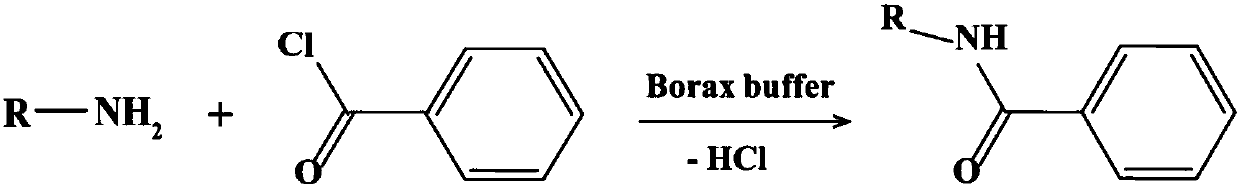
Patents
Literature
142 results about "Tyramine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tyramine (/ˈtaɪrəmiːn/ TY-rə-meen) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
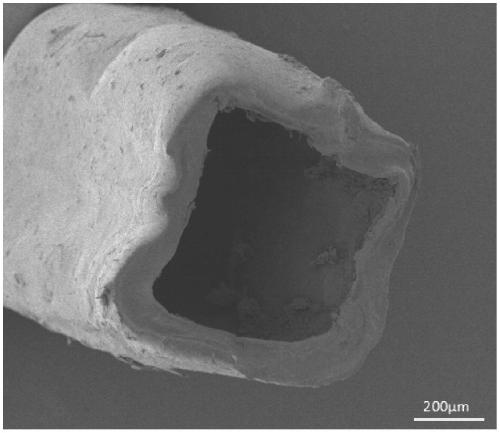
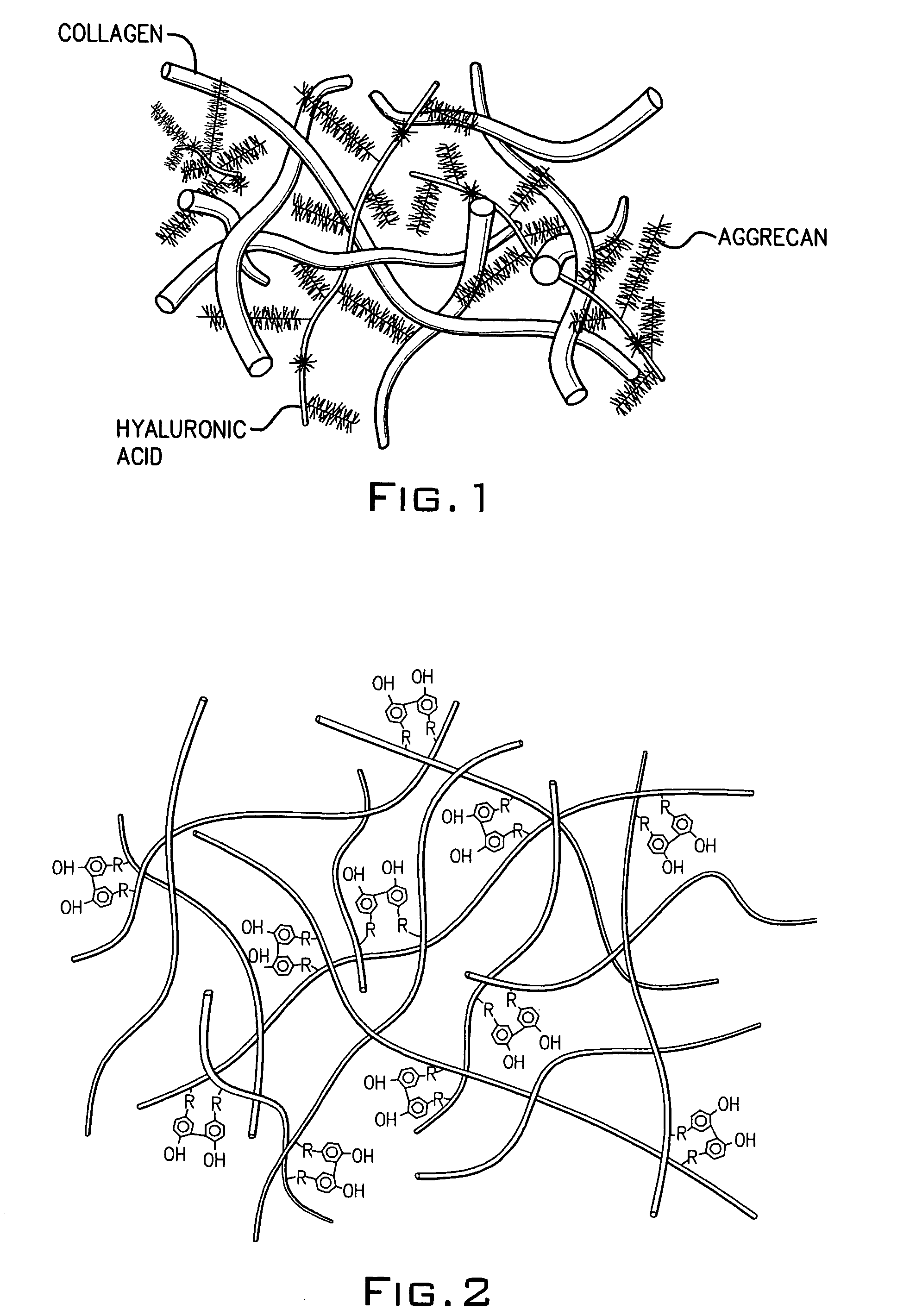
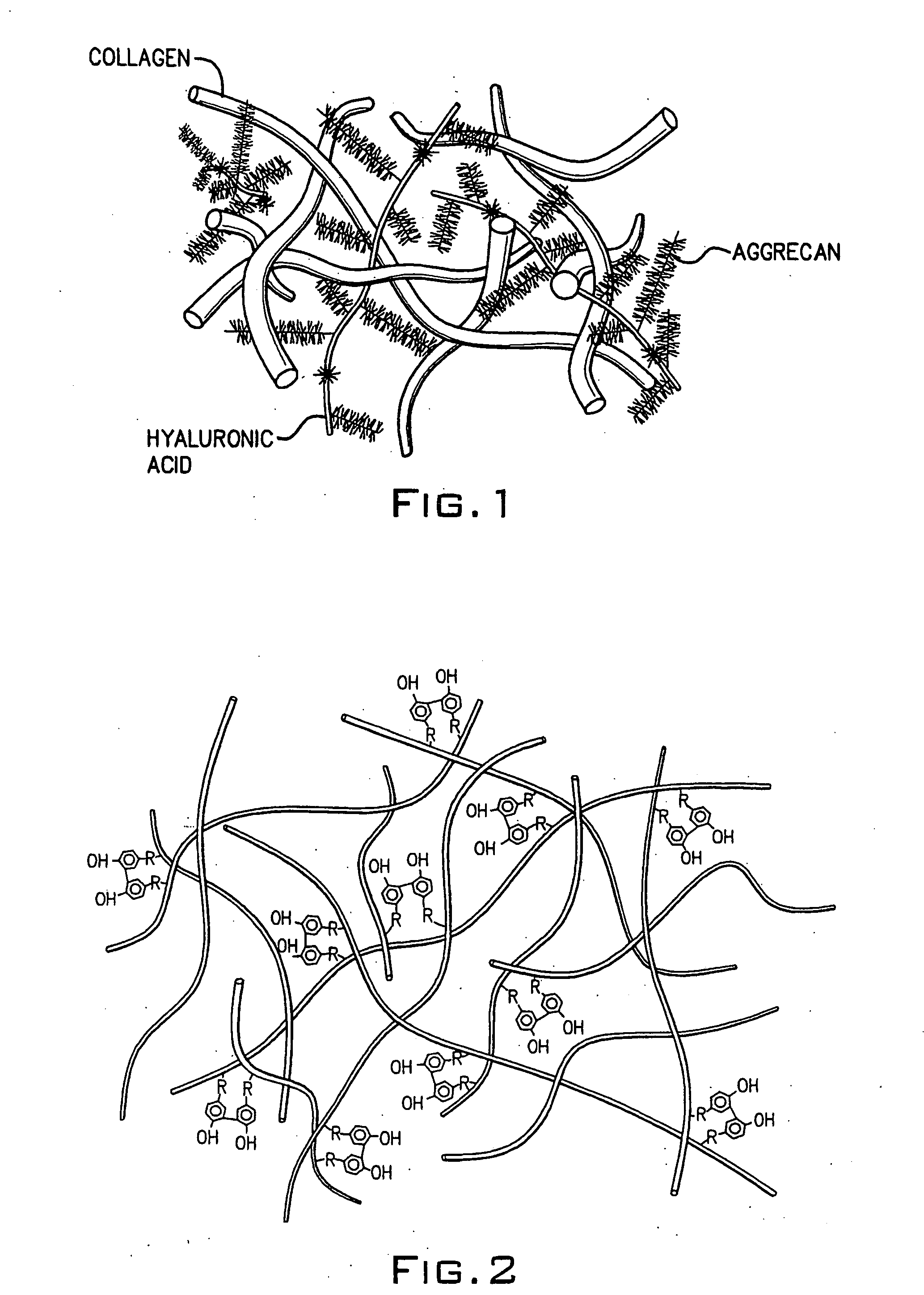
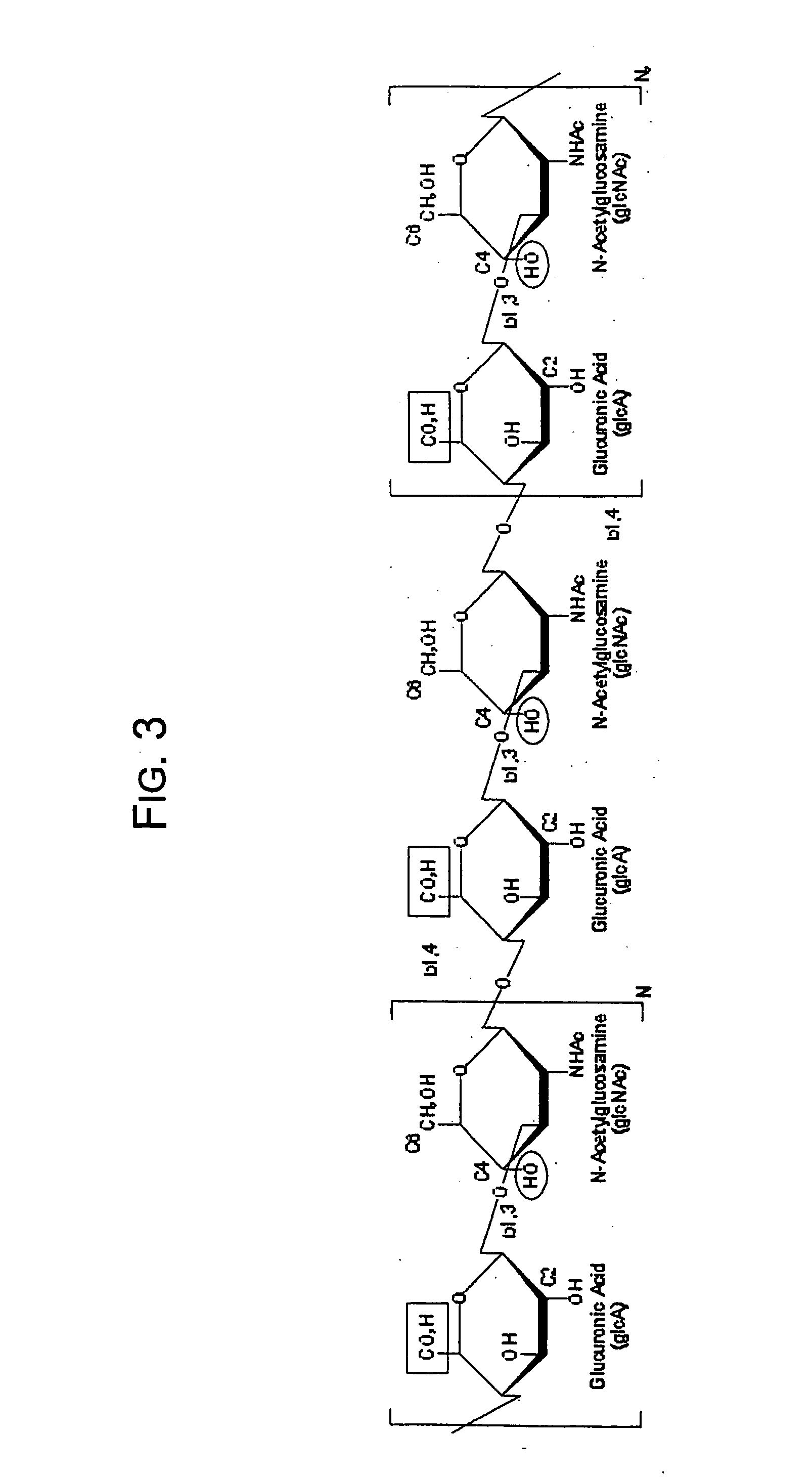
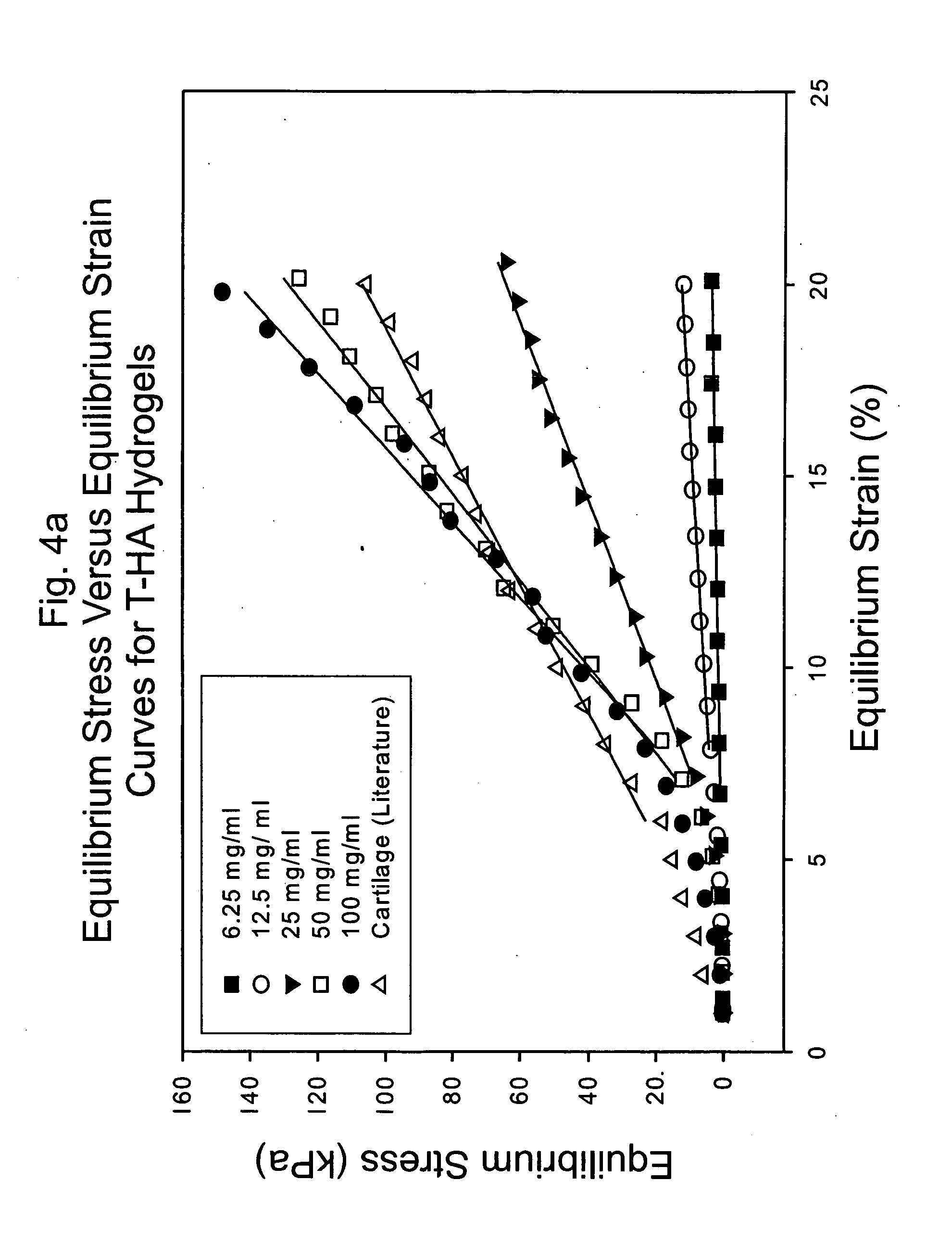
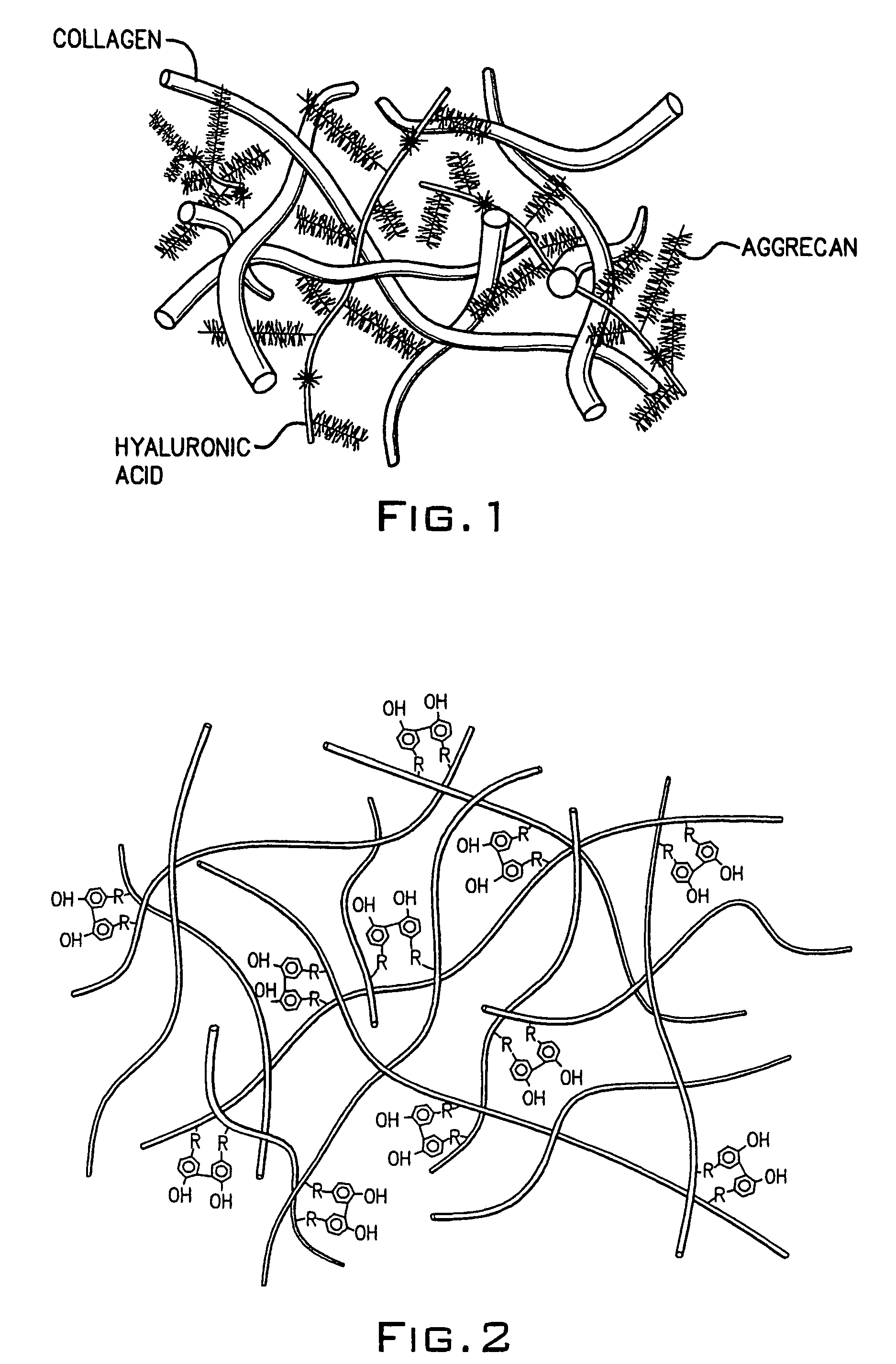
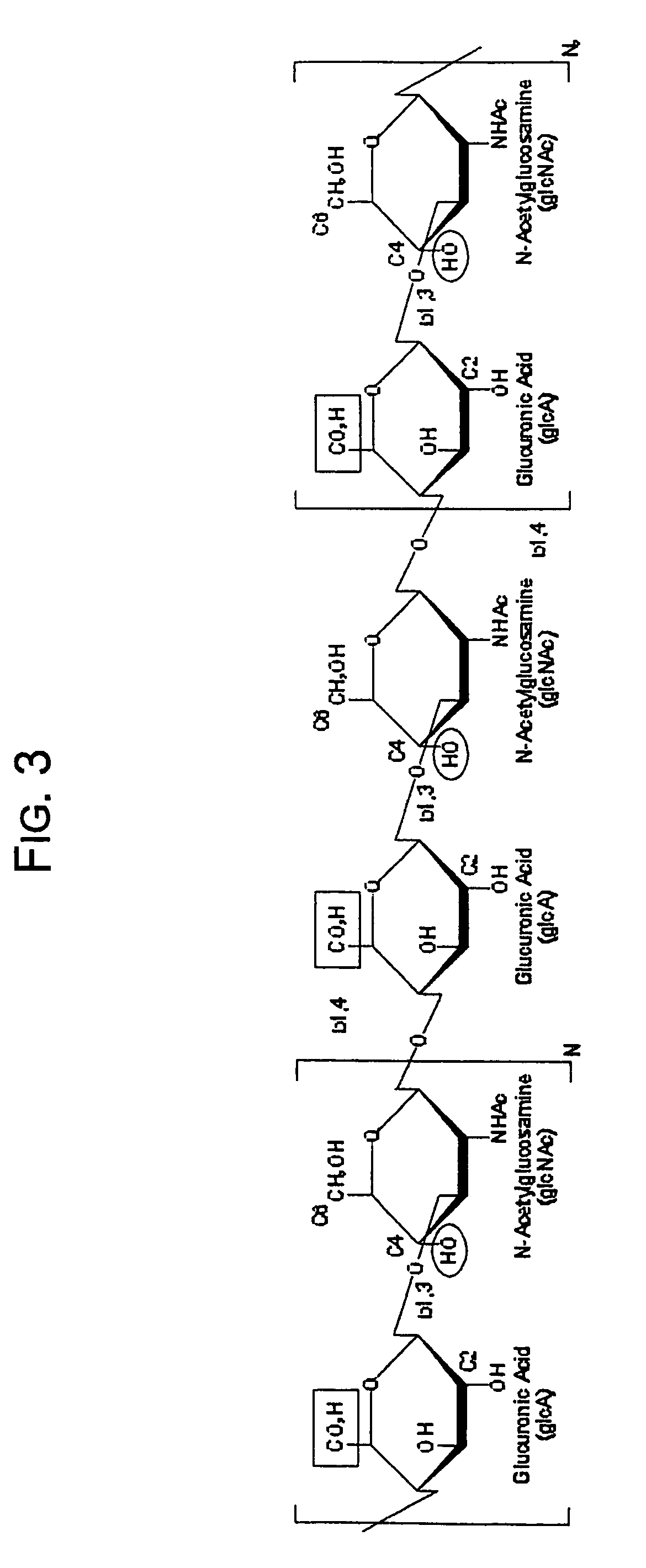
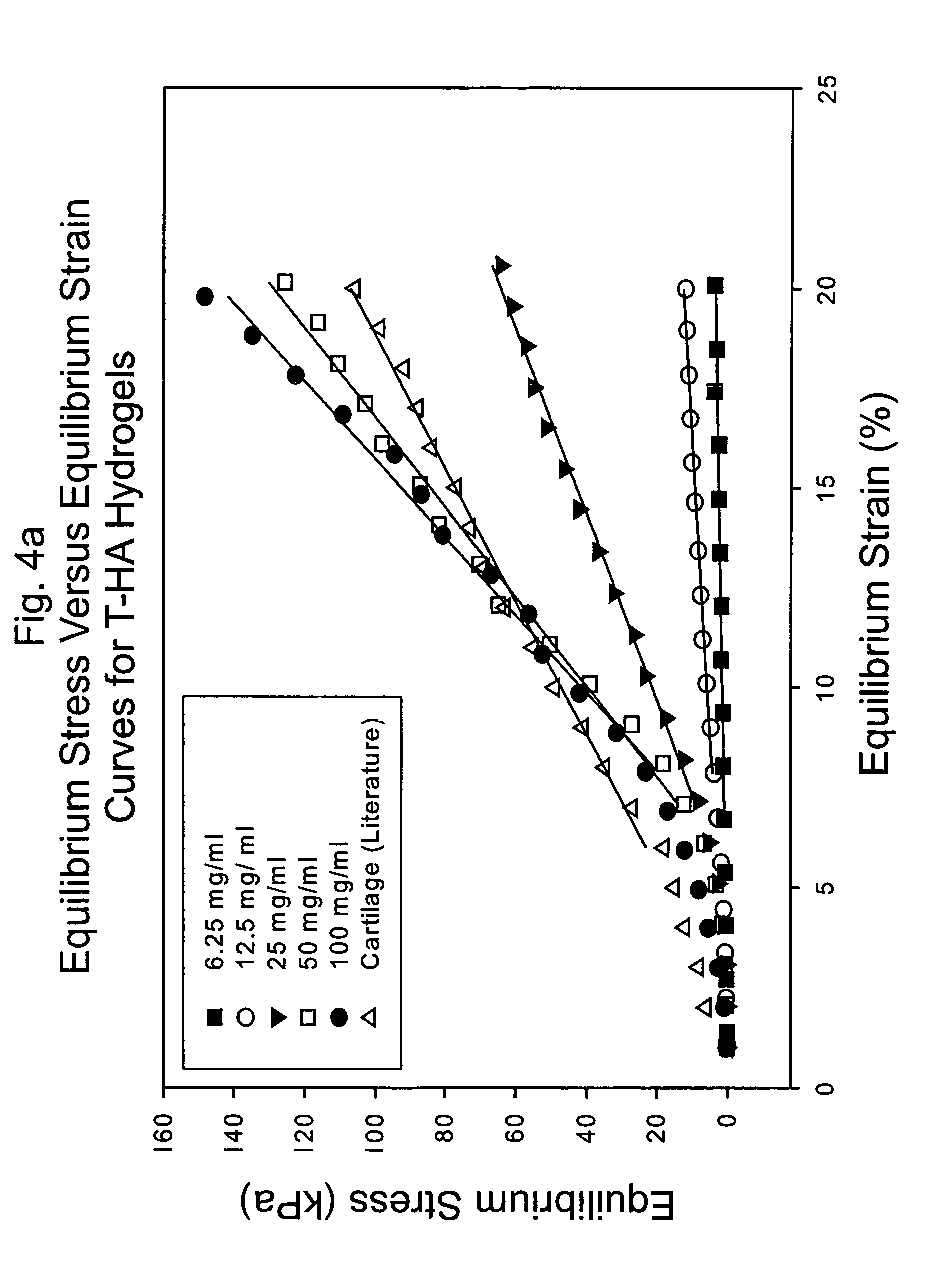
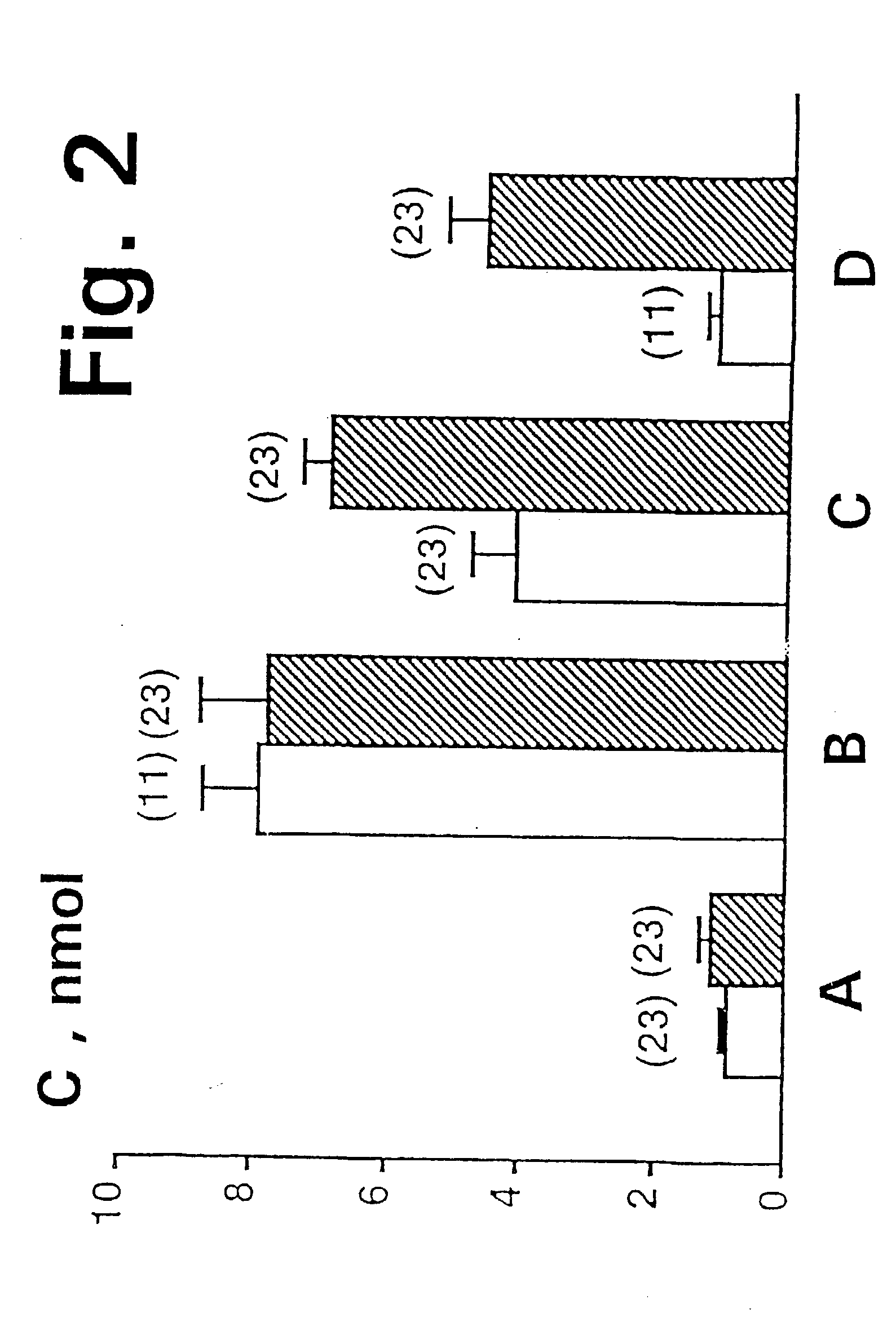
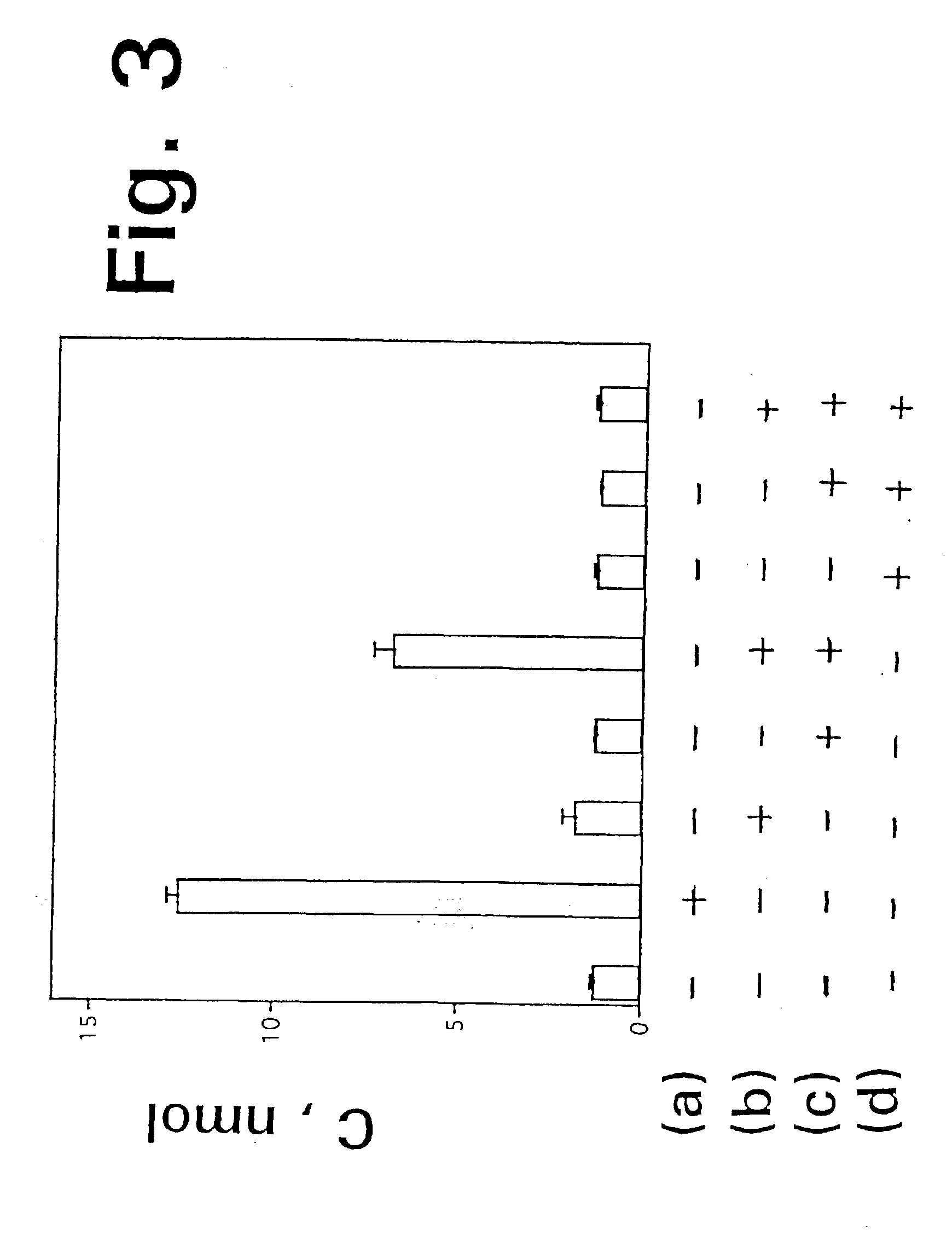
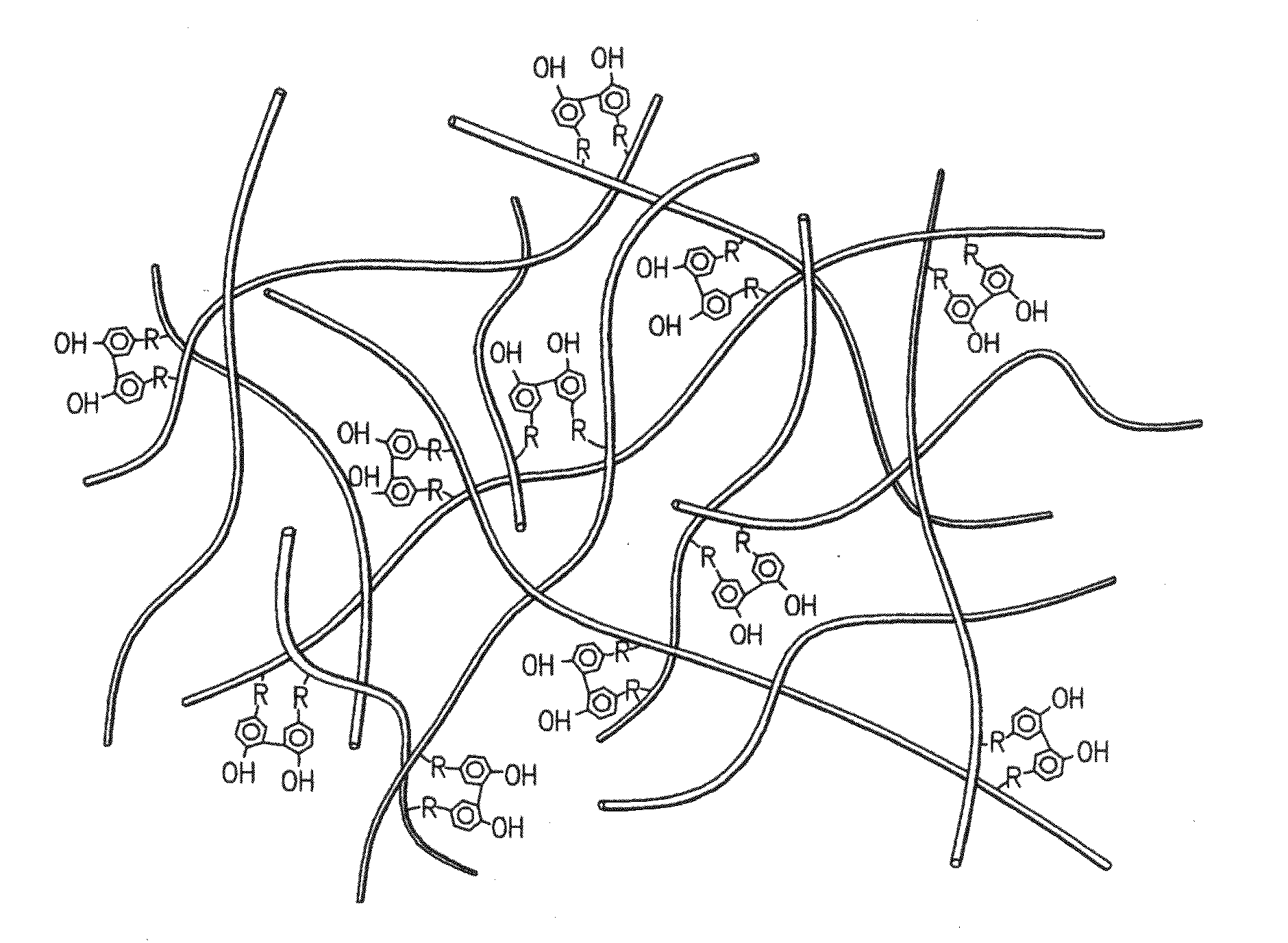
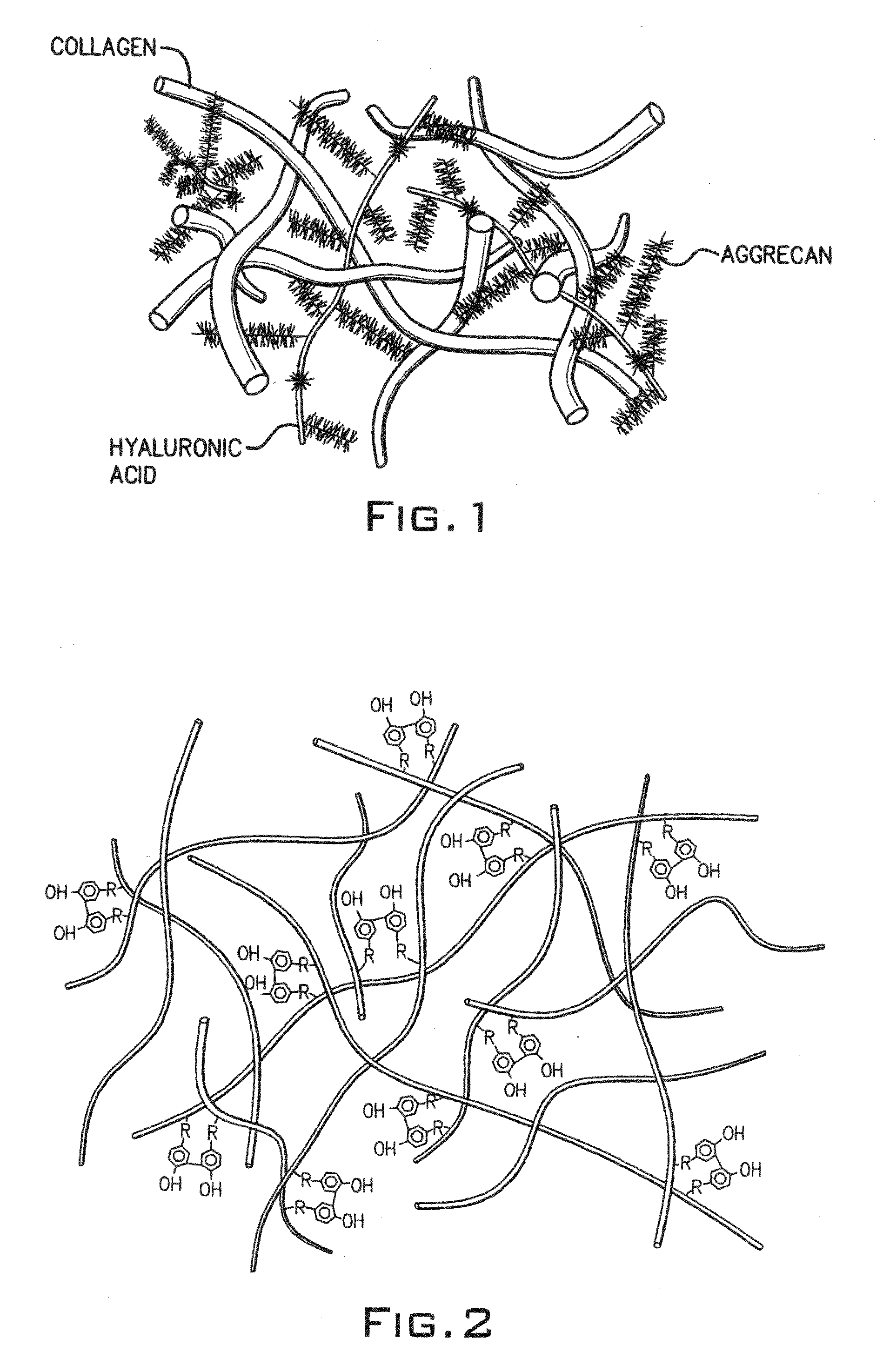
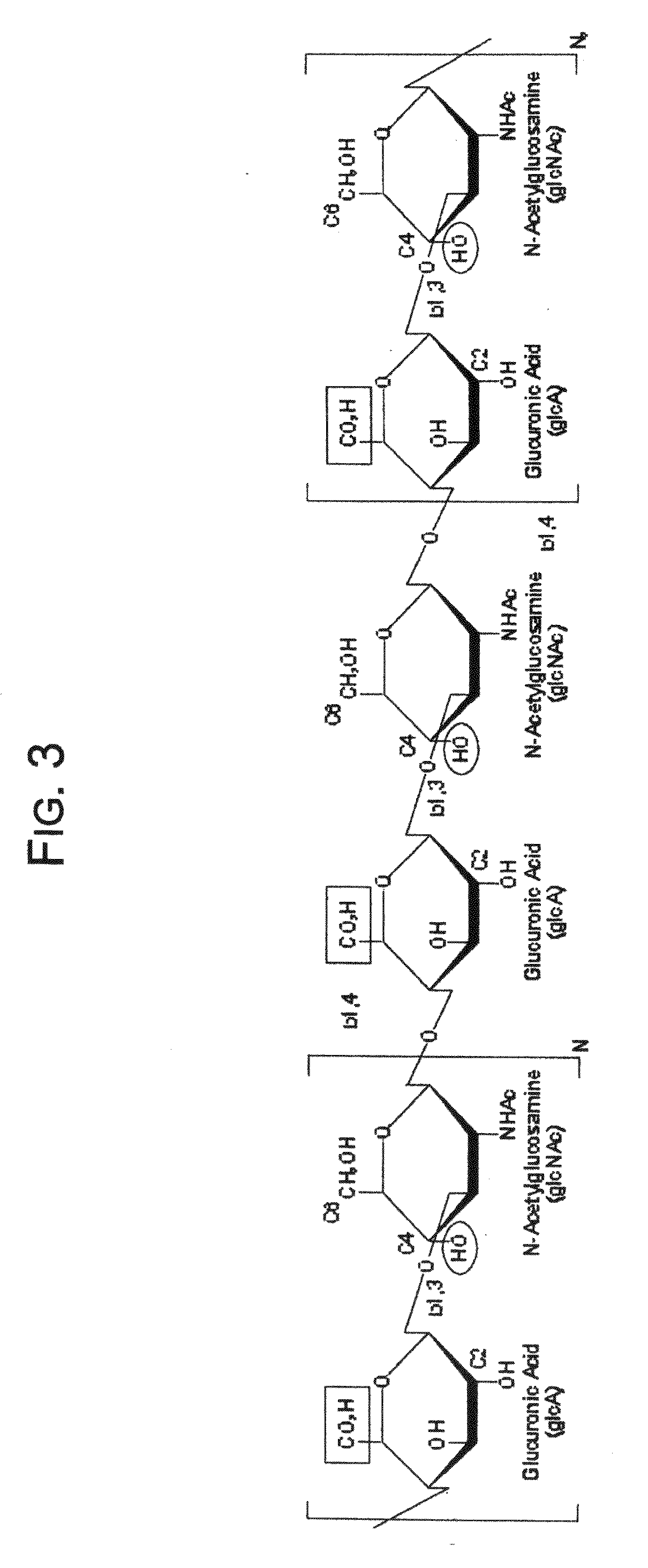
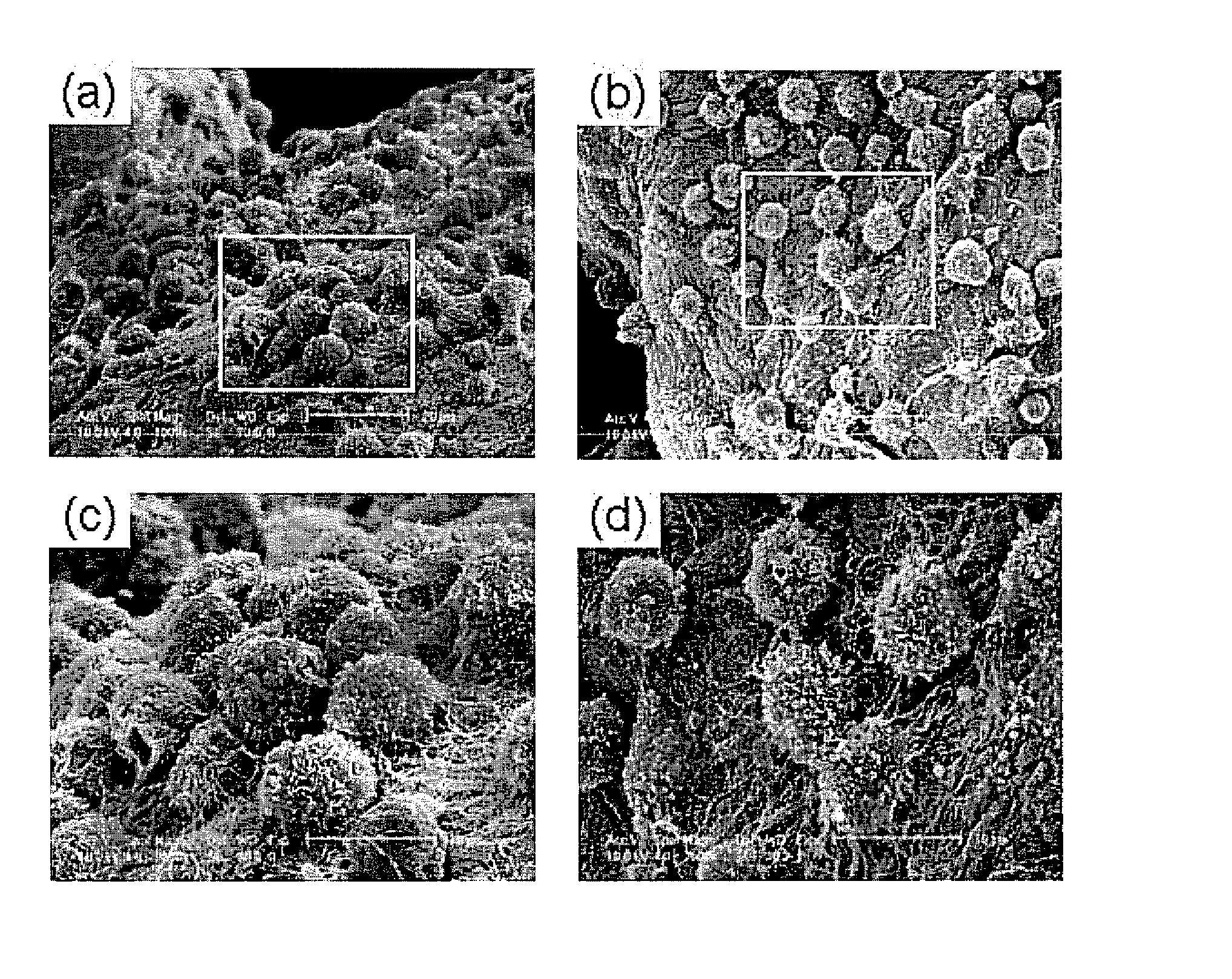
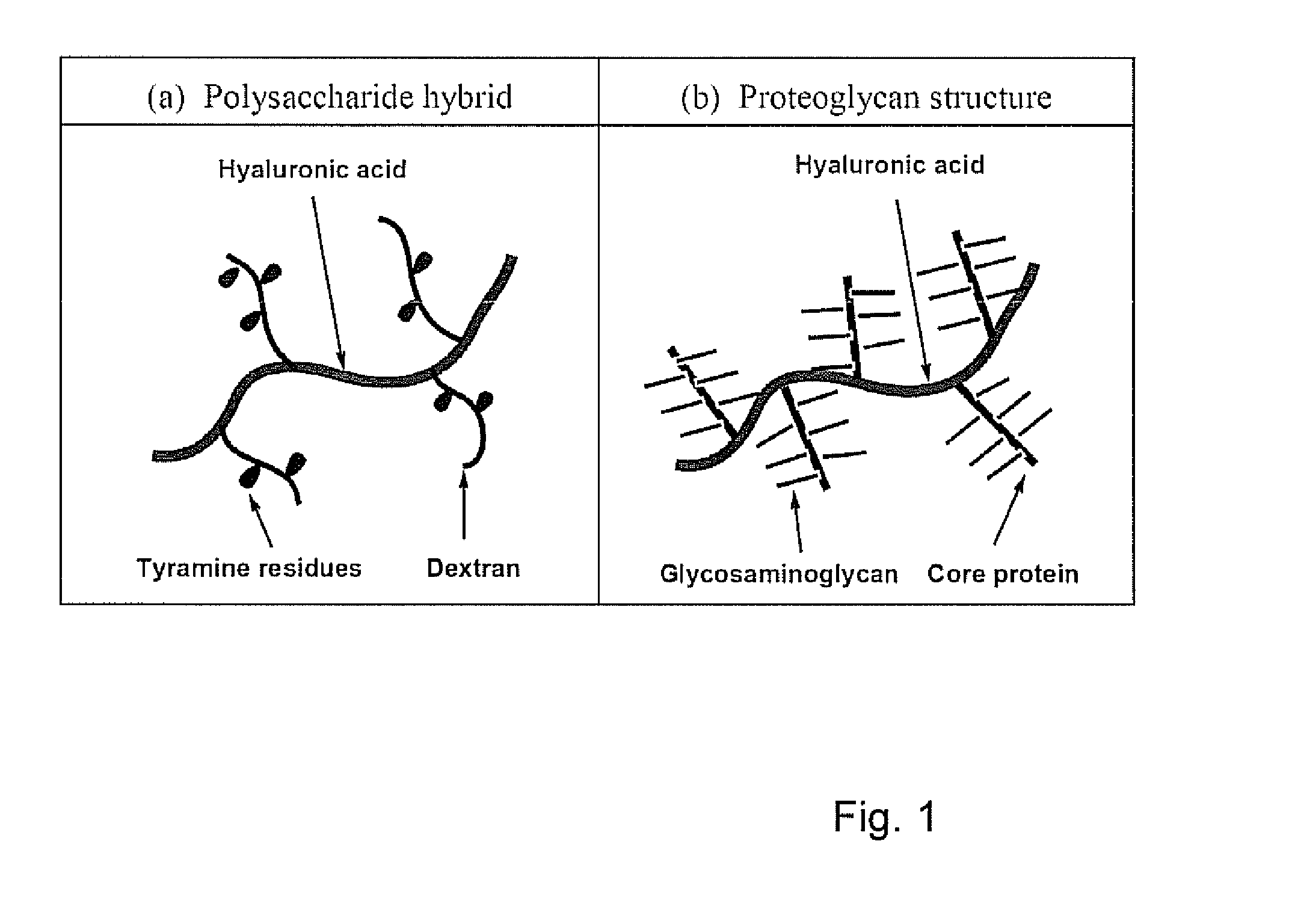
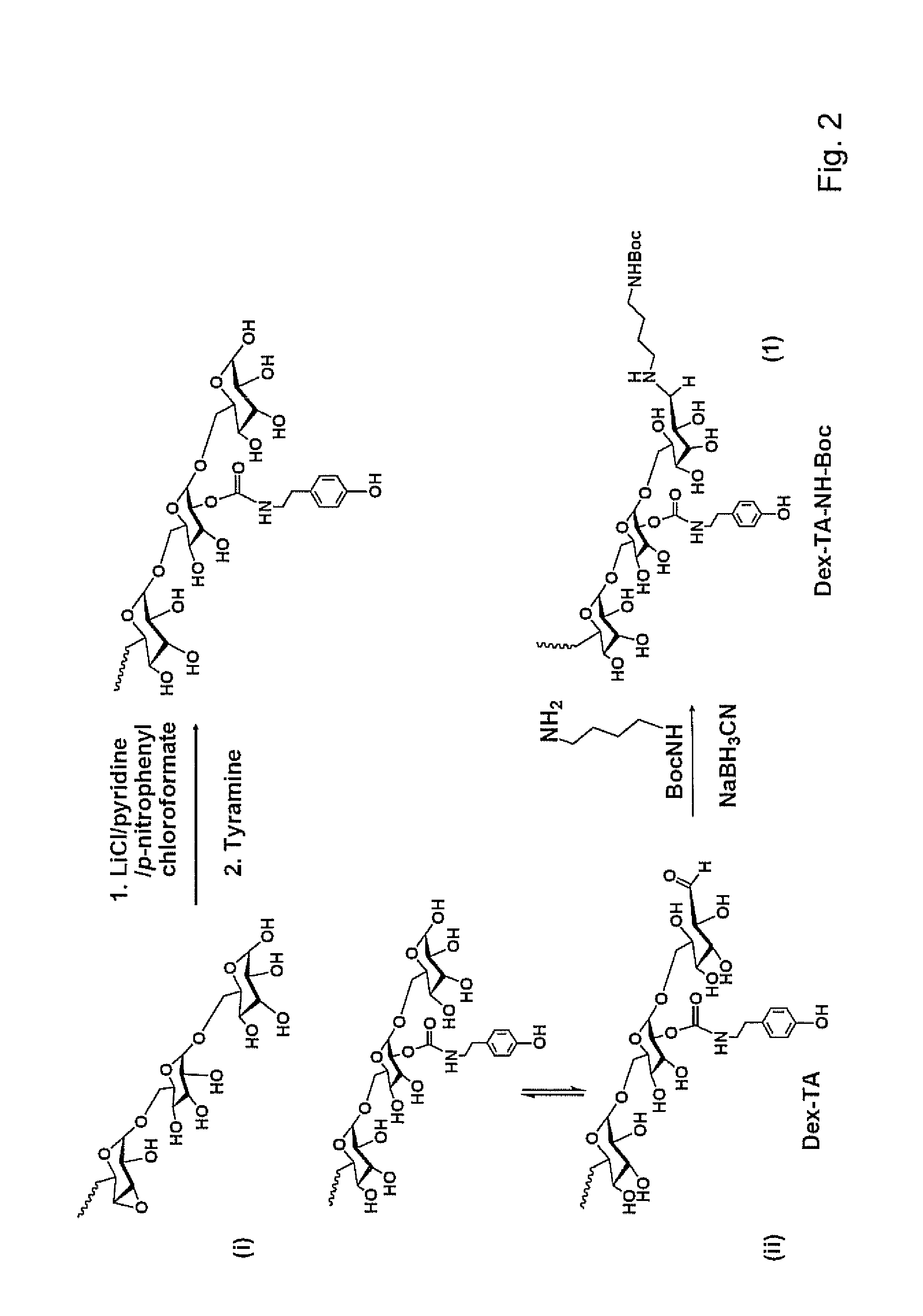
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, such as artificial or synthetic cartilage. The network is made by first providing a polyamine or polycarboxylate macromolecule (having a plurality of amine or carboxylic acid groups respectively attached along the length of the molecule), reacting this macromolecule with a hydroxyphenyl compound having a free carboxylic acid group in the case of a polyamine or a free primary amine group in the case of a polycarboxylate, and substituting the hydroxyphenyl compound onto the macromolecule via a carbodiimide-mediated reaction pathway to provide a hydroxyphenyl-substituted macromolecule. This macromolecule is then linked to other such macromolecules via an enzyme catalyzed dimerization reaction between two hydroxyphenyl groups attached respectively to different macromolecules under metabolic conditions of temperature and pH. In a preferred embodiment, the macromolecular network is made up of tyramine-substituted hyaluronan molecules that are linked by dityramine bonds to provide a stable, coherent hydrogel with desired physical properties. A method of preparing such a network is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
ActiveUS20060084759A1Skeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingCross-linkPeroxidase
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, particularly to provide a synthetic, implantable tissue matrix material for a wide variety of tissue types. In particular, artificial or synthetic cartilage, vocal cord material, vitreous material, soft tissue material and mitral valve material are described. In an embodiment, the network is composed of tyramine-substituted and cross-linked hyaluronan molecules, wherein cross-linking is achieved via peroxidase-mediated dityramine-linkages that can be performed in vivo. The dityramine bonds provide a stable, coherent hyaluronan-based hydrogel with desired physical properties.