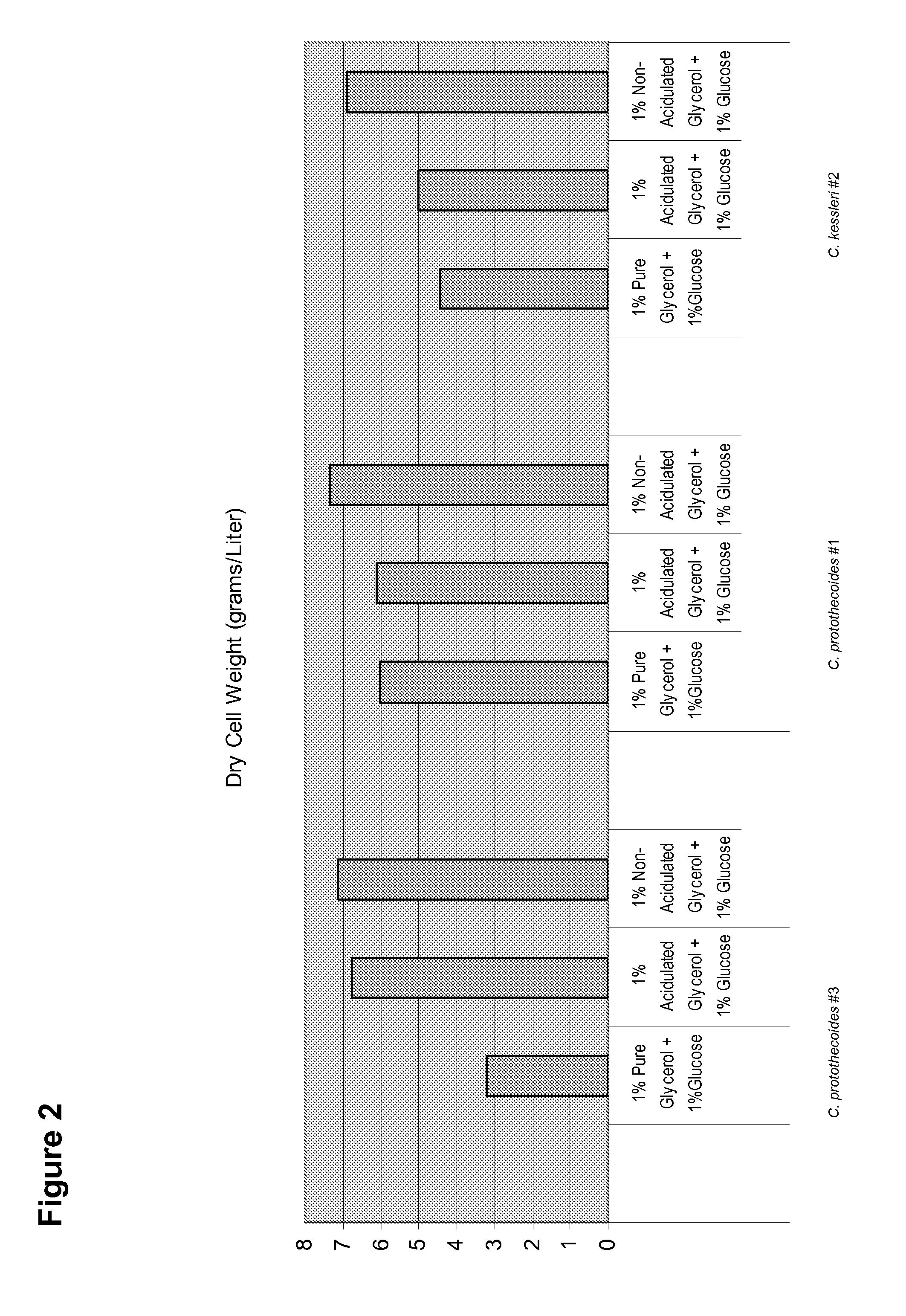
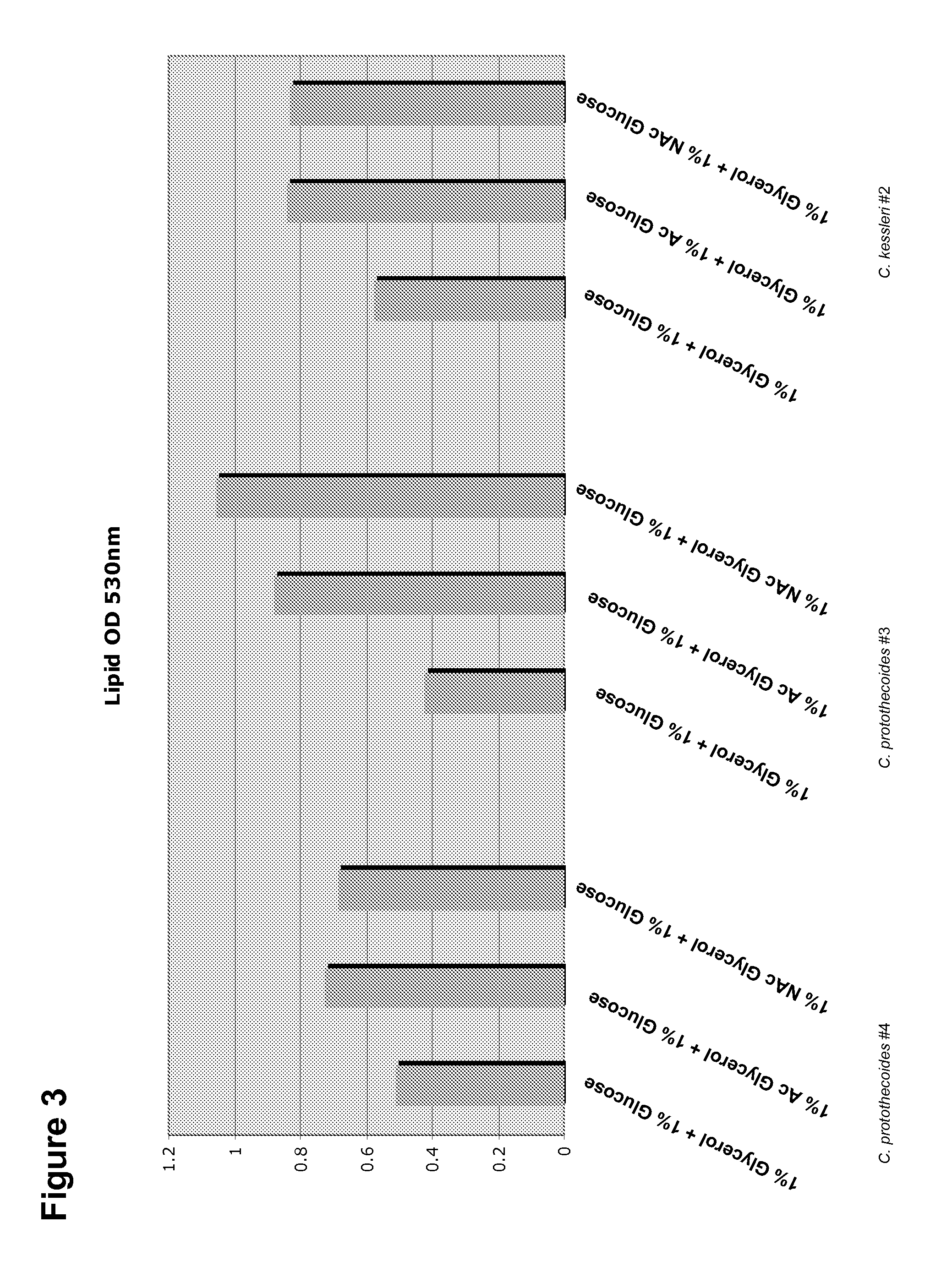
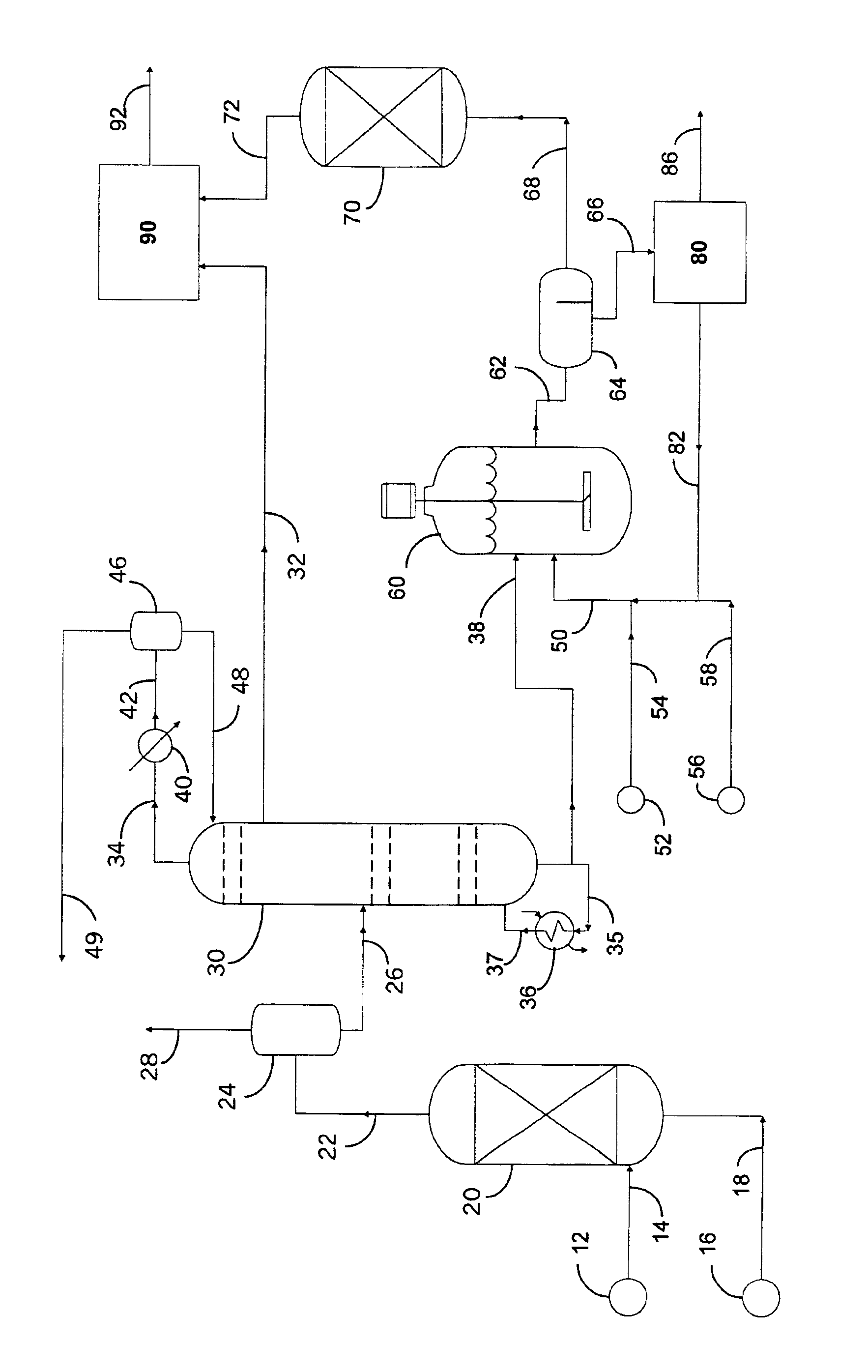
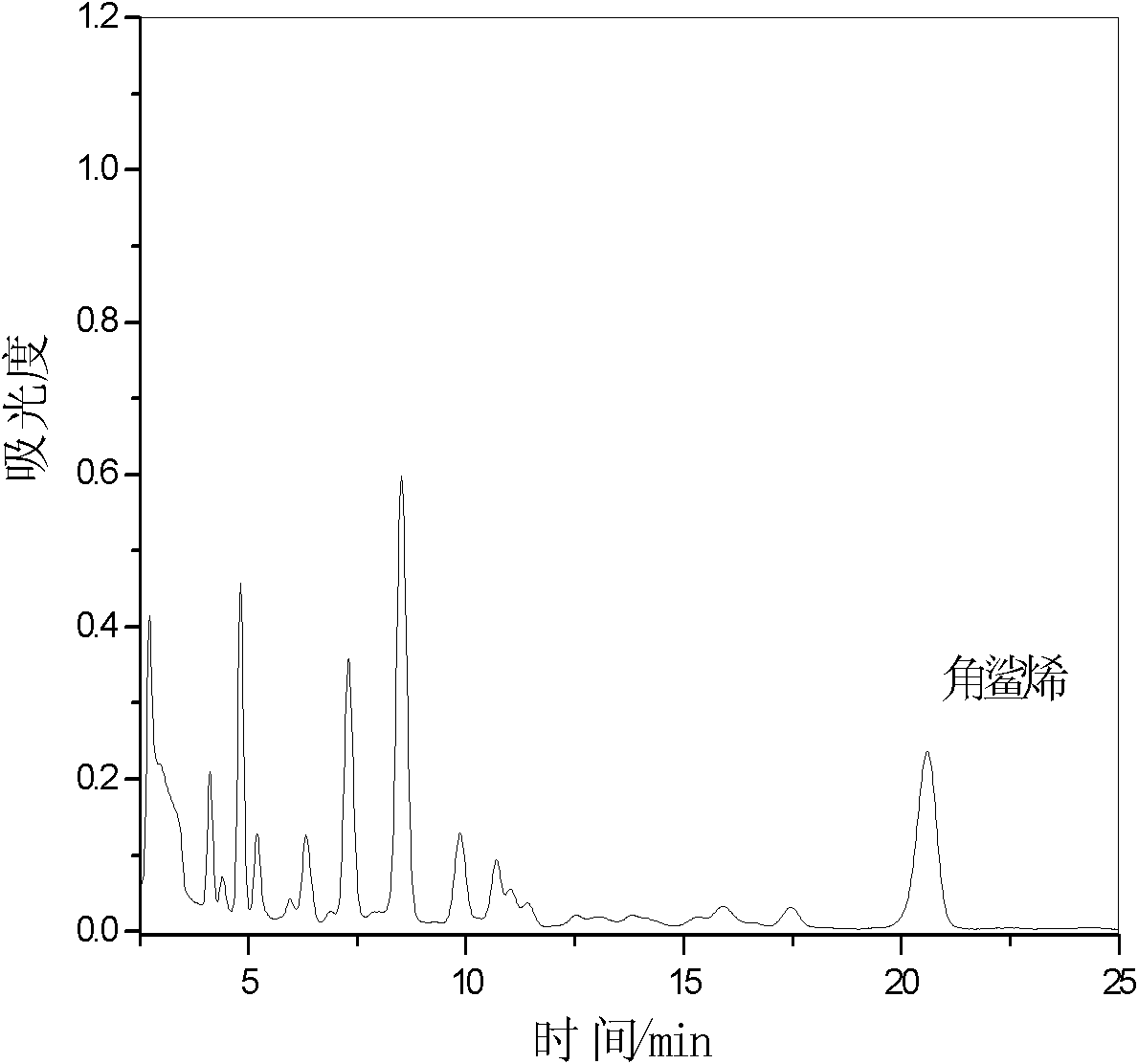
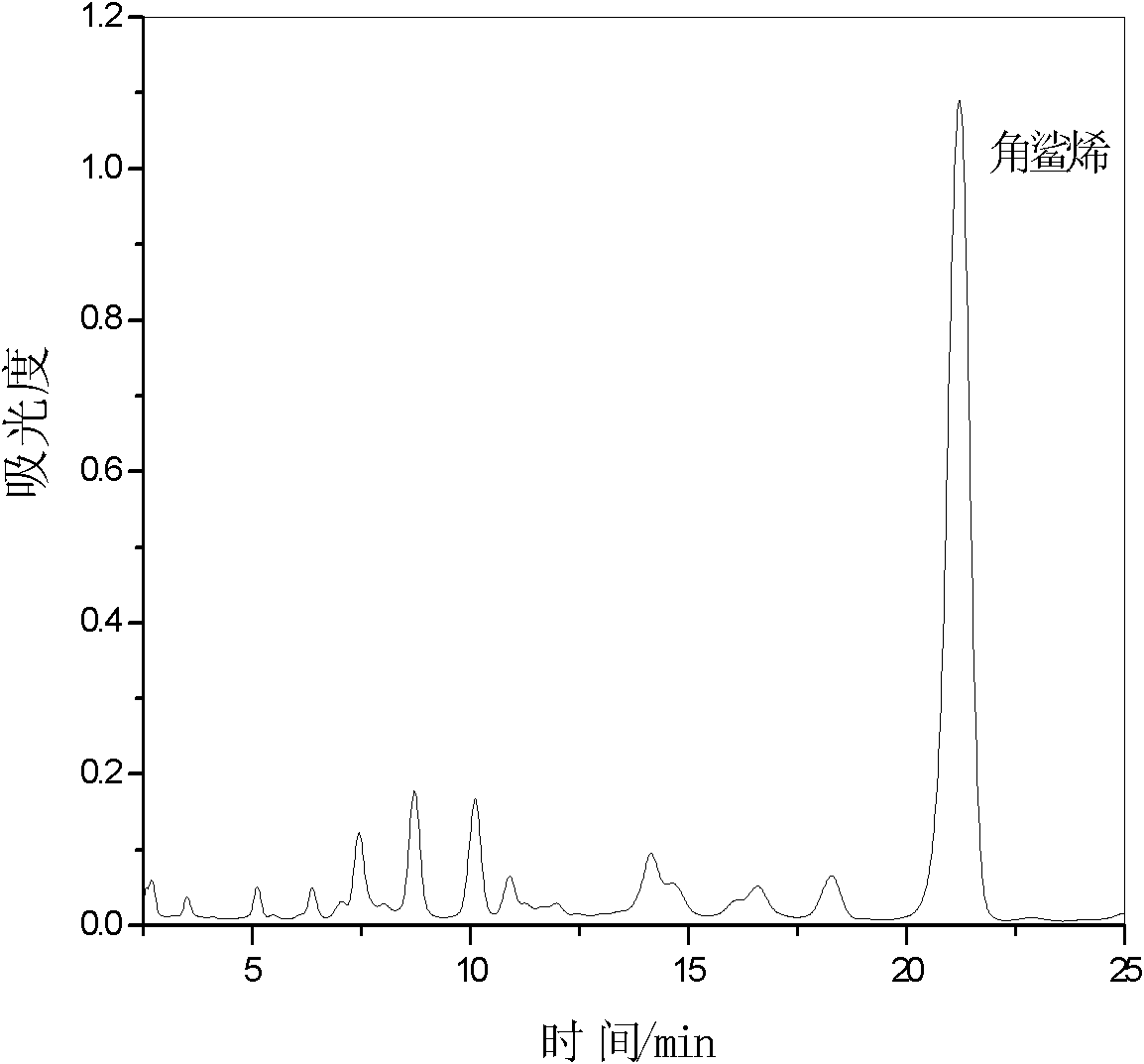
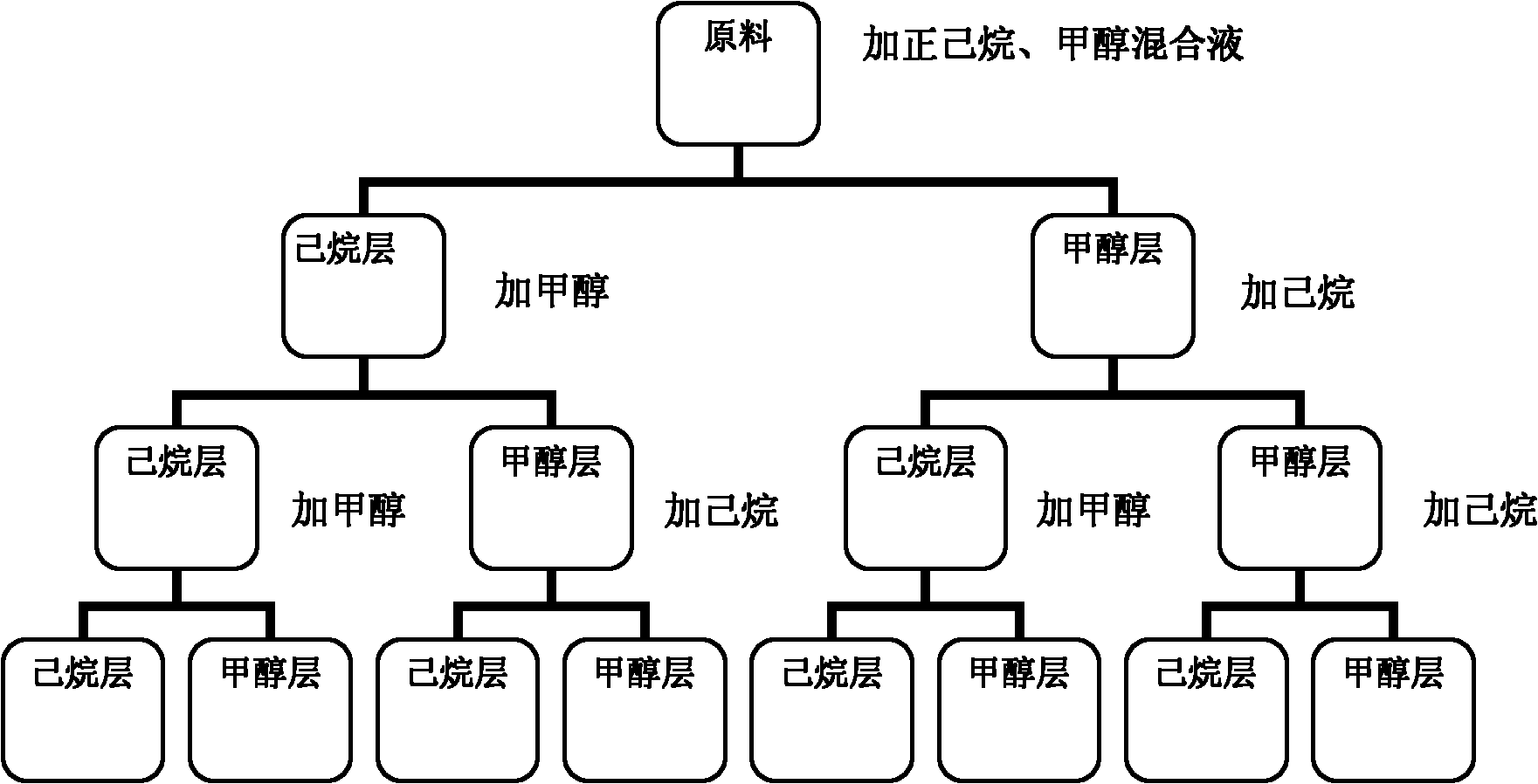
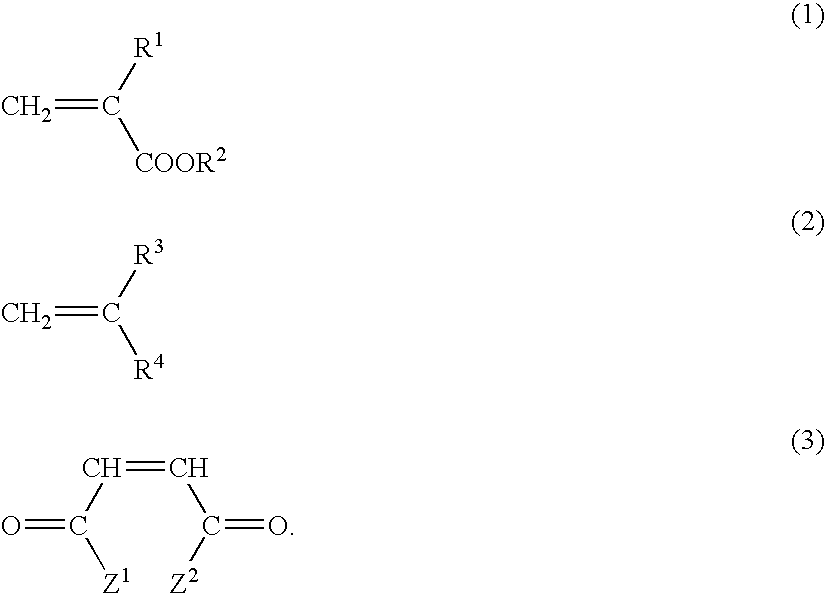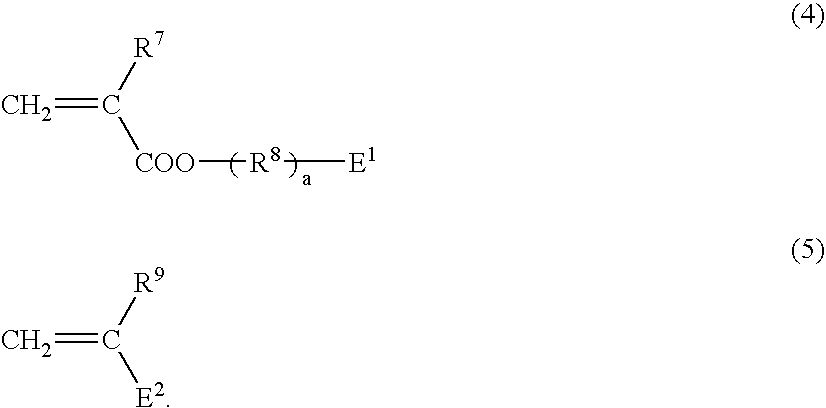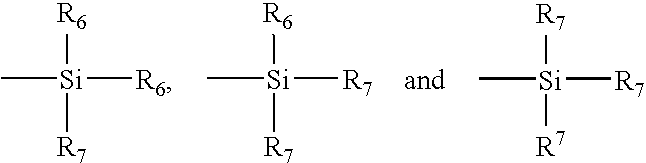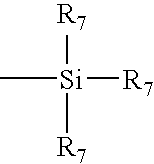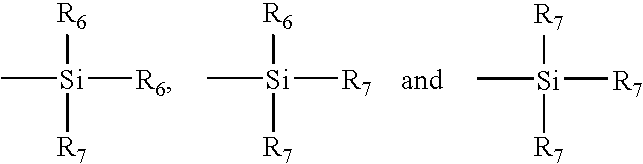Patents
Literature
3641 results about "Components of crude oil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Components of Crude Oil Crude oil is essentially a mixture of many different hydrocarbons, all of varying lengths and complexities. In order to separate the individual components that make up the raw natural resource, the crude oil must be fractionally distillated so that chemical components can be removed one at a time according the their boiling points. a) Light Distillates: i) Naphtha - Made into gasoline/petrochemicals ii) Kerosene b) Middle distillates i) Light gas oil - made into jet/diesel furnace fuels ii) Heavy gas oil - further processing to produce naphtha and other products. The components of crude oil are petrol, tar, oil, dissolved gases and kerosene also known as petroleum. c) Residue Further processed into refinery fuels, heavy fuel oil, waxes, greases, asphalts [the lighter the stuff the higher the price]
Fuel Composition
ActiveUS20080229654A1Maximize product yieldYield maximizationFatty acid isomerisationFatty acid oxidationIsomerizationVegetable oil
Compositions and methods for forming hydrocarbon products from triglycerides are disclosed. In one aspect, the methods involve the thermal decomposition of fatty acids, which can be derived from the hydrolysis of triglycerides. The thermal decomposition products can be combined with low molecular weight olefins, such as Fischer-Tropsch synthesis products, and subjected to molecular averaging reactions. Alternatively, the products can be subjected to hydrocracking reactions, isomerization reactions, and the like. The products can be isolated in the gasoline, jet and / or diesel fuel ranges. Thus, vegetable oils and / or animal fats can be converted using water, catalysts, and heat, into conventional products in the gasoline, jet and / or diesel fuel ranges. These products are virtually indistinguishable from those derived from their petroleum-based analogs, except that they can have virtually no aromatic, sulfur or nitrogen content, they are derived, in whole or in part, from renewable resources, and can also be derived from domestically available coal and / or natural gas.
