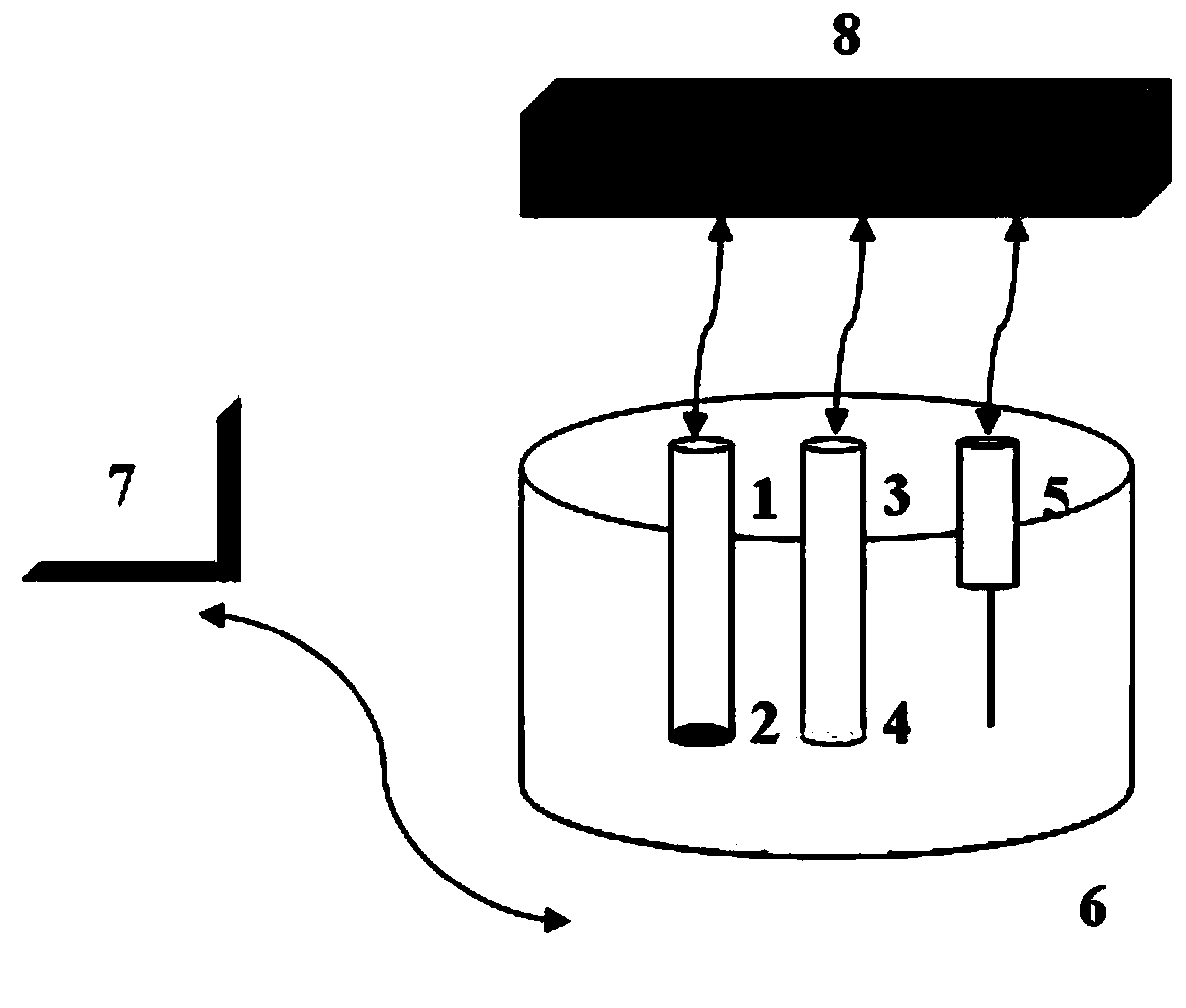
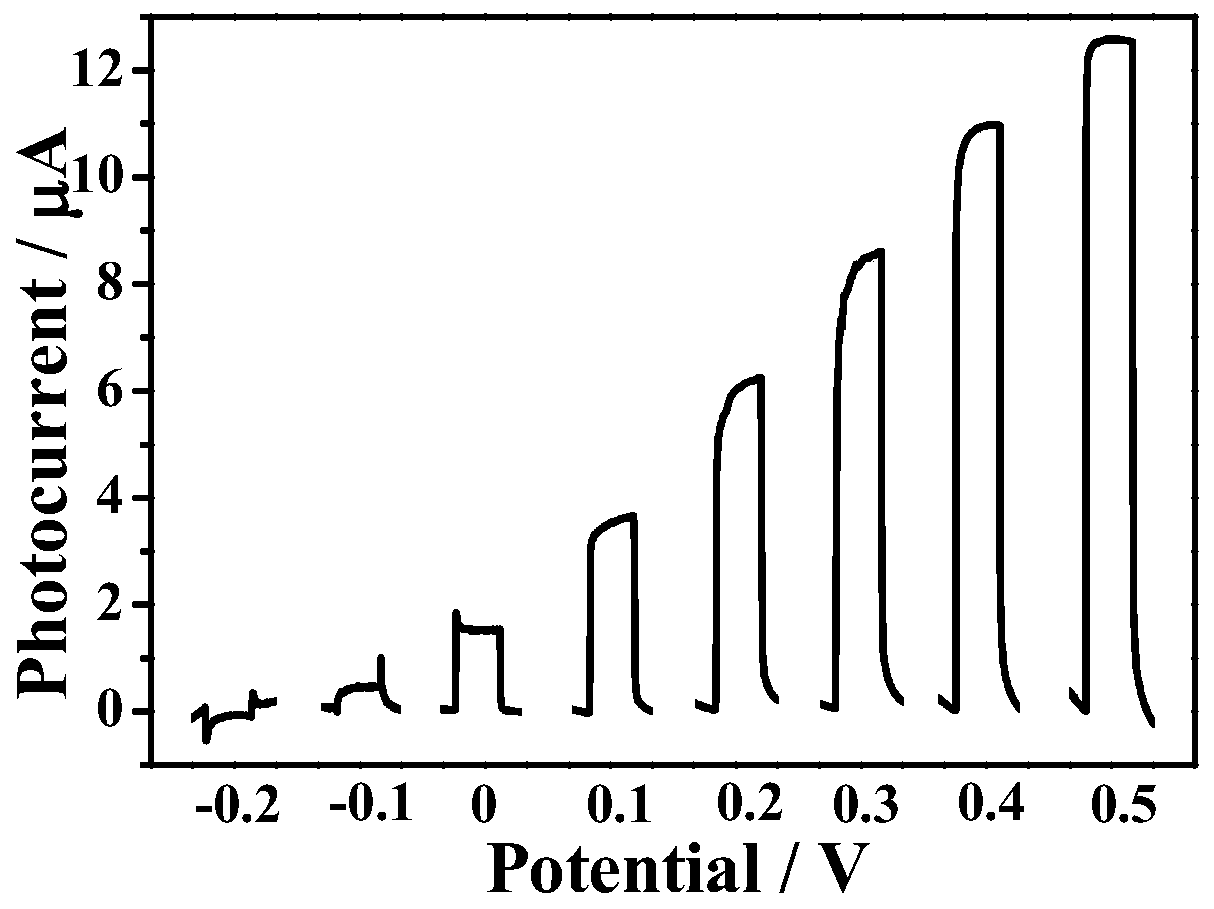
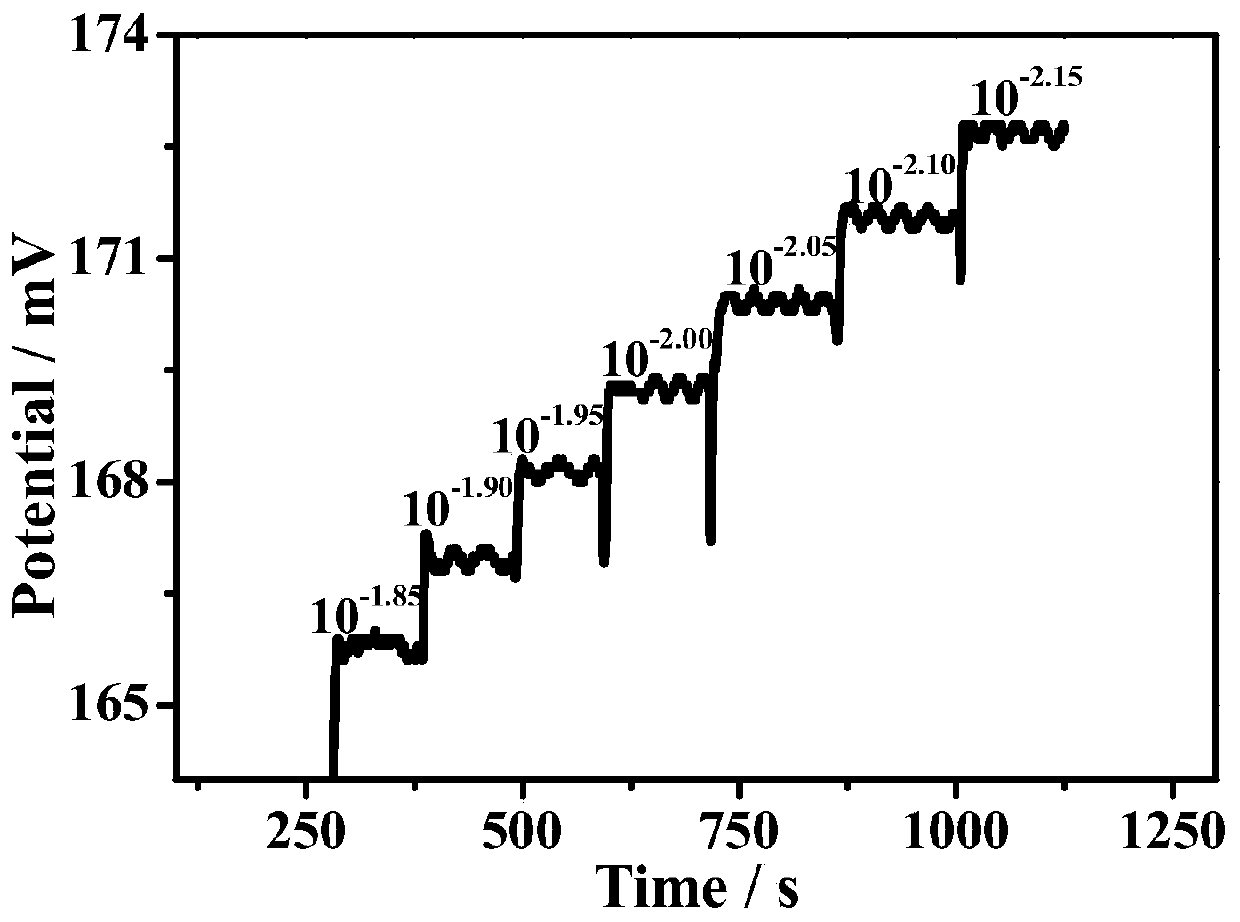
Patents
Literature
921 results about "Photoelectrochemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
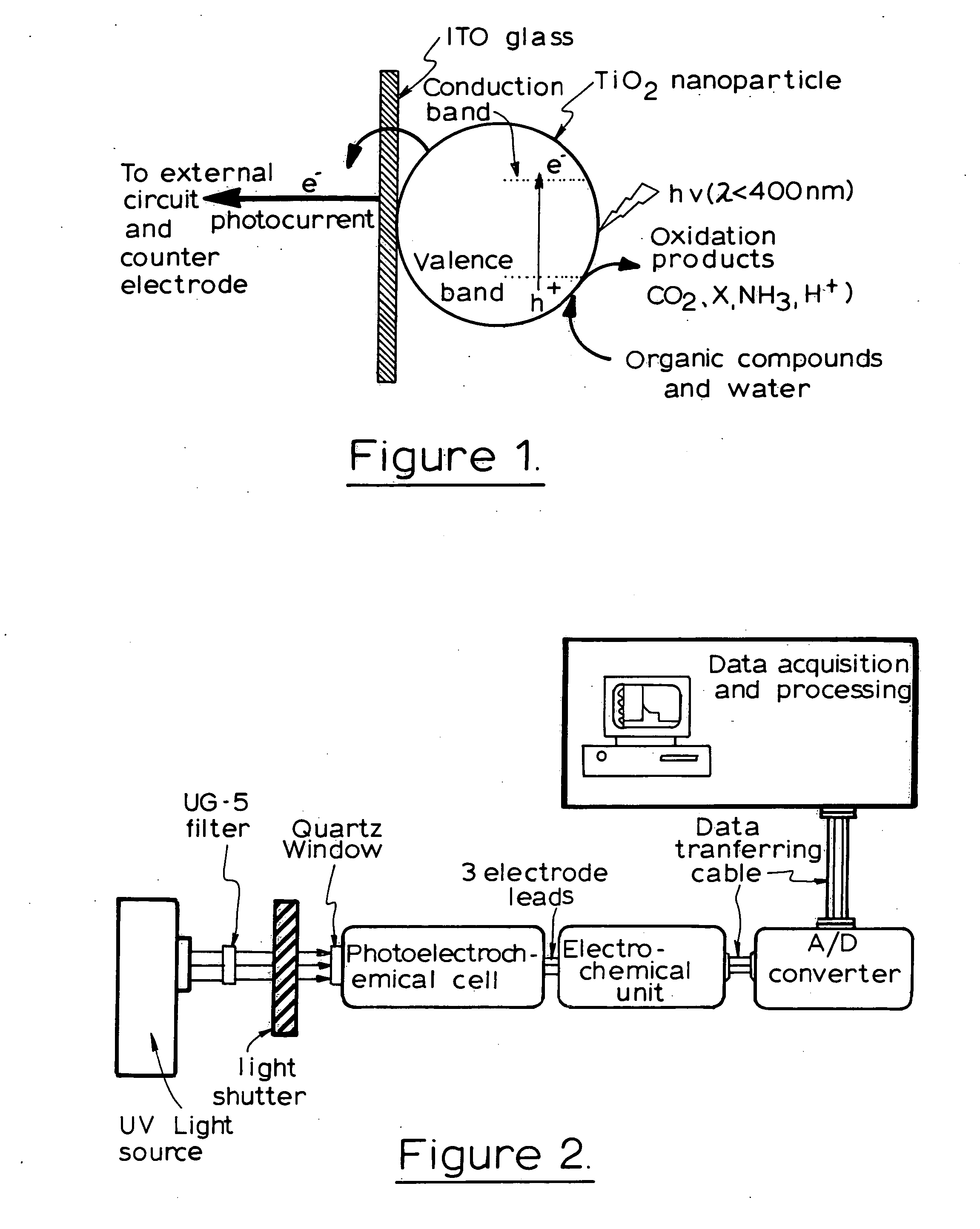
Photoelectrochemistry is a subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems. It is an active domain of investigation. One of the pioneers of this field of electrochemistry was the German electrochemist Heinz Gerischer. The interest in this domain is high in the context of development of renewable energy conversion and storage technology.
Photoelectrochemical determination of chemical oxygen demand
ActiveUS20060240558A1High sensitivityWide linear rangeChemical analysis using catalysisChemical analysis using combustionSupporting electrolytePotential measurement
