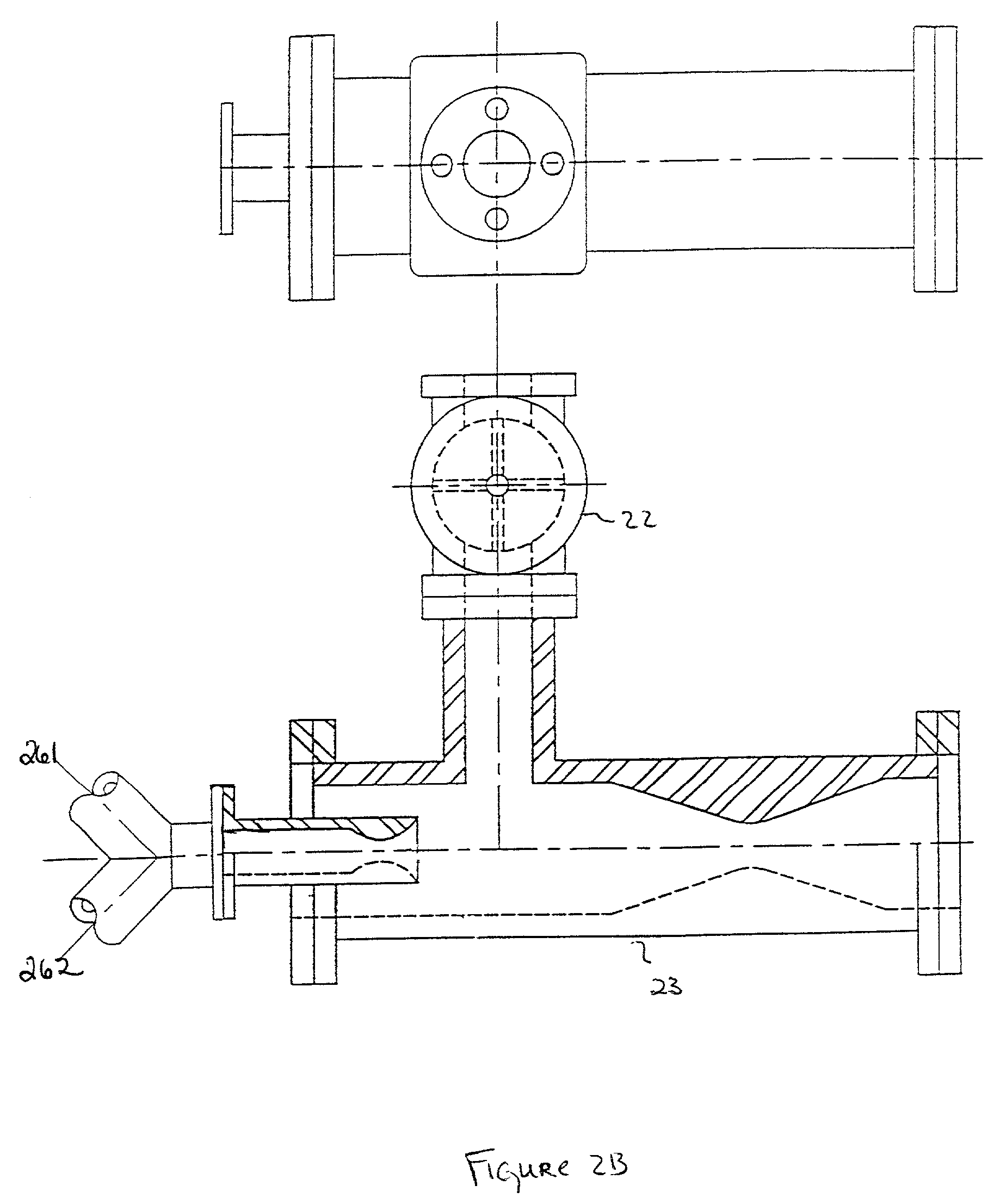
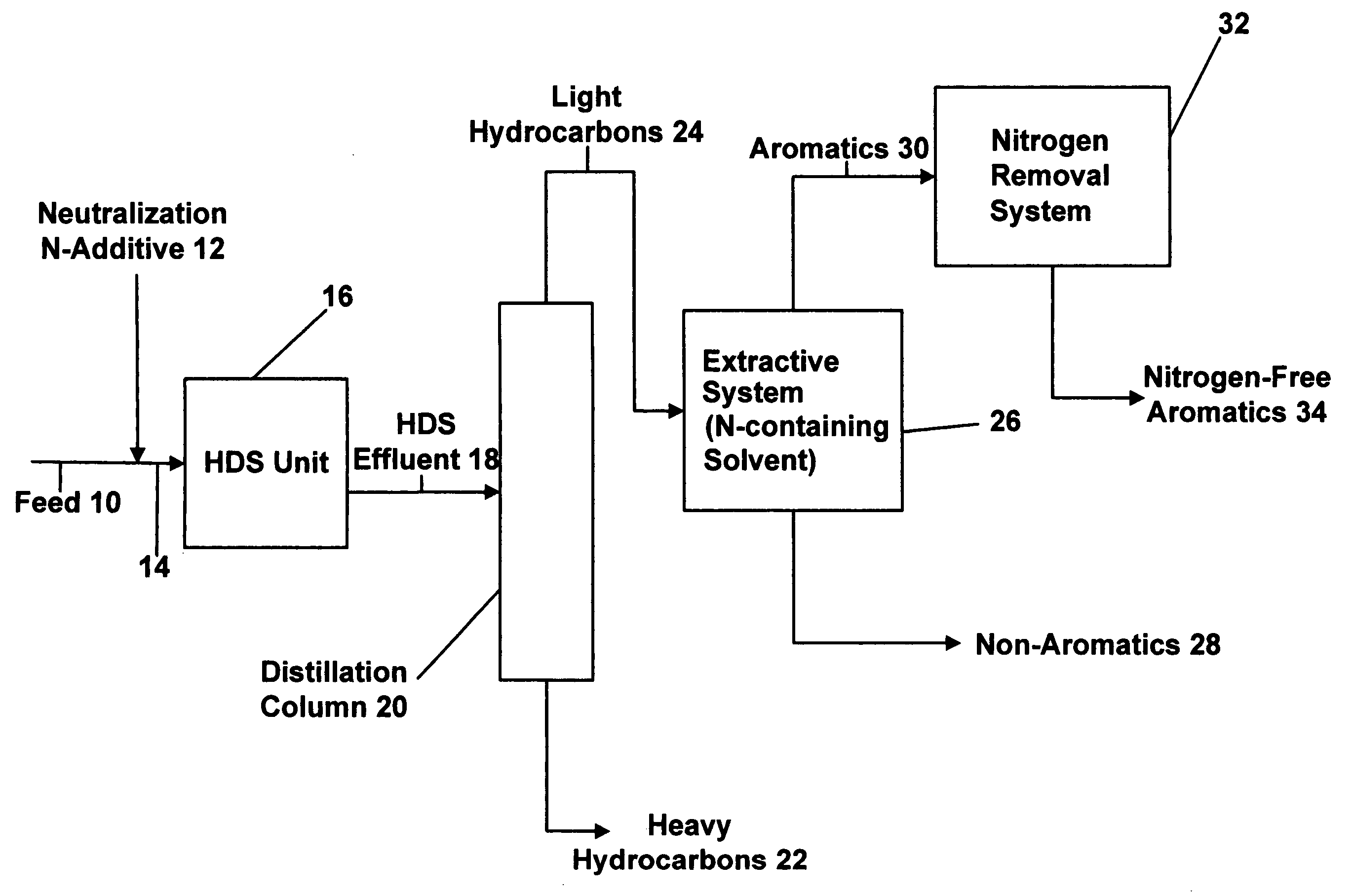
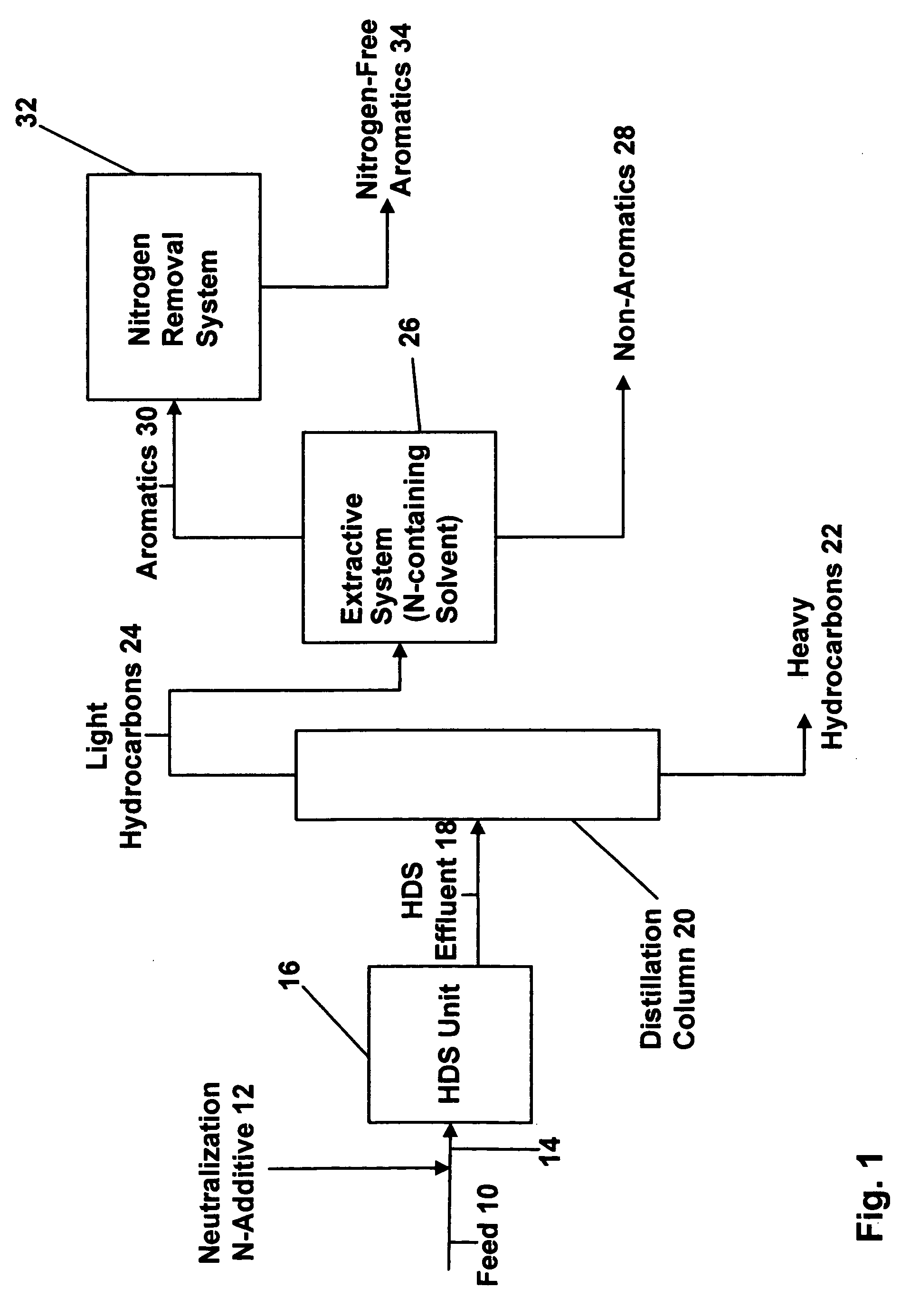
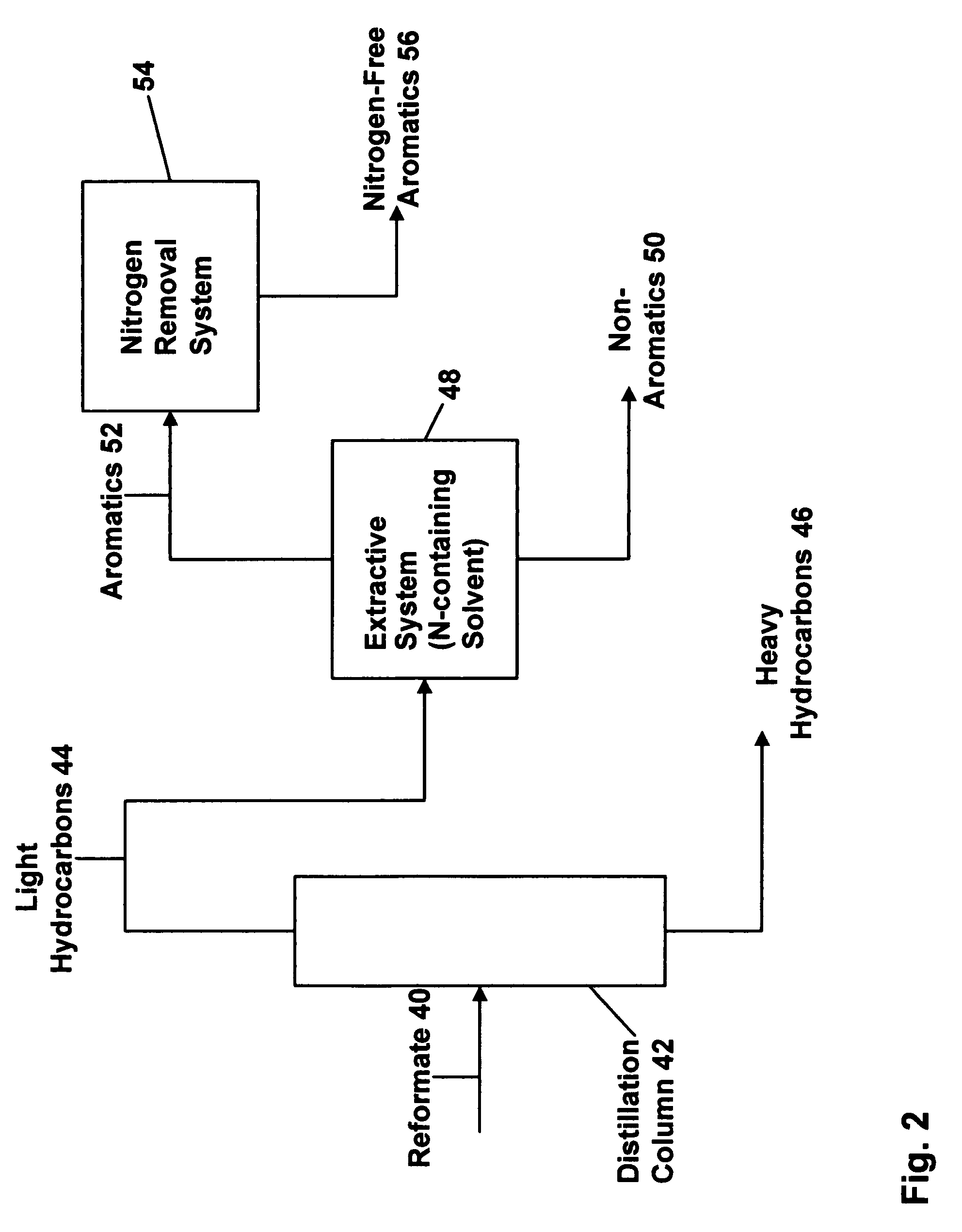
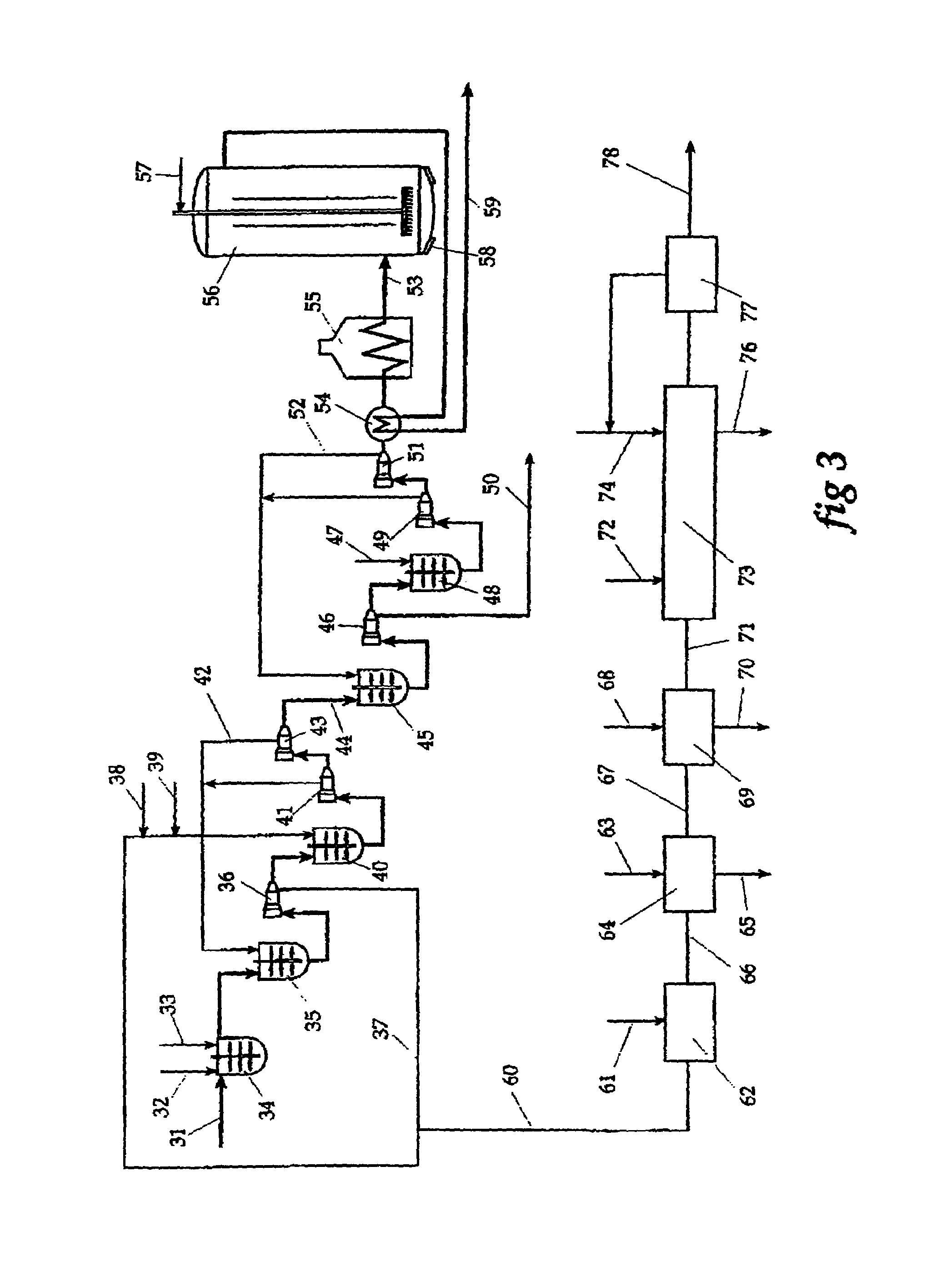
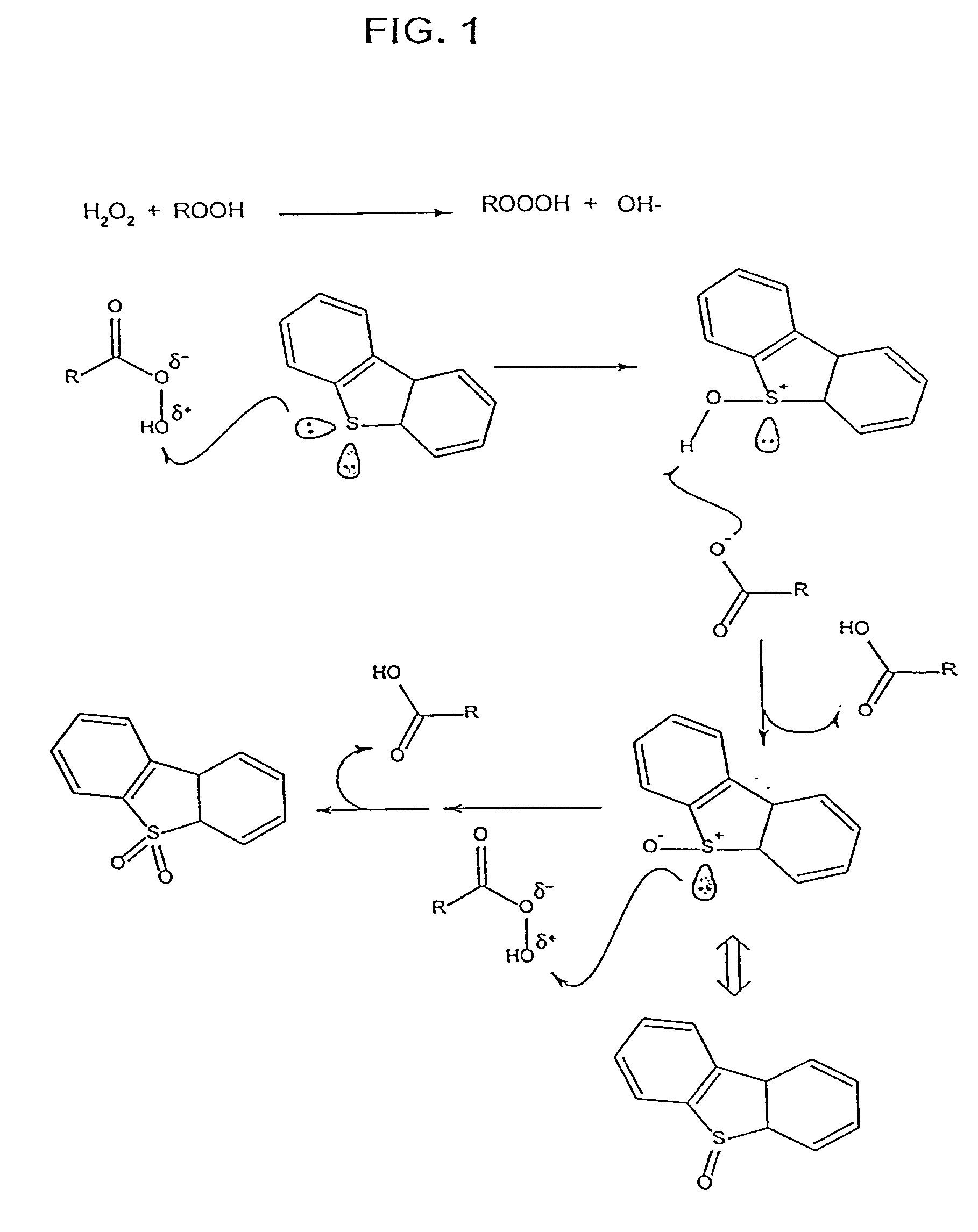
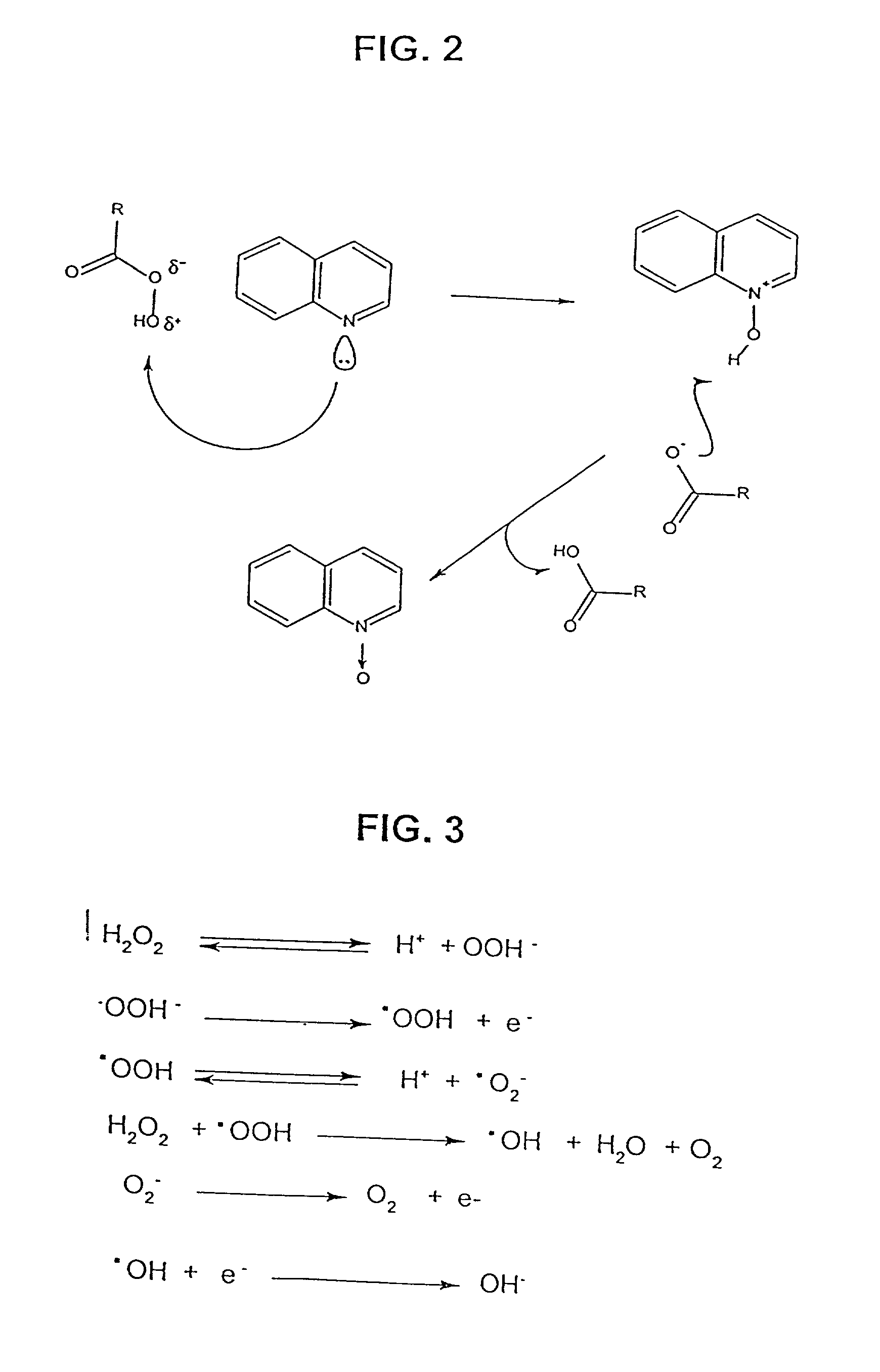
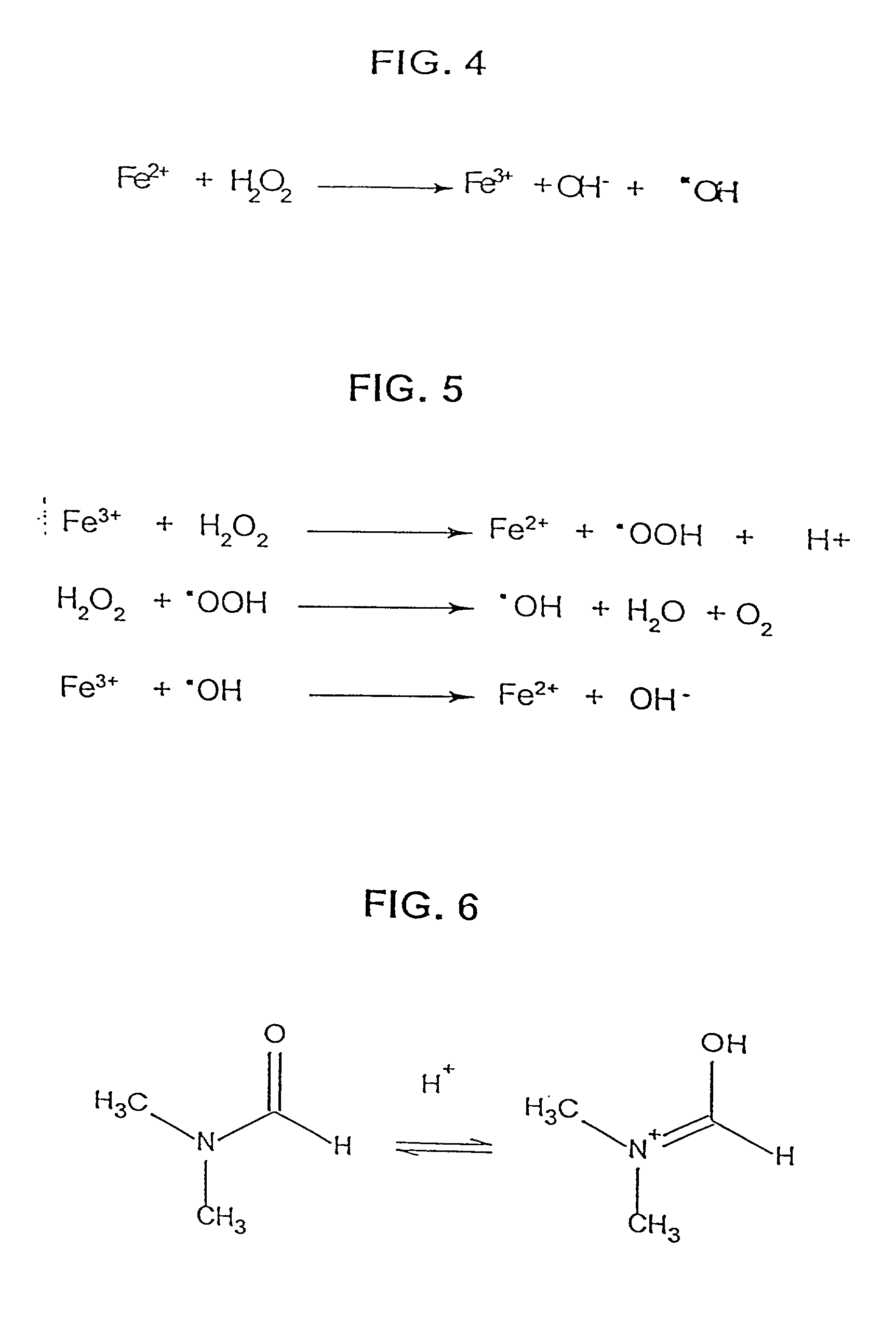
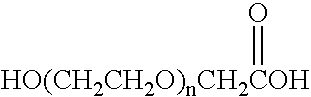Patents
Literature
325results about "Refining with acid-containing liquids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process of paraffin hydrocarbon isomerisation catalysed by an ionic liquid in the presence of a cyclic hydrocarbon additive
InactiveUS6797853B2High selectivityHigh degree of branchingHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneIonic liquid
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
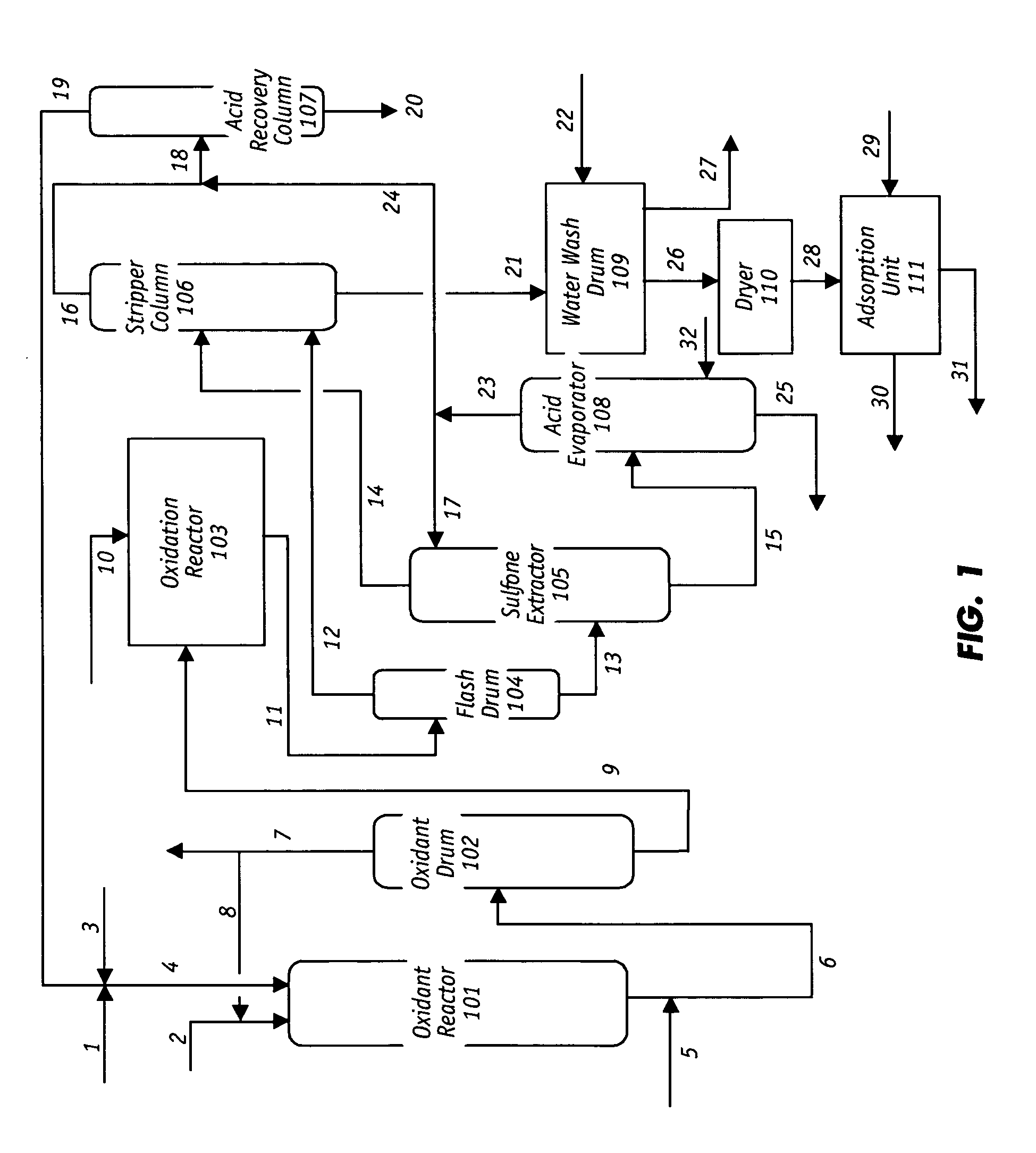
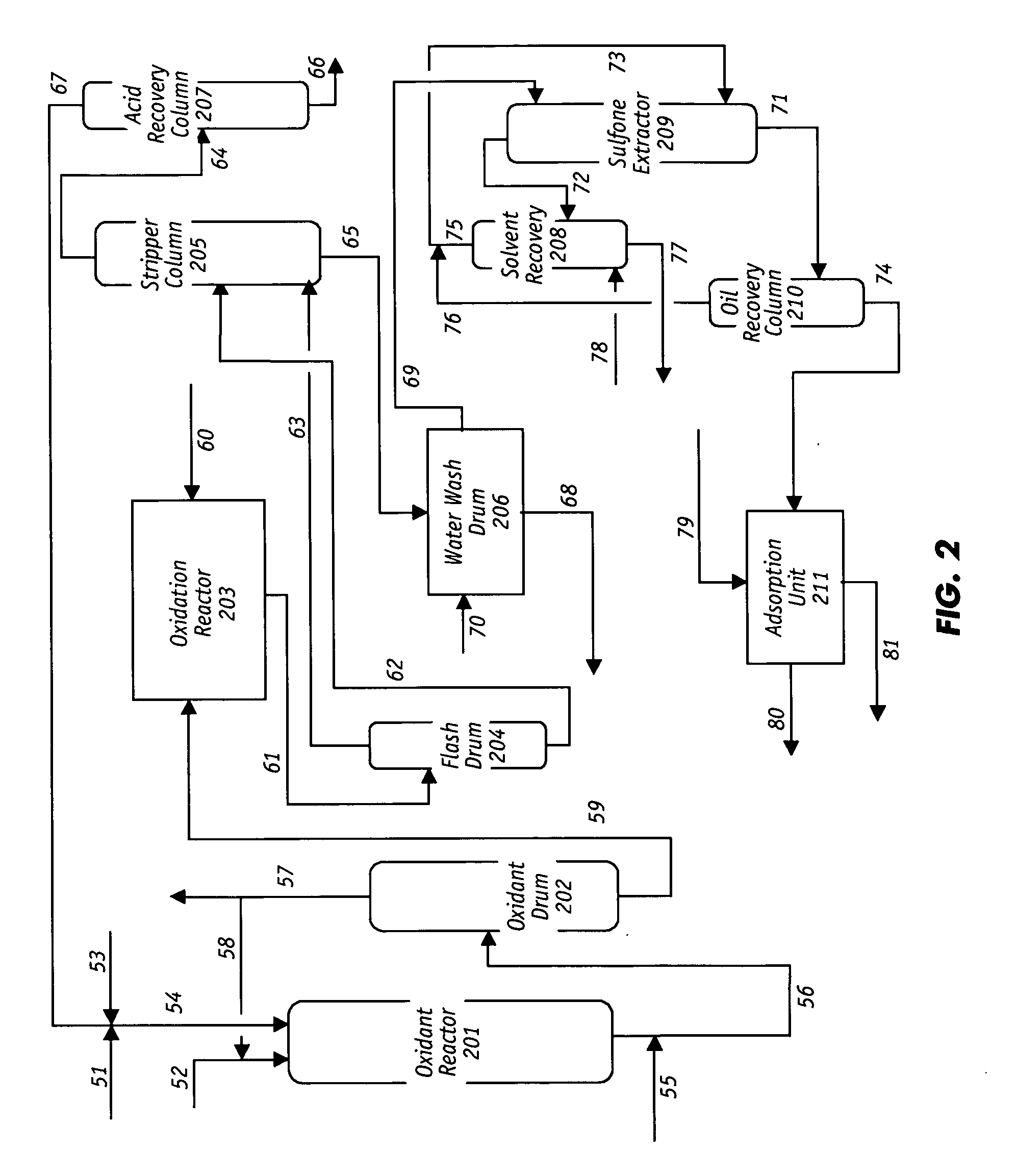
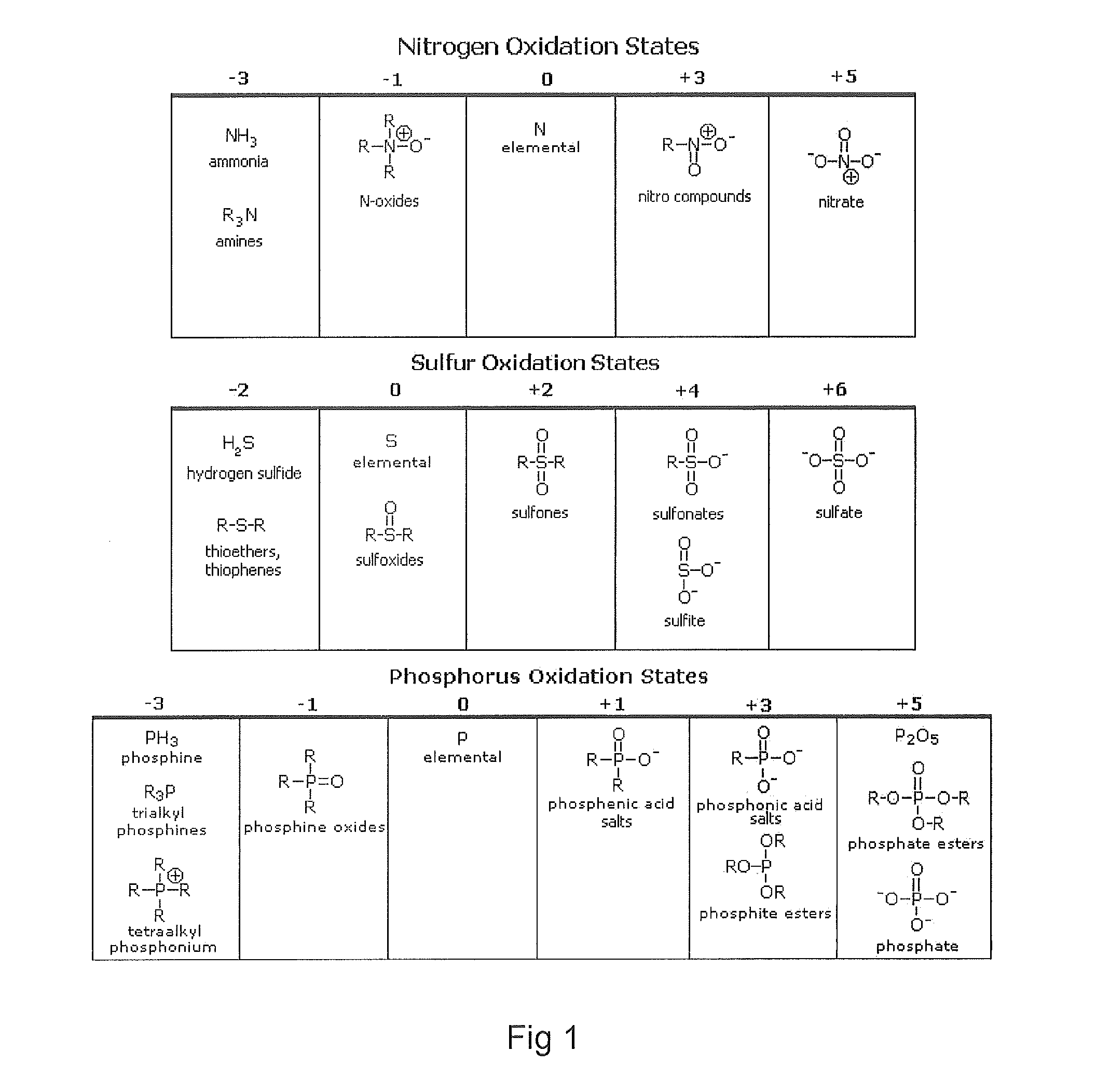
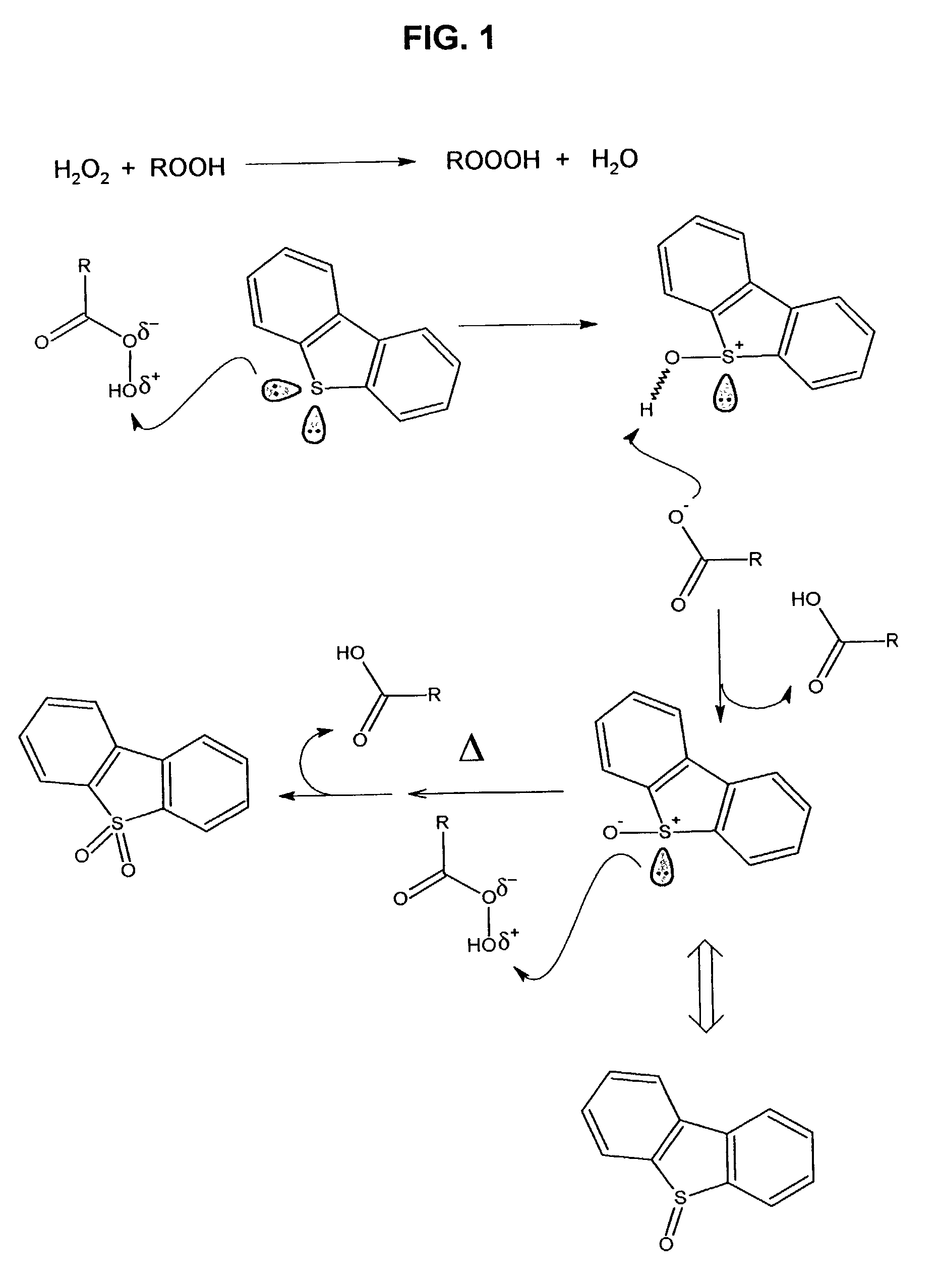
Process for the catalytic oxidation of sulfur, nitrogen and unsaturated compounds from hydrocarbon streams
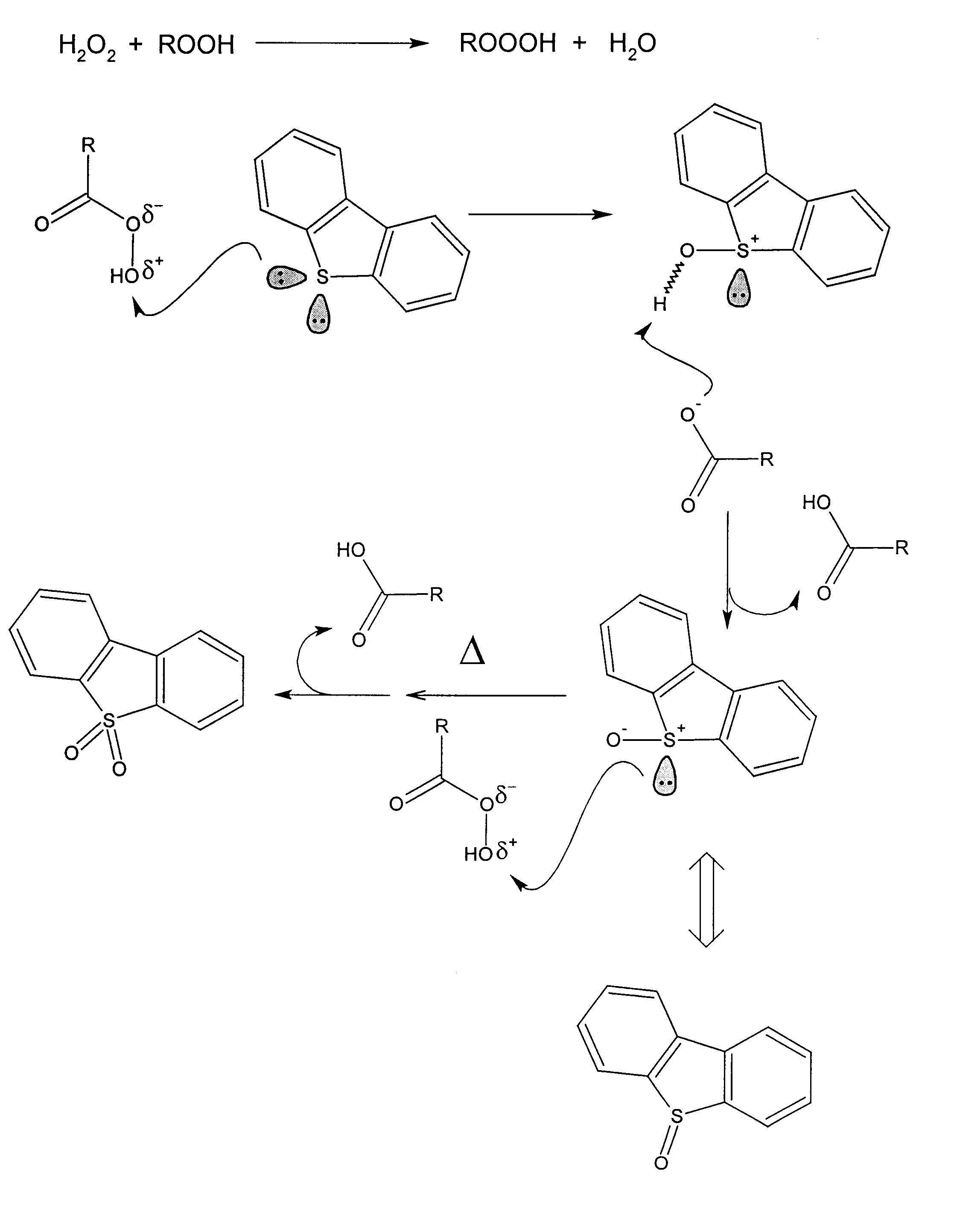
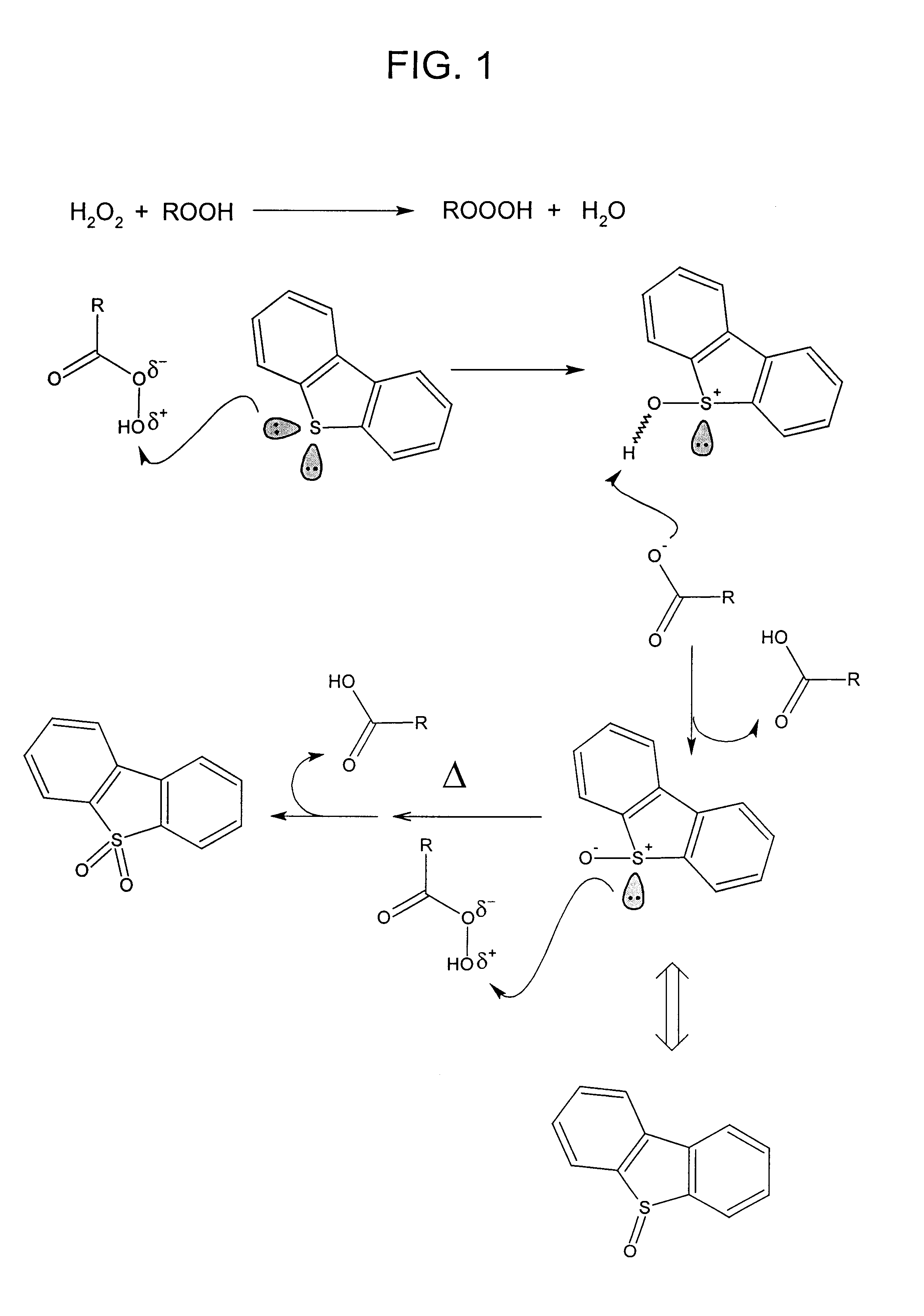
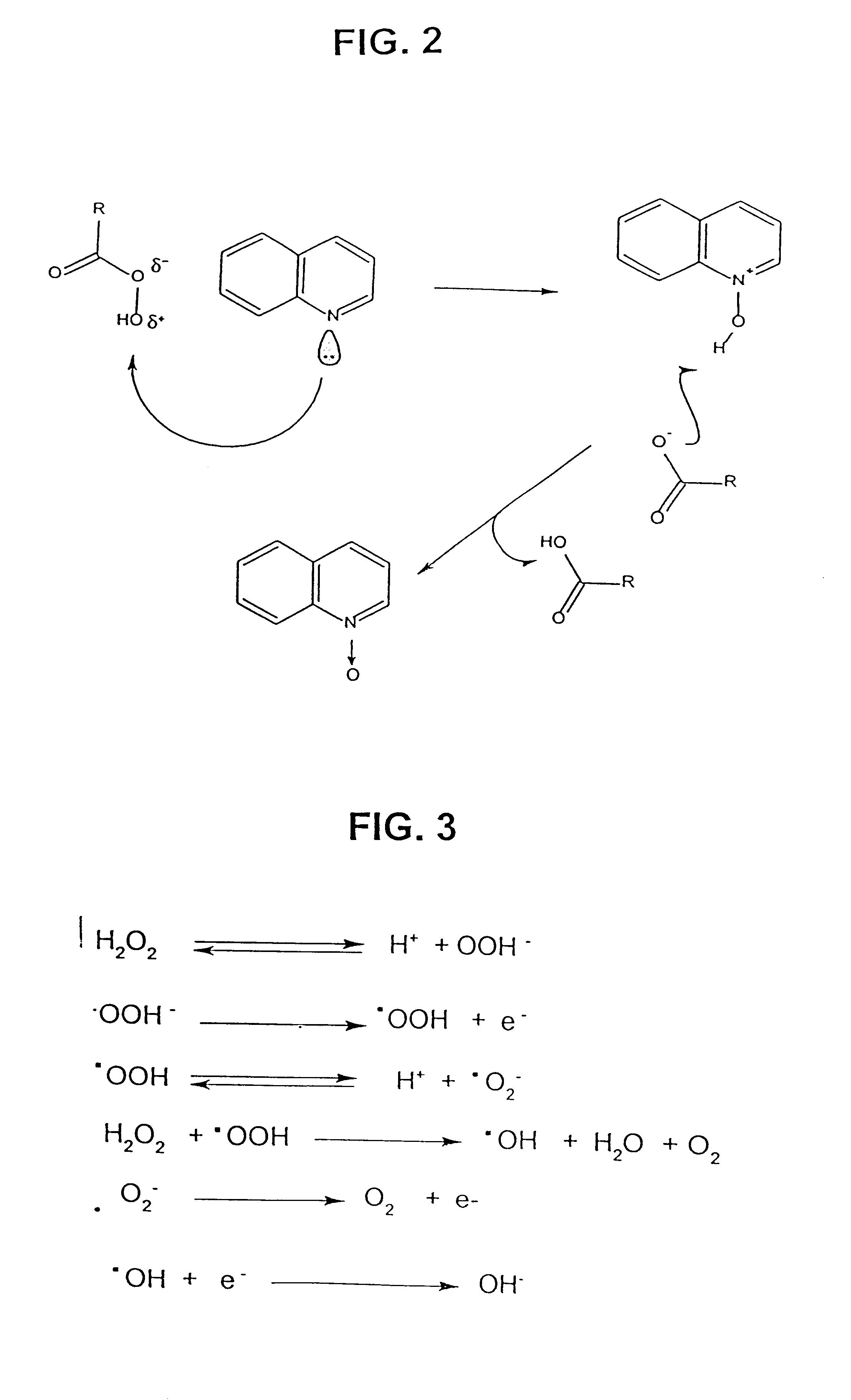
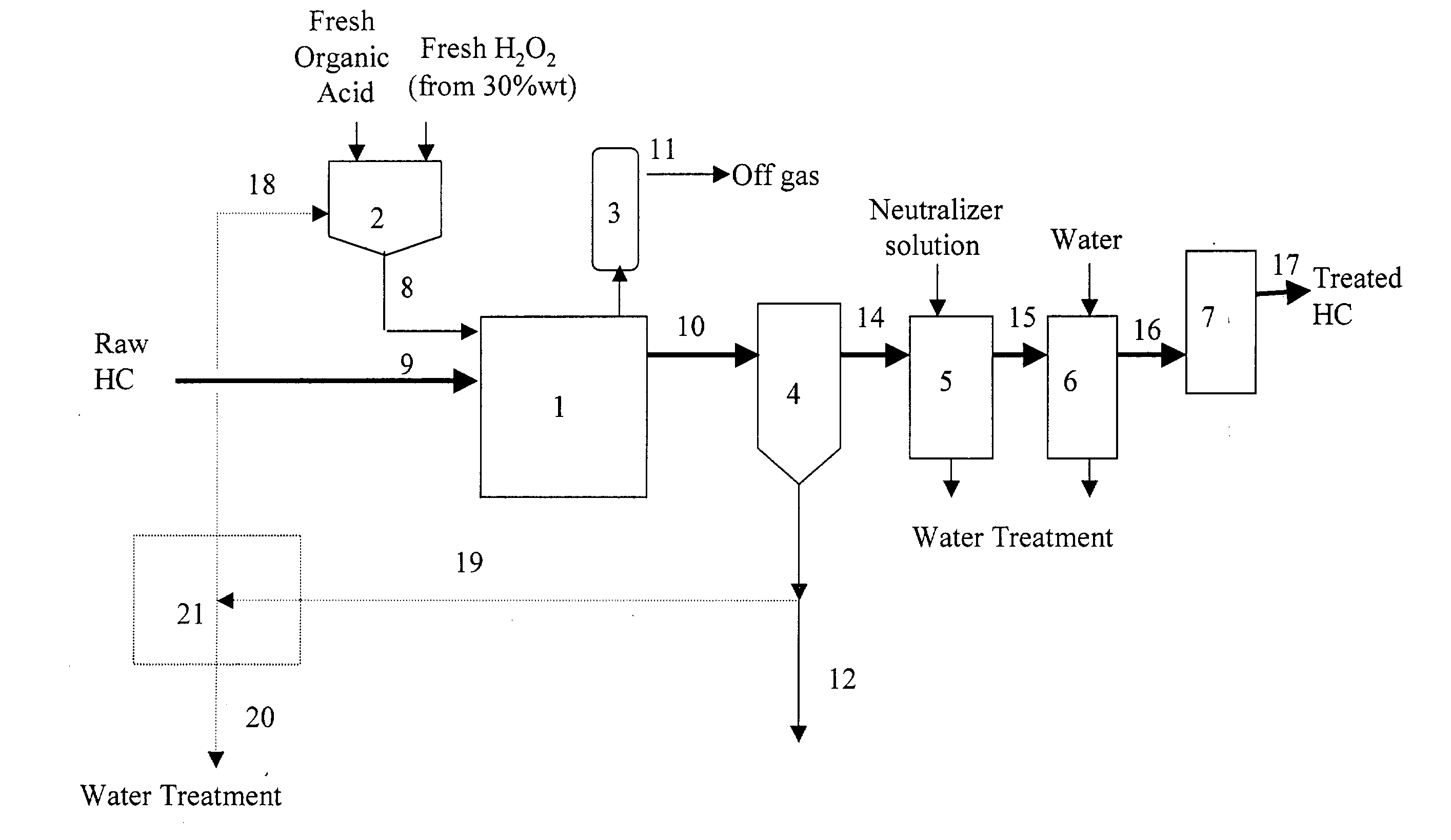
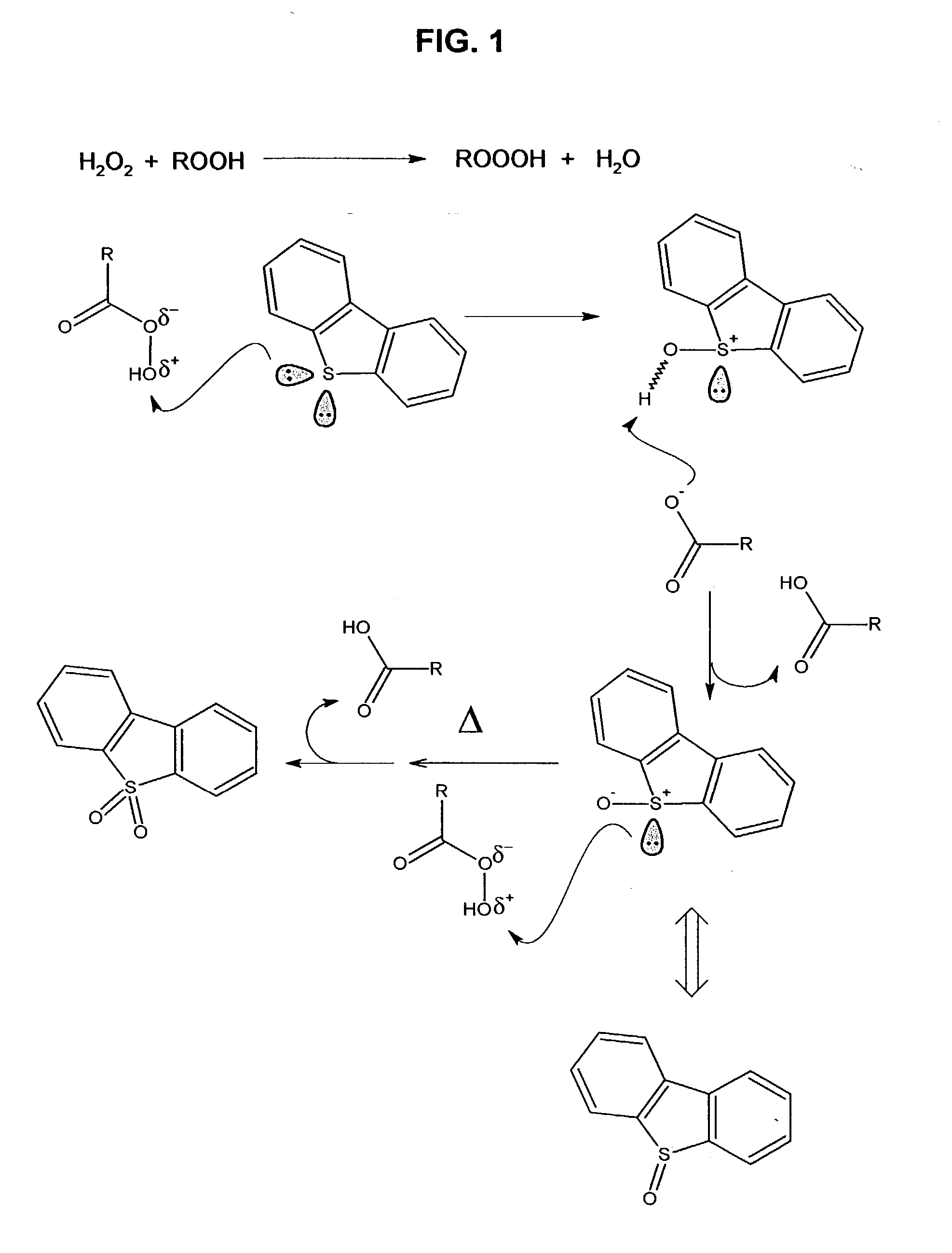
A process for the catalytic oxidation of sulfur and nitrogen contaminants as well as unsaturated compounds present in a hydrocarbon fossil oil medium is described, the process comprising effecting the oxidation in the presence of at least one peroxide, at least one acid and a pulverized raw iron oxide. The process shows an improved oxidation