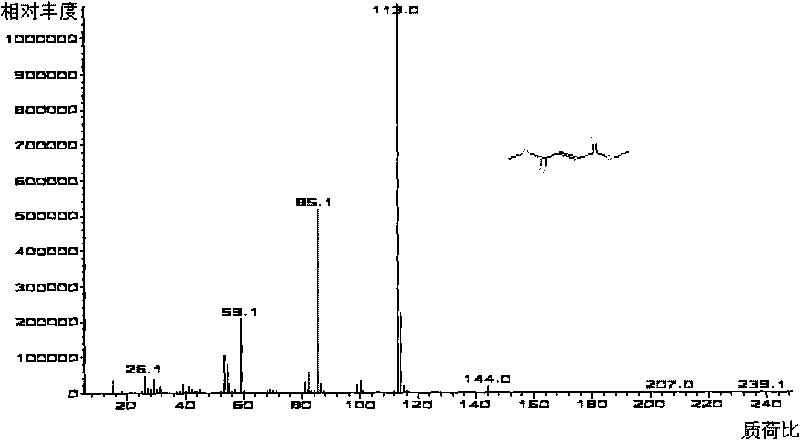
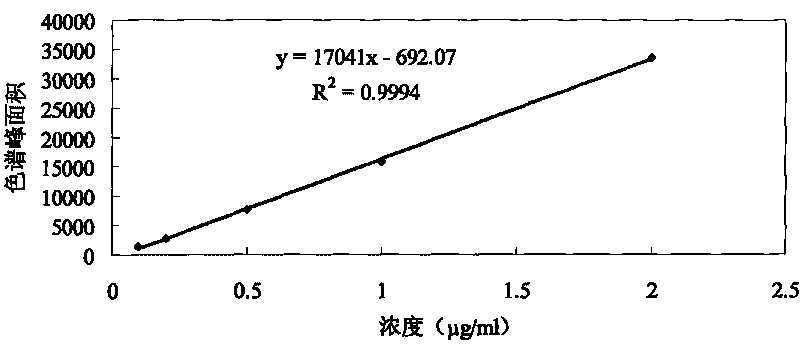
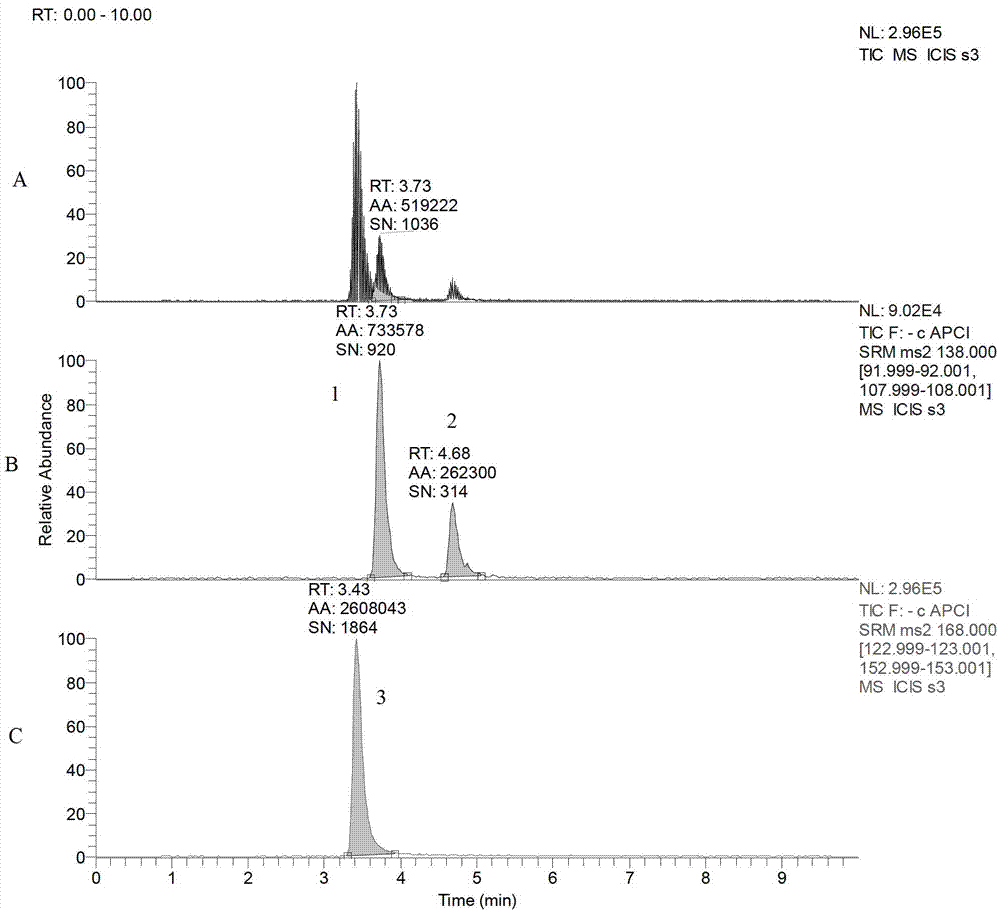
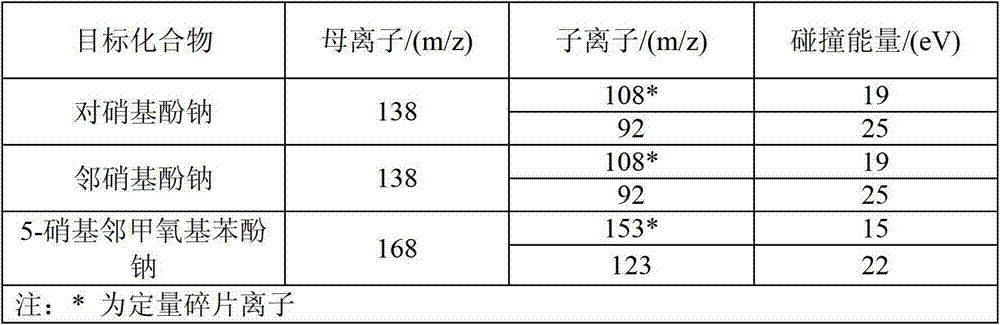
Patents
Literature
414results about How to "Qualitatively accurate" patented technology
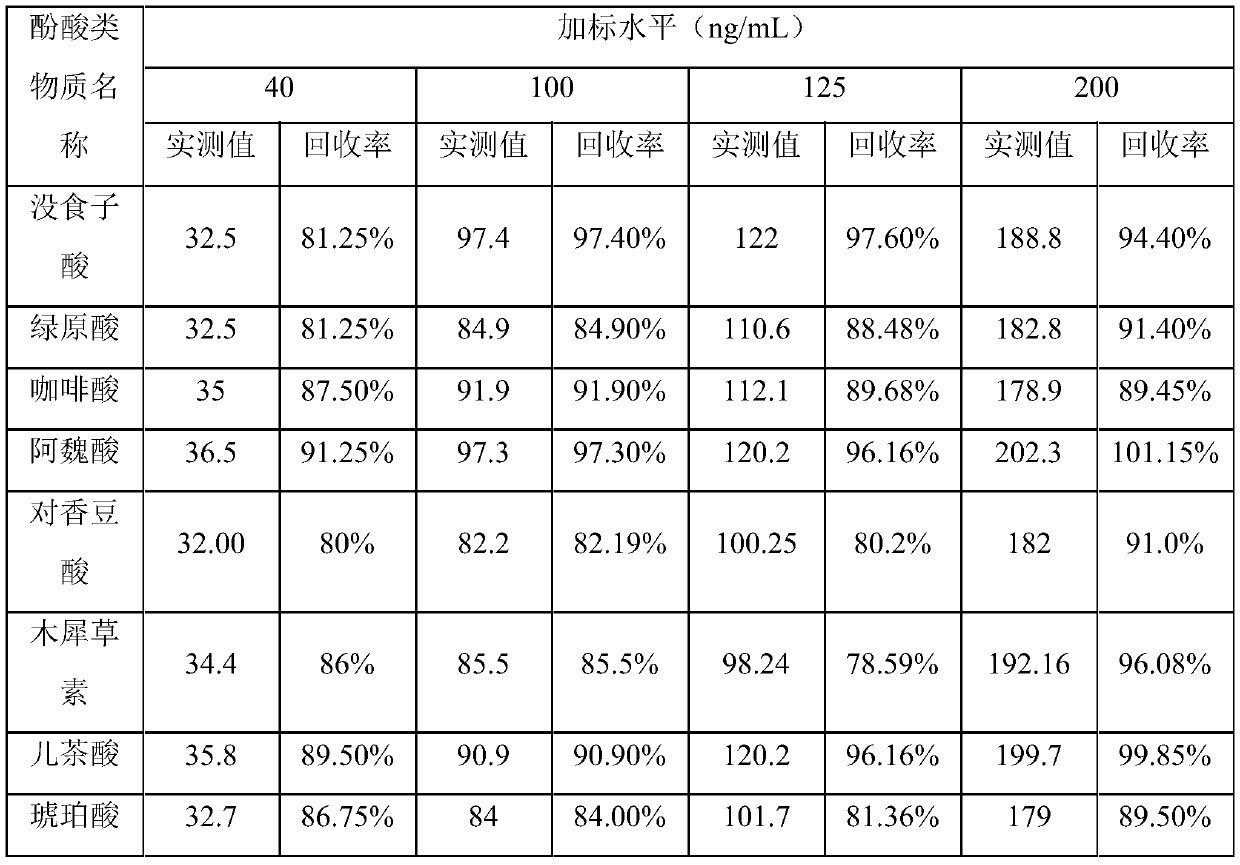
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
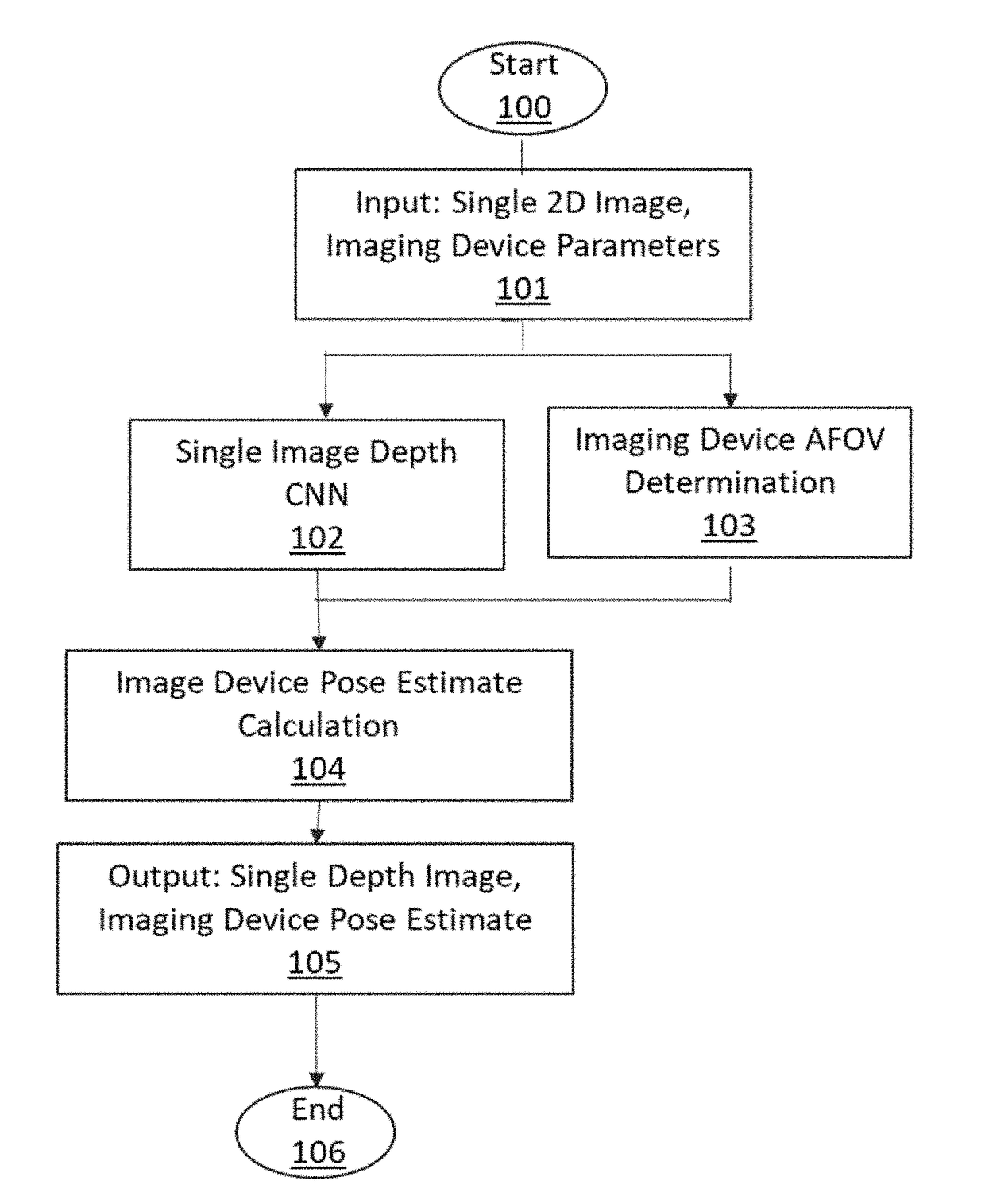
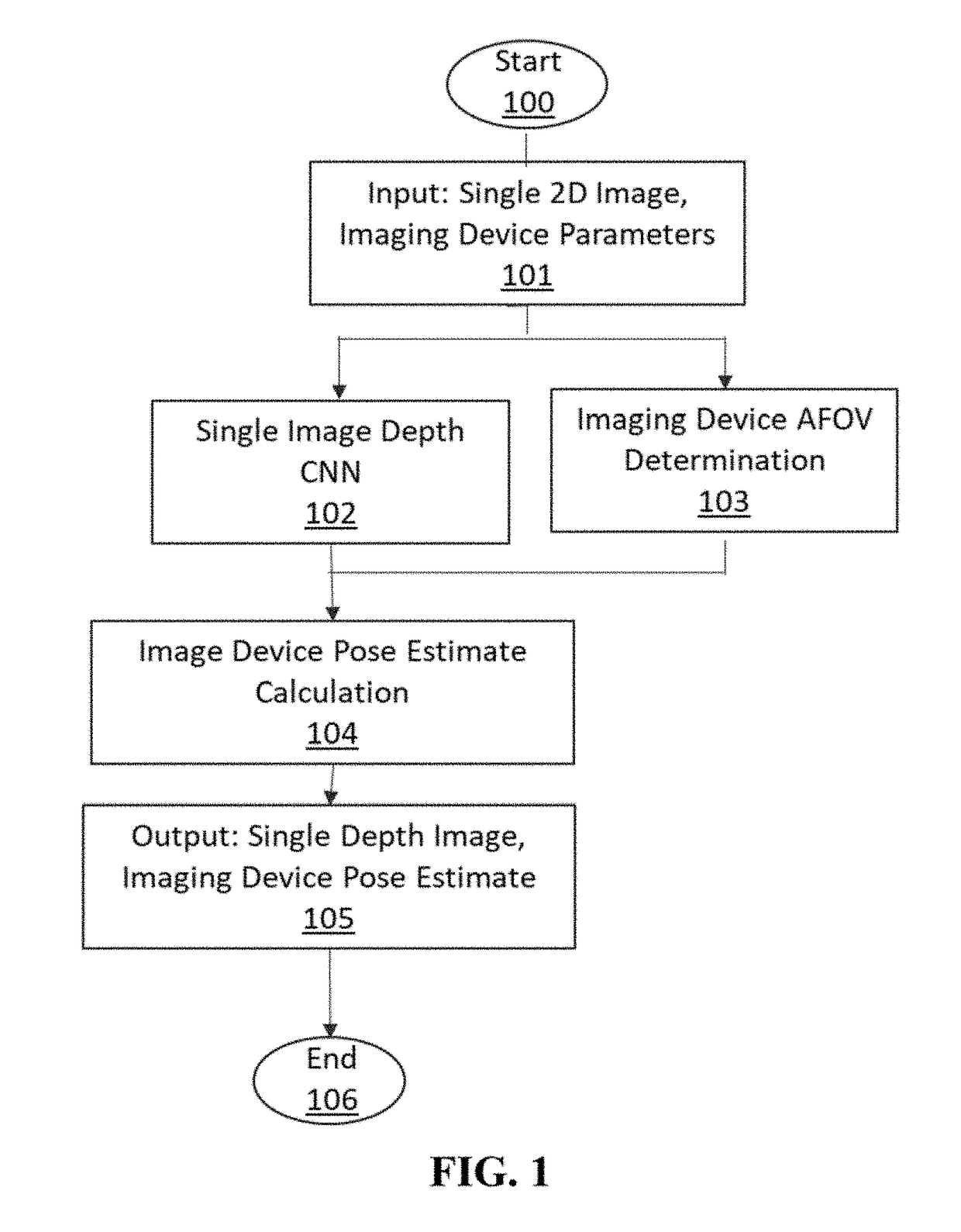
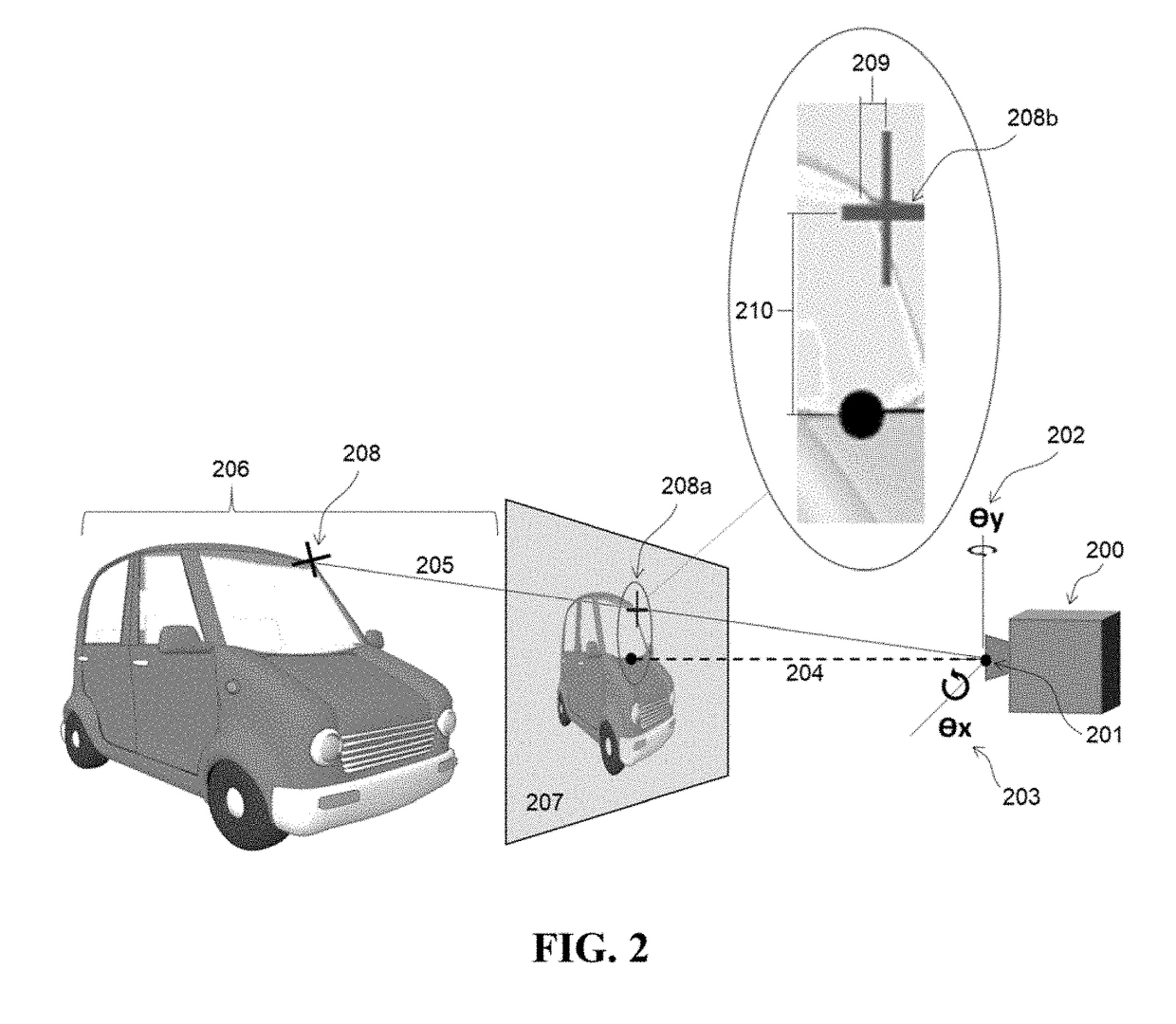
Machine learning based model localization system
ActiveUS20180189974A1Improve refinementEfficient reconstructionImage enhancementImage analysisImage sensor3d image
A method for deriving an image sensor's 3D pose estimate from a 2D scene image input includes at least one Machine Learning algorithm trained a priori to generate a 3D depth map estimate from the 2D image input, which is used in conjunction with physical attributes of the source imaging device to make an accurate estimate of the imaging device 3D location and orientation relative to the 3D content of the imaged scene. The system may optionally employ additional Machine Learning algorithms to recognize objects within the scene to further infer contextual information about the scene, such as the image sensor pose estimate relative to the floor plane or the gravity vector. The resultant refined imaging device localization data can be applied to static (picture) or dynamic (video), 2D or 3D images, and is useful in many applications, most specifically for the purposes of improving the realism and accuracy of primarily static, but also dynamic Augmented Reality (AR) applications.
