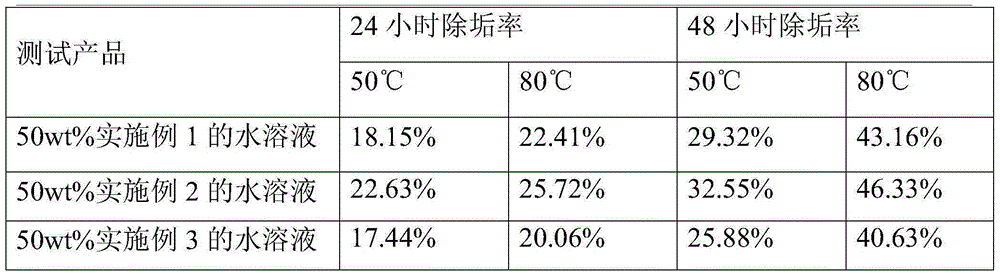
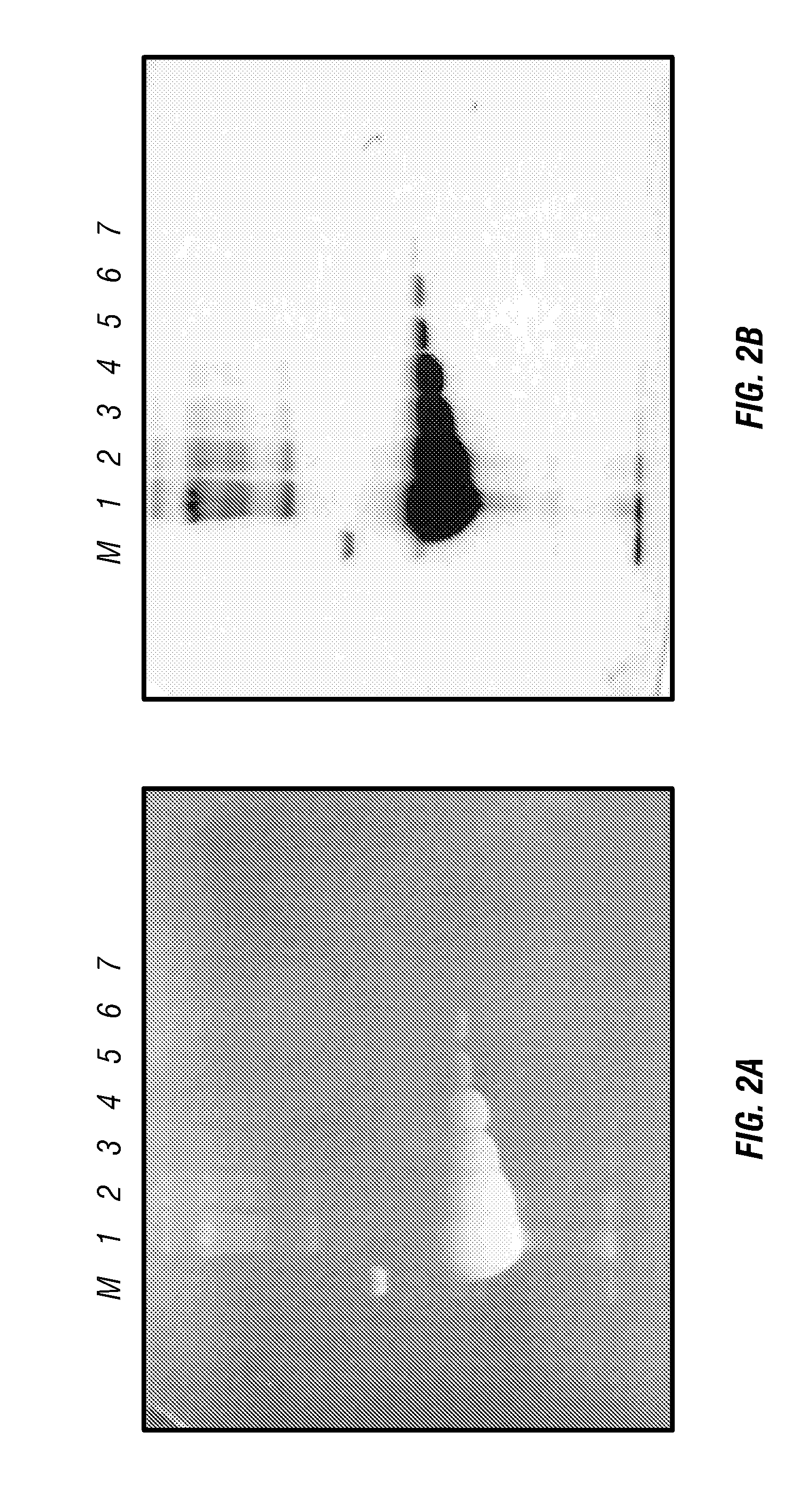
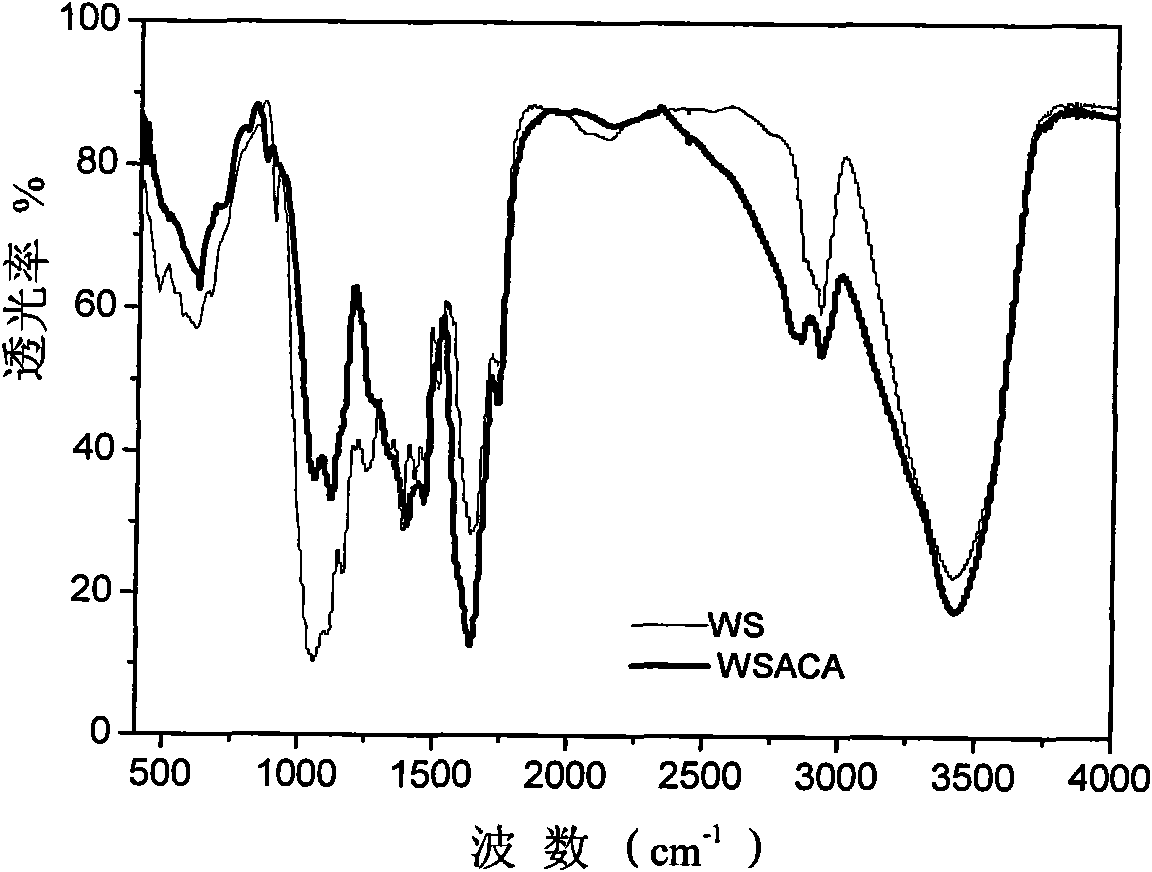
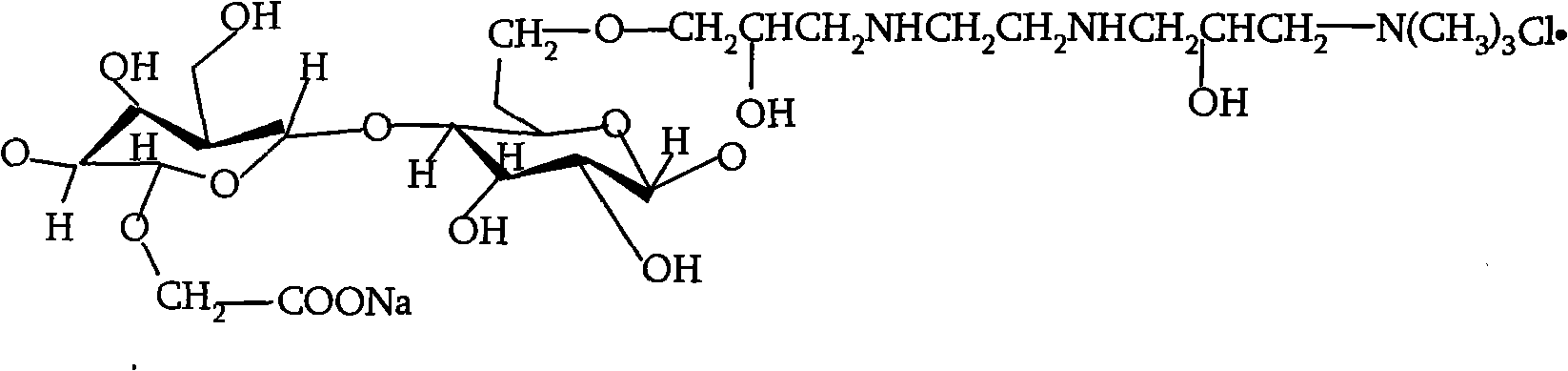
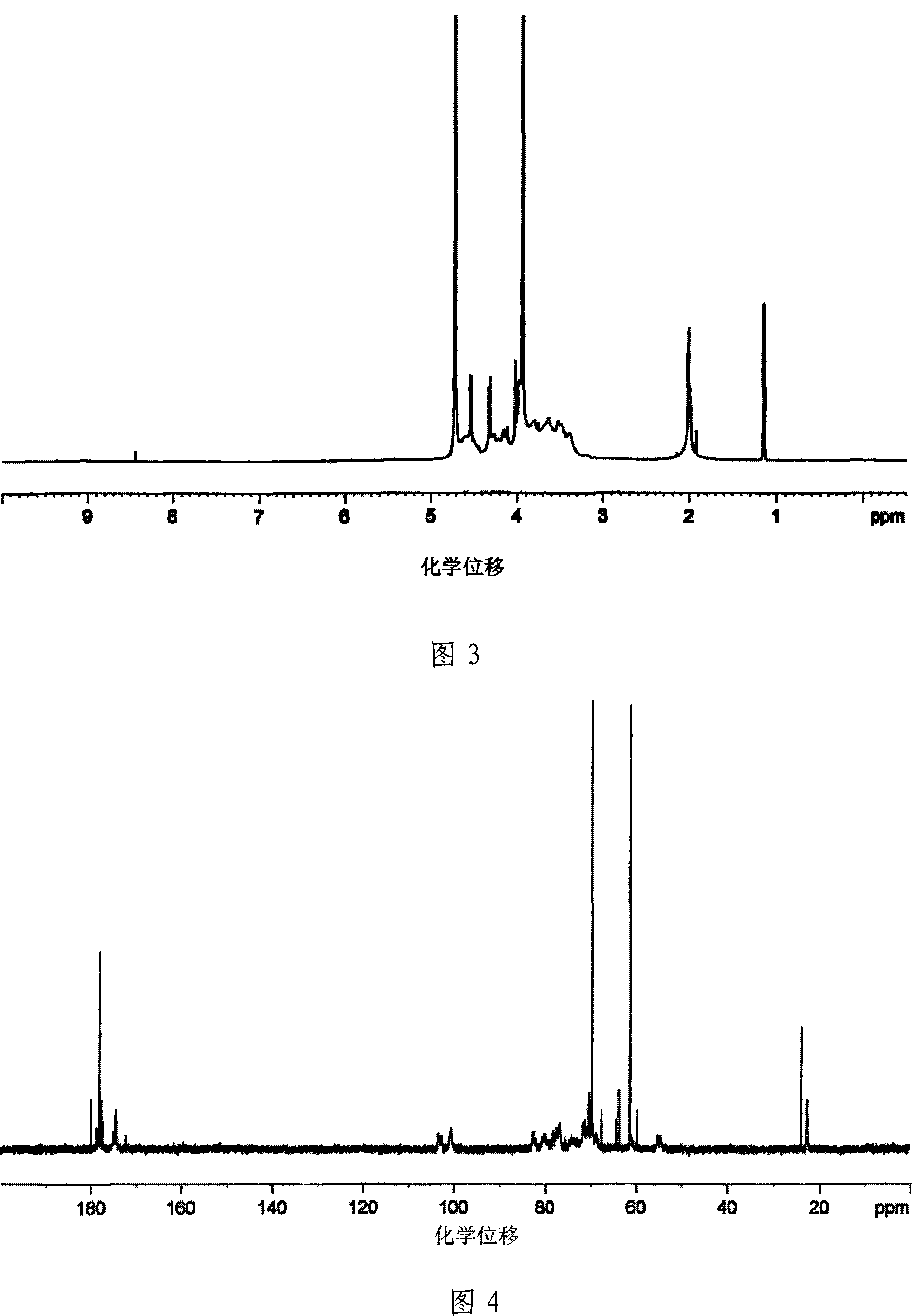
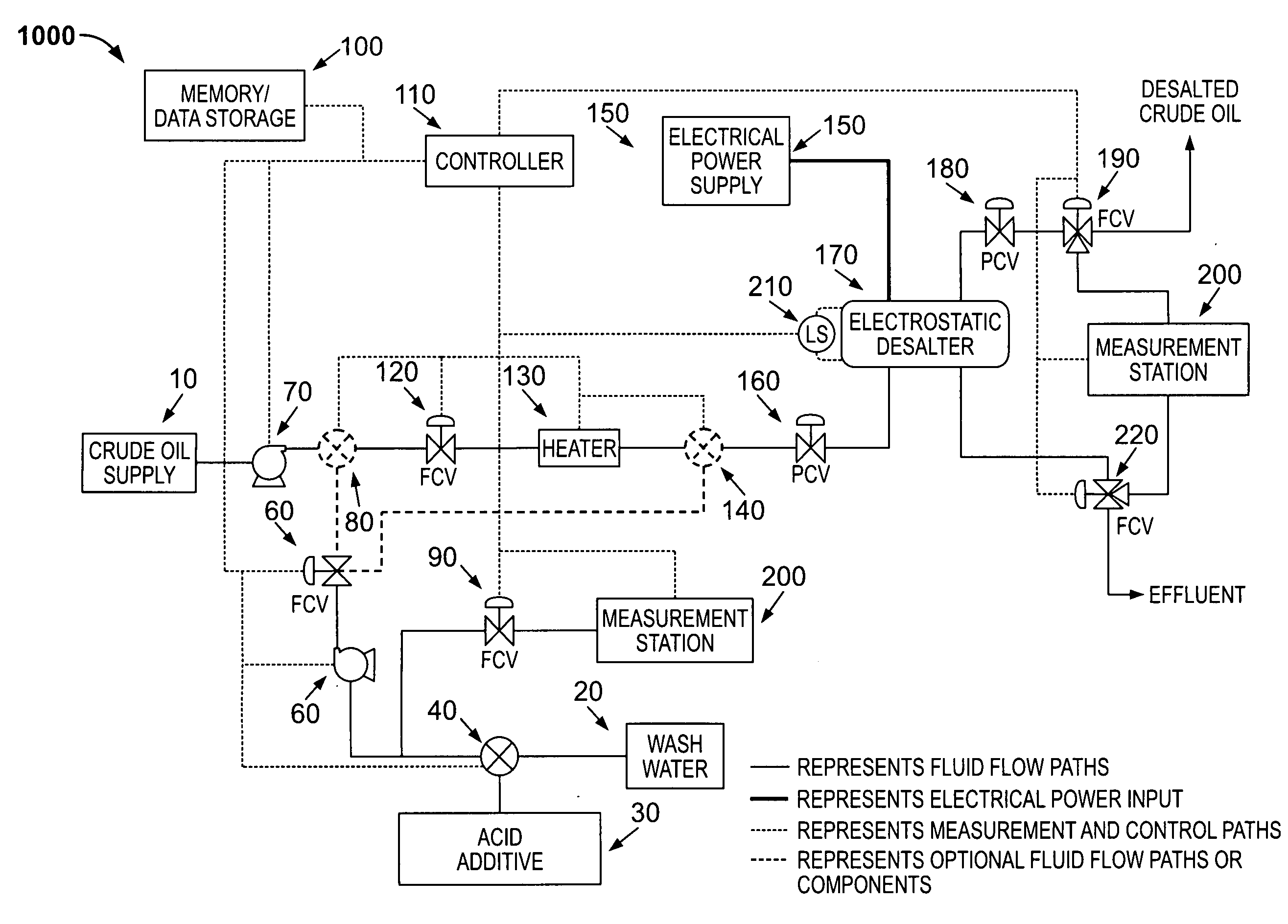
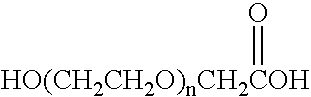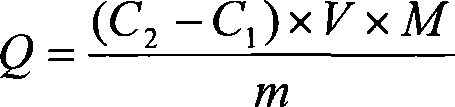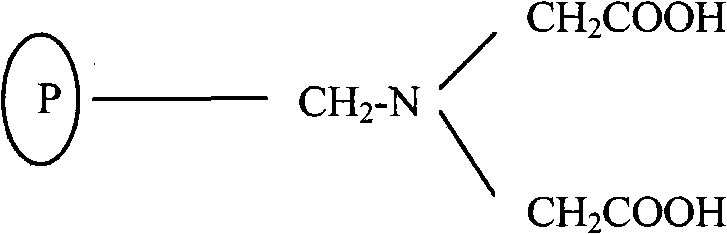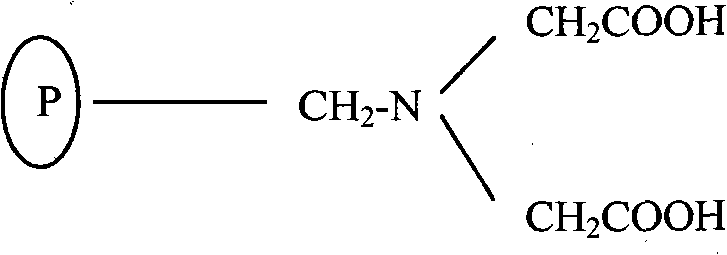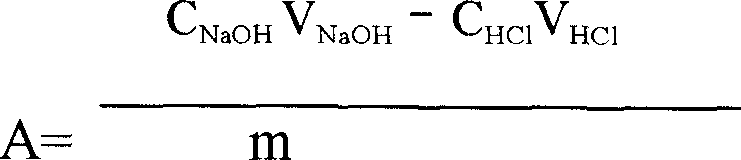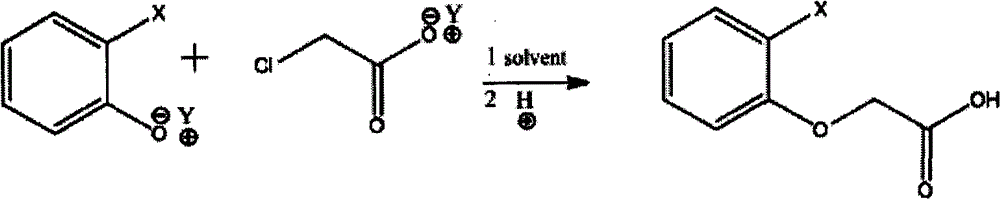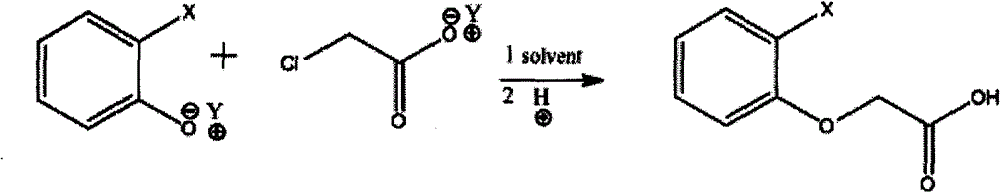Patents
Literature
1619 results about "Chloroacetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is the organochlorine compound with the formula ClCH₂CO₂H. This carboxylic acid is a useful building-block in organic synthesis.
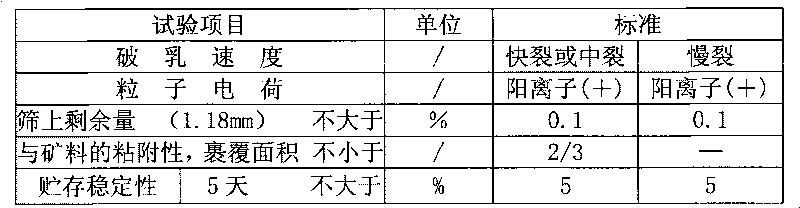
Cationic asphalt emulsifier and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101745340AWide selectionWide applicabilityTransportation and packagingMixingChloroacetic acidsFatty alcohol
The invention relates to cationic asphalt emulsifier and preparation method and application thereof. The main agent of the cationic asphalt emulsifier is prepared through the reaction of quaternarization reagent and intermediate at molar ratio of 0.5-3:1, wherein the intermediate is produced in the reaction of organic acid mixture and organic amine at molar ratio of 1: 1-3. The adjuvant agent of the cationic asphalt emulsifier is the combination of, based on the main agent by weight, 0.1-2.5% of nonionic surfactant and 0.1-2.5% of modifier. The organic acid mixture is the mixture of linear, branched or naphthene-containing organic acid with small relative pace steric effect and organic acid with big relative space steric effect at molar