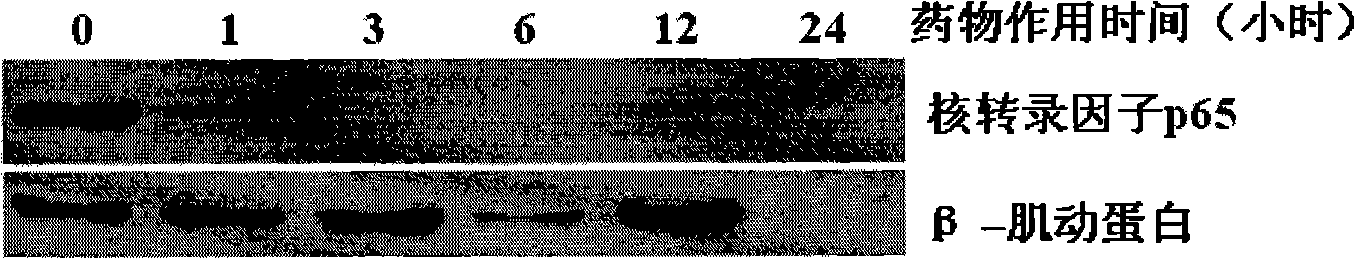
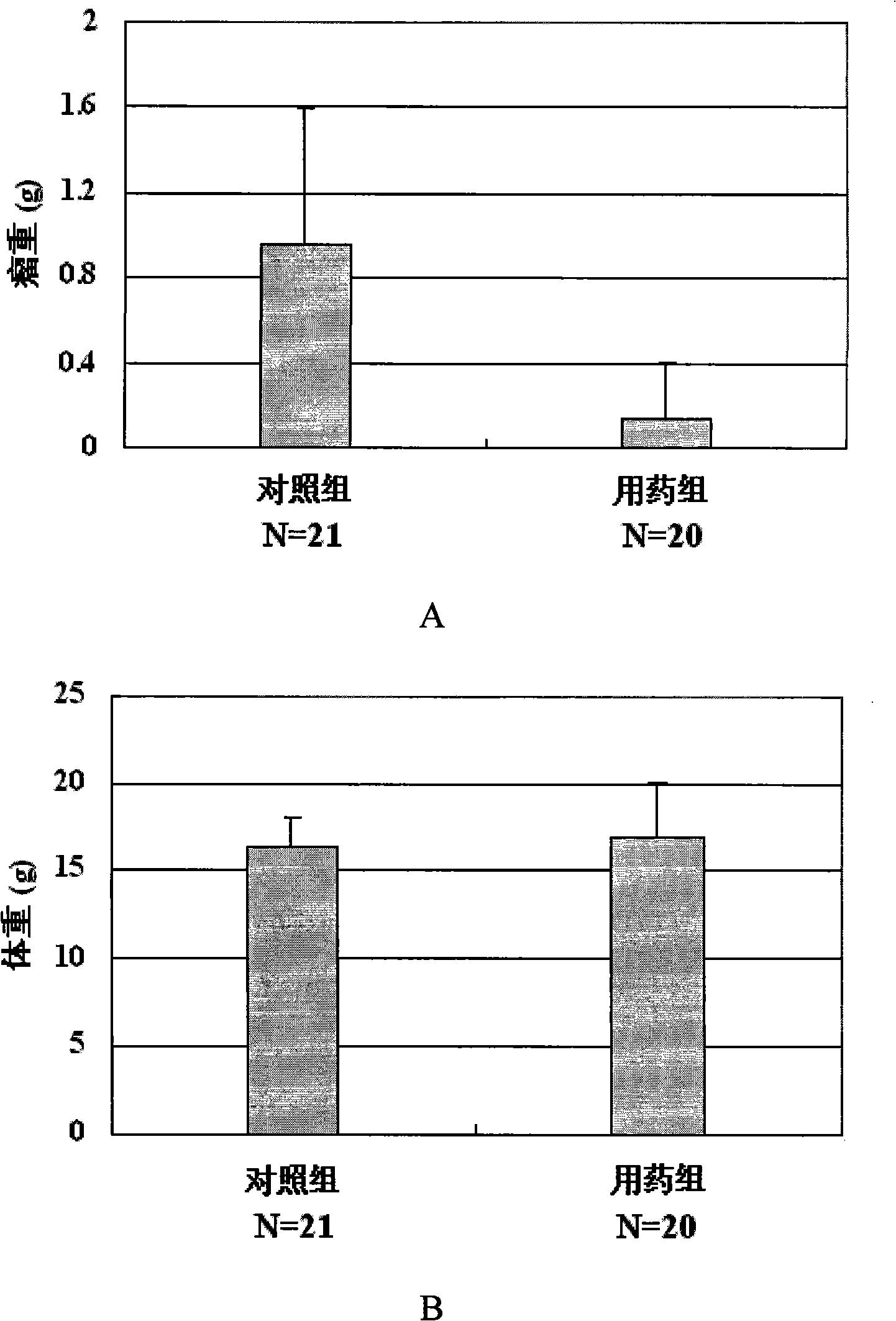
The invention provides an application of a type of berbamine derivatives and salts thereof in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of tumors, which is mainly applied in the preparation of the drugs for the prevention and treatment of nuclear transcription factor NF-kBp65 activity-related diseases and BCR / ABL transcription activity-related diseases. The drugs are combined and prepared by the compounds of the invention and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The preparation forms comprise solid preparations, semi-solid preparations or liquid preparations. The type of berbamine derivatives and the salts thereof provided by the invention have broader and stronger anti-leukemia and anti-solid-tumor activity, the tumors proved to be sensitive are leukemia, multiple myeloma, liver cancer, osteosarcoma and breast cancer; the toxicity and the side effects are lighter. An in vitro cell culture system and animal experiments confirm that the berbamine derivatives and the salts thereof have no significant toxicity or side effects to the growth of normal human hematopoietic cells and experimental animals under the anti-tumor dosage, which are superior to the commonly used chemotherapy drugs.
Owner:HANGZHOU BENSHENG PHARMA
New wheat gene TaMYB3 for regulating synthetization and metabolization of anthocyanin
The invention provides a transcription factor TaMYB3 of a MYB class, which is separated from the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety and is used for regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. TaMYB3 is positioned between 0.62 and 0.95 of a long arm physical map of wheat 4B chromosome. The subcellular fraction of a protein product is positioned on a cell nucleus. Shown by a derived amino acid sequence, the TaMYB3 codes a MYB class transcription factor regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB3 in the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety increases under the induction of light. The TaMYB3 can promote skin cells of the plateau 115 kernels after dark treatment to synthetize anthocyanin under the existence of transcription factors ZmR of corns bHLH during transient expression. Single TaMYB3 genes and single ZmR genes can not induct the synthetization of anthocyani, which shows that the TaMYB3 genes have the transcriptional activity of regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. barly strip mosaic virus (BSMV) mediates the expression quantity decrease of the TaMYB3 in the plateau 115 kernels, and reduces the quantity of anthocyanin in kernels. This shows that the TaMYB3 participates in the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in the plateau 115 kernels.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for synthesizing cDNA