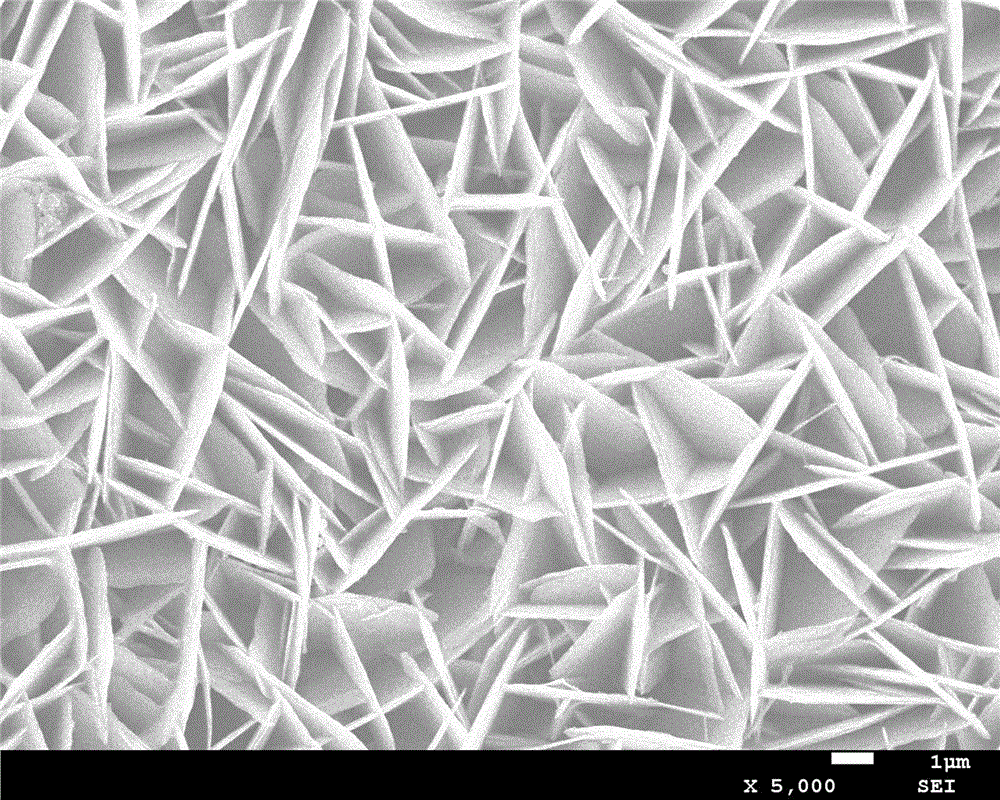
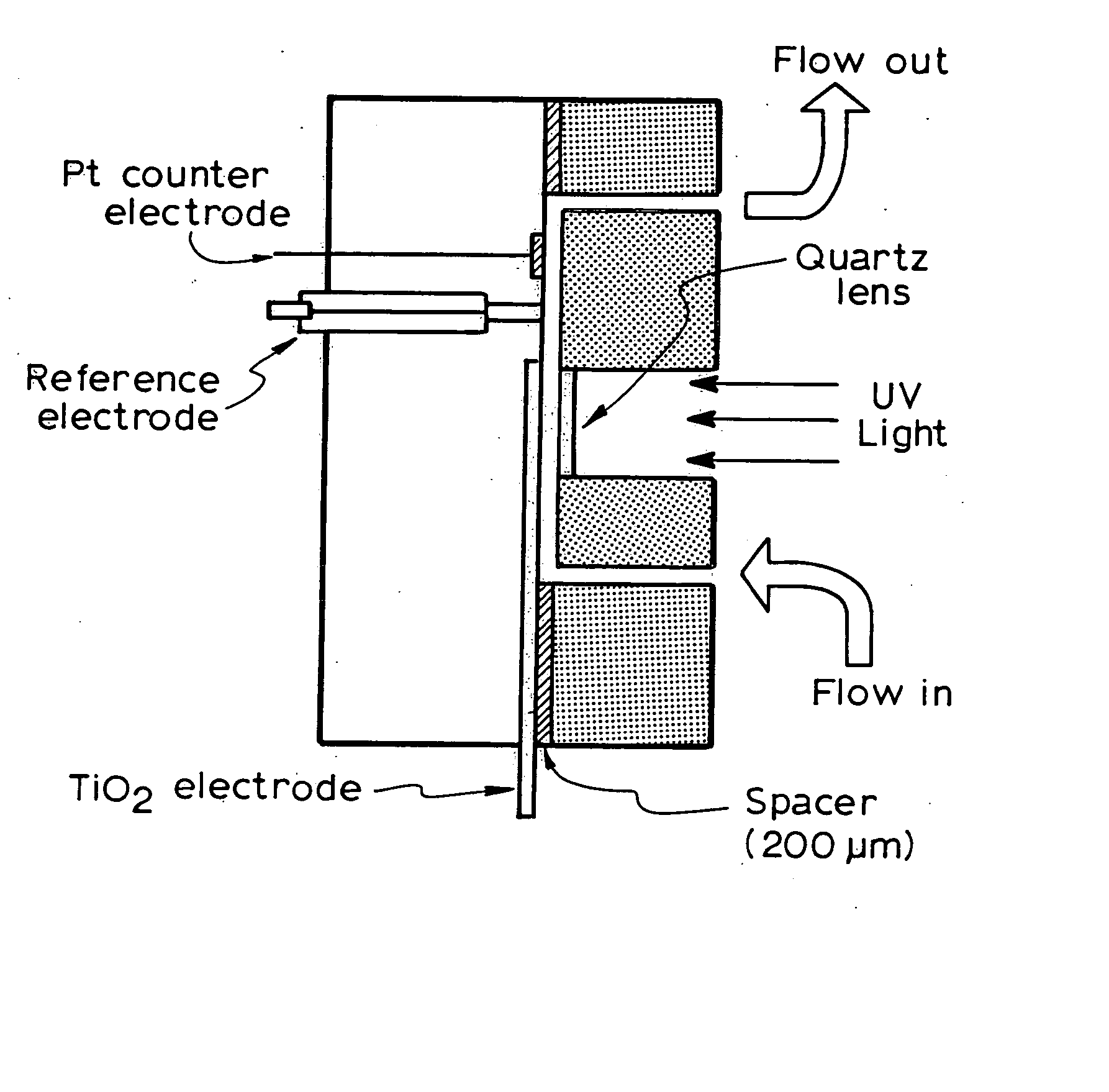
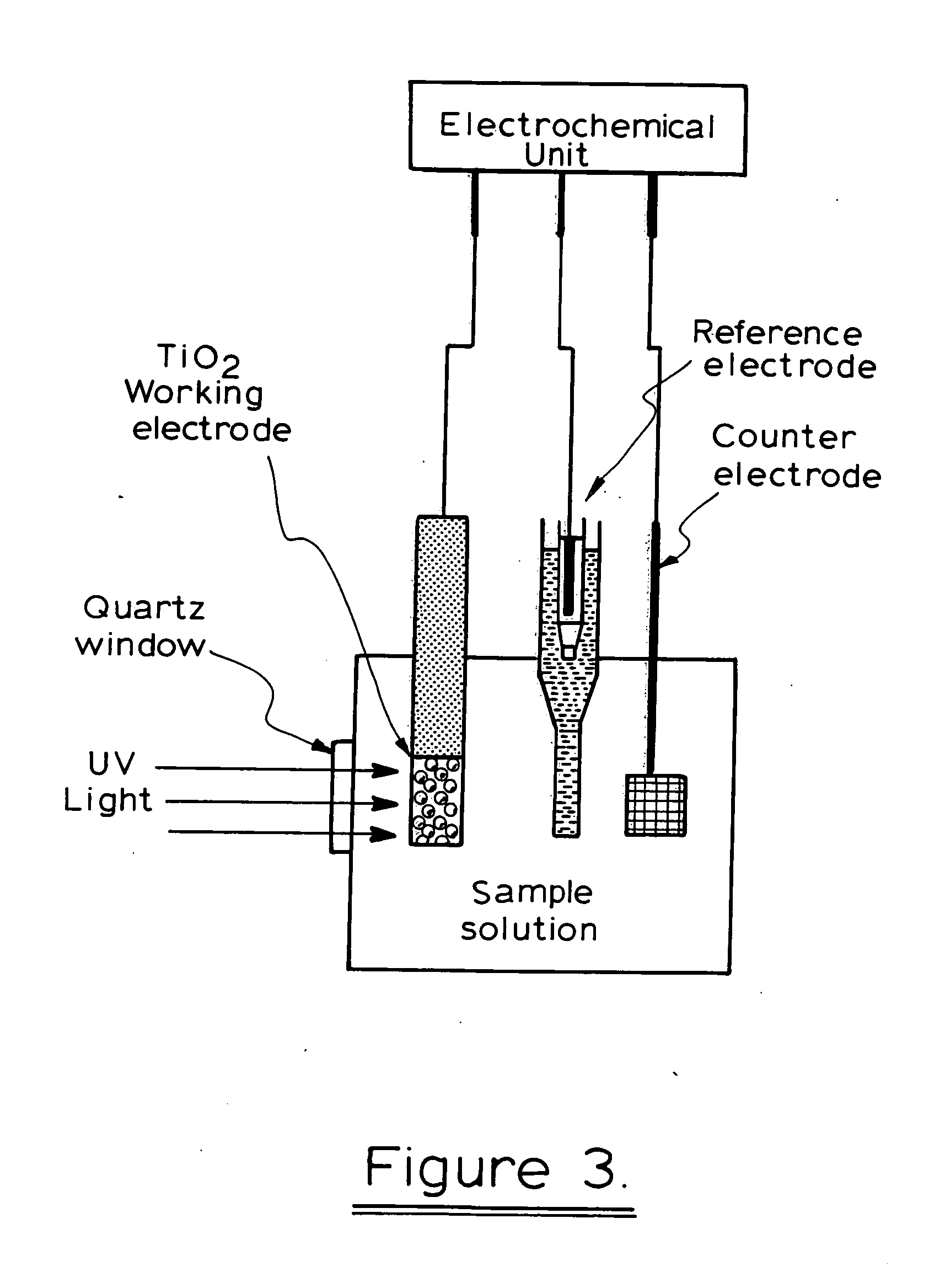
A photoelectrochemical assay apparatus for determining chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a water sample which consists of a) a measuring cell for holding a sample to be analysed b) a titanium dioxide nanoparticle photoelectric working electrode and a counter electrode disposed in said cell, c) a UV light source adapted to illuminate the photoelectric working electrode d) control means to control the illumination of the working electrode e) potential measuring means to measure the electrical potential at the working and counter electrodes f) analysis means to derive a measure of oxygen demand from the measurements made by the potential measuring means. The method of determining chemical oxygen demand of a water sample, comprises the steps of a) applying a constant potential bias to a photoelectrochemical cell, containing a supporting electrolyte solution; b) illuminating the working electrode with a UV light source and recording the background photocurrent produced at the working electrode from the supporting electrolyte solution; c) adding a water sample, to be analysed, to the photoelectrochemical cell; d) illuminating the working electrode with a UV light source and recording the total photocurrent produced; e) determining the chemical oxygen demand of the water sample according to the type of degradation conditions employed. The determination may be under exhaustive degradation conditions, in which all organics present in the water sample are oxidised or under non-exhaustive degradation conditions, in which the organics present in the water sample are partially oxidised.