ratio of 1: 3- 3: 1. The quaternarization reagent is epichlorohydrin, hydrochloric acid, chloromethane, dimethyl sulfate or chloroacetic acid. The modifier is one or more of aluminum sulfate, ammonium chloride and calcium chloride and the nonionic surfactant is fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether. The emulsifier has no bad effects to the property of the asphalt, has wide application range and can satisfy different construction conditions.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
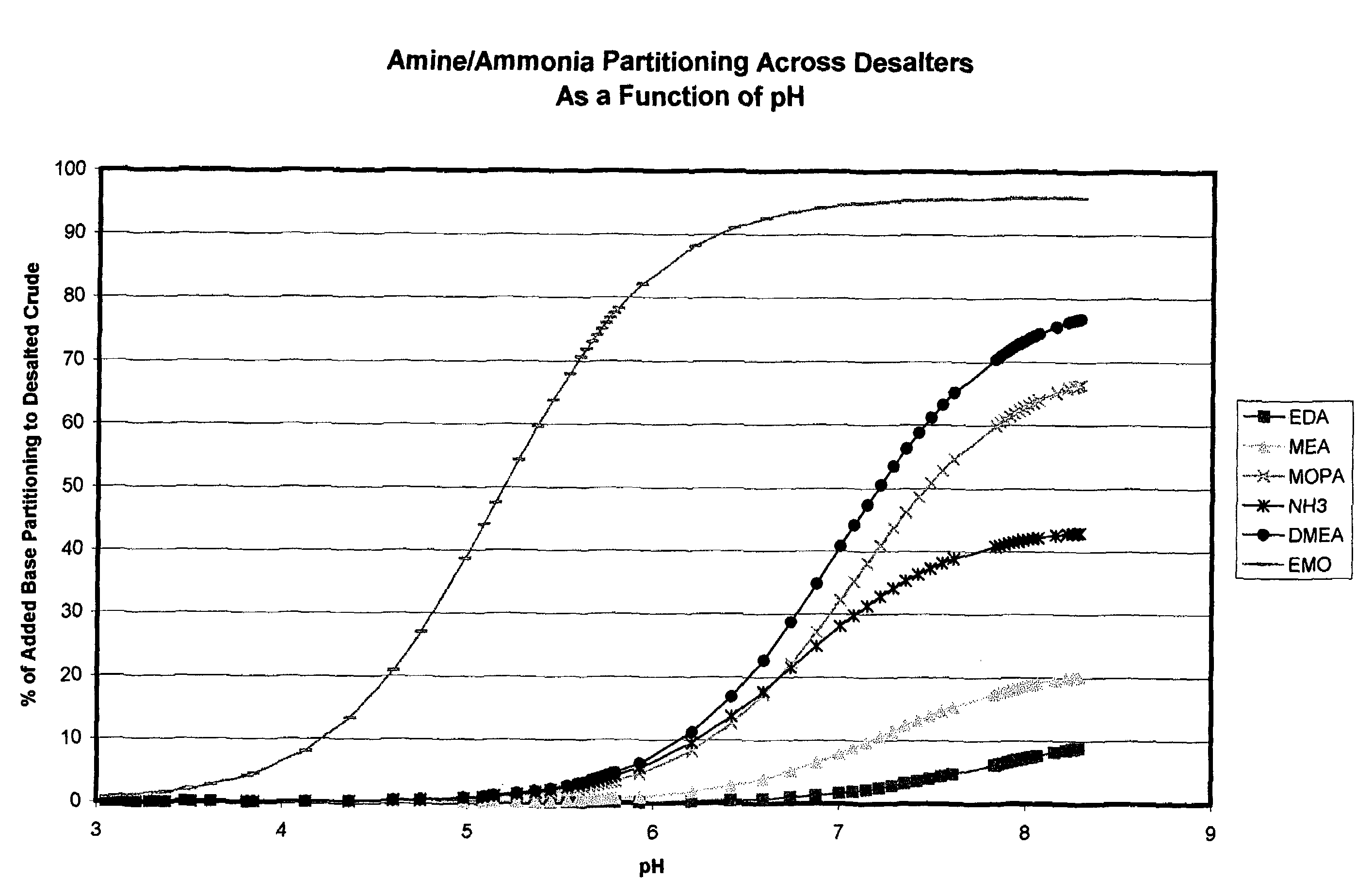
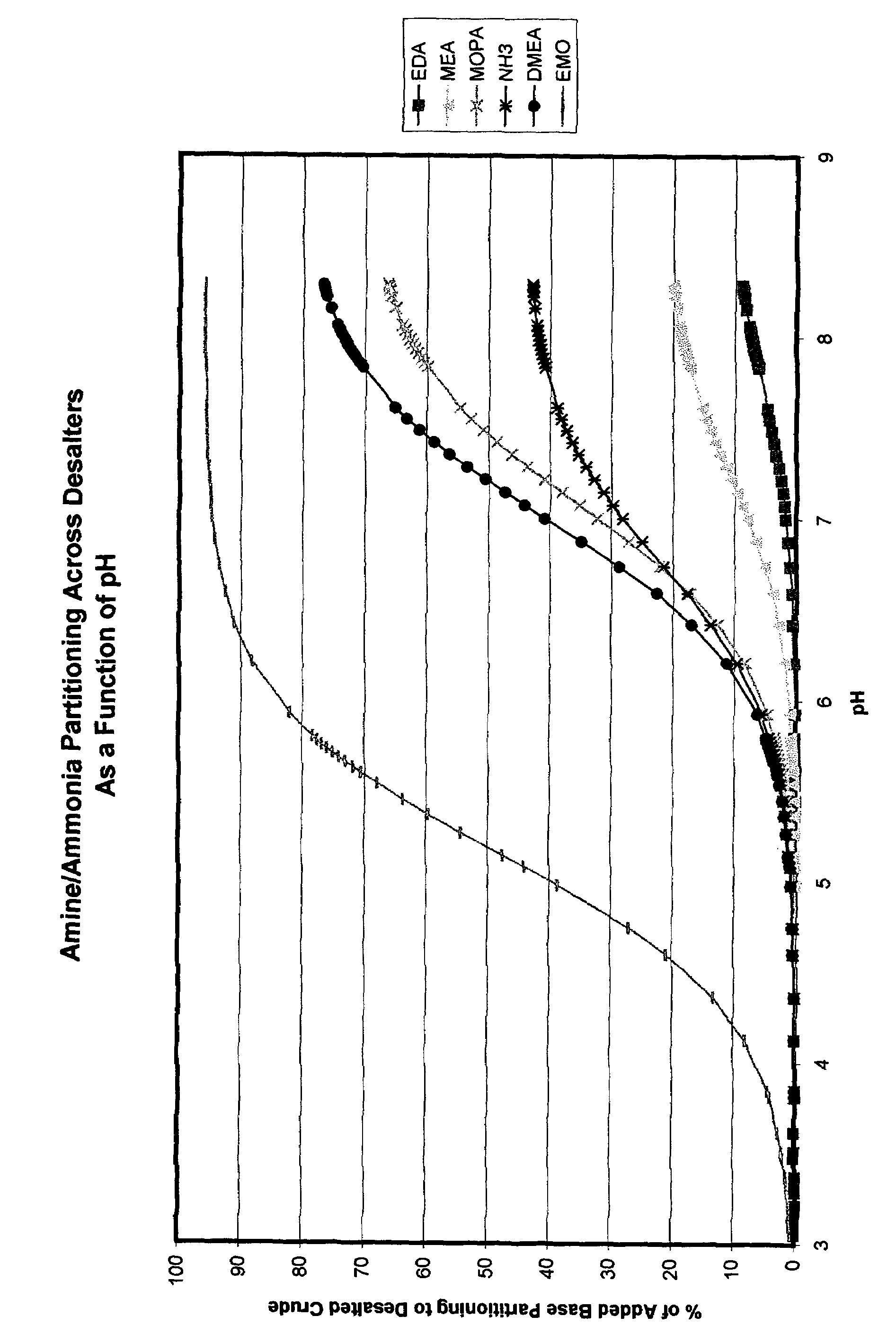
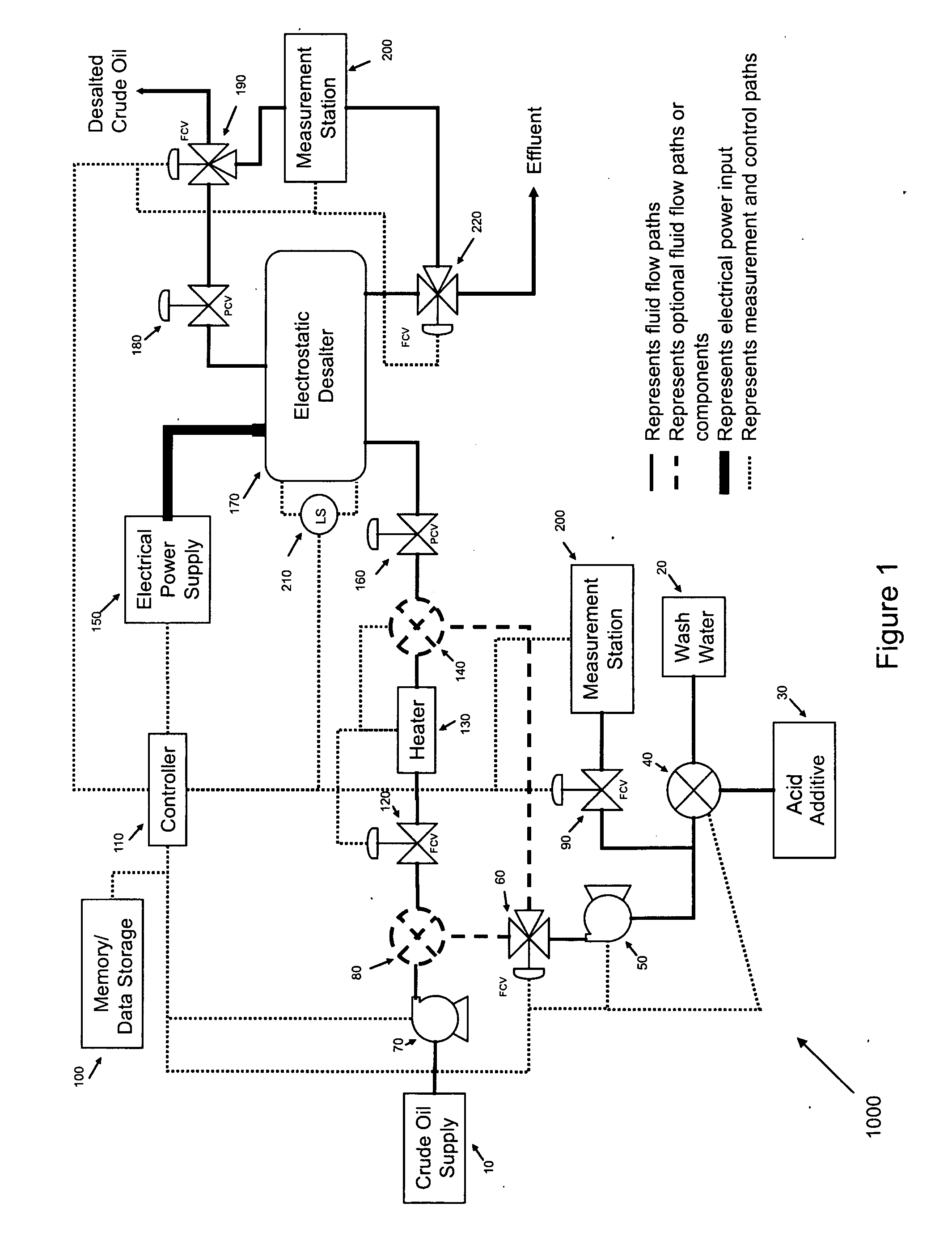
Additives to enhance metal and amine removal in refinery desalting processes
ActiveUS7497943B2Dewatering/demulsification with chemical meansDewatering/demulsification with electric/magnetic meansWash waterChloroacetic acids
It has been discovered that metals and / or amines can be removed or transferred from a hydrocarbon phase to a water phase in an emulsion breaking process by using a composition that contains water-soluble hydroxyacids. Suitable water-soluble hydroxyacids include, but are not necessarily limited to glycolic acid, gluconic acid, C2-C4 alpha-hydroxy acids, poly-hydroxy carboxylic acids, thioglycolic acid, chloroacetic acid, polymeric forms of the above hydroxyacids, poly-glycolic esters, glycolate ethers, and ammonium salt and alkali metal salts of these hydroxyacids, and mixtures thereof. The composition may also include at least one mineral acid to reduce the pH of the desalter wash water. A solvent may be optionally included in the composition. The invention permits transfer of metals and / or amines into the aqueous phase with little or no hydrocarbon phase undercarry into the aqueous phase. The composition is particularly useful in treating crude oil emulsions, and in removing calcium and other metals therefrom.