Owner:MANOR FINANCIAL INC
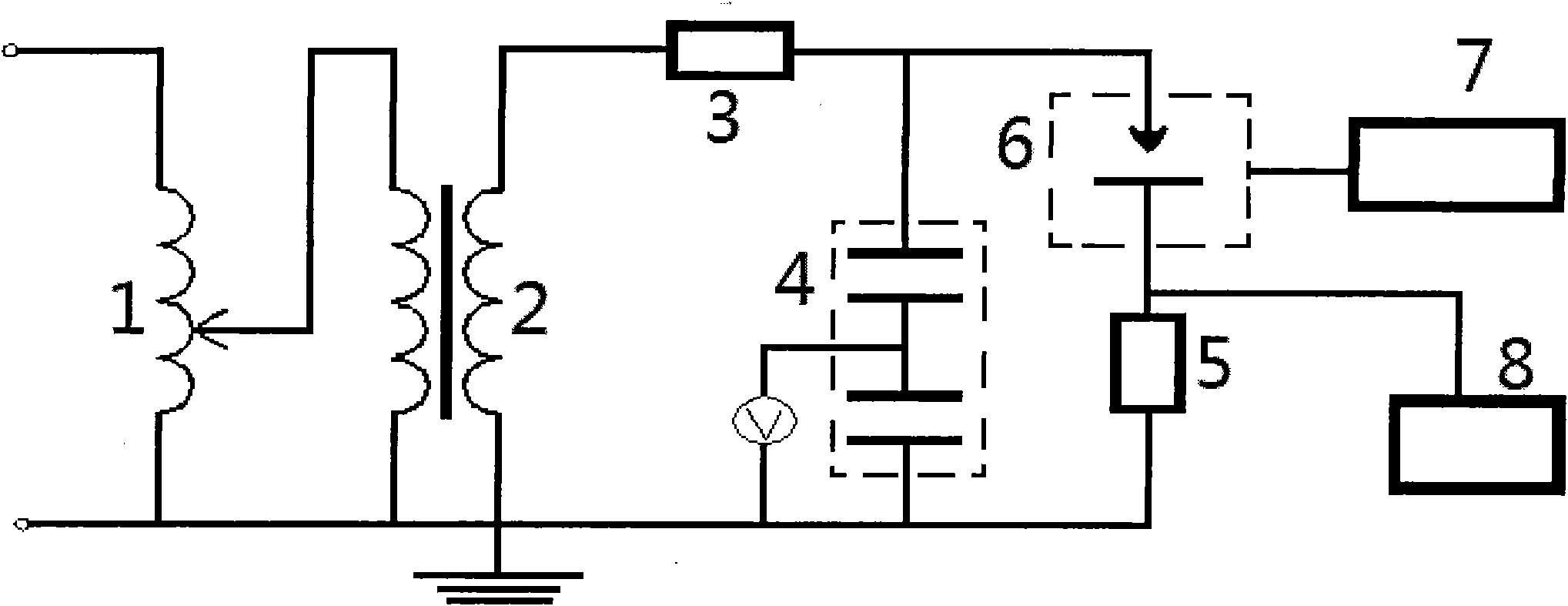
Infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy detection device and method for decomposed components of sulfur hexafluoride under partial discharge
InactiveCN101982759AQualitatively accurateAccurate quantitative analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsAnti jammingSulfur hexafluoride
The invention relates to an infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy detection device and method for decomposed components of sulfur hexafluoride under partial discharge, belonging to the technical field of partial discharge on-line monitoring of SF6 gas insulating electrical equipment. The device of the invention mainly comprises an induction voltage regulator, a corona free experimental transformer, a partial discharge free protective resistor, a standard capacitive voltage divider, a non-inductive resistor, a GIS analog element, a wide-frequency high-speed ultrahigh-capacity digital storage oscillograph and an infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy system. In the method of the invention, infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy detection is carried out on the decomposed gas of SF6 under partial discharge in the GIS analog element by the device of the invention. The invention has high sensitivity, little gas consumption, multiple detection components and strong anti-jamming capability, can effectively detect SF6, CF4, SO2F2, SOF2, SO2, HF and the like as low as 0.01 muL / L, and is suitable for on-line detection. The invention can be widely used for detection of partial discharge decomposed gas of SF6 in the SF6 gas insulating electrical equipment, especially the GIS equipment.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
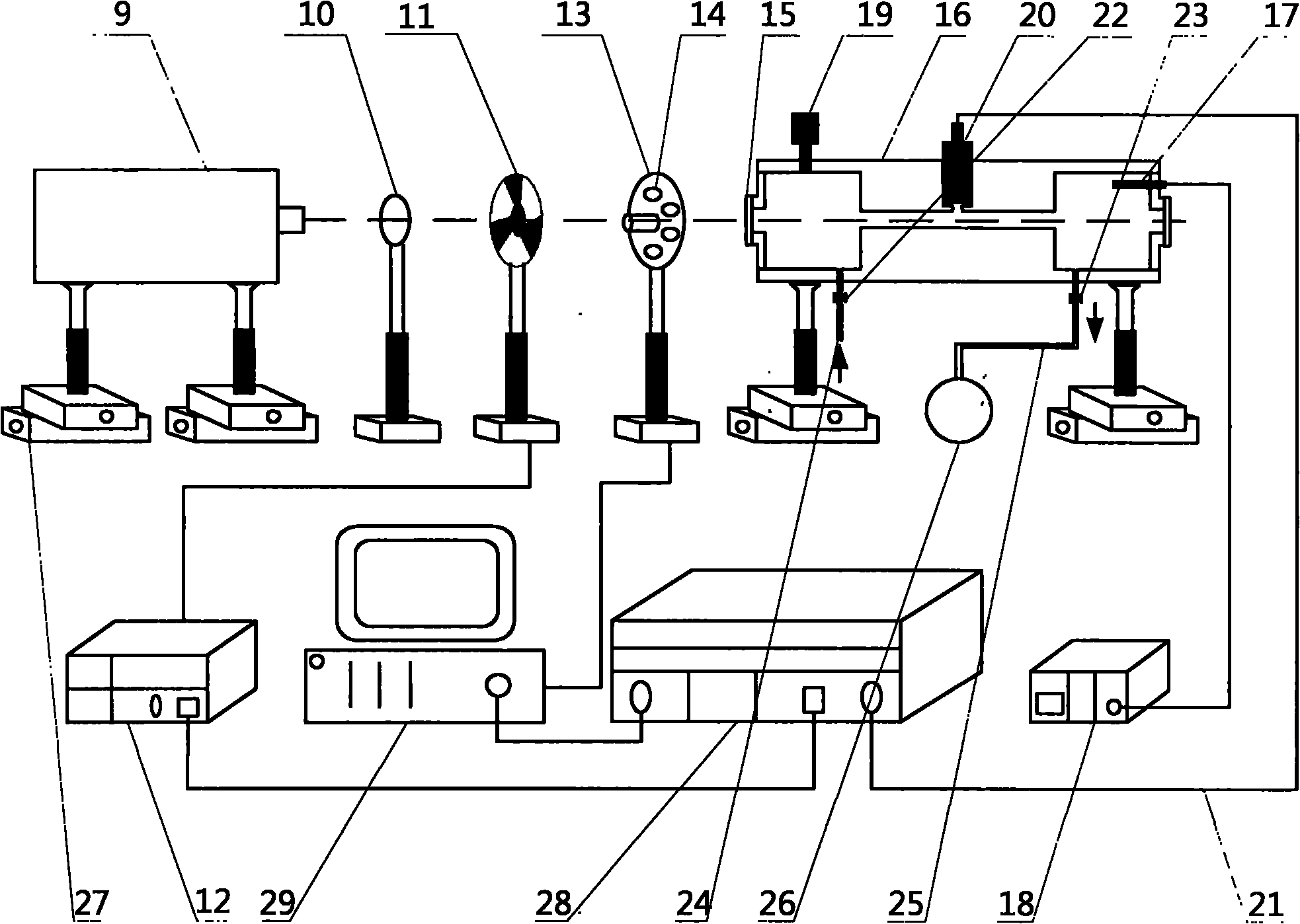
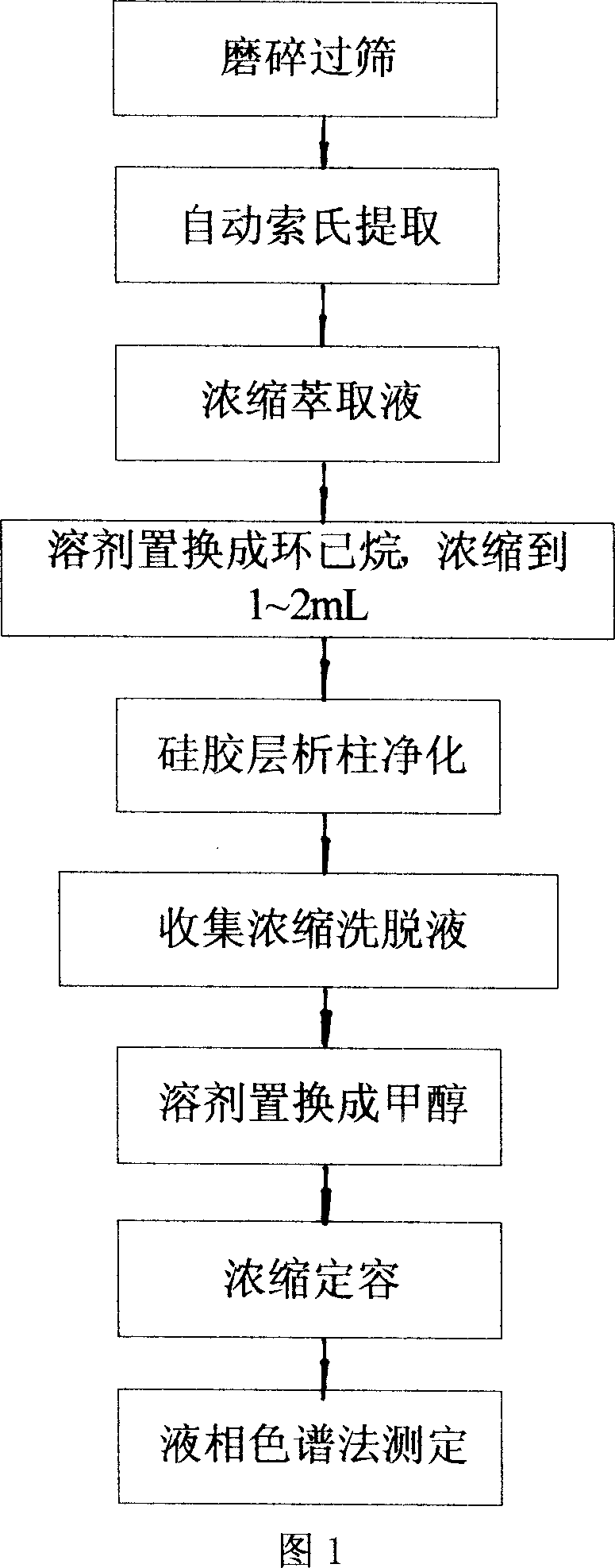
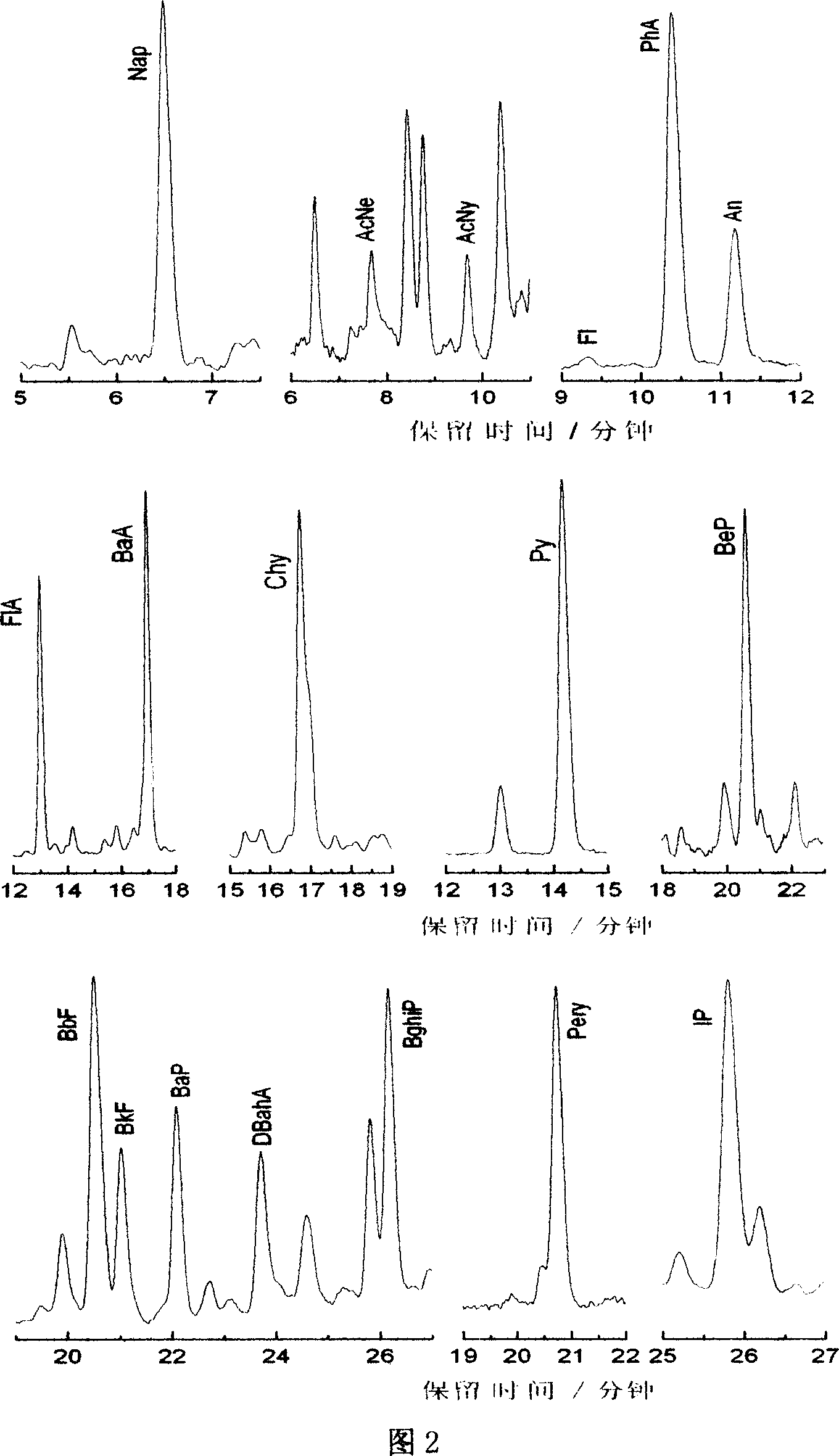
Extraction purifying measuring method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil
InactiveCN101013114AReduce generationReduce extraction timeComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationSilica gelSolvent
The PAHs extraction purification determination method in the soil relates to 18 trace PAHs analysis and determination method in the soil. Using automatic Soxhlet extraction instrument to extract PAHs organic in the soil samples, and then using silica gel column chromatography to purify the extracted liquid, remove the polar and non-polar interference during extraction, and finally, using HPLC (with diode array detector) to analyze qualitatively and quantitatively 18 PAHs. In this invention, the extraction solvent consumption is small, and it can be used for large volume sample extraction, with quick sample analysis speed, low-cost sample pretreatment, and for the 5 group 13 isomers in 18 PAHs, it can not only accurately qualitatively but also accurately quantitatively determine, with low detection limit, high sensitivity, and with the exception of fluorine and perylene, the detection limit of the other 16 PAHs all below 10ng / g-dw. It is a rapid, sensitive and accurate analytical method for the trace PAHs, applied to farmland, wasteland, urban green belt and other soil.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Automatic constant temperature type photoacoustic detection device for SF6 decomposed components and experiment method thereof
InactiveCN102519904AEfficient detectionQualitatively accurateMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateHollow article cleaningThermodynamicsMonitoring system
The invention which relates to an automatic constant temperature type photoacoustic detection device for SF6 decomposed components and an experiment method thereof belongs to the technical field of SF6 gas insulation device partial discharge online monitoring. The device is characterized in that an automatic constant temperature system is arranged in present infrared photoacoustic spectrum monitoring systems; and according to the method, the device is utilized to detect the SF6 gas partial discharge decomposed components in a GIS (gas insulated substation) simulation element under automatic preset temperature constancy conditions. According to the invention, the influence of external environment can be eliminated, the gas components of SO2, CO2, CF4, SO2F2, SOF2 and the like with the concentrations of low to 0.01muL / L can be effectively detected, the accuracy, the detection precision and the stability are high, and performances of a solid state relay are stable, so the long-term effective working of the automatic constant temperature system can be guaranteed. The device which can be widely applied to the field of the SF6 gas insulation equipment partial discharge online monitoring is especially suitable for detecting the SF6 gas partial discharge decomposed components in the GIS.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Magnetic fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography quantitative detection method
The invention discloses a magnetic fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography quantitative detection method. In the method, respective excellent characteristics of magnetic nano particles and quantum dots are fully utilized, and an immunochromatography technology is combined to realize fluorescent quantitative detection on the basis of optimizing the structure and ingredients of a test strip. The method has a function of amplifying signals; and compared with the conventional colloidal gold immunochromatography method, the method has the advantages of high mark stability, low non-specificity, high sensitivity, wide linear range and accurate quantification. The invention provides a simple, accurate, specific and cheap detection tool for blood samples, urine samples, spittle, excrement and the like, so the method can be widely applied to the fields of medical technology, food safety, veterinary drug residues, environmental monitoring, drug detection and the like.