InactiveUS6485917B1Improve fidelityAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiologyExonuclease
A method for synthesizing cDNA characterized by performing a reverse transcription reaction in the presence of an enzyme having a reverse transcriptional activity and another enzyme different from the former one which as a 3'-5' exonuclease activity.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Marker, method and an assay for detection and monitoring of latency and activation of human immunodeficiency virus
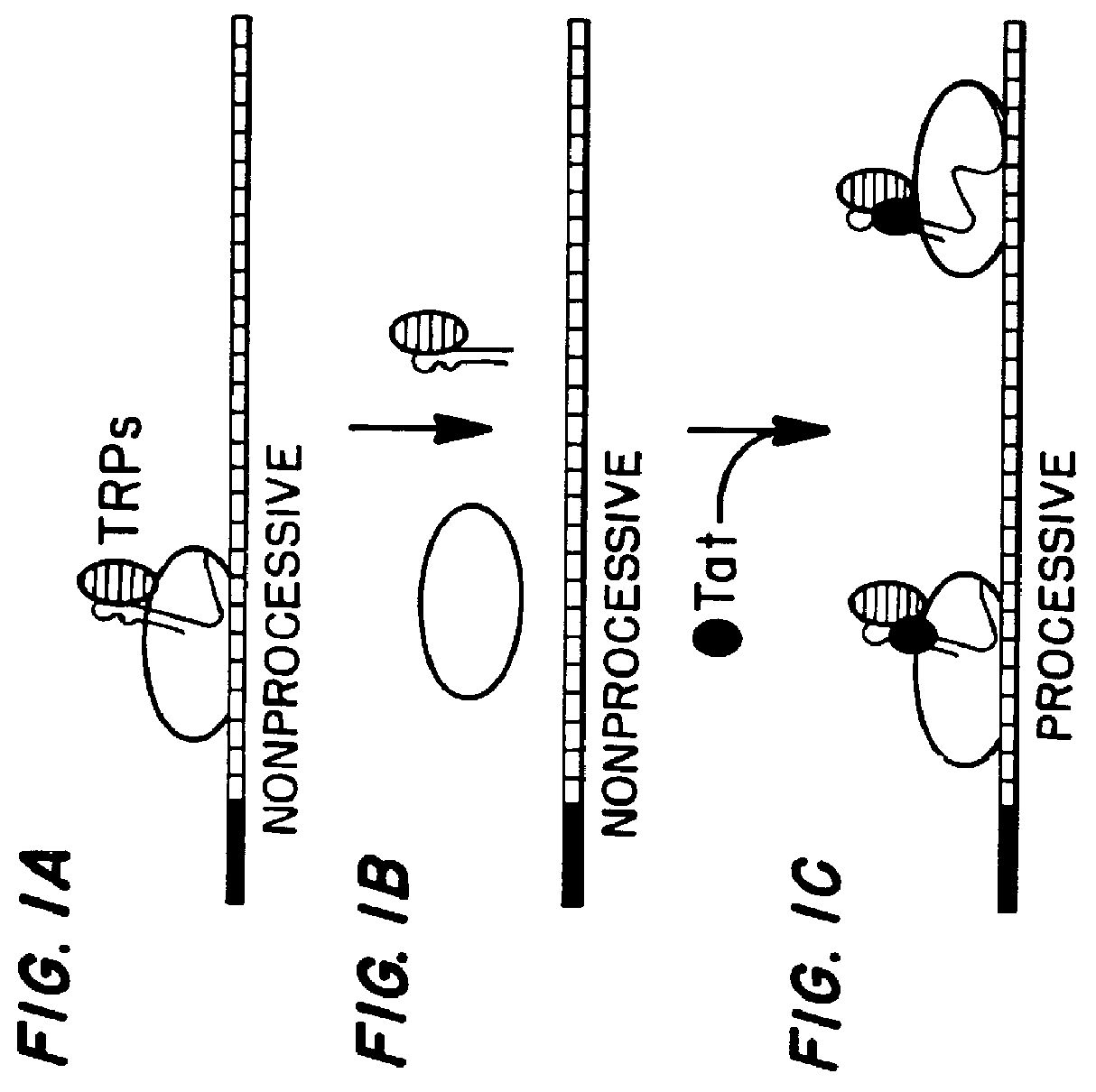
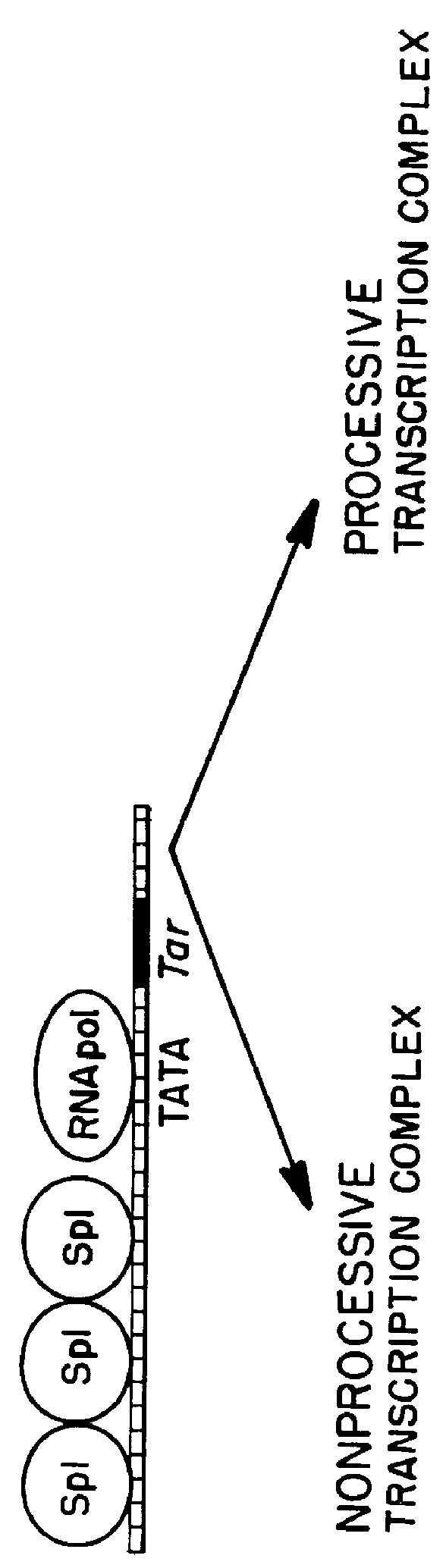
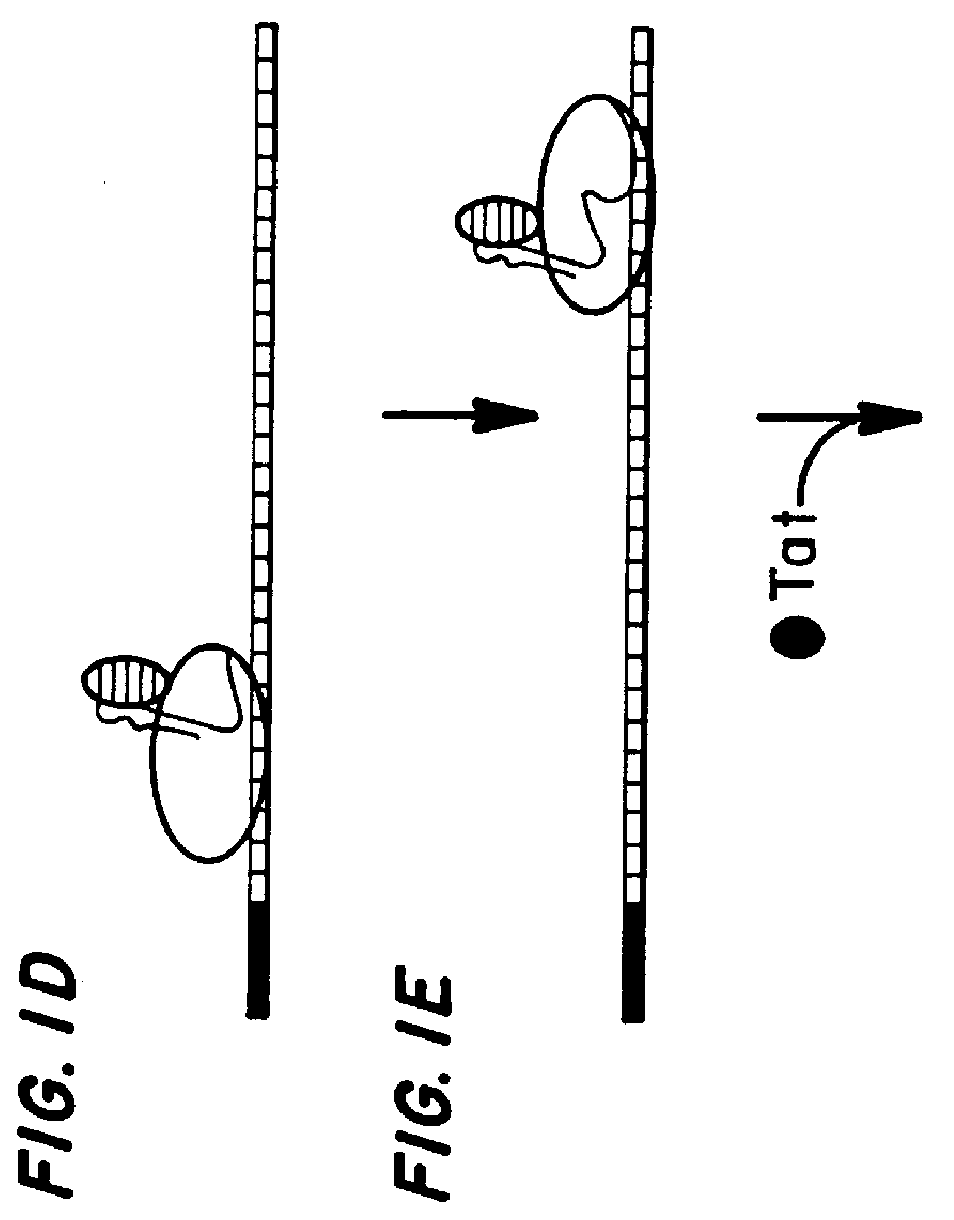
A TAR marker, method for detection and monitoring of HIV latency and activation and an assay for detection of the marker. The assay sensitively detects HIV transcription and monitors HIV transcriptional activity by detecting the presence of TAR fragments and full length transcripts, quantifying both and determining the ratio of short to long transcripts. A low ratio correlates with a latent-type transcriptional activity of HIV whereas the appearance of long transcripts signifies increased efficiency of transcriptional activity of HIV and the transition from latency to activation. The size difference between the TAR fragments appearing predominantly in latency and the full length transcripts appearing predominantly during the HIV activation is detected by RT-PCR assay that utilizes novel primers and probes. The obtained ratio is a sensitive tool in detection of HIV infection, the analysis of load of latent and active virus and monitoring the transition from the latent to active state of HIV replication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
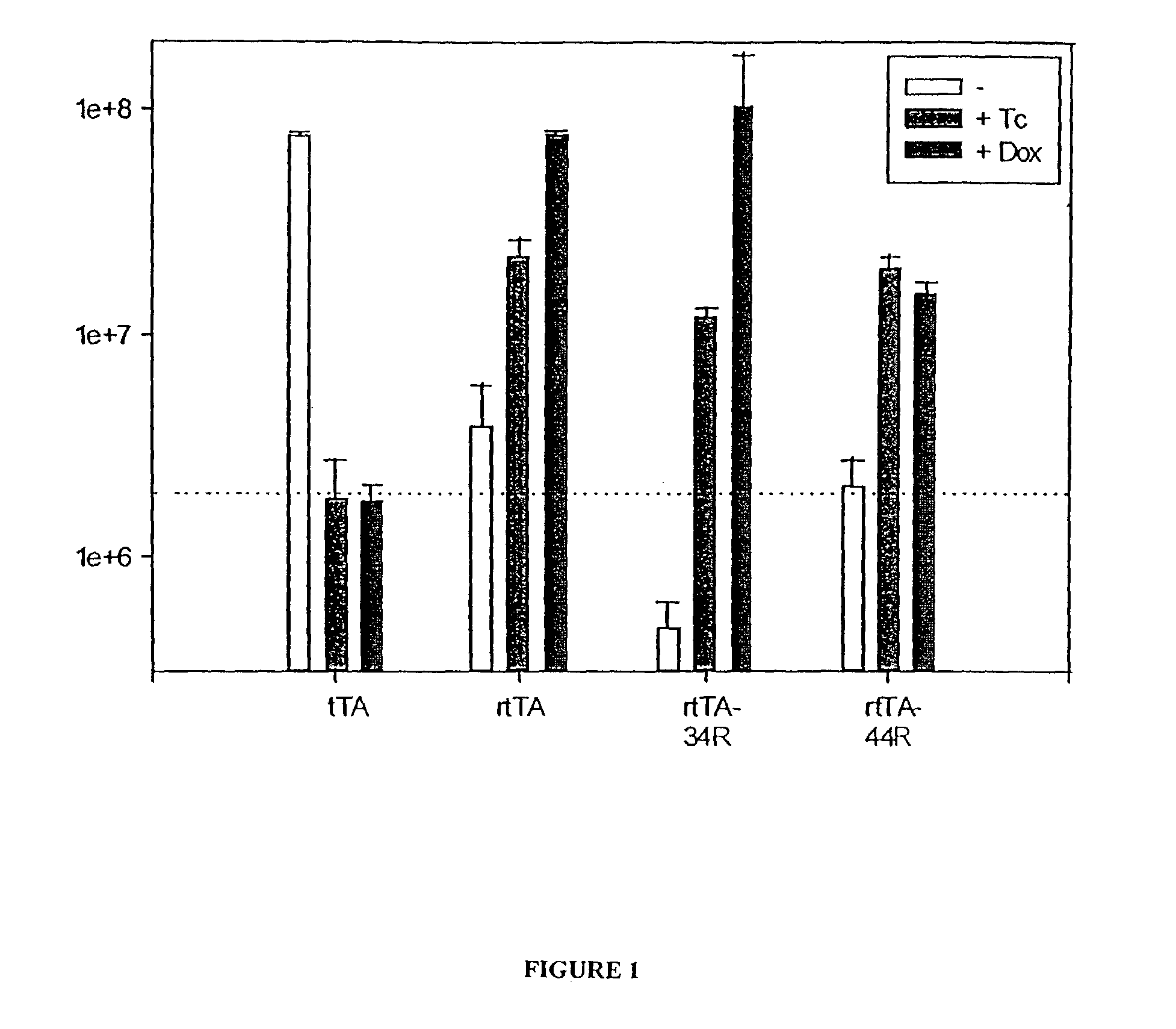
Tet repressor-based transcriptional regulatory proteins
InactiveUS7541446B2Decreased basal transcriptional activityIncrease transcriptional activityOrganic active ingredientsFungiTetracycline ControlTET repressor
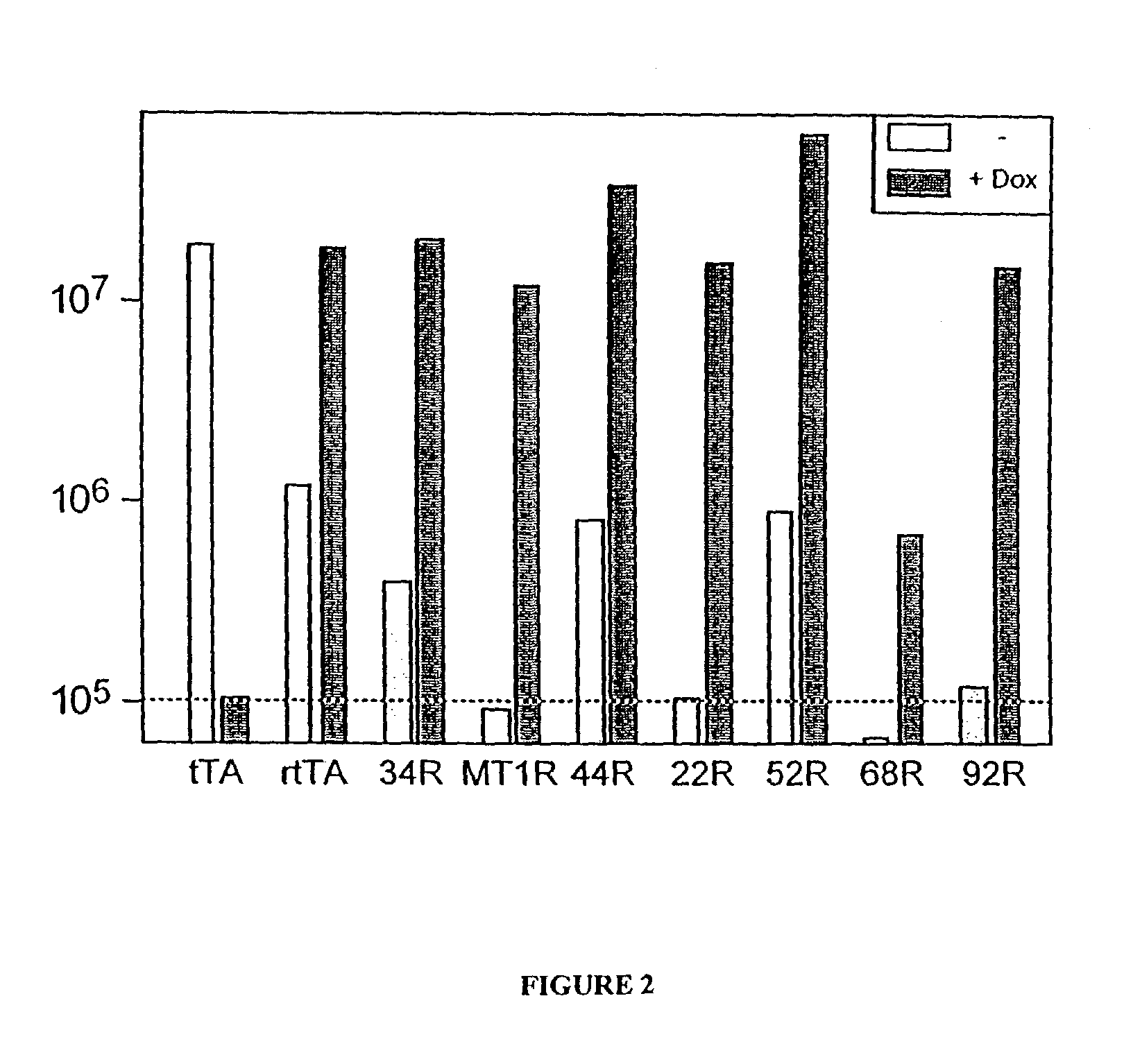
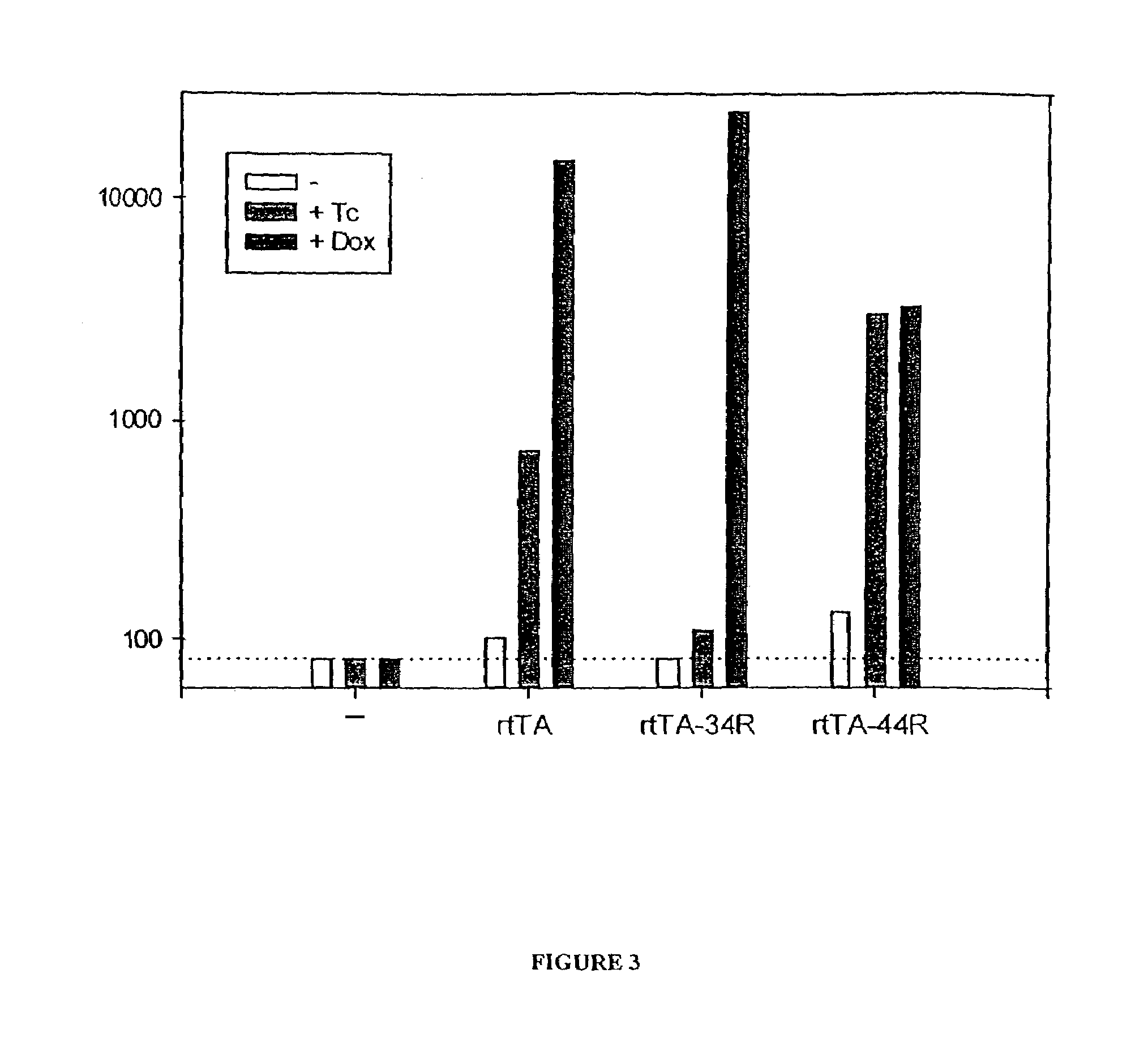
The present invention provides a panel of transcriptional activator fusion proteins which comprises both tetracycline controlled transactivator proteins and reverse tetracycline transactivator proteins. These transactivators have novel phenotypes such as altered basal transcriptional activity in the absence of doxycycline, altered induced transcriptional activity in the presence of doxycycline, or differential induction by tetracycline and analogs of tetracycline.
