Method for atom force microscope inducing single molecule DNA positoning mutation
An atomic force microscope and single-molecule technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as the inability to induce mutagenesis of a single DNA molecule, and achieve the effects of position determination, controllable operation, and easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
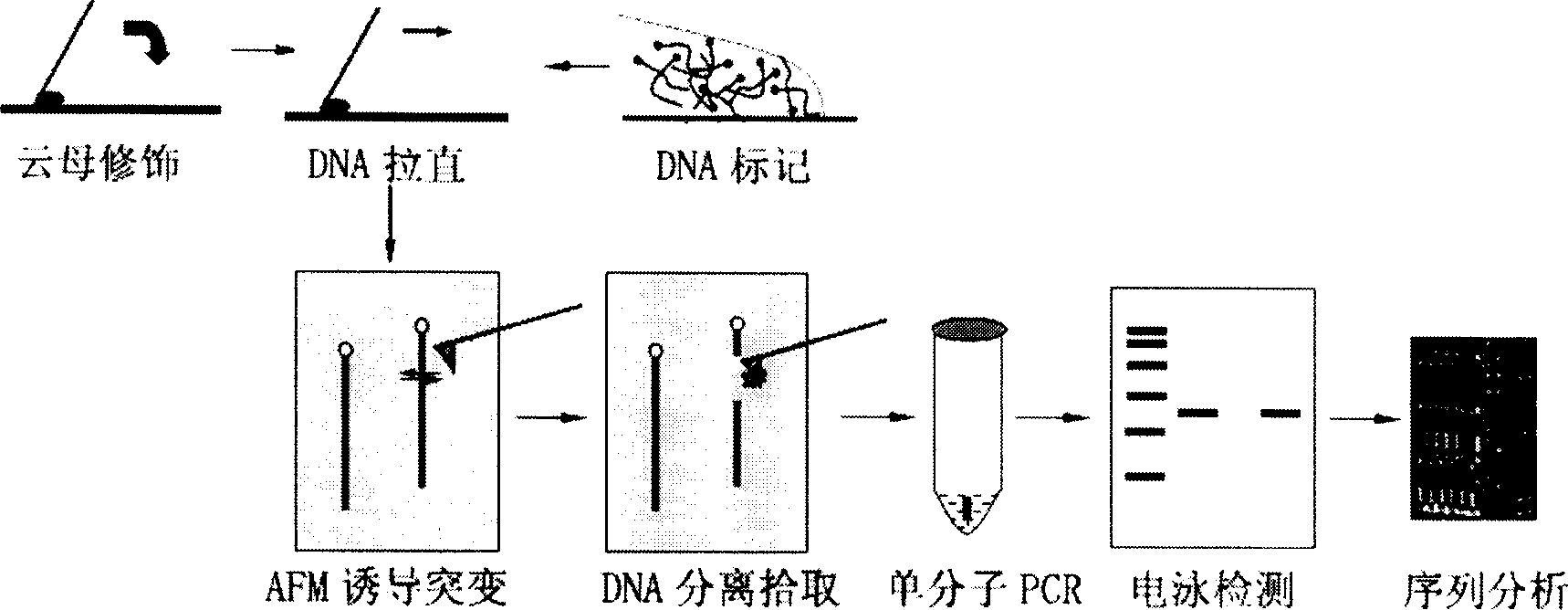
[0042] AFM localization of a sequence on the embodiment pBR322 plasmid DNA mechanically induced mutation
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the positioning and detection of mechanically induced mutations and detection of pBR322 DNA by AFM include the following steps:
[0044] 1. Prepare a mica substrate modified with aminosilane (APTES), and modify the substrate with 3-amino-propyl-triethoxysilane (APTES) with a volume concentration of 1%. The specific steps are:
[0045] 1) Dilute APTES with water to a volume concentration of 1%, and pipette 20 μl and drop it on a clean parafilm;
[0046] 2) The newly dissociated mica (20mm×20mm) was blown off with an ear washing ball to remove debris, and covered on the APTES droplet;
[0047] 3) Modify at room temperature for 5 minutes, rinse with double distilled water 4 times, place on filter paper, and blow dry with clean nitrogen;
[0048] 4) The modified mica was baked in an oven at 120°C for 2 hours, and then irradiated with ultr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com