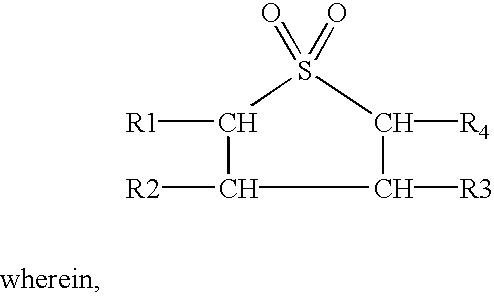
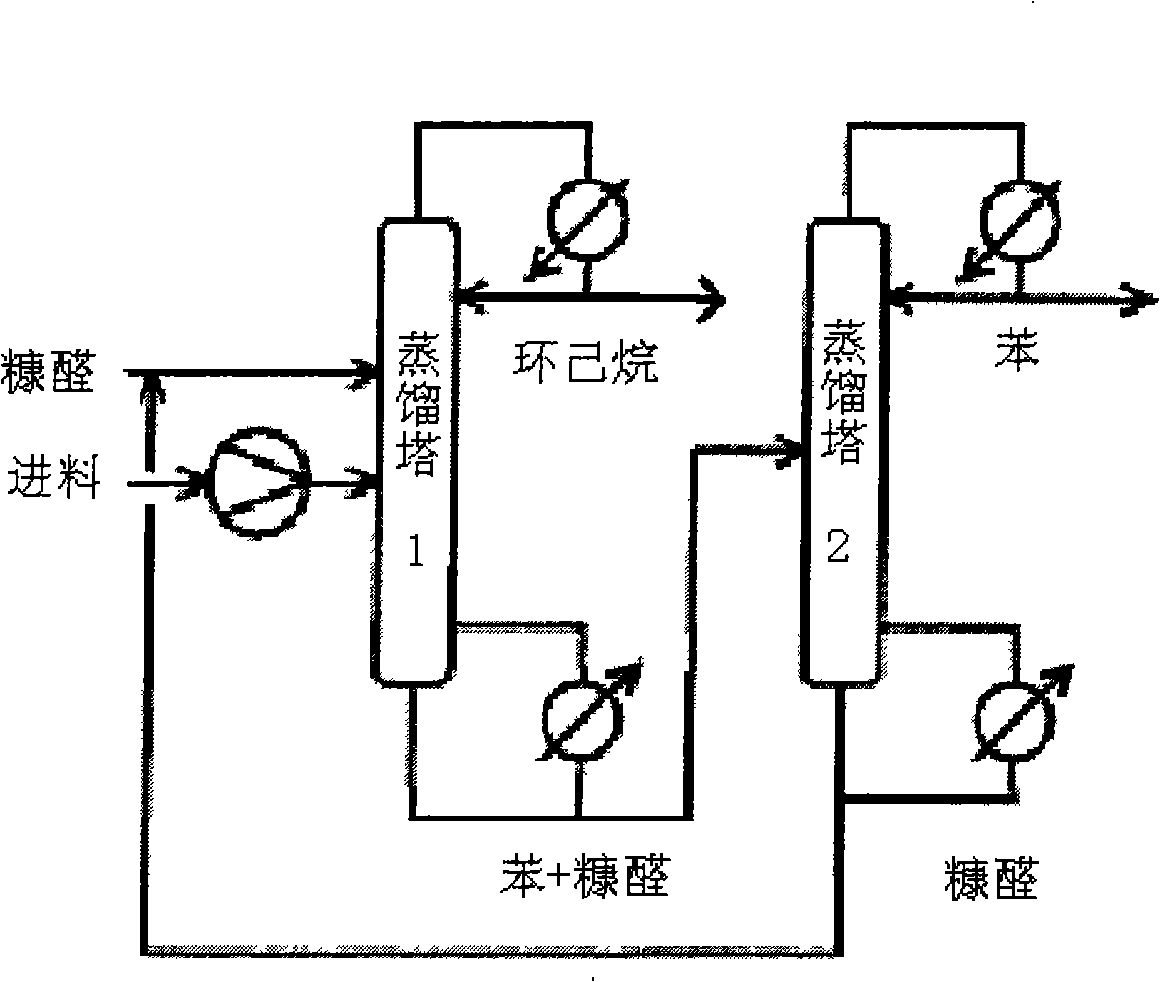
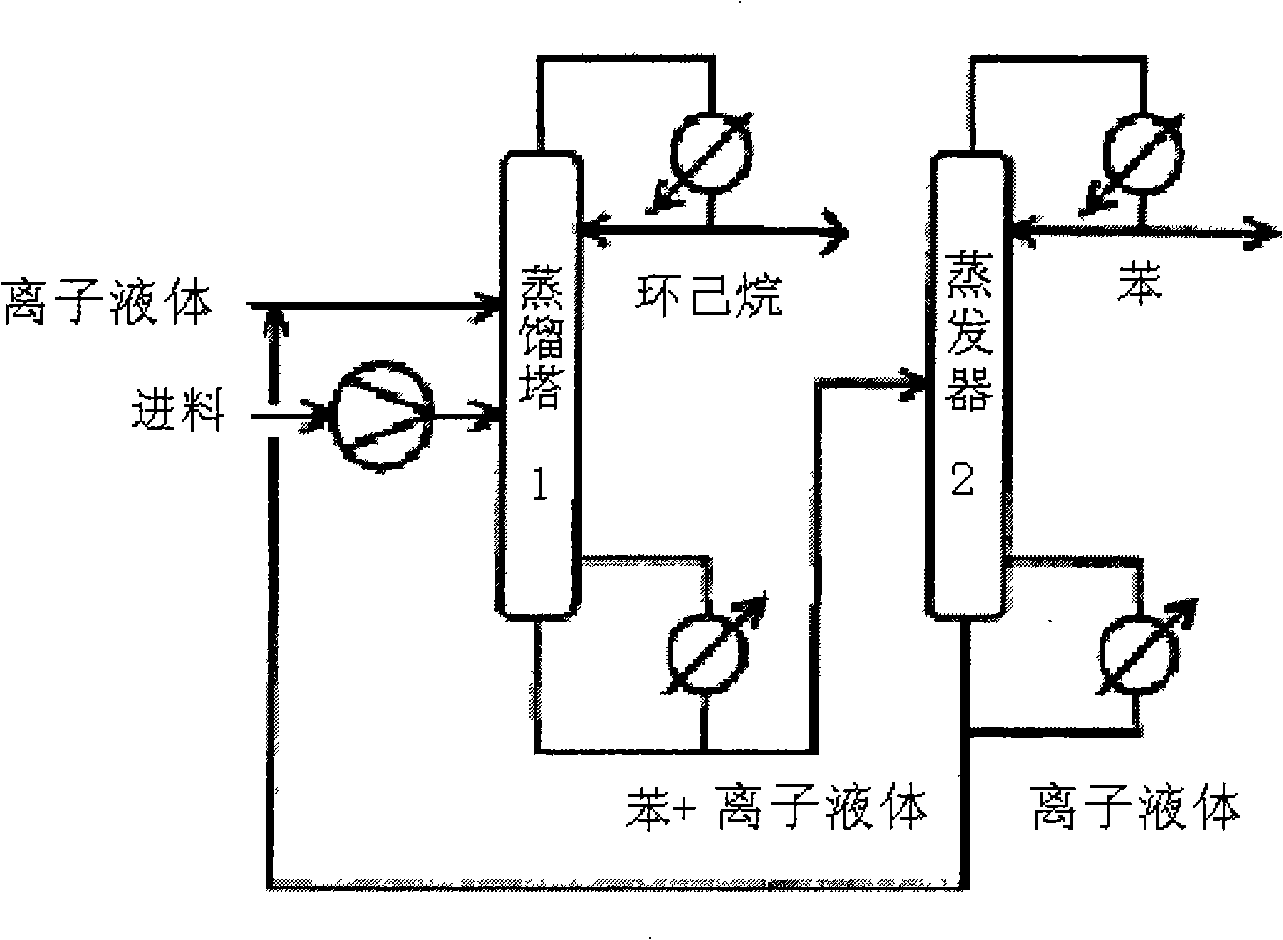
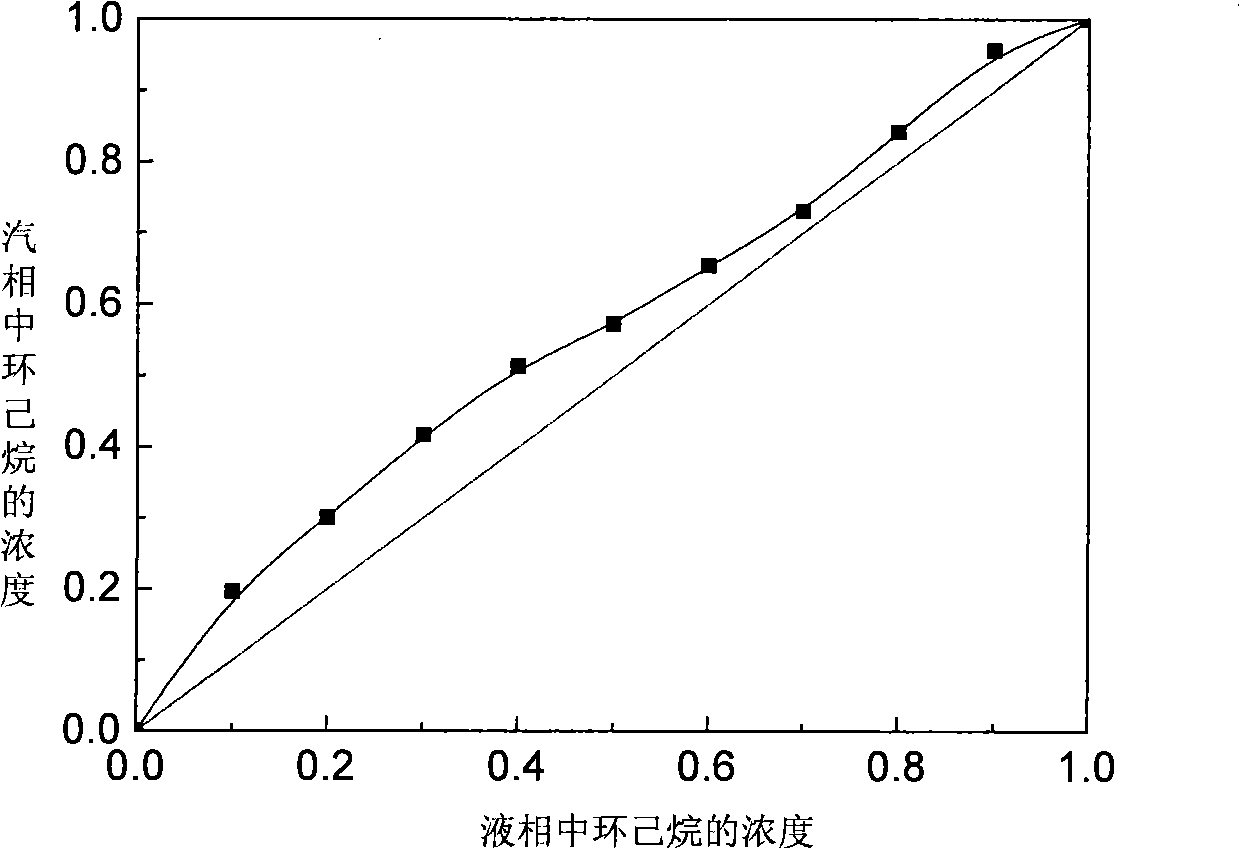
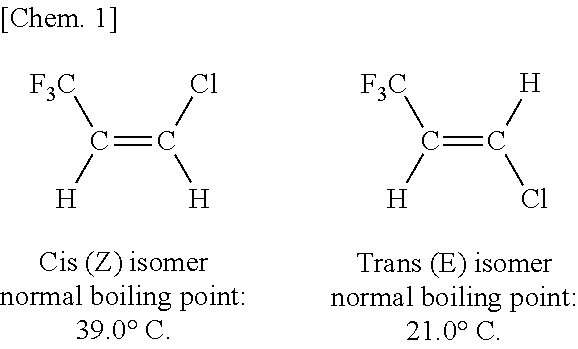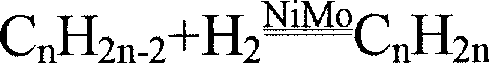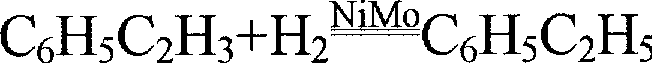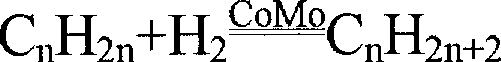Patents
Literature
1039 results about "Extractive distillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
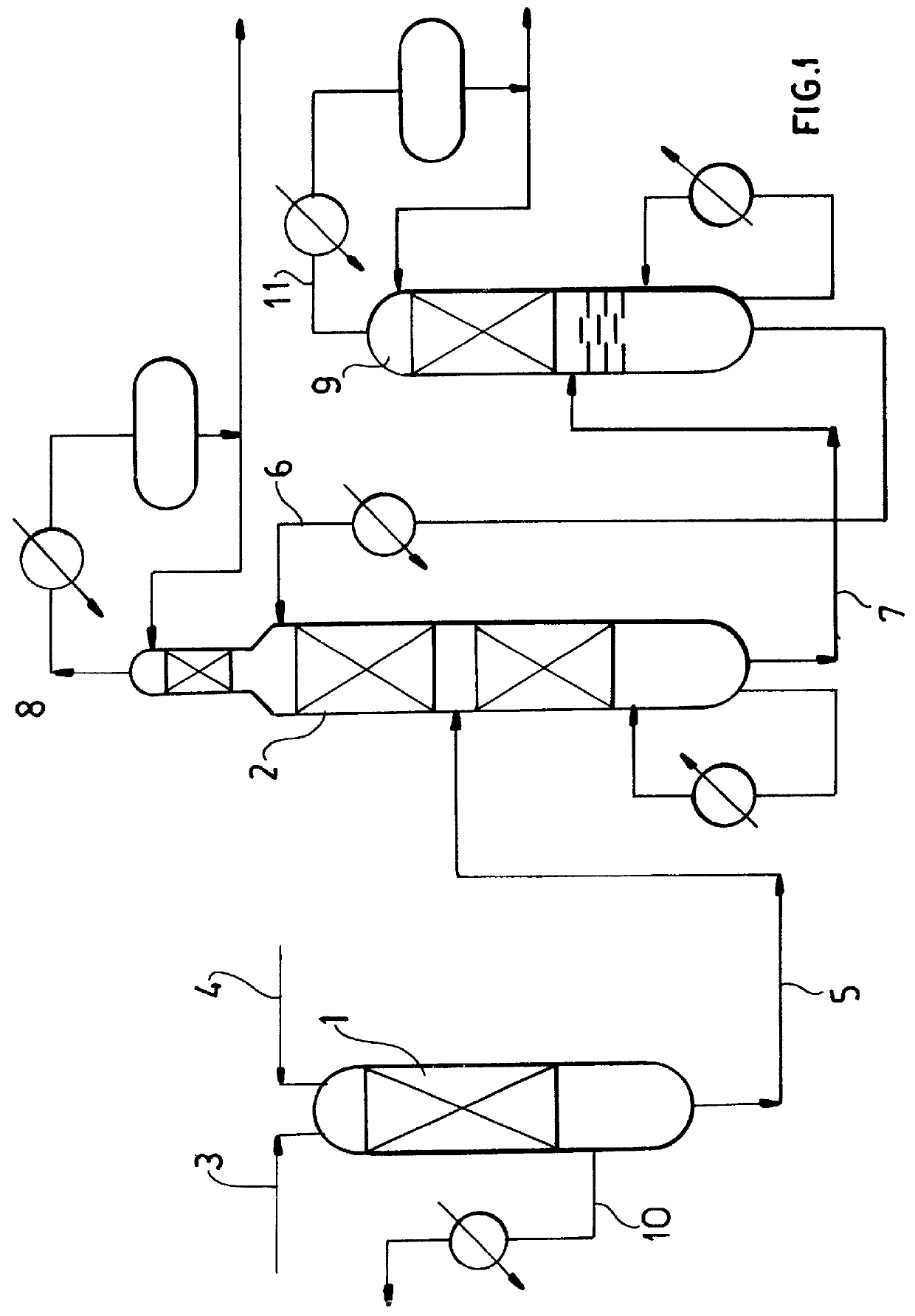
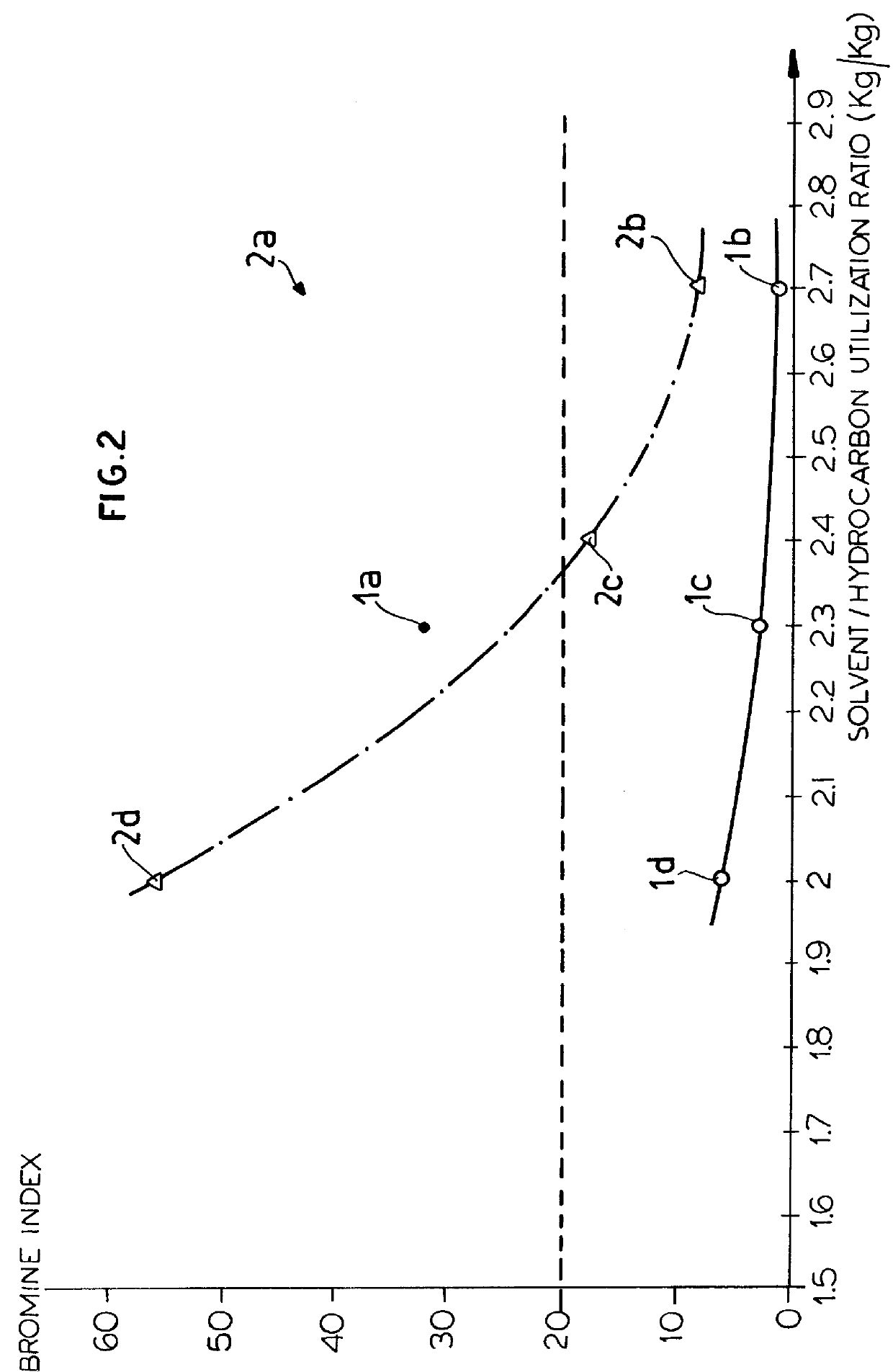
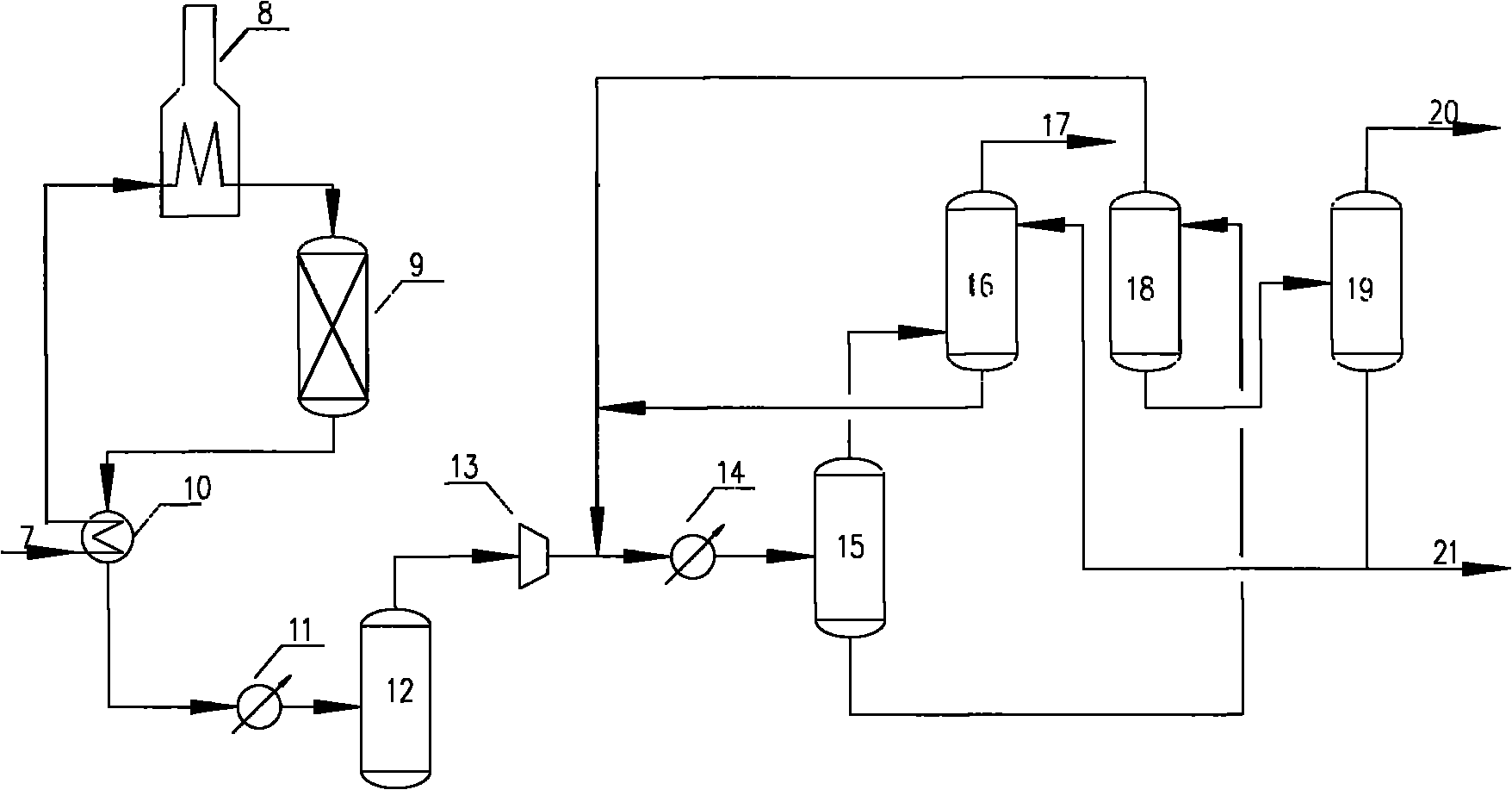
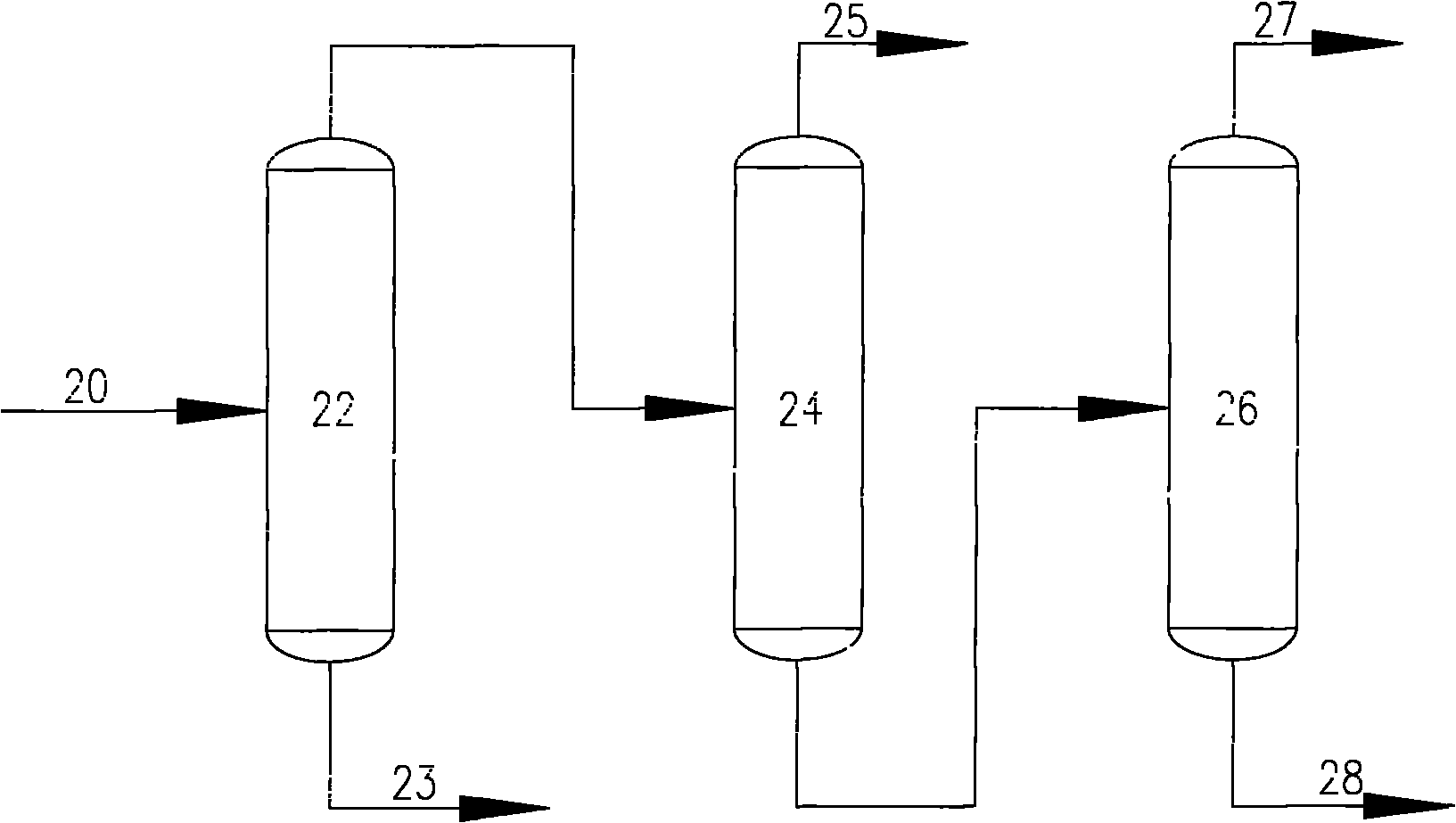
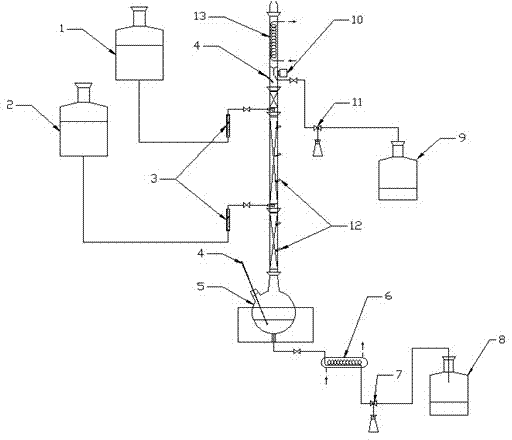
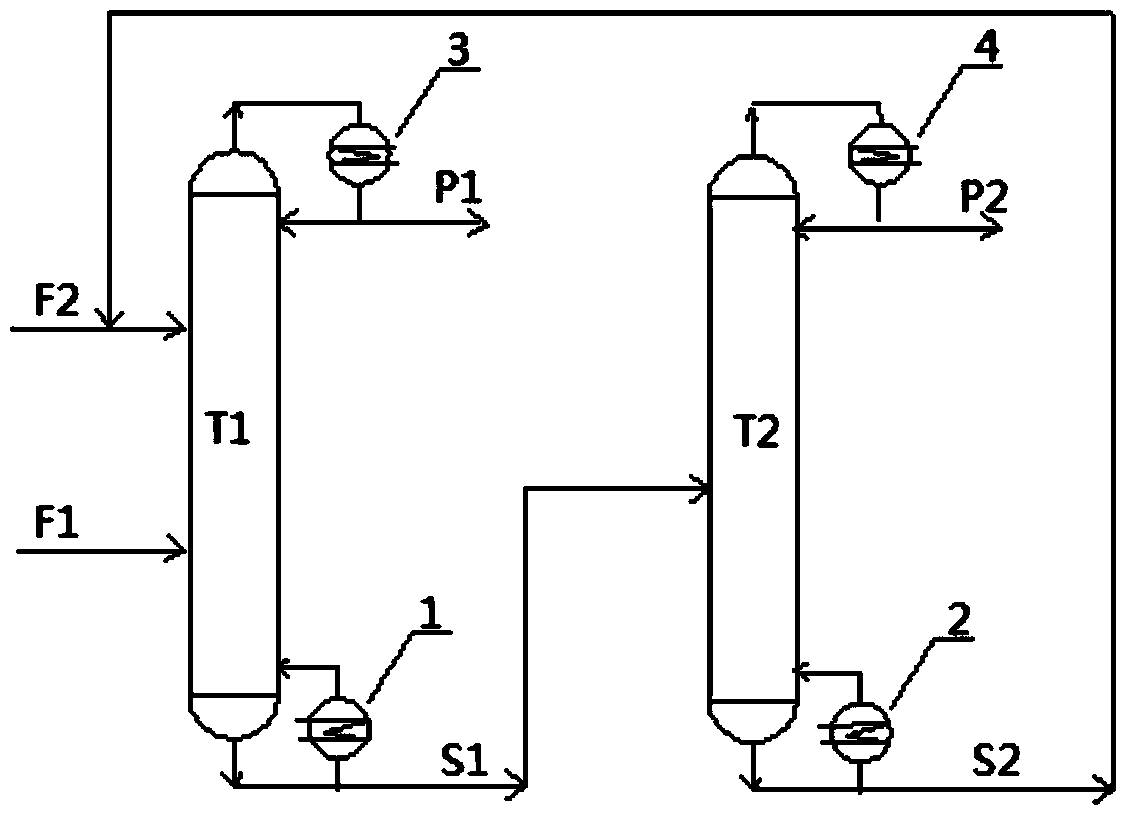
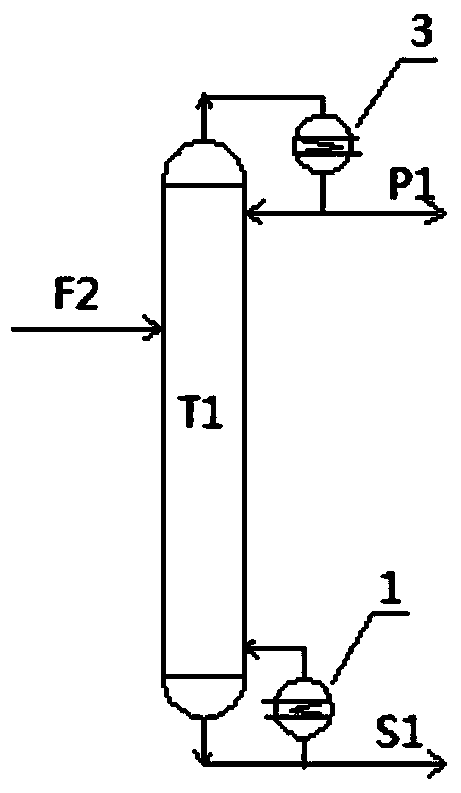
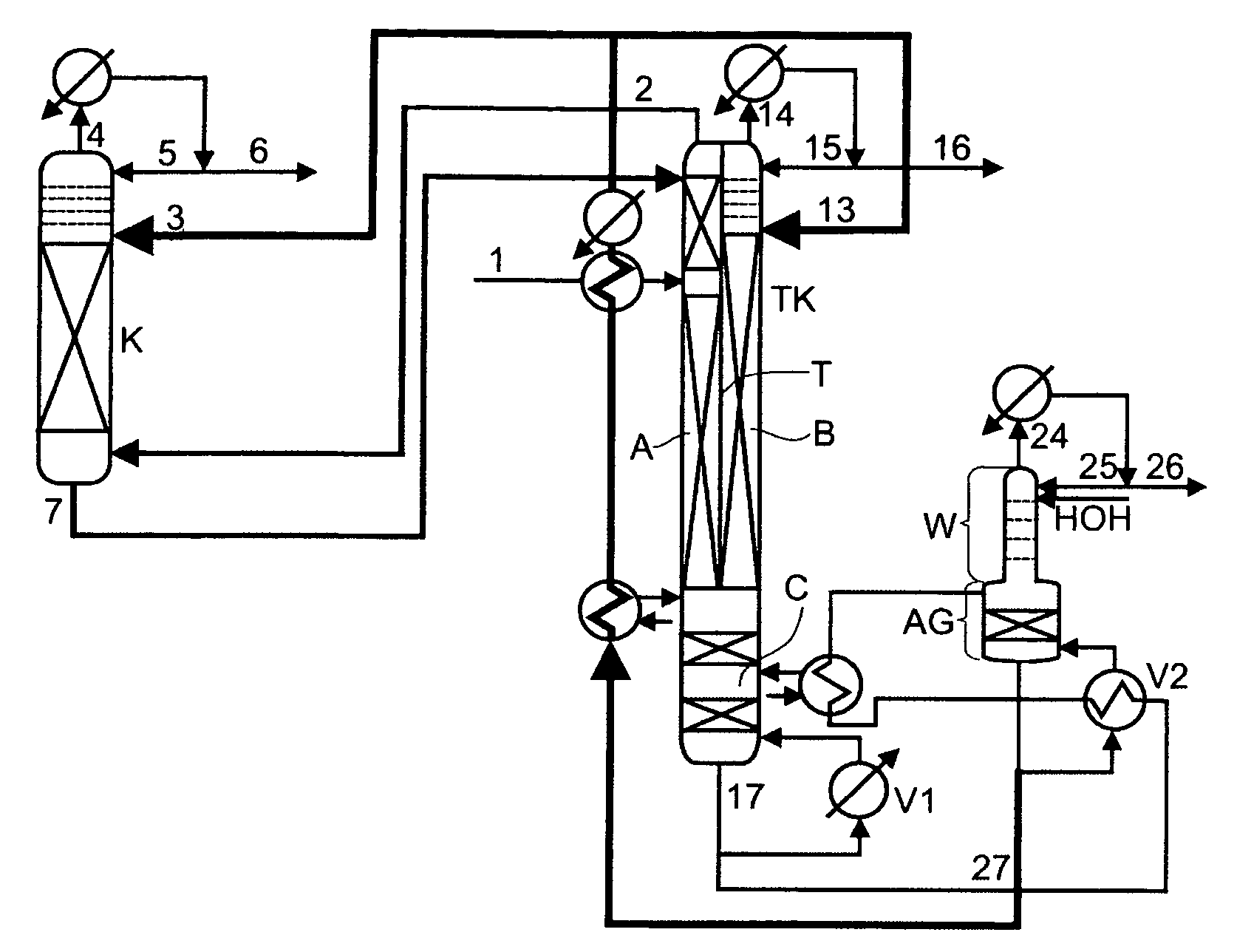
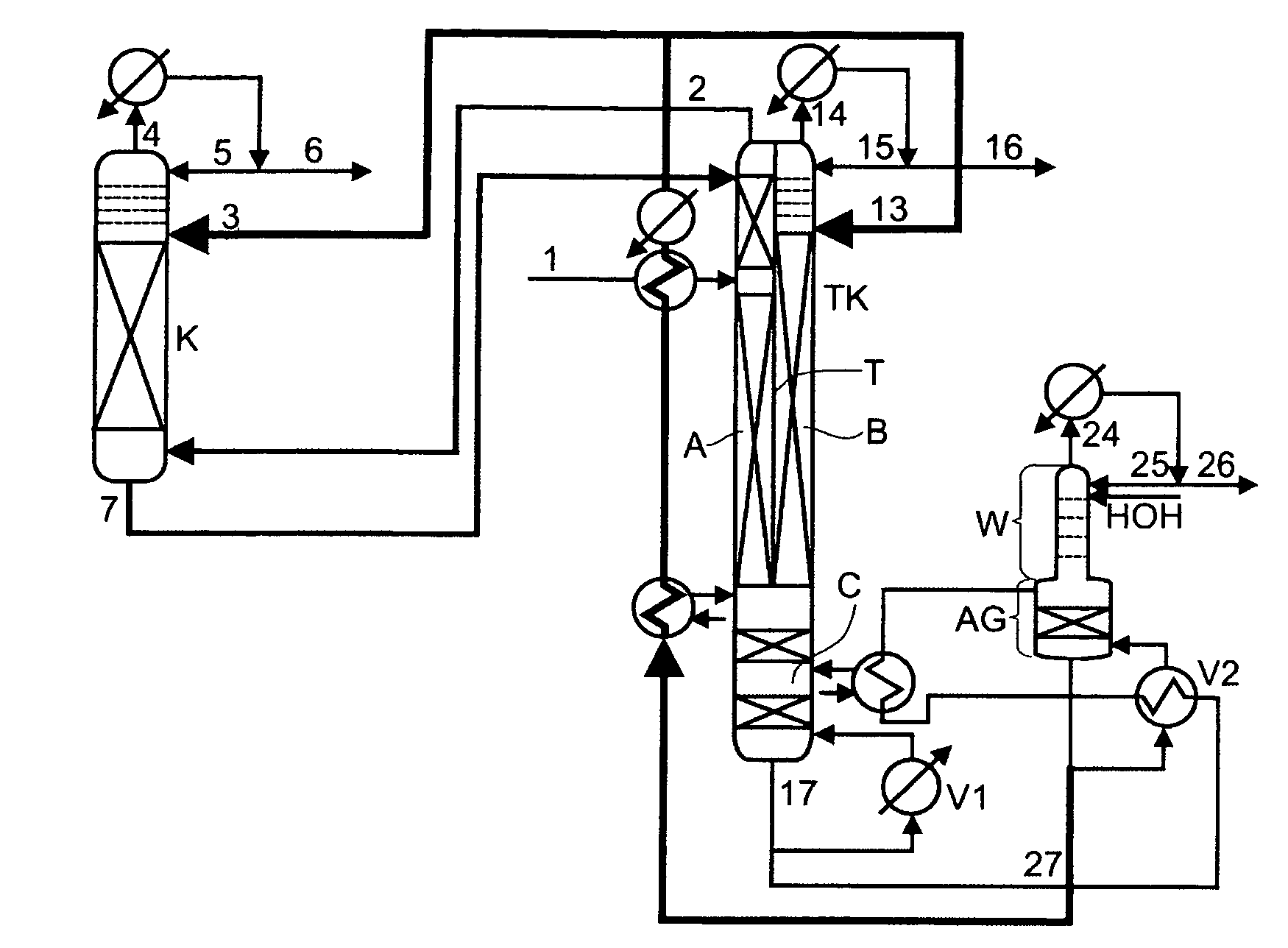
Extractive distillation is defined as distillation in the presence of a miscible, high-boiling, relatively non-volatile component, the solvent, that forms no azeotrope with the other components in the mixture. The method is used for mixtures having a low value of relative volatility, nearing unity. Such mixtures cannot be separated by simple distillation, because the volatility of the two components in the mixture is nearly the same, causing them to evaporate at nearly the same temperature at a similar rate, making normal distillation impractical.
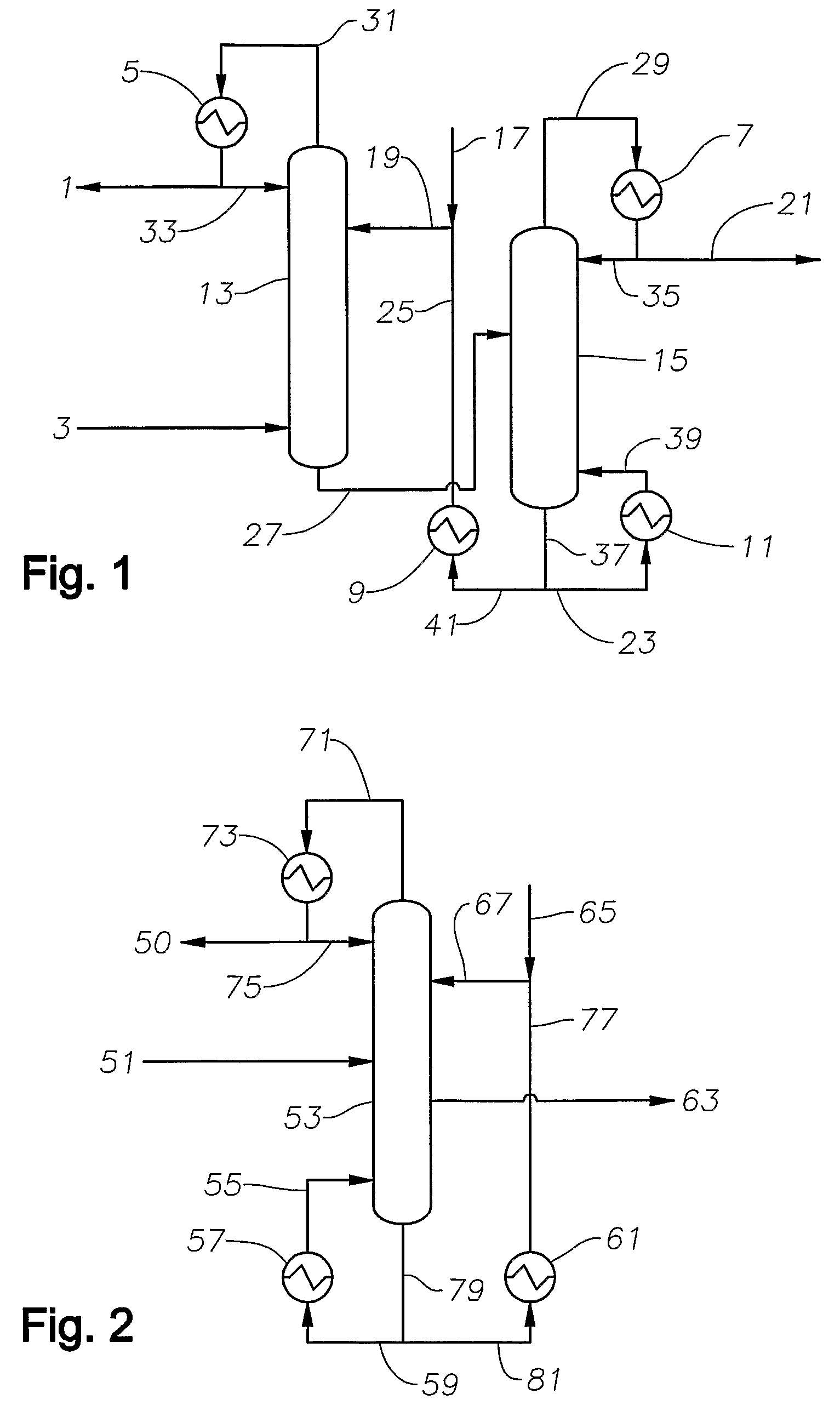
Preparation of olefins
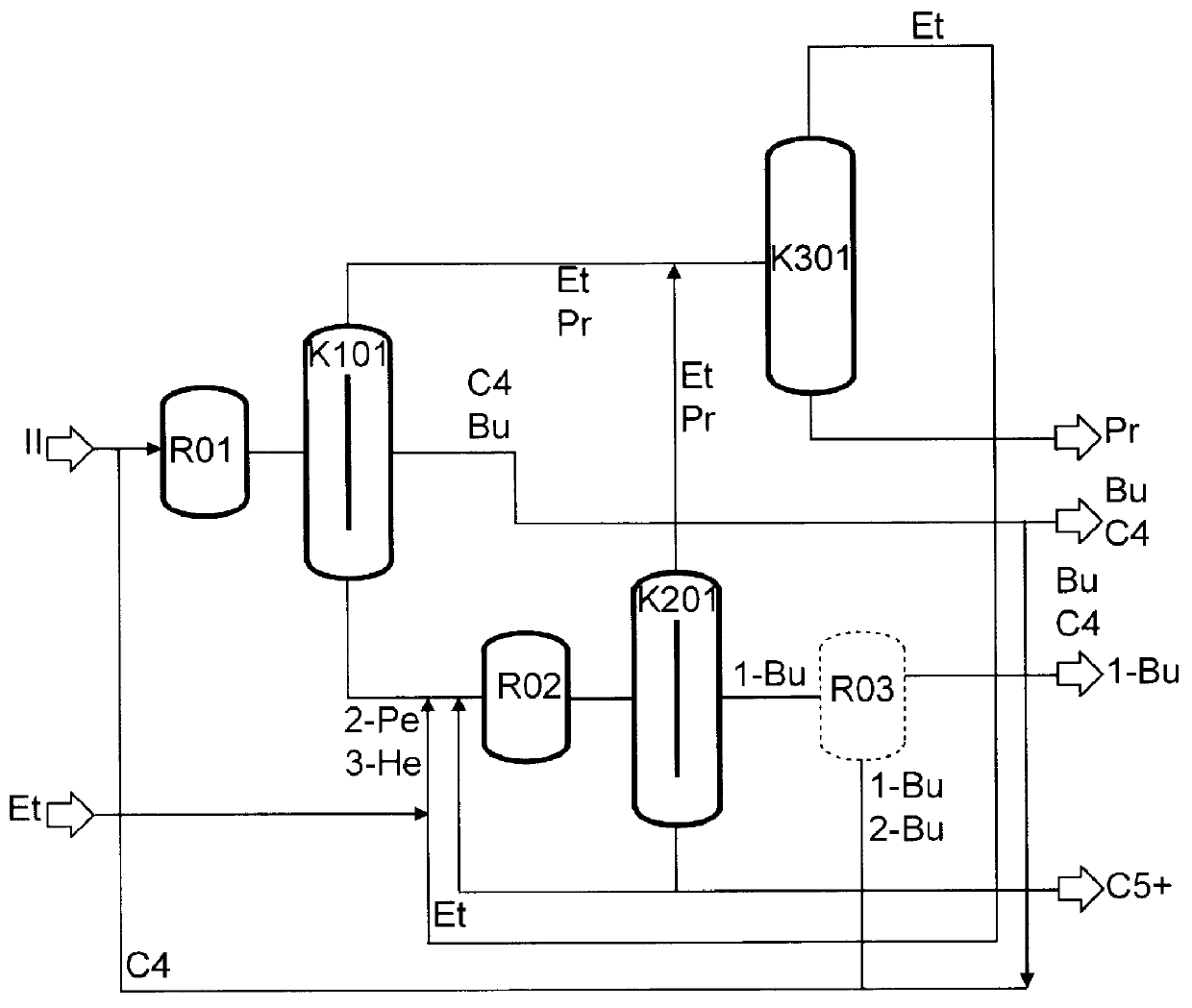
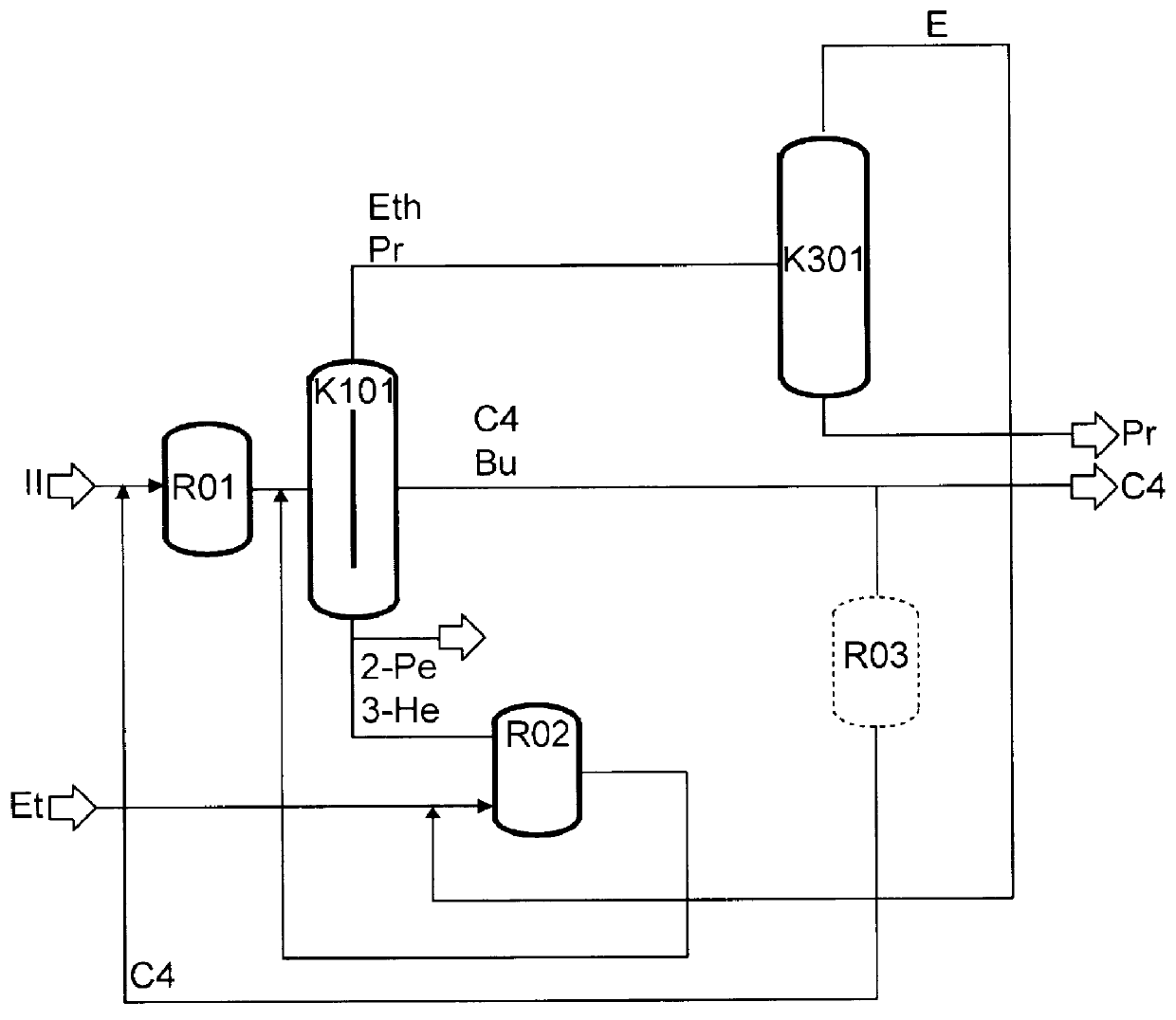
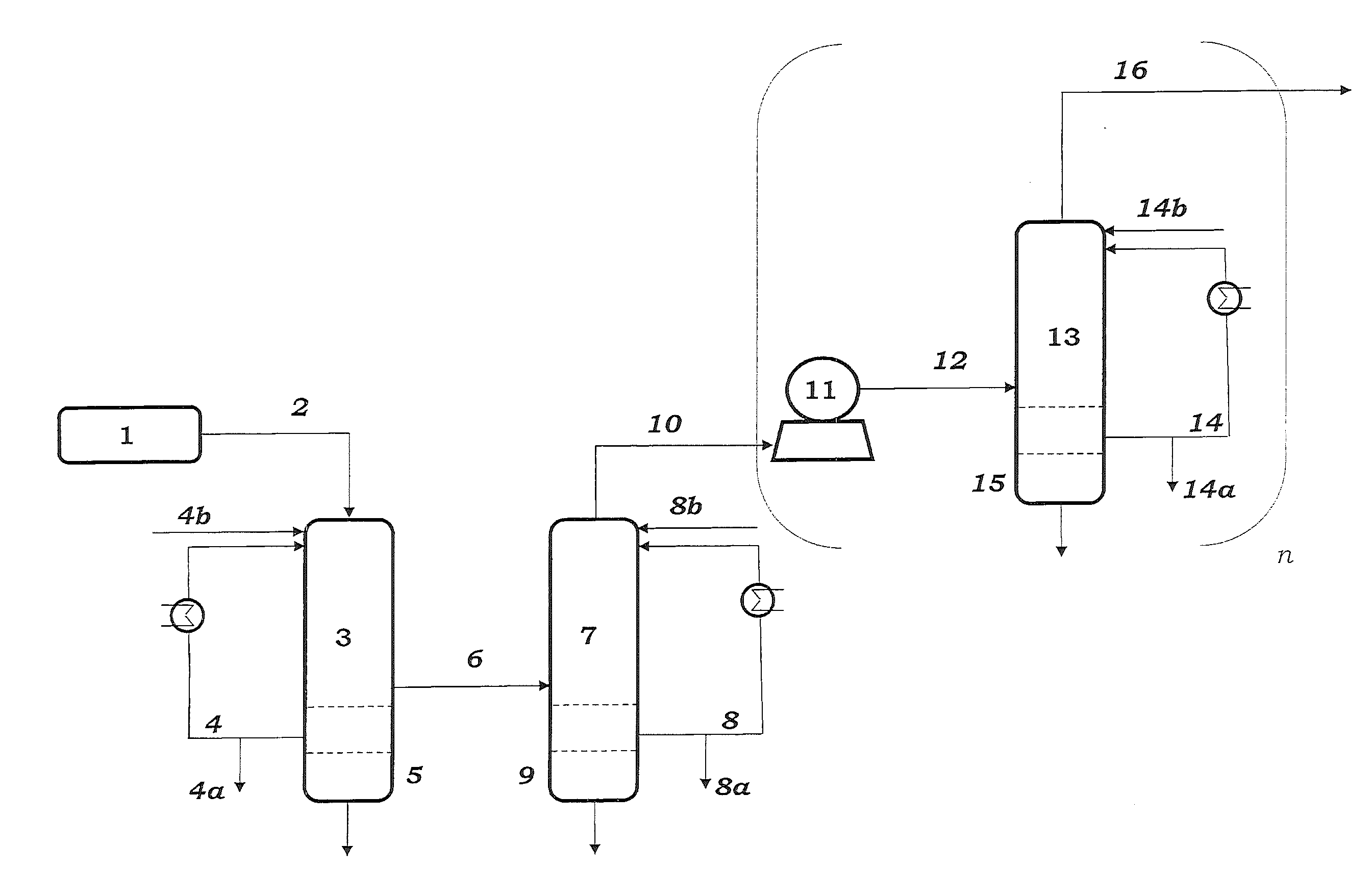
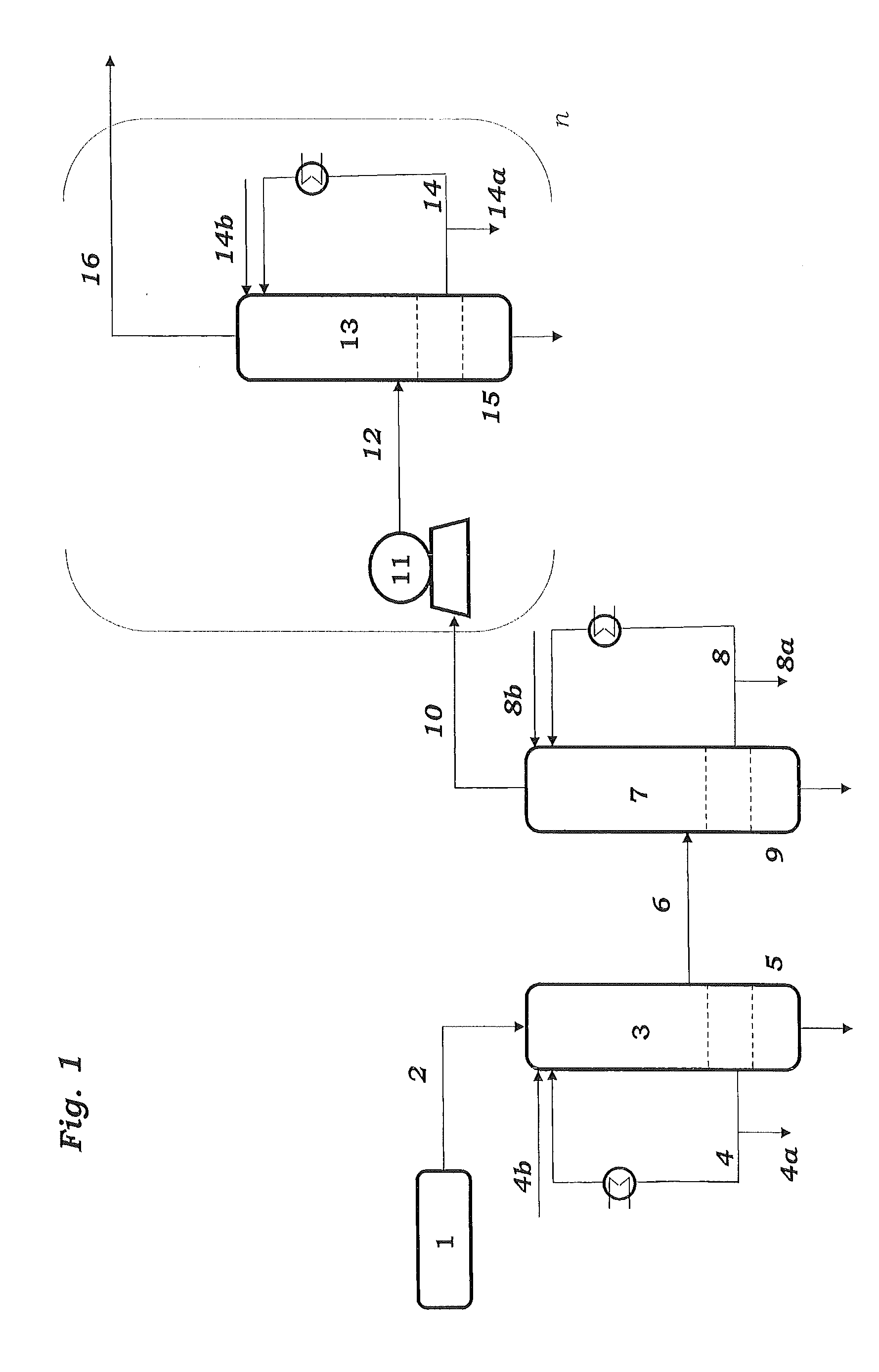
The preparation of olefins from steam cracker or refinery C4 streams is carried out by selective hydrogenation of butadienes and acetylenic impurities in the steam cracker or refinery C4 stream, with simultaneous or subsequent, at least partial isomerization of 1-butene to 2-butene, followed by removal of i-butene from the C4 stream by reaction with an alcohol to form an ether, followed by removal of oxygen-containing impurities from the C4 stream using adsorber materials, followed by two-stage metathesis of the butenes in the C4 stream by conversion of 1-butene and 2-butene present in the C4 stream into propene and 2-pentene and subsequent reaction of the 2-pentene with ethene in the presence of a metathesis catalyst to form propene and 1-butene. Optionally, butadiene may be removed from the C4 stream by extractive distillation in a preliminary step.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for generating pure benzene from reformed gasoline
InactiveUS6124514AReduce benzene contentAchieve separationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingBenzeneExtractive distillation
A process is disclosed for generating pure aromatic compounds from a reformed gasoline which contains aromatic compounds, olefins, diolefin, and triolefins, which comprises the steps of: (a) selectively hydrogenating the olefins, diolefins and triolefins in the reformed gasoline to obtain a mixture of hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds and aromatic compounds; and (b) separating the aromatic compounds from the hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds in the mixture formed during step (a) by either extractive distillation, liquid-liquid extraction or both to obtain the pure aromatic compounds.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for Preparing Butadiene by Oxidative Dehydrogenation of N-Butenes with Monitoring of the Peroxide Content During Work-Up of the Product
InactiveUS20140200381A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationWater vaporDesorption
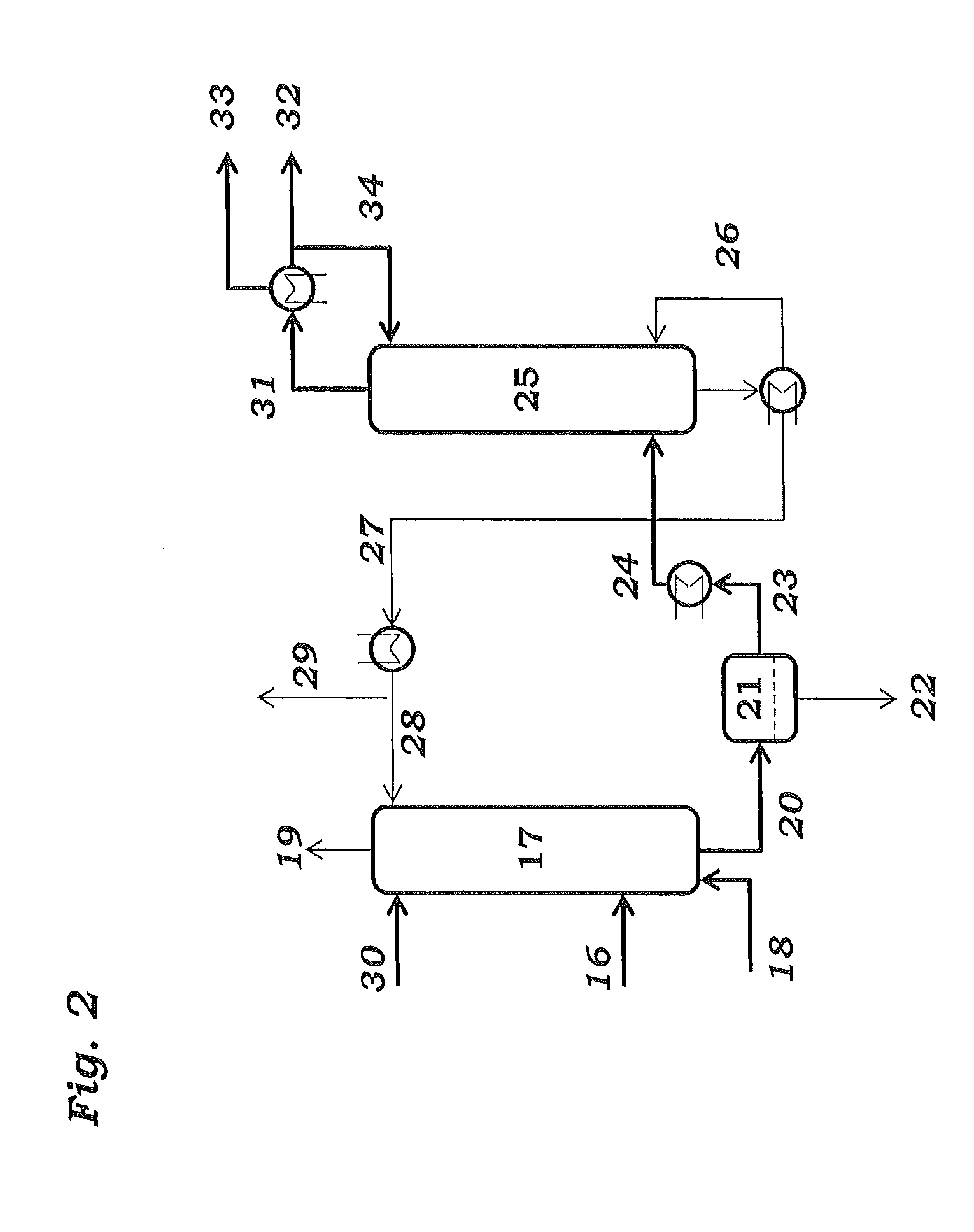