power towards the contaminants typically present in a fossil oil medium, this deriving from the combination of the peroxyacid and the hydroxyl radical generated in the reaction medium due to the presence of an iron oxyhydroxide such as a limonite clay, which bears a particular affinity for the oil medium. The process finds use in various applications, from a feedstock for refining until the preparation of deeply desulfurized and deeply denitrified products.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Distillate fuel blends from Fischer Tropsch products with improved seal swell properties
InactiveUS6890423B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic naphtha reformingPolymer scienceEngineering
The invention provides distillate fuel blend components with improved seal swell and lubricity properties obtained from Fischer Tropsch products. The blends contain a highly paraffinic distillate fuel component and distillate-boiling alkylcycloparaffins and / or distillate-boiling alkylaromatics. The invention further provides processes for obtaining such blends using the products of Fischer Tropsch processes. Finally, the invention provides methods for improving seal swell and lubricity properties for distillate fuels.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
Process and system for continuously extracting oil from solid or liquid oil bearing material
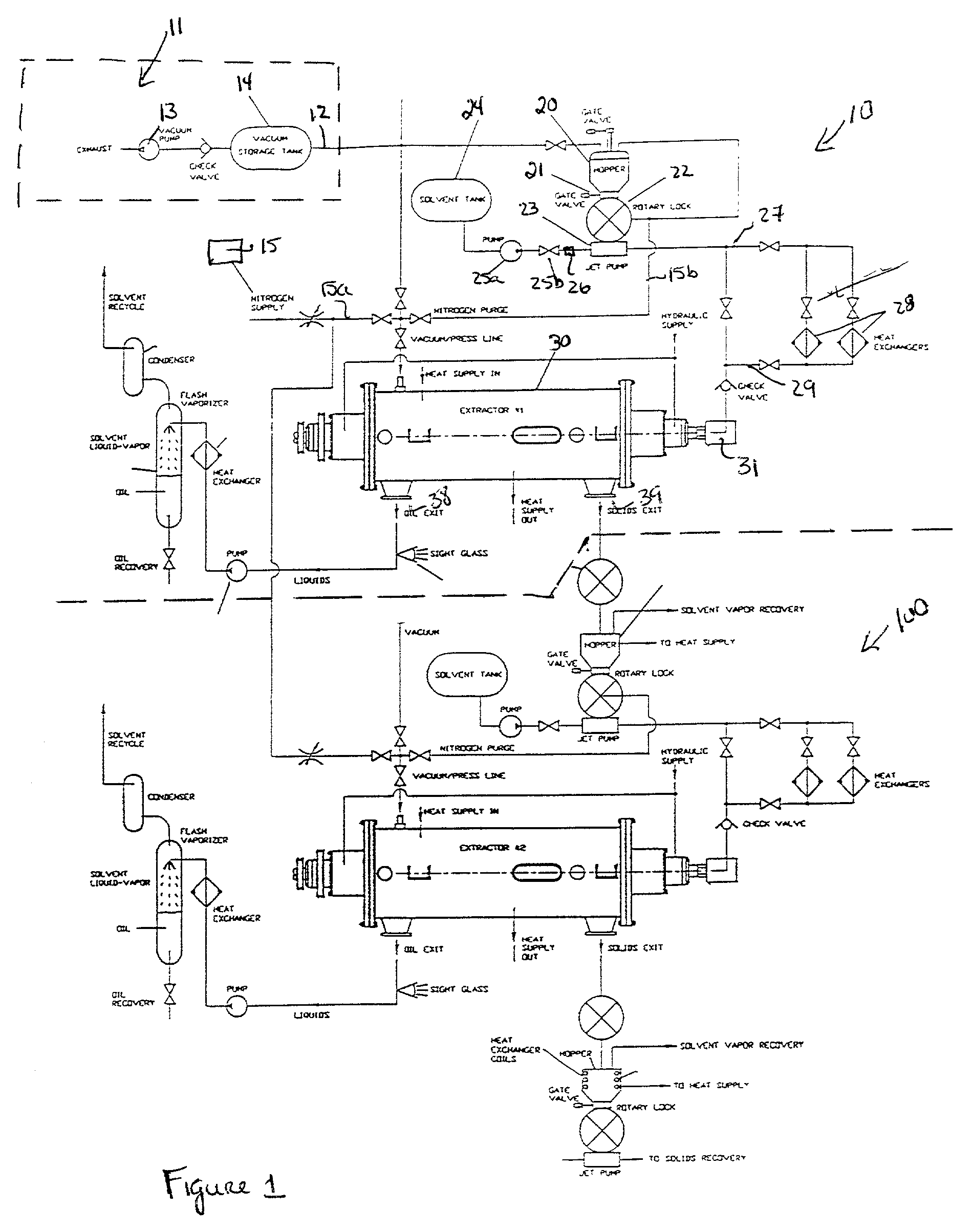
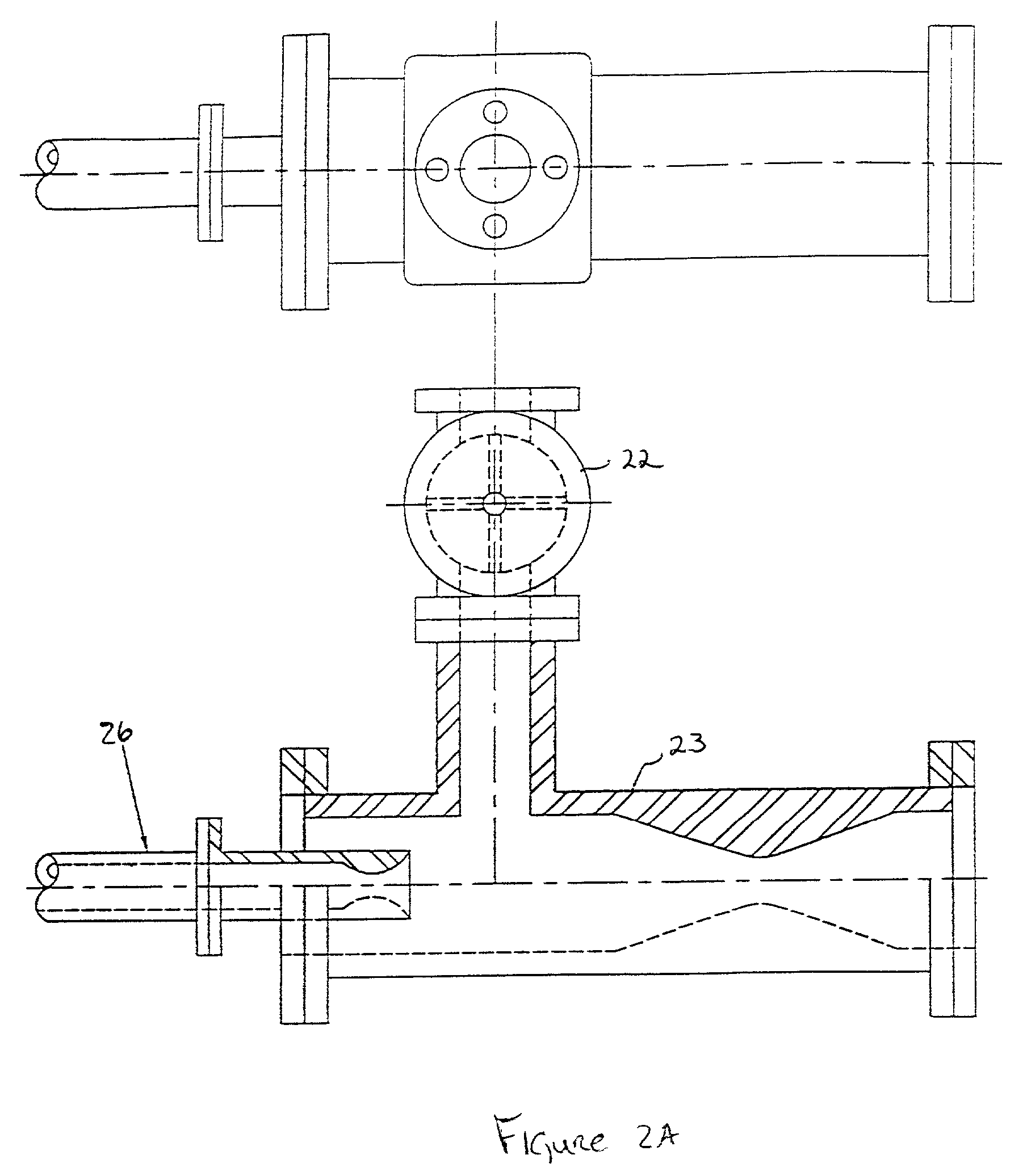
InactiveUS7008528B2Eliminating formationEasy to optimizeRefining with acid-containing liquidsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionSufficient timeLiquid state