Owner:TET SYST
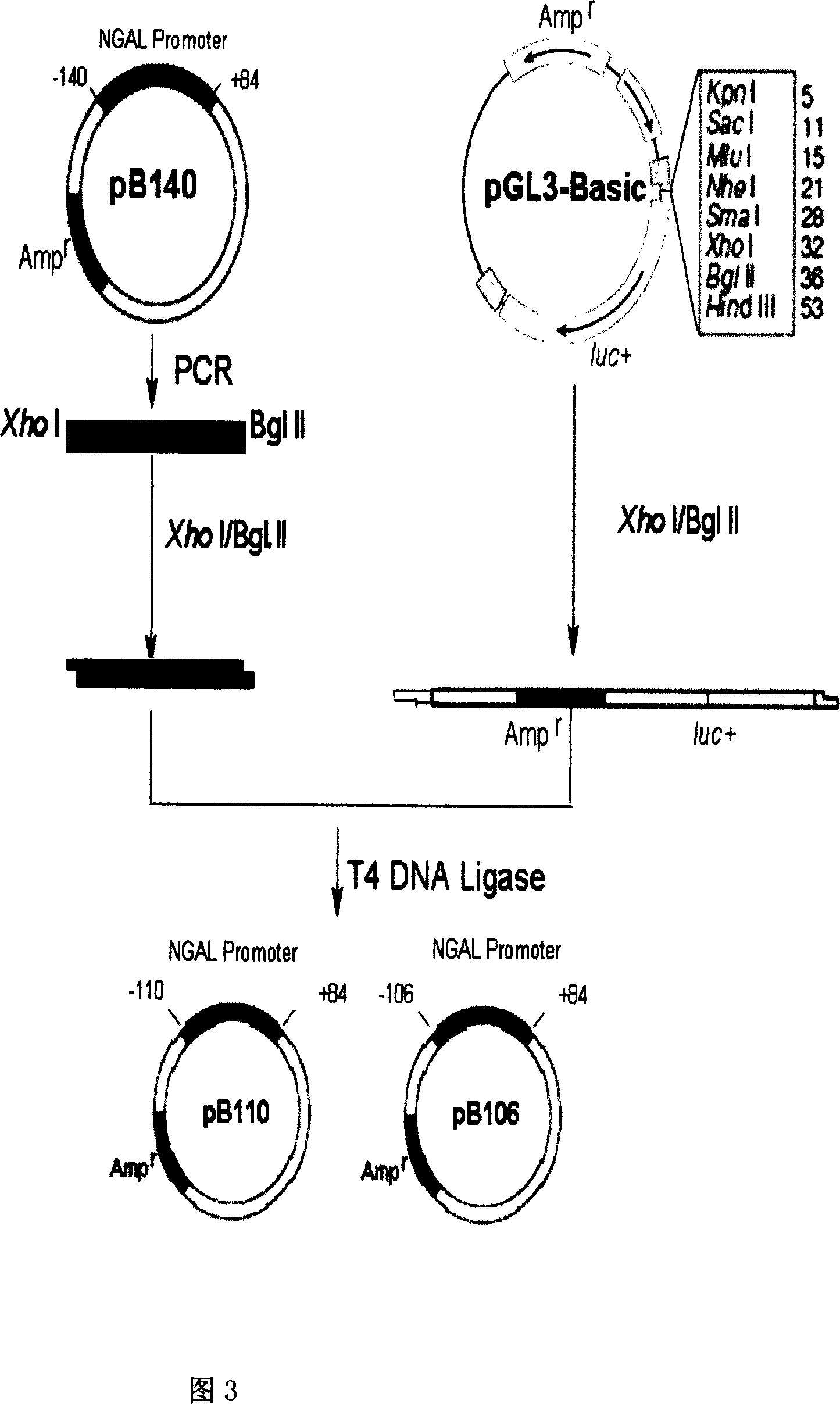
Transcriptional control element of human lung carcinoma cell NGAL gene promoter region
InactiveCN1974768AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionRegulation of gene expressionTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
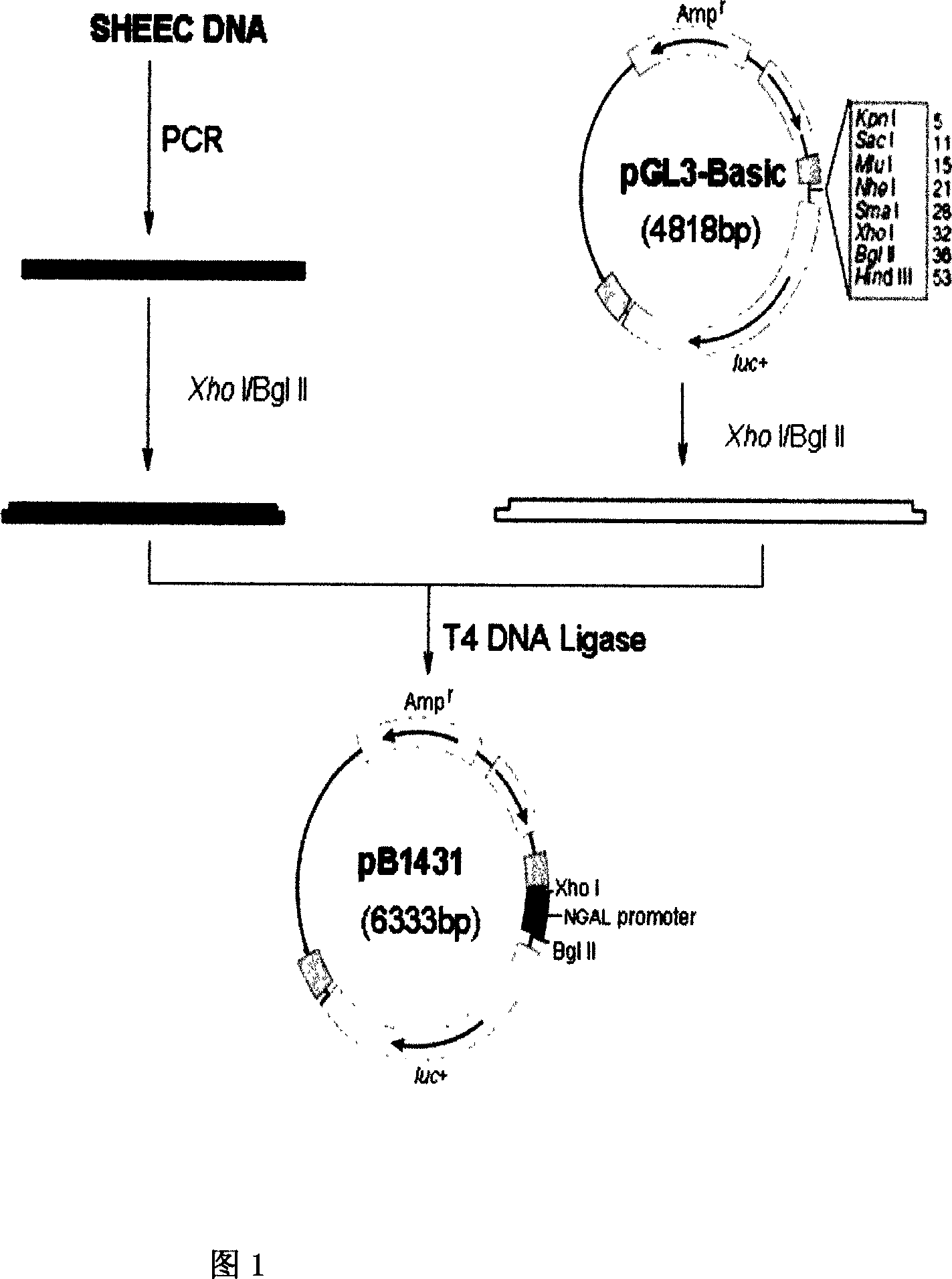
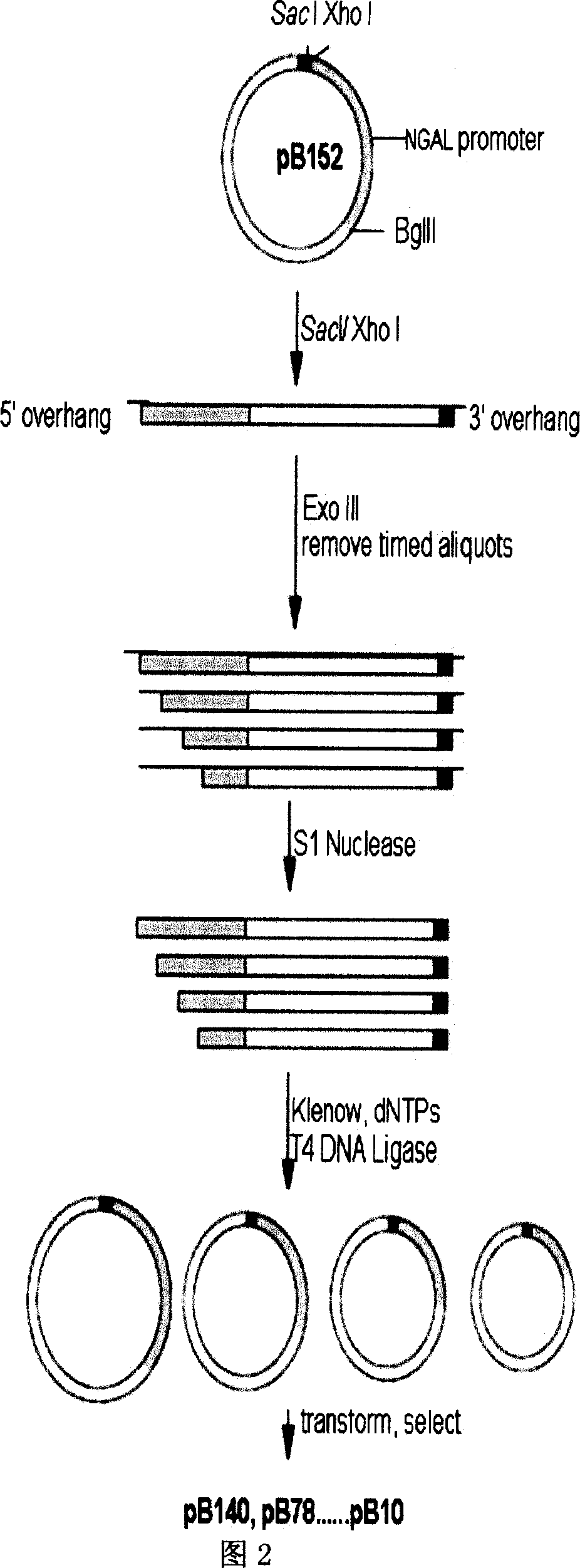
The present invention relates to gene expression controlling technology, and discloses one kind of transcriptional control element of human lung carcinoma cell NGAL gene promoter region. The present invention identifies human lung carcinoma cell NGAL gene promoter region for the first time, inserts the promoter sequence with gradually deleting 5' end sequence and partial modified controlling element to the upstream of the report gene to constitute serial eukaryotic expression plasmids, transfects mammal cell for instantaneous expression, and determines the key control element of human NGAL gene promoter in lung carcinoma cell transcription activity. The present invention is significant in the research of NGAL in the tumor cell expression control mechanism and NGAL targeting clinical treatment.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
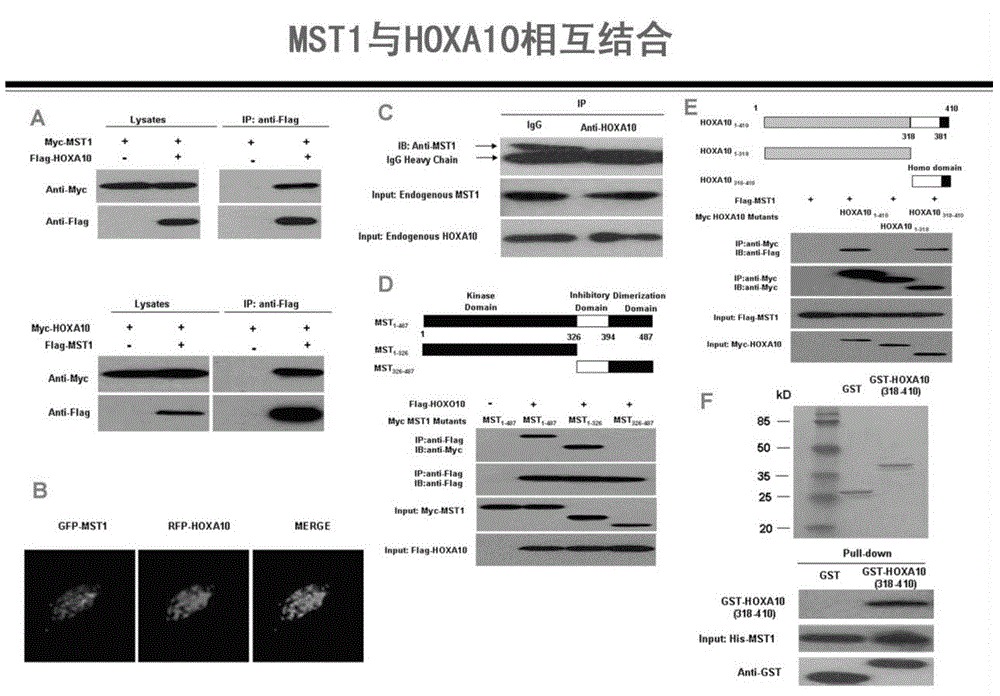
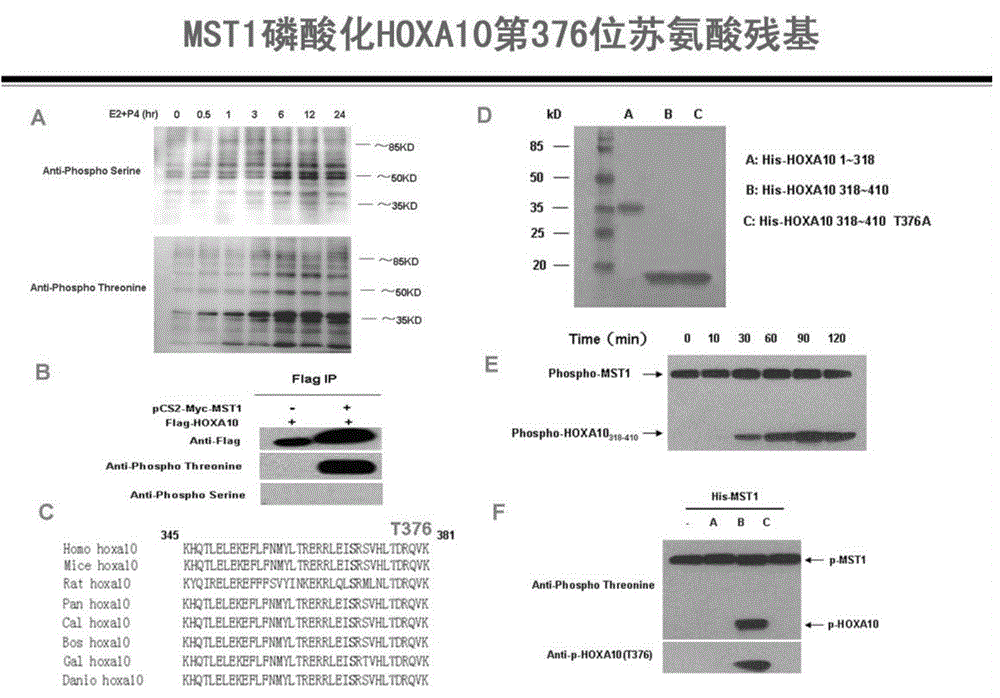
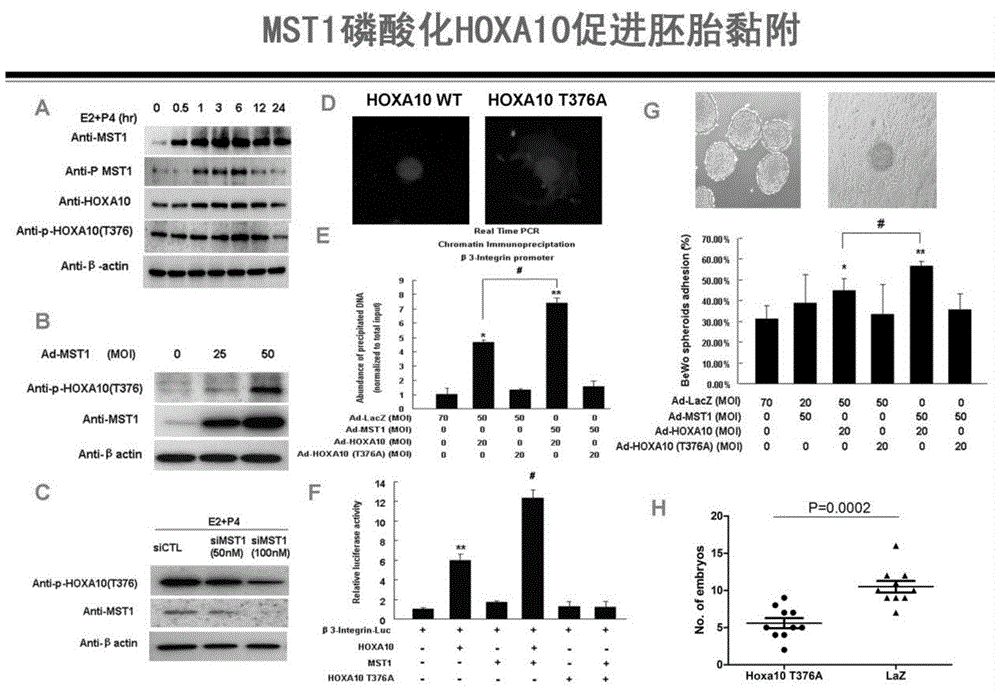
Method for detecting endometrial receptivity through MST1 and phosphorylated MST1
ActiveCN105988002AQuick and easy expressionEasy and fast retouching levelMaterial analysisCarcinoma cell linePhosphorylation
The invention provides a method for detecting endometrial receptivity through MST1 and phosphorylated MST1. The method comprises the steps that a human endometrial carcinoma cell line Ishikawa and HEK293T cells are kept and cultured in a 10% FBS and mycillin containing double-antibody DMEM / F12 culture solution; an immunoblotting experiment is carried out; co-immunoprecipitation is carried out; immunohistochemistry is carried out; adjustment of MST1 on the transcriptional activity of HOXA10 is analyzed through chromosome co-immunoprecipitation (ChIP) / PCRs; human choriocarcinoma cell (BeWo) sphere adhering experiments are carried out. According to the method, the expression level of MST1 and MST1 phosphorylation modification in endometrial tissue is detected conveniently and fast, and the receptivity state of the endometrium can be directly reflected.