The invention relates to a process for preparing butadiene from n-butenes, which comprises the following steps:A) provision of a feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes;B) introduction of the feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes and an oxygen-comprising gas into at least one dehydrogenation zone and oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butenes to butadiene, giving a product gas stream b comprising butadiene, unreacted n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;C) cooling and compression of the product gas stream b in at least one cooling stage and at least one compression stage, with the product gas stream b being brought into contact with a circulated coolant to give at least one condensate stream c1 comprising water and a gas stream c2 comprising butadiene, n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;D) separation of incondensable and low-boiling gas constituents comprising oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases as gas stream d2 from the gas stream c2 by absorption of the C4-hydrocarbons comprising butadiene and n-butenes in a circulated absorption medium, giving an absorption medium stream loaded with C4-hydrocarbons and the gas stream d2, and subsequent desorption of the C4-hydrocarbons from the loaded absorption medium stream to give a C4 product gas stream d1;E) separation of the C4 product stream d1 by extractive distillation using a solvent which is selective for butadiene into a stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent and a stream e2 comprising n-butenes;F) distillation of the stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent to give a stream f1 consisting essentially of the selective solvent and a stream f2 comprising butadiene;where samples are taken from the circulated coolant in step C) and / or the circulated absorption medium in step D) and the peroxide content of the samples taken is determined by means of iodometry, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) or microcalorimetry.
Owner:BASF AG
Energy-saving and emission-reducing technique for producing propane epoxide by using hydrogen peroxide epoxidation propylene
InactiveCN101693703ASuitable for industrial productionEther separation/purificationChemical industryThermal energyExtractive distillation
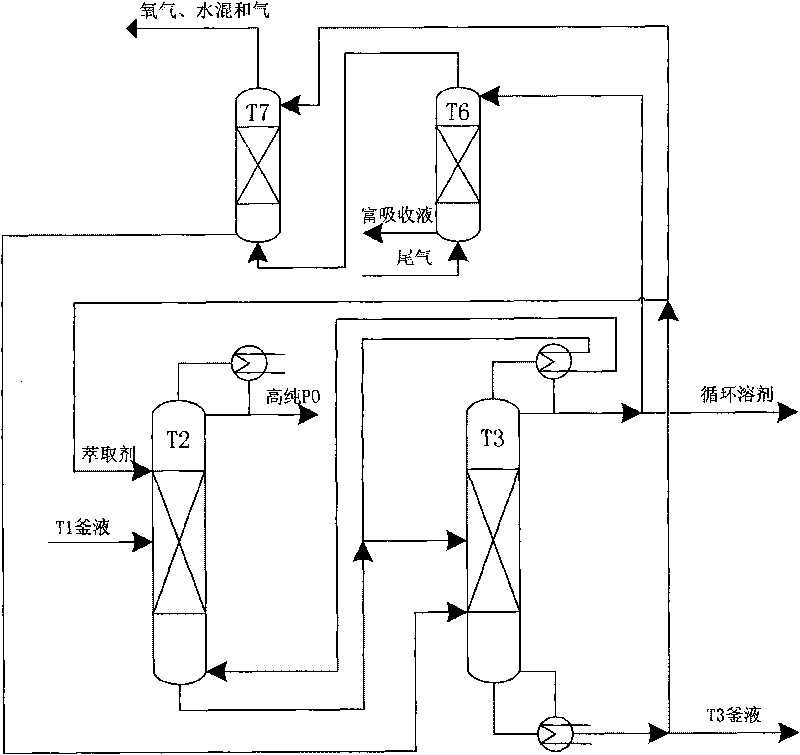
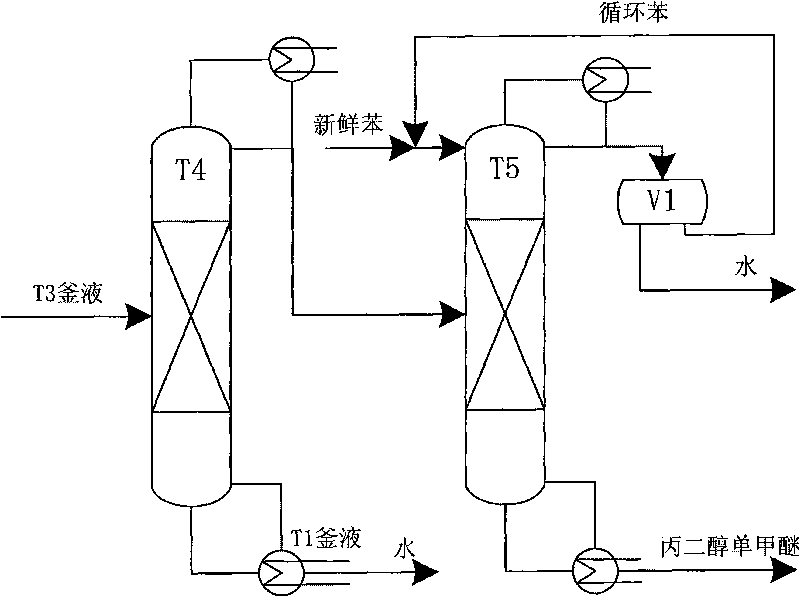
The invention relates to an energy-saving and emission-reducing technique for producing propane epoxide by using hydrogen peroxide epoxidation propylene, belonging to the field of petrochemical technology. The technique comprises a reaction part, a separation part and a tail gas treatment part, and is characterized in that propylene and hydrogen peroxide have an epoxidation reaction through a Ti-Si molecular sieve at medium pressure and low temperature; the propylene and solvent have higher recovery rate, the propane epoxide meeting the requirement of commercial-grade purity can be obtained by extractive distillation, and the joint product of propylene glycol monomethyl ether can be prepared by azeotropic distillation and purification; after part of tail gas is condensed and absorbed and the propylene is recovered, the tail gas reaches the standard and is discharged; extracting agent, absorbing agent and entrainer which are needed by the technique are in closed cycle in the process flow; and medium-pressure operation is adopted by a propylene tower to ensure water-cooling on the top of the tower, and thermal energy can be recovered by multiple-effect rectification and matching of streams. The technique has the effect and the advantage that the new energy-saving and environment-friendly technique for producing the propane epoxide can generate remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for the purification of crude propene oxide
