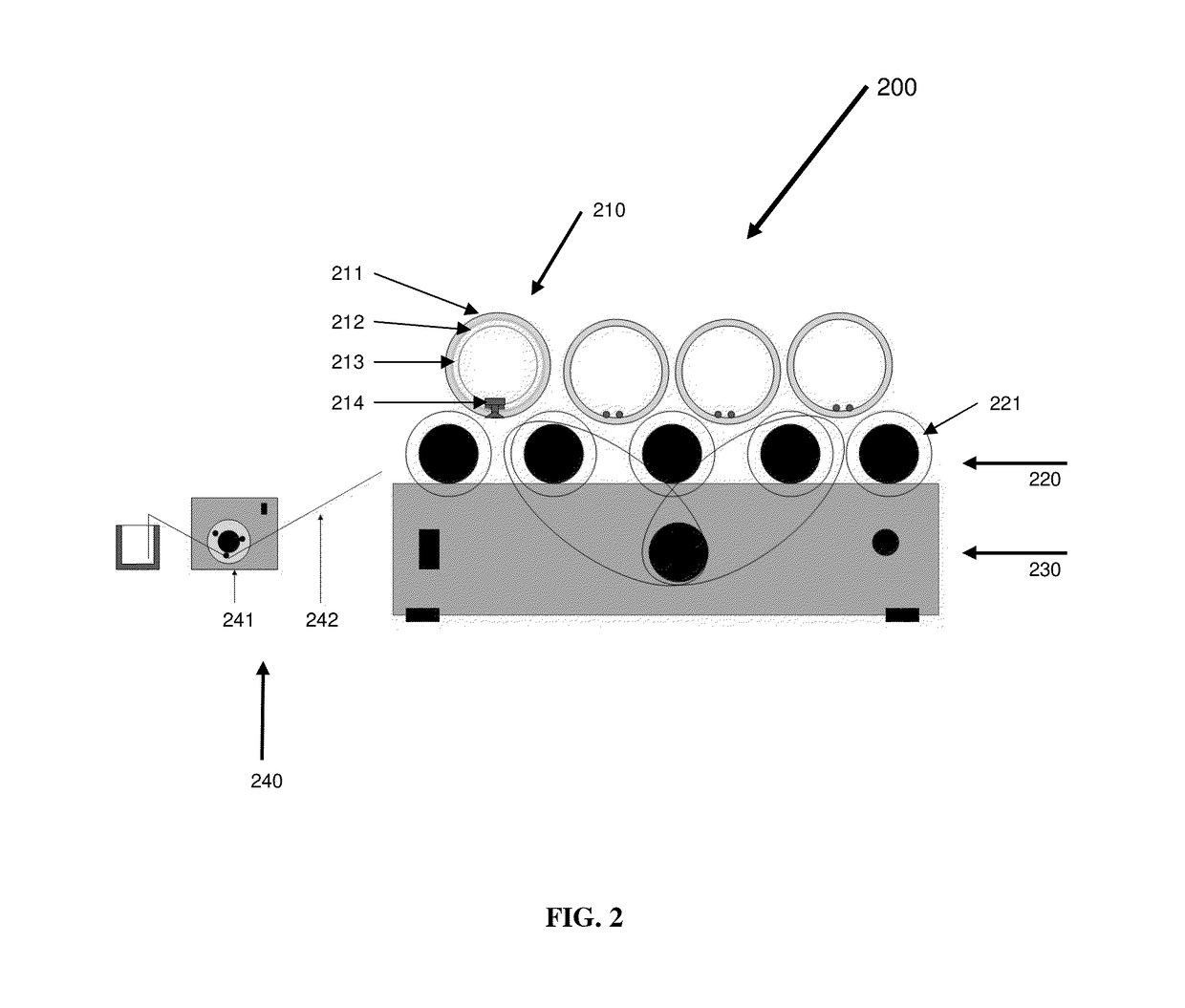
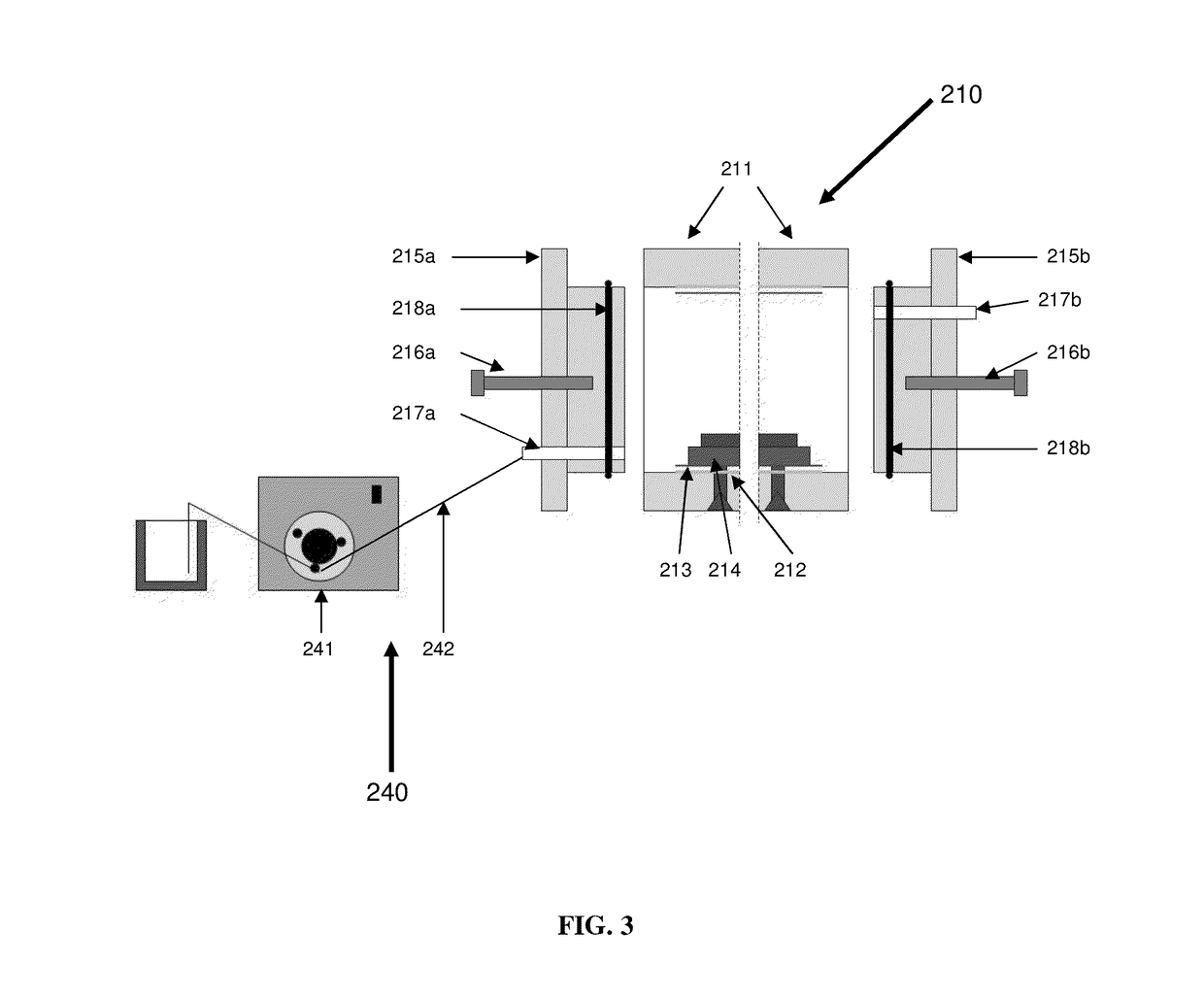
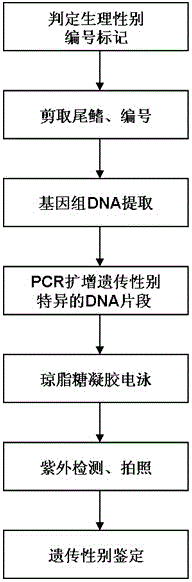
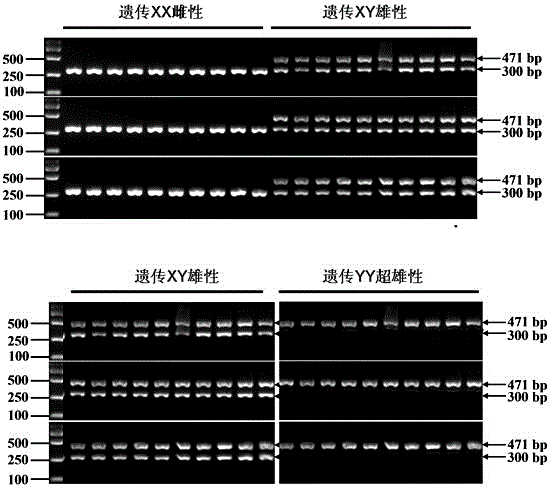
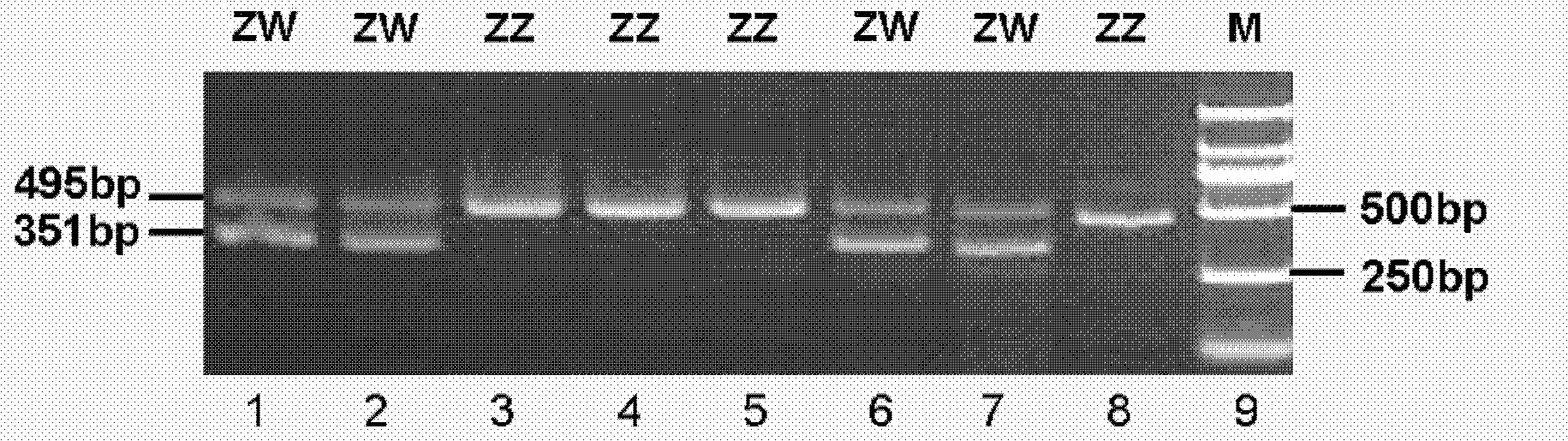Patents
Literature
1631 results about "Agarose gel electrophoresis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size (isoelectric focusing agarose electrophoresis is essentially size independent), and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix.
Method used for detecting HLA-B*5801 alleles
ActiveCN103484533AReliable resultsFlexible detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomicsA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of pharmacogenomics and genetic diagnosis, and relates to a method used for detecting HLA-B*5801 alleles. The method comprises following steps: a DNA sample to be detected is taken, three pairs of specific primers and a pair of internal primers are taken, amplification of DNA segments is realized by using sequence specific primer method, and then the results of the amplification are analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis; or sample DNA is extracted, a pair of specific primers, a pair of internal primers and three fluorescence probes are taken, amplification of DNA segments is realized by Taqman probe method using a fluorescence ration PCR instrument, and then the amplification curve is analyzed so as to obtain results. Results analysis methods such as agarose gel electrophoresis, high resolution melting curve and SYBRGreen fluorogenic quantitative PCR are employed in the method. The method has advantages of speediness, convenience, flexibility, high resolution and no contamination; is suitable for detection of HLA-B*5801 alleles in samples such as peripheral blood and hair; and can be used for determining the probability of severe skin adverse reaction of patients with gout or hyperuricemia caused by taking of allopurinol.