A process for continuously extracting oil from a solid or liquid oil-bearing material comprises (a) removing air from the extraction system, (b) introducing an inert gas into the extraction system at a pressure sufficient to maintain a normally gaseous solvent in liquid state, (c) introducing an oil-bearing material into a silo, (d) passing the oil-bearing material from the to a jet pump mixing device, (e) introducing a liquified normally gaseous solvent into the jet pump mixing device, (f) mixing the oil-bearing material and the solvent in the jet pump mixing device for a time sufficient to permit complete wetting of oil-bearing material by the solvent to form a mixture, (g) heating the mixture to near supercritical conditions; (h) passing the mixture through an extractor having a screw conveyor adapted to rotate at a first rpm range and a centrifugal drum adapted to rotate at a second rpm range, (i) treating the mixture within the extractor in such a manner that supercritical temperature and pressure are attained, wherein treating the mixture includes a combination of increasing the rpms of the centrifugal drum, increasing the temperature inside the extractor and increasing the inert gas pressure inside the extractor, (j) extracting oil from the mixture by pressure diffusion provided by the combination of increased rpms, increased temperatures and increased inert gas pressures at supercritical conditions, (j) removing liquids extracted from the mixture through a liquids exit port, and (k) removing solids extracted from the mixture through a solids exit port.
