Patents
Literature
41 results about "Dna targeting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
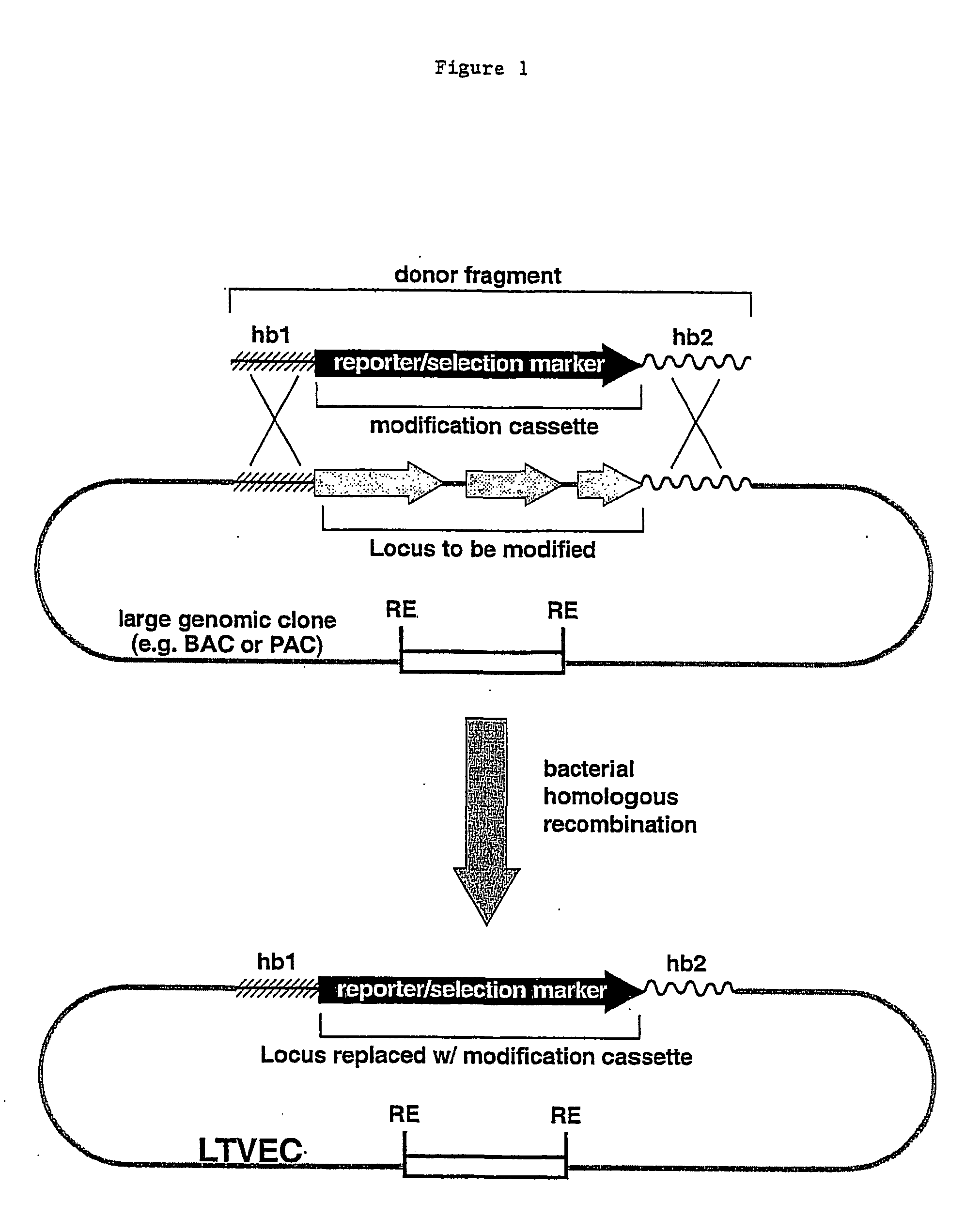
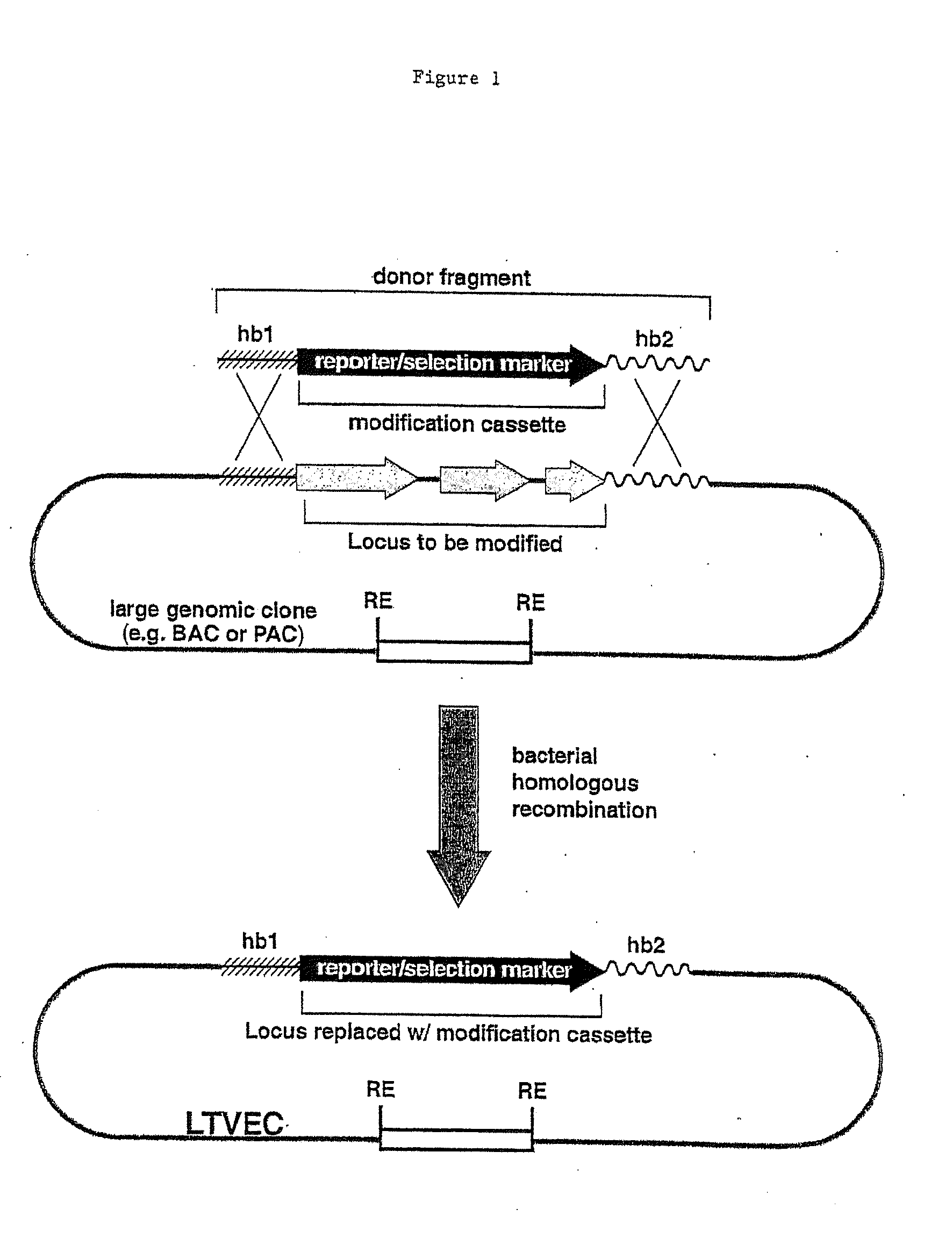
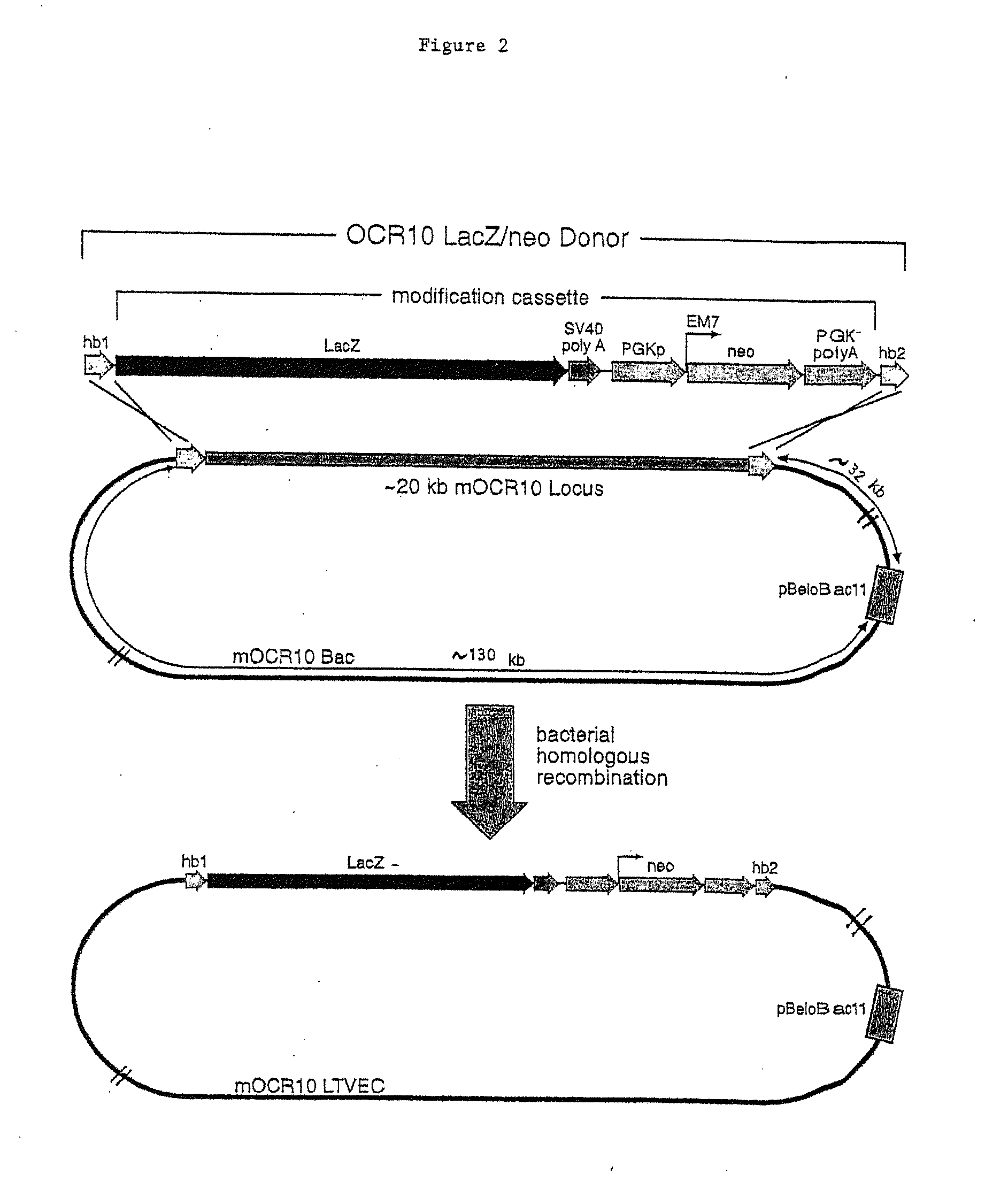
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
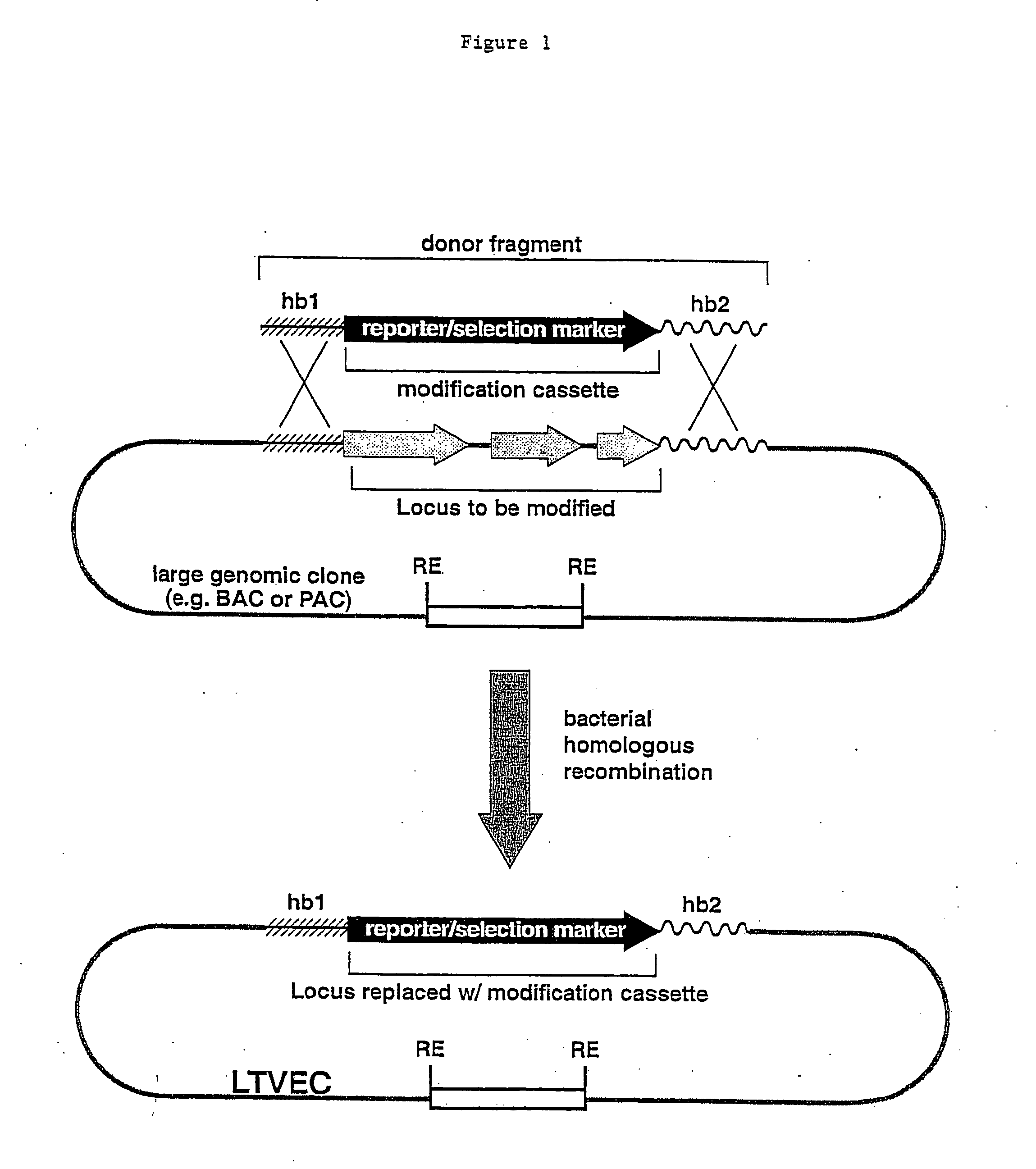
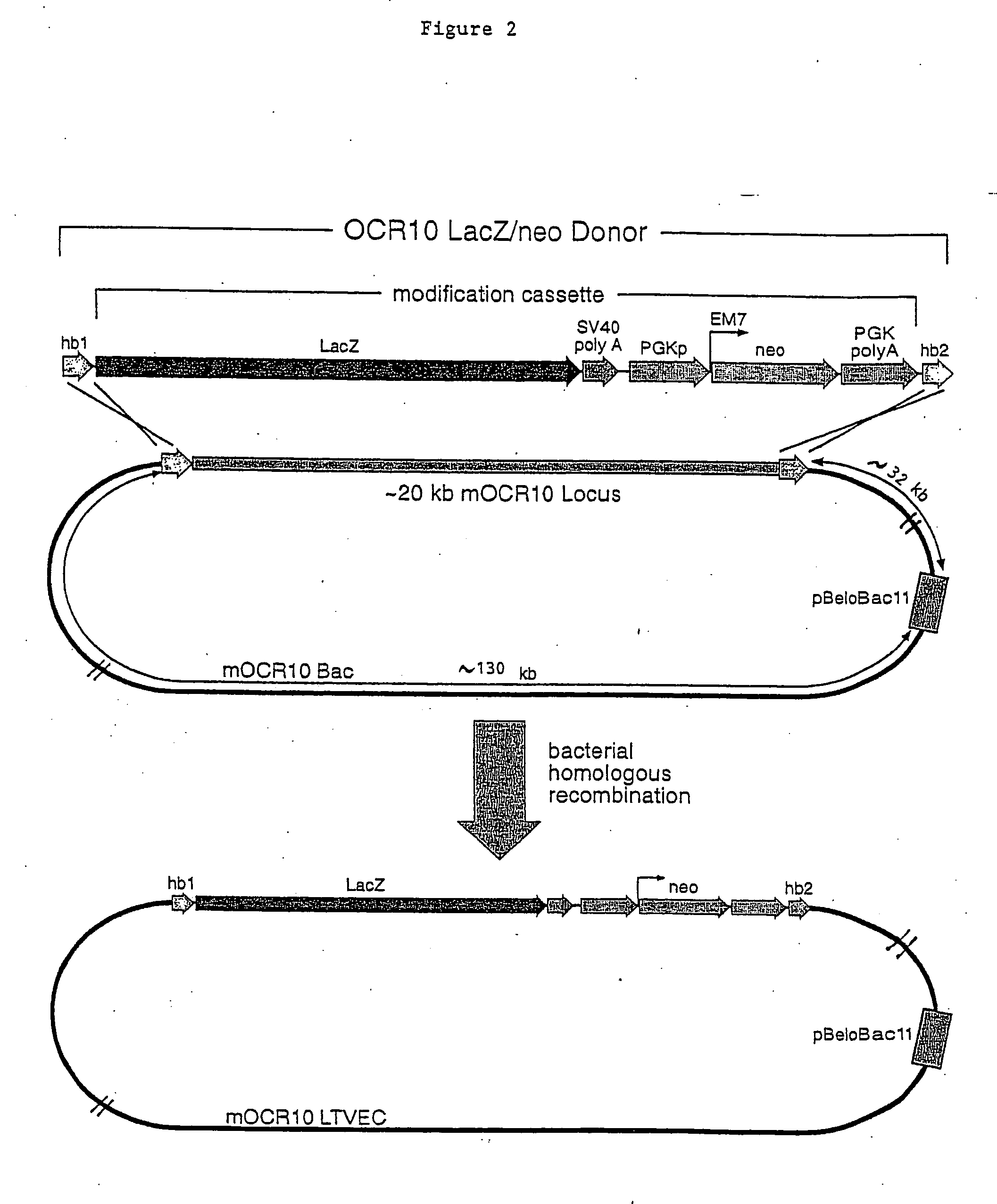
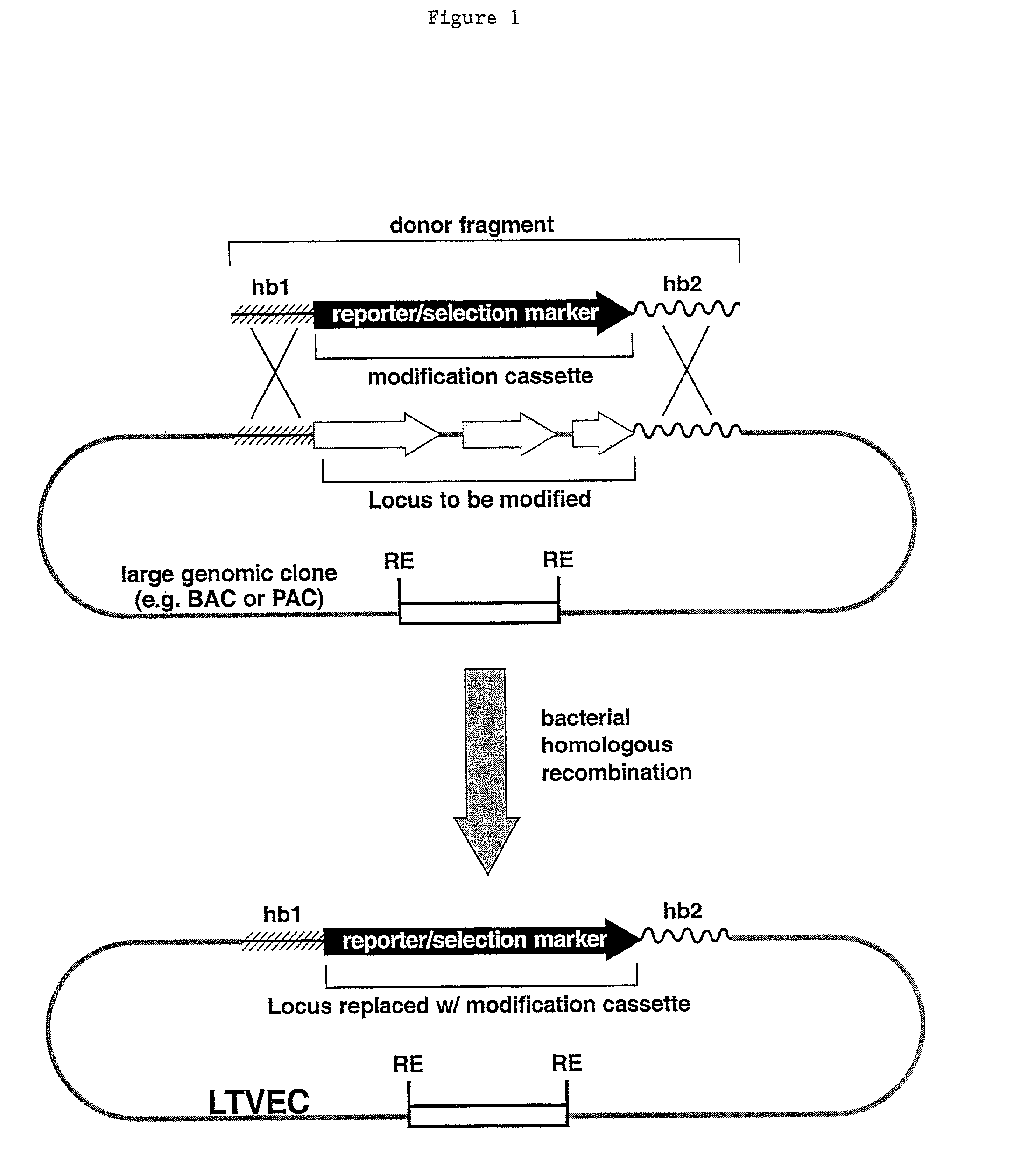
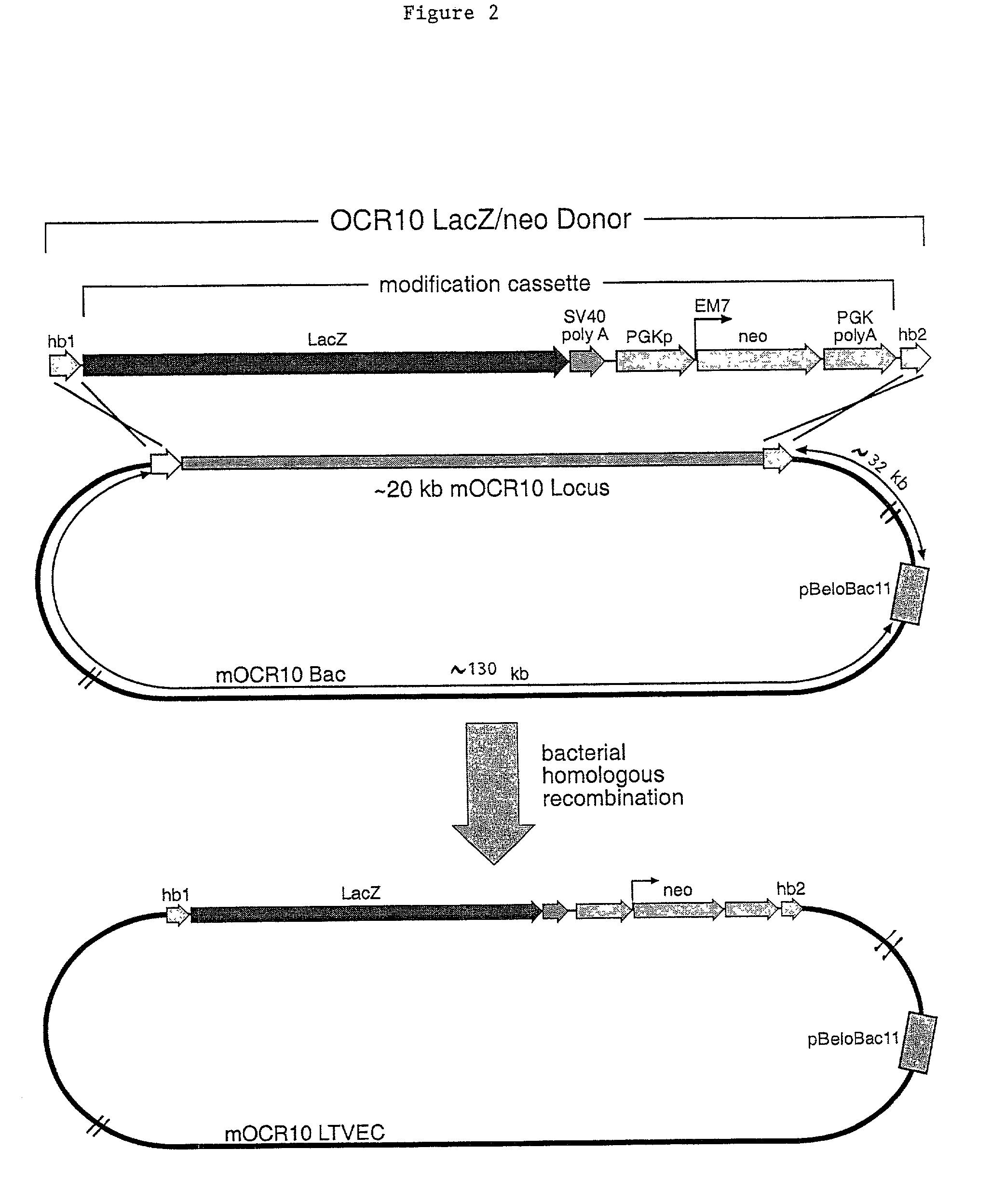
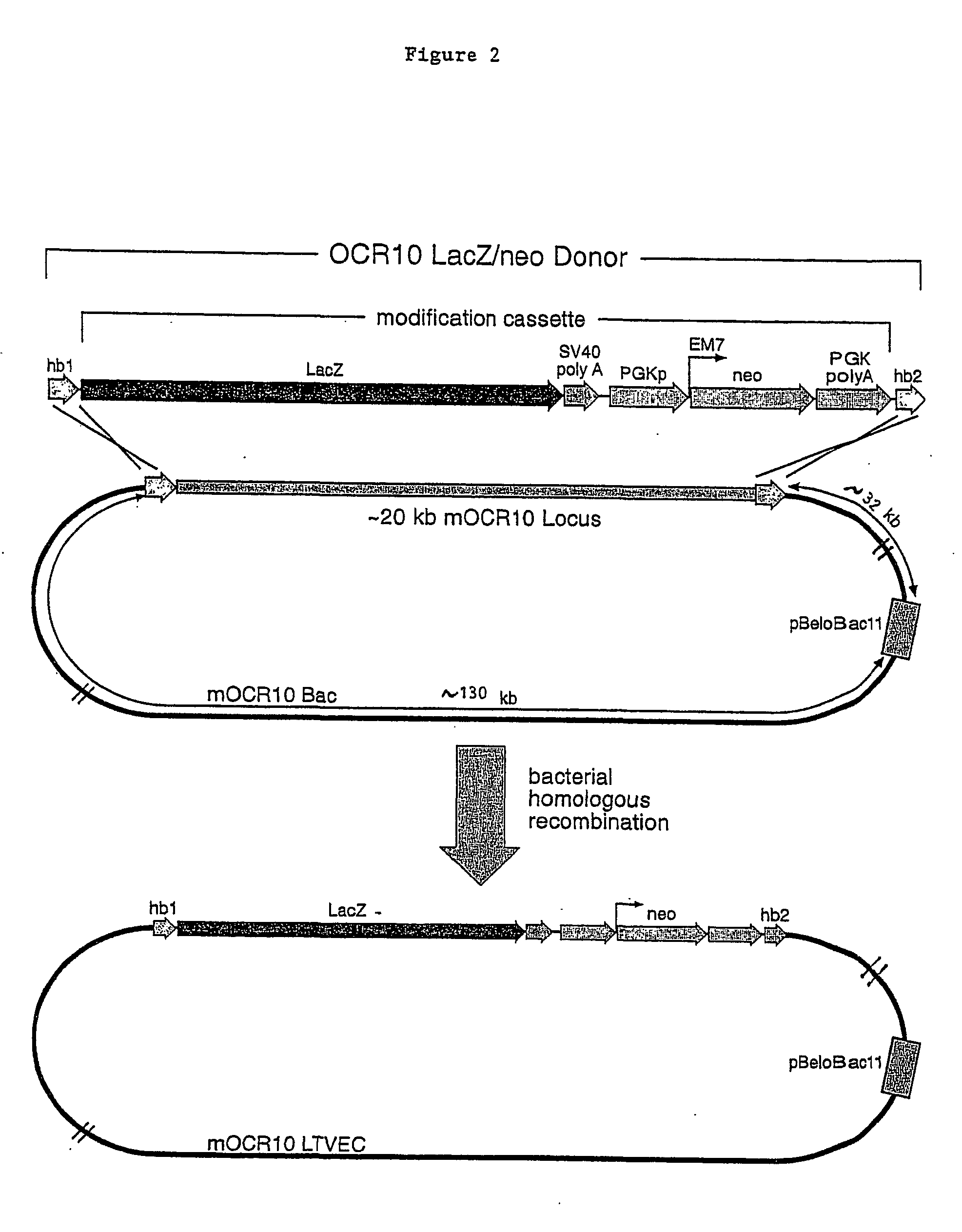
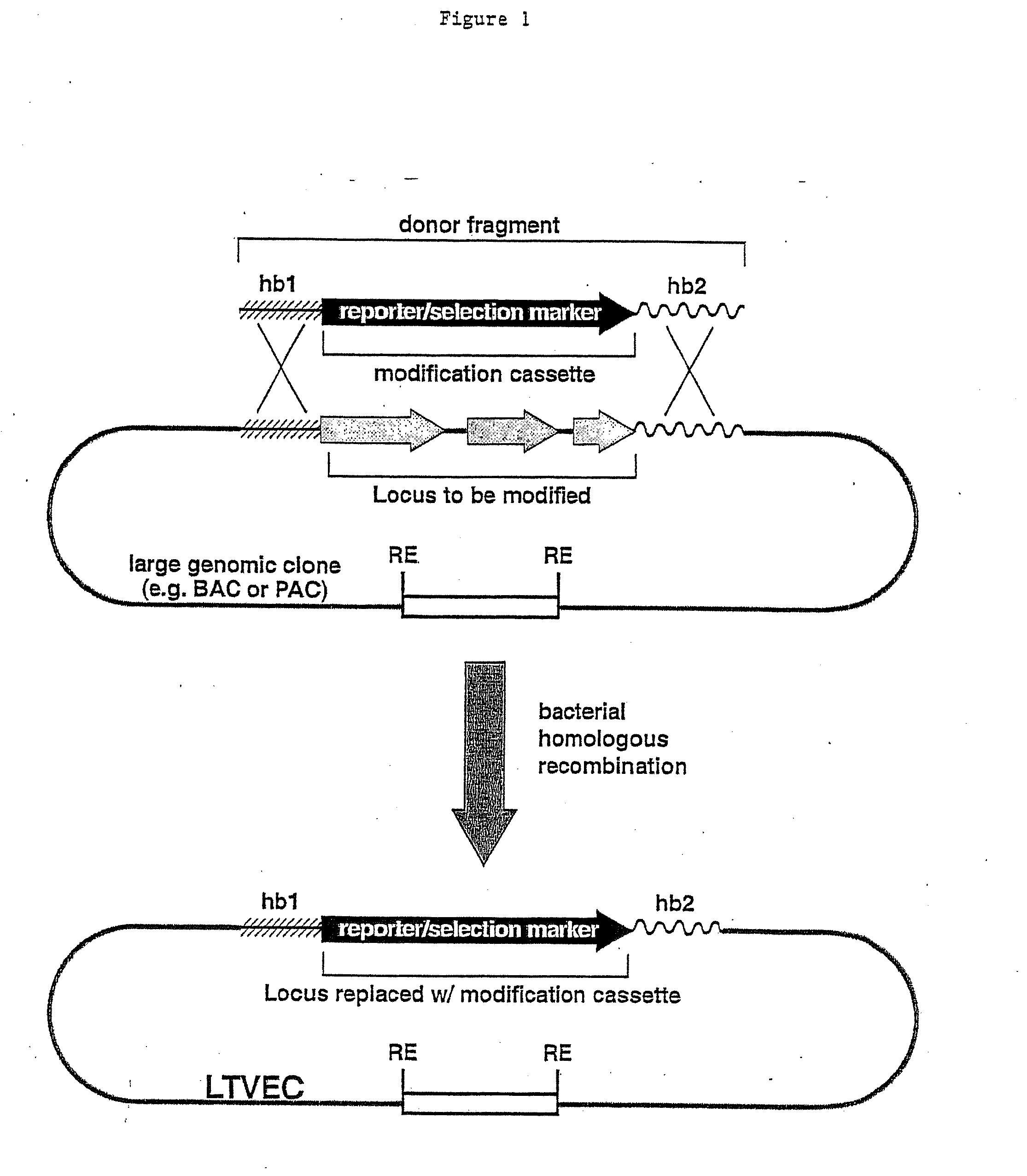
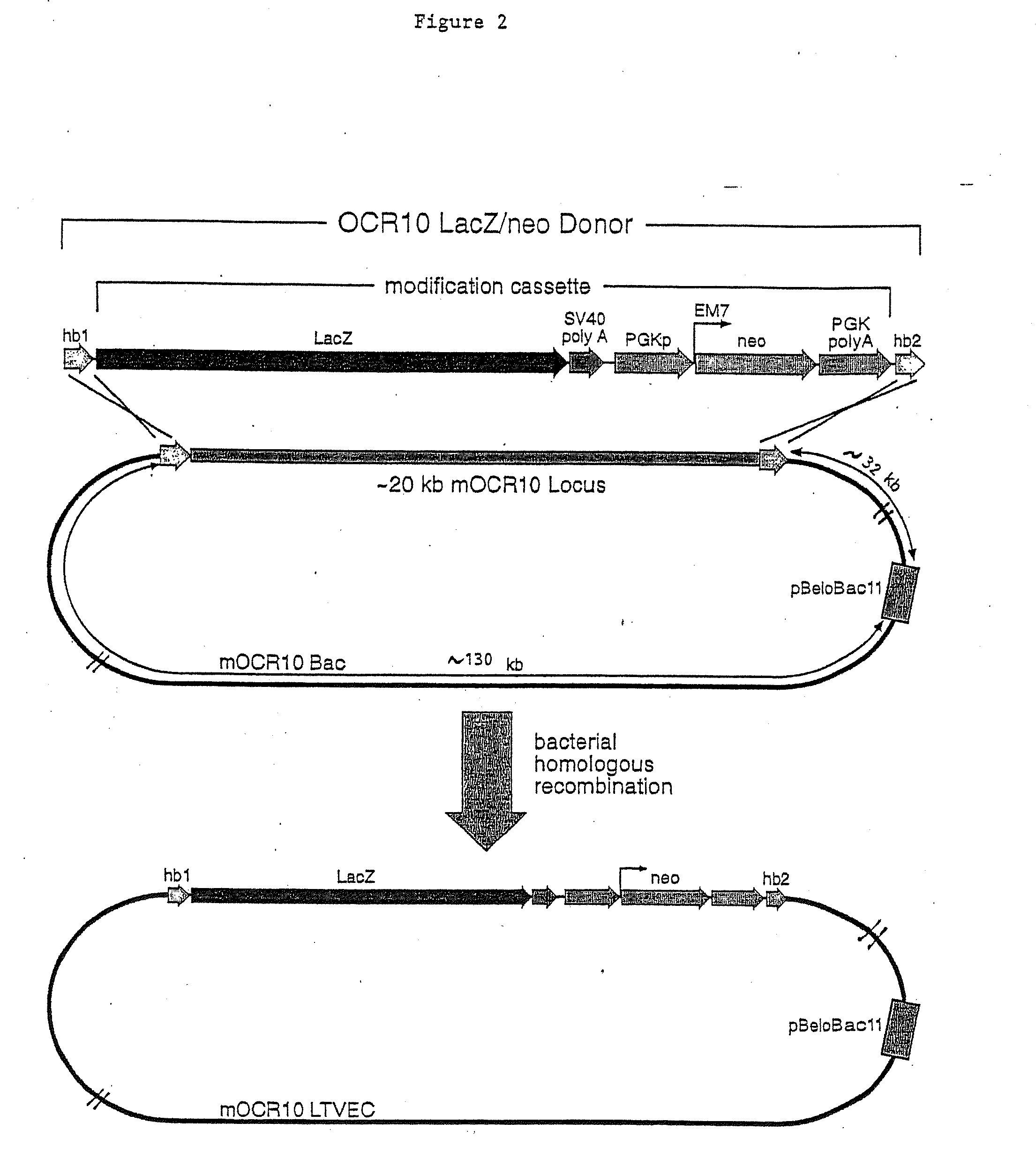
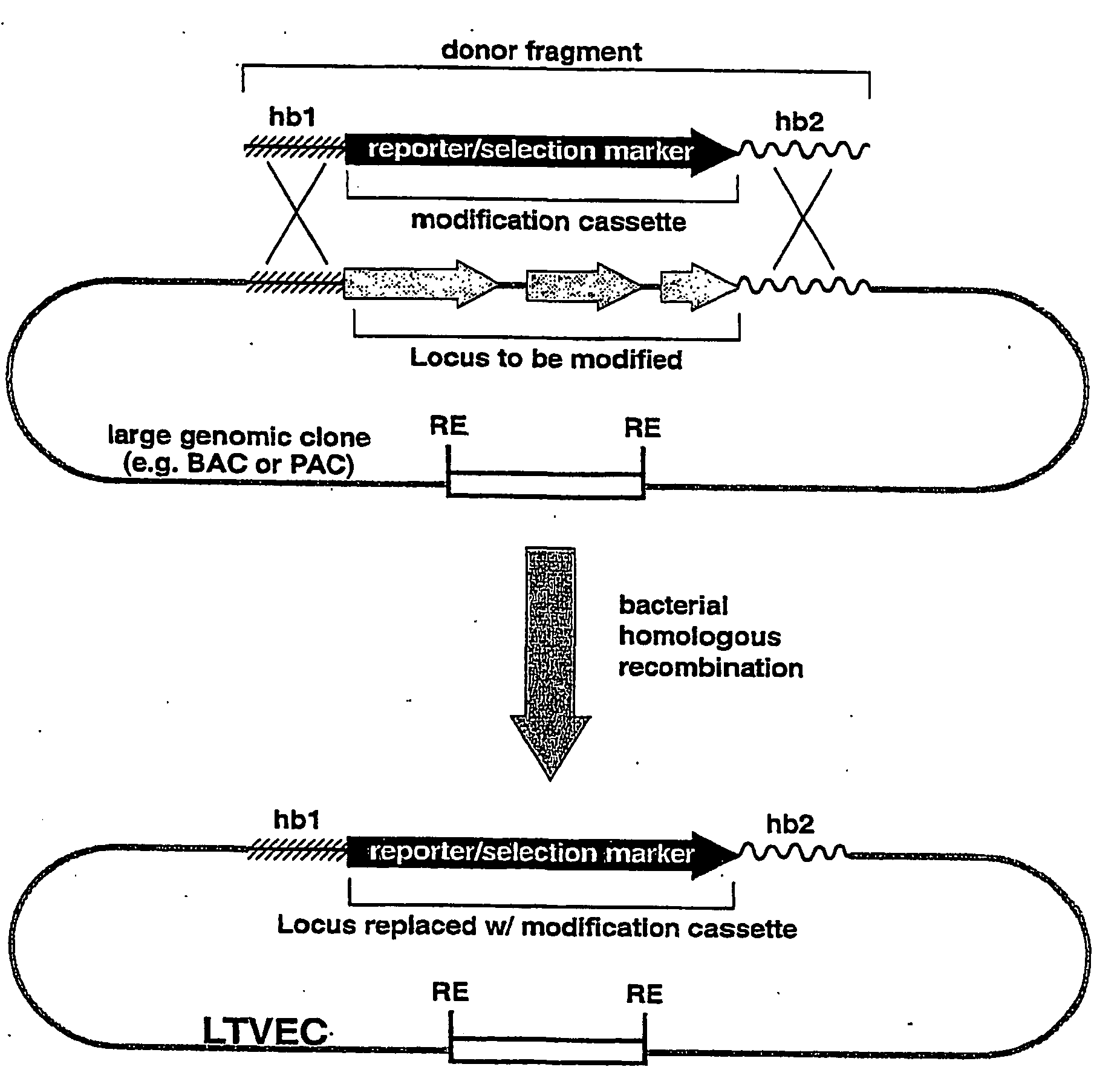
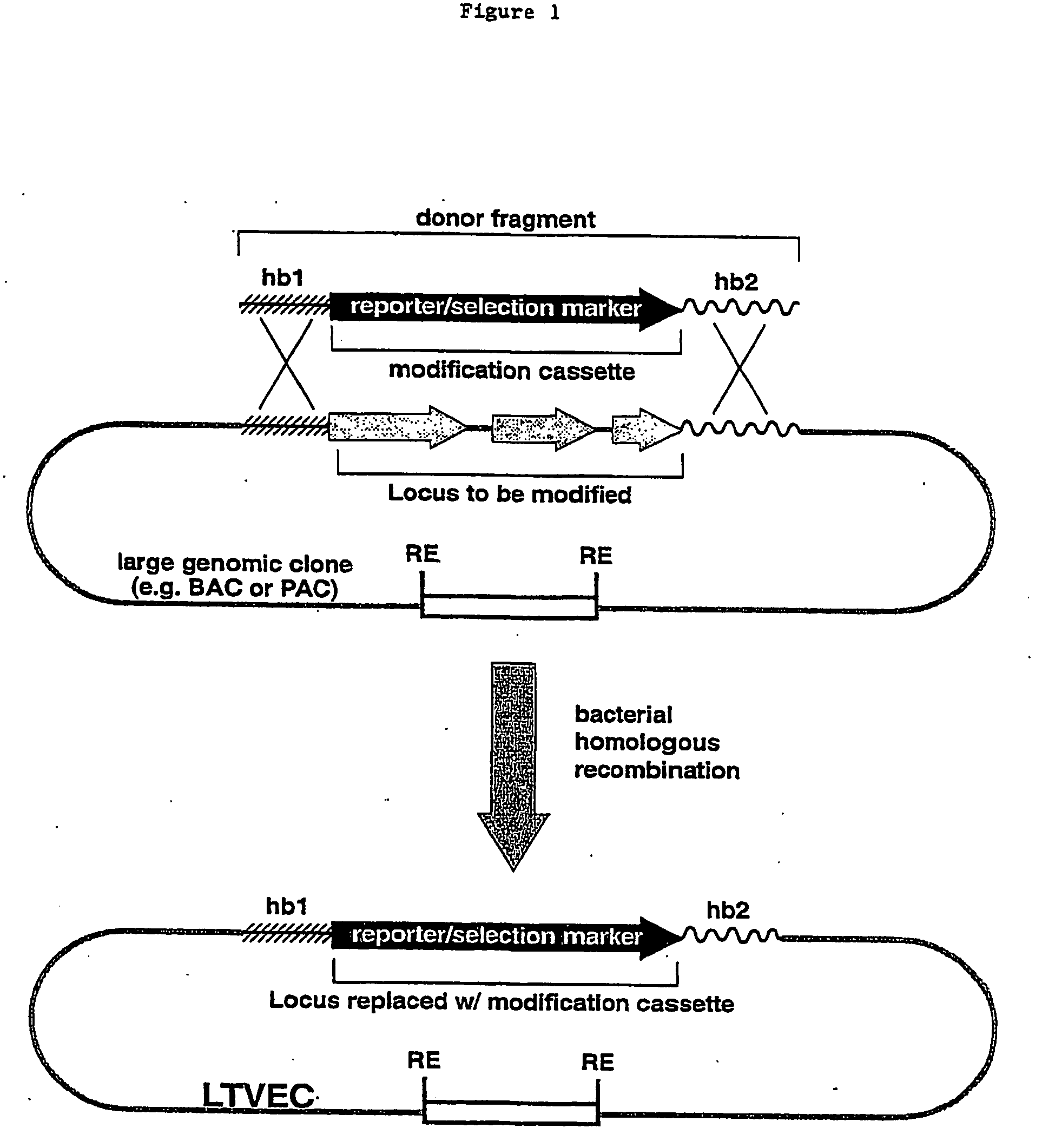
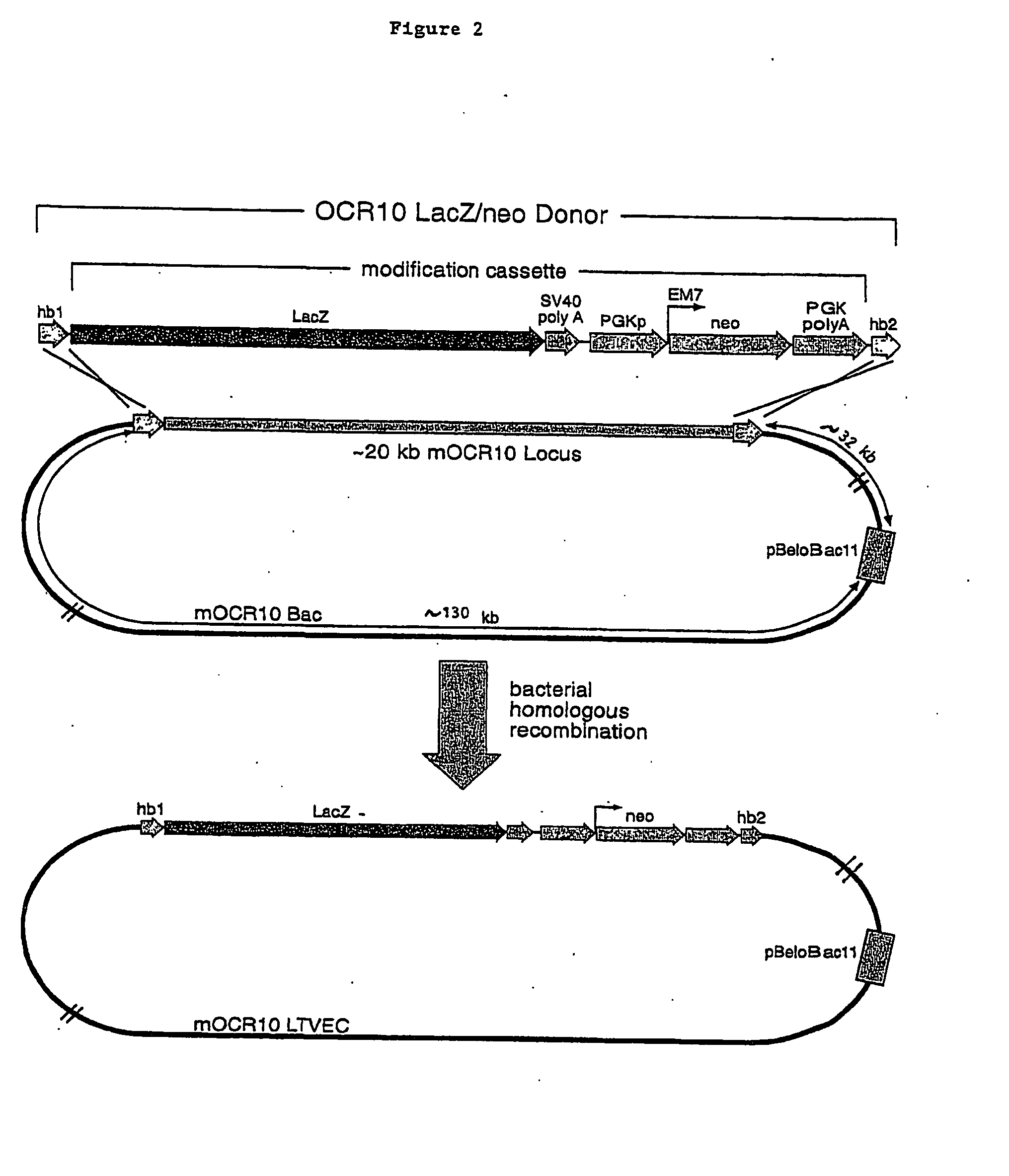
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
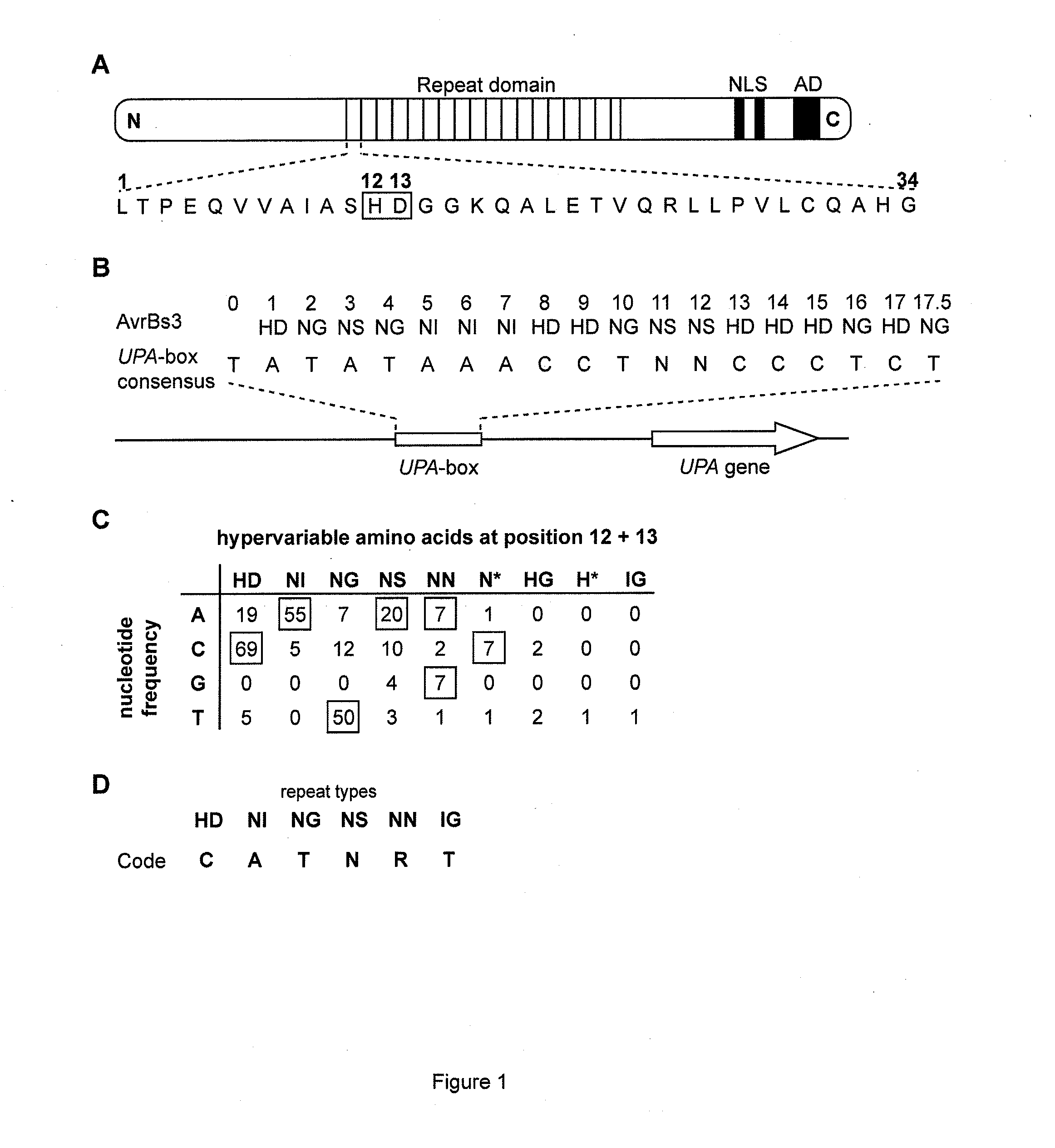
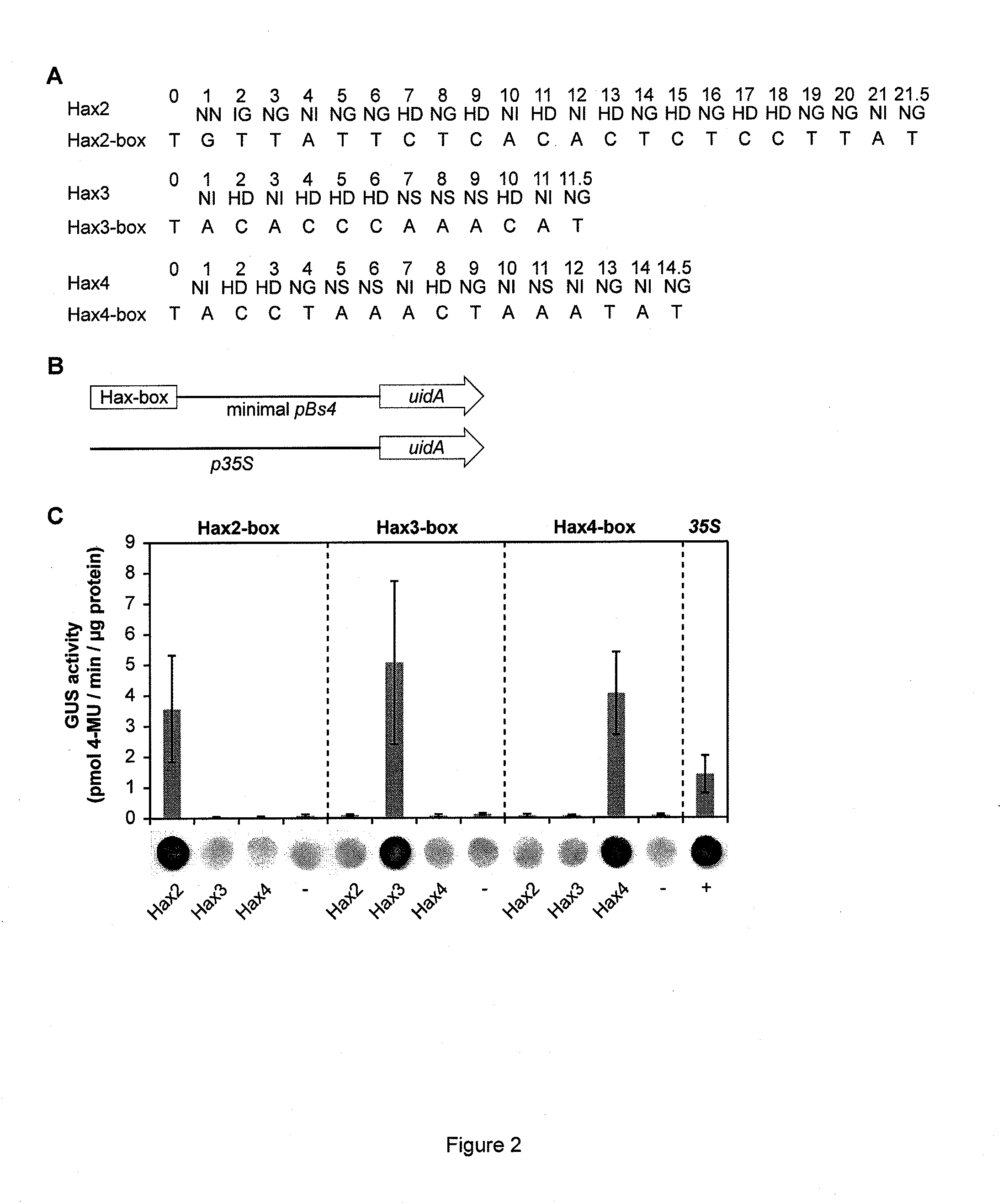
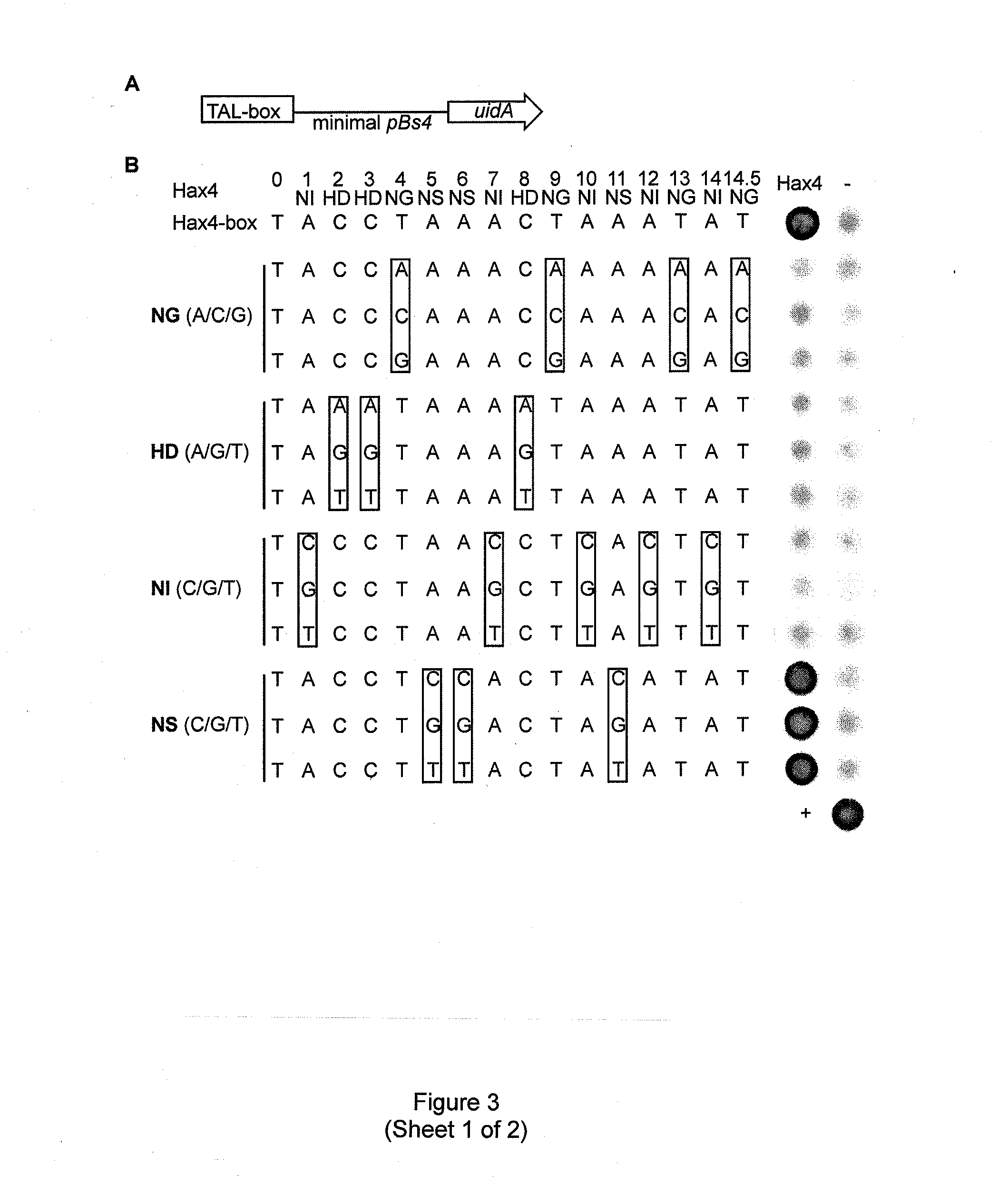
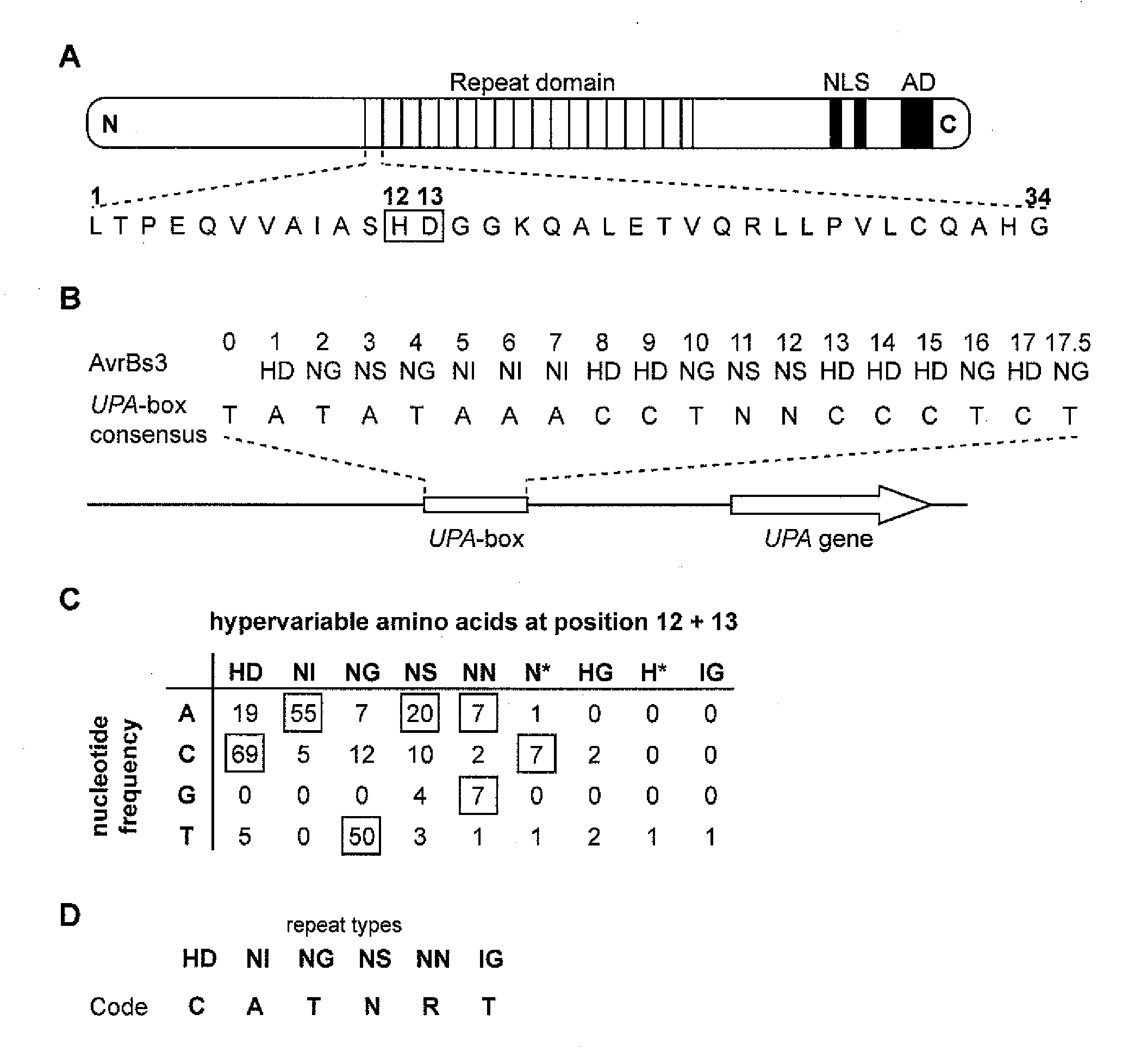
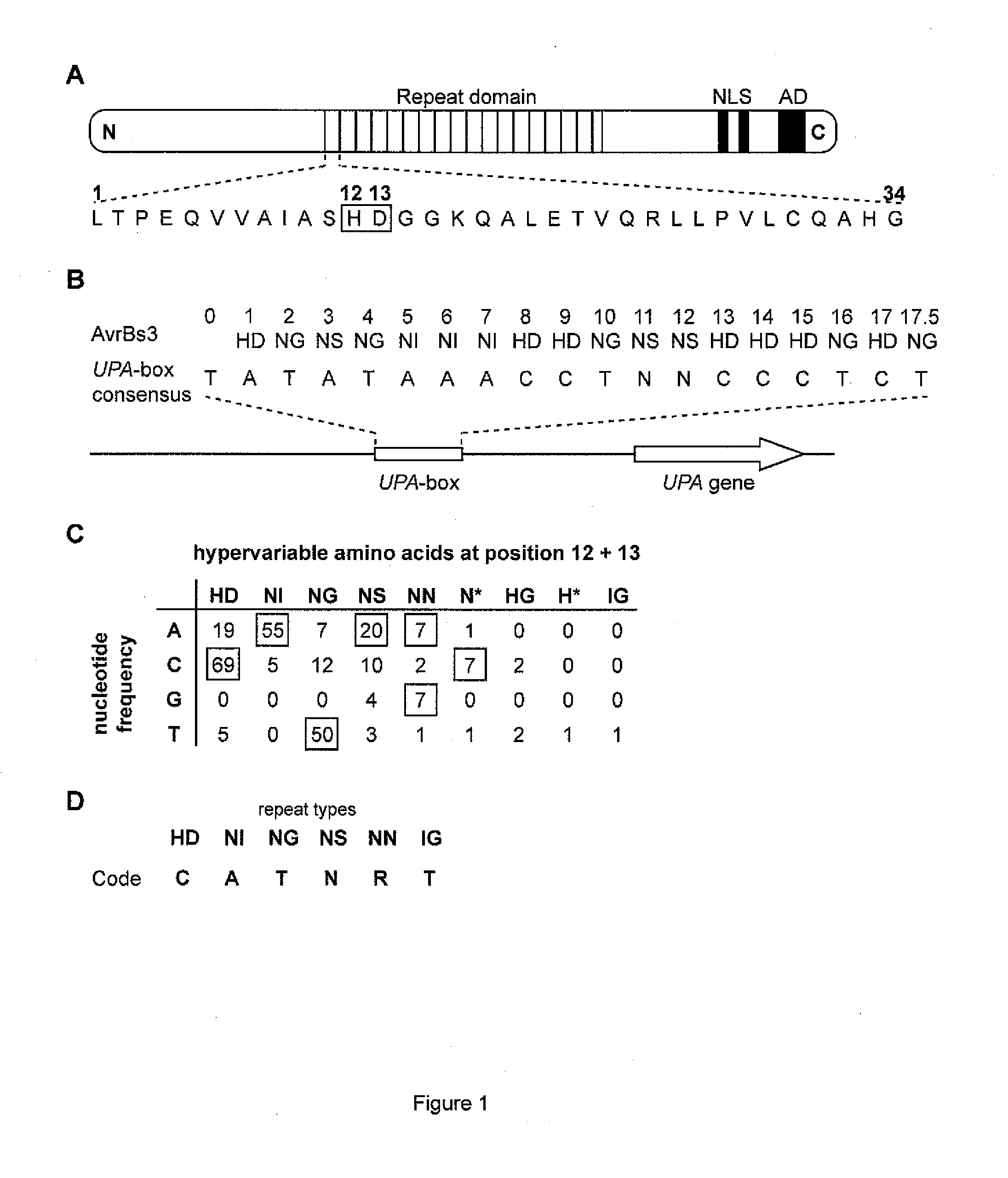
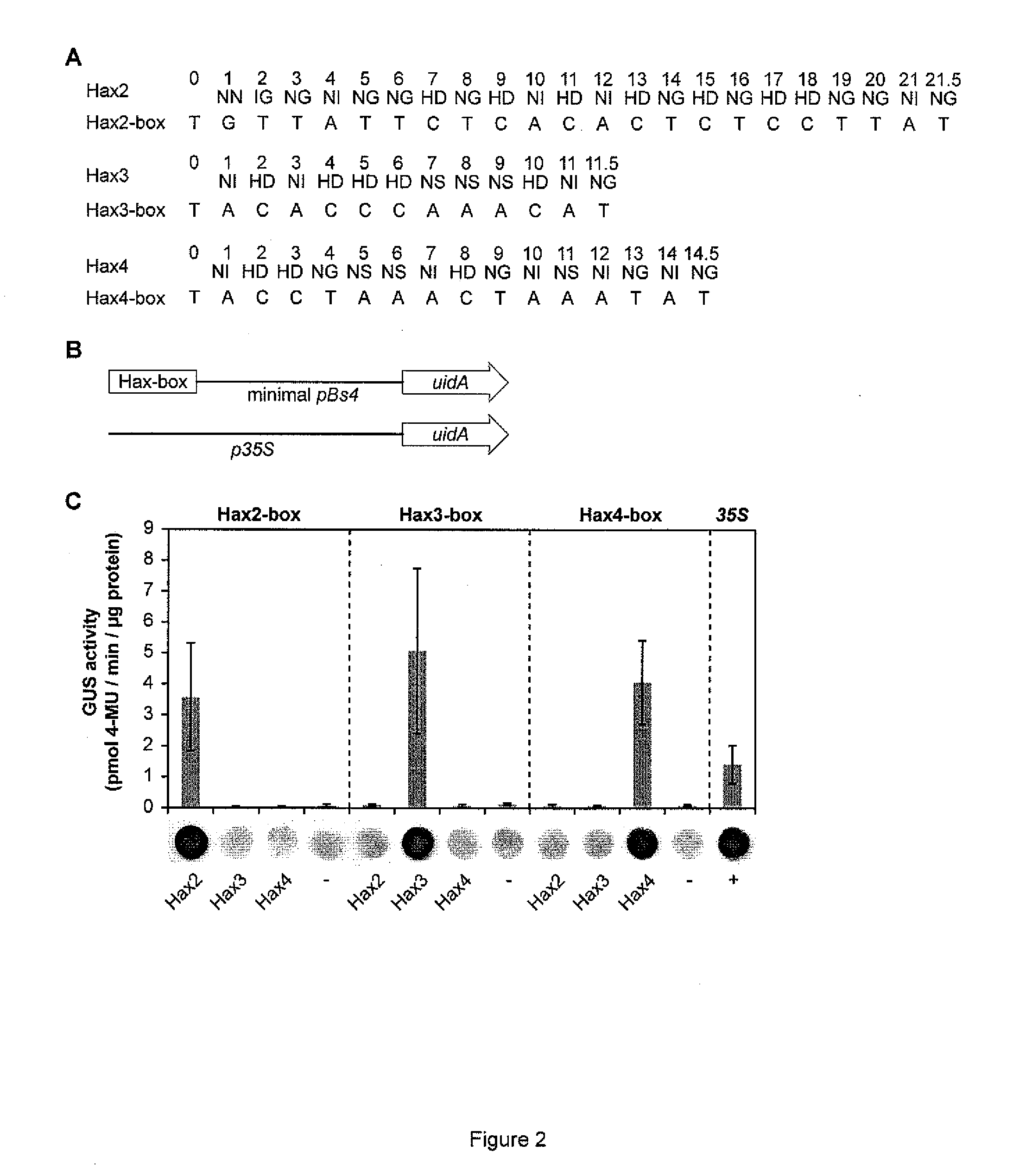
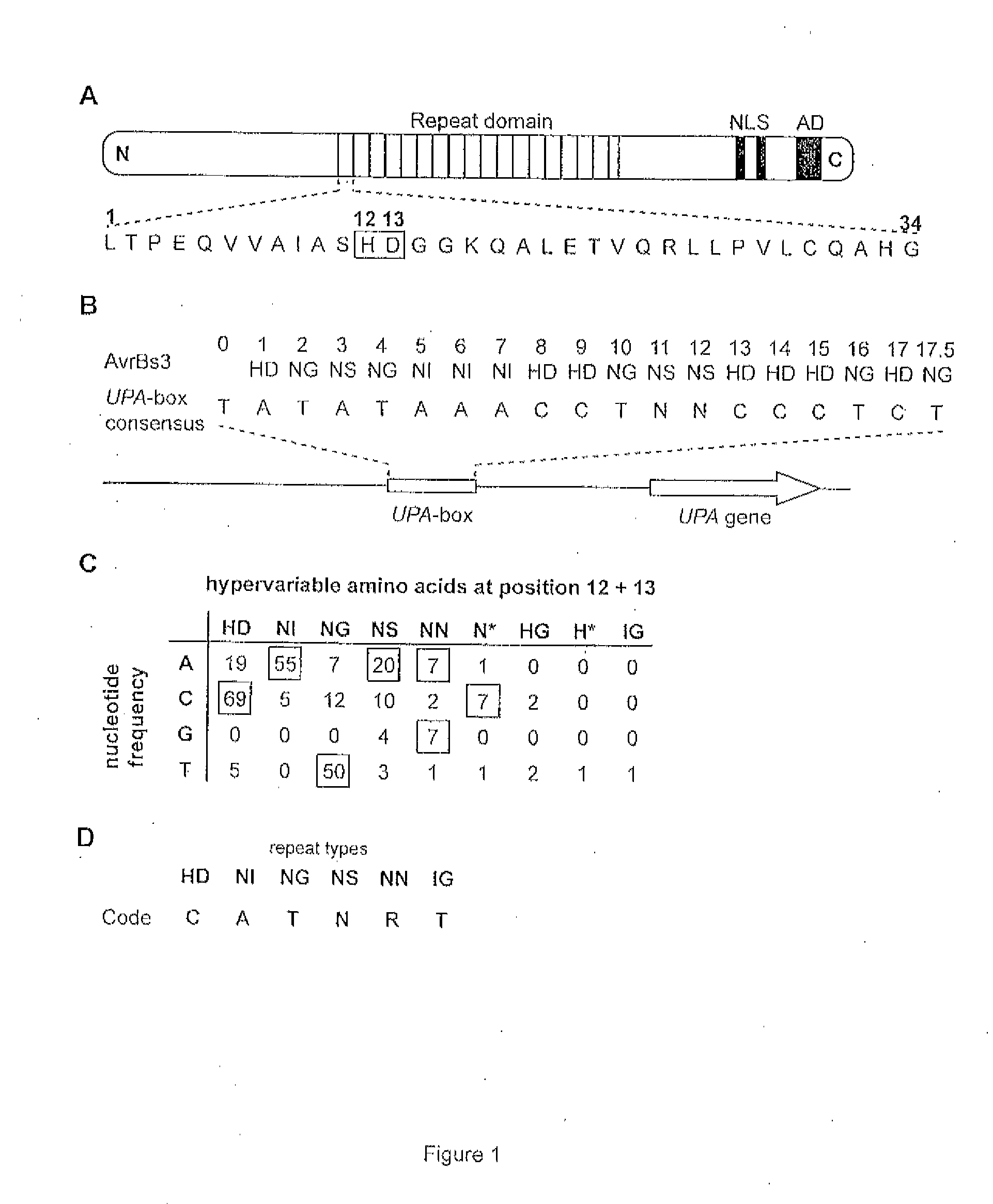
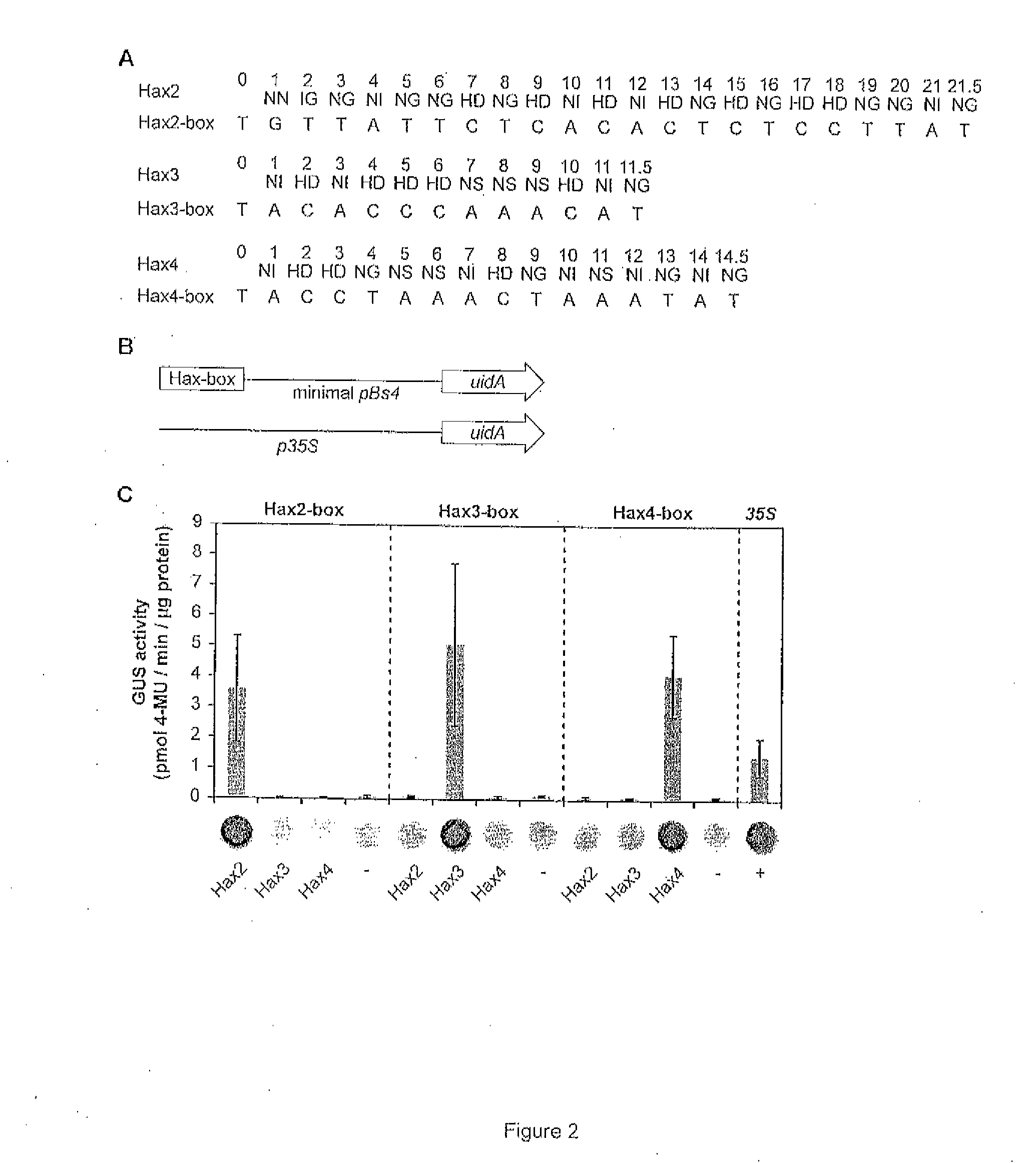
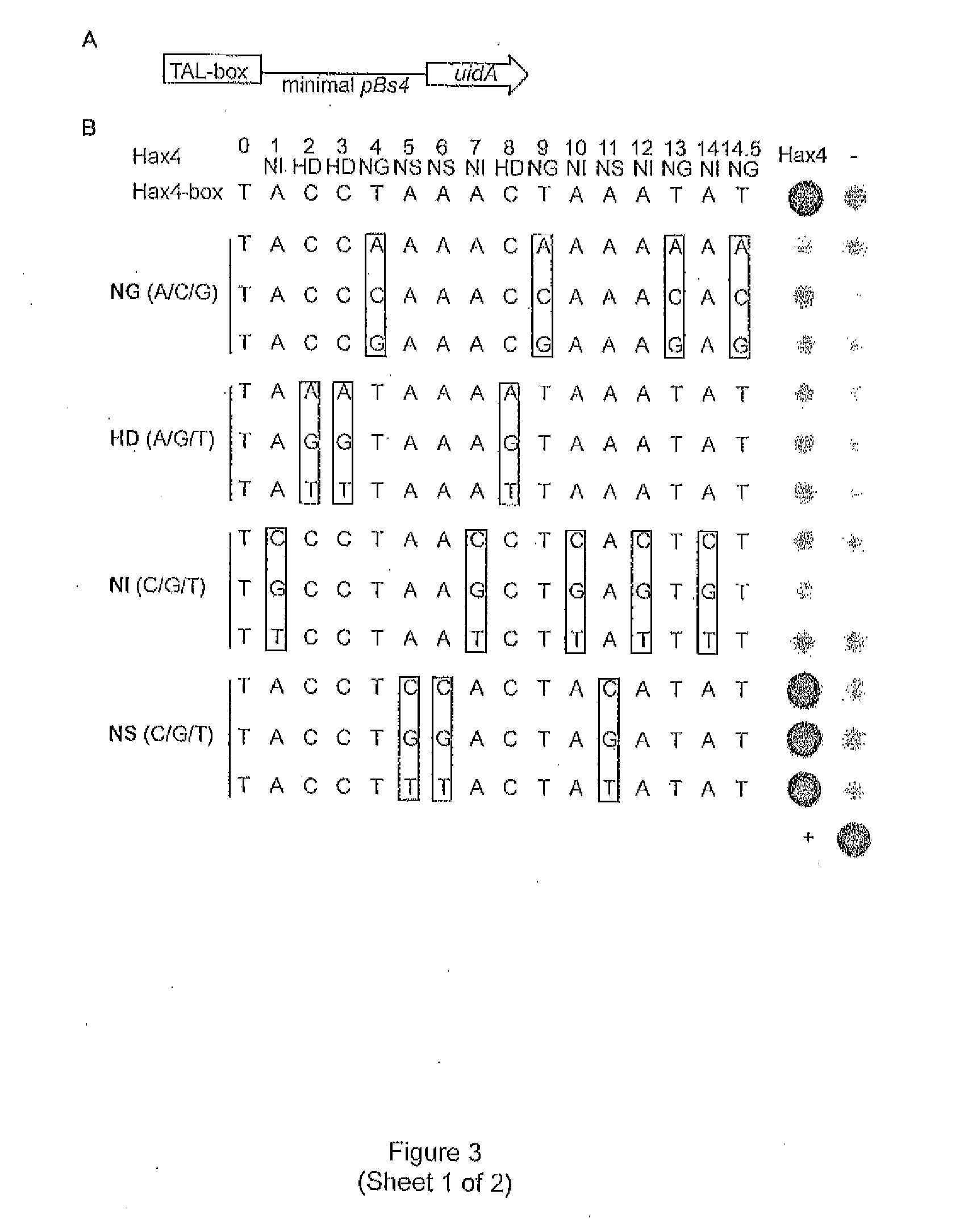
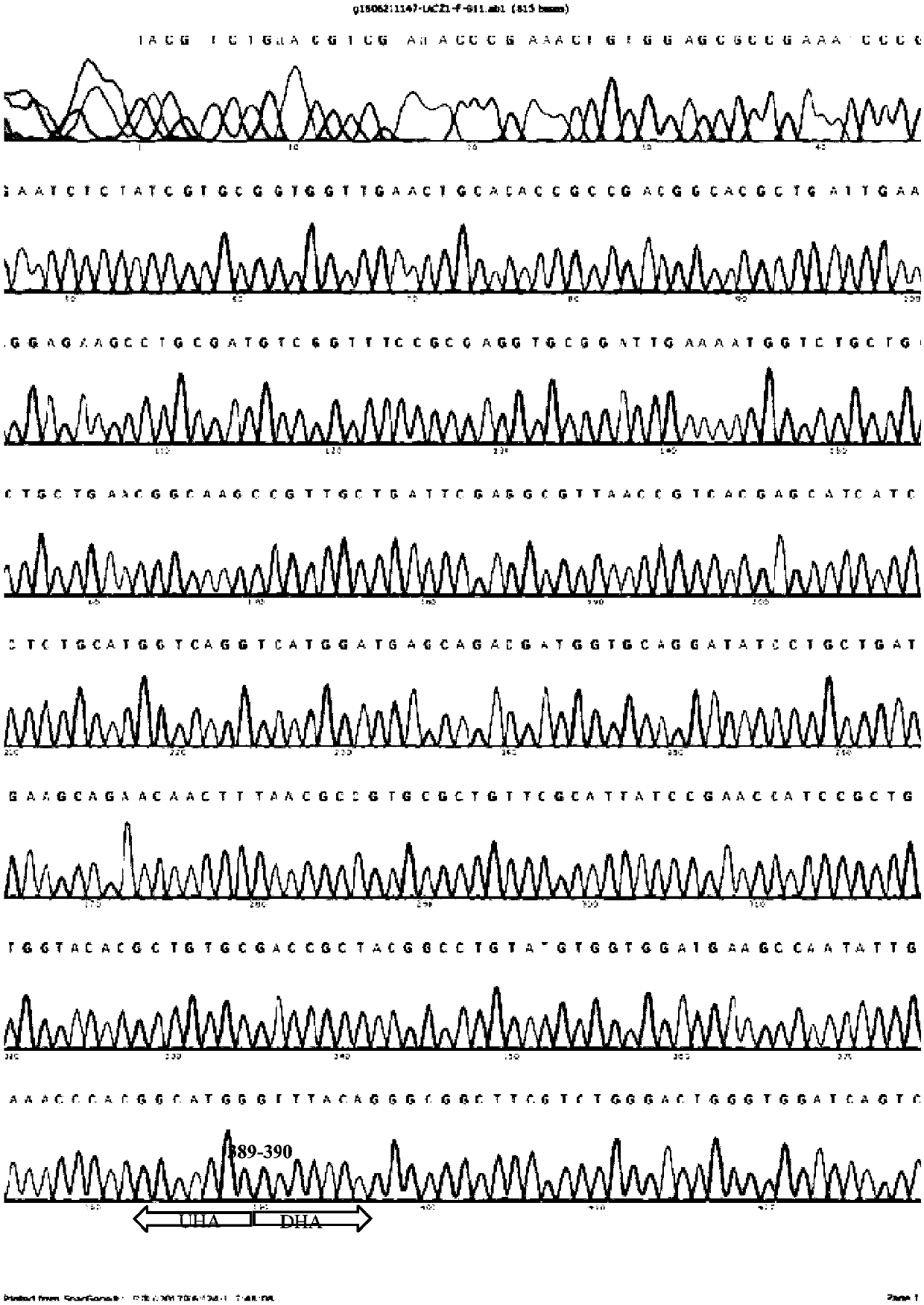
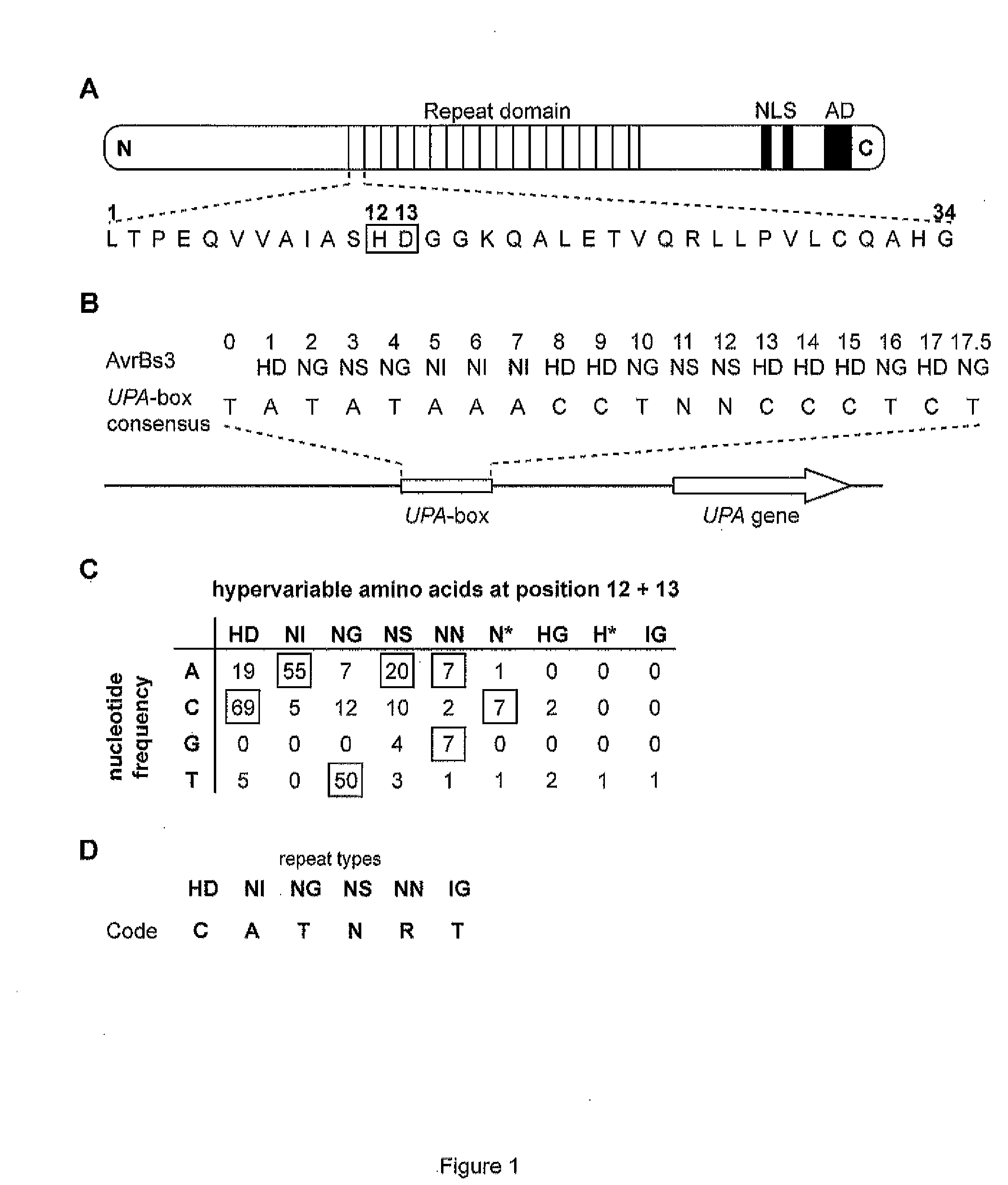
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
InactiveUS20110239315A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFungiBacteriaDNA-binding domainDna targeting
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +2
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
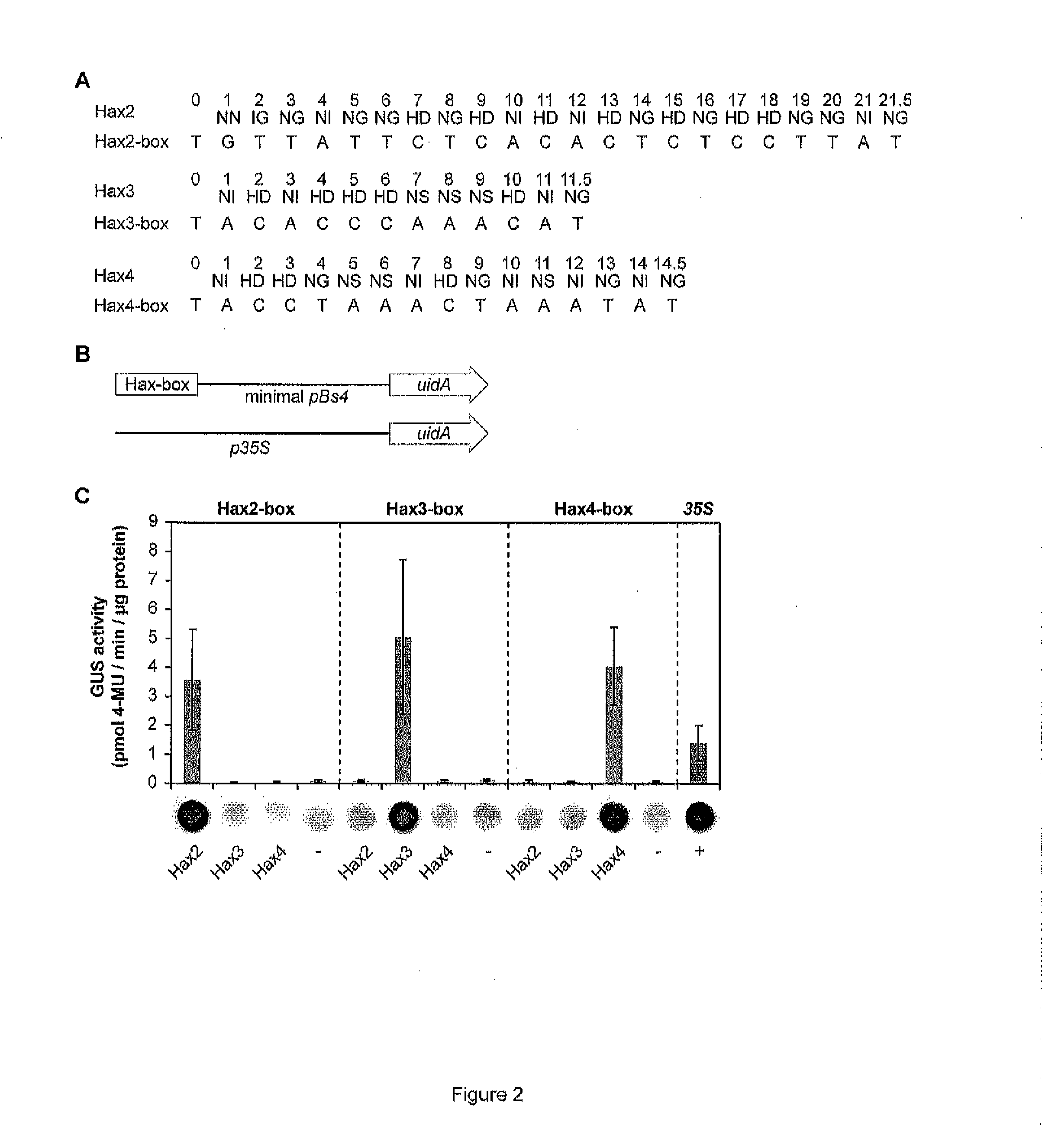
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
ActiveUS20120064620A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesDNA-binding domainDna targeting
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +3
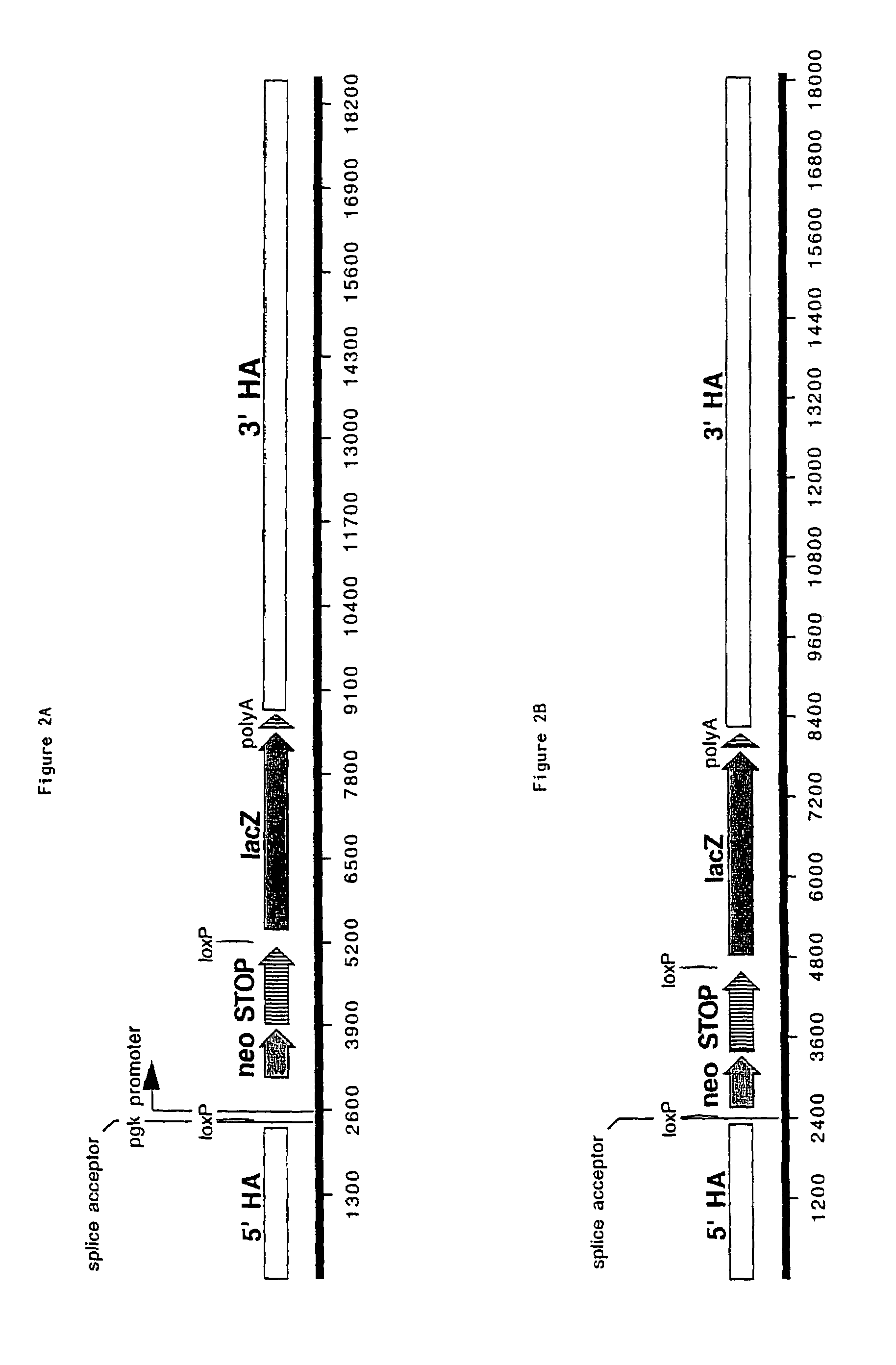
