Patents
Literature
168 results about "Silver stain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
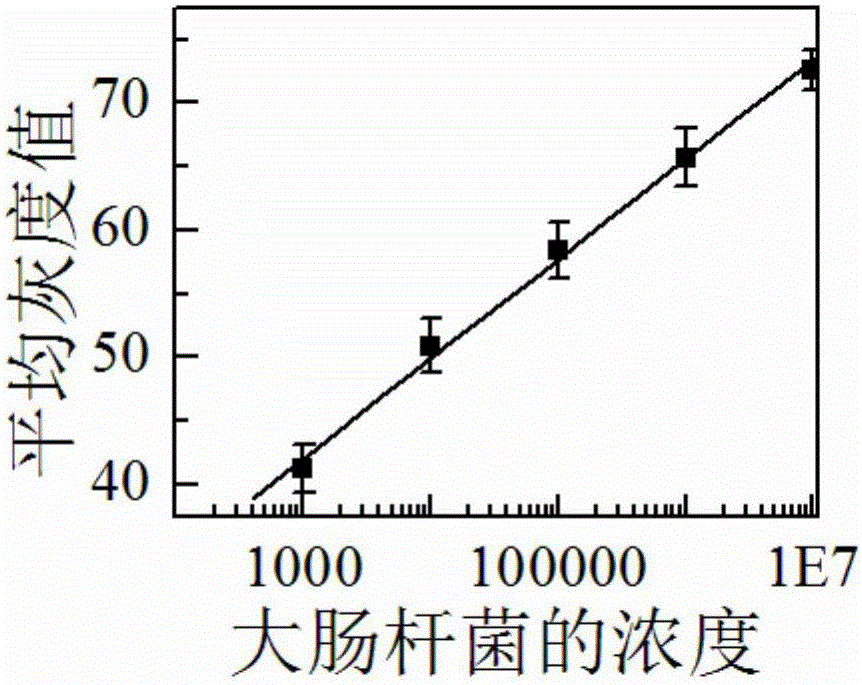
Silver staining is the use of silver to selectively alter the appearance of a target in microscopy of histological sections; in temperature gradient gel electrophoresis; and in polyacrylamide gels.
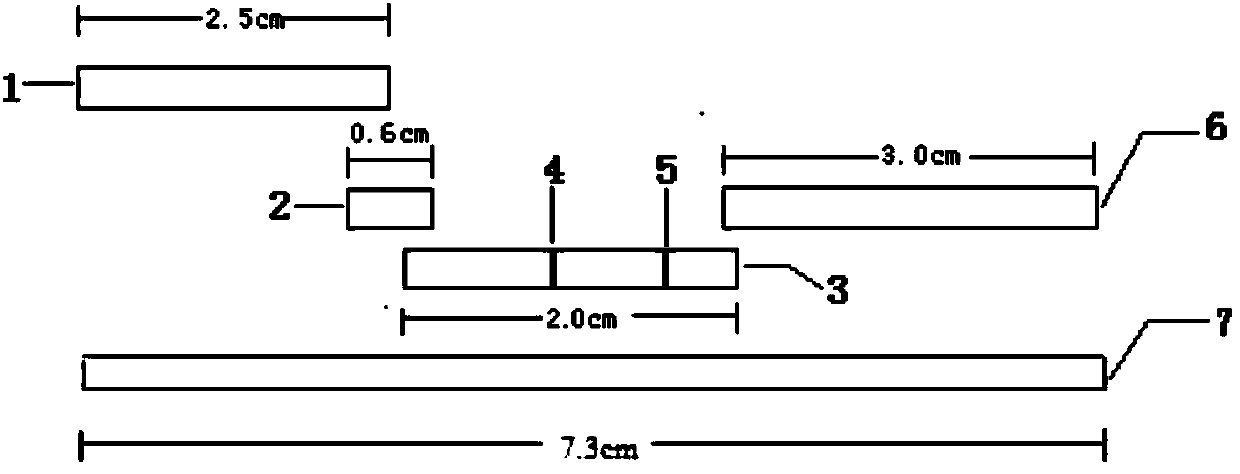
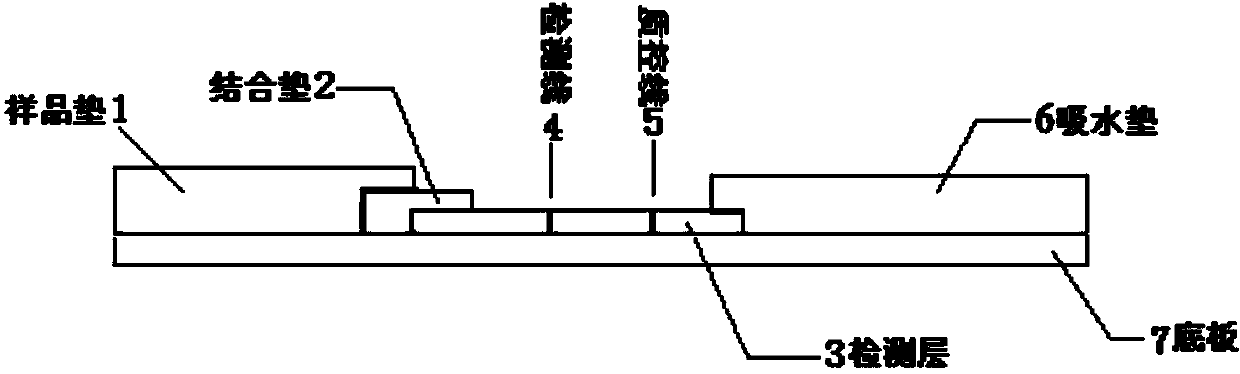
Human mycoplasma pneumoniae gold-marked silver-stained immunochromatographic assay kit and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a human mycoplasma pneumoniae gold-marked silver-stained immunochromatographic assay kit and a preparation method and application thereof. The assay kit comprises a detection card and a silver-stained sensitivity-enhanced pad, wherein the detection card is composed of a bottom plate, a sample pad, an absorbent pad, a conjugate pad and a detection layer; the conjugate pad is coated with a colloidal gold-marked polyclonal antibody mixture of colloidal gold marked rabbit anti-human mycoplasma pneumoniae P1 protein and P30 protein; the detection layer is composed of a solid phase nitrocellulose membrane with a detection line and a quality control line; the detection layer is bonded on the bottom plate, the conjugate pad and the absorbent pad are partially overlapped with the detection layer respectively and are bonded with the detection layer and the bottom plate respectively; the sample pad and the conjugate pad are partially overlapped to be bonded with the conjugate pad and the bottom plate respectively; and the silver-stained sensitivity-enhanced pad consists of a AgNO3 pad and a restoring pad. The human mycoplasma pneumoniae gold-marked silver-stained immunochromatographic assay kit can effectively improve the detection sensitivity of the human mycoplasma pneumoniae, has the strong specificity and has the high application value in the aspects of clinical diagnosis of human mycoplasma pneumoniae, etiology identification, epidemiological investigation and the like.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH +1
Nanotechnology-based trace protein detection method
InactiveCN101943703AWide linear rangeLow detection limitColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAntigenBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention relates to a nanotechnology-based trace protein detection method, which combines enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology, tyramine signal amplification technology and the aggregation phenomenon of gold nanoparticles modified by different biological molecules, so an experimental method used for detecting trace proteins such as prostate specific antigen (PSA) and the like is established. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing an antibody aiming at the protein to be detected (such as the PSA) on the surface of a substrate; incubating another antibody with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) activity of the protein to be detected (such as the PSA) after capturing the protein to be detected in a sample, wherein the HRP catalyzes biotin-tyramide to generate biotin deposition under certain conditions; further amplifying a signal by using the aggregation phenomenon of the gold nanoparticles modified by biotin-labeled DNA and the gold nanoparticles modified by streptavidin; performing silver staining; and performing data analysis on an experimental result by using software. The method has the advantages of extremely low detection limit, wider detection range, capacity of detecting the antigen in a rabbit serum with complex compositions, and important application prospect.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Nano probe based method for detecting trace proteins by using microfluidic chip
InactiveCN102147414AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresDecorative surface effectsBiological testingAntigenProtein target
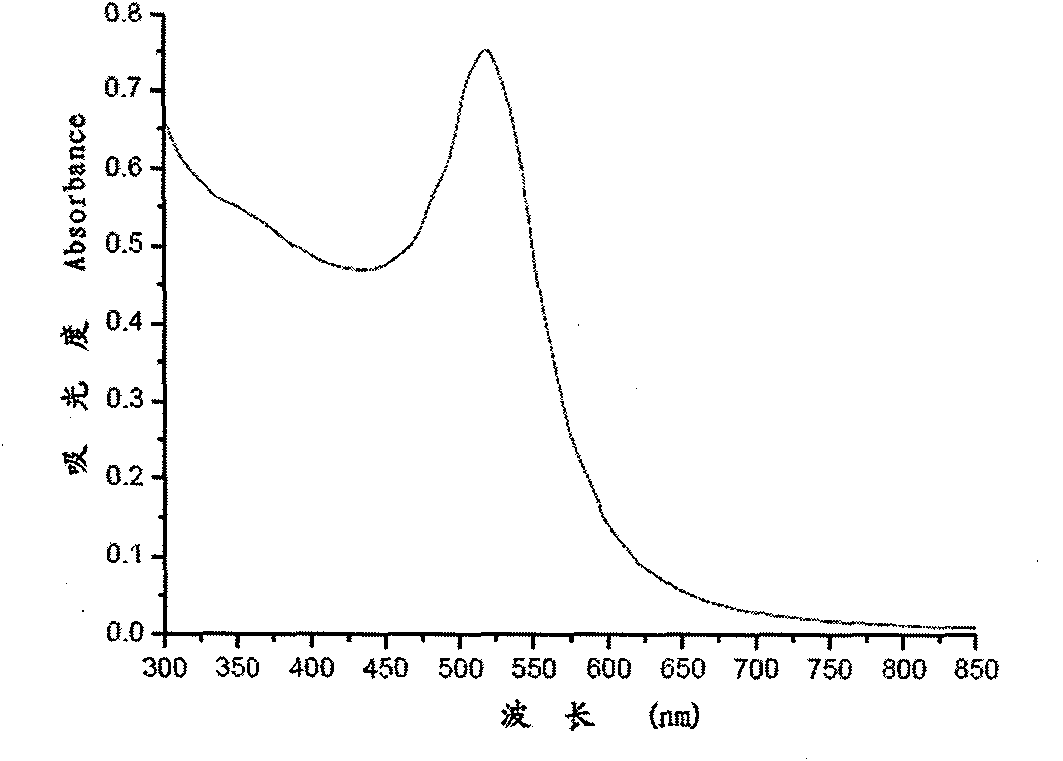
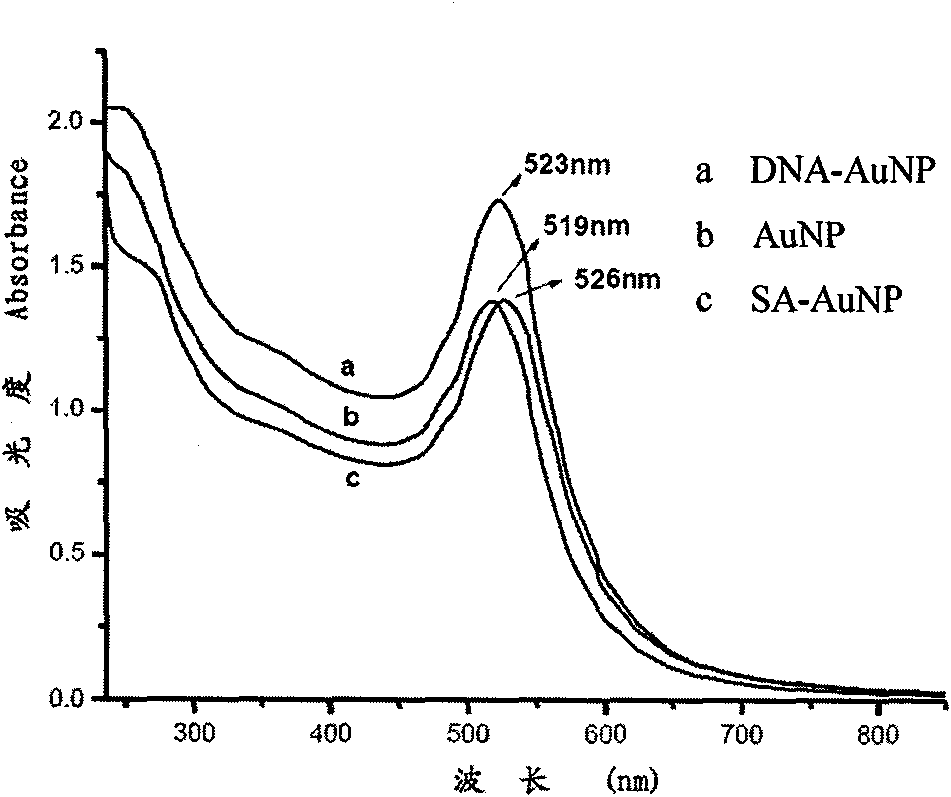
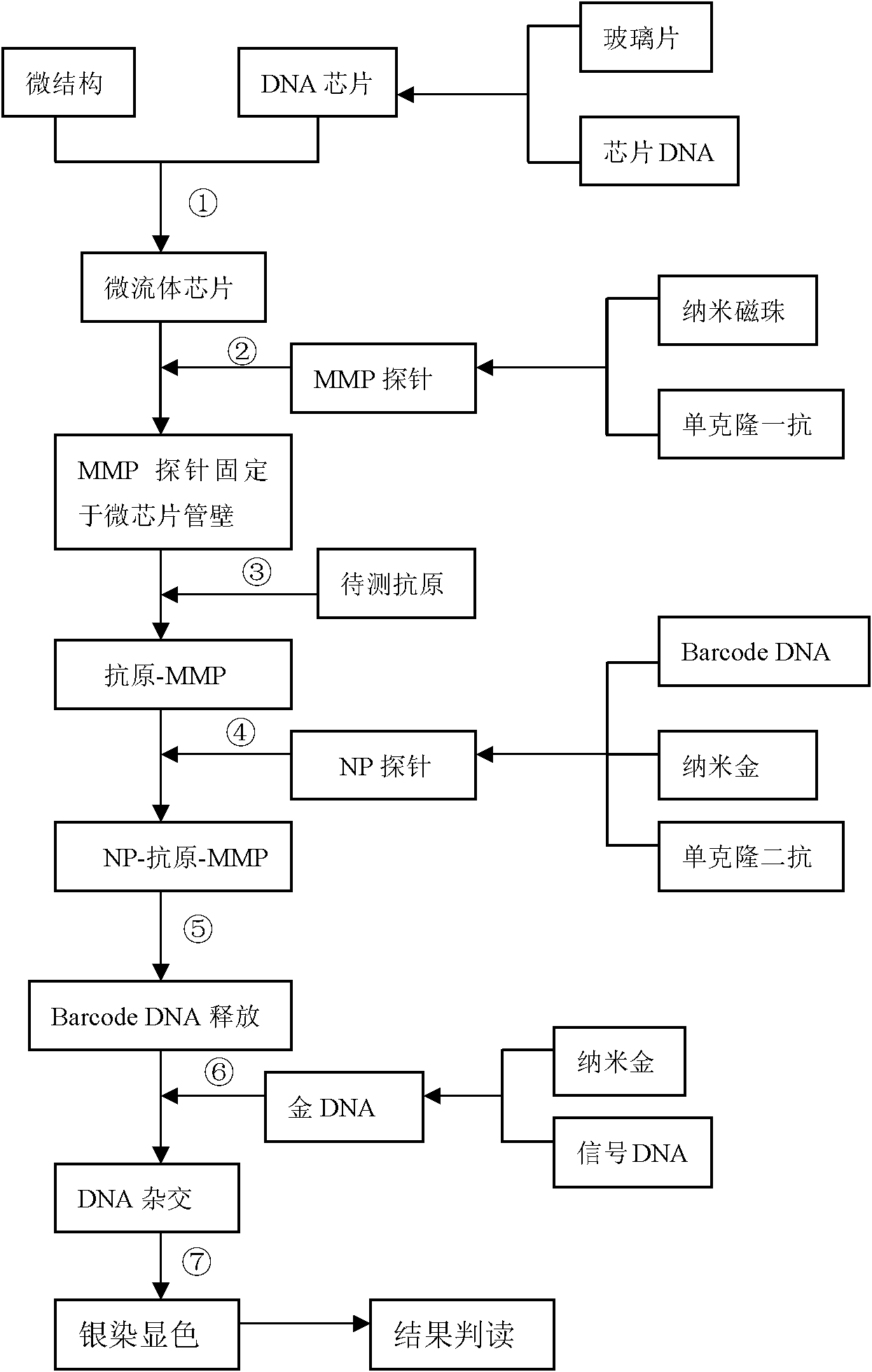