InactiveCN1714087ACarbonyl compound separation/purificationPurification methodsExtractive distillation
The present invention relates to a method for purifying crude propylene oxide containing methanol and acetaldehyde by extractive distillation operated continuously, wherein an extraction solvent capable of reducing the volatility of methanol is used, and the crude propylene oxide is fed into a distillation column above the feed point of the crude propylene oxide A compound containing unsubstituted NH2 groups and capable of reacting with acetaldehyde is added to obtain purified propylene oxide containing less than 100 ppm methanol and less than 100 ppm acetaldehyde. The present invention also relates to a method for catalytic epoxidation of propylene comprising said purification step.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH +1
Continuous extractive distillation separation method of dimethyl carbonate-methanol azeotropic mixture
InactiveCN103159586AIncrease relative volatilityAchieve recyclingOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationExtractive distillationTransesterification
The invention discloses a continuous extractive distillation separation method of a dimethyl carbonate-methanol azeotropic mixture, and relates to a continuous extractive distillation method. The technical process of the method is as follows: ethylene glycol is used as an extraction agent at normal pressure; the solvent ratio is 1-3; the separated dimethyl carbonate-methanol azeotropic mixture is fed from the middle part of a tower, the extraction agent is fed from the top of the tower, and the reflux ratio is 2; high-purity methanol is extracted from the tower top of an extractive distillation tower, and the dimethyl carbonate and the extraction agent are extracted from the tower bottom; the fraction at the tower bottom enters an extraction agent recovery tower, and the reflux ratio is 3; and dimethyl carbonate is extracted from the tower top, and the extraction agent extracted from the tower bottom can be recycled. The method disclosed by the invention adopts ethylene glycol as an extraction agent, and improves the separation effect of the dimethyl carbonate-methanol azeotropic mixture; and since ethylene glycol is a co-production product in synthesizing dimethyl carbonate by a transesterification method, the source is conveniently available, and the cost caused by introducing other substances is avoided.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
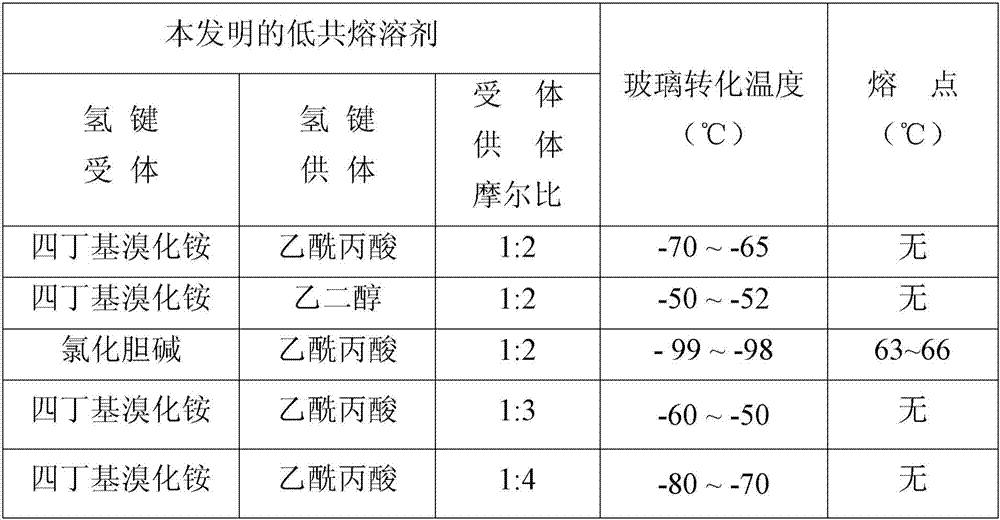
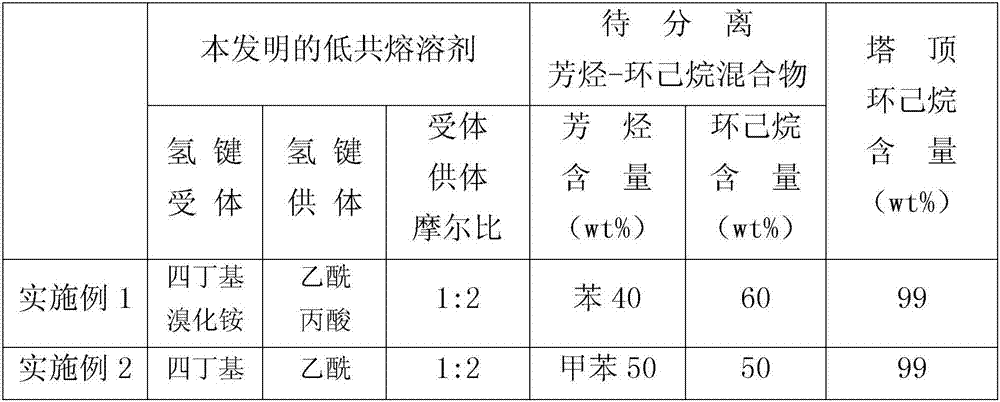
Low eutectic solvent for aromatic hydrocarbon separation and application thereof to extractive distillation
ActiveCN107311833AOvercome dosageOvercoming a large amountDistillation purification/separationExtractive distillationExtractive distillationReactive distillation
The invention discloses a low eutectic solvent for aromatic hydrocarbon separation. The low eutectic solvent is obtained by mixing hydrogen bond receptors and hydrogen bond donors according to a certain ratio (the molar ratio of 1: 1 to 1:10), and stirring till being in a uniform transparent state at 70-100 DEG C. The low eutectic solvent is low in toxicity, environment-friendly and high in efficiency, and can be applied to the process of separating aromatic hydrocarbons from non-aromatic hydrocarbons in coal tar and petroleum oil.