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Preparation and application of carboxymethyl cellulose of wheat straw
InactiveCN101985479AReduce dosageImprove stabilityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsChloroacetic acidsChloroacetic acid
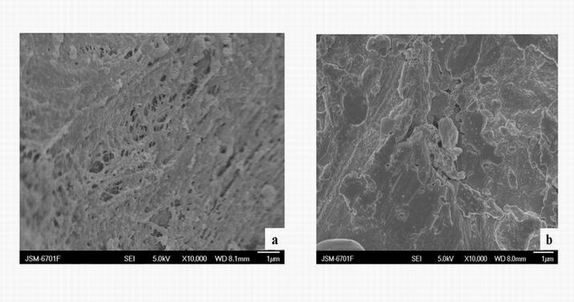
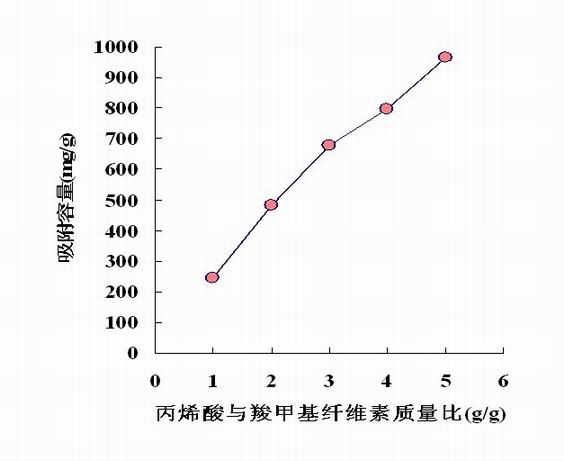
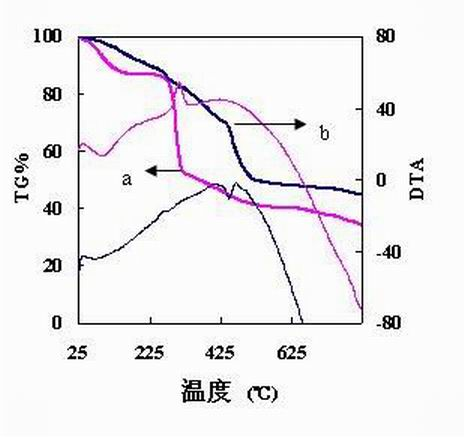
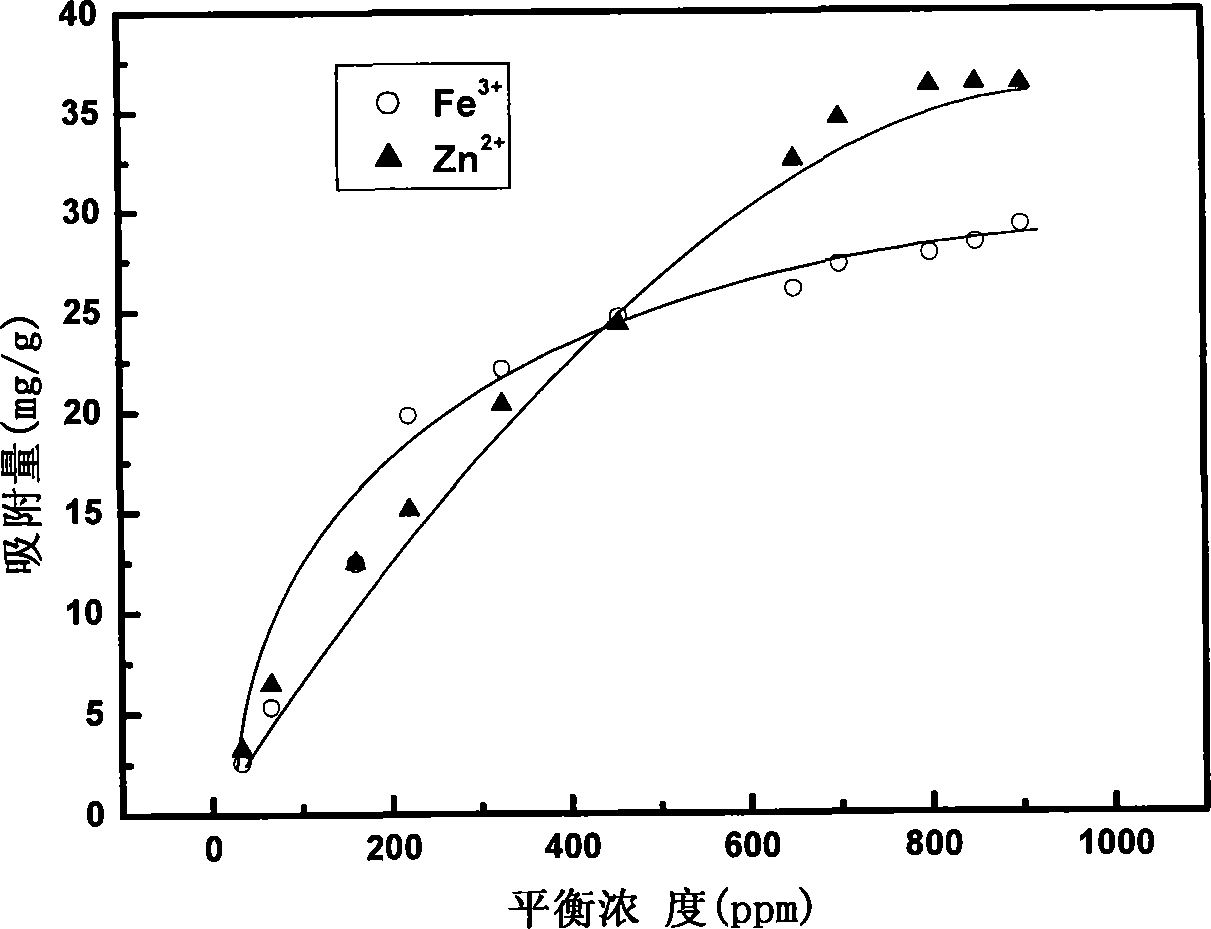
The invention discloses carboxymethyl cellulose of wheat straw. The wheat straw is crushed and subjected to pretreatment with dilute alkali, bleaching and alkalization, and then reacts with chloroacetic acid before being etherified so as to obtain the carboxymethyl cellulose of the wheat straw; and the carboxymethyl cellulose of the wheat straw is subjected to graft copolymerization together with acrylic acid to obtain a carboxymethyl cellulose-based polymer adsorbent. The adsorbent is applied to the treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal ions, has high adsorbability and large adsorption capacity and ensures high metal ion removal rate. After treatment, the adsorbent has high stability and can completely meet the requirements of heavy-metal wastewater treatment; and the treated wastewater is clear and transparent without odor and can meet the national emission standard. The invention has the advantage that the resources of raw materials are wide, the cost is low, the use of waste is realized, and secondary pollution caused by burning of the wheat straw is avoided, thus being conducive to environmental protection.