Owner:BRADIN DAVID
Corn plants and products with improved oil composition
InactiveUS6248939B1Increase contentHigh oleic acid producing characteristicsMutant preparationAnimal feeding stuffChemical compositionComponents of crude oil
This invention relates to corn (Zea mays L.) seed and grain having a significantly higher oleic acid content than conventional corn by virtue of heritable genes for increased oil and oleic acid content and / or lowered levels of linoleic acid. The present invention also relates to the production of high oil, high oleic grain, its oil, its progeny and its use.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Soaps Produced from Oil-Bearing Microbial Biomass and Oils
ActiveUS20090305942A1Improve efficiencyLow costSoap detergents with organic compounding agentsBiofuelsMicroorganismMicrobial oil
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Oil suspension preparation using resin-based vegetable oil as carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101984809AGood cost advantageWide variety of sourcesBiocideFungicidesVegetable oilBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention provides an oil suspension preparation using resin-based vegetable oil as a carrier and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a pesticide preparation. The oil suspension preparation using the resin-based vegetable oil as the carrier comprises the following raw material components in percentage by mass: 1 to 50 percent of pesticide active ingredient, 1 to 10 percent of emulsifying agent, 2 to 8 percent of wetting dispersant, 0 to 5 percent of suspension stabilizer, 0 to 0.2 percent of organic silicon defoaming agent and the balance of resin-based vegetable oil. After the pesticide active ingredient, the emulsifying agent, the wetting dispersant, the suspension stabilizer, the organic silicon defoaming agent and the resin-based vegetable oil are mixed uniformly, the mixture is put into a high-speed shearing ball milling device for ball milling so as to obtain the oil suspension preparation using the resin-based vegetable oil as the carrier.
Owner:FUJIAN NUODE BIOTECH
Catalyst for cleaning up the exhaust gases of a diesel engine
InactiveUS6677264B1Reduced activityReduce componentsMolecular sieve catalystsInternal combustion piston enginesCatalytic functionComponents of crude oil
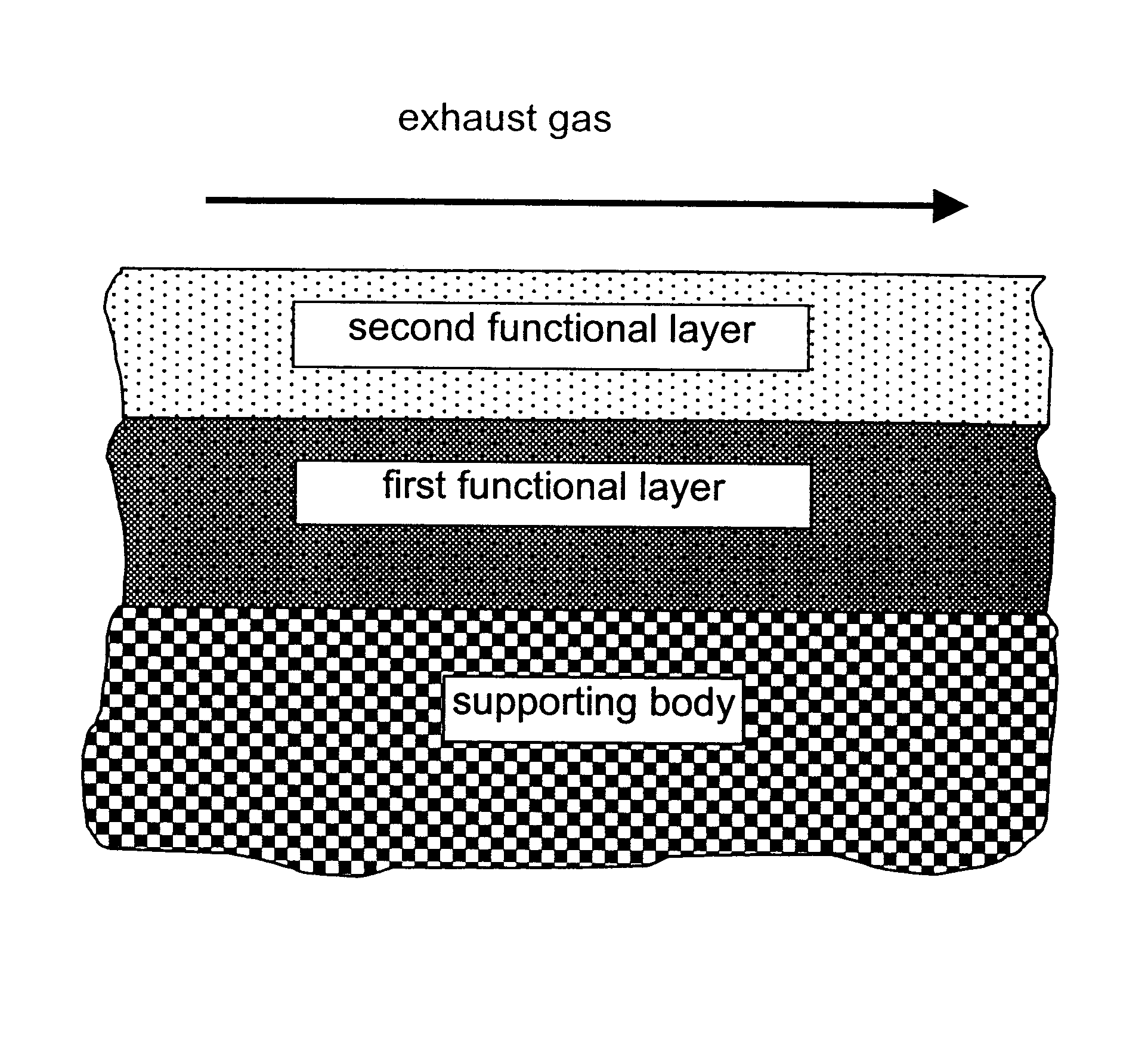
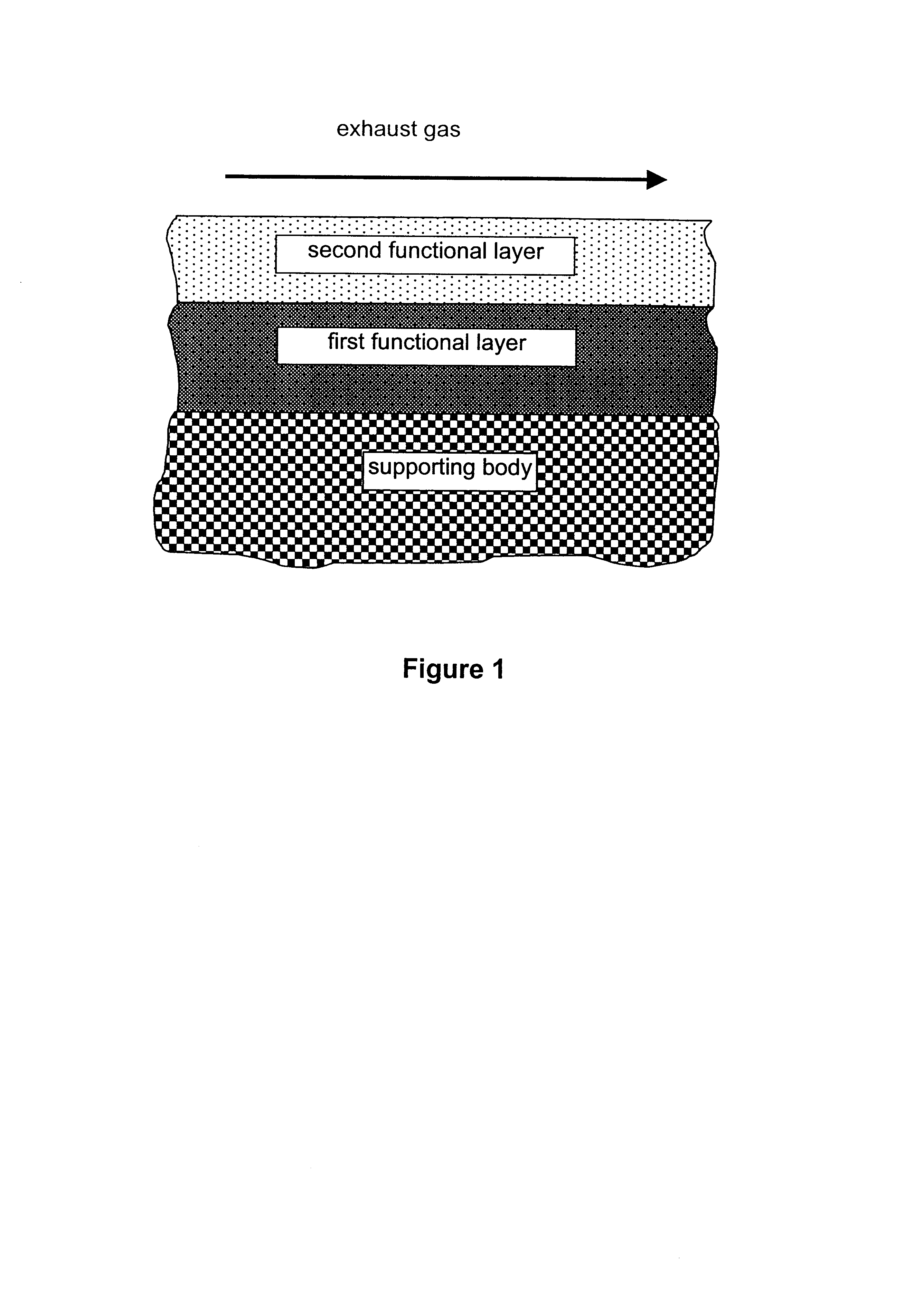
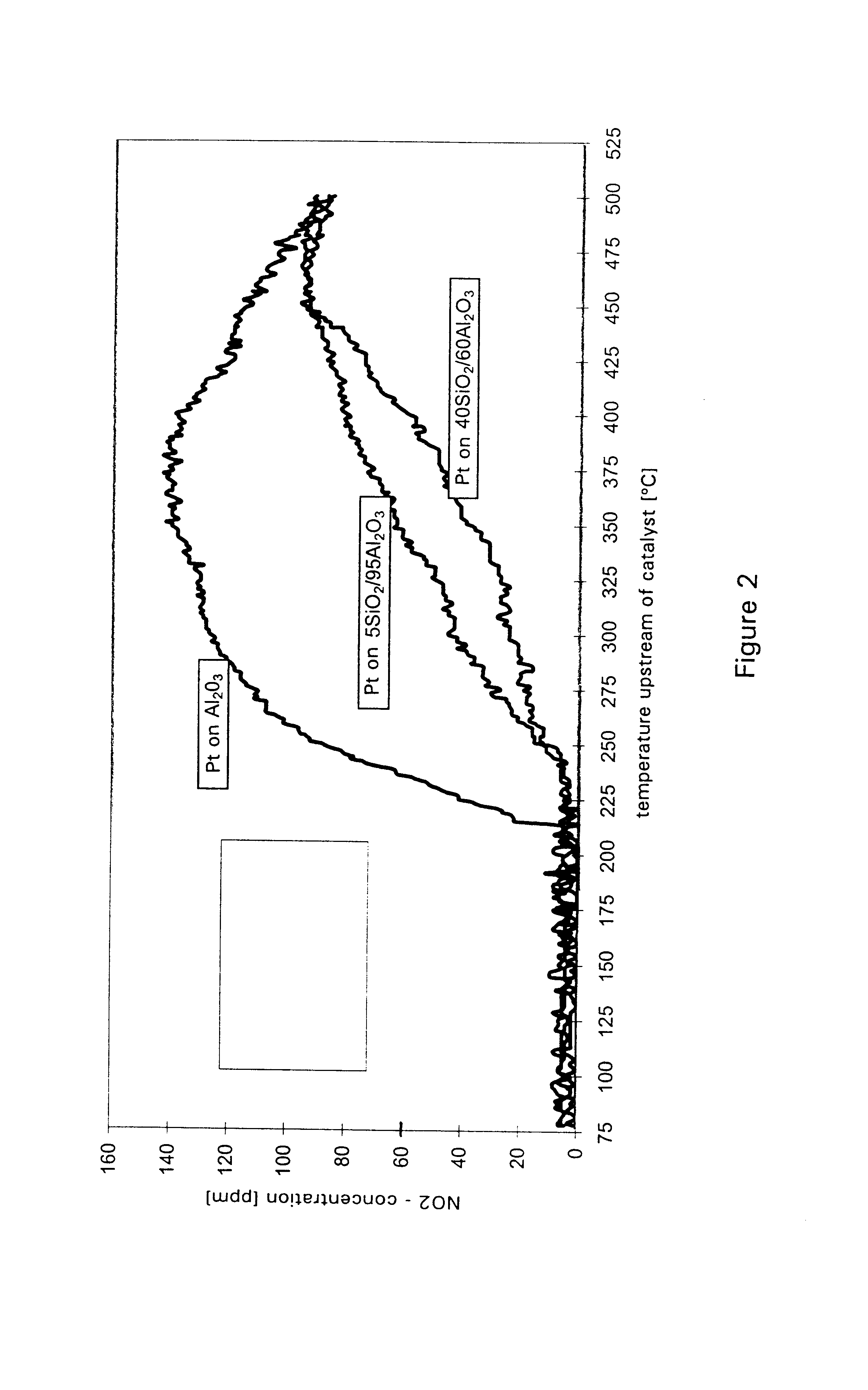
