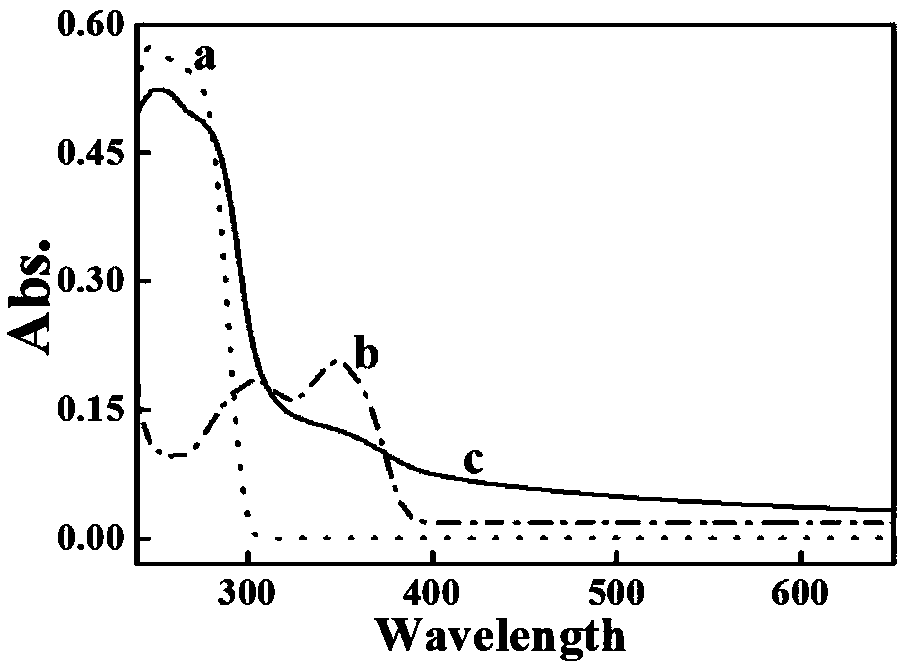
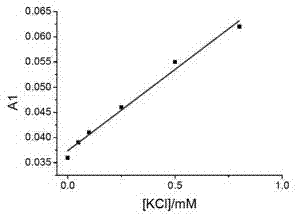
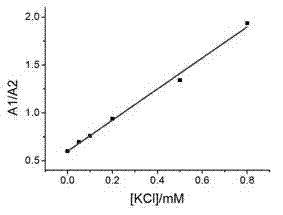
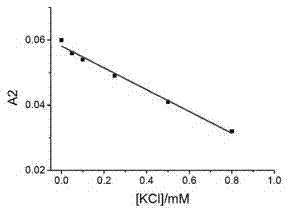
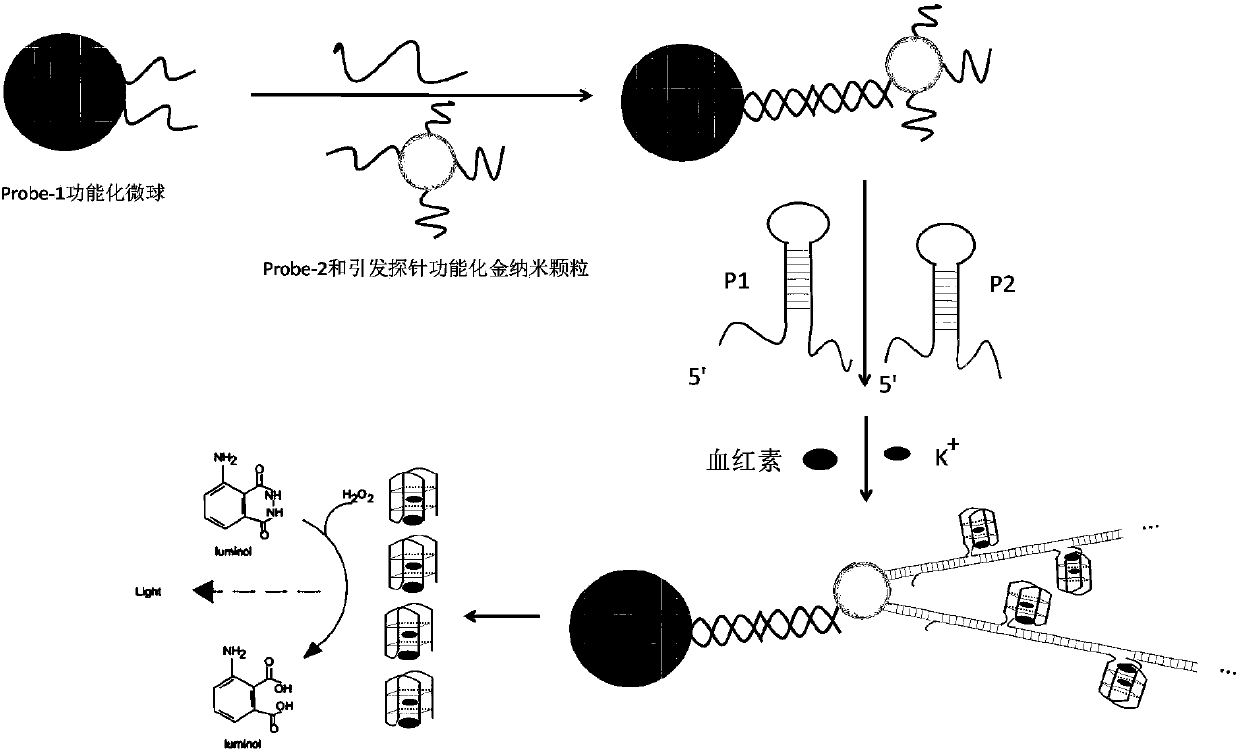
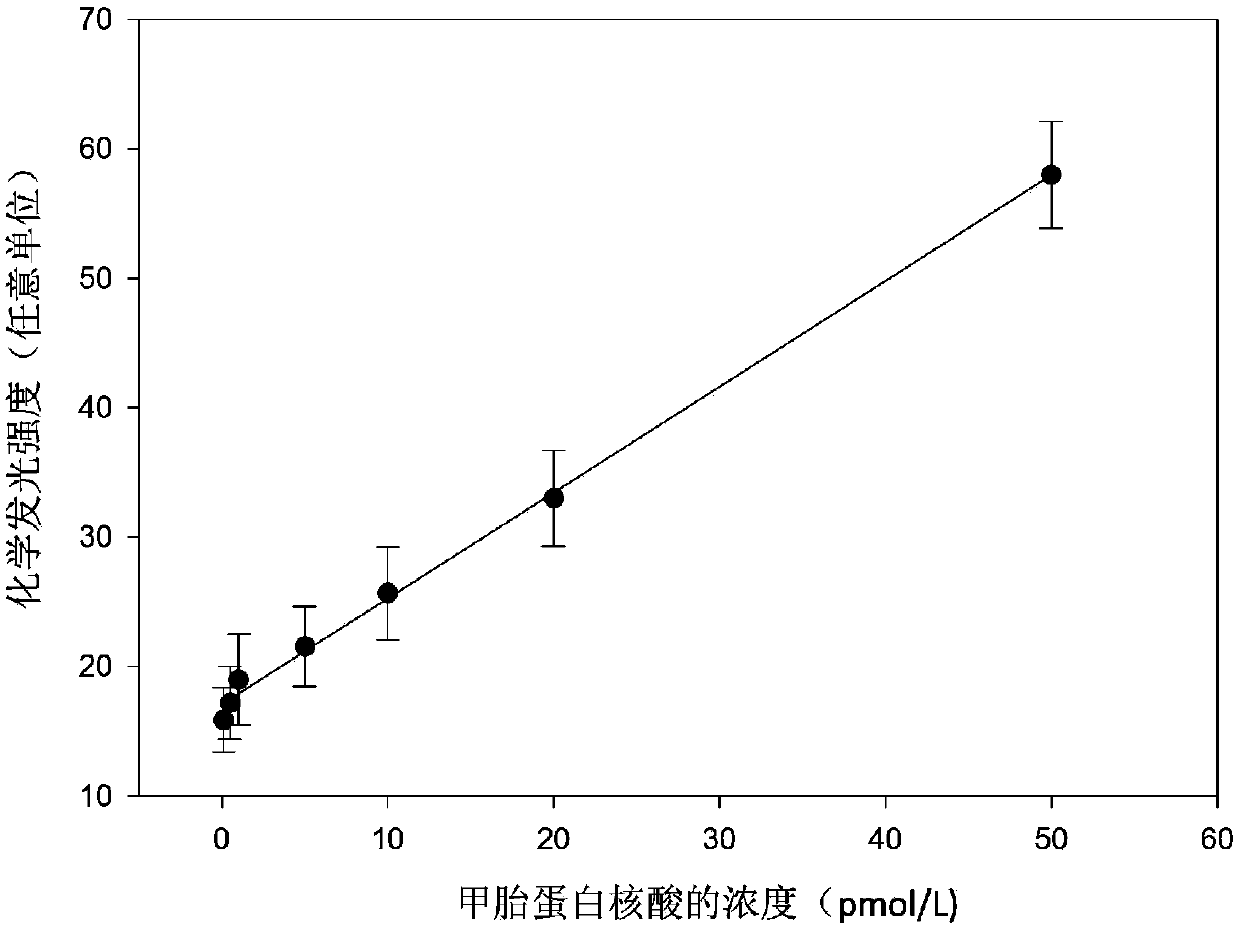
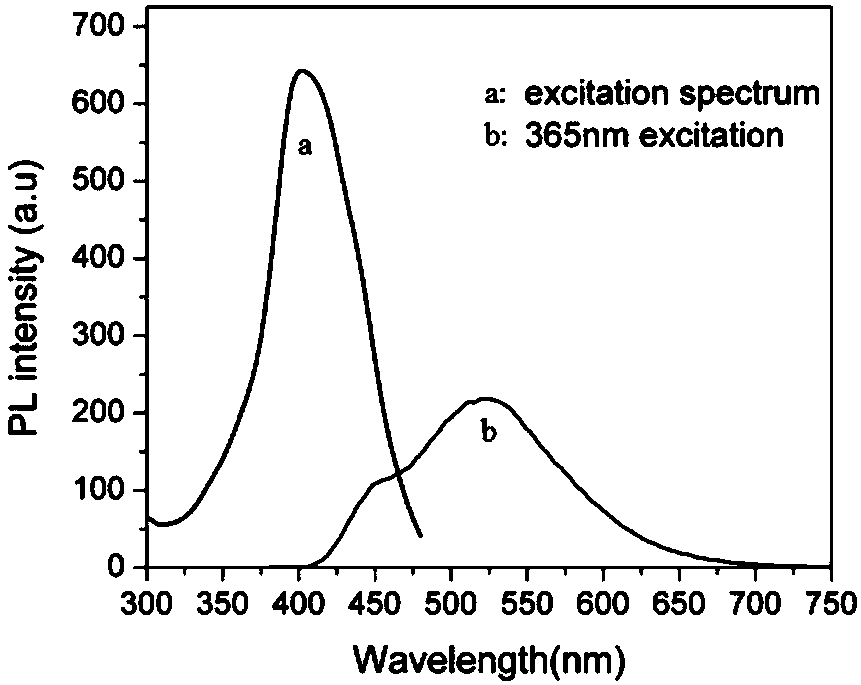
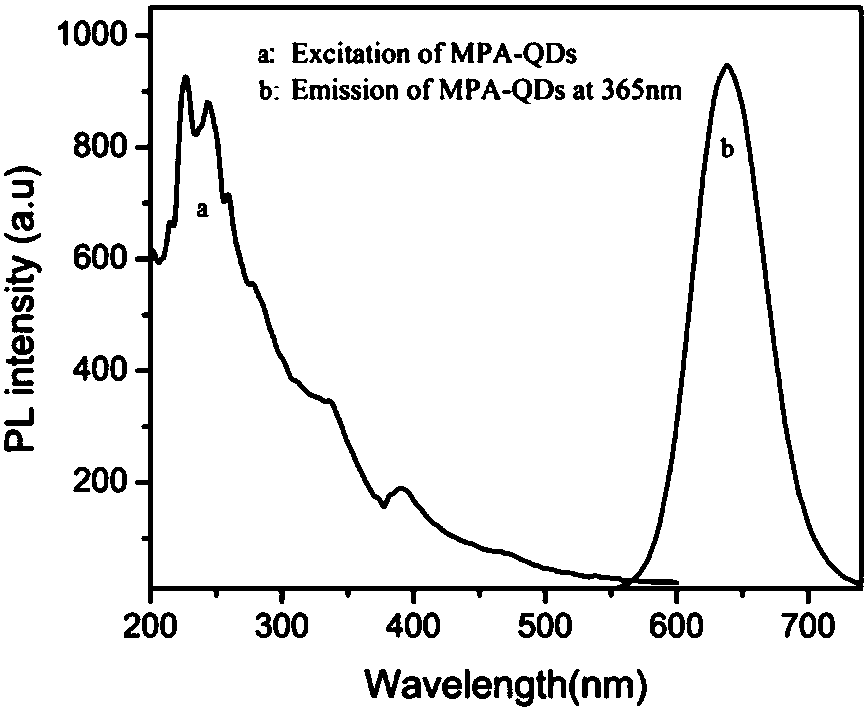
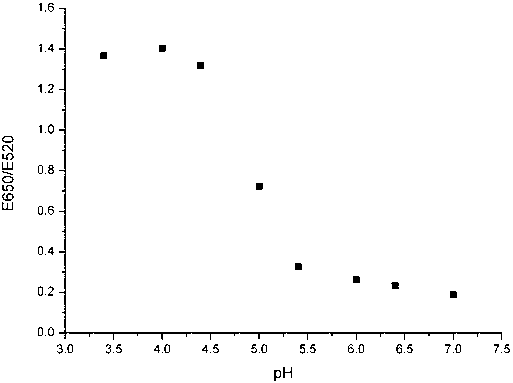
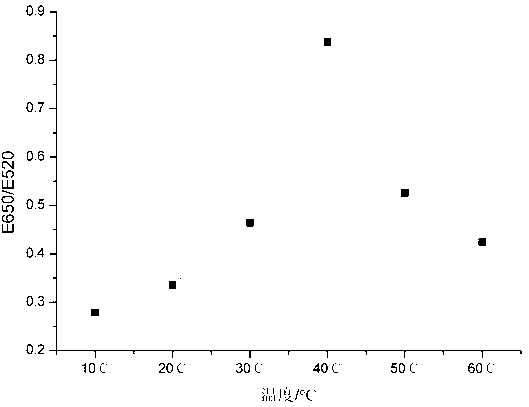
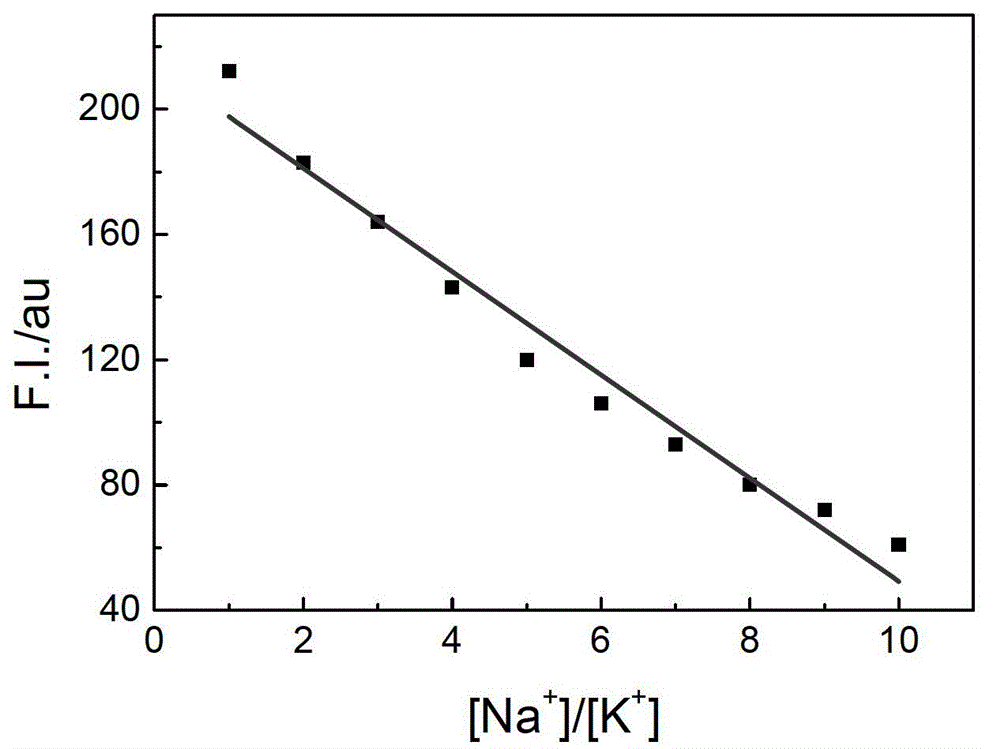
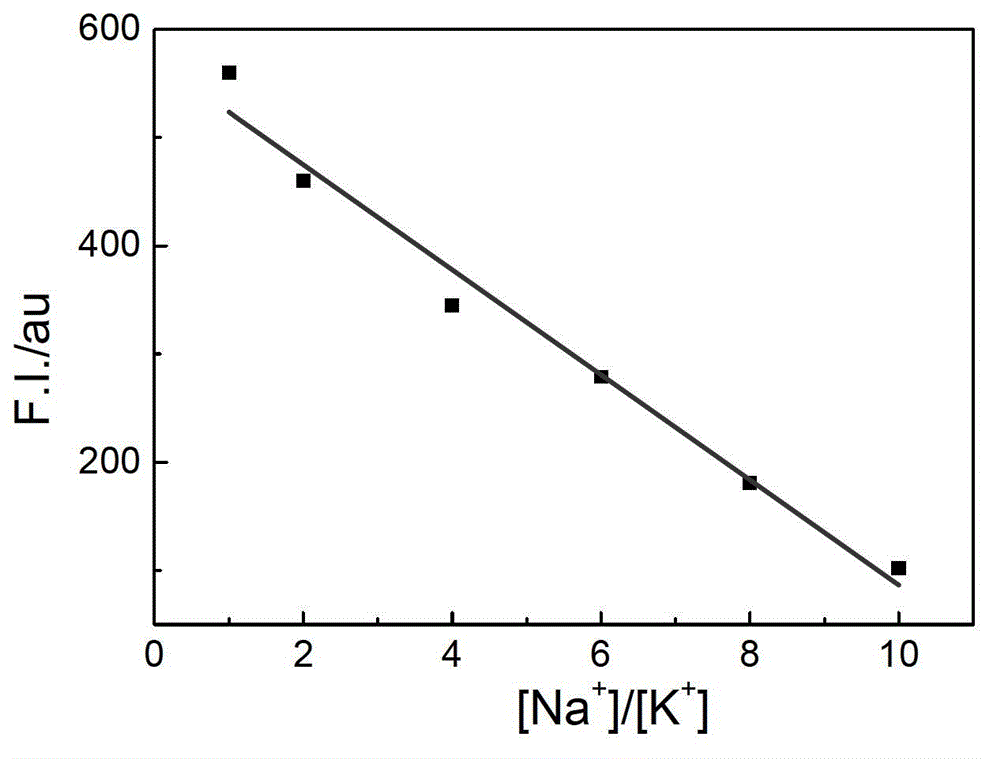
Patents
Literature
237results about How to "Realize visual detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
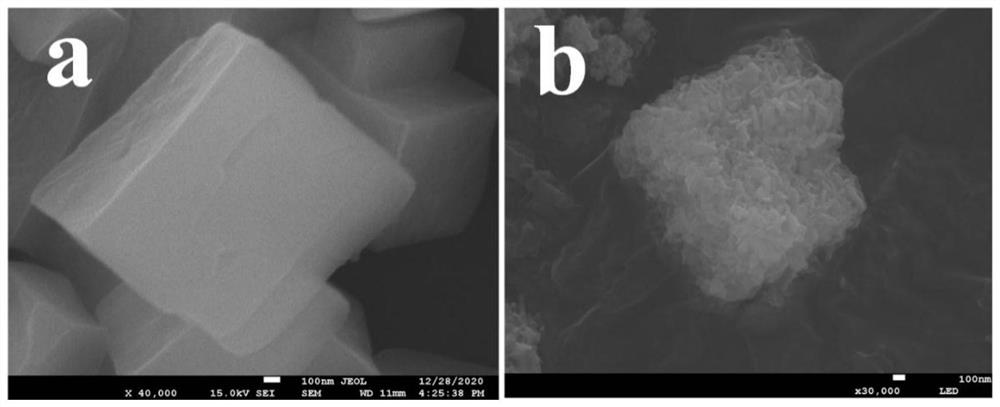
Spatially-separated pump-probe transient absorption spectrograph and realization method
ActiveCN103868595AMotivating realizationImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyBeam splitterVertical plane
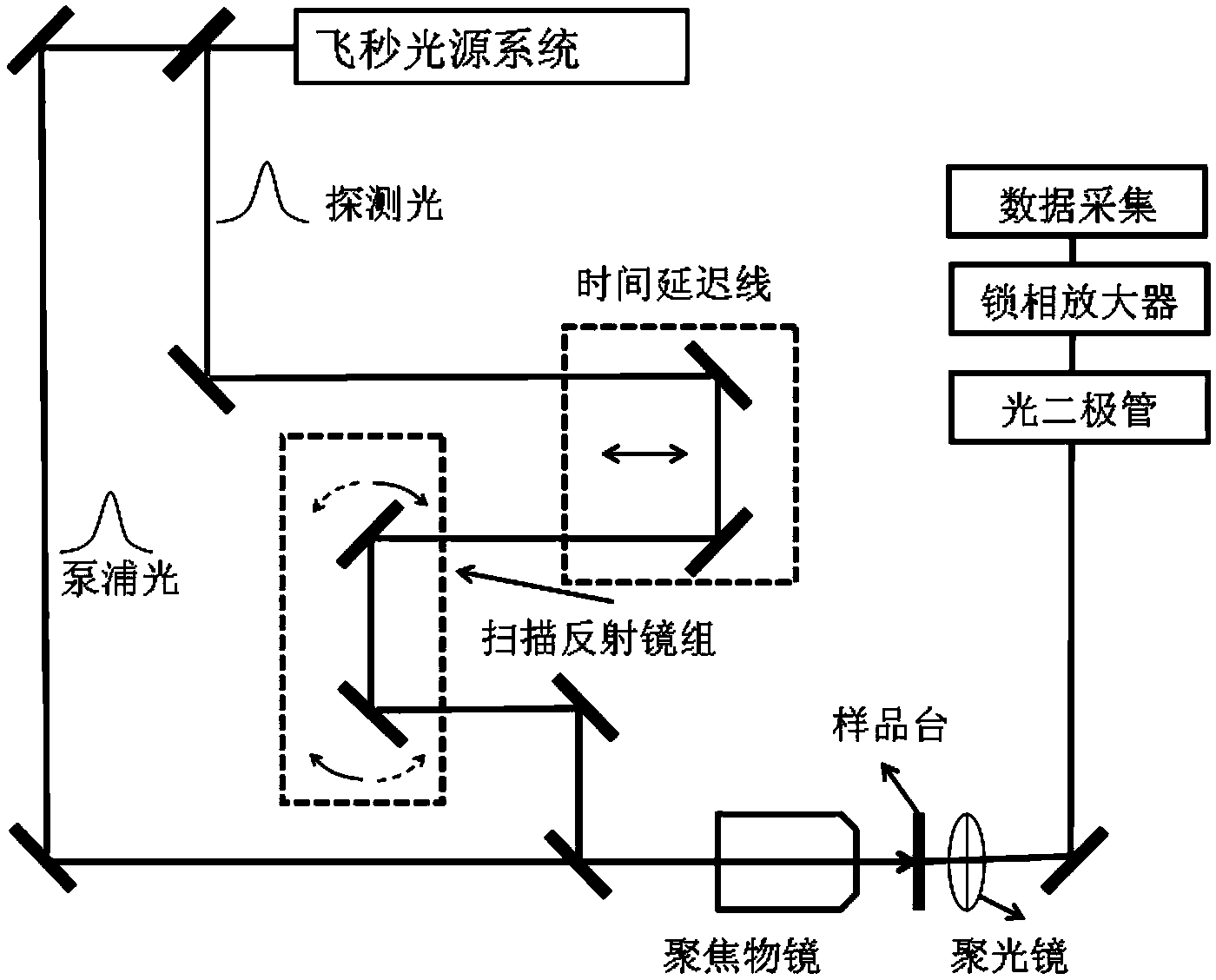
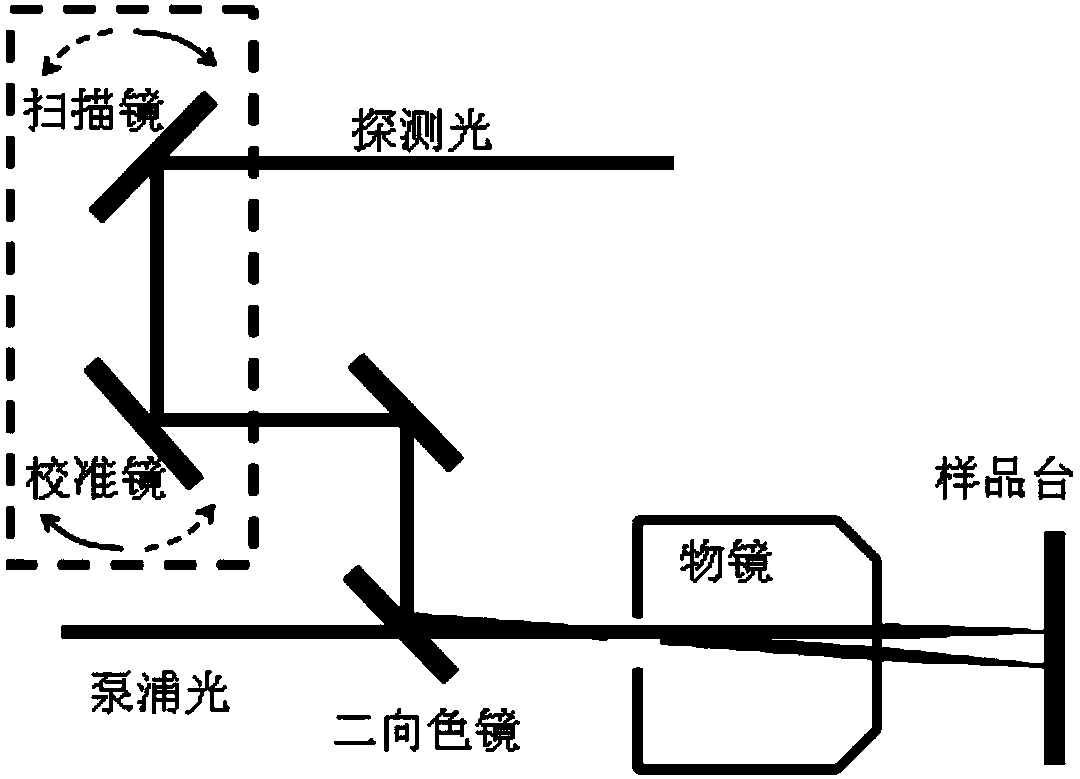
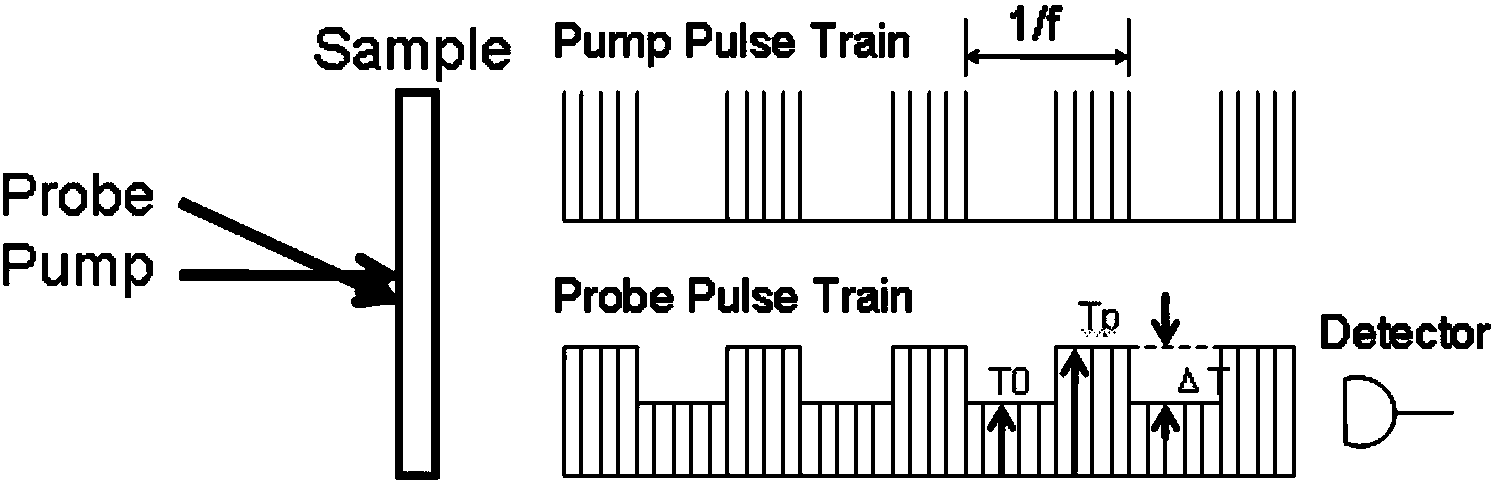
The invention discloses a spatially-separated pump-probe transient absorption spectrograph and a realization method. The realization method is characterized by generating a light source through a femtosecond light source system; realizing the beam splitting of pump light and probe light through a beam splitter; realizing the different time delay of the probe light through a time delay line; realizing the two-dimensional rotation and the calibration of the probe light within a horizontal plane and a vertical plane through a sweep reflector group; calibrating which means guaranteeing the incidence of the rotated probe light into a aperture within the front section of an objective lens; finally, obtaining a two-dimensional image formed on a sample under the combined action of the probe light and the pump light by a data collection system. According to the spatially-separated pump-probe transient absorption spectrograph and the realization method, the extremely high spatial discrimination can be realized, and moreover, the visual probe of carriers, excitors or plasmons can be realized.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Dual-emission ratio-type quantum dot fluorescence probe, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104198447AGood optical performanceReduce the impactFluorescence/phosphorescenceDrug contentPhotochemistry
The invention relates to a dual-emission ratio-type quantum dot fluorescence probe for visual detection of aspirin, a preparation method and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of preparation of material and detection of content of medicines. The preparation method of the probe includes following steps: preparing a precursor NaHTe solution from sodium borohydride, tellurium powder and water under an ultrasonic environment; adding the precursor to an aqueous solution of CdCl2.2.5H2O in the presence of thioglycollic acid; carrying out a reflux reaction with a nitrogen protecting condition to obtain required green fluorescence quantum dot and red fluorescence quantum dot; by means of a sol-gel method, wrapping the red fluorescence quantum dot with silicon spheres with amino group being connected; dispersing a green fluorescence quantum dot solution and the red fluorescence quantum dot wrapped with the silicon spheres in an MES buffer solution with addition of an EDC / NHS solution; and carrying out a reaction at room temperature in a dark place to obtain the dual-emission ratio-type quantum dot fluorescence probe. The dual-emission ratio-type quantum dot fluorescence probe is used in detection of the content of the aspirin through fluorescence quantitation and visualized analysis. The quantum dot fluorescence probe is quite good in optical performance and stability and has a capability of visualizedly detecting the aspirin.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method and application of modified glassy carbon electrode