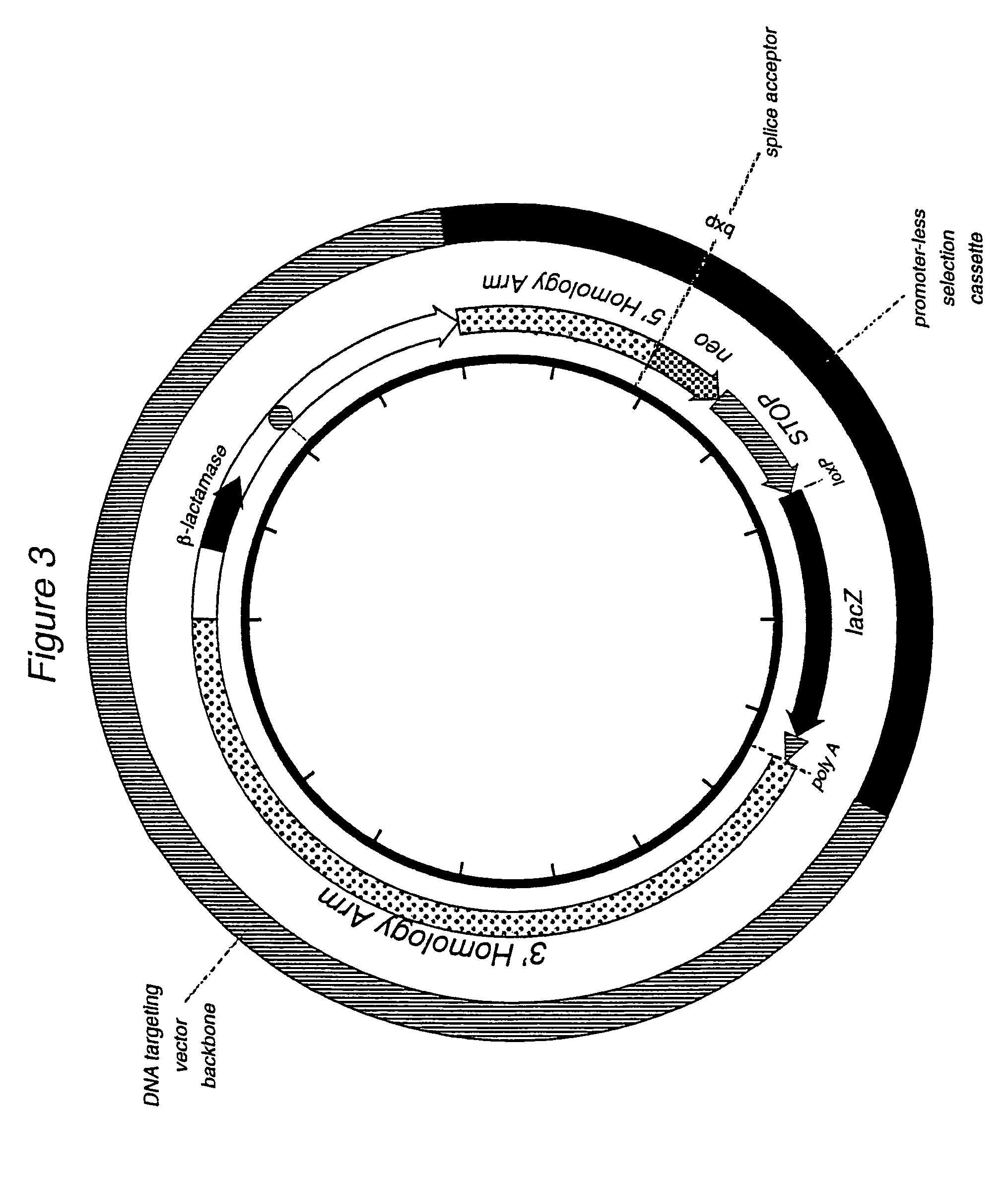
Method for targeting transcriptionally active loci
The present invention provides a method of achieving very high targeting efficiency by utilizing targeting vectors that utilize promoter-less selection cassettes and which are engineered to targeted into transcriptionally active loci. In particular, the invention provides a method for targeting promoter-less selection cassettes into transcriptionally active loci in stem cells or other eukaryotic cells with much greater efficiency than previously observed with other methods, thus reducing the number of drug-resistant clones to be screened or eliminating the need to screen for targeted cells altogether. The invention also encompasses the DNA targeting vectors, the targeted cells, as well as non-human organisms, especially mice, created from the targeted cells.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
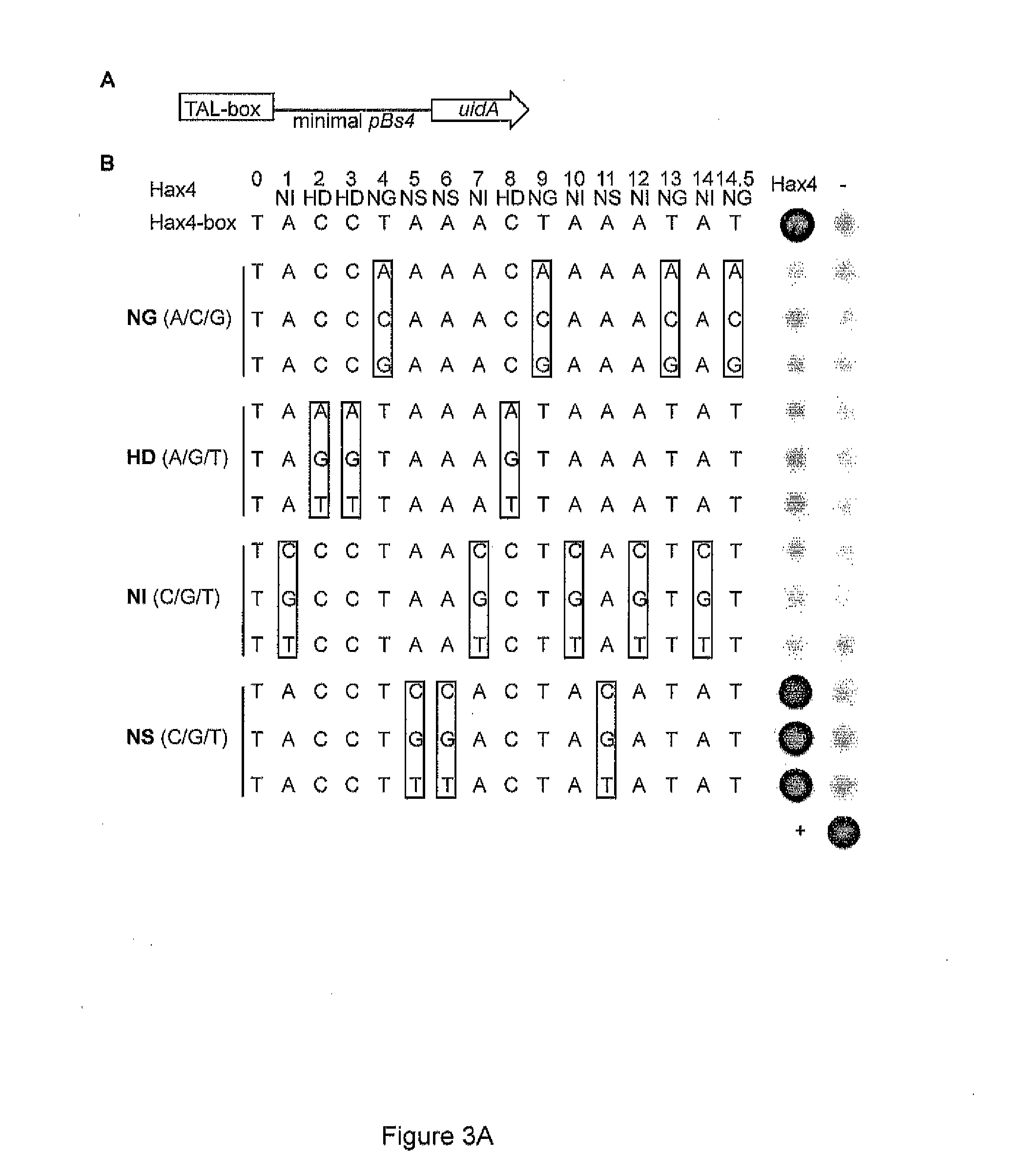
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
ActiveUS20120110685A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFungiBacteriaDNA-binding domainModular design
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +3
Methods of Modifying Eukaryotic Cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
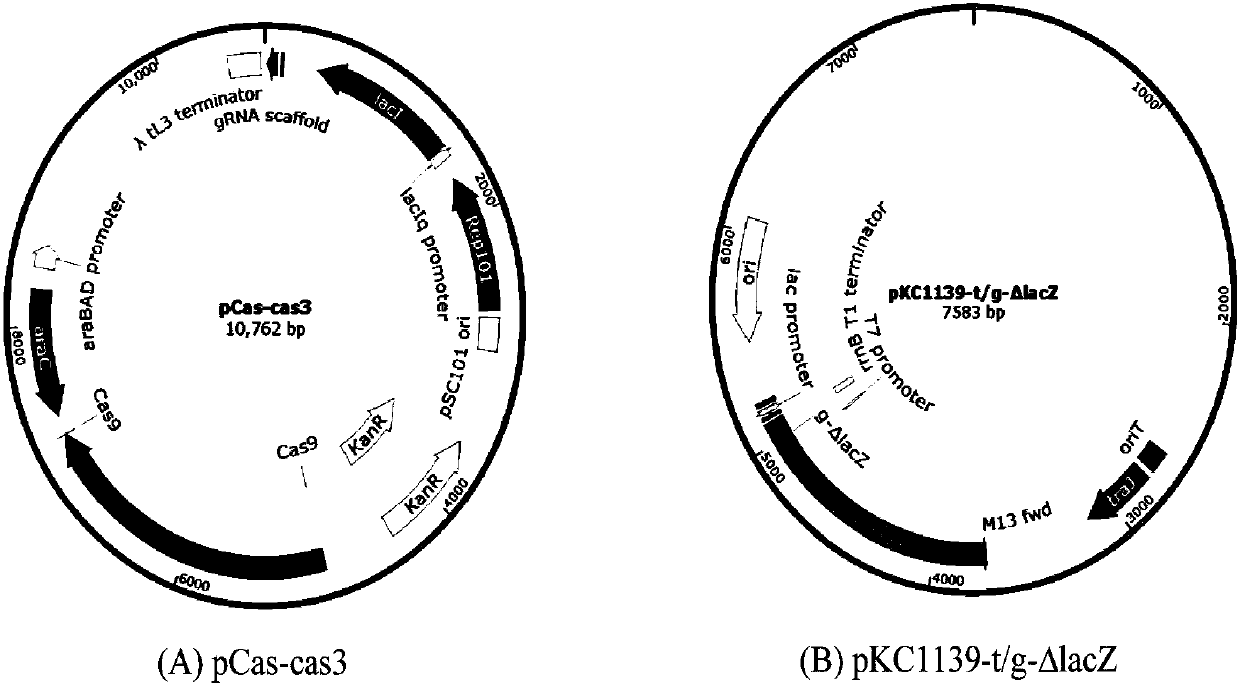
Gene editing method based on gene cas3 of I-B type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557373ASmall molecular weightGene editing is correctHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiological cellEucoenogenes