Owner:江苏华朵生物科技有限公司
Novel wheat gene TaMYB7D capable of adjusting and controlling synthesis and metabolism of anthocyanin
InactiveCN104894142ARegulates transcriptional activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a novel wheat gene TaMYB7D capable of adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, wherein the novel wheat gene TaMYB7D is obtained through separation of the purple-grain wheat variety highland 115. The TaMYB7D is located on a wheat chromosome 7D, and a protein product subcell is located in a cell nucleus. A deduced amino acid sequence shows that TaMYB3 encodes an MYB transcription factor capable of adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB7D in the coleoptiles of a purple wheat variety highland 115 grain can be increased under the induction of light. During transient expression, the TaMYB7D and the pericarpic cell of the highland 115 grain synthetize anthocyanin. Moreover, coseparation occurs between the color of the coleoptiles of the highland 115 grain and the expression of the TaMYB-7D, that is, the TaMYB7D has transcriptional activity used for adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and is the major gene of the purple coleoptiles of the TaMYB7D highland 115 grain.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
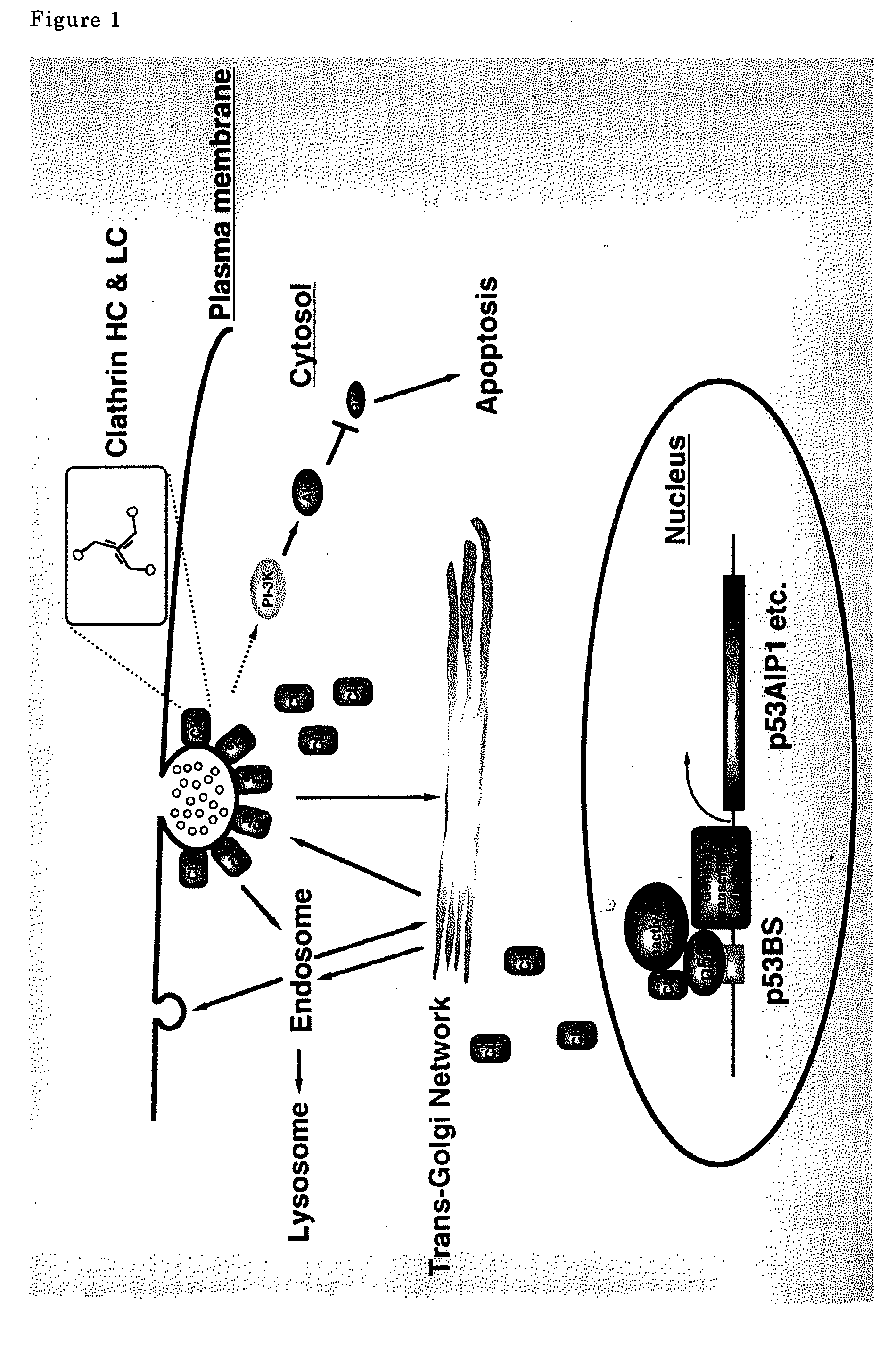
Transcriptional factor inducing apoptosis in cancer cell
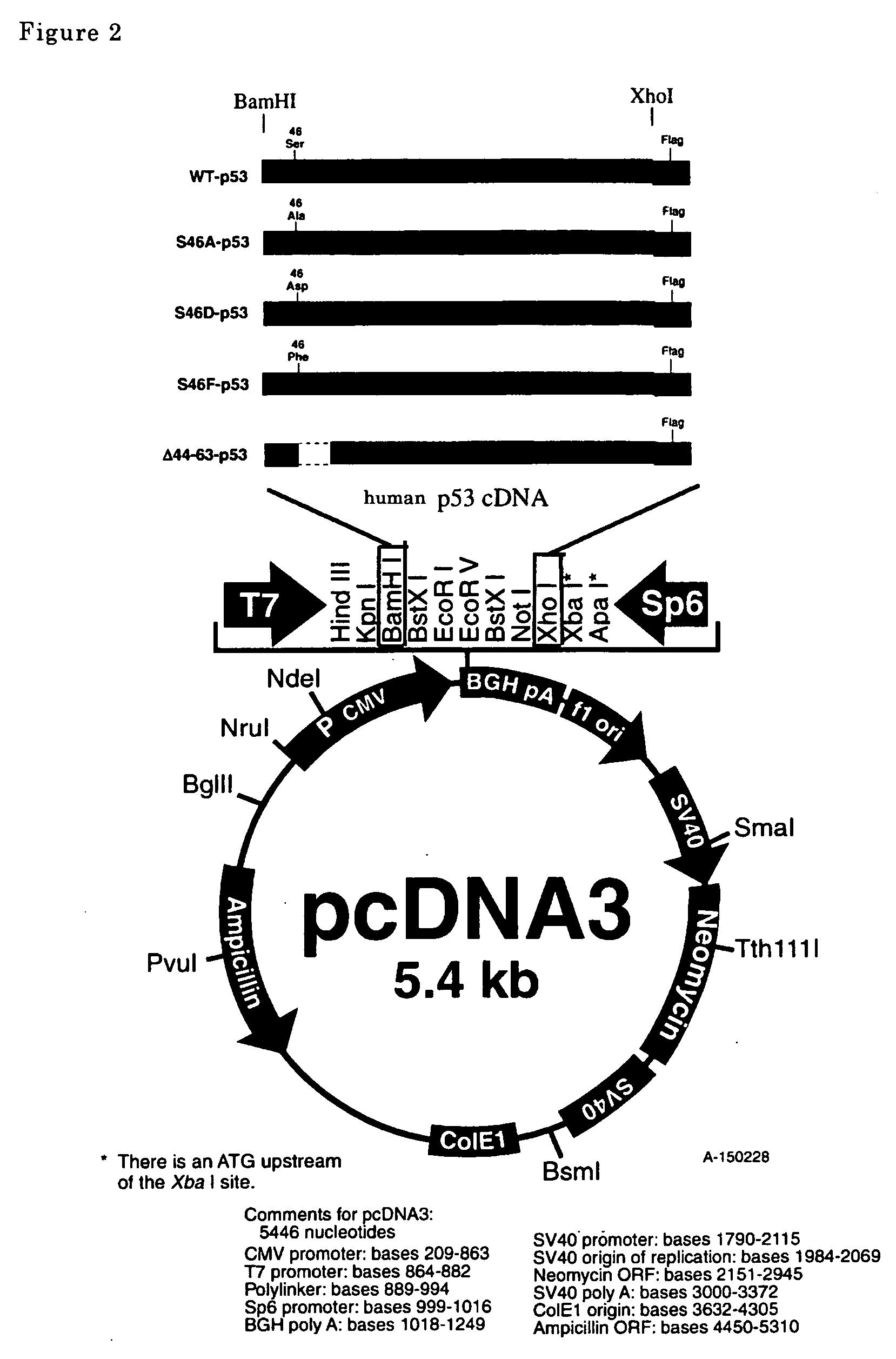
A new method for treating cancer by inducing apoptosis exclusively in cancer cells and killing them is provided. The present invention relates to a transcriptional factor, comprising p53 or a mutated type p53, wherein one or more amino acids are deleted, substituted or added with respect to the amino sequence of p53, and clathrin heavy chains and having an activity to induce apoptosis of cancer cells. The transcriptional factor enhances the transcriptional activity of p53AIP1 promoter and induces apoptosis of cancer cells.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) with constitutive promoter activity, application of DNA and pichia pastoris expression vector
ActiveCN102994501ALittle change in transcriptional activityIncrease transcriptional activityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisBase J
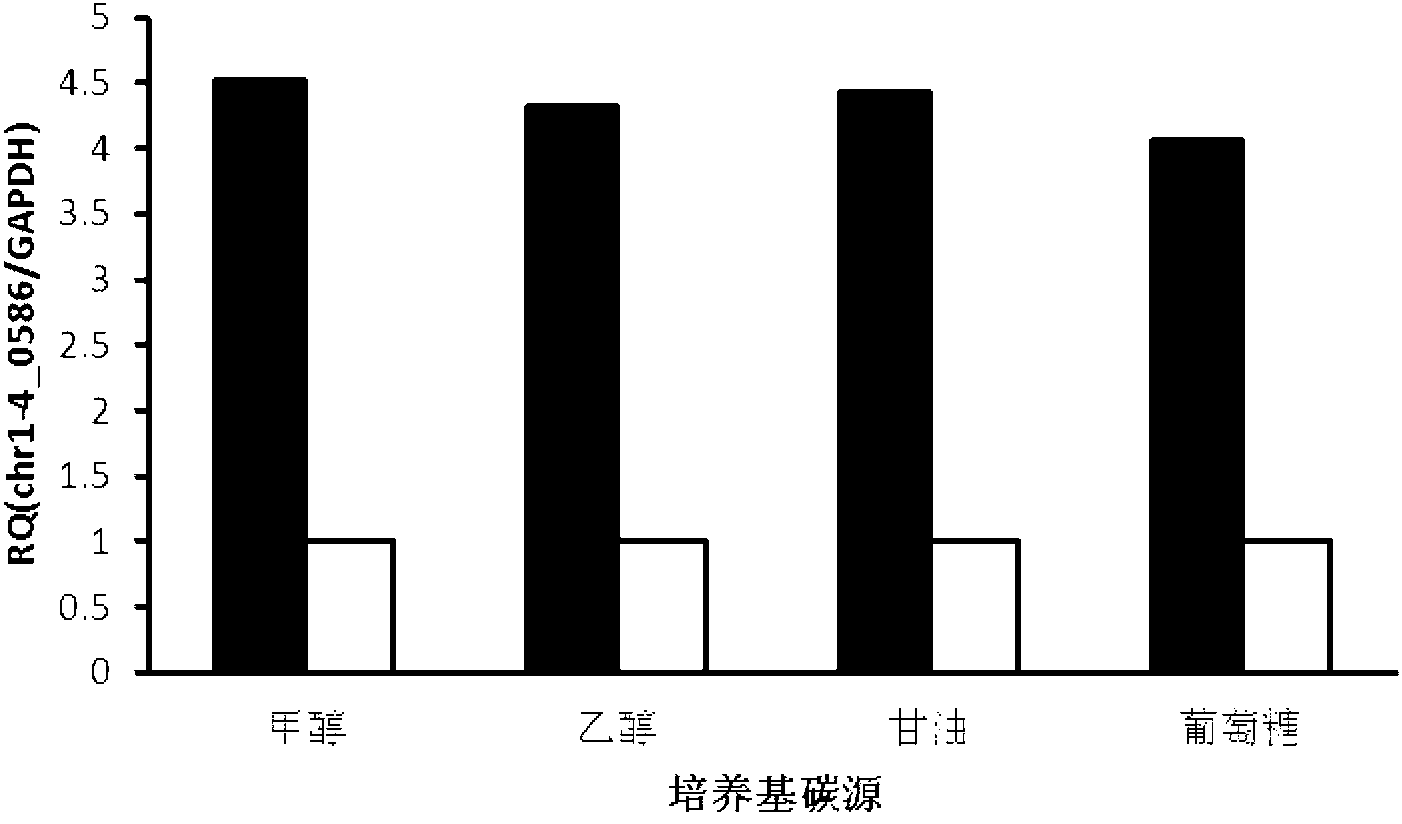
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) with constitutive promoter activity, application of the DNA and a pichia pastoris expression vector. The DNA has a base sequence as shown in SEQ No.1 (Sequence Number); and the application of the DNA relates to the application of the DNA in construction of the pichia pastoris (Pinchia Pastoris) expression vector. The DNA disclosed by the invention has the constitutive promoter activity, and can activate the transcription of a downstream structural gene without an inductor; the transcriptional activity shows little change in four different culture mediums, namely, ethanol, methanol, glucose and glycerol; the promoter activity is efficient, and the efficiency of the initiation transcription is four times more than the pichia pastoris GAPDH (Reduced Glyceraldehyde-phosphate Dehydrogenase) promoter. The pichia pastoris expression vector, constructed by the DNA disclosed by the invention, can efficiently express the extrinsic protein without methanol induction, and the efficiency of expressing the extrinsic protein (Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein) is about 6 to 8 times that of the expression system of the GAPDH promoter and 1.5 to 2 times that of the expression system of a TEF1 (Transcription Enhancer Factor 1) promoter.