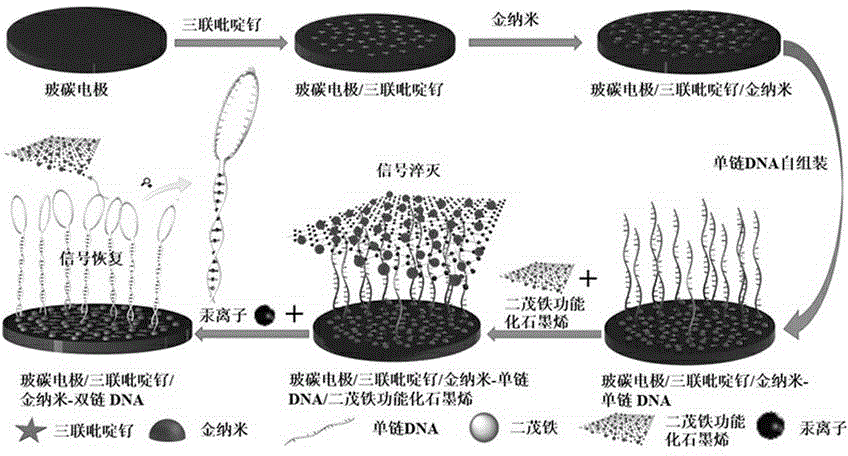
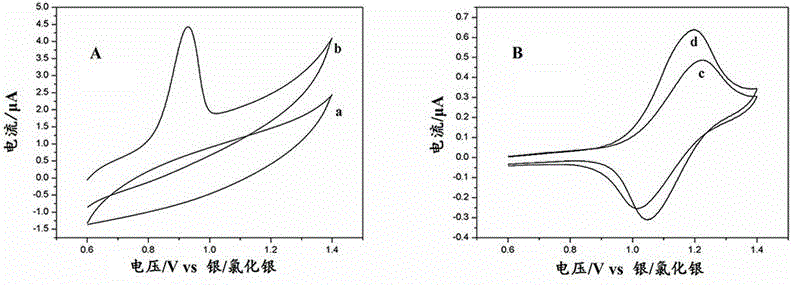
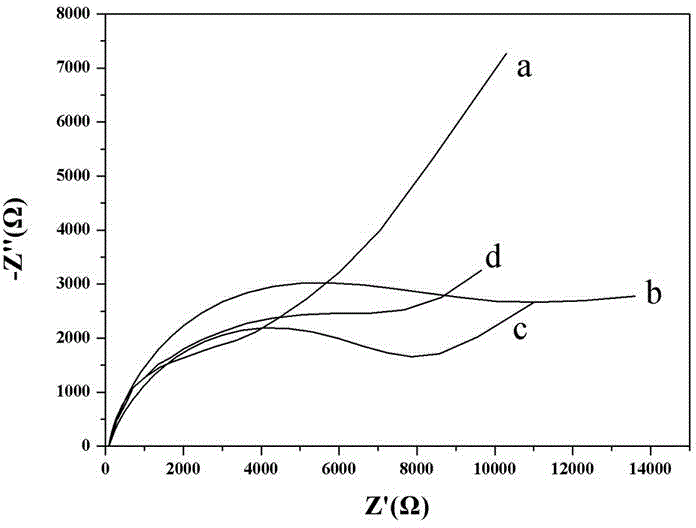
ActiveCN103913496ARealize visual detectionImprove stabilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMercuric ionSample water
The invention discloses a preparation method for a Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle-DNA-ferrocene functionalized graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. The method comprises the following concrete steps: polishing of a glassy carbon electrode; coating of Ru(bpy)3<2+> to prepare a Ru(bpy)3<2+> modified glassy carbon electrode; coating of gold nanoparticles to prepare a Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode; coating of single-stranded DNA to prepare a Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle-DNA modified glassy carbon electrode, wherein the sequence of the single-stranded DNA is rich in T bases, a stable double-stranded DNA structure can be formed after bonding with Hg2+, and the 5' end of the sequence of the single-stranded DNA is connected with an SH-(CH2)6 group; and coating pf ferrocene functionalized graphene so as to prepare the Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle-DNA-ferrocene functionalized graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. The modified glassy carbon electrode prepared in the invention can be used for detecting the content of mercury ions in a water sample and has good electrochemiluminescence performance, excellent stability and reproducibility and high sensitivity; and operation of the method is easy and convenient.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
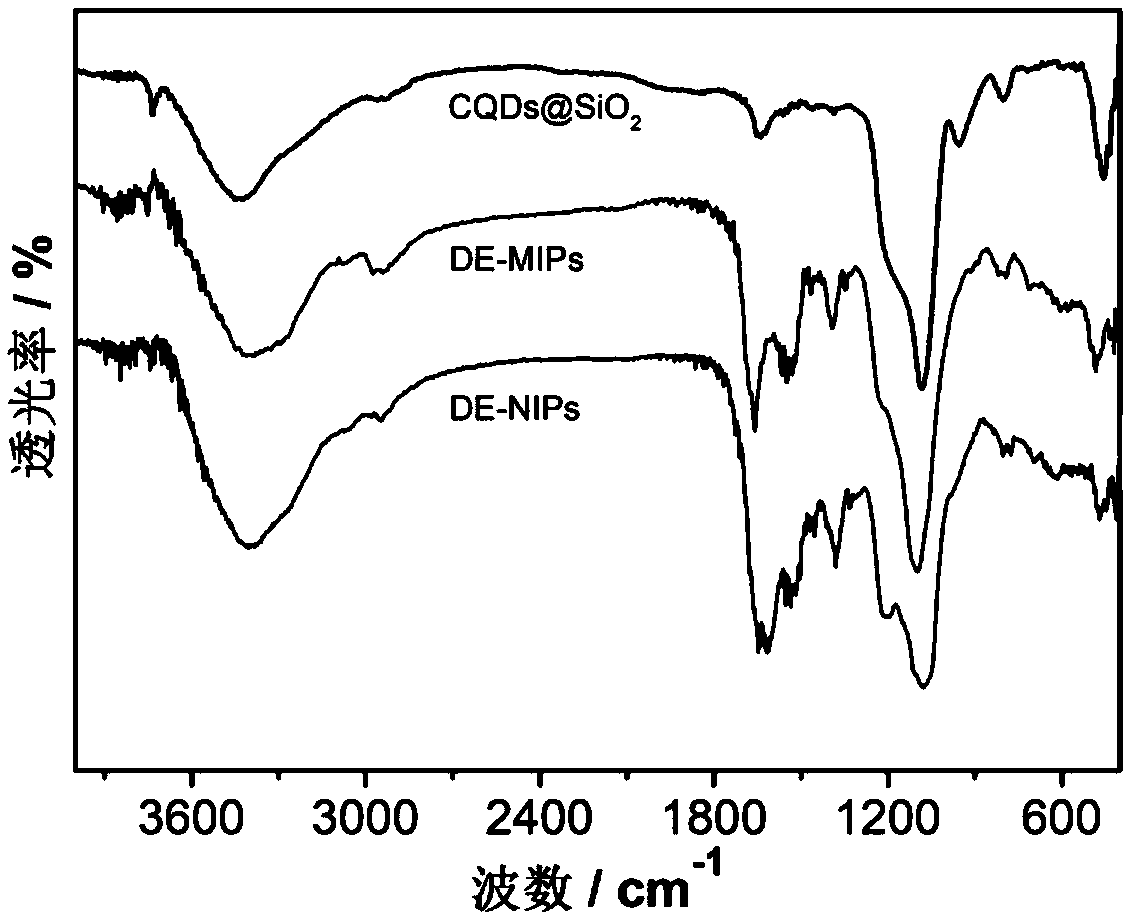
Dual-emission fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109370565AHigh selectivityAvoid interferenceMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescence/phosphorescenceCadmium CationSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of bio-functional materials, in particular to dual-emission fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and a preparation methodand application thereof. carbon quantum dots are coated with silica nanospheres to form a core of a ratio fluorescence probe; red cadmium telluride quantum dots are used as response signals, acrylamide and 4-vinylbenzeneboronic acid are used as bifunctional monomers, N,N-methylene bisacrylamide is used as a crosslinker, dopamine is used as templating molecules, dual-emission fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles having specific recognition sites for dopamine are synthesized in an alcohol phase under initiating of azodiisobutyronitrile, and fluorescent detection test paper with visualizing effect is prepared then by means of impregnating so as to provide visual detection for DA (dopamine); the fluorescent detection test paper is applied to the detection of DA in a human serum sample, and the results prove that the fluorescent detection test paper prepared herein is suitable for half-quantitative detection of DA in actual complex samples.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
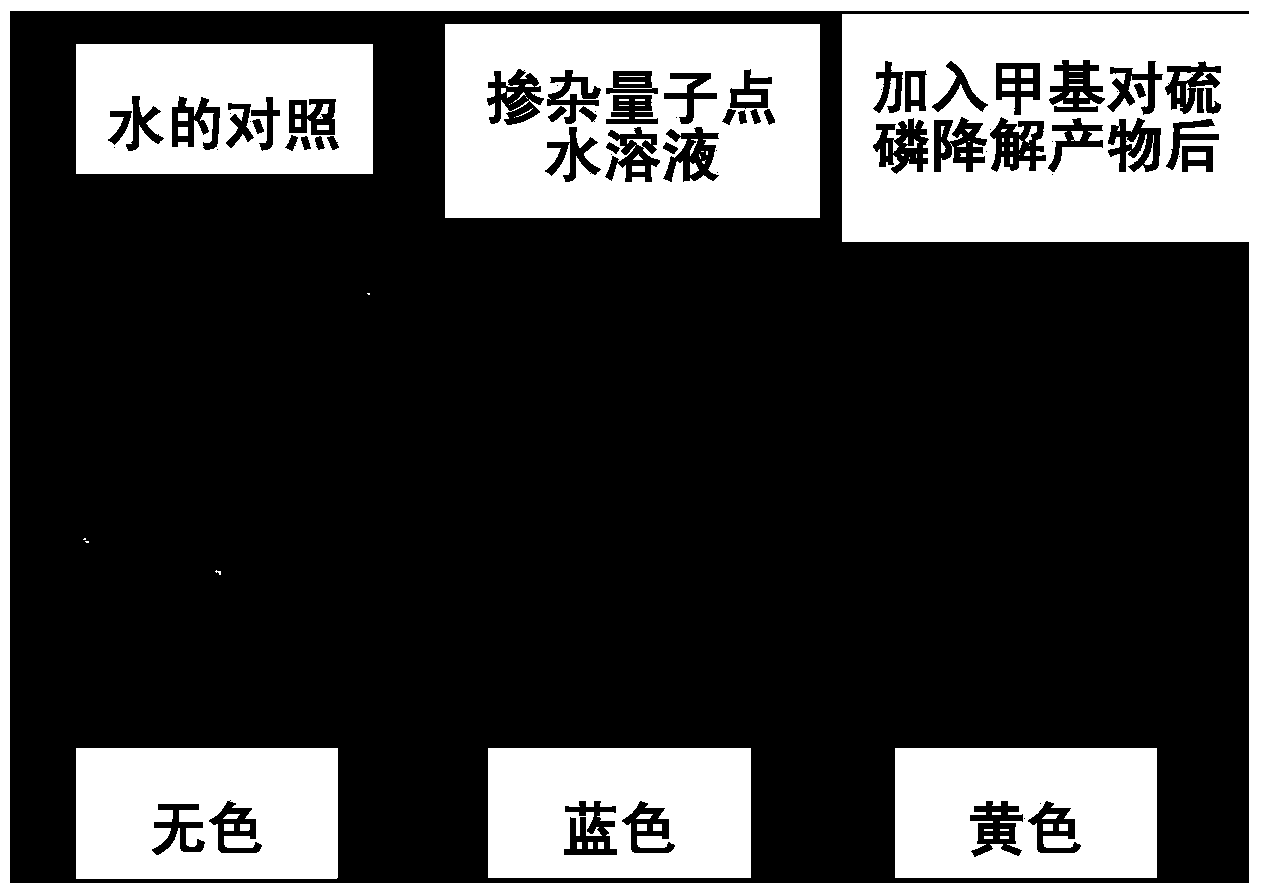
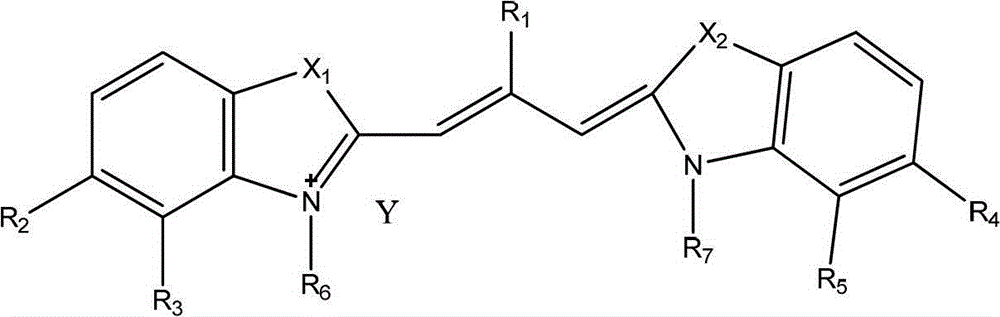
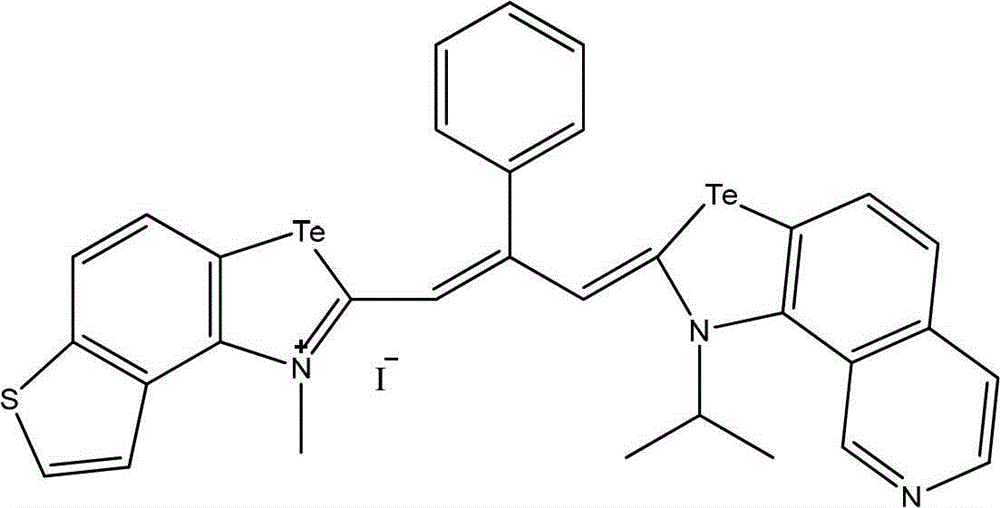
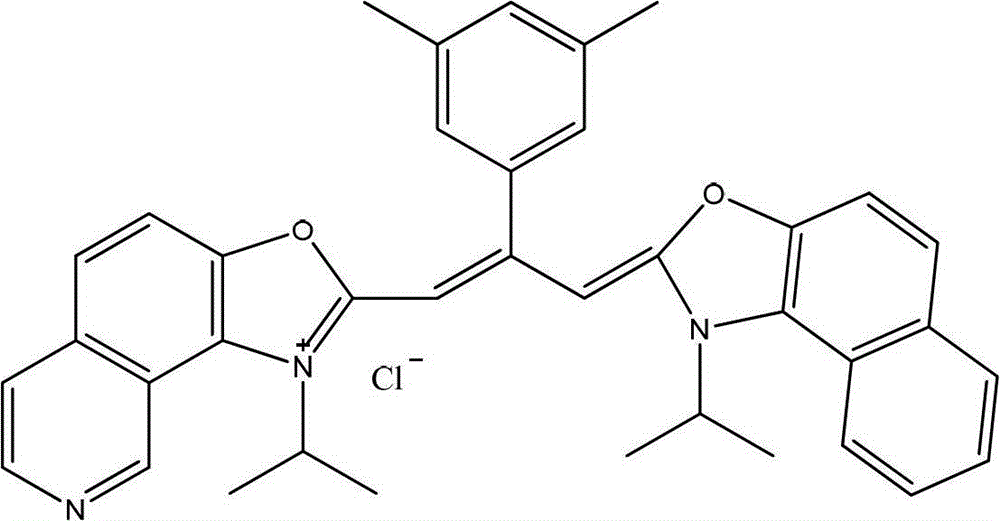
Method for visualized detection of organophosphorus pesticide residue by doped quantum dot ratio fluorescence technique