A catalyst for purifying exhaust gases of a diesel engine. The catalyst contains two functional layers superimposed on an inert supporting body, whereby the first layer, which is situated directly on the supporting body, has a nitrogen oxide storage function and the second layer, which is in direct contact with the exhaust gas, has a catalytic function. The second functional layer additionally has a hydrocarbon-storage function and its catalytic function is provided by catalytically active noble metals of the platinum group which are deposited in highly dispersed form on finely divided, acidic carrier materials. Nitrogen oxides in the oxygen-rich exhaust gas of a diesel engine can be converted with optimal utilization of the reductive constituents contained in the exhaust gas. For this purpose, no reducing agents going beyond the reductive components (carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons) which are contained as a consequence of incomplete combustion need to be added to the exhaust gas. Nevertheless, rates of conversion in respect of the nitrogen oxides are obtained, averaged over practical driving cycles, which lie distinctly above the rates of conversion of conventional reduction catalysts.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Method and apparatus for measuring the properties of petroleum fuels by distillation
InactiveUS20070050154A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityChemical property predictionMaterial thermal analysisBoiling pointDistillation
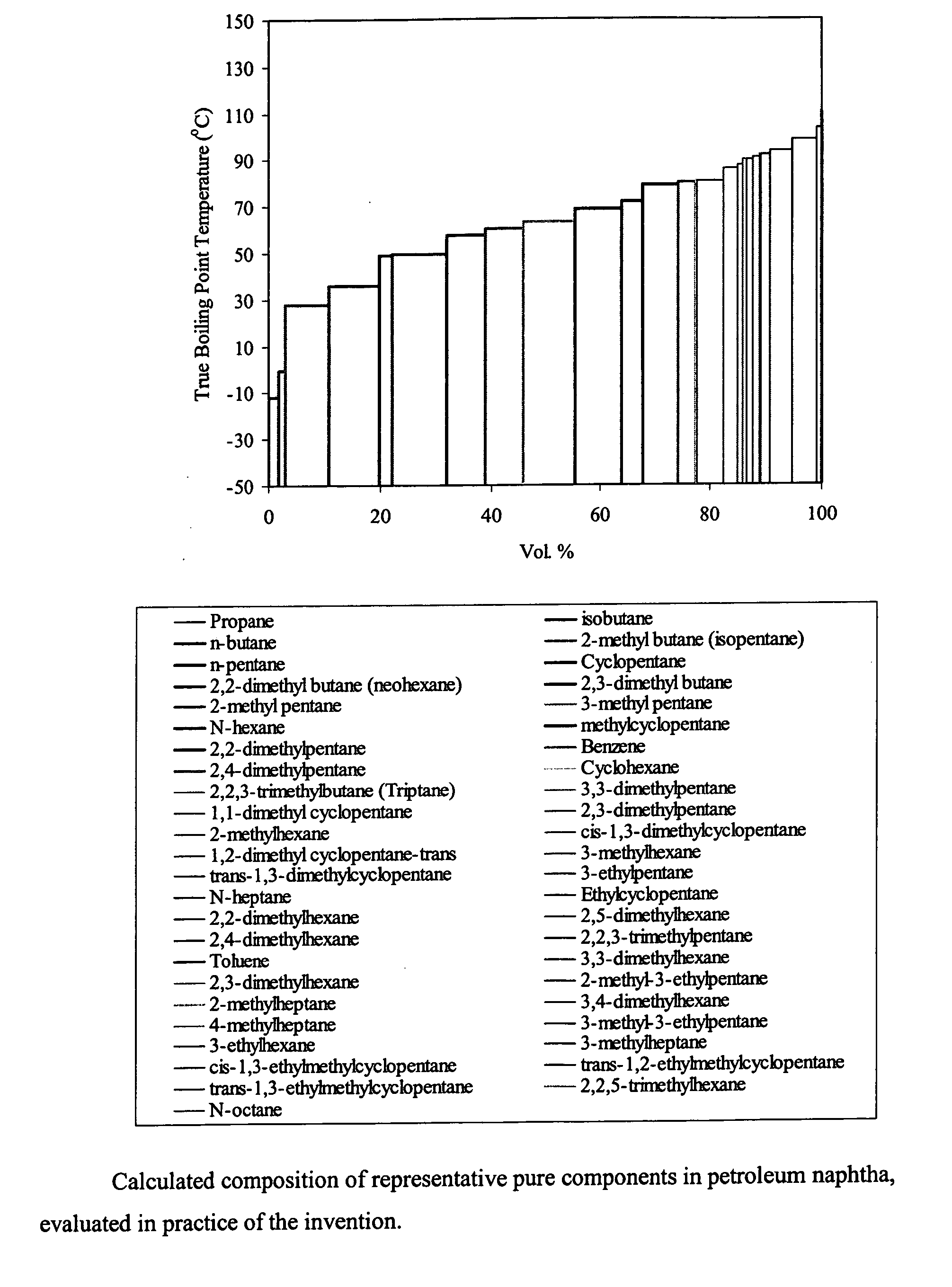
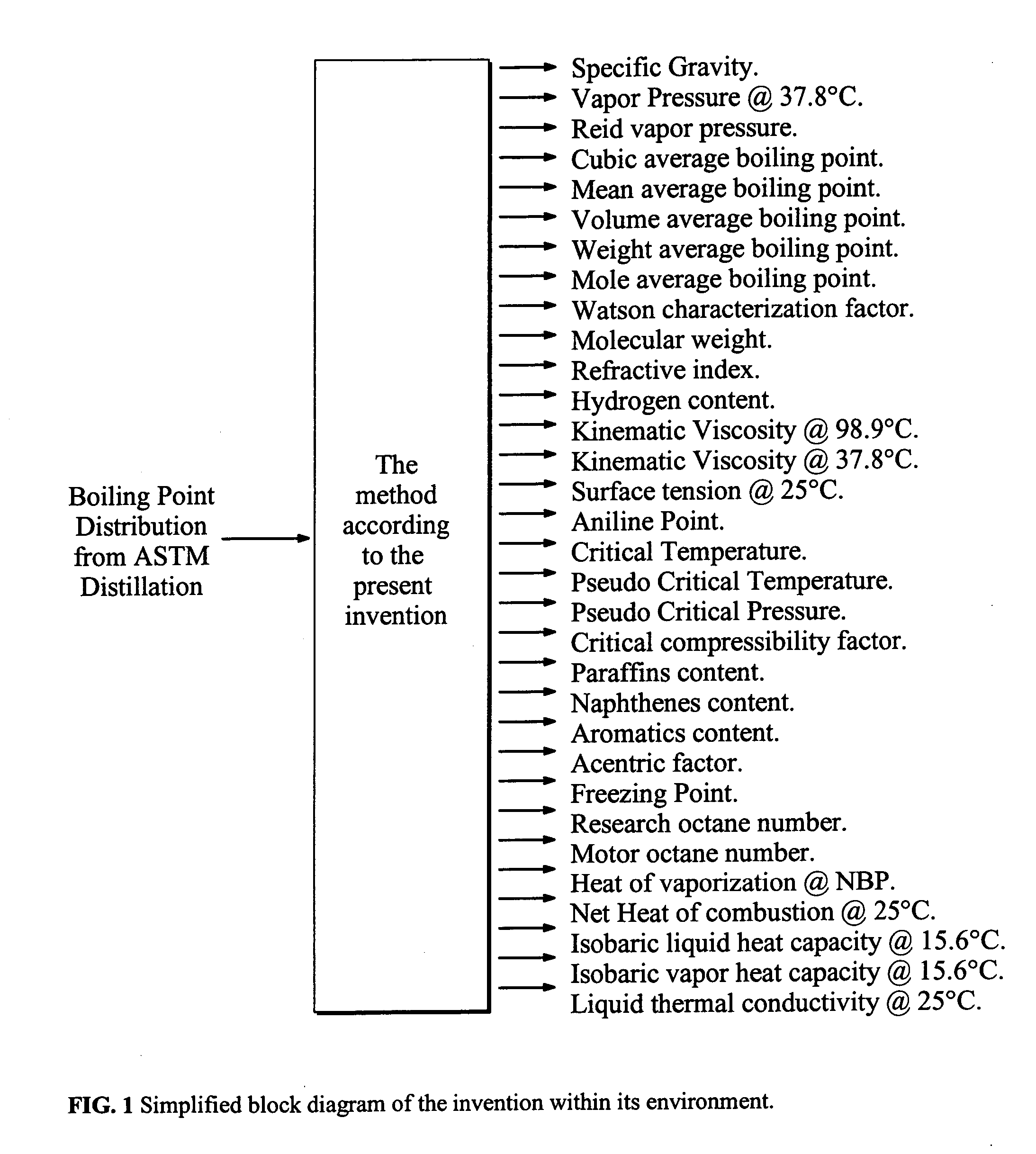
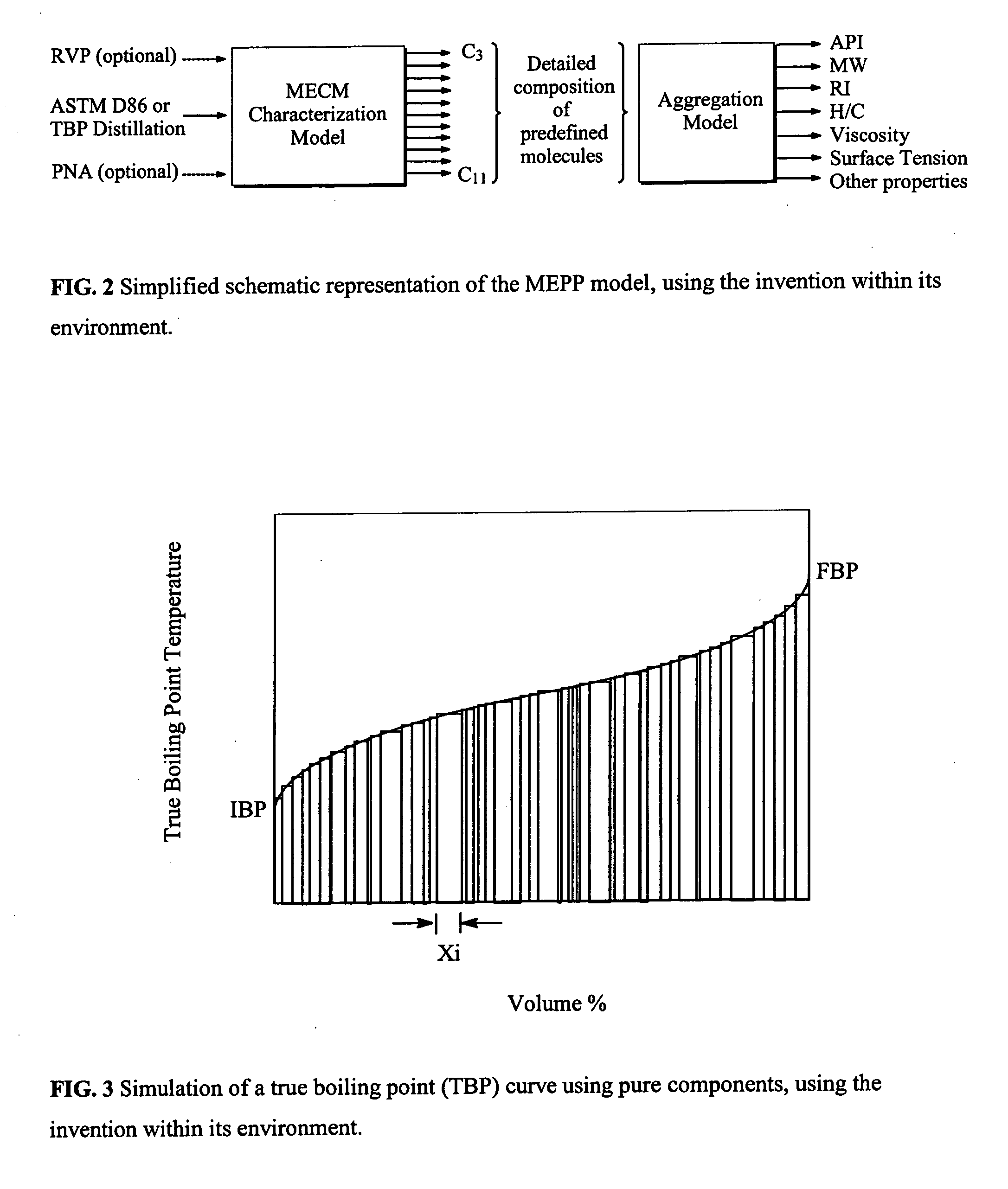
It is a purpose of this invention to accurately measure the properties of petroleum and petroleum fractions from a small volume of sample oil in a short period of time with less cost and energy for the analysis by vaporizing and distilling the respective components contained in the sample to be measured by a distillation apparatus. The components in the sample oil are first separated and vaporized by the distillation apparatus and the boiling point distribution of the respective components is measured. The property estimation means is equipped with a property estimation model for evaluating the property estimate value outputted from the property estimation model. The method is incorporated into standard or otherwise any distillation test apparatus to provide accurate measure of the thermodynamic and transport properties of undefined multicomponent mixtures such as crude oil, petroleum fractions, gas condensates and the like.