Owner:安徽同科生物科技有限公司
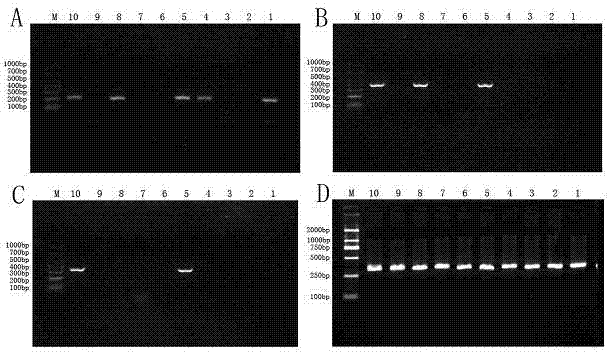
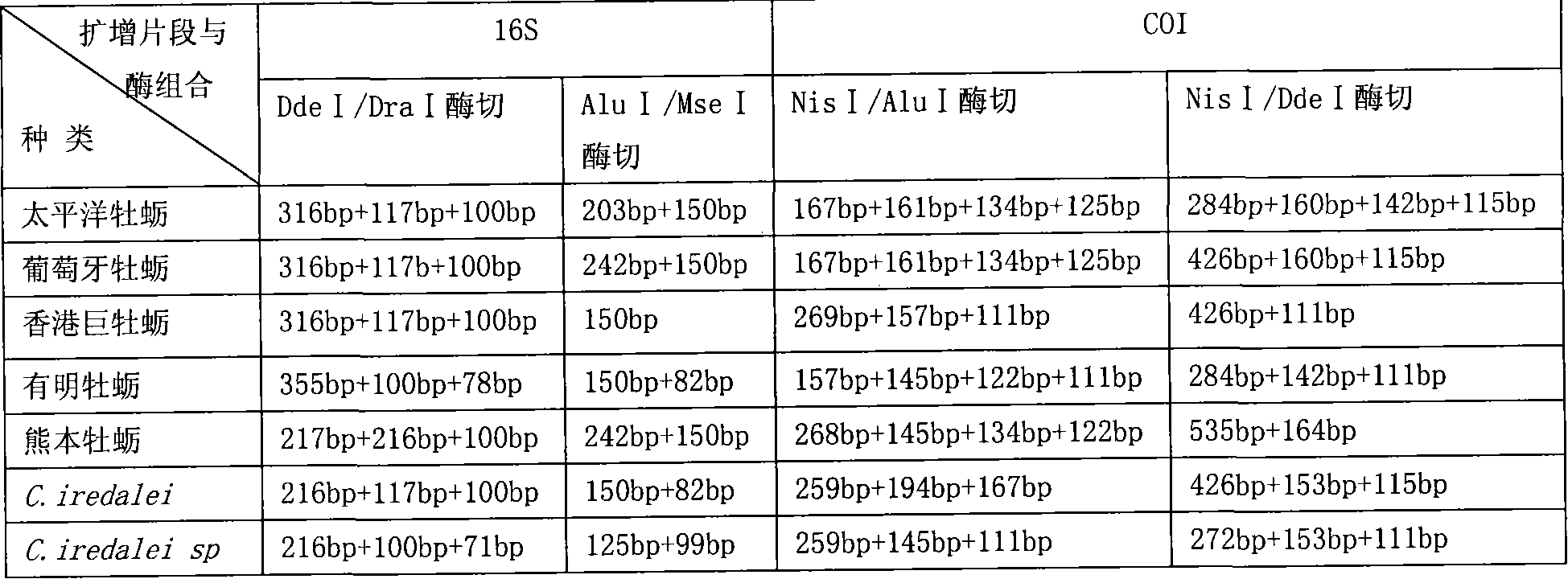
PCR-RFLP identification method for seven crassostrea oyster on south China coast
ActiveCN101130815AAccurate identificationImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsCrassostrea
The present invention relates to a PCR-RFLP identification method for 7 kinds of Chinese south inshore oysters. Said identification method includes the following several main steps: making genome DNA extraction, PCR amplification of object fragment, selecting proper incision enzyme combination, utilizing selected incision enzyme to enzyme-cut the PCR product and utilizing agarose gel electrophoresis to make detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primer, method and kit for detecting animal clonorchiasis sinensis specificity
InactiveCN101586161AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence databaseUltraviolet lights
The present invention discloses a primer, a method and a kit for detecting the animal clonorchiasis sinensis specificity, a nucleotide sequence of an upstream primer of the primer is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, a nucleotide sequence of a downstream primer is represented by SEQ ID NO:2. the present invention implements an PCR amplification to a detectingformwork DNA by the primer, an amplifying outcome yield is processed by an agarose gel electrophoresis and observed under an ultraviolet light, if it is a positive result, there will be a specificity amplifying band, otherwise there will not be a band. According to an ITS zone sequence database OF THE animal clonorchiasis sinensis, the invention designs the primer, builds a rapid, special and sensitive PCR method, and it is capable of authenticating the animal clonorchiasis sinensis accurately. The operation of the kit of the invention is simple and programmable, the method specificity is strong, the sensibility is high, the result judgement is objective, and the invention is capable of being used for diagnosing the animal clonorchiasis sinensis and inquiring epidemiology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for identifying salmonella enteritidis, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella pullorum and salmonella gallinarum
InactiveCN103131784AShorten diagnostic timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSerotype
The invention relates to a multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for identifying salmonella enteritidis, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella pullorum and salmonella gallinarum. The multi-PCR method comprises the following steps of: with the extracted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a bacterium to be detected as a template, carrying out mPCR (multiple polymerase chain reaction) amplification on five pairs of primers as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-10; and carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis on mPCR amplification products, and then determining according to electrophoresis results. According to the multiple PCR method, the synthesized primers are used for carrying out PCR amplification, a diseased material can be directly ground and amplified by adopting the established multiple PCR, different salmonella serotypes can be detected in one system, serum glass plate agglutination is completed in only about six hours compared with three days for the traditional serum glass plate agglutination after separation pure culture in clinical detection, the diagnosis time is greatly shortened, and a basis is provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Construction and identification method of molecular marking fingerprint of Dendrobium huoshanense and similitude species thereof
InactiveCN101451163AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention relates to a method for constructing and identifying molecular marker fingerprint chromatogram of Dendrobium huoshanense and similar species thereof, which solves the problems that a method of identifying medicinal plants in the prior art has high cost, complicated procedures and long time consumption. The method comprises the steps of: 1, the collection of Dendrobium huoshanense samples; 2 the extraction and purification of DNA of genomes of the samples; 3. ISSR-PCR amplification; 4, agarose gel electrophoresis; 4, the construction of ISSR molecular marker fingerprint chromatogram of the samples to be tested; and 5, the identification of Dendrobium huoshanense germplasm by utilizing the constructed ISSR molecular marker fingerprint chromatogram. The method has the advantages that the method saves the time and the cost, and can obtain an accurate and reliable identification chromatogram through the extraction to DNA of Dendrobium plants, the ISSR-PCR amplification, and the agarose gel electrophoresis; the method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, quickness, good repetitiveness, and high resolution on the identification of raw materials which are easy to confuse in appearance; and the method can identify in a seedling stage, which has important effect on ensuring the accuracy and stability of base resources of medicinal materials.