The invention relates to a method for visualized detection of organophosphorus pesticide residue by a doped quantum dot ratio fluorescence technique. Being a standard curve method, the method includes preparation and quenching of a double-fluorescence emission quantum dot, establishment of a standard curve and detection of organophosphorus pesticide residue. The method is characterized in that: the standard curve is determined under ultraviolet irradiation and is a curve about the corresponding relationship of a fluorescence ratio and a sample concentration, i.e. the standard curve is established by adding sample solutions with gradient concentrations into a quenched doped quantum dot probe dispersion fluid with a concentration of 30-40mcg / ml in order under ultraviolet irradiation, and determining fluorescence ratios successively. For the quenched doped quantum dot, a quenching agent is employed to quench the double-fluorescence of the doped quantum dot probe dispersion fluid to fluorescence intensity that no longer reduces. The method provided in the invention realizes sensitive and high selectivity detection of organophosphorus pesticide residue.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Potassium ion concentration detection method
ActiveCN102866148AStrong specificityRealize visual detectionMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCyaninePotassium ions
The invention relates to a potassium ion concentration detection method. The characteristic for forming the conversion of a G-four chain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) structure by controlling potassium ions and the characteristic for recognizing the conversion of the G-four structure through cyanine dye supramolecular aggregate are utilized, a sample to be tested is placed into DNA and cyanine dye mixed solution capable of forming the G-four chain, and the concentration range of the potassium ions in the sample can be semiquantitatively judged according to the color of the solution. Due to adopting the method, the visible detection of the potassium ion concentration can be realized, and detection test paper can be developed. A reagent is simple in ingredients, the reaction process is simple, no special or additional instrument is needed, the detection cost is low, and the method is convenient for being popularized to use in the industry.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cascade intrusion signal amplification reaction combined nanogold-oligonucleotide probe visual nucleic acid detection method
InactiveCN102827922ALow costNo cross contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
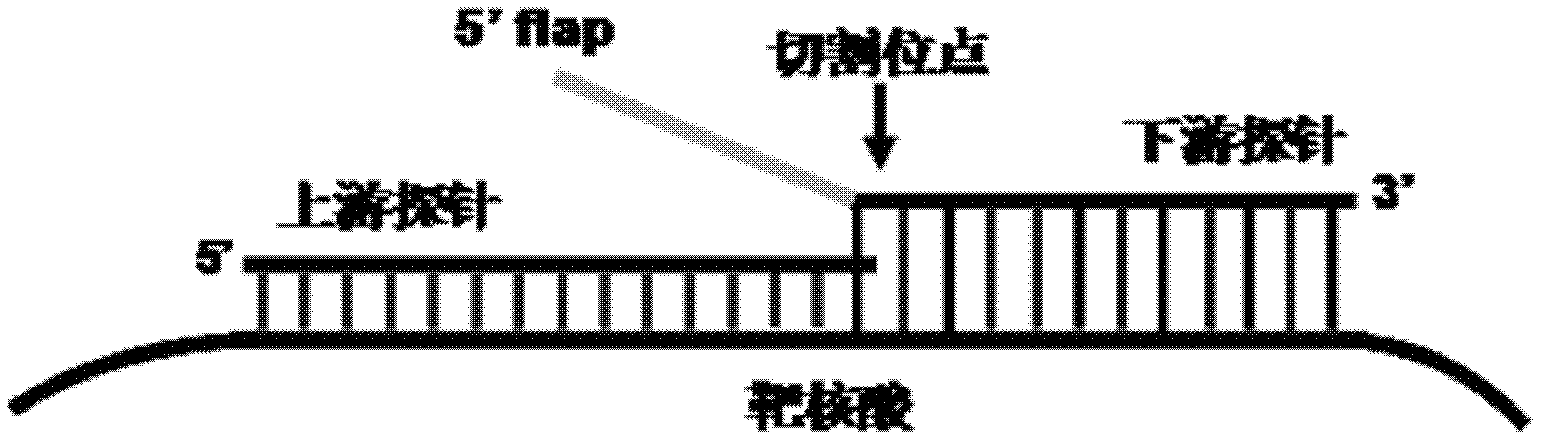
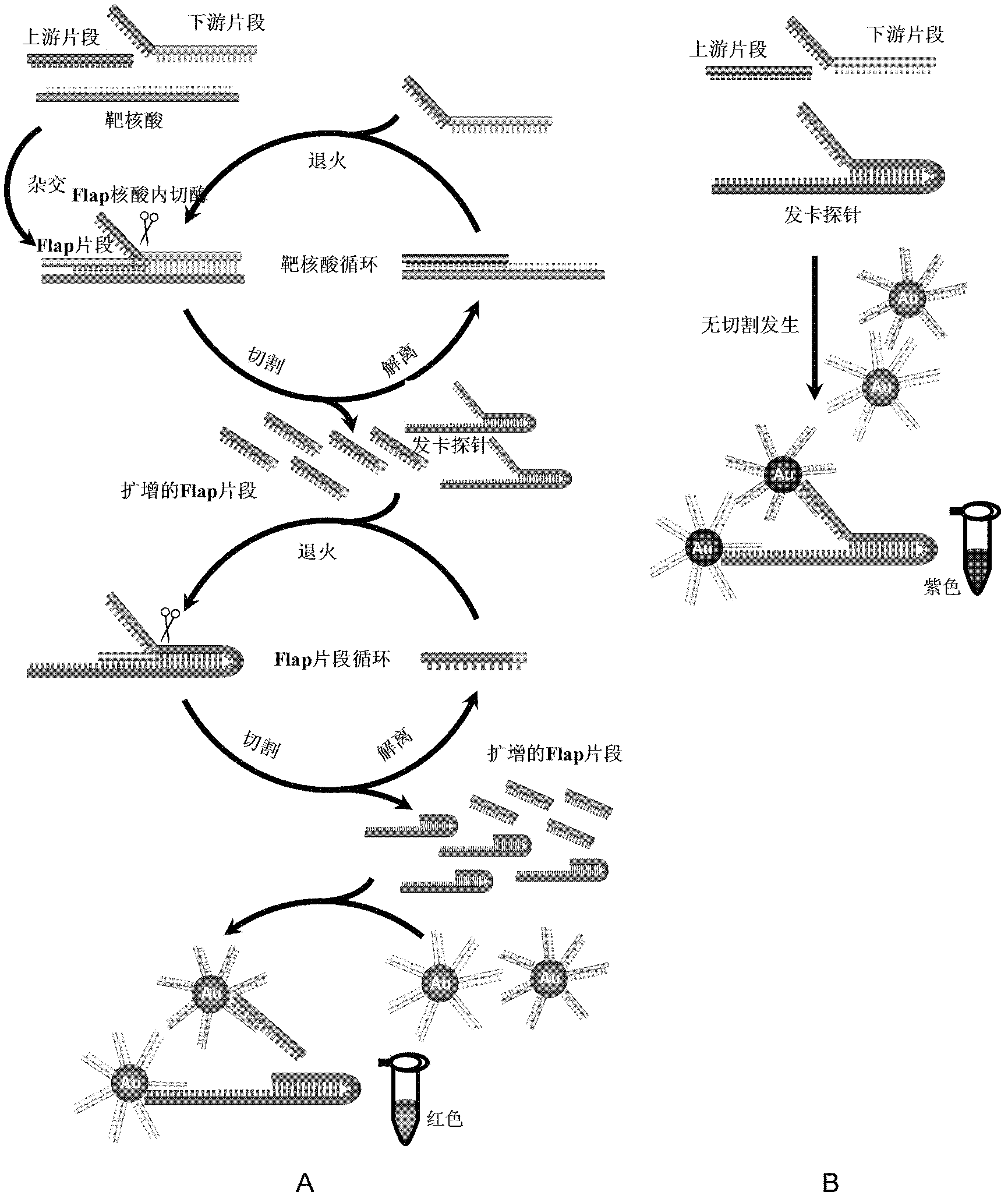
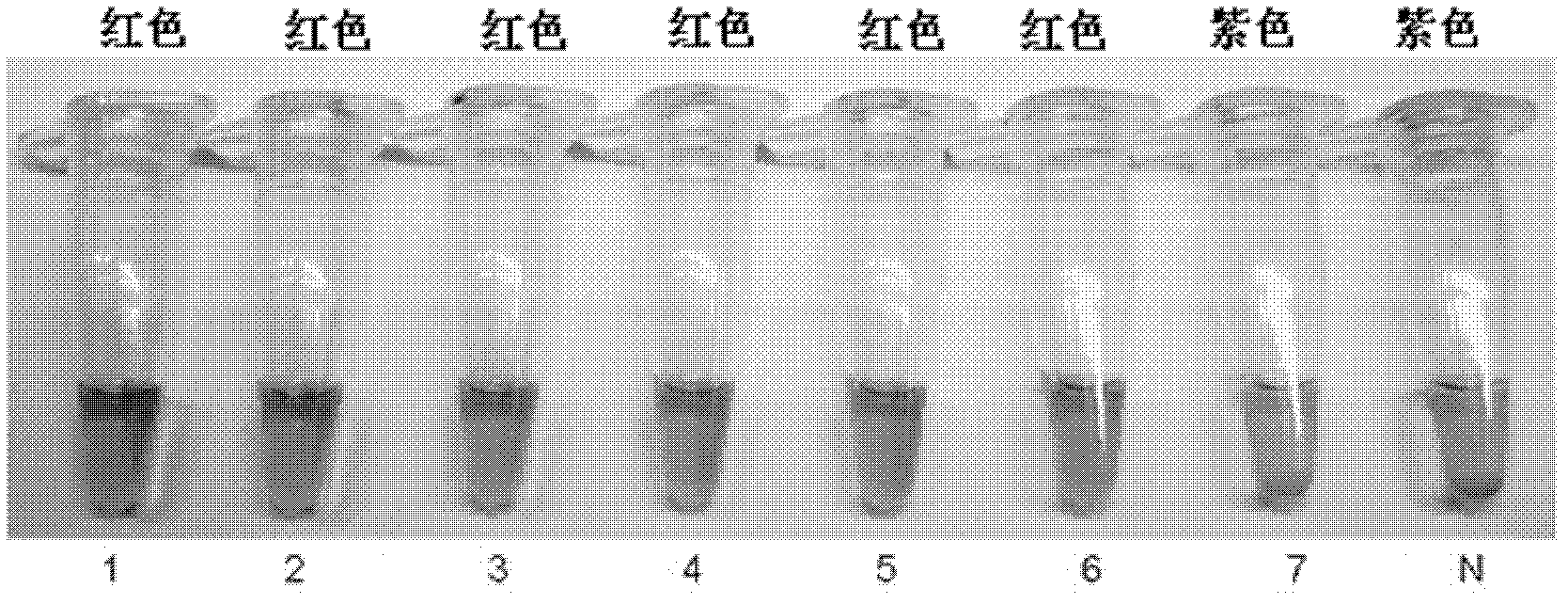
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to cascade intrusion signal amplification reaction combined nanogold-oligonucleotide probe visual detection. The cascade intrusion signal amplification reaction combined nanogold-oligonucleotide probe visual nucleic acid detection method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: 1) first-step intrusion signal amplification reaction, during which accumulation of flap fragments is formed; 2) flap fragment circulation phase, during which complementary hybridization of the flap fragments and hairpin probes is performed to form a flap fragment-hairpin probe special structure, and the hairpin probes are cut after the structure is recognized by enzymes; and 3) nanogold-oligonucleotide probe detection phase, during which results of the cascade intrusion signal amplification reaction are visually detected by the utilization of two different oligonucleotide modified nanogold probes. By the utilization of the detection method provided by the invention, visual detection of a nucleic acid target sequence can be carried out. In addition, as the intrusion signal amplification reaction has high specificity, differentiated detection of the nucleic acid sequences with single-base differences near intrusion sites can be realized.