Owner:579453 ONTARIO INC
Organic wastewater treatment film reactor utilizing sunlight-assisted electro-catalysis
InactiveCN102603037AAccelerated adsorption/desorption rateThe actual user interface increasesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentPhoto assistedPorous channel
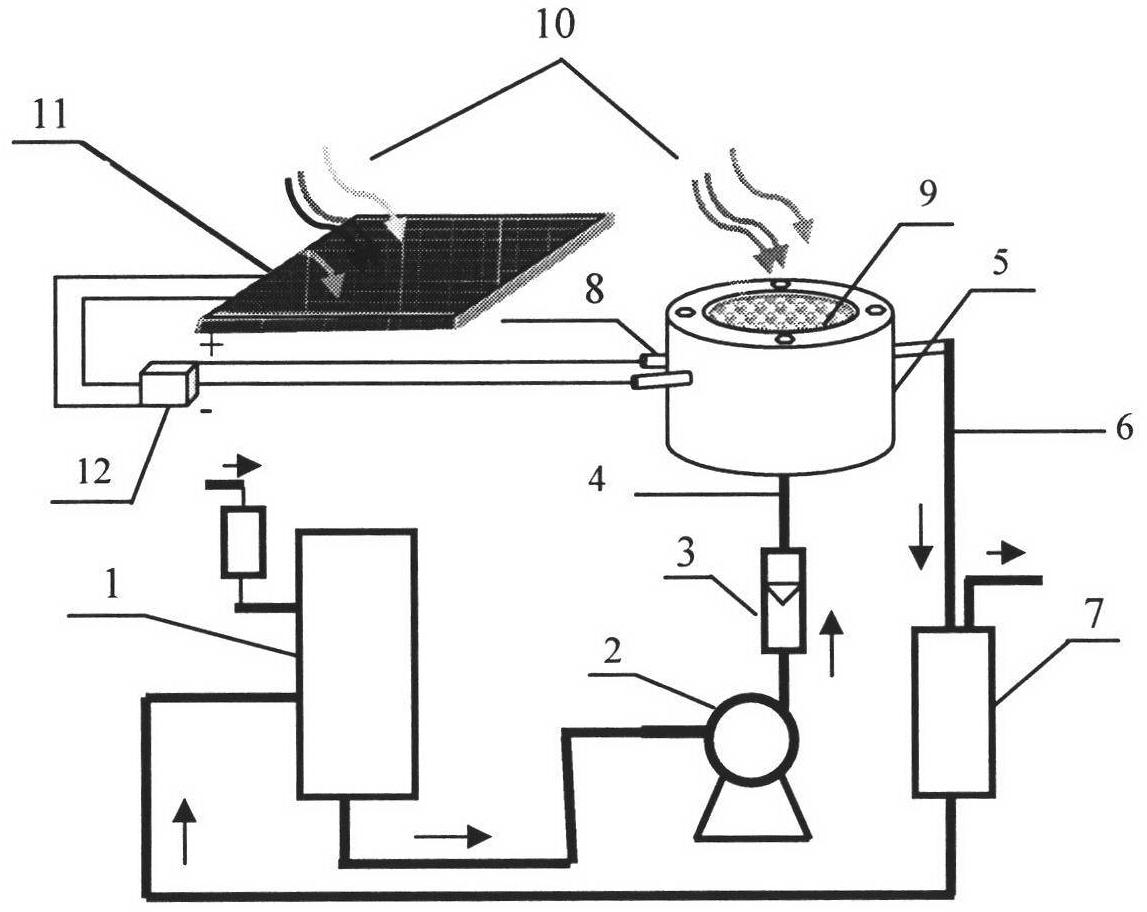
The invention relates to an organic wastewater treatment film reactor utilizing solar energy photo-assisted electro-catalysis, which comprises a storage tank of water to be processed, a flow controllable constant flow pump, a photoelectric chemical reactor, a clear water storage tank and a solar battery component, wherein a photo anode and a cathode are correspondingly arranged in the reactor; the photo anode takes a porous metal membrane as a base body, and a TiO2 nano tube or a TiO2 mesoporous membrane is formed on the surface of a porous titanium membrane (net) by an electrochemical anisotropic etching technology; a porous channel film is used as the base body; a metal oxide coating electrode with high electrochemical catalytic activity and high electrical conductivity is prepared by a dipping film-forming method, simultaneously, by doping and modifying operations, the electrode material has photo catalytic activity and the reaction efficiency is improved. The reactor integrates electrochemistry, photocatalysis and film separation technologies; the three technologies are coupled to enhance a synergistic effect; the wastewater treatment efficiency can be improved; a solar component is adopted as a power supply; the clean solar energy is utilized to the maximal degree, and the organic wastewater treatment film reactor has social benefits of reducing environment load and economic benefits of reducing cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
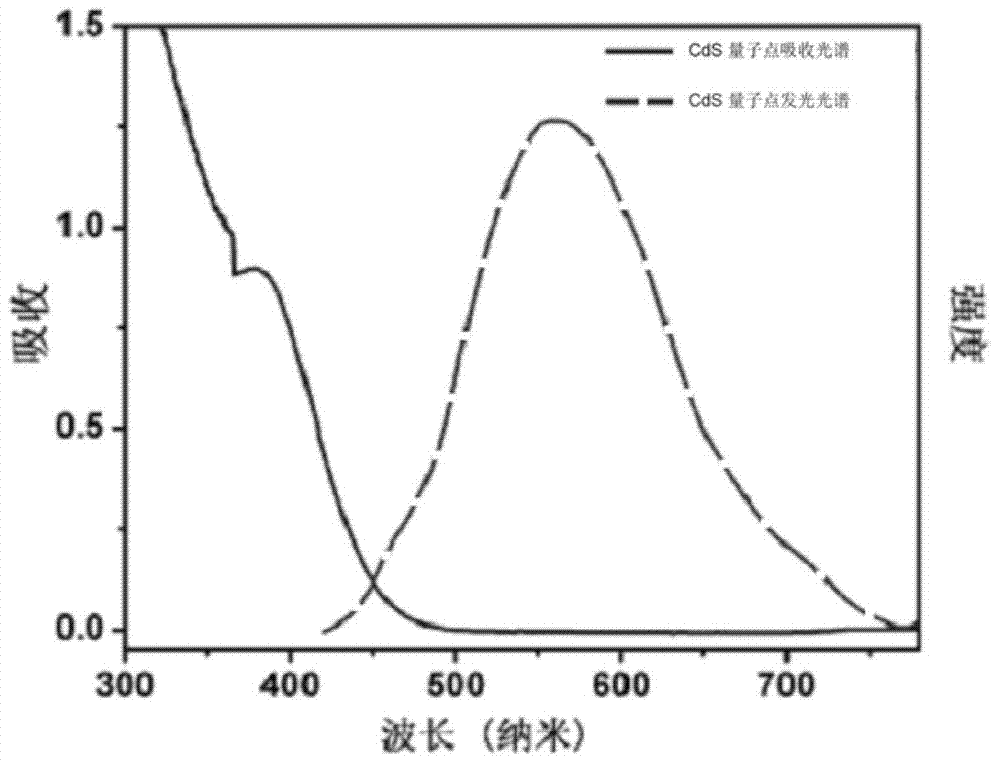
Making method and application of CdS sensitized TiO2 environmental estrogen photoelectrochemical sensor
ActiveCN104297305AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySave raw materialsMaterial electrochemical variablesAntigenAntigen capture
The invention relates to a making method and an application of a CdS sensitized TiO2 environmental estrogen photoelectrochemical sensor. The method uses TiO2 as an antigen capture substrate material, a CdS photoelectric active material is in situ generated on the surface of a Cd2<+> functional TiP nanomaterial maker modified electrode through a direct Na2S dropping technology, and CdS is irritated by an LED lamp of visible light wavelength to be converted to a photoelectric current signal. The substrate material TiO2 can be well matched with CdS energy band, so the photocurrent conversion signal of CdS is further improved, thereby the competitive photoelectrochemical immunosensor for ultra sensitive detection of estradiol, estriol, diethylstilbestrol, bisphenol A, nonylphenol, oestrone and other environmental pollutants is made.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
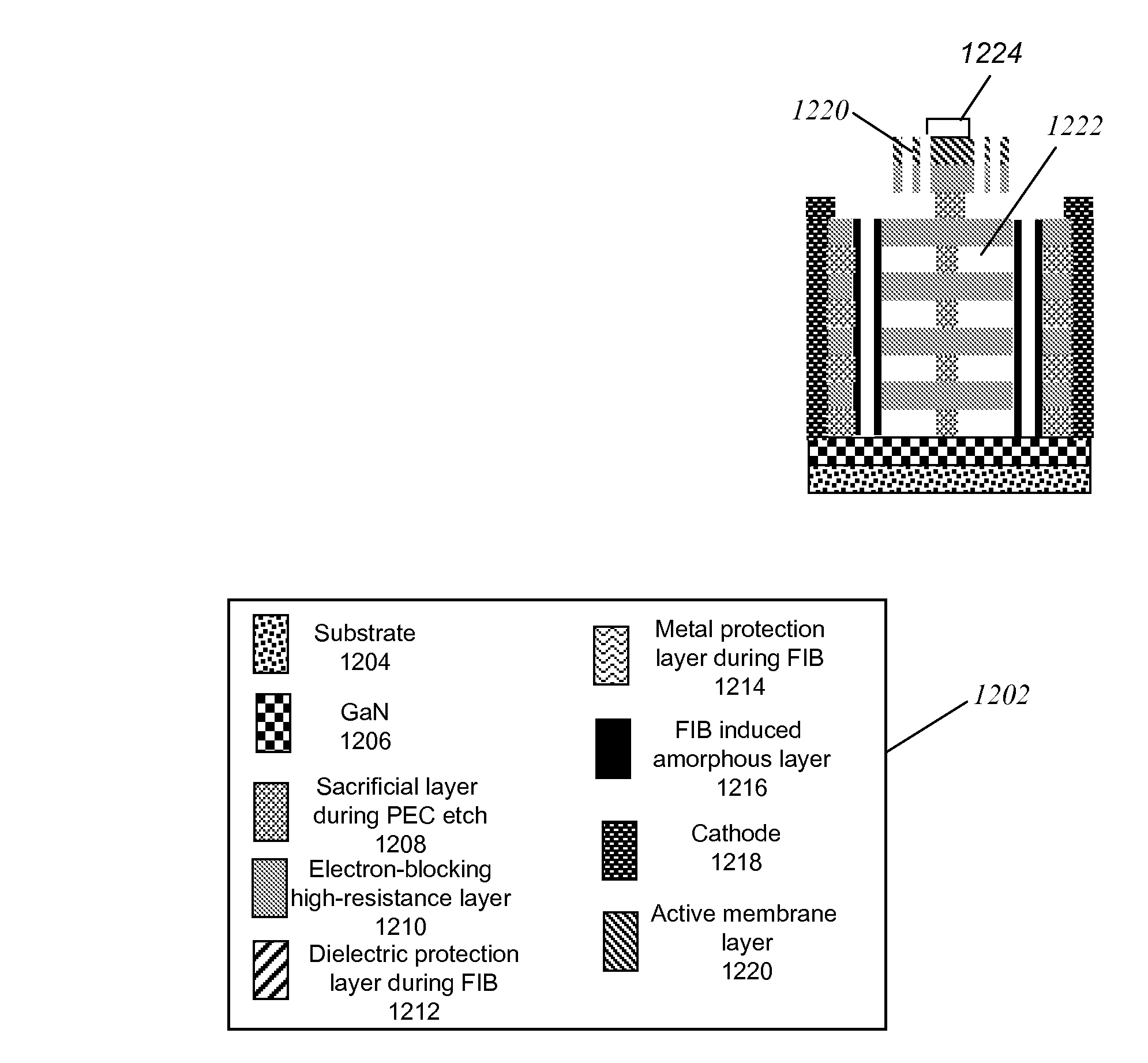
Ion beam treatment for the structural integrity of air-gap iii-nitride devices produced by the photoelectrochemical (PEC) etching