Owner:烟台中科恩吉科创新产业园管理有限公司
Iso-butane, n-butane and butylene separation and purification method
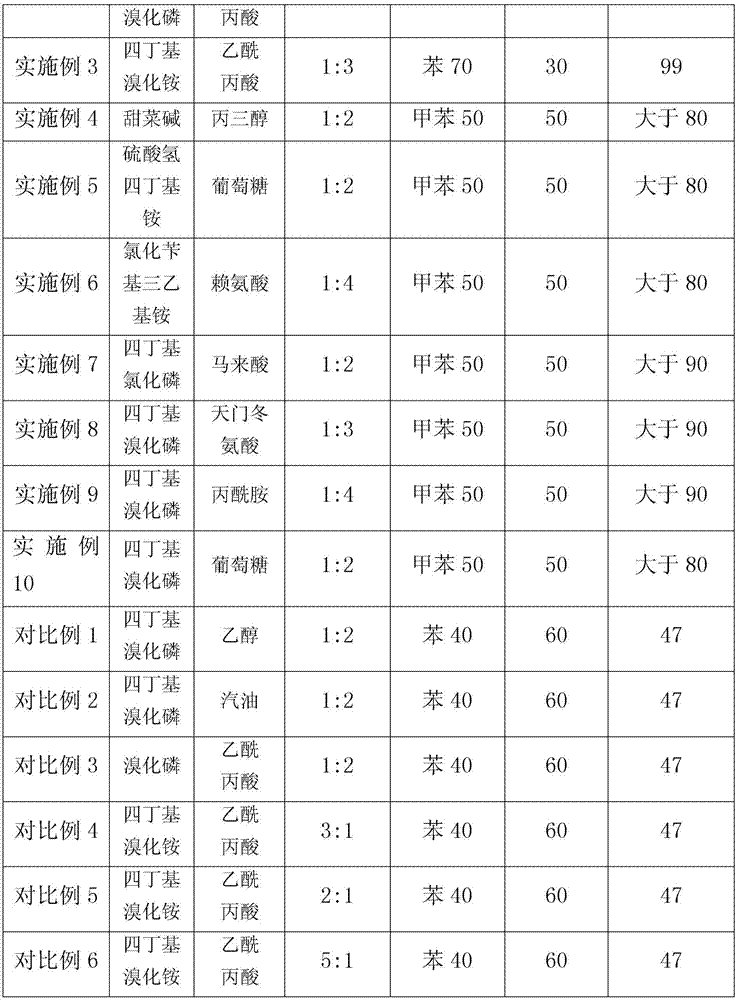
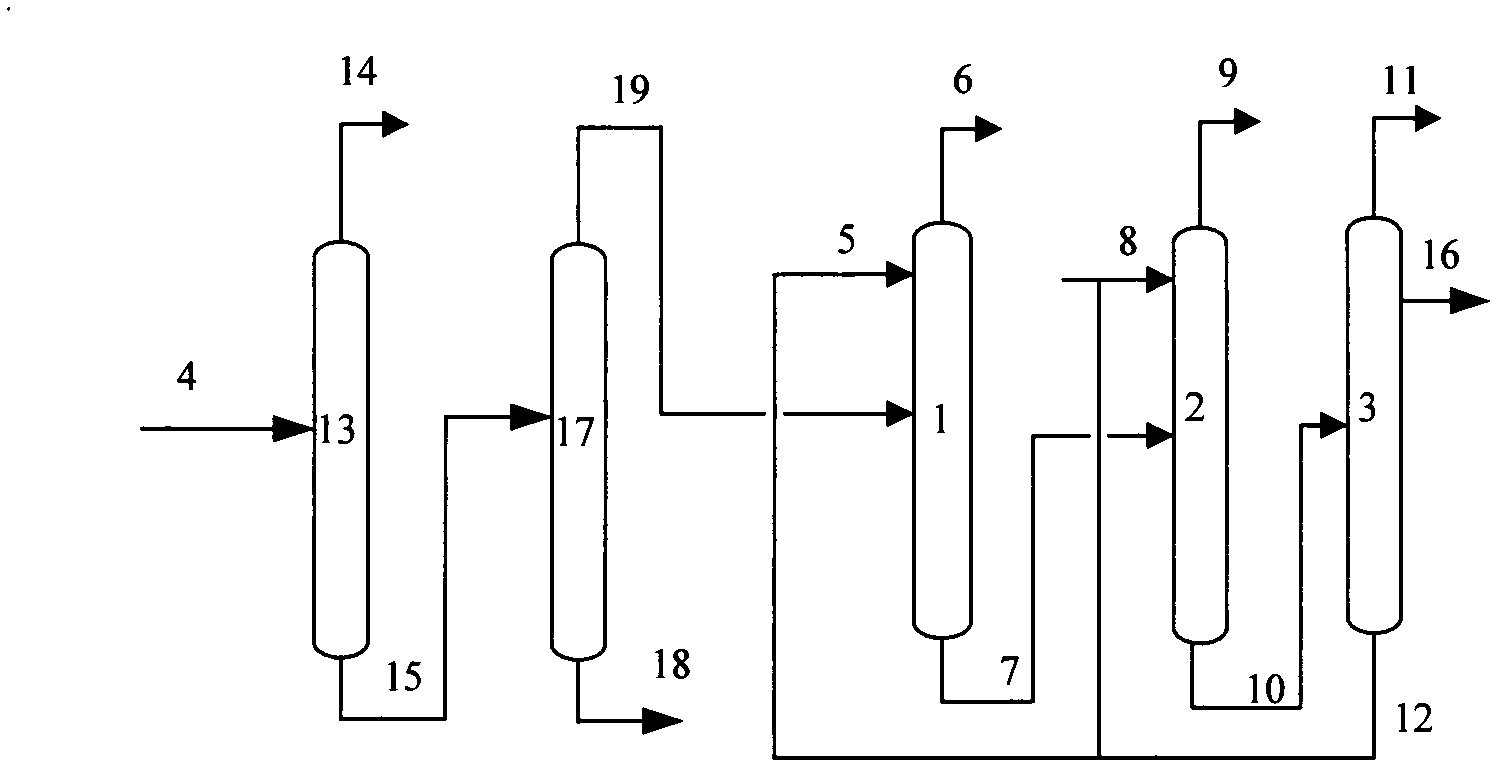
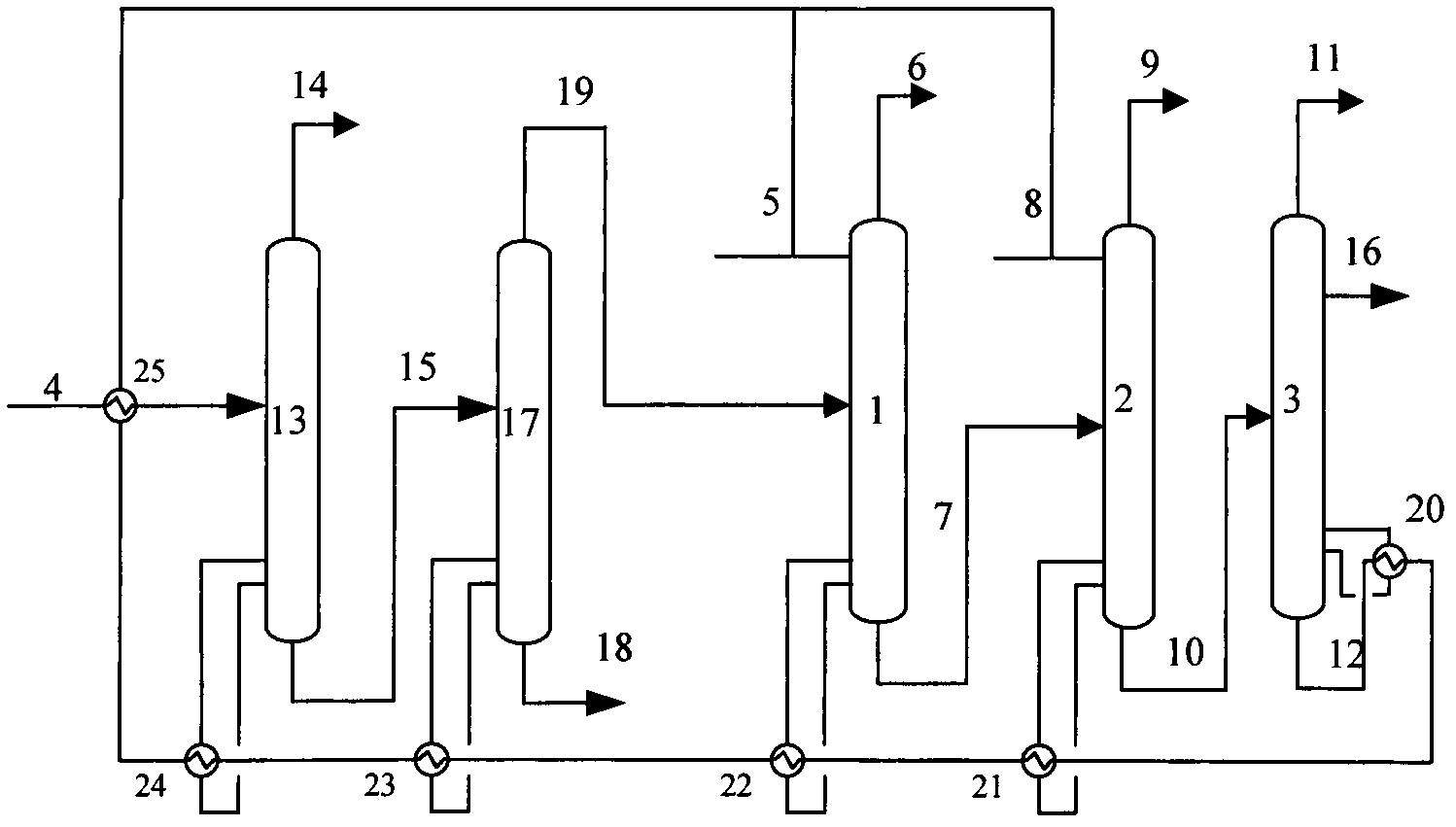
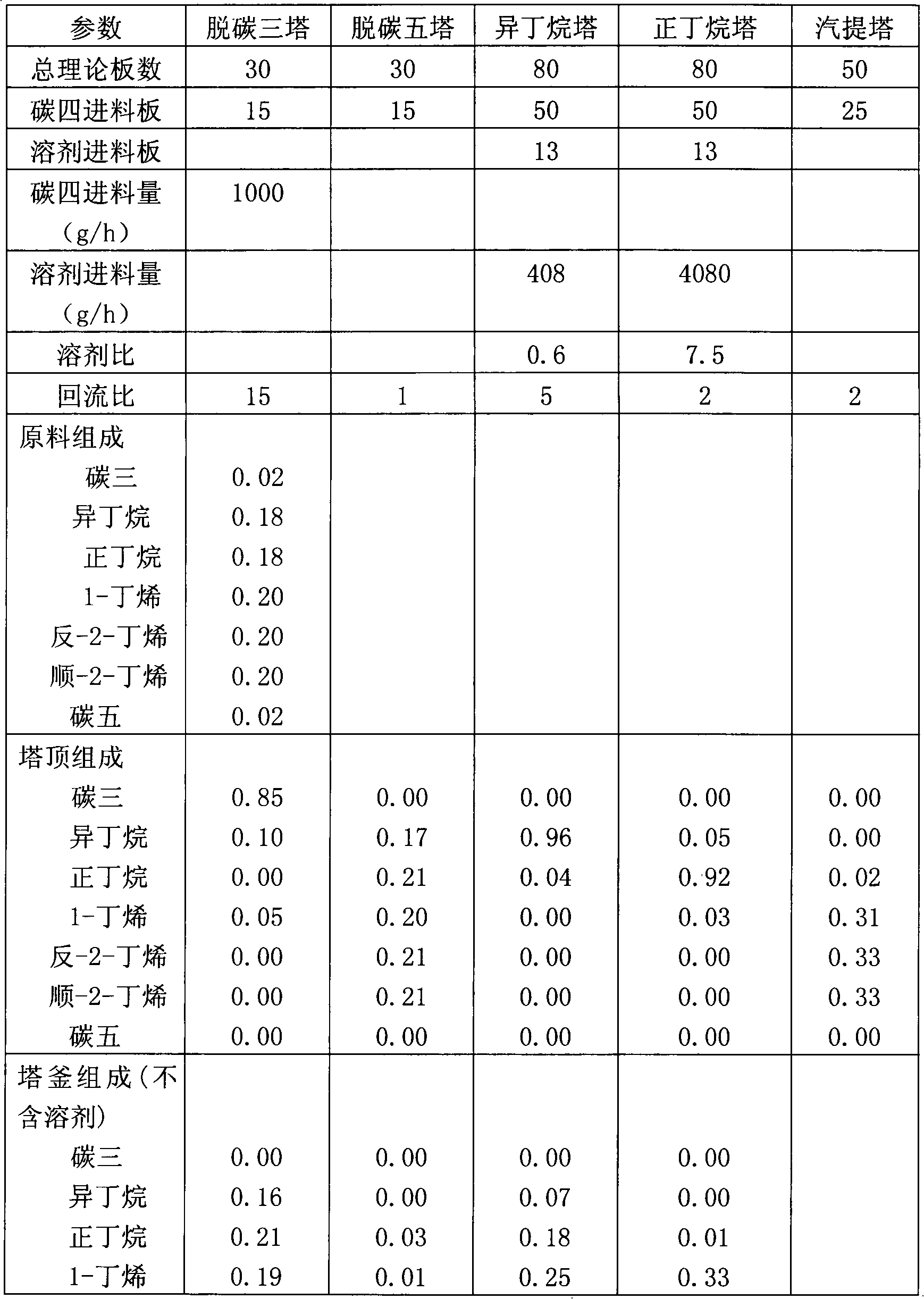
InactiveCN102603454ALess investmentReduce energy consumptionDistillation purification/separationButenePurification methods
The invention provides an iso-butane, n-butane and butylene separation and purification method. C4 raw materials are successively put into a C3 decarburization tower, a C5 decarburization tower, an iso-butane tower, an n-butane tower and a stripping tower to obtain high-purity iso-butane, n-butane and butylene. Solvents are cyclically utilized. The iso-butane, n-butane and butylene separation and purification method has the technical advantages that not only can equipment investment be reduced, but also the advantages of extractive distillation are used and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Extractive distillation process for recovering aromatics from petroleum streams
InactiveUS7666299B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyHydrocarbon oils refiningAlkaneExtractive distillation
A process for recovering polar hydrocarbons from non-polar hydrocarbons, such as aromatics from non-aromatics, naphthenes from paraffins and isoparaffins, or olefins from paraffins and isoparaffins, in feed mixtures containing at least a measurable amount of heavier hydrocarbons. This improved extractive distillation (ED) process recovers aromatic hydrocarbons including benzene, toluene, and xylenes from the C6-C8 petroleum streams containing a measurable amount of C9+ hydrocarbons. The ED process also recovers benzene and toluene from the C6-C7 petroleum streams containing a measurable amount of C8+ hydrocarbons. The ED solvent utilized to recover and purify the aromatic hydrocarbons from the petroleum stream with a heavier than intended feedstock of hydrocarbons is also regenerated and recovered.
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
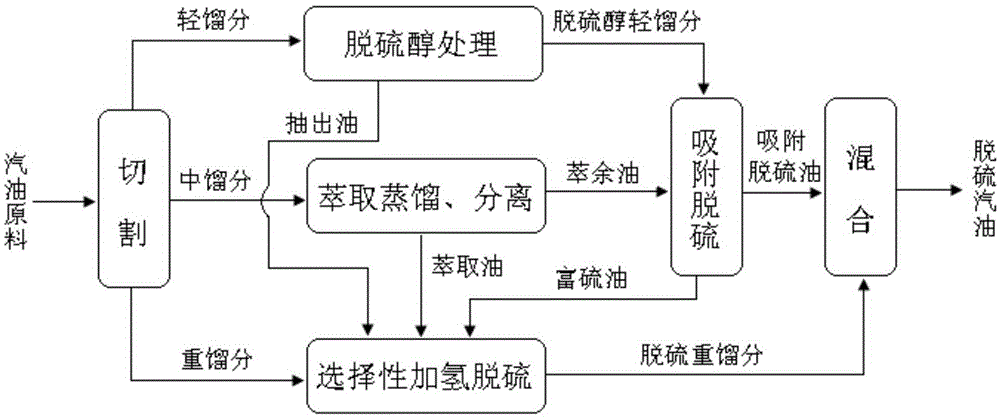
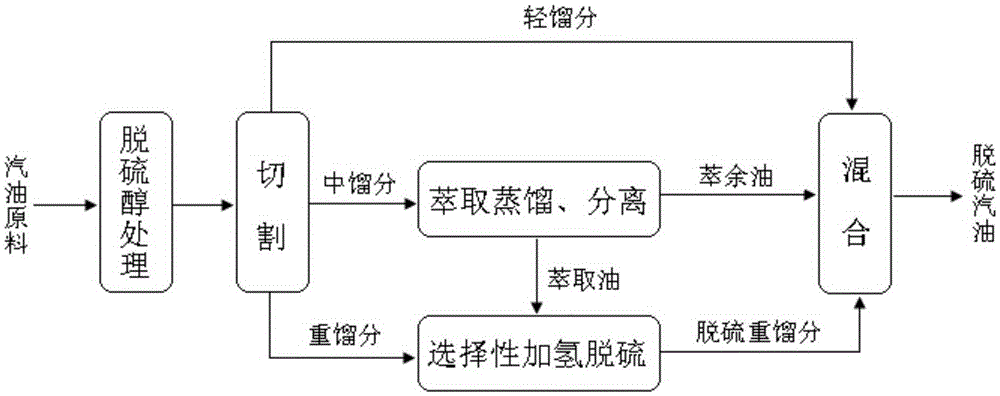
Coupling method of catalytic cracking gasoline desulfurization
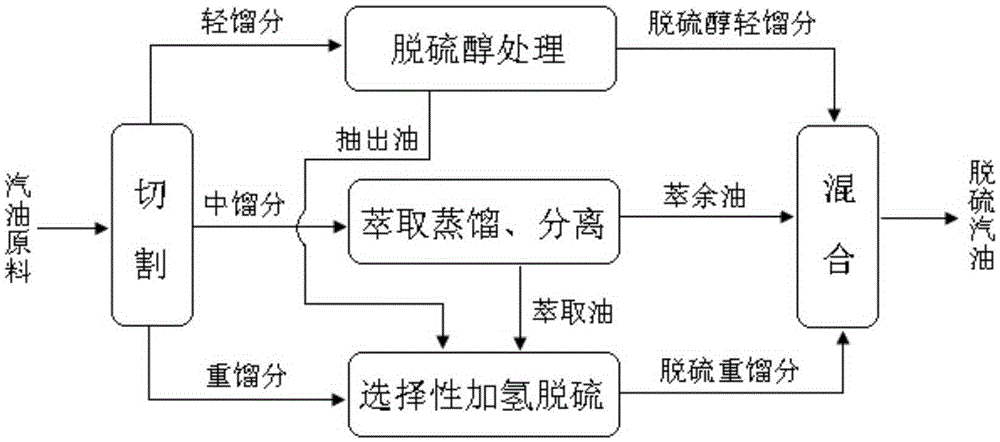
ActiveCN105296000AEasy to removeRemoval is not easy to achieveTreatment with hydrotreatment processesOrganic solventExtractive distillation
The invention provides a coupling method of catalytic cracking gasoline desulfurization. The coupling method comprises the following steps: cutting gasoline raw materials into light fractions, medium fractions and heavy fractions; carrying out extractive distillation on the medium fractions by an organic solvent to obtain olefin-contained raffinate and extracts which contain sulfide and arene; separating the organic solvent in the extracts to obtain extraction oil; carrying out selective hydrodesulfurization on the extraction oil and the heavy fractions to obtain the desulfurization heavy fractions; mixing the light fractions, the raffinate and the desulfurization heavy fractions to obtain desulfurization gasoline, wherein the cutting temperature of the light fractions and the medium fractions is 35 to 60DEG C, and the cutting temperature of the medium fractions and the heavy fractions is 140 to 160DEG C. According to the coupling method of the gasoline desulfurization, the octane value loss of a gasoline product can be obviously reduced, and desulfurization load is drastically lowered while deep desulfurization is realized. The yield of the product is greater than 95%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