Owner:HUADONG RES INST FOR MEDICINE & BIOTECHNICS
Potassium ion concentration detection method
ActiveCN102735664AStrong specificityRealize visual detectionMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCyaninePotassium ions
The invention relates to a potassium ion concentration detection method. According to the method, characteristics comprising that potassium ion regulation allows G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation to be formed and cyanine dye supermolecular aggregates identify the G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation are utilized, a sample to be detected is added to a mixed solution of G-quadruplex DNA and the cyanine dye, the absorbance value at 560-590nm, 500-540nm or 610-670nm or the fluorescence intensity value at 580-640nm is determined, and the corresponding potassium ion concentration value can be obtained through finding the value corresponding to the absorbance value or the fluorescence intensity value on a standard curve. The method has a high specificity, so the method is not affected by sodium ions in the sample; and reagent components is simple, and the reaction process is simple, so errors generated by operations can be effectively reduced, and the test accuracy is high. The method can be rapidly realized through a common ultraviolet-visible absorption detector, a spectrophotometer or a fluorescent spectrometer without special or extra instruments, so the detection cost is low, thereby the popularization and the application of the method in industries are convenient.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and Cu<2+> detection application of rare earth ratiometric fluorescent probe
ActiveCN108517208ABlock deliveryAchieve high sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescence/phosphorescenceRare earth ionsGuanosine monophosphate
The invention discloses a preparation method and a Cu<2+> detection application of a rare earth ratiometric fluorescent probe, and belongs to the technical field of environmental detection. The preparation method of the luminol-Tb-GMP fluorescent probe is established through the self-polymerization coordination effect among luminol, GMP and Tb<3+> by using luminol and guanosine monophosphate (GMP)as dual ligands and using a rare earth ion Tb<3+> as a luminescent center ion. The luminol-Tb-GMP fluorescent probe combines the dual fluorescent signals of luminol and Tb<3+>, and simultaneously emits dual fluorescent signals of the luminol and Tb<3+> under the same excitation wavelength. When Cu<2+> exists, the luminol and GMP have a strong coordination effect on the Cu<2+> in order to preventelectrons from being transferred from the amino group of the GMP to Tb<3+>, so fluorescence quenching of the Tb<3+> is caused, and the fluorescence intensity of the luminol is unchanged, thereby a Cu<2+> detection method based on the fluorescence signal ratio of the luminol and Tb<3+> is established. Additionally, the green fluorescence of the Tb<3+> gradually weakens and the blue fluorescence ofthe luminol gradually appears with the increase of the Cu<2+> concentration, so the visual detection of the Cu<2+> can be achieved. The luminol-Tb-GMP fluorescent probe also can be applied to the sensitive detection of the Cu<2+> in an environmental water samples and a biological sample.