Owner:陈乃富
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker combination and identification method of small Meishan pig and raw meat product
ActiveCN107699624AEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyRaw meat
The invention provides an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker combination and identification method of a small Meishan pig and a raw meat product. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a genome DNA of raw pork or a meat product, performing AGE (agarose gel electrophoresis) and Sanger sequencing after performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the genome DNA,and identifying the small Meishan pig and the meat product thereof according to an SNP genotype of a characteristic site of a sequencing result, wherein in the step of Sanger sequencing, peculiar mutation occurs at identified sites: SNP6, SNP12, SNP16, SNP71 and SNP79. According to the method, the problem that an identification method of the small Meishan pig and the meat product thereof does notexist in the prior art is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Multiple RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) detection method for SPVD (sweet potato virus disease)
ActiveCN102108419AEffectively distinguish strain typesTimely warning of the degree of dangerMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerDisease
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting polymorphism of flora of prawn culture water body
InactiveCN101724690AEffective qualitativeEffective quantitative analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePrawnFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting polymorphism of a flora of a prawn culture water body. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting total genomic DNA of mixed microbes in a prawn culture water body sample; (2) designing a specificity T-RFLP-PCR universal primer and performing PCR circulating reaction; (3) purifying a product and performing enzyme cutting on DNA by a specific restriction enzyme Hae III; (4) performing ionophortic separation on DNA segments by 1 percent agarose gel, performing fluorescent scanning on the DNA segments; (5) analyzing a polymorphism structure of a microbe flora; and (6) performing quantitative detection on predominant bacteria of the flora through fluorescence in situ hybridization technology. The method improves detection technology combining T-RFLP-PCR with FISH, uses fluorescence to mark a specific primer; and compared with the modern technology, the method has the characteristics of high repeatability, sensitivity, rapidness, accuracy, stability and the like, and can qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the ecological diversity of the microbes in the prawn culture water body along with time change and the dynamic change of a composite structure of the predominant flora.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Sudden cardiac death mutant gene detection kit
ActiveCN104561310AChange bad habitsAchieve the purpose of preventionMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh risk populationsCvd risk
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and medical science, and in particularly relates to a sudden cardiac death mutant gene detection kit which is high in accuracy and good in predictability. The kit is used for performing polymorphism detection on 12 SNP sites of 8 major genes related to sudden cardiac death; three forward and reverse specific primers are respectively adopted for each SNP site by combining the characteristics of specific allelic gene PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and temperature gradient descent PCR; and the mutation of the 12 SNP sites can be simultaneously determined by virtue of program amplification of the temperature gradient descent PCR and agarose gel electrophoretic analysis. The detection kit provided by the invention is strong in specificity, high in detection rate, high in efficiency and low in cost, and can be used for screening high-risk population of sudden cardiac death, evaluating the risk degree of having the sudden cardiac death for a detected patient, and making clear pathogenic factors of patient sudden death from a gene level, thereby providing a new way of preventing, diagnosing and treating clinical sudden death.
Owner:谢怡
Transgenic soybean detection method and the primer
InactiveCN1769488AShorten the timeImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransfer geneElectrophoresis
This invention relates to a transfer gene soybean checking method and its eduction, which includes:1 distilling soybean DNA;2 PCR expanding reaction, the total volume of the system is 25ul, each component and its final concentration is as follows: cushion solution 10mM, dNTP0.2mMú¼Mg2+1.5mMú¼the up eduction and the down eduction are 0.2mMú¼Taq 1Uú¼DNA50ng respectively, the special eduction react under the condition of the special PCR reaction by filling ddH20 up to the 25ul; after the reaction ending, distills the systerm solution 10ul and makes electrophoresis detection with 2.0úÑ agarose gelatin, and makes record; 3judging whether the soybean is the transfer gene soybean according to the record that whether it can display a 337bp unusual zoster. The related matter includes the up eduction and the down matter, whichare:Fú‘5'-CACTGACGTAAGGGATGA-3 18nt Tmú‘55.0ú¼Rú‘5'-TGTGCTGTAGCCACTGAT-3'18nt Tmú‘55.0.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting pseudomonas syringaepv altinidia through recombinase-mediated isothermal amplification technology
InactiveCN104762409ASpecificImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesWater bathsMolecular level