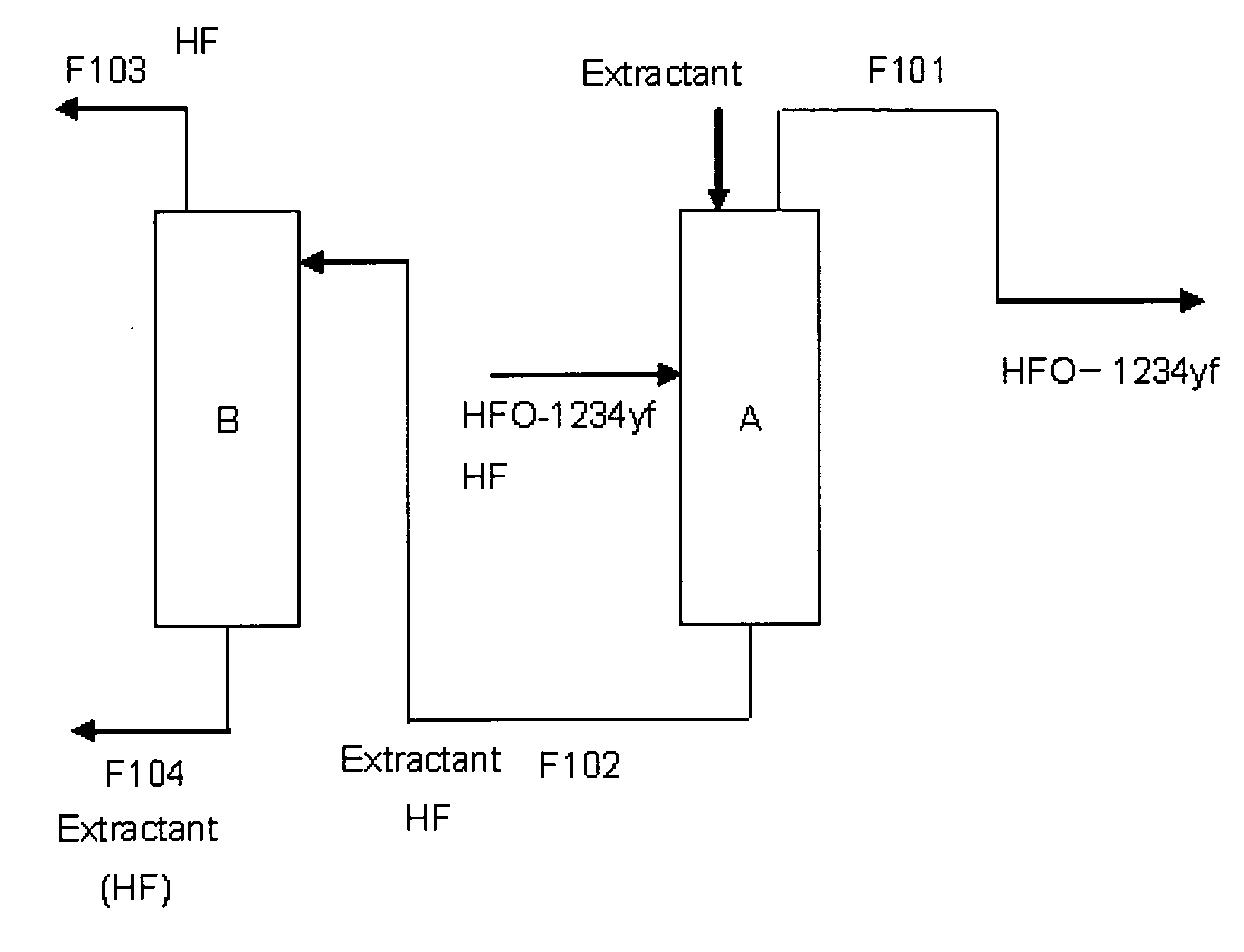
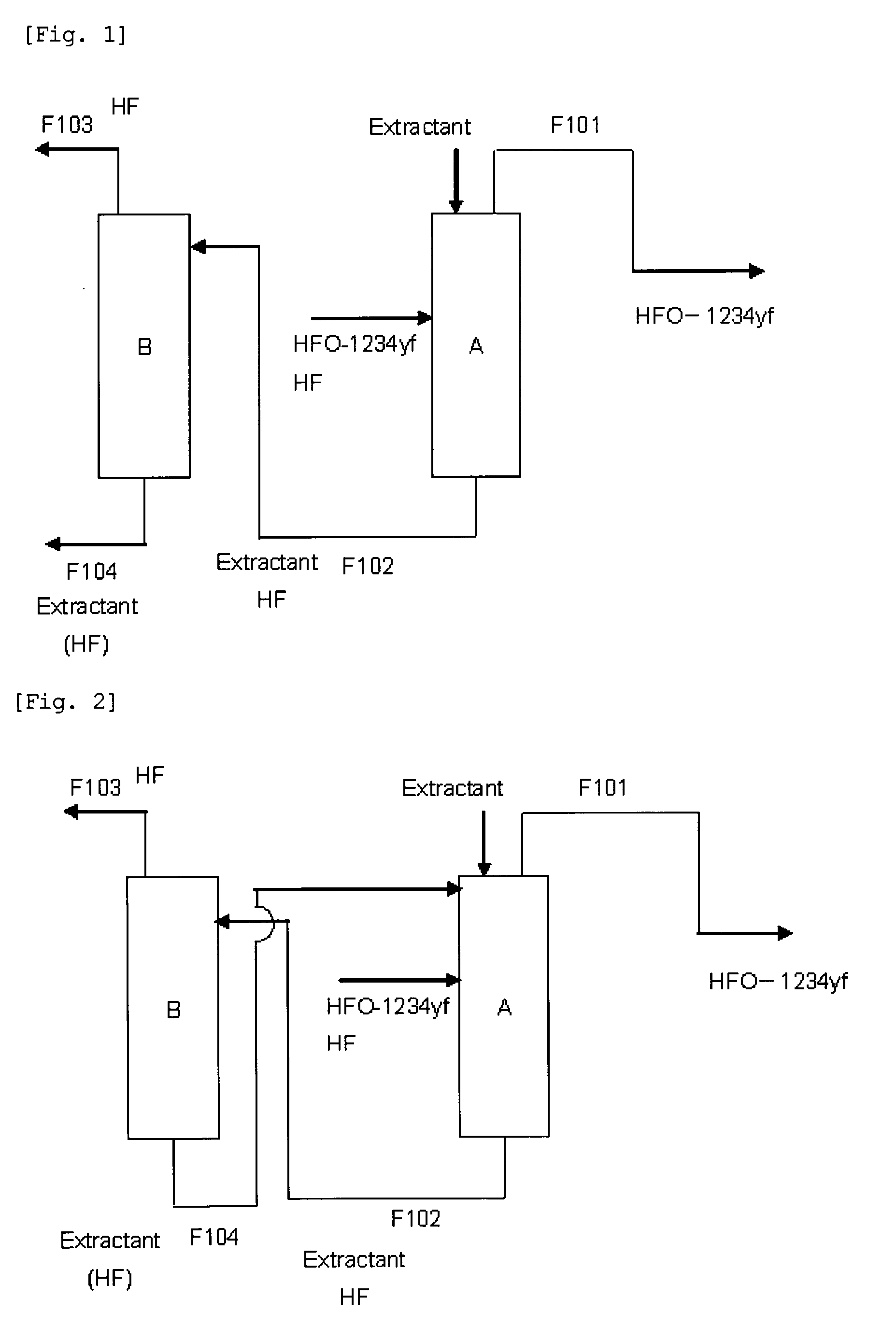
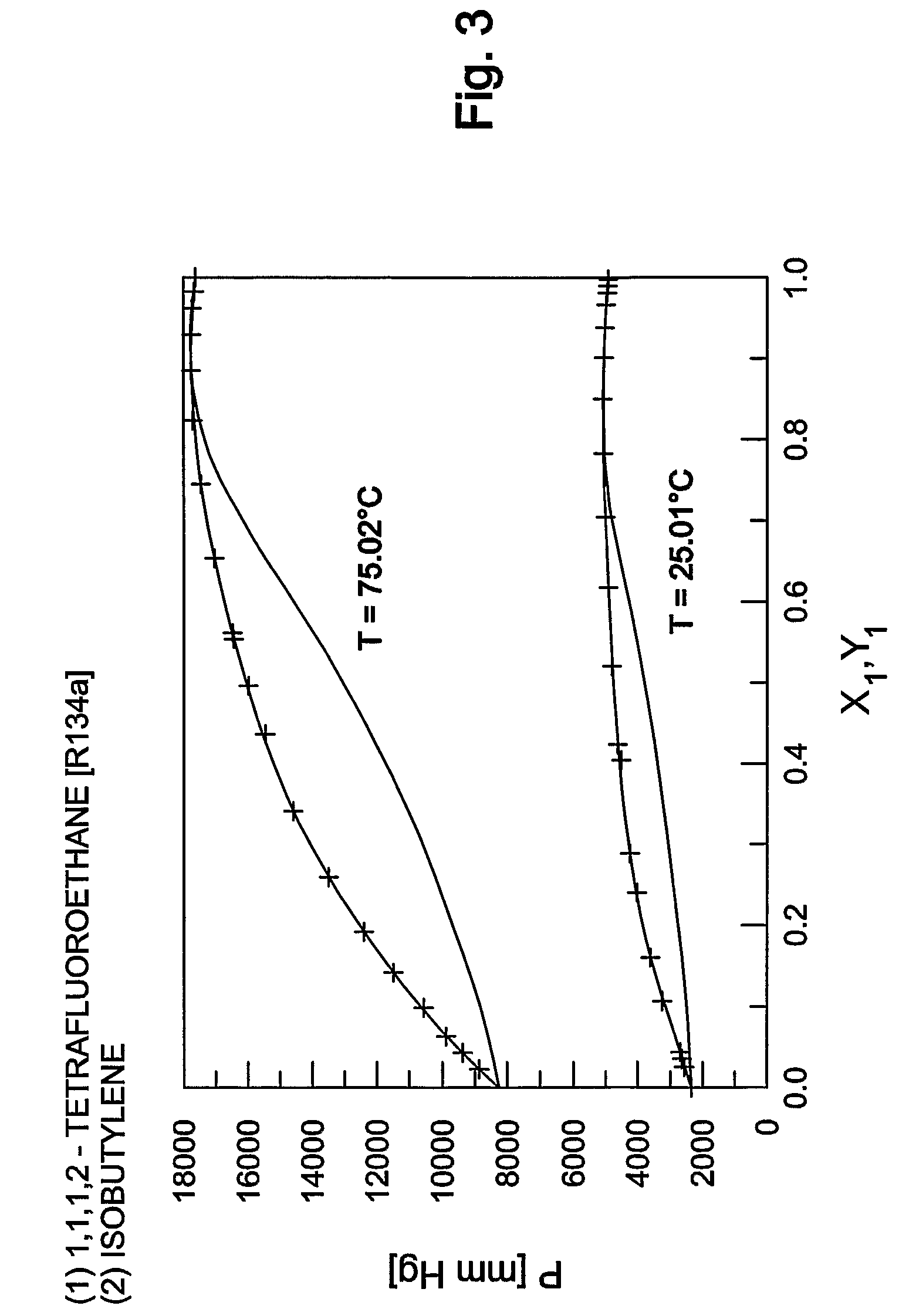
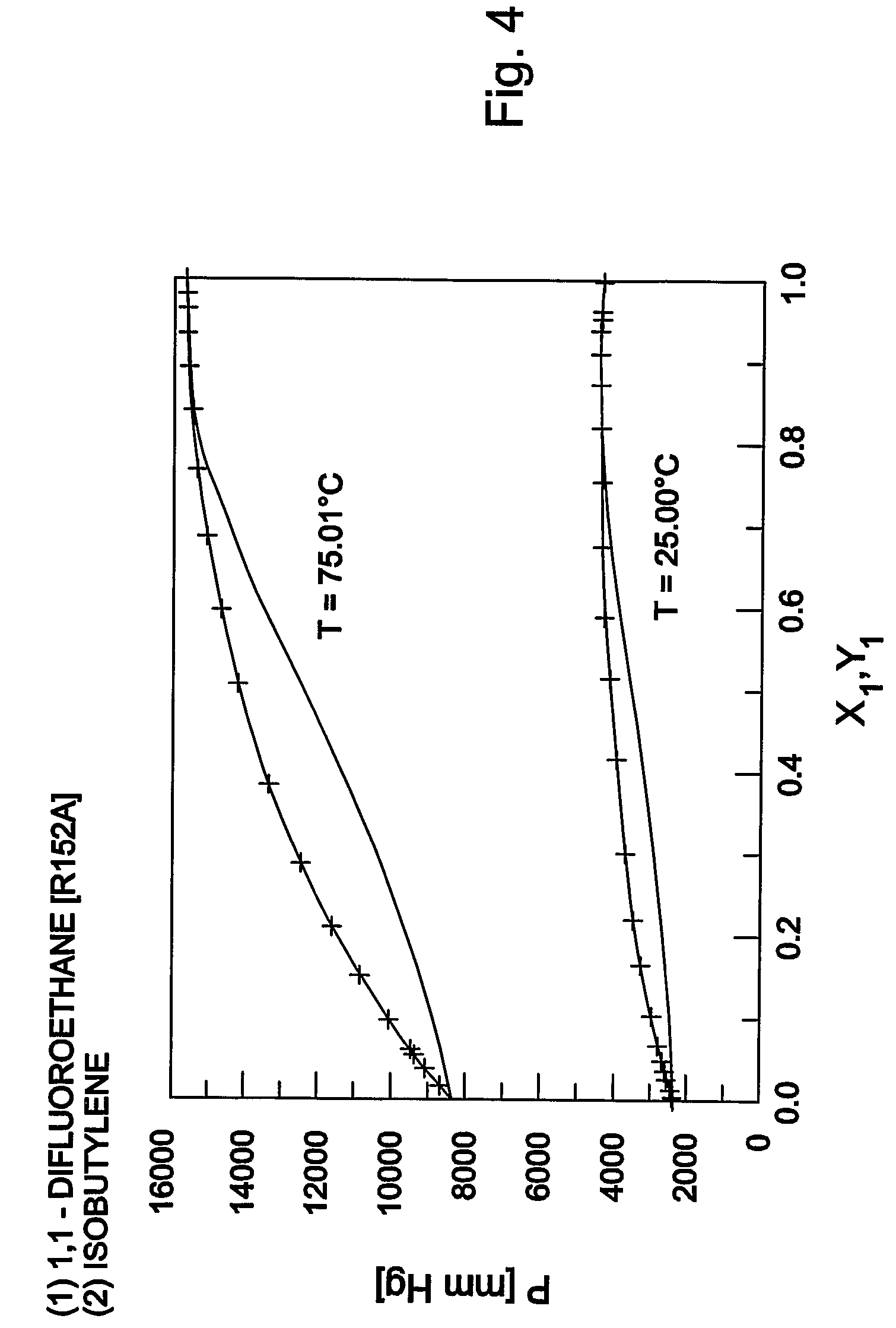
Purification method of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene
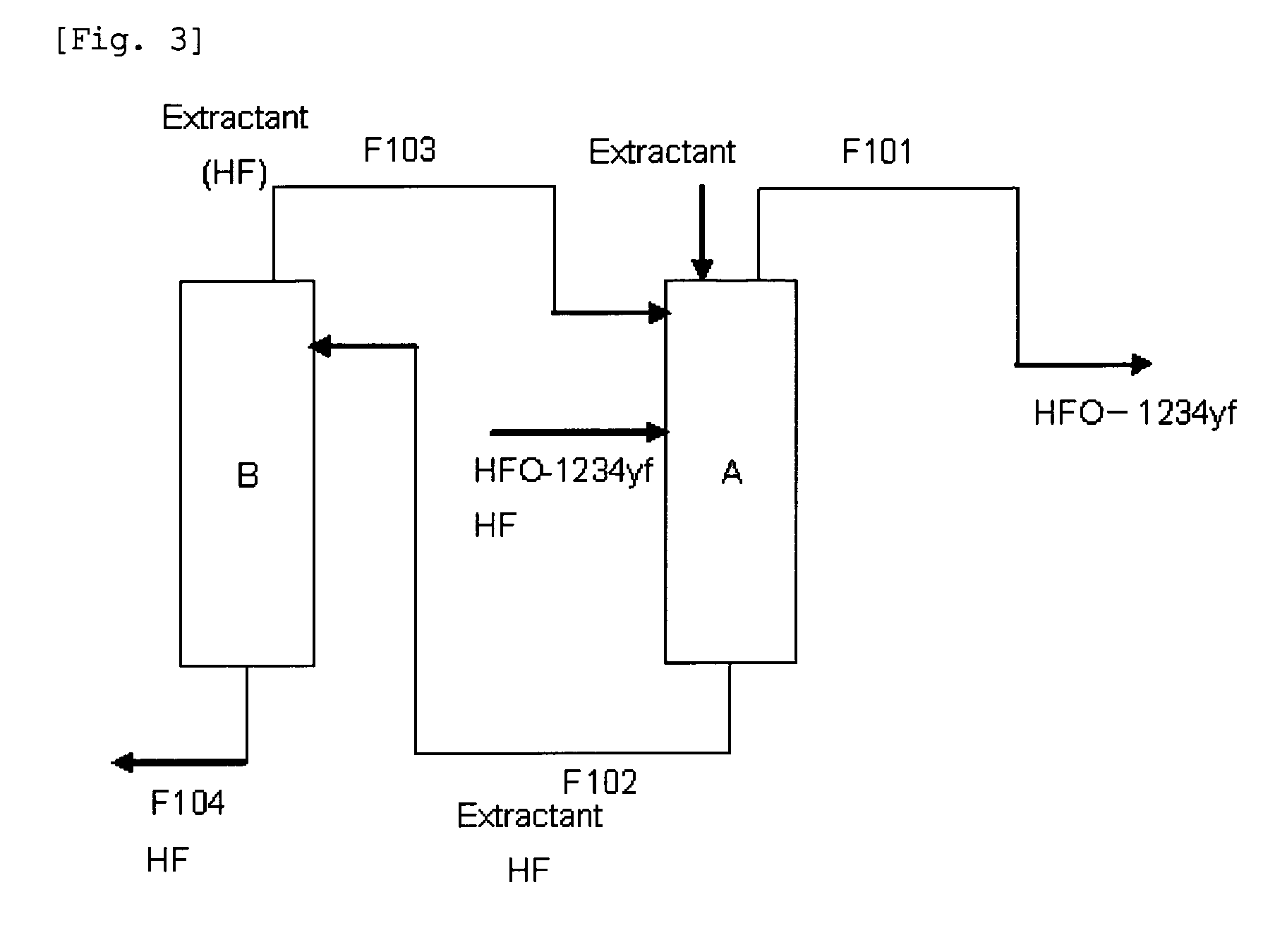
ActiveUS20130105296A1Efficient methodReduce the amount of wasteHydrogen fluorideHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationPurification methodsExtractive distillation
This invention provides a method for purifying HFO-1234yf by removing HF from a mixture of HFO-1234yf and HF under simple and economically advantageous conditions. According to the present invention, this is a purification method for 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene, (1) the purification method comprising the step of subjecting a mixture comprising 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene and hydrogen fluoride to extractive distillation in a distillation column A using an extractant, thereby obtaining a fraction I that contains 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene and has a lower ratio of hydrogen fluoride to 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene than that of the mixture, while obtaining a fraction II that contains hydrogen fluoride and has a lower ratio of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene to hydrogen fluoride than that of the mixture; (2) the extractant comprising at least one member selected from the group consisting of: (i) alcohols represented by ROH, wherein R is a C1-5 alkyl group, (ii) ethers represented by ROR′, wherein R and R′ are the same or different, and each is a C1-4 alkyl group, (iii) fluorinated alcohols represented by RfOH, wherein Rf is a C1-3 fluoroalkyl group, (iv) ketones represented by RCOR′, wherein R and R′ are the same or different, and each is a C1-4 alkyl group, (v) esters represented by RCOOR′, wherein R and R′ are the same or different, and each is a C1-4 alkyl group, (vi) polyols represented by R(OH)n, wherein R is a C1-4 alkyl group, and n is an integer of 2 to 3, and (vii) ethylene glycols represented by R1O(CH2CH2O)nR2, wherein R1 and R2 are the same or different, and each is hydrogen or a C1-4 alkyl group, and n is an integer of 1 to 3.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
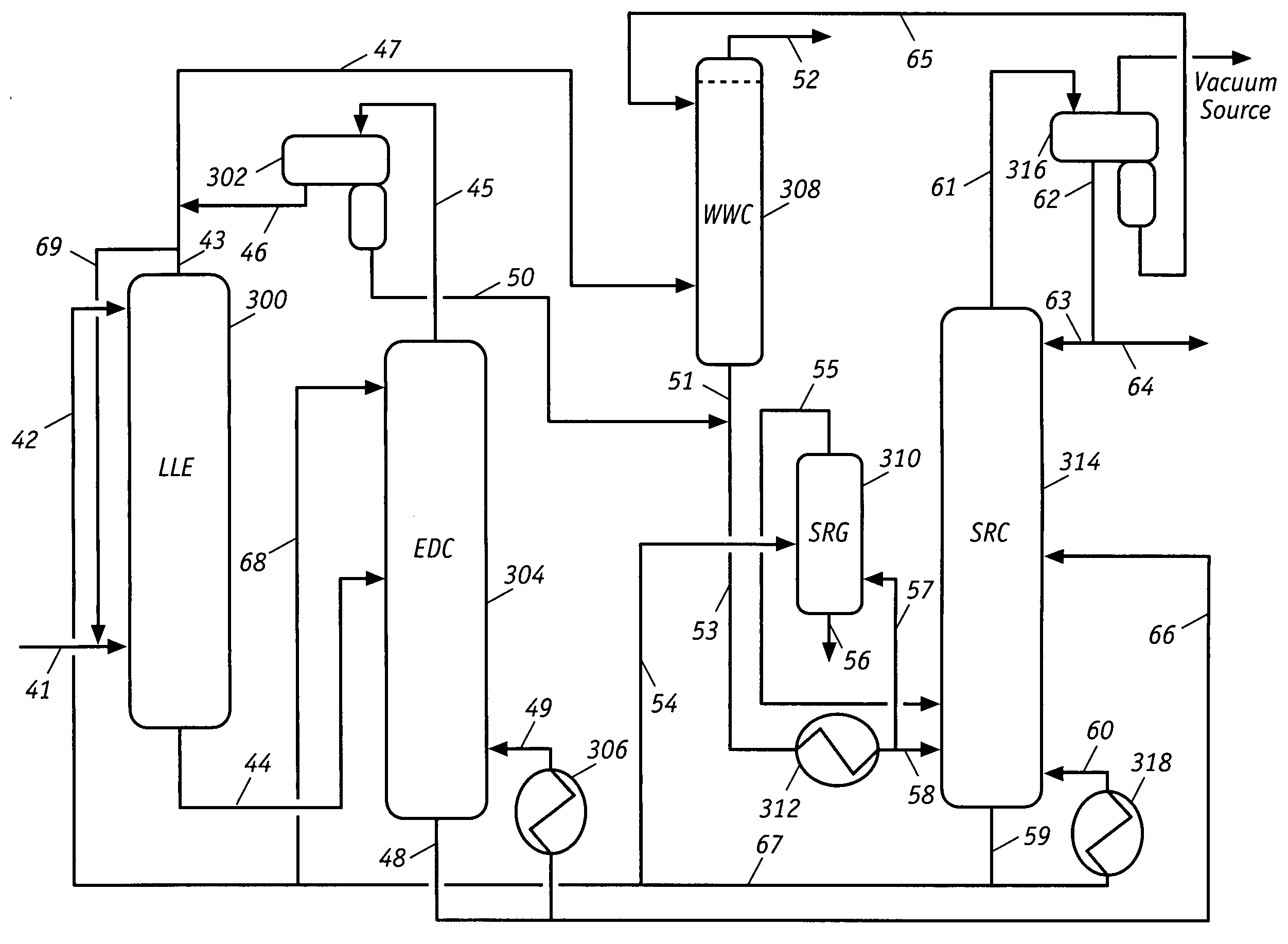
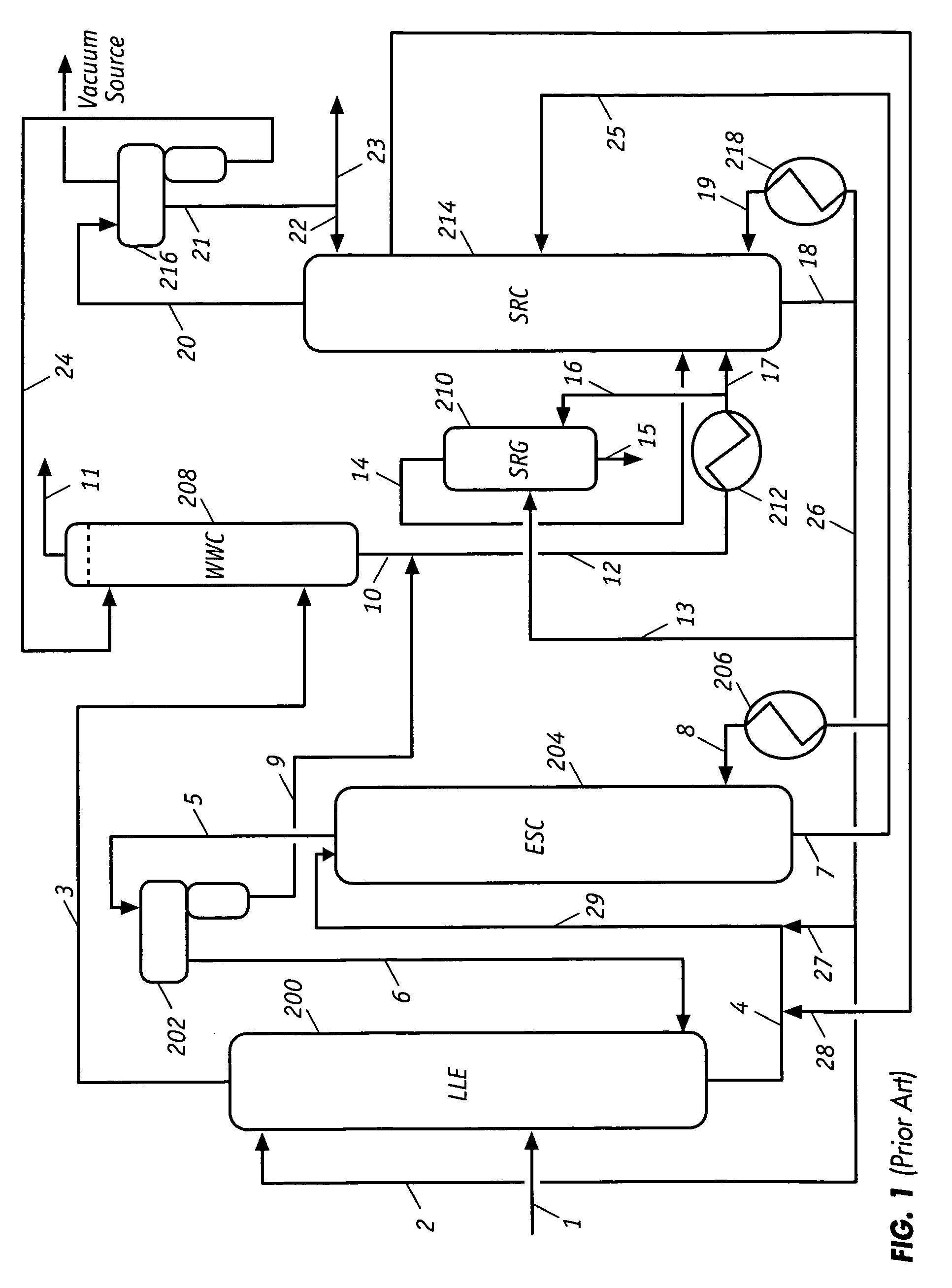
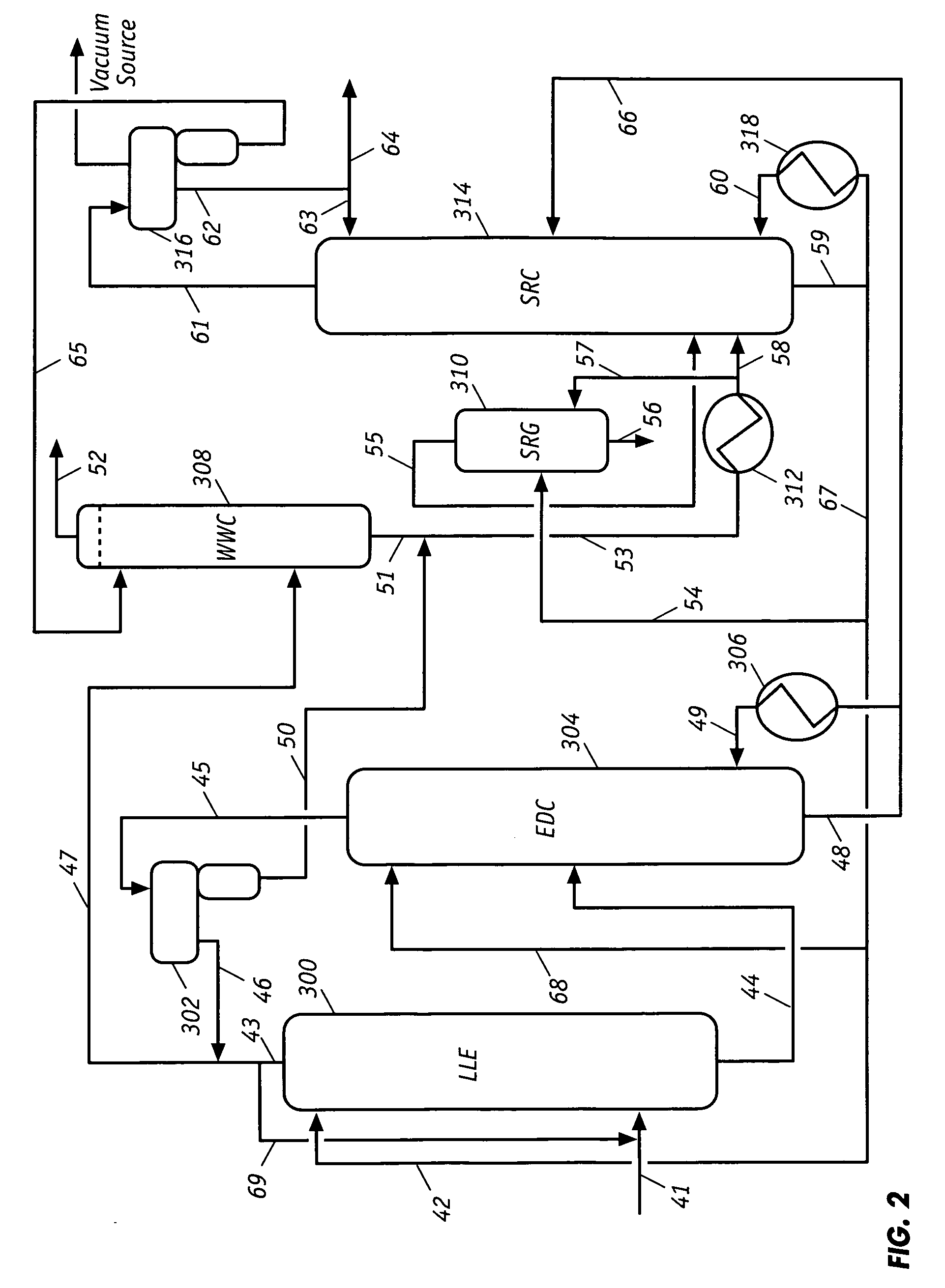
Extractive distillation processes using water-soluble extractive solvents
ActiveUS20090105514A1Reduce steam consumptionGood solvent resistanceHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsExtractive distillationWater soluble
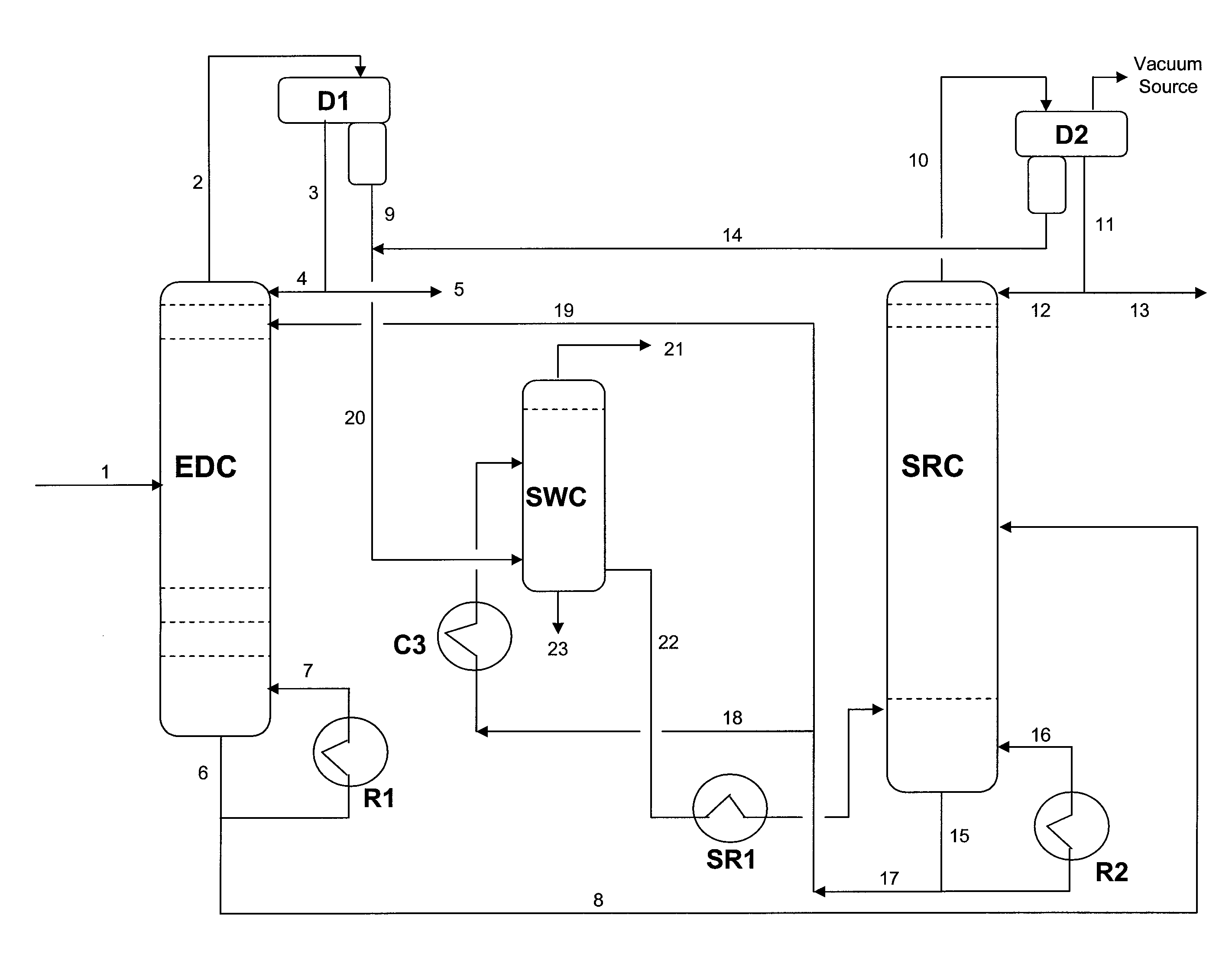
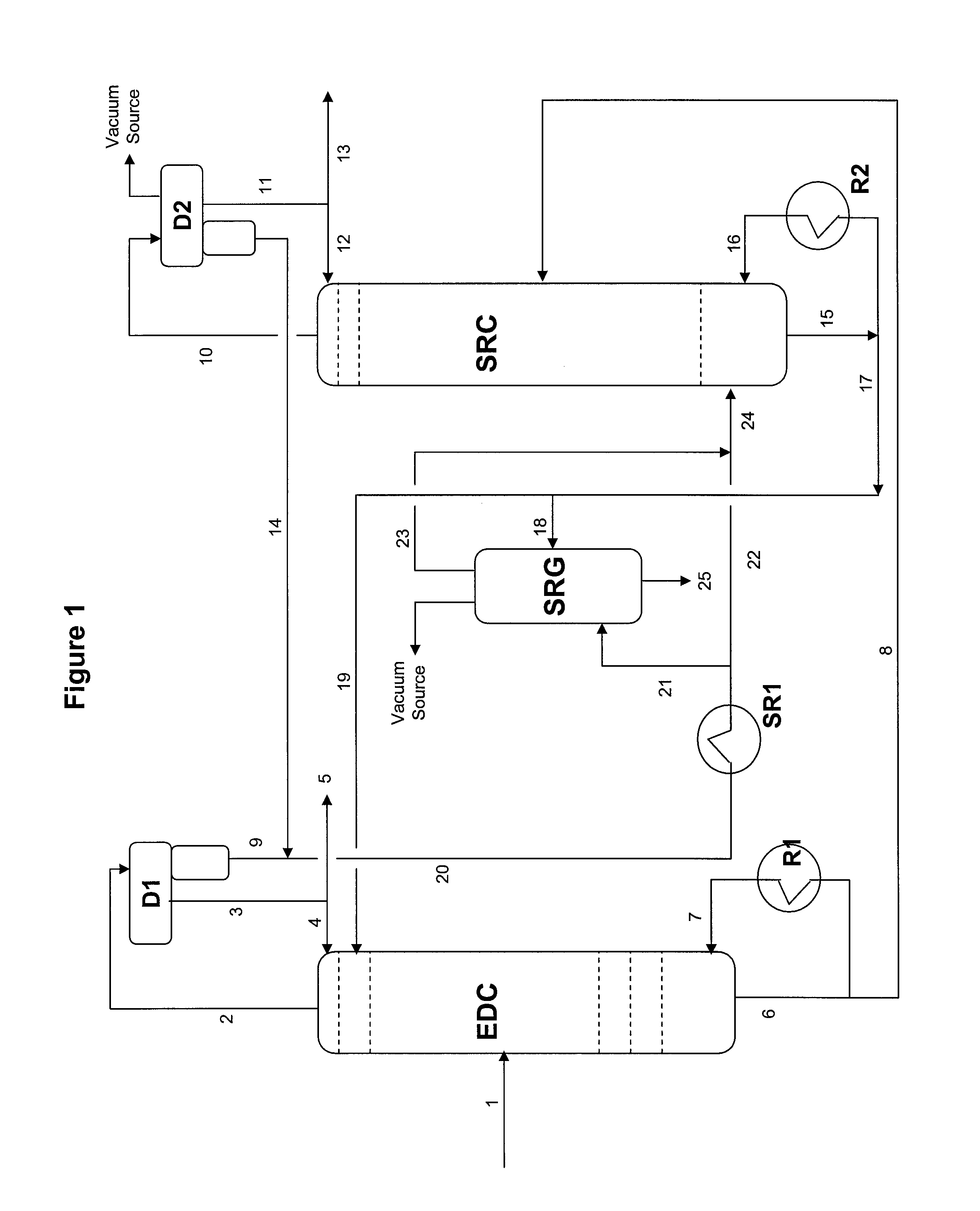
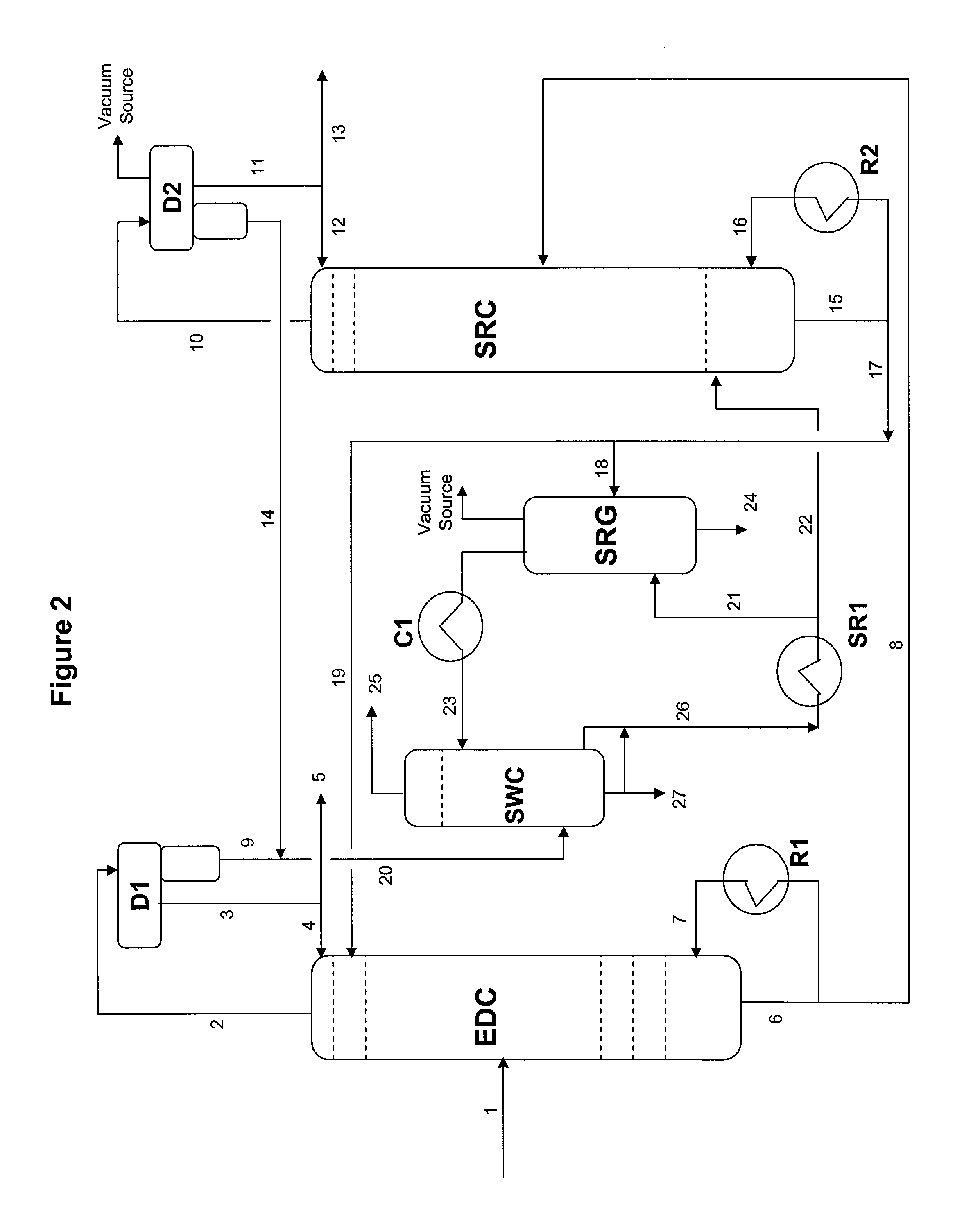