Owner:BEIJING KANGMEI TIANHONG BIOTECH
Method for detecting concentration of nine compound coloring agents in auxiliary materials for reconstituted tobacco
InactiveCN105403630AQualitatively accurateQuantitatively accurateComponent separationSpectrum analyzerSunset yellow
The invention relates to a method for detecting concentration of nine compound coloring agents in auxiliary materials for reconstituted tobacco. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a mixture mother liquor of nine compound coloring agents, namely, lemon yellow, amaranth, indigo blue, carmine, sunset yellow, allura red, brilliant blue, acid red and erythrosine, and a sample solution; preparing a standard operation solution; and adopting a liquid chromatogram-series triple quadrupole spectrum analyzer for analyzing and detecting the concentration of the nine compound coloring agents in the sample solution. The method provided by the invention is accurate and reliable, is high in sensitivity and is very suitable for the analysis for the nine compound coloring agents in the auxiliary materials for the complex matrix reconstituted tobacco.
Owner:YUNNAN REASCEND TOBACCO TECH GRP +1
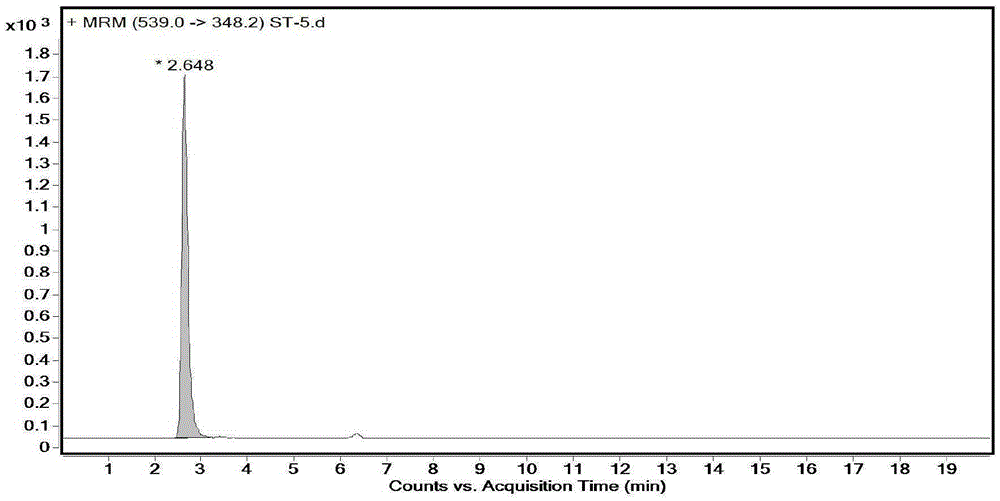
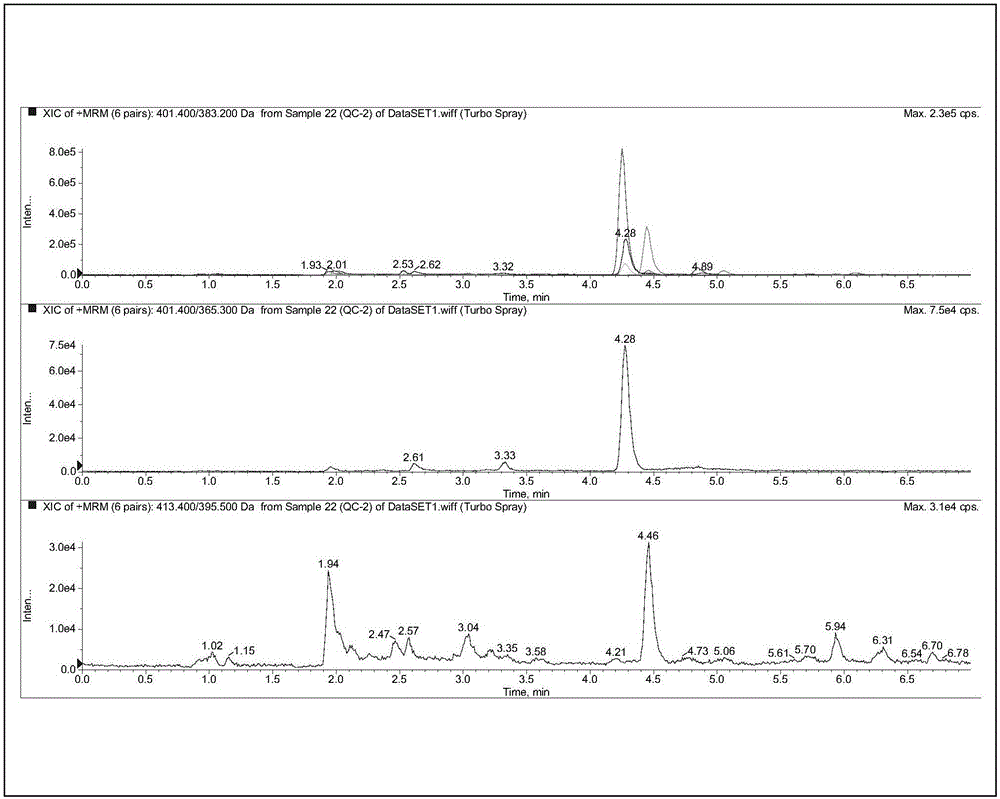
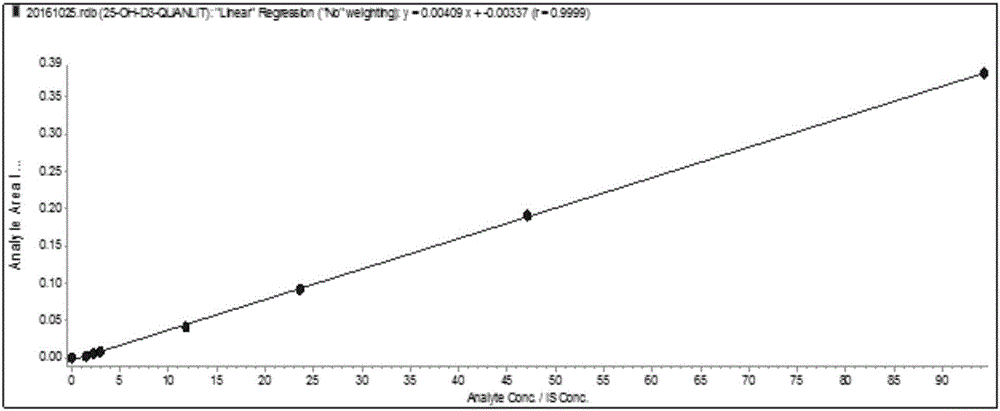
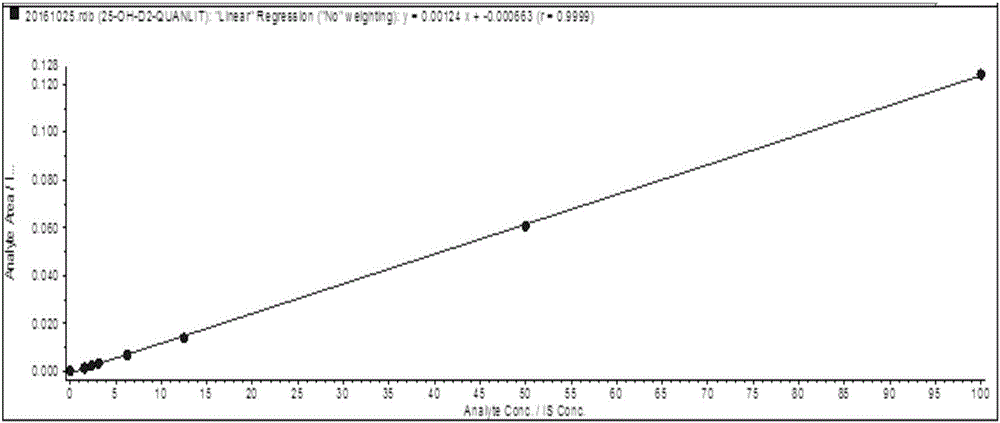
Method for detection of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in serum
ActiveCN106526026AHigh detection throughputEasy to handleComponent separationInterference resistanceSerum samples
The invention relates to a method for detection of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in serum. The method comprises sample pretreatment: adding an acetonitrile solution containing a 25-hydroxyvitamin D internal standard substance into a serum sample, carrying out protein precipitation, carrying out centrifugation, taking the supernatant and diluting the supernatant through acetonitrile to obtain a sample to be detected, wherein a volume ratio of the serum sample to the acetonitrile solution is 1: 1-4 and a volume ratio of the supernatant to acetonitrile is 1: 1-4, and enrichment, separation and detection: carrying out enrichment, separation and detection on the sample to be detected through a two-dimensional liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer. The method is simple, greatly shortens the detection time, improves the detection flux of the sample and has a high detection precision, a low cost, specificity and strong matrix interference resistance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIOHOP TECH INC
Analytical processing method and device of medical image data
InactiveCN104750951AGet clearGet quicklyImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionTemporal information
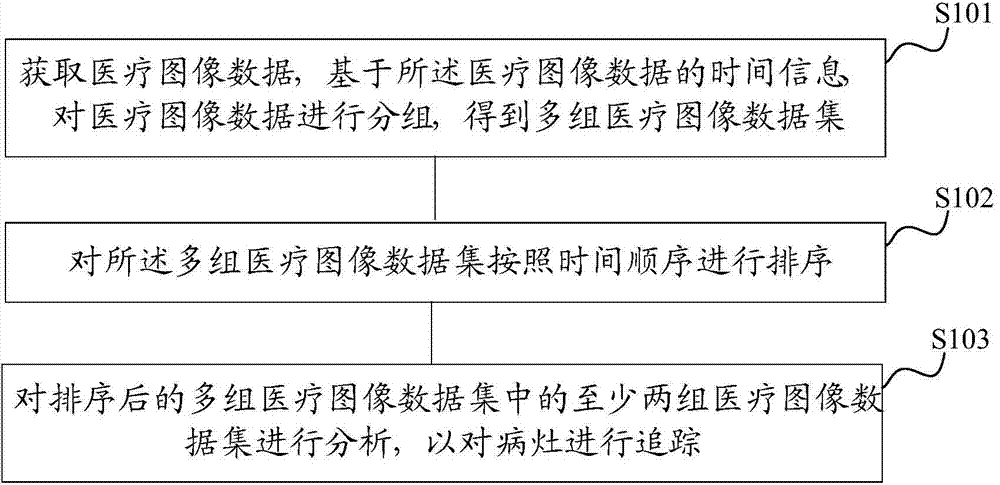
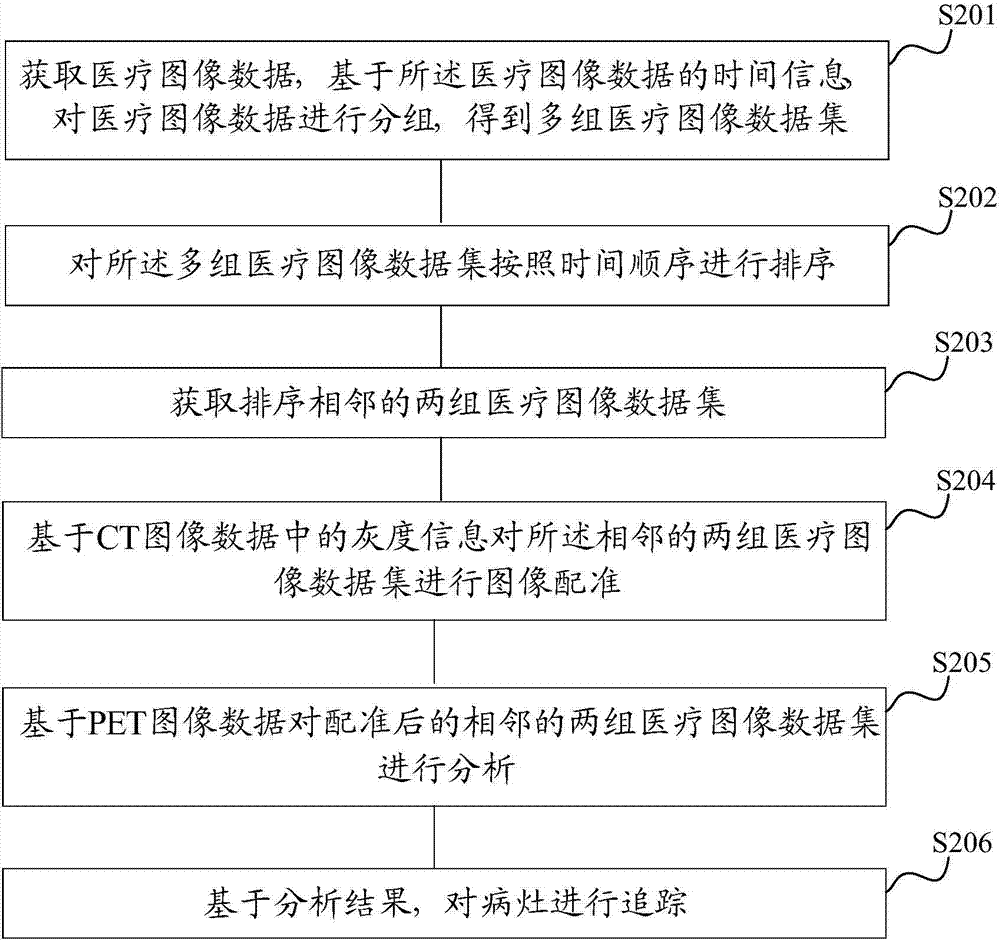
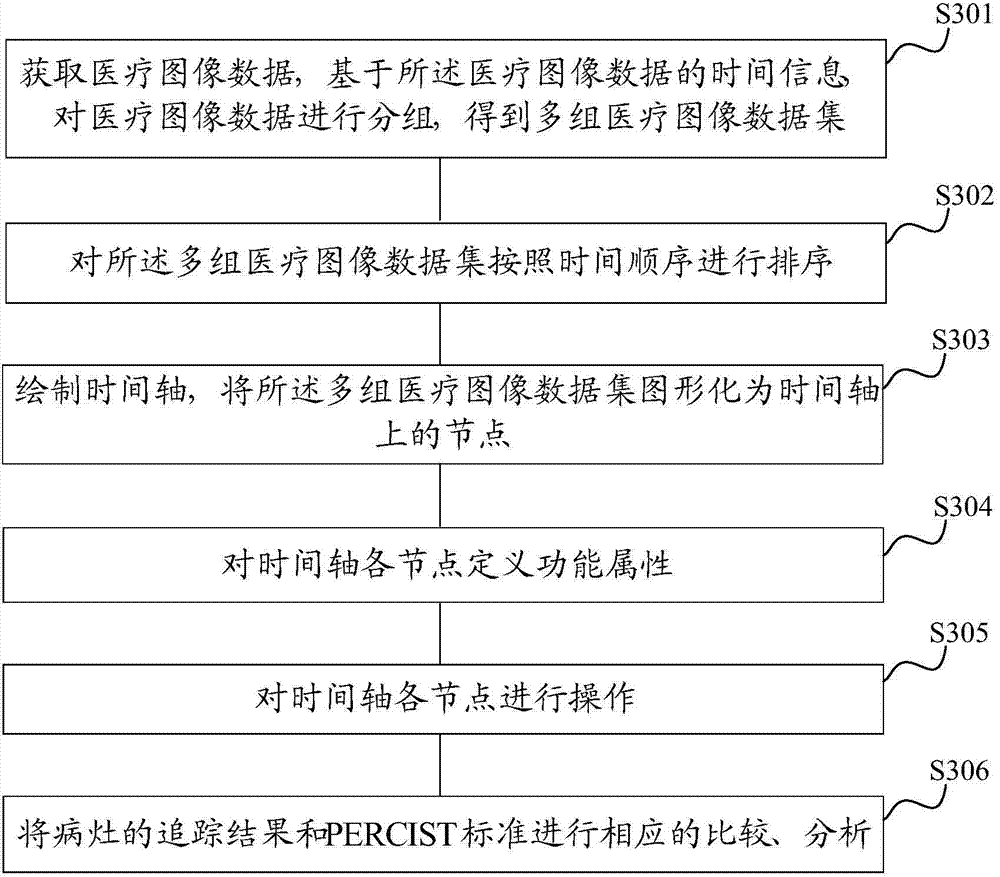
The invention discloses an analytical processing method and device of medical image data. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining medical image data, and grouping the medical image data on the basis of the time information of the medical image data to obtain multiple groups of medical image data sets, wherein the same group of medical image data set owns the same time information; sorting the multiple groups of medical image data sets according to a time sequence; and analyzing at least two groups of medical image data sets in multiple groups of sorted medical image data sets to trace focuses. The method can effectively process the medical image data at multiple time points, so that the complex medical image data can be mutually related, doctors can clearly, quickly and conveniently obtain the mutually-related medical image data so as to conveniently check, compare and analyze multiple groups of medical image data at different time points, and finally, the focuses can be accurately traced on the basis of an analysis result.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Railway roadbed geological radar defect map analysis method and device
ActiveCN107748392AUnable to resolveResolve accuracyDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionNon destructiveRadar
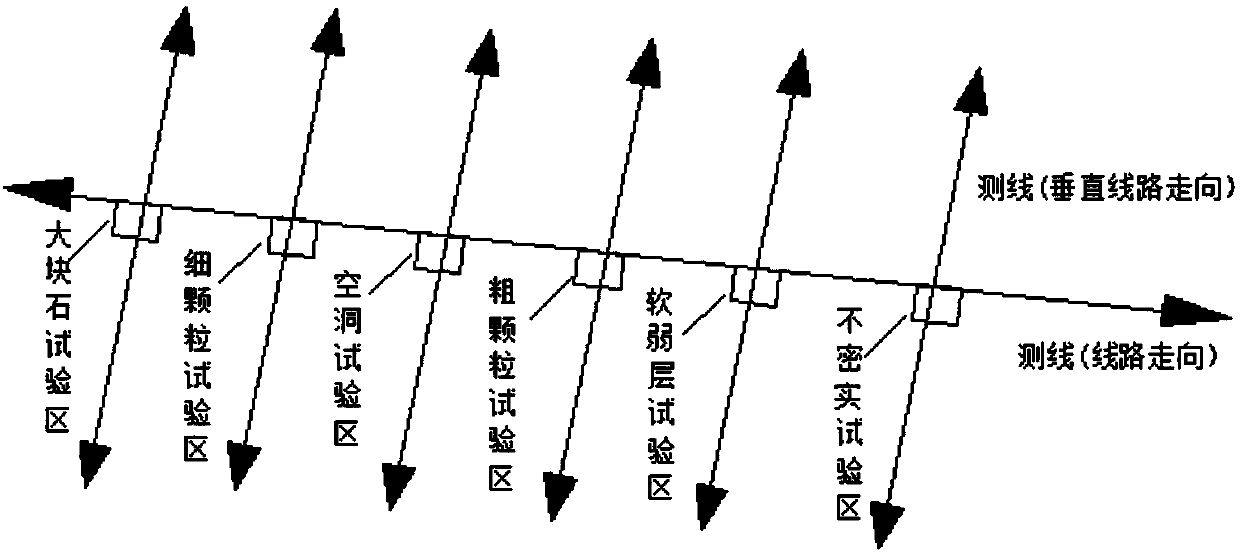
The invention relates to the technical field of railway engineering detection, and provides a railway roadbed geological radar defect map analysis method and device in allusion to problems existing inthe prior art. The railway roadbed geological radar defect map analysis method comprises the steps of forming forward modeling on geological radar electromagnetic waves, preliminarily establishing aroadbed defect map, analyzing feature laws of the simulated defect map in various types of geological radar images, and forming a railway roadbed simulated geological radar typical defect map featurelibrary; setting a typical roadbed defect test area, and performing field testing by using geological radar nondestructive testing equipment, and respectively generating profile grayscale maps or waveform maps of a compaction area and the roadbed typical defect test area correspondingly; and performing comparative analysis on the generated profile grayscale maps or waveform maps of the compactionarea and the roadbed defect test area according to the simulated geological radar typical defect map feature library, and summarizing a railway roadbed actual measurement geological radar typical defect map feature library; and performing rapid non-destructive detection and defect judgment on the actual railway roadbed according to the geological radar typical defect map feature library.
Owner:CONSTR COMPANY OF CHINA RAILWAY NO 8 ENGNEERING GRP
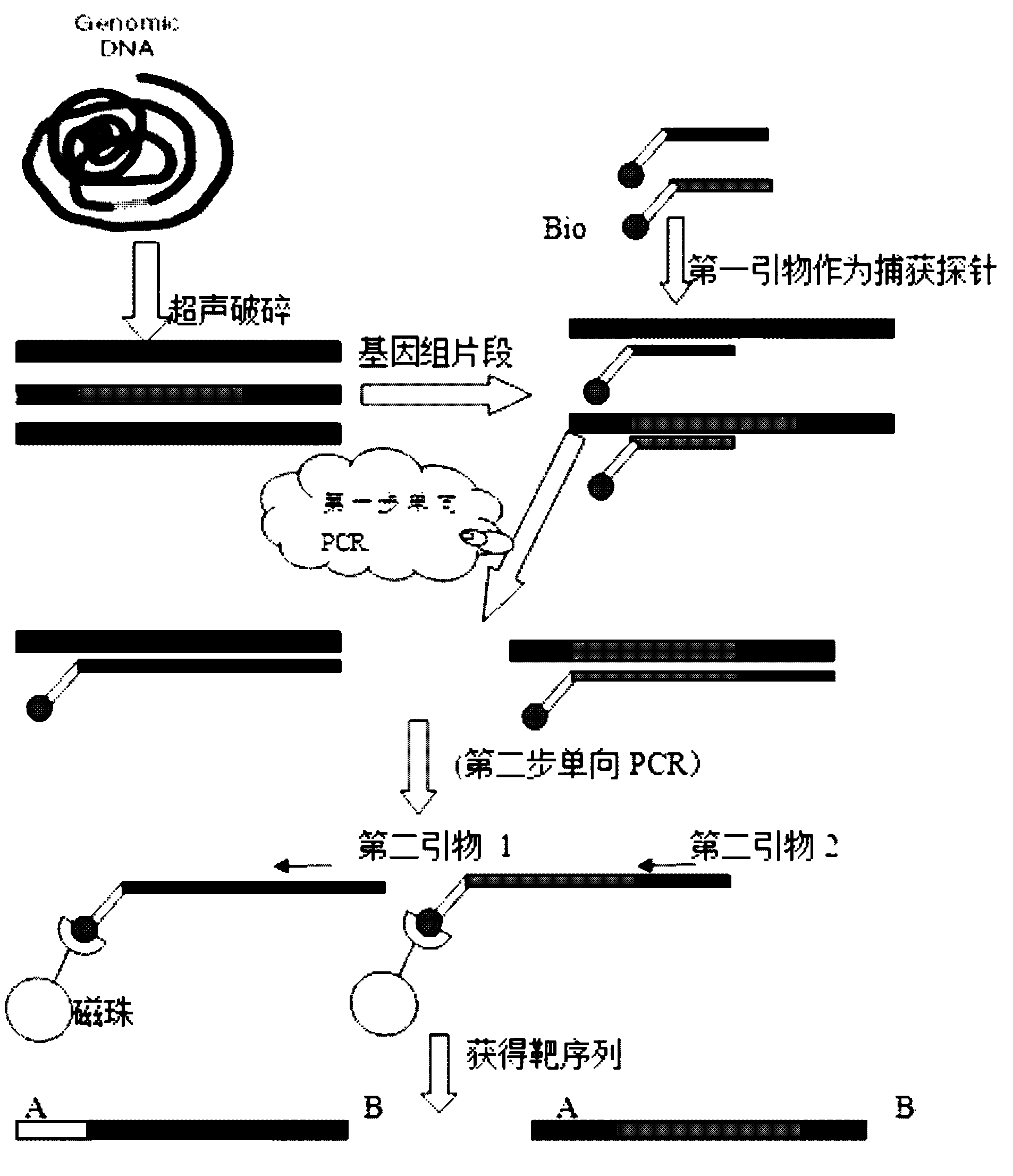
Method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting nucleic acid based on high-flux sequencing technology
ActiveCN102628082AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseHigh flux
The invention discloses a method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting nucleic acid based on a high-flux sequencing technology. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a single-chain DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) library with a method for capturing a specific nucleic acid target through multi-gene multi-region two-step and one-direction amplification; sequencing the obtained single-chain DNA library based on a high-flux sequencing technology; and qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing nucleic acid according to a sequencing result to obtain a qualitative and quantitative detection result of nucleic acid. Compared with an ordinary real-time Q-PCR (Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) quantifying method, the method has the advantages of lower cost, wider application, increase in the quantifying sample flux of nucleic acid and capability of accurately qualifying and quantifying the series of nucleic acids.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD
Method for screening pesticide and veterinary drugs in infant formula food by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole static electric field track ion trap mass spectrum
The invention discloses a method for screening pesticide and veterinary drugs in infant formula food by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole static electric field track ion trap mass spectrum, and belongs to the technical field of food safety inspection. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a sample by an optimized QuEChERS method; screening by applying ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole static electric field track ion trap mass spectrum; selecting a positive ion or negative ion mode for scanning by adopting full-scan / data dependence acquisition, full-scan / variable data independence acquisition and full-scanning / full-ionic acquisition fragmentation acquisition scan modes to obtain complete primary and secondary maps; and processing the primary and secondary maps by applying Exact Finder 2.5 software to extract compound information. According to the method, information in the established spectrum library is compared with the screening result of a to-be inspected object so as to ensure the composition of pesticide and veterinary drugs in an infant formula food. The mass spectrum instrument used in the method has the main advantages of high resolution ratio, accurate qualitative and quantitative results, high sensitivity, high quality precision and the like. The method can be applied to analysis of complex substrates.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for simultaneously detecting multiple anti-tumor drugs in blood sample
InactiveCN110927297AEasy to handleImprove throughputComponent separationBusulfanTandem mass spectrometry
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting multiple anti-tumor drugs in a blood sample. A pretreated sample to be detected is detected by adopting ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS / MS). The pretreatment process comprises the following steps: adding serum into a mixed solution of methanol and acetonitrile, oscillating and centrifuging,taking out the centrifuged supernatant, drying, dissolving the dried powder into a methanol aqueous solution, and filtering to obtain a sample to be detected. The method can be used for simultaneously detecting 13 kinds of anti-tumor drugs such as methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil, apatinib, busulfan, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, docetaxel, gemcitabine, imatinib, illinotecan, lenalidomide, oxaliplatin, paclitaxel and the like in blood.
Owner:JINAN YING SHENG BIOTECH
Method for synchronously detecting six sweetening agents in distilled spirit by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer
ActiveCN104634895AQualitatively accurateQuantitatively accurateComponent separationLinear relationshipQuadrupole
The invention discloses a method for synchronously detecting six sweetening agents (namely acesulfame, saccharin sodium, sodium cyclamate, aspartame, trichlorosucrose and neotame) in a distilled spirit by using an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer. The method comprises the following steps: performing nitrogen blowing on a wine sample to remove alcohol, separating the wine sample by using an ultra-high performance liquid chromatograph, and then performing multi-reaction ion monitoring mode detection by using a triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer. The six sweetening agents have good linear relationships in a range of 50-1000ng / mL, correlation coefficients r2 of the six sweetening agents are more than 0.993, the average recovery rate of the sample is 90-120%, and the limit of detection is 2.69-5.16ng / mL. The method disclosed by the invention is accurate, reliable, simple and fast, and can be used for synchronously detecting the six sweetening agents in the distilled spirit.
Owner:ANHUI GUJING DISTILLERY +1
Method suitable for simultaneously detecting 9 N-nitrosamines in food contact rubber products
InactiveCN104076106AQualitatively accurateQuantitatively accurateComponent separationNitrosoN-nitrosamine
The invention discloses a method suitable for simultaneously detecting 9 N-nitrosamines in food contact rubber products. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a sample to be tested to establish a migration system to obtain a migration extract; utilizing the migration extract to prepare a sample solution to be tested to obtain a supernatant / filtrate; preparing 9 N-nitrosamines into a standard solution to further prepare a standard working solution with the gradient of 0.01-0.40 [mu]g / mL; injecting the gradient standard solution and the supernatant / filtrate into a liquid Chromatogram-tandem mass spectrograph, and testing the cation multi-reaction monitoring model to finally obtain the respective contents of 9 N-nitrosamines in the sample to be tested. The 9 N-nitrosamines are N-Nitrosodimethylamine, N-Nitroso-ethyl methylamine, N-Nitrosomorpholine, N-Nitrosopiperidine, N-Nitrosopyrrolidine, N-Nitroso-diethylamine, N-Nitrosodibutylamine, N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine and N-Nitroso-diphenylamine.
Owner:THE INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT ZHEJIANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for utilizing ultra-effective bonded phase chromatography to serially connect QDa while quickly detecting seven biogenic amines in white spirit
ActiveCN105866302AEasy to useEasy to operateComponent separationTesting beveragesBiogenic amineChromatography column
The invention discloses a method for utilizing an ultra-effective bonded phase chromatography to serially connect QDa while quickly detecting seven biogenic amines in white spirit and belongs to the technical field of detection. The method is characterized by the following steps: after extracting a to-be-detected wine sample with acetonitrile, taking BEH C18 bonded phase chromatographic column as a separating column and carbon dioxide (A)+ isopropanol (B) as flowing phase for performing gradient eluting, and adopting a QDa mass spectrometry detector for detecting after separating the sample through the ultra-effective bonded phase chromatography (UPC2). The method provided by the invention is simple, quick, accurate, reliable and applicable to the simultaneous detection for the contents of seven biogenic amines (histamine, putrescine, cadaverine, phenylethylamine, spermidine, tyramine and octopamine) in white spirit.