Owner:GANSU TIPTOP PLANT TECH CORP
Method for preparing etherification luffa and application of it in metallic ion adsorption
InactiveCN101239306AEasy to makeImprove performanceOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCelsius DegreeChloroacetic acids
The present invention provides a etherifying luffa method and an application in the metal ion adsorption, belonging to natural high polymer material modification or wastewater disposal technical field. The method is mixing the natural luffa with m moderate NaOH alcohol solution, alkalization under the temperature 25-80 Celsius degree, or alkalization by microwave interval radiation, then obtaining alkalization luffa by reflowing, washing, filtering, drying in the thermostatic waterbath; the etherifying luffa is obtained by dispersing with NaOH solution, reacting with the chloroacetic acid alcoholic solution, filtering, washing, drying. The luffa comes from variety of natural resources, and biodegradation, and treating process is relatively simple, partly substituting high molecular synthetic material in aspect of the sewage treatment, and having advantages such as friendly to the environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Modifying method for wood elements
InactiveUS6632326B1Good dimensional stabilityReduce processing timeCellulosic pulp after-treatmentLiquid surface applicatorsManufacturing cost reductionAcetic acid
The present invention's modifying method for wood elements includes a step for soaking wood elements in one or a mixture of acetic anhydride, acetic acid, or chloroacetic acid; and a step for acetylating the impregnated wood elements in a gaseous phase. This method makes it possible to reduce the time required for the step of acetylating the wood elements, simplifies the process, reduces fabrication costs, and enables fabrication of a wood fiberboard having high dimensional stability.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Preparation method of grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant
InactiveCN101880356AHigh molecular weightEnhanced bonding and bridging flocculationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSolubilityAcetic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of a grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant, comprising the following steps: carrying out graft copolymerization between carboxymethyl chitosan and polyacrylamide to obtain the grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant, wherein the substituted ratio of a carboxyl group is 5%-90%, and the mass of the polyacrylamide is 40%-80% of the grafting amphoteric chitosan flocculant. The carboxymethyl chitosan can be obtained by separation after carboxylation reaction between chitosan and chloroacetic acid. The chitosan can adopt various commercially available products, and preferably, molecular weight of the chitosan is not less than 50,000, more preferably 750,000-850,000. The carboxymethyl chitosan grafting polyacrylamide flocculant prepared by the method of the invention improves water solubility of the chitosan, is applicable to treating water with different electric charges, and has good salt tolerance; and the flocculant can be also widely applied to an acid medium and an alkaline medium, and has wide adaptability to the pH value range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Making method of and use of antibiotic surgical dressing
InactiveCN1833731AHigh strengthImprove antibacterial propertiesAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberAcetic acid
An antibacterial medical dressing for the operation wound is prepared from chitosan fibers through alkalizing to become alkaline chitosan fibers, and etherifying reaction on chloroacetic acid to become carboxymethyl chitosan fibers. When said fibers are encountered with water, it is swelling to become elastic gel. It is possible to add additive for higher curative effect.
Owner:李毅彬
Preparation Method of an Anti-Microbial Wound Dressing and the Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080241229A1Improve the environmentPromote wound healingAdhesive dressingsAbsorbent padsFiberWound dressing
The present invention discloses a method for the preparation of an anti-microbial wound dressing comprises alkalizing chitosan fiber to obtain alkalized chitosan fiber which is then etherified with chloroacetic acid to produce carboxymethyl chitosan fiber. Said fiber is made into dressing by fiber opening, web formation and needling. Alternatively chitosan fiber can be made into chitosan non-woven fabric by non-woven technique first which is then carboxylmethylated. The fabric is then made into wound dressing by cutting, packaging and sterilizing. The present invention also discloses the uses of the anti-microbial wound dressing made according to said method. The dressing according to the present invention can be applied in surgical wound, burn, and other chronic wound. Said dressing, when covering wound, is able to prevent moisture losses in body fluid, provide a favorable moist environment necessary for wound healing and maintain a fluid-free, maceration-free, germ-free wound surface. Said dressing is antiphlogistic, hemostatic and antalgic and promotes wound healing.
Owner:MEDTRADE PROD
Novel chelate resin and production method and application thereof
ActiveCN101735372AHigh removal rateSimple process controlOther chemical processesMetal impuritiesChloroacetic acids
The invention provides a chelate resin and a production method and the application thereof, and the novel chelate resin can effectively remove impurities in trichlorosilane; the preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) zinc chloride is used as catalyzer, a white ball and chloromethyl ether are reacted to obtain chloromethylate white ball; (2) the chloromethylate white ball and hexamine are reacted, and then concentrated hydrochloric acid-ethanol mixing solution is used for decomposing, so as to obtain primary amine resin; (3) the primary amine resin is added in the chloroacetic acid aqueous solution, and the reaction is carried out for 10-30 hours at 55-70 DEG C to obtain the chelate resin; the chelate resin can effectively remove the metal impurities such as boron, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, copper, ferrum and other impurities in trichlorosilane, the removal rate can reach more than 99 percent; the chelate resin has high processing capacity with 200t per cube and is the optimal choice for improving the product quality.
Owner:SUNRESIN NEW METERIALS CO LTD XIAN
Barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent for near-well area and preparing method of barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent
ActiveCN105112036APrevents accumulation of scaleReduce secondary damageDrilling compositionCarboxylic saltChloroacetic acids
The invention discloses a barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent for a near-well area and a preparing method of the barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent. The barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent comprises a polyamine carboxylate solution, nonionic surfactant accounting for 3%-10% of the total mass of the polyamine carboxylate solution and an emulsion breaker accounting for 2%-8% of the total mass of the polyamine carboxylate solution. The polyamine carboxylate solution is prepared from polyamine midbody and chloroacetic acid salt through a reaction, wherein the polyamine midbody is prepared through organic amine and epoxy chloropropane with the mole ratio of 1.05-1.5:1 through a reaction, and the chloroacetic acid salt is prepared from chloroacetic acid and alkali with the same mole ratio through a reaction. The barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent for the near-well area has a good removing effect on indissolvable salt such as barium sulfate, strontium sulfate and calcium sulfate, and the descaling rate is higher than 40%. Meanwhile, the barium-strontium-calcium descaling and blockage removing agent has the expansion preventing and inhibiting performance, the clay expansion reducing rate is higher than 80%, corrosion to equipment is slight, and water locking can be avoided. Blockage removing can be effectively achieved on a reservoir stratum near a well, the permeability of the reservoir stratum is improved, and thus the recovery ratio of oil and gas resources is increased.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Polyurethane base biological fixing carrier and sewage treating method
InactiveCN1587106ASustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentCross-linkChloroacetic acids
The present invention discloses one kind of polyurethane base biological immobile carrier. The carrier has three kinds of structures: macroporous polyurethane network; polyurethane cross-linked chitosan and coated active carbon; and microporous network formed with chitosan and cross-linked glutaraldehyde, chloropropylene oxide or chloroacetic acid. These three kinds of network interpenetrate to form the polymer capable of fixing bioactive molecule. The carrier of the present invention has the features of coexisting macropores and micropores, coexisting hydrophilicity and reaction property, coexisting powerful adsorption and strong polarity, high biological bearing capacity, good compatibility, high physical, chemical and mechanical performance, etc., and is suitable for various bioreactors for treating sewage.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Preparation of surfactant of double long-chain alkyl lycine and applications thereof
InactiveCN101549266ASufficiently lipophilicEnhanced overall recoveryTransportation and packagingMixingAlkali freePolyacrylamide
The invention relates to preparation of a surfactant of double long chain alkyl lycine and applications thereof, belonging to the field of colloid and interface chemistry. The surfactant is prepared by reaction of double long-chain alkyl methyl tertiary amine and chloroactic acid and is an ampholytic surfactant t and the number of carbon atoms of the long-chain alkyl is 8 to 18. By being used by combination with other surface active agents, the surfactant is used as an alkali-free oil-displacing agent; wherein the molar fraction of the surface active agent of double-long chain alkyl lycine is 0.10 to 0.60, and can reduce the interfacial tension of Daqing crude oil / formation water interface to 10mN / m order of magnitude under the conditions that the total mass concentration of the active surface agent is 0.01 percent to 0.5 percent, 1000ppm of polyacrylamide is added, alkali is not added and the temperature is 45 DEG C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Making method of and use of antibiotic surgical dressing
InactiveCN1833732AEasy to usePrevent moisture lossAdhesive dressingsAbsorbent padsWound healingAcetic acid
An antibacterial medical dressing is prepared from chitosan fibers through alkalizing, etherifying reaction on chloroacetic acid to obtain carboxymethyl chitosan fibers, opening, netting, needling, and cutting by needed sizes, packing and disinfecting. It can be used for preparing the surgical dressing for wound, bum and scald, the anti-inflammatory staltic fiberous ball, anti-inflammtory drainage sliver, and operation dressing.
Owner:李毅彬
High substitution degree carboxymethyl indianbread polysaccharide and its preparation method and uses
ActiveCN1970579AIncrease the reaction concentrationIncreased degree of carboxymethyl substitutionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityAlcohol
The invention discloses a carboxymethyl pachyman (CMP) with high-degree of substitution and making method and application, which is characterized by the following: adopting water or water alcohol solution as dielectric; proceeding substitution reaction for pachyman, chloroacetic acid and fitful excessive sodium hydroxide to obtain CMP without vibrating technique and equipment; improving CMP D / S and solubility to reach injection need.
Owner:HUNAN BUTIAN PHARMA
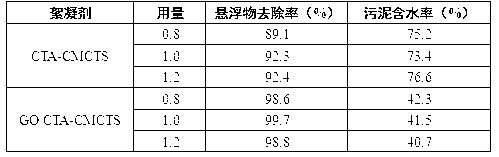
Preparation method of graphene oxide/amphoteric chitosan intercalation composite for sewage treatment
ActiveCN103240063AEnhance sexualityWell formedOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCarboxyl radicalUltrasound - action
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene oxide / amphoteric chitosan intercalation composite for sewage treatment. At present, the dewatering effect of a cationic type polymeric flocculant is limited. The preparation method has the steps of oxidizing graphite by virtue of concentrated sulfuric acid, sodium nitrate and potassium permanganate to prepare graphene oxide; modifying chitosan by virtue of chloroacetic acid and a quaternization reagent to obtain amphoteric chitosan; and then under the action of ultrasonic waves, realizing intercalation compounding of the graphene oxide and the amphoteric chitosan, and carrying out dispersion to obtain a graphene oxide nanometer ion dispersion liquid. According to the preparation method, by virtue of an intercalation method, controllable dispersion of a graphene oxide sheet layer and grains is realized; as being provided with active groups of carboxyl groups, hydroxy groups, quaternary ammonium groups and the like, the surface of the graphene oxide in a dispersed state can adsorb suspended pollutants in wastewater; and the graphene oxide / amphoteric chitosan intercalation composite can be applied to wastewater treatment and has the advantages of little dosage, high efficiency and low water content of sludge, and the preparation method has the characteristics that the preparation technology is unique, equipment is easily botained, and the operation is simple.