Extractive distillation processes whereby water-soluble extractive distillation (ED) solvents are regenerated and recovered employ improved operations of the extractive distillation column (EDC) so that polar hydrocarbons are recovered and purified from mixtures containing polar and less polar hydrocarbons and measurable amounts of hydrocarbons that are heavier than intended feedstock and / or polymers that are generated in the ED process. The improved process can effectively remove and recover the heavy hydrocarbons and / or remove polymer contaminants from the solvent in a closed solvent circulating loop through mild operating conditions with no additional process energy being expended. With the improved process, the overhead reflux of the EDC may be eliminated to further reduce energy consumption and to enhance the loading and performance within the upper portion of the EDC, especially when two liquid phases exists therein.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
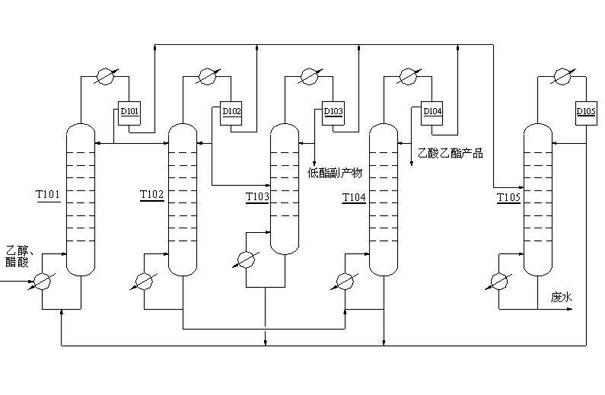
Technology of extractive distillation separation of ethyl acetate-ethanol-water
ActiveCN102627556AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationExtractive distillationEconomic benefits
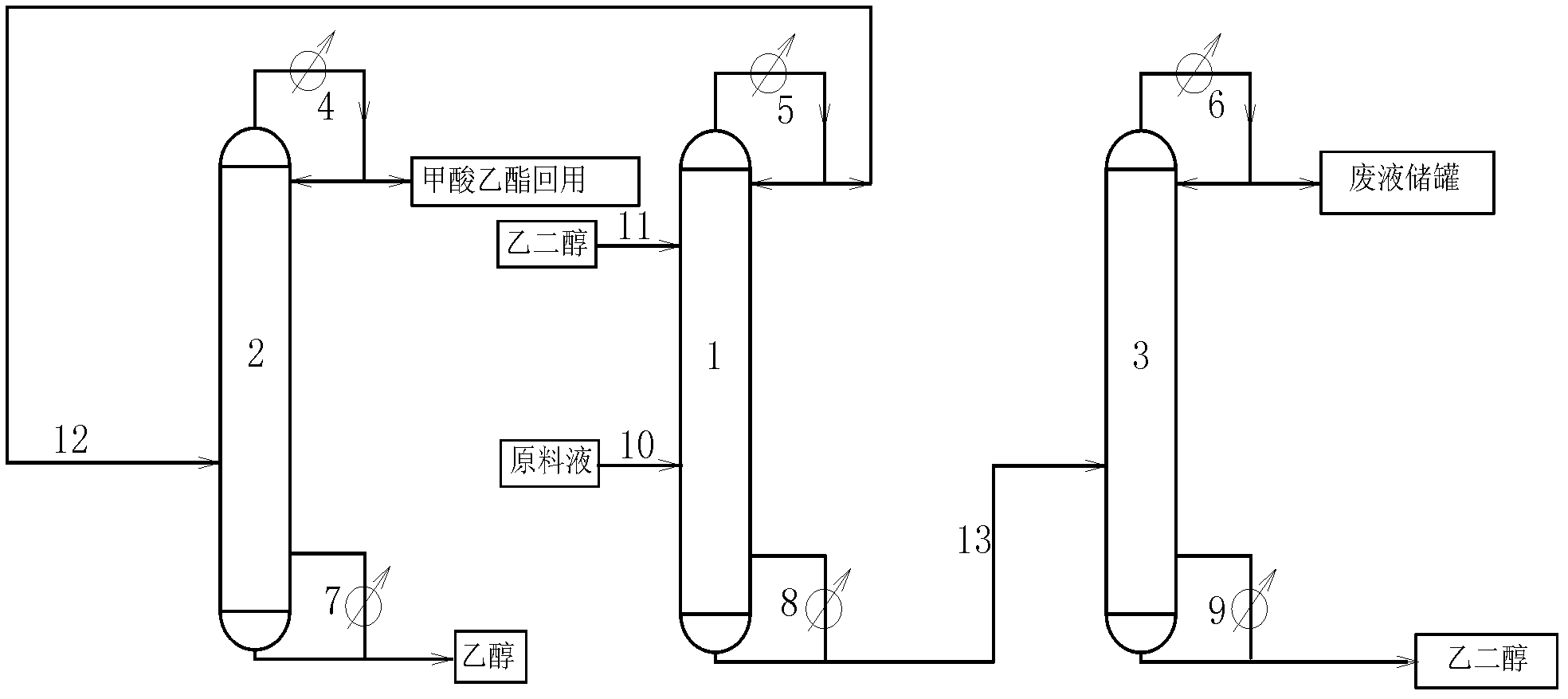
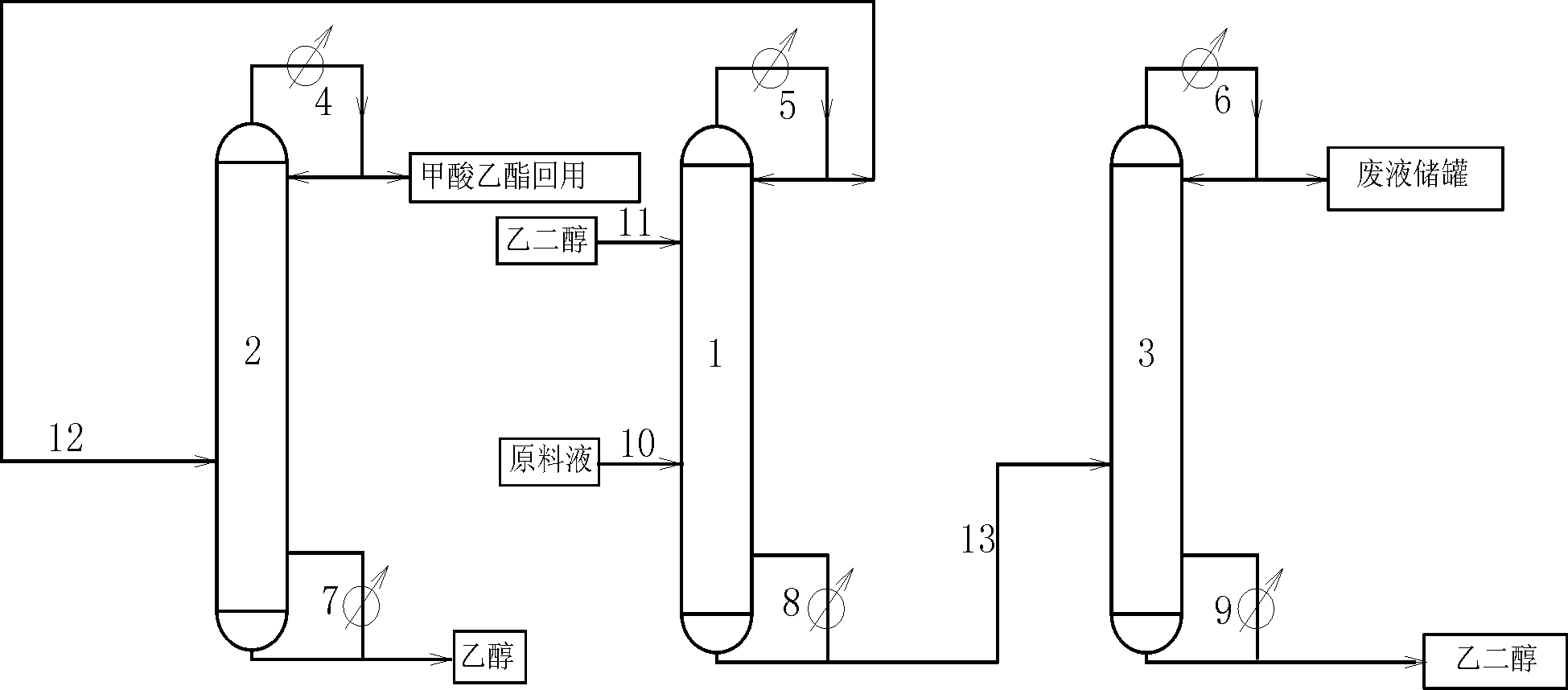
The invention belongs to the extractive distillation process, in particular to a technology of extractive distillation separation of ethyl acetate-ethanol-water. The technology employs glycol as an extractant and joint operation of three tower model including a dehydration tower, a ethyl formate recovery tower and a glycol recovery tower to separate the three substances. The invention can ensure recycling of the extractant. A tower top 2 of the ethyl formate recovery tower obtains 90.7% of ethyl formate, a yield near 100%, and 99.6% of ethanol. Both ethyl formate and ethanol are able to be recycled, s as to save resources, reduce environmental pollution and produce enormous economic benefits.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Treatment of phenol containing decanedioic acid waste water by extractive distillation
InactiveCN1450006AAvoid SaponificationLow processing and running costsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPhosphoric Acid EstersPhosphate
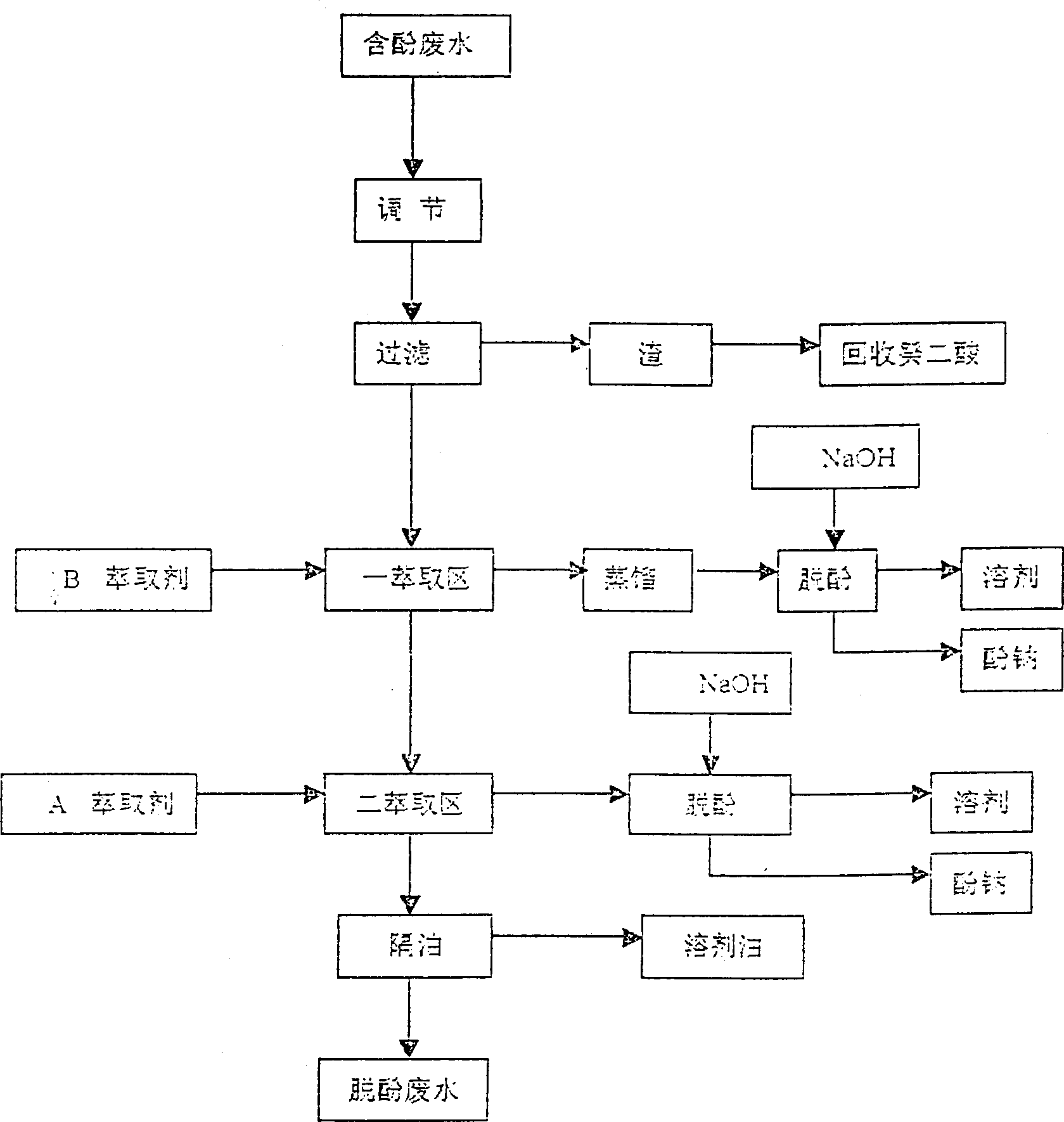
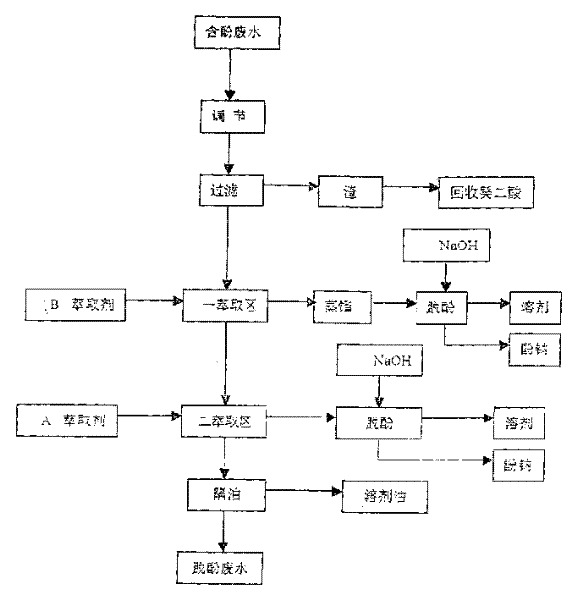
The method for treating waste water containing phenol which is produced in the course of producing sebacic acid includes five steps: regulation, filtration, extraction, removing phenol and isolating oil. After the phenol-containing waste water is filtered and its insoluble material is removed, in first extraction zone the high carbon alcohol is used as extraction agent to remove the organic material from waste water and effectively reduce content of phenol, the load extraction agent is fed into distillation procedure, the distilled high carbon alcohol can be reextracted and can be circularly used, and the organic material being in the waste water can be recovered in the form of high-boiling material, and the second extraction zone the mixture of phosphate and kerosene is used as extraction agent to make counter-current extraction with the phenol-containing waster water.