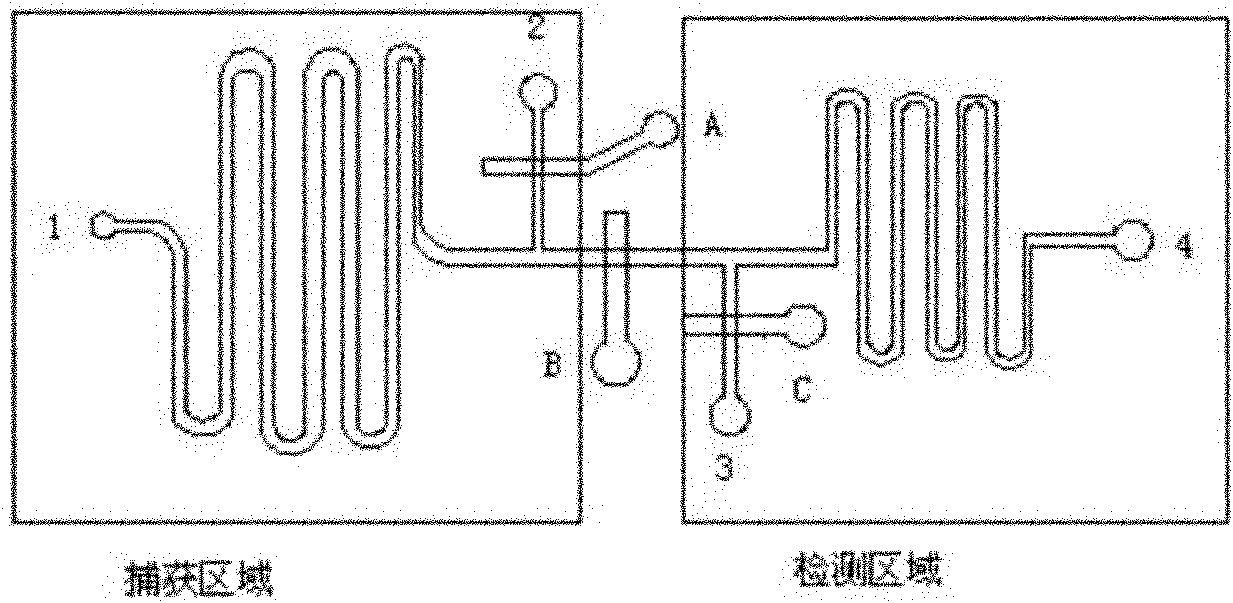
The invention relates to a nano probe based method for detecting trace proteins by using a microfluidic chip, which is characterized by comprising the steps: manufacturing a microstructure by using a standard photoetching process, and sealing a glass sheet (spotted with a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probe) and the microstructure to prepare a required microfluidic chip; simultaneously labeling a monoclonal secondary antibody and a Barcode DNA with a signal amplification function on a nano gold particle, and labeling a monoclonal primary antibody on a magnetic bead; and detecting the trace target proteins in a microfluidic chip channel by means of immunoreaction of antigens and antibodies as well as gradual amplification and silver staining development of signals. The nano probe based method provided by the invention integrates the procedures of enrichment, separation and detection of biological samples, has the characteristics of specificity, rapidness and high sensitivity, and is expected to be applied to the diagnosis and detection of trace proteins (the antigens or antibodies) in clinical laboratory medicine. The sensitivity can reach a pg / ml level and is improved by 1000 times compared with the common ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method in clinical application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
African swine fever virus nucleic acid amplification primer, detection method and kit
InactiveCN101921878AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGold particlesHybrid compound
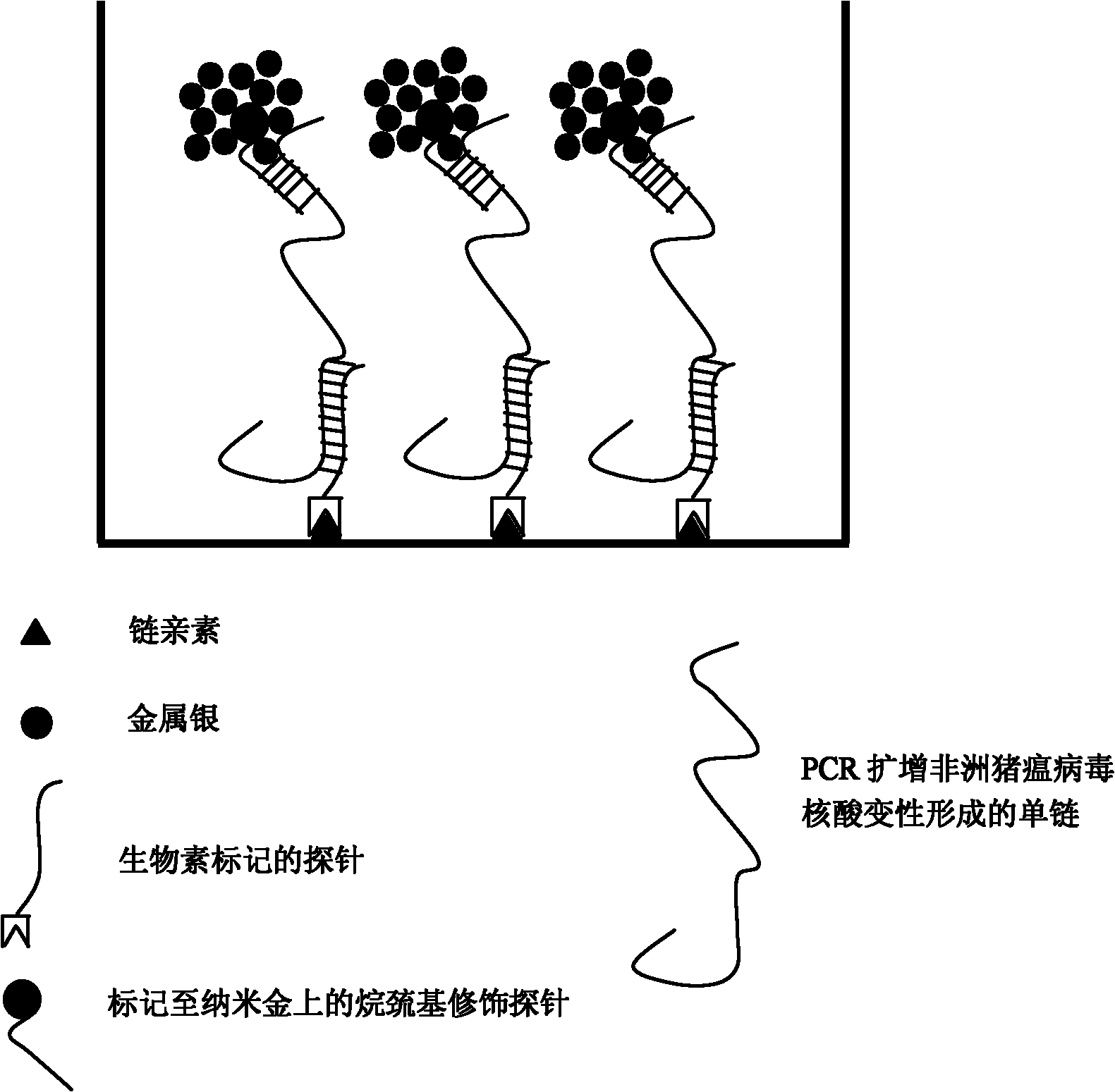
The invention relates to an African swine fever virus nucleic acid amplification primer, a detection method and a kit. The primer pair and the specific nucleic acid probe are selected from SEQ ID NO: 1-12. The detection method comprises the following steps: (a) amplifying nucleic acid in the sample to be detected by using a PCR primer; (b) labeling the detection probe labeled by alkyl sulfydryl group on nano gold particles; (c) hybridizing the capture probe labeled by biotin and the detection probe labeled by nano gold in step (b) with a metamorphic PCR product; (d) adding the hybrid system in step (c) to a Streptavidin-coated ELISA plate to capture the hybrid compound; (e) carrying out silver enhancement to capture nano gold; (f) and stoping the silver enhancement reaction, and visually inspecting the grey scale judgment result. The invention has the characteristics of high detection sensitivity, strong detection specificity and low detection cost, can effectively eliminate false positive or false negative result when the PCR method is used for detecting African swine fever virus, and quickly detect the African swine fever virus nucleic acid.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Molecule detection signal amplification technique
InactiveCN102492772AAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionRealize visual detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexAntigen
The invention relates to novel molecule detection signal amplification technique, which is characterized in that the molecule detection signal amplification technique is a biomolecule detection method with high sensitivity which is formed by streptavidin, an antigen, an antibody, polypeptide and the like which are marked by quantum dots through tyramine signal amplification and silver strengthening dyeing signal amplification. The detection method comprises the following steps: the biomolecule to be detected is combined with nucleic acid, the antibody, the antigen, the polypeptide and the like which are fixed on a solid phase material, the quantum dots are introduced to molecule to be detected through biomolecule specificity combination, silver strengthening dyeing is carried out on the quantum dots by using silver dyeing reagents, and signals are amplified. Obtained signals can be scanned through common optical scanners, analyzed through common imaging instruments or observed through naked eyes. The detection method achieves high sensitivity detection of the biomolecule on one hand, and reduces application cost of biomolecule detection on the other hand.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Fast typing detection method of high-flux visualized HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) gene chip