The invention discloses a novel gene editing system which is established based on gene cas3 of an I-B type CRISPR-Cas system in a chromosome of Virginia streptomycete IBL14, the gene editing of an I type CRISPR-Cas system to a biological cell genome is realized for the first time, and new supplement and choice are provided for the gene editing system which is established by II type commercializedCas9. In the system, a target DNA can be specifically cut by the Cas3 through crRNA guide or t-DNA location. By adopting the system, error-free, simple and rapid gene editing can be performed on prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. The optimized gene editing system is expected to be superior to the commercialized gene editing system which is established based on Cas9 in multiple fields due to low molecular weight and ability to be guided by DNA.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
ActiveUS20120122205A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA-binding domainModular design
Owner:BONAS ULLA +3
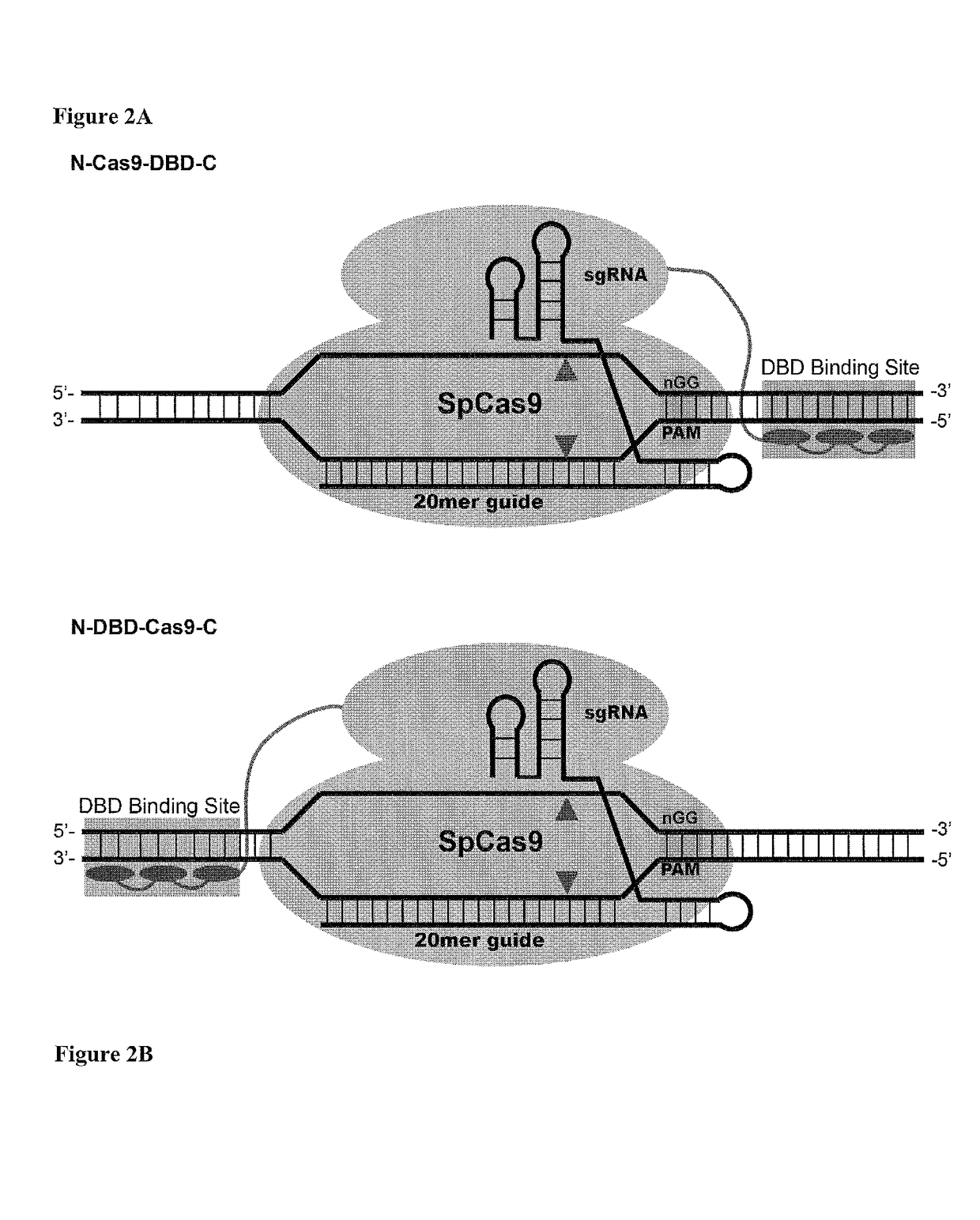
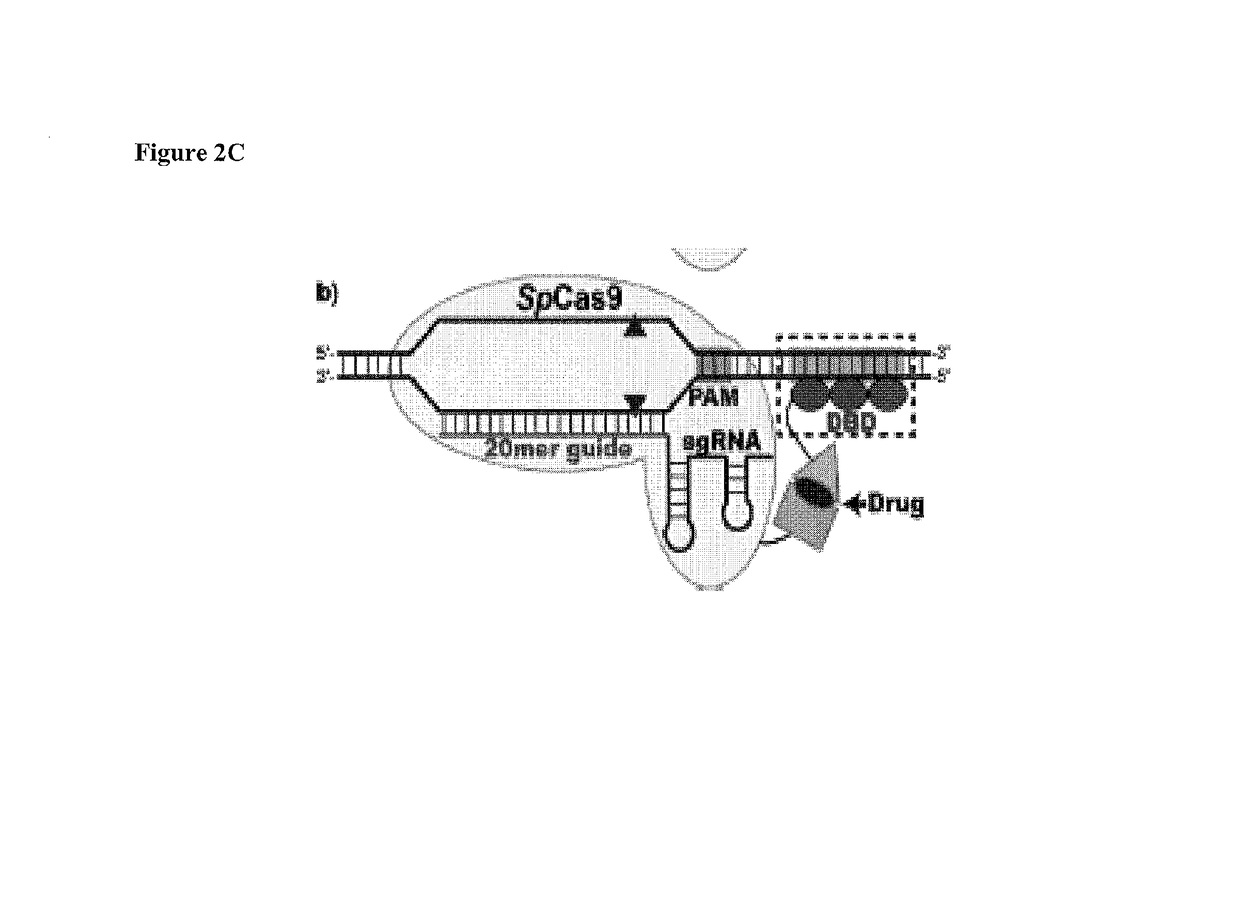
Cas9-DNA Targeting Unit Chimeras
ActiveUS20160177278A1High precisionIncrease diversityFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingDna targeting
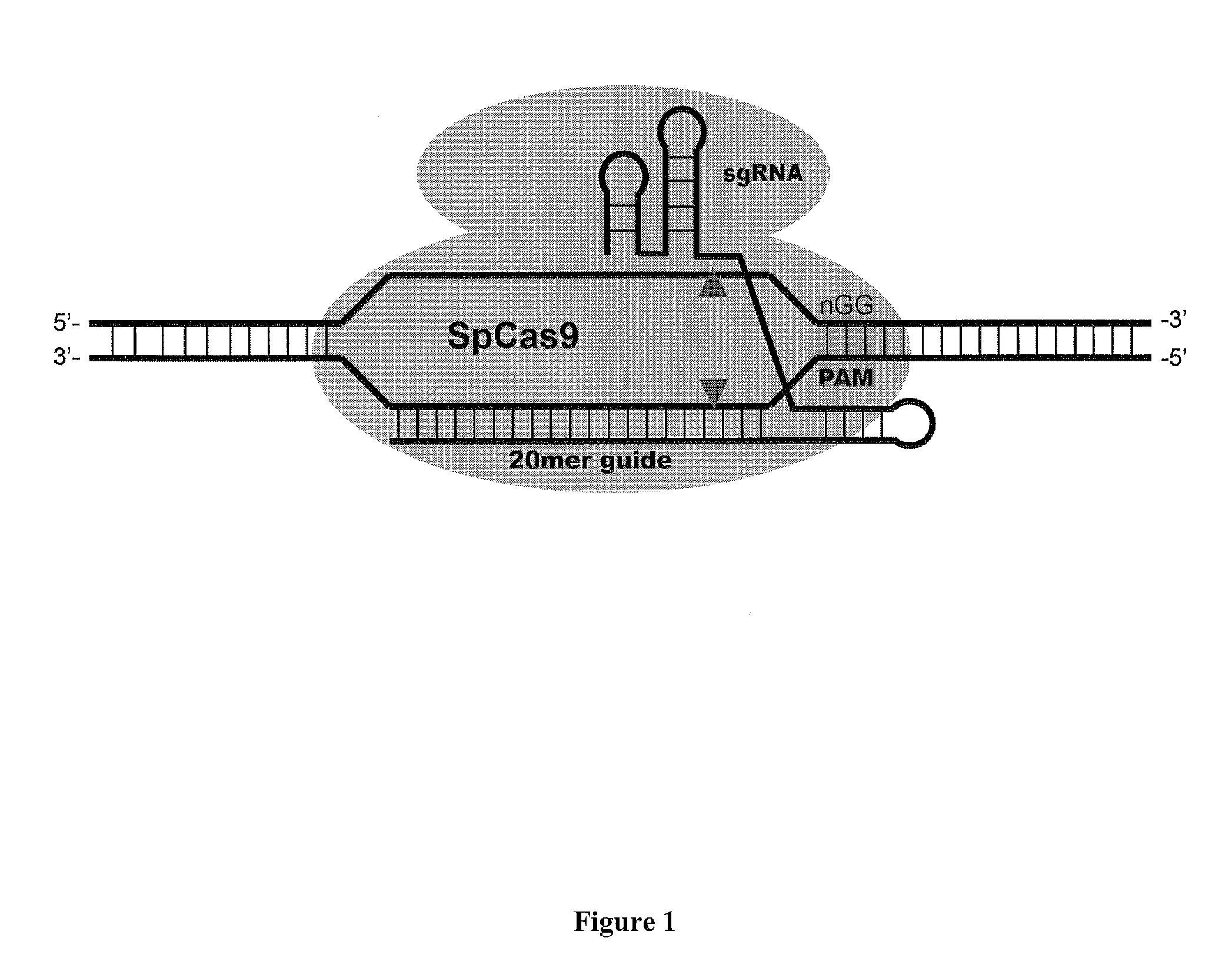
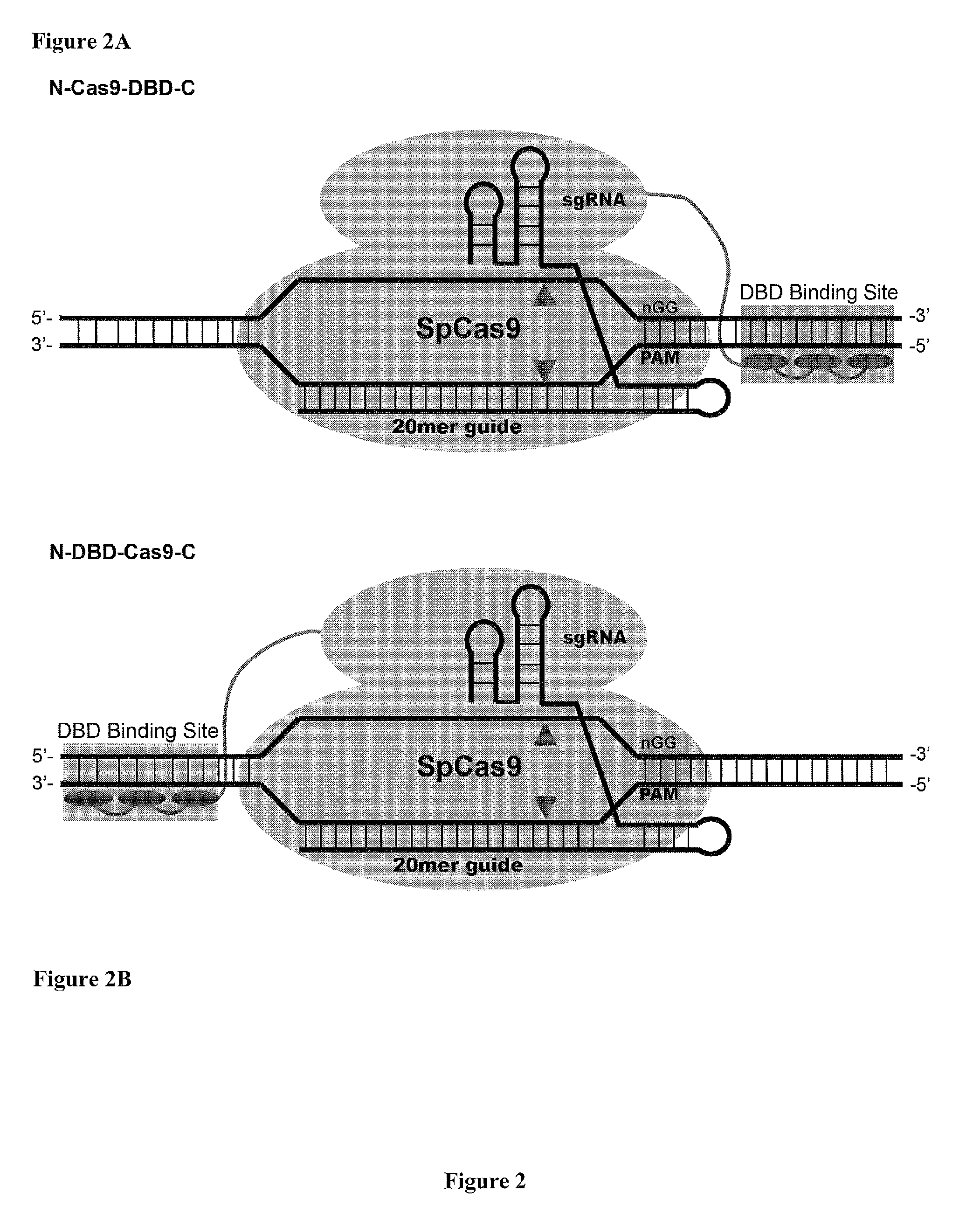
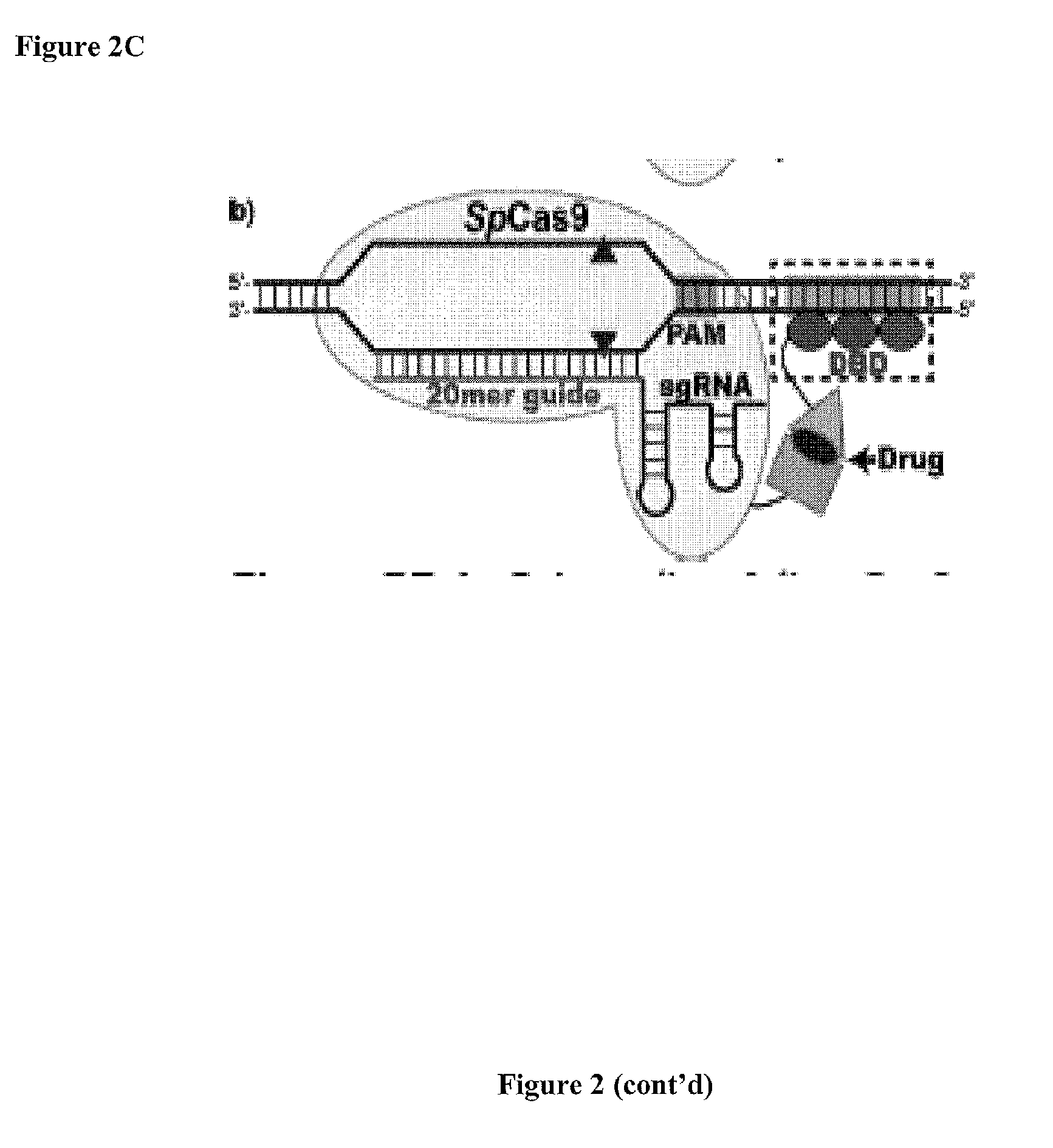
The present invention provides a Cas9 platform to facilitate single-site nuclease gene editing precision within a human genome. For example, a Cas9 nuclease / DNA-targeting unit (Cas9-DTU) fusion protein precisely delivers a Cas9 / sgRNA complex to a specific target site within the genome for subsequent sgRNA-dependent cleavage of an adjacent target sequence. Alternatively, attenuating Cas9 binding using mutations to the a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) recognition domain makes Cas9 target site recognition dependent on the associated DTU, all while retaining