Owner:MITCHELL ALLEN R +1
Process for producing petroleum oils with ultra-low nitrogen content
ActiveUS20070000809A1Highly effectiveSpeed up the extraction processHydrocarbon distillationTreatment with plural serial refining stagesLow nitrogenSolvent
A highly effective liquid-liquid extraction process to remove nitrogen compounds and especially basic nitrogen compounds from aromatic light petroleum oils with excellent recovery employs de-ionized water, which can be acidified, as the extractive solvent. The product is an aromatic hydrocarbon with ultra-low amounts of nitrogen poisons that can deactivate acidic catalysts. The extracted oils are suitable feedstock for the subsequent catalytic processes that are promoted with the high performance solid catalysts, which are extremely sensitive to nitrogen poison.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
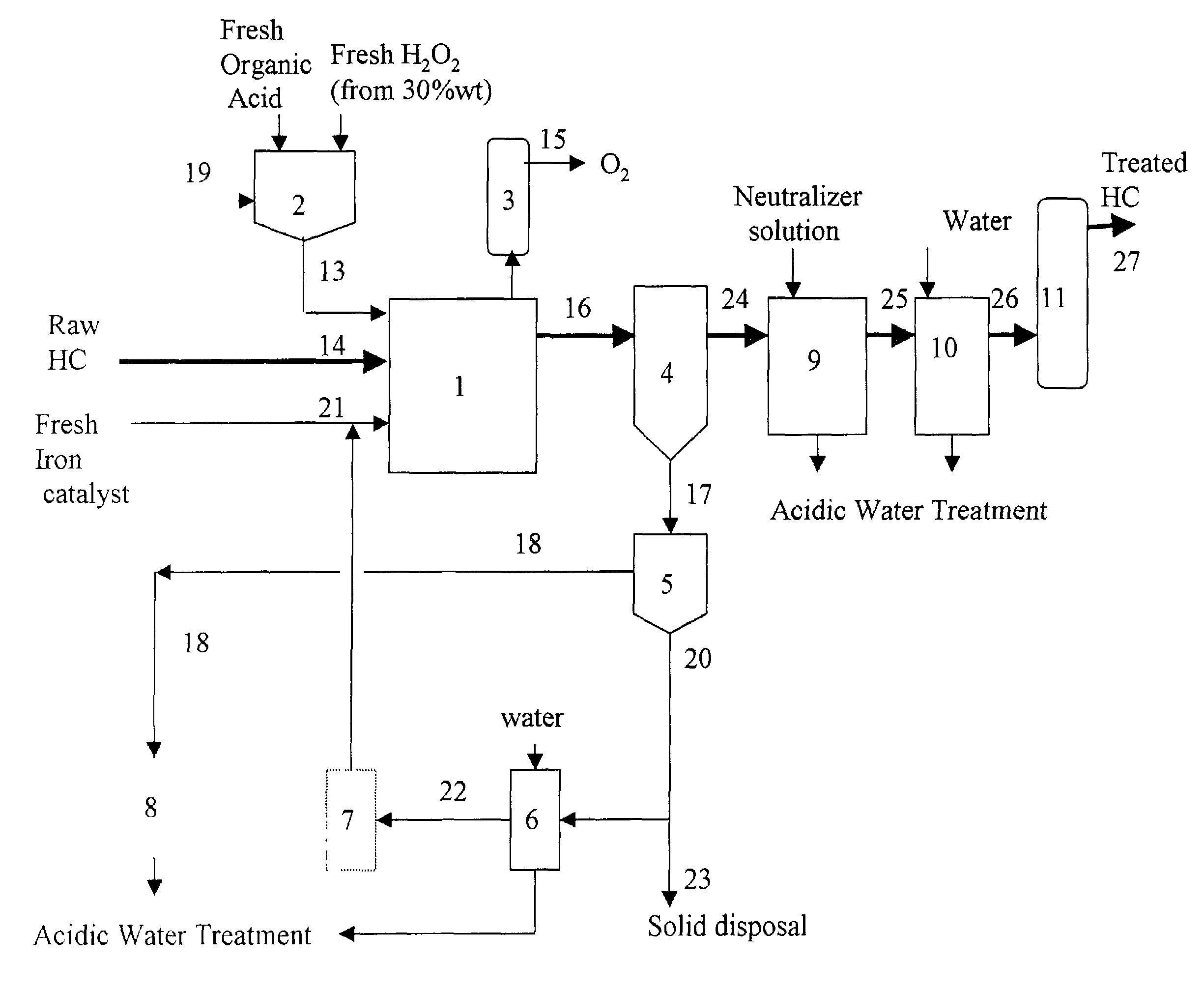
Oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation of petroleum oils
InactiveUS20070102323A1Reduce the temperatureShort stayOrganic chemistryRefining with oxygen compoundsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSolvent
An improved oxidative process that employ a robust, non-aqueous, and oil-soluble organic peroxide oxidant for effective desulfurization and denitrogenation of hydrocarbons including petroleum fuels, hydrotreated vacuum gas oil (VGO), non-hydrotreated VGO, petroleum crude oil, synthetic crude oil from oil sand, and residual oil. Even at low concentrations and without the assistance of catalysts, the non-aqueous organic peroxide oxidant is extremely active and fast in oxidizing the sulfur and nitrogen compounds in the hydrocarbon feedstocks. Furthermore, the process generates a valuable organic acid by-product that is also used internally as the extractive solvent for effective removal of the oxidized sulfur and nitrogen from the hydrocarbons without the need of a final adsorption step. Novel process steps are also disclosed to substantially prevent yield loss in the oxidative process.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION
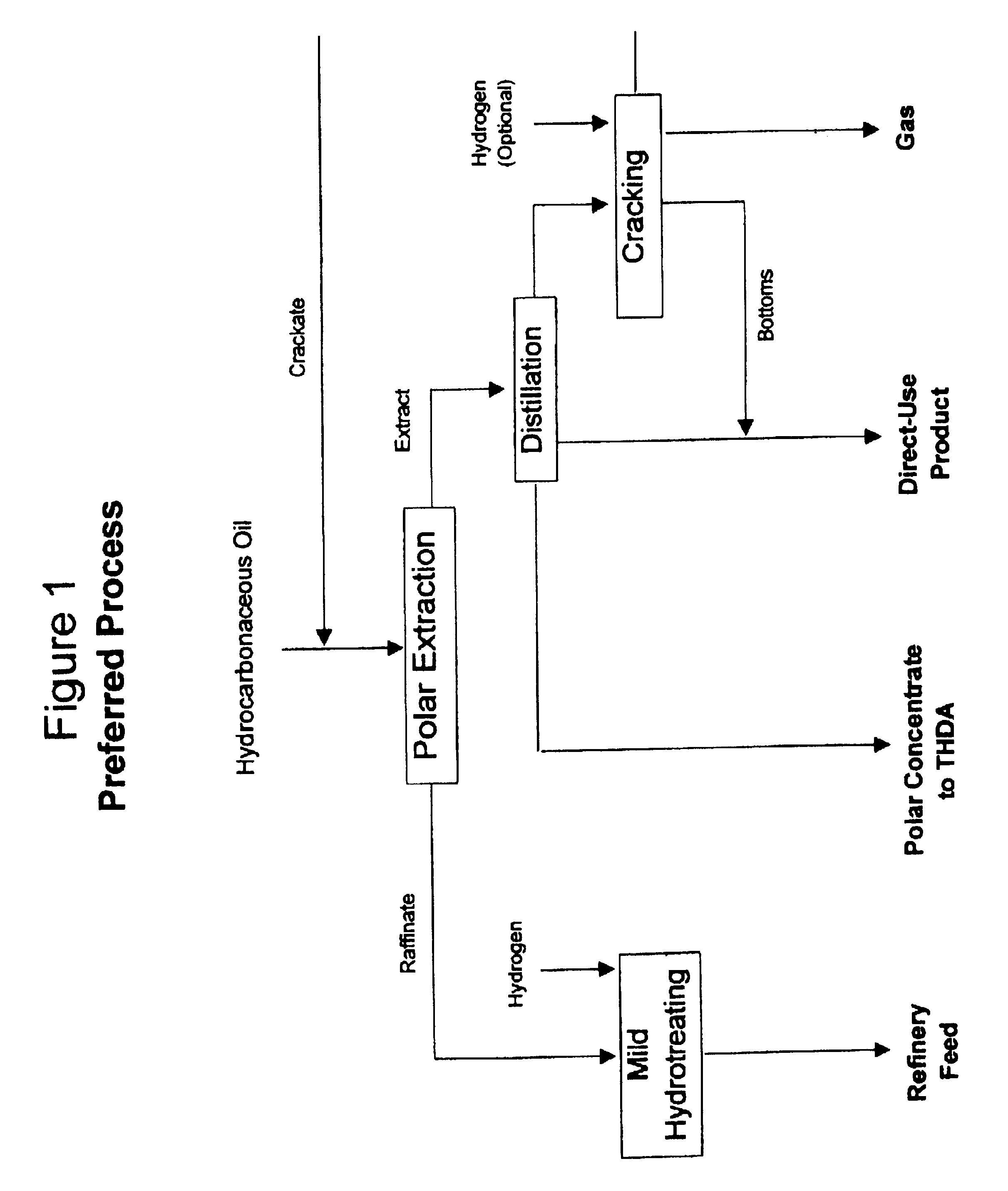
Process for enhancing the value of hydrocabonaceous natural recources
InactiveUS6875341B1Little and valueReduce total process throughputRefining with acid-containing liquidsHydrocarbonsSolubilitySolvent free
Owner:JWBA
Preparation of components for transportation fuels
InactiveUS6881325B2Environmentally friendlyRefining with oxygen compoundsRefining with acid-containing liquidsPhosphomolybdic acidComponents of crude oil
Economical processes are disclosed for the production of components for refinery blending of transportation fuels by selective oxidation of feedstocks comprising a mixture of hydrocarbons, sulfur-containing and nitrogen-containing organic compounds. Oxidation feedstock is contacted with a soluble quaternary ammonium salt containing halogen, sulfate, or bisulfate anion, and an immiscible aqueous phase comprising a source of hydrogen peroxide, and at least one member of the group consisting of phosphomolybdic acid and phosphotungstic acid, in a liquid reaction mixture under conditions suitable for reaction of one or more of the sulfur-containing and / or nitrogen-containing organic compounds. Blending components containing less sulfur and / or less nitrogen than the oxidation feedstock are recovered from the reaction mixture. Advantageously, at least a portion of the immiscible acid-containing phase is recycled to the oxidation.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Hydrocarbon oil demetalizing agent, and preparing method and use method thereof
InactiveCN1454967AEasy to separateReduce oil contentRefining with non-metalsRefining with acid-containing liquidsPetroleumChemistry
The present invention relates to a hydrocarbon oil demetallization agent, its preparation method and application method. Said hydrocarbon oil demetallization agent comprises demetallization agent, demulsifier and demetallization adjuvant. Its application method includes the following steps: fully mixing hydrocarbon oil demetallization agent or its aqueous solution and hydrocarbon oil according to a certain ratio and adopting conventional electric desalting process to make treatment so as to obtain demetallized hydrocarbon oil. At the same time of desalting it can remove other metal ions of calcium, magnesium, iron, vanadium and nickel, etc. from hydrocarbon oil, so that its oil and water separation effect is good.
Owner:PETROCHINA KARAMAY PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Additives to enhance metal and amine removal in refinery desalting processes
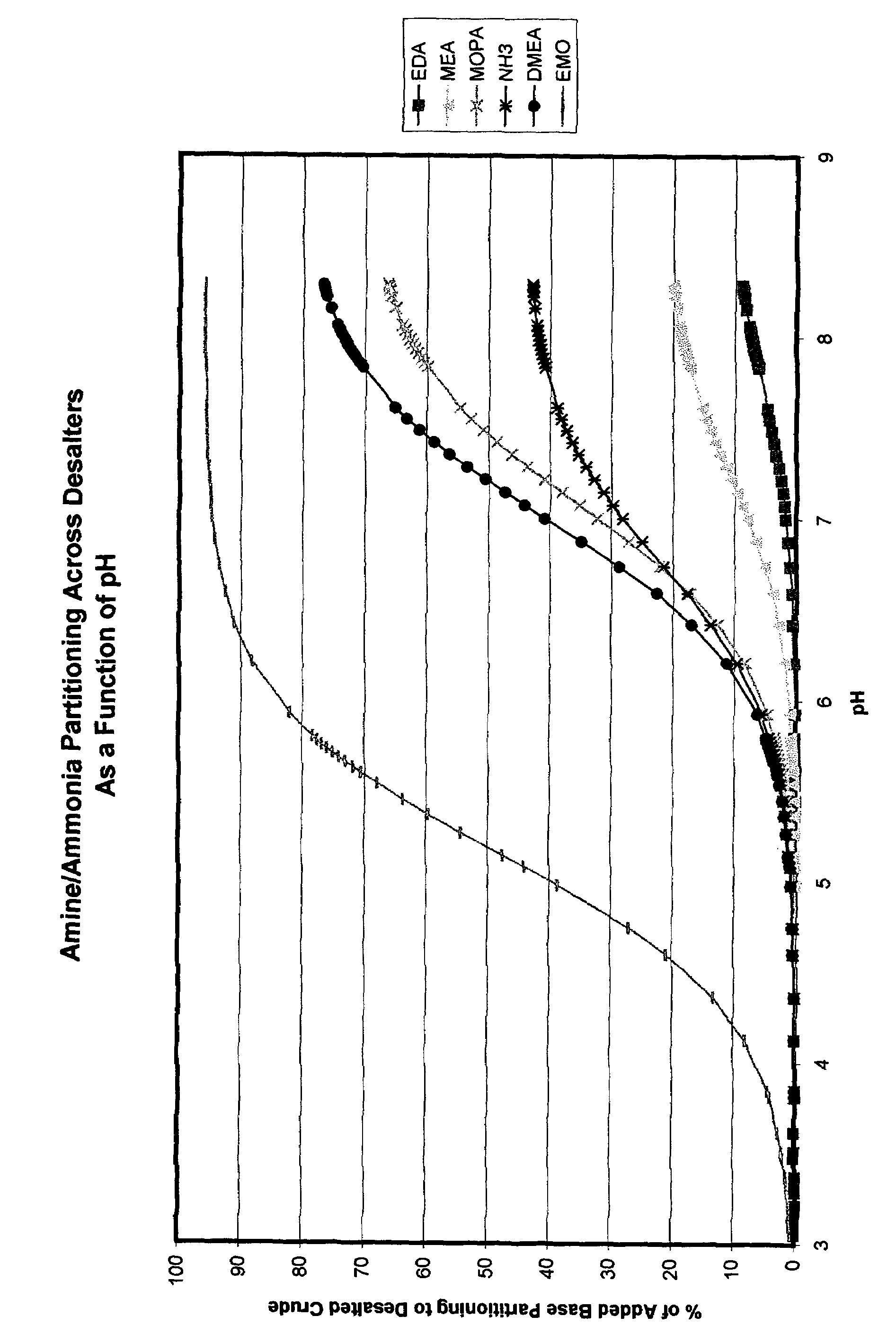