Owner:SHANXI LIFEGEN
Colloidal gold immune chromatographic test paper box of silver staining enhancement technology and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a colloidal gold immune chromatographic test paper box of a silver staining enhancement technology. The test paper box is characterized by mainly comprising a colloidal gold immune chromatographic test paper strip, a silver salt-coated bottom membrane and a top membrane which contains a reducing agent for silver salt reduction reaction. The test paper box has the advantages of easiness for operation, judgment and storage, high sensitivity, high stability, quick detection, clear result, no need of any instrument or equipment and the like, is particularly suitable for field test of clinical and sudden events and is suitable for large-scale application of epidemiological survey.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for showing fingerprints on various object surfaces and keeping DNA information
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection, in particular to a method for showing fingerprints on various object surfaces and keeping DNA information. The method adopts metaliding, takes functionalized gold nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles as probes, and is combined with argentation to realize that the latent fingerprints and blood fingerprints on different object surfaces can be shown in one method. The gold and silver nanoparticles are adsorbed due to the action with the ingredients of the latent and blood fingerprints, silver ions in silver staining solution can be catalyzed to be reduced on the surfaces of the fingerprints, and the generated silver covers the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles, thus enhancing the detection signals. After the blood fingerprints are shown in the method, the DNA sequence can be further detected. In the invention, the reducing agent in the silver staining solution is further expanded, when vitamin C is taken as the reducing agent, the cost is lower, the reaction condition is wild, the operation is simpler, and further environmental protection can be realized. The method has high sensitivity and wide application range, and can show old fingerprints.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Nanometer detecting probe chip without amplifying genom DNA and detection method
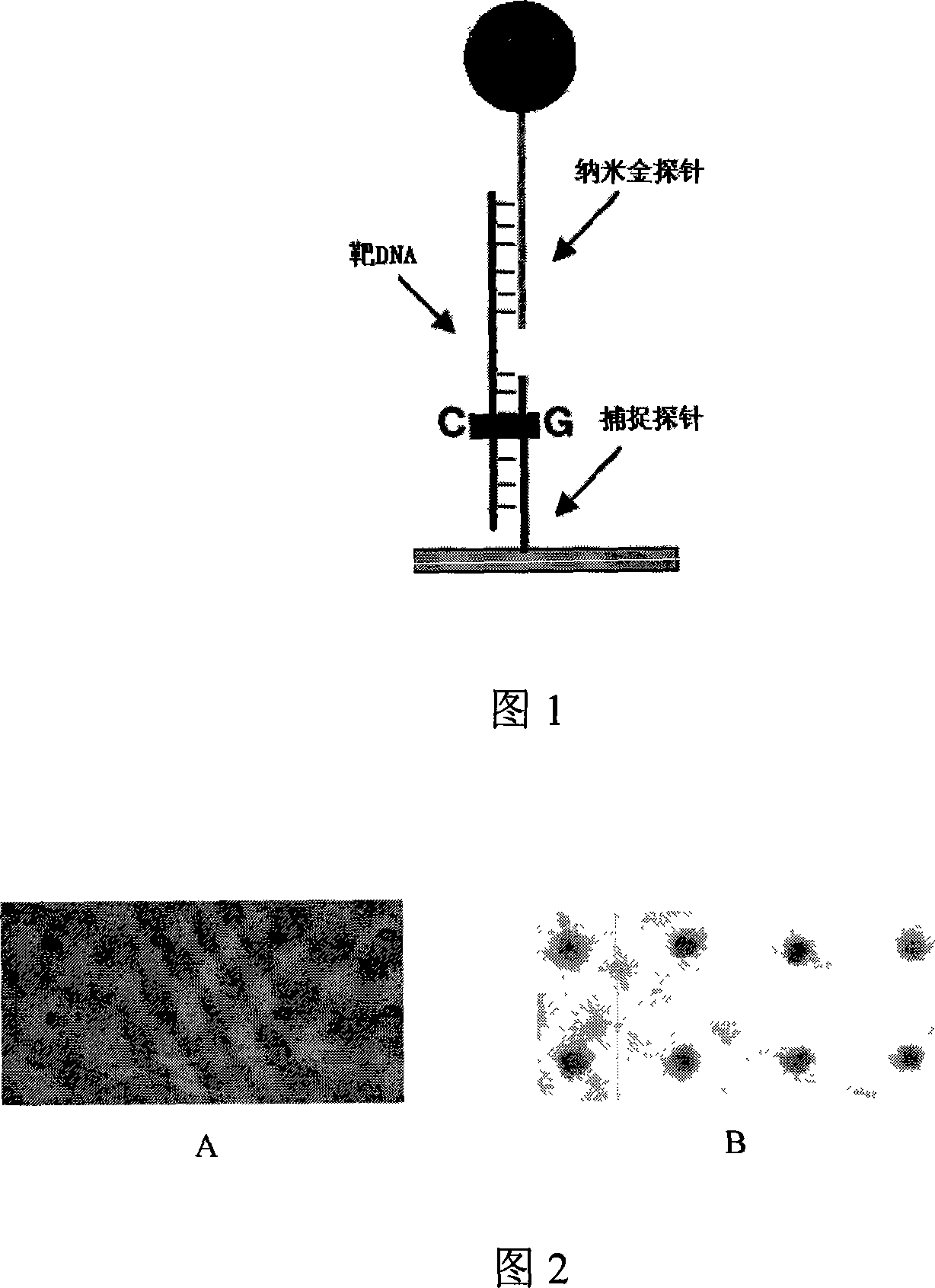
ActiveCN101182579AThe detection sensitivity exceedsGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceOptical scanners
The invention relates to a nanosized probe chip which does not need to magnify the genome DNA and a detection method; the invention is characterized in that the detection of nucleic acid with unmarked target produces high-sensibility identification signal through two steps of continuous sandwich crossbreed reaction with the capture probes which are equipotentially and specialally fixed on the surface of the chip and special oligonucleotide probes of the marked nanosized gold with the magnification effect of the nanosized gold signal which is enhanced by silver stein; and then microscope is used directly for observation or ordinary optical scanner is used for scanning to directly obtain the corresponding crossbreed results; the detection report can be obtained through the analysis of relevant software. Compared with the traditional method based on fluorescent signal detection, the method greatly increases the sensibility and specials of the detection and can detect the targeted gene and single base group mutation of unmagnified genome DNA sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
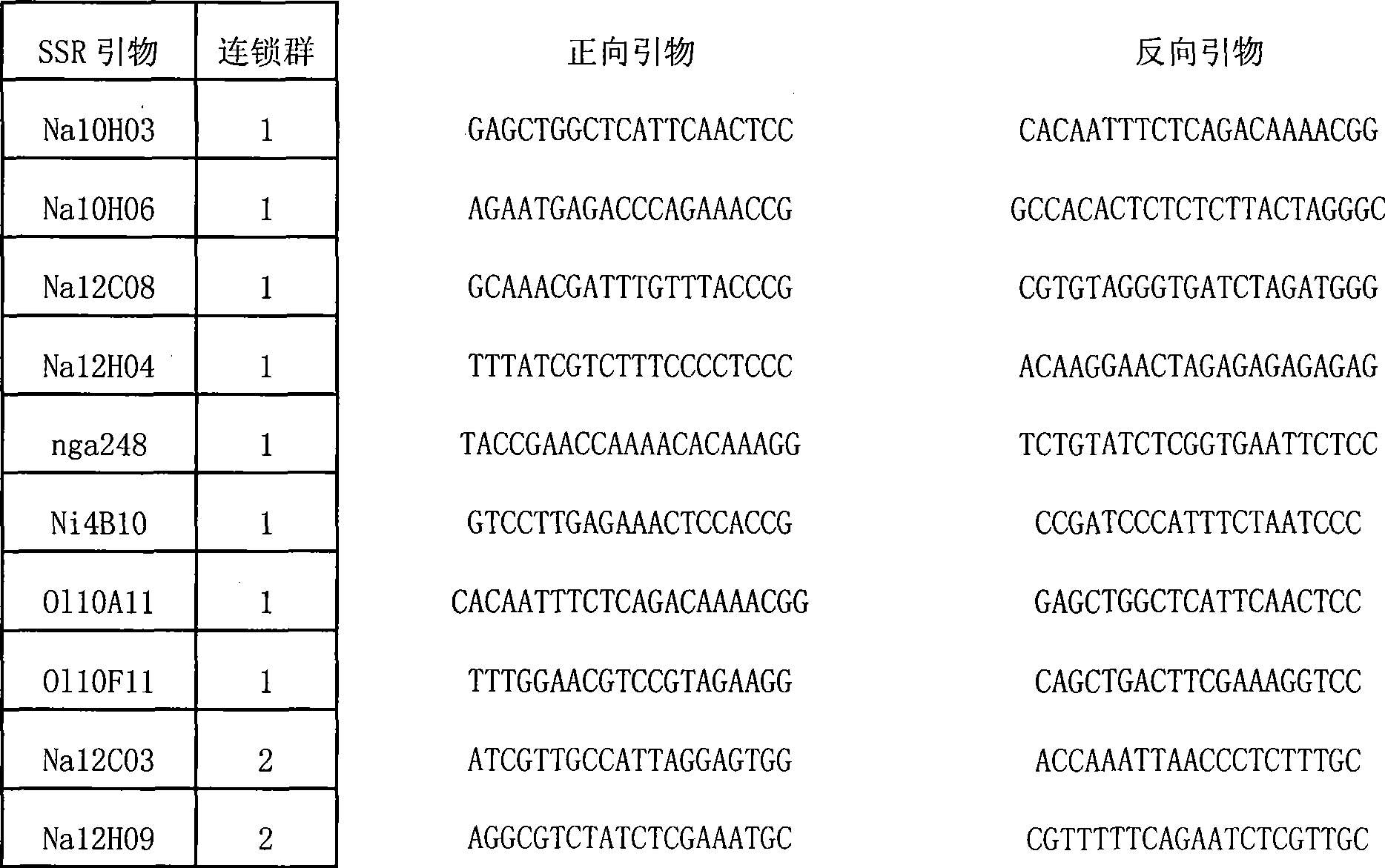