Owner:ANHUI GUJING DISTILLERY +1
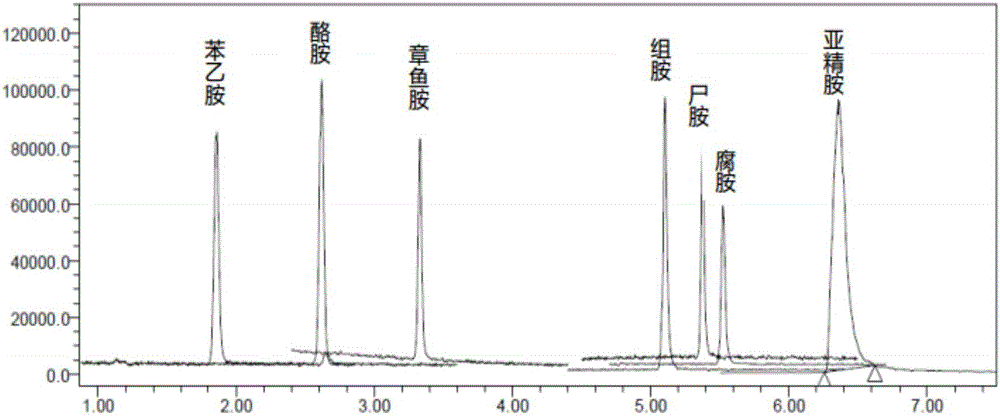
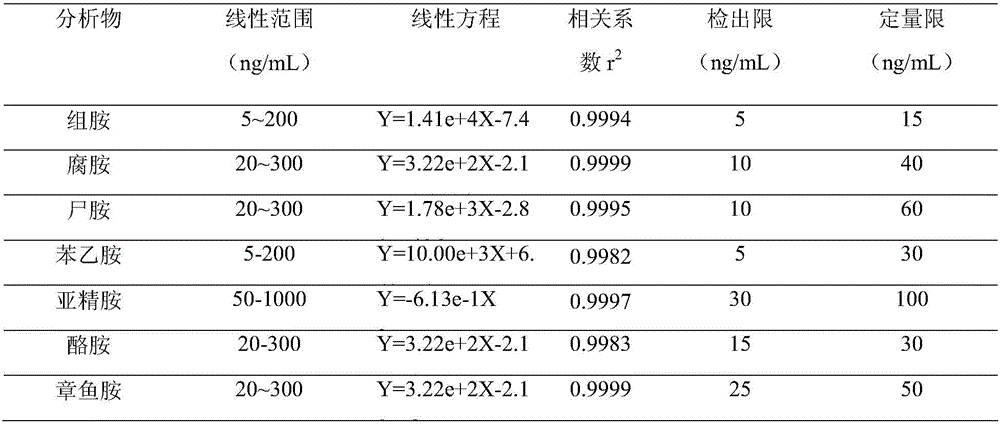
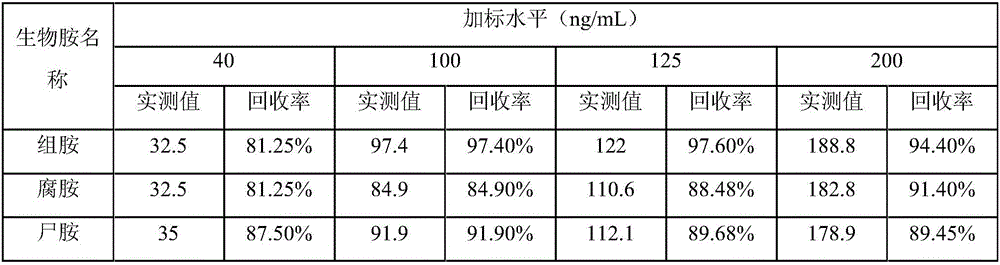
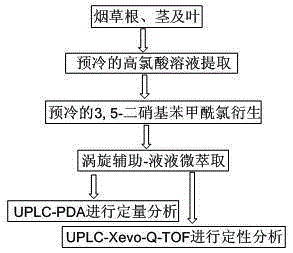
Detection method of polyamine substances in tobacco roots, stems and leaves
ActiveCN105424823AIncrease relative volatilityQualitatively accurateComponent separationNicotiana tabacumFractional factorial design
The invention discloses a detection method of polyamine substances in tobacco roots, stems and leaves. The method comprises the steps that vortex extraction is conducted on tobaccos to obtain polyamines through a pre-cooled perchloric acid solution, derivatization is conducted through 3,5-dinitro benzoyl chloride, extraction and concentration are conducted on a derivative product through vortex auxiliary-liquid-liquid microextraction, and detection is conducted through an ultra-efficient liquid chromatography-photodiode array detector. In addition, in order to obtain the best enrichment factors and the recovery rate in vortex auxiliary-liquid-liquid microextraction, method optimization is conducted through fractional factorial design and Doehlert design. Compared with other methods of analyzing and detecting the polyamines, the detection method of the polyamine substances in the tobacco roots, stems and leaves has the advantages of being rapid in derivative reaction, stable in product, high in sensitivity, good in reproducibility, green and friendly to environment and the like, and accurate qualitativeness and quantification can be conducted on the polyamines in the tobacco roots, stems and leaves. In addition, other four kinds of polyamines, namely, tyramine, 1,3-propylene diamine, high spermidine and canavalmine are identified through high-resolution mass spectrometry, wherein the canavalmine is found in the tobaccos for the first time.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Method for detecting related substances of ibuprofen and its sodium salt and preparation
The invention provides a method for detecting related substances of ibuprofen or its sodium salt and preparation. The related substances comprise impurities A, B, C, D, E and F. The method comprises (1) preparation of a test sample solution: taking an appropriate amount of ibuprofen or ibuprofen sodium raw materials, putting the materials into a certain volume of a container, dissolving the materials, diluting the solution until a desired volume marked by a scale, shaking the solution, and filtering the solution to obtain a certain concentration of the test sample solution, and (2) sample detection: pouring the test sample solution into a chromatographic instrument, and acquiring a chromatogram map of the related substances separated effectively under chromatographic conditions of use of a chromatographic column containing octadecyl silane chemically bonded silica as a filler having size of 250*4.6mm and pore sizes of 5 micrometers and having a column temperature of 20 to 40 DEG C, use of a mobile phase having a volume ratio of organic phase acetonitrile to a water phase phosphoric acid aqueous solution of 32% to 48% and phosphoric acid content of 0.01 to 0.1% in the phosphoric acid aqueous solution, a flowing rate of 1.0 to 2.3 ml / min, and a detection wavelength of 205 to 225nm. The method can realize effective separation of a variety of impurities.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Mass spectrum qualitative and quantitative analysis method for free fatty acids based on double-derivatization technology
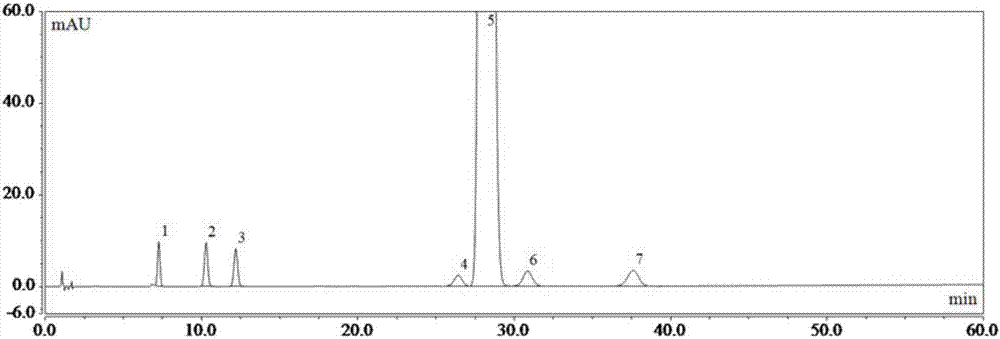
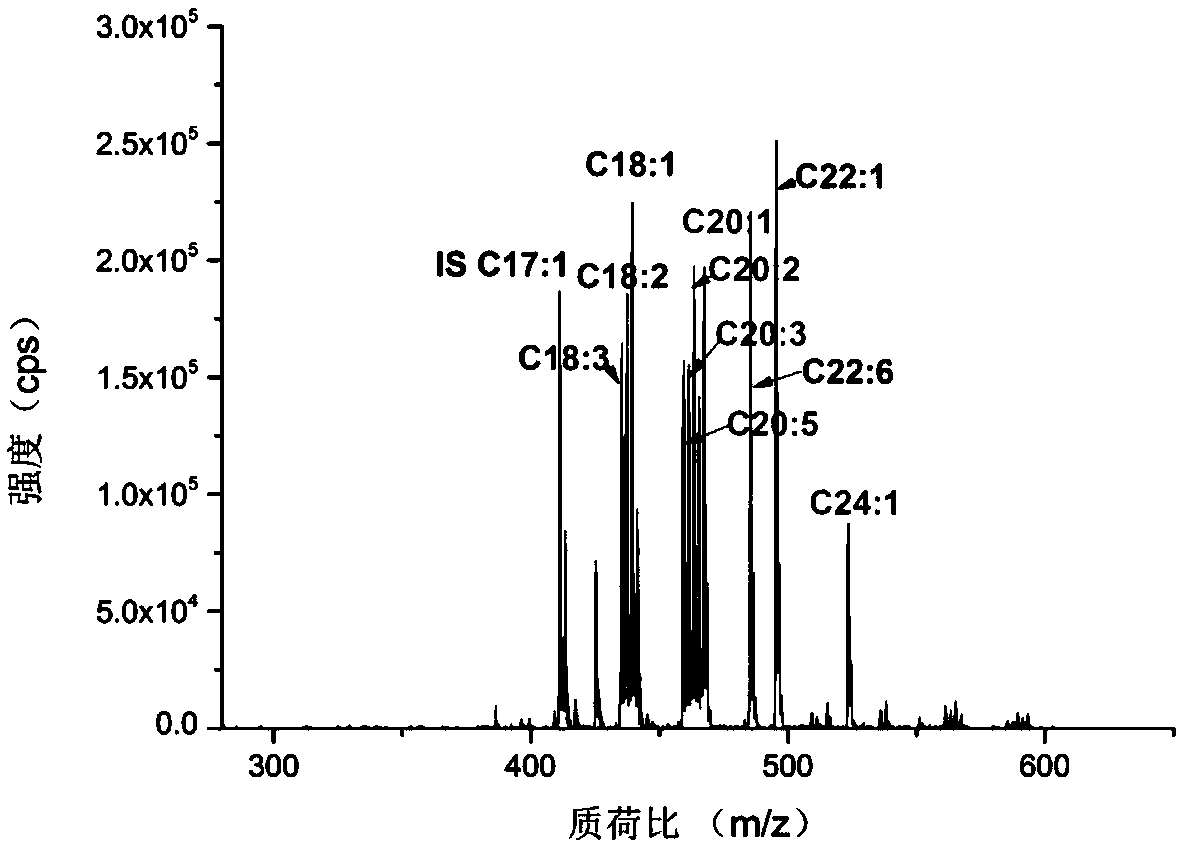
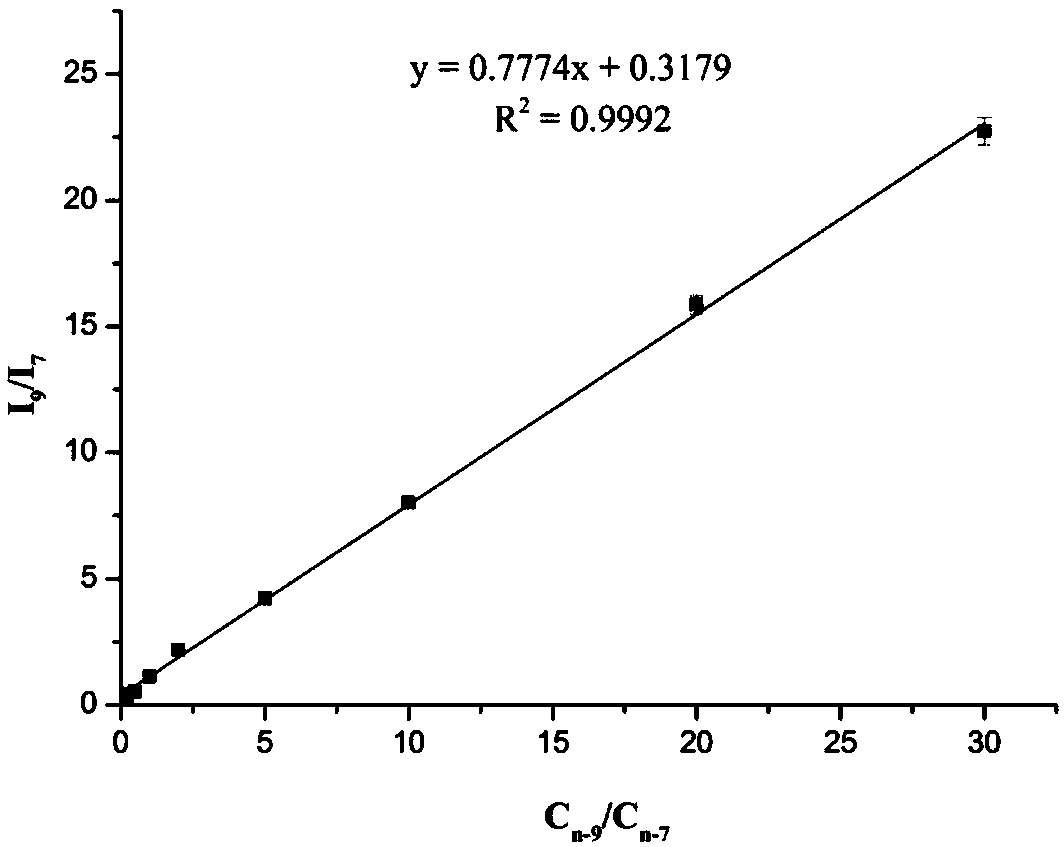
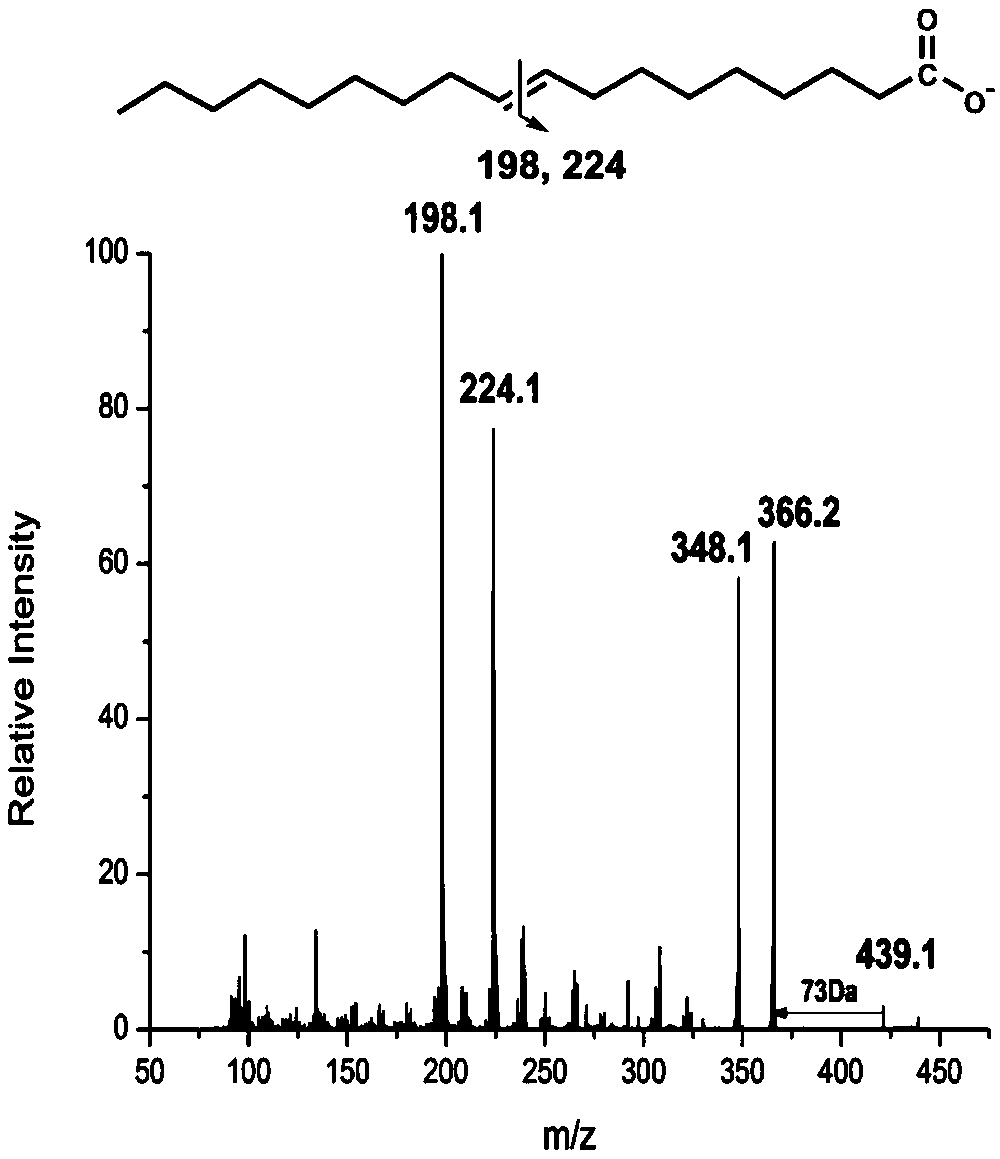
ActiveCN109374723AQualitatively accurateAccurate quantitative analysisPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDouble bondDerivatization
The invention relates to a mass spectrum qualitative and quantitative analysis method for free fatty acids based on a double-derivatization technology. The mass spectrum qualitative and quantitative analysis method comprises the following steps: 1) a photochemical derivatization reaction of double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids; 2) an N,N-diethylethylenediamine derivatization reaction of carboxyl terminals of the fatty acids; 3) a qualitative method for precise structures of the fatty acids; and 4) a quantitative method for the fatty acids. The method disclosed the invention is used for precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of the free fatty acids in actual samples, so that the problems that double-bond positions of the unsaturated fatty acids, particularly polyunsaturated fattyacids, are difficult to authenticate and the fatty acids are low in ionization efficiency and poor in detection sensitivity under a negative ion mode are solved, and high-sensitivity and accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis for the free fatty acids in the actual samples is realized.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