ActiveUS7497943B2Dewatering/demulsification with chemical meansDewatering/demulsification with electric/magnetic meansWash waterChloroacetic acids
It has been discovered that metals and / or amines can be removed or transferred from a hydrocarbon phase to a water phase in an emulsion breaking process by using a composition that contains water-soluble hydroxyacids. Suitable water-soluble hydroxyacids include, but are not necessarily limited to glycolic acid, gluconic acid, C2-C4 alpha-hydroxy acids, poly-hydroxy carboxylic acids, thioglycolic acid, chloroacetic acid, polymeric forms of the above hydroxyacids, poly-glycolic esters, glycolate ethers, and ammonium salt and alkali metal salts of these hydroxyacids, and mixtures thereof. The composition may also include at least one mineral acid to reduce the pH of the desalter wash water. A solvent may be optionally included in the composition. The invention permits transfer of metals and / or amines into the aqueous phase with little or no hydrocarbon phase undercarry into the aqueous phase. The composition is particularly useful in treating crude oil emulsions, and in removing calcium and other metals therefrom.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Treatment of crude oils
InactiveUS6955753B1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolvent extractionHydrogenPetroleum
A process and apparatus to extract and recover heavy metals and sulfur from crude oil or petroleum fuel products including the steps of emulsifying the crude oil with an emulsifying agent, adding a leach solution to the emulsified crude oil and leaching the emulsified crude oil at elevated temperature and pressure to give a leached emulsified crude oil. The leach solution may be acid or alkali. A proportion of the leach solution is extracted for recovering heavy metals. There can also be a microwave hydro-treating step using hydrogen gas at a temperature below 220° C. to ensure there is no quality degradation in the crude feed to produce a desulfurized crude oil and a hydrogen sulphide by-product and recovering sulfur from the hydrogen sulphide by-product.
Owner:RODOLFO ANTONIO M GOMEZ
Process for the catalytic oxidation of sulfur, nitrogen and unsaturated compounds from hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS20020189975A1Refining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsCatalytic oxidationPeroxy acid
A process for the catalytic oxidation of sulfur and nitrogen contaminants as well as unsaturated compounds present in a hydrocarbon fossil oil medium is described, the process comprising effecting the oxidation in the presence of at least one peroxide, at least one acid and a pulverized raw iron oxide. The process shows an improved oxidation power towards the contaminants typically present in a fossil oil medium, this deriving from the combination of the peroxy-acid and the hydroxyl radical generated in the reaction medium due to the presence of an iron oxyhydroxide such as a limonite clay, which bears a particular affinity for the oil medium. The process finds use in various applications, from a feedstock for refining until the preparation of deeply desulfurized and deeply denitrified products.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Method for cavitation-assisted refining, degumming and dewaxing of oil and fat
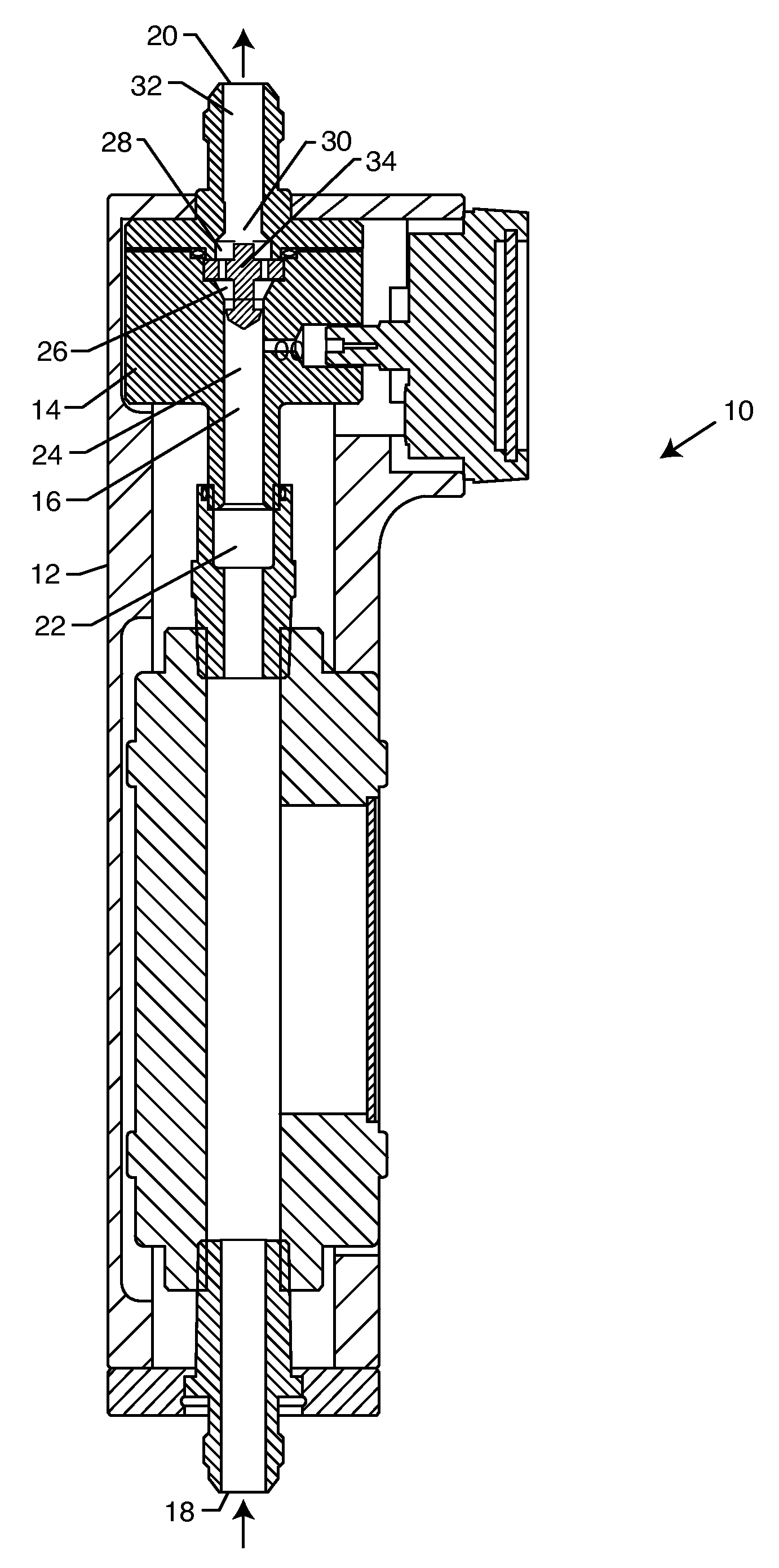
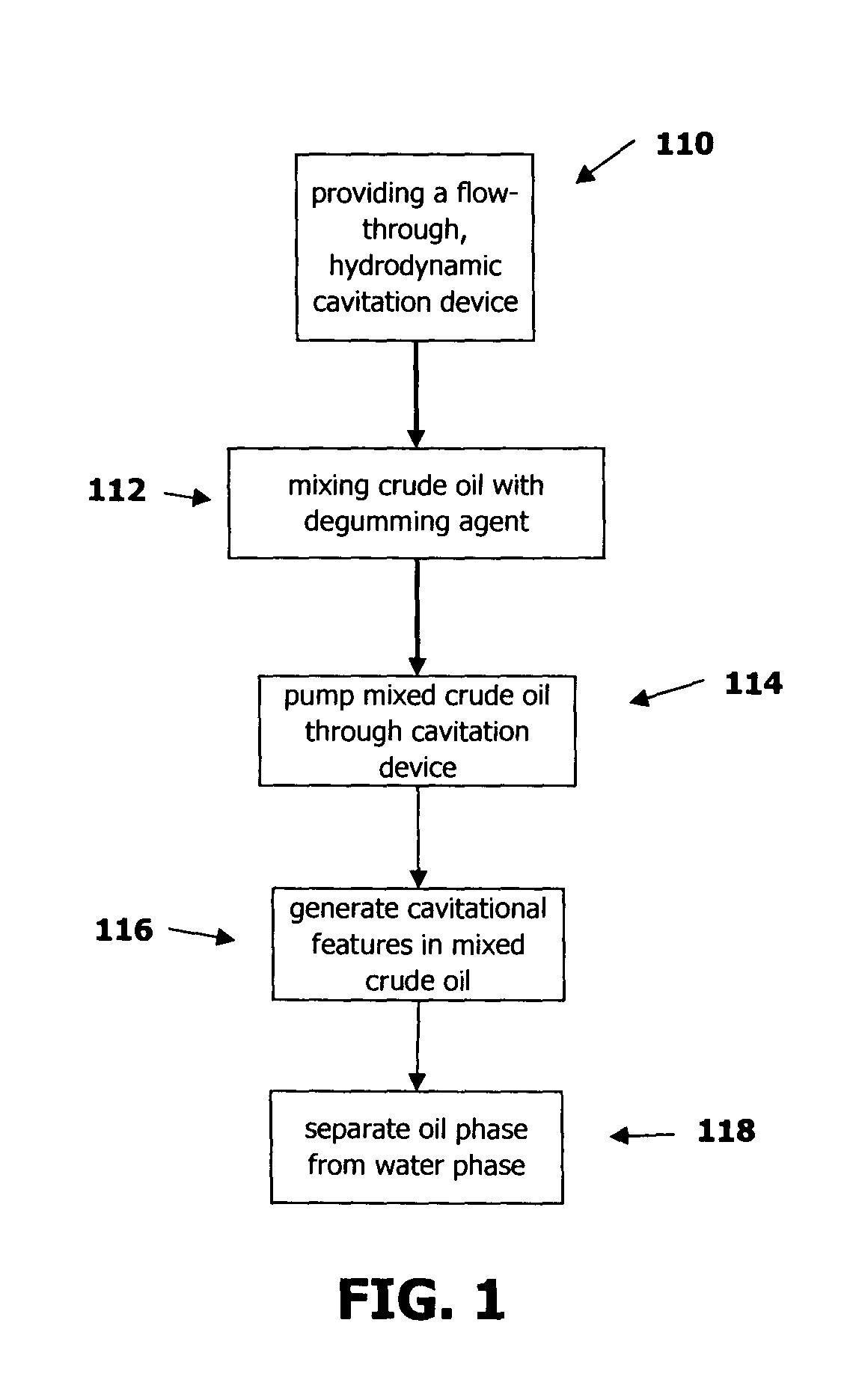
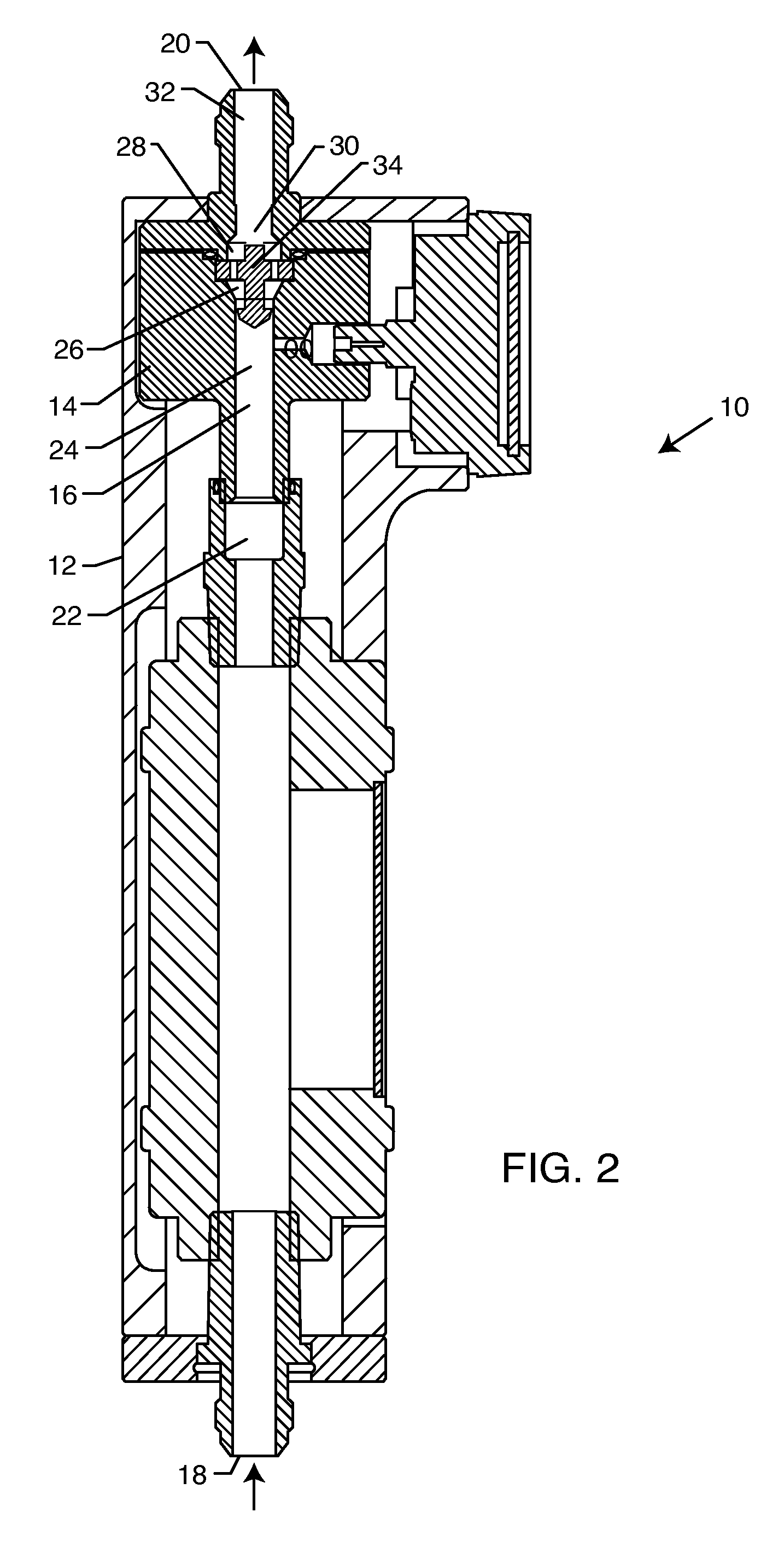
ActiveUS20090314688A1Improve throughputPrevent oxidationLiquid-gas reaction as foam/aerosol/bubblesFatty acid esterificationCavitationOil phase
A method for degumming and / or refining crude oil containing impurities involving mixing the crude oil with degumming agents, i.e., water or acid, and subjecting the mixture to flow-through, hydrodynamic cavitation processing. The cavitational processing transfers impurities in the crude oil to a water phase for easier separation. The water phase may be separated from the oil phase by commonly available separation methods.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
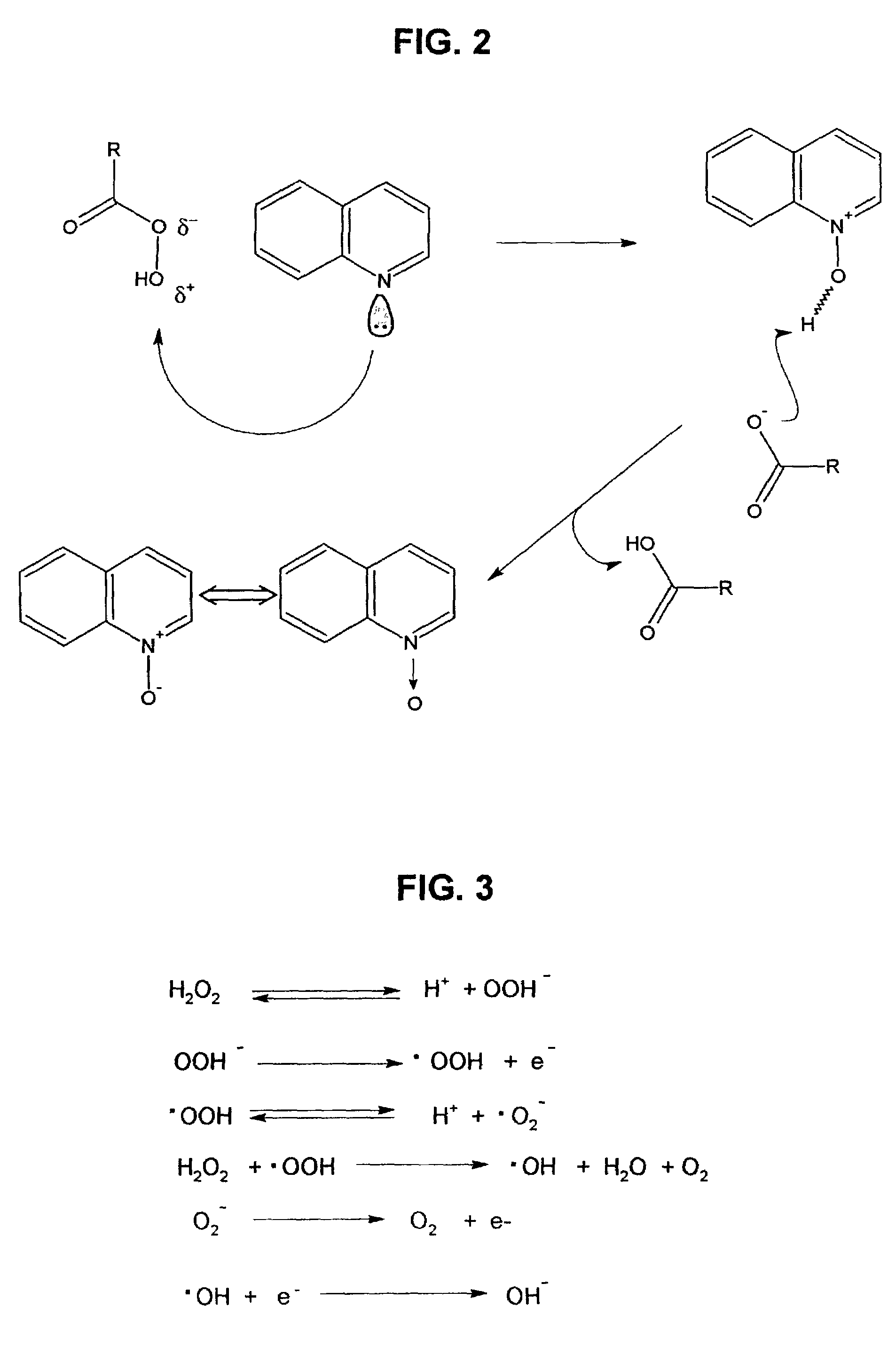
Process for the extractive oxidation of contaminants from raw hydrocarbon streams
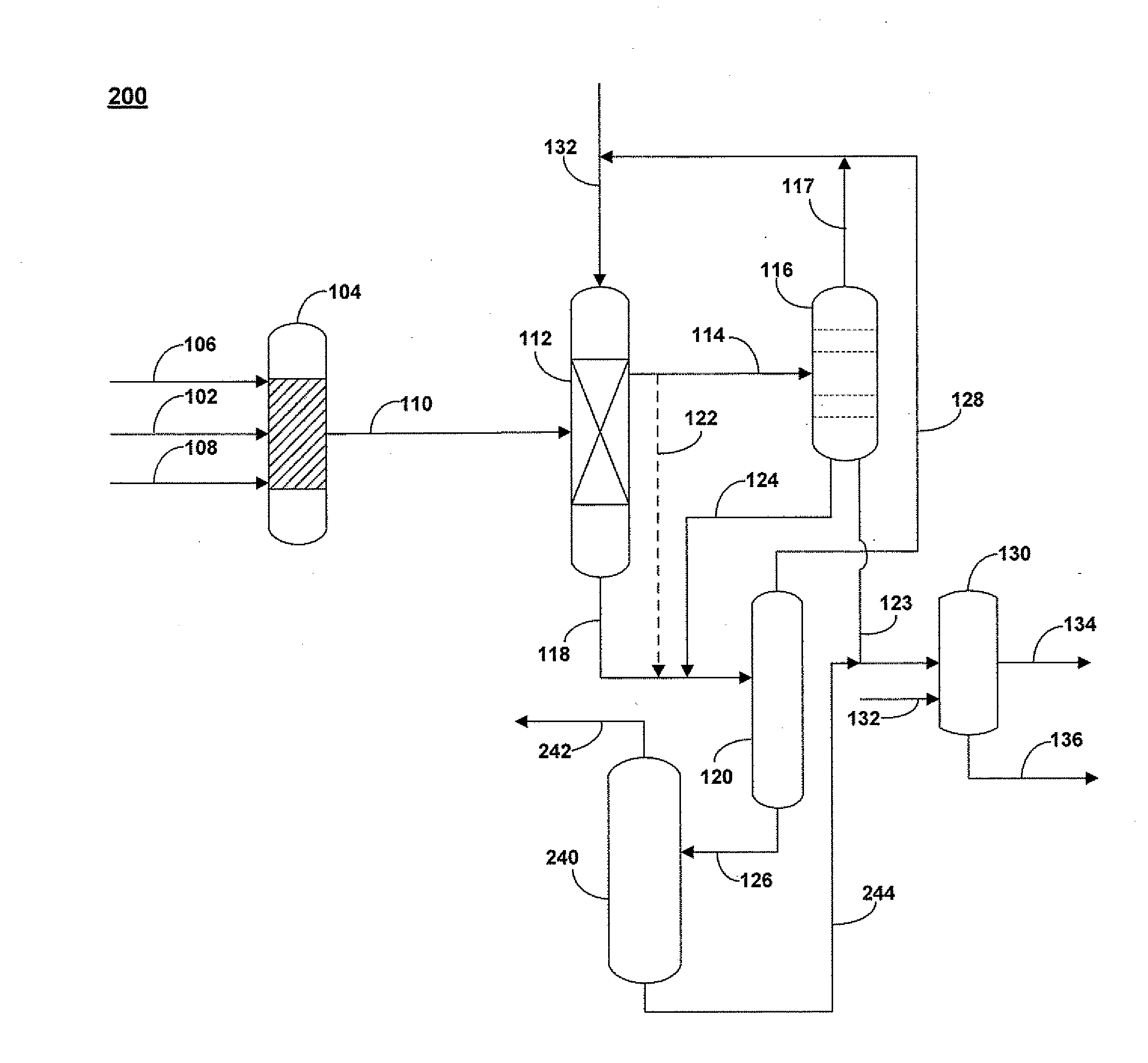
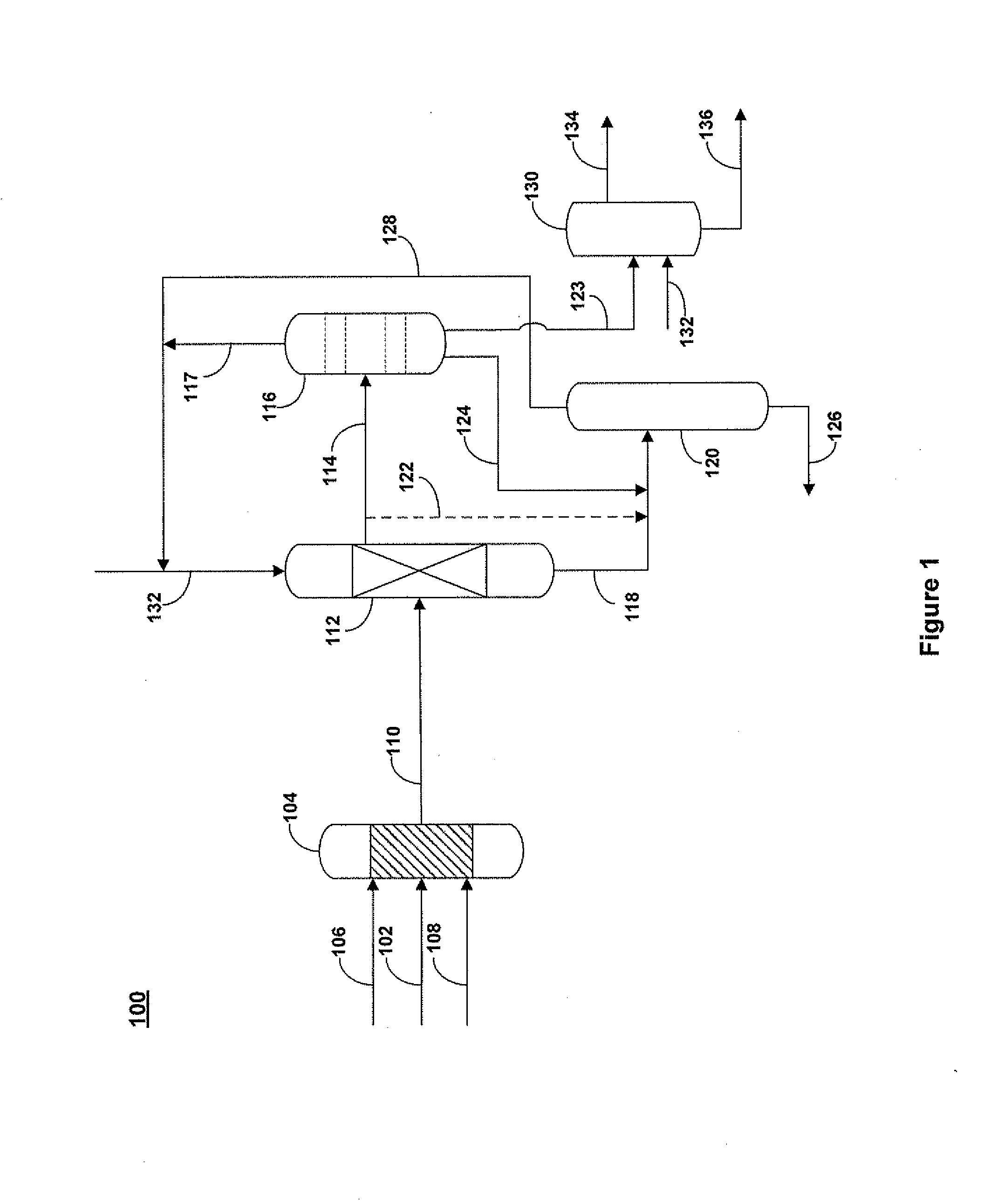