Cas9's sgRNA-mediated DNA cleavage fidelity. Cas9-DTU fusion proteins have improved target site binding precision, greater nuclease activity, and a broader sequence targeting range than standard Cas9 systems. Existing Cas9 or sgRNA variants (e.g., truncated sgRNAs (tru-gRNAs), nickases and FokI fusions) are compatible with these improvements to further reduce off-target cleavage. A robust, broadly applicable strategy is disclosed to impart Cas9 genome-editing systems with the single-genomic-site accuracy needed for safe, effective clinical application.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Methods of Modifying Eukaryotic Cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Preparation method of DNA targeting nano medicine-carrying molecule for brain tumor
InactiveCN104645338ARealize the drug loading processGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPhosphoric acidCytotoxicity
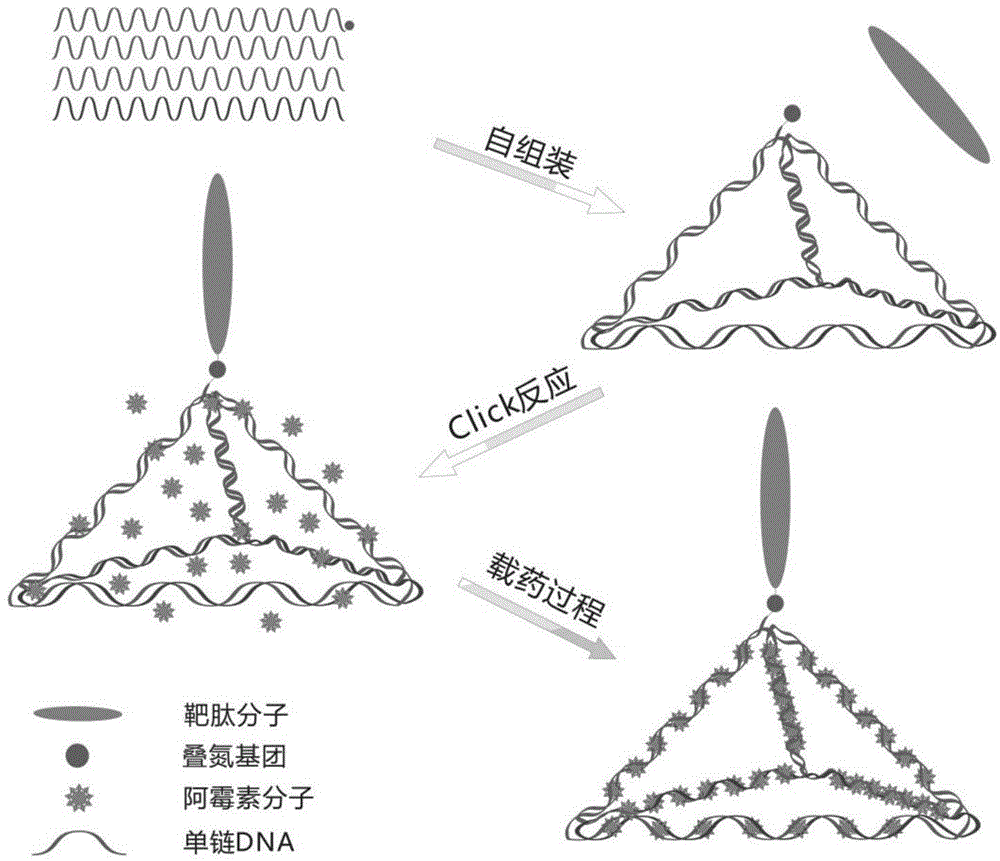
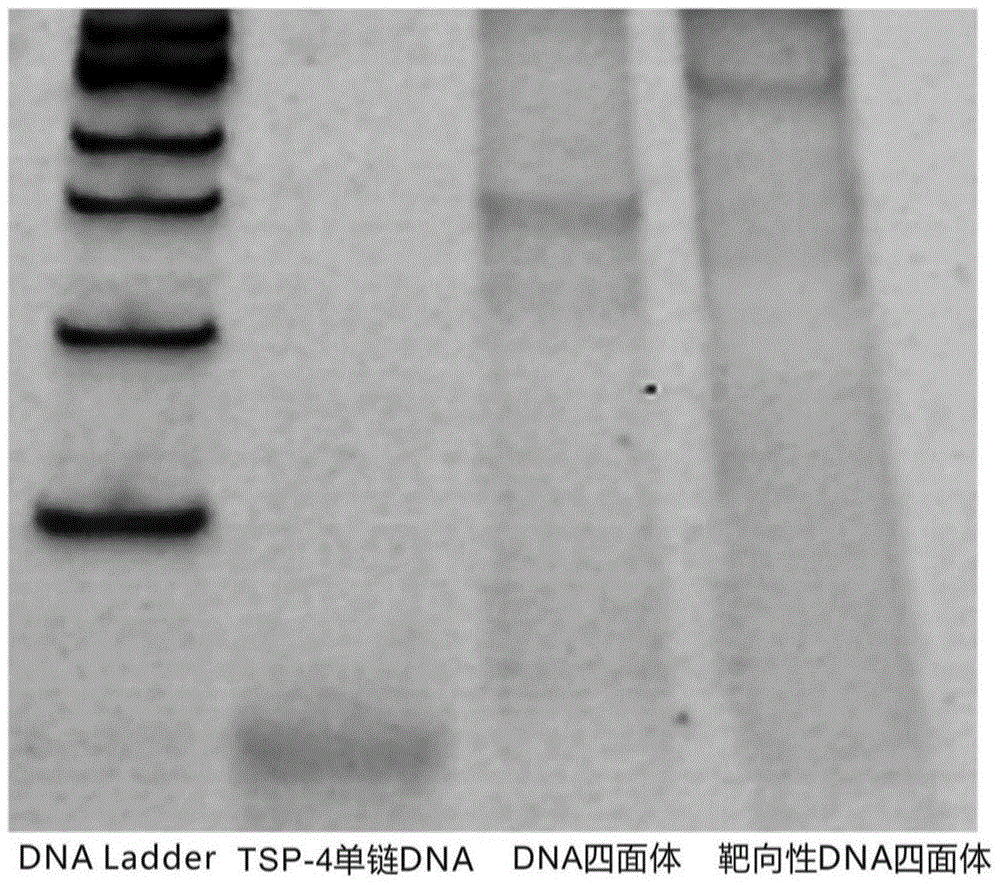
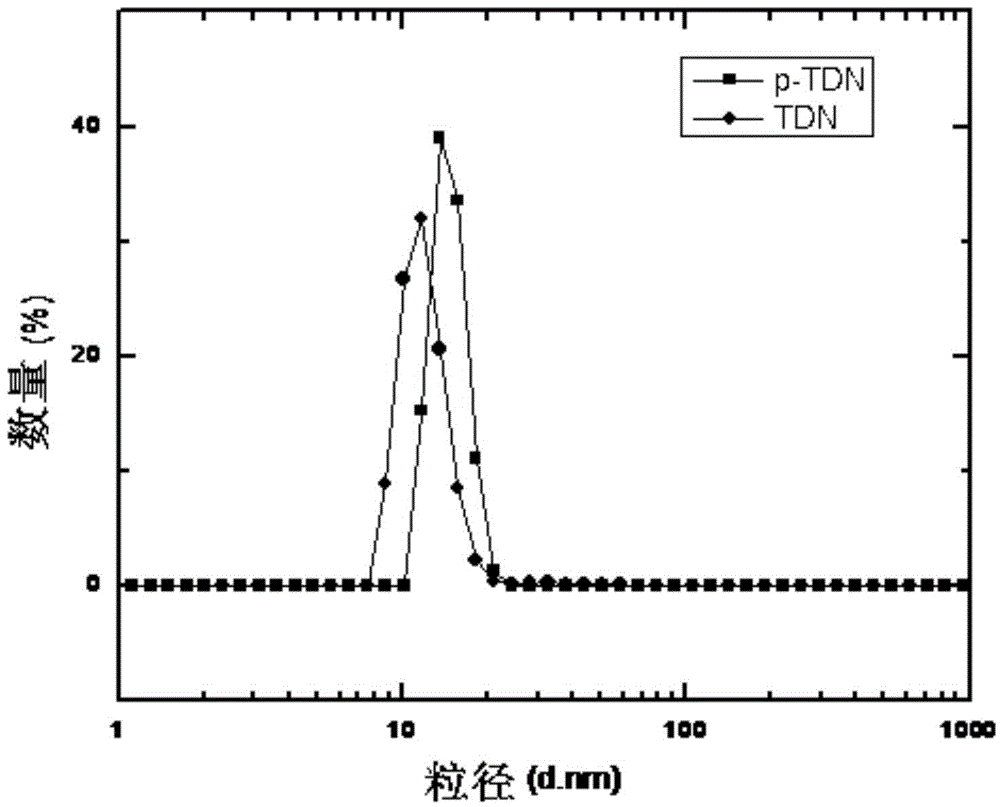
The invention discloses a preparation method of a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) targeting nano medicine-carrying molecule for a brain tumor. The preparation method comprises the steps that a DNA single strand is added to a Tris-MgCl solution and mixed, and reacts to form a DNA tetrahedron solution; the DNA tetrahedron solution and a targeting peptide solution are added to a mixed solution of a PBS (Phosphoric acid solution), a CuSO4 solution, a TCEP (Tris-(2-carboxyethyl)-phosphine) solution and a TBTA (Tert-Butyl 2,2,2-trichloroacetimidate) solution, and subjected to thermostatic reaction; a targeting DNA tetrahedron solution is obtained; a tumor medicine is added to the targeting DNA tetrahedron