InactiveUS20080182420A1Avoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhotoelectrochemical etchingPhotonics
A method for ensuring the structural integrity of III-nitride opto-electronic or opto-mechanical air-gap nano-structured devices, comprising (a) performing ion beam implantation in a region of the III-nitride opto-electronic and opto-mechanical air-gap nano-structured device, wherein the milling significantly locally modifies a material property in the region to provide the structural integrity; and (b) performing a band-gap selective photo-electro-chemical (PEC) etch on the III-nitride opto-electronic and opto-mechanical air-gap nano-structured device. The method can be used to fabricate distributed Bragg reflectors or photonic crystals, for example. The method also comprises the suitable design of distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) structures for the PEC etching and the ion-beam treatment, the suitable design of photonic crystal distributed Bragg reflector (PCDBR) structures for PEC etching and the ion-beam treatment, the suitable placement of protection layers to prevent the ion-beam damage to optical activity and PEC etch selectivity, and a suitable annealing treatment for curing the material quality after the ion-beam treatment.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen by photoelectro-chemically decomposing water, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN104762634AEasy to separateImprove transmission performanceEnergy inputElectrode shape/formsHydrogenPhotocathode
A photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen by photoelectro-chemically decomposing water is characterized in that the photoelectrode is composed of a photocathode and a photoanode, wherein the photocathode and a photoanode are provide with quantum dots being assembled with assistance of a double-functional molecule. The invention achieves the establishment and the application of the photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen on the basis of semiconductors, quantum dots and catalysts. The photoelectrode is high in stability, is free of a sacrificial agent, is simple in operation, is good in repeatability, is strong in universality and is high in utilization rate on visible light. In addition, the catalyst is free of requirement of noble metals, is low in cost and is easy to obtain.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
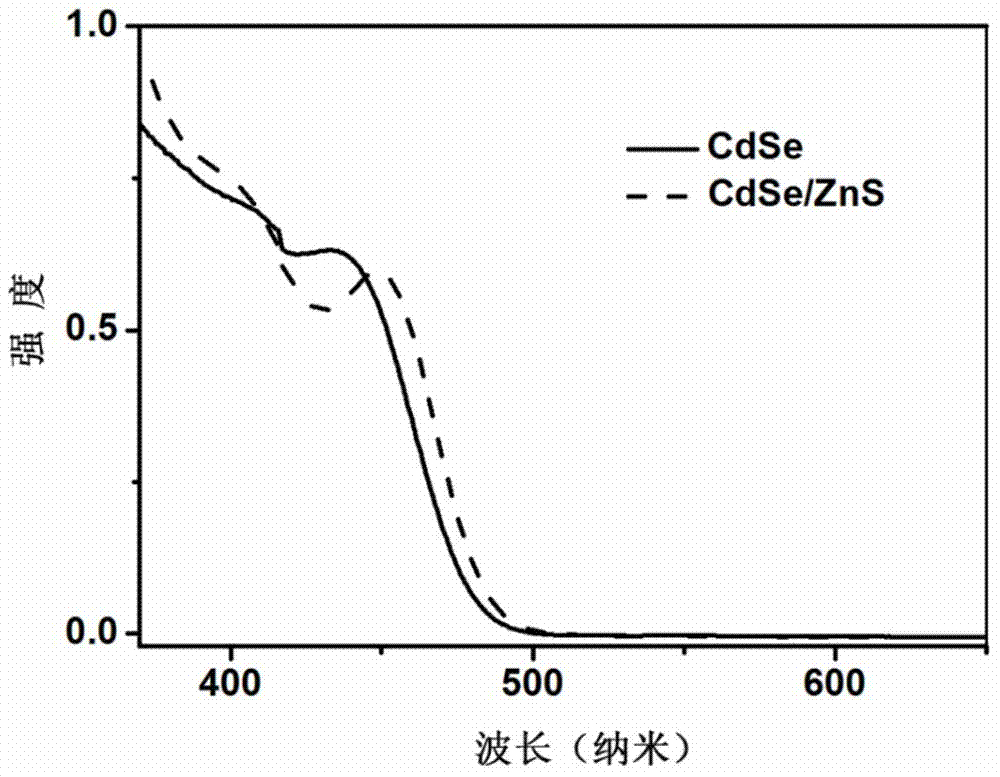
Preparation method for double-functional mark photo-electrochemical sensor and application
InactiveCN104133069AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