A process for the extractive oxidation of contaminants from raw hydrocarbon streams rich in heteroatomic polar compounds is described, the said process involving the extractive oxidation of sulfur and nitrogen compounds from said streams, the said process comprising treating said streams with a peroxide solution / organic acid couple, the weight percent of the peroxide solution and organic acid based on raw hydrocarbon being at least 3 for both the peroxide and organic acid solution, under an acidic pH, atmospheric or higher pressure and ambient or higher temperature. As a result of the reaction, the oxidized heteroatomic compounds, having strong affinity for the aqueous phase, are extracted into said aqueous phase, while the oxidized hydrocarbon is neutralized, water washed and dried, the resulting end product being a hydrocarbon stream from which have been removed 88.1 wt % or more of total nitrogen compounds and basic nitrogen up to 99.1 wt %, both calculated as mass contents, total Sulfur 23.3% removal, and removal of total olefins is limited to 6.5 weight %. The treated product is further directed to any refining process.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
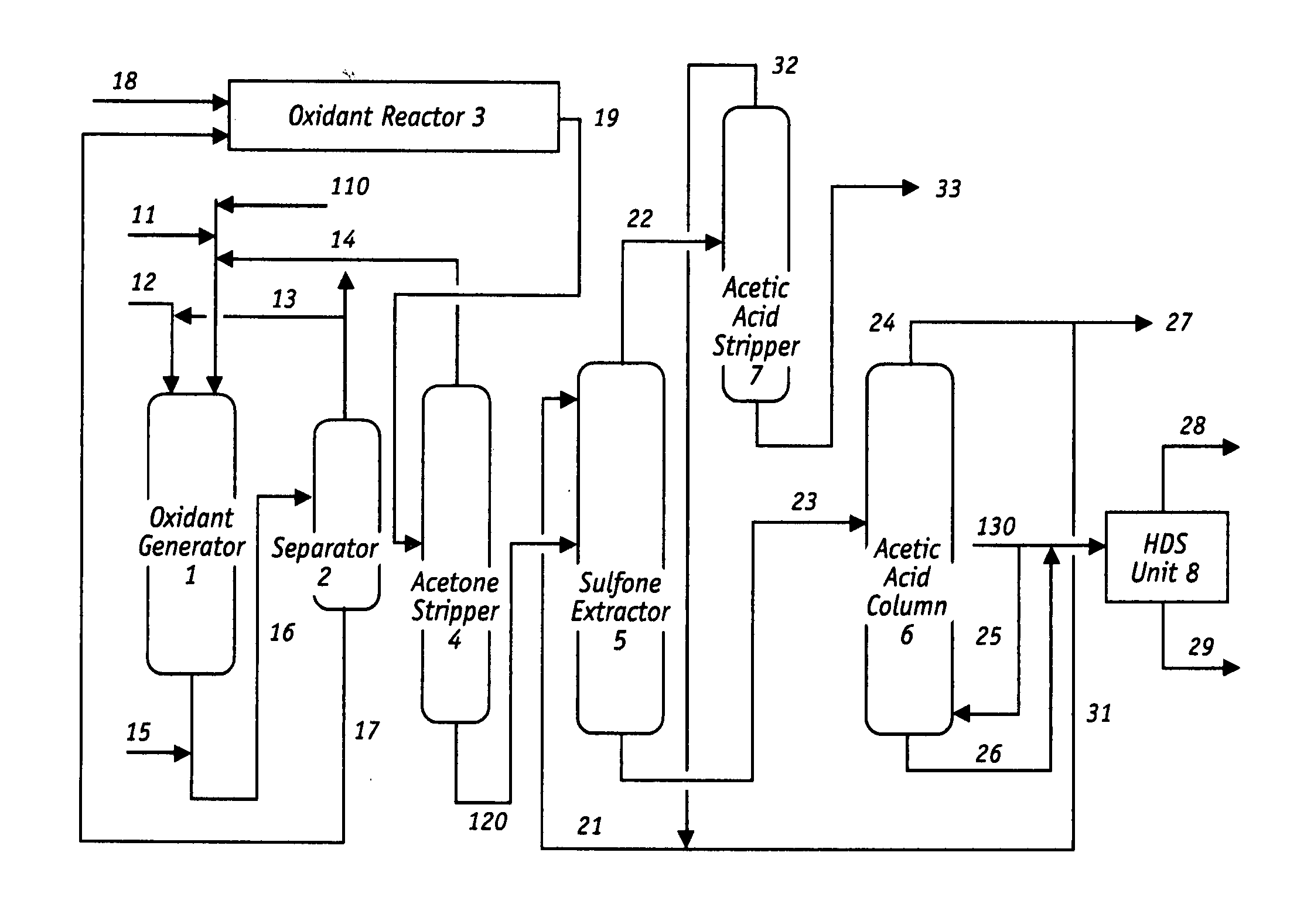
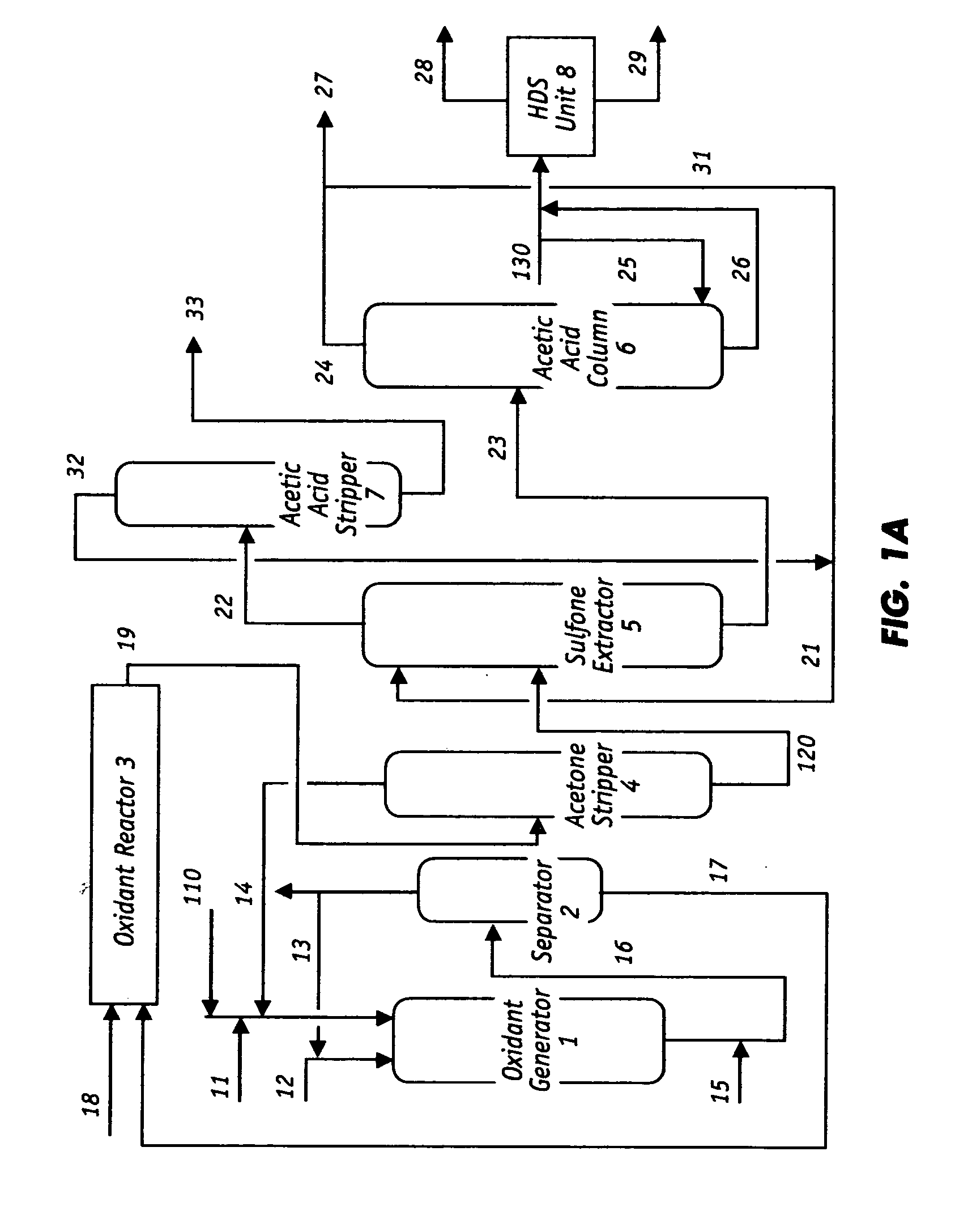
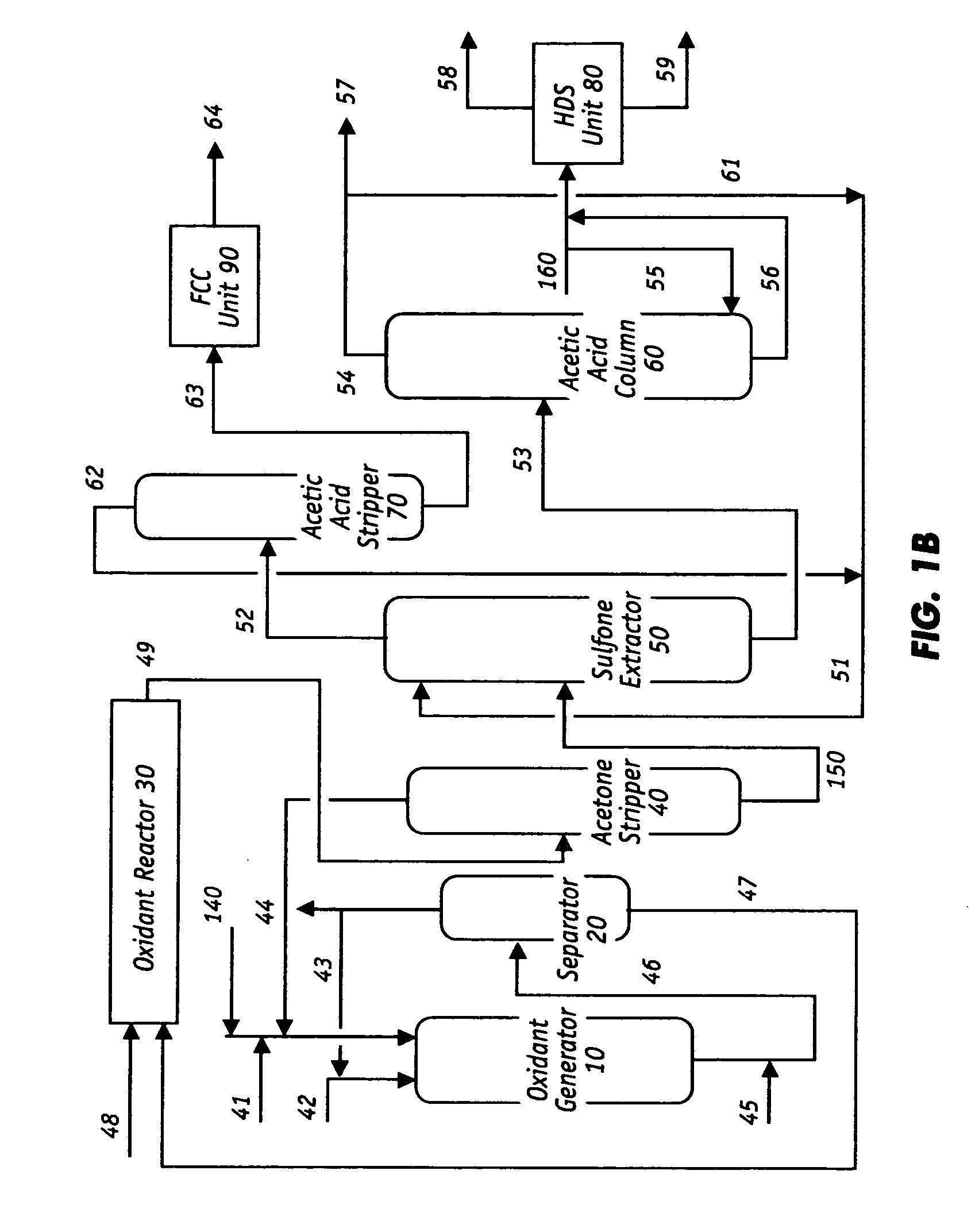
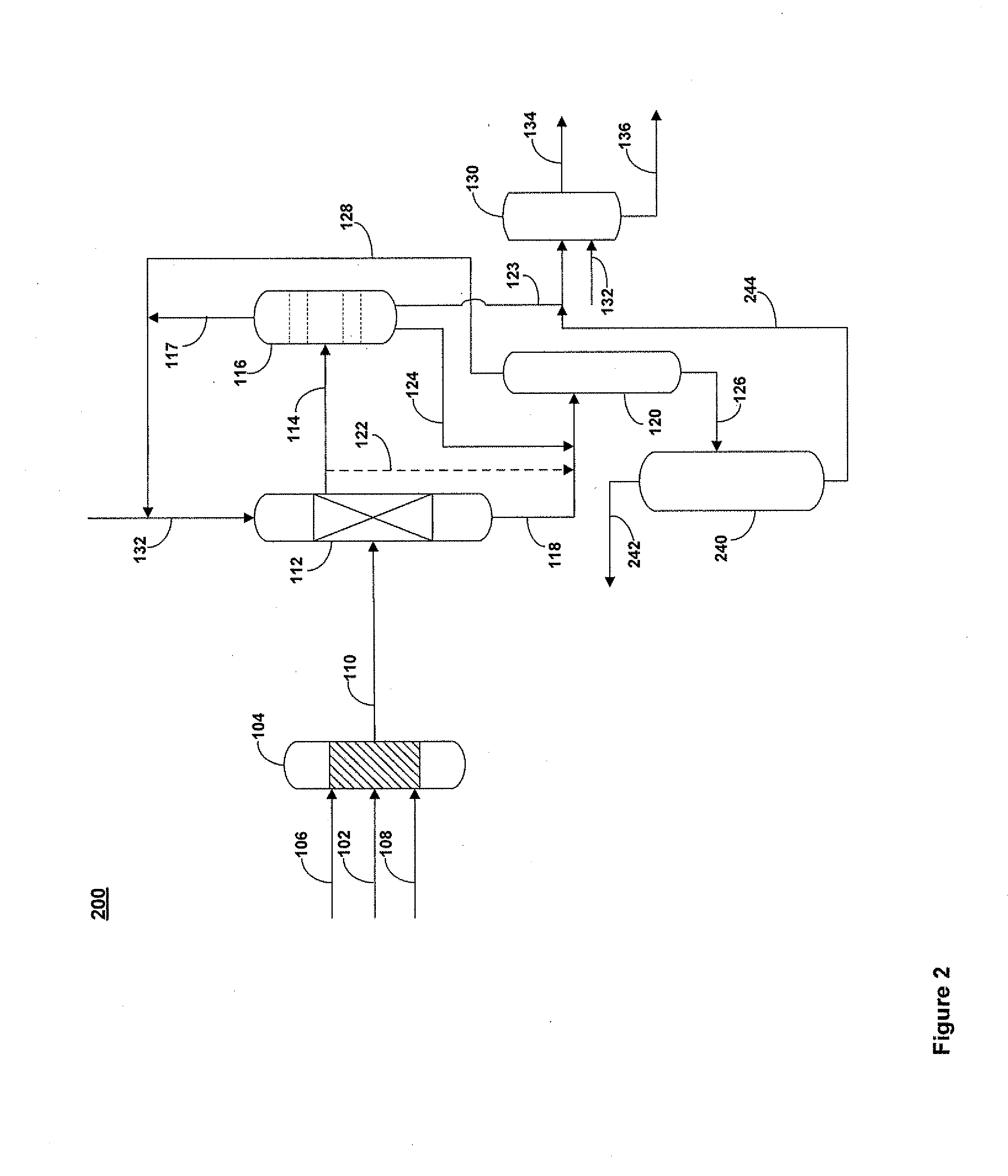
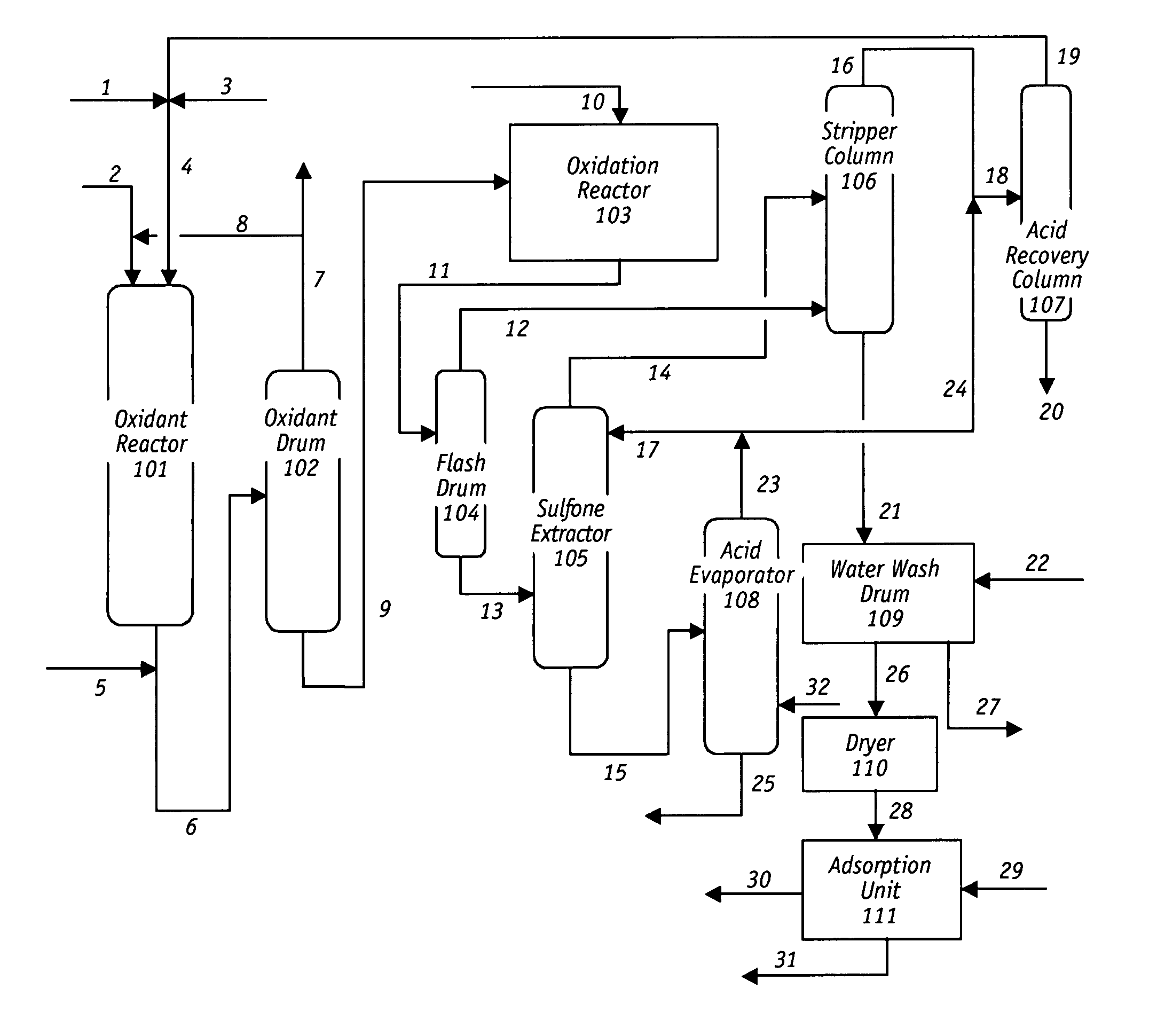
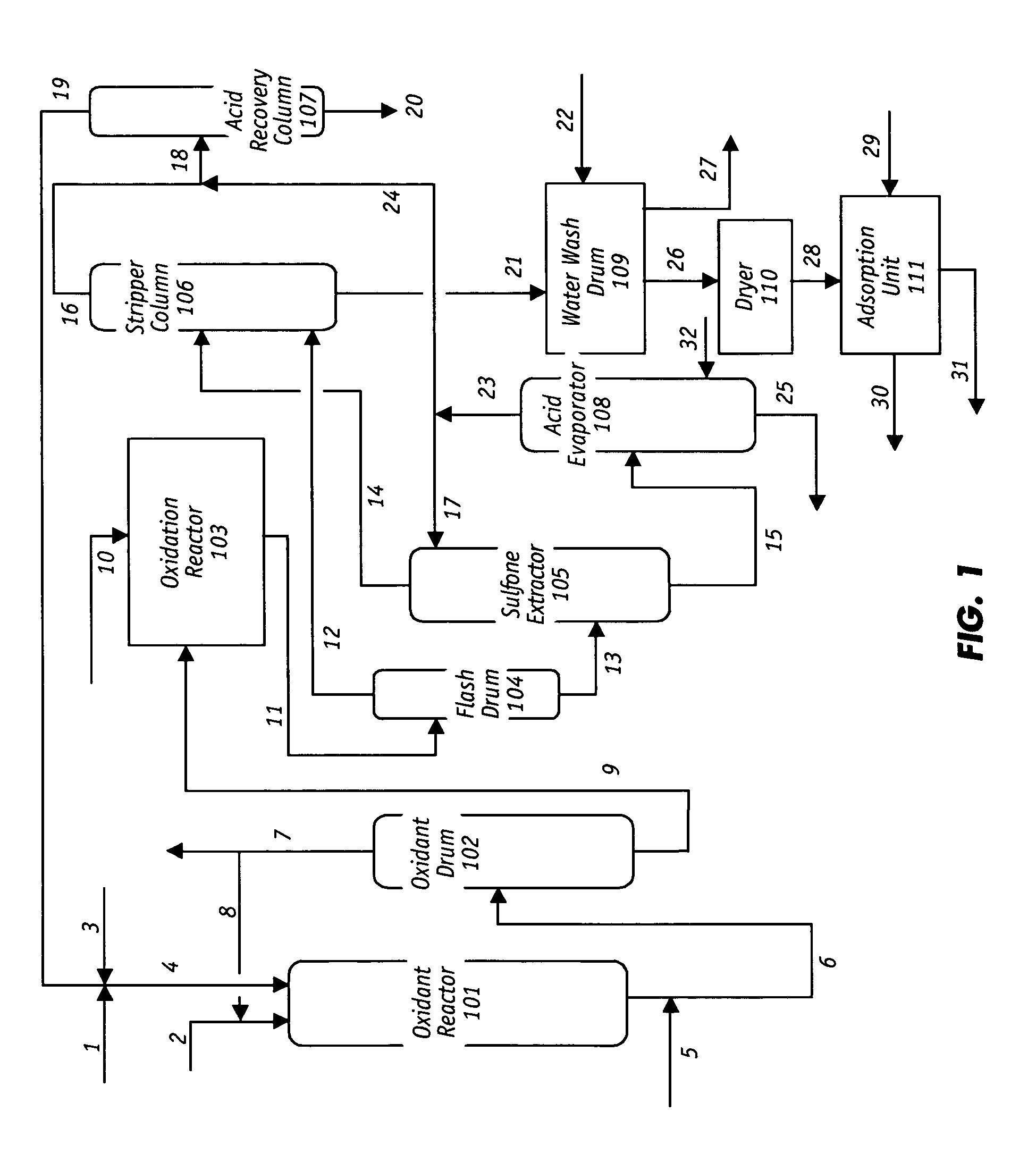
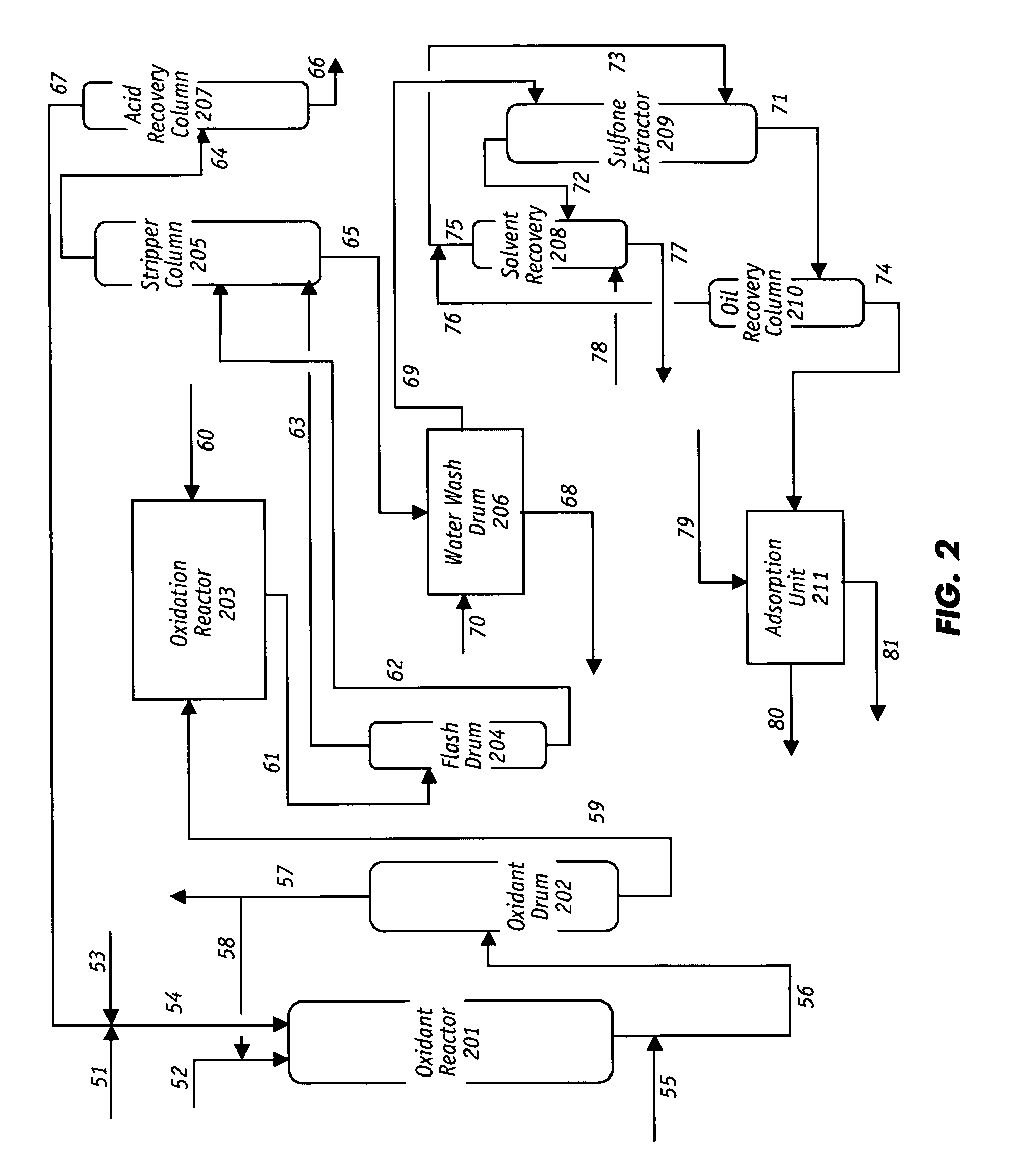
Desulfurization and Sulfone Removal Using A Coker
ActiveUS20120055845A1Refining with oxygen compoundsTreatment with plural serial refining stagesSulfurSolvent
A method and apparatus for upgrading a hydrocarbon feedstock is provided. The method includes the steps of (a) supplying a hydrocarbon feedstock to an oxidation reactor, wherein the hydrocarbon feedstock is oxidized in the presence of a catalyst under conditions sufficient to selectively oxidize sulfur compounds present in the hydrocarbon feedstock; (c) separating the hydrocarbons and the oxidized sulfur compounds by solvent extraction; (d) collecting a residue stream that includes the oxidized sulfur compounds; and (e) supplying the residue stream to a coker to produce coker gases and solid coke.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation of petroleum oils
InactiveUS20060108263A1Active and fast in oxidizing the sulfurReduce the temperatureOrganic chemistryRefining with oxygen compoundsPtru catalystEnvironmental engineering
A robust, non-aqueous, and oil-soluble organic peroxide oxidant is employed for oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation of hydrocarbon feedstocks including petroleum fuels. Even at low concentrations, the non-aqueous organic peroxide oxidant is extremely active and fast in oxidizing the sulfur and nitrogen compounds in the hydrocarbon feedstocks without catalyst. Consequently, the oxidation reactions that employ the non-aqueous organic peroxide oxidant take place at substantially lower temperatures and shorter residence times than reactions in other oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation processes. As a result, a higher percentage of the valuable non-sulfur and non-nitrogen containing components in the hydrocarbon feedstock are more likely preserved with the inventive process. Desulfurization and denitrogenation occur in a single phase non-aqueous environment so that no phase transfer of the oxidant is required.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION
Process for Oxidative Desulfurization and Sulfone Disposal Using Solvent Deasphalting
ActiveUS20120055843A1High purityWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSulfur-dioxide/sulfurous-acidSulfurSolvent
A method and apparatus for upgrading a hydrocarbon feedstock is provided. The method includes the steps of (a) supplying a hydrocarbon feedstock to an oxidation reactor, wherein the hydrocarbon feedstock is oxidized in the presence of a catalyst under conditions sufficient to selectively oxidize sulfur compounds present in the hydrocarbon feedstock; (c) separating the hydrocarbons and the oxidized sulfur compounds by solvent extraction; (d) collecting a residue stream that includes the oxidized sulfur compounds; and (e) supplying the residue stream to a deasphalting unit.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
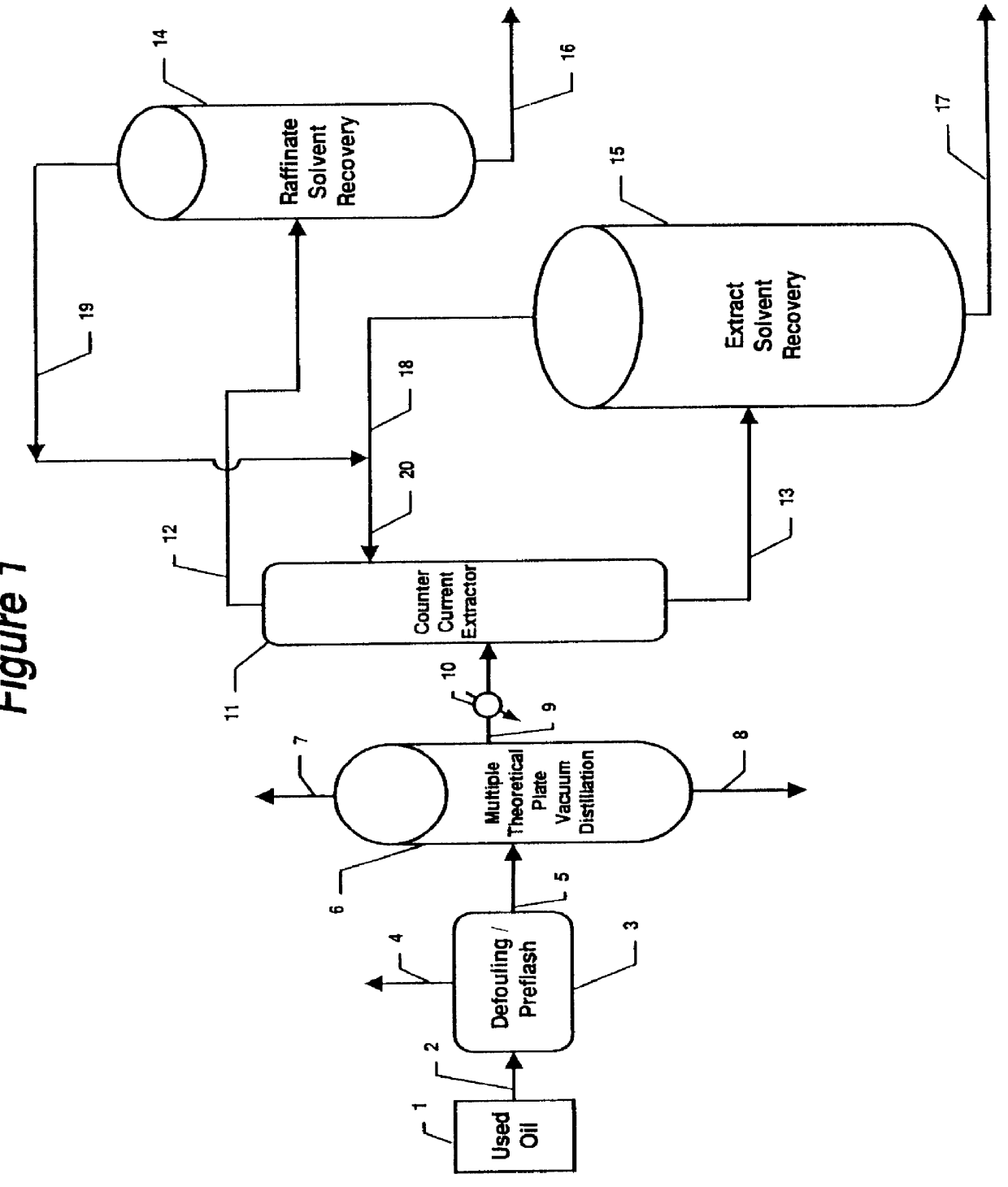
Method of rerefining waste oil by distillation and extraction
InactiveUS6117309AHigh yieldLower the volumeRefining with acid-containing liquidsLubricant compositionTheoretical plateDistillation
Owner:SARP
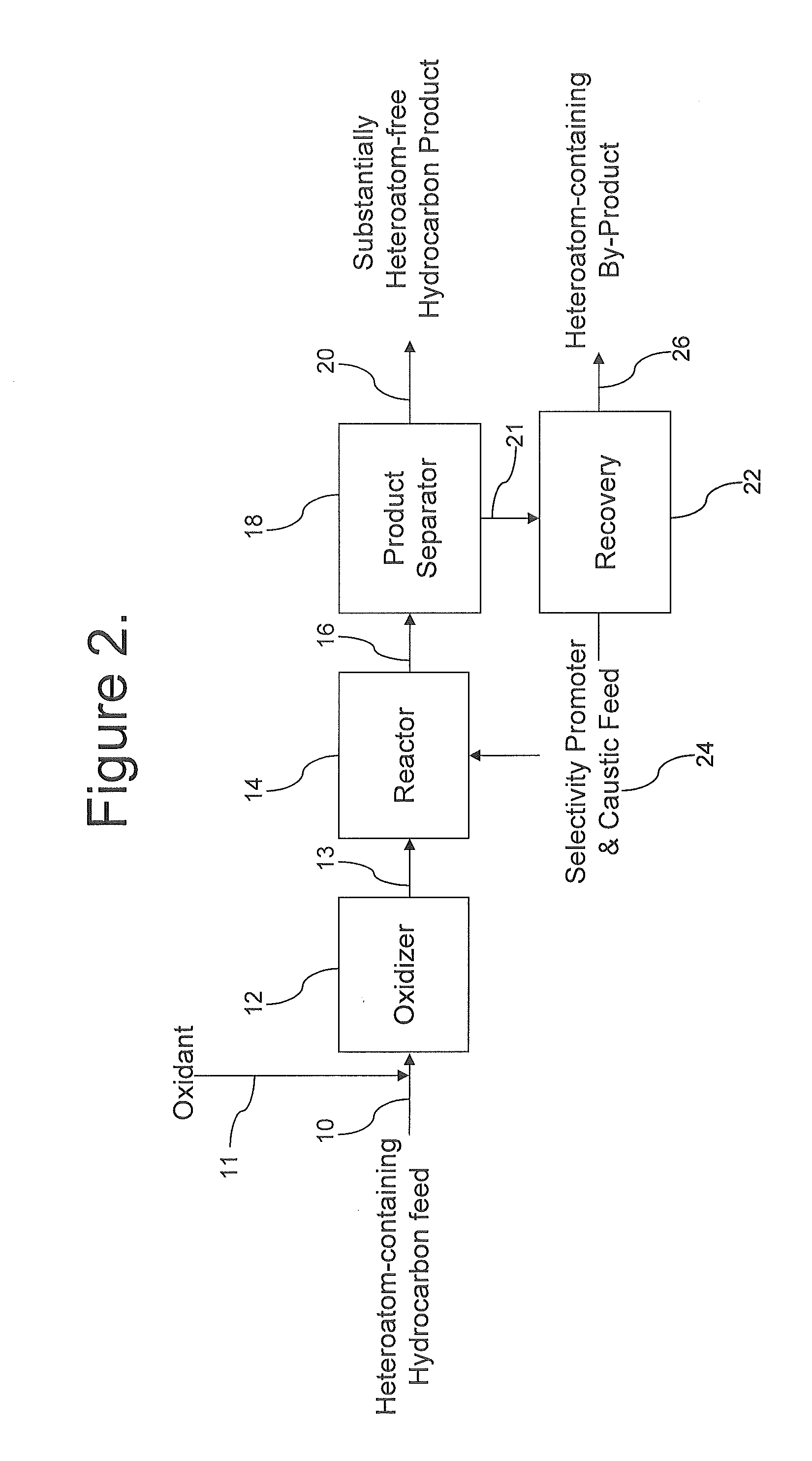
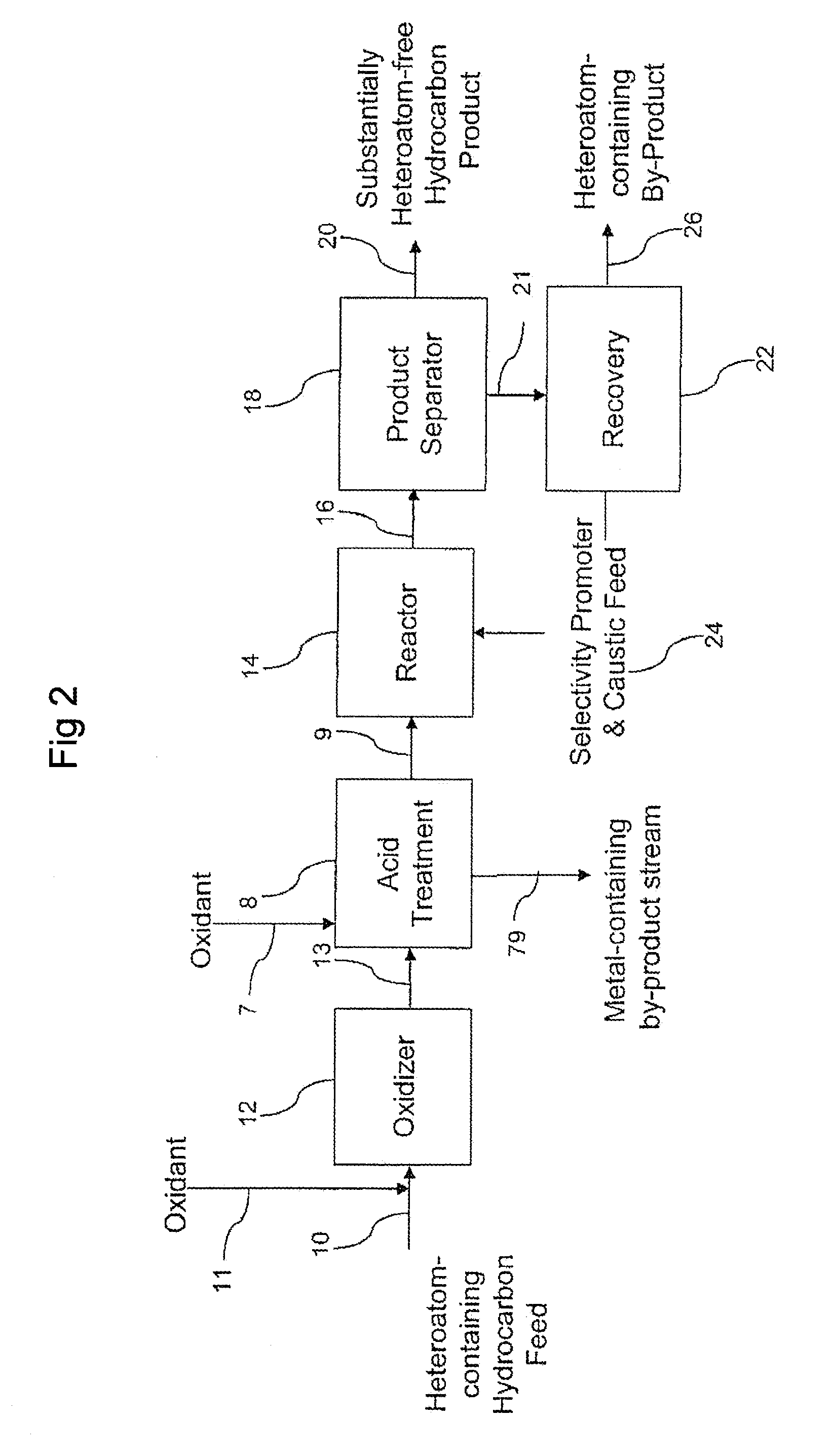
Methods for upgrading of contaminated hydrocarbon streams
A method of upgrading a heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed by removing heteroatom contaminants is disclosed. The method includes contacting the heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed with an oxidant to oxidize the heteroatoms, contacting the oxidized-heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed with caustic and a selectivity promoter, and removing the heteroatom contaminants from the heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed. The oxidant may be used in the presence of a catalyst.