Owner:DONGYING DAOYI BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
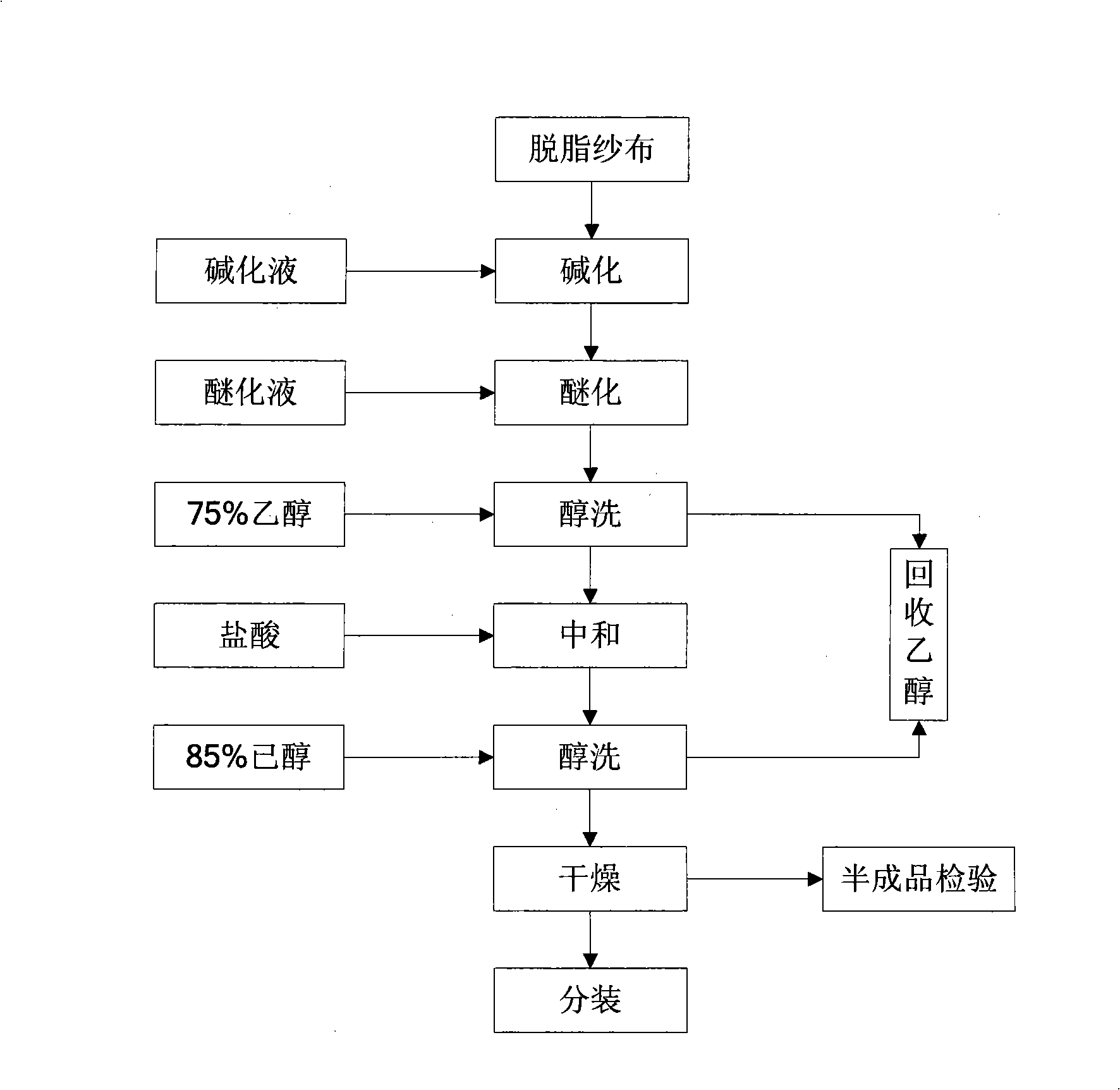
Soluble stanching gauze and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101491688AGood hygroscopicityProtect the woundAbsorbent padsVegetal fibresSolventChemistry
The invention relates to a hemostatic medicament, in particular to a soluble hemostatic gauze and a preparation method thereof. The soluble hemostatic gauze contains an absorbent gauze, sodium hydroxide, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose which is generated by, reaction of chloroactic acid in an alcohol solvent; and the weight ratio of the three raw material components is 1: 1.8: 2.35. The methodfor preparing the soluble hemostatic gauze comprises the following steps of water scrubbing, alkalization, etherification, alcohol washing, neutralization, and drying as well as weighing, cutting, and packaging after a prepared semi-finished product is qualified through the inspection. The soluble hemostatic gauze can be applied to exodontia, dermatological surgery, trauma hemostasis, and wound surface protection.
Owner:HENAN FENGHUANG DRUGS MFR
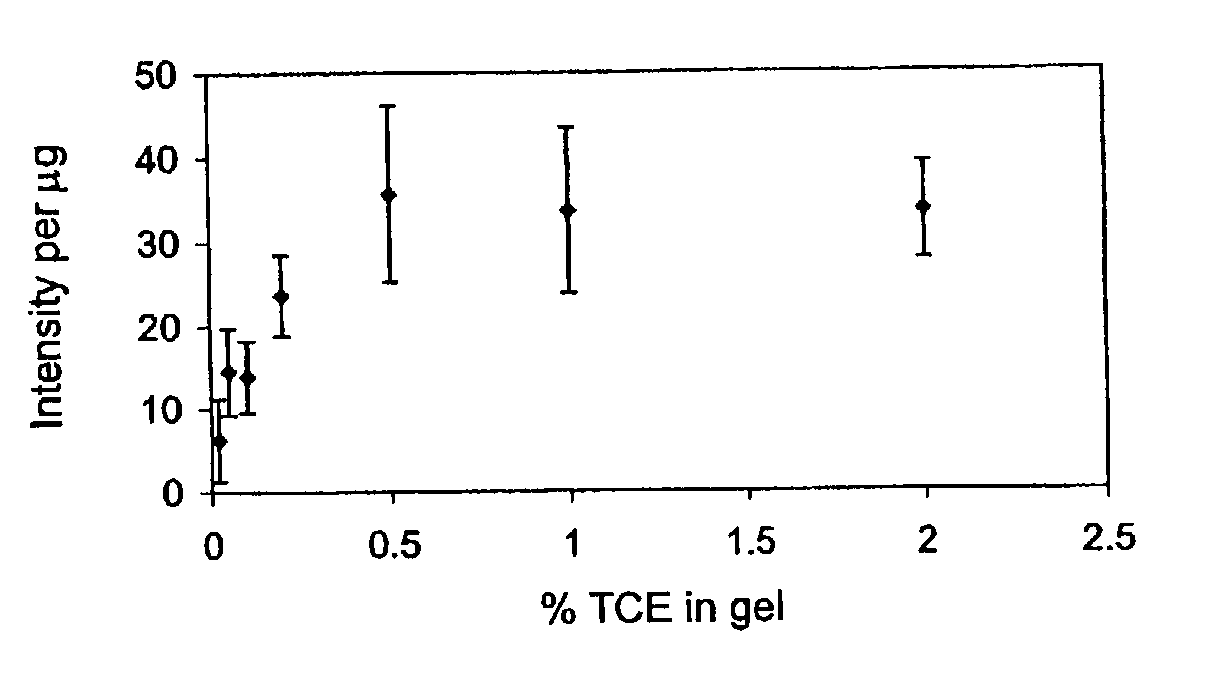
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
ActiveUS7569130B2Laborious labelingLaborious staining stepElectrolysis componentsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
InactiveUS20100089753A1Without laborious labeling and staining stepElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
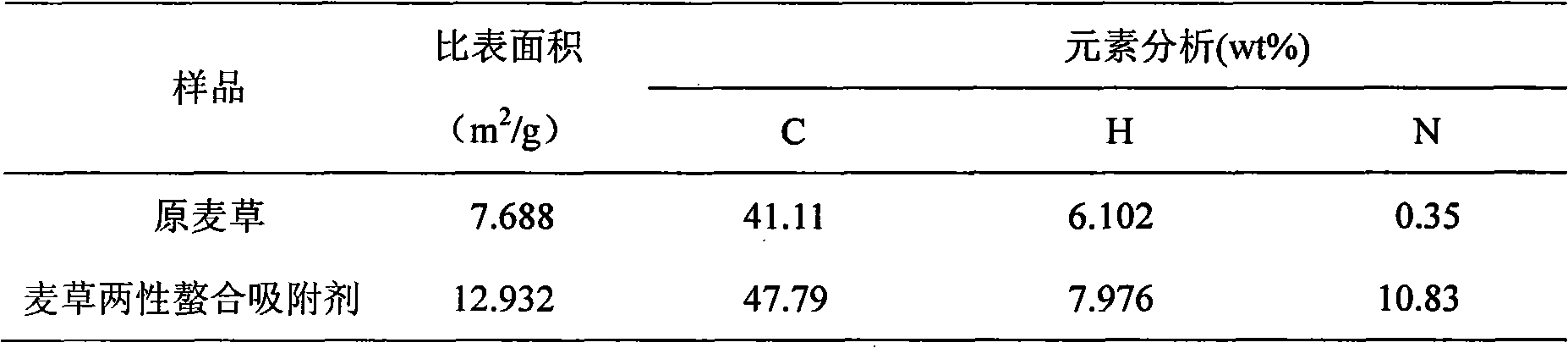
Preparation method and application of amphoteric chelate sorbent containing agricultural straw
InactiveCN101862642AEasy to handleSimple production processOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCross-linkEthylenediamine
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an amphoteric chelate sorbent containing agricultural straw. The sorbent is brownish-yellow solid powder, the nitrogen content is 10.83wt%, and the specific surface area is 12.93m<2> / g. The sorbent is prepared by taking agricultural straw, epoxy chloropropane and monochloroacetic acid as raw materials, taking trimethylamine or triethylamine as a grafting reaction agent and taking ethylenediamine, diethylenetriamine or triethylenetetramine as a cross-linking agent. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple production processes, economy, practicability, reproducibility and the like and can be suitable for large-scale production. The sorbent prepared by the invention has the characteristics of good stability, good adsorption effect, wide application range and the like, can be widely applied to treatment of waste water containing heavy metal ions, and has better treatment effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Acrylic chelating fibre for removing heavy metal ion in water and preparation
InactiveCN101264438AExtensive and excellent complexing performance of heavy metal ionsEasy to makeOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionChloroacetic acidsChloroacetic acid
The invention discloses an acrylic chelating fiber for removing heavy metal ions in water and the preparation method, belonging to chelating fiber technology. The chelating fiber adopts acrylic fiber as matrix, and the matrix loads poly (carboxymethyl) amino functional group by means of covalent bond. The preparation method of the acrylic chelating fiber comprises the following steps: enabling amination reaction of the acrylic fiber and polyamine or polyamine water solution; enabling carboxy methylation reaction with the alkali-bearing chloroacetic acid water solution after washing and drying, so as to obtain the acrylic chelating fiber with poly (carboxymethyl) amino functional group. The acrylic chelating fiber has the advantages of wide and excellent performance for complexing heavy metal ions, high complex capacity and high complex speed of metal ion, simple preparation and low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and device for automated control of enhanced metal and amine removal from crude oil
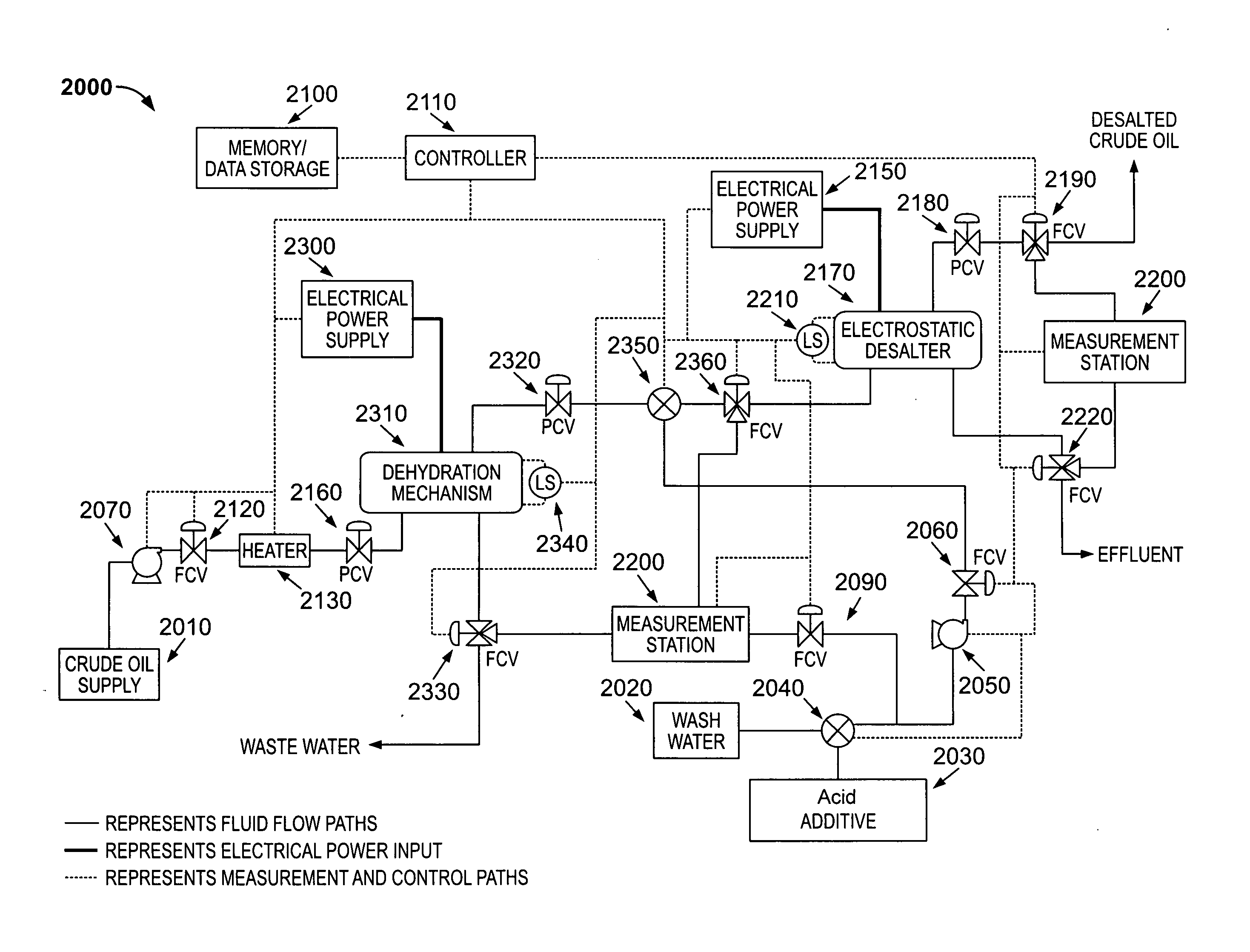
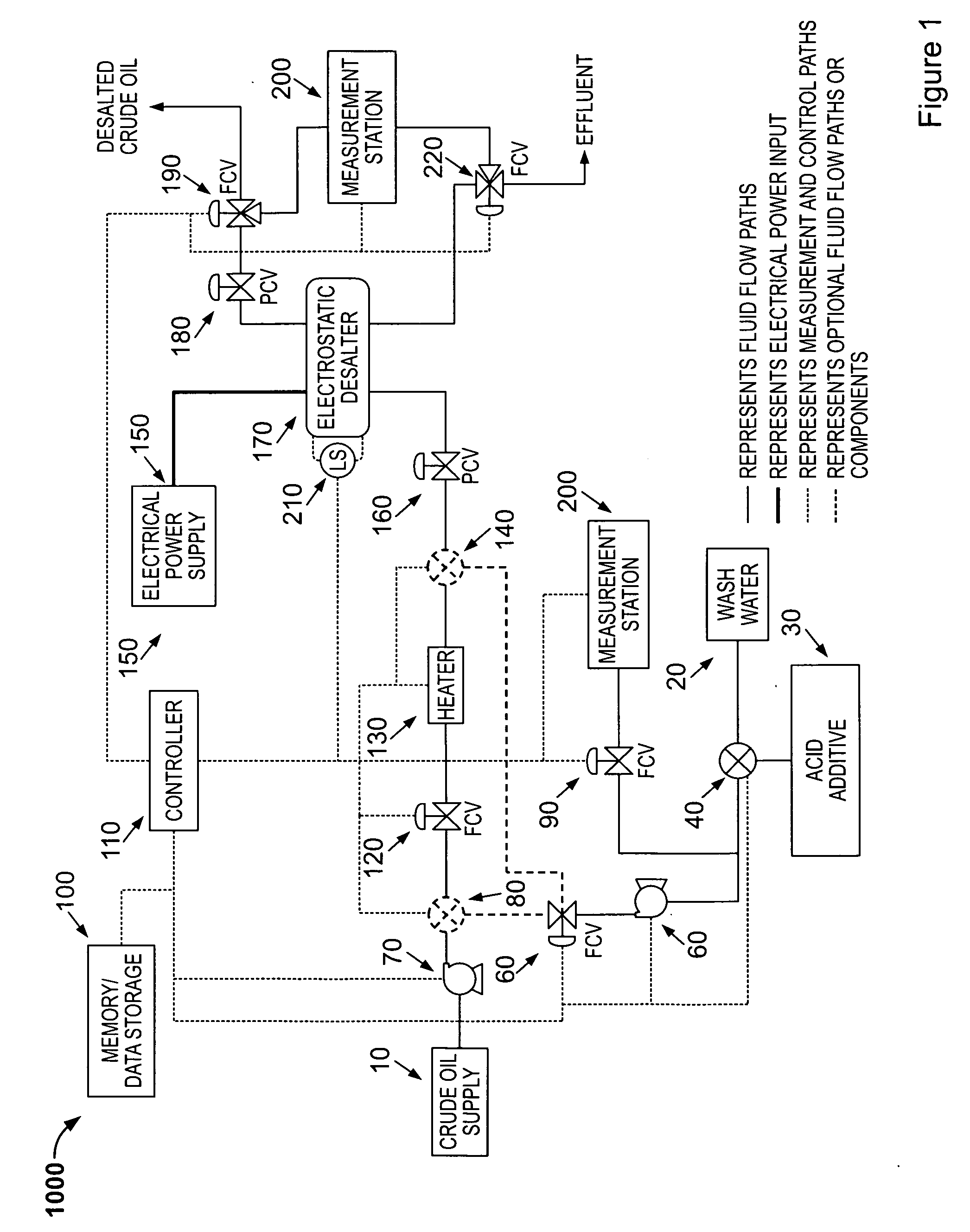
InactiveUS20110100877A1Sampled-variable control systemsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionAutomatic controlWash water