Owner:林影 +1
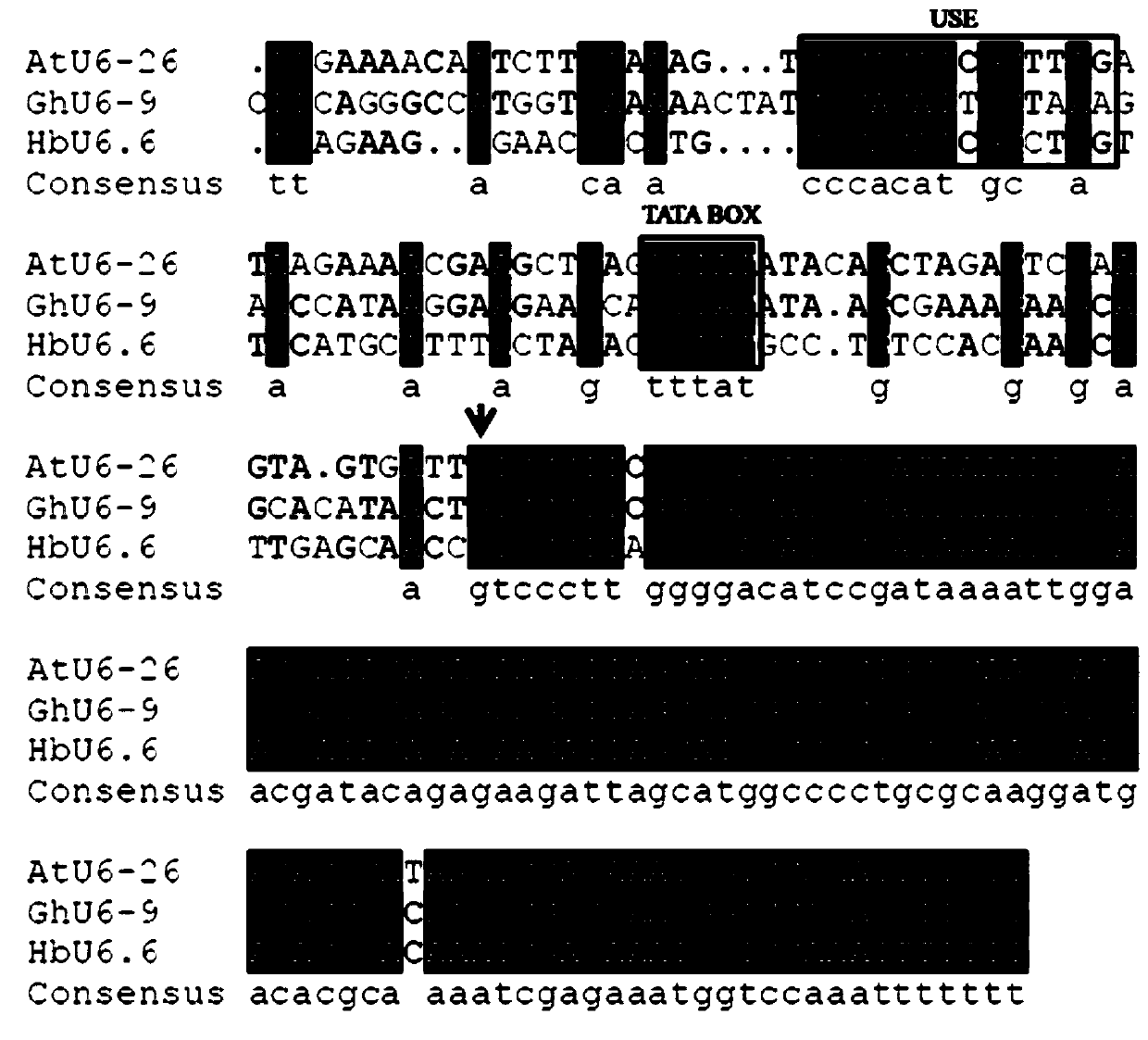
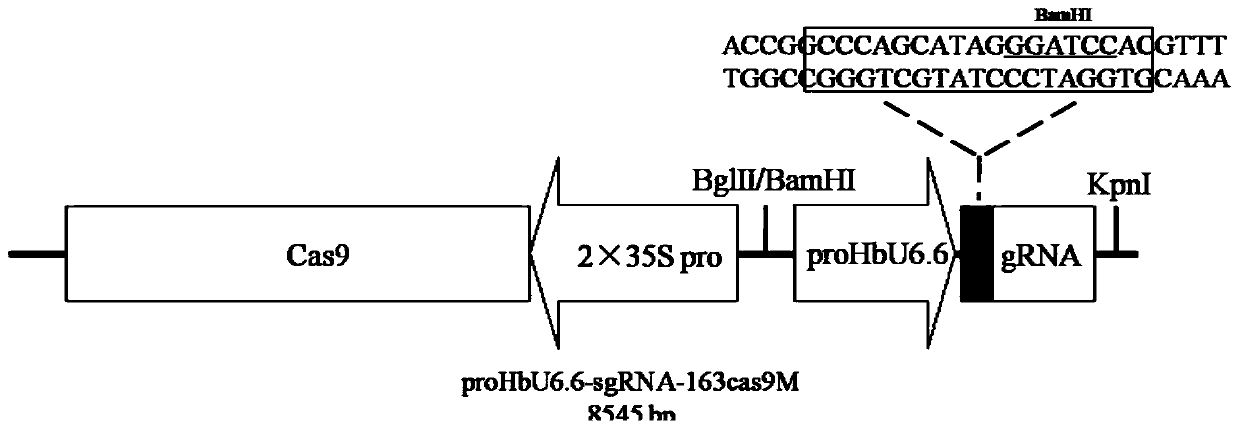
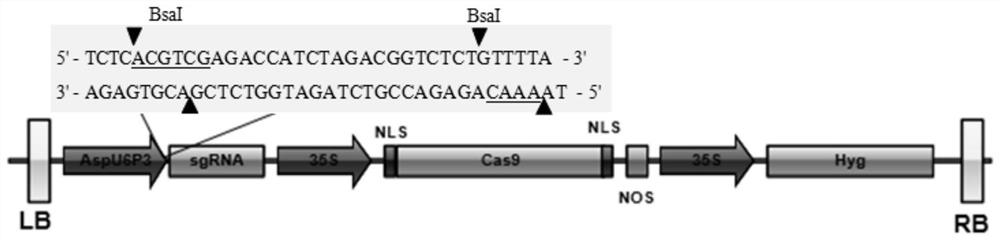
Rubber tree U6 gene promoter proHbU6.6 and cloning and application of rubber tree U6 gene promoter proHbU6.6
ActiveCN110144353AIncrease transcriptional activityRealize editingPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPara rubber treePolymerase L
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, particularly relates to a rubber tree RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymerase type III promoter, in particular to a rubber tree U6 gene promoter proHbU6.6 and further discloses a cloning method and an application of the rubber tree U6 gene promoter proHbU6.6. The rubber tree RNA polymerase type III promoter, namely the rubber tree endogenous U6 promoter proHbU6.6 is obtained by cloning in a Para rubber tree for the first time; the promoter is a rubber tree endogenous RNA polymerase type III promoter, has high transcriptional activity,and can drive expression of downstream sgRNA (small guide ribonucleic acid); the activity of the promoter and feasibility of the promoter applied to a rubber tree CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated nuclease 9) gene editing system are demonstrated by instantaneous conversion of rubber tree protoplast; and CRISPR / Cas9 mediated rubber tree genometarget editing is achieved.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method of protein synthesis
The present invention relates to a method of protein synthesis and, more particularly, to a method of effective protein synthesis by regulating the expression of a protein in a host cell, wherein said host cell is transformed with an expression vector comprising a promoter as well as a DNA fragment for a gene that encodes a desired protein, wherein said promoter has an inductive activity for transcription during the resting stage of cell growth and also the induction of said protein expression can be controlled by varying culturing conditions.
Owner:HALLA PATENT & LAW FIRM
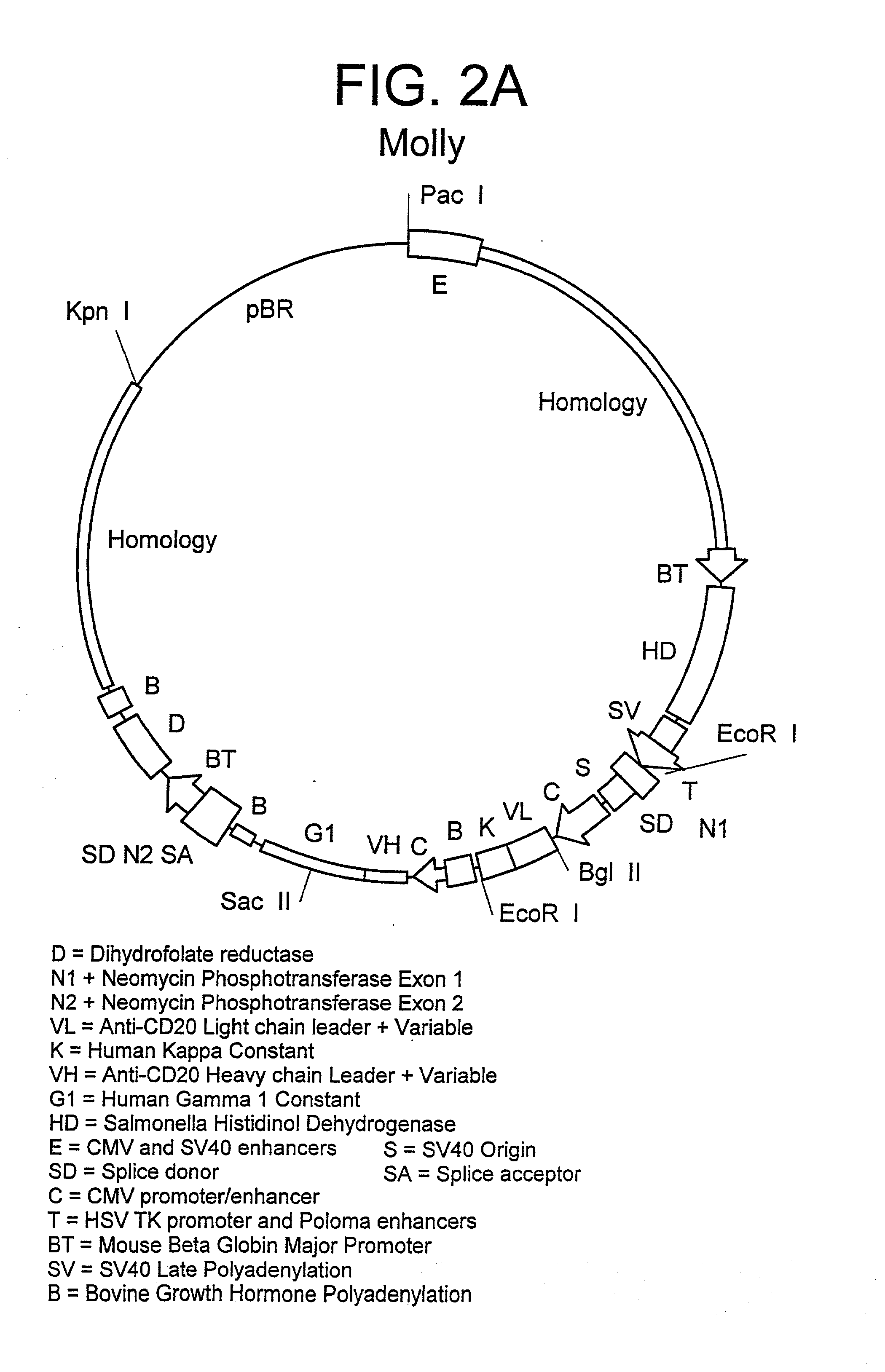
Expression vector for producing protein derived from foreign gene in large quantity using animal cells, and use thereof
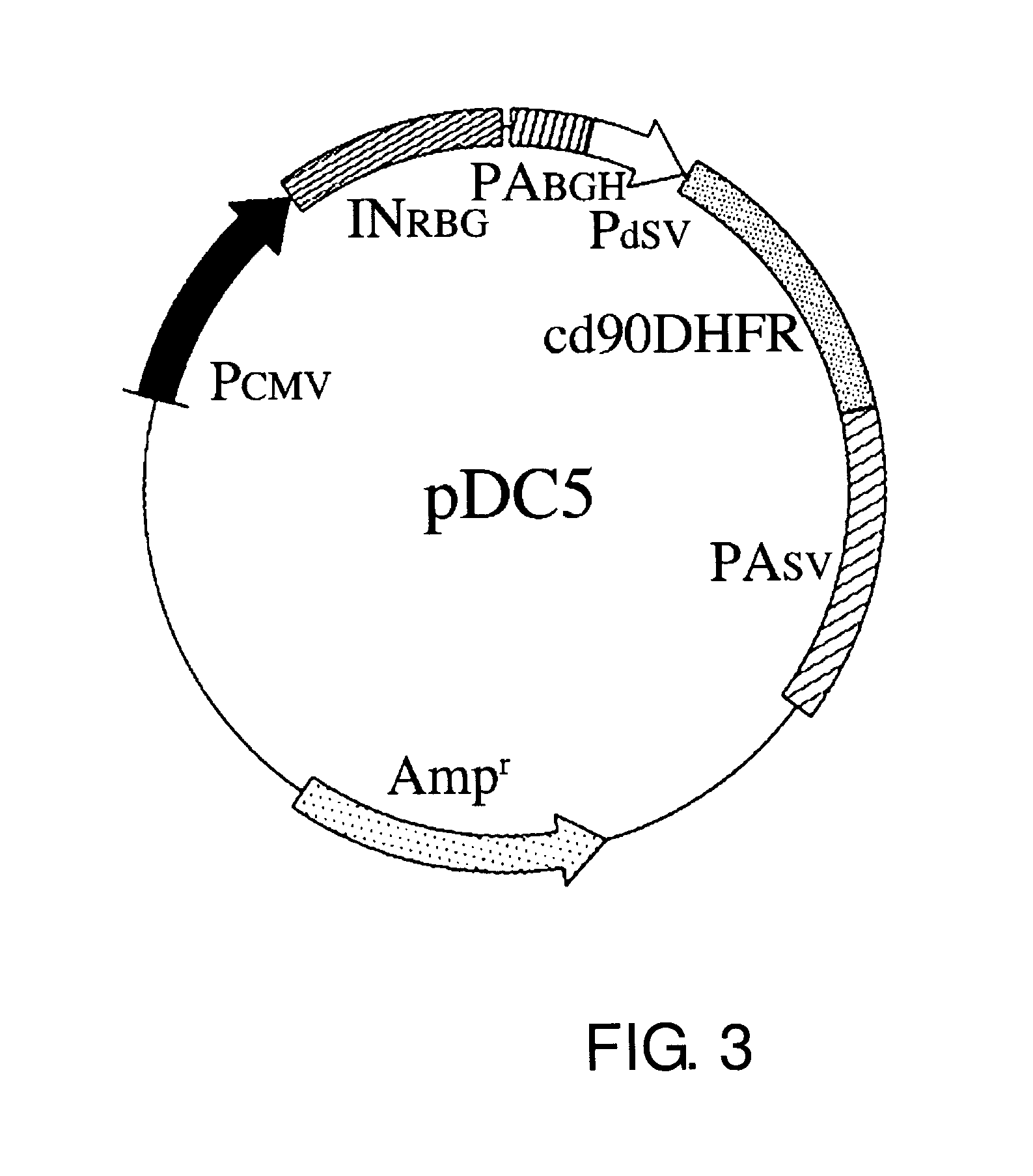
ActiveUS9096878B2Increase probabilityImprove the level ofVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyadenylationMammal
The present inventors conducted dedicated studies and successfully constructed expression vectors that enable high-level production of foreign gene-derived proteins in mammalian host cells, which comprise a translation-impaired dihydrofolate reductase gene cistron whose expression has been attenuated by altering the codons to the least frequently used codons in mammals; and a gene cassette which has a cloning site for incorporation of a foreign gene between a highly transcriptionally active promoter and a highly stable polyadenylation signal.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
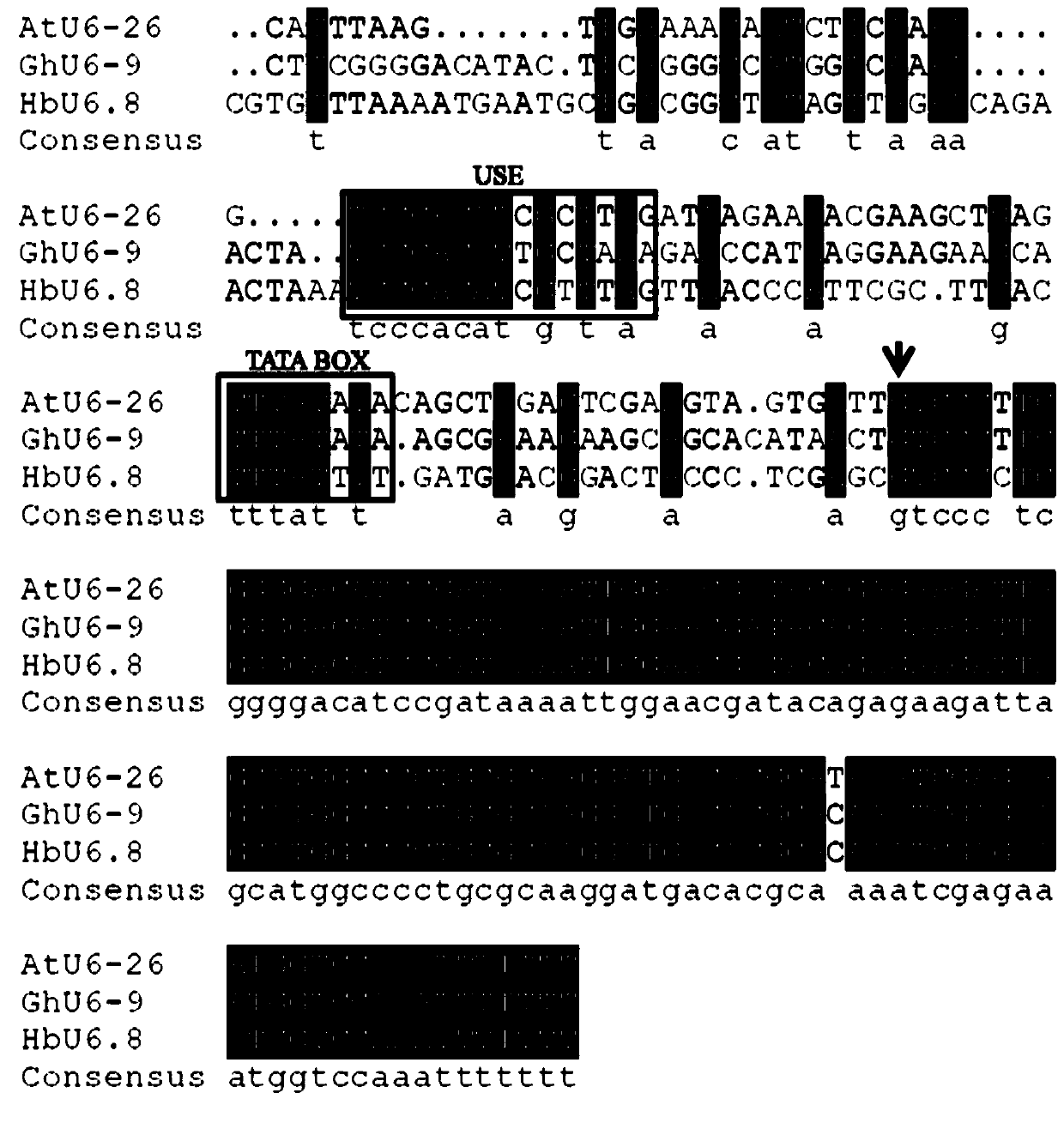
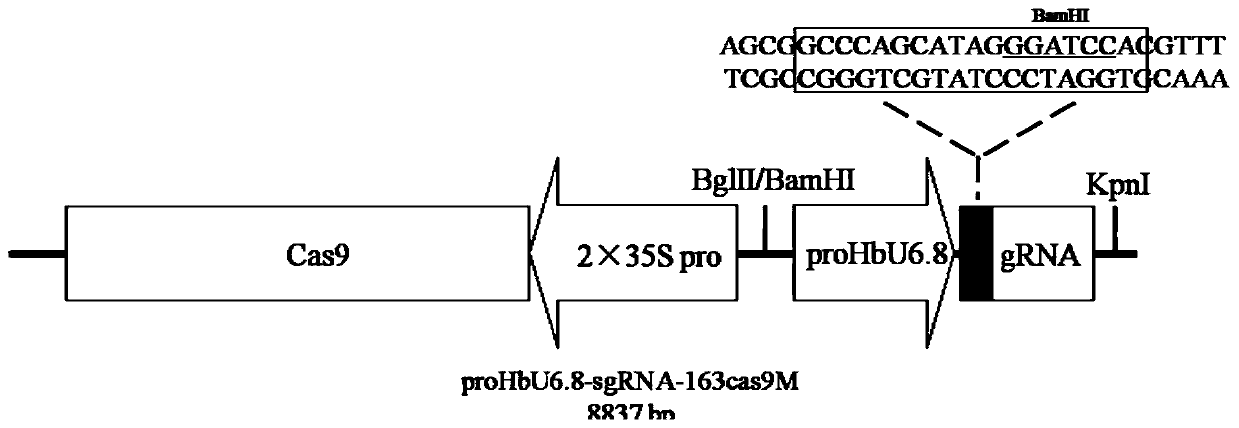
Rubber tree U6 gene promoter proHbU6.8 and cloning and application thereof
ActiveCN110157709AIncrease transcriptional activityRealize editingVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementU6 promoterGene engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and relates to a rubber tree RNA polymerase III type promoter, in particular to a rubber tree U6 gene promoter proHbU6.8. The invention further discloses a cloning method and application of the promoter. The rubber tree RNA polymerase III type promoter-rubber tree endogenous U6 promoter proHbU6.8 is obtained through cloning in a Brazil rubber tree for the first time. The promoter is the rubber tree endogenous RNA polymerase III-type promoter, the promoter has high-efficiency transcriptional activity, the expression of downstreamsgRNA can be driven, the activity of the promoter and the application feasibility of the promoter in a rubber tree CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system are verified through transient transformation rubbertree protoplasm, and CRISPR / Cas9-mediated rubber tree genome targeted editing is achieved.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Cellular Arrays