Owner:RUIJIN SHENGYUAN METAL NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Potassium ion concentration detection kit and system thereof
ActiveCN102735623AStrong specificityRealize visual detectionMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPotassium ionsReagent
The invention relates to a potassium ion concentration detection kit and a system thereof. The kit and the system, which utilize characteristics comprising that potassium ion regulation allows G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation to be formed and cyanine dye supermolecular aggregates identify the G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation, have high specificities, and are not affected by sodium ions in a sample. Reagent components are simple and the reaction process is simple, so errors generated by operations can be effectively reduced, and the test accuracy is high. The kit and the system of the invention allow rapid detection to be realized without special or extra apparatuses, and the detection cost is low, so the popularization and the application of the kit and the system are convenient.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular imprinting ratio fluorescent sensor, preparation and application thereof
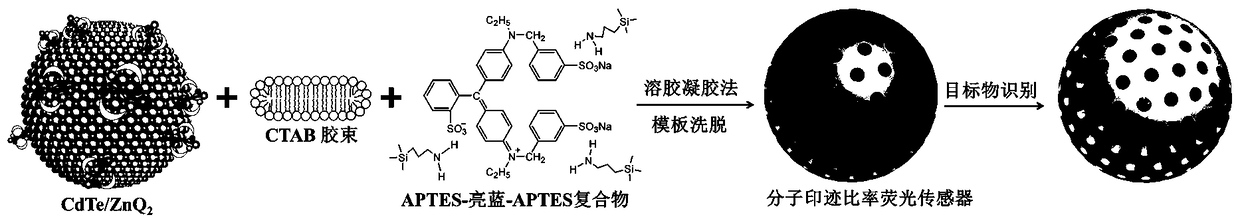
ActiveCN109239045AExtensive testingFluorescence intensity unchangedFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrosphereWavelength
The invention belongs to the fields of chemistry, materials and food safety, and relates to a molecular imprinting ratio fluorescent sensor, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the molecular imprinting ratio fluorescent sensor includes the steps that molecular imprinting is carried out through sol-gel polymerization, single-component dual-fluorescence emission cadmium telluride / 8-hydroxyquinoline zinc nanoparticles provide fluorescence signals, holes after eluting bright blue are recognition sites, a mesoporous structure is formed after hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide is eluted, and bright blue imprinted microspheres with the mesoporous structure are obtained, that is, the molecular imprinting ratio fluorescent sensor based on the single-component dual-fluorescence emission nanoparticles. According to the molecular imprinting ratio fluorescent sensor, preparation and application thereof, the obtained sensor prepared by the preparation method candetect bright blue with high selectivity and sensitivity, and provides color evolution and self-correction functions; and in addition, by effectively adjusting the emission wavelength of the sensor,the molecular imprinting ratio fluorescent sensor can be more widely used in detection of various colored substances.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
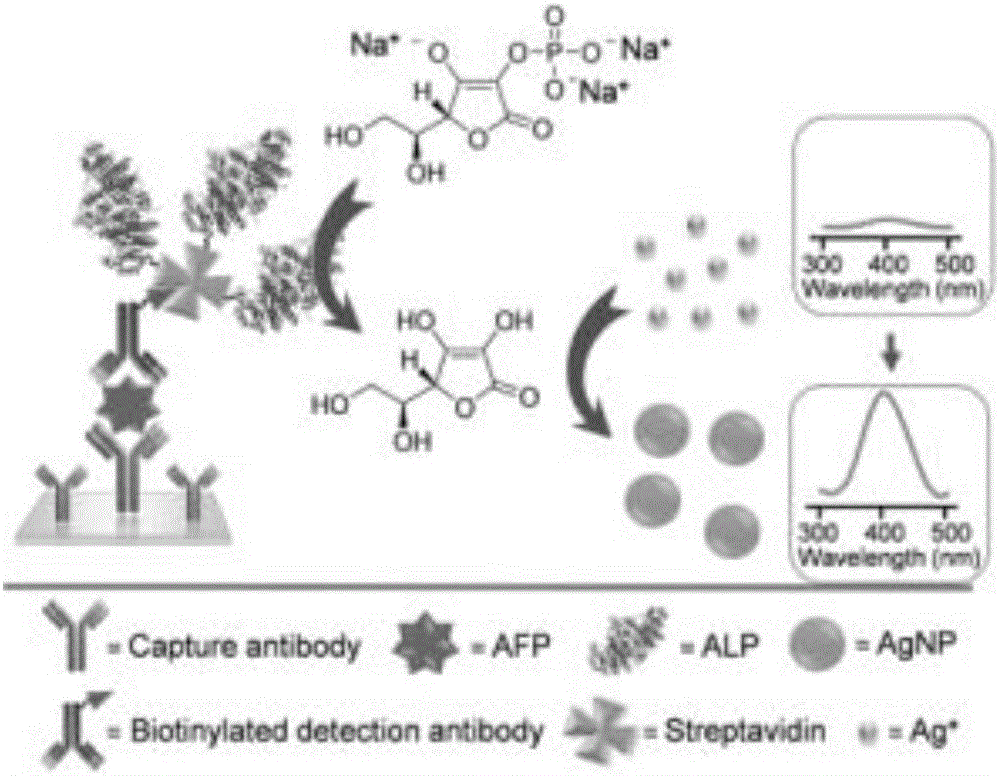
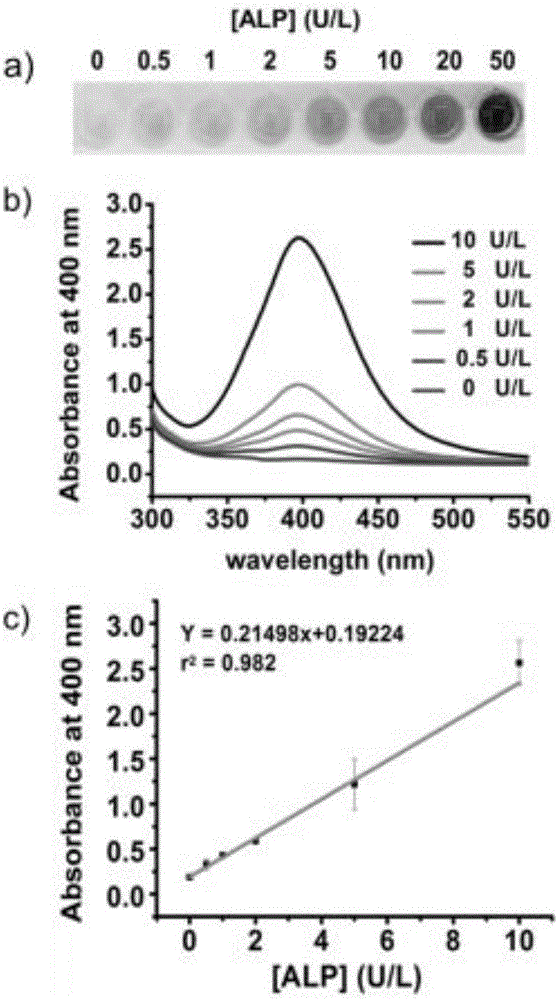
Noble metal nanoparticle based visual detection method and application
ActiveCN106248597ARealize visual detectionThe detection method is simpleColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingChemistryEnzyme
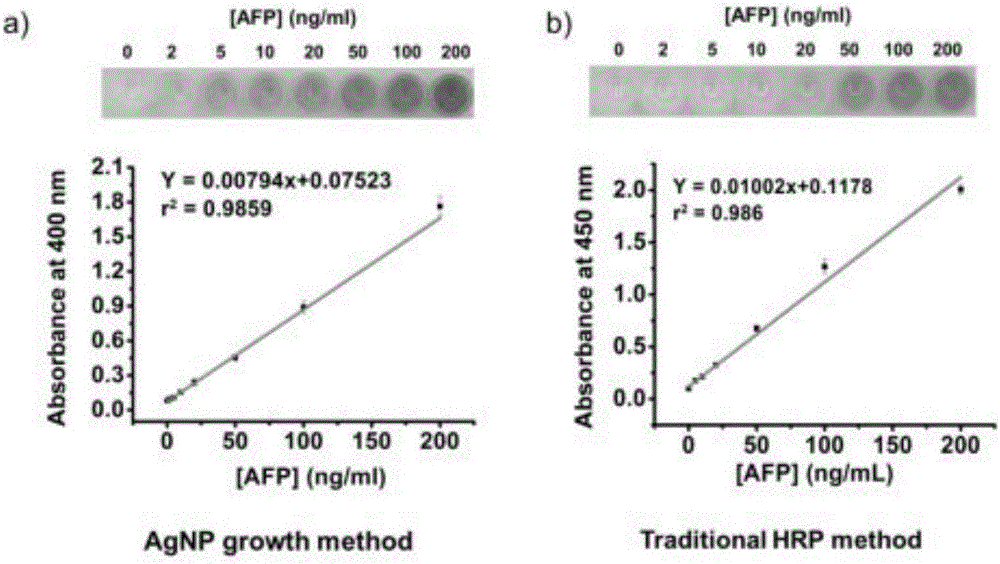
The invention discloses a noble metal nanoparticle based visual detection method and an application, and relates to the field of immunity detection and analysis. The method combines the high catalytic performance of an enzyme and the high extinction coefficient of a noble metal nanoparticle, the visual detection concentration of the enzyme is greatly reduced, meanwhile, the small change of the concentration of the enzyme is conveniently distinguished through the color of an obtained nano-gel, and the concentration of the enzyme is semi-quantitatively detected directly through naked eyes within a certain concentration range of the enzyme. The method is combined with a traditional enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and various tumor makers, bacteria and viruses are visually detected with high sensitivity. The method is based on the fact that the direct in-situ growth of the nanoparticle leads to the remarkable color change from colorless solution to colored solution, no complicated probe modification process or no precise instrument and equipment is needed, therefore, the method is simple and is low in energy consumption, and the method has a very high practical value.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
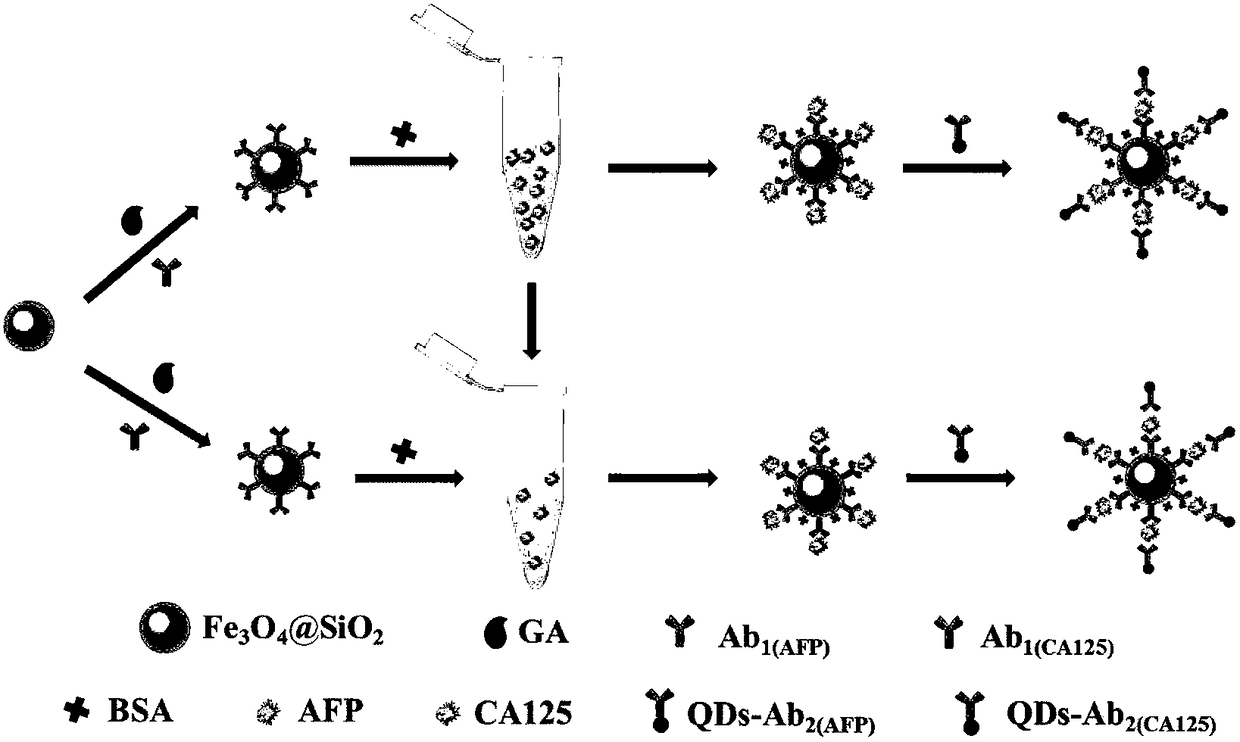
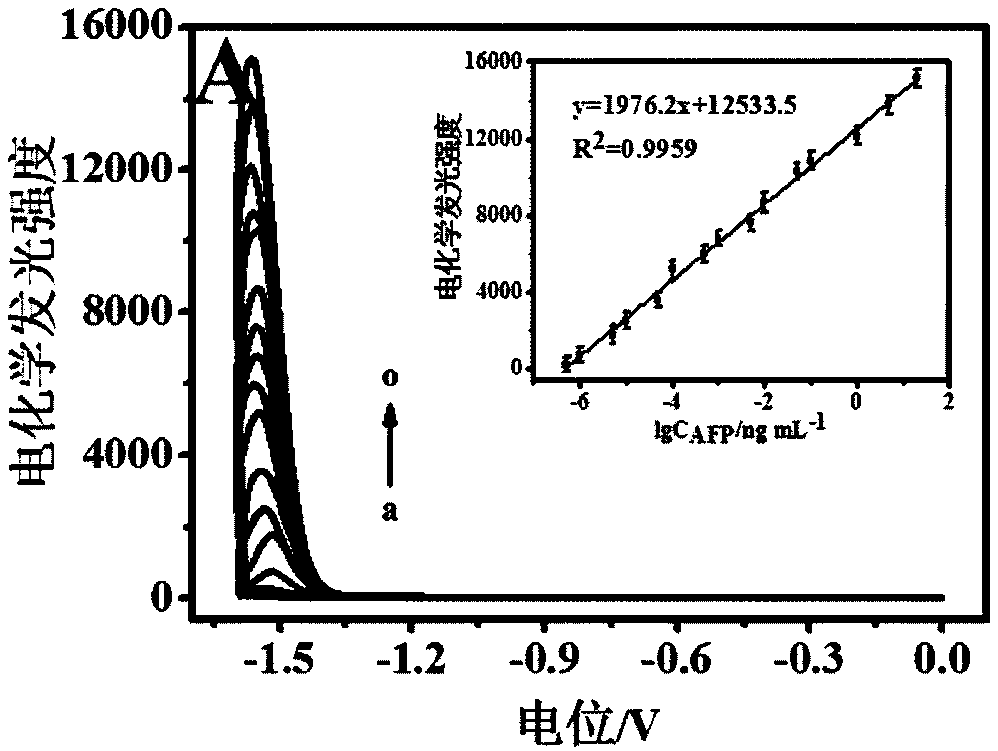
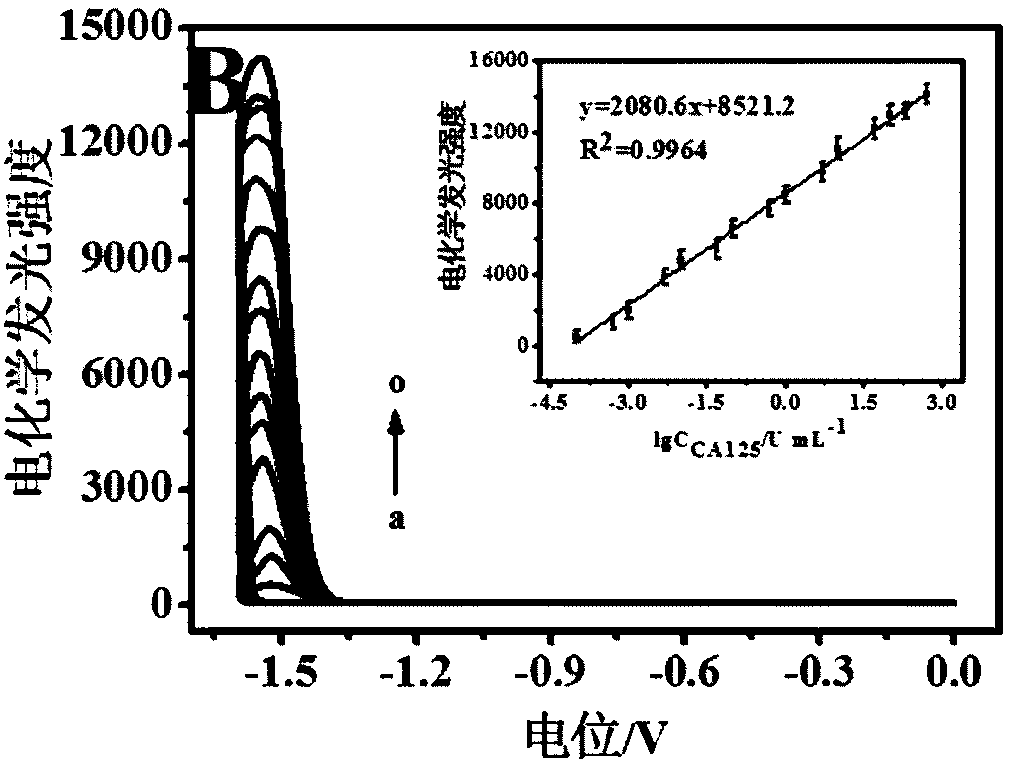
Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on CdZnTeS quantum dots as well as preparation method and application of electrochemiluminescence immunosensor
ActiveCN108226461AExcellent electrochemiluminescent propertiesStrong electrochemiluminescent propertiesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingAntigenMedicine
The invention discloses an electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on CdZnTeS quantum dots. The electrochemiluminescence immunosensor comprises CdZnTeS-Ab2, Fe3O4@SiO2-Ab1 with closed non-specificbinding sites, and antigens respectively connected with the CdZnTeS-Ab2 and the Fe3O4@SiO2-Ab1 by mutual action between antigens and antibodies; the CdZnTeS-Ab2 is secondary antibodies marked by CdZnTeS quantum dots; the Fe3O4@SiO2-Ab1 is Fe3O4@SiO2 with the surface being modified with primary antibodies. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the electrochemiluminescence immunosensor. The electrochemiluminescence immunosensor, the preparation method and the application disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that the electrochemiluminescence immunosensor is established on the basis of mutual action between the antigens and the antibodies, so that the specificity of detection is greatly improved, the detection speed is fast, the sensitivity is high, the specificity is good, the detection limit is low, the detectable linear range is wide, the operation is simple and visual detection can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