The invention discloses a method for detecting pseudomonas syringaepv altinidia through the recombinase-mediated isothermal amplification technology and belongs to the technical field of phytobacteriology diagbosis. The method mainly includes the steps that general DNA of the pseudomonas syringaepv altinidia is extracted, an RPA reaction and 2.5% agarose gel electrophoresis detection are performed, and fast detection of the pseudomonas syringaepv altinidia is performed in the aspect of the molecular level. The method has the advantages of being fast, sensitive, convenient to use and specific. Compared with a conventional PCR method, primers obtained through the method in a screened mode have high specificity and stability on amplification of target fragments, amplification time is short, annealing is not needed during the reaction, the high activity of the RPA reaction can be kept when required temperature can be maintained under any condition of a constant-temperature incubator, a water bath kettle and human body temperature, and no expensive instruments are needed. Due to the method, a detection system of the pseudomonas syringaepv altinidia is successively established, the practicability of the system is verified through sample detection, and the method for detecting the pseudomonas syringaepv altinidia is fast and effective.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers, method and kit for identifying duck gender
InactiveCN102618659AEasy to operateRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobiologyNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers for identifying duck gender. The nucleotide sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO.2 in a sequence table. In addition, the invention also provides a method for identifying the duck gender by using the PCR primers for identifying the duck gender and a kit containing the PCR primers for identifying the duck gender. The method comprises the following steps of: performing PCR amplification by using total DNA of a duck to be detected as a template and adopting the PCR primers for identifying the duck gender, detecting the PCR amplification product by adopting agarose gel electrophoresis, and judging the duck gender. The PCR primers are reasonably designed by using a CHD1 gene sequence concurrent in a duck sex chromosome W and a chromosome Z, and the gender of the individual duck is determined by combining the PCR amplification and the agarose gel electrophoresis; and the method is easy and convenient to operate, has the advantages of quick identification, accurate result and the like, and overcomes the defects that the conventional method wastes time and labor and easily produces errors.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
Method for quickly, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products
InactiveCN101712987AQualitatively accurateSimplify testing proceduresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyLactobacillus plantarum
The invention relates to a method for quickly, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products. The method comprises the following steps: aiming at the lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products, independently designing a species specificity primer of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the lactobacillus plantarum, carrying out species specificity PCR and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction by using the primer, and analyzing through an agarose gel electrophoresis pattern and a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR pattern, thereby establishing the method for simply, conveniently, quickly, accurately, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
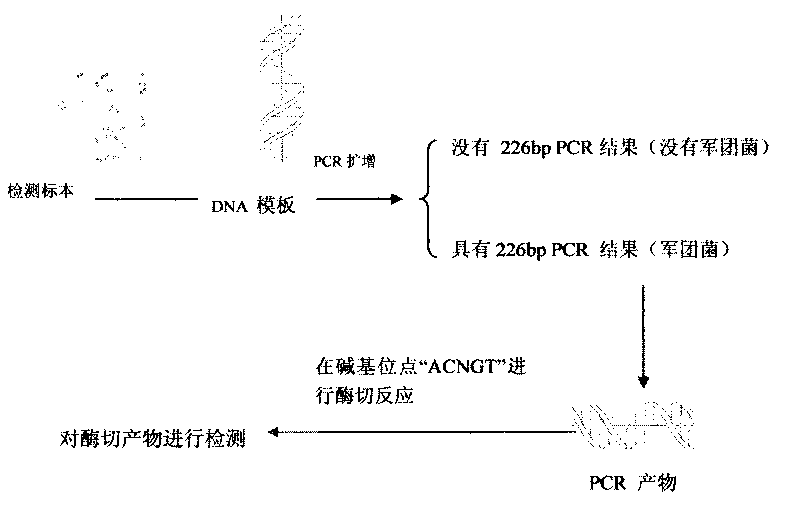
Legionnella rapid detecting and parting method
ActiveCN101717815AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDigestionBiology
The invention discloses a legionnella rapid detecting and parting method, comprising the steps of: (1) extracting a genom DNA of a detecting sample, (2) performing PCR by using genom DNA as a template in order to acquire PCR products, (3) performing agarose gel electrophoresis analysis to the PCR products in order to determine if legionnella exists, (4) performing digestion reaction to the detected positive PCR products and then performing agarose gel electrophoresis analysis to the digestion reaction products and parting molecule. Compared with the prior art, the legionnella rapid detecting and parting method of the invention can rapidly and simply detect the legionnella and can part the molecule thereof into legionella pneumophilia and non-pneumophilia legionella.
Owner:重庆金域医学检验所有限公司
Phytophthora nicotianae molecule detection primer and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103555823AStrong specificityGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a Phytophthora nicotianae molecule detection primer and a detection method thereof, specially used for the specific molecule detection of Phytophthora nicotianae. A pair of specific primers of the Phytophthora nicotianae (comprising an upstream primer YhF:5'-GACATGATATCAACTGTTCTGCAG-3' and a downstream primer YhR:5'-CCTTGGATCTTCTCTCGATAAG-3') are mainly designed, and an amplified product having a fragment length of 342bp can be specially amplified on the pure DNA and bacteria bearing pathogenic tissues of the Phytophthora nicotianae through PCR amplification and agarose gel electrophoresis. The primer and the method can be used for the rapid, sensitive and specific detection of the Phytophthora nicotianae in Phytophthora nicotianae infected plant tissues in the production practices, can be used for the early stage diagnosis of field diseases and the monitoring and identification of pathogens, and provide reliable technologic and theoretic bases for the control of diseases caused by the Phytophthora nicotianae.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Method for detecting goat TMEM95 gene subtle copy number variation through PCR technology and application thereof
InactiveCN105624314AImproved production traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionPcr ctpp