solution; constant temperature oscillation, centrifugation, and supernatant removal are conducted; and an obtained sediment is the DNA targeting nano medicine-carrying molecule. According to the preparation method, peptide molecules having specificity in the tumor are modified on DNA tetrahedrons via a point-and-click reaction, so that construction of a targeting DNA nano-carrier is realized; and the targeting DNA medicine-carrying molecule has extremely high specific recognition function, low cytotoxicity and good structural stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
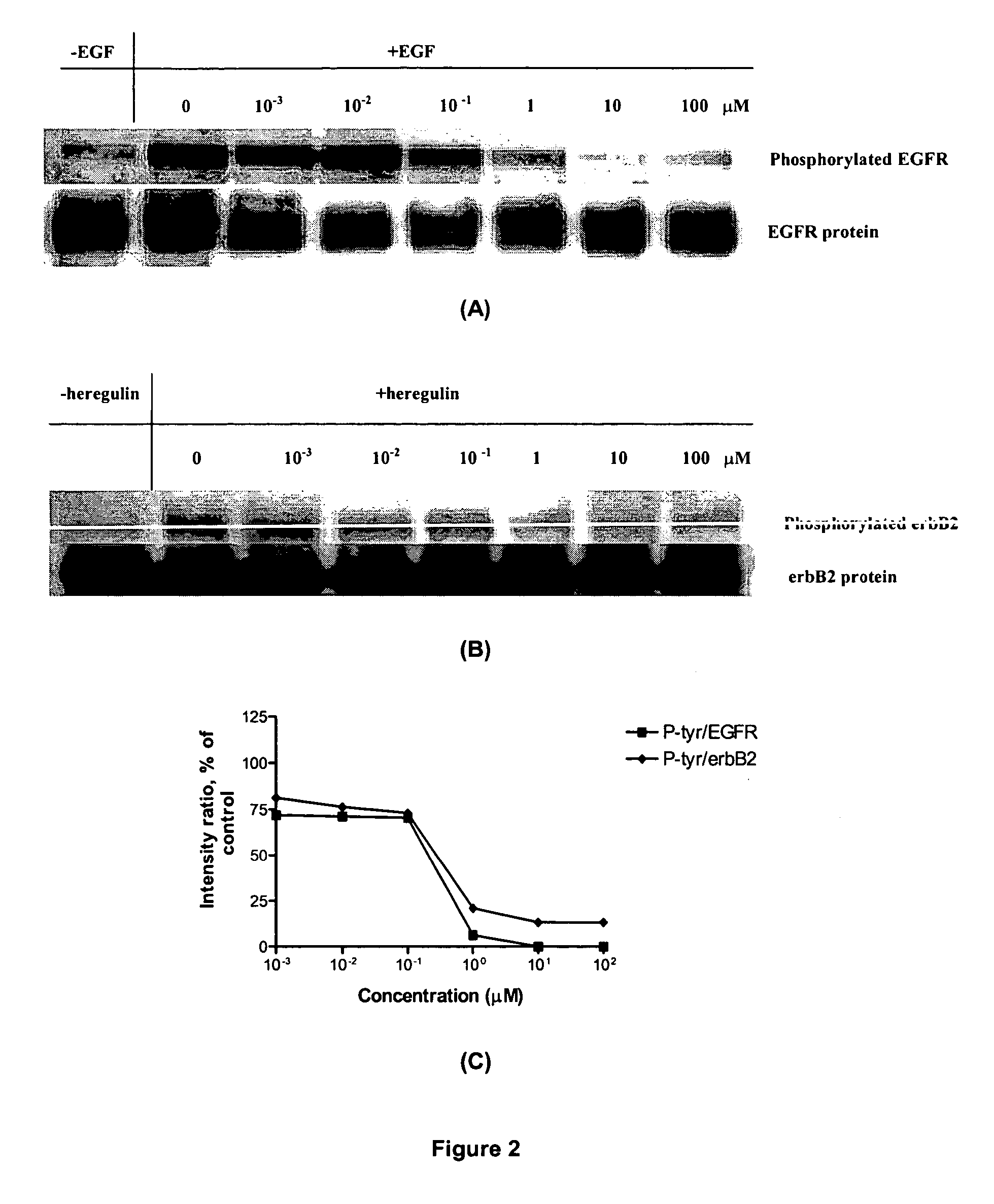
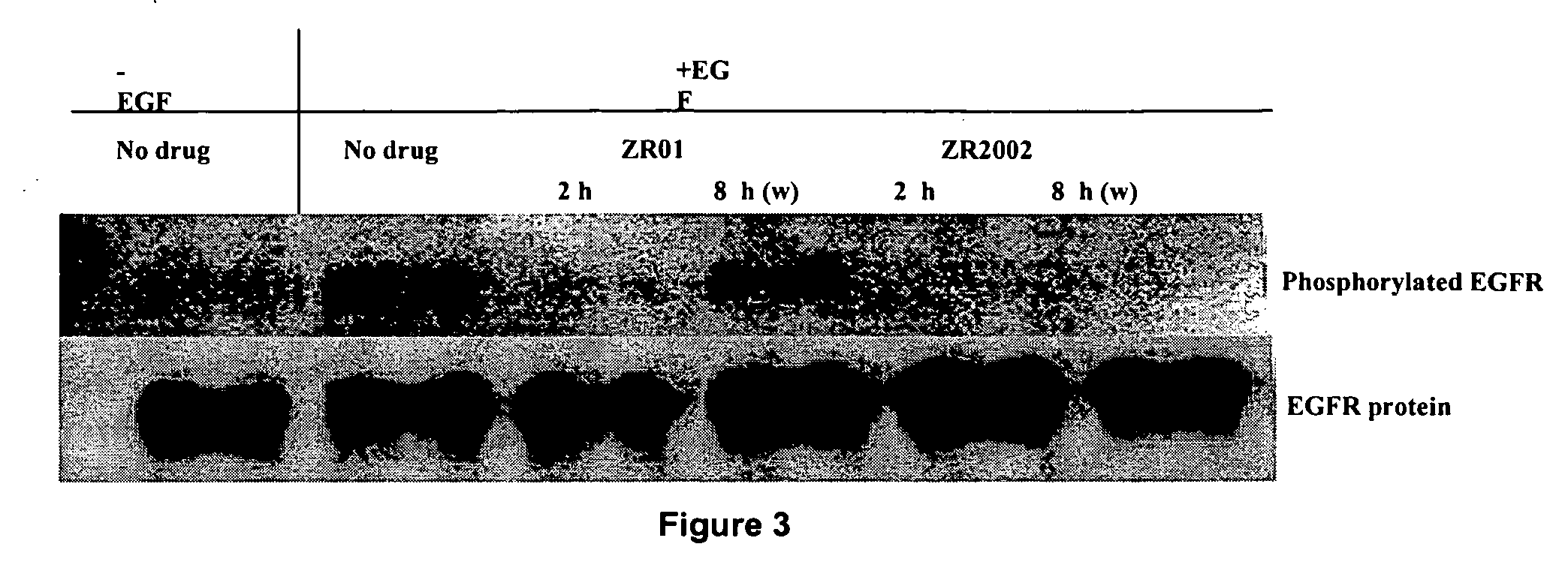
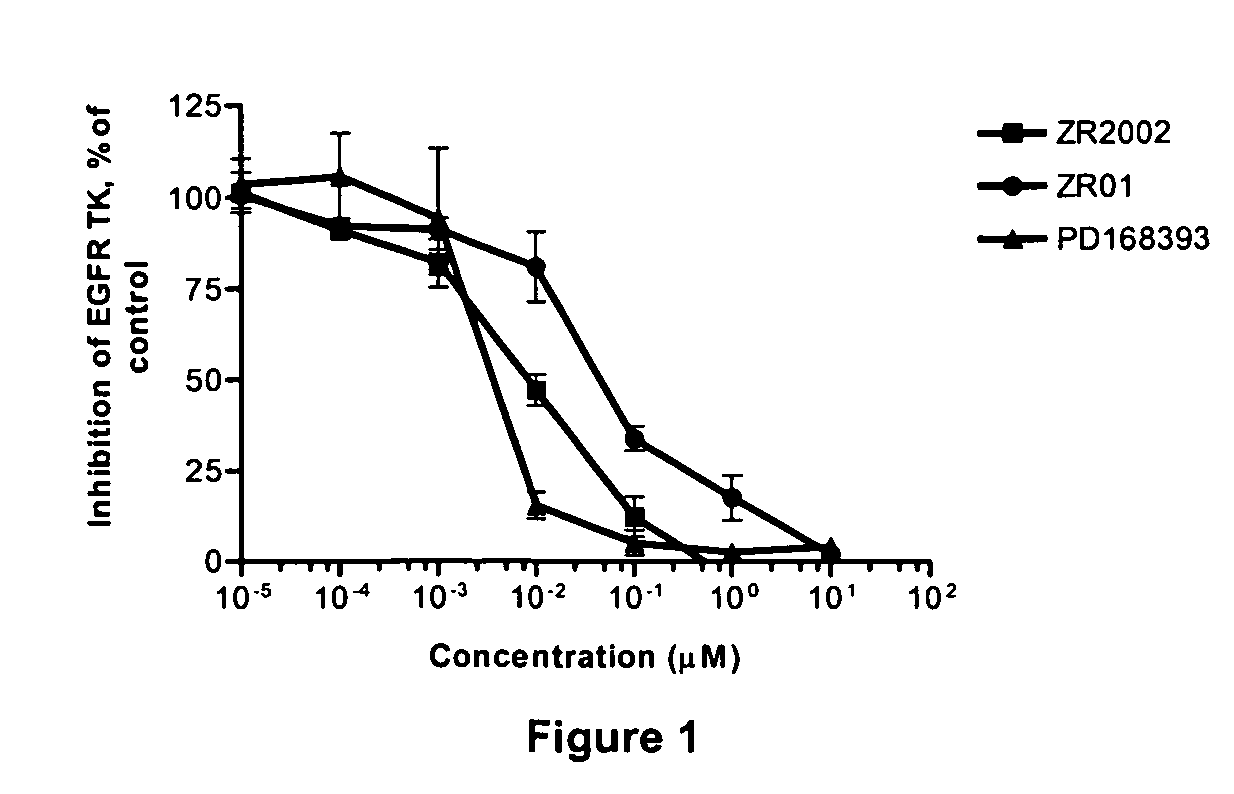
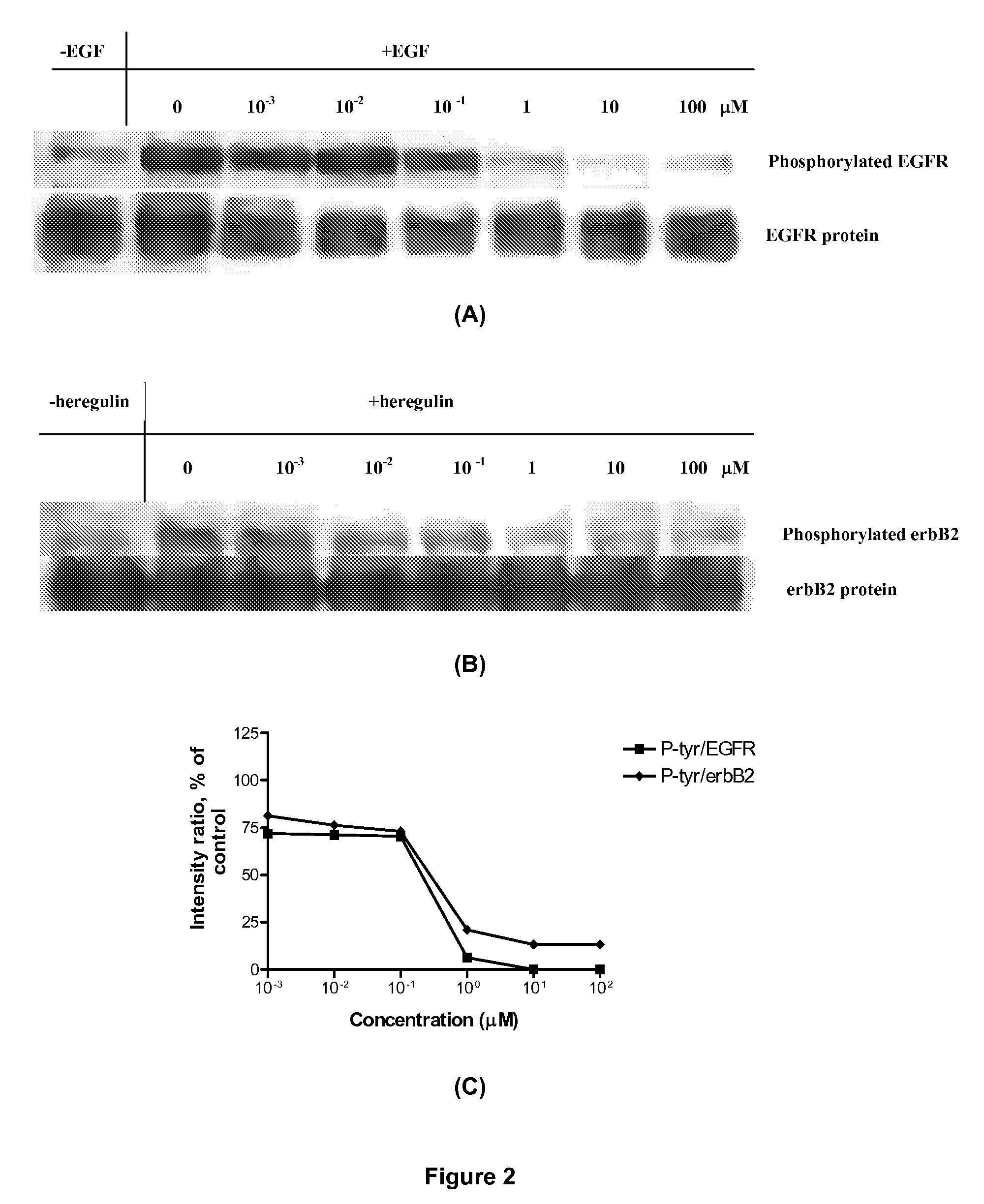
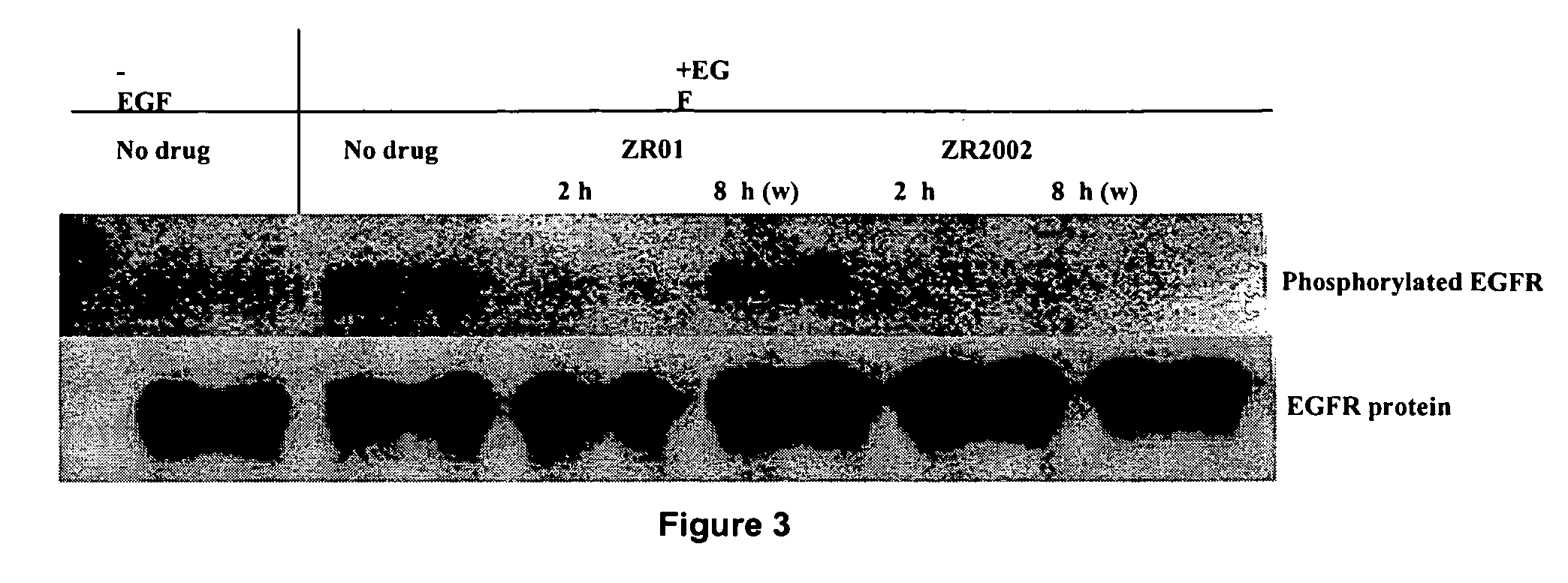
Novel combi-molecules having EGFR and DNA targeting properties
InactiveUS20060003970A1Inhibit phosphorylationInhibits downstream signallingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthDna targeting
A series of new chemical agents that demonstrate anti-tumor activity are described. The new chemical agents combine two major mechanisms of anti-tumor action. In an embodiment, the agents are capable of both inhibiting EGFR and damaging DNA while also, upon degradation, degrading to an inhibitor of EGFR and to an agent capable of damaging DNA. Moreover, a novel series of molecules capable of releasing two moles of EGFR inhibitor and a potent bi-functional alkylating agent are also described.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
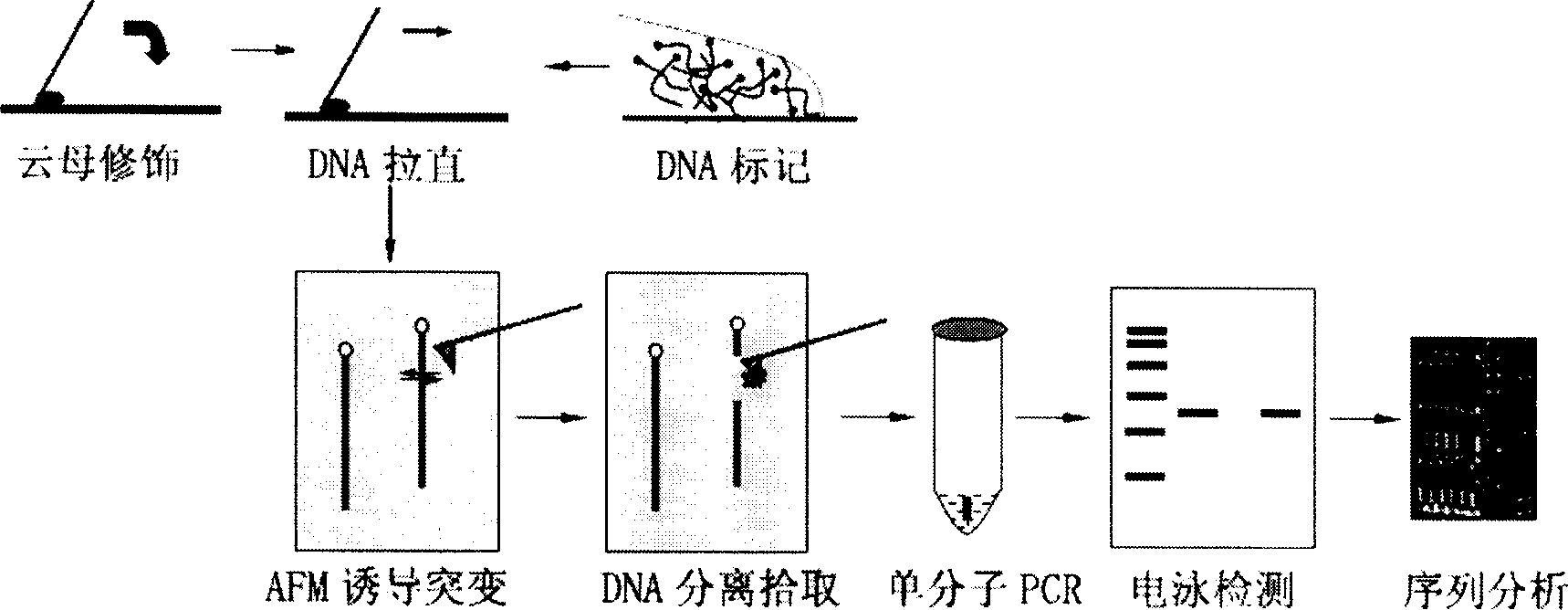
Method for atom force microscope inducing single molecule DNA positoning mutation
InactiveCN1766104AGood effectEasy to operate and controlDNA preparationDNA fragmentationDna targeting