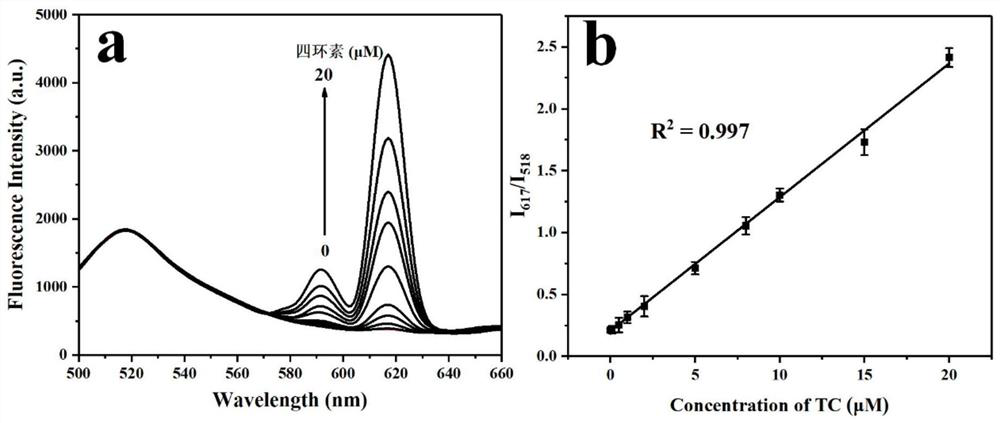
Preparation method of ratio-type fluorescent probe and application of ratio-type fluorescent probe in detection of tetracycline antibiotics
ActiveCN113201325AReduce distractionsReliable resultsFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsAptamerFluoProbes
The invention belongs to the technical field of sensors, and relates to a preparation method and application of a ratio type fluorescent probe. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving fluorescein, zinc acetate and terephthalic acid in DMF (Dimethyl Formamide), carrying out ultrasonic treatment and heating, and after a reactant is cooled, conducting washing and drying to obtain an FSS-coated MOF-5 fluorescent material; and dissolving the FSS-coated MOF-5 fluorescent material in water, adding guanosine monophosphate and europium nitrate under a stirring condition, and conducting washing, centrifuging and drying to obtain the FSS-coated MOF-5-coated GMP / Eu fluorescent probe. The ratio type fluorescent probe prepared by the invention can realize specific detection of tetracycline antibiotics, does not need specific biological materials such as antigens, antibodies or aptamers and the like, and can reduce the time and cost for preparing a specific fluorescent sensor; meanwhile, various color changes can be generated under an ultraviolet lamp, so that semi-quantitative visual detection of tetracycline is realized; and the detection is rapid and accurate, the operation is simple, the probe is not easily influenced by the environment, and the quality and safety of food are guaranteed.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method and use method of visual detection chip for multiple pesticide residues based on membrane material
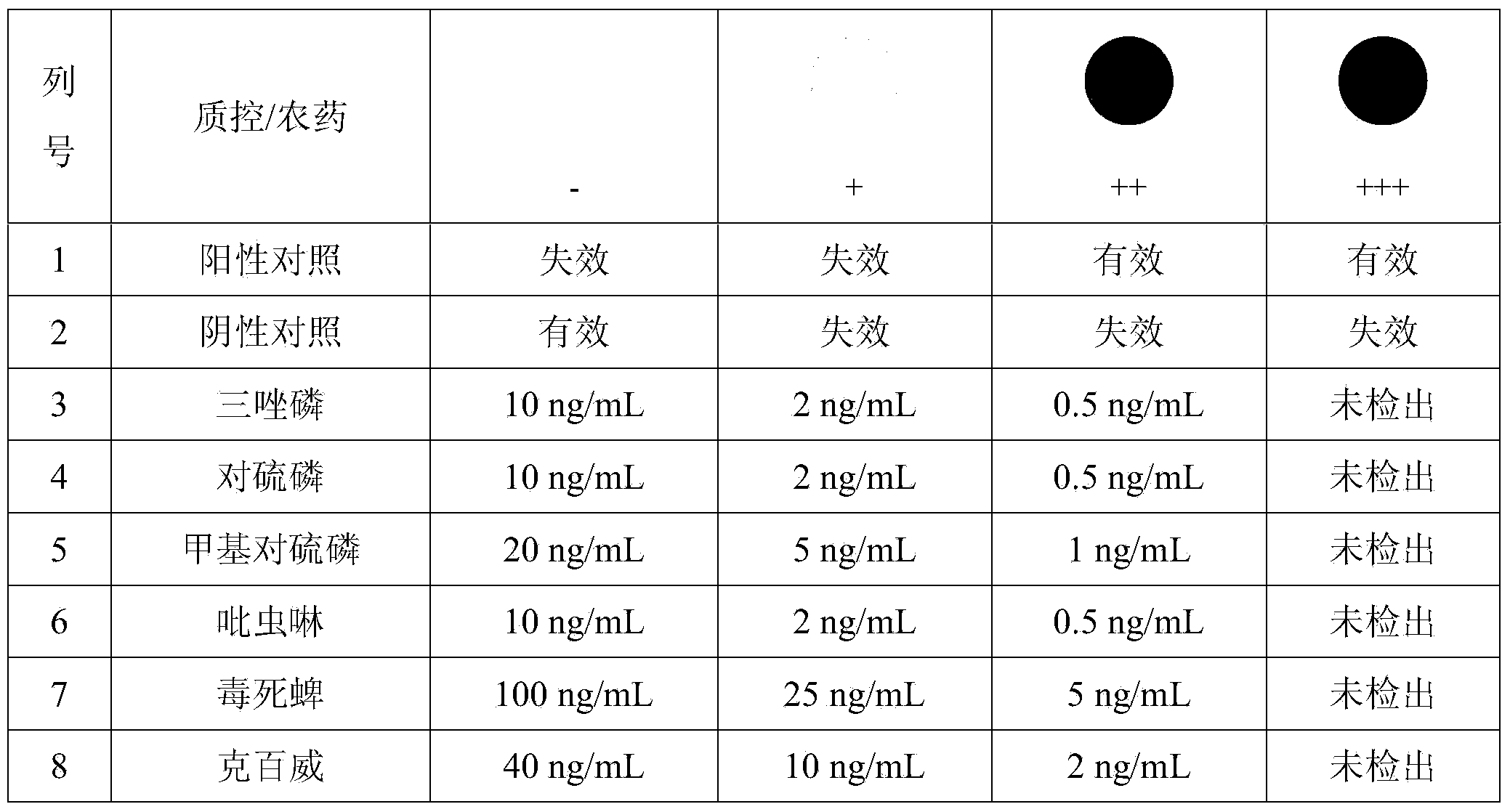
InactiveCN104165986AGuaranteed uniformityGuaranteed stability and reliabilityBiological material analysisPhosphatePesticide residue
The invention discloses a preparation method of a visual detection chip for multiple pesticide residues based on a membrane material. The preparation method comprises the steps of spotting a detection point and quality-control points on a carrier to form a point array, the carrier being a nitrocellulose membrane; washing with a cleaning solution; drying in the air; sealing uncombined regions by using bovine serum albumin; washing with the cleaning solution; and drying in the air to obtain the visual detection chip for the multiple pesticide residues. The quality-control points comprises a positive quality-control point and a negative quality-control point; the positive quality-control point is goat anti mouse IgG; the negative quality-control point is 0.01 M phosphate buffer solution PBS (pH7.4); and the detection point is a pesticide hapten-chicken ovalbumin conjugate. The invention also provides a use method of the visual detection chip for the multiple pesticide residues. According to the invention, visualization of an enhanced gold mark color development and high throughput of a chip technology are integrated together, and an immune chip capable of determining by naked eyes and detecting a plurality of pesticide residues at the same time is prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nano di-cyclic aptamer probe and application thereof
ActiveCN106520764AInhibitory activityRealize visual detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerCancer cell
The invention discloses a nano di-cyclic aptamer probe and application thereof. The nano di-cyclic aptamer probe (G-dApR) is very stable and is not degraded by in-vivo DNA. Meanwhile, the biological activity of target cells can be effectively inhibited by combining specific recognition with a leukemia cell surface highly-expressive biomarker. The design of the probe is researched and developed based on two advanced technologies in the field of tumors, namely a ligand technology and a nanotechnology. Firstly, a conventional linear aptamer structure is transformed into a structure including a functional zone (specific) and a di-cyclic DNA zone (stable) by adopting a nucleic acid modification means, and the biological stability is greatly improved; secondly, the probe is finally established by combining a cyclic aptamer and a dendritic nano material PAMAM. The shortcoming that an aptamer is unstable is greatly overcome, an effective means is provided for leukemia detection, and high-sensitivity diagnosis and treatment integrated clinical application is achieved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Kit for detecting circulating nucleic acid based on micro-fluidic chip and G-quadruplex-protoheme DNA enzyme, and preparation method and application of kit
ActiveCN107828861ARealize visual detectionSolve high-throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrofluidic chipMicro fluidic
The invention provides a kit for detecting circulating nucleic acid based on a micro-fluidic chip and G-quadruplex-protoheme DNA enzyme, and a preparation method and application of the kit, and belongs to the technical field of biomolecular detection. The kit for detecting the circulating nucleic acid comprises a micro-fluidic detection chip, gold nanoparticle liquid, a first hairpin probe reagent, a second hairpin probe reagent and a light-emitting system, wherein the micro-fluidic detection chip is coated with functionalized microspheres; the functionalized microspheres are used to modify afirst probe on the surface of the microsphere through a biotin-avidin system; the surface of the gold nanoparticle liquid is modified by a second probe and a triggering probe. The reagent provided bythe invention is applied to detection on the circulating nucleic acid. The kit can solve the problem that high throughput and high sensitivity are difficult to coexist under the condition of a trace amount of samples in the technical field of micromedical analysis or the field of minimally invasive or non-invasive diagnosis.