Owner:KWAIT UNIV
Heavy oil reforming method, an apparatus therefor, and gas turbine power generation system
InactiveUS20060011511A1Reduce equipment costsReduce runningThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrogenScavengerCombustor
Owner:HOKARI NOBUYUKI +4
Soaps produced from oil-bearing microbial biomass and oils
ActiveUS8119583B2Low costImprove efficiencySoap detergents with organic compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsMicrobial oilGlycerol
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Lubricating oil composition
ActiveUS20080110799A1Excellent in thermal/oxidation stabilityInhibit of acid numberLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAdditivesInternal combustion engineSoot
The present invention provide a lubricating oil composition suitable for internal combustion engines, which composition is excellent in thermal / oxidation stability and can inhibit the increases of the viscosity and acid number even in the presence of NOx and can be used for a long period of time or provide a lubricating oil composition particularly suitable for diesel or direct injection engines equipped with an exhaust-gas after-treatment device such as DPF or various catalysts, which composition is excellent in high-temperature detergency and base number retention properties and further can achieve the effect of inhibit wear caused by soot contamination in the oil occurring significantly when the content of phosphorus compounds such as ZnDTP is decreased, at a high level and can inhibit the exhaust-gas after-treatment device from being adversely affected. The lubricating oil composition comprises a lubricating base oil containing, a specific amount of a base oil with specific properties, and two or more types of additives selected from specific additives.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
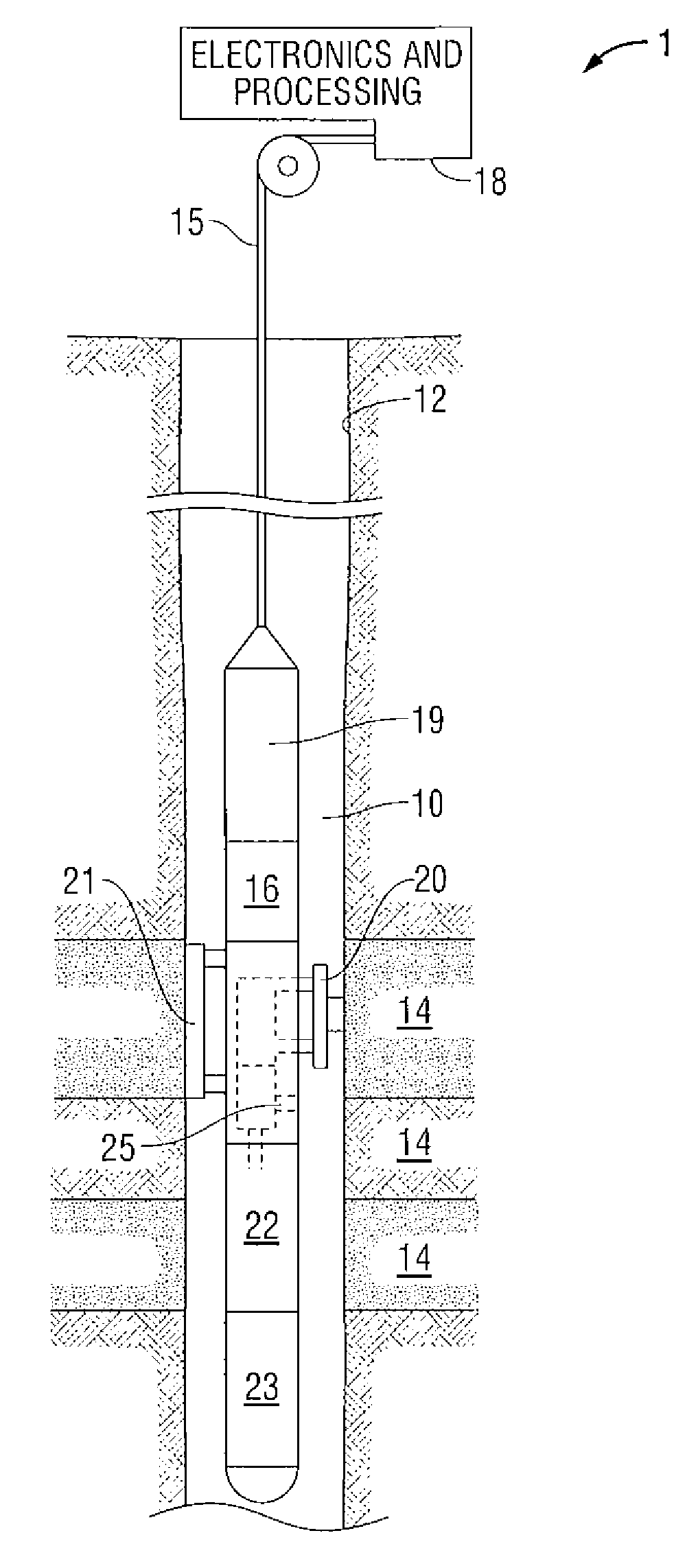
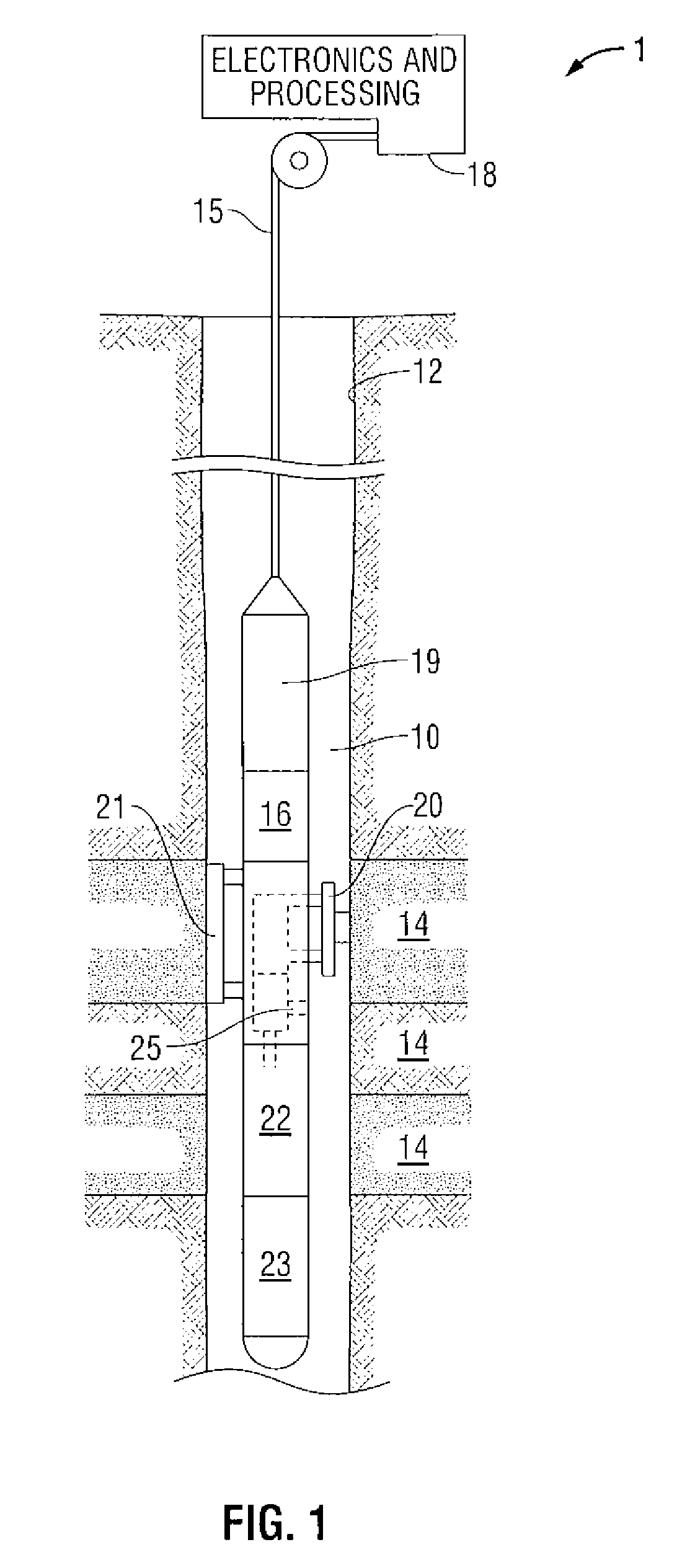
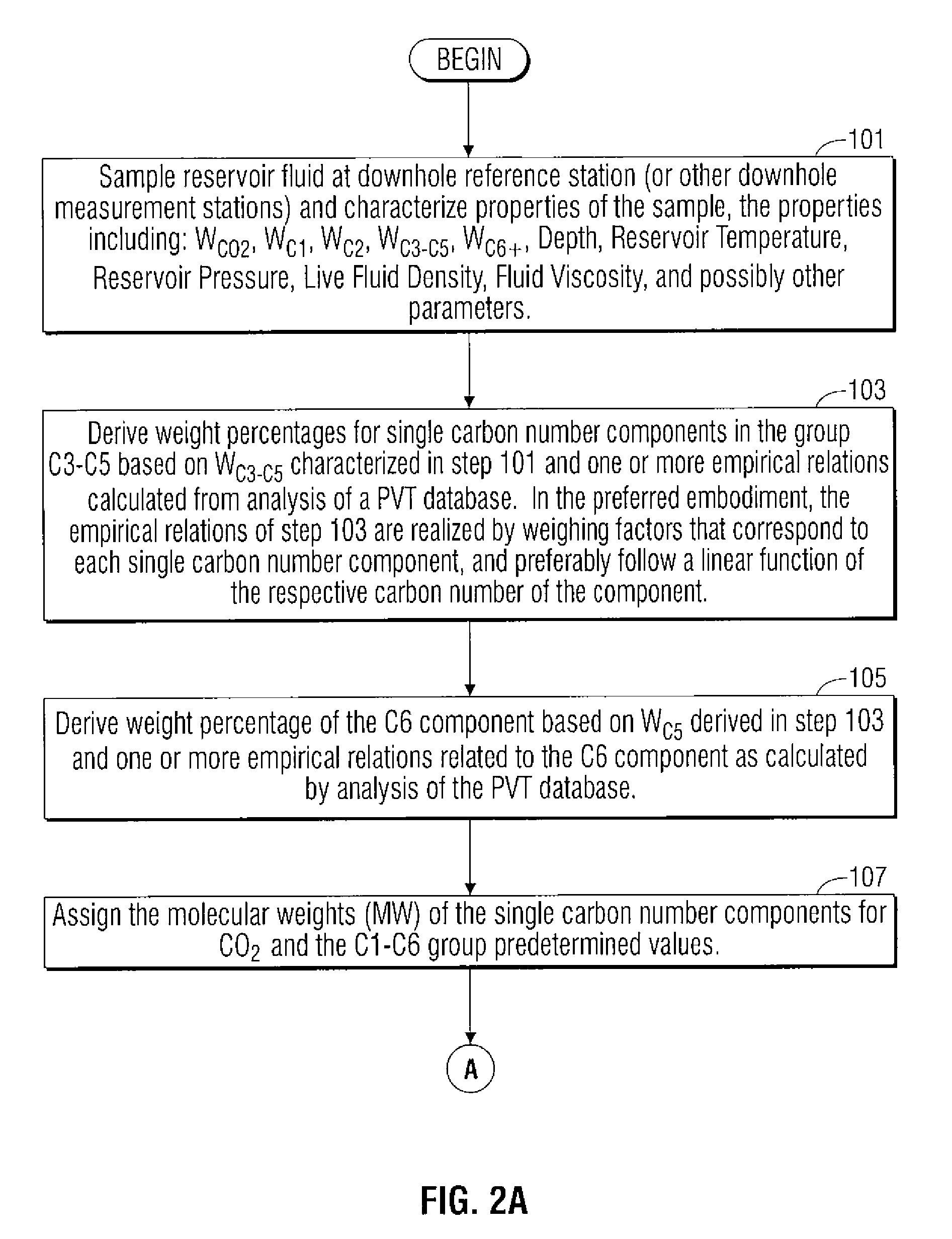
Methods and apparatus for characterization of petroleum fluid and applications thereof
ActiveUS20090192768A1Accurately reflectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationSoil sciencePetroleum
An improved method and system for characterizing the compositional components of a hydrocarbon reservoir of interest and analyzing fluid properties of the reservoir of interest based upon its compositional components.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Pneumatic tire having a component containing low PCA oil
There is disclosed a pneumatic tire having a component comprising a vulcanizable rubber composition comprising, based on 100 parts by weight of elastomer (phr), from about 40 to about 90 phr of a solution polymerized styrene-butadiene having a styrene content of greater than 38 percent by weight; from about 10 to about 60 phr of at least one additional elastomer; and from about 10 to about 70 phr of a process oil having a glass transition temperature of from about −80° C. to about −40° C. and a polycyclic aromatic content of less than 3 percent by weight as determined by the IP346 method.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Process for Preparing Butadiene by Oxidative Dehydrogenation of N-Butenes with Monitoring of the Peroxide Content During Work-Up of the Product
InactiveUS20140200381A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationWater vaporDesorption
The invention relates to a process for preparing butadiene from n-butenes, which comprises the following steps:A) provision of a feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes;B) introduction of the feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes and an oxygen-comprising gas into at least one dehydrogenation zone and oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butenes to butadiene, giving a product gas stream b comprising butadiene, unreacted n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;C) cooling and compression of the product gas stream b in at least one cooling stage and at least one compression stage, with the product gas stream b being brought into contact with a circulated coolant to give at least one condensate stream c1 comprising water and a gas stream c2 comprising butadiene, n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;D) separation of incondensable and low-boiling gas constituents comprising oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases as gas stream d2 from the gas stream c2 by absorption of the C4-hydrocarbons comprising butadiene and n-butenes in a circulated absorption medium, giving an absorption medium stream loaded with C4-hydrocarbons and the gas stream d2, and subsequent desorption of the C4-hydrocarbons from the loaded absorption medium stream to give a C4 product gas stream d1;E) separation of the C4 product stream d1 by extractive distillation using a solvent which is selective for butadiene into a stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent and a stream e2 comprising n-butenes;F) distillation of the stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent to give a stream f1 consisting essentially of the selective solvent and a stream f2 comprising butadiene;where samples are taken from the circulated coolant in step C) and / or the circulated absorption medium in step D) and the peroxide content of the samples taken is determined by means of iodometry, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) or microcalorimetry.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for preparing vegetable oil fractions rich in non-tocolic, high-melting, unsaponifiable matter
InactiveUS7288278B2Fatty acid hydrogenationEdible oils/fats ingredientsHigh concentrationVegetable oil
A vegetable oil fraction rich in non-tocolic, high-melting, unsaponifiable matter is prepared by the following steps: A vegetable oil having a slip melting point of not more thatn 30° C. and a content of unsaponifiable matter of at least 0.5% by weight is hydrogenated to fully saturate the fatty acids of the glycerides and to reach a slip melting point of at least 57° C. To the hydrogenated oil is added from 1 to 75% by weight of the unhydrogenated starting oil or another oil having a slip melting point of not more than 30° C. in order to act as a carrier and vehicle for the unsaponifiable matter. Then, a solvent is added to the oil mixture in a ratio between oil and solvent from 1:2 to 1:20, and the mixture is heated to transparency. The oil / -solvent-mixture is cooled in one or more steps to a final temperature in the range from −35 to +30° C., and the precipitated high-melting fraction(s) is (are) filtered off. The filtrate is desolventised, leaving a fraction rich in unsaponifiable matter. By this process very high concentrations of in particular the non-tocolic, higher melting unsaponifiables can be achieved, and the composition of the glyceridic part of the enriched fraction can betailored to specific applications. Also, a novel blood cholesterol-lowering effect of the unsaponifiable constituents from shea butter has been found.