Owner:AUTERRA INC
Process for the upgrading of raw hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS7153414B2Increase polarityPromote oxidationRefining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsTotal nitrogenSlurry
A process for the upgrading of raw hydrocarbon streams rich in heteroatomic polar compounds and / or unsaturated moieties involving the extractive oxidation of sulfur, nitrogen, conjugated dienes and other unsaturated compounds from said streams, the said process comprising treating said streams with a peroxide solution / organic acid couple and an iron oxide catalyst which is a limonite ore, under an acidic pH, atmospheric pressure and ambient or higher temperature. As a result of the reaction, the oxidized heteroatomic compounds, having strong affinity for the aqueous slurry phase, are extracted into said aqueous phase, while the oxidized hydrocarbon is separated from catalyst by decanting, neutralizing, water washing and drying, the resulting end product being a hydrocarbon stream from which have been removed 90% or more of total nitrogen compounds and basic nitrogen up to 99.7%, both calculated as mass contents.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation of petroleum oils
InactiveUS7276152B2Active and fast in oxidizing the sulfurReduce the temperatureOrganic chemistryRefining with oxygen compoundsSulfurNitrogen
A robust, non-aqueous, and oil-soluble organic peroxide oxidant is employed for oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation of hydrocarbon feedstocks including petroleum fuels. Even at low concentrations, the non-aqueous organic peroxide oxidant is extremely active and fast in oxidizing the sulfur and nitrogen compounds in the hydrocarbon feedstocks without catalyst. Consequently, the oxidation reactions that employ the non-aqueous organic peroxide oxidant take place at substantially lower temperatures and shorter residence times than reactions in other oxidative desulfurization and denitrogenation processes. As a result, a higher percentage of the valuable non-sulfur and non-nitrogen containing components in the hydrocarbon feedstock are more likely preserved with the inventive process. Desulfurization and denitrogenation occur in a single phase non-aqueous environment so that no phase transfer of the oxidant is required.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION
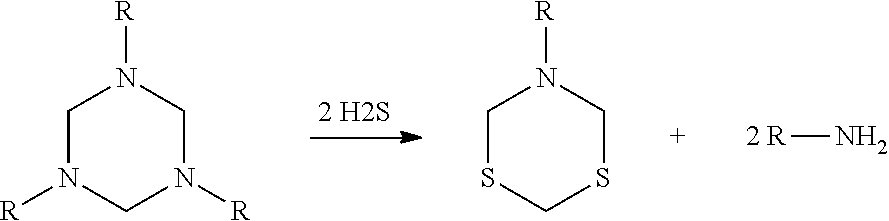
Hexahydrotriazines, synthesis and use
InactiveUS20130118996A1Organic chemistryRefining with acid-containing liquidsTriazineAldehyde formation
Methods for making asymmetrical triazines are provided. The methods comprise first forming a mixture of at least two primary amines then reacting the mixture with an aldehyde. Methods for removing sulfides from hydrocarbon streams are also provided. The triazines may be added to the hydrocarbon stream in a molar ratio of triazine:H2S of about 10:1 to about 1:2.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
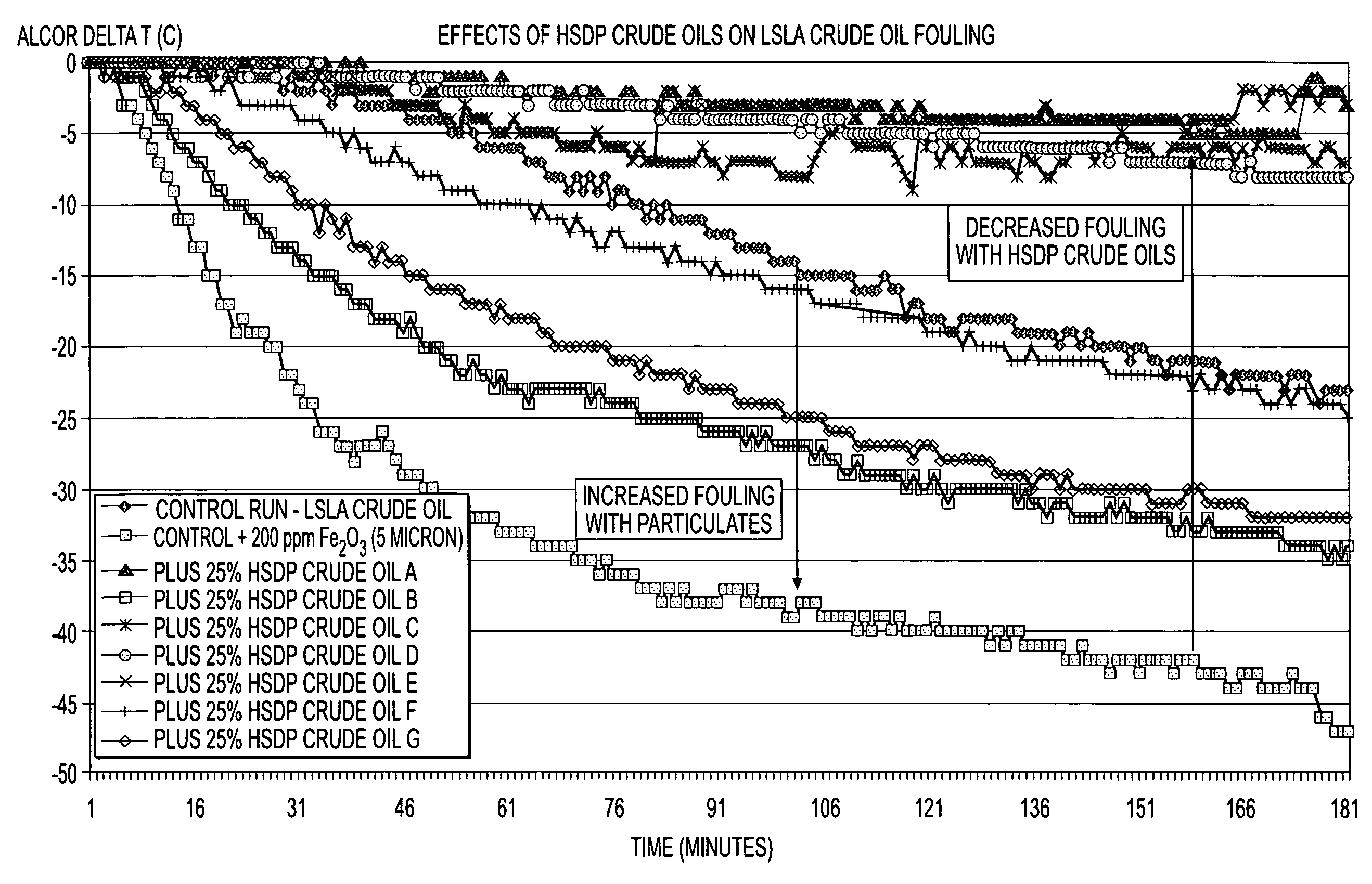
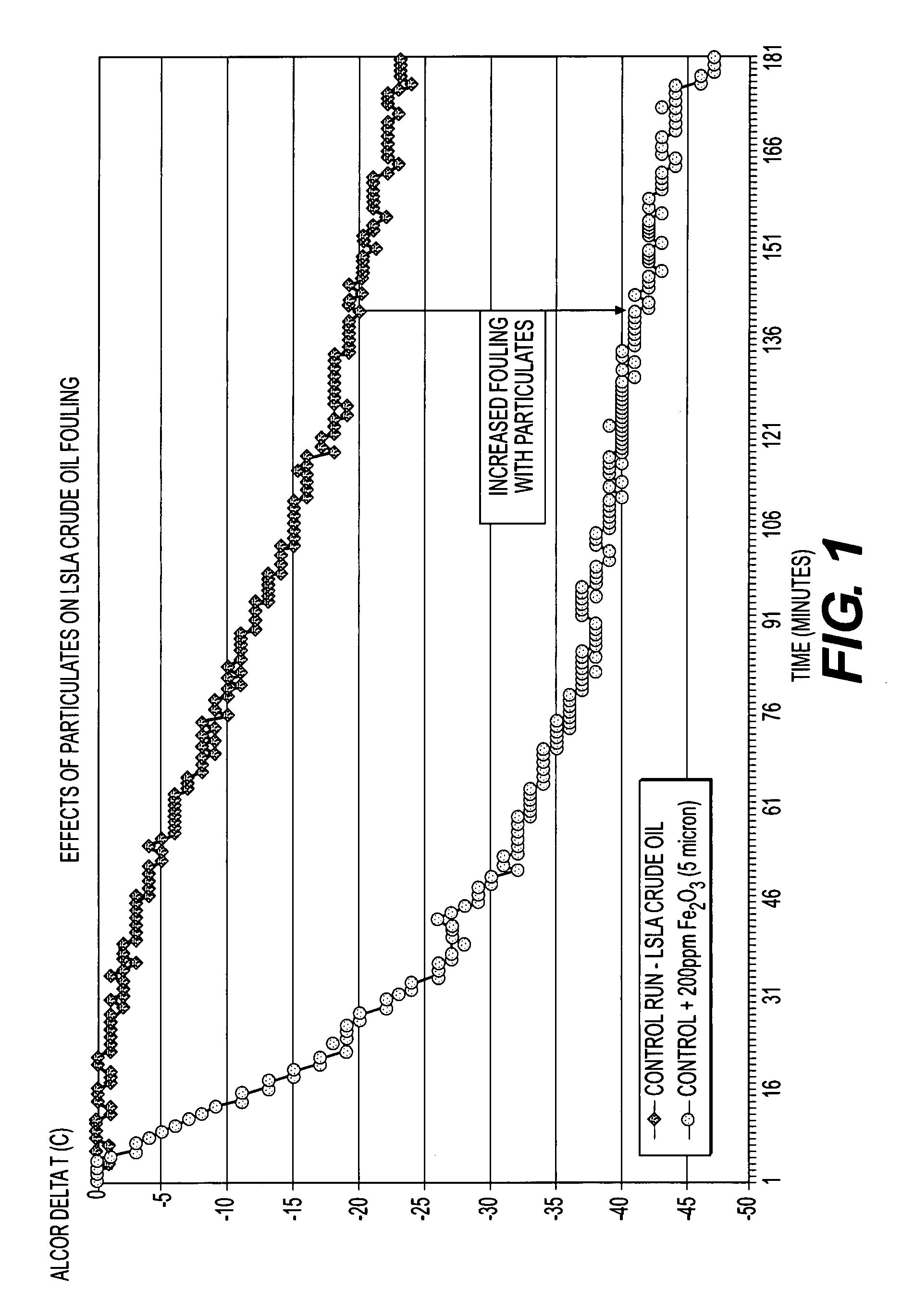
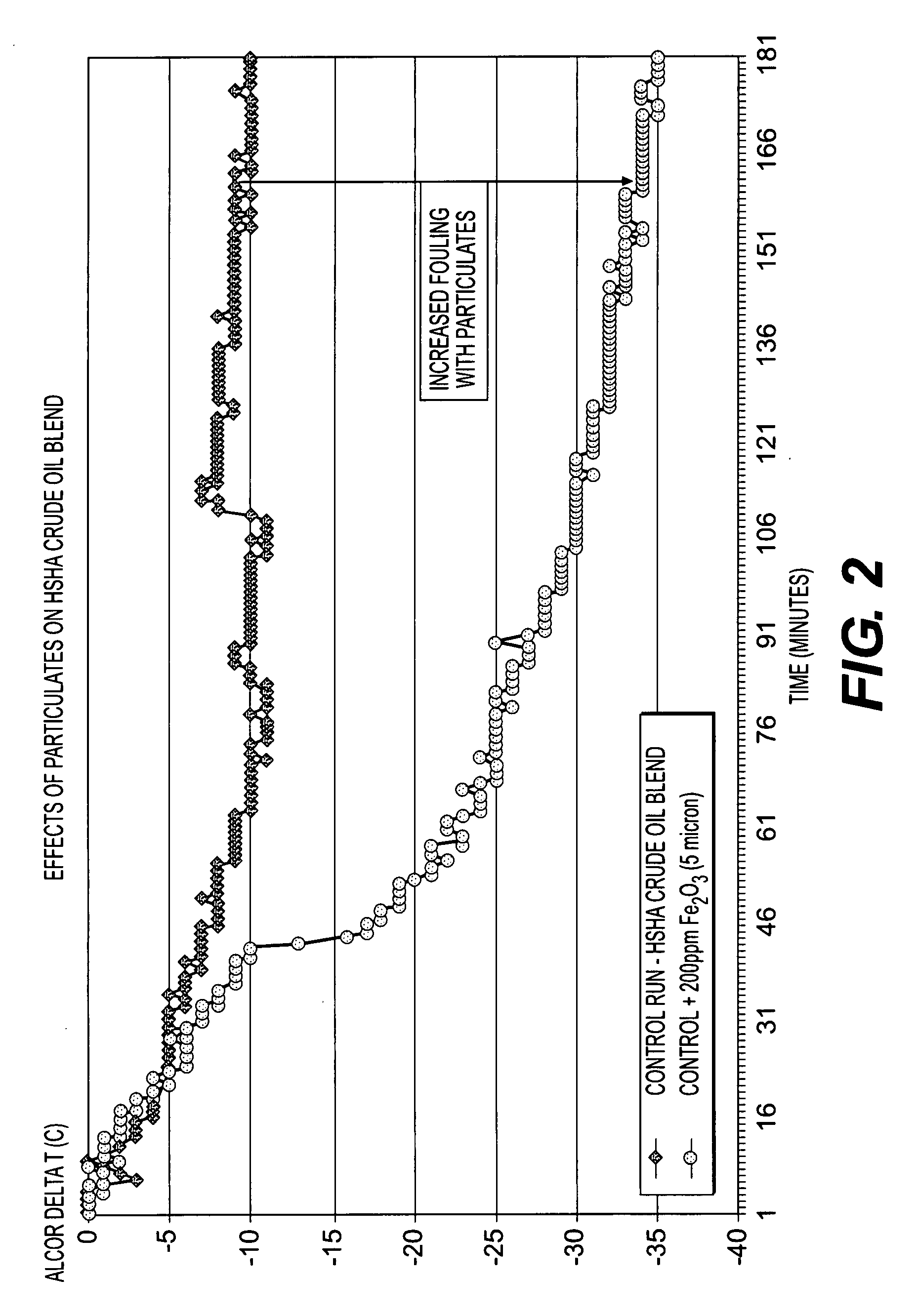
Method of blending high tan and high SBN crude oils and method of reducing particulate induced whole crude oil fouling and asphaltene induced whole crude oil fouling
InactiveUS20080041762A1Reduce dirtHigh molecular weightLiquid organic insulatorsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsParticulatesSediment
A high solvency dispersive power (HSDP) crude oil is added to a blend of incompatible oils to proactively address the potential for fouling heat exchange equipment. The HSDP component dissolves asphaltene precipitates and maintains suspension of inorganic particulates before coking affects heat exchange surfaces. An HSDP oil is also flushed through heat exchange equipment to remove any deposits and / or precipitates on a regular maintenance schedule before coking can affect heat exchange surfaces.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Solid acid assisted deep desulfurization of diesel boiling range feeds
InactiveUS20090065398A1Improve efficiencyRefining with acid-containing liquidsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesLow nitrogenSulfur
The instant invention relates to a process to produce low sulfur diesel products through the hydrodesulfurization of low nitrogen diesel boiling range feedstreams in the presence of solid acidic materials.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
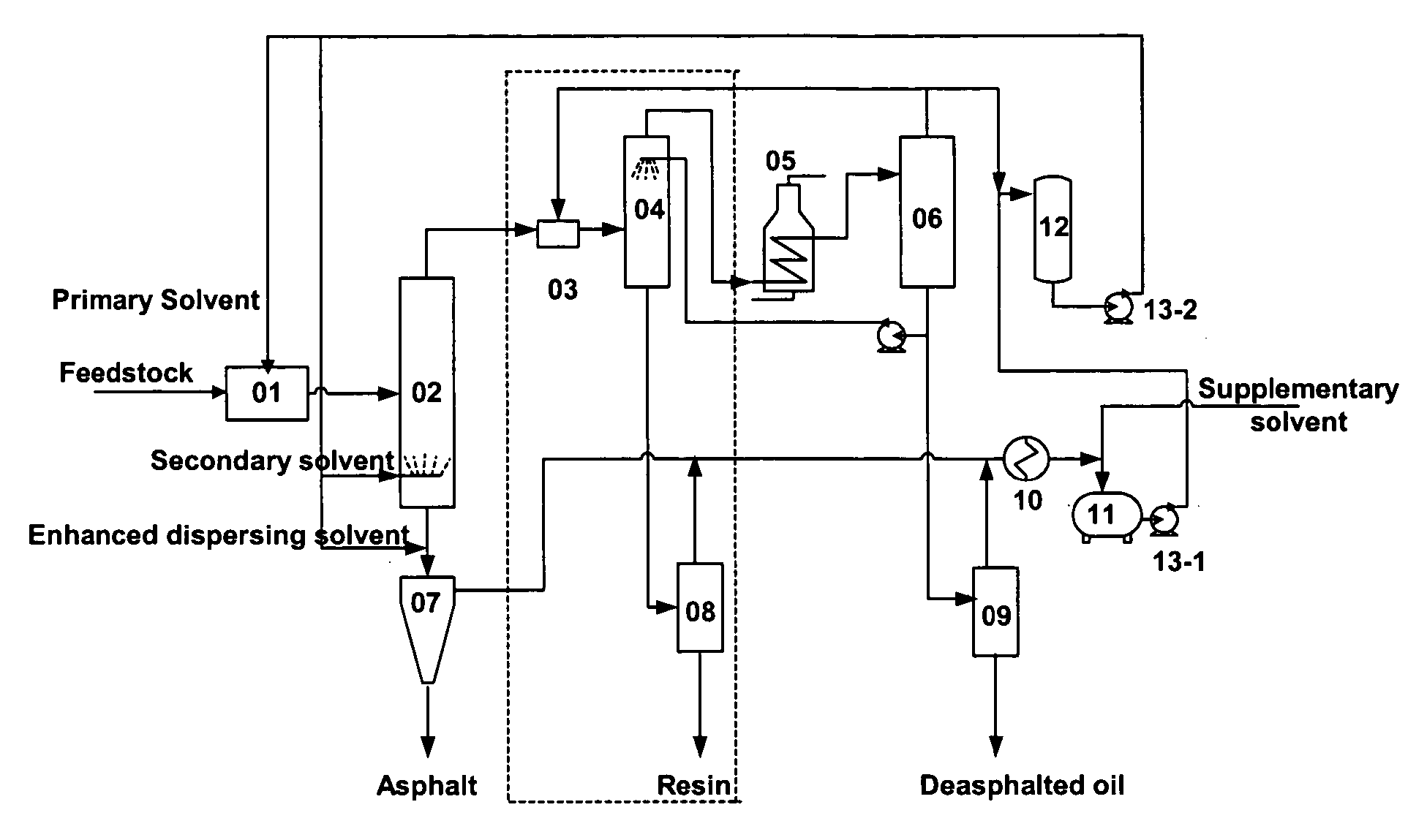
Deep separation method and processing system for the separation of heavy oil through granulation of coupled post-extraction asphalt residue
ActiveUS20070007168A1High yieldSimple processWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by solidifying/disintegratingSolid particleOil phase
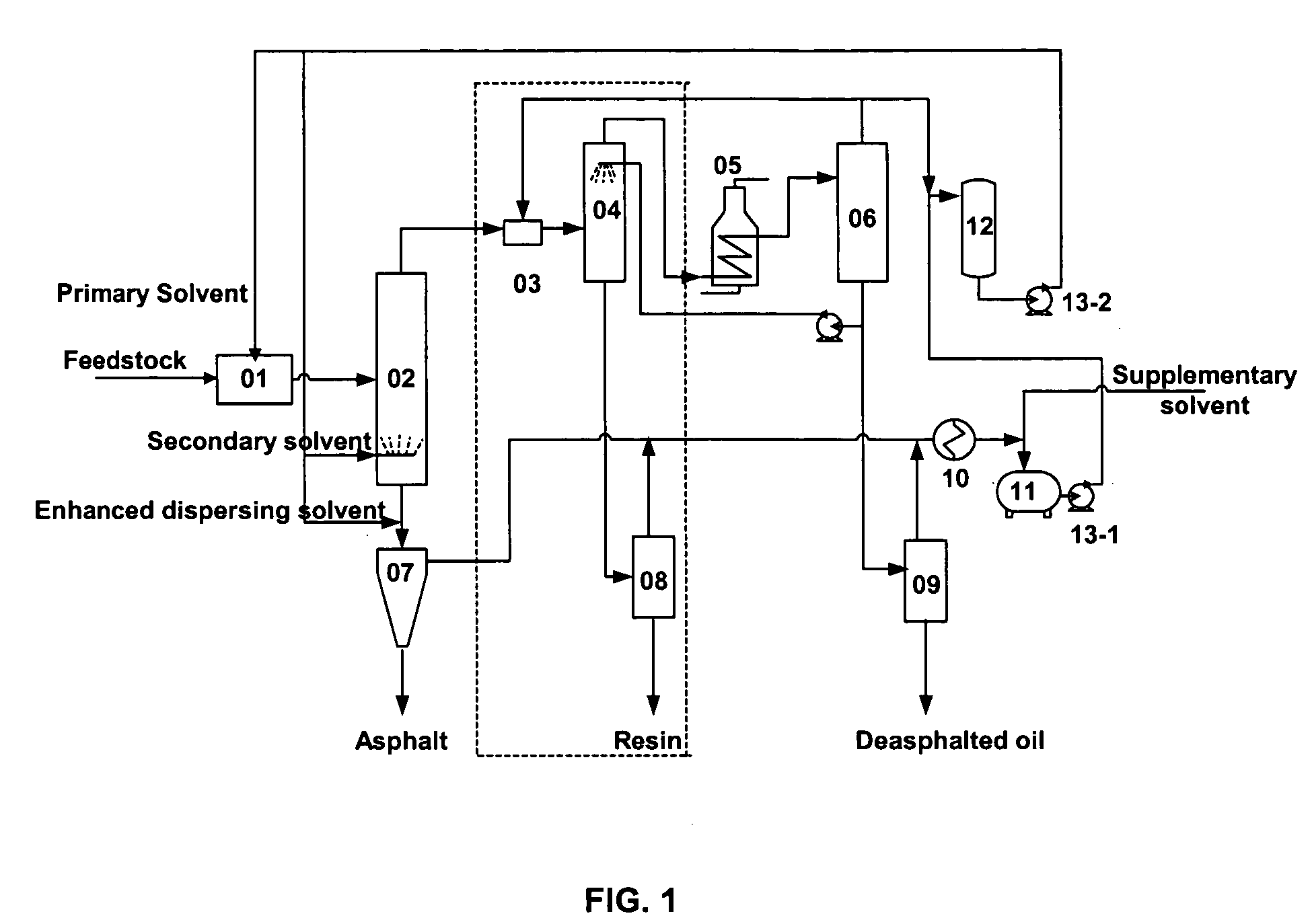
The present invention is a separation method and system in which granulation of coupled post-extraction asphalt residue is used to achieve deep separation of heavy oil. A dispersion solvent is introduced into the asphalt phase after separation by solvent extraction and the asphalt phase undergoes rapid phase change in a gas-solid separator and is dispersed into solid particles while the solvent vaporizes, resulting in low temperature separation of asphalt and solvent with adjustable size of the asphalt particles. The separation method of this invention also includes a three-stage separation of heavy oil feedstock, in which the deasphalted oil phase separated from heavy oil is treated with supercritical solvent and results in the further separation of the resin portion of the deasphalted oil, maximizing the yield and quality of the deasphalted oil. The processes and systems in this invention use atmospheric pressure and a low temperature gas-solid separator instead of a high temperature and high pressure furnace and do not require the feed pre-heating or heat exchange equipment at the inlet of resin separator column, resulting in a simplified process flow and reduced investment.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