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Lactobacillus plantarum with function of reducing contents of biogenic amines in foods and application of lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN105132308AAcid resistantHas the ability to clearBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and discloses lactobacillus plantarum with a function of reducing contents of biogenic amines in foods and application of the lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum is resistant to acids and capable of strongly removing eight types of biogenic amines (including tryptamine, phenethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine, spermidine and spermine) in vitro. After 1*1010CFU / ml of the lactobacillus plantarum and the eight types of biogenic amines are co-cultured for 24h, wherein the concentration of each type of the biogenic amines is 100mg / L, and the total amine concentration is 800mg / L, the total amine content is reduced by 70% approximately, the content of each type of the biogenic amines is reduced by 30%-100%, and the removal rate of histamine highest in toxicity is up to 96.69%. Further, the lactobacillus plantarum is capable of lowering pH to 4 in eight hours owing to quickness in acid generation, thereby having favorable fermentation potential. The lactobacillus plantarum is used for degradation of the biogenic amines in foods, especially in fermented foods and extensive in application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Regulation of appetite, body weight and athletic function with materials derived from citrus varieties
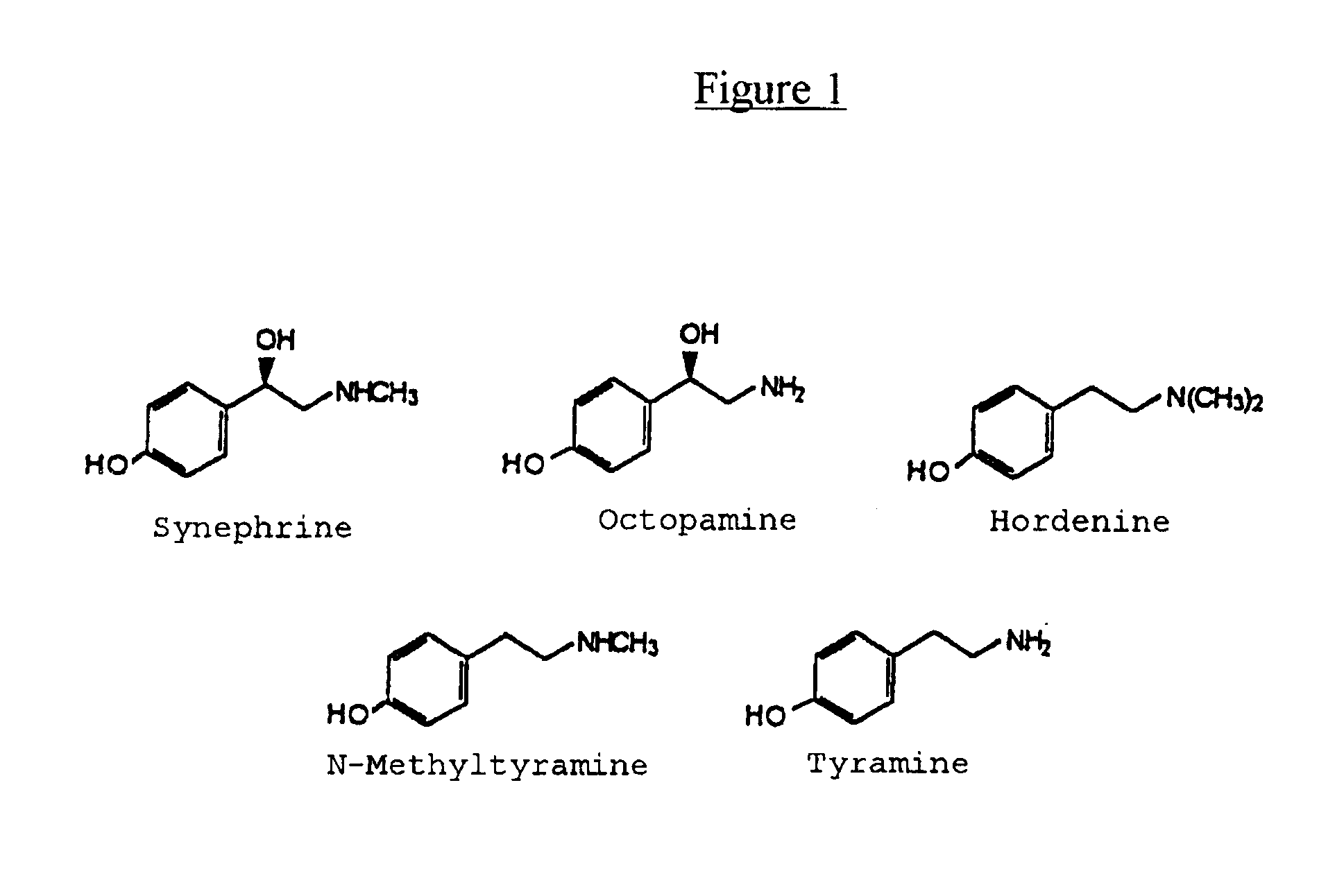
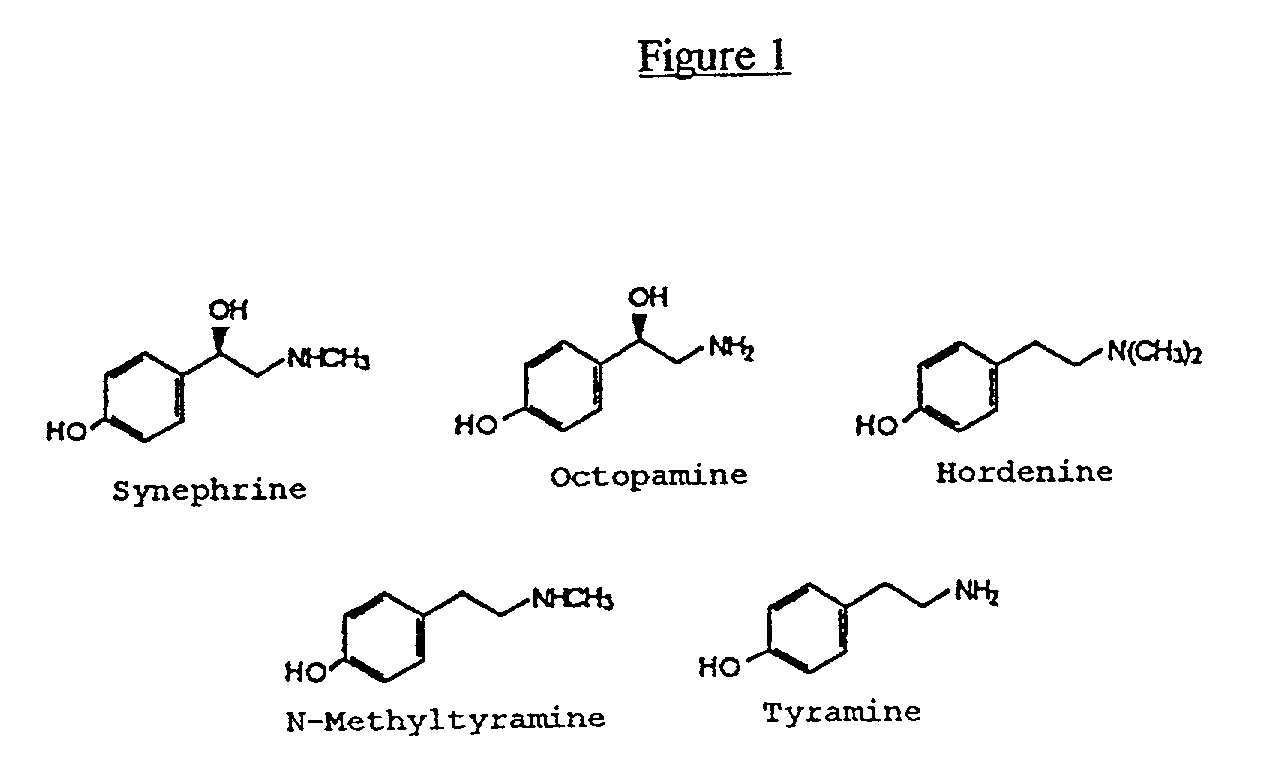
Materials derived from Citrus plants can be administered orally to humans for the purpose of producing or maintaining weight loss as well as for improving the person's physical performance and increasing the person's lean muscle mass. The Citrus materials include those portions of the plant that are normally considered waste or inedible, such as the leaves, peel, and immature, unripe fruit. The materials contain at least one of the alkaloids from the group consisting of synephrine, hordenine, octopamine, tyramine and N-methyltyramine (1). Two species, Citrus aurantium and Citrus reticulata, are particularly useful. The materials can be administered in their natural form or as extracts, and can be administered in various ways including capsules and tablets. The Citrus materials may also be used as a tea. For weight loss and weight control, the materials can be administered concurrently with caloric restriction or in the absence of caloric restriction. The materials may also be administered for the purpose of increasing muscle mass concurrently with a high protein diet as well as with an exercise program.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
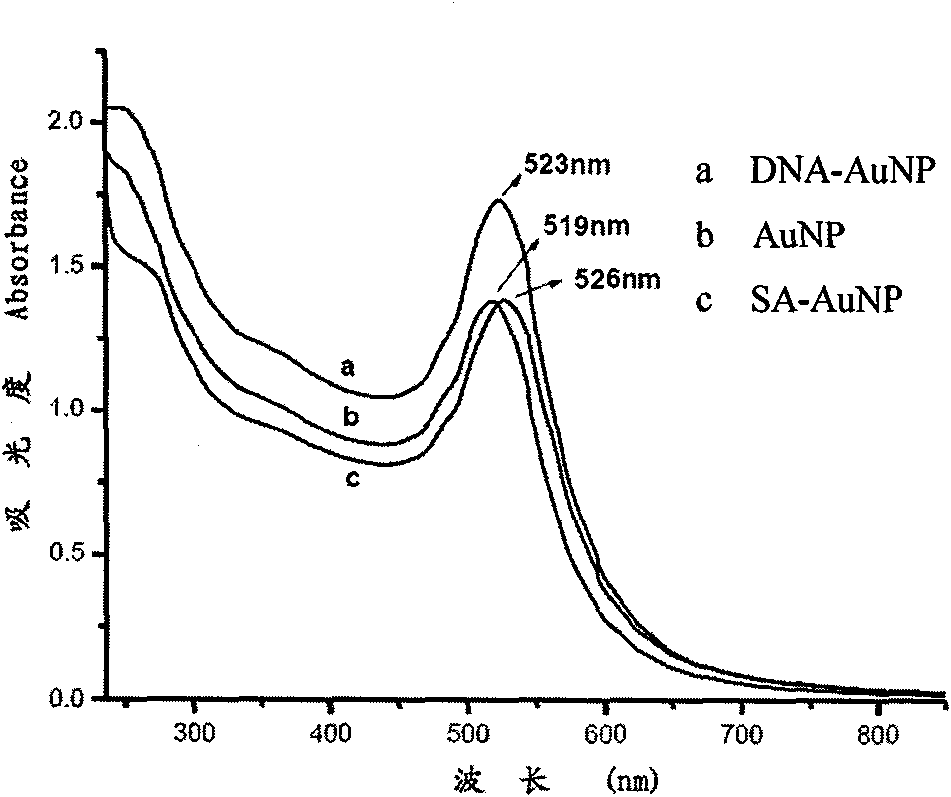
Nanotechnology-based trace protein detection method
InactiveCN101943703AWide linear rangeLow detection limitColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAntigenBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention relates to a nanotechnology-based trace protein detection method, which combines enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology, tyramine signal amplification technology and the aggregation phenomenon of gold nanoparticles modified by different biological molecules, so an experimental method used for detecting trace proteins such as prostate specific antigen (PSA) and the like is established. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing an antibody aiming at the protein to be detected (such as the PSA) on the surface of a substrate; incubating another antibody with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) activity of the protein to be detected (such as the PSA) after capturing the protein to be detected in a sample, wherein the HRP catalyzes biotin-tyramide to generate biotin deposition under certain conditions; further amplifying a signal by using the aggregation phenomenon of the gold nanoparticles modified by biotin-labeled DNA and the gold nanoparticles modified by streptavidin; performing silver staining; and performing data analysis on an experimental result by using software. The method has the advantages of extremely low detection limit, wider detection range, capacity of detecting the antigen in a rabbit serum with complex compositions, and important application prospect.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Methods of screening tyramine- and octopamine-expressing cells for compounds and compositions having potential insect control activity
A screening method for identifying compounds that are effective insect control agents includes providing cells expressing an octopamine receptor, adding the compounds to the cells, and measuring the effects of the compounds and compositions. The effects of the compounds may be determined by measuring the binding affinity of the compounds to the octopamine receptor or measuring the change in intracellular cAMP or Ca2+ levels.
Owner:TYRATECH
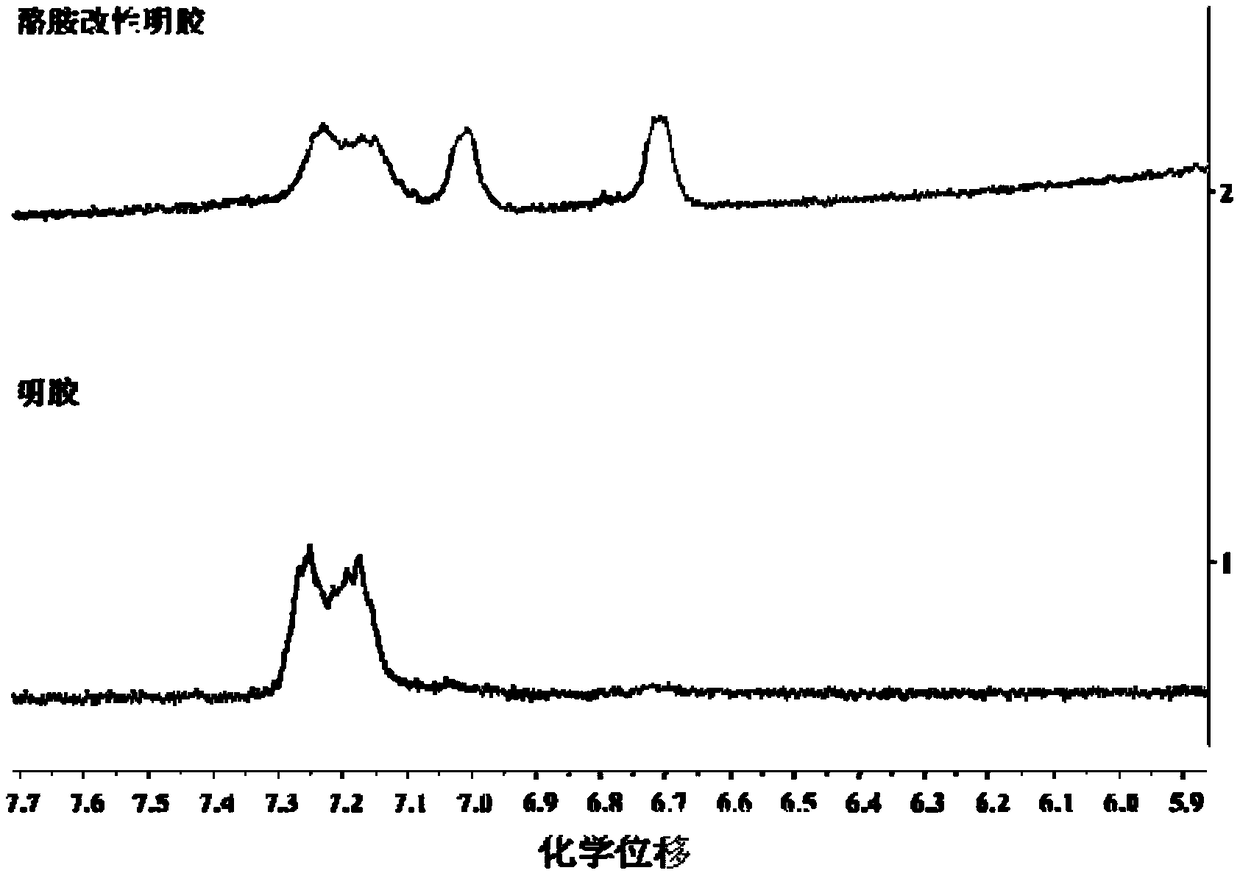
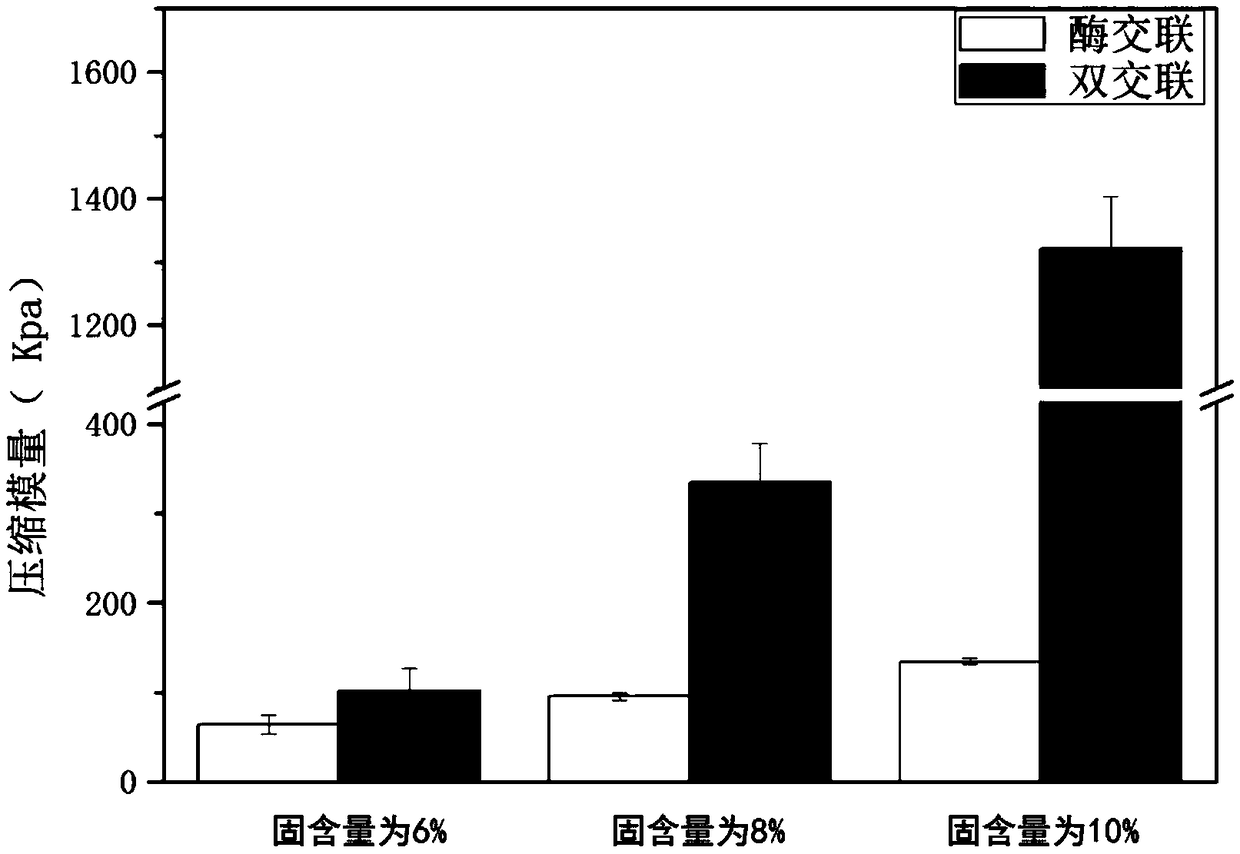
Silk fibroin-gelatin double crosslinked hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a silk fibroin-gelatin double crosslinked hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing tyramine grafting modified gelatin;(2) preparing a silk fibroin solution; (3) preparing thermoreversible silk fibroin / tyramine modified gelatin hydrogel; and (4) preparing silk fibroin-gelatin double crosslinked hydrogel. The method of the invention has simple process, and the prepared double crosslinked silk fibroin-gelatin composite hydrogel has stronger mechanical properties than the gelatin or silk fibroin hydrogel alone, hasthe advantages of gelatin or silk fibroin hydrogel, and makes up for the defects of gelatin or silk fibroin hydrogel. The hydrogel with excellent biocompatibility and mechanical properties has a broadapplication prospect in the field of tissue engineering vascularization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Molecule detection signal amplification technique
InactiveCN102492772AAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionRealize visual detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexAntigen
The invention relates to novel molecule detection signal amplification technique, which is characterized in that the molecule detection signal amplification technique is a biomolecule detection method with high sensitivity which is formed by streptavidin, an antigen, an antibody, polypeptide and the like which are marked by quantum dots through tyramine signal amplification and silver strengthening dyeing signal amplification. The detection method comprises the following steps: the biomolecule to be detected is combined with nucleic acid, the antibody, the antigen, the polypeptide and the like which are fixed on a solid phase material, the quantum dots are introduced to molecule to be detected through biomolecule specificity combination, silver strengthening dyeing is carried out on the quantum dots by using silver dyeing reagents, and signals are amplified. Obtained signals can be scanned through common optical scanners, analyzed through common imaging instruments or observed through naked eyes. The detection method achieves high sensitivity detection of the biomolecule on one hand, and reduces application cost of biomolecule detection on the other hand.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, particularly to provide a synthetic, implantable tissue matrix material for a wide variety of tissue types. In particular, artificial or synthetic cartilage, vocal cord material, vitreous material, soft tissue material and mitral valve material are described. In an embodiment, the network is composed of tyramine-substituted and cross-linked hyaluronan molecules, wherein cross-linking is achieved via peroxidase-mediated dityramine-linkages that can be performed in vivo. The dityramine bonds provide a stable, coherent hyaluronan-based hydrogel with desired physical properties.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
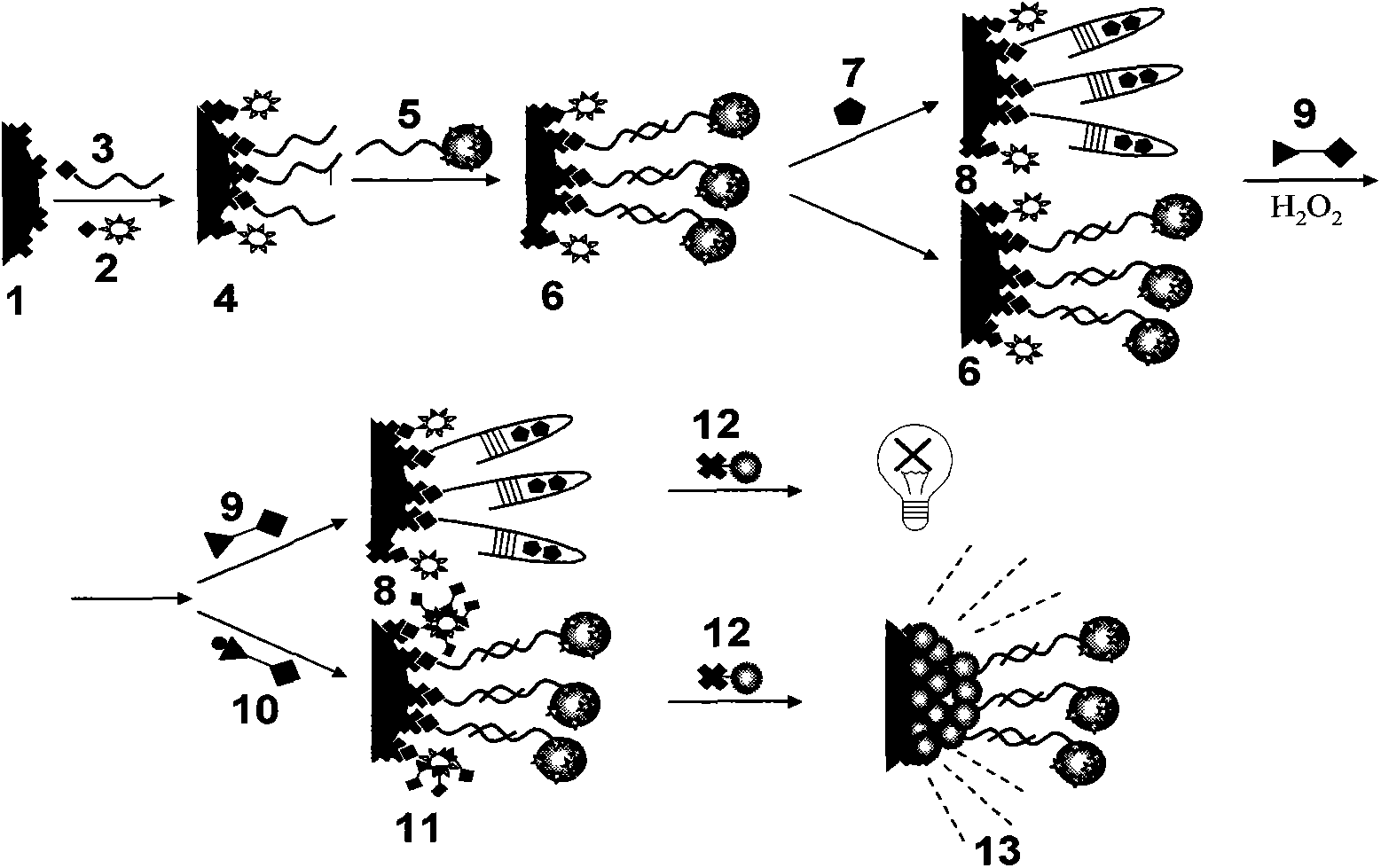
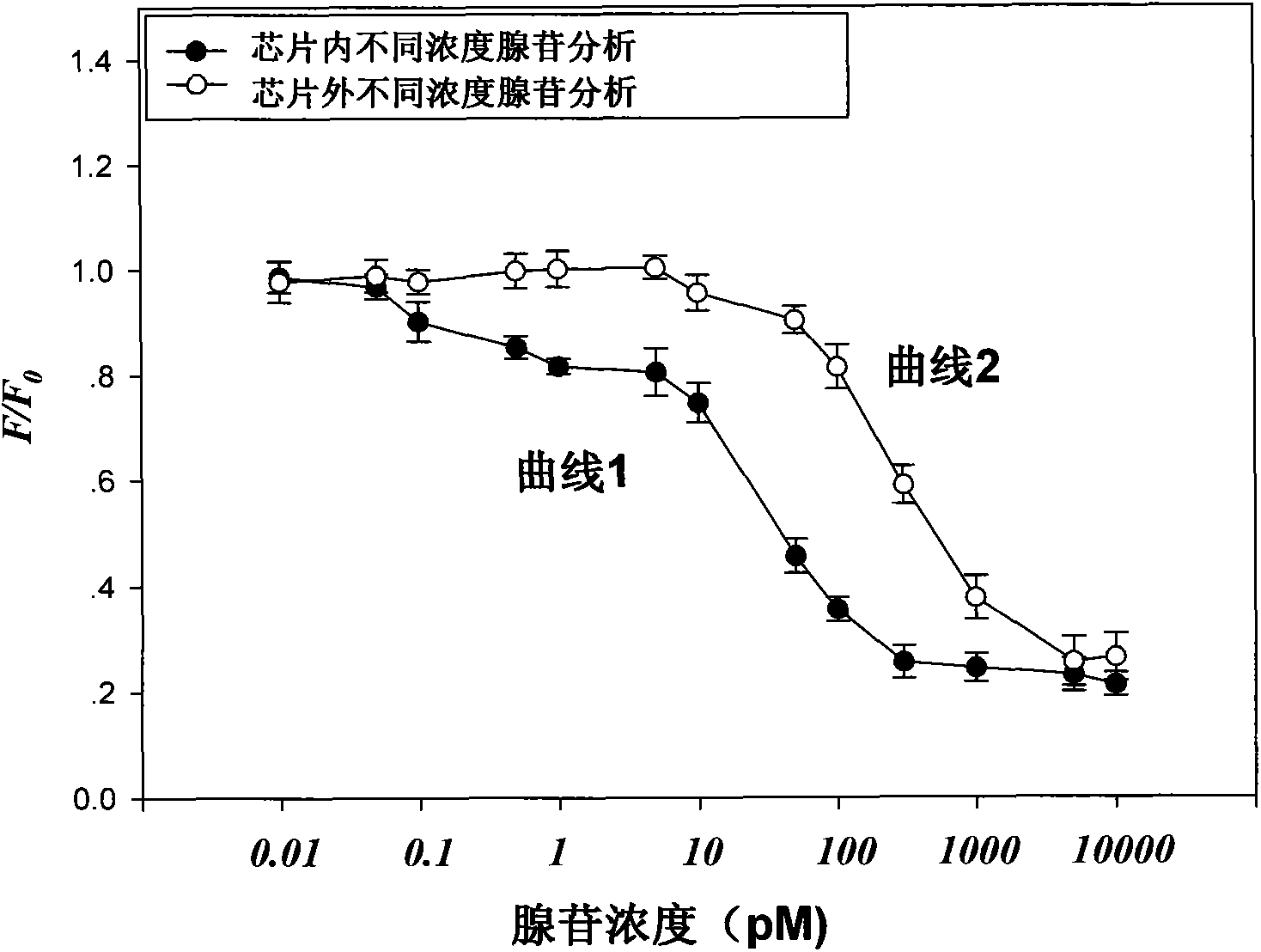
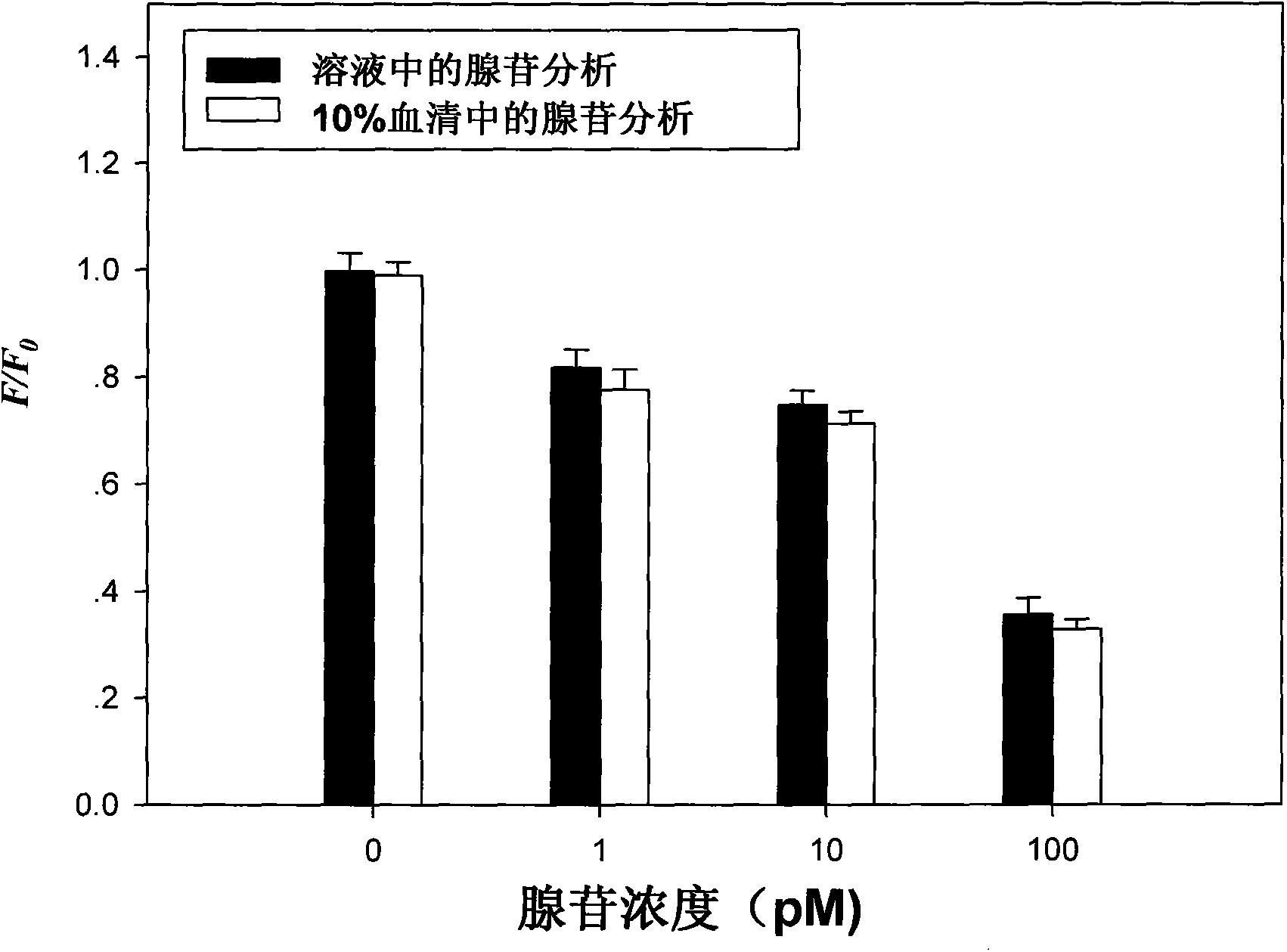
Adenosine detecting method based on micro-fluidic chip and nucleic acid adapter technology
InactiveCN103713138AAccurate quantitative analysisResolve detectionBiological testingFluorescencePeroxidase
The invention discloses an adenosine detecting method based on a micro-fluidic chip and a nucleic adapter technology. Biotin-modified adenosine nucleotide adapter and biotin-modified casein are fixed on the surface of an avidin-modified microsphere to form a functional microsphere through a biotin-avidin combining method; capture probes modified with horseradish peroxidase and sulfydryl are modified on nanometer particles as signal marks; functional nanometer particles flow to a micro-fluidic microsphere array to detect a detection area of a chip and hybrid with a microsphere array; after elution, an adenosine solution flows to be incubated with hybridized microspheres; a peroxidase substrate solution flows in; biotinylated tyramine is combined with the casein on the surface of the microsphere; the avidin-marked quantum dot flows in after elution; qualification and quantification are carried out on the adenosine by calculating a ratio of a fluorescence amount of the microsphere surface after adenosine inflows and a fluorescence amount of the microsphere surface before the adenosine inflows. The adenosine detecting method provided by the invention can be used for detecting and analyzing a target at high sensitivity, so that the specific and accurate quantitative analysis of the adenosine in a serum sample is realized.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