The invention provides a preparation method for a double-functional mark photo-electrochemical sensor and application and belongs to the technical fields of nano-functional materials, clinical analysis, bio-sensing and electrochemistry. A TiO2-CdSe semiconductor compound is prepared based on a ligand principle between TiO2 and carboxyl; a remarkably-enhanced photoelectric conversion effect of the prepared TiO2-CdSe semiconductor compound is displayed on a visible region; a photocurrent value is 10 times as much as that of a single TiO2 photocurrent value; the TiO2-CdSe semiconductor compound has large specific surface area and good biocompatibility and is used for marking a second antibody (Ab2) of CA125 so that a TiO2-CdSe-Ab2 hatched matter is prepared. The difference between the double-functional mark photo-electrochemical sensor and other electrochemical or photo-induced electrochemical sensors is as follows: the TiO2-CdSe semiconductor compound can be used for not only carrying out photoelectric conversion and but also generating Cd2<+>, so that an immunosensor taking the TiO2-CdSe semiconductor compound as a second antibody marker can adopt an electrochemical analysis technology and a photo-induced electrochemical analysis technology to rapidly, sensitively and accurately detect the CA125. The method has certain guiding significance and application value on early diagnosis of cancers.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
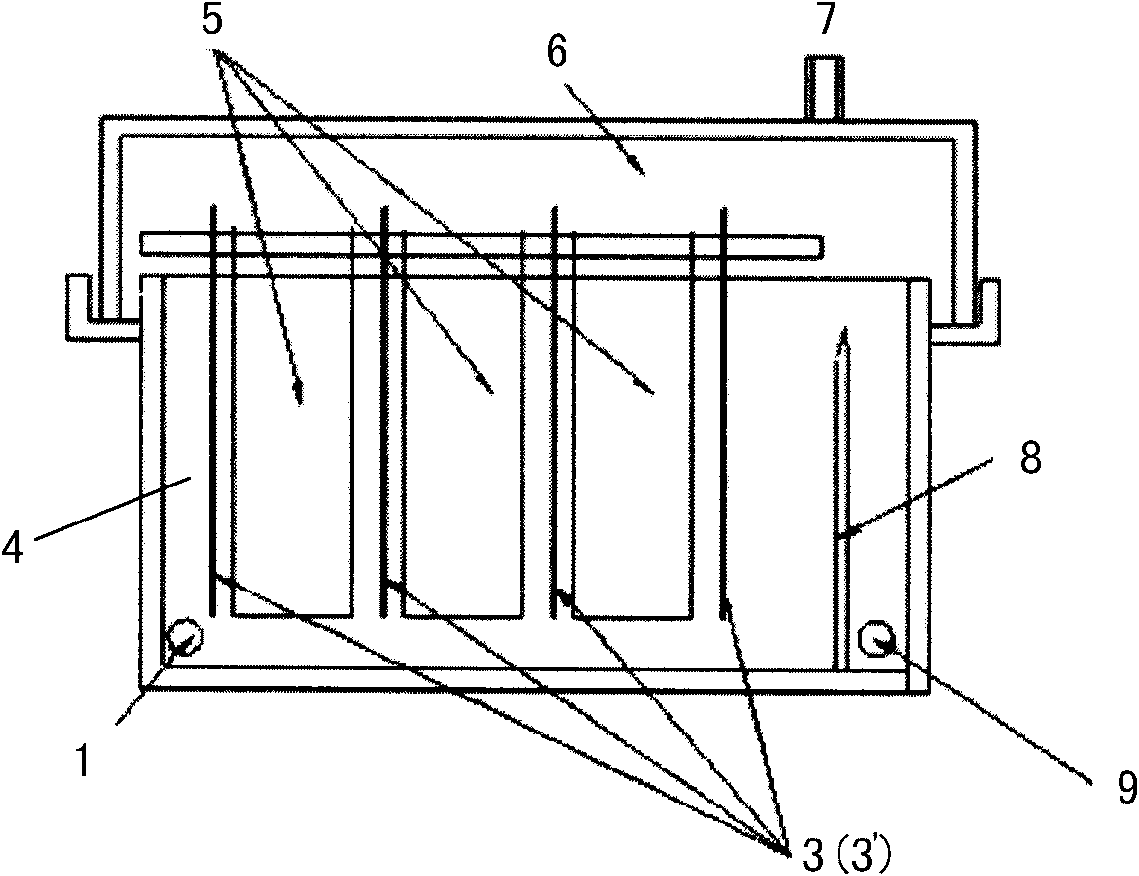
Method and device for realizing photoelectrochemical micro-etch processing of masked electrode
The invention provides a method and a device for realizing the photoelectrochemical micro-etch processing of a masked electrode, and relates to the micro processing field in the manufacturing technology. A masked electrode used by the invention comprises a glass substrate, an indium tin oxide (ITO) layer and a photoresist mask layer, wherein the conductive light-permeable ITO layer is used as a tool electrode for electrochemical processing and can be permeated by a laser beam, and the photoresist mask layer can limit the action zones of the laser beam and the electrochemical electrode to achieve the double effects of a beam mask and an electric field mask. When the laser beam permeates the masked electrode, a mask pattern is imaged on the surface of a workpiece, the force effect of a shock wave generated by the irradiation of the laser between the workpiece and the electrolyte enables the passivation layer to be removed by the generation of stress corrosion. Meanwhile, the workpiece material at the laser-irradiated part is removed by etching under the action of the photoelectrochemical reaction. The invention can effectively enhance the processing efficiency, the micro processing degree and the processing precision of the complex pattern, and is applicable to the micro processing of the conductive metal material.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Hybrid solid state/electrochemical photoelectrode for hydrogen production
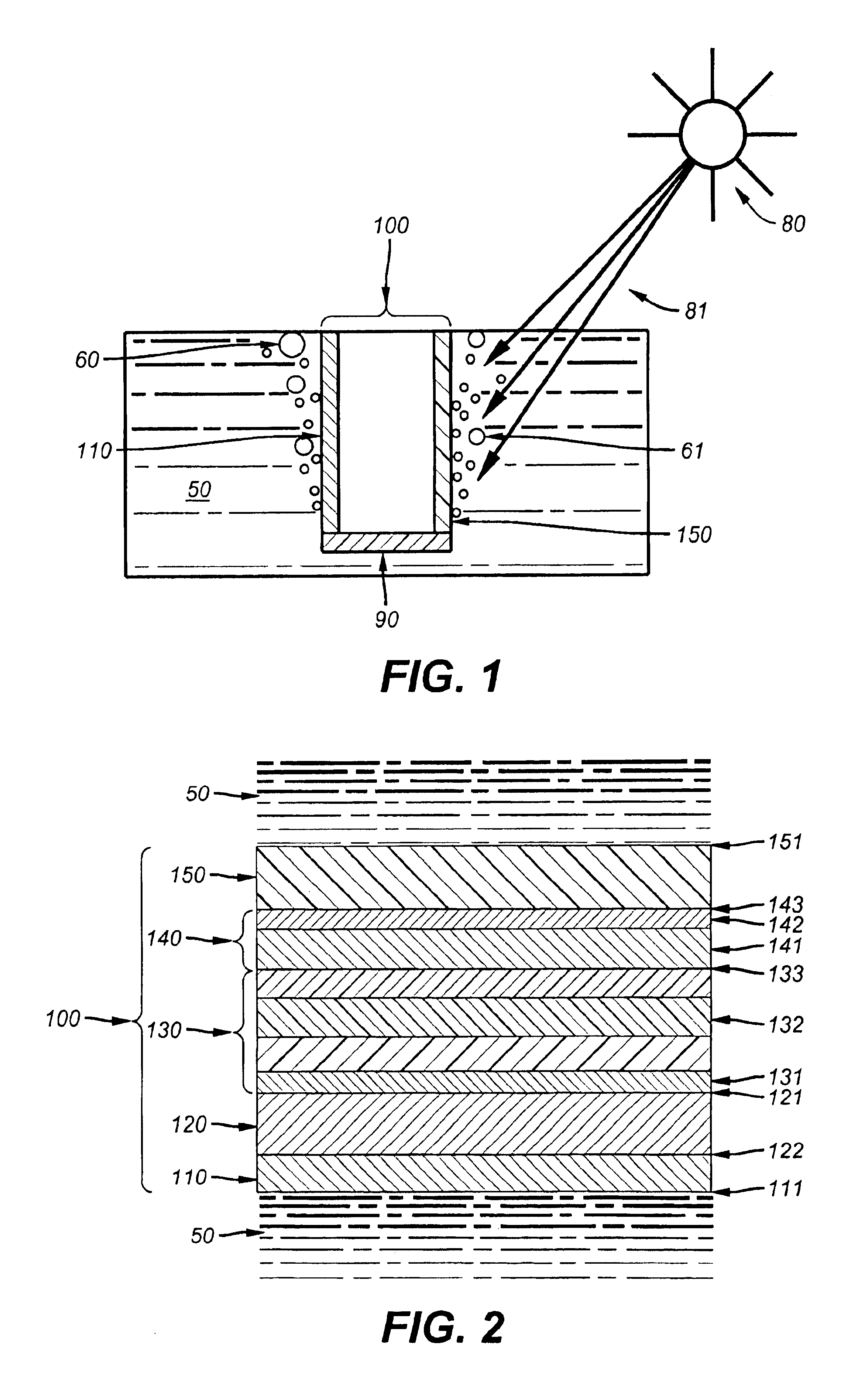
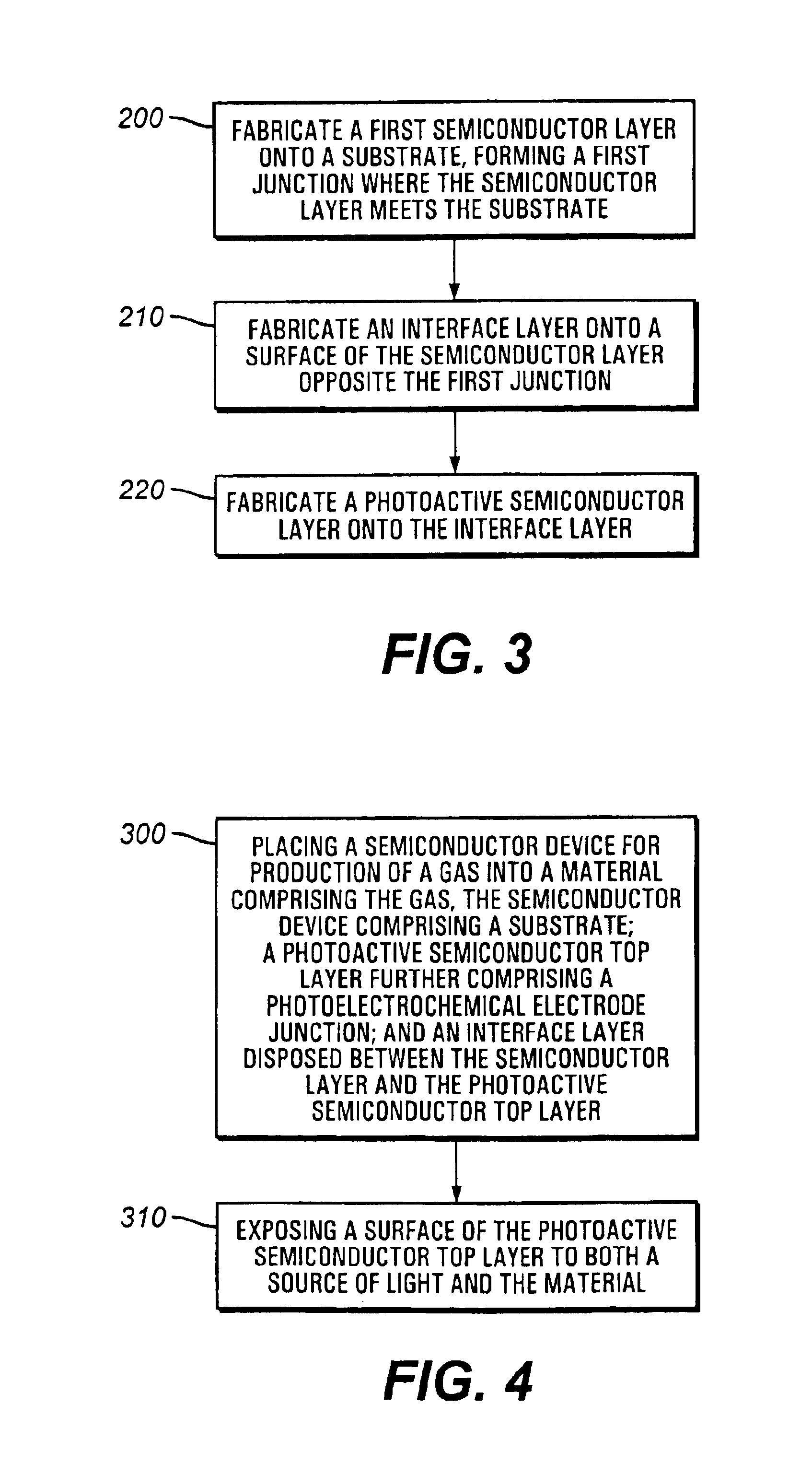