A method for removing calcium, iron, other metals, and amines from crude oil in a refinery desalting process includes the steps of adding a wash water to the crude oil; adding the wash water to the crude oil to create an emulsion; adding to the wash water, the crude oil or the emulsion an acid additive consisting of at least one of the following: oxalic acid, citric acid, water-soluble hydroxyacid selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, gluconic acid, C.sub.2-C.sub.4 alpha-hydroxy acids, malic acid, lactic acid, poly-hydroxy carboxylic acids, thioglycolic acid, chloroacetic acid, polymeric forms of the above hydroxyacids, poly-glycolic esters, glycolate ethers, and ammonium salt and alkali metal salts of these hydroxyacids, and mixtures thereof; heating at least one of the crude oil, the wash water or the emulsion to a desired temperature; resolving the emulsion containing the acid additive into a hydrocarbon phase and an aqueous phase using electrostatic coalescence, the metals and amines being transferred to the aqueous phase; measuring at least one desalting process characteristic at at least one process point; performing a statistical calculation of the desalting process performance based upon the measuring; and adjusting a control setting of the desalting process as a function of the statistical calculation. Other methods and devices are also provided.
Owner:ASSATEAGUE OIL
Moisture absorption humectant and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101225125AIncrease production costImprove moisture absorption and moisturizing performanceAcetic acidFiltration
The invention relates to a moisture absorbing humectant of polysaccharides and a preparation method, belonging to the fields of daily chemicals and medical industry; wherein, carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid is adopted for the moisture absorbing humectant; the preparation method comprises steps as follows: 1 to 5-hour reaction is carried out for the hyaluronic acid swollen in alkaline isopropyl alcohol solution and the chloroacetic acid with a molar mass ratio between 1 to 6 and 1 to 4 in the excessive alkaline isopropyl alcohol solution under temperatures between 35 and 75 DEG centigrade, and then pumping filtration and drying are carried out to acquire the moisture absorbing humectant. With the carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid acquired through effective synthesis, the production cost hardly increases, while the moisture absorption and maintaining performance is remarkably improved, so as to enhance the activity and indirectly reduce the production cost. By adopting the carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid with better moisture absorption and maintaining performance than that of the hyaluronic acid as the moisture absorbing humectant, the preparation method for moisture absorbing humectant of polysaccharides has the advantages of low cost and high yielding.
Owner:烟台大境生物科技有限公司
Inhibiting agent for separating copper-molybdenum mineral and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an inhibiting agent for separating a copper-molybdenum mineral and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking aminoacetic acid or alanine, ethyl isothiocyanate, triethylamine, water and acetone according to a molar ratio of 1-2:1-2:3-4:4-6:3-5, and mixing the aminoacetic acid or alanine, the ethyl isothiocyanate, the triethylamine, the water and the acetone, heating the mixture at the temperature of between 60 and 80 DEG C to perform reaction for 2 to 3 hours; reducing the temperature to distill off 60 to 80 percent of the triethylamine and the acetone; cooling the mixture at the normal temperature; adding 10 to 15 ml of saturated monochloroacetic acid solution into the remainder to react for 1.5 to 2 hours with stirring; and cooling to crystallize the mixture to obtain a white solid namely the inhibiting agent of a copper mineral. The inhibiting agent has high inhibiting effect on the copper mineral in a copper-molybdenum collective concentrate to reduce the content of the copper mineral in a molybdenum concentrate and improve the grade of the molybdenum concentrate. The inhibiting agent has a small used amount, and is nontoxic and pollution-free.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
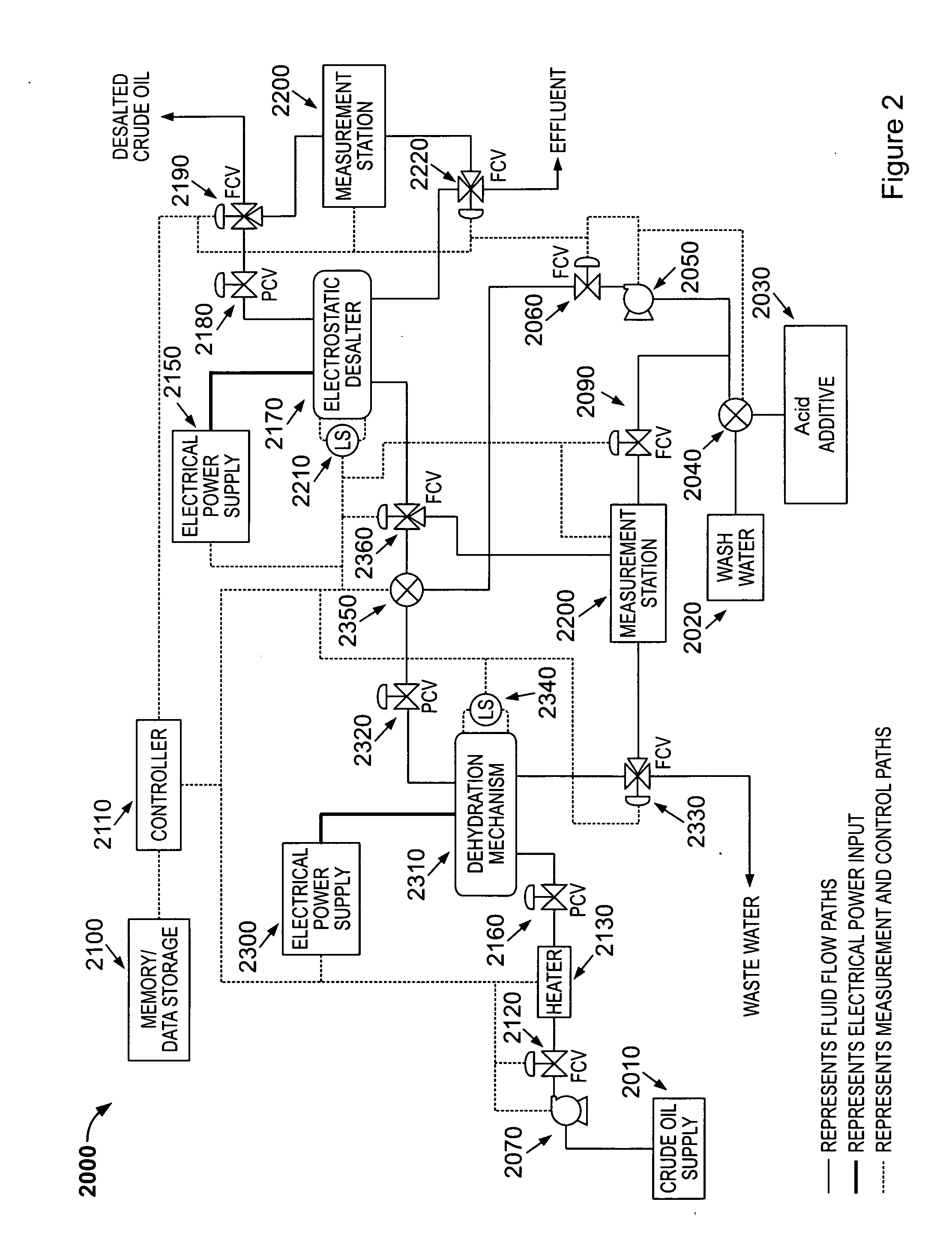
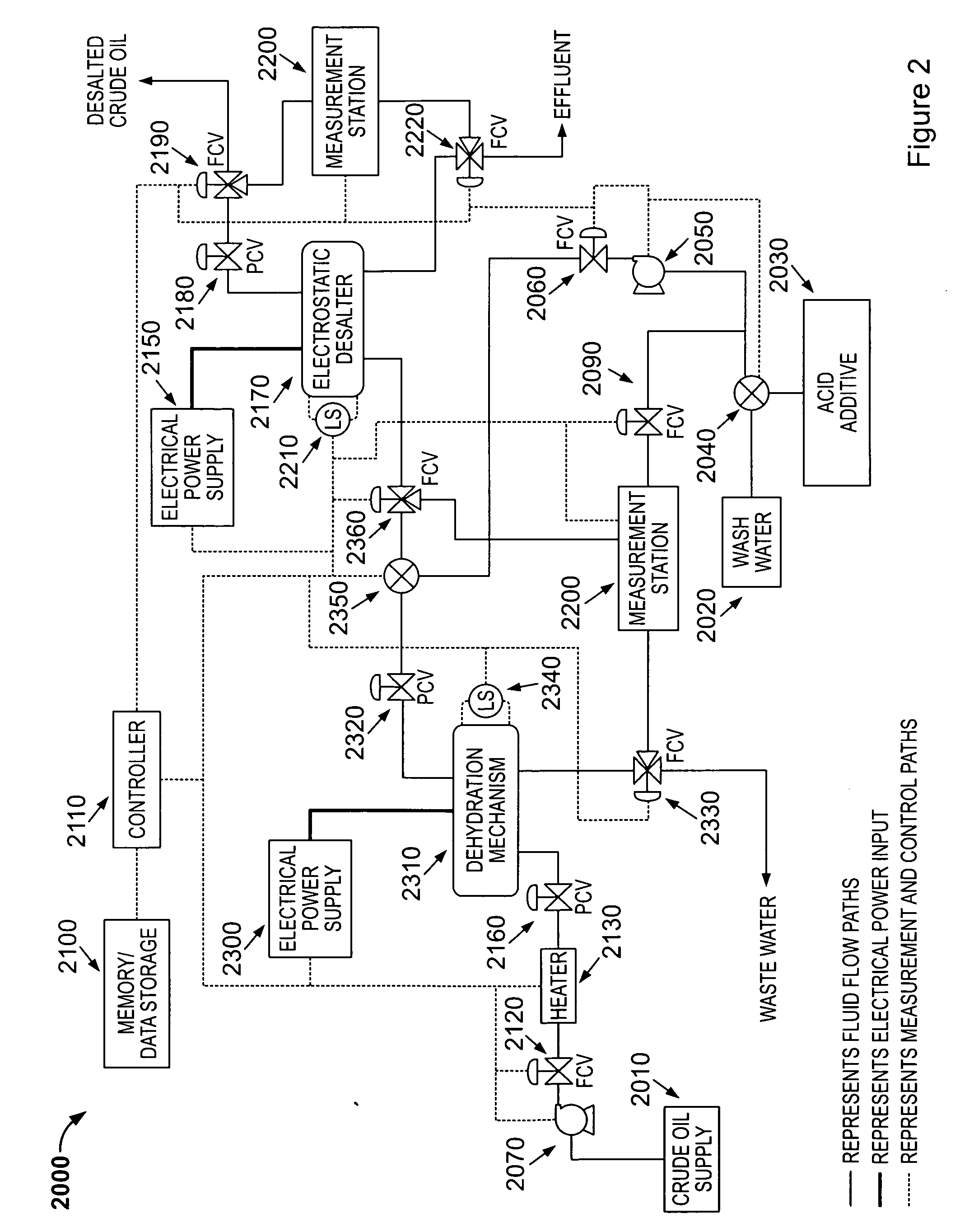
Method and device for electrostatic desalter optimization for enhanced metal and amine removal from crude oil
InactiveUS20110120913A1Working-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolvent extractionChloroacetic acidsAlpha hydroxy acid