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cas9-DNA targeting unit chimeras
ActiveUS10190106B2High precisionIncrease diversityFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingDna targeting
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
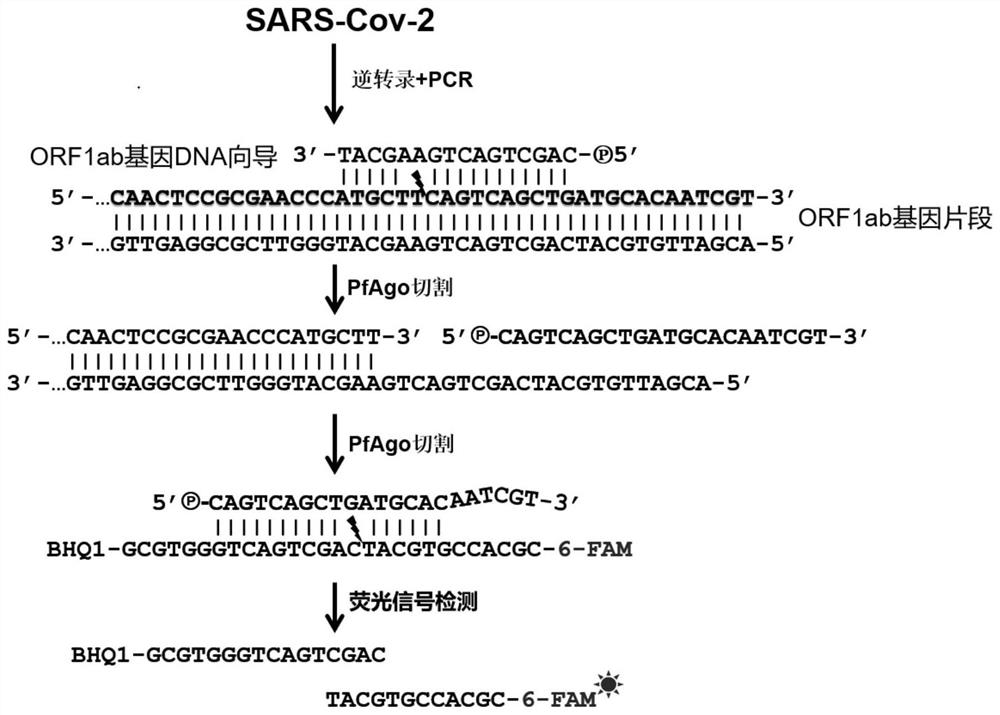
Primer group and kit for nucleic acid detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus and application of primer group and kit
ActiveCN112029903ASimple and fast amplificationGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionDna targeting
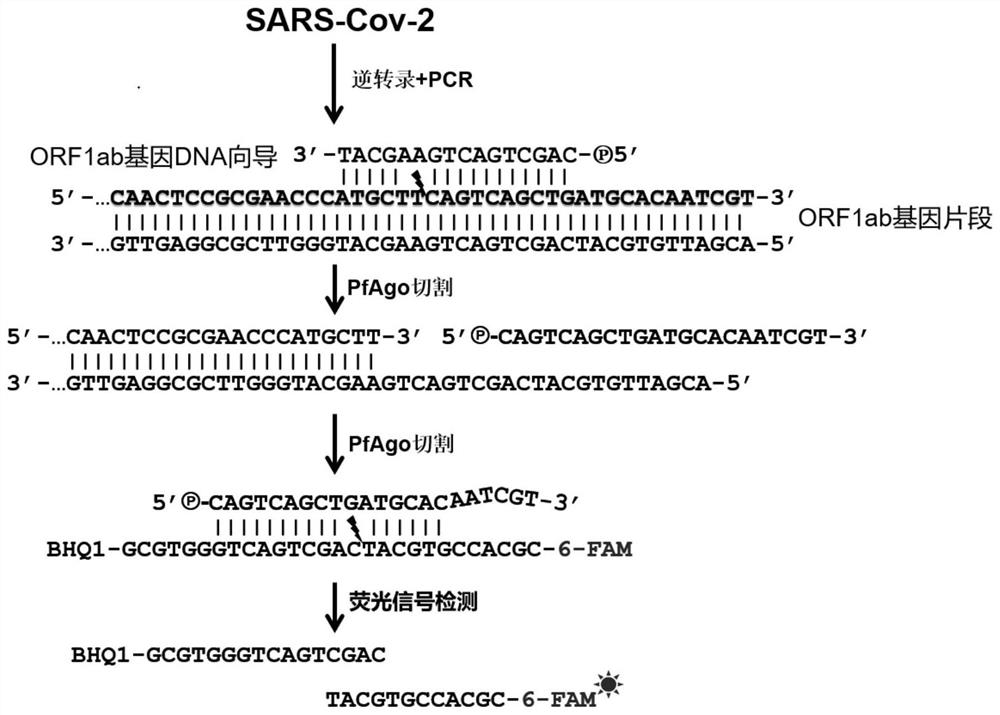
The invention discloses a primer group and a kit for nucleic acid detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus and application of the primer group and the kit. The primer group for an N gene and an ORF1ab gene of the SARS-CoV-2 virus is designed, and the kit comprises the primer group, guide DNA targeting a target gene, a molecular beacon with a fluorescent marker and PfAgo enzyme. The primer group provided by the invention can be used for simply and quickly amplifying new coronavirus nucleic acid, and has the characteristics of good repeatability, high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
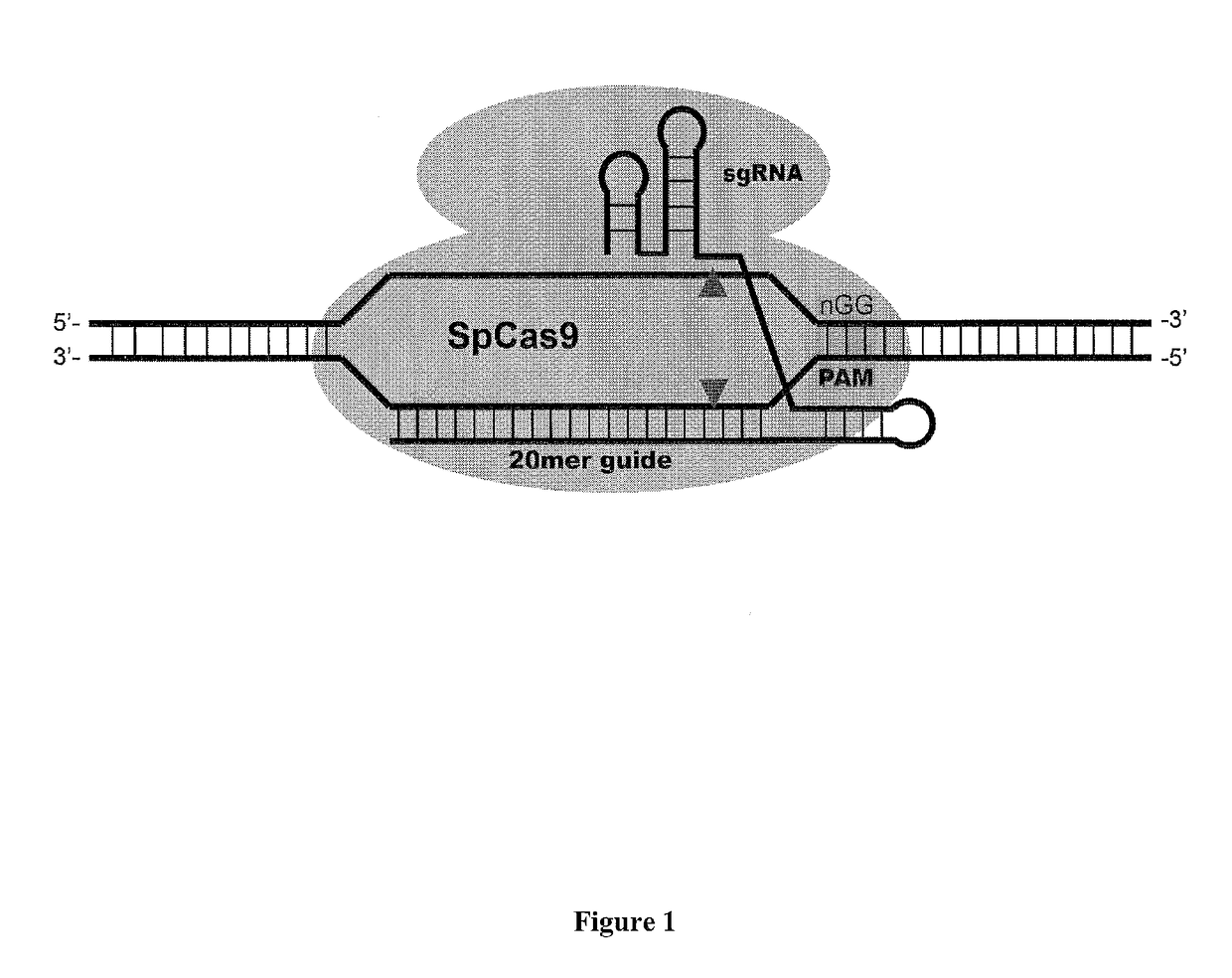
Truncated crispr-cas proteins for DNA targeting
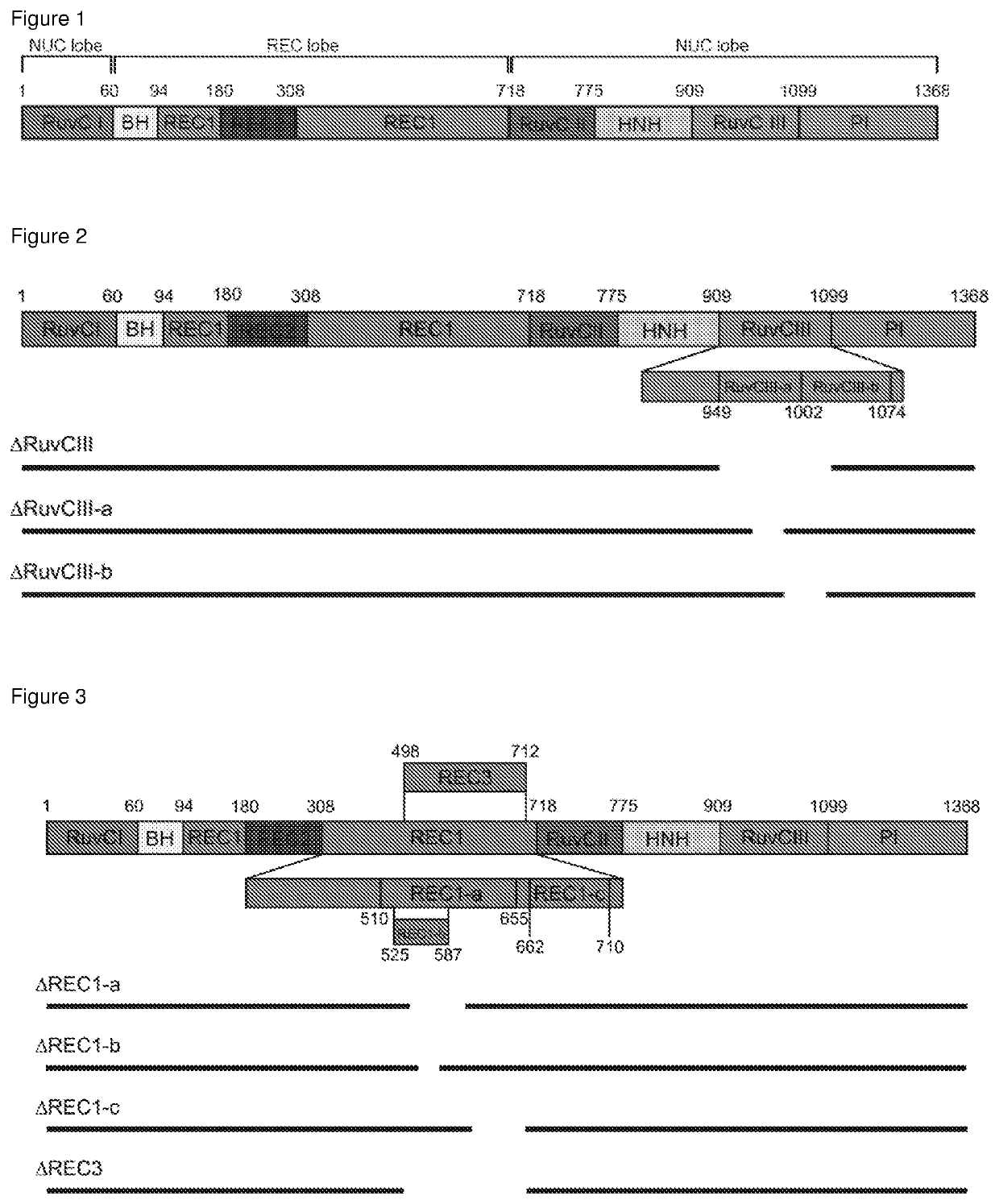
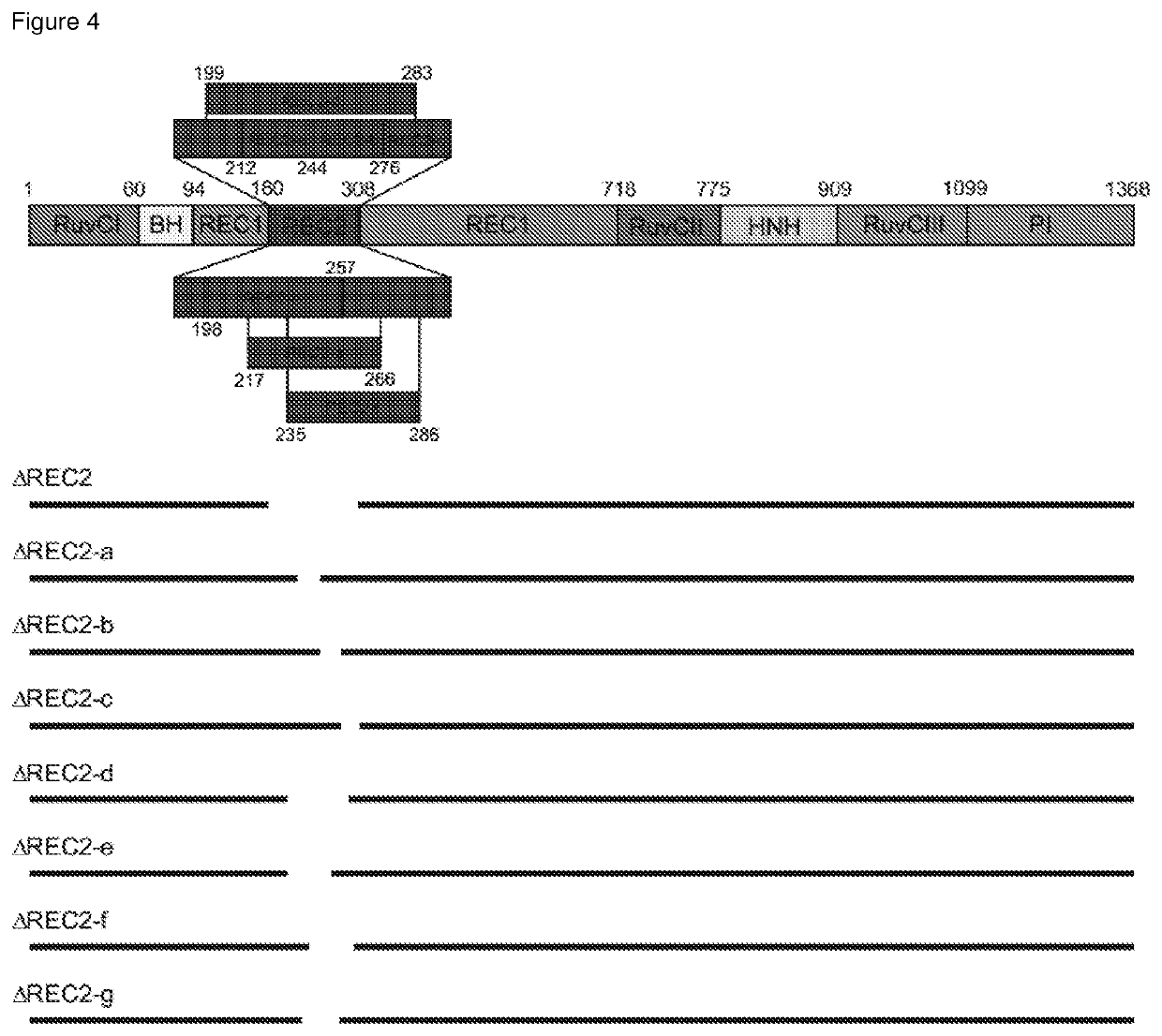
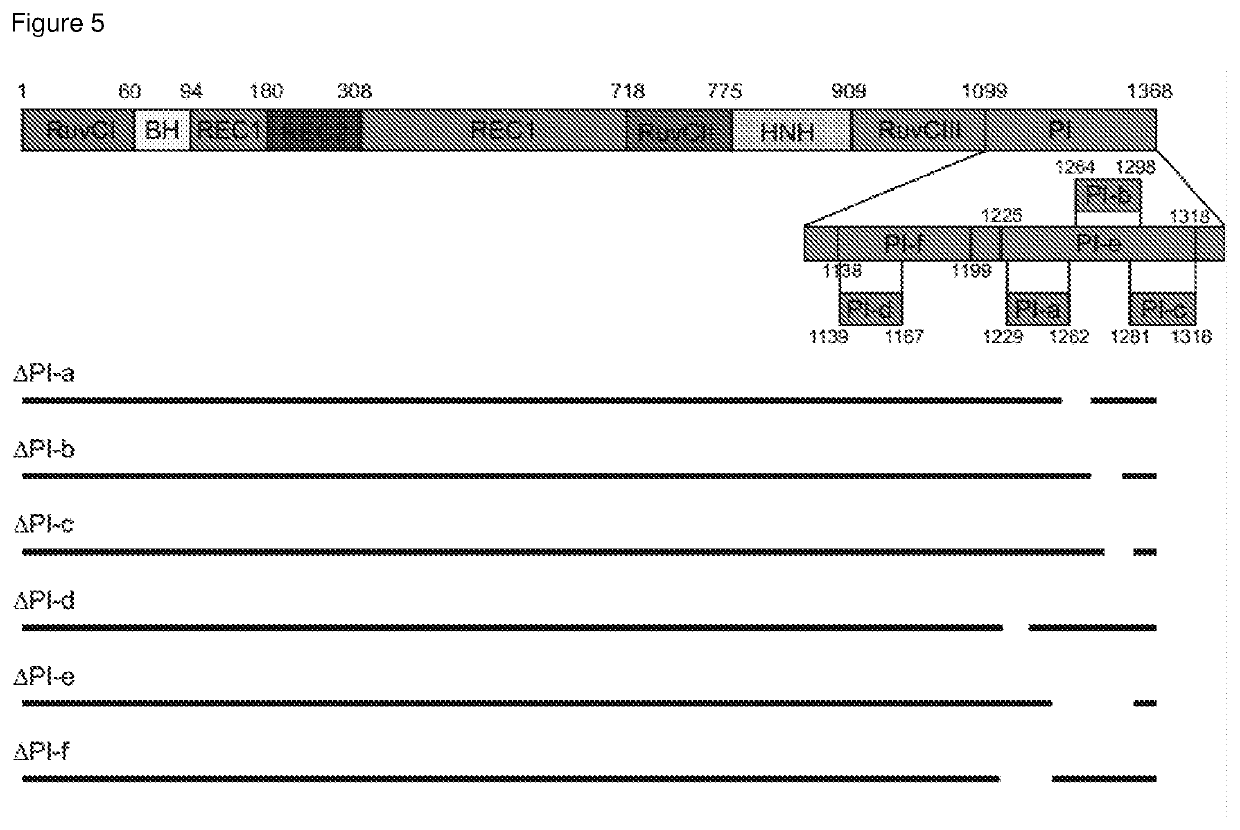
The present invention relates to a polypeptide comprising at least one at least one deletion selected from the group consisting of ΔHNH (Δ775-909), ARuvCIII-b (Δ1002-1074), AREC1-a (Δ510-655), AREC1-b (Δ525-587), AREC1-c (Δ662-710), AREC2 (Δ180-308), AREC2-a (Δ212-244), AREC2-b (Δ244-276), AREC2-c (Δ276-308), AREC2-d (Δ199-283), AREC2-e (Δ198-257), AREC2-f (Δ235-286), AREC2-g (Δ217-266), AREC3 (Δ498-712) and combinations thereof, wherein the position numbering is in accordance with SEQ ID NO: 1 encoding for S. pyogenes Cas9, and wherein the polypeptide has CRISPR-Cas DNA-binding activity. The polypeptide may further comprises a missense mutations selected from G12R, T13K, T13R, N14K, N497K, T657K, T657R, N767K, T770K, T770R, Q920K, Q920R, S1109R, D1135K, D1135R, S1338R and combinations thereof. Also claimed are nucleic acid molecules encoding for said polypeptides, compositions and method of site-directed engineering of a target DNA thereof.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
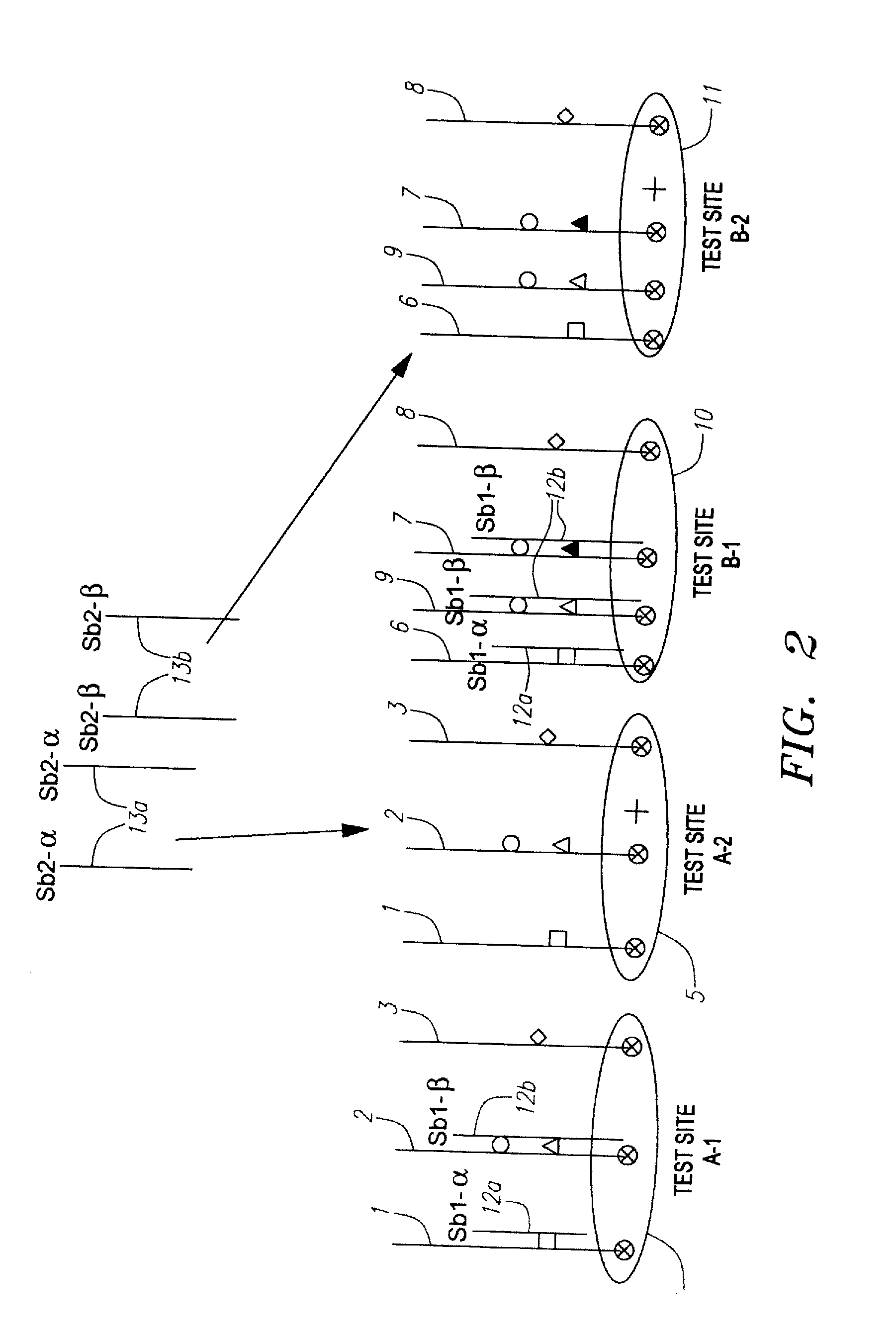
Methods and apparatus for screening and detecting multiple genetic mutations
InactiveUS7601493B2Avoid reactionEffective strategyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiscriminatorSingle mutation
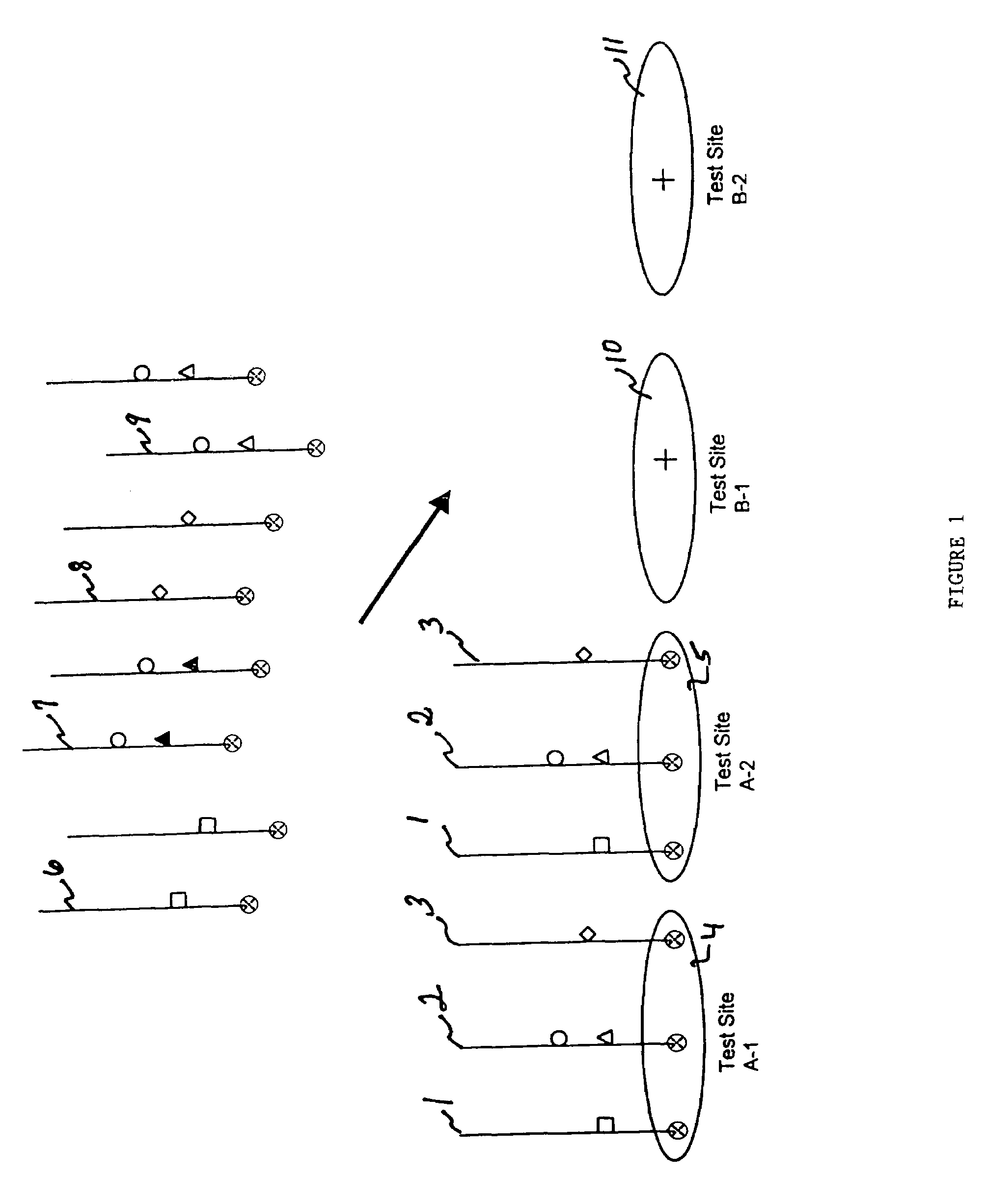
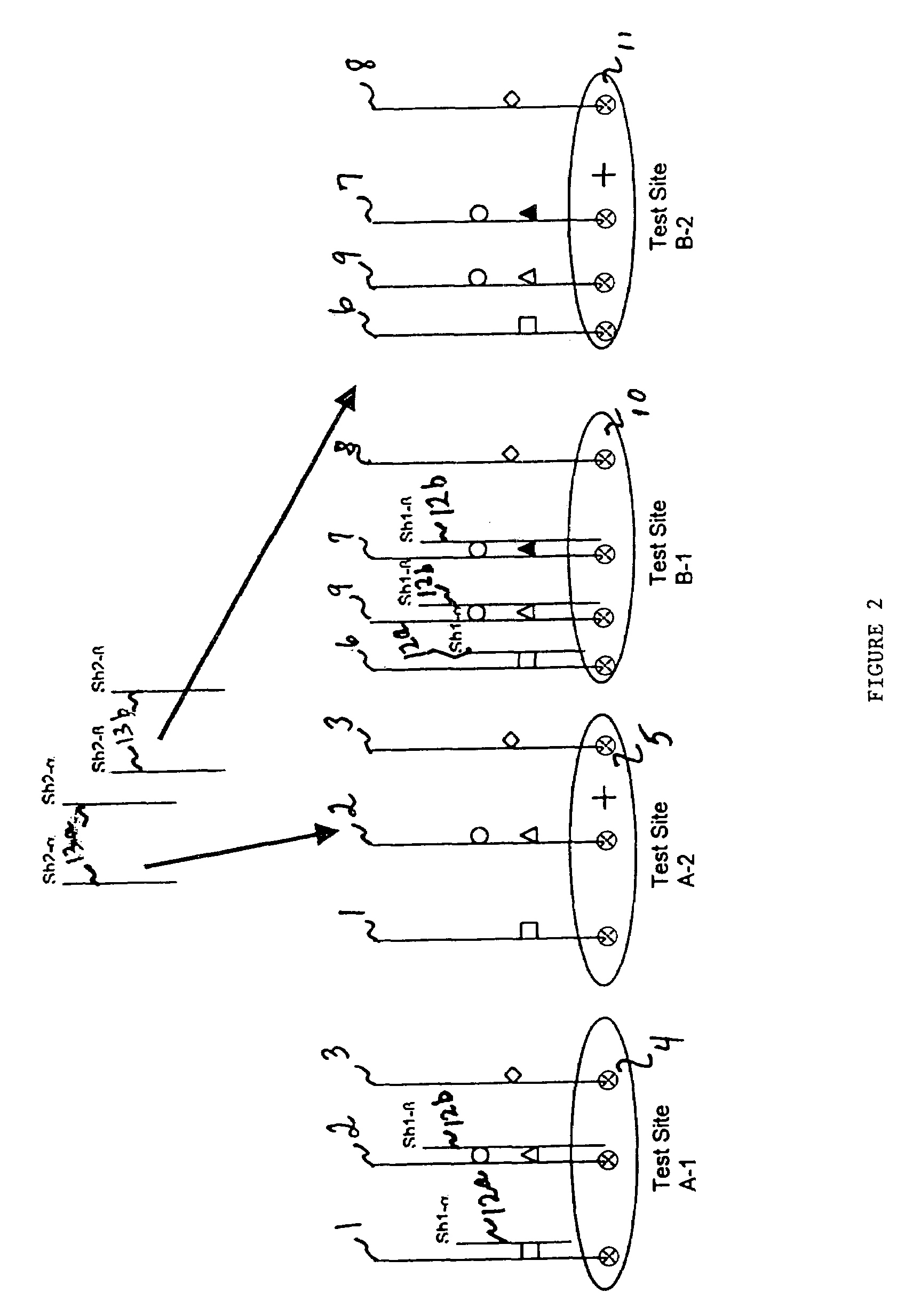
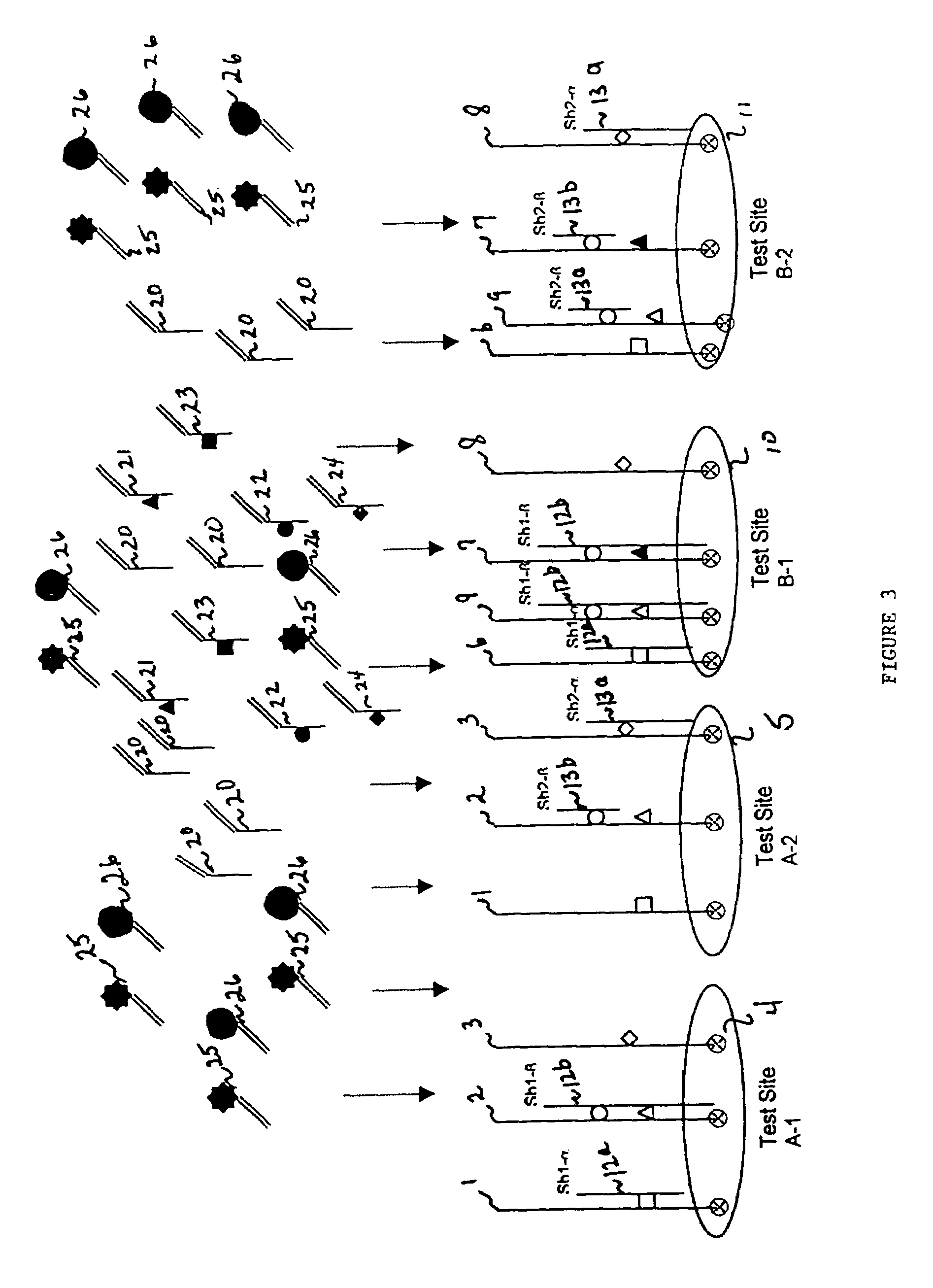
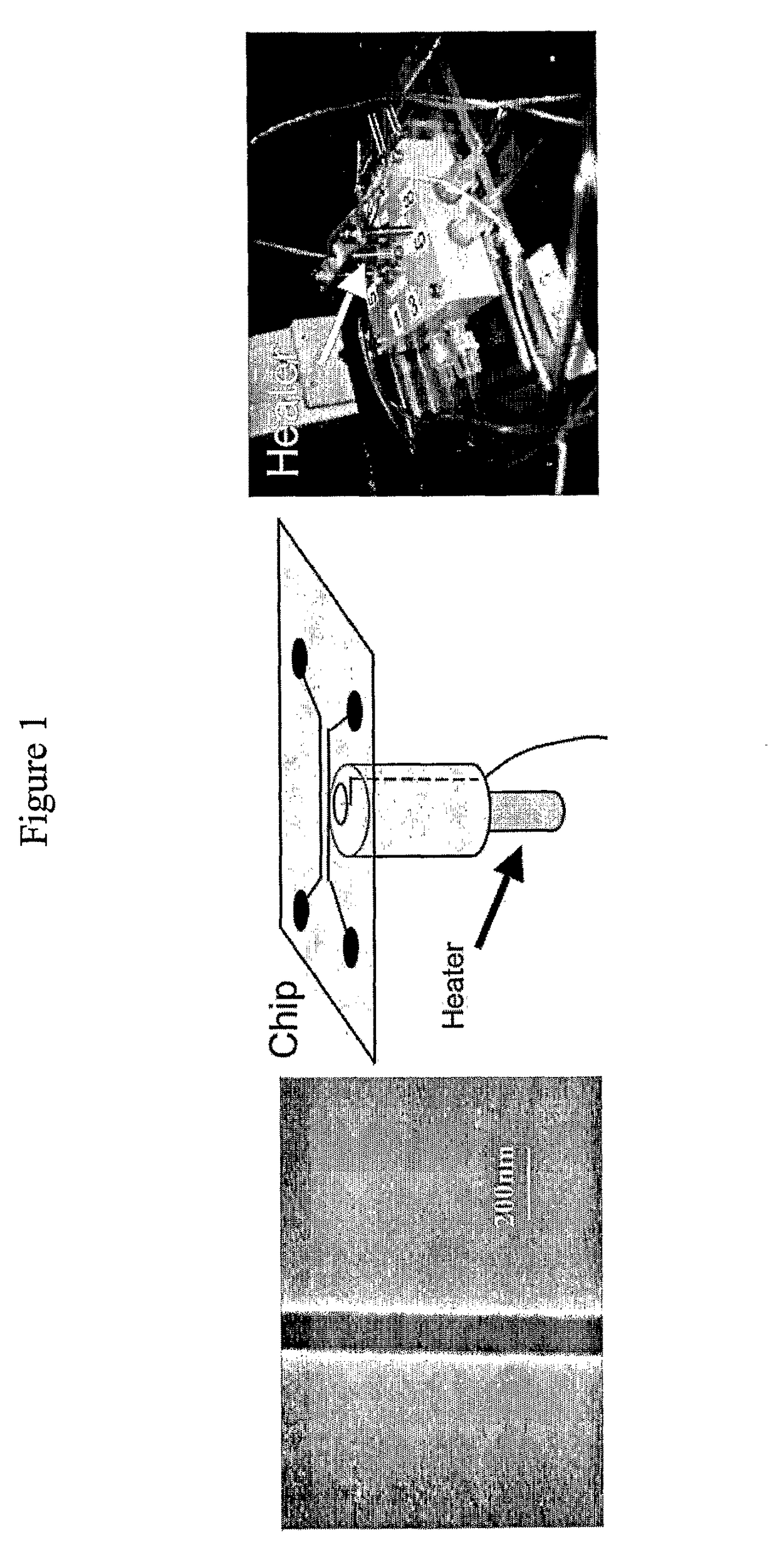
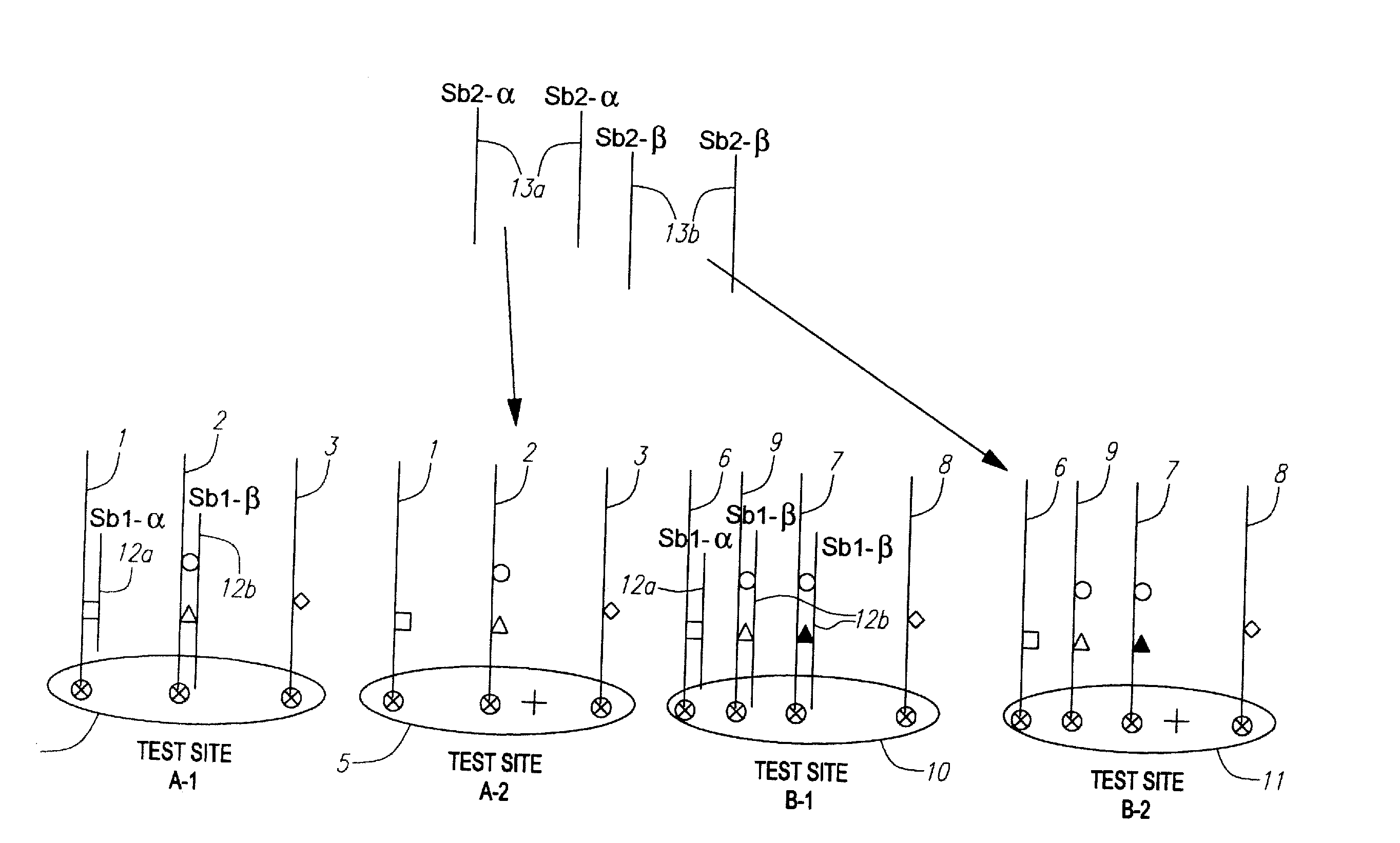
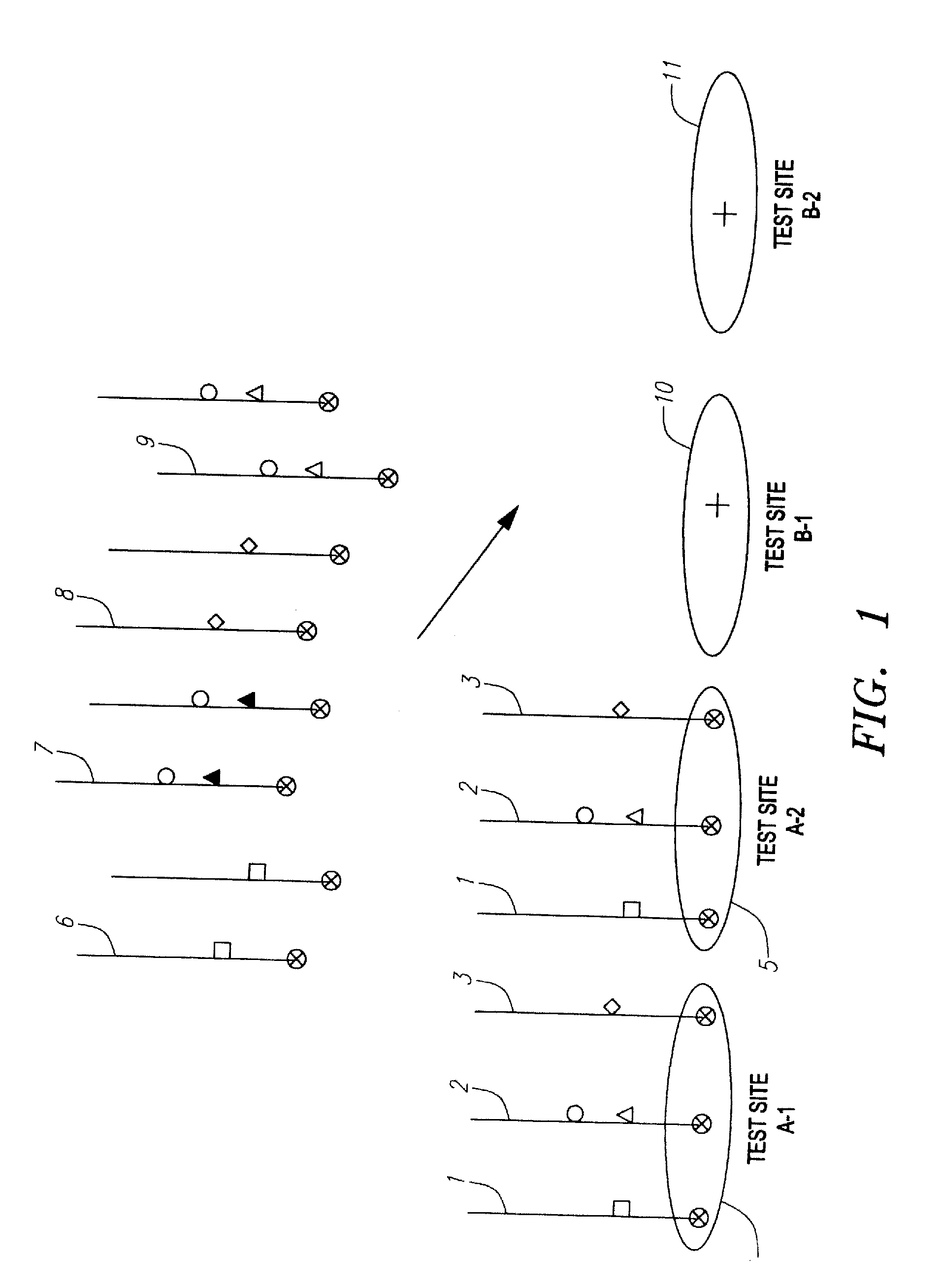
An assay system and methods are described where patient samples containing genomic DNA are analyzed for the presence of known genetic polymorphisms using a universal reporter strategy. In a preferred embodiment, the amplified DNA is localized at test sites in an array of sites on a microchip followed by a series of hybridization reactions that screen for the presence of a single mutation from among a number of mutations, and allow the identification of specific mutations. In addition to universal reporters, the assay may use blockers and discriminators for screening and identification of known polymorphisms.