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device for production of a gas from a material comprising the gas using light as the sole power source. In an embodiment, the semiconductor comprises a substrate; a solid-state semiconductor layer disposed on the substrate; a photoactive semiconductor top layer further comprising a photoelectrochemical electrode junction; and an interface layer disposed between the solid-state semiconductor layer and the photoactive semiconductor top layer. A surface of the photoactive semiconductor top layer is exposed to both a source of light such as the sun and to the material, e.g. a liquid electrolyte. The gas is liberated from the material, e.g. hydrogen liberated from a liquid electrolyte. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Preparation of three-dimensional photoelectrochemical paper chip and application of three-dimensional photoelectrochemical paper chip in tumor detection
The invention discloses a preparation method for a three-dimensional photoelectrochemical paper chip and a method for measuring six tumor markers in a sample through a photoelectrochemical sensor. A hydrophobic region and a hydrophilic region are formed on paper by adopting a wax printing technology; a corresponding reference electrode and working electrodes are printed on the paper through proper ink; a working region is functionalized for antigen recognition; the prepared paper chip is folded to form a three-electrode system; a buffering solution containing ascorbic acid is dropwise added into a reaction region; under the irradiation of an ultraviolet lamp, the high-sensitivity detection on an object to be measured is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Photoelectrochemical system for hydrogen production from water
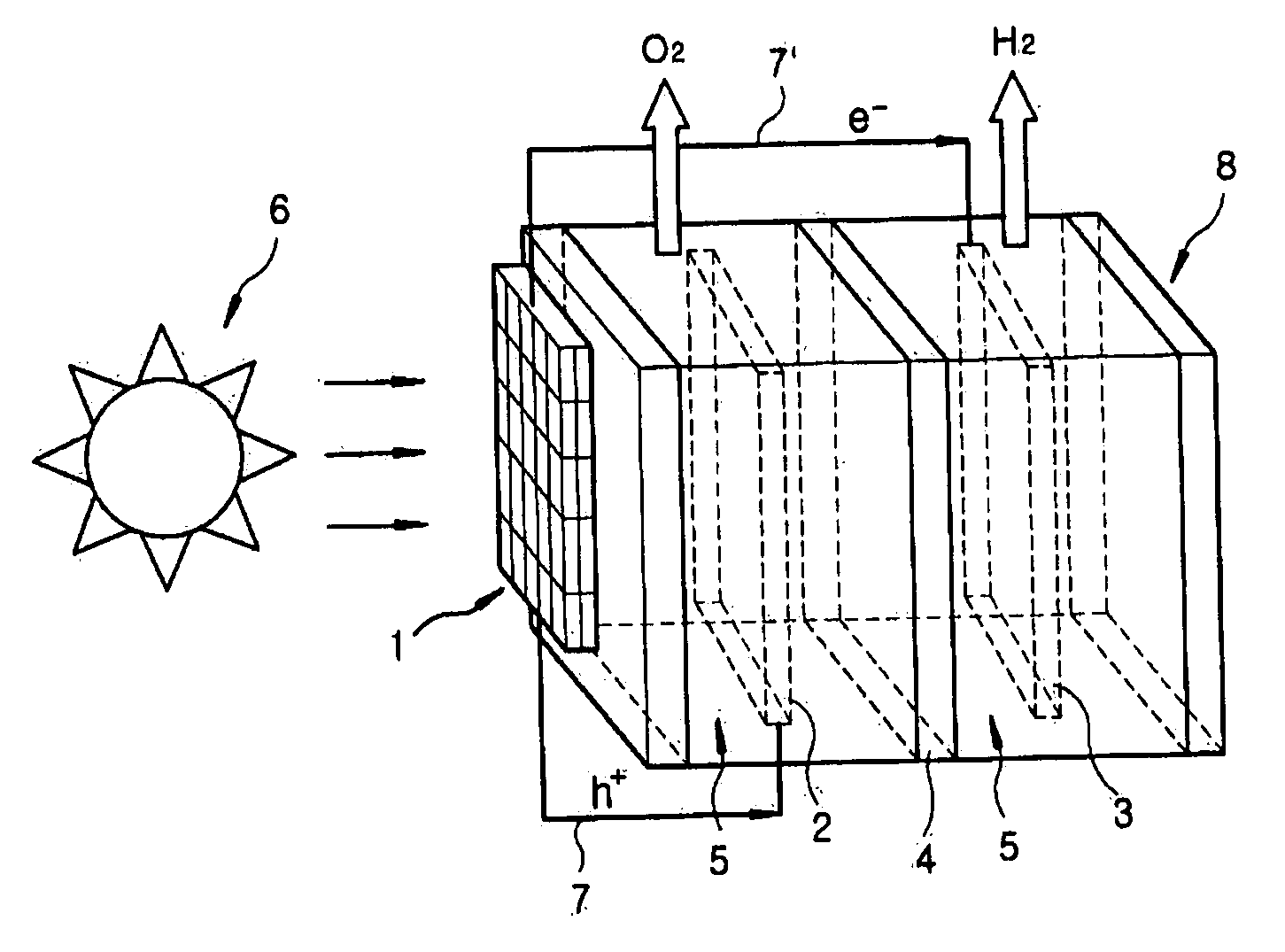
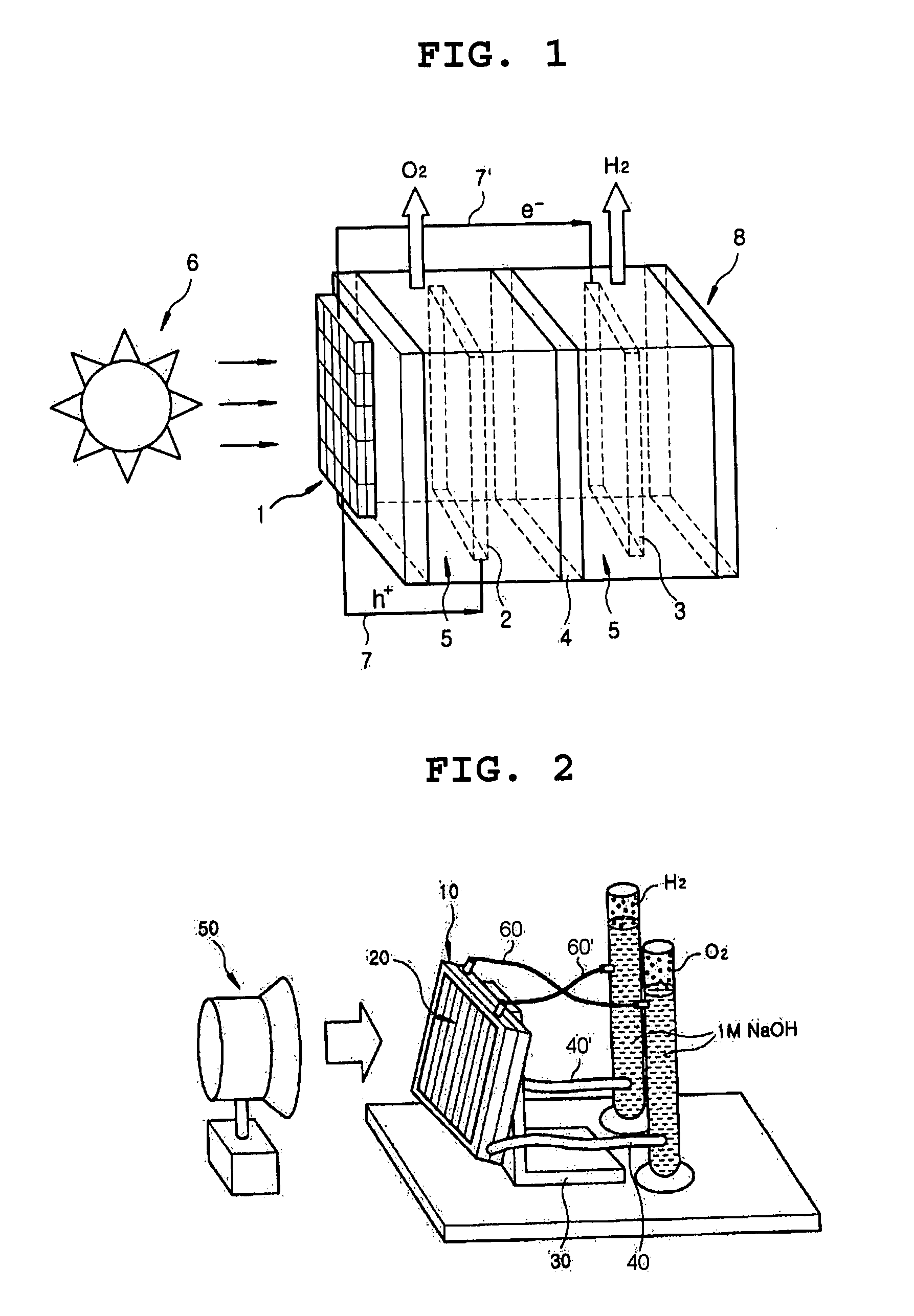
The present invention provides a photoelectrochemical (PEC) system for the production of hydrogen from water, which comprises (A) an electrolytic bath comprising an electrode for catalytic oxidation, an electrode for catalytic reduction, an ion separation film disposed between the two electrodes, and an aqueous electrolyte solution into which the two electrodes and the ion separation film are immersed, and (B) a photoelectrode positioned at the outside of the electrolytic bath and electrically connected to the two electrodes. The inventive PEC system is characterized by disposing a photoelectrode at the position which does not contact aqueous electrolyte solution, thus preventing the lowering of the photoelectrode activities, and maximizing the hydrogen production efficiency.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for production of nanoporous electrodes for photoelectrochemical applications
InactiveUS20090114275A1Enhance surfactant adsorptionElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPorous electrode
The invention relates to a two-step method for production of low temperature mechanically stable and electrically efficient nanoporous electrodes, in particular titania nanoporous electrodes, for photoelectrochemical applications. The method of the invention comprises electrophoretic deposition (EPD) of nanosize titania crystals from a stable suspension containing thereof on a conductive substrate, and formation of mechanical and electrical contact between them. The invention further relates to nanoporous electrodes obtained by this method and to dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) fabricated therefrom.