A method for removing calcium, iron, other metals, and amines from crude oil in a refinery desalting process includes the steps of: running a plurality of tests to determine at least one statistically significant processing characteristic of the refinery desalting process; adding a wash water to the crude oil; adding the wash water to the crude oil to create an emulsion; adding to the wash water, the crude oil or the emulsion an acid additive consisting of at least one of the following: oxalic acid, citric acid, water-soluble hydroxyacid selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid, gluconic acid, C.sub.2-C.sub.4 alpha-hydroxy acids, malic acid, lactic acid, poly-hydroxy carboxylic acids, thioglycolic acid, chloroacetic acid, polymeric forms of the above hydroxyacids, poly-glycolic esters, glycolate ethers, and ammonium salt and alkali metal salts of these hydroxyacids, and mixtures thereof; resolving the emulsion containing the acid additive into a hydrocarbon phase and an aqueous phase; and adjusting a control setting of the processing characteristic as a function of the tests.
Owner:ASSATEAGUE OIL
Preparation method of flurbiprofen axetil
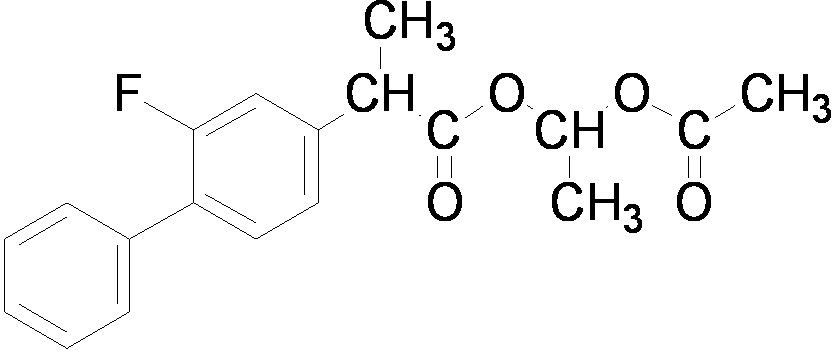
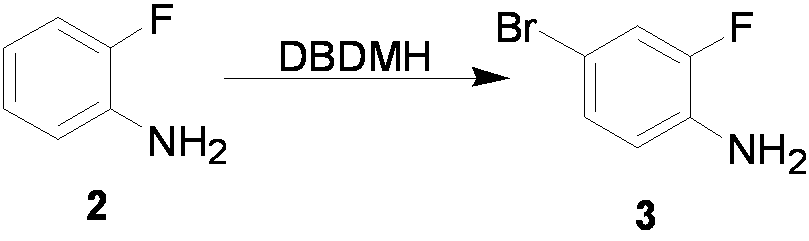
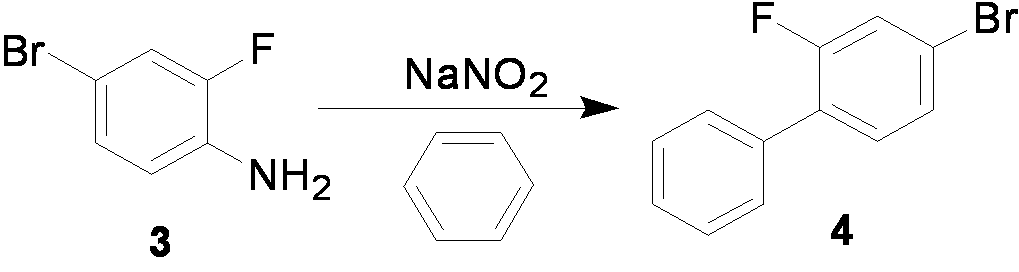
ActiveCN103012144AConvenient sourceMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPropanoic acidDistillation
The invention relates to a preparation method of flurbiprofen axetil. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing 4-bromine-2-fluoroanili from fluoroaniline under the action of 1,3- dibromo-5,5-dimethyl hydantoin; condensing 4-bromine-2-fluoroanili with benzene under the action of a catalyst and sodium nitrite to synthesize 4-bromine-2-fluorobiphenyl; carrying out grignard reaction and acidity reaction on the 4-bromine-2-fluorobiphenyl and 2-bromine sodium propionate under the action of a catalyst to generate 2-(2- fluorine-4-biphenylyl) propionic acid; condensing the 2-(2- fluorine-4-biphenylyl) propionic acid with 1-chloroacetic ethyl acetate to generate a target compound flurbiprofen axetil; and carrying out molecular distillation on the flurbiprofen axetil crude product to obtain a flurbiprofen axetil final product.
Owner:哈药集团股份有限公司 +1
Method for preparing collagen sugar
InactiveCN101270061AReduce lossHigh reaction yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationGlycineAcetic acid
The present invention discloses a preparation method of glycine. In the preparation method, chloroacetic acid and ammonia are used as raw materials; urotropine is used as the catalyst of the reaction; low-carbon alcohol solvent is used as a reaction medium; organic amine is added into the reaction system to be used as an acid binding agent; after the reaction is completed, the glycine with high content can be prepared through filtration. The preparation method solves the problems of the solvent that can not be recycled, serious solvent consumption, high cost, low yield, serious three-waste pollution and so on in the prior art. And the preparation method is suitable for the industrial production of the glycine.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
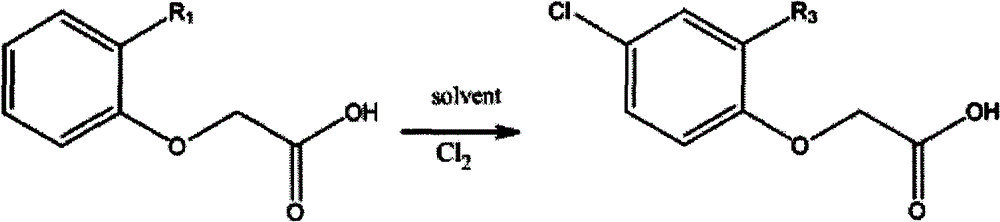
Method for synthesizing phenoxyacetic acid derivative
ActiveCN103058855AAvoid external dischargeMeet production balanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationChloroacetic acidsEthyl Chloride
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a phenoxyacetic acid derivative. The method comprises the steps of mixing a salt compound of phenol or methyl phenol and a salt compound of chloroacetic acid, putting the mixture in a solvent to carry out a heating reaction, acidifying with an inorganic acid to obtain phenoxyacetic acid, dissolving the phenoxyacetic acid in a solvent, adding a catalyst to the solvent, passing chlorine in the solvent and carrying out a heating chlorination, cooling and crystallizing to obtain a chlorinated phenoxyacetic acid derivative or a methyl phenoxyacetic acid derivative. Compared with a conventional method, the method provided by the invention can recycle the solvent of the reaction system and wastewater for cycle use during the reaction process, can meet self-production balance and realize recycle and reuse of a sealed system, and has a yield higher than 95%, a content larger than 98%, the recycle and reuse utilization rate of the solvent higher than 95% and emission reduction of the waste water in the whole production process higher than 95%.