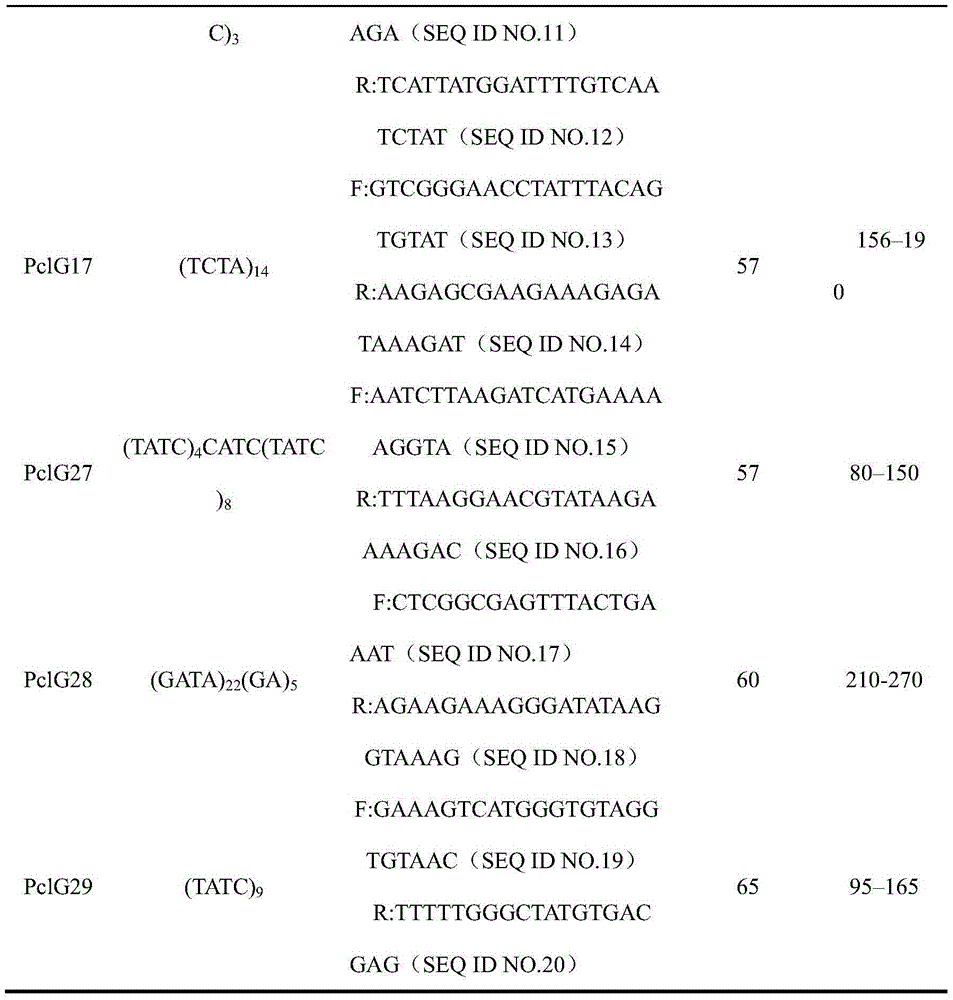
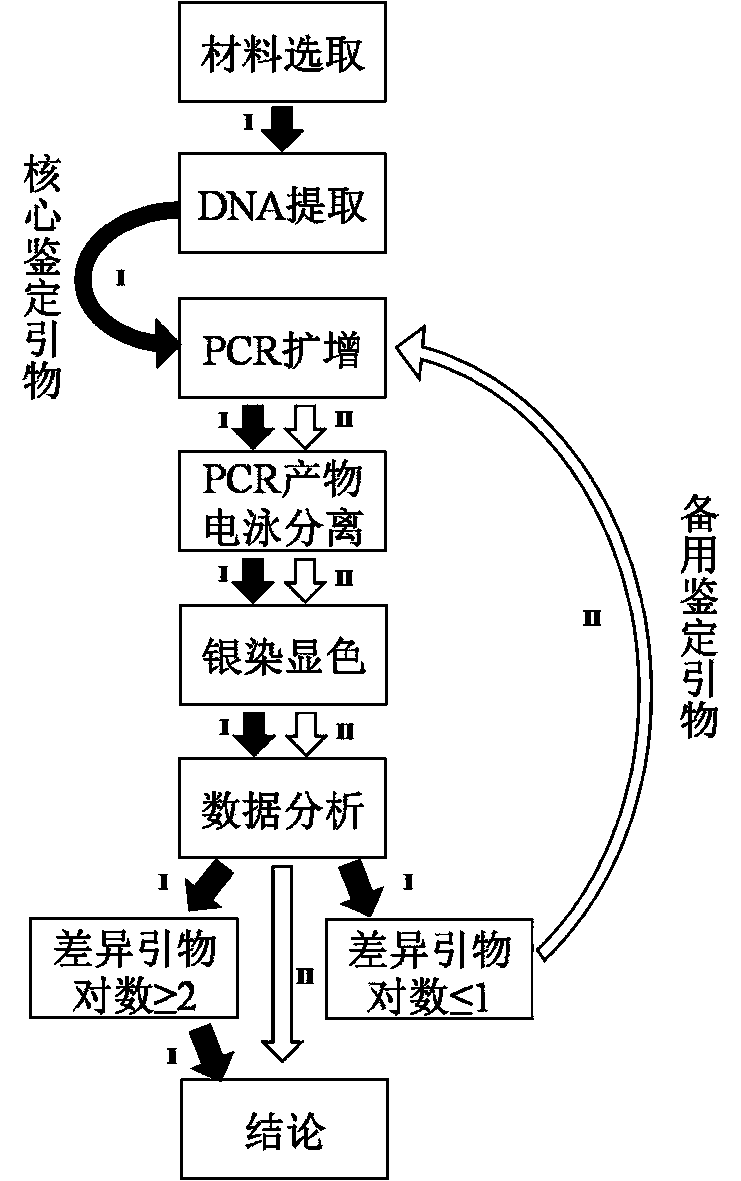
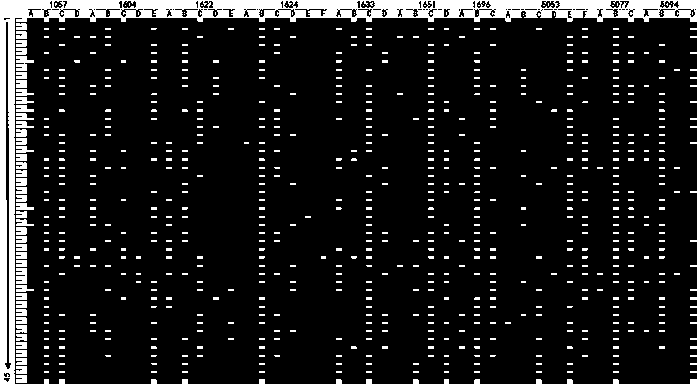
Method for identifying barley varieties by SSR (simple sequence repeat) primers and applications of method
ActiveCN102787172ANot easy to influenceImprove test efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHordeum vulgare
The invention relates to a method for identifying barley varieties by SSR (simple sequence repeat) primers. The method comprises steps as follows: extracting DNA of samples to be tested; using 14 pairs of basic core SSR primers and 14 pairs of extended core SSR primers to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification; performing gel electrophoresis, modified polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and silver staining on the PCR amplified product; analyzing an SSR band, wherein the samples to be tested are at least two barley varieties; when the number of different sites of the varieties is larger than or equal to 3, the varieties are judged as different varieties; when the number of the different sites of the varieties is 1 or 2, the varieties are judged as similar varieties; and when the number of the different sites of the varieties is 0, the varieties are judged as suspected identical varieties. The method provided by the invention can be used for identifying the barley varieties to be tested and the known barley varieties, or establishing a barley variety database; the method has advantages of high efficiency, accuracy, low cost and convenient operation; and with the adoption of the method, the authenticity of the barley varieties is effectively monitored, crop varieties are protected, and fake varieties are prevented from entering the market.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA detection method based on gene chip with nanometer gold detecting probe
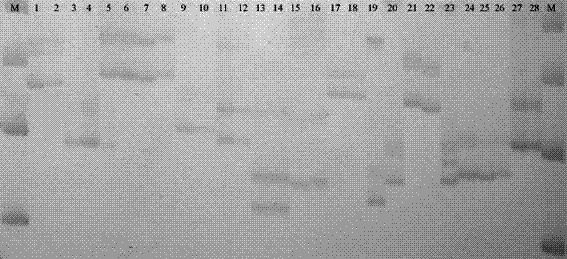
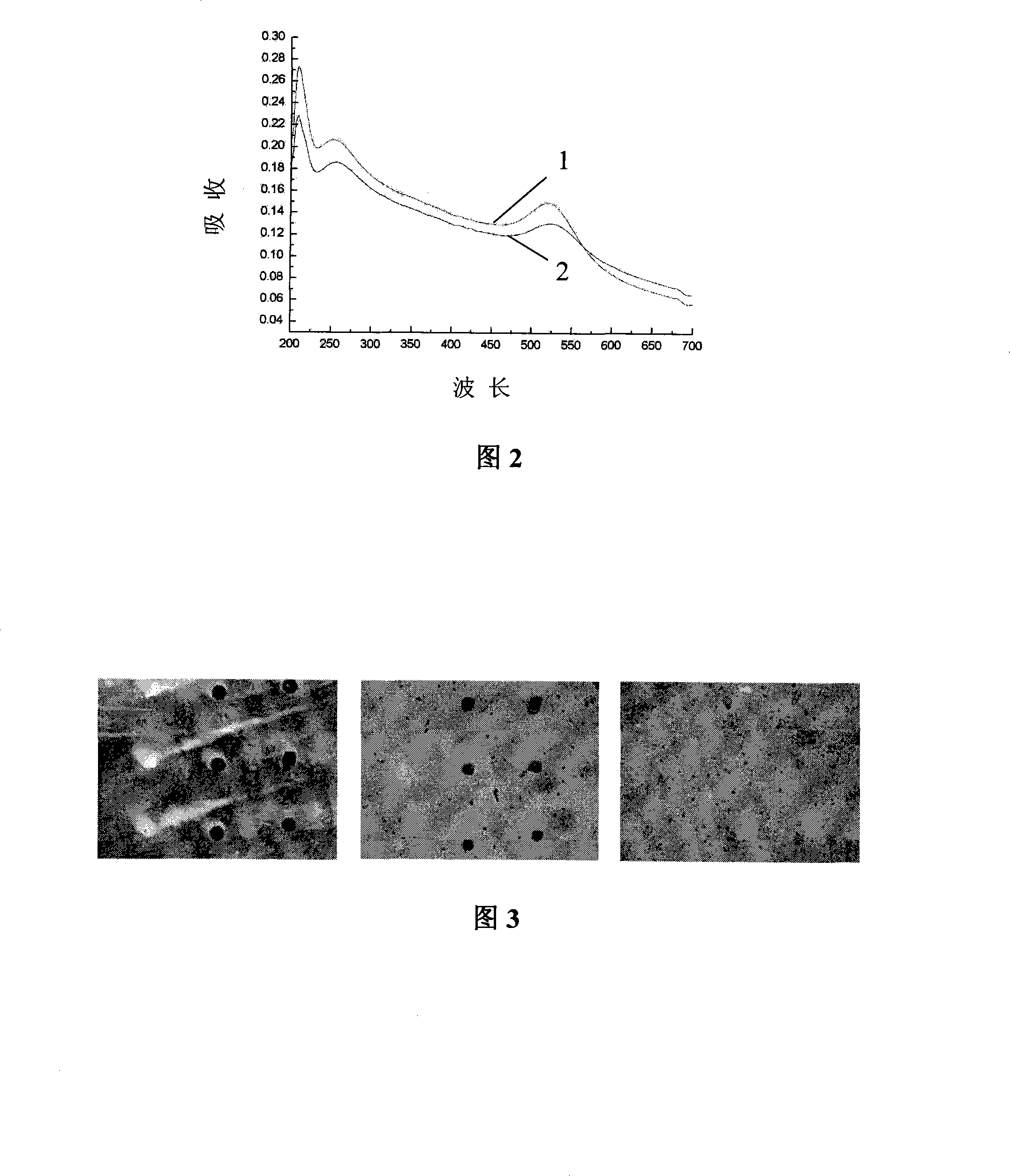
The invention relates to a high-sensibility DNA detection method based on the gene chip of nanosized gold probe; the method is characterized in that the nanosized gold is centrifugally condensed and enriched with a low temperature and then sterile deionized water or TE (pH7.4) is used for re-suspension according to a consistency; and then the nanosized gold is added with an amount of DNA signal probes which is used for modifying hydrosulphonyl; in this way, the amount of the DNA used for modifying the hydrosulphonyl is greatly saved; after the mark is made, the mark and the detected object molecules are placed on the chip for one-step crossbreed; the capture probes of the detected DNA and the chip and the signal probes for marking the nanosized gold are used for the crossbreed at the same time; and then the chip is washed and dried after the crossbreed and improved silver stein preparation is added on the chip for silver stein color development; in this way, the crossbreed signal strength is greatly enhanced and the detection sensibility is promoted; people can observe with naked eyes or use CCD for scanning and taking pictures. The detection method provided by the invention is characterized by greatly reduced DNA probe number, high sensibility and convenient signal detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for identifying celery cabbage-brassica oleracea alien addition lines
InactiveCN101423867AFacilitate communicationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisMolecular level