Owner:AAK DENMARK
Plant and process for removing carbon dioxide from gas streams
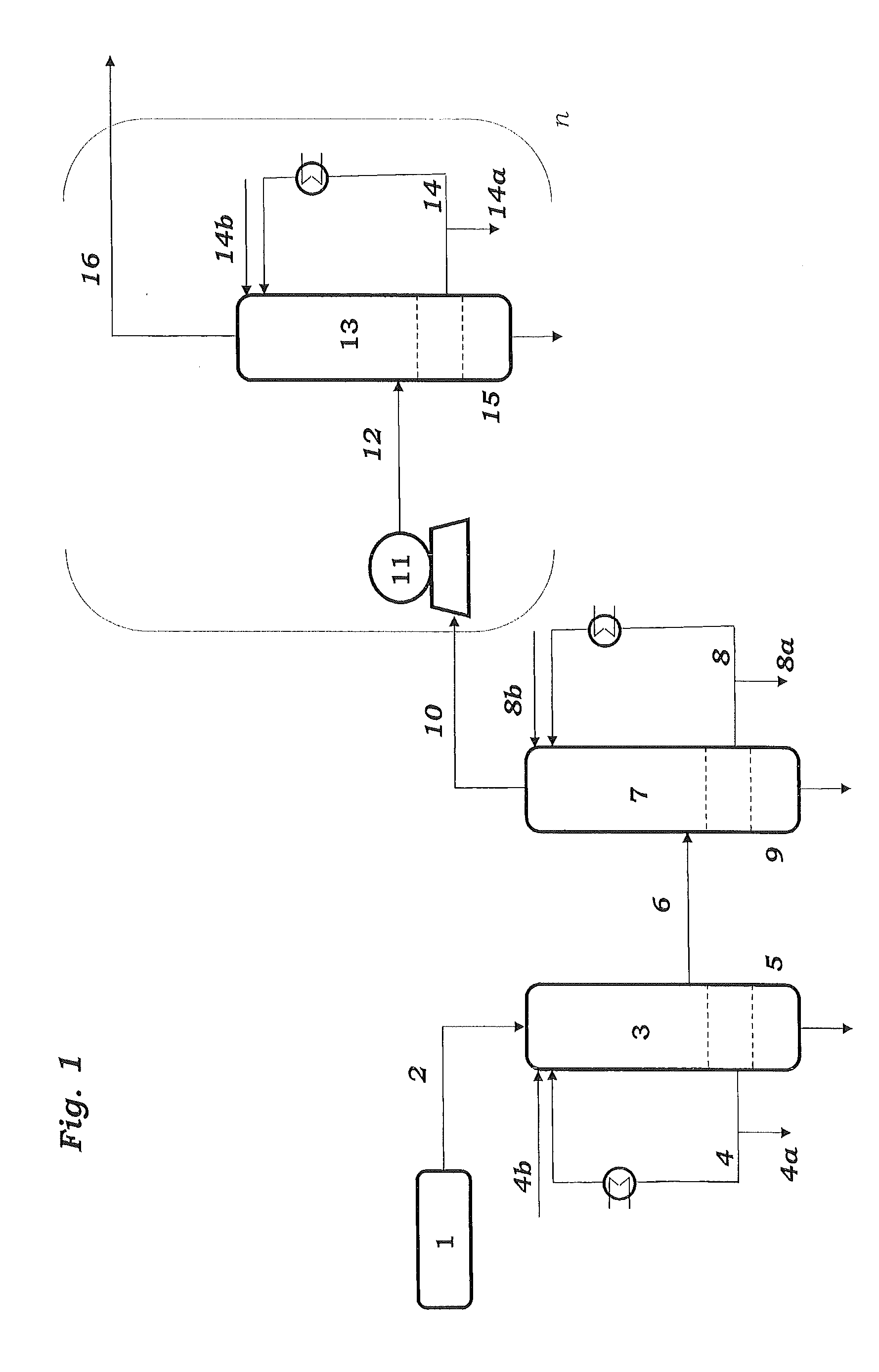
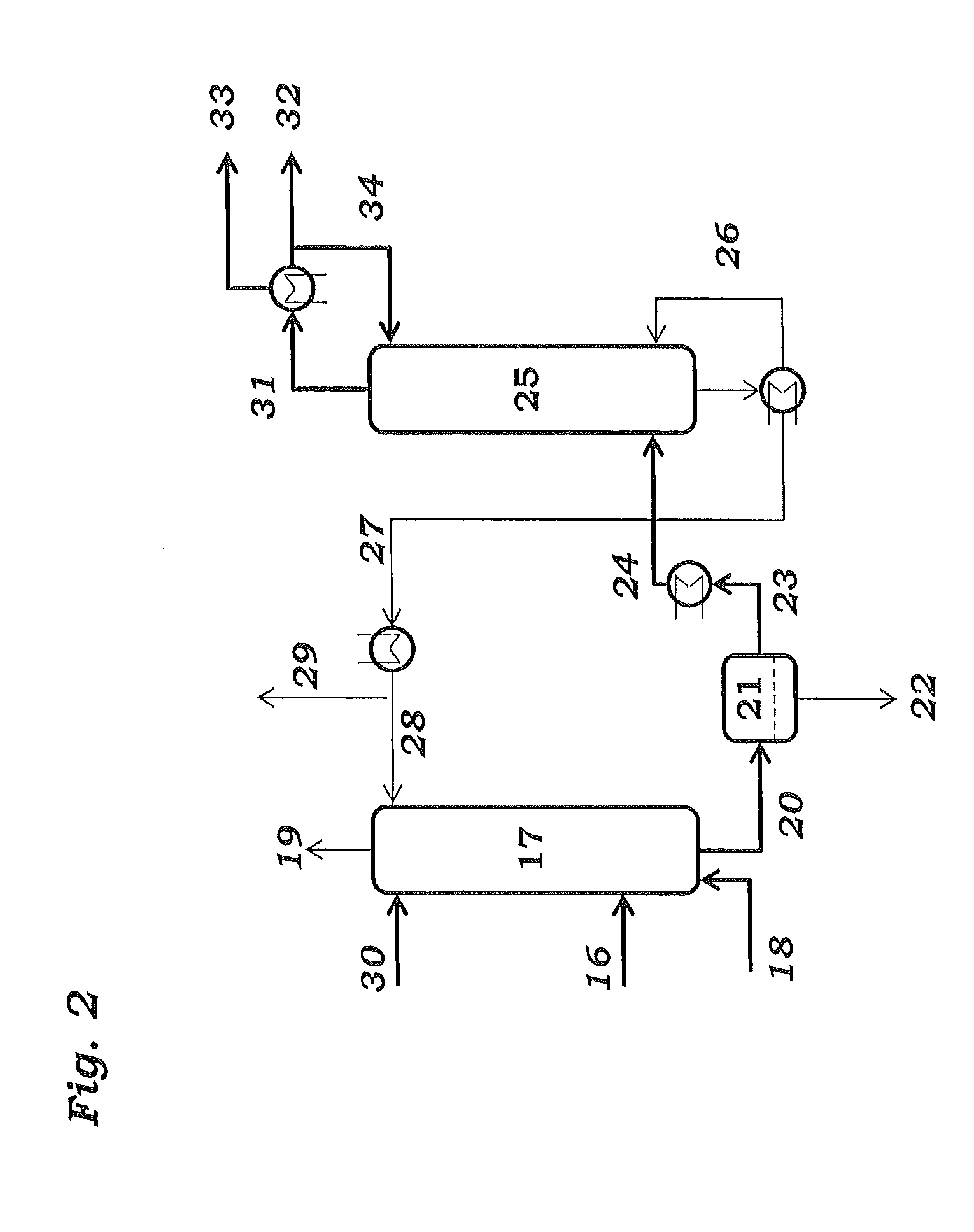
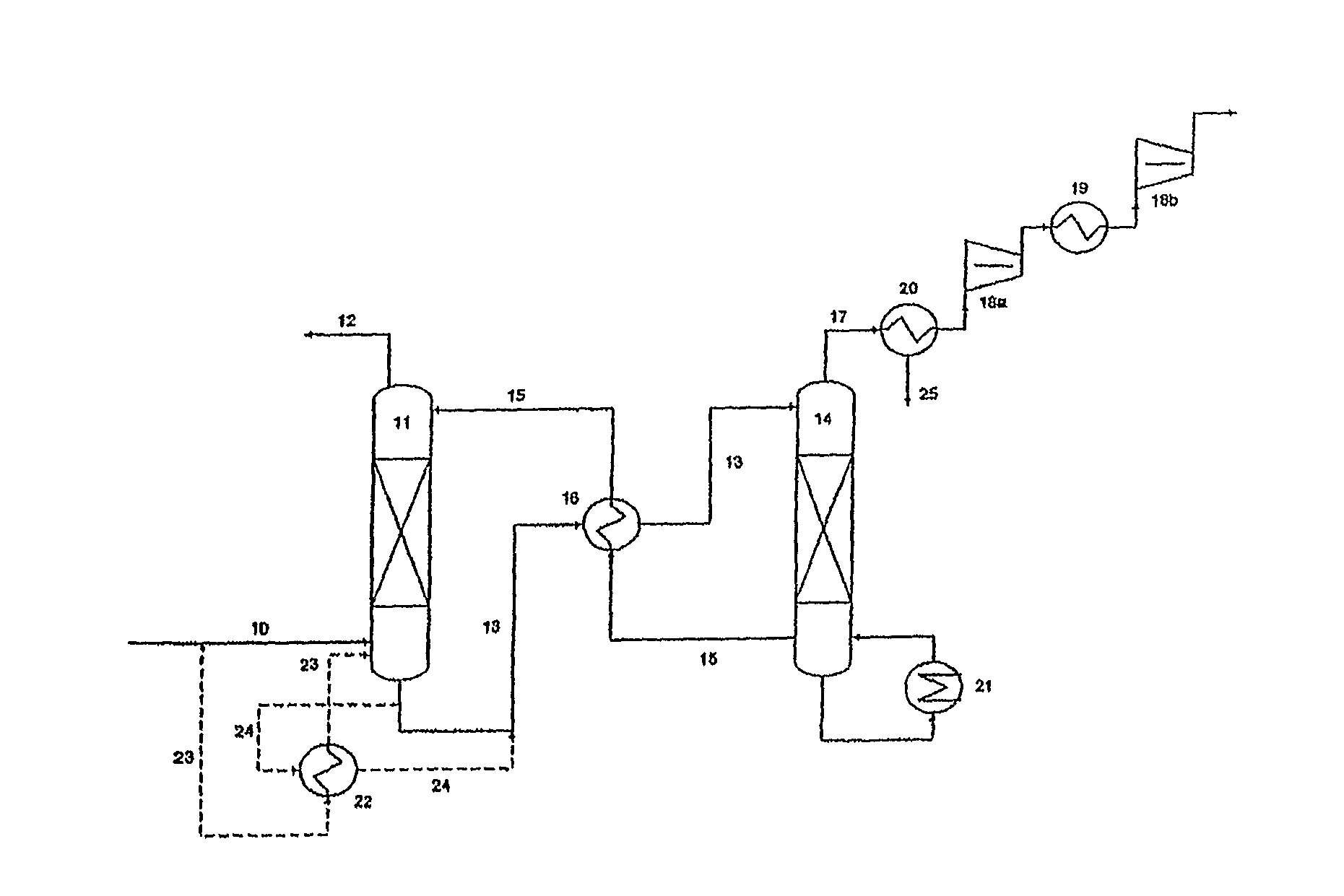
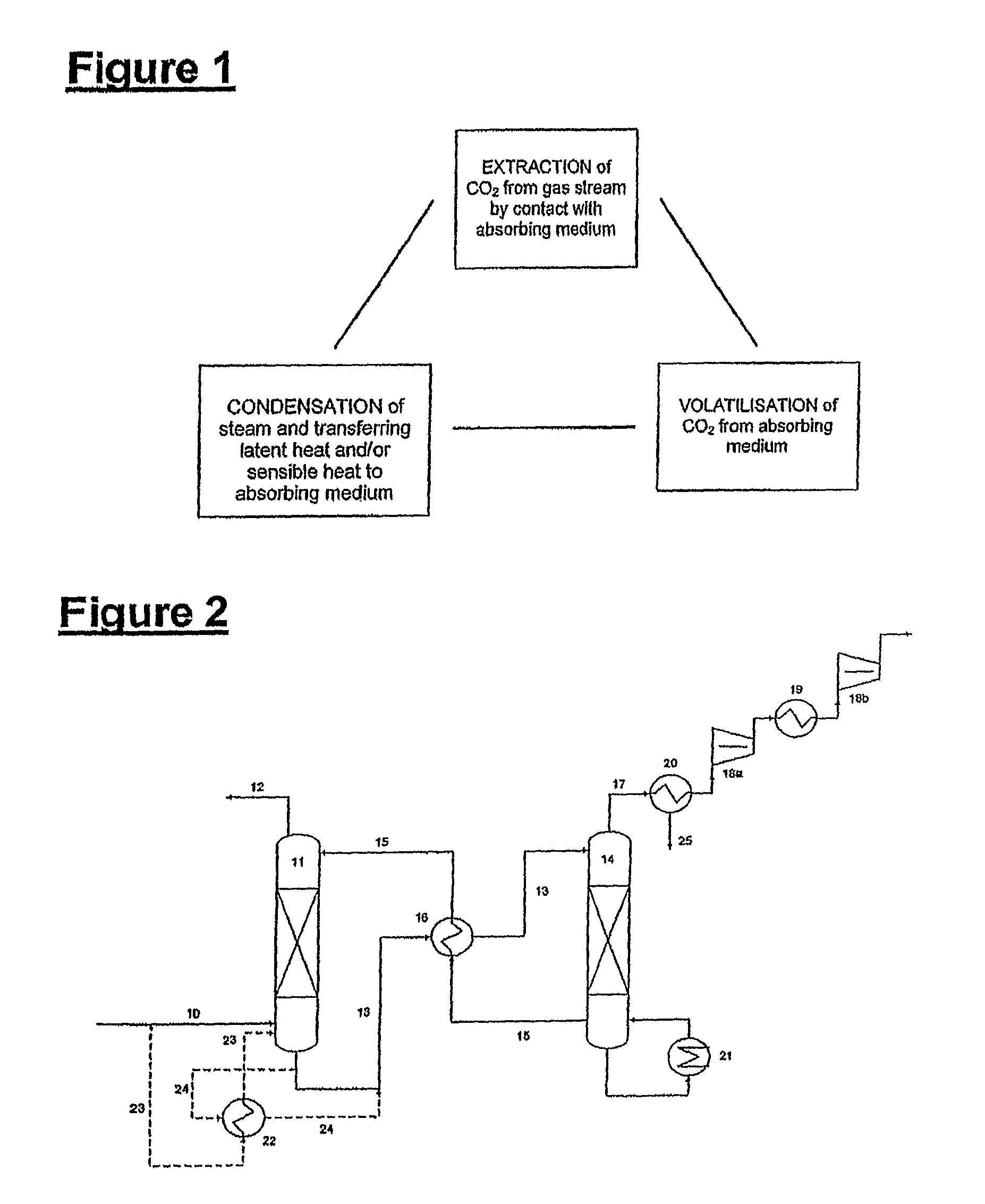
ActiveUS7976803B2Minimizing overall energy requiredAssist in volatilizationFluidized bed combustionIndirect heat exchangersComponents of crude oilCoal
Owner:KC8 CAPTURE TECH LTD
Treatment of spent caustic refinery effluents
InactiveUS7214290B2Avoid spreadingDrying using combination processesLiquid degasificationLiquid wasteCombustion
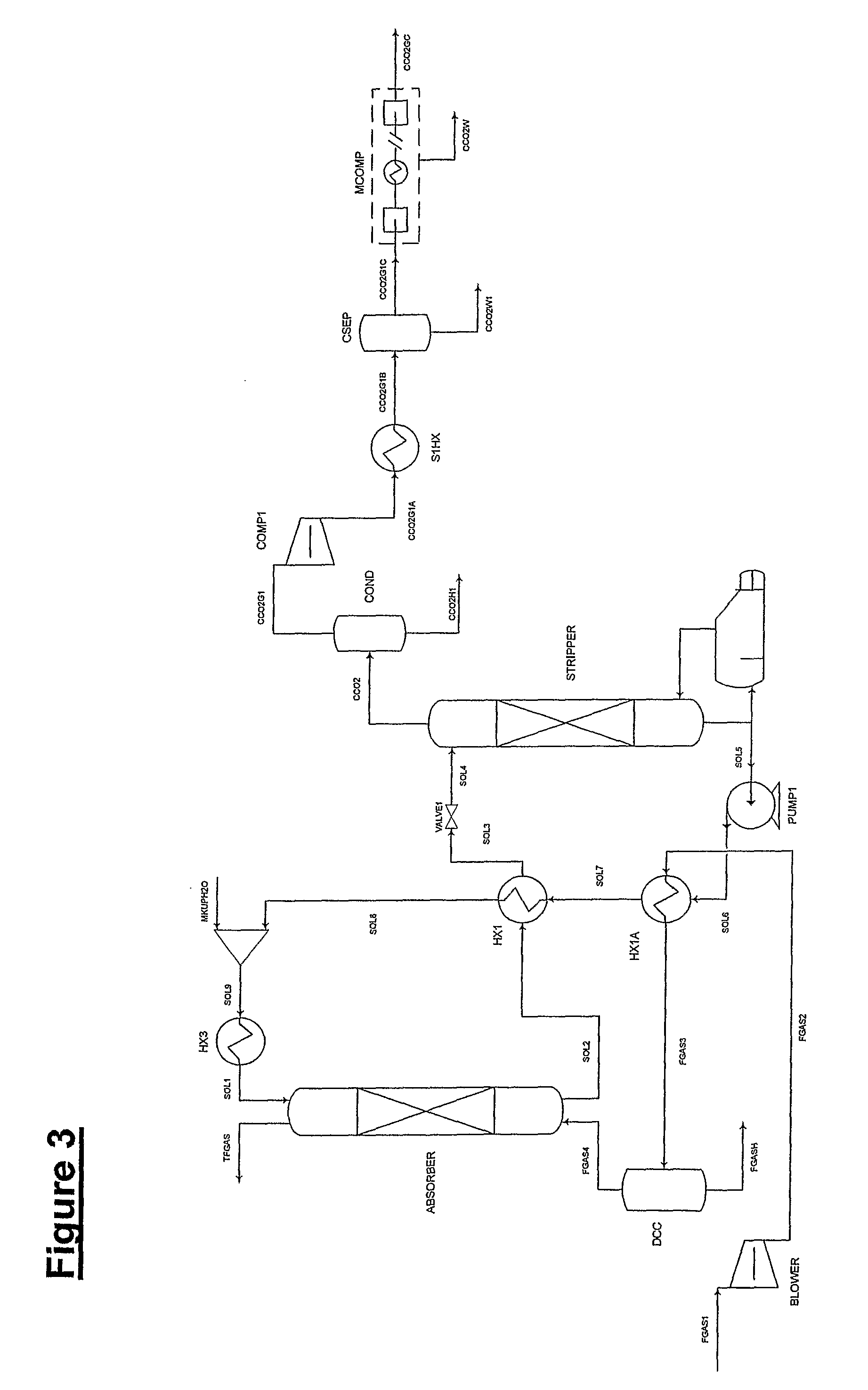
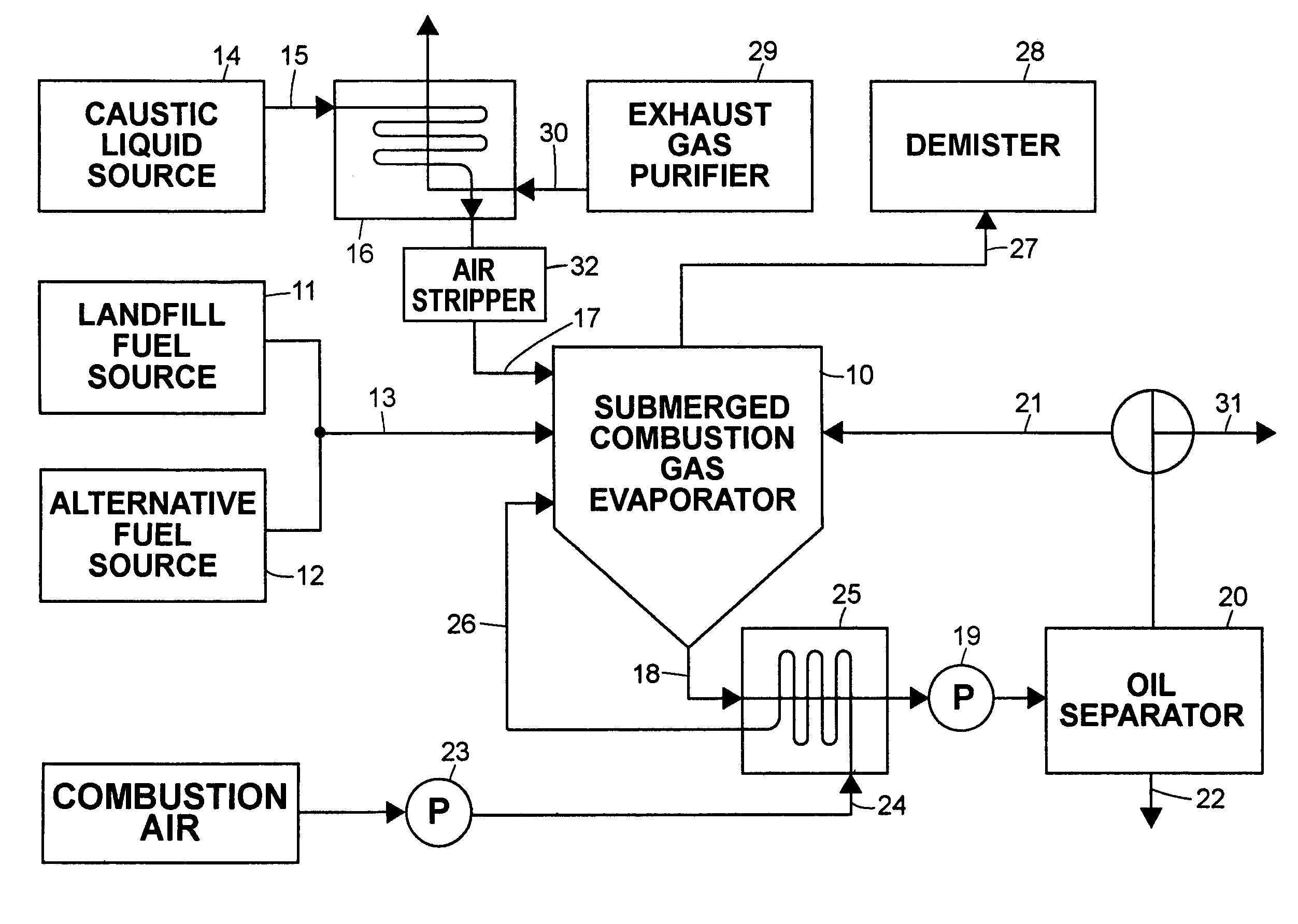
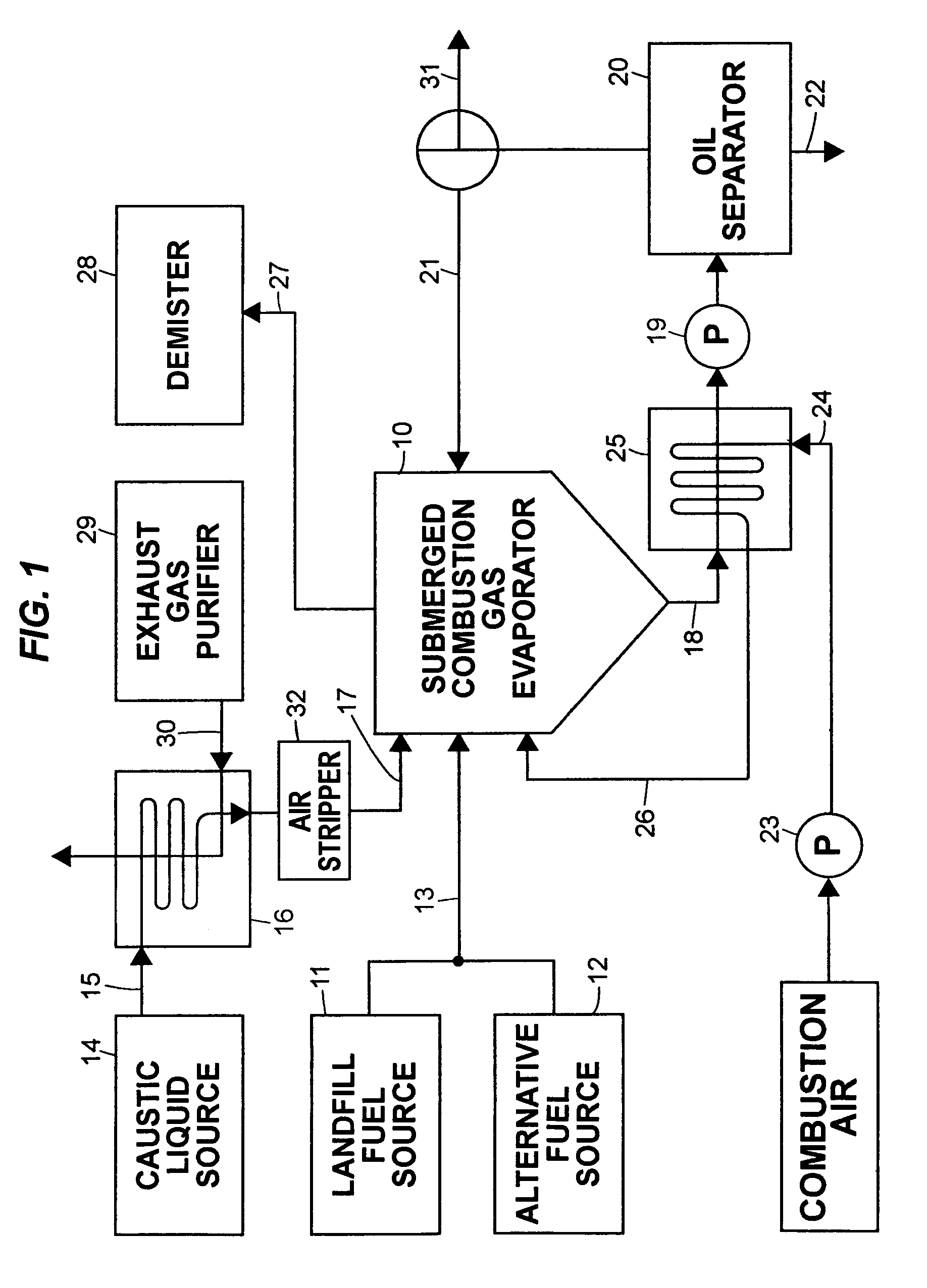
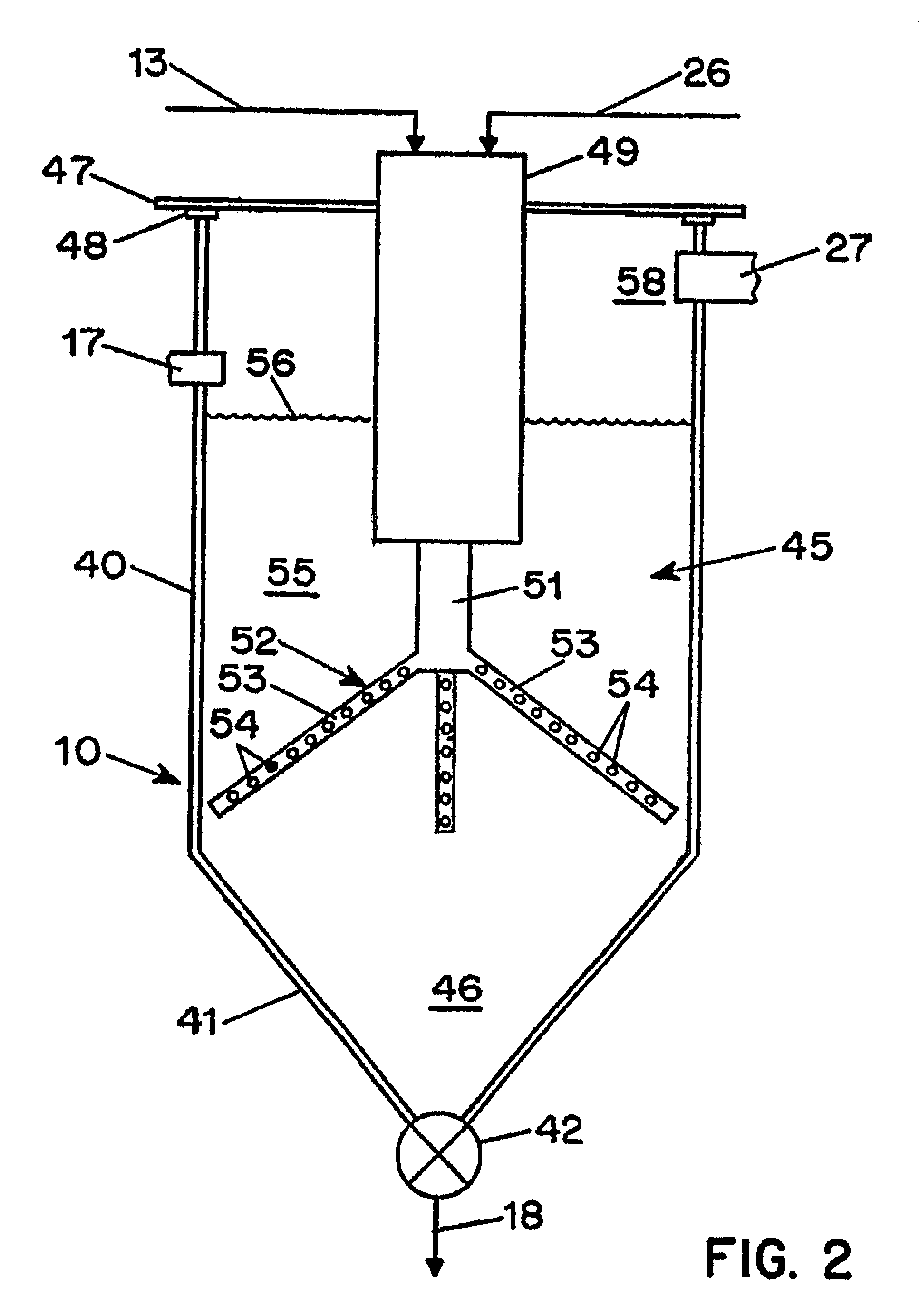
In the methods for treatment of caustic effluents described in the specification, a spent caustic refinery effluent is supplied to a submerged combustion gas evaporator in which hot combustion gas containing carbon dioxide is injected into the caustic liquid to concentrate the liquid and convert a hydroxide constituent to a carbonate. Where the caustic effluent is from a petroleum refinery, oil in the waste liquid is separated from the aqueous constituent before, during or after concentration.
Owner:GEI LIQUID SOLUTIONS +1
Reducing mercury emissions from the burning of coal
ActiveUS7758827B2Reduce waste disposal costsReduce concrete costsSolid waste managementUsing liquid separation agentCombustionHalogen
Sorbent components containing calcium, alumina, silica, and halogen are used in combination during coal combustion to produce environmental benefits. Sorbents are added to the coal ahead of combustion and / or are added into the flame or downstream of the flame, preferably at minimum temperatures to assure complete formation of the refractory structures that result in various advantages of the methods. When used together, the components ● reduce emissions of mercury and sulfur; ● reduce emissions of elemental and oxidized mercury; ● increase the efficiency of the coal burning process through de-slagging of boiler tubes; ● increase the level of Hg, As, Pb, and / or Cl in the coal ash; ● decrease the levels of leachable heavy metals (such as Hg) in the ash, preferably to levels below the detectable limits; and ● make a highly cementitious ash product.
Owner:NOX II LTD