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE
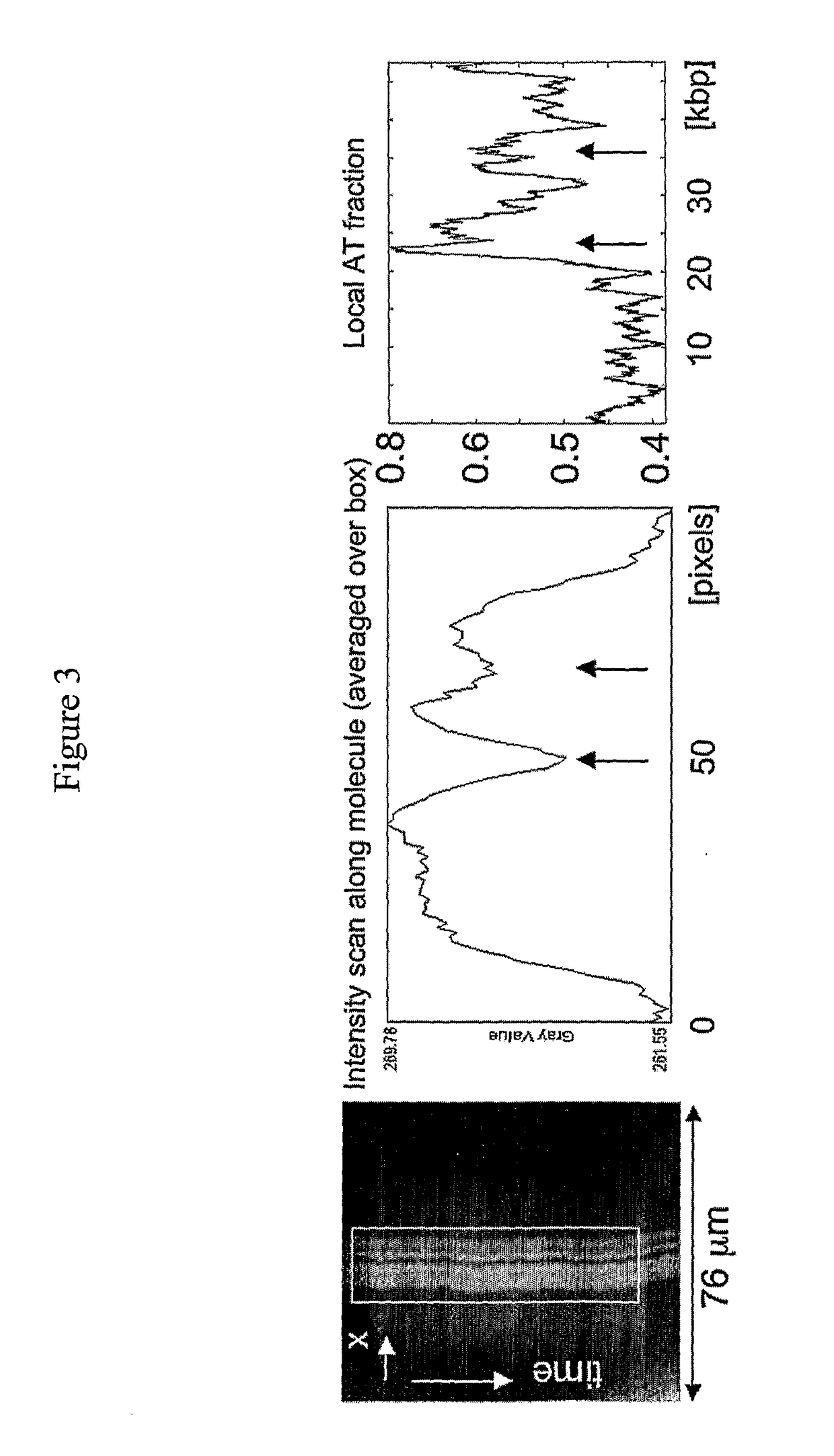
Method for the mapping of the local AT/GC ratio along DNA
ActiveUS9597687B2Low costIncrease speedHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis dnaDna targeting
Owner:TEGENFELDT JONAS +2
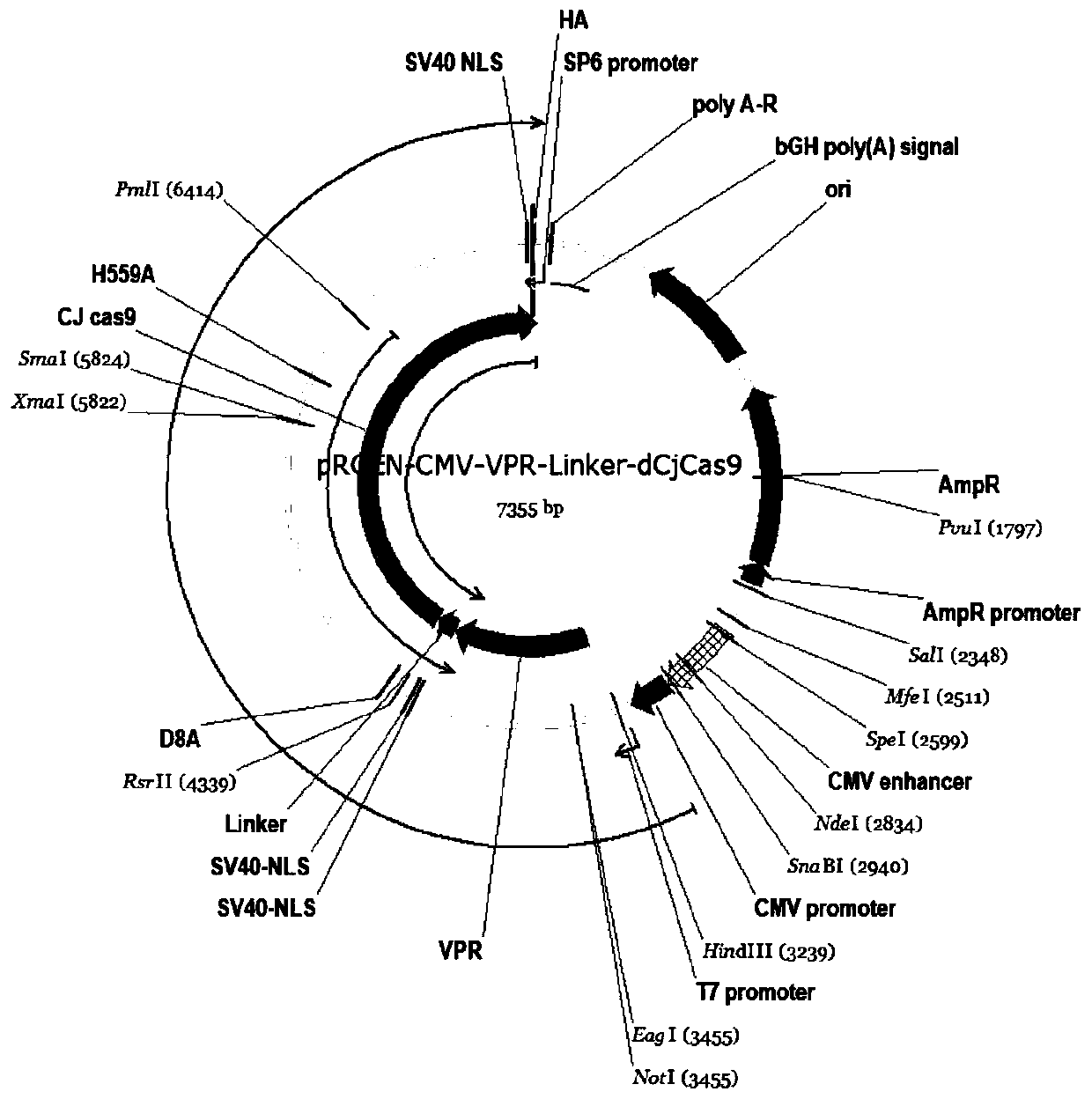
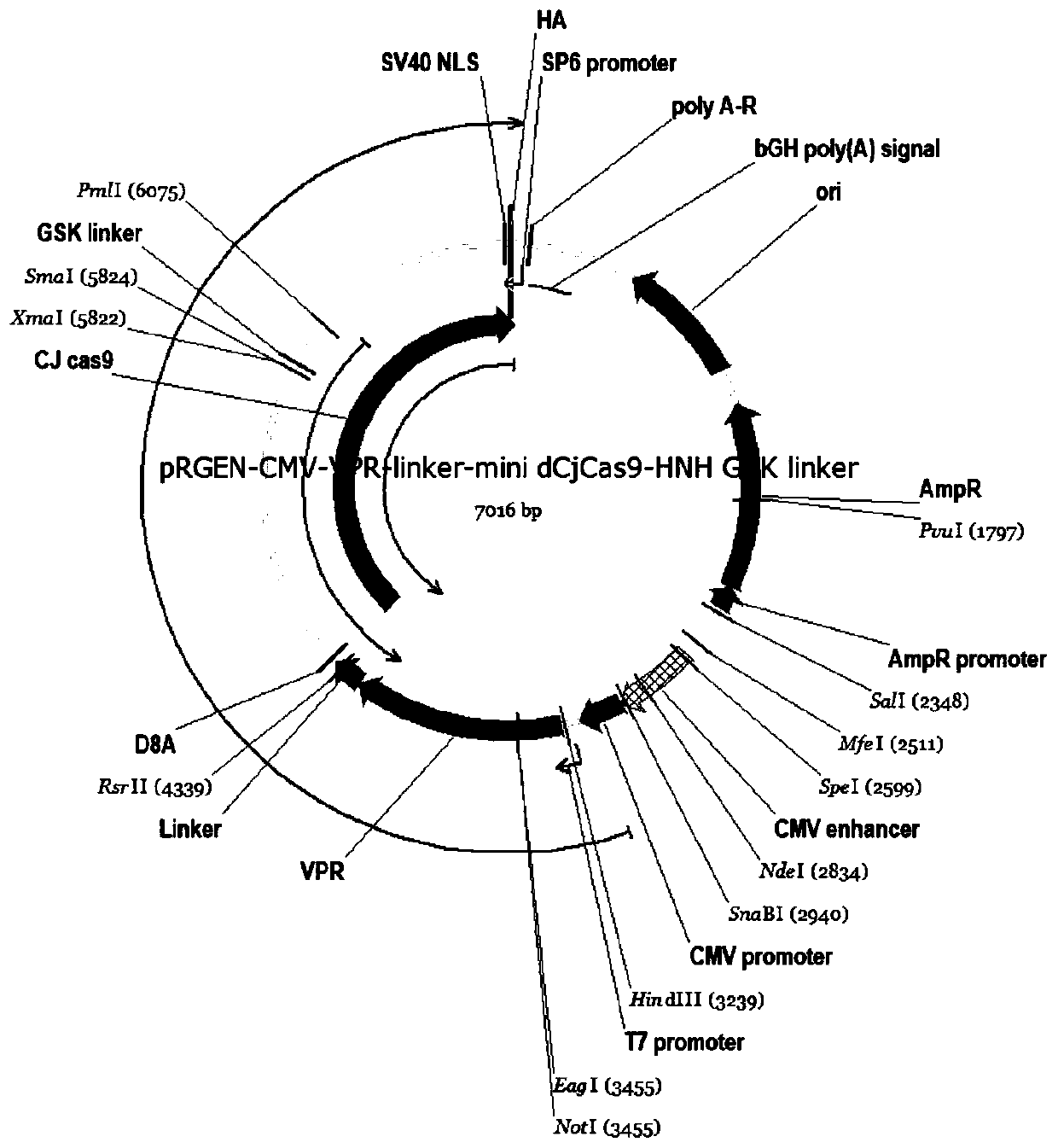
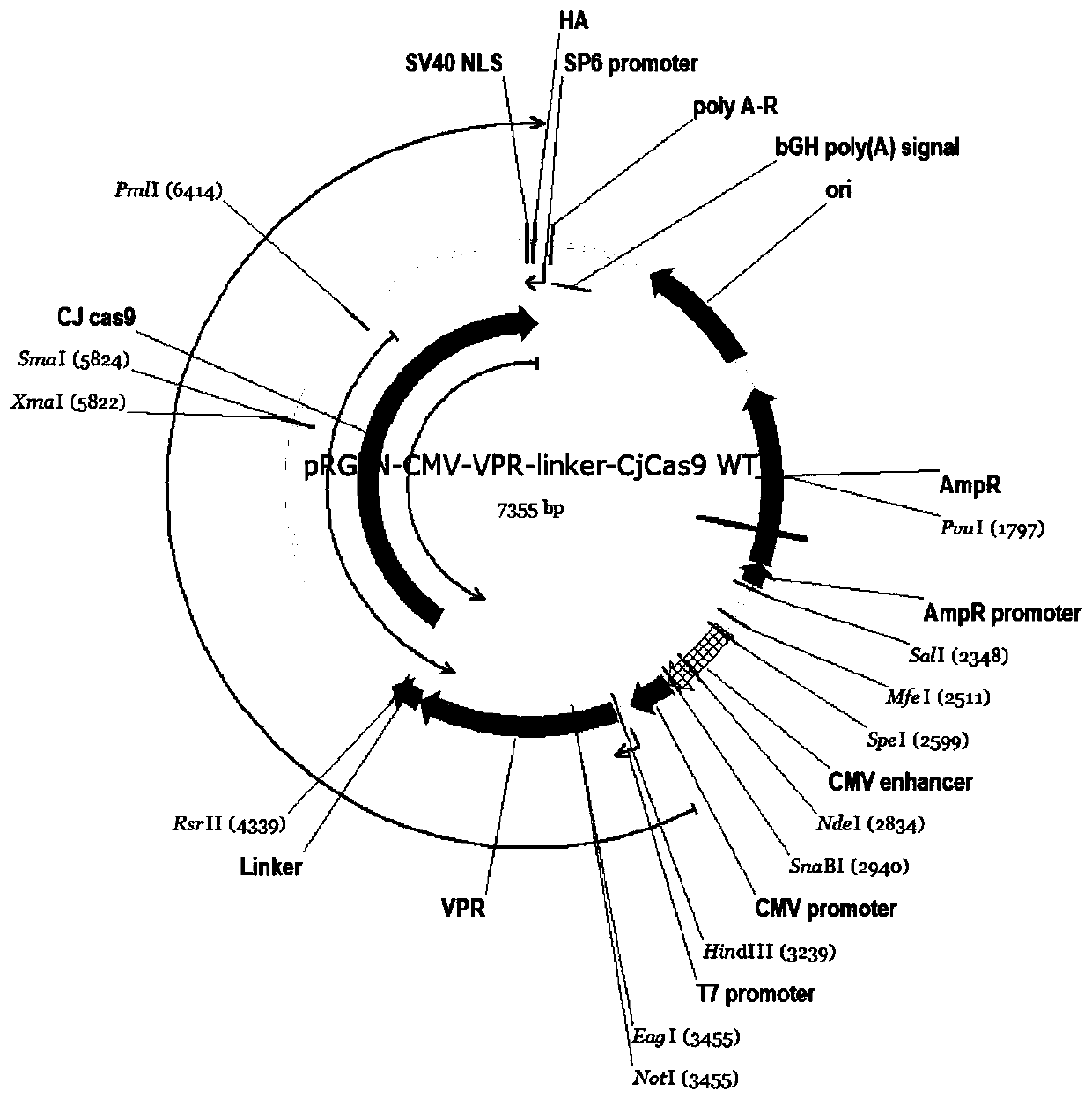
Fusion protein based on CjCas9 and VPR core structure domains, corresponding DNA targeting activation system and application of system
ActiveCN110358753AReduce volumeStrong specificityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousWild type
The invention discloses a fusion protein based on CjCas9 and VPR core structure domains, a corresponding DNA targeting activation system and application of the system. The fusion protein comprises twoheterologous polypeptide structure domains, and one polypeptide structure domain comprises VPR protein with the transcription activation activity; the other polypeptide structure domain comprises theCjCas9 protein, the CjCas9 protein is in a dCjCas9 subtype or a mini-dCjCas9 subtype or a CjCas9 wild type, and the dCjCas9 subtype contains D8A and H559A single-locus amino acid mutation; the mini-dCjCas9 subtype contains D8A single-locus amino acid mutation and deficiency of most HNH structure domains. The DNA targeting activation system comprises the fusion protein and one or more kinds of guide RNA, and the guide RNA comprises a sequence with the length of 14-22 bp and a framework sequence with the length of 80 bp, wherein the sequences are designed for a target gene promoter area. The DNA targeting activation system is applied to targeting activation of a gene. The DNA targeting activation system has the advantages of being small in size, capable of achieving high specificity, a highactivation effect and easy synthesis, low in cost and the like.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Combi-molecules having EGFR and DNA targeting properties
A series of new chemical agents that demonstrate anti-tumor activity are described. The new chemical agents combine two major mechanisms of anti-tumor action. In an embodiment, the agents are capable of both inhibiting EGFR and damaging DNA while also, upon degradation, degrading to an inhibitor of EGFR and to an agent capable of damaging DNA. Moreover, a novel series of molecules capable of releasing two moles of EGFR inhibitor and a potent bi-functional alkylating agent are also described.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Methods and apparatus for screening and detecting multiple genetic mutations
InactiveUS20100167960A1Avoid reactionEffective strategyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibraries apparatusDiscriminatorHybridization reaction
An assay system and methods are described where patient samples containing genomic DNA are analyzed for the presence of known genetic polymorphisms using a universal reporter strategy. In a preferred embodiment, the amplified DNA is localized at test sites in an array of sites on a microchip followed by a series of hybridization reactions that screen for the presence of a single mutation from among a number of mutations, and allow the identification of specific mutations. In addition to universal reporters, the assay may use blockers and discriminators for screening and identification of known polymorphisms.
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE
A kind of ratiometric pH probe with organelle or protein targeting function and its application
InactiveCN111533761BHigh fluorescence quantum yieldEasy to functionalizeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsLysosome localizationProtein target
A kind of ratio-type pH probe with cell organelle or protein targeting function and its application belongs to the field of fine chemical industry. In the field of biological imaging, the visualization of cell activities is of great significance. Ratio pH probes located in organelles mainly achieve organelle targeting by connecting specific Tags, such as introducing morpholine to achieve lysosome positioning, introducing triphenylphosphine to achieve mitochondrial targeting, and using Hoechst to achieve DNA targeting, etc. . The introduction of Tag sites directly on the basis of ratiometric pH probes often has a series of problems such as increased synthesis steps and increased separation difficulty, so it is very important to develop a general platform. BODIPY and rhodamine have the advantages of high molar extinction coefficient and fluorescence quantum yield, narrow spectrum, and spectral matching, which are very suitable for the construction of ratiometric pH probes with FRET mechanism. These compounds have high biocompatibility and can specifically bind to ratiometric pH. , and also has the function of organelle targeting.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
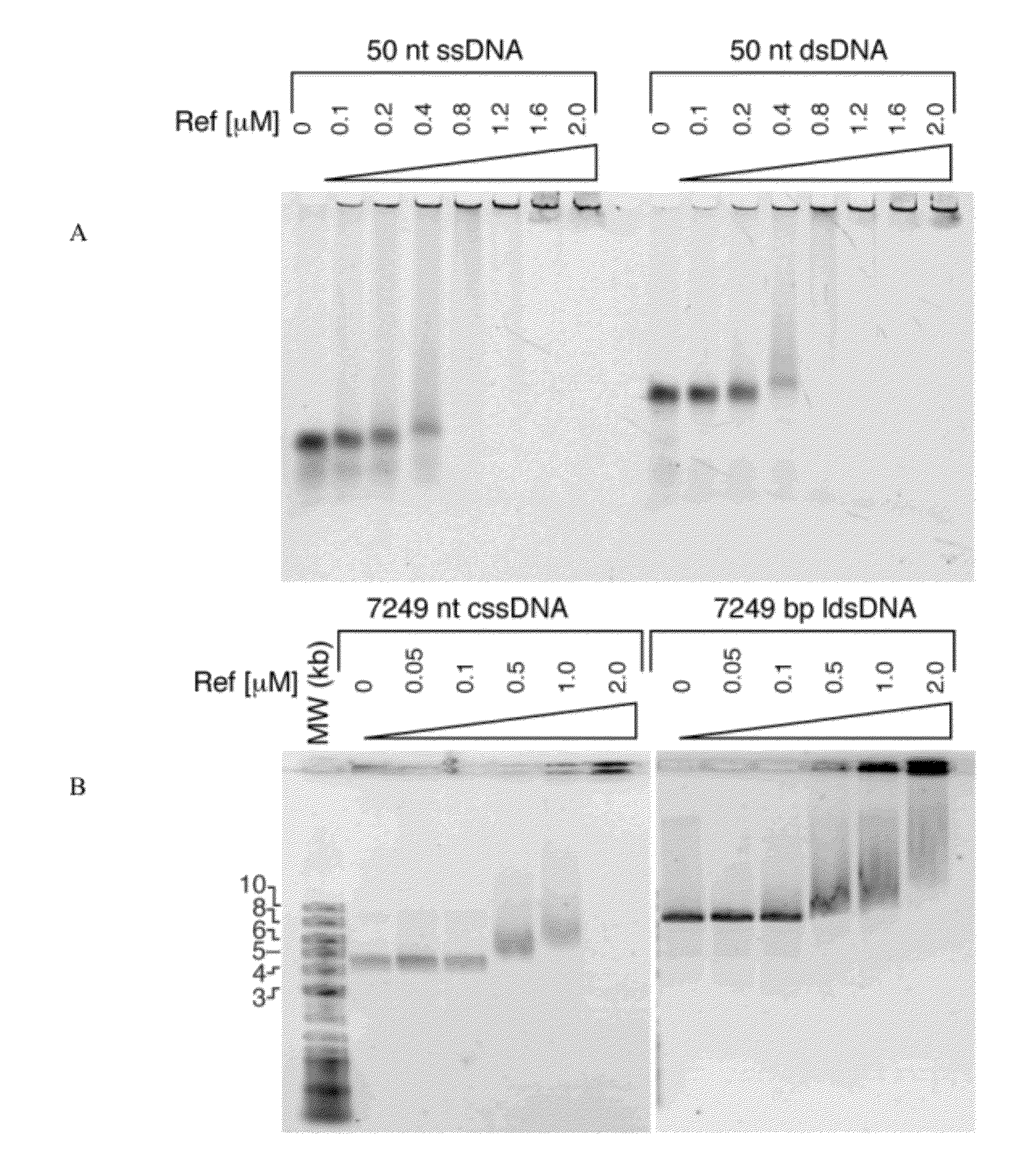
Targeted DNA capture method mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN111471745BImprove accuracyImprove capture efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDna targeting
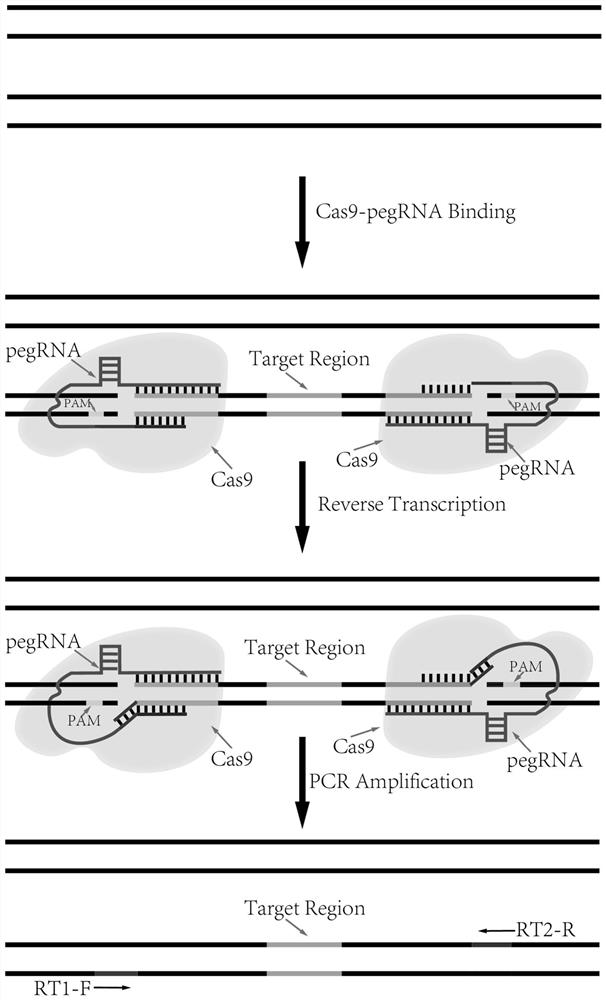
The invention discloses a DNA targeted capture method mediated by the CRISPR / Cas9 system. A sgRNA is designed for the upstream and downstream of the target DNA region respectively, and different capture sequences and a segment of the sgRNA are added to the 3' ends of the two sgRNA sequences. The reverse complementary sequence constitutes the pegRNA. When the pegRNA-Cas9 protein complex is targeted to bind the target DNA, through pegRNA-mediated site-specific insertion, different capture sequences are inserted in the upstream and downstream of the target DNA region, and then through the capture sequence. The primers are used for PCR amplification, targeted enrichment and isolation of target DNA from the DNA library or the whole genome, which can be directly used for subsequent capture sequencing. Compared with other enrichment methods, the method provided by the invention is simple, fast, specific and sensitive, and has broad application advantages in DNA sequence analysis.
Owner:武汉影子基因科技有限公司
A kind of primer set, kit and application thereof for sars-cov-2 virus nucleic acid detection
ActiveCN112029903BSimple and fast amplificationGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionDna targeting
The invention discloses a primer set, a kit and an application thereof for detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus nucleic acid. The present invention designs a primer set for the N gene and ORF1ab gene of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and the kit includes the primer set, a guide DNA targeting the target gene, a fluorescently labeled molecular beacon and a PfAgo enzyme. The primer set provided by the invention can simply and quickly amplify the nucleic acid of the new coronavirus, and has the characteristics of good repeatability, high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
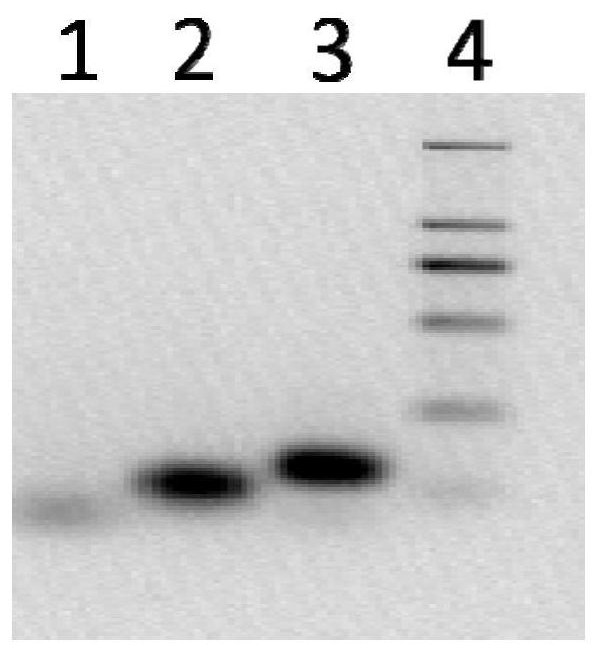
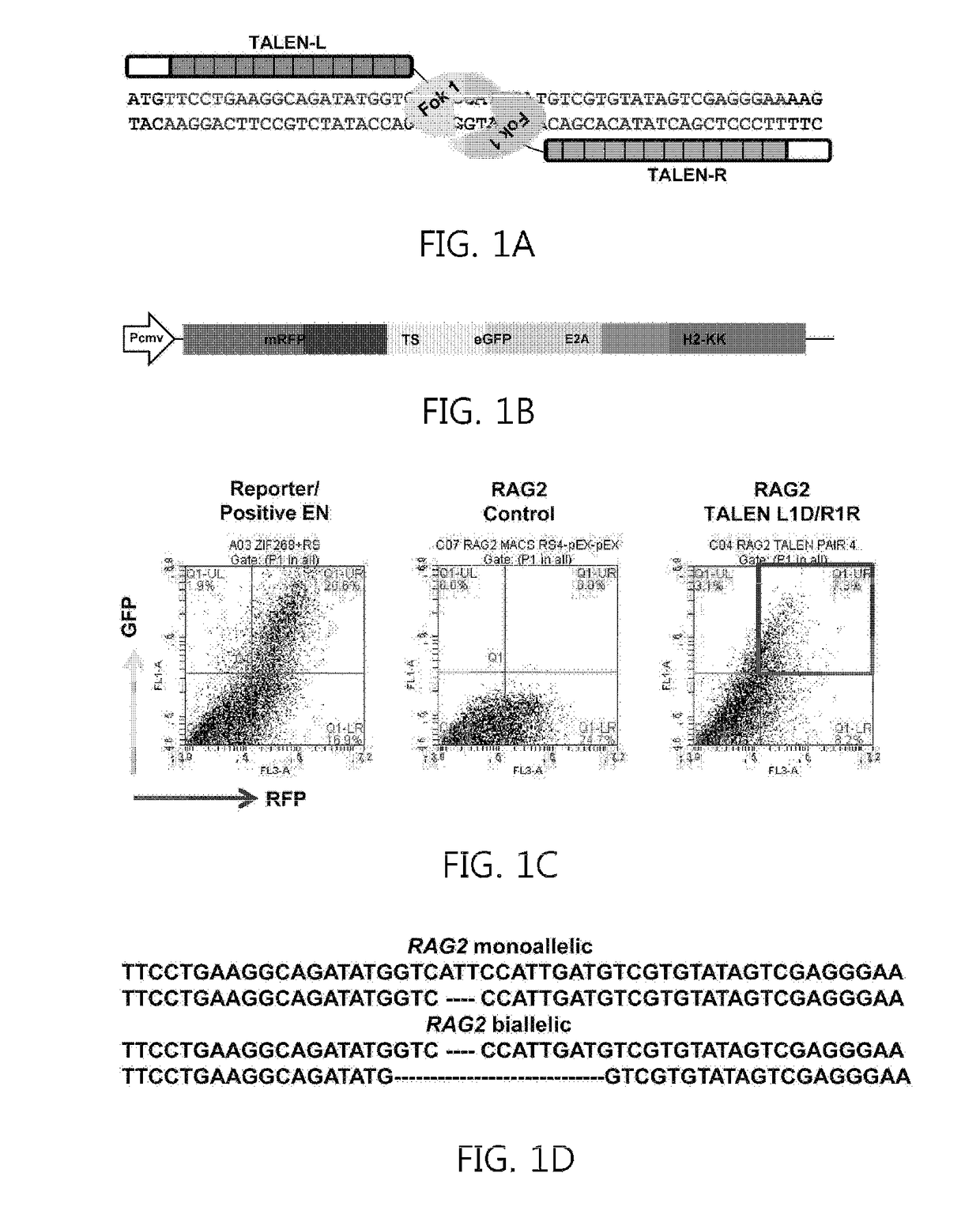
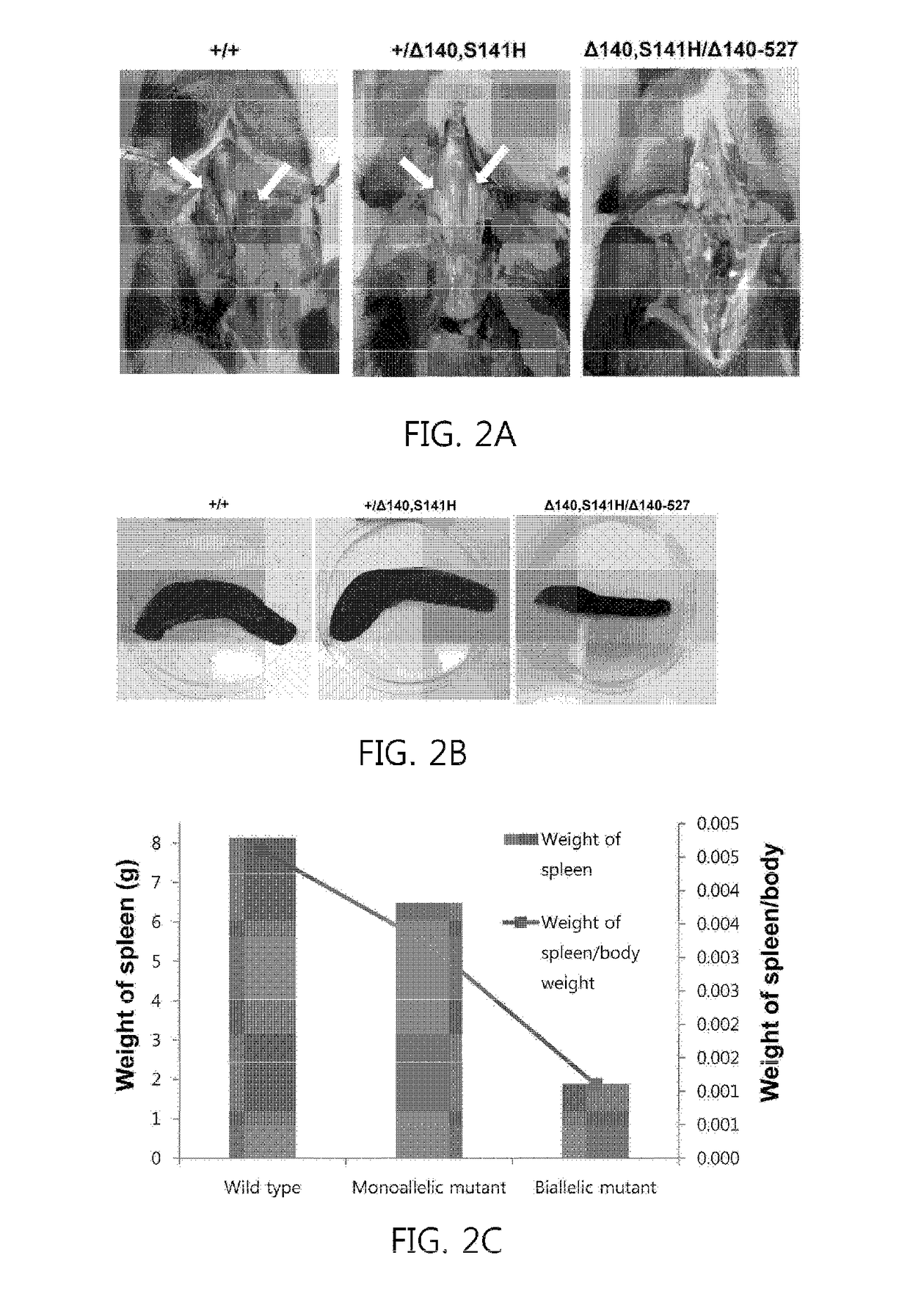
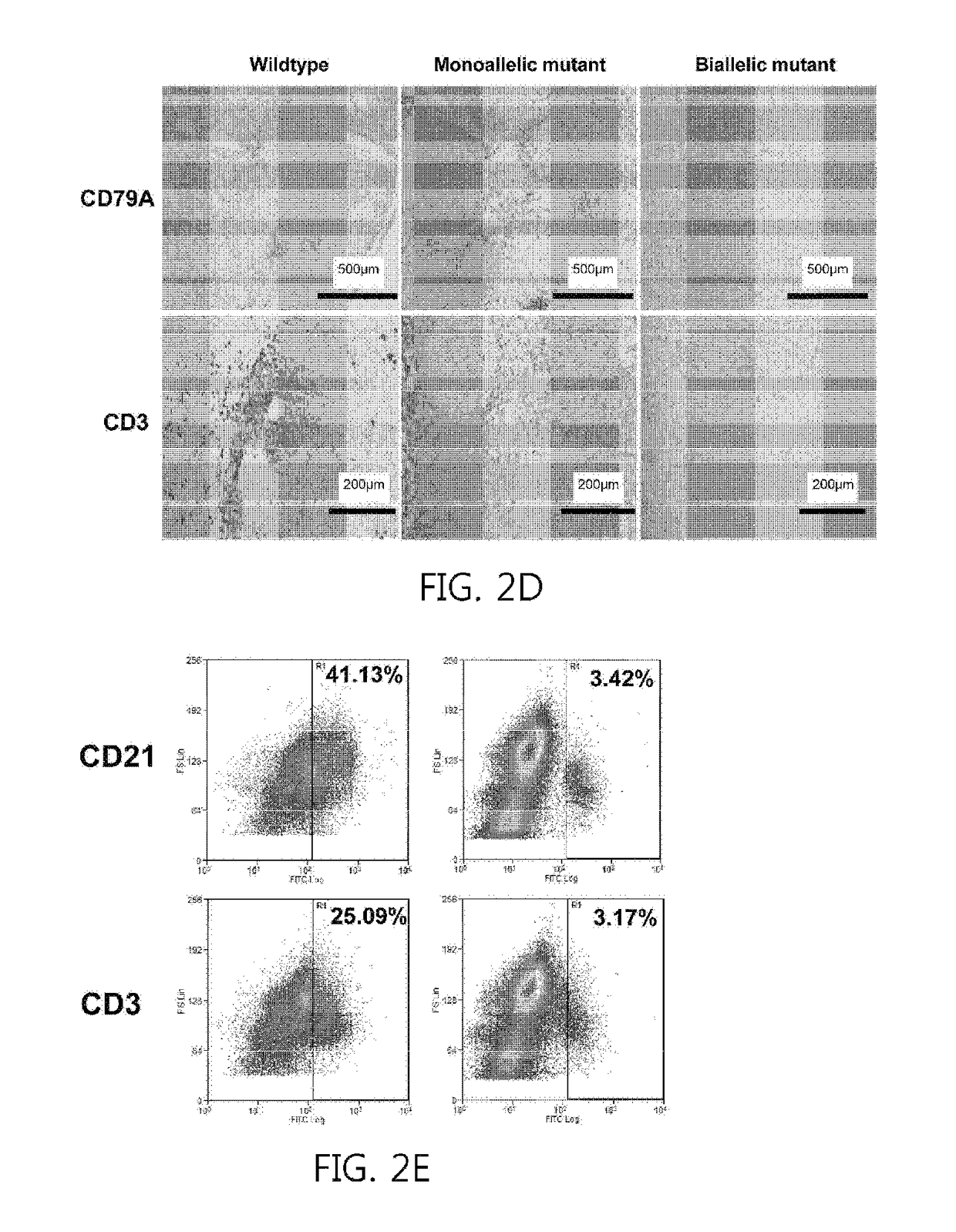
Recombination activating gene 2 gene targeting vector, production of SCID-like miniature pigs by TALEN-mediated gene targeting and use thereof
ActiveUS9807987B2Genetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNADna targetingRecombination-activating gene
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI +1
Compositions and methods for targeting cancer-specific sequence variations
ActiveUS11492670B2Avoids off-target binding and its resulting side effectHigh degreeHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer targetingDna targeting
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for targeting cancer-specific DNA sequences, such as copy number amplifications and other types of cancer-specific sequence variations, such as cancer-specific polymorphisms, insertions, or deletions. The present invention provides hereto sequence-specific DNA targeting agents targeting a sequence within the amplified DNA region or a sequence otherwise specific for a cancer cell compared to a non-cancer cell. The invention further relates to methods for treating cancer, comprising administering such sequence-specific DNA targeting agents. The invention further relates to methods for preparing sequence-specific DNA targeting agent, as well as screening methods using the DNA targeting agents.
Owner:INST CARLOS SLIM DE LA SALUD A C +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com