Owner:HAIHUA TIANHE ORGANIC CHEM SHANDONG
Method for producing butadiene by oxidatively dehydrogenating butene and used catalyst
ActiveCN103102238AHigh yieldHigh selectivityHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsExtractive distillationLattice oxygen
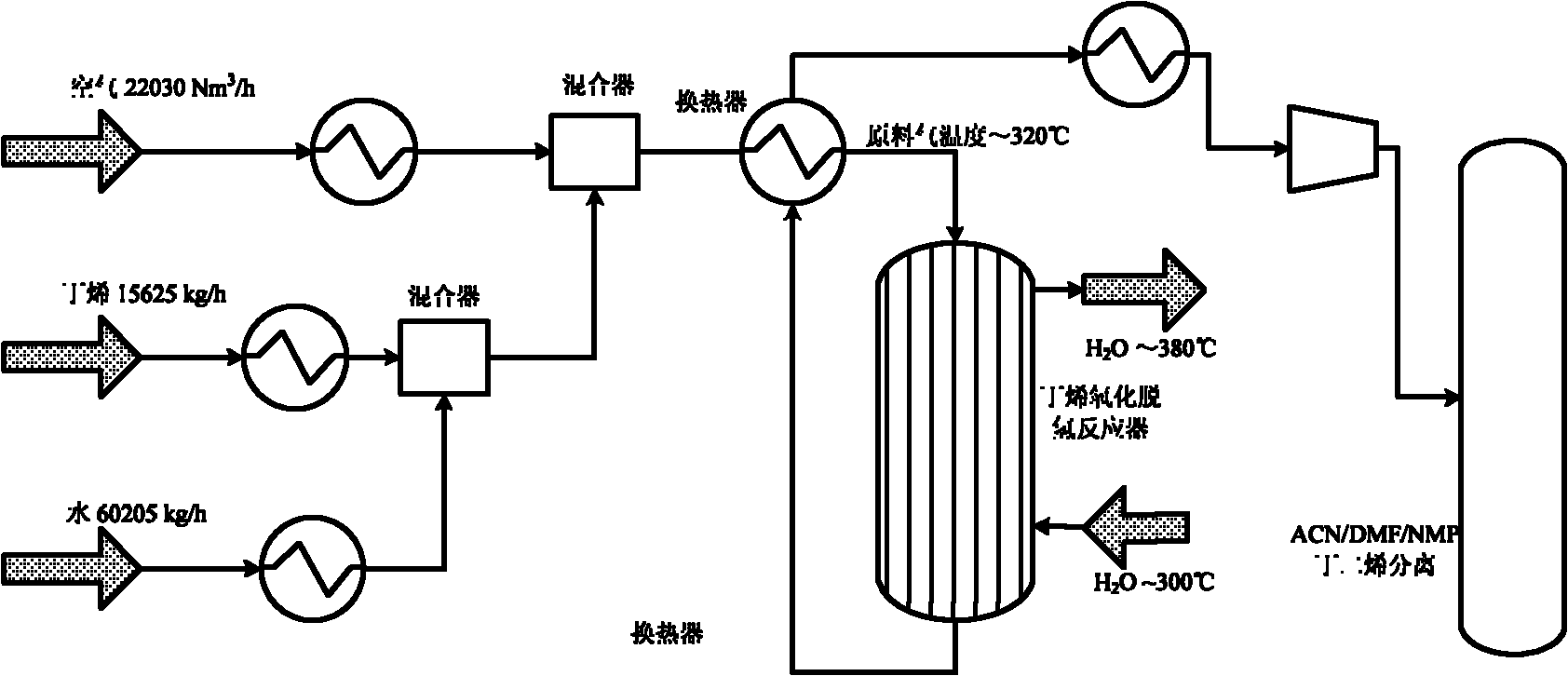
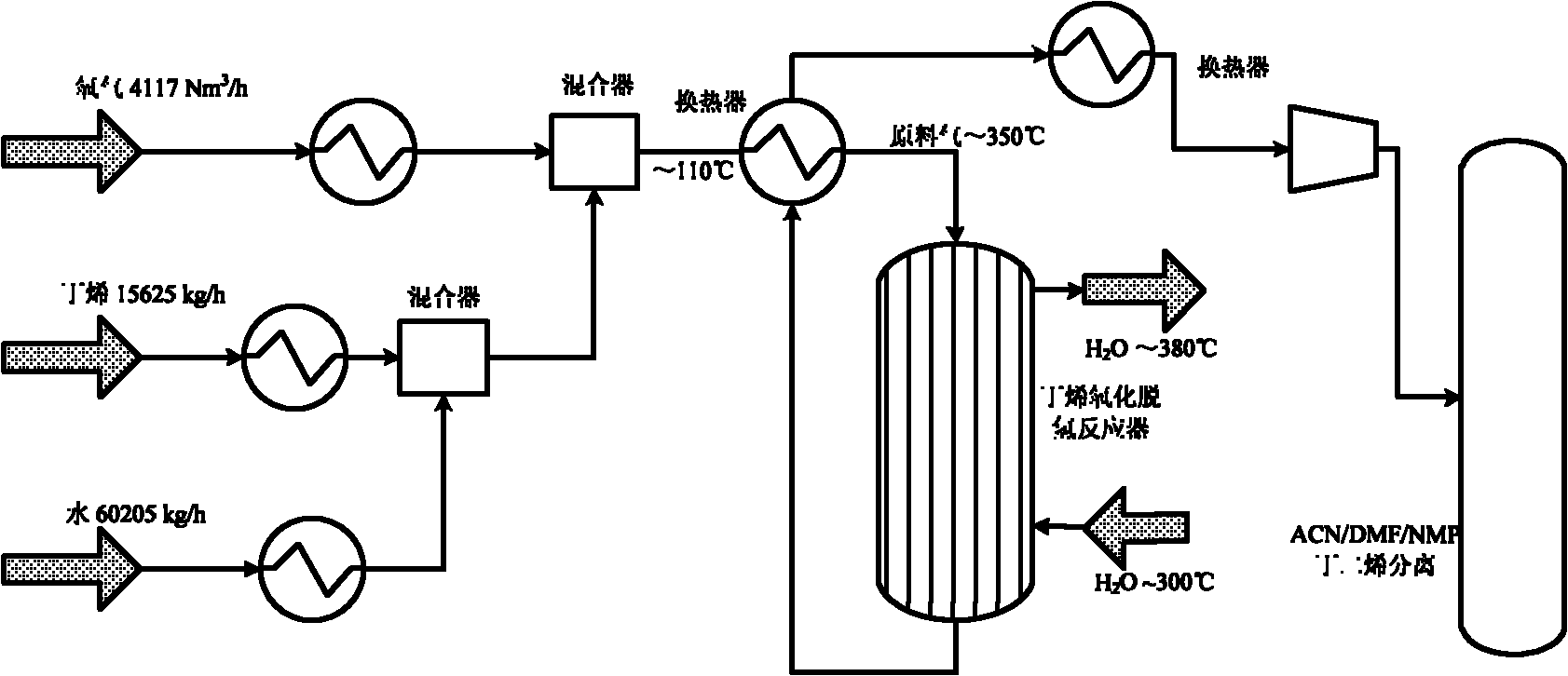
The invention discloses a method for producing butadiene by oxidatively dehydrogenating butane and a used catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of using product gas heat and reaction heat to exchange heat with raw material butene, water, oxygen or air, and then catalytically converting on a fixed bed to effectively prepare butadiene. The invention in particular relates to an alpha-Fe2O3, ZnFe2O4 composite oxide lattice oxygen catalyst. The raw material gas preheated to a certain temperature is heated to the temperature for reaction by adopting the sensible heat of the reaction product gas, the temperature of the reactor is controlled by steam heat-exchange, the raw material gas is heated by the sensible heat of the product gas and the stable operation of the reactor is realized, the oxidatively dehydrogenated rough butadiene logistics generated gas is separated through the processes of compression, oil-absorption and de-absorption, and extractive distillation of a butadiene solvent so as to efficiently, continuously and stably prepare the butadiene product, the once through yield of the butadiene is more than 80%.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Process for separating aromatics by extractive distillation and a composite solvent used therein
InactiveUS7078580B2Improve solubilityWide boiling rangeDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsSulfolaneAlkalinity
This application relates to a composite solvent for separating aromatics by extractive distillation, comprising a main solvent, a solutizer and a modifier. Said solutizer is selected from any one or mixtures of any two of C8–C11 aromatics having different number of carbon atoms, the content of which is 3–39 wt %, and the number of carbon atoms of the lowest aromatic in the solutizer should be greater than that of the highest aromatic in the aromatics to be separated. When the solutizer is selected from any one of C8–C11 aromatics, the composite solvent contains 0.01–10.0 wt % of the modifier; when the solutizer is selected from mixtures of any two of C8–C11 aromatics having different number of carbon atoms, the composite solvent contains 0–10.0 wt % of the modifier. Said main solvent and modifier are independently selected from sulfolane derivatives, N-formyl morpholine, and N-methyl pyrrolidone, provided that the acidity and basicity of the modifier are opposite to those of the main solvent. When the composite solvent is used to recover aromatics by extractive distillation, it is possible to moderate the operation conditions of solvent recovery, increase the yield of aromatics, and make the separated aromatics to be neutral.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Application of ionic liquid used as solvent in benzene and cyclohexane extraction, rectification and separation
InactiveCN101265152AAdjustable selectivityImprove thermal stabilityDistillation purification/separationBulk chemical productionExtractive distillationIonic liquid
The invention discloses the application of ionic liquid which is used as a solvent for separating benzene and cyclohexane by extractive distillation, and relates to the application that the ionic liquid is used as the solvent during the process of separating the benzene and the cyclohexane by extractive distillation. Cationic in the ionic liquid is imidazole cationic, anion in the ionic liquid isfluorophoshoric acid anion or halide anion, and ionic liquid solvent is one ionic liquid or two or more than two compounded ionic liquid; the water content of the ionic liquid is 0 percent to 20 percent, and the addition amount ranges in the molar concentration from 5 percent to 90 percent; light-component cyclohexane with low boiling point is obtained at the top of a rectification column and themixture of the ionic liquid and the benzene is obtained in a column reactor during the separating process; the mixture passes through an evaporator or is performed through steam stripping separation.The extractive distillation technology of the ionic liquid solvent increases the separation precision, and obviously simplifies process flow agents, reduces equipment investment and lowers the separation energy consumption at the same time, thereby getting very remarkable economic benefits.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method of Purifying (Z)-1-Chloro-3,3,3-Trifluoropropene
InactiveUS20110270001A1Easy to separateImprove purification effectHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationHydrogen atomAlcohol
Disclosed is a method of purifying (Z)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene of the formula [1], comprising: distilling a mixture containing (Z)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene and 1-chloro-1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropane (CF3CH2CHClF), wherein the distilling is performed by extractive distillation of the mixture in the coexistence of at least one kind of compound selected from the group consisting of halogenated hydrocarbons of the formula [2], halogenated unsaturated hydrocarbons, nitriles, ketones, carbonates, ethers, esters and alcohols as an extractant[Chem. 8]CFnCl3-nCHXCClFmH2-m [2]where X represents a hydrogen atom (H), a fluorine atom (F) or a chlorine atom (Cl); n represents an integer of 0 to 3; and m represents an integer of 0 to 2.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Low-energy extractive distillation process for dehydration of aqueous ethanol
ActiveUS8002953B2Energy efficiencyReduce energy inputFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationGas phaseExtractive distillation
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
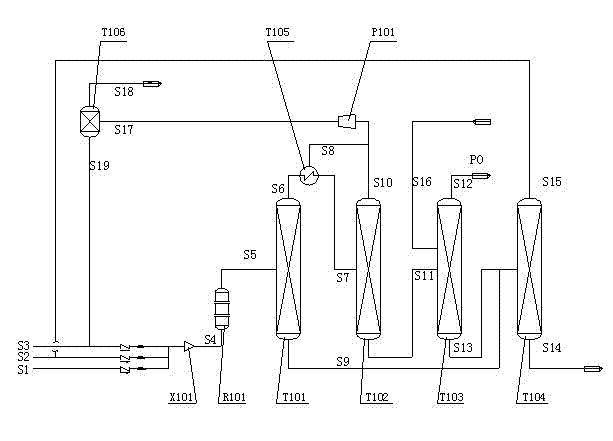
Process for hydrofining coking crude benzene
ActiveCN101519338AReduce lossesHigh retention rateDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsHydrogenExtractive distillation
The invention discloses a process for hydrofining coking crude benzene, which consists of a raw-materialnits preseparating unit, a hydrofining unit, a predistillation unit, an extractive distillation, an aromatic-hydrocarbon refining unit and a xylene distillation unit, wherein supplementary hydrogen needed in reaction is supplied from the outside; a reaction part in the hydrofining unit adopts three-stage hydrogenation; and the temperature of second-stage hydrogenation and third-stage hydrogenation is 230 to 290 DEG C and 220 to 315 DEG C respectively. The process has the advantages that the temperature adopted in both the second-stage hydrogenation and the third-stage hydrogenation is greatly lower than the reaction temperature of the prior process; the process effectively reduces benzene transformed into cyclohexane, reduces the secondary cracking reaction of the cyclohexane, reduces the loss of aromatic compound, and improves the retention rate of aromatic hydrocarbon which can reach over 99.6 percent; meanwhile, the three-stage hydrogenation adopted in the reaction part prolongs the process of hydrogenation and ensures that sulfur-containing nitrogen-containing organic compounds can also be transformed into inorganic sulfur or inorganic nitrogen compounds at a lower temperature, so that the aim of purification is achieved; and the total content of both sulfur and total in a hydrofined product is less than 1 ppm.
Owner:中国寰球工程有限公司辽宁分公司
Method for producting propylene by catalytic pyrolysis of liquefied gas
InactiveCN101844960ABulk chemical productionHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon crackingCatalytic pyrolysisExtractive distillation
The invention relates to a method for producting propylene by catalytic pyrolysis of liquefied gas, which mainly solves the problems that the existing process limits the source of raw materials and components, the yield of the propylene is low and the one-way service life of the catalyst is short. The common civil-use liquefied gas is preprocessed through depropanization, extractive distillation and the like, then is heated to be 500-600 DEG C after being exchaning heat with a reaction product, and carries out the pyrolysis reaction under the condition with 0.4MPa and mass space velocity of 0.8h-1; after being cooled, the gas-liquid separation is carried out on the reaction product to enter an absorption and stable system to be further separated to obtain the high-octane gasoline component and liquefied petroleum gas containing rich propylene and butylenes; and the liquefied petroleum gas is further separated to obtain fine propylene. The invention makes full use of the common civil-use liquefied gas in markets to product propylene with a high added value, can be used in an industrial unit for producting propylene, can relieve the contradiction between supply and demand of propylene, can improve the economic benefit of petroleum chemical enterprises, better solves the problems of deep processing of liquefied petroleum gas and increasing production of propylene.
Owner:上海傲佳能源科技有限公司
Method for continuously extracting, rectifying and separating mixed alcohols from water
InactiveCN103193590ABroaden your optionsEasy to industrializeOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationN-Propyl alcoholIsobutyl alcohol
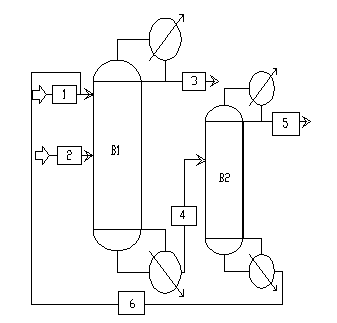
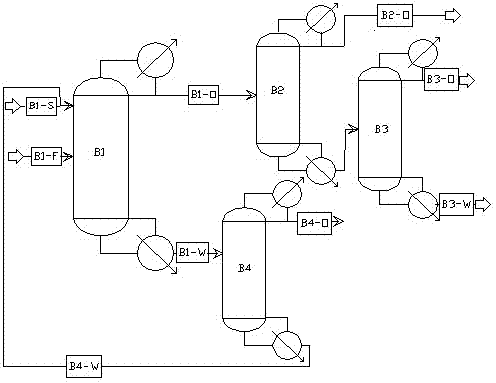
The invention discloses a method for continuously extracting, rectifying and separating mixed alcohols from water, relates to a chemical separating method, and in particular to a method for continuously extracting, rectifying and separating mixed alcohols such as aqueous mixtures of ethanol, n-propyl alcohol, isobutyl alcohol and the like. According to the method, extractive distillation and common rectifying are combined together, and a multi-column combined step-by-step separating method is adopted to separate mixed alcohols from water step by step and recycle components with high purity. The method comprises steps of: with ethylene glycol as an extraction agent, separating the mixed alcohols from water in an extractive rectifying column B1, wherein the column B1 adopts normal pressure rectification, the reflux ratio is 1:1-10:1, the mixed alcohols can be get from the column top, and a mixture of a solvent and water can be get from the column bottom; recovering most of the solvent from a solvent recovering column B4 and recycling the solvent; and effectively separating the mixed alcohols through columns B2 and B3. According to the method, extractive distillation and common rectifying are combined together, the extraction agent is used to avoid the azeotrope of alcohols and water, and continuous separation of multiple columns are adopted to recover the components with high purity step by step, so that the method has high economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Processes utilizing extractive distillation
InactiveUS7699962B2Distillation purification/separationHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationExtractive distillationMIXTURE COMPONENT
The invention relates to methods for separating mixture components such as reactor effluent components. In particular, the invention relates to the use of an extractive agent such as a hydrocarbon in an extractive distillation process to separate monomers such as a C4-C7 isoolefins such as isobutylene from mixtures such as reactor effluents including one or more hydrofluorocarbon(s) (HFC).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for preparing epoxypropane by directly using epoxidation propylene through hydrogen peroxide
ActiveCN102898405AMeet high power requirementsReduce conversionOrganic chemistryChemical industrySocial benefitsMolecular sieve
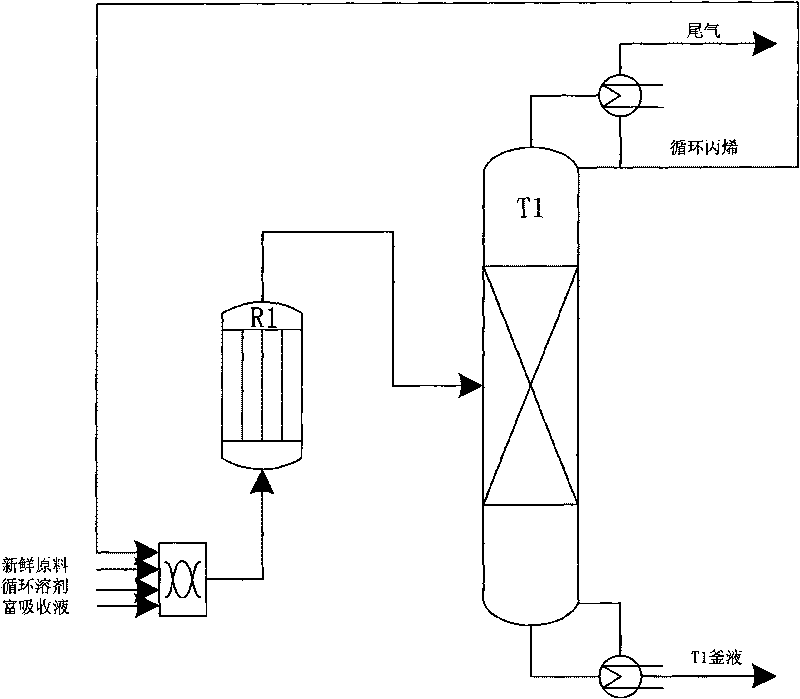
The invention relates to a process for preparing epoxypropane by directly using epoxidation propylene through hydrogen peroxide. The process comprises the following steps of: (1) sufficiently mixing propylene and hydrogen peroxide, conducting an epoxidation reaction in a fixed bed reactor filled with titanium silicon molecular sieves and generating epoxypropane coarse products; (2) pumping the epoxypropane coarse products into a coarse tower trough a pump and conducting crude separation on unreacted propylene and epoxypropane; (3) enabling coarse component products to pass through a propylene flashing tower and then enter a light component recovery tower; (4) compressing the propylene separated by the coarse tower and the light component recovery tower and light components through a compressor, entering a non-condensable gas separation tower, enabling the propylene to enter a recycling and reusing system from the bottom of the separation tower, and enabling tail gas to be discharged through a tail gas absorption device; and (5) conducting extractive distillation on the epoxypropane treated by the light component recovery tower in a epoxypropane purification tower to obtain high purity epoxypropane products. The process is energy-saving, environment-friendly, safe, suitable to industrial production and capable of producing obvious economic and social benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU YIDA CHEM
Method for separating ethyl acetate-ethyl alcohol compound
InactiveCN103467286AReduce dosageEasy to recycleOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationExtractive distillationEthyl acetate
The invention provides a method for separating ethyl acetate-ethyl alcohol, which comprises the following steps: adopting ethyl acetate-ethyl alcohol compound in any proportion as a raw material, taking ionic liquid or a double solvent composed of ionic liquid and an organic solvent as an extraction agent, and extracting ethyl acetate and ethyl alcohol in sequence after the raw material goes through an extractive distillation stage and an extraction agent recycle stage, wherein the extraction agent is used circularly after being extracted in the recycle stage. Compared with the prior art, the new method has the advantages that the energy can be conserved by more than 40%, the environment pollution can be avoided, the product purity is high, the industrialization is facilitated, the equipment cost is low, and the economic benefit is good.