Controlled releasing microcapsule for scale prevention, wax prevention or viscosity reduction of oil well
InactiveCN102250604AAchieve slow releaseAchieve long-term effectiveDrilling compositionBorehole/well accessoriesPetrochemicalComponents of crude oil
The invention relates to the technical field of petrochemical engineering, in particular to a controlled releasing microcapsule for scale prevention, wax prevention or viscosity reduction of an oil well. The invention discloses a solid controlled releasing microcapsule for scale and corrosion prevention in the production process of crude oil and wax prevention or viscosity reduction in the production process of the crude oil as well as a preparation method thereof. Filler comprising an inorganic framework and agent components is arranged in a macromolecule composite membrane. The controlled releasing microcapsule has a stable structure comprising an inside inorganic framework support and an outer-layer macromolecular composite membrane wrapping film, can be used for realizing the slow release of the agent and achieving the aim of maintaining the agent effective for a long term as well as the functions of corrosion inhibition and dispersion. With proper volume and density, the controlled releasing microcapsule can be prevented from being taken away by an extraction solution and can be added through a sleeve; and the controlled releasing microcapsule is simple in process and is strong in maneuverability. According to the controlled releasing microcapsule, volatile matters and harmful components which do harm to the human health are avoided; various components can be basically and slowly dissolved; the labor intensity of workers is reduced; and one-time agent addition can ensure stable operation for 30-90 days.
Owner:门正国
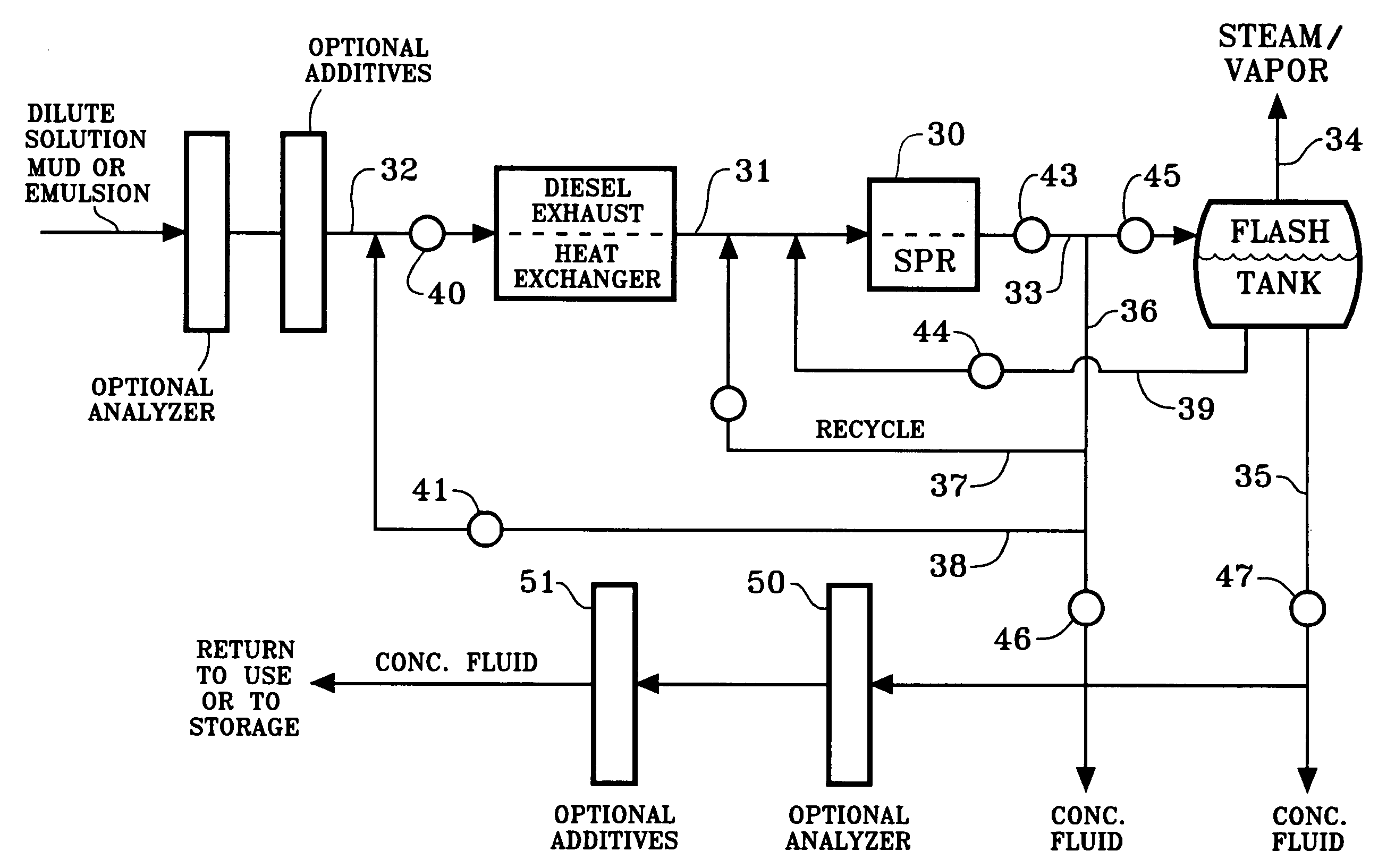
Conserving components of fluids
InactiveUS7201225B2Efficient designSurveyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationProcess engineeringComponents of crude oil
A cavitation device is used to heat, concentrate and recycle or otherwise reuse dilute and other oil well fluids, brines and muds, and solution mining fluids, all of which commonly contain ingredients worthy of conservation. The cavitation device is powered by a Diesel engine whose exhaust may be used to heat the incoming fluid, and the product of the cavitation device is directed to a flash tank.