The invention discloses a method for detecting goat TMEM95 gene subtle copy number variation through the PCR technology and application thereof. According to the method, goat whole genome DNA, containing the TMEM 95 gene, in a Chinese region serves as a template, a primer pair P1 serves as a primer, part of a sequence of the goat TMEM 95 gene is amplified through PCR, and then a PCR amplification segment is subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis; according to an agarose gel electrophoresis result, non-coding region 58bp subtle copy number variation of the goat TMEM 95 gene is identified; because the TMEM 95 gene has an important regulation function on growth traits and milk production traits, the detection method lays a foundation for building of the relation between the TMEM95 gene subtle copy number variation and production traits, therefore the method can be conveniently used for assisted selection of markers of production traits of goats in China, and goat species with good genetic resources are built easily.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Primer for detecting orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides molecules and quick detection method
InactiveCN102534017AStrong specificityImprove practicalityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGel electrophoresisPlantlet
The invention relates to a primer for detecting orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides molecules and a using method of the primer, which is specially used for detecting orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides specific molecules and belongs to the fields of detection, identification and prevention and treatment of crop diseases. A pair of specific primers of orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides comprising an upstream primer P1:5'-GGCCTCCCGCCTCCGGGCGGGTC-3' and a downstream primer P2:5'-TGAGGGCCTACATCAGCT-3' are subjected to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and agarose gel electrophoresis and can specifically amplify a specific amplification product with the segment length of 304bp in a plant infected with orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides with pure DNA and germs and a culture medium. The specific molecule detection primer and the using method thereof can be used for detecting the orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides in the plant infected with the orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides and the culture medium quickly, sensitively and specifically, can also be used for performing early diagnosis on field diseases and monitoring and identifying germs, and provides reliable technological and theoretical basis for preventing and treating diseases caused by the orchid colletotrichum gloeosporioides.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Preparation method of Phellinus linteus mycelium
InactiveCN102363749AHigh purityQuality improvementFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTotal rna
The invention aims at providing a preparation method of a Phellinus linteus mycelium. The method comprises the following steps of: activating Phellinus linteus spawn; executing plate cultivation of potato dextrose agar culture medium; scraping the Phellinus linteus mycelium to inoculate the scraped Phellinus linteus mycelium to the potato dextrose agar culture medium for shake cultivation; collecting the Phellinus linteus mycelium; extracting Phellinus linteus mycelium total RNA; and observing result via agarose gel electrophoresis. The spawn used in the preparation method is the Phellinus linteus spawn (Phellinus baumii Pilate) collected in the CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is Phellinus linteus DL101 CCTCC M 2011137. The preparation method is simple to operate and has straightforward principle, and a simple and convenient method for obtaining large-scale high-purity Phellinus linteus mycelium and high-quality Phellinus linteus total RNA in the future is provided, and the basis for fundamental research and application development of the Phellinus linteus is also provided.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
ISSR fingerprint construction method for identifying reality of rice variety
InactiveCN101956016ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementUltraviolet lightsIssr pcr
The invention discloses an ISSR fingerprint construction method for identifying the reality of a rice variety and provides a quick and accurate rice variety ISSR fingerprint construction method and use thereof. The method comprises the following steps: extracting DNA of young rice seedlings by an improved CTAB method; performing ISSR-PCR amplification by using the DNA of the young seedlings as a template; performing the 1.5-percent agarose elelectrophoretic detection of the product of the PCR, and taking an image in ultraviolet light; and constructing the DNA fingerprint of the rice variety for identifying the reality of the rice variety. In the invention, the DNA fingerprint contains basic information including rice variety code, amplified band types, site code of each band and '0' and '1' arrays. The method has the characteristics of simple operation, visualization, practicality and the like and promotes the wide use of the ISSR molecular mark technology in the accurate, quick, simple and convenient identification of the reality of the rice variety.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
One group of specific primers for identifying leech as well as identification method thereof
InactiveCN107937566AFlexible dosage rangeLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMedicinal herbsNucleotide
The invention relates to a method for identifying leech by one group of specific primers and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine identification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a DNA test sample solution; secondly, taking the DNA test sample solution as a template, selecting specific nucleotide sequence obtained through design and screening as primers to perform PCR amplification; thirdly, performing agarose gel electrophoresis analysis and gel imaging system detection on products; and finally, judging the true and false and the adulteration condition of the leech according to the detection result. The specific primer amplification method is simple in operation, sequencing is not needed, the result is intuitive, and the adulteration product can be detected and identified; meanwhile, the method is high in anti-interference ability and high in repeatability, can be used for accurately identifying leech foundation and medicinal materials, provides an efficient and rapid method for detecting the leech products, and has a relatively good application value.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Molecular biology identification method for dry sea cucumbers