Owner:南通清源信息科技有限公司
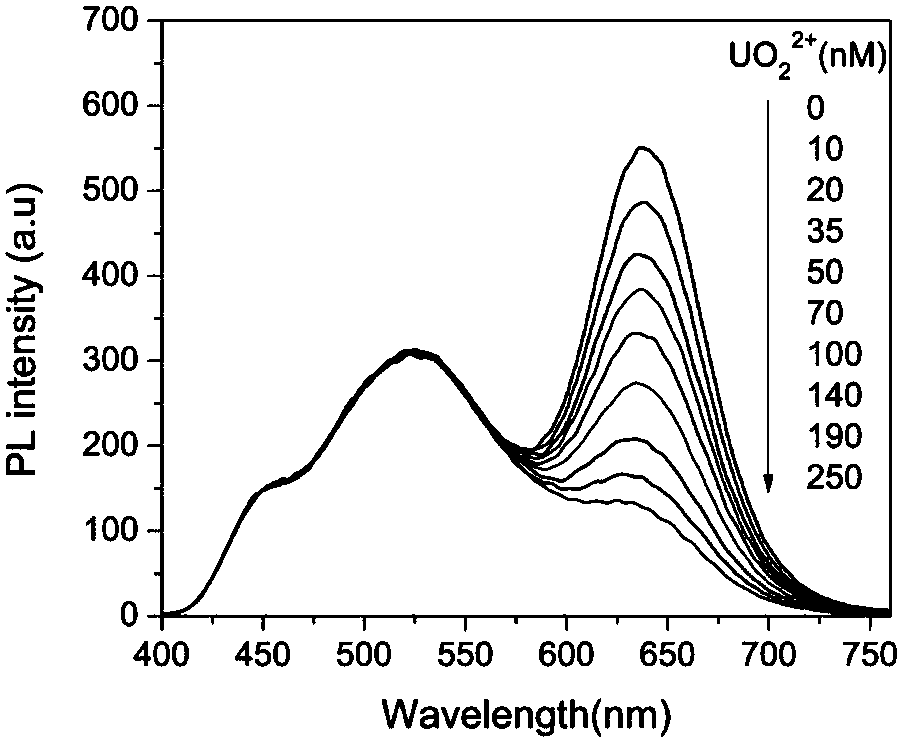
Double-channel fluorescent uranyl ion probe and application thereof
InactiveCN107828417ARealize visual detectionAvoid interferenceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsPhysicsInstrumentation
The invention belongs to the field of analysis methods of radioactive elements, and particularly relates to a method for analyzing and detecting trace radioactive elements by a double-channel fluorescent uranyl ion probe. The probe is established on the basis of a semiconductor quantum dot-carbon quantum dot double-channel fluorescent signal with a method mainly comprising the following steps: (1)synthesizing a green fluorescent carbon quantum dot; (2) synthesizing a red fluorescent cadmium quantum dot; (3) preparing the probe. The detection principle is that uranyl ions can quench fluorescence of the red quantum dot, while the green fluorescence signal of the carbon quantum dot remains stable and unchanged, and quantitative detection of a to-be-detected sample is realized by testing thelinear relationship between concentration of the sample and the ratio of the red fluorescence signal to the green fluorescence signal. With adoption of the method, use of large-scale instruments can be avoided to a certain extent, all that is required is only one hand-held ultraviolet lamp for visual detection, operation is simple, convenient and quick, the pretreatment process is omitted, and high-sensitivity selective detection of the trace uranyl ions in a solution can be realized.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Label color band for detecting hydrogen and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108593637AQuick responseRealize visual detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHydrogen concentrationEmissivity
The invention relates to the technical field of gas detection, in particular to a label color band for detecting hydrogen and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a noble metal quantum dot is modified on the surface of a hydrogen sensitive material substrate by an ultraviolet reduction method to obtain the label color band for detecting hydrogen. In the label color band for detecting hydrogen, after the hydrogen-sensitive material is reacted with the hydrogen, the change of the optical signals such as the emissivity, the transmittance, the wavelength and the like is caused, so that the corresponding hydrogen concentration in the environment is detected, the noble metal quantum dots are modified on the surface of the hydrogen-sensitive materialby adopting the ultraviolet reduction method, the sensitivity of the label color band to the hydrogen is improved while the specific surface area of the sensitive layer is increased, and the hydrogencan be adsorbed more quickly and the response can be carried out.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Construction method for disposing road cracks by using waterborne polyurethane
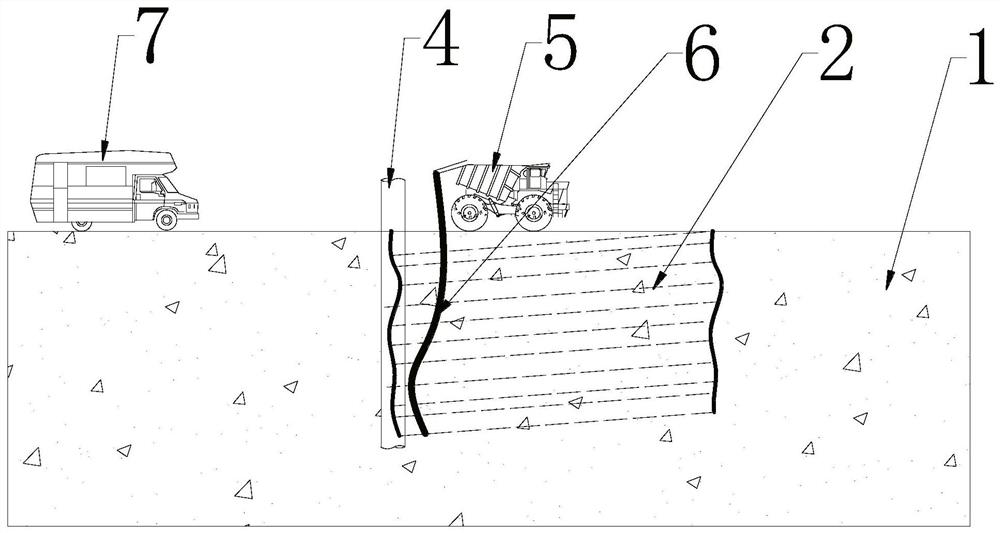
PendingCN112609553AFully grasp the traitsFully grasp the parametersRoads maintainenceEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention discloses a construction method for disposing road cracks by using waterborne polyurethane. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nondestructive testing on road cracks, drawing a crack distribution diagram, cutting and slotting cracks with the width of less than 3mm as required, drilling grouting holes at intervals along the trend of the cracks, installing grouting pipes, injecting water into the cracks; and then injecting a waterborne polyurethane grouting material, enabling the slurry to react with water in the cracks to generate gel to fill the cracks, sealing the grouting holes after grouting is completed, and finally performing rechecking to confirm that repairing is completed. The method has the advantages that visual detection of road cracks can be achieved, follow-up grouting repair is effectively guided, the characteristics that the waterborne polyurethane material is high in water reaction speed and short in gelation time are ingeniously utilized, roadbed and pavement cracks can be rapidly and comprehensively repaired, the material cannot generate a corrosion effect. And the road crack disease is effectively solved, and wide applicability is achieved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RAILWAY VOCATIONAL & TECH COLLEGE
Visualized molecularly imprinted nanosensor and preparation and application thereof
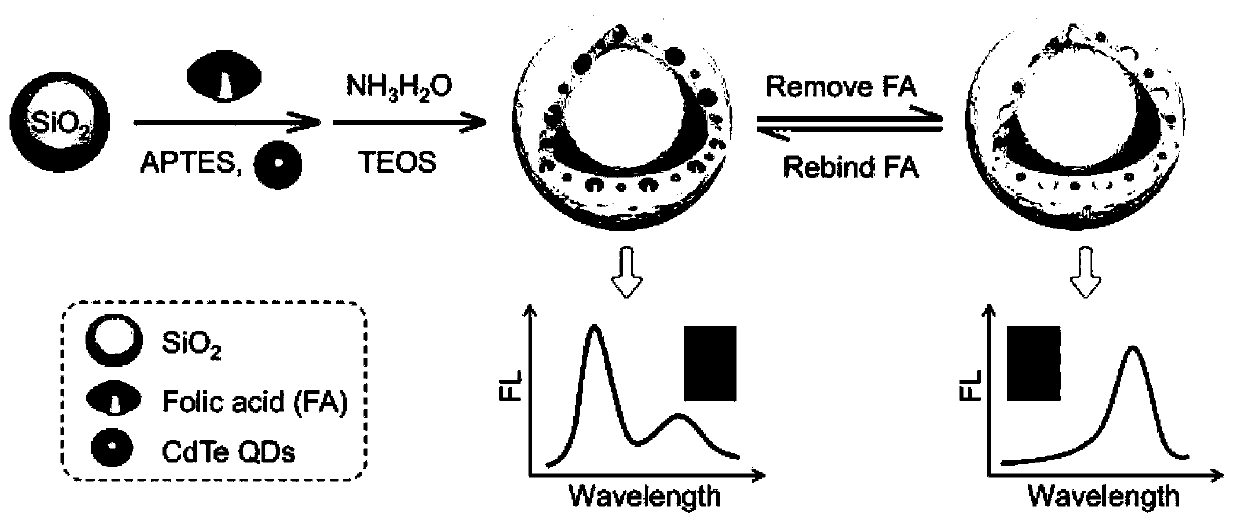
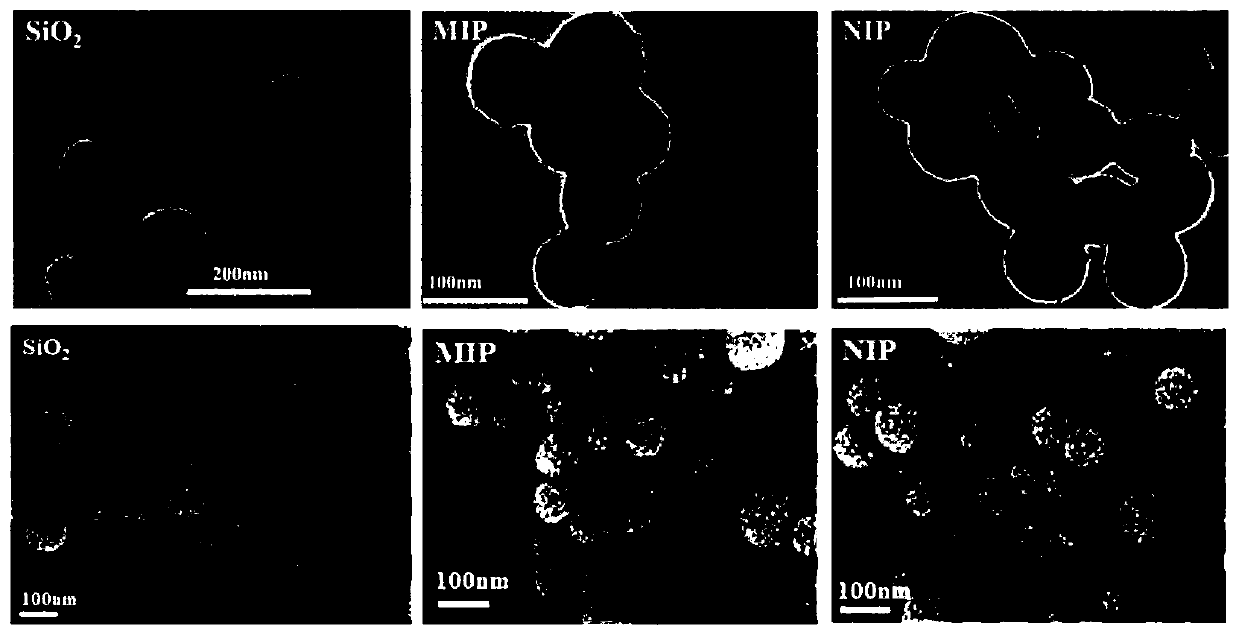
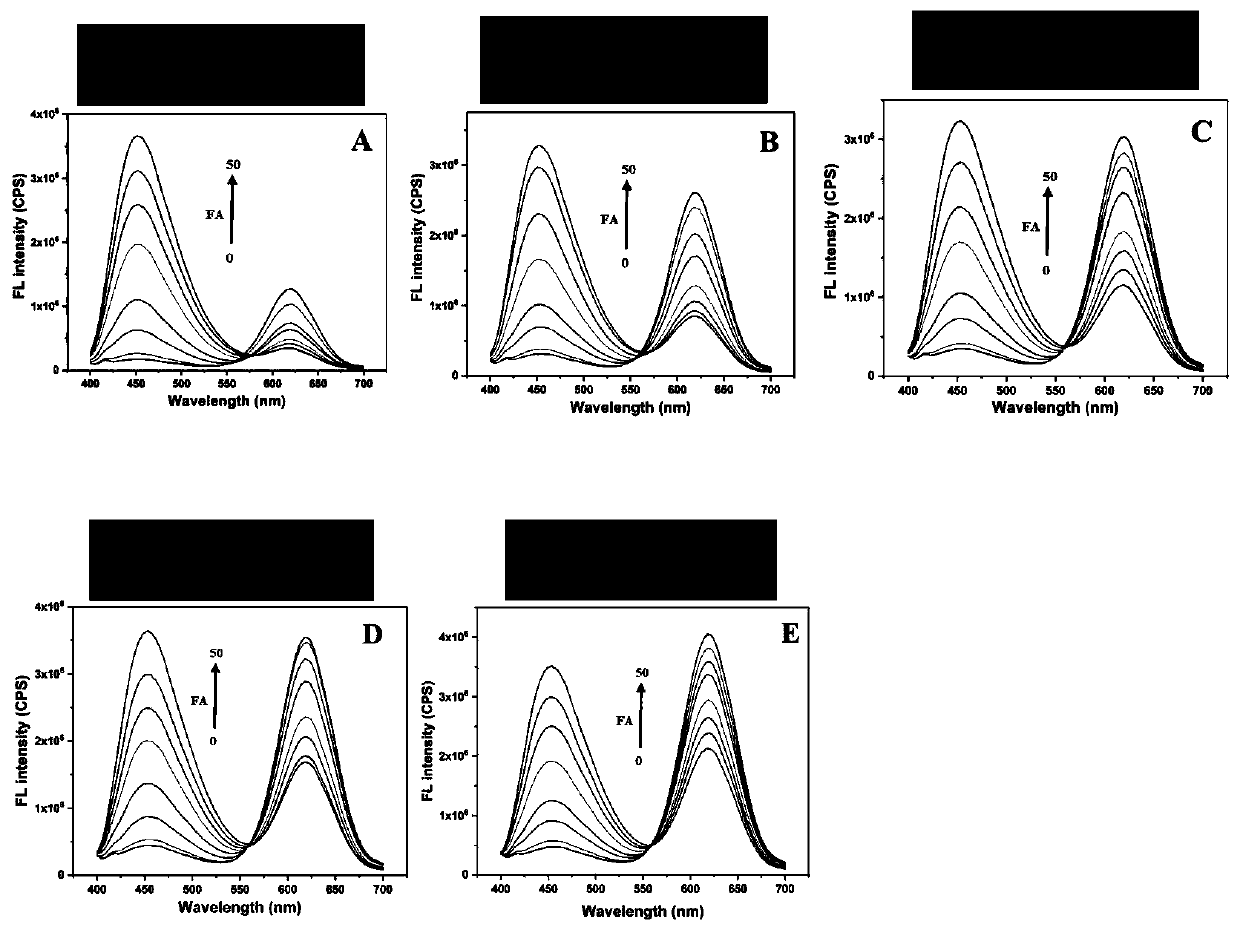
ActiveCN110186884AIncrease mass transfer rateEasy to synthesizeFluorescence/phosphorescenceSilica nanoparticlesTwo step
The present invention belongs to the fields of material, analytical chemistry and food safety, in particular to a molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor based on dual fluorescence emission, a preparation method and an application thereof in visual detection of folic acid in food. The surface of silica nanoparticles is subjected to imprinting polymerization with the sol-gel methodin one step; red fluorescent cadmium telluride quantum dots (CdTe QDs) and folic acid with spontaneous blue fluorescence are embedded; holes of eluted folic acid are used as recognition sites; then the dual fluorescence emission molecularly imprinted nanosensor with a core-shell structure is obtained, which is the visualized molecularly imprinted nanosensor. The preparation method of the invention is simpler than the conventional two-step method for preparing the molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent sensor; cumbersome synthesis steps are avoided; and the experimental period is shortened. In addition, the sensor prepared by the method of the invention can be used for detecting folic acid with a high sensitivity, a high selectivity and self-correction; abundant fluorescence color evolution is provided; and the visual detection for a target is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Hydrogel microcarrier and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112048033AEasy to decodeReduce testing costsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseActive agent
The invention discloses a hydrogel microcarrier and a preparation method and application thereof.The hydrogel microcarrier takes an oil phase solution as a carrier, an aqueous phase solution containing an initiator and two or more gelatinizing materials is dispersed in the oil phase solution, and the density-coded hydrogel microcarrier is formed by changing the concentration ratio of different gelatinizing materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing two or more gelatinizing materials with different concentration ratios with an initiator to obtain a water-phase solution; dissolving a surfactant and TEMED in an oil medium to obtain an oil phase solution, wrapping a water phase solution in the oil phase solution to form hydrogel liquid beads, and curing the hydrogel liquid beads to form the density-coded hydrogel microcarrier. The hydrogel microcarrier can realize multiple detection of disease-related proteins and visual detection of tumor-derived exosomes, andhas the advantages of simple decoding, low detection cost and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
LAMP kit for Vibrio cholera in aquatic product
ActiveCN104212885AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyAquatic product
The invention discloses an LAMP kit for Vibrio cholera in an aquatic product. The kit comprises a reaction buffer solution, specific primers for detecting the Vibrio cholera, a BstDNA polymerase, a Vibrio cholera DNA positive template and ultrapure water; and the specific primers for detecting the Vibrio cholera comprise a pair of inner primers FIP and BIP and a pair of outer primers F3 and B3. The kit has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and fastness, and can be used for real-time rapid and accurate detection of Vibrio cholera of a base.
Owner:舟山出入境检验检疫局综合技术服务中心
Method for detecting nucleic acid based on exponential hairpin assembly and colorimetry
ActiveCN103820541ARealize visual detectionReduce demandMicrobiological testing/measurementVisual inspectionReaction speed
The invention relates to a method for detecting nucleic acid based on exponential hairpin assembly and colorimetry. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: 1) hybridizing target nucleic acid molecules and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) on nanogold; 2) initiating four hairpin DNAs to perform self-assembly reaction by the target nucleic acid molecules and generating large DNA polymers; 3) adding salts of divalent cations or monovalent cations into a reaction solution, and performing different degrees of aggregation on the nanogold combined with the target nucleic acid molecules, wherein the color of the nanogold changes from red to blue. According to the method, a system is simple, and the four hairpin DNAs are designed easily; the visual inspection of a target can be realized; the method has high temperature adaptability, high reaction speed, high sensitivity, high specificity and short reaction time, and can be applied to the field of clinical detection, food safety detection, environment monitoring and the like; the detection limit reaches 8.45 pM.