InactiveUS20080108513A1Promotes an increase in inductionMicroorganism librariesDirected macromolecular evolutionIntracellularPharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to characterizing transcription within cells. In particular, the present invention provides transfected cell arrays (e.g., two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional arrays) and systems, kits and methods utilizing the same (e.g., for transcriptional activity characterization). Compositions and methods of the present invention find use in, among other things, research, drug discovery and clinical (e.g., diagnostic, preventative and therapeutic) applications.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
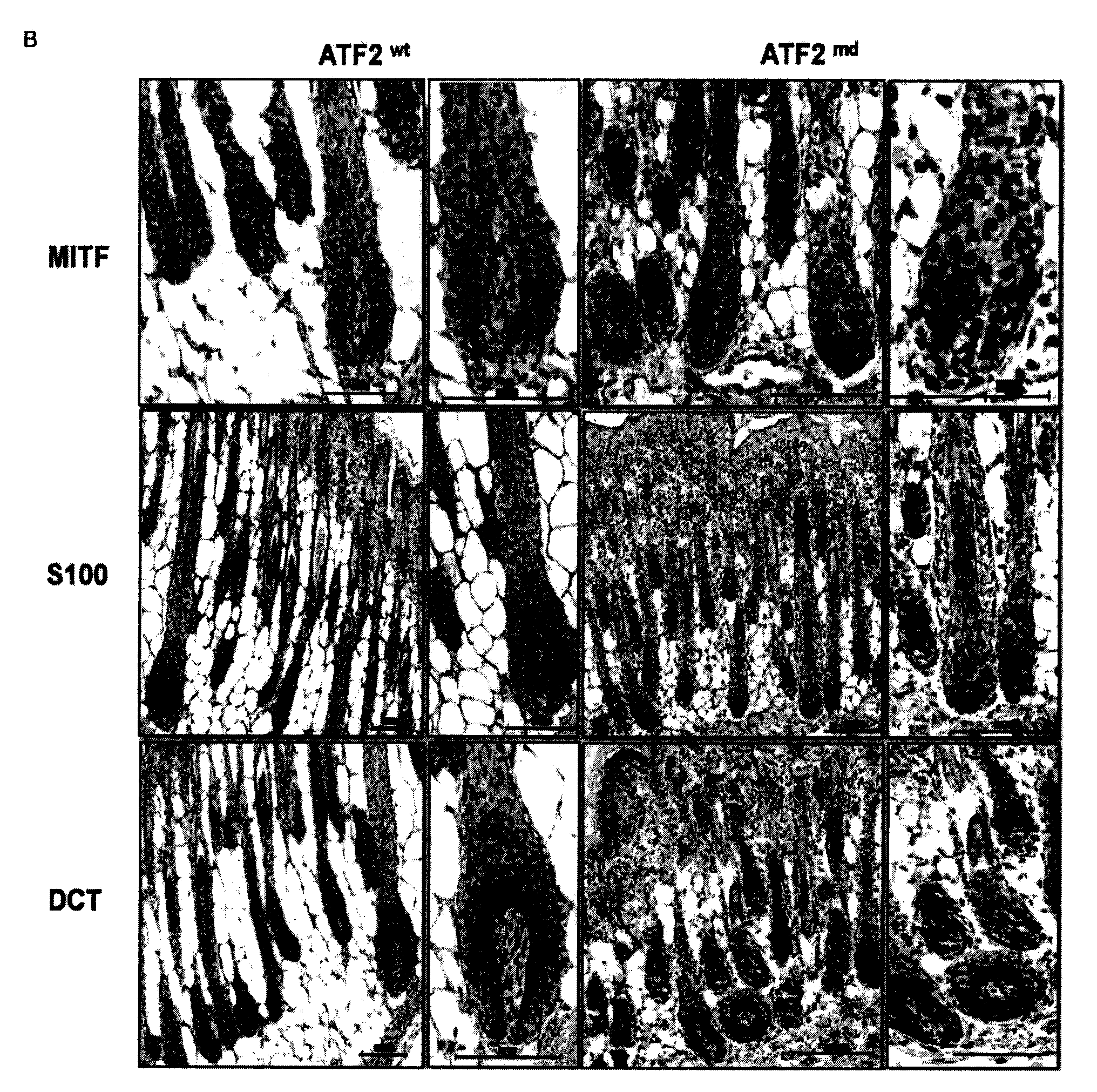
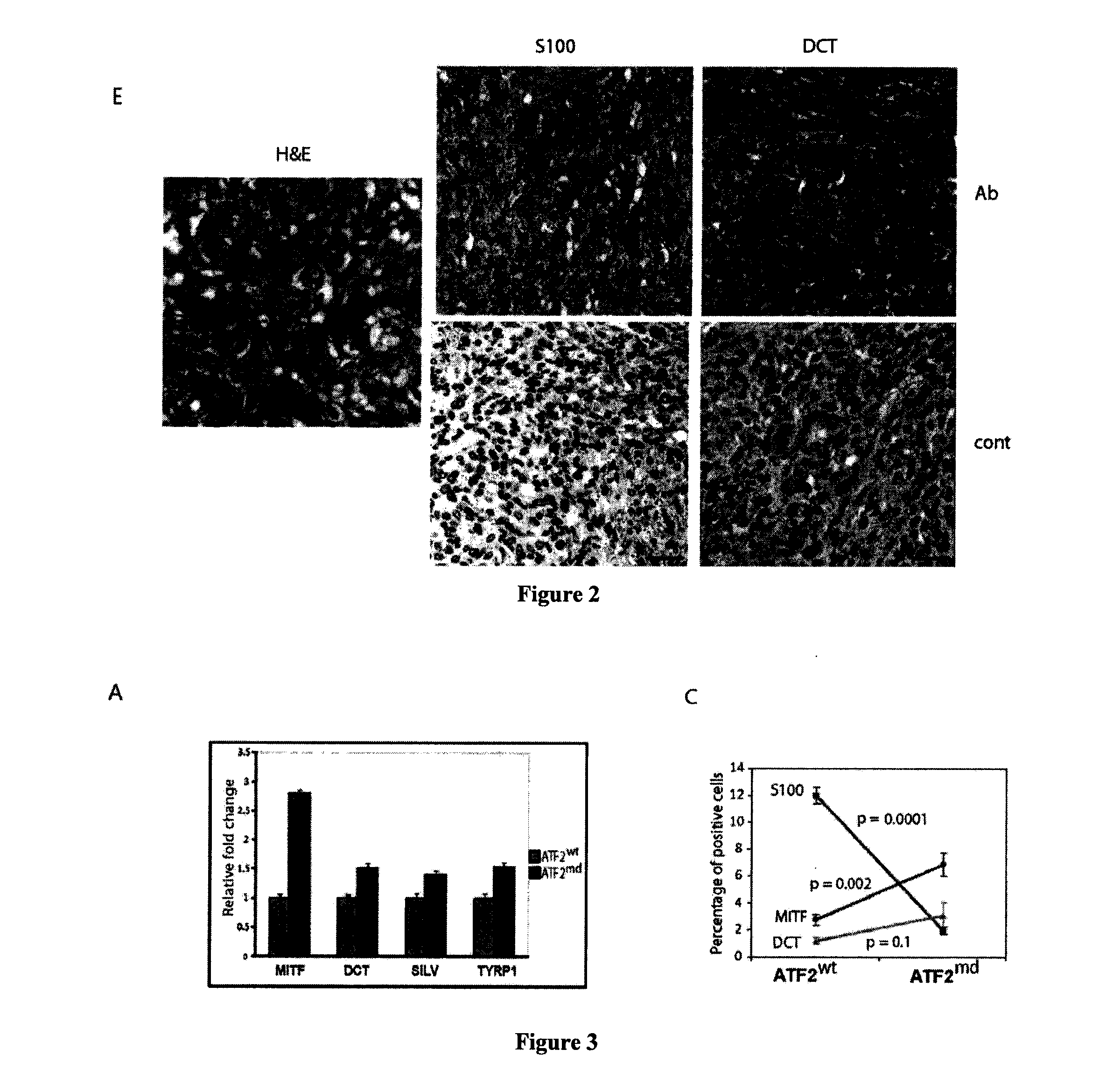
Methods of diagnosis and treatment of melanoma
InactiveUS20120095078A1High expressionNegatively regulatesOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMelanocyteLine of therapy
Methods for the diagnosis or prognosis of melanoma by detecting expression of ATF2 and MITF in melanocytes are provided herein. Also provided are methods of treating a melanocyte proliferative disorder with agents that modulate the transcriptional activity of ATF2 and / or MITF activity.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM MEDICAL RES INST
Novel method for integrating genes at specific sites in mammalian cells via homologous recombination and vectors for accomplishing the same
InactiveUS20020192820A1Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalReactive site
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Method for detecting activity of human BAFF-R gene promoter
InactiveCN101781679AEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture cellTranscriptional regulation
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of a human BAFF-R gene promoter, which comprises the following steps: designing a primer, cloning a BAFF-R gene 5' flanking region, constructing a sequence-loss plasmid of the BAFF-R gene 5' flanking region, culturing cells, recombining a report gene plasmid transiently transfected cell, detecting luciferase activity and the like. The method is easy to operate and accurate, detects the difference between transcriptional activities of a BAFF-R gene 5' upstream sequence in different cells and in different areas, determines the area where a core promoter of a BAFF-R gene is, and lays a foundation for studying the effect of a BAFF-R gene transcriptional regulation element and clarifying the expression regulation mechanism of the gene.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
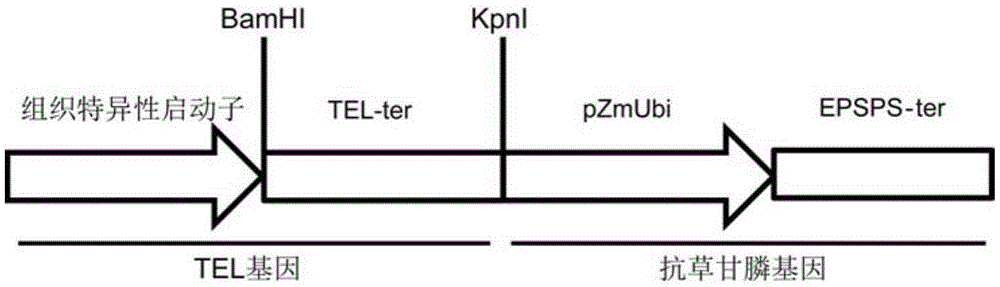
Application of tissue-specific promoter to regulation and control of crop yield
InactiveCN106544344AImproved yield-related traitsIncrease productionAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceTassel
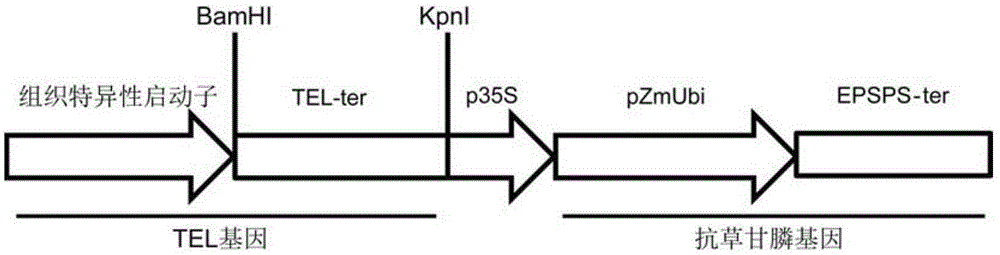