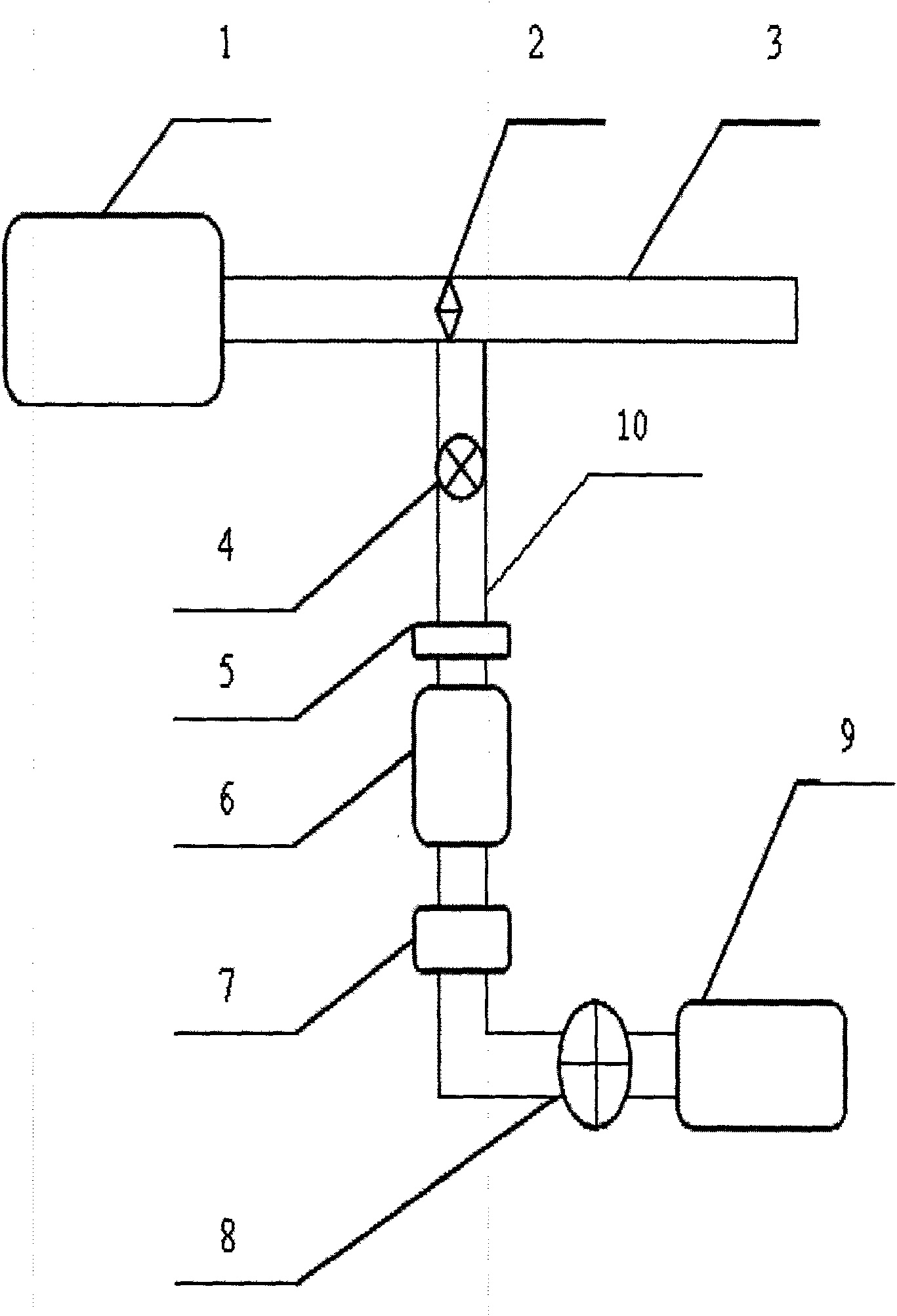
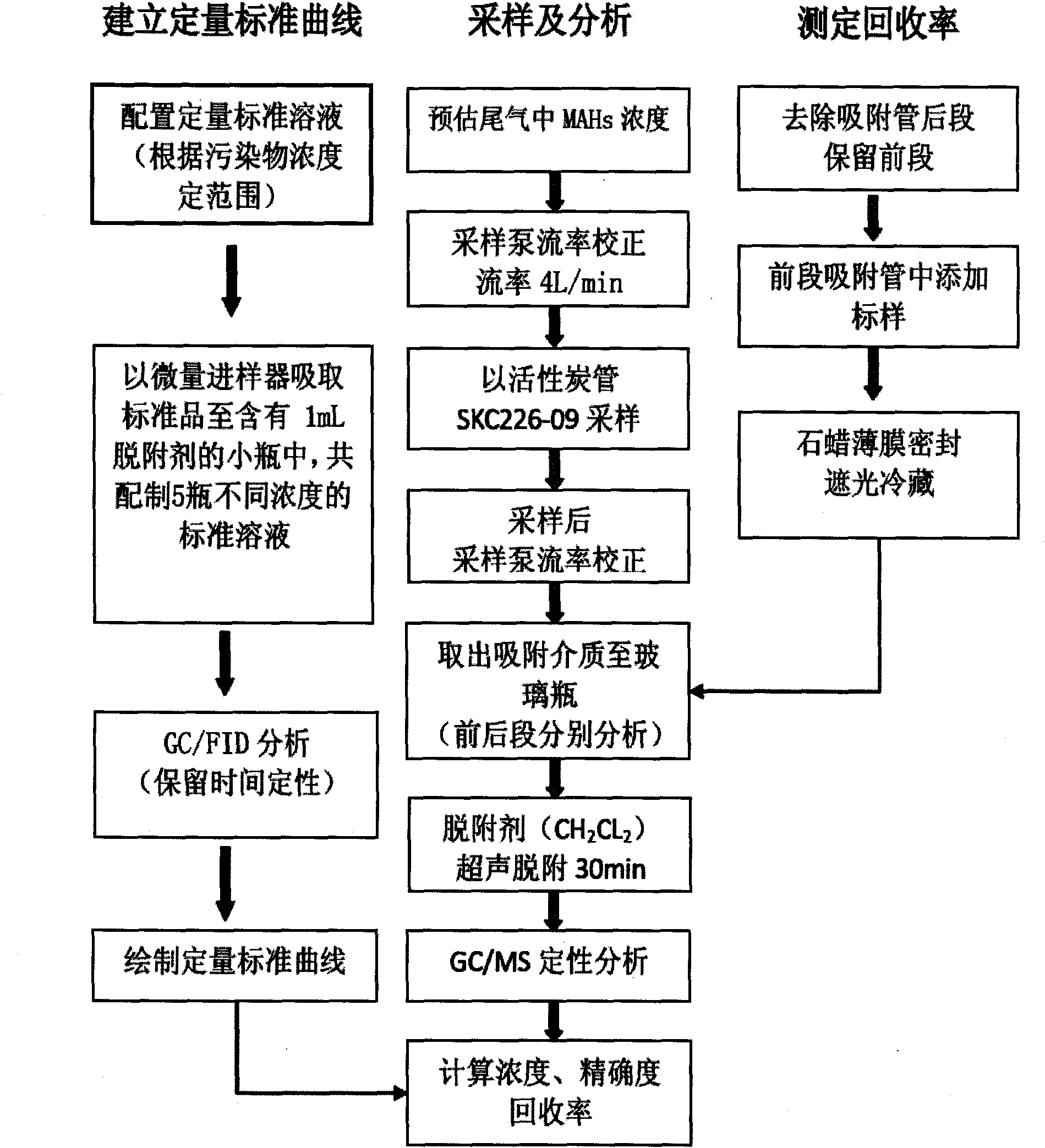
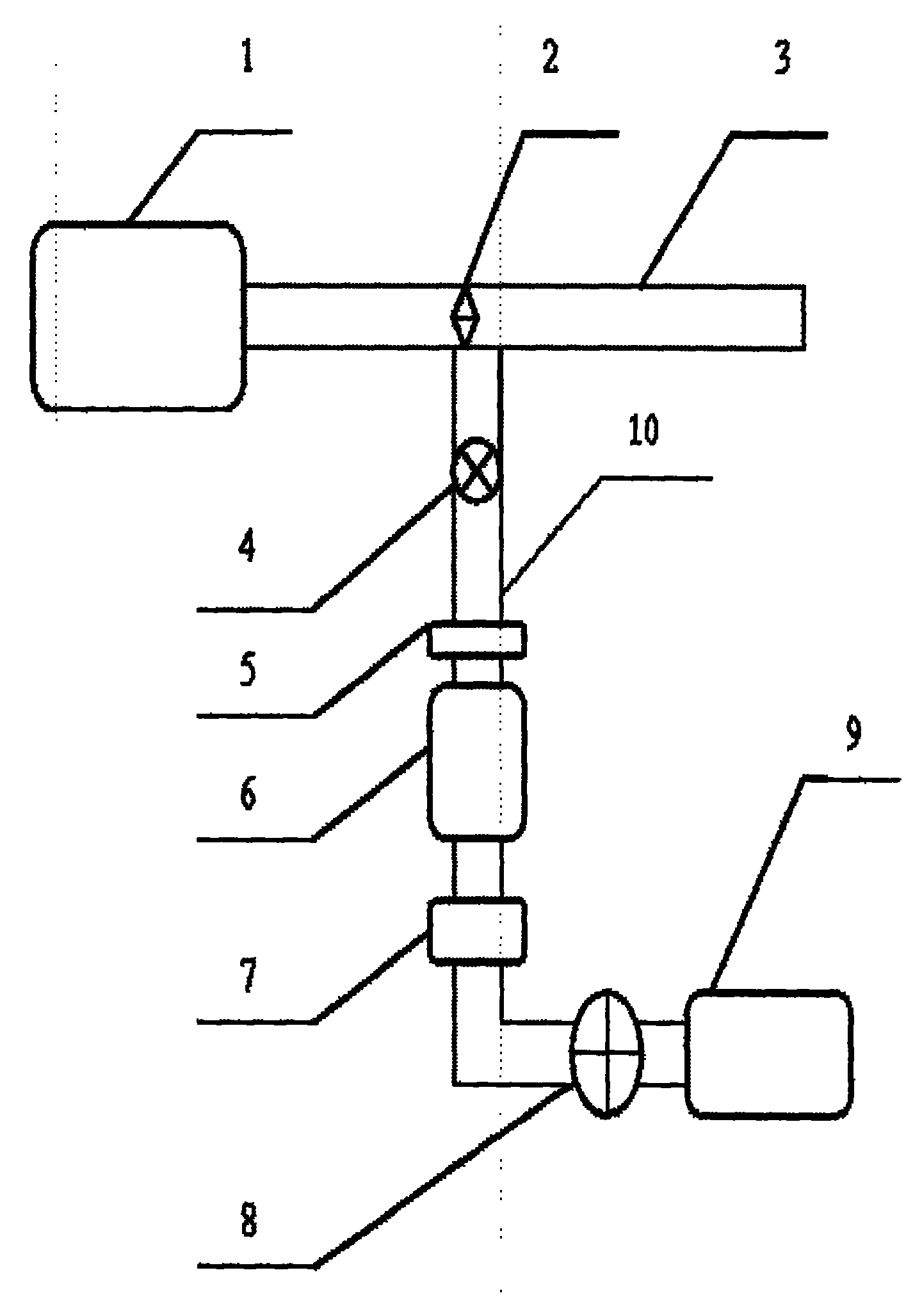
Method for detecting monocyclic aromatic pollutants in engine tail gas
InactiveCN101776661AQuick QualificationRapid Quantitative AnalysisComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesRelative standard deviationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for detecting monocyclic aromatic pollutants in engine tail gas. The method comprises the following steps: collecting tail gas to be detected by using an engine tail gas sampling unit, and putting the active-carbon tail gas to be detected in a test tube as the sample; adding dichloromethane into the sample, putting the test tube in an ultrasonic extractor to carry out ultrasonic extraction, filtering the extract liquor, evaporating and setting to the marked volume to concentrate the extract liquor, and preserving at low temperature; carrying out chromatographic analysis on the extract liquor preserved at low temperature; and carrying out linear regression by using the concentration of monocyclic aromatics as the horizontal ordinate and the peak area as the vertical coordinate to calculate a standard operation curvilinear equation, substituting the chromatographic result into a standard operation curvilinear equation, and calculating the concentration of monocyclic aromatics in the sample. The invention can quickly and accurately carry out qualitative and quantitative analysis on monocyclic aromatics and has the advantages of high sensitivity and selectivity and good reproducibility; and the relative standard deviation does not exceed 6.5%, the detection limit is 0.003-0.009 mg / m3, and the recovery rate is 87.5-95.2%.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
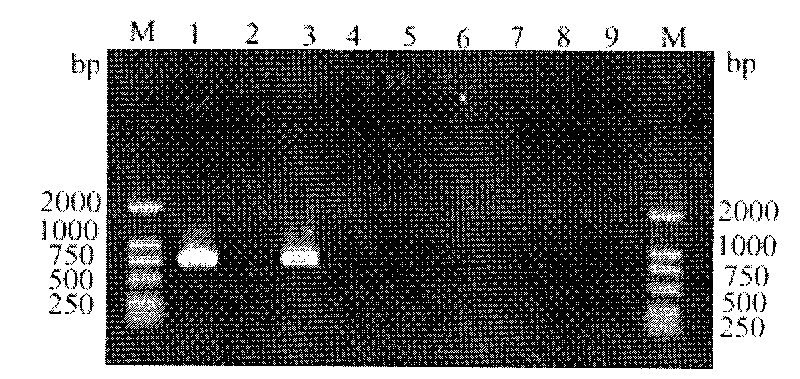
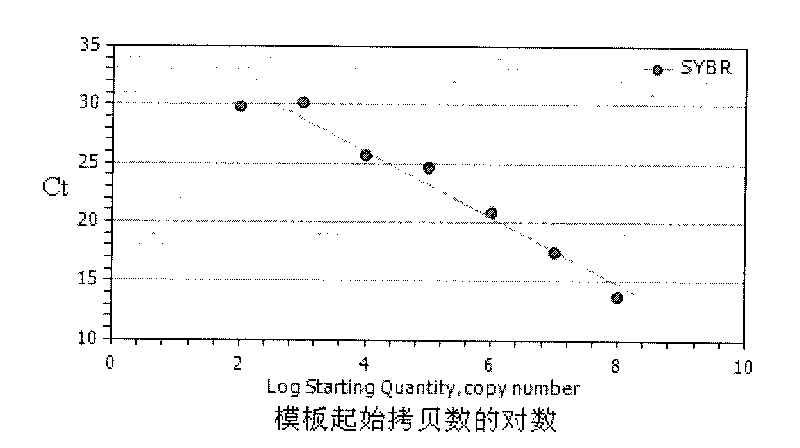
Method for quickly, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products
InactiveCN101712987AQualitatively accurateSimplify testing proceduresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyLactobacillus plantarum
The invention relates to a method for quickly, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products. The method comprises the following steps: aiming at the lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products, independently designing a species specificity primer of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the lactobacillus plantarum, carrying out species specificity PCR and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction by using the primer, and analyzing through an agarose gel electrophoresis pattern and a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR pattern, thereby establishing the method for simply, conveniently, quickly, accurately, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring lactobacillus plantarum in probiotic dairy products.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Experiment system for simulating cable burning under fire environment and method thereof
InactiveCN105489103AAvoid pollutionQualitatively accurateEducational modelsHeat flowSmoke composition
The invention discloses an experiment system for simulating cable burning under the fire environment and a method thereof. The experiment system for simulating cable burning under the fire environment comprises a weighing device which is provided with a sample frame used for fixing cable samples; a heating device which comprises a radiation heating shell and an igniter, wherein the radiation heating shell covers the weighing device, and the igniter is arranged in the cavity of the radiation heating shell and used for igniting the cable samples fixed on the sample frame; multiple thermocouples and heat flow meters; and a smoke collection device which comprises a smoke collection hood and a smoke composition analyzer, wherein the smoke collection hood is connected with the radiation heating shell of the heating device, and smoke emitted by burning of the cable samples is guided to the smoke composition analyzer through the smoke collection hood. According to the experiment system for simulating cable burning under fire environment and the method thereof, more accurate nature determination and classification of the burning characteristics of the cables are facilitated so that deeper research and analysis can be performed in the aspect of cable fire dynamics.