The invention discloses a method for identifying Chinese cabbage-cabbage addition lines. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting 91 pairs of primers in different linkage groups of cabbage according to a published cabbage genetic map; (2) extracting genetic groups DNA of different Chinese cabbages and cabbages to carry out PCR amplification; (3) electrophoretically separating an amplified product in modified polyacrylamide gel of 6 percent to carry out silver staining; (4) screening SSR primers in the linkage groups of the cabbage different from the Chinese cabbage; and (5) identifying the Chinese cabbage-cabbage addition lines by the SSR primers in the linkage groups of the cabbage different from the Chinese cabbage. The method has the advantages that the method can quickly and accurately identify important genetic analysis materials for the Chinese cabbage and the cabbage, such as coenospecies, addition lines, alien substitution lines, translocation lines and the like on molecular level, and lays foundation for modifying Chinese cabbage genetic background by cabbage gene.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Nano gold mark silver dyeing detection method of gene chip
InactiveCN1392269AReduce use costLong validity periodMicrobiological testing/measurementOptical scannersBiotin
The present invention relates to gene chip detection method and is one using no radioactive label and no fluorescent label. The detection method includes the following steps: extracting the tested target gene in sample, labeling the gene with digoxin or biotin to obtain labeled DNA or RNA for hybridization with the gene chip; making nano gold labeled digoxin antibody to combined with digoxin or nano gold labeled avidin to combine with biotin; dyeing the hybridized gene chip with silver dyeing reagent; direct microscope oservation, CCD record of signal or scanning detection with common opticalscanning instrument to obtain corresponding crossing result; and further analysis by using relative software.
Owner:刘全俊 +2
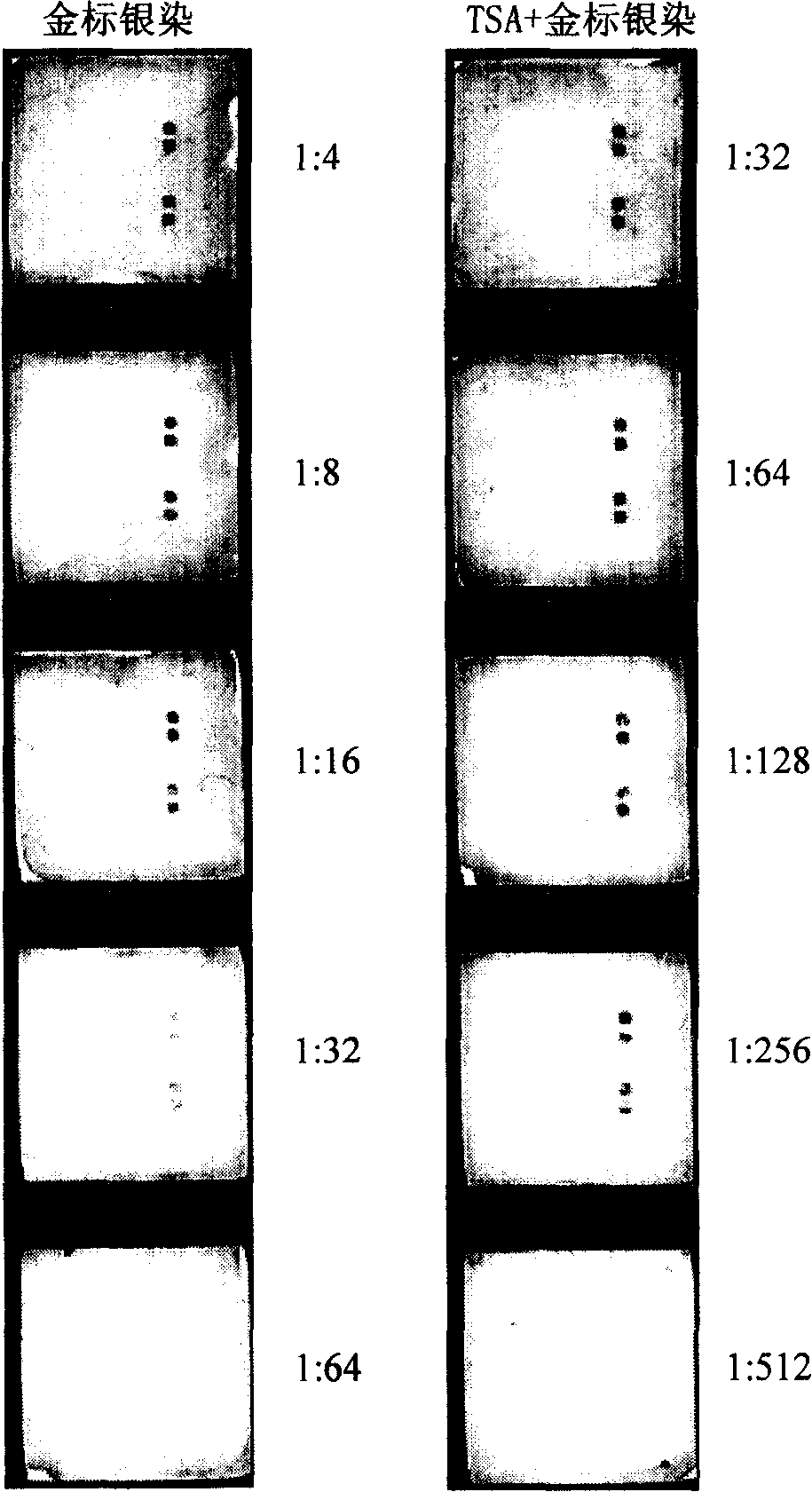
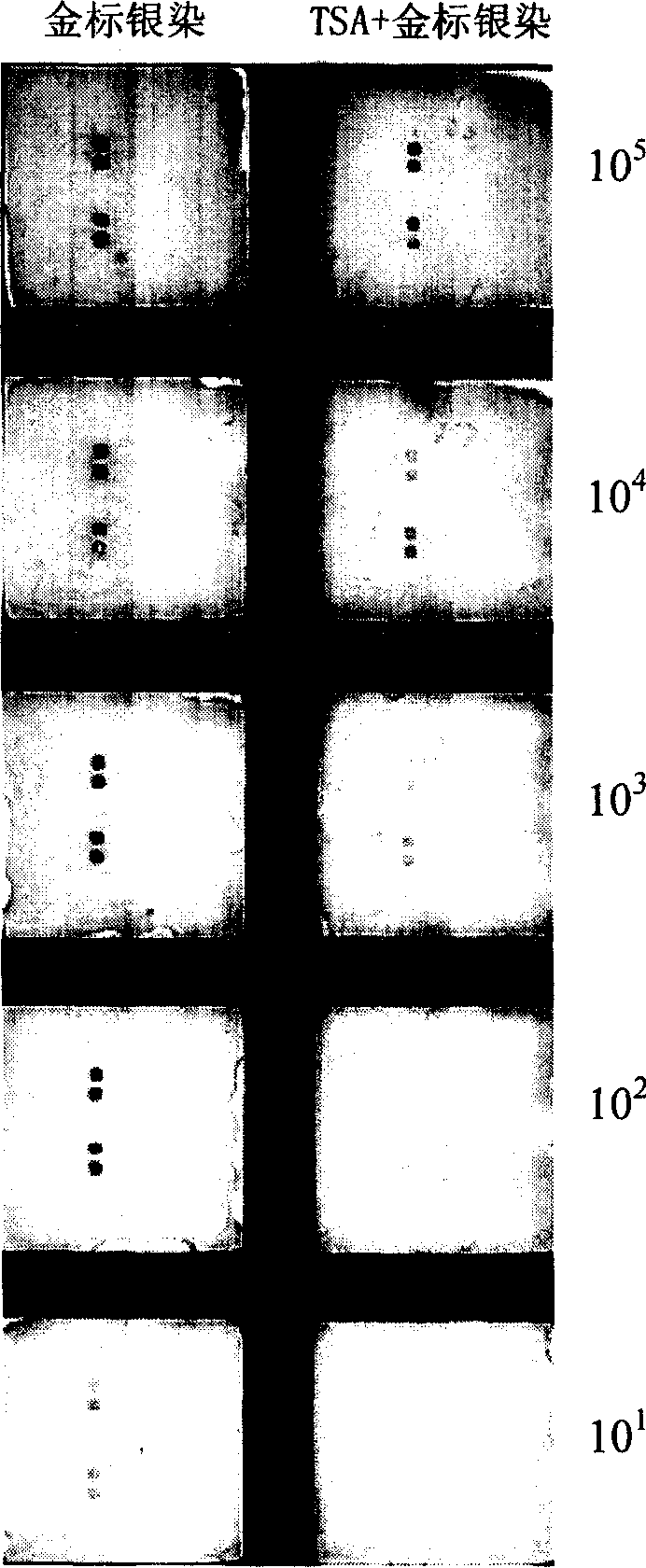
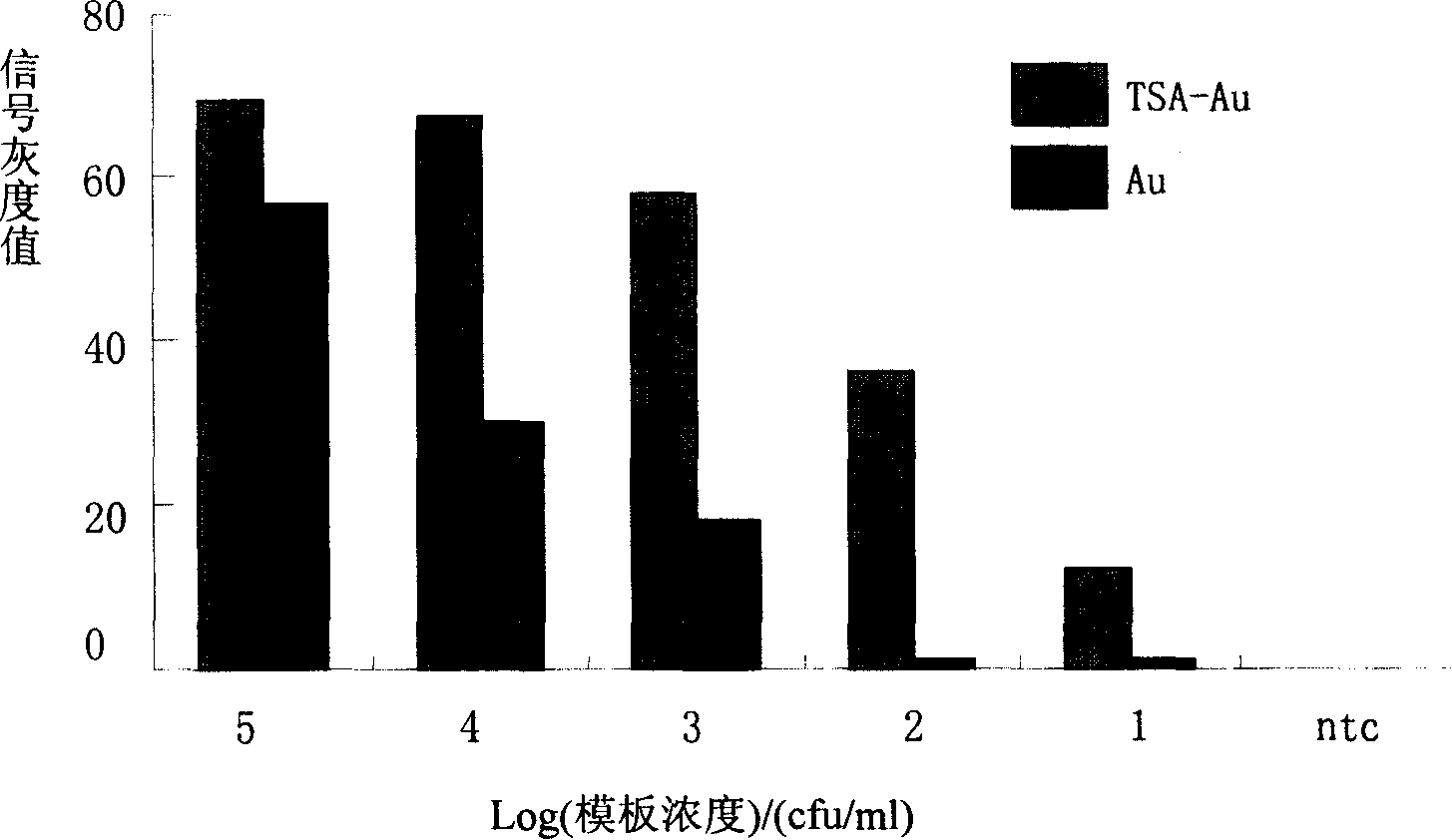
TSA- nano-gold making silver-staining testing method of gene chip
InactiveCN101162201AHigh detection sensitivityLong validity periodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexGold particles
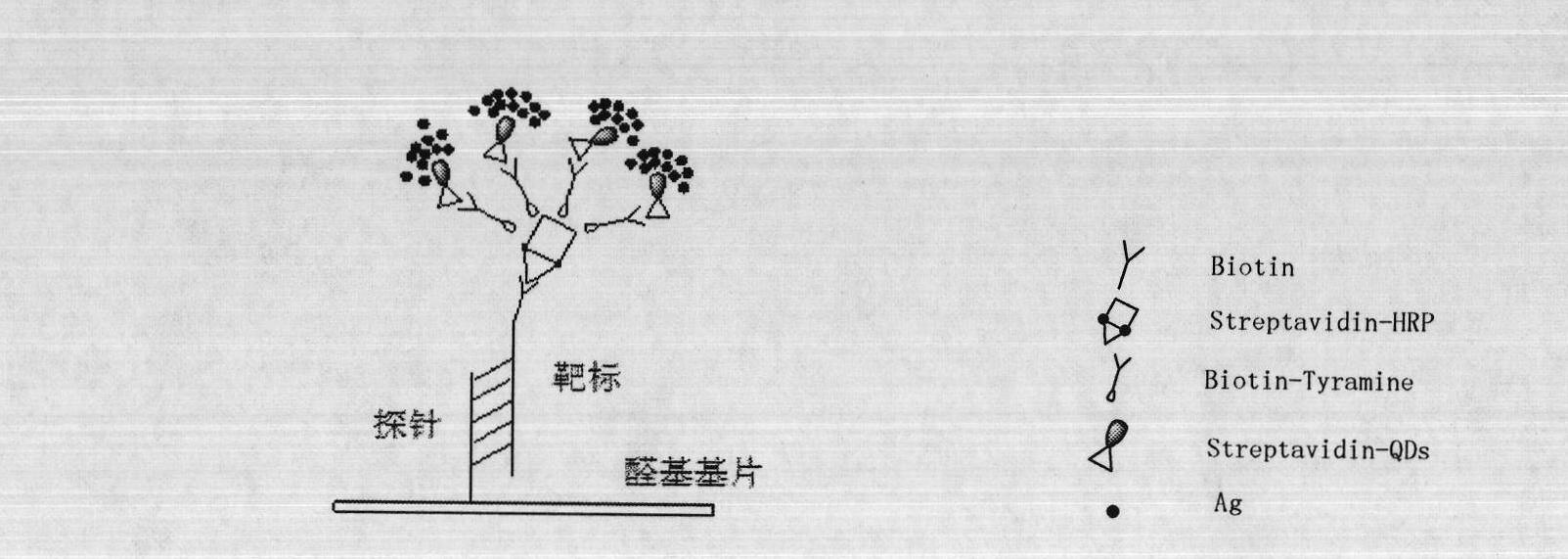
The invention relates to a detection method with a gene chip, in particular to a visualized detection method which can improve the sensitivity of gold label silver stain of a gene chip to a great extent. The detection method mainly comprises the following steps that: gene marker biotin molecule of a sample to be tested is used to hybridize with the gene chip. At first, TSA treatment is performed on the hybridized chip; vast Tyramine is precipitated around a reaction site under the catalysis of enzymes; gold nanoparticles with streptavidin are added and nanoscale gold particles are connected to target molecules; silver stain reagent is used to color the hybridized gene chips to observe and analyze signals. A TSA procedure is added in the method provided by the invention based on a single gold label silver stain detection, the Biotin-Tyramine reagent used for TAS is simple to prepare, avoids purification and is easy to preserve and stable in performance. Compared with the single gold label silver stain detection method, the detecting sensitivity of the gene chips can be improved by ten to one hundred times.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Multiple PCR reagent kit detecting breast cancer susceptibility gene mutation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101200766AQuick checkFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementBreast cancer susceptibility genesBrca1 gene
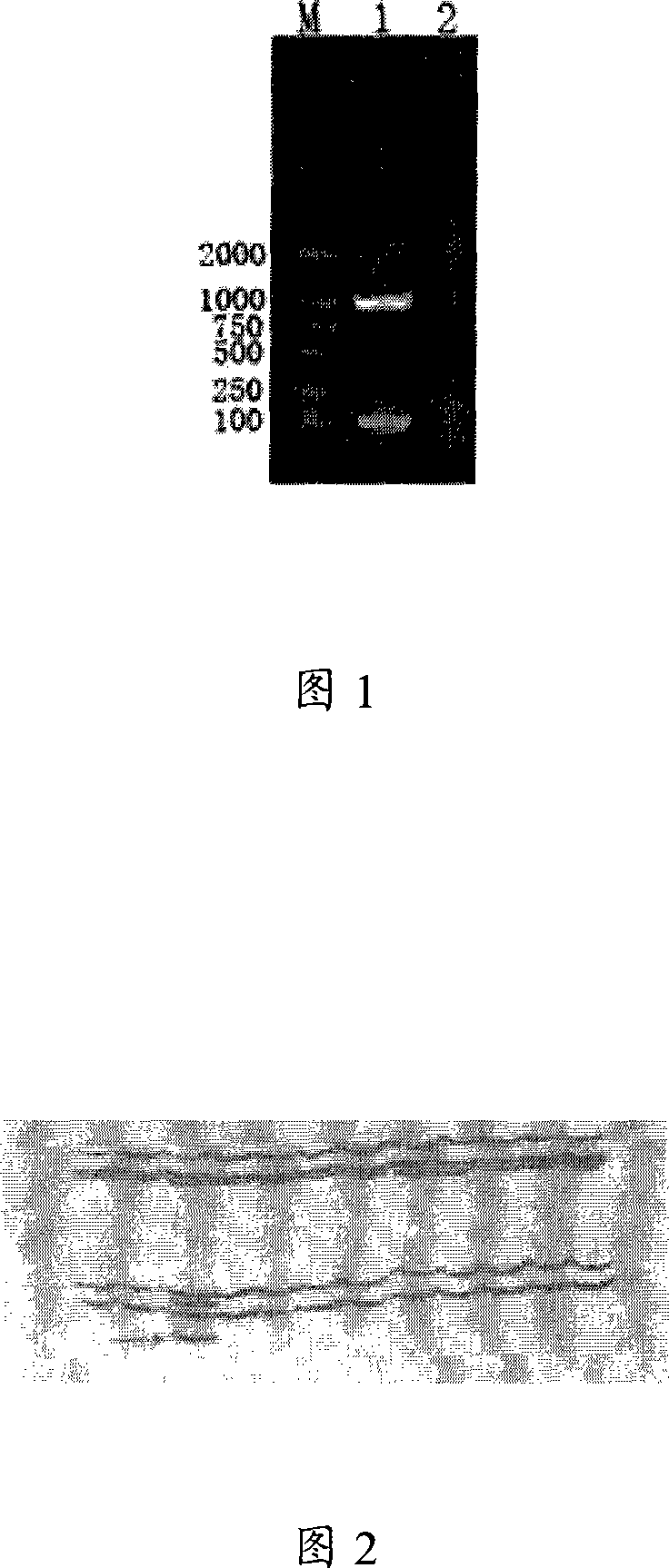
The invention discloses a multiple PCR kit for detecting the eleventh exon mutation of breast cancer susceptibility gene and a preparation method thereof. The PCR amplification primers of the kit are composed of primers pair 1 which consist of SEQIDNO:1 and SEQIDNO:2 and primers pair 2 which consist of SEQIDNO:3 and SEQIDNO:4. The multiple PCR kit of the invention combines the SSCP technology with the DNA silver staining and can simultaneously screen the mutation conditions of the eleventh exon of BRCA1 gene and the eleventh exon of BRCA2 gene. The invention has the advantages of strong sensitivity, high accuracy, simple and convenient property, etc. and has important significance on the early detection and the forecast of the breast cancer.