The invention discloses application of a tissue-specific promoter to the regulation and control of the crop yield. According to the application, the tissue-specific promoter is used for regulating and controlling the expression of a crop TEL gene to realize the improvement of the crop yield, wherein the tissue-specific promoter comprises a promoter with transcriptional activity on at least one or more than one tissue or organ of a crop stem tip mitogenetic region, a flower tip mitogenetic region, a flower primordium, an inflorescence, a tassel, a seed and a root; the effect that a series of adverse influence brought by a constitutive promoter can be effectively avoided by regulating and controlling the overexpression of the TEL gene in plants by the tissue-specific promoter is disclosed for the first time; the crop yield relevant property is effectively improved, so that a novel balance is formed in aspects of source, translocation and sink; and the crop yield is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU RUIFENG BIOTECH LIMITED
Method for synthesizing cDNA
InactiveUS20030077762A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyExonuclease
A method for synthesizing cDNA characterized by performing a reverse transcription reaction in the presence of an enzyme having a reverse transcriptional activity and another enzyme different from the former one which as a 3'-5' exonuclease activity.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Asparagus U6 gene promoter AspU6p3 and cloning and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, particularly relates to an asparagus RNA polymerase III type promoter, more particularly relates to an asparagus U6 gene promoter AspU6P3, and further discloses a cloning method and application of the asparagus U6 gene promoter AspU6P3. The asparagus RNA polymerase III-type promoter, namely the asparagus endogenous U6 promoter AspU6P3, is cloned from asparagus (aka the king of vegetables) cultivated species for the first time; the promoter is the asparagus endogenous RNA polymerase III-type promoter and has efficient transcriptional activity, and can drive expression of downstream sgRNA; in addition, The activity of the endogenous U6 promoter AspU6P3 and the feasibility of the endogenous U6 promoter AspU6P3 applied to an asparagus CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system are verified through an asparagus stable genetic transformation system, and CRISPR / Cas9 mediated asparagus genome targeted editing is realized for the first time.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV +1
Application of bavachinin and analogs of bavachinin
ActiveCN105982884AWide range of synergiesIncrease transcriptional activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBavachininSide effect
The invention discloses application of bavachinin and analogs of bavachinin. According to the application, bavachinin or / and analogs of bavachinin serve as active ingredients to prepare compositions for enhancing exciting activity of PPARalpha or / and PPARgamma. Research results show that bavachinin and analogs of bavachinin can remarkably improve the transcriptional activity of a PPARgamma exciting agent to PPARgamma, enhance the transcriptional activity of a PPARalpha exciting agent to PPARalpha and serve as active ingredients of PPARalpha or / and PPARgamma exciting agents to prepare compositions for preventing or treating the metabolic syndrome, the application range of bavachinin and analogs of bavachinin can be widened, and decrement and synergism of PARalpha or / and PPARgamma exciting agents can be achieved to reduce the toxic and side effects of PARalpha or / and PPARgamma exciting agents and achieve wide clinical application of PARalpha or / and PPARgamma exciting agents.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
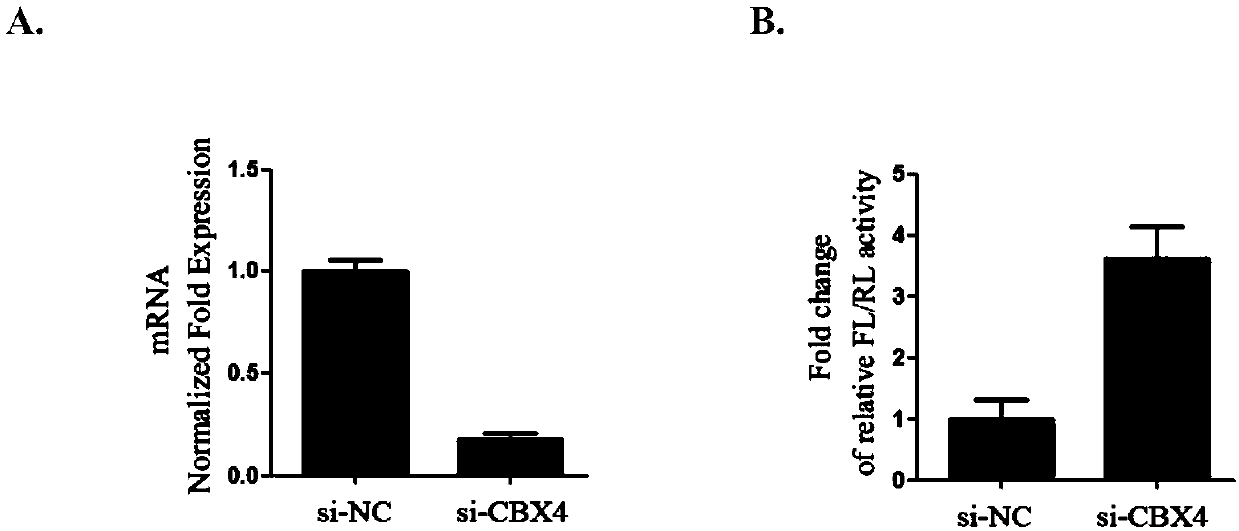
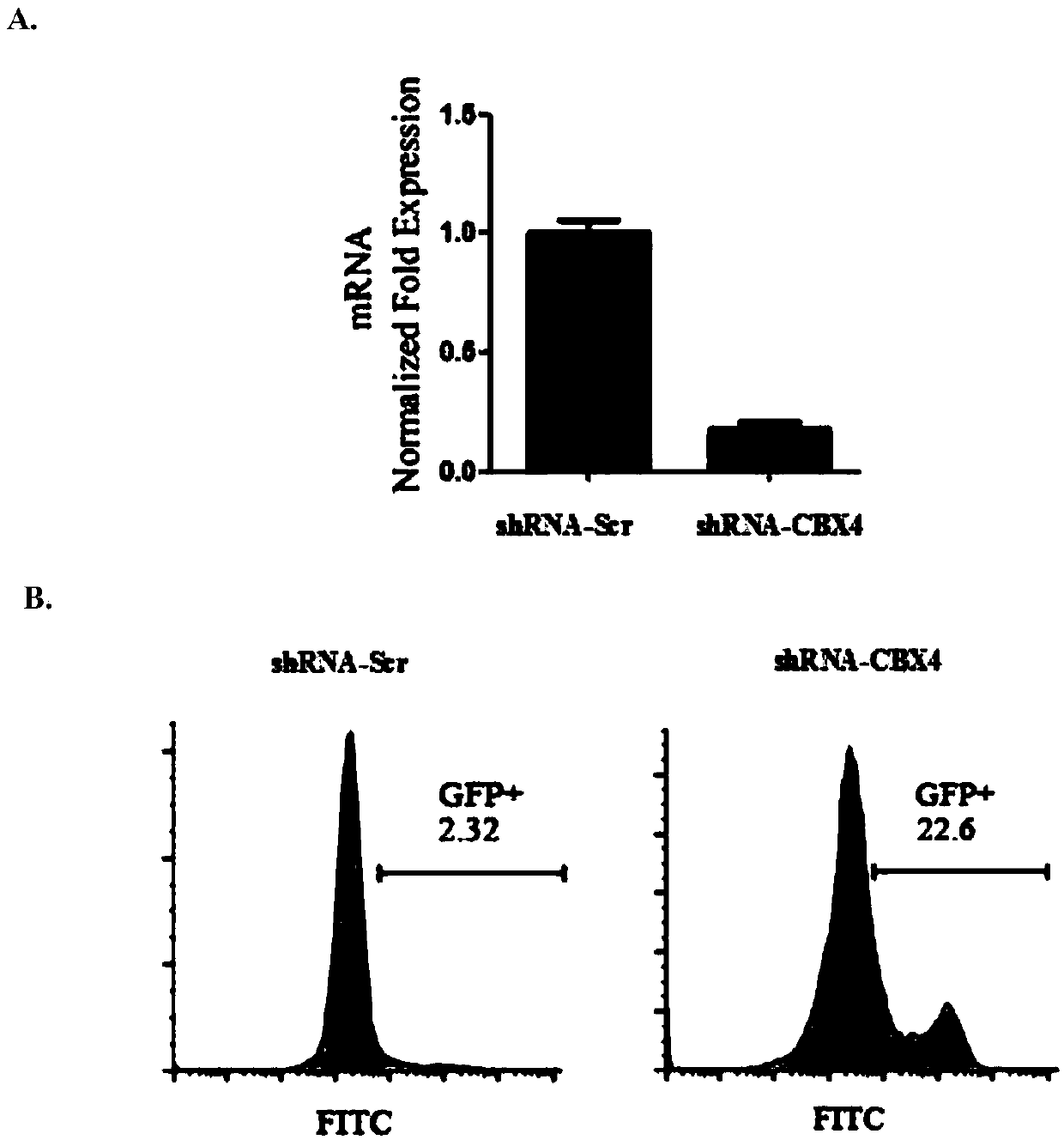
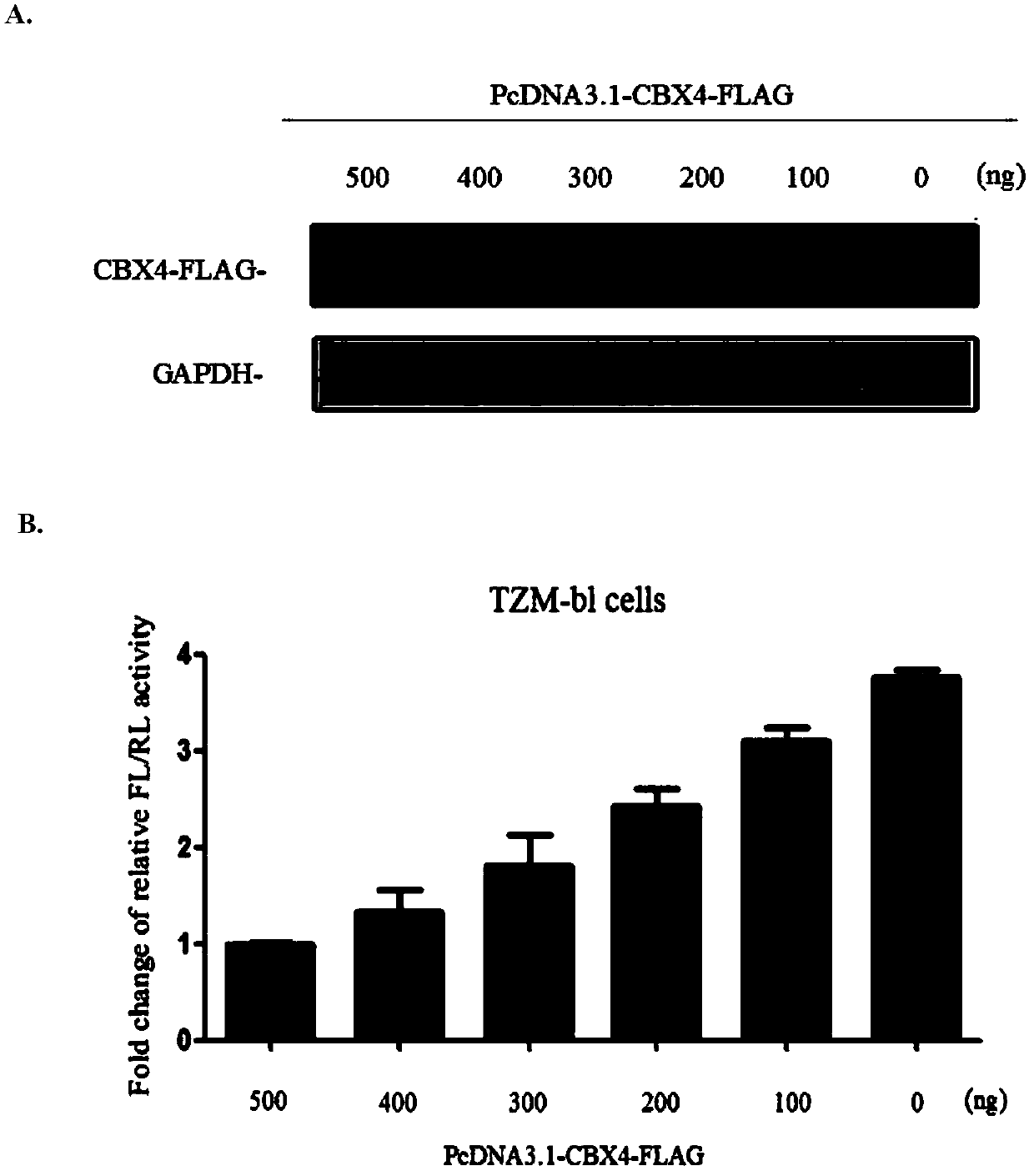
Application of CBX4 used as HIV-1 latent infection activation target