Chitosan hydrogel, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104710653AGood physical and chemical propertiesGood biological propertiesOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryNon toxicityPolyethylene glycol
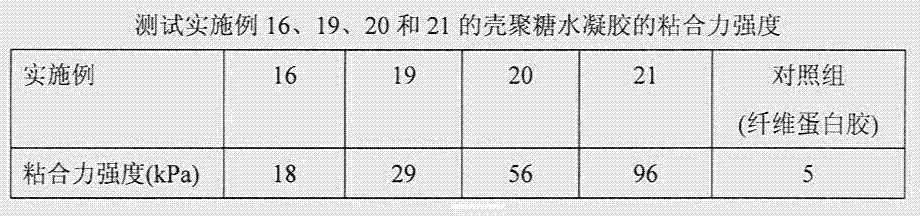
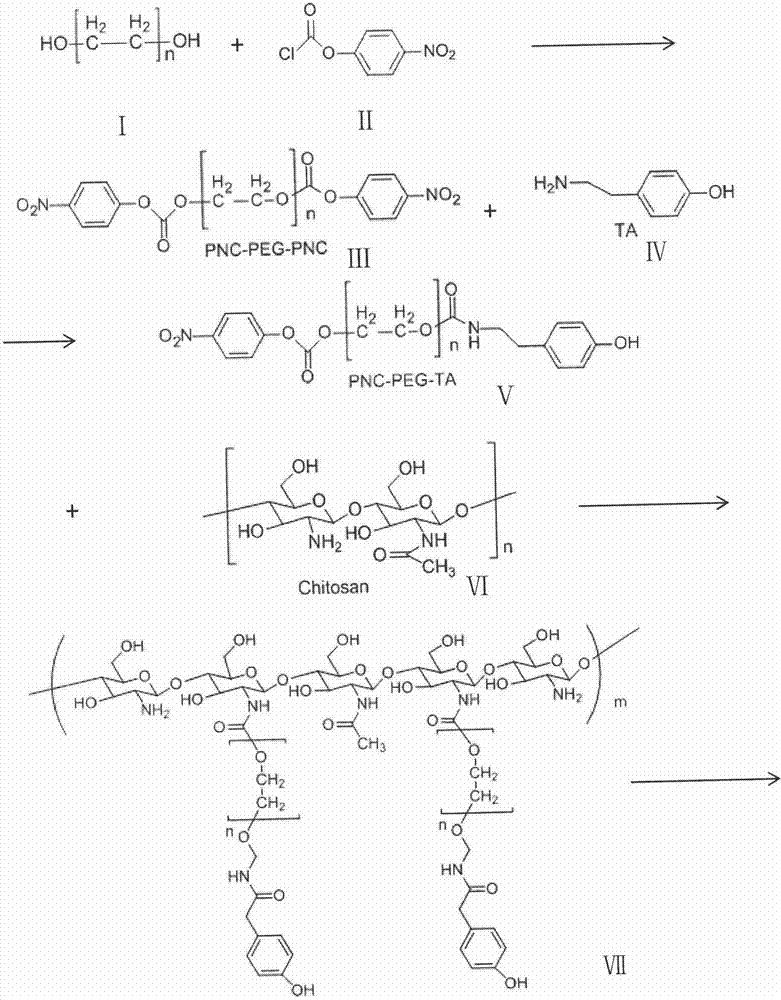
The invention discloses a chitosan hydrogel. The structural unit of the chitosan hydrogel is shown in the specification; and in the structural unit, m is a natural number in a range of 400-700, and n is a natural number in a range of 30-100. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the chitosan hydrogel, and an application of the chitosan hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: polyethylene glycol and tyramine molecules are grafted to a chitosan molecular chain in order to obtain a highly-water-soluble chitosan derivative, and the derivative is processed under the action of a crosslinking reagent to obtain the chitosan hydrogel. The process of the preparation method is simple, and the prepared chitosan hydrogel has the advantages of good physical, chemical and biological performances, good histocompatibility, environmental protection, and non-toxicity, and can be safely and effectively applied in restoration of wound tissues.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
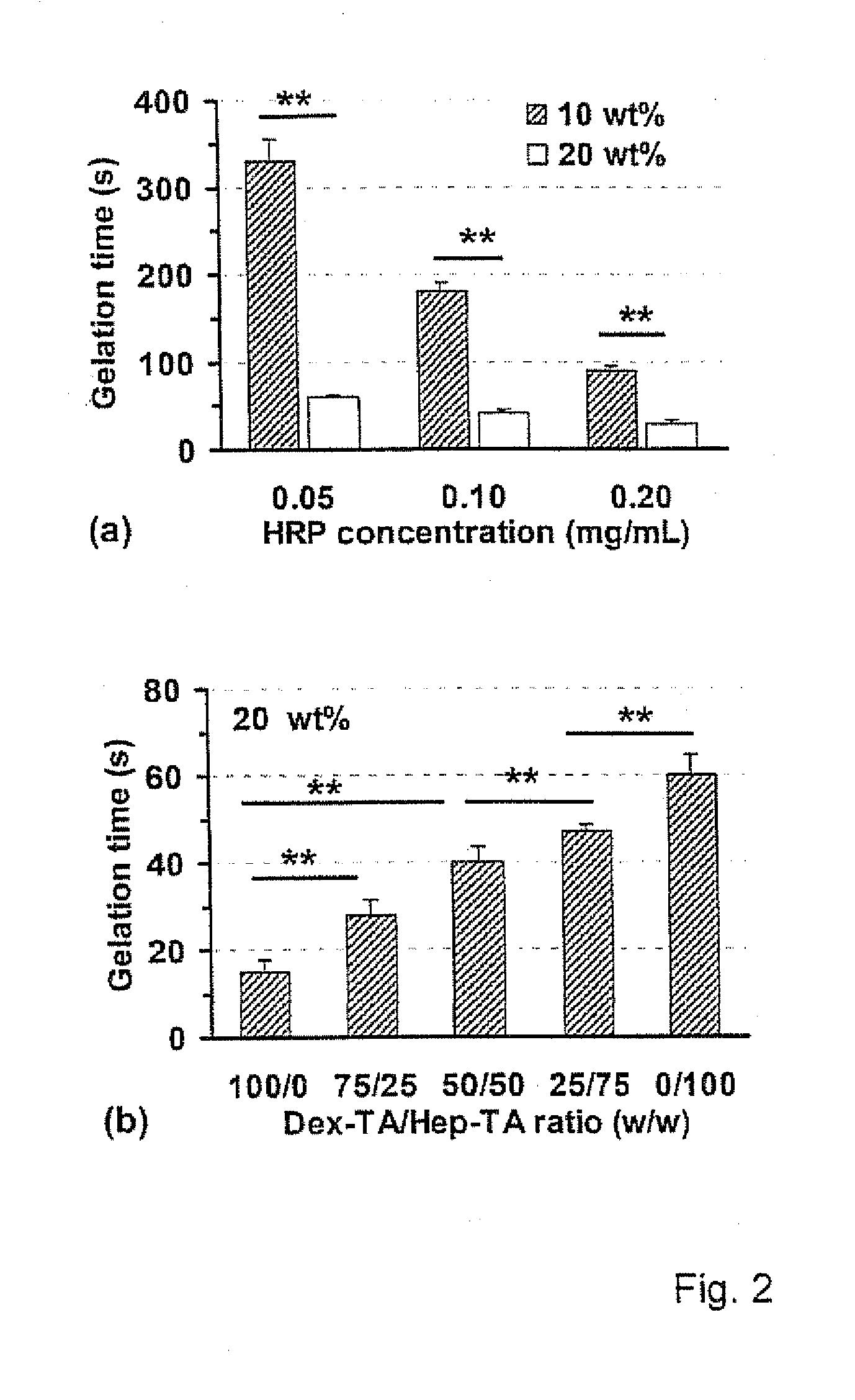
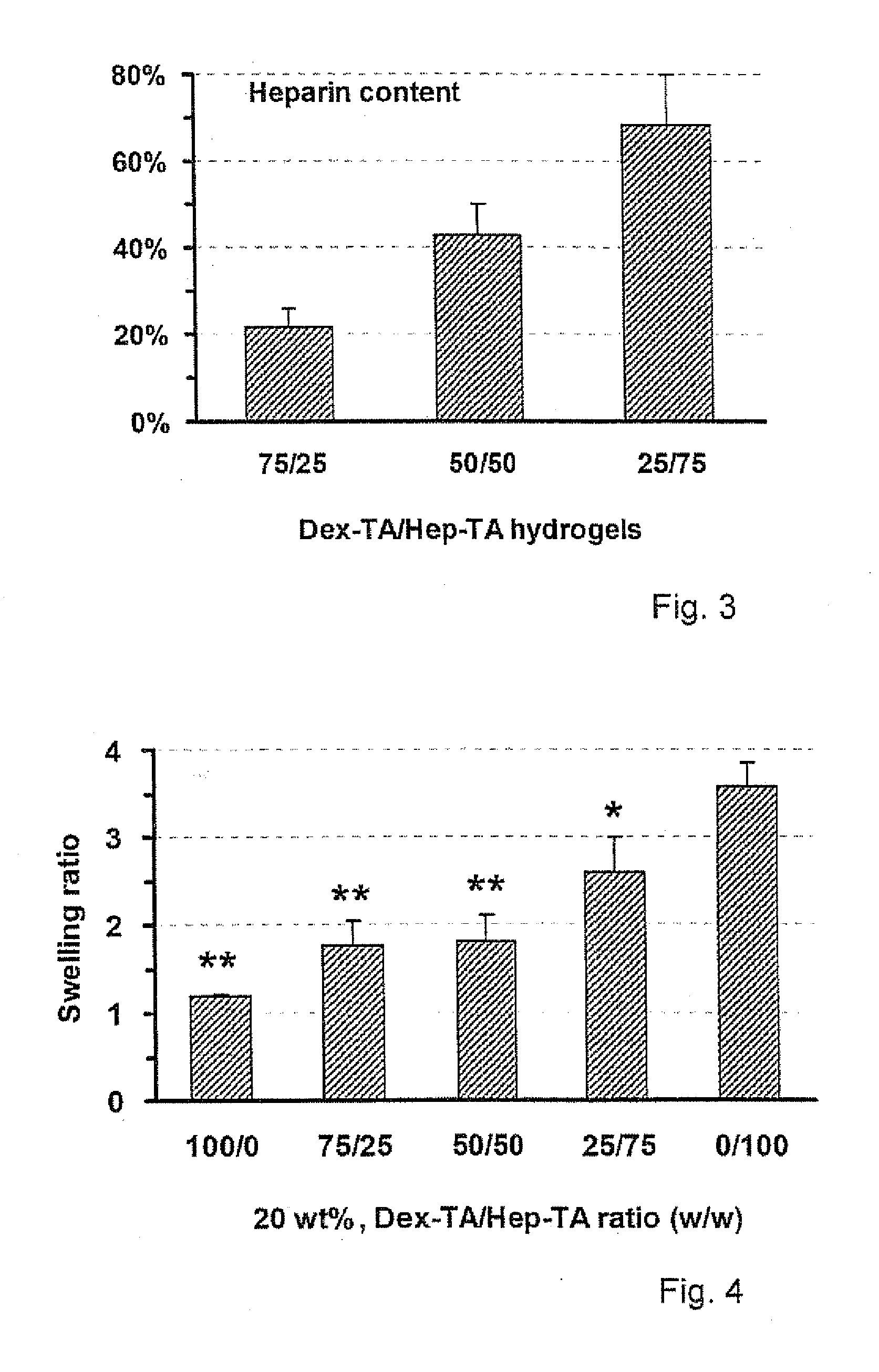
Hydrogels based on polymers of dextran tyramine and tyramine conjugates of natural polymers
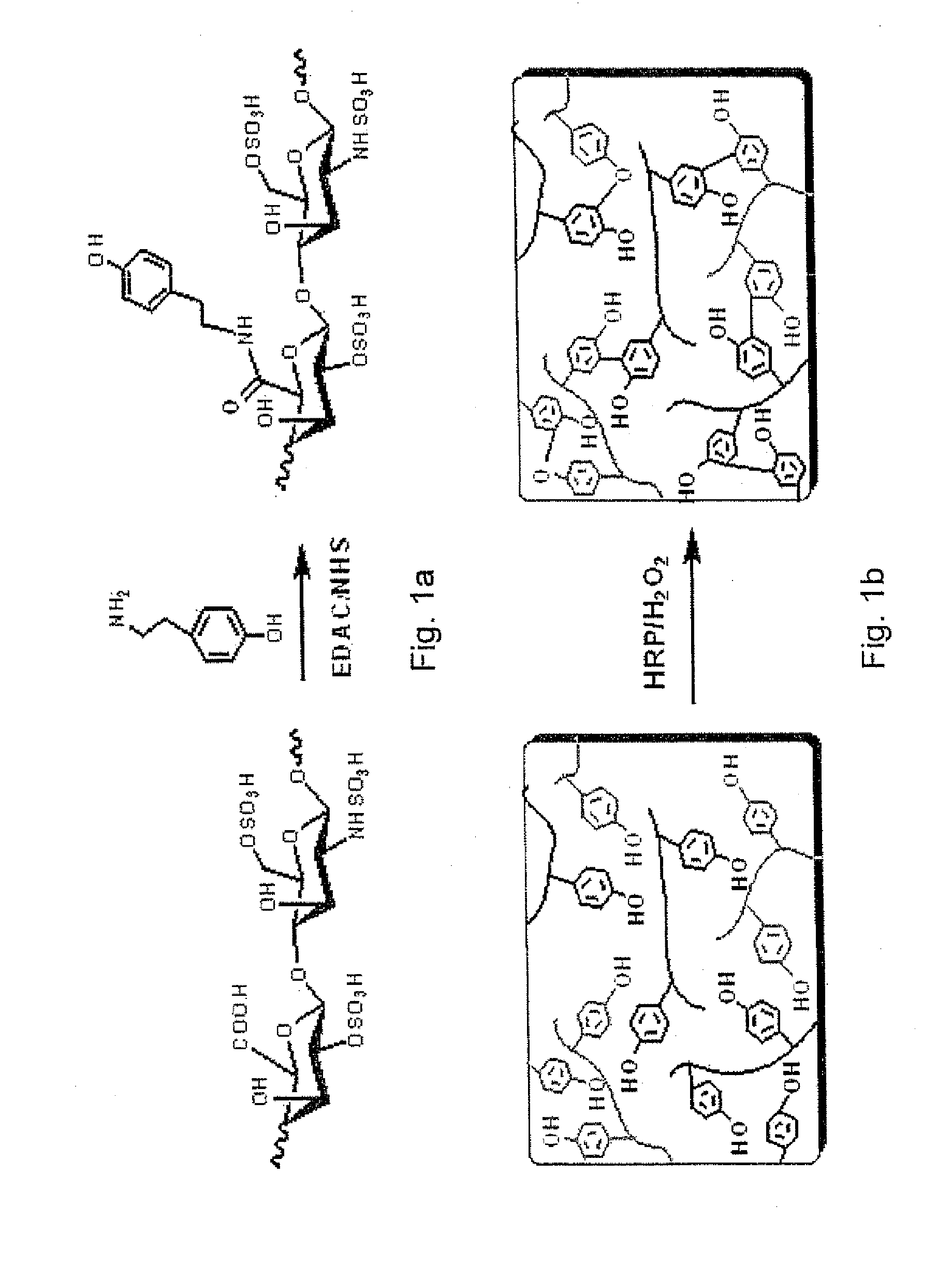
The invention relates to composition comprising a dextran-tyramine conjugate and a conjugate selected from the group consisting of chondroitin sulphate-tyramine, collagen-tyramine, chitosan-tyramine, chitosan-phloretic acid, gelatine-tyramine, heparan sulphate-tyramine, keratin sulphate-tyramine, hyaluronic acid-tyramine and heparin-tyramine.
Owner:HY2CARE BV
Lactobacillus plantarum and its application in the high-acid yellow wine production for acid modulation
ActiveCN106350465AReduces biogenic amine levelsLittle difference in production processBacteriaAlcoholic beverage preparationPutrescineChemistry
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum and its application in the high-acid yellow wine production for acid modulation, belonging to the field of rice wine brewing technology. The lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.12757, isolated from rice wine fermented mash. The lactobacillus plantarum comprises of total acid of rice wine produced of more than 17.5g / L (in lactic acid), lactic acid content of 70% or more accounting for the total organic acid, 14% (v / v) or more of alcohol content, 52mg / L biogenic amine content (the total amount of putrescine, histamine and tyramine), far lower than the rancid rice wine in the storage process, which can produce high-acid rice wine for acid modulation, greatly facilitating the production of low-grade rice wine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
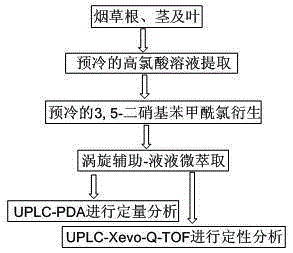
Detection method of polyamine substances in tobacco roots, stems and leaves
ActiveCN105424823AIncrease relative volatilityQualitatively accurateComponent separationNicotiana tabacumFractional factorial design