Owner:TIANJIN CLEANTECH TECH
Process for obtaining crude 1,3-butadiene from a C4 cut
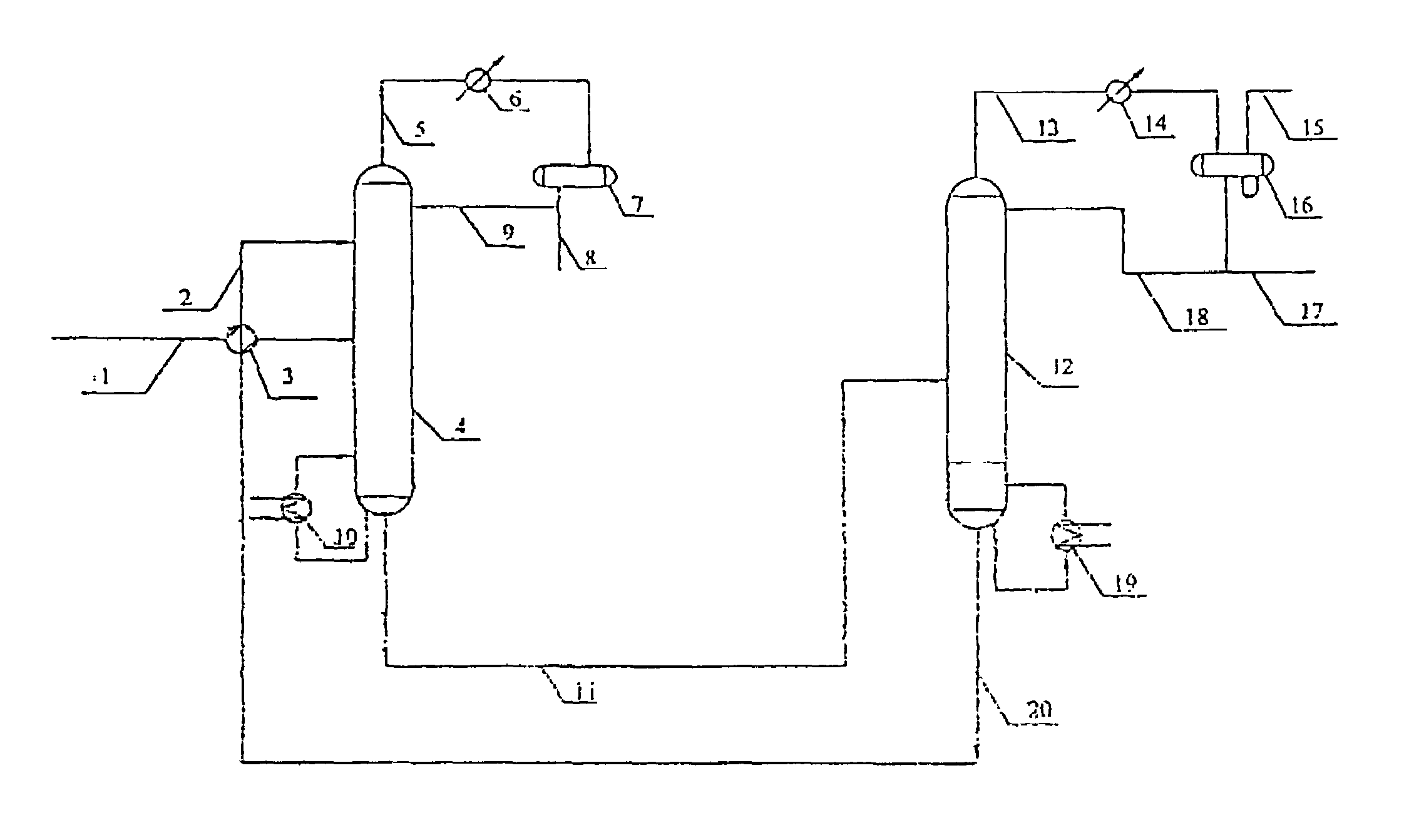
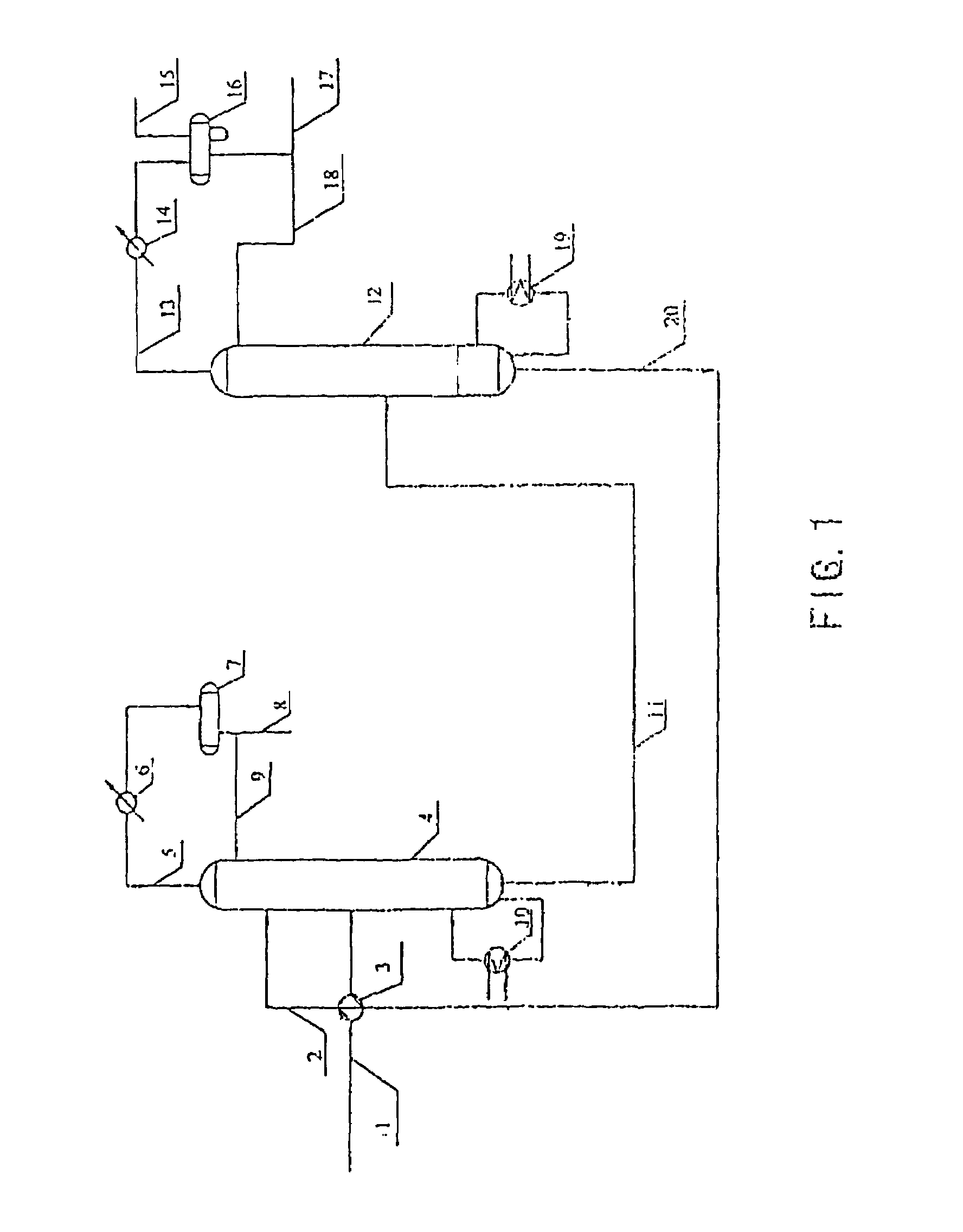
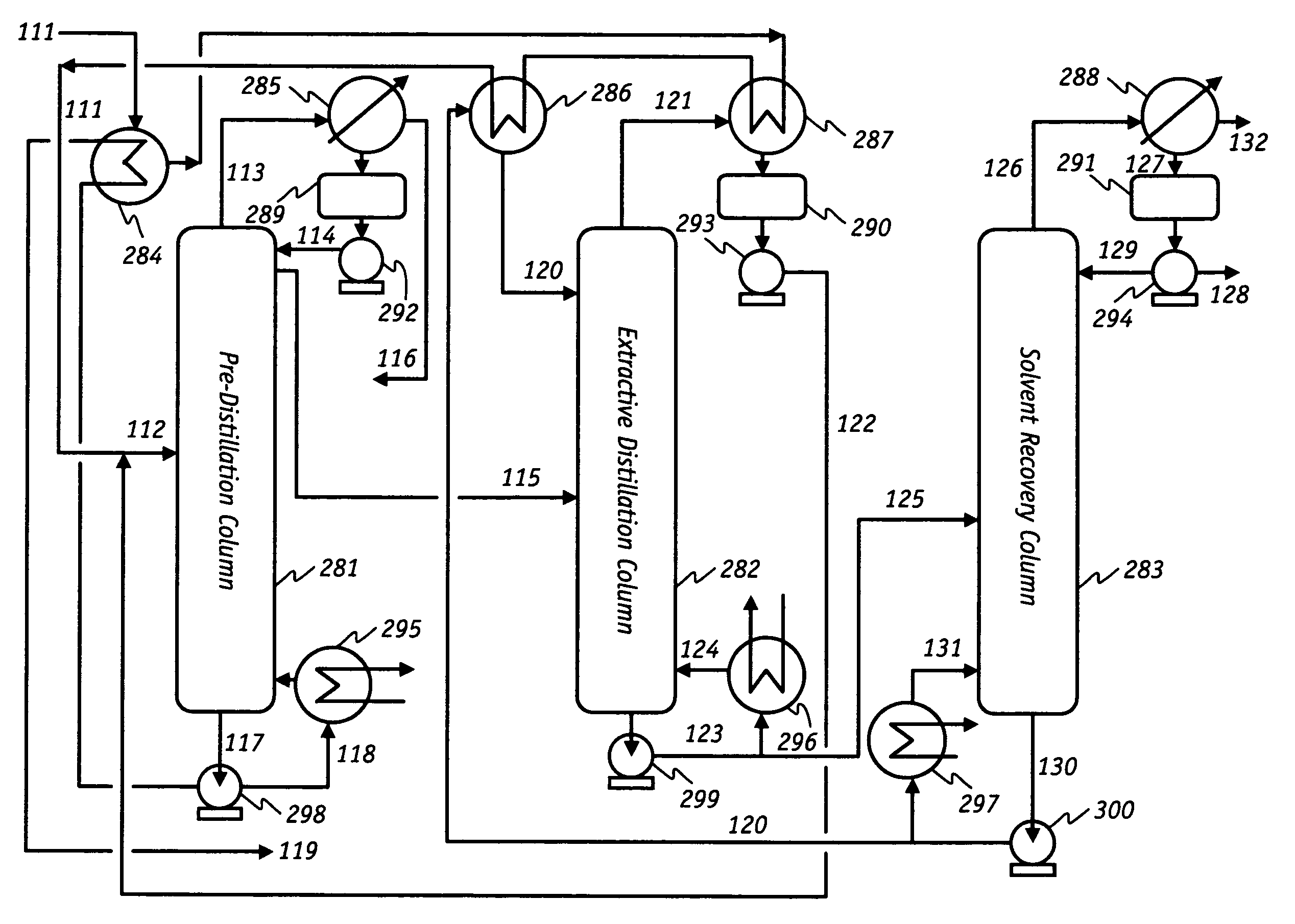
ActiveUS7692053B2Distillation regulation/controlDistillation purification/separationSecondary componentExtractive distillation
1,3-butadiene is obtained by extractive distillation with a selective solvent from a C4 cut comprising C4 acetylenes as secondary components in a dividing wall column having a bottom evaporator, in which a dividing wall is disposed in the longitudinal direction of the column to form a first subregion, a second subregion and a lower combined column region. The column is disposed upstream of an extractive wash column. The energy input into the dividing wall column via the bottom evaporator is controlled in such a way that a bottom stream containing solvent, C4 acetylenes and 1,3-butadiene restricted such that the loss of 1,3-butadiene is economically acceptable, is drawn off and fed to an acetylenes outgasser where the C4 acetylenes are stripped out overhead and purified solvent is obtained as the bottom stream.
Owner:BASF AG
Separation method for mixed C4
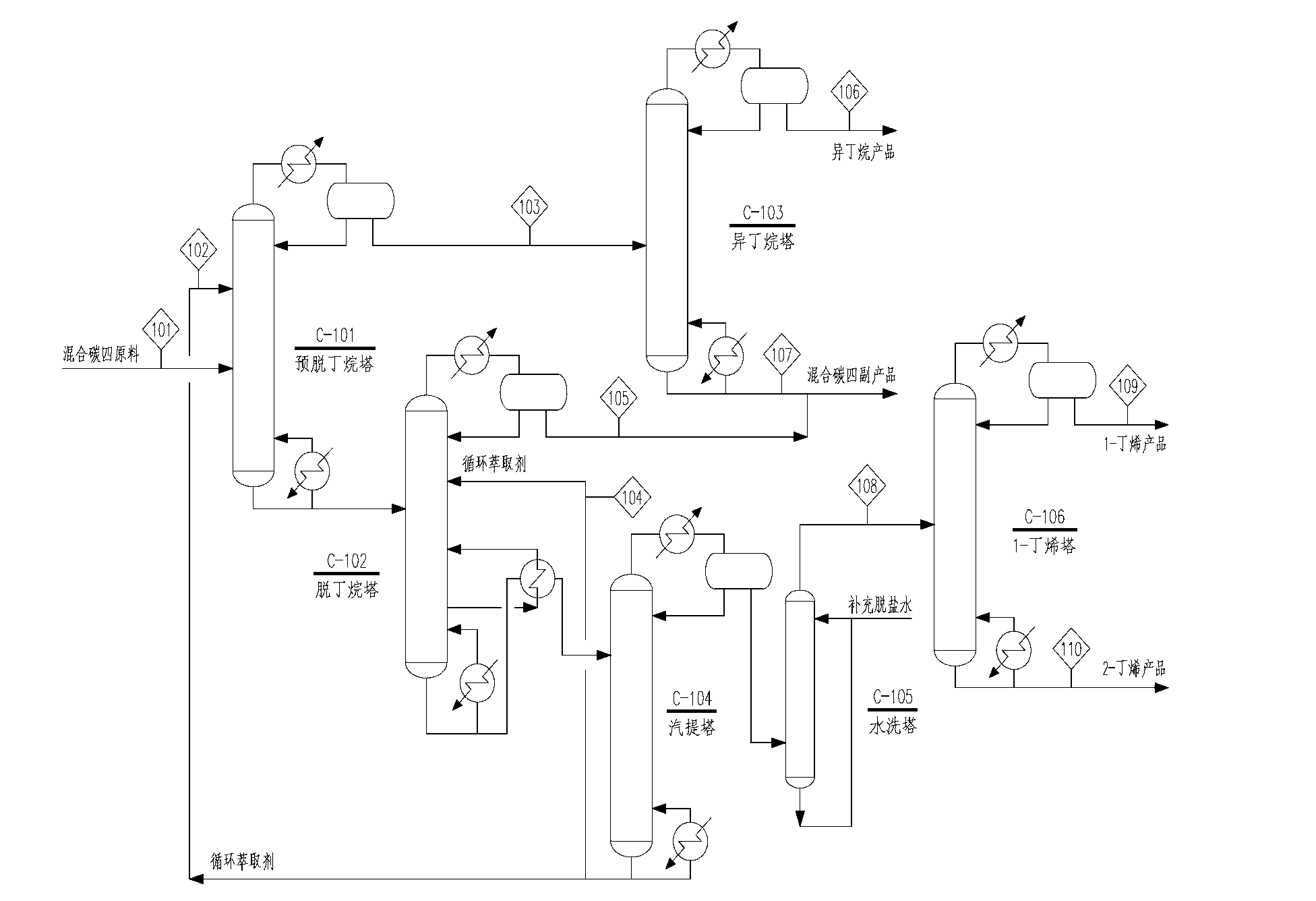
ActiveCN102992933AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costChemical industryDistillation purification/separationButeneHigh concentration
The invention discloses a separation method for mixed C4, which comprises the following steps of separating butene and butane from mixed C4 through extractive distillation, wherein the mixed C4 contains n-butane, iso-butane, 1-butylene and 2-butylene after removal of components such as C3, butadiene, alkyne, isobutene, C5 and the like, furthermore, separating to obtain iso-butane, 1-butylene and 2-butylene and the byproduct of crude n-butane through ordinary distillation, wherein the solvent for extractive distillation is publicly known in the industry, non clear-clear separation method is adopted in extractive distillation technology, namely, the combination of preextraction distillation and extractive distillation. Due to the adoption of the separation method, after the mixed C4 is processed, products of iso-butane, 1-butene and 2-butene of high concentration can be obtained simutaneously, therefore, the separation method has the advantages of being energy-saving, good in economic efficiency, high in resource utilization rate, and the like, reducing the cost and is of great significance in comprehensive utilization of mixed C4 resource.
Owner:EAST CHINA ENG SCI & TECH +1
Novel energy efficient and throughput enhancing extractive process for aromatics recovery
InactiveUS20090255853A1Satisfactory aromatic puritySatisfactory recoveryHydrocarbon distillationRefining with acid-containing liquidsSulfolaneExtractive distillation
An energy efficient, high throughput process for aromatics recovery can be readily implemented by revamping existing sulfolane solvent extraction facilities, or constructing new ones, so as to incorporate unique process operations involving liquid-liquid extraction and extractive distillation. Current industrial sulfolane solvent based liquid-liquid extraction processes employ a liquid-liquid extraction column, an extractive stripping column, a solvent recovery column, a raffinate wash column, and a solvent regenerator. The improved process for aromatic hydrocarbon recovery from a mixture of aromatic and non-aromatic hydrocarbons requires transformation of the extractive stripping column into a modified extractive distillation column. The revamping incorporates the unique advantages of liquid-liquid extraction and extractive distillation into one process to significantly reduce energy consumption and increase process throughput. The revamp entails essentially only piping changes and minor equipment adjustments of the original liquid-liquid extraction facility, and is therefore, reversible.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
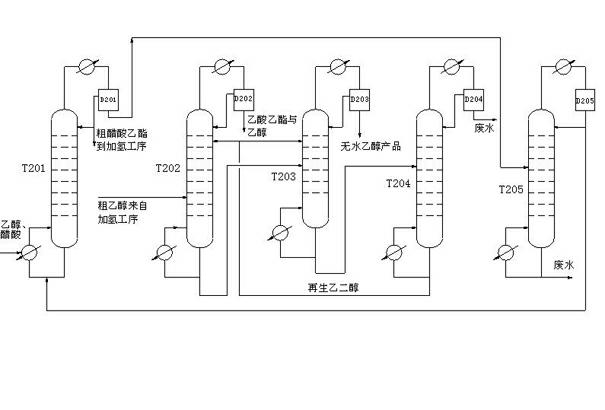
Method for simplifying rectification process for preparing ethanol through hydrogenation of acetic acid
ActiveCN102399130AMeet separation requirementsLess investmentOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAnhydrous ethanolAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for simplifying a rectification process for preparing ethanol through hydrogenation of acetic acid. An extractive distillation mode is adopted, and an ethanol product with higher purity can be obtained; a rectifying device can meet the separation requirement on an acetic ether product and an ethanol product; in addition, the acetic ether and the ethanol are separated by the same separation equipment; when the ethanol is produced, crude acetic ether and absolute ethanol products are obtained in the device, and when the ethanol is not produced, the device can produce the qualified acetic ether product, so that the device investment is saved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
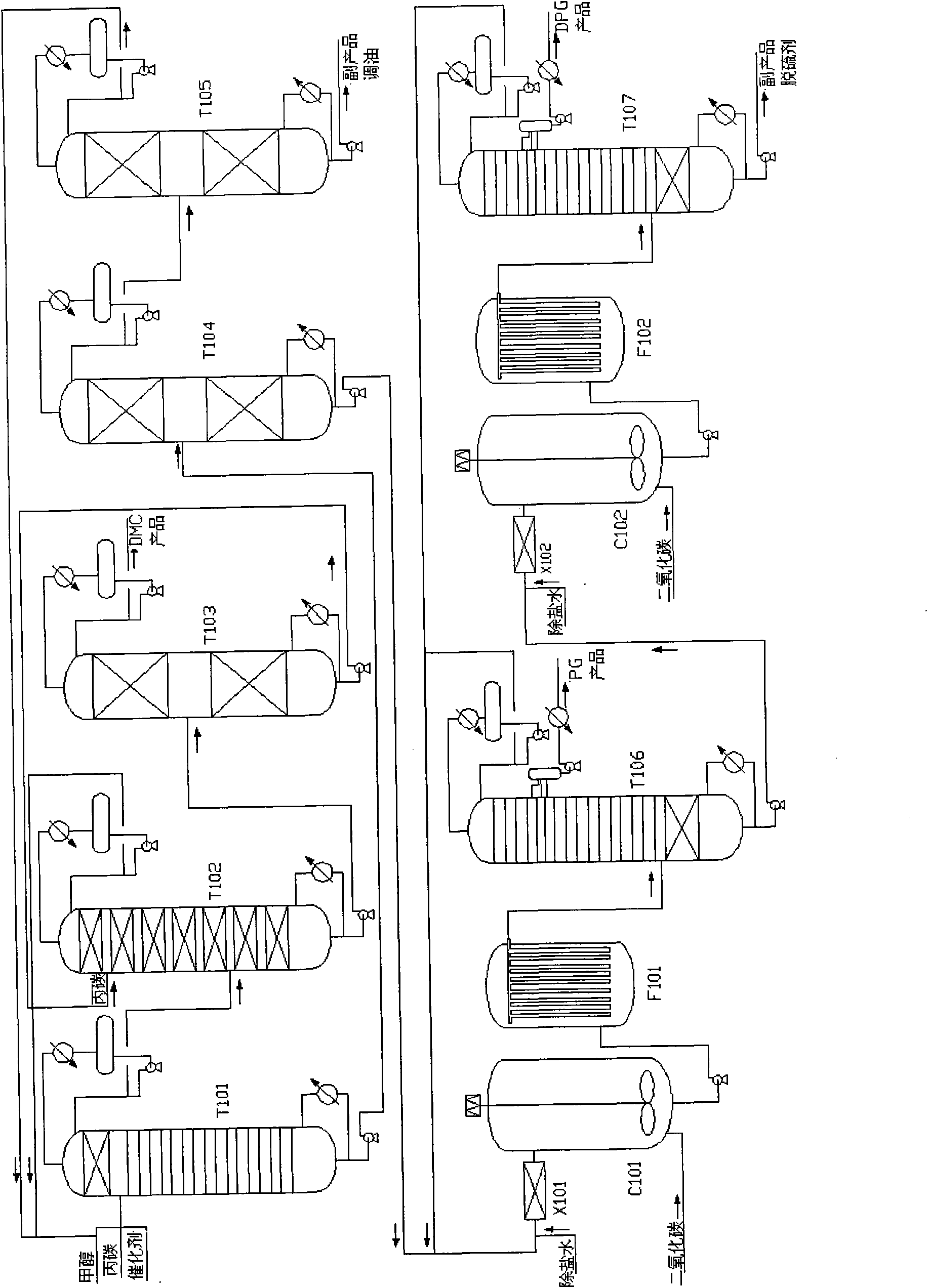
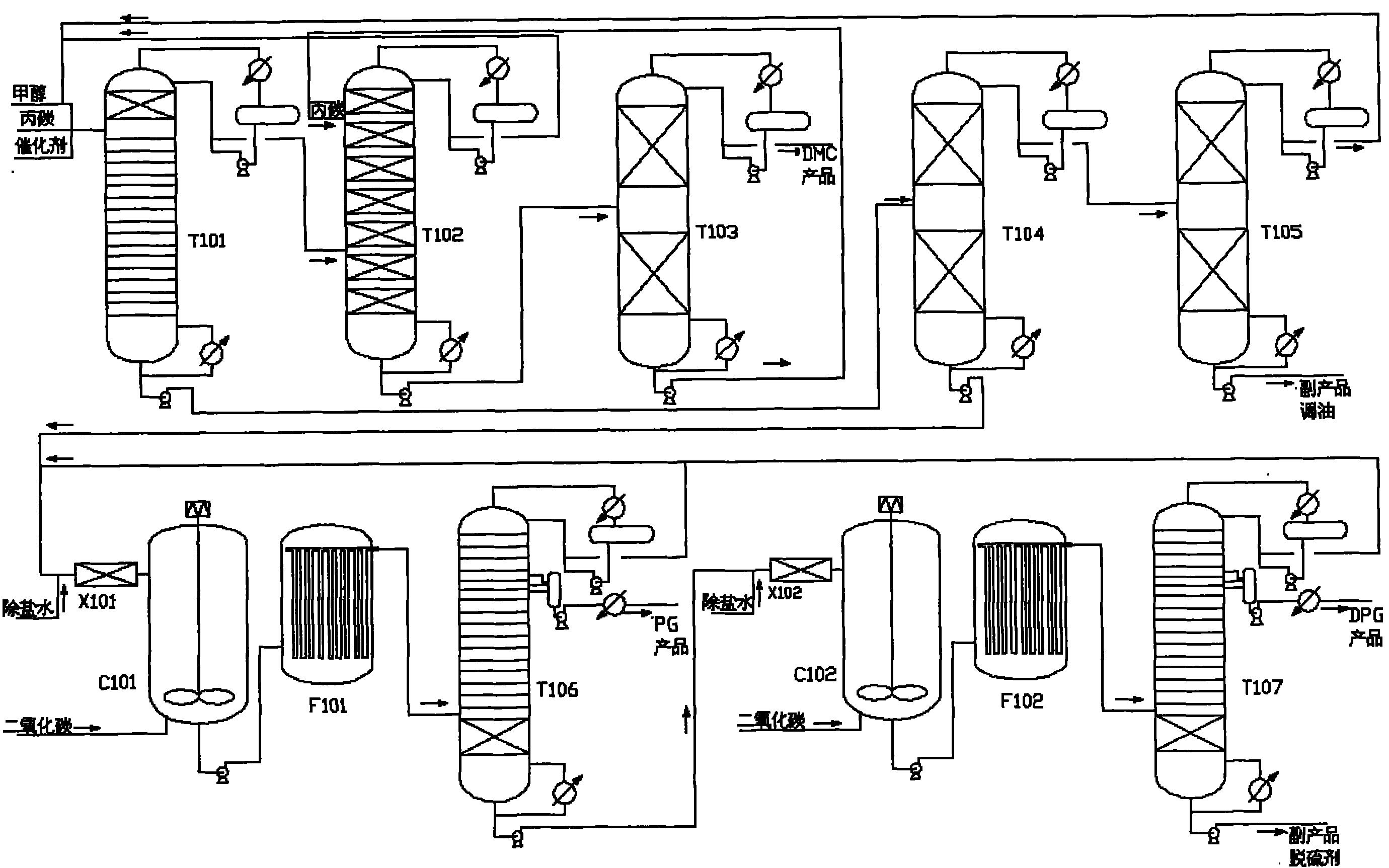
Novel technique for purifying high-quality propylene glycol in production process of dimethyl carbonate
ActiveCN101774888AHigh yieldSolve the emission problemChemical industryHydroxy compound separation/purificationFiltrationExtractive distillation
The invention relates to a technique for coproduction of dimethyl carbonate and propylene glycol, in particular to a novel technique for purifying high-quality propylene glycol in the production process of dimethyl carbonate. The technical scheme includes the steps of reactive distillation, extractive distillation, separation of the dimethyl carbonate, the recovery and refining of carbinol, primary carbonization, first filtration of sodium carbonate crystals and refining of the propylene glycol. The invention solves the problem of low recovery rate of the propylene glycol, and the recovery rate of the propylene glycol can be above 95%. Meanwhile, the propylene glycol has more stable quality, with the purity reaching 99.99% and the chroma less than 10, thereby the propylene glycol totally meets the requirements for medical auxiliary material, daily cosmetics, top grade unsaturated resin and polyether. Meanwhile, the purity of the byproduct dipropylene glycol can be above 99.50%, thus improving the benefit of the equipment.
Owner:DONGYING HI TECH SPRING CHEM IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com