The invention discloses application of CBX4 used as an HIV-1 latent infection activation target. It is found through researches that inhibition of CBX4 has good HIV-1 latent activation capability andknock-down of CBX4 can effectively promote transcription of HIV-1 LTR. Then, it is found in a J-lat 10.6 HIV-1 latent infection cell model that through knock-down of CBX4, CFP gene expression is up-regulated and HIV-1 can be effectively activated. Through overexpression of CBX4 protein in TZM-bl cell, transcriptional activity of LTR of HIV-1 can be effectively reduced. Through further detection, it is found that reduced CBX4 protein expression will reduce H3K9 trimethylation of HIV-1 LTR and enrichment of H3K27 trimethylation so as to activate HIV-1 latent infection. The CBX4, which is used asa brand new HIV-1 latent infection activation target, has important research and development value and significance of development in the aspect of HIV-1 latent infection activation.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
RNA polymerase transcription promoters and nucleic acid sequencing method
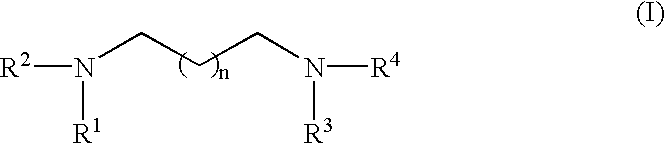
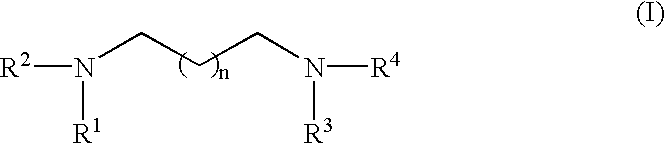
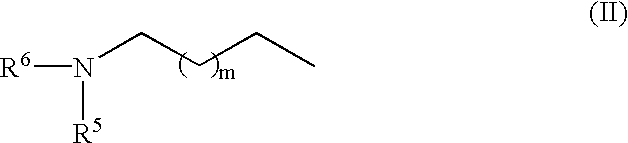
InactiveUS6627399B1Cosmetic preparationsSugar derivativesPolyamine CompoundTranscription factor activity
An RNA polymerase transcription accelerator comprising a compound represented by the following Formula (I) or salts thereof.A method of sequencing DNA in which nucleic acid transcripts are obtained using an RNA polymerase and a DNA fragment as a template, the resulted nucleic acid transcripts are separated, the nucleic acid sequence is determined from the separated fractions wherein the nucleic acid transcription reaction is carried out in the presence of a compound selected from a group of compounds represented by the above formula (I).The polyamine compounds above have outstanding accelerating activity on transcription activity of RNA polymerase. Therefore, use of the polyamine compounds in a DNA sequencing method using RNA polymerase can make a length of DNA sequence that can be determined in one sequencing longer.
Owner:RIKEN
Methods of diagnosing, prognosing and treating breast cancer
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
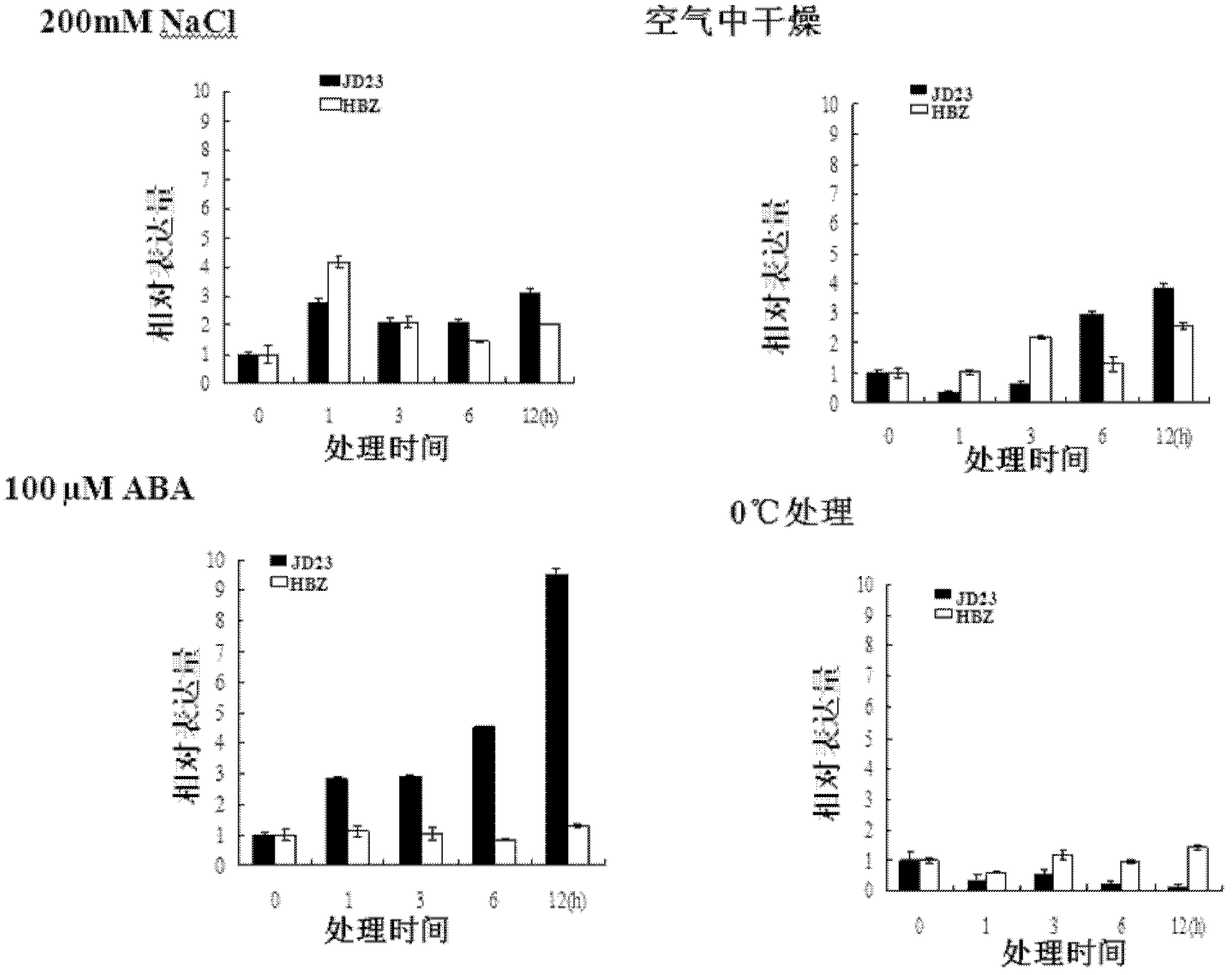
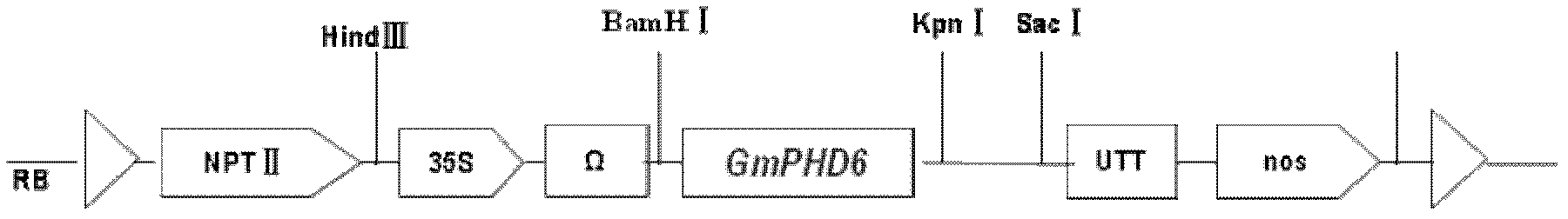
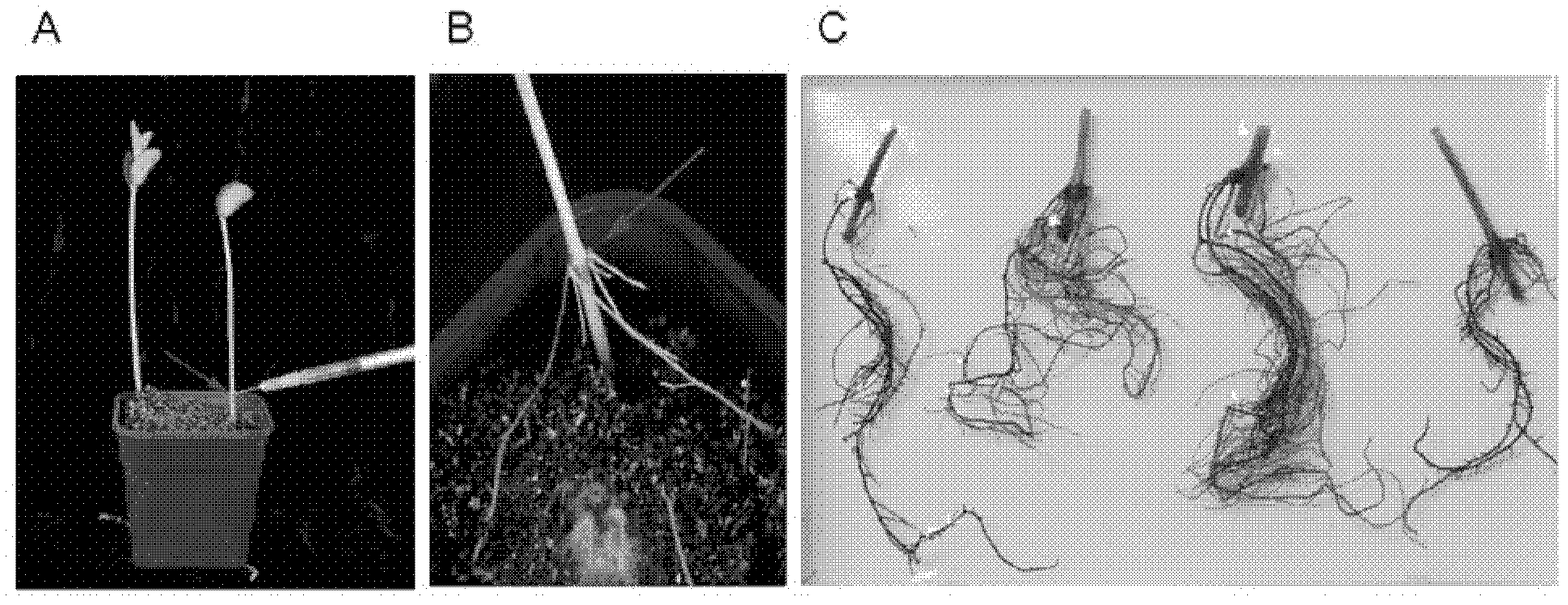
Soybean transcription active protein GmPHD6, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a soybean transcription active protein GmPHD6, and a coding gene and application thereof. The soybean PHD transcription factor is: (a) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown as Sequence 2 in a sequence table; or (b) a protein which is derived from the Sequence 2, is formed by the amino acid sequence shown as the Sequence 2 in the sequence table through the substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or some amino acid residues and is related to stress tolerance of plants. Experiments of the invention prove that the soybean PHD transcription factor GmPHD6 and the coding gene thereof can be used for the cultivation of stress-tolerant plant species, especially stress-tolerant soybean species such as salt-tolerant and drought-tolerant soybeans.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel enhancer and application thereof
ActiveCN104975018AImprove expression levelHigh expressionVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiotechnologyForeign protein
The invention relates to an artificially synthesized DNA enhancer and application thereof. The enhancer can be added to a recombinant protein expression vector of a mammalian cell and used for enhancing the intensity of transcriptional activity of a promoter, so that the secretory expression of proteins from mammals and other sources can be enhanced and the expression quantity of foreign proteins in animal cells can be improved greatly.
Owner:SUNSHINE GUOJIAN PHARMA (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com