InactiveCN101659993AHigh purityHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationElectrophoresisEnzyme
The invention relates to a molecular biology identification method for dry sea cucumbers, which comprises the following steps: extracting genome DNA of dry sea cucumbers by a high salt method; amplifying CO I genetic fragments by using a degenerate primer PCR; carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection on enzyme-digested products; and determining the result by the quantity and the length of electrophoretic bands. The method is used for identifying different varieties of sea cucumbers, has the characteristics of high accuracy and speed as well as convenience and is more accurate and reliable when compared with the traditional morphological identification.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Haplotype primer for identifying Q-shaped bemisia tabaci and identification method
InactiveCN102676680ASimple and Stable Molecular MarkersSolving the difficult problem of differentiating haplotype Q Bemisia tabaciMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNADigestion
The invention relates to a haplotype primer for identifying Q-shaped bemisia tabaci and an identification method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting Q-shaped bemisia tabaci genomic DNA; (2) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on mitochondrial COI (cytochrome oxidase subunit I) genes of the Q-shaped bemisia tabaci genomic DNA by taking the Q-shaped bemisia tabaci genomic DNA as a template; (3) digesting a PCR product prepared in step (2) by a restriction enzyme Hin1II (N1aIII) to obtain a digestion product; and (4) carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis analysis on the digestion product prepared in step (3). The restriction enzyme is a common restriction enzyme, a simple and stable digestion mark is provided for screening two types of haplotype Q-shaped bemisia tabaci, at the same time an identification technology for the two types of haplotype Q-shaped bemisia tabaci is developed and established, and a foundation is established for future population dynamic identification and biology and invasion mechanism researches of the two types of haplotype Q-shaped bemisia tabaci.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
A method for extracting microbial total rna in forest soil and litter
The invention discloses a method for extracting microbial total RNA in forest soil and litter, which comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out freeze-drying on a forest soil or litter sample, grinding, and uniformly mixing; 2, adding pyrocarbonic acid diethyl ester treating water into the powdered sample, and standing over night at -70 DEG C; 3, adding glass beads, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide buffer, lauryl sodium sulfate, diatomite and phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol, and uniformly mixing; 4, severely shaking the mixed liquid, and centrifuging to obtain the supernate; 5, adding guanidinium isothiocyanate into the supernate, and centrifuging to obtain the supernate; 6, adding chloroform / isoamyl alcohol into the supernate, and centrifuging to obtain the supernate; 7, addingpolyethylene glycol 6000 into the supernate, standing, centrifuging, and removing the supernate; 8, washing, dissolving, and carrying out DNA enzyme digestion to obtain an RNA solution; and 9, detecting the integrality of the RNA through agarose gel electrophoresis, and using a nucleic acid protein determinator to detect the concentration and purity of the RNA. The RNA extracted by using the method has high yield, good integrality and better purity.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Specific primer sequence capable of being applied in method for identifying different fish, and DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecular marker method for identifying different fish
ActiveCN103589801AConservativeVariabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNAGel electrophoresis
The invention discloses a specific primer sequence capable of being applied in a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecular marker method for identifying different fish. The specific primer sequence comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer. The DNA molecular marker method for identifying different fish by using the specific primer sequence comprises the steps that a specific primer is designed according to a 5S rDNA genic conservative coding region sequence of the given fish; a genome of a fish material to be identified is extracted; a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system is designed by taking DNA of the genome as a template; a 5S rDNA gene of the system is amplified; a DNA segment mode of the sample 5S rDNA gene is obtained after PCR amplified reaction, agarose gel electrophoresis and DNA gel recovery kit purification by utilizing the polymorphyism of a nontranscribed spacer of the 5S rDNA gene; and finally the kind of the fish material to be identified is judged by comparing the DNA segment mode in gel imaging with the given fish. The method has the advantages that the method is rapid, accurate, and easy and simple to operate.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Quick extracting method for lotus rhizome tissue total RNA
InactiveCN1587405AQuality improvementHigh purityFermentationPlant genotype modificationTotal rnaUltraviolet
The quick extracting process of lotus rhizome tissue total RNA includes the steps of: compounding test chemical preparation and processing test articles; sampling tender leaf and leaf stalk; extracting, precipitating and centrifuging to obtain total RNA; identifying total RNA with ultraviolet spectrophotometer and formaldehyde denatured agarose gel electrophoresis detection. The obtained data and electrophoresis results show that the lotus rhizome tissue with complete total RNA has high purity and high yield. The present invention has simple test process, convenient and safe operation, accurate and effective result and high repeatability. The method is also suitable for the total RNA extraction of other plant tissue with rich polysaccharide and polyphenol.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