The invention discloses a detection method of polyamine substances in tobacco roots, stems and leaves. The method comprises the steps that vortex extraction is conducted on tobaccos to obtain polyamines through a pre-cooled perchloric acid solution, derivatization is conducted through 3,5-dinitro benzoyl chloride, extraction and concentration are conducted on a derivative product through vortex auxiliary-liquid-liquid microextraction, and detection is conducted through an ultra-efficient liquid chromatography-photodiode array detector. In addition, in order to obtain the best enrichment factors and the recovery rate in vortex auxiliary-liquid-liquid microextraction, method optimization is conducted through fractional factorial design and Doehlert design. Compared with other methods of analyzing and detecting the polyamines, the detection method of the polyamine substances in the tobacco roots, stems and leaves has the advantages of being rapid in derivative reaction, stable in product, high in sensitivity, good in reproducibility, green and friendly to environment and the like, and accurate qualitativeness and quantification can be conducted on the polyamines in the tobacco roots, stems and leaves. In addition, other four kinds of polyamines, namely, tyramine, 1,3-propylene diamine, high spermidine and canavalmine are identified through high-resolution mass spectrometry, wherein the canavalmine is found in the tobaccos for the first time.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Formula of multifunctional polymethylmethacrylate
The invention discloses a formula of multifunctional polymethylmethacrylate. The formula comprises polymethyl methacrylate and additives, wherein the additives include a fire retardant, an antistatic agent, a dispersing agent, a colorant and a coupling agent; the fire retardant is triphenyl phosphate; the antistatic agent is ethyoxyl lauro tyramine; the dispersing agent is triethylhexyl phosphoric acid; the colorant is palm oil acid diester; and the coupling agent is ammonia propyltriethoxysilane. Prepared polymethylmethacrylate has the characteristics of flame retardance, static electricity resistance, good internal dispersity, diversified colors, low production cost and the like.
Owner:常熟市慧丰塑料制品有限公司
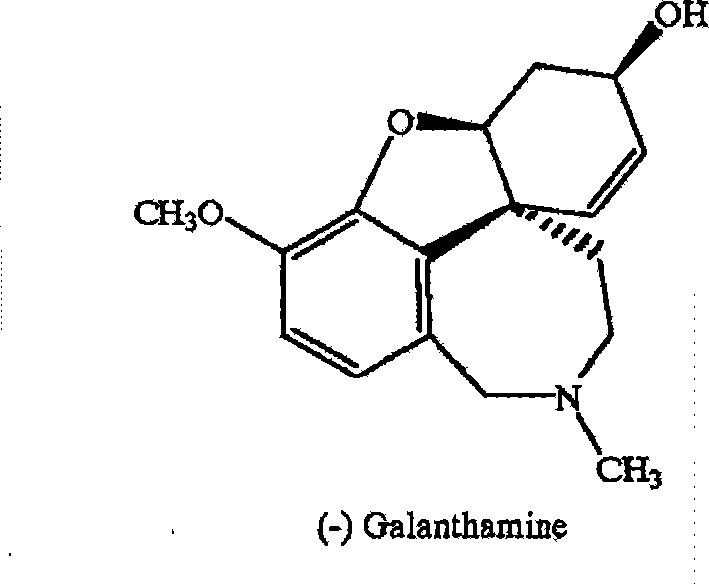
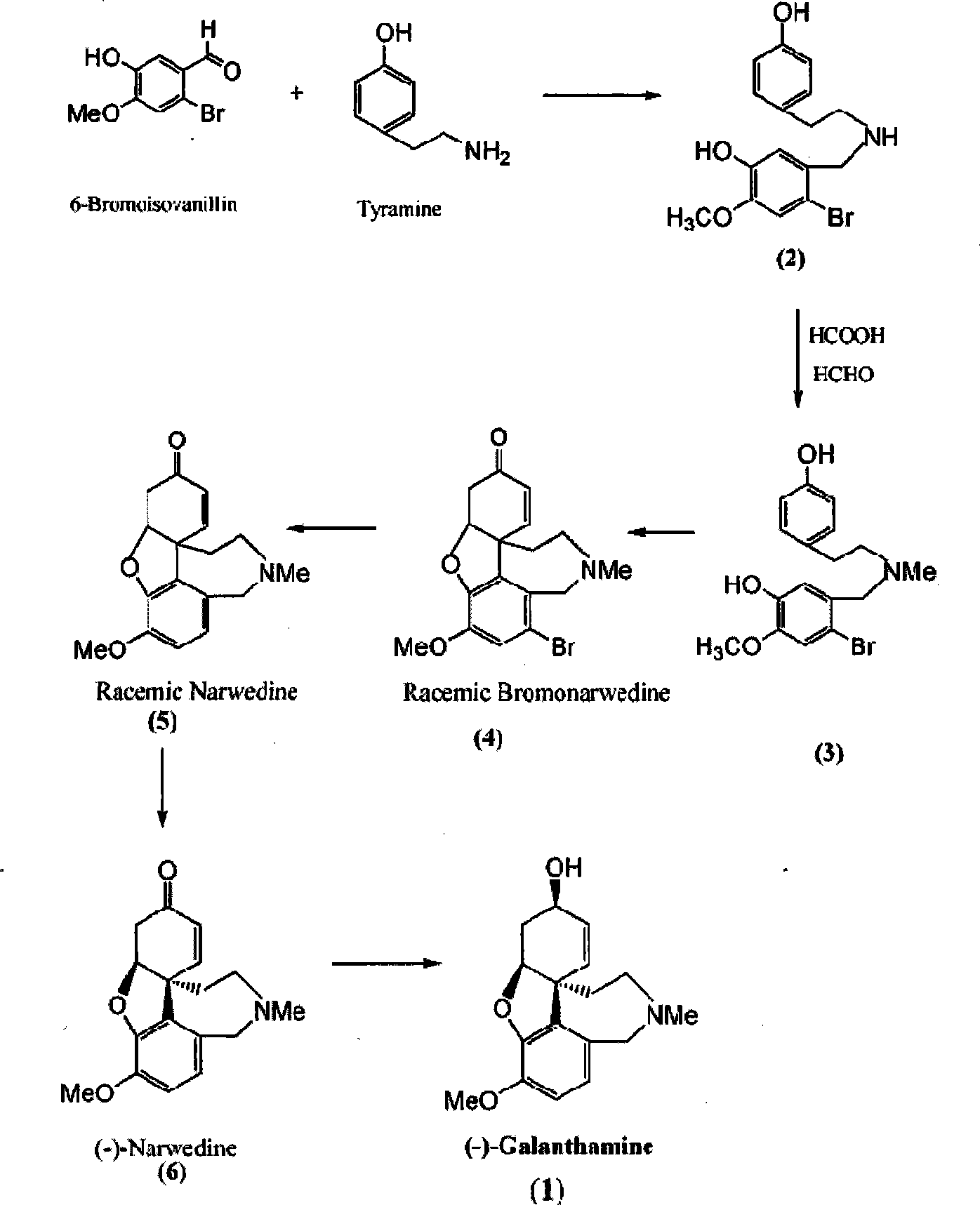
Chiral synthesis method for (-)-galantamin hydrobromide
InactiveCN101239983AFavorable manufacturing methodNervous disorderAsymmetric synthesesHydrobromideEphedrine
Ethamine compound is obtained by condensing starting materials of 6-bromoisovanillin and tyramine under catalysis of NaBH4 in carbinol. In formylation of ethamine compound, aminic acid and formaldehyde of same amount are used to produce formyl compound, with temperature between 90 DEG C. and 110 DEG C., 8h. Racemic bromonarwedine is obtain by oxidation and cyclization of the formyl compound. Racemic narwedine is obtained by reduction reaction under catalysis of NaCO2H, PPh3, Pd(OAc)2. Racemic narwedine is transformed into (-)-narwedine by a process of crystal inoculation. (-)-narwedine is reduced into unsaturated ketone by (-)-N-methyl ephedrine as chiral reagent, whereby optically active alcohol is obtained, and (-)-galanthamine is also obtained.