Owner:BEIJING MOKOBIO LIFE SCI CO LTD
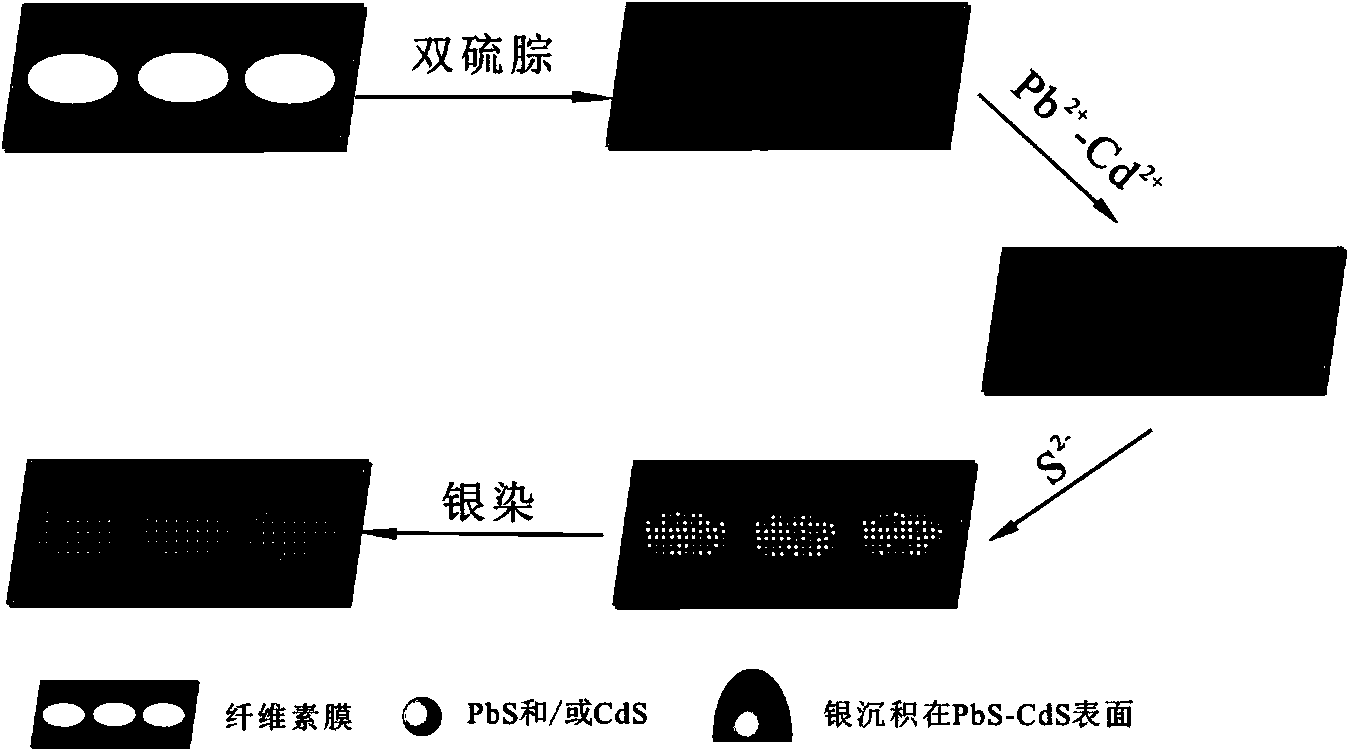
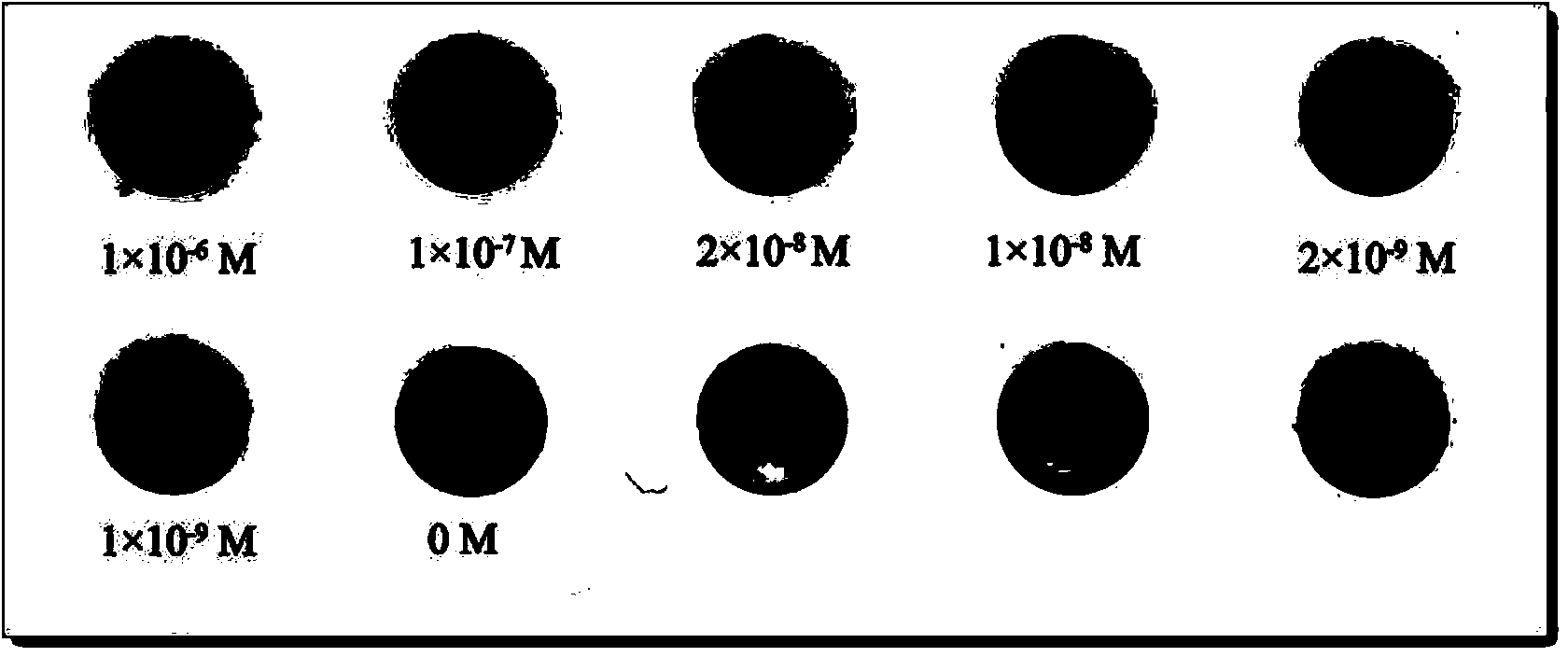
Ultra-trace lead-cadmium ion detection method and detection test strip
InactiveCN104048959AAchieving visual magnificationSensitive detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBuffer solutionTest strips
The invention discloses an ultra-trace lead-cadmium ion detection method and a detection test strip. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) acidifying a sample; (2) removing Hg2+ and Zn2+ in the sample; (3) diluting the sample by utilizing a buffer solution to obtain a neutral sample; (4) enabling the neutral sample obtained in the step (3) to be contacted with dithizone to generate a lead-cadmium ion-dithizone complex; (5) adding sulfide solution so as to enable the lead-cadmium ion-dithizone complex to be completely reacted to generate PbS and / or CdS; (6) carrying out silver staining reaction on the mixture containing PbS and / or CdS obtained in the step (5), and determining the concentration of lead and cadmium ions in the to-be-detected sample according to the grey scale of a reaction product. The test strip comprises a substrate film and a dithizone layer, wherein the dithizone layer is compounded onto the substrate film, and the test strip is packaged in a vacuum manner. The detection method and the detection test strip are sensitive inn detection, simple in judgment, capable of reaching the standard of naked eye detection, strong in applicability and stable inn performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
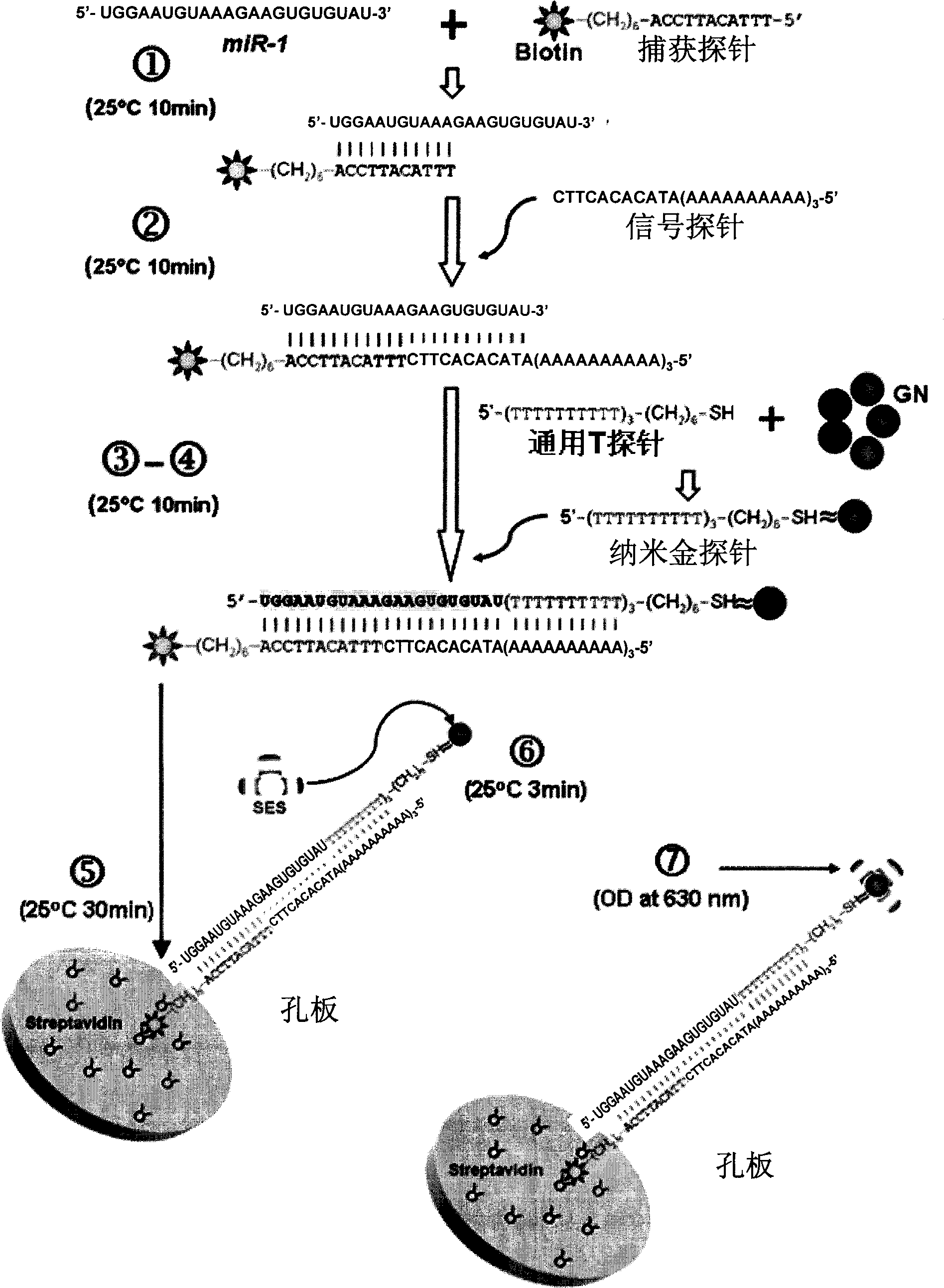
Nucleotide sequence for detecting mircoRNA content in samples and detecting method
ActiveCN101538615AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceNucleotide
The invention provides a nucleotide sequence and a kit for detecting mircoRNA content in samples as well as a mircoRNA detecting method which is based on the complementary combination of nucleic acid base pairing identification and utilizes silver-staining enhanced nano gold to mark a probe, the method is simple and practicable and can obtain detection signals with high sensitivity and high specificity without expensive equipment of radioactive labels, fluorescence and the like.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method used for identifying different families of procambarus clarkii
InactiveCN105602946AAvoid inbreedingPrevent breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStainingProcambarus clarkii
The invention discloses a method used for identifying different families of procambarus clarkii. The method comprises following steps: half-sib families are established artificially; DNA is extracted from the tail muscle of procambarus clarkii; 10 pairs of selected microsatellite primers are used for PCR amplification of the extracted DNA; obtained PCR products are subjected to electrophoretic analysis and silver staining; silver staining results are subjected to digital analysis; genetic distances of individuals are measured using a genetic software, a UPGMA cluster analysis diagram is drawn based on the genetic distances, and the individuals from different families can be distinguished based on cluster analysis results. The method can be used for distinguishing the families of procambarus clarkii quickly and accurately, and preventing inbreeding effectively, and possesses high application value in breeding of procambarus clarkii families.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
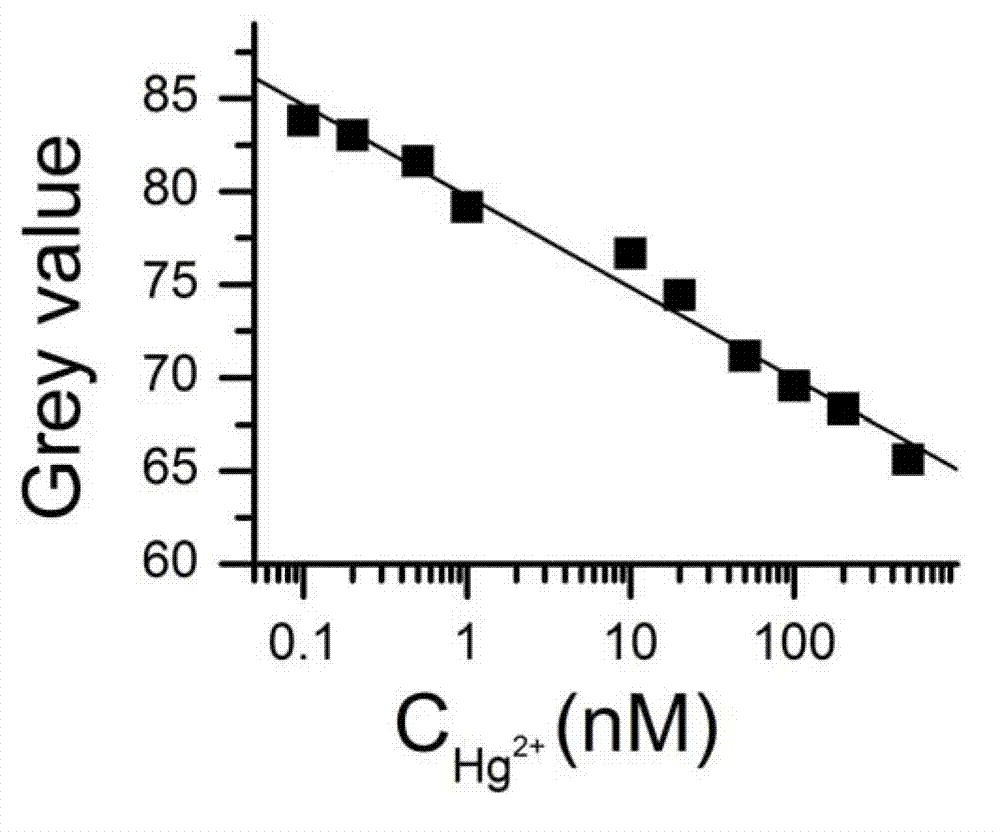
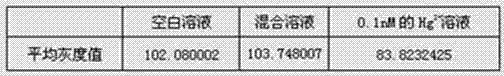
Method for quantitative detection of mercury ions through gold label silver stain and kit thereof
InactiveCN102759526AAccurate concentrationEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationDistilled waterRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for the quantitative detection of mercury ions through gold label silver stain and a kit thereof. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: heating, washing and drying a glass slide, immersing the glass slide in an APTES (3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane) solution, performing silanization treatment on the glass slide at room temperature, then cleaning the glass slide with ethanol, and drying in vacuum at 110-130 DEG C for 1-3h to obtain the silanization glass slide; mixing DNA and a nanogold solution, vibrating to reach a uniform state, incubating at room temperature, and adding water for dilution to obtain a specific DNA-nanogold probe solution; mixing the specific DNA-nanogold probe solution with a sample solution, dripping the mixture on the silanization glass slide, drying a sample point at room temperature completely, dripping a silver staining reagent, standing in a black box, then, immediately rinsing the glass slide with distilled water and drying; and finally, performing quantitative analysis on gold label silver stain signals, and calculating to obtain the accurate concentration of the mercury ions in the sample solution to be detected. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high selectivity, availability for quantitative analysis of mercury ion concentration, simplicity for operation and availability for field detection.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
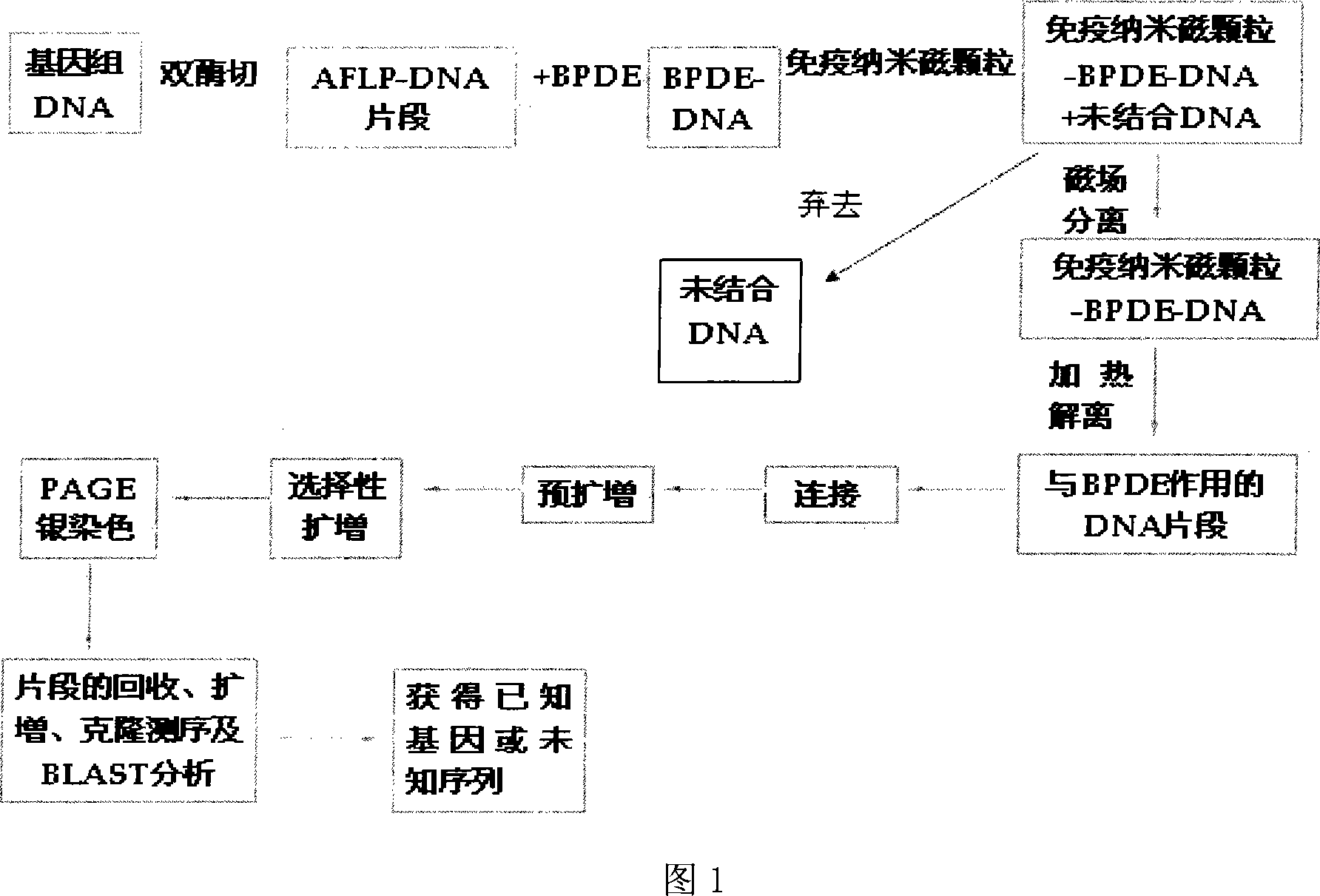
Whole-genom sifting method for BPDE carcinogen related gene
InactiveCN101113474AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCarcinogenScreening method
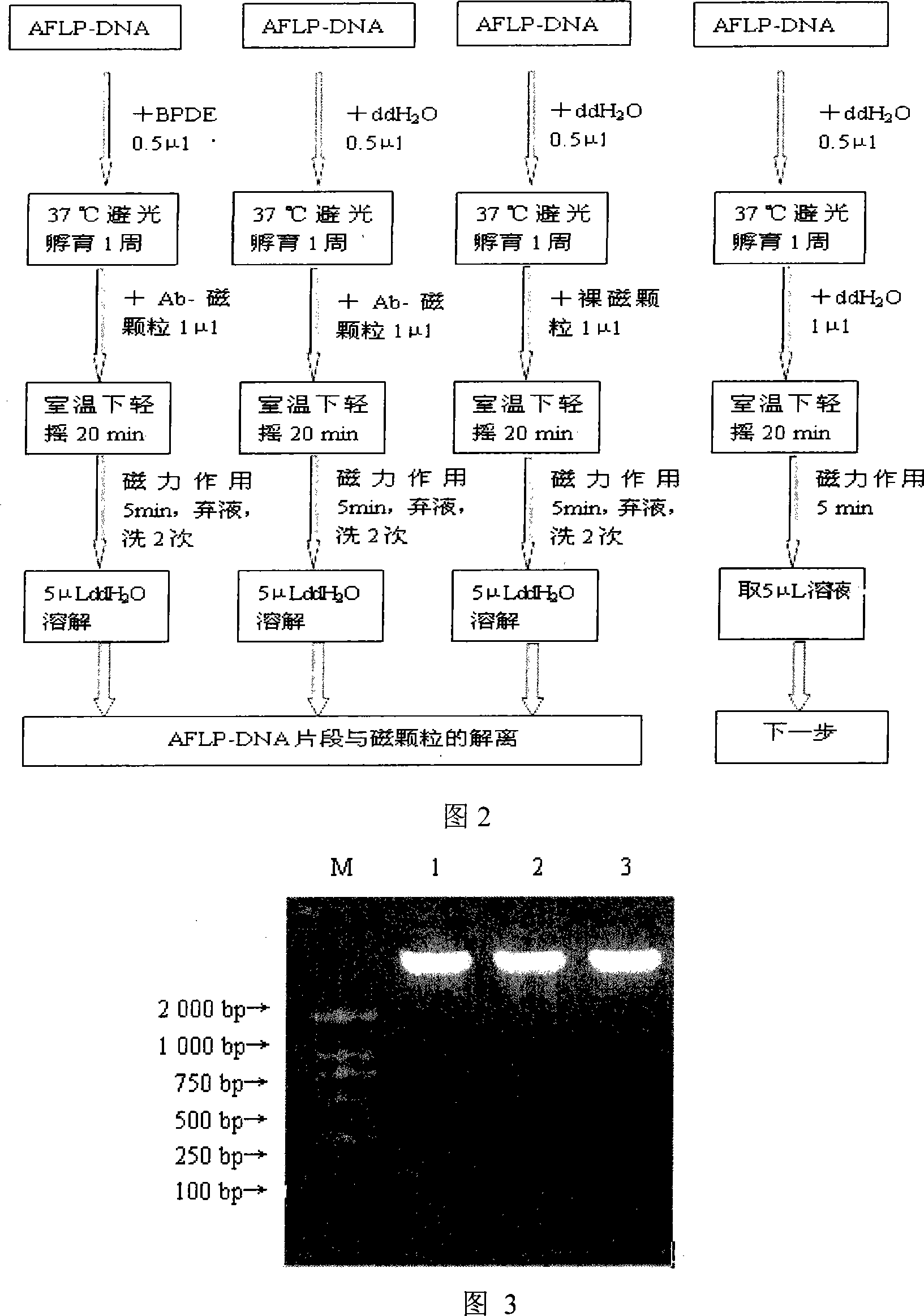
The invention discloses a whole genome screening method for screening relative BPDE oncogenes and comprises the steps that: (1) genome DNA is extracted from normal lung tissue; (2) AFLP DNA fragment is prepared; (3) immunomagnetic of AFLP DNA fragment interacting with BPDE is enriched and separated; (4) AFLP PCR is increased; (5) denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and silver stain visualization are done to selective PCR amplification products of AFLP; (6) differential fragment is recycled, amplified, cloned and tested for sequence and homologous similarity and analysis are done. The whole genome screening method for screening relative BPDE oncogenes of the invention is the high effective and specific method and more BPDE susceptible oncogenes are screened in the whole genome level, which provides a basis for stating BPDE carcinogenic molecular mechanism.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