Owner:JIANGXI TIANYU CHEM CO LTD
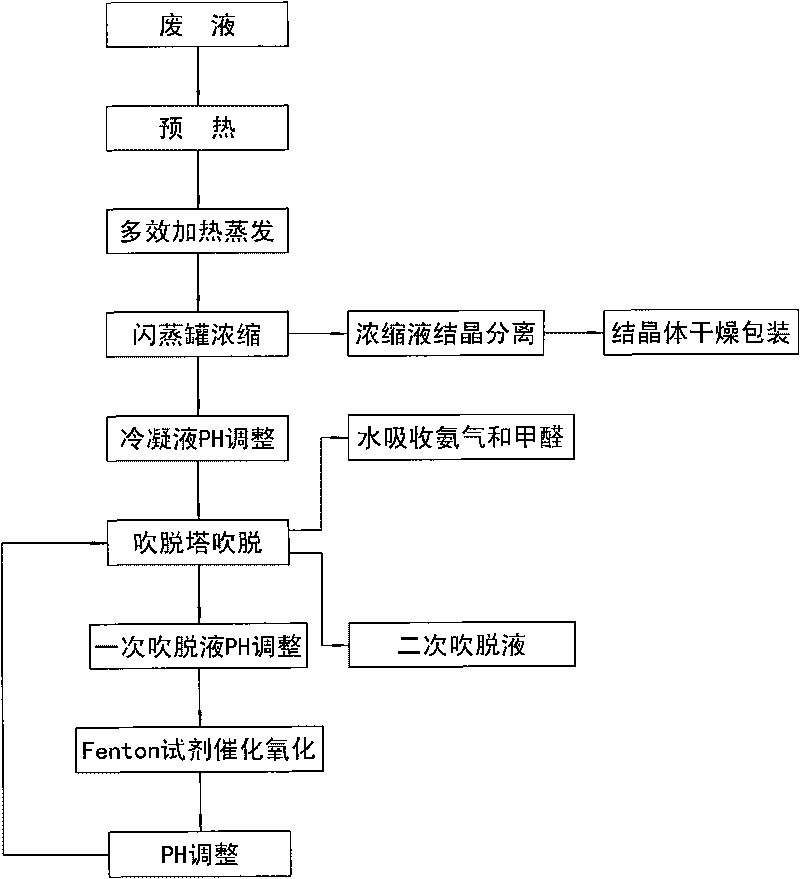
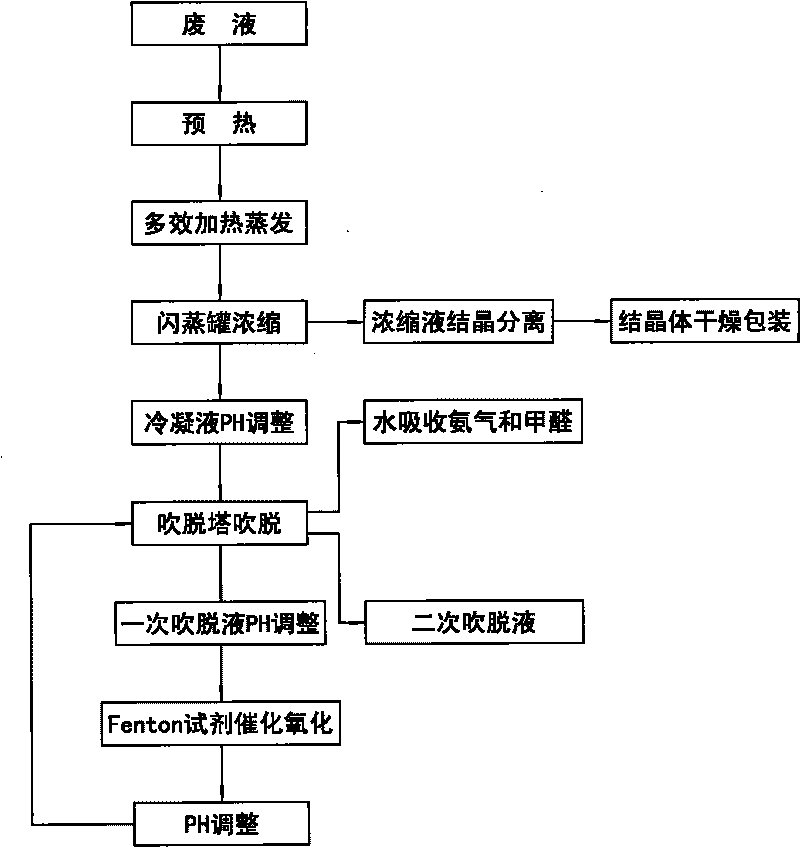
Method for treating wastewater from preparation of glycine by chloroacetic acid ammonolysis process
InactiveCN101717165AReduce energy consumptionReduce corrosionWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteFenton reagent
The invention discloses a method for treating wastewater from the preparation of glycine by the chloroacetic acid ammonolysis process, comprising the following steps: throwing waste liquid into a multi-effect falling film vacuum evaporation system, preheating the waste liquid in the multi-effect falling film vacuum evaporation system, heating and evaporating the waste liquid with a multi-effect falling film evaporator, putting the waste liquid in a flashing pot, concentrating the waste liquid until achieving the ammonium chloride concentration of 35-45%, crystallizing the concentrated solution with a crystallizer at normal temperature, drying and packaging the crystalline solid, adjusting the pH value of condensate which is generated by the multi-effect falling film vacuum evaporation system to 10-11 with NaOH, stripping the condensate in a stripping tower, absorbing methanol and ammonia which are generated from stripping with water, adjusting the pH value of primary stripping solution to 2-4 with dilute sulfuric acid, catalyzing and oxidizing the primary stripping solution with Fenton reagent at 30-40 DEG C, adjusting the pH value of the catalyzed and oxidized primary stripping solution to 10-11 with dilute sulfuric acid, throwing the primary stripping solution into the stripping tower, stripping the primary stripping solution for the second time in the stripping tower, absorbing methanol and ammonia which are generated from the primary stripping solution stripping with water, and discharging secondary stripping solution.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
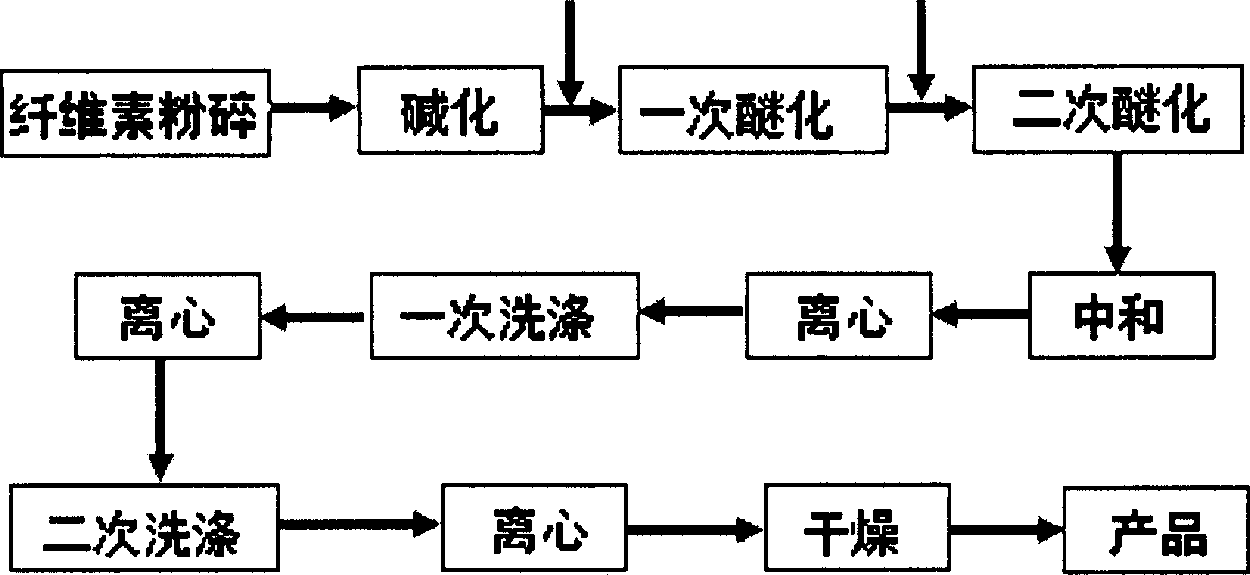
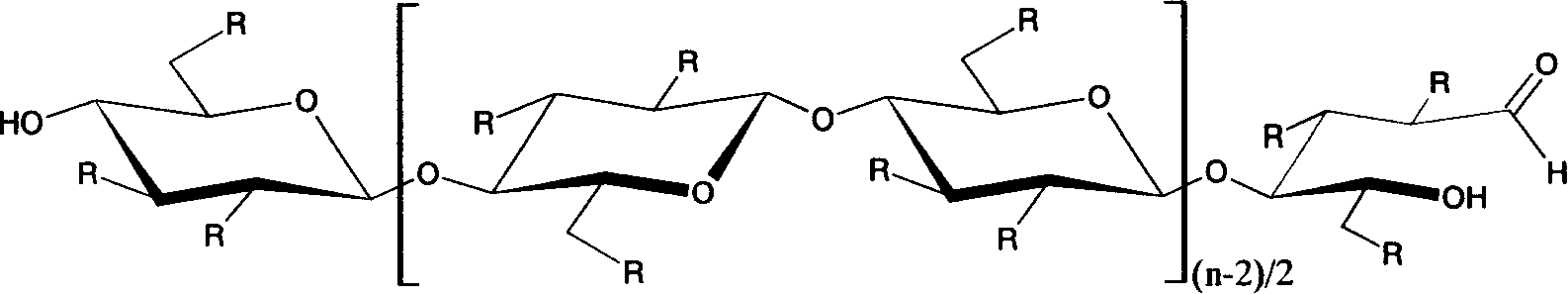
Method for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose in high degree of substitution
InactiveCN1916027AHigh degree of substitutionHigh degree of etherificationCarboxymethyl celluloseOrganic solvent
This invention provides a method for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose with ultrahigh substituent degree. The method comprises: (1) treating cotton and lignocellulose with 18-50% NaOH aqueous solution; (2) adding chloroacetate, chloroacetic acid or its sodium salt, and etherifying under stirring in an organic solvent under inert gas protection; (3) adding an alkali, heating for second etherification, neutralizing, washing and drying to obtain carboxymethyl cellulose with carboxymethyl mol substituent degree not lower than 2.0.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
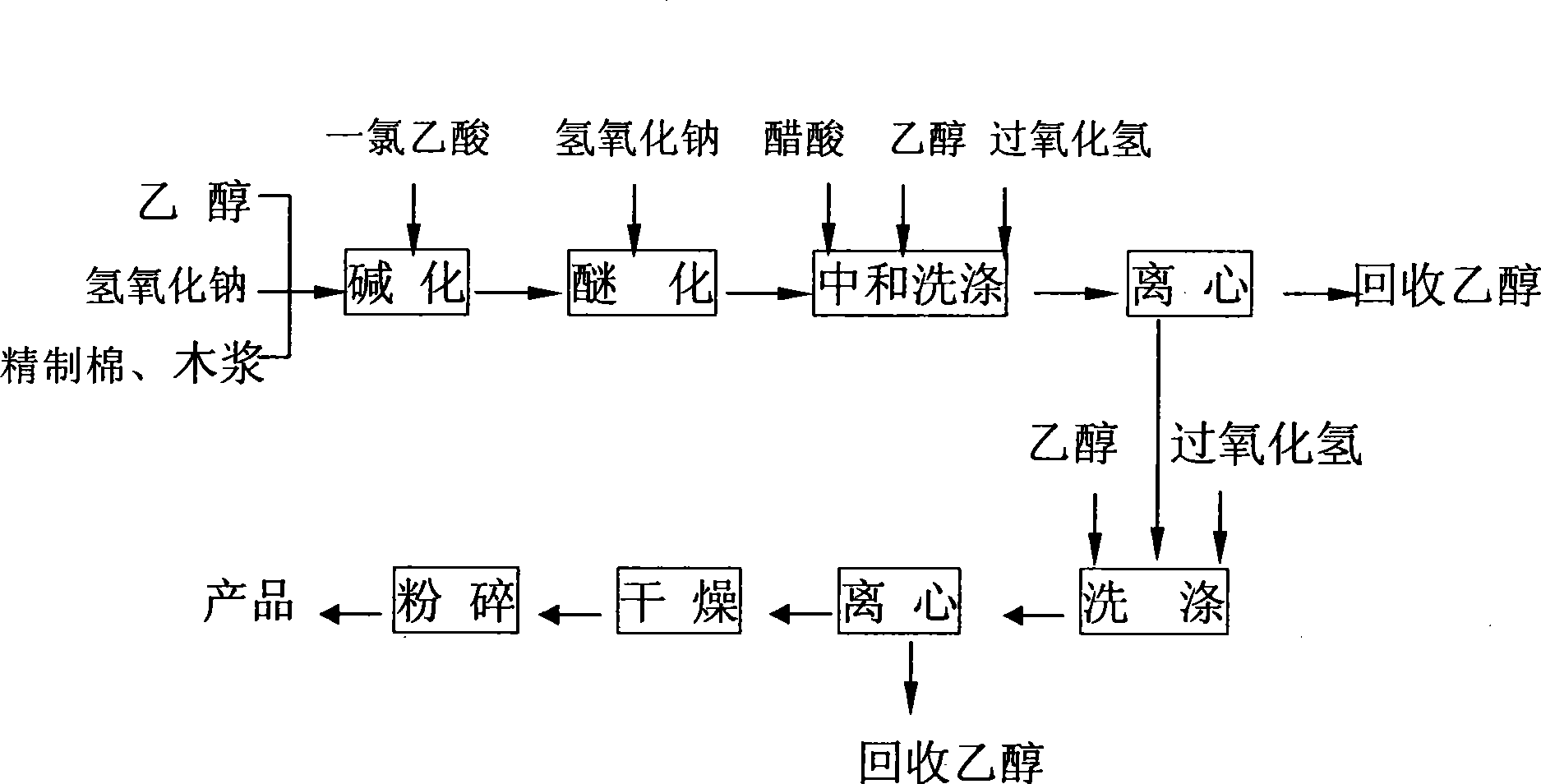
Preparation method of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for food
The present invention relates to a food sodium carboxymethylcellulose preparation method, which includes: principally adding a mixed cellulosic material composed of 100 parts of wood pulp and purified cotton with a mixing ratio of 0.25-1.5:1, ethanol solvent and sodium hydroxide aqueous solution into a kneader, performing quaternization for 50-100 minutes under the mixing condition of 20-40 EDG C, and then respectively slowly adding chloroacetic acid ethanol solution and sodium hydrate aqueous solution, and performing etherifying response for 40-100 minutes under the mixing condition of 75-80 EDG C, and then cooling down for discharging; preparing sodium carboxymethylcellulose by using acetic acid to neutralize the obtained material, and simultaneously using ethanol aqueous solution for washing twice, adding aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution once or twice at the same time of washing and the other steps. The preparation method has simple method, low-cost, high yield, convenient operation; its products have lower viscosity, low prices, and widely application in various types of food and drinks as a stabilizer of emulsion and suspension, playing a thickening role.
Owner:上海长光企业发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com