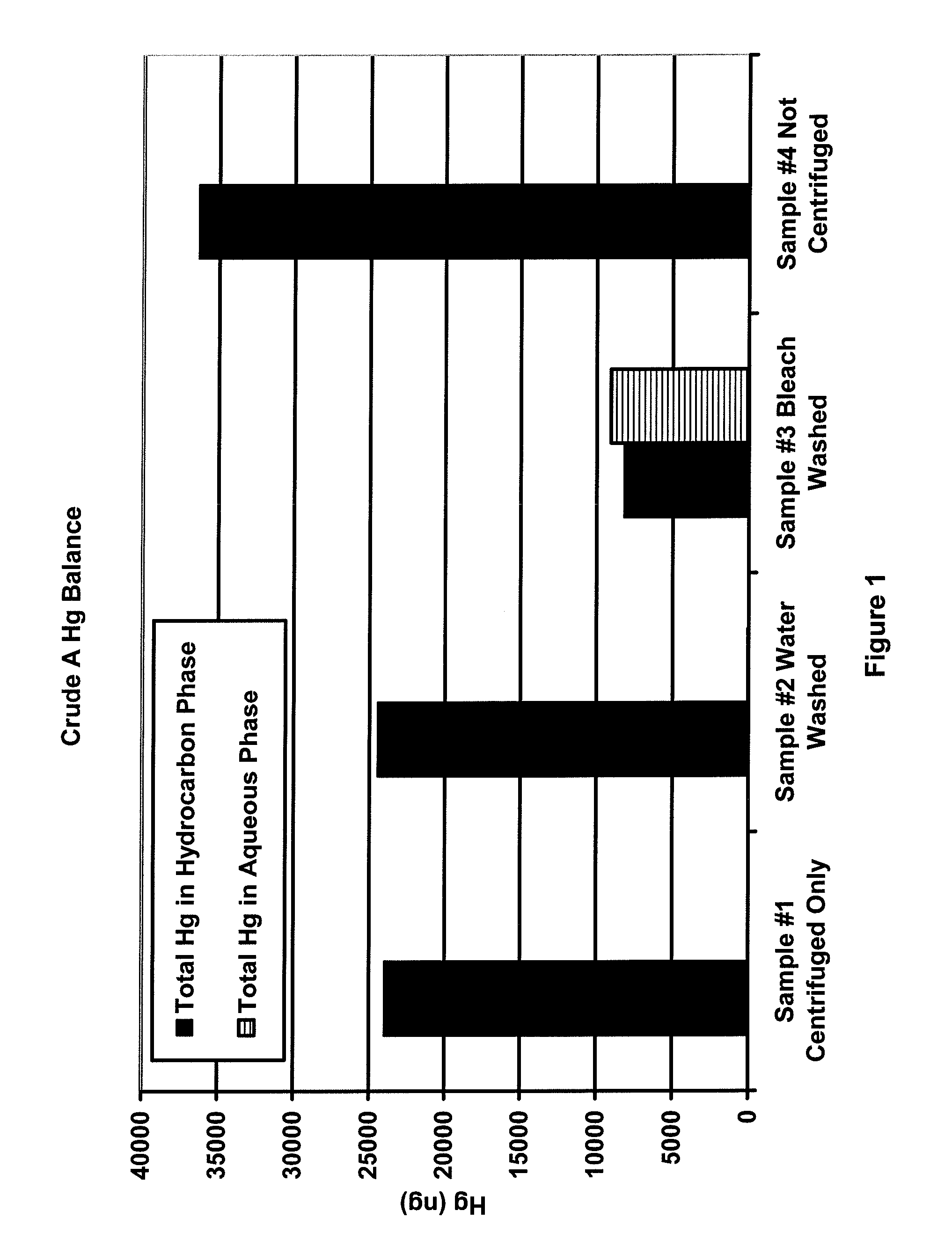
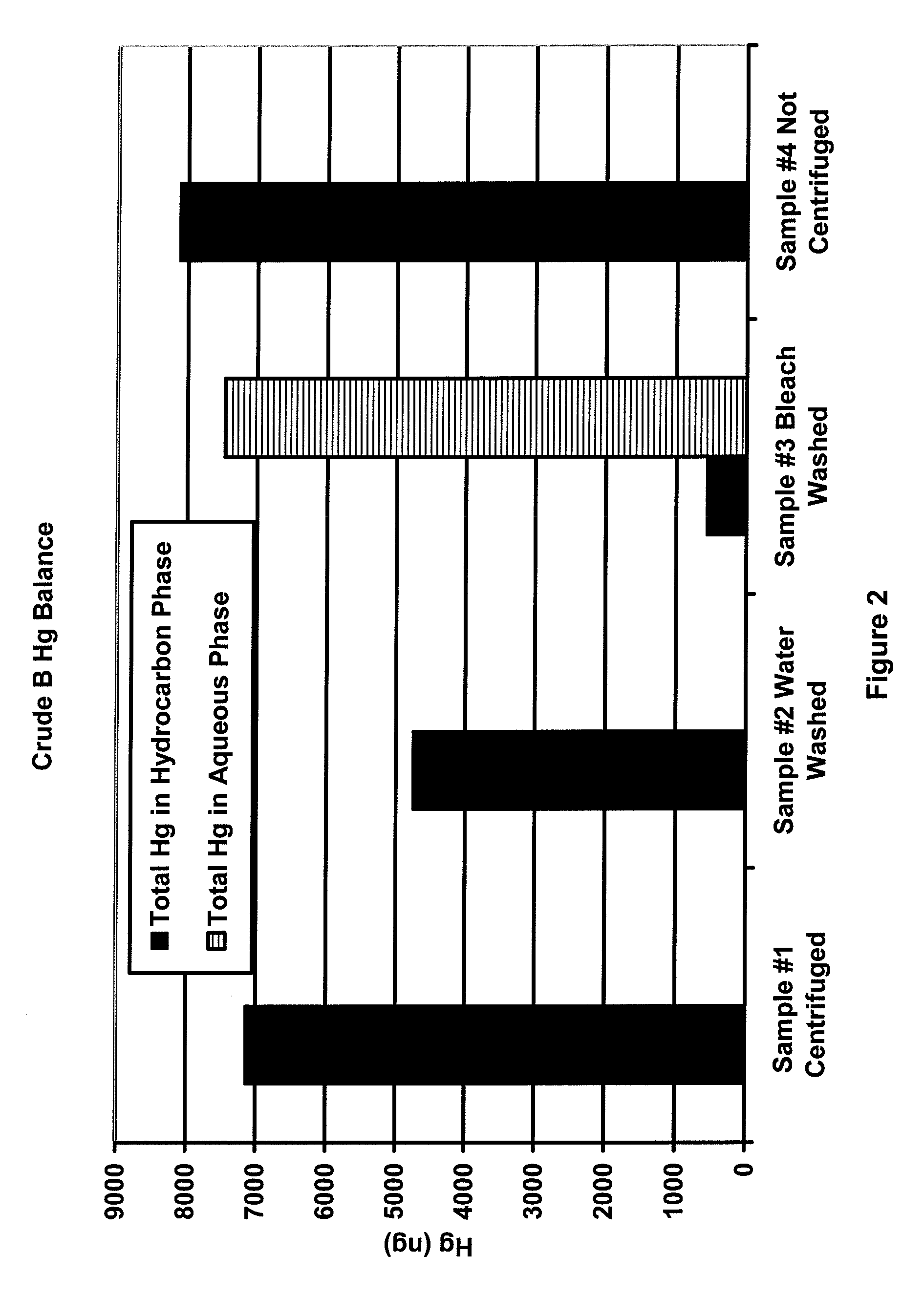
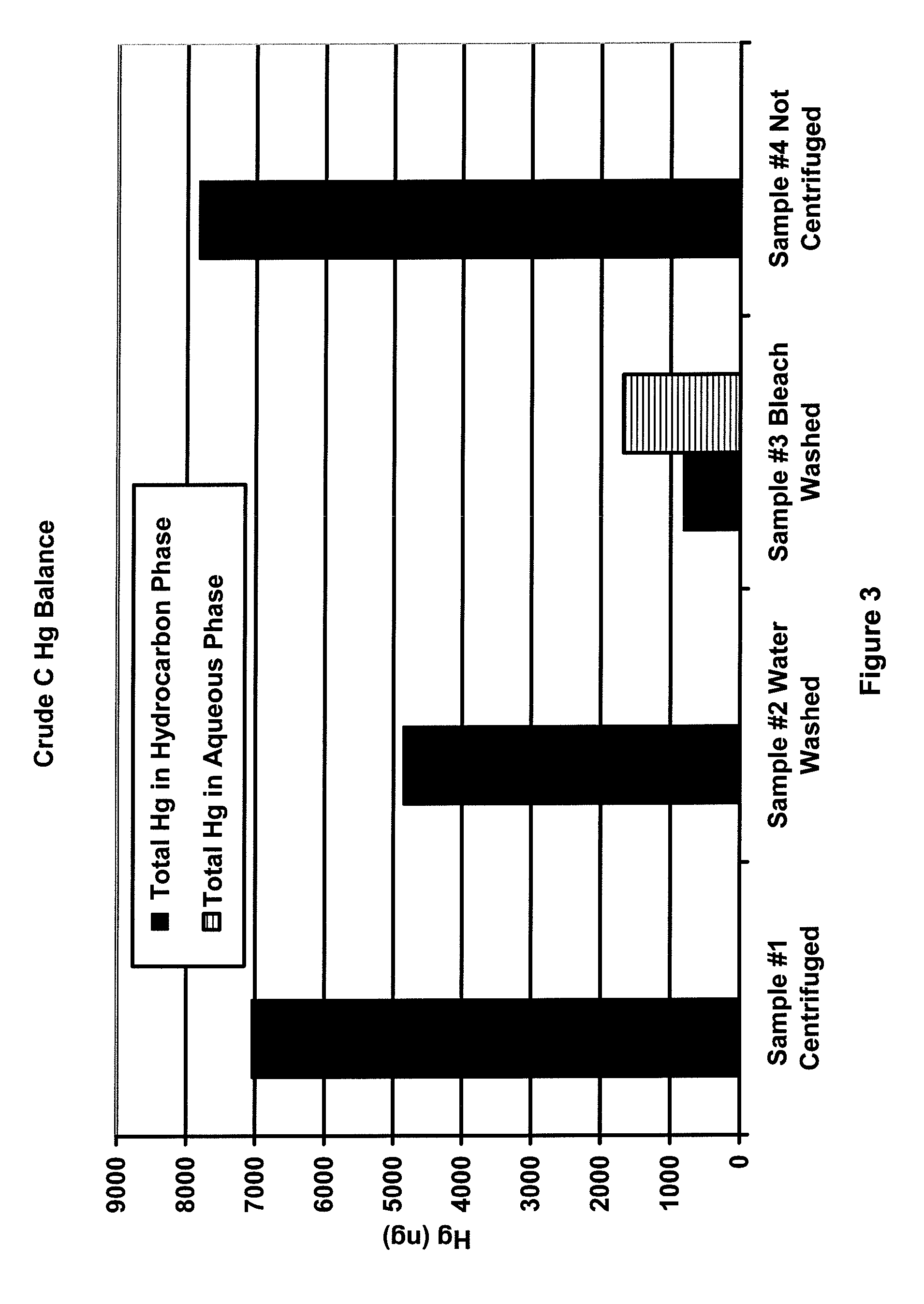
Mercury removal process
A process is disclosed for decreasing the level of elemental mercury contained in a liquid hydrocarbon stream by a) contacting the liquid hydrocarbon stream with a water stream containing an oxidizing agent for conversion of at least a portion of the Hg(0) to Hg(II); b) extracting at least a portion of the Hg(II) from the liquid hydrocarbon stream into the water stream, thereby forming a treated liquid hydrocarbon stream and a waste water stream containing water and Hg(II); and c) separating the treated liquid hydrocarbon stream from the waste water stream.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
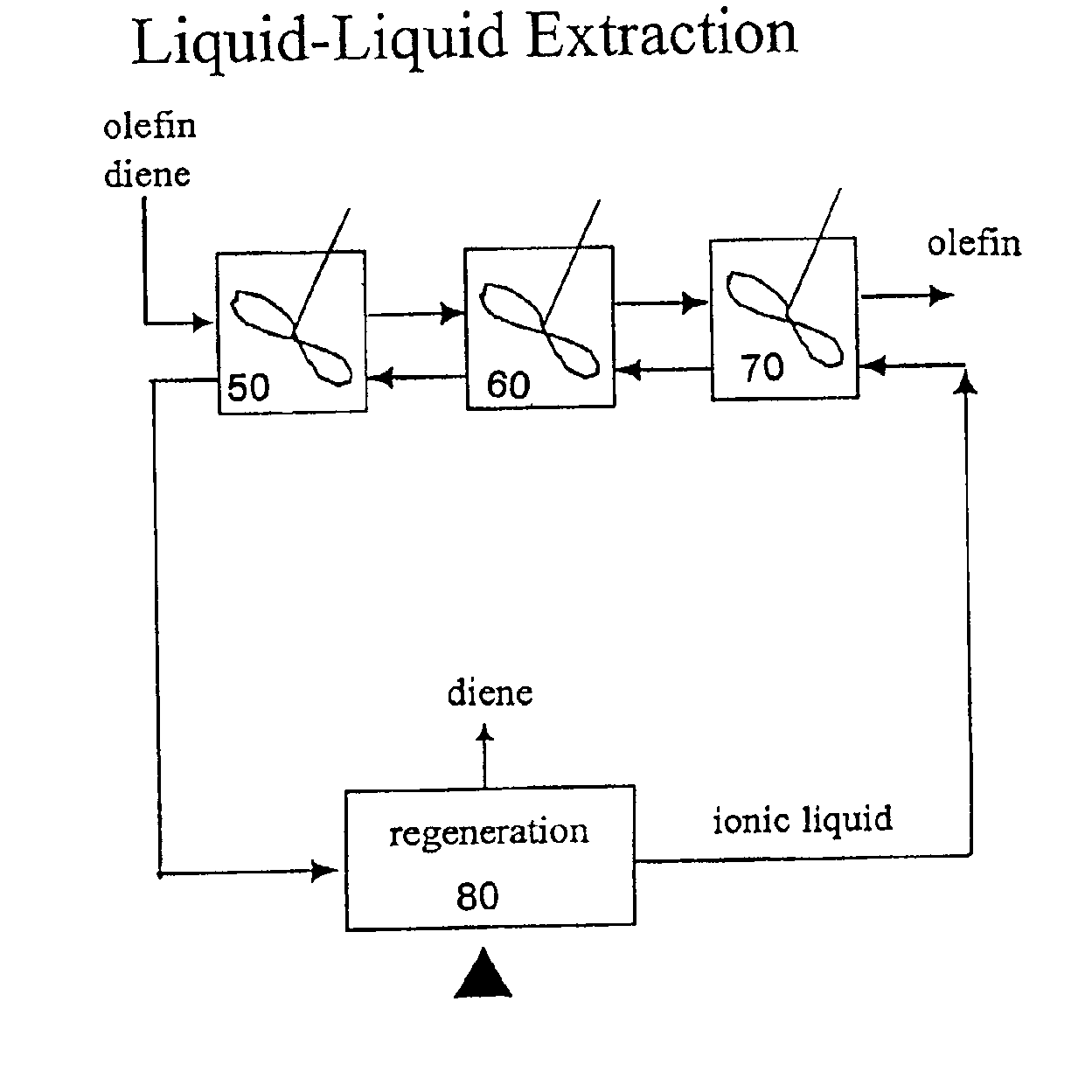
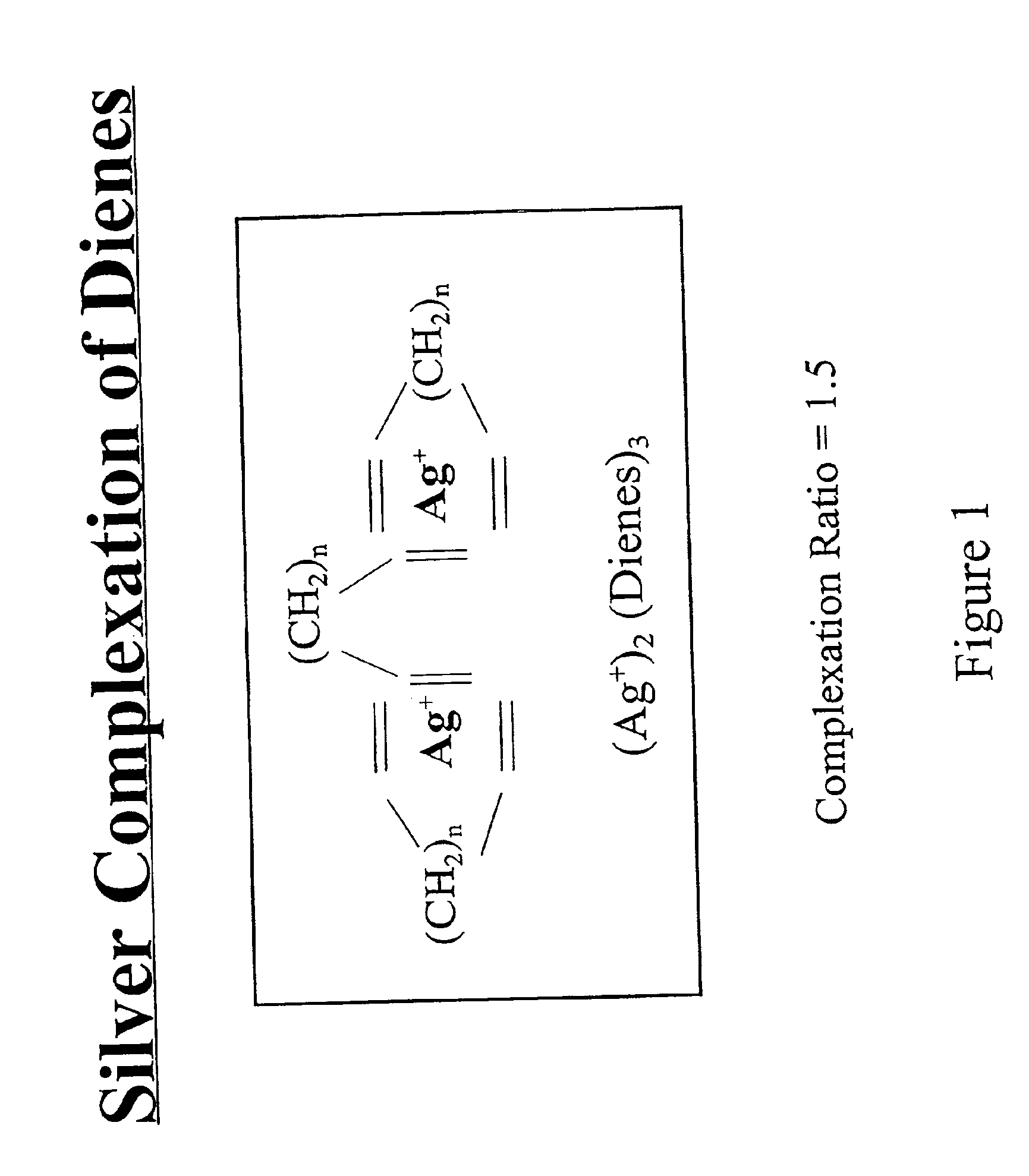
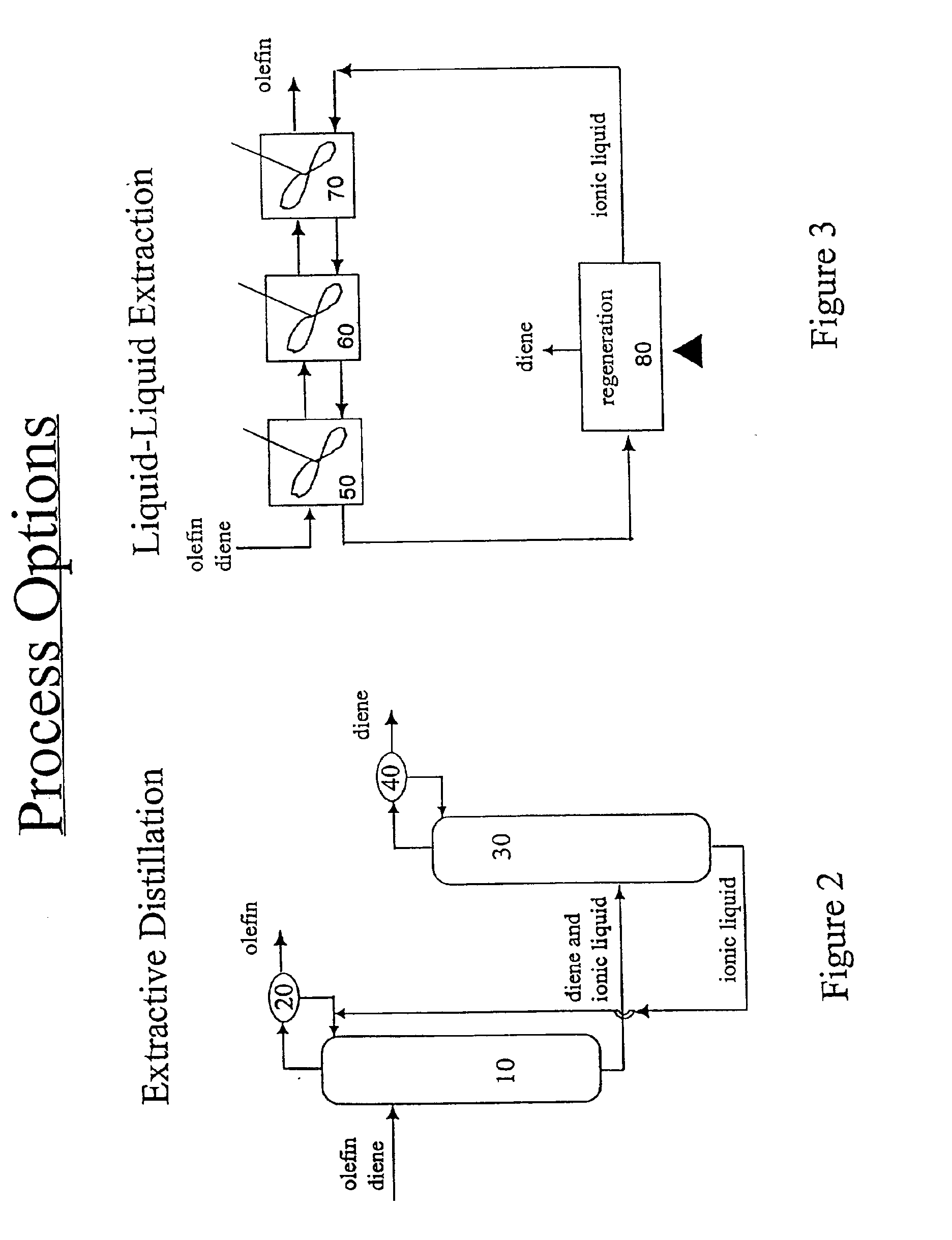
Separation of dienes from olefins using ionic liquids
InactiveUS6849774B2Facilitate desorptionDesorbed more readilyRefining with metal saltsRefining with acid-containing liquidsGas phaseIonic liquid
Methods for separating di-olefins from mono-olefins, and olefins from non-olefins such as paraffins, oxygenates and aromatics; are provided. The methods use metal salts which complex both mono-olefins and di-olefins, but which selectively complex di-olefins in the presence of mono-olefins. The metal salts are dissolved or suspended in ionic liquids, which tend to have virtually no vapor pressure. Preferred salts are Group IB salts, more preferably silver and copper salts. A preferred silver salt is silver tetrafluoroborate. A preferred copper salt is silver CuOTf. Preferred ionic liquids are those which form stable solutions, suspensions or dispersions of the metal salts, which do not dissolve unwanted non-olefins, and which do not isomerize the mono- or di-olefins. The equivalents of the metal salt can be adjusted so that di-olefins are selectively adsorbed from mixtures of mono- and di-olefins. Alternatively, both mono- and di-olefins can be adsorbed, and the mono-olefins selectively desorbed. The latter approach can be preferred when non-olefins are also to be separated. The mono- and di-olefin-containing mixture can be in the gas phase or in the liquid phase. The flow of mono- and di-olefin-containing mixture over / through the ionic liquid can be, for example, co-current, counter-current, or staged in stirred tanks, with countercurrent being preferred.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
ITFM extraction of oil seeds
InactiveUS7156981B2Superior, high purity, bright proteinsIncrease in absorbable proteinHydrocarbon distillationEssential-oils/perfumesProtein insertionProtein isolate
A process for the producing edible protein-containing meal for human and animal consumption and high quality food grade oils from oil seed using iodotrifluoromathane as the solvent is shown. The meal has a significantly improved level of dietary available (absorbable) protein. The process involves the preparation of protein isolates by a procedure which is conducted at room temperature, thus decreases protein degradation and denaturing which is caused by elevated temperatures. The process also provides for extraction of substantially all oils and fats, which interfere with the formation of the protein micelle, from the protein meal providing a cleaner, purer product with high levels of absorbable protein. Such protein isolates can then be used as such or added to formulated foods in order to increase the total protein content of that food. The protein produced and the oils recovered have compositions which are also unique and unobtainable by prior processing methods.
Owner:BIO EXTRACTION INC
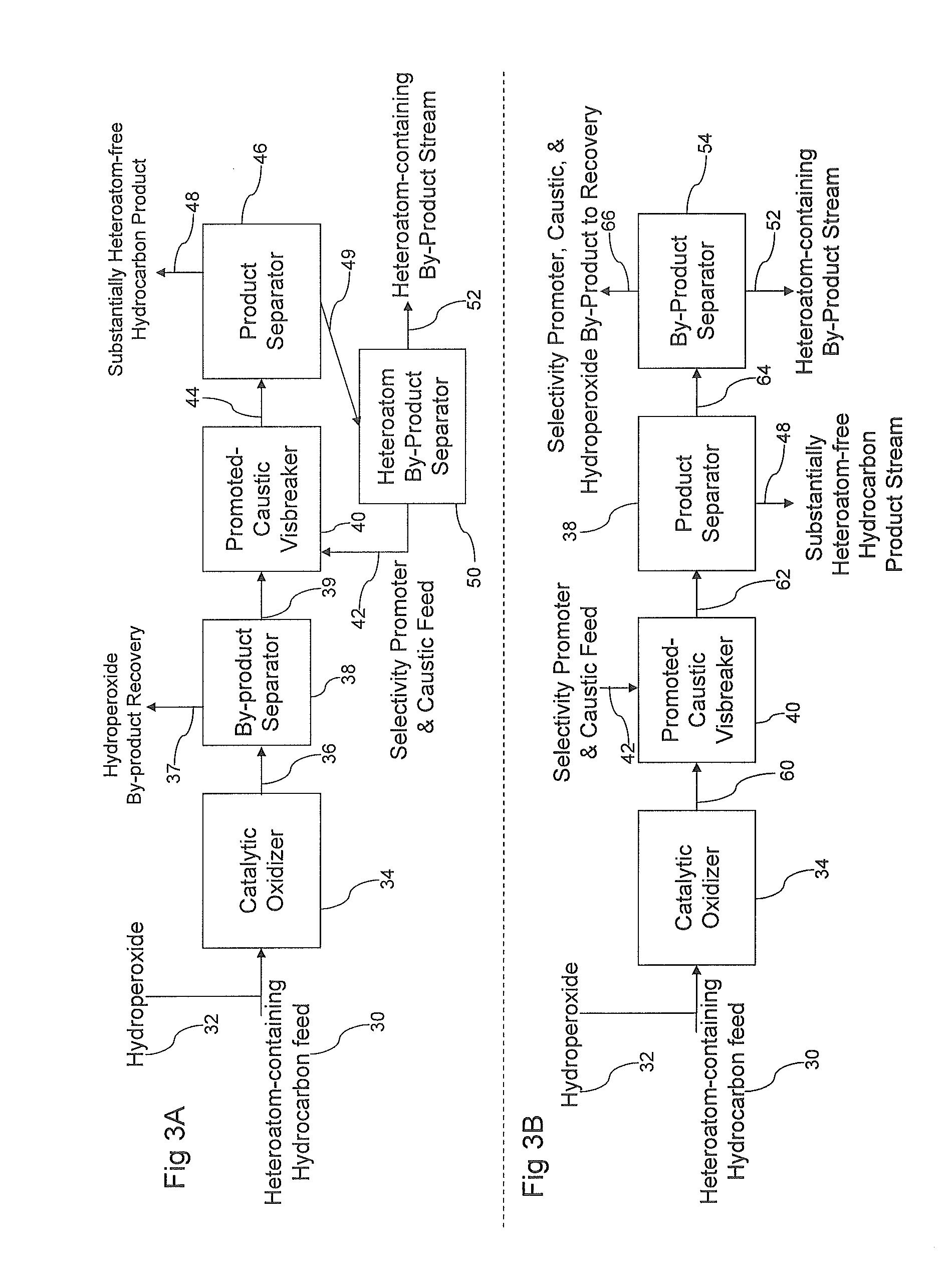
Methods for upgrading of contaminated hydrocarbon streams
ActiveUS20110108464A1Hydrocarbon distillationRefining with acid-containing liquidsHeteroatomOxidizing agent
A method of upgrading a heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed by removing heteroatom contaminants is disclosed. The method includes contacting the heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed with an oxidant and an immiscible acid to oxidize the heteroatoms, contacting the oxidized-heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed with caustic and a selectivity promoter, and removing the heteroatom contaminants from the heteroatom-containing hydrocarbon feed. The oxidant may be used in the presence of a catalyst.
Owner:AUTERRA INC
Reactive Extraction of Sulfur Compounds from Hydrocarbon Streams
InactiveUS20070227950A1Hydrocarbon purification/separationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryAlkaline earth metalHypochlorite
A process to substantially reduce the sulfur content of a liquid hydrocarbon stream by contacting the hydrocarbon stream with an aqueous stream containing a mixture of one or more extraction agents selected from hypochlorites, cyanurates and alkali metal and alkaline earth metal hydroxides, optionally in the presence of a catalyst, to remove sulfur compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Popular searches
Hydrocarbon by hydrogenation Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalysts Catalysts Hydrocarbon preparation catalysts Catalyst regeneration/reactivation Metal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalysts Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon addition Naphtha treatment Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Fatty-oils/fats production
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com