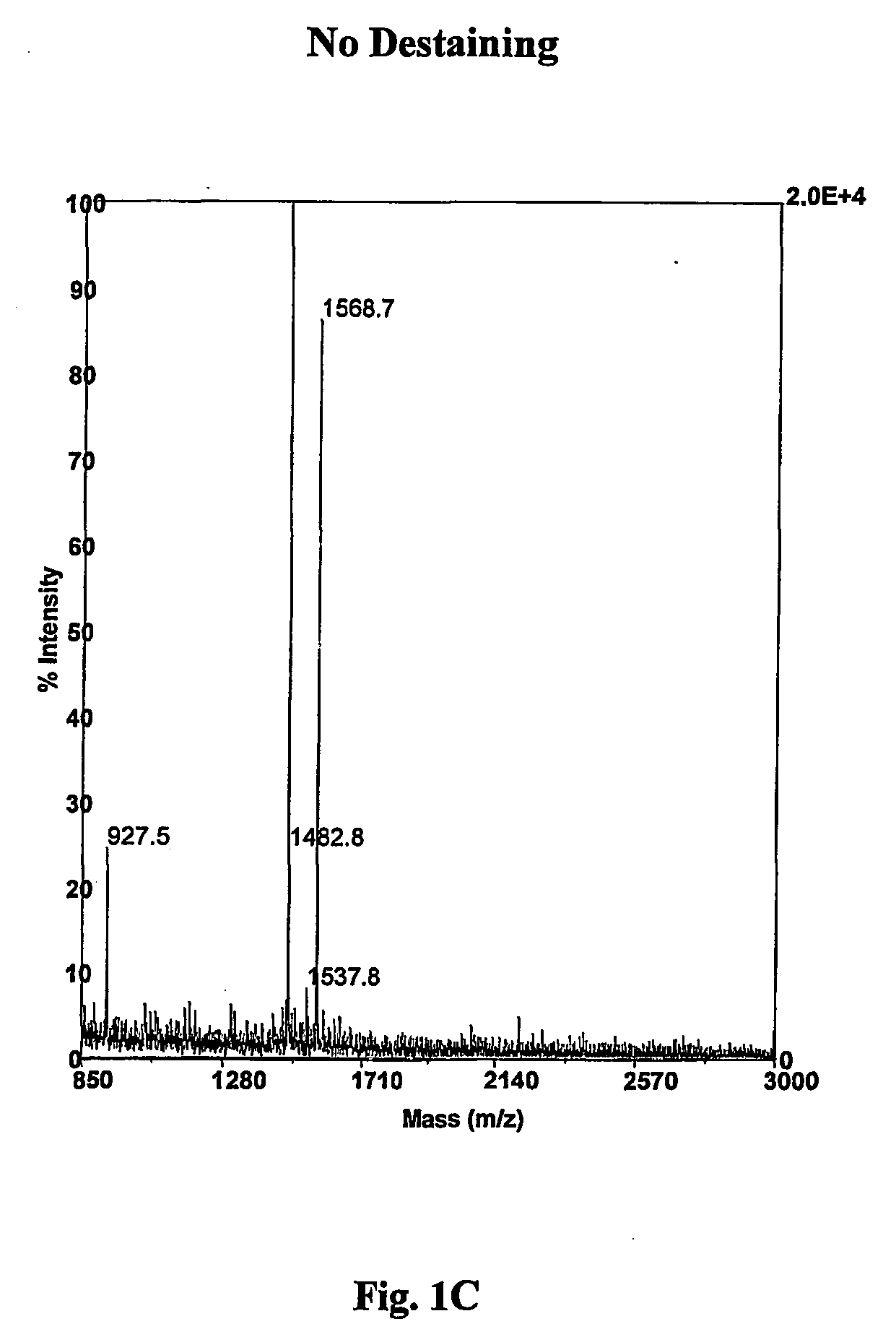
Silver destaining method
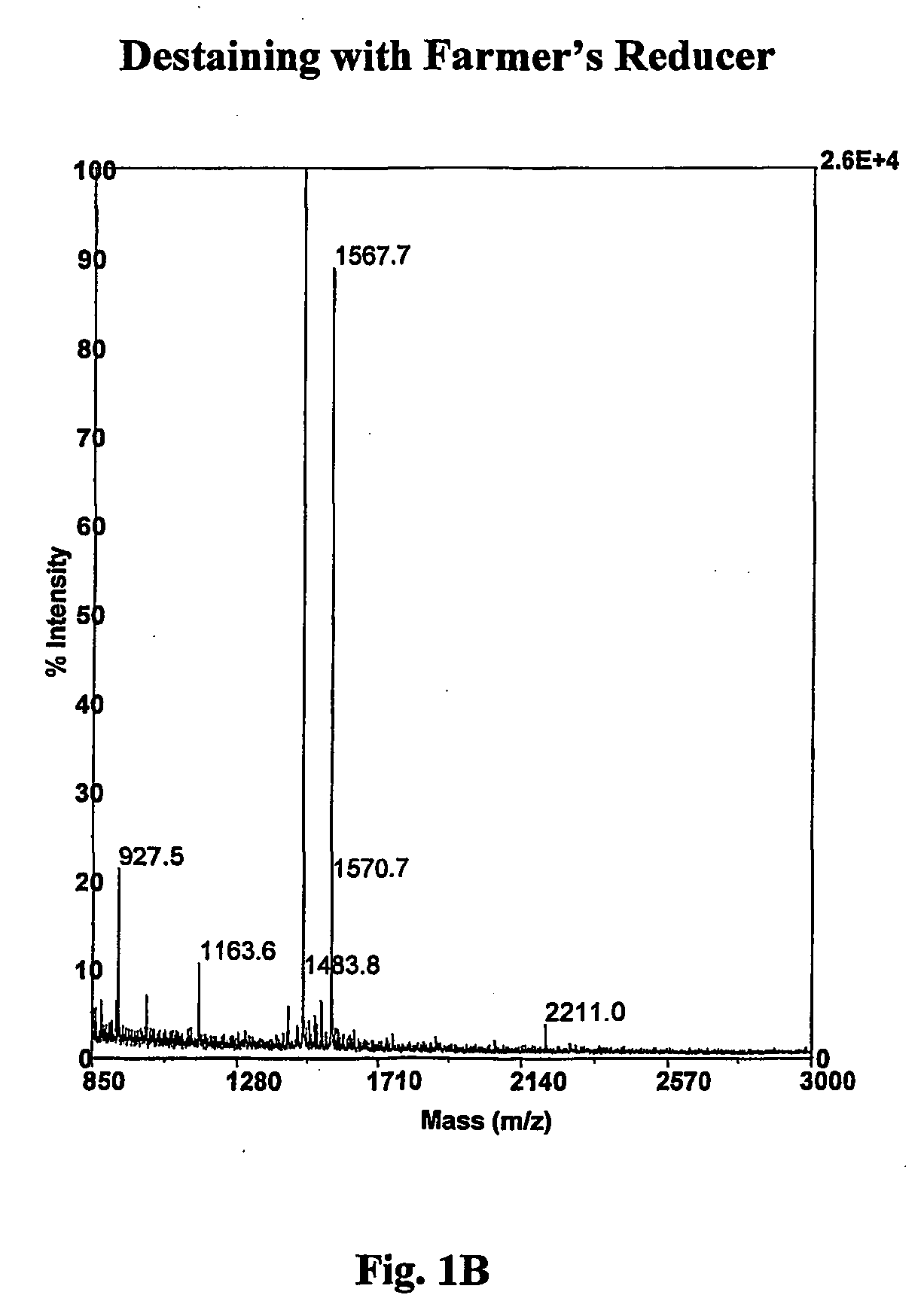
InactiveUS20050230255A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryStain
A method for removing transition metal stains from biological samples including protein, DNA, and RNA has been found. In particular, a hydrogen peroxide mediated silver stain removal method for PAGE gels is disclosed which is safer, more effective, and more convenient than other methods of the prior art. This silver destaining method is compatible with mass spectrometry analyses of in gel digested PAGE gels.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) core primer group and method thereof for identifying tea variety
InactiveCN104004756AImprove identification efficiencyAvoid identification errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationElectrophoresisDNA extraction
The invention relates to an SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) core primer group and a method thereof for identifying a tea variety, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) material selection; (2) genome DNA extraction; (3) PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification of a target product; (4) electrophoretic separation of a PCR product; (5) silver staining development; (6) data analysis; and (7) result judgment. The SSR core primer group and the method thereof for identifying the tea variety, which are disclosed by the invention, have the characteristics of easiness and convenience for operation, accuracy in result, high repeatability, high identification capacity, low cost and the like and are suitable for identifying the tea variety.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
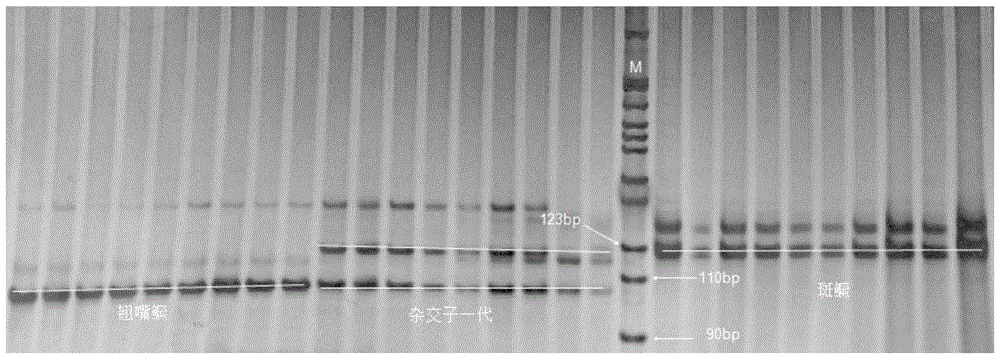
Molecular identification method used for siniperca chuatsi, siniperca scherzeri and hybrid f1 of siniperca chuatsi and siniperca scherzeri
InactiveCN104630335ASmooth responseGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerMolecular identification
The invention discloses a molecular identification method used for siniperca chuatsi, siniperca scherzeri and a hybrid f1 of the siniperca chuatsi and the siniperca scherzeri. The molecular identification method used for the siniperca chuatsi, the siniperca scherzeri and the hybrid f1 of the siniperca chuatsi and the siniperca scherzeri comprises the following steps: 1) extracting a genome DNA of a to-be-detected mandarin fish (the siniperca chuatsi, the siniperca scherzeri and the hybrid f1 of the siniperca chuatsi and the siniperca scherzeri) sample; 2) with the extracted genome DNA of the to-be-detected sample as a template, amplifying a DNA target fragment by adopting polymerase chain reaction (PCR), wherein a pair of microsatellite primer sequences used in the PCR are as follows: a forward primer sequence, namely 5'ATGTAACCGTAAGTGACCTC3', and a reverse primer sequence, namely 5'TGTTGTTCAGACGATGACGA3'; 3) carrying out electrophoretic separation on the PCR product by adopting 8% non-denatured polyacrylamide gel, then carrying out silver staining, and photographing to record an electrophoresis result; and 4) comparing with a map of a standard digestion fragment, reading out the position of a target stripe of the to-be-detected mandarin fish sample, and respectively identifying the to-be-detected mandarin fish sample to be the siniperca chuatsi, the siniperca scherzeri or the hybrid f1 of the siniperca chuatsi and the siniperca scherzeri. The molecular identification method used for the siniperca chuatsi, the siniperca scherzeri and the hybrid f1 of the siniperca chuatsi and the siniperca scherzeri is easy and simple to operate, the defects of morphological identification are made up, and the problems that a hybrid mandarin fish (the hybrid f1 of the siniperca chuatsi and the siniperca scherzeri) is difficult to identify and varieties are miscellaneous during aquaculture are solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Maize phosphate starvation responses intron length polymorphism marker for corn
The invention discloses a maize phosphate starvation responses intron length polymorphism marker. Specific primers, namely PSR-ILP markers, are designed in exon areas on two sides of a cross-intron of a phosphate starvation responses gene. PCR detection, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and silver-stain development are carried out in 30 skeleton inbred lines widely applied to production and breeding of corn in China, fragments with different amplified lengths are obtained in different inbred lines, and the silver-stain development is carried out on the PSR-ILP markers in different inbred lines. The molecular marker which is simple to operate, low in cost, and strong in applicability, is provided for QTL positioning of the corn phosphate starvation responses gene and auxiliary breeding of the molecular marker, and a foundation is laid for efficient breeding of phosphate in maize.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for rapidly improving number of eggs produced by Bian chicken through DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) labeling
The invention relates to the field of poultry breeding, and in particular relates to a method for screening the number of eggs produced by Bian chicken through DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) labeling. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the chicken genome DNA of a sample to be detected; amplifying with a specific primer to obtain a target segment of an MSTN gene; carrying out enzymedigestion on the target segment with restriction enzyme BbvI; after gel electrophoresis, carrying out silver staining development so as to obtain an enzyme digestion map of DNA; and judging the number of the eggs produced by the sample to be detected according to the quantity and size of strips in the map. The detection method selected by the invention is simple and rapid, is not influenced by external environment, and can be used for molecular genetic labeling of the number of the eggs produced by Bian chicken to carry out marker-assisted selection.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method and application of food-borne pathogen immunosensor based on gold label silver stain signal amplification technology