Owner:泰州市宝嵘新材料有限公司
Enzymatic catalysis crosslinking reduction-responsive hyaluronic acid microgel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105969825AQuick releaseFast curing ratePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFermentationTumor targetBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses enzymatic catalysis crosslinking reduction-responsive hyaluronic acid microgel and a preparation method thereof. The hyaluronic acid microgel is prepared by taking sulfhydrylation hyaluronic acid as a raw material, taking horseradish peroxidase as a catalyst, taking tyramine hydrochloride as an enzymatic catalysis reaction substrate and combining the method that horseradish peroxidase is catalytically crosslinked with sulfydryl to generate a disulfide bond through an inverse emulsion method. The disulfide bond crosslinking structure in the microgel can be broken in the presence of reductive substances such as dithiothreitol, reductive glutathione hormone and L-cysteine, and then the good reduction responsiveness is given to the microgel. The hyaluronic acid microgel can achieve controlled release on the reduction responsiveness of loaded doxorubicin hydrochloride and can be applied to controlled release of tumor-targeted drugs. According to the preparation method, a crosslinking agent does not need to be additionally added into an inverse emulsion system to cure the microgel, the toxicity influence of the crosslinking agent is avoided, the biocompatibility of the microgel is guaranteed, the reaction conditions are mild, and the technological processes are simple.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Methods for inducing weight loss in a human with materials derived from citrus varieties
Materials derived from Citrus plants can be administered orally to humans for the purpose of producing or maintaining weight loss as well as for improving the person's physical performance and increasing the person's lean muscle mass. The Citrus materials include those portions of the plant that are normally considered waste or inedible, such as the leaves, peel, and immature, unripe fruit. The materials contain at least one of the alkaloids from the group consisting of synephrine, hordenine, octopamine, tyramine and N-methyltyramine (1). Two species, Citrus aurantium and Citrus reticulata, are particularly useful. The materials can be administered in their natural form or as extracts, and can be administered in various ways including capsules and tablets. The Citrus materials may also be used as a tea. For weight loss and weight control, the materials can be administered concurrently with caloric restriction or in the absence of caloric restriction. The materials may also be administered for the purpose of increasing muscle mass concurrently with a high protein diet as well as with an exercise program.
Owner:ADVANTRA Z INC
Piper hancei total alkaloid extract and uses thereof
The invention discloses a total alkaloids extractive of piper hancei and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of medicine, and in particular relates to a total alkaloids extractive of traditional Chinese medicine piper hancei and application thereof. The extractive is obtained from the traditional Chinese medicine piper hancei, and comprises the following alkaloid components: sinoacutine amide, hairy grama piperine, long pepper amide A, pepper a-amanitine, Guinea pepper, piperine, piperettine, piperovatine, N-p-tonka-bean acyl tyramine, N-trans- asafetida acyl tyramine, birthwort lactam AIIIa, birthwort lactam II, and 2E, 4E-N- isobutyl-7-3,4-methinedioxy phenyl-2, 4-diene heptamide, long pepper nerinine and a derivate thereof, wherein the total content of the total alkaloids components is counted by 5 to 100 percent by weight.
Owner:JIANGXI HERBFINE HI TECH
Enzyme for degrading biogenic amine in soy sauce
The invention discloses enzyme for degrading biogenic amine in soy sauce, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation. A sequence of multi-copper oxidase crude enzyme provided by the inventionis as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The enzyme disclosed by the invention has different degrees of degradation functions on biogenic amine of tryptamine, phenylethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine and spermidine in the soy sauce, wherein the concentration of the tyramine of which the content in the soy sauce is the most is 540.71 mg / L. After adding the multi-copper oxidase crude enzymeprovided by the invention, the content of the biogenic amines is reduced by 100 mg / L within 24 hours; compared with an existing technology for reducing the content of the biogenic amine by 58.57 mg / Lby adding pure enzyme in a biogenic amine mixed solution for 24 hours, the degradation time is short, and the effect is good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Combination of amines and vanadium (IV)/(V) compounds for the treatment and/or prevention of diabetes mellitus
Combinations comprising vanadium (IV) / (V) compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable amines selected from the group of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) substrates are insulin mimickers. Preferred vanadium (IV) / (V) compounds are vanadyl salts, vanadyl complexes and vanadates (e.g. sodium orthovanadate). Preferred amines are tyramine and benzylamine. A here-discovered synergism between the vanadium compound and the amine makes the effective concentration of vanadate in the combination one order of magnitude lower than the corresponding of vanadate alone. Consequently the combination has much lower toxicity than the known vanadium compound alone, which is a crucial advantage of the former for its use in the treatment and / or prevention of Diabetes mellitus.
Owner:UNIV DE BARCELONA
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, particularly to provide a synthetic macromolecular network for a wide variety of tissue types. In particular, artificial or synthetic cartilage, vocal cord material, vitreous material, soft tissue material and mitral valve material are described. In an embodiment, the network is composed of tyramine-substituted and cross-linked hyaluronan molecules, wherein cross-linking is achieved via peroxidase-mediated dityramine-linkages that can be performed in vivo. The dityramine bonds provide a stable, coherent hyaluronan-based hydrogel with desired physical properties.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
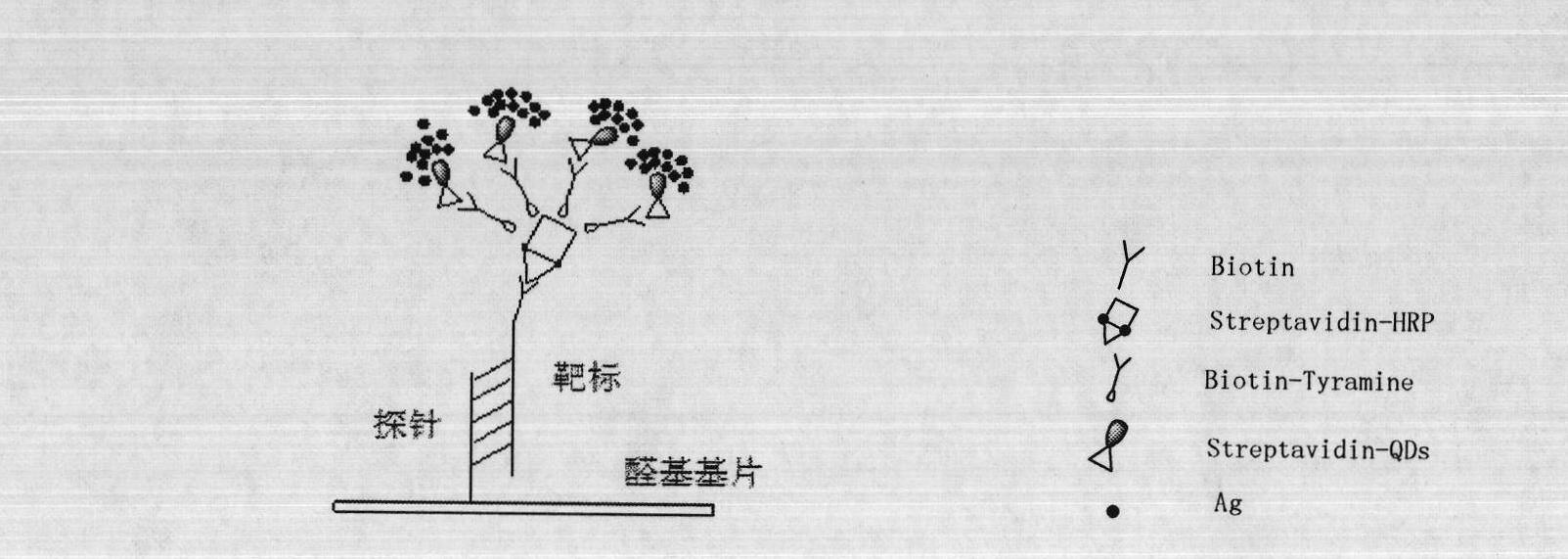
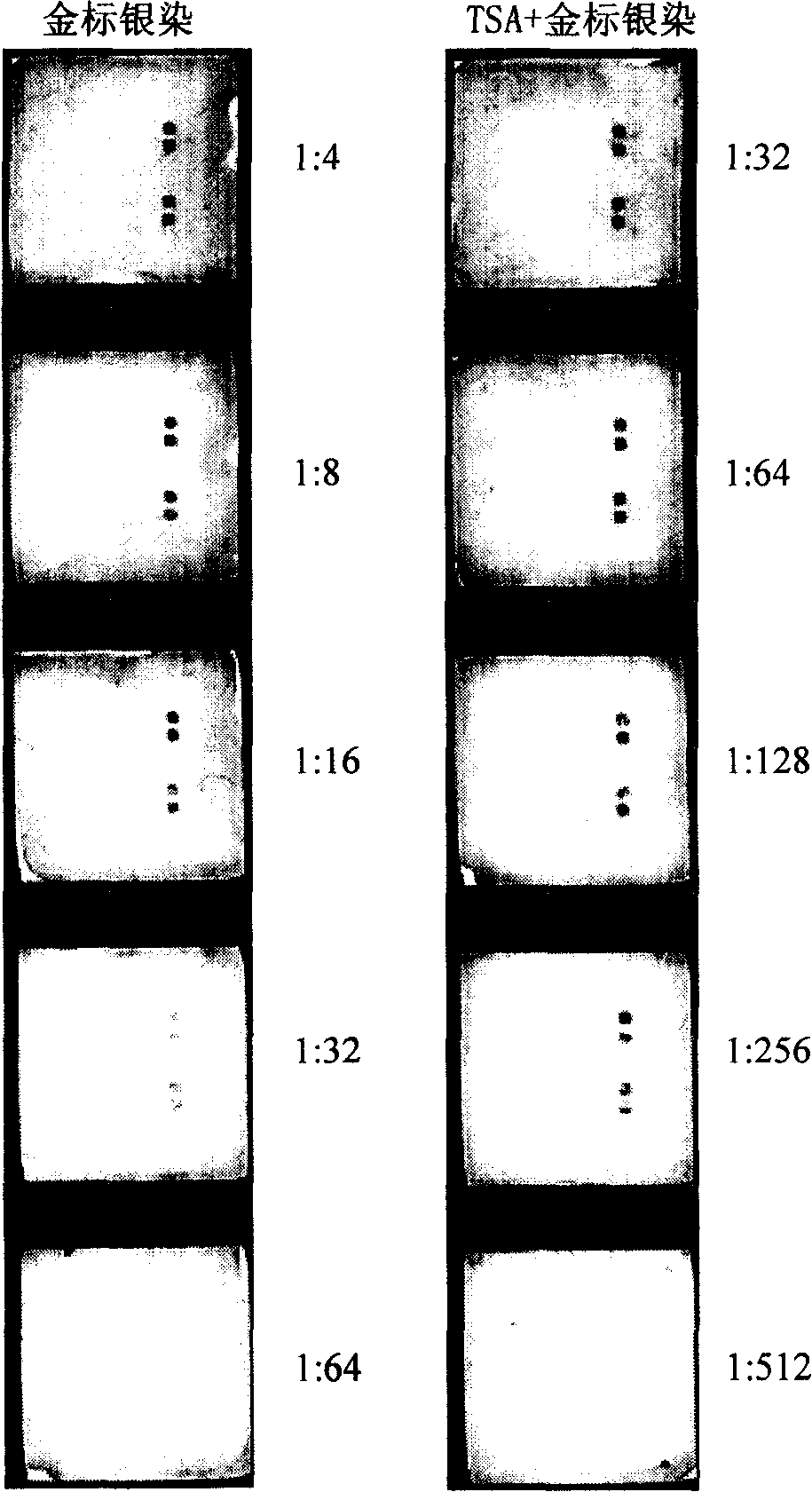
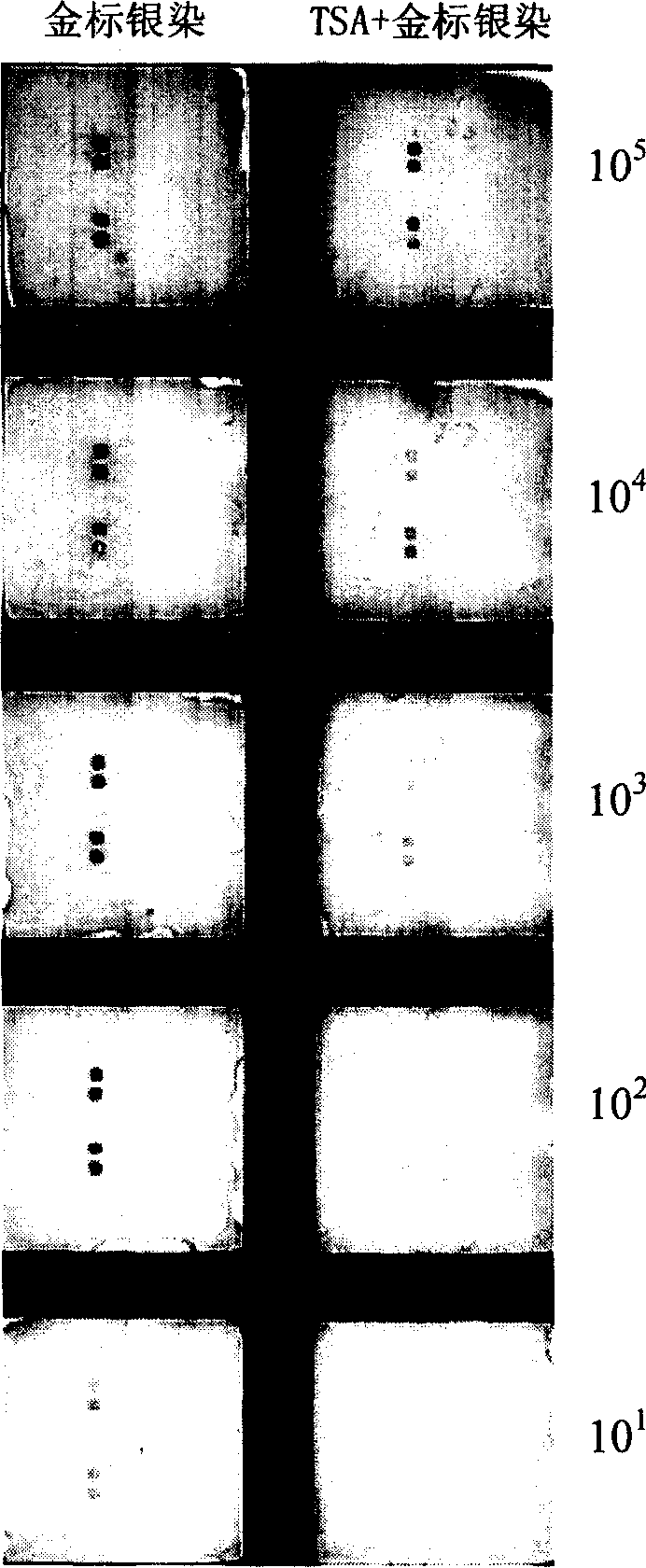
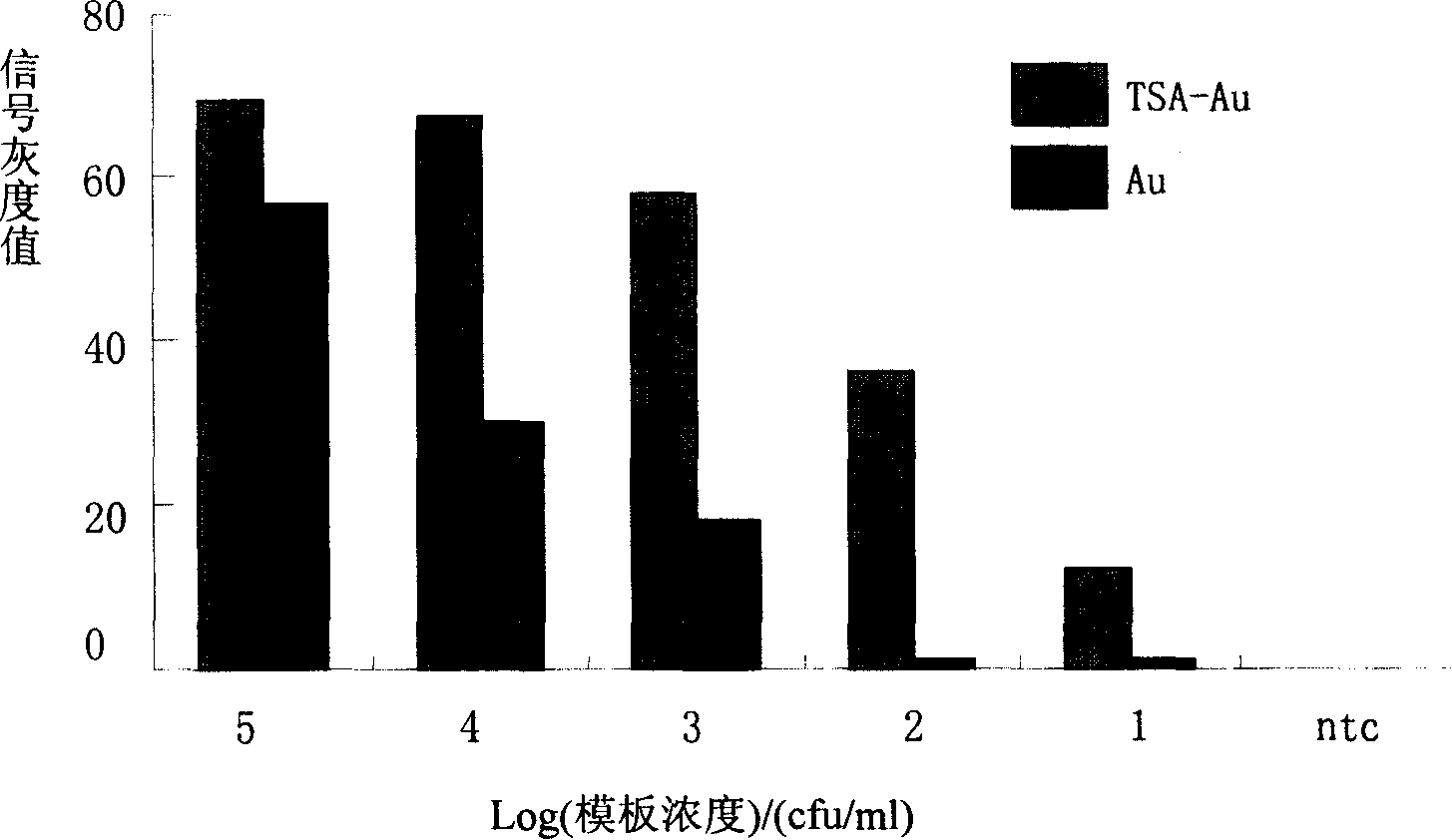
TSA- nano-gold making silver-staining testing method of gene chip
InactiveCN101162201AHigh detection sensitivityLong validity periodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexGold particles
The invention relates to a detection method with a gene chip, in particular to a visualized detection method which can improve the sensitivity of gold label silver stain of a gene chip to a great extent. The detection method mainly comprises the following steps that: gene marker biotin molecule of a sample to be tested is used to hybridize with the gene chip. At first, TSA treatment is performed on the hybridized chip; vast Tyramine is precipitated around a reaction site under the catalysis of enzymes; gold nanoparticles with streptavidin are added and nanoscale gold particles are connected to target molecules; silver stain reagent is used to color the hybridized gene chips to observe and analyze signals. A TSA procedure is added in the method provided by the invention based on a single gold label silver stain detection, the Biotin-Tyramine reagent used for TAS is simple to prepare, avoids purification and is easy to preserve and stable in performance. Compared with the single gold label silver stain detection method, the detecting sensitivity of the gene chips can be improved by ten to one hundred times.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Method for artificially synthesizing galanthamine
The invention discloses a method for artificially synthesizing galanthamine, which uses isovanillin and bromine as the raw materials. After the raw materials are subjected to substitution reaction, the reaction and industrial chemicla tyramine are subjected to amination and formylation to obtain formamide, the formamide is subjected to reaction to obtain a derivative of racemic narwedine, the derivative of racemic narwedine is reduced into racemic narwedine, N-methylephedrine is used to reduce unsaturated ketone and tartaric acid is used to carry out resolution to obtain levogyrate galanthamine. The method not only can conveniently and rapidly prepare the galanthamine, but also adopts artificial preparation so as to have little limination in the preparation process.
