Detection method of polyamine substances in tobacco roots, stems and leaves
A detection method, technology of tobacco roots, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
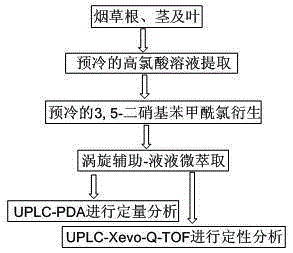
[0027] The detection method of polyamine substances in tobacco roots, stems and leaves of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0028] (1) Weigh 100mg of freeze-dried samples (roots, stems or leaves) in a 10mL centrifuge tube, then add 1mgmL of 5uL 0.1M hydrochloric acid -1 Hexamethylenediamine hydrochloride, then add 6mL of pre-cooled 0.3M perchloric acid aqueous solution to extract by vortexing at 2000rpm for 30min, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 5min, and pass the supernatant through a 0.45um water filter membrane;
[0029] (2) Take 2mL of the filtrate in a 10mL centrifuge tube, put it in an ice bath to cool for 5min, then add 400uL of 4M sodium hydroxide solution, vortex and mix well, then add 50mM 3,5-dinitrate prepared in pre-cooled 1050uL of acetonitrile Base benzoyl chloride, vortex mix, react in ice bath for 2min, add 500uL 2M hydrochloric acid aqueous solution to stop the reaction;
[0030] (3) Add 1mL ultrapure water to the derivatized product, adjust i...
Embodiment 2
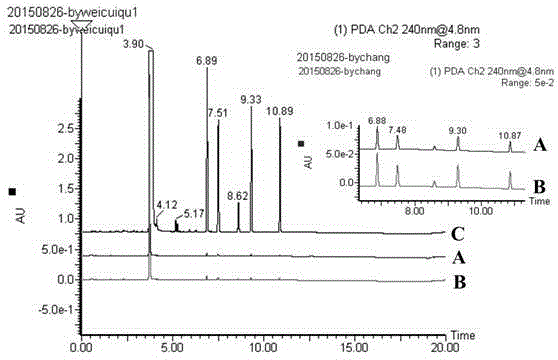
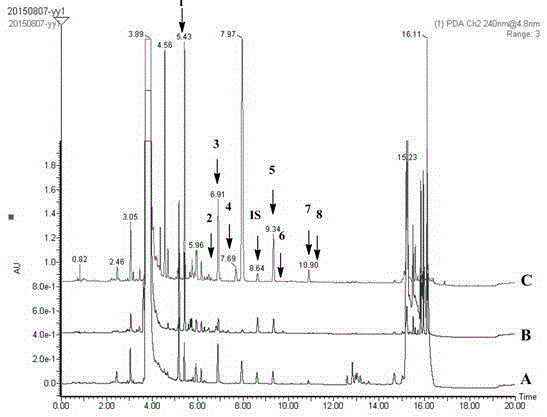
[0048] The polyamines in different parts of the same tobacco were detected by the method as in Example 1, and the measurement results are shown in Table 6. From the detection results, it can be known that the content of polyamines in leaf buds is the highest, especially the content of tyramine. The composition of polyamine content in leaves was leaf bud>upper leaf>middle leaf>lower leaf. Generally speaking, the content of polyamine in young leaves was higher than that in old leaves. The root has relatively high tyramine content, but other polyamine content is low, which is similar to the polyamine composition of the lower leaves, and the polyamine content in the stem is higher than that of the root, which is similar to the polyamine composition of the middle leaves.
[0049] Table 6 Polyamine content composition between different parts of the same tobacco
[0050]
[0051] a Data are mean ± SD of 5 determinations; ND, not detected.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| correlation coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com