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a food-borne pathogen immunosensor based on the gold label silver stain signal amplification technology. The preparation method is characterized by including the steps that a glass slide is silanized; a carbon nitride material is subjected to carboxylation and then mixed with a colloidal gold solution, the mixture is stirred, and a multifunctional carbon nitride solution is obtained; the multifunctional carbon nitride solution is combined with a food-borne pathogen primary antibody, and a food-borne pathogen primary antibody probe is obtained; a coupling reagent, a food-borne pathogen secondary antibody, a food-borne pathogen antigen and the food-borne pathogen primary antibody probe are sequentially dripped onto the silanized glass slide, and the food-borne pathogen immunosensor based on the gold label silver stain signal amplification technology is obtained. Quantitative detection and analysis are carried out by adding a silver stain reagent, and the preparation method and application of the food-borne pathogen immunosensor have the advantages that specificity and sensitivity are high, the result is accurate and reliable, cost is low, and operation is easy and fast.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Gallinaceous visfatin gene 9bp indel polymorphism detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN101805787AOvercoming the limitations of difference detectionOvercome limitationsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionSmall fragment
The invention relates to a gallinaceous visfatin gene 9bp indel polymorphism detection method and application thereof. The detection method comprises the following steps of: designing a primer in the position of a gallinaceous visfatin gene 9bp indel locus; then carrying out PCR amplification; and detecting the polymorphism of the gene 9bp indel by the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, wherein the gene is of a DD genotype when 9bp is deleted, the gene is of an II genotype when 9bp is inserted, and the heterozygous individual at the locus is of an ID genotype. The correlation analysis combining the detection results and economic characters of chickens is used for the assistant selection and the molecular breeding of chickens. The detection method does not need be subject to the enzyme digestion, thereby saving the cost and the time; the detection is carried out by adopting the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, thereby overcoming the limitation of the agarose electrophoresis to the small-fragment nucleotide difference detection. The method has the advantages of high resolution, high detection sensitivity and accurate genotype judgment; and the gel has on requirements for the staining method, and the ethidium bromide (EB) staining and the silver staining are both applicable.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method for marking non-heading cabbage molecule by utilizing SAMPL technique
The invention relates to a method for loose head cabbage molecular markers by utilizing the SAMPL technology comprising DNA extraction, DNA enzyme digestion-connection system optimization, SAMPL pre-amplification system optimization, SAMPL amplification system optimization, electrophoresis, silver staining color development and cluster analysis, wherein, a DNA sample is performed enzyme digestion through using EcoRI, MseI or PstI enzyme, and then corresponding joints of EcoRI,MseI or PstI are connected on the DNA sample through using T4-DAN ligase; the SAMPL pre-amplification is performed through using a 10mu L reaction system; a pre-amplification primer is corresponding to the chosen enzyme in the enzyme digestion; the SAMPL amplification is performed through using a 20mu L reaction system, one amplification primer is corresponding to the pre-amplification primer, and the other is an SAMPL primer. The method for loose head cabbage molecular markers by utilizing the SAMPL technology performs optimization and primer design for the complicated system of the SAMPL, constructs an SAMPL reaction system applicable to loose head cabbages and realizes loose head cabbage molecular markers.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
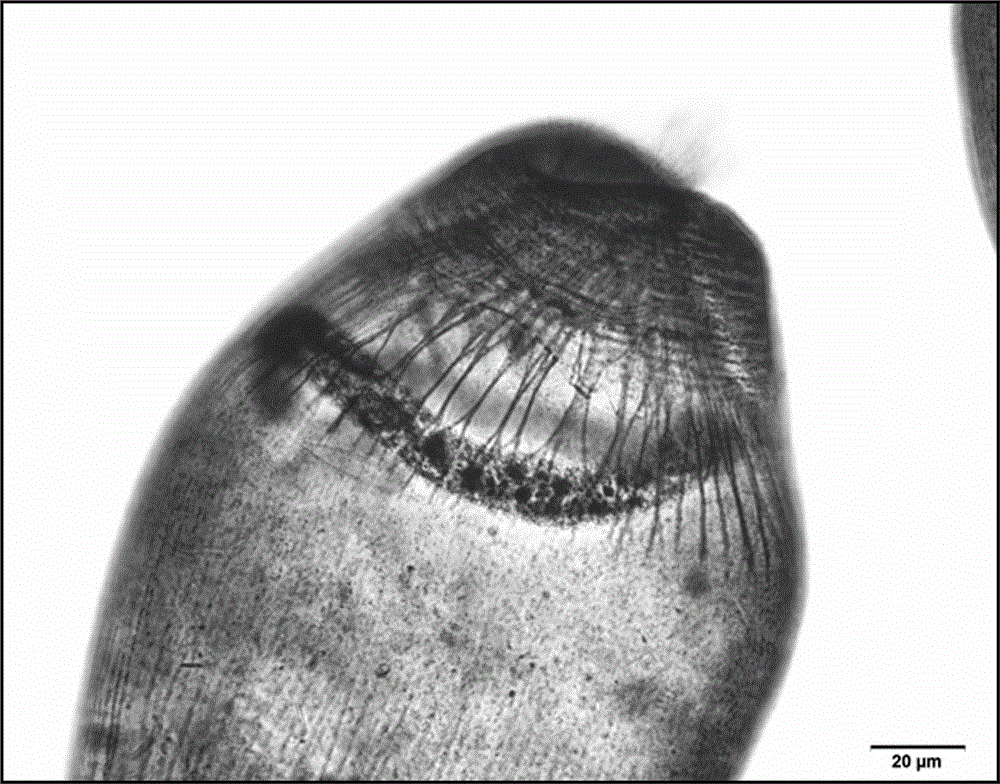
Staining method of ciliates
ActiveCN104568556AShorten experiment timeImprove dyeing efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationStainingCytology
The invention discloses a staining method of ciliates, belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides a staining method of ciliates to solve the problems that a traditional ciliate staining method is long in staining time and fussy in staining step, and cytostome and cilium cannot be clearly displayed. A saturated ethyl alcohol mercuric chloride solution is adopted as a fixing agent to carry out pre-fixation on ciliate bodies. In addition, before the pre-fixation operation, to-be-produced ciliate bodies are attached to a to-be-dyed glass slide; a plurality of steps such as dropwise adding protein glycerinum water and collodion are omitted. The staining method disclosed by the invention is convenient to operate; the sensitivity and the staining effect of silver staining of the ciliate protein are greatly improved; and rapid, efficient and accurate display of infraciliature in morphological classification and cytological studies of the ciliates is achieved.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for rapidly screening bian chicken weight gain degree by molecular marking
The invention relates to the field of poultry breeding, and particularly relates to a method for rapidly screening bian chicken weight gain degree by DNA molecular marking. The method comprises the following steps: extracting chicken genome DNA of a sample to be detected, performing specific primer amplification to obtain a MSTN gene target fragment, performing restriction endonuclease BbvI digestion of the target fragment, performing gel electrophoresis and silver staining for color development to obtain a DNA restriction enzyme map, determining the speed of weight gain of the sample to be detected based on the strip quantity and size in the map. The detection method adopted by the invention is simple and rapid, is not affected by external environment, can be used for molecular genetic marking of bian chicken weight selection, and can be used for marker assisted selection.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com