Owner:青岛简码基因科技有限公司
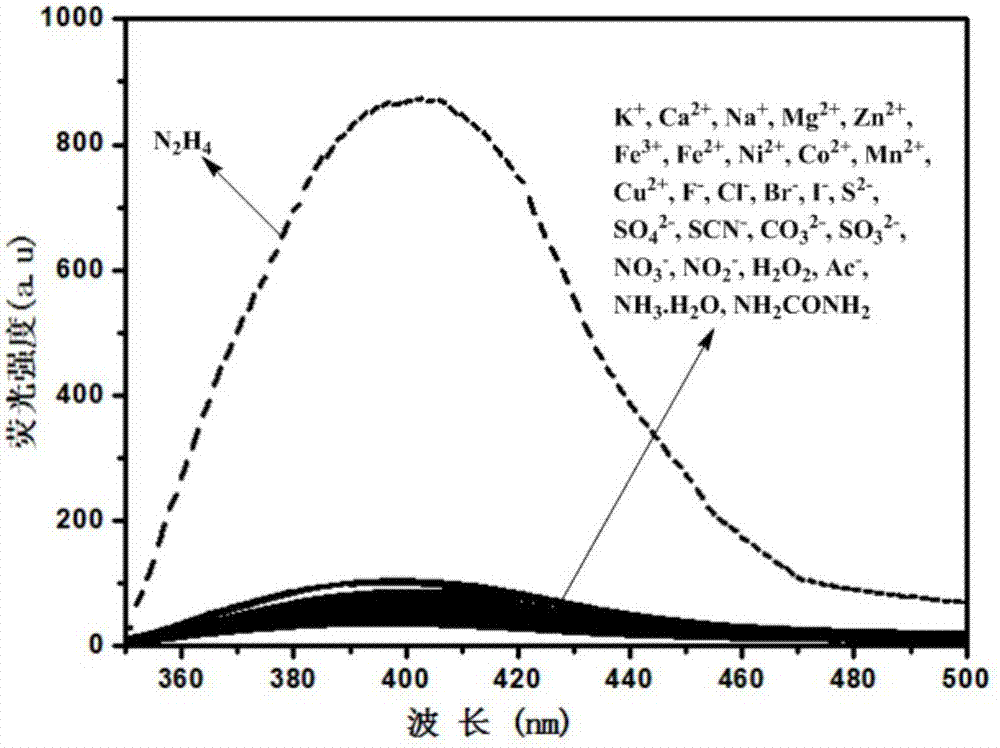
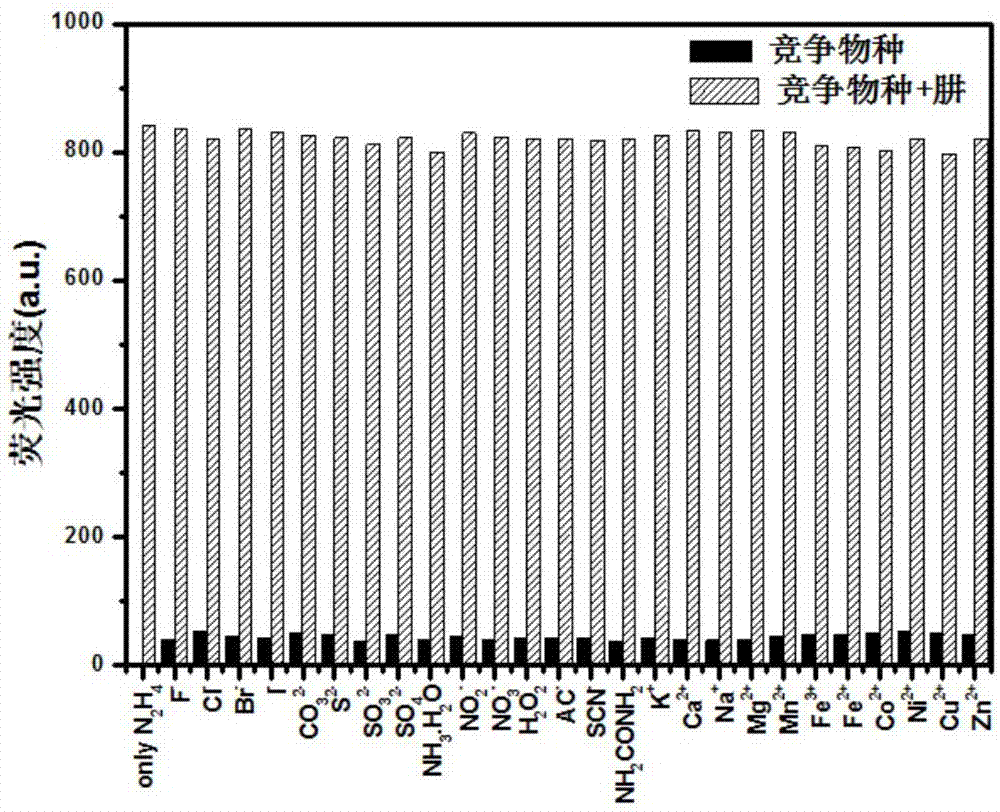
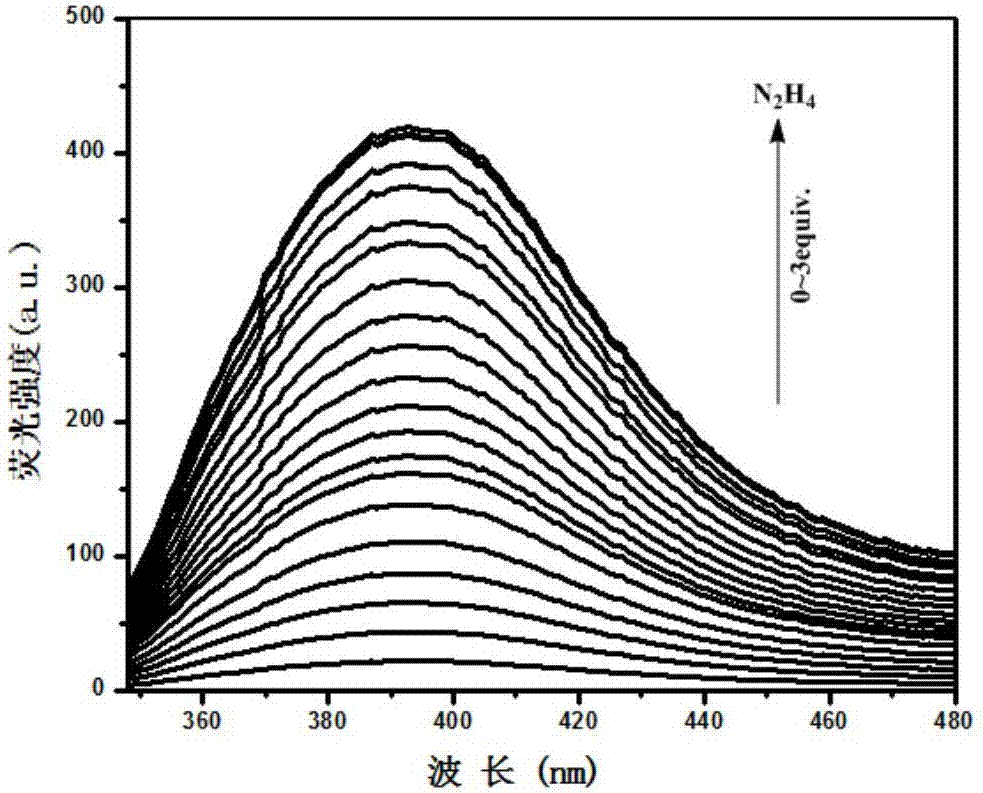
Fluorescence probe for visually detecting hydrazine based on benzothiazole as well as preparation method and use of fluorescence probe
InactiveCN107880034AGood choiceRealize visual detectionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceAnti jammingHydrazine compound
The invention provides a fluorescence probe ZY9 for visually detecting hydrazine based on benzothiazole as well as a preparation method and use of the fluorescence probe ZY9. The fluorescence probe ZY9 can be prepared through the reaction of 2-(4-aminophenyl)benzothiazole and phthalic anhydride in a certain proportion and is easy to synthesize and purify, relatively high in yield and low in cost;the hydrazine fluorescence probe is a fluorescence enhanced fluorescence probe, has relatively selectivity and sensitivity to hydrazine, is strong in anti-jamming capability and high in response speedand can be used for visually detecting hydrazine through the significant change of the fluorescence color; the probe is good in stability and can be stored for a long time for use; besides, the probeis suitable for detecting the content of hydrazine and realizing the fluorescence imaging of hydrazine in a living cell level, and hydrazine in a water solution with a certain concentration can be detected by virtue of probe test paper. A hydrazine detection method provided by the invention has the advantages of easiness and convenience in operation, easiness in popularization and the like and has wide application prospects in the fields of environment and biological science.
Owner:HUBEI POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Apple stem groove virus visual detection system based on CRISPR-Cas12a technology and detection method thereof
ActiveCN110567951ARealize visual detectionPrevent cross-linking reactionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designConserved sequence
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to an apple stem groove virus visual detection system based on the CRISPR-Cas12a technology and a detection method thereof. CrRNA isdesigned according to an ASGV conserved sequence, AuNP-DNA for colorimetric detection is manufactured, the influence of a Cas12a protein in-vitro cleavage reaction time and linker DNA concentration on a detection effect is explored, and the optimal ASGV visual detection system and the detection method thereof are established. The method is carried out under a constant-temperature reaction condition, a virus is recognized through a CRISPR-Cas12a-crRNA complex to improve the specificity, the linker DNA has universality, expensive double-labeled probes are not needed, a plurality of samples canbe detected within 40 minutes by means of low-speed centrifugation, the lower detection limit is 5.62*102 copies / reaction, and the sensitivity is 100 times higher than that of RT-PCR.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting lipase activity
ActiveCN103063597AGood water solubilityReduce dosageColor/spectral properties measurementsCarboxylic acidMercaptoacetic acid
The invention provides a method for detecting lipase activity. The method comprises the following steps: mercaptoacetic acid methyl ester is utilized for modifying nanogold; in the presence of lipase, mercaptoacetic acid is generated by hydrolysis, and thus carboxylate radicals are exposed; intense hydrogen-bond interaction exists among carboxylate radicals, and thus the distance between nanogold is shortened to gather and blue the nanogold. On one hand, the strength of the lipase activity can be directly identified by naked eyes from the color and on the other hand, the lipase activity can be sensitively detected by an ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometer. The method can be used for detecting the lipase activity from the aspects of time, temperature, quantity and the like and the experimental phenomenon is obvious. The method has the advantages of being simple to operate without substrate emulsification, small in dosage, being beneficial to being obviously observed by naked eyes and low in cost. The method has not only good research value academically, but also wide application in production application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for detecting ratio of sodium ions to potassium ions, kit and system
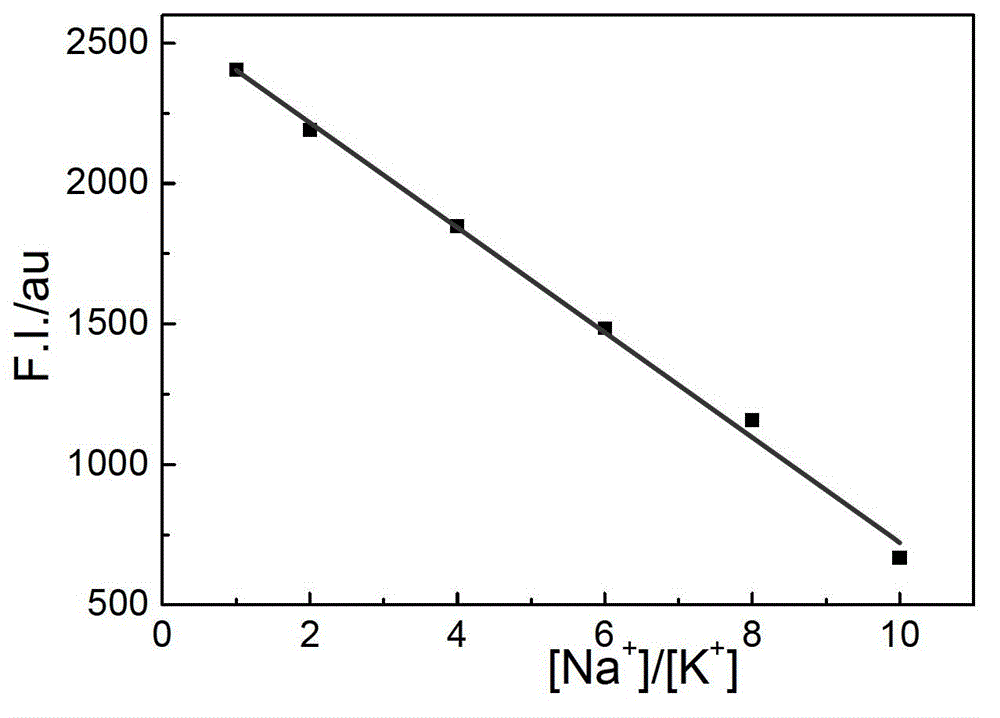
ActiveCN103063629AStrong specificityRealize visual detectionMethine/polymethine dyesFluorescence/phosphorescencePotassium ionsLength wave
The invention relates to a method for detecting a ratio of sodium ions to potassium ions, a kit and a system. The invention relates to a method for detecting mol ratio of sodium ions to potassium ions in solution, comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a plurality of solution samples according to difference of ratios of sodium ions to potassium ions, wherein each solution sample contains cyanine dye with the same concentration and DNA molecules capable of respectively forming different G-quadruplex structures with the existence of sodium ions and potassium ions; (2) detecting fluorescence intensity level where wavelength is collected; (3) plotting by using the ratio of sodium ions to potassium ions in each solution sample as a horizontal ordinate or a vertical ordinate and using the fluorescence intensity level where wavelength is collected detected in the step (2) as a horizontal ordinate or a vertical ordinate so as to obtain a specification curve of ratios of sodium ions to potassium ions; (4) adding the DNA molecules in a liquid sample to be detected, and adjusting the pH value so as to obtain a test solution; (5) detecting the fluorescence intensity level of the wavelength where the wavelength is collected; and (6) finding out corresponding ratio of sodium ions to potassium ions in the test solution in the specification curve of ratios of sodium ions to potassium ions.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Protein glycosylation detection kit and detection method, and application
ActiveCN109307773AImprove label stabilityGood biocompatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCell membraneIn vivo
The invention discloses a protein glycosylation detection kit and a detection method, and an application. Specific protein targeting, an HCR-based non-enzymatic amplification strategy, and the proteinglycosylation detection kit and detection method for detecting and imaging specific protein glycosylation on a cell membrane surface in living cells and living bodies by using the HCR-based non-enzymatic amplification strategy, and detection applications in various application occasions such as an in vitro application occasion and an in vivo application occasion are achieved by using technical means such as modification of azido glycosyl on the surface of a protein by a glycosyl-labelled nucleic acid sequence, introduction of a protein probe nucleic acid sequence, and introduction of a hybridization chain reaction reagent.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Agent for loop-mediated isothermal amplification and kit and application thereof
InactiveCN109161582ALow costGuaranteed SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoparticleLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to an agent for loop-mediated isothermal amplification. The agent comprises at least one of nanoparticles, dithiothreitol, peptide bovine serum, tetramethylammonium chloride andtrehalose. The invention also relates to a kit containing the abovementioned agent and the application thereof. The kit further comprises a 10x constant-temperature buffer, a dNTP mixture, MgSO4, a Bst DNA polymerase, an indicator and water; a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction system prepared through the kit comprises the following components by final concentration: 0-10mg / mL of nanoparticles, 0-10M of dithiothreitol, 0-10g / mL of peptide bovine serum, 0-100mM of tetramethylammonium chloride, 0-50mM of trehalose, 1.0-3.0mM of dNTP mixture, 4-10mM of MgSO4, and 0.1-0.5U / uL of DNA polymerase. According to the agent, the kit and the application thereof, the detection quality is ensured while the problem of high cost of an LAMP agent is high is solved; the kit has the same detection effect as an imported agent; the sensitivity, the specificity and the stability meet the clinical test demand; the detection cost is greatly decreased; and the application prospect is good.
Owner:关明 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com