Owner:TOTAL SEPARATION SOLUTIONS
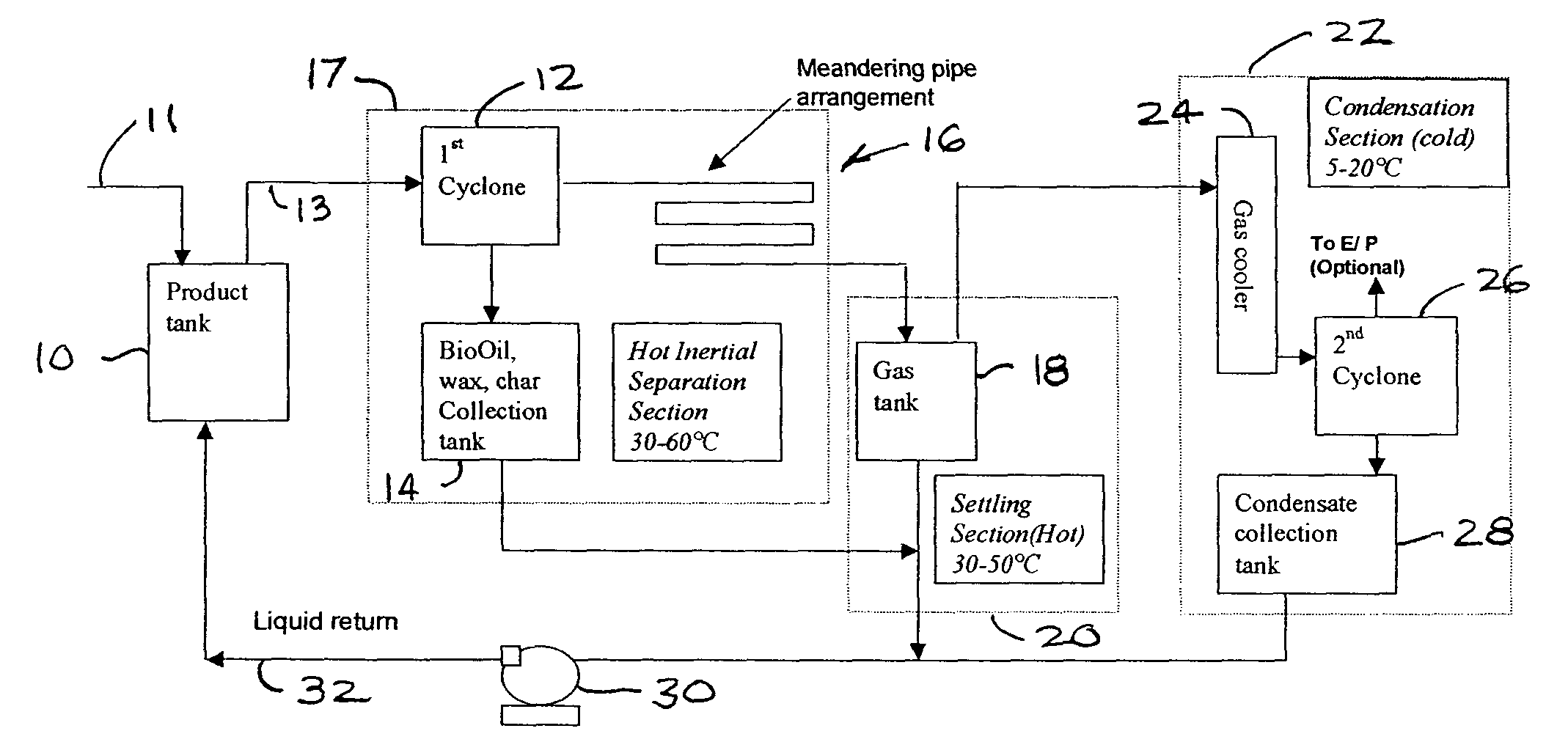
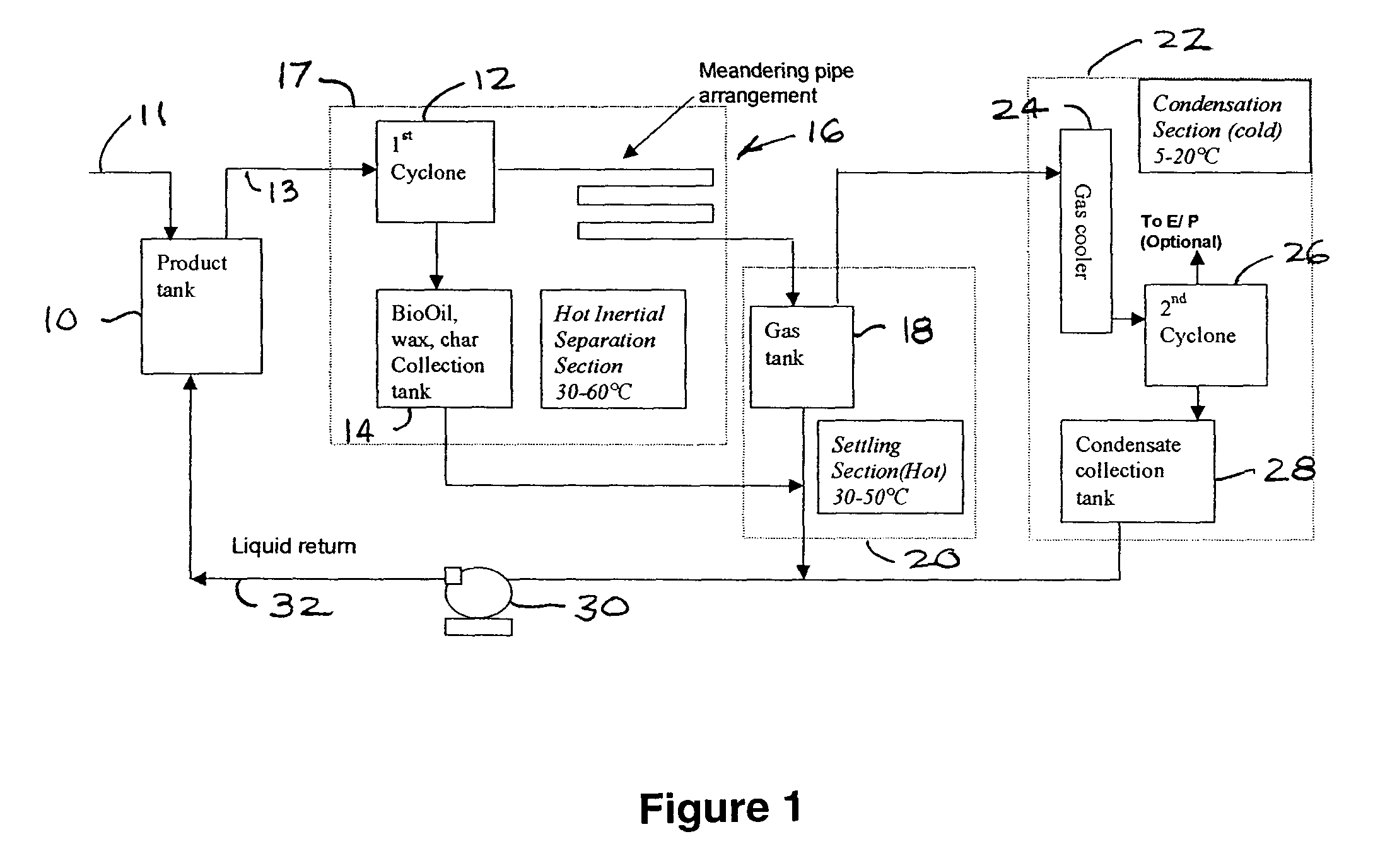
Apparatus for separating fouling contaminants from non-condensable gases at the end of a pyrolysis/thermolysis of biomass process
InactiveUS7004999B2Extended retention timeSlow downCombination devicesLiquid degasificationProduct gasComponents of crude oil
A method of continuously capturing BioOil and its constituents from a gas stream produced in a fast pyrolysis / thermolysis process, in a usable liquid form so as to produce a non-condensable gas free of fouling contaminates. The method includes separating BioOil and its constituents from a gas stream using hot inertial separation to maintain the temperature of said BioOil and its constituents above a temperature at which the thick and / or sticky constituents cause inefficient operation of the equipment but low enough so that they do not undergo rapid degradation. Next the gas velocity is reduced to a temperature sufficiently low to allow droplets in the gas stream to settle out but high enough so that a viscosity of said droplets remains low enough to avoid inefficient operation of the separation equipment. Finally, liquid is condensed out of the gas stream.
Owner:DYNAMOTIVE ENERGY SYST CORP
Dual Function Proppants
ActiveUS20130056204A1Improve conductivityIncrease valueFluid removalFlushingMulti pollutantIon exchange
Proppants for use in fractured or gravel packed / frac packed oil and gas wells are provided with a contaminant removal component to remove one or more of the contaminants found in subterranean water / hydrocarbon from a production well. The water / hydrocarbon cleaning proppant solids may be used as discrete particles in a proppant formulation, as a coating on proppant solids in pores of a porous proppant solid or as part of the proppant's internal structure. The contaminant removal component removes contaminants, especially dissolved contaminants, in the subterranean water or hydrocarbon before the water / hydrocarbon leaves the well. For those contaminant removal components that can be regenerated, such as ion exchange resins, a measured quantity of an acidic regeneration solution can be injected into the fractured stratum for regeneration and recovered when the well resumes production.
Owner:PREFERRED TECH
Comprehensive system for the storage and transportation of natural gas in a light hydrocarbon liquid medium
ActiveUS20100000252A1Rapid economic developmentRaise the ratioSolidificationLiquefactionProcess systemsLiquid medium
This invention provides a means of loading, processing and conditioning raw production gas, production of CGL, storage, transport, and delivery of pipeline quality natural gas or fractionated products to market. The CGL transport vessel utilizes a pipe based containment system to hold more densely packed constituents of natural gas held within a light hydrocarbon solvent than it is possible to attain for natural gas alone under such conditions. The containment system is supported by process systems for loading and transporting the natural gas as a liquid and unloading the CGL from the containment system and then offloading it in the gaseous state. The system can also be utilized for the selective storage and transport of NGLs to provide a total service package for the movement of natural gas and associated gas production. The mode of storage is suited for both marine and land transportation and configured in modular form to suit a particular application and / or scale of operation.
Owner:SEAONE HLDG
Process for preparing biological diesel oil from waste animal and plant oil
InactiveCN1382762AEliminate emissionsSimple production processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockOil and greaseBiodiesel
A process for preparing biologic diesel oil from waste plant or animal oil includes alcoholysis and esterifying reactions under the existance of acidic catalyst, separating out the excessive non-product part to obtain coarse product, adding saturated equeous solution of edible salt containing sodium carbonate (10%), neutralizing reaction, adding industrial sodium carbonat4e, heating distillation and collecting the gas-phase fraction at 22-320 deg.C to obtain biologic diesel oil. Its advantages are high performance no pollution, and simple preparing process.
Owner:叶活动 +1
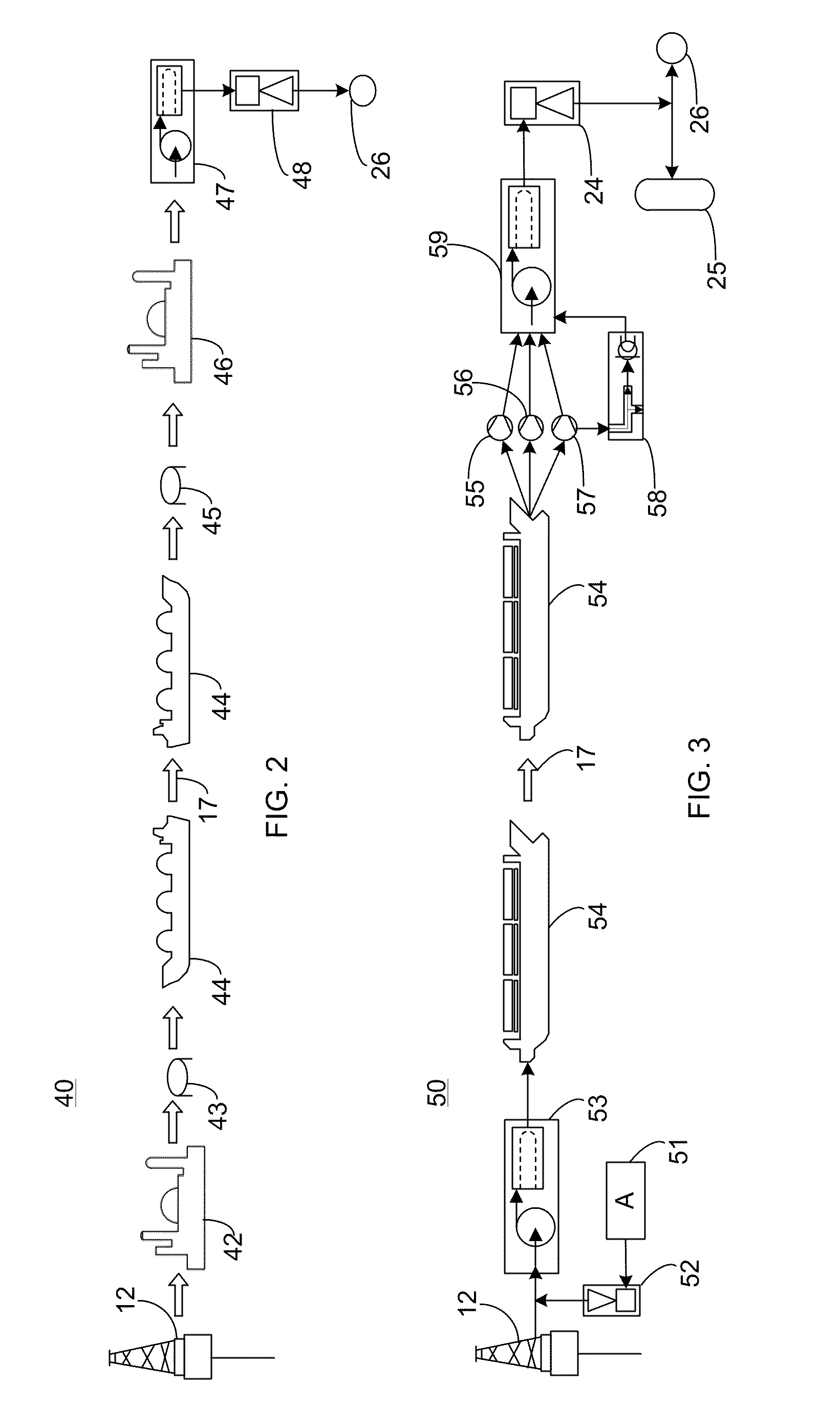
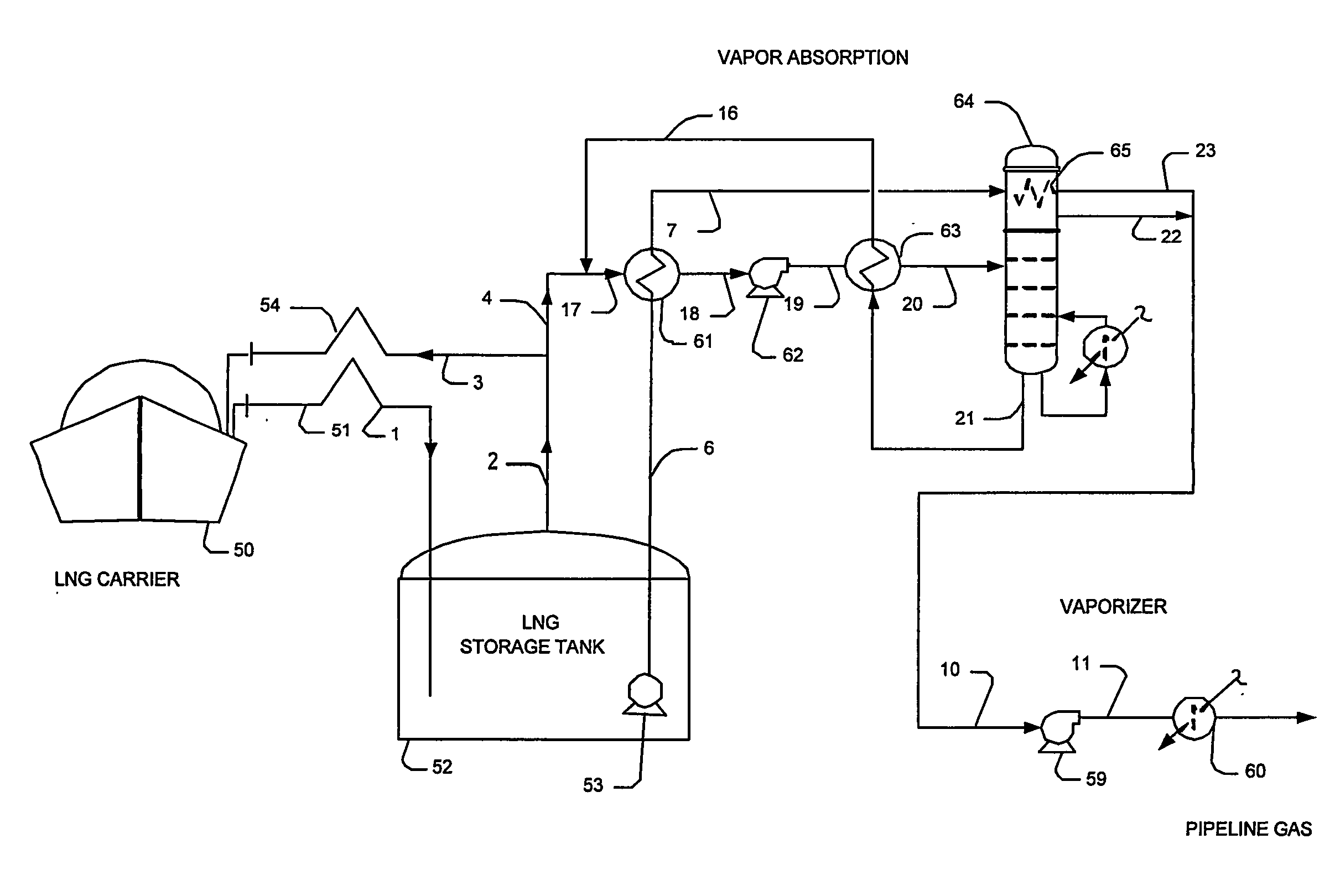
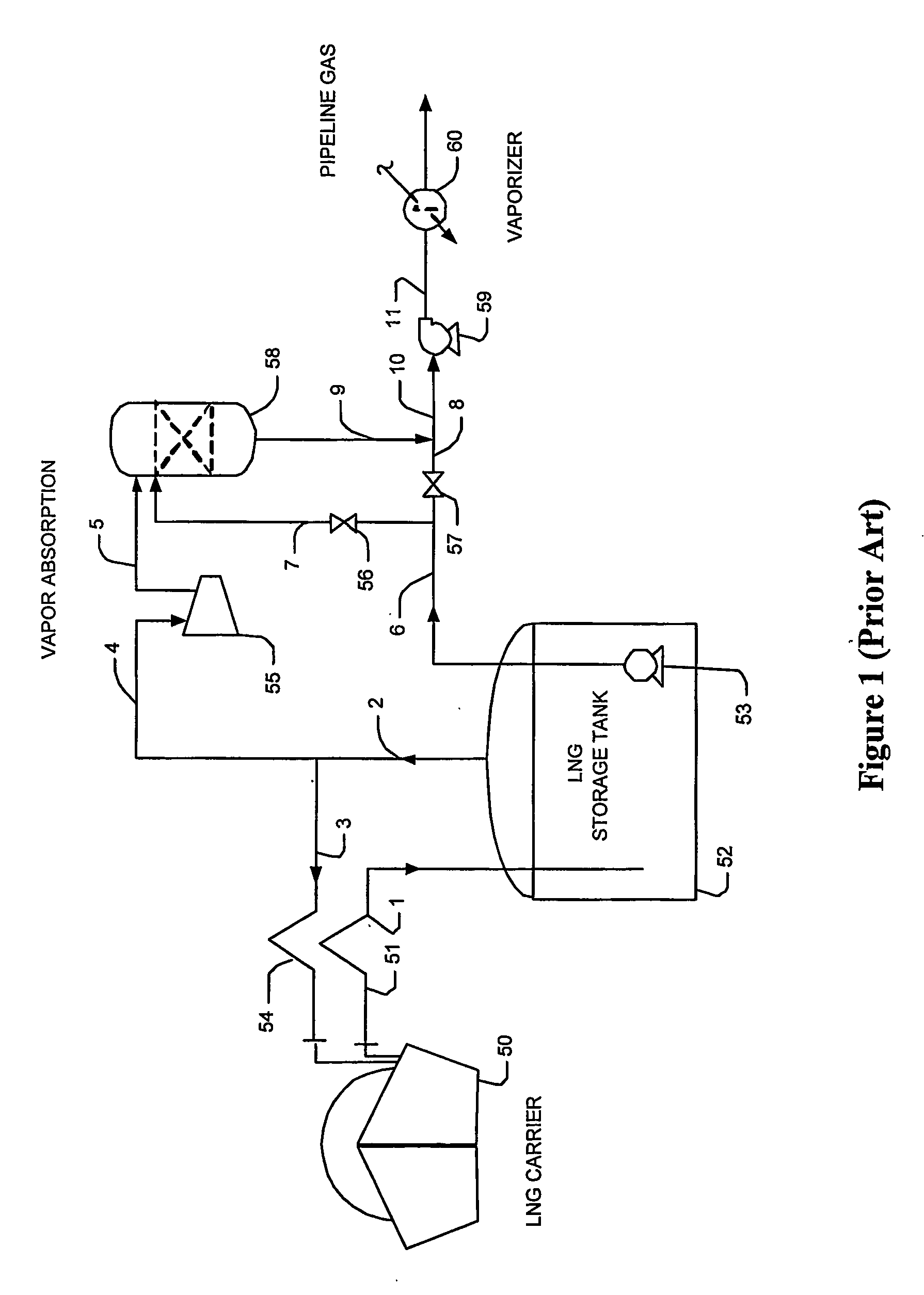
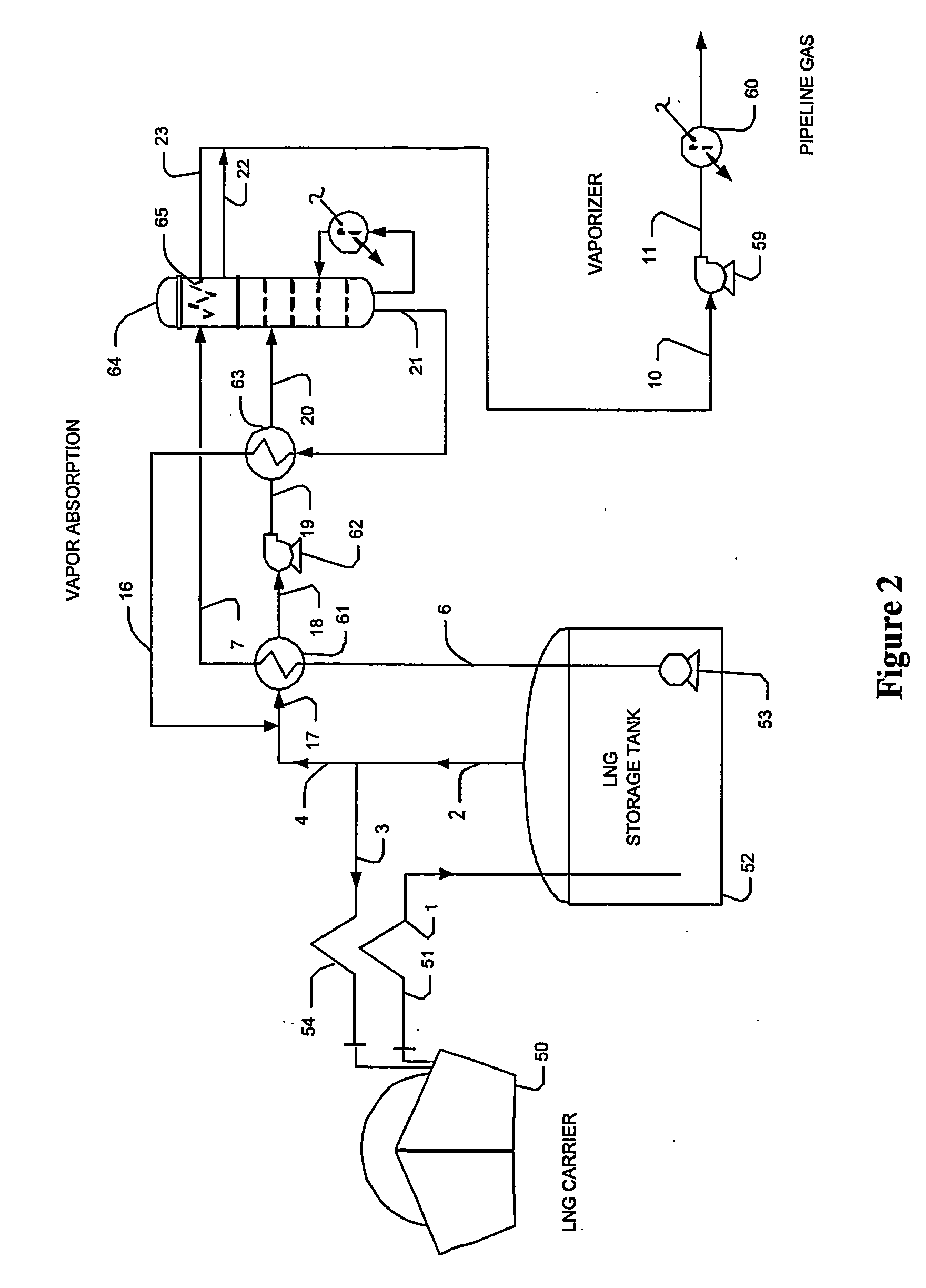
Lng vapor handling configurations and methods
InactiveUS20070125122A1Easy to condenseSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringComponents of crude oil
LNG vapor from an LNG storage vessel is absorbed using C3 and heavier components provided by a fractionator that receives a mixture of LNG vapors and the C3 and heavier components as fractionator feed. In such configurations, refrigeration content of the LNG liquid from the LNG storage vessel is advantageously used to condense the LNG vapor after separation. Where desired, a portion of the LNG liquid may also be used as fractionator feed to produce LPG as a bottom product.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
Preparation of components for transportation fuels
InactiveUS6881325B2Environmentally friendlyRefining with oxygen compoundsRefining with acid-containing liquidsPhosphomolybdic acidComponents of crude oil
Economical processes are disclosed for the production of components for refinery blending of transportation fuels by selective oxidation of feedstocks comprising a mixture of hydrocarbons, sulfur-containing and nitrogen-containing organic compounds. Oxidation feedstock is contacted with a soluble quaternary ammonium salt containing halogen, sulfate, or bisulfate anion, and an immiscible aqueous phase comprising a source of hydrogen peroxide, and at least one member of the group consisting of phosphomolybdic acid and phosphotungstic acid, in a liquid reaction mixture under conditions suitable for reaction of one or more of the sulfur-containing and / or nitrogen-containing organic compounds. Blending components containing less sulfur and / or less nitrogen than the oxidation feedstock are recovered from the reaction mixture. Advantageously, at least a portion of the immiscible acid-containing phase is recycled to the oxidation.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Equipment and method for extracting perfume plant essential oil by reduced pressure steam distillation
InactiveCN102250689AWide applicabilityEasy and flexible operationEssential-oils/perfumesWater vaporOil phase