Owner:泰州市宝嵘新材料有限公司
Dextran-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels
The invention provides a copolymer of hyaluronic acid (HA) grafted with a dextran-tyramine (Dex-TA) conjugate.
Owner:UNIV OF TWENTE INST FOR BIOMEDICAL TECH & TECHN MEDICINE MIRA
Multicopper oxidase recombinase capable of degrading biogenic amine
ActiveCN108165515AStrong performance in degrading biogenic aminesBroad degradation spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTryptamine
The invention discloses a multicopper oxidase recombinase capable of degrading biogenic amine, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation. According to a degradation method, an appropriate amount of the multicopper oxidase recombinase is added into soy sauce, biogenic amine is degraded by the multicopper oxidase recombinase into aldehydes and ammonias, and degradation of biogenic amine isrealized, wherein the multicopper oxidase recombinase is obtained via heterologous expression of multicopper oxidase recombinase genes from Lactobacillus paracasei in Escherichia coli. The multicopperoxidase recombinase possesses relatively excellent biogenic amine degradation capacity, is capable of degrading tryptamine, phenylethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine, spermine, and spermidine in 24h, and the highest degradation efficiency is 75%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
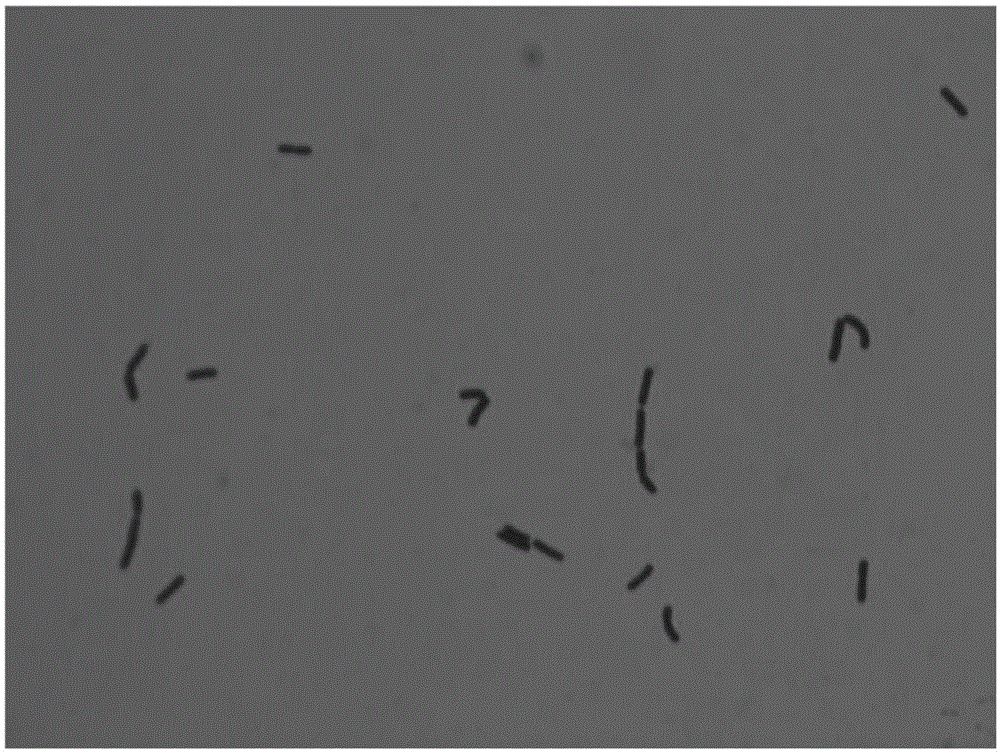
ActiveCN101701201AReduce manufacturing costSave energyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationTyrosine
The invention relates to an enterococcus faecalis with the collection number of CGMCC No.3164. A bacterial colony is cultured on an MRS agar culture medium at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 24 hours to be gathered; the bacterial colony is white, thallus is ovate, extends along chain direction, is in pair or in short chain, is Gram-negative, generates lactic acid when fermenting glucose and is elliptic under a common microscope. When being applied, the bacterial colony is inoculated into a test tube filled with culture medium A to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for 24 hours; after being repeatedly activated five times, the bacteria solution is inoculated into a culture medium B to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for four days; the cultivated bacteria solution is decentralized at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes; and supernate is extracted to obtain high concentration tyramine solution. The culture medium A is an MRS liquid culture medium of 0.1% of tyrosine, and the culture medium B is an MRS liquid culture medium of 0.005% of pyridoxal phosphate and 0.1% of tyrosine.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Non-toxic photoelectrochemistry competition immunoassay method of zearalenone based on peptide sensor
InactiveCN108535345AHigh porosityFast transmissionBiological material analysisBiological testingCysteaminePhotoelectrochemistry
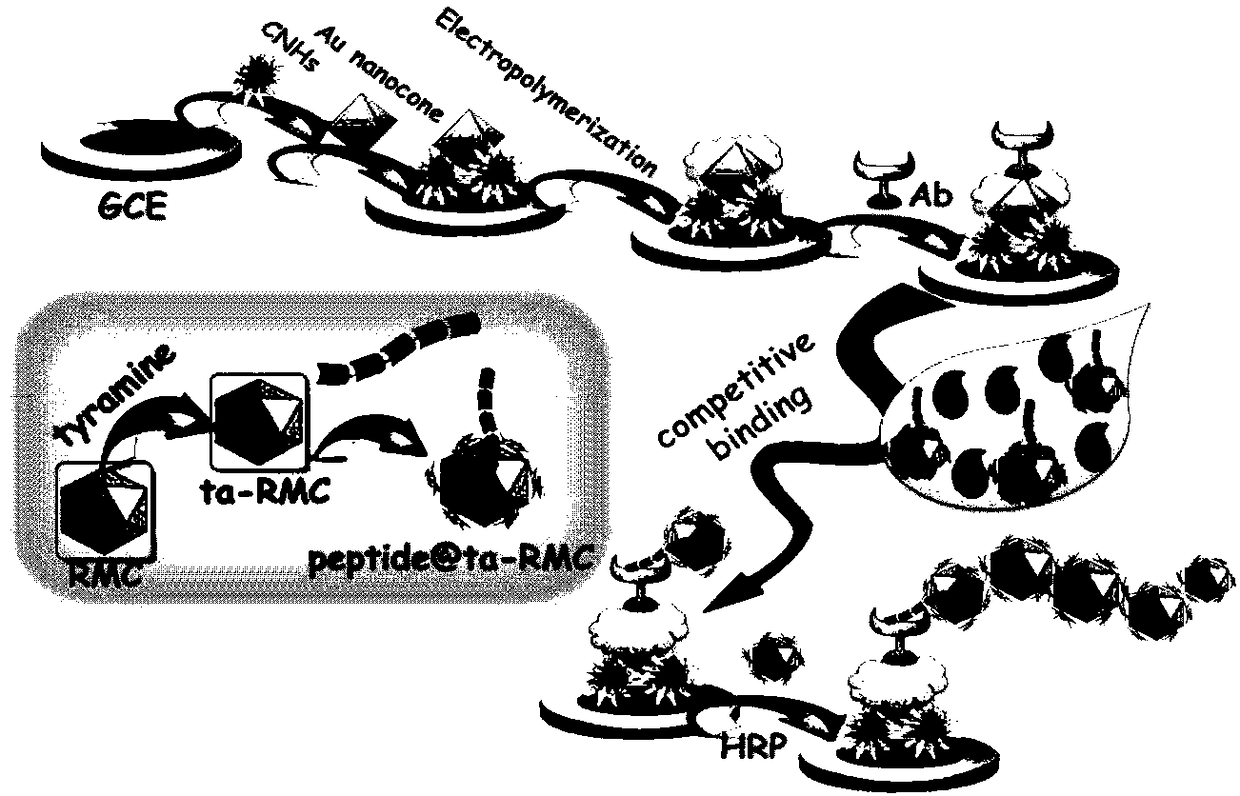
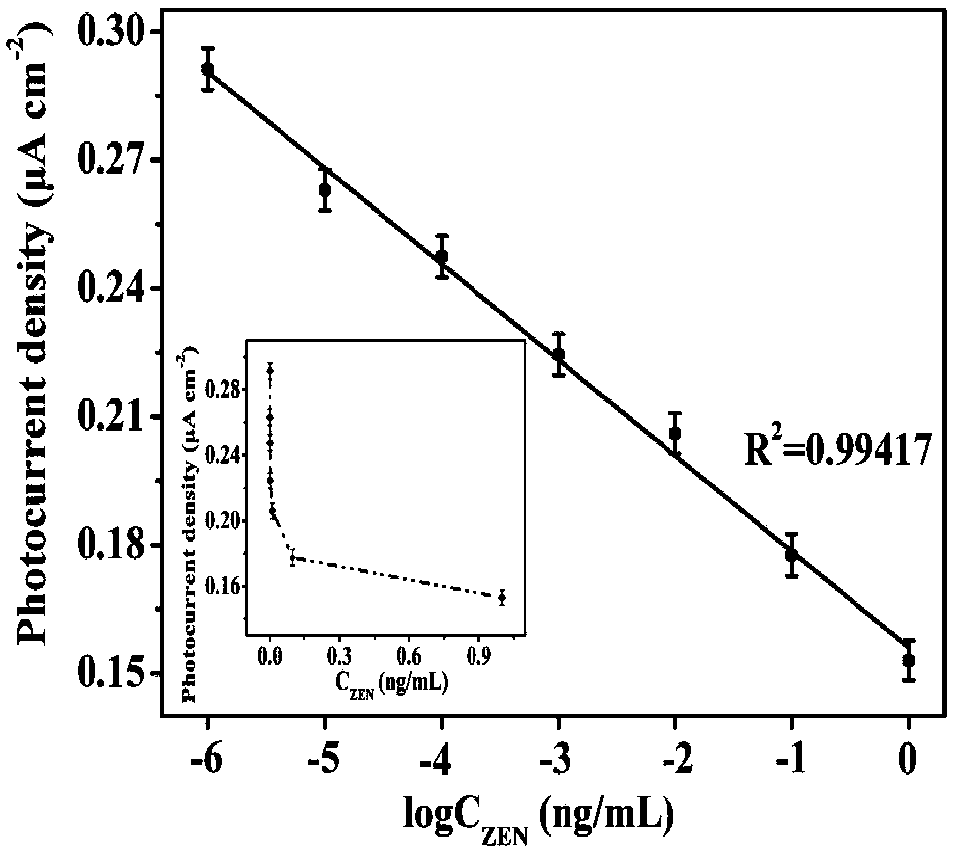
The invention discloses a non-toxic photoelectrochemistry competition immunoassay method of zearalenone based on a peptide sensor. According to a sensing interface building method, carbon nanohorns, cysteamine functional golden cone and polyglycine are used as substrates; corn zeranol antibodies (Ab) are further immobilized; tyramine functionalized nanometer rutile type TiO2 mesoscopic crystals are used for immobilizing peptide chains with the specific sequences as a photoelectric probe; the peptide chain has the effect of simulating the zearalenone, the zearalenone can compete with the markedphotoelectric probe to combine the corn zeranol antibodies immobilized on the sensing interface. The photoelectric probe combined onto the sensing interface can further combine with tyramine-Rutile TiO2 mesoscopic crystal compounds under the catalysis effect of horseradish peroxidase; optoelectronic signals can be further amplified. On the basis, the non-toxic photoelectrochemistry competition immunoassay method on the corn zeranol can be built.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
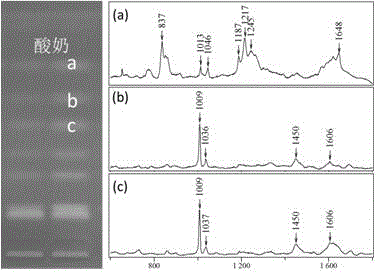
Method for rapidly detecting multiple biogenic amines in dairy product by virtue of combination of high performance thin layer chromatography and adjustable surface enhanced raman spectroscopy
ActiveCN106706834ASuppress masking effectWell-characterized Raman fingerprintsComponent separationVisual field lossSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
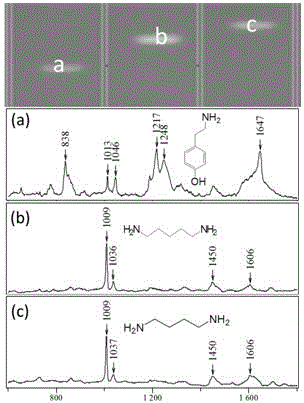
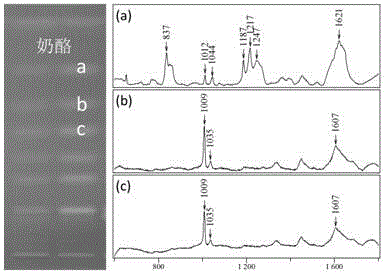
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting multiple biogenic amines in a dairy product by virtue of combination of high performance thin layer chromatography and adjustable surface enhanced raman spectroscopy, and belongs to the technical field of food detection. The method comprises the steps of preparation of nano silver colloid, preparation of samples, separation based on high performance thin layer chromatography, HPTLC-SERS detection and the like. The HPTLC-SERS detection method for identifying structures of the multiple biogenic amines (tyramine, putrescine and cadaverine) is established, and has the advantages of economical efficiency, rapidness, simplicity and convenience; furthermore, by virtue of the selectivity enhancement function of a new synergist, the application range of HPTLC-SERS detection is expanded, and a new visual field is opened for directly and rapidly detecting a chromatoplate for chemical derivatization.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
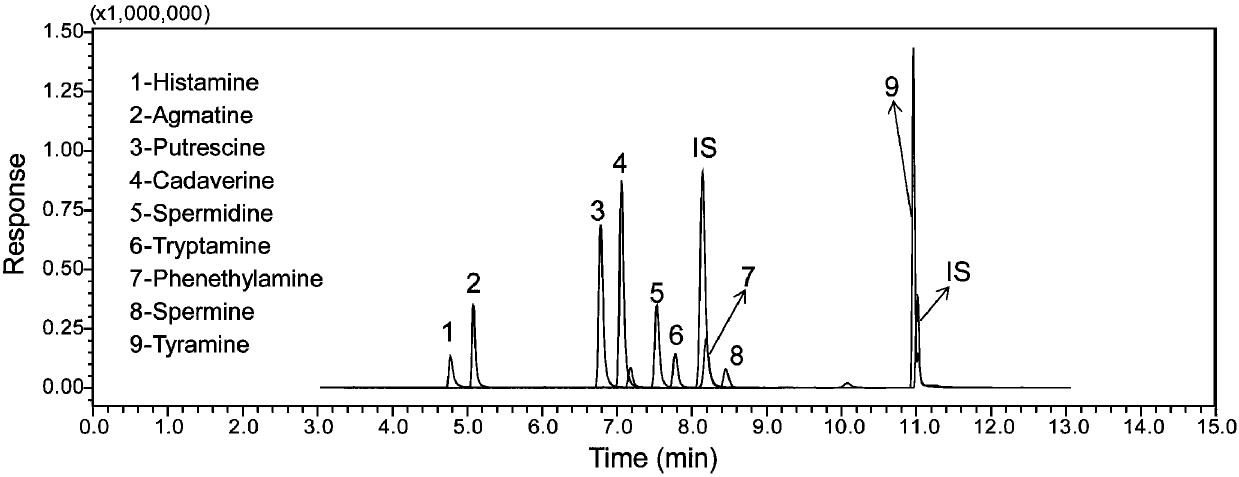
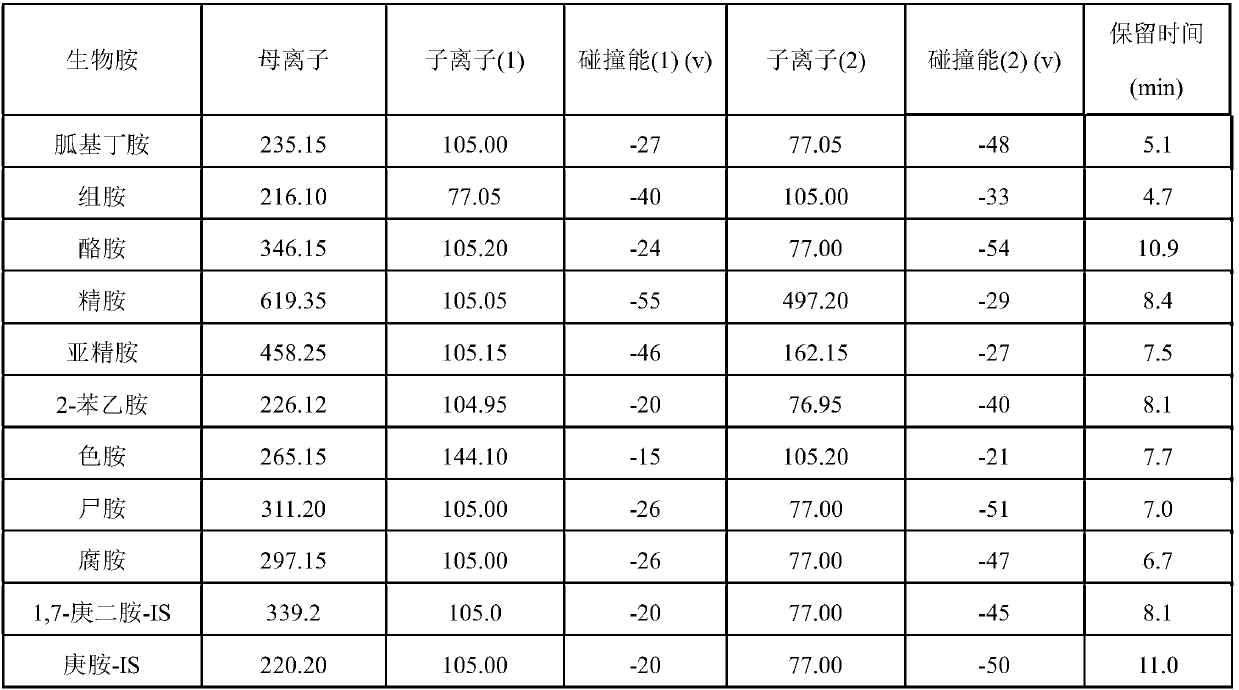
Rapid analysis method of biogenic amine in fish
ActiveCN107782834AReduce the impactHigh sensitivityComponent separationTryptamineSulfosalicylic acid
The invention discloses a rapid analysis method of biogenic amine in fish. The common biogenic amine (nine types of biogenic amine comprising agmatine, histamine, tyramine, spermine, spermidine, 2-phenylethylamine, tryptamine, cadaverine and putrescine) is analyzed in a targeted manner by taking 5-sulfosalicylic acid as an extraction solvent, adopting bead agitating and grinding as an extraction method, taking benzoyl chloride as a derivatization reagent and adopting an LC (liquid chromatogram)-triple tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. The biogenic amine is detected in a multi-reactions monitoring manner by taking ion pairs with optimum response, which are obtained by optimization, as quantitative ion pairs and taking ion pairs with following response as auxiliary qualitative ion pairs.According to the method, the sample extraction time and the biogenic amine derivation time can be greatly shortened, so that the analysis time of the whole analysis process is greatly shortened. The analysis method has the advantages of being simple in sample pretreatment, rapid in derivation, high in detection sensitivity, high in repeatability and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com