Owner:INST OF IND TECH GUANGZHOU & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
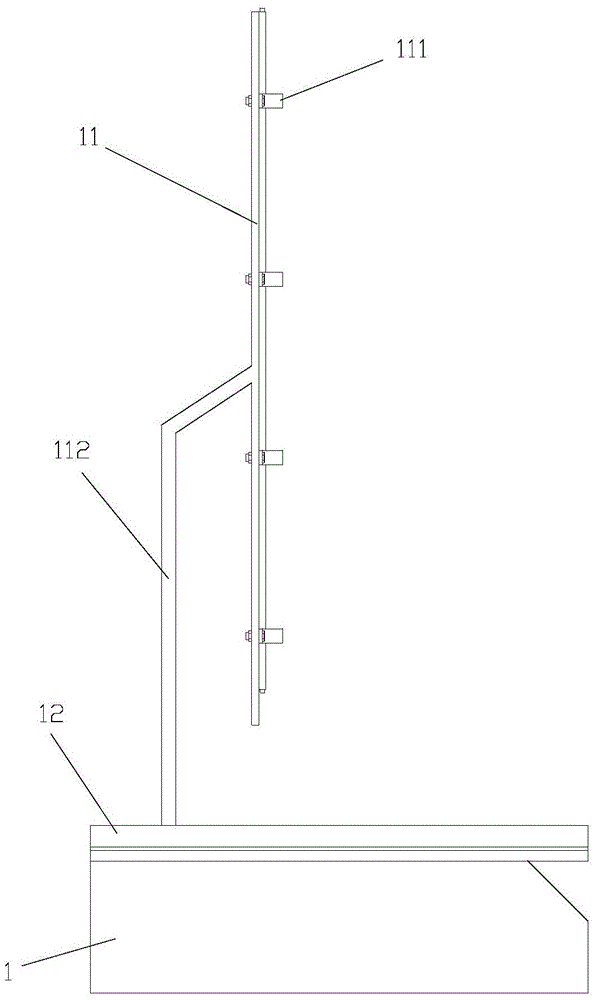
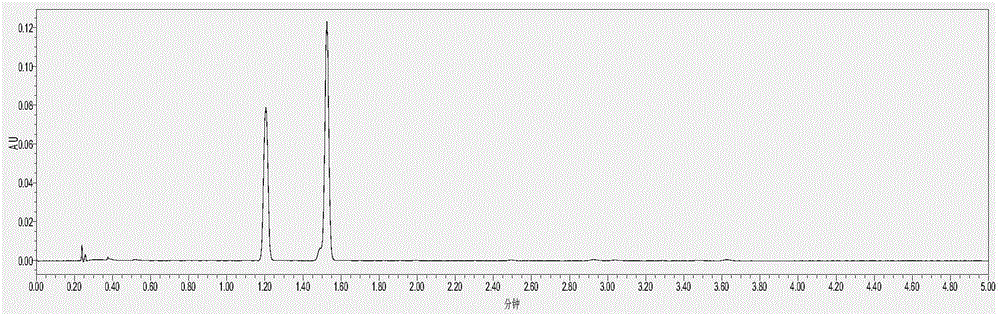
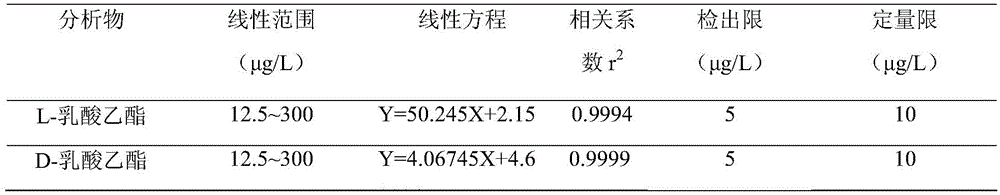
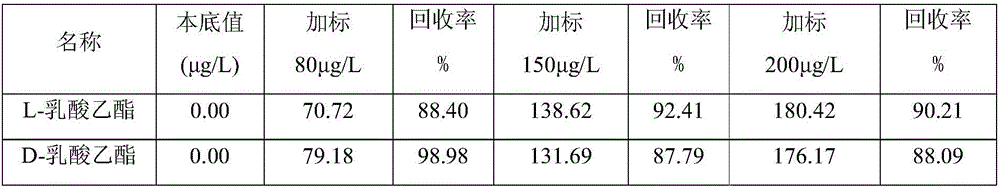
Method using ultra-performance convergence chromatography to fast detect chiral ethyl lactate in Baijiu
ActiveCN105891375AQualitatively accurateQuantitatively accurateComponent separationGradient elutionNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method using ultra-performance convergence chromatography to fast detect chiral ethyl lactate in Baijiu and belongs to the technical field of detection. The method is characterized in that the chiral ethyl lactate includes L-ethyl lactate and D-ethyl lactate; a Baijiu sample is dried by blowing through nitrogen after being extracted by ethyl acetate and dissolved with methanol, a special ACQUITY UPC2Trefoil CEL1 chiral chromatographic column of 2.5 micrometers is used as the separation column, and carbon dioxide (A) plus methanol (B) are used as the flowing phase to perform gradient elution; the sample is detected by a diode array detector after being separated by ultra-performance convergence chromatography (UPC2). The method is simple and fast and capable of accurately qualitatively and quantitatively detecting the chiral ethyl lactate in Baijiu, and a scientific basis is provided for the accurate determination and fast detection of the two kinds chiral ethyl lactate in Baijiu.
Owner:ANHUI RUISIWEIER TECH
Method for qualitatively and quantitatively testing and analyzing impurities in steel
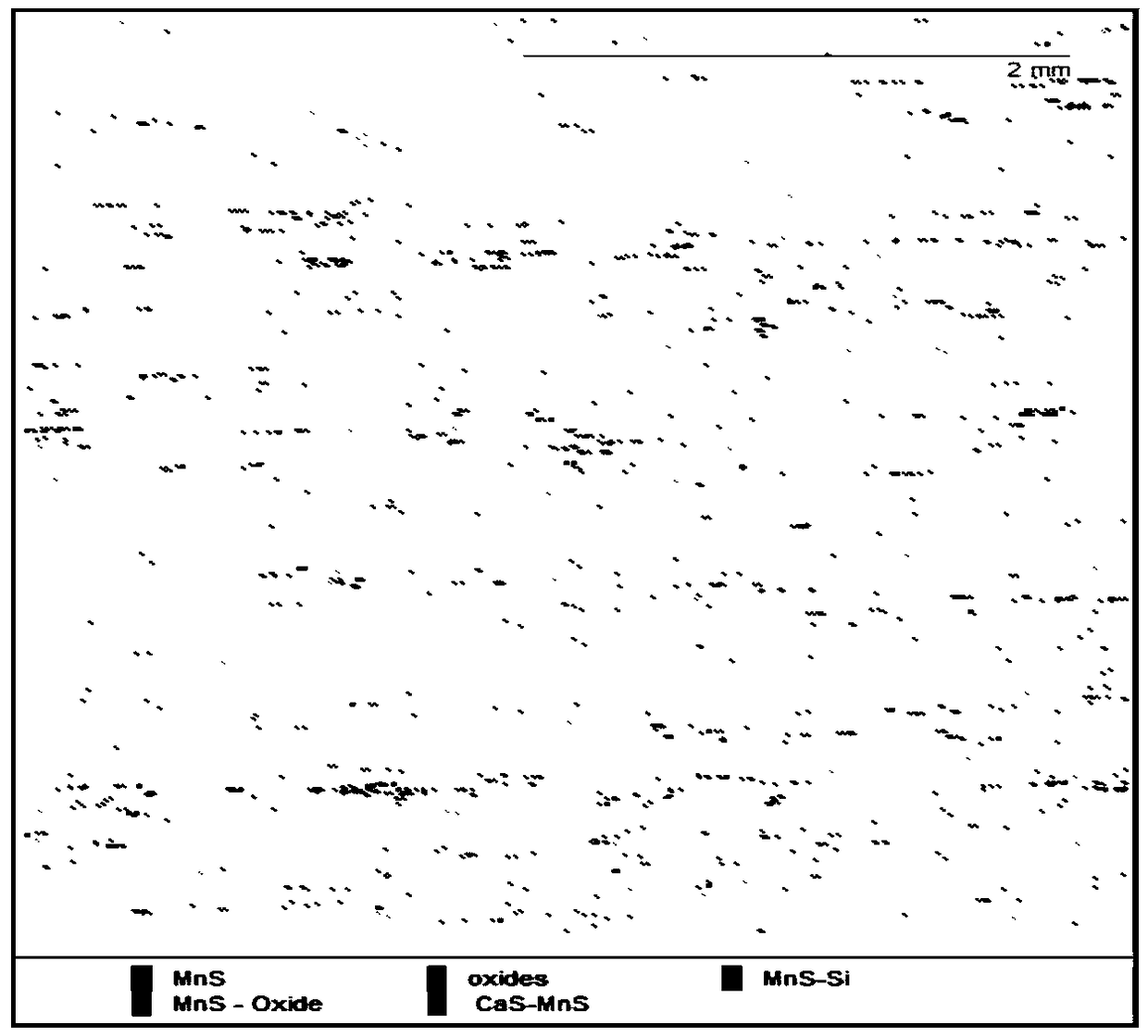
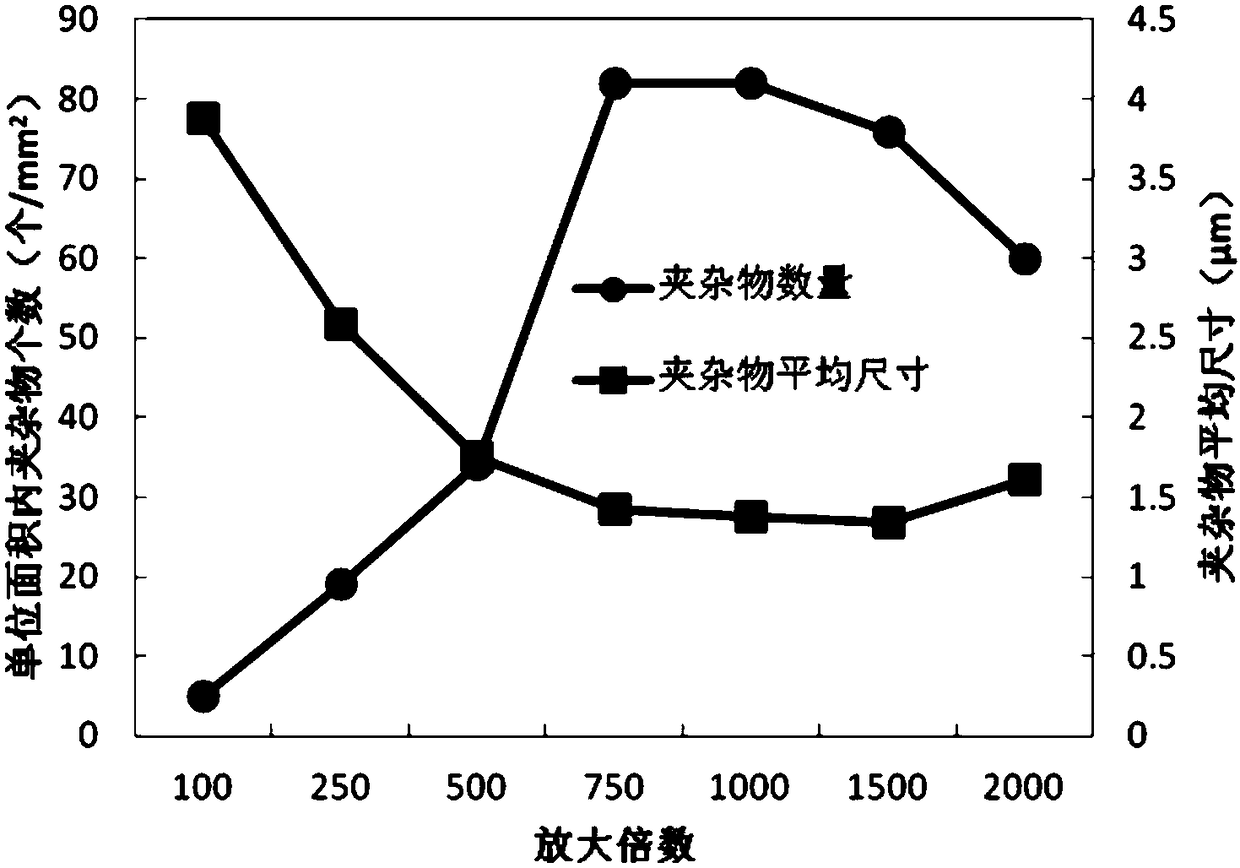
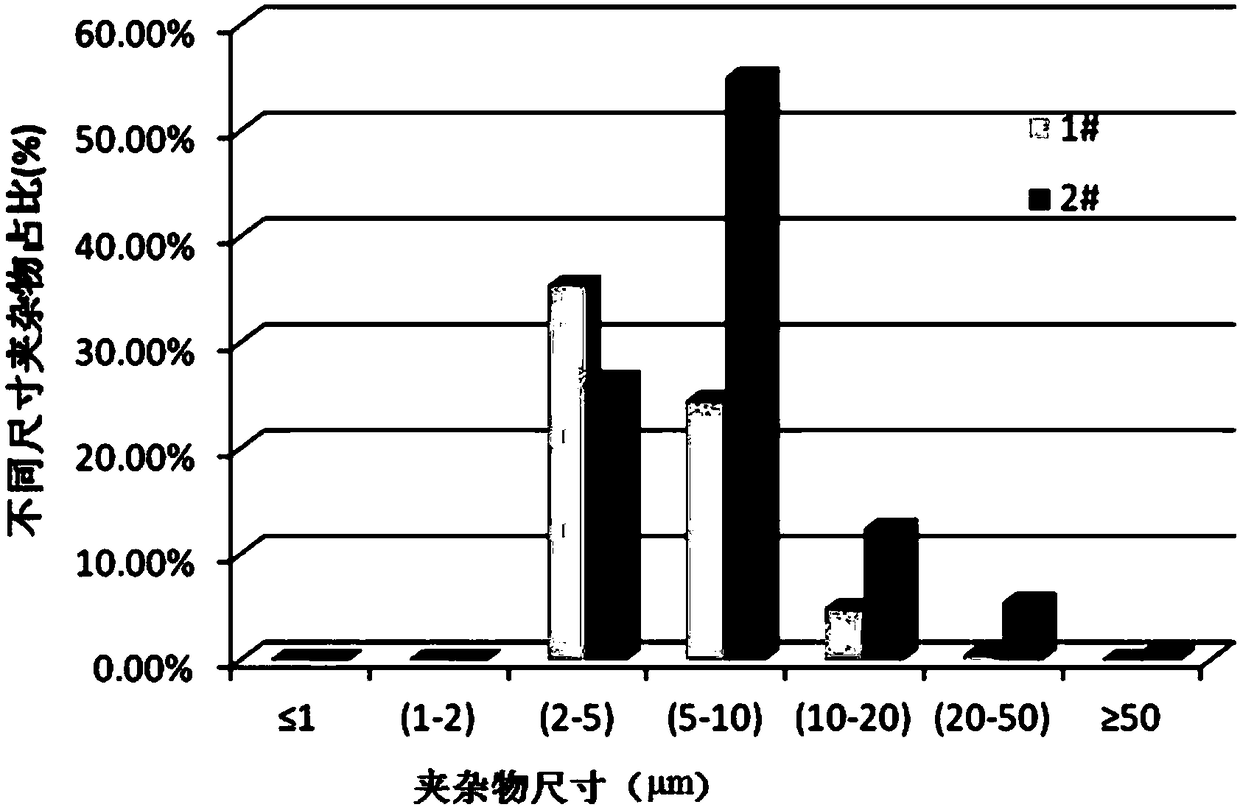
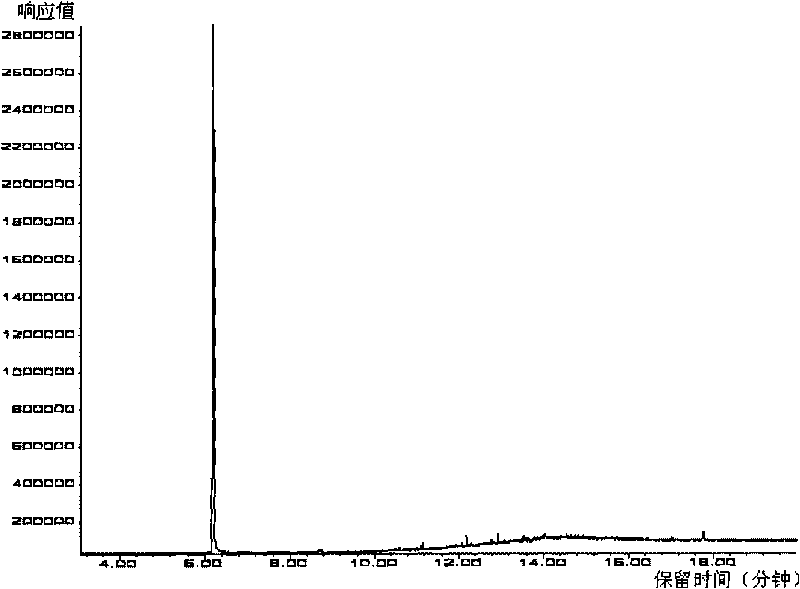
ActiveCN108593649AQualitatively accurateHuman factors are smallMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionEvaluation resultTest sample
The invention provides a method for qualitatively and quantitatively testing and analyzing impurities in steel. The method includes the following steps of firstly, preparing a to-be-tested sample, wherein the to-be-tested sample is ground and polished, and the surface is clean, smooth and free of peculiar objects; secondly, observing the to-be-tested sample in a metallographic microscope, and determining the size range of the impurities; thirdly, adjusting testing parameters of a scanning electron microscope according to the impurity size range determined in the second step, and conducting scanning electron microscope testing and EDS energy spectrum component analysis on the to-be-tested sample to obtain size, shape and component data of the impurities in steel. By setting the component content standard, size and length standard and shape standard of the impurities in steel in application software and related accessories of the scanning electron microscope and setting the proper testing parameters according to the size of the impurities in steel, the properties of the impurities in steel can be accurately, qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed, analyzing and testing are accurate and comprehensive, artificial influence factors are small, and the evaluation result is specific, precise and visual.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Method for measuring dimethyl fumarate in product by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN101701943AQualitatively accurateReduce consumptionComponent separationGas phaseMass chromatography
The invention discloses a method for measuring dimethyl fumarate in a product by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps of: pretreating a dimethyl fumarate product to be detected by using an ultrasonic extraction method; setting the temperature of a sample injection port of a gas chromatography-mass spectrometer to be 240-280 DEG C, a flow rate to be 0.8-1.5 ml / min and the temperature of a port to be 280-300 DEG C, and selecting a weak polar column for a chromatographic column; enabling a sample to enter the chromatographic column through the sample injection port, and carrying out temperature programming on the temperature of the chromatographic column to separate the components of the sample by the chromatographic column; and enabling the components separated by the chromatographic column to enter a mass spectrometric detection part through the port of the gas chromatography-mass spectrometer, wherein an electron impact ion source is adopted as the ion source of the mass spectrometric detection. The method for measuring the dimethyl fumarate in the product by the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry has low detection limit, good detection effect, little consumption of analysis solvent and low detection cost.