The invention provides a piece of equipment and a method for extracting volatile essential oil from natural perfume plants by using the technology of reduced pressure steam distillation extraction. The equipment provided in the invention comprises a steam distillation system and a vacuum system, wherein the steam distillation system is composed of a steam generator, a material retort, a condenser, an oil-water separator and connecting pipelines, and the vacuum system comprises a vacuum unit or a suction pump, a pressure regulator valve, connecting pipelines and the like. The method comprises the following steps that: plant raw materials to be extracted for essential oil in the material retort is controlled to be at a certain temperature and under certain pressure so as to reduce changes of aroma components in perfume plants in the process of extraction as much as possible; extracted volatile components of essential oil is mixed with steam to form mixed steam of water and oil; the mixed steam enters into the condenser for condensation and then enters into the oil-water separator for separation; an oil phase is collected after separation and the oil phase is plant essential oil; the separated water phase is flower water. The essential oil and flower water obtained by the extraction method have pure aroma, suffer little loss for head volatile thereof, and are applicable to the industries of perfumes, essence, cosmetics, daily chemicals, etc.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY +2
Method for extracting squalene from vegetable oil deodorized distillate
InactiveCN101830770AIdeal yieldIncrease contentDistillation purification/separationExtraction purification/separationHigh concentrationVegetable oil
The invention relates to a method for extracting squalene from vegetable oil deodorized distillate. A process method of combining molecular distillation with extraction and crystallization is used to extract high-concentration squalene and recover natural vitamin E and phytosterol with a certain purity from vegetable oil deodorized distillate. The method comprises the following steps of: carryingout a saponification reaction of the raw material; twice molecularly distilling unsaponifiable matter obtained by extraction; using the distillate obtained during the second distilling as a raw material for cold crystallization to obtain phytosterol; recovering squalene and mixed tocopherol from the filtrate; and extracting with multi-stage solvents to respectively enrich squalene and vitamin E in two phases. The process has simple flows, low-prices raw material and higher separation efficiency and recovery rate and comprehensively utilizes useful contents in the deodorized distillate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Encapsulation of food ingredients
InactiveUS20030185960A1Small particle sizeGood emulsificationSugar food ingredientsFatty substance preservation using additivesMaillard reactionAdditive ingredient
Oxygen sensitive oils or oils containing oil soluble oxygen sensitive substances are encapsulated in proteins which have been reacted with carbohydrates that contain reducing sugar groups. An aqueous mixture of a protein preferably casein and a carbohydrate preferably a sugar is heated within the range of 60 to 160° C. so that Maillard reaction products are formed in the aqueous mixture. The oil phase, up to 50% by weight is then emulsified with the aqueous phase to form micro encapsulated oil particles. The formation of MRP may also be done after emulsification prior to drying. The emulsions can be used as food ingredients or dried to form powders
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Lubricating oil composition and watch using the same
InactiveUS6858567B2Long lifeChange propertiesLiquid carbonaceous fuelsHorological bearingsEtherViscosity index
The first lubricating oil composition of the invention comprises a polyol ester (A) as a base oil, a specific amount of a viscosity index improver (B) and a specific amount of an anti-wear agent (C), and the second lubricating oil composition of the invention comprises a paraffinic hydrocarbon oil (F) having at least 30 carbon atoms and a specific amount of a viscosity index improver (B), so that these compositions exert effects that they enable a life of watch battery to last long, they enable a watch to operate in the temperature range of −30 to 80° C. with one kind of a lubricating oil, and they are free from change of properties over a long period of time. The third lubricating oil composition of the invention comprises an ether oil (G) as a base oil, a specific amount of an anti-wear agent (C) comprising a neutral phosphoric ester and / or a neutral phosphorous ester, and an antioxidant (E), so that this composition is free from change of properties over a long period of time and is favorable as a watch lubricating oil. The watch of the invention is a watch having a movable portion for which at least one composition selected from the above compositions is used.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Oil tank sludge removal method
InactiveUS20060042661A1Reduce operating costsThorough removalHollow article cleaningOrganic baseSludge
A method for removing sludge from a petroleum storage tank is based on a two-step approach utilizing solvent extraction to dissolve organic components of the sludge followed by water wash to remove inorganic materials. Sludges contain both organic-based solids (e.g., waxes and asphaltenes) as well as inorganic-based solids (known to exist as salts such as chlorides, carbonates, and oxides). The organic components of the sludge are dissolved using petroleum-based solvent streams that have been identified to possess high solvent power. The dissolved material can then be processed and recovered in the refinery using conventional refining operations. A water wash following removal of the organic materials is effective to remove the inorganic materials that can then be disposed of without the complications of the having to treat the oily organics along with them. A beneficial part of the method includes mixing and heating to improve the dissolution of soluble materials in both steps of the process.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Combined treatment method for oilfield solid waste
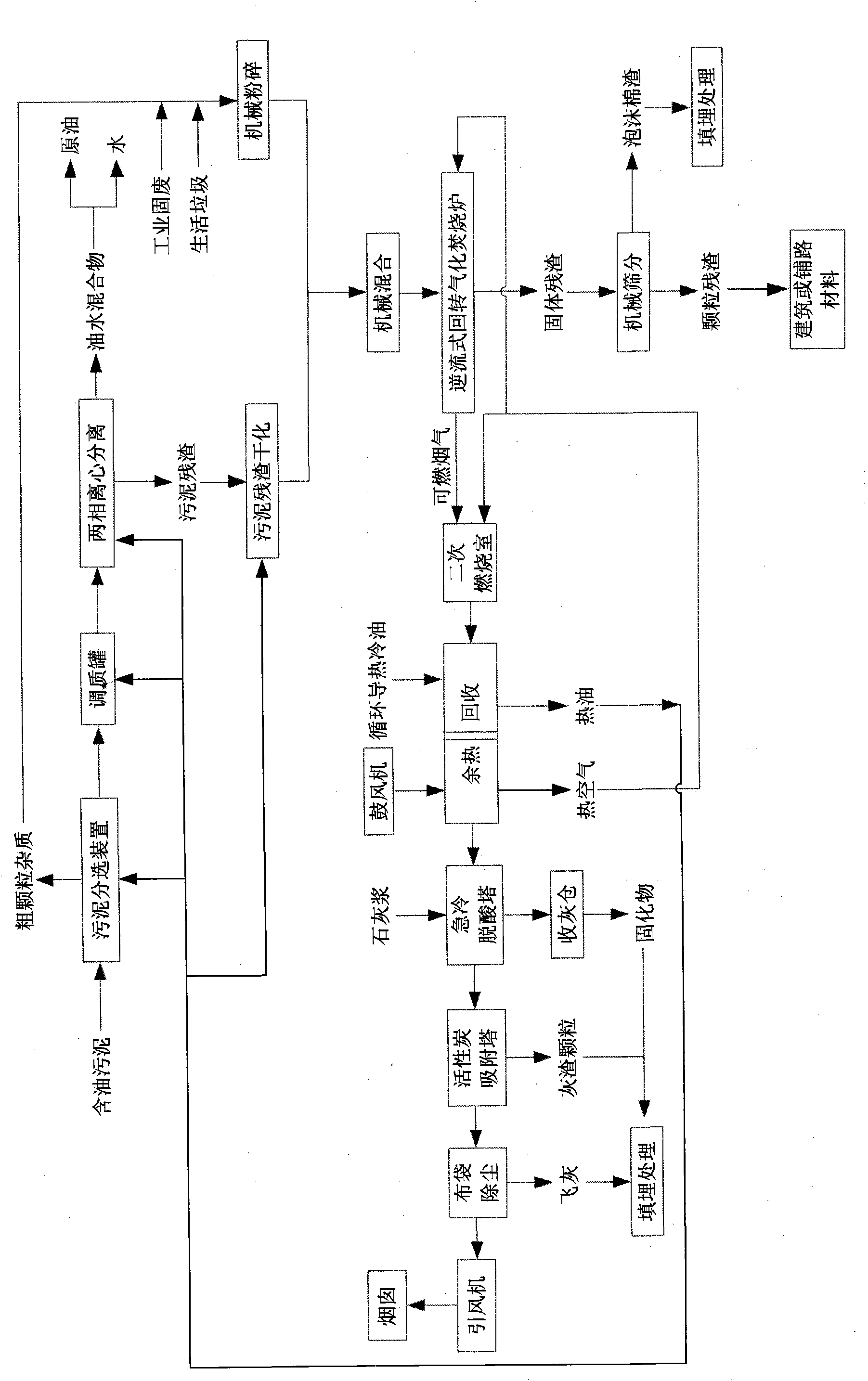
InactiveCN101963358AHigh recovery rateLess investmentIncinerator apparatusCombustion chamberOil sludge
The invention provides a new combined treatment process for oilfield solid waste (oil sludge, industrial solid waste and household garbage). In the process, liquid-solid separation is performed on the oil sludge of an oilfield by adopting a conditioning-centrifugal separation process; the separated liquid enters oil-water separation equipment constructed on the oilfield for recovering crude oil; the oil recovery rate is up to 65 to 90 percent; after drying separated solid residue, the separated solid residue and pre-crushed industrial solid waste and household garbage are mixed and enter a countercurrent-type rotary gasification incinerator; combustible components in the oilfield solid waste are decomposed and gasified into combustible gases which are combusted partially in the incinerator; the combustible gases are combusted completely in a secondary combustion chamber; high-temperature smoke gas afterheat is recovered by a conduction oil afterheat boiler and air preheating equipment; and low-temperature smoke gas of which the afterheat is recovered is harmlessly exhausted after being treated by a sharp-quenching deacidification tower, an activated carbon adsorption tower and a bag-type dust remover. The process realizes the purposes of decrement, harmlessness and resources of oilfield solid waste treatment.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com