PCR-RFLP rapid detection method for common sturgeons
InactiveCN103436610AAccurate identificationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseSturgeon
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and taxonomy and discloses a PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) rapid detection method for common sturgeons as well as a primer and a kit for the rapid detection method. The PCR-RFLP rapid detection method for the common sturgeons comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a sample to be detected as a template; secondly, carrying out PCR amplification reaction to obtain a PCR product by taking the genome DNA as the template; thirdly, digesting the PCR product by using restriction endonuclease to obtain a digested product; fourthly, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection on the PCR product and the digested product and identifying species according to electrophoretogram. According to the PCR-RFLP rapid detection method disclosed by the invention, the simplicity in operation is realized; a small amount of fin rays or muscle is needed to be sheared on the basis of ensuring the survival of fingerling; the identification of fingerlings of the common sturgeons is quickly and accurately carried out; the accuracy and the reliability of the identification result are improved; the working efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:徐鹏
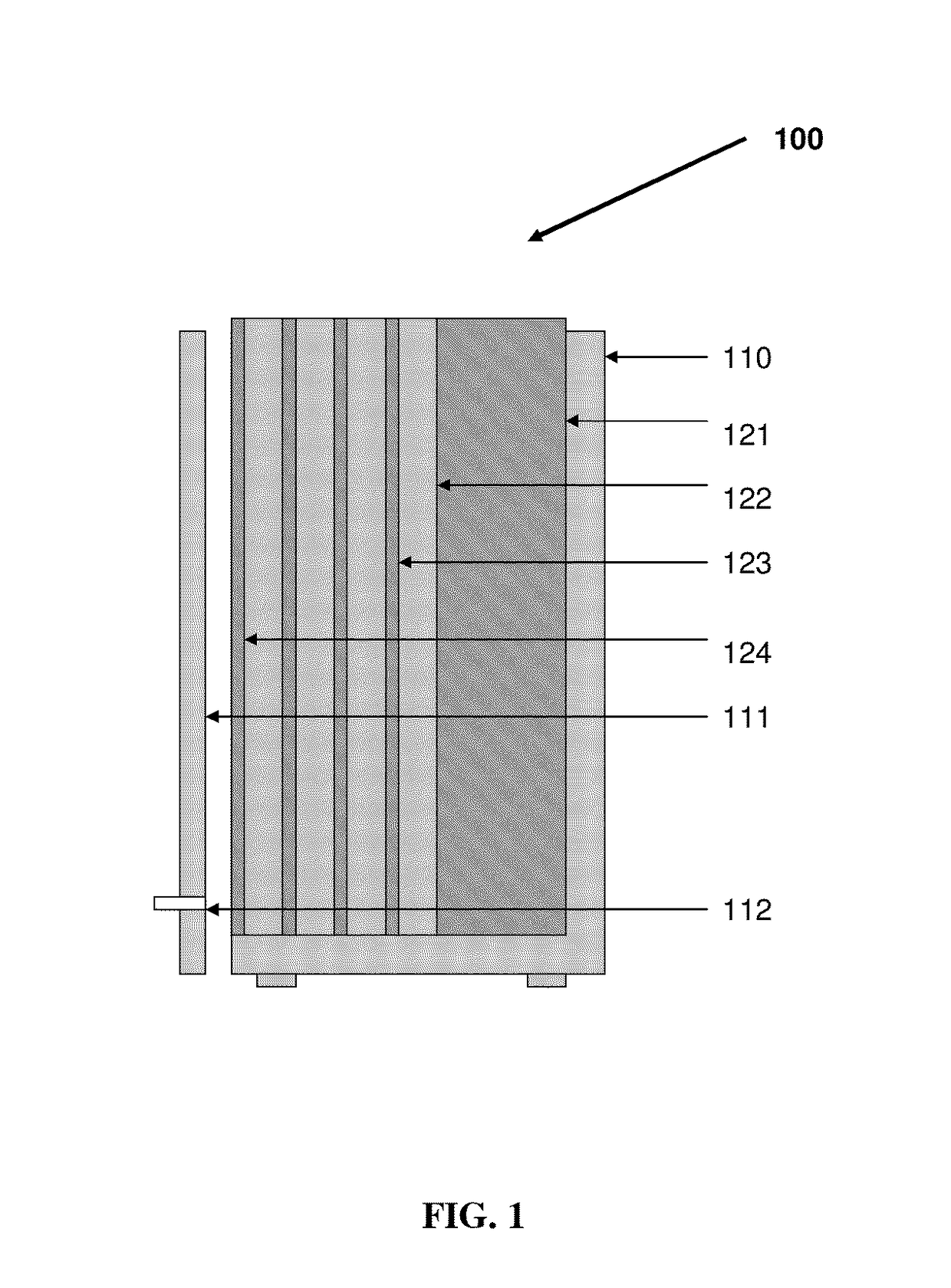
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS8470541B1Evaluating efficacyOptimize patient therapyElectrophoretic profilingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
PCR primer pair used for identifying genetic sex of Pseudobagrus ussuriensis, and rapid identification method thereof
InactiveCN106011300AAll-male parthenogenesisShorten breeding timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationZooidPhysiology
The invention discloses a PCR primer pair used for identifying the genetic sex of Pseudobagrus ussuriensis, and a rapid identification method thereof. The identification method comprises the steps of examined individual tissue drawing, genome DNA extraction, sex specific DNA fragment PCR amplification, agarose gel electrophoresis, ultraviolet light detection shooting and examined individual genetic sex determination. High-quality genome DNA is extracted through an optimized process, a sex specific DNA fragment is amplified, and the existence or not and the existence characteristic of the sex specific fragment are detected under ultraviolet lights, so the genetic constitution of Pseudobagrus ussuriensis is identified, and the genetic sex is discriminated in 1-2d. The PCR primer pair and the rapid identification method provide a rapid identification method for identifying sex reversal fish and super-male fish, provide technical support for breeding all-male fish, and have the advantages of breeding time shortening, great increase of the output, breeding cost reduction, and profound economic and social values.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Method for taking DNA as text information efficient storage medium
InactiveCN110427786AIncrease synthesis costRaise the cost of sequencingDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionChinese charactersA-DNA
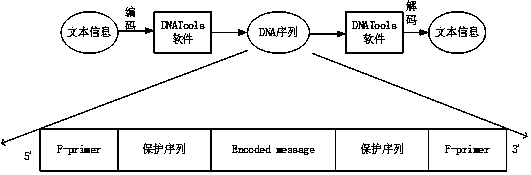
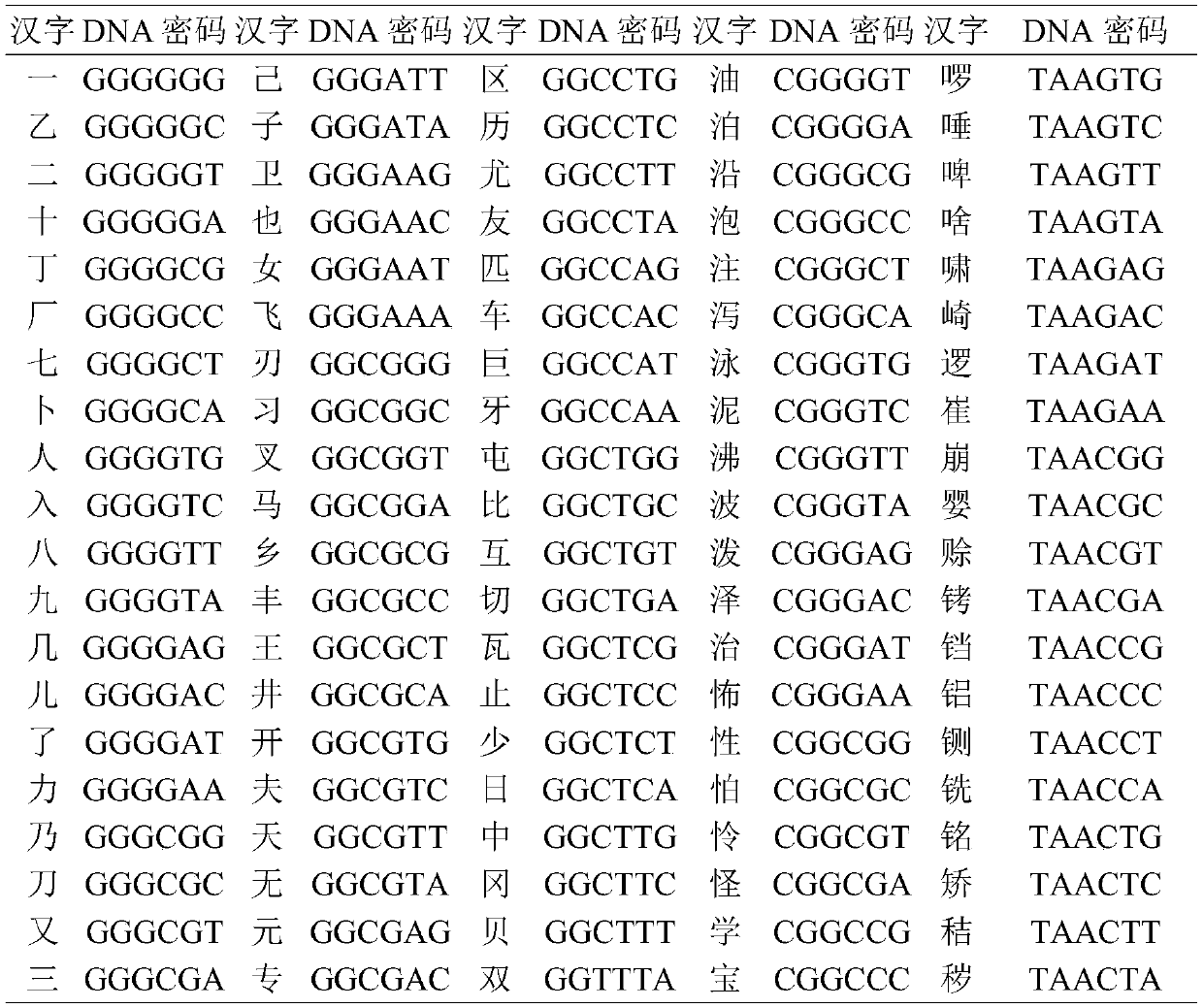
The invention provides a method for taking DNA as an efficient text information storage medium, which is used for storing text information and is beneficial to culture protection. The method for taking DNA as a text information efficient storage medium comprises a storage process and a decoding process. The storage process comprises the following steps: establishing an information sequence, dividing text content into a plurality of storage units, and converting each storage unit into a DNA sequence by utilizing DNA tool software, thereby converting the whole text into a plurality of DNA sequences; adding 20bp protection sequences to the two ends of the information sequence respectively; adding primer binding regions at two ends of the protection sequence. The decoding process comprises thefollowing steps: culturing bacteria, extracting plasmids, carrying out polymerase chain reaction to obtain an amplification product, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis and imaging identification on the amplification product, sequencing the amplification product by using a Sanger sequencing method, and reducing the DNA sequence obtained by sequencing into a Chinese character text by using DNATools software.
Owner:西藏自治区人民政府驻成都办事处医院
Molecular detection method for desulfovibro
ActiveCN105112543ADetection time is shortEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationElectrophoresisVolumetric Mass Density
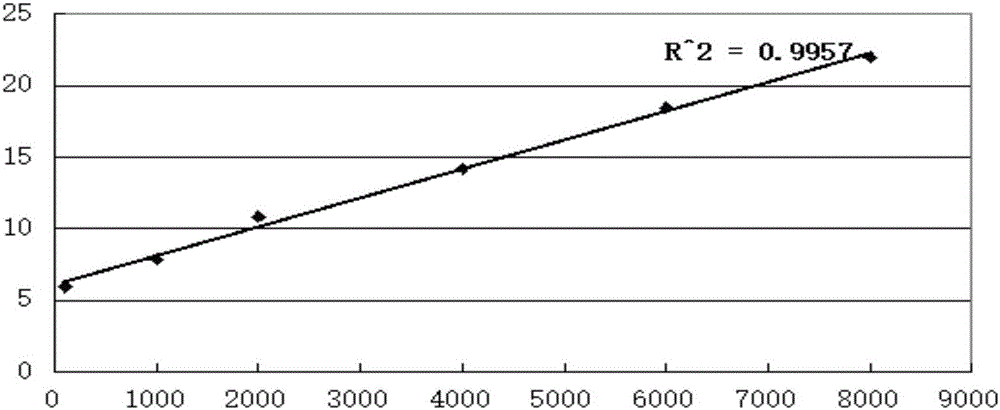
The invention discloses a molecular detection method for desulfovibro. The nucleotide sequences of the specific primer pair adopted by the detect method are SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a standard curve and a linear equation for quantitative detection of desulfovibro; (2) pretreating a sample; (3) taking the pre-treated sample as a mold plate, establishing a PCR reaction system by utilizing the primer pair, and carrying out PCR amplification; (4) carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection; (5) analyzing the electrophoresis result by utilizing a gel imaging system to obtain a relative strip density value, and quantitatively determining the concentration of the desulfovibro by looking up the standard curve and the linear equation. The quantitative molecular detection method has the advantages that the time consumption is low; the operation is simple; the sensitivity is high; the test charge is low; the detection effect is broad-spectrum; desulfovibro in various samples can be quantitatively detected.
Owner:北京世纪金道石油技术开发有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com