Owner:NINGBO PTS PROD TECH SERVICE
Method for detecting residual quantity of sodium nitrophenol in aquatic product
ActiveCN103091422AHigh sensitivityEasy to prepareComponent separationHazardous substancePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for detecting residual quantity of sodium nitrophenol in an aquatic product and belongs to the technical field of detection of aquatic products. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting and purifying a sample; drawing a standard curve; and determining and quantifying apparatus conditions. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an APCI (Atmosphere Pressure Chemical Ionization) ion source is selected by a mass spectrometer, so that the sensitivity of sodium orotho-nitrophenolate is improved by dozens of times; neutral alumina is adopted for purifying, so that interfering substances such as fat in the sample can be effectively removed, and the concentration time is shortened; sodium hydroxide is added during the concentration process, so that the sodium orotho-nitrophenolate exits in the sample in the form of sodium salt, thereby enabling the recovery rate of the sodium orotho-nitrophenolate to be more than 70%. Phosphoric acid is added after the concentration for neutralizing the excessive sodium hydroxide, so that the pH of the purifying liquid kept at about 3, and the requirements of upper solid-phase extractor column can be satisfied. The method disclosed by the invention fills up the blank that no method is provided for detecting residual quantity of sodium nitrophenol in aquatic products and other animal foods at present, and has great significance in accurately and scientifically evaluating the quality safety of the aquatic products and making the novel standards of harmful substances in the aquatic products.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for quickly, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus casei in probiotic dairy products
InactiveCN101712989AQualitatively accurateSimplify testing proceduresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGenus specific primersLactobacillus casei
The invention relates to a method for quickly, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus casei in probiotic dairy products. The method comprises the following steps: aiming at the Lactobacillus casei in probiotic dairy products, independently designing a species specificity primer of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the Lactobacillus casei, carrying out species specificity PCR and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction by using the primer, and analyzing through an agarose gel electrophoresis pattern and a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR pattern, thereby establishing the method for simply, conveniently, quickly, accurately, qualitatively and quantitatively measuring Lactobacillus casei in probiotic dairy products.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of identifying illegal cooking oil by means of Raman spectra technique
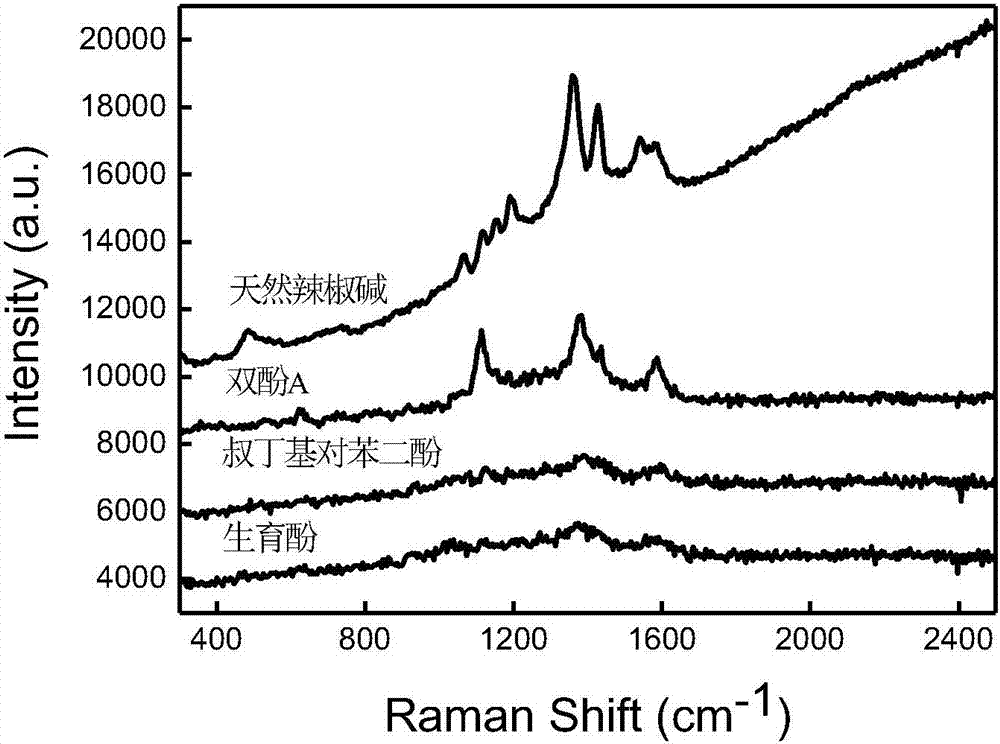
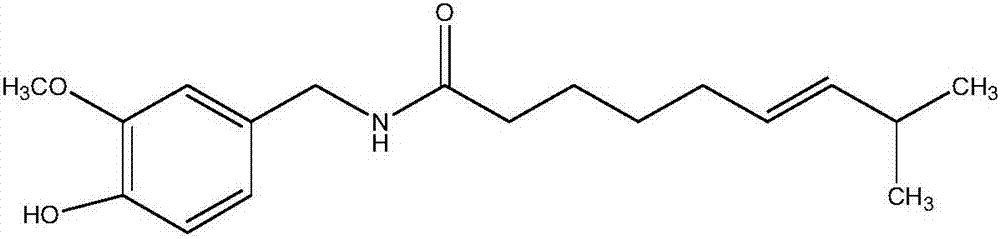
ActiveCN107144558AEffective monitoringSimple and fast operationRaman scatteringSensitive analysisCapsaicin
The invention relates to a method of identifying illegal cooking oil by means of a Raman spectra technique and belongs to the technical field of food fast detection. The method comprises the following steps: measuring 2-5mL of edible oil needed to be detected, adding an extraction reagent A double in volume, whirling the mixture for 5-10min and then performing magnetic field assisted separation to extract natural capsaicin from the edible oil; then analyzing the extracted natural capsaicin by using 2-5mL of methanol to obtain a methanol extraction liquid; then adding the methanol extraction liquid into a derived solution B the same in volume, and performing a whirling reaction at room temperature for 1-3min; and finally adding an SERS enhancing reagent C the same in volume to the reaction solution, performing the whirling reaction at room temperature for 1-3min, and performing SERS detection; if characteristic peaks of natural capsaicin are shown in the SERS spectrogram, the detected edible oil is illegal cooking oil. The invention provides a simple, quick and super-sensitive analysis method for identifying illegal cooking oil, which has the characteristics of being distinct in target object, strong in characteristics, accurate in quality and simple in operation.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for rapidly detecting 8 phenolic acids in liquor product by serial connection of ultra-performance convergence chromatography and QD
InactiveCN109828044AEasy to useMeet the low limit detection requirementsComponent separationMass spectrometry detectorGradient elution
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting 8 phenolic acids in a liquor product by serial connection of an ultra-performance convergence chromatography and a QD. After a liquor sample to be detected is extracted by methanol, a dedicated chromatographic column of the BSS C18 convergence is taken as a separation column, carbon dioxide (A)+methanol (B) are taken as a mobile phase for gradient elution, a sample is separated by the ultra-performance convergence chromatography (UPC2), and then a QDa mass spectrometry detector is employed for detection. The method is simple and rapid andconvenient, and accurate and reliable, and can be used for detection of the content of the 8 phenolic acids in liquors.
Owner:ANHUI GUJING DISTILLERY +1
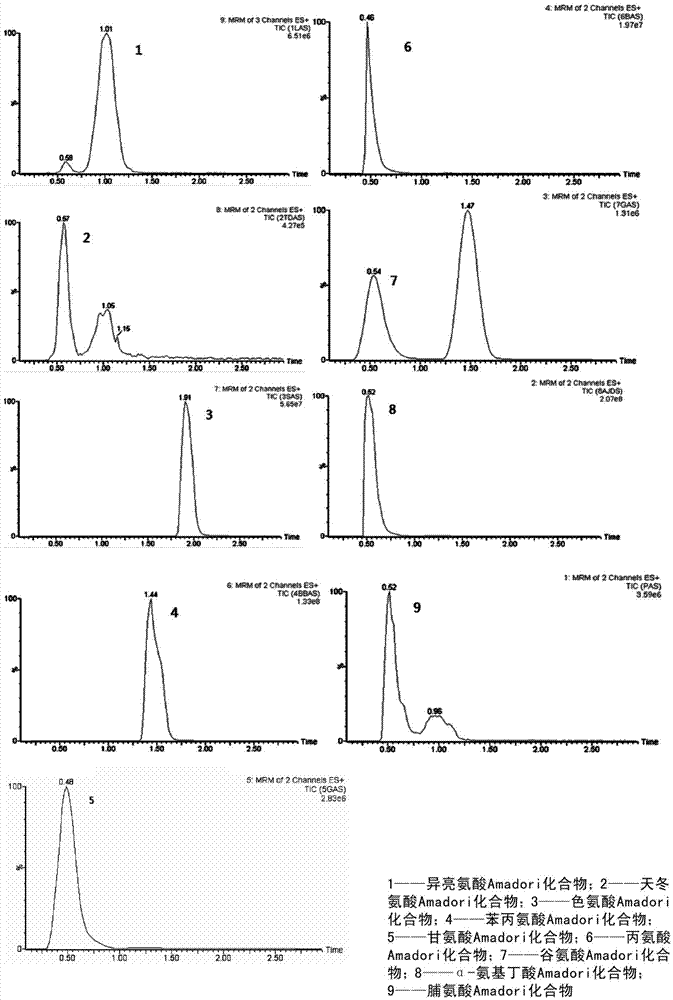
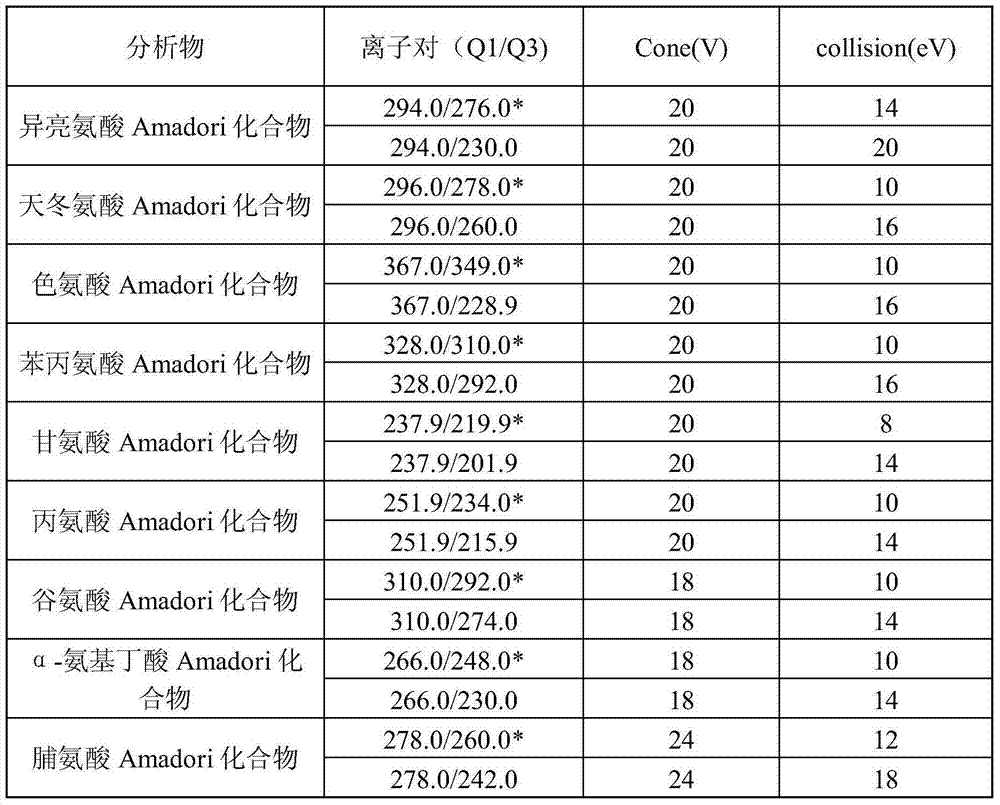
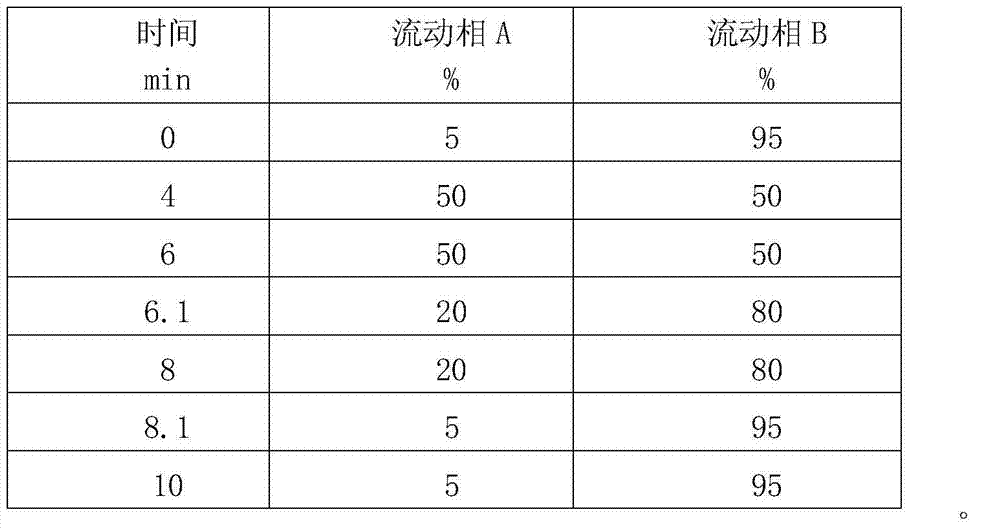
Method for simultaneously measuring Amadori compounds in tobaccos
ActiveCN103499658AEfficient extractionAchieving co-detectionComponent separationAdditive ingredientImpurity
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring Amadori compounds in tobaccos, relates to a method for measuring important ingredients in tobaccos, and particularly relates to a method for simultaneously measuring nine Amadori compounds in tobaccos by the aid of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The method includes steps of 1, sample extracting: smashing tobacco samples, extracting the tobacco samples by methanol-aqueous solution, filtering the tobacco samples and collecting filter liquor; 2, purifying: adding normal hexane into the filter liquor, repeatedly extracting the filter liquor, removing impurities such as coloring matters in the filter liquor, concentrating the filter liquor by methanol-aqueous phases until the filter liquor is dry, diluting the filter liquor by methanol-aqueous solution until the volume of the diluted filter liquor meets requirements, and filtering the filter liquor by an organic filter membrane to obtain test samples; 3, measuring: analyzing the test samples via HPLC-MS / MS (high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry / mass spectrometry), and performing multi-reaction monitoring scanning on the test samples in a cation ionization mode. The method has the advantages that the Amadori compounds in complicated systems of the tobaccos can be effectively extracted and analyzed and can be detected jointly, the sensitivity and the interference resistance are high, and the method has popularization and application value.
Owner:HONGTA TOBACCO GRP
Rapid Qualitative and Quantitative Determination of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Additive Premix Samples
ActiveCN102296117ASimplify testing proceduresImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSubstance useQuantitative determination
The invention belongs to the detection technical fields of feed science and feed additives, and more specifically relates to a rapid qualification and quantitation measurement method of saccharomyces cerevisiae in an additive premix sample. According the invention, cDNA gradient dilution is taken as an external standard substance used for distinguishing dead bacteria and live bacteria for accurately detecting the amount of the live bacteria in a sample to be measured. The invention is capable of measuring saccharomyces cerevisiae in premix sample with simple, rapid and accurate qualification and quantitation without pure culture of saacharomyces cereisiae, the whole process has the advantages of simple detection process, high detection efficiency, high accuracy and short detection period; and the invention provides a guarantee a long term development for a microecological preparation industry.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com