Owner:3GSOLAR PHOTOVOLTAICS
Preparing method of photoelectrochemical sensor based on sandwich cardiac troponin T marked by Ag2Se@CdSe and application
InactiveCN104849331AGood photoelectric conversion characteristicsImprove photoelectric signal responseBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesCardiac muscleEngineering
The invention relates to a preparing method of a photoelectrochemical sensor based on sandwich cardiac troponin T marked by Ag2Se@CdSe and application, and belongs to the technical field of novel functional materials and biosensing detection. According to concrete contents of the preparing method and the application, CeO2-TiO2 composite nanometer materials with photoelectrocatalytic activity are used as optical activity substrate materials; Ag2Se@CdSe is used as an antibody marker; the sandwich photoelectrochemical sensor is prepared through the signal amplification effect of the marker Ag2Se@CdSe on the substrate materials, and is used for the high-sensitivity detection of the cardiac troponin T of myocardial damage specific marker. The method has the important significance on the early diagnosis and treatment of acute myocardial infarction.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Novel Pb2+ supersensitive detecting method based on photoelectrochemical sensing
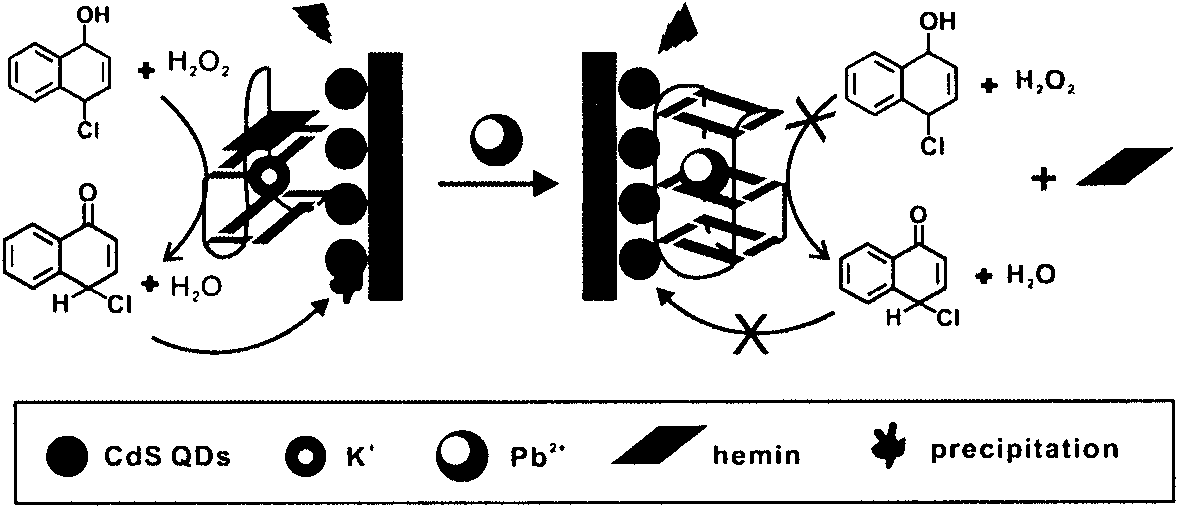
The invention relates to construction of a photoelectrochemical sensor which is based on conformation transition of G-quadruplex DNAzyme, and belongs to the field of photoelectrochemical sensor technology of analytical chemistry, wherein the conformation transition is induced by Pb2+, and the photoelectrochemical sensor is capable of realizing supersensitive sensing of Pb2+ effectively. K+ is replace by Pb2+ to induce the conformation transition of G-quadruplex DNAzyme so as to decrease enzymatic activity, so that enzyme biological catalytic precipitation reaction on an ITO electrode which is modified by CdS quantum dots is influenced, and photoelectrochemical sensing detection of Pb2+ is realized. G-quadruplex DNAzyme is applied in a photoelectrochemical sensing system for detection of Pb2+ for the first time; the photoelectrochemical sensor possesses advantages of high selectivity and high ensitivity; and detection limit of Pb2+ reaches to 1.0*10<-8>M.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV
Photoelectrode using metal nitride as conductive substrate and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a photoelectrode and a preparation method thereof. A metal nitride substrate serves as a current collection body and is tightly contacted with a photoactive layer which is a non-complete oxide semiconductor with or without the decoration of a promoter, so that the photoelectrochemical photoelectrode is formed. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing the conductive metal nitride substrate, wherein the lowest sheet resistance of the conductive metal nitride substrate is 1.8 ohm per square, the electrical resistivity is 0.16 mohm per centimeter, the conductive metal nitride substrate is superior to commercial FTO and ITO; and secondarily, depositing or coating the semiconductor or a precursor containing a semiconductor metal constituent, performing high-temperature processing in an inert atmosphere or a hydride atmosphere of the semiconductor nonmetal constituent. The metal nitride substrate can keep conductivity after being subjected to high-temperature processing in the inert or hydride atmosphere (such as to 900 DEG C in ammonia gas), and is applicable for high-temperature preparation process of a non-all oxide semiconductor photoelectrode, and the whole photoelectrode preparation process is easy to industrialize. The photoelectrode can be used for application such as water decomposition, hydrogen preparation and carbon dioxide conversion by means of solar energy in photoelectrochemistry.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
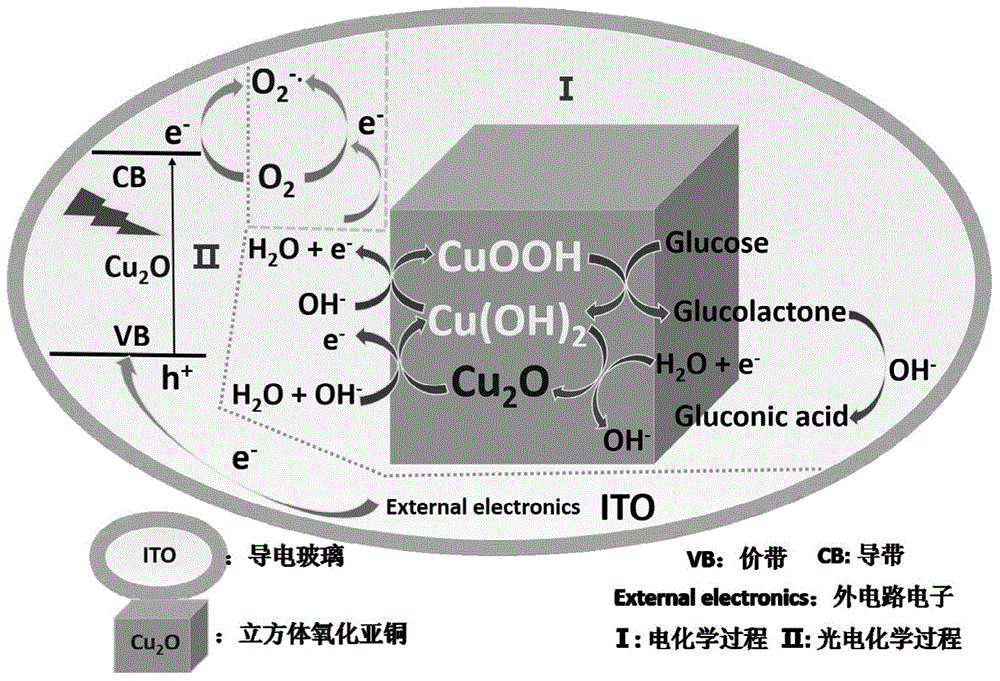
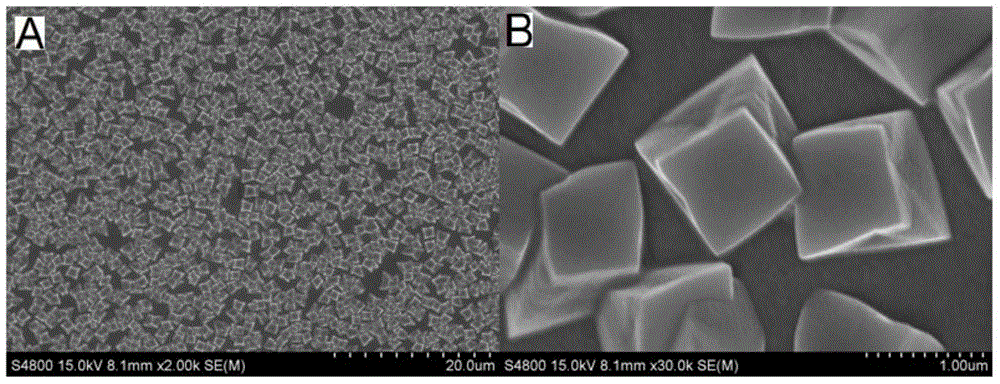
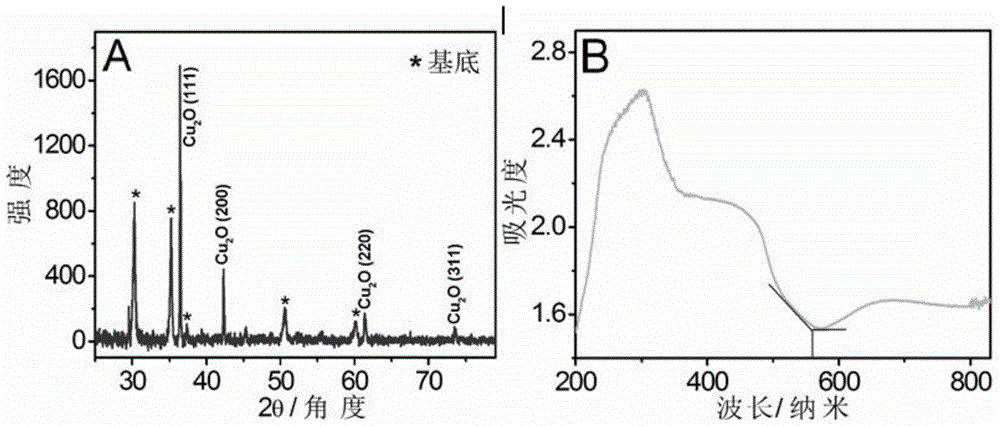
Construction method and detection method of cuprous oxide membrane-based enzyme free-oxygen sensitive glucose photo electrochemical sensor
InactiveCN104569096ALow detection signal backgroundLow costMaterial electrochemical variablesPhotocathodeOxygen
The invention discloses a construction method of a cuprous oxide membrane-based enzyme free-oxygen sensitive glucose photo electrochemical sensor. The construction method comprises the following steps: with an ITO conductive glass as a working electrode, a platinum wire as a counter electrode and a silver / silver chloride electrode as a reference electrode, inserting the three electrodes into a sodium hydroxide solution containing 0.05mol / L copper sulfate and 0.1mol / L sodium citrate, and regulating a pH value to be 11; under the conditions that the deposition temperature is 60 DEG C, the deposition potential is -0.4V and the deposition time is 20 minutes, forming a cuprous oxide membrane on the surface of the ITO conductive electrode; and rinsing residual solution on the surface with pure water, drying for 1h at the temperature of 100 DEG C, and forming a stable cuprous oxide membrane-based photocathode. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, photocurrent detection based on light excitation is low in detection signal background and can have high detection sensitivity and stability without needing expensive instrument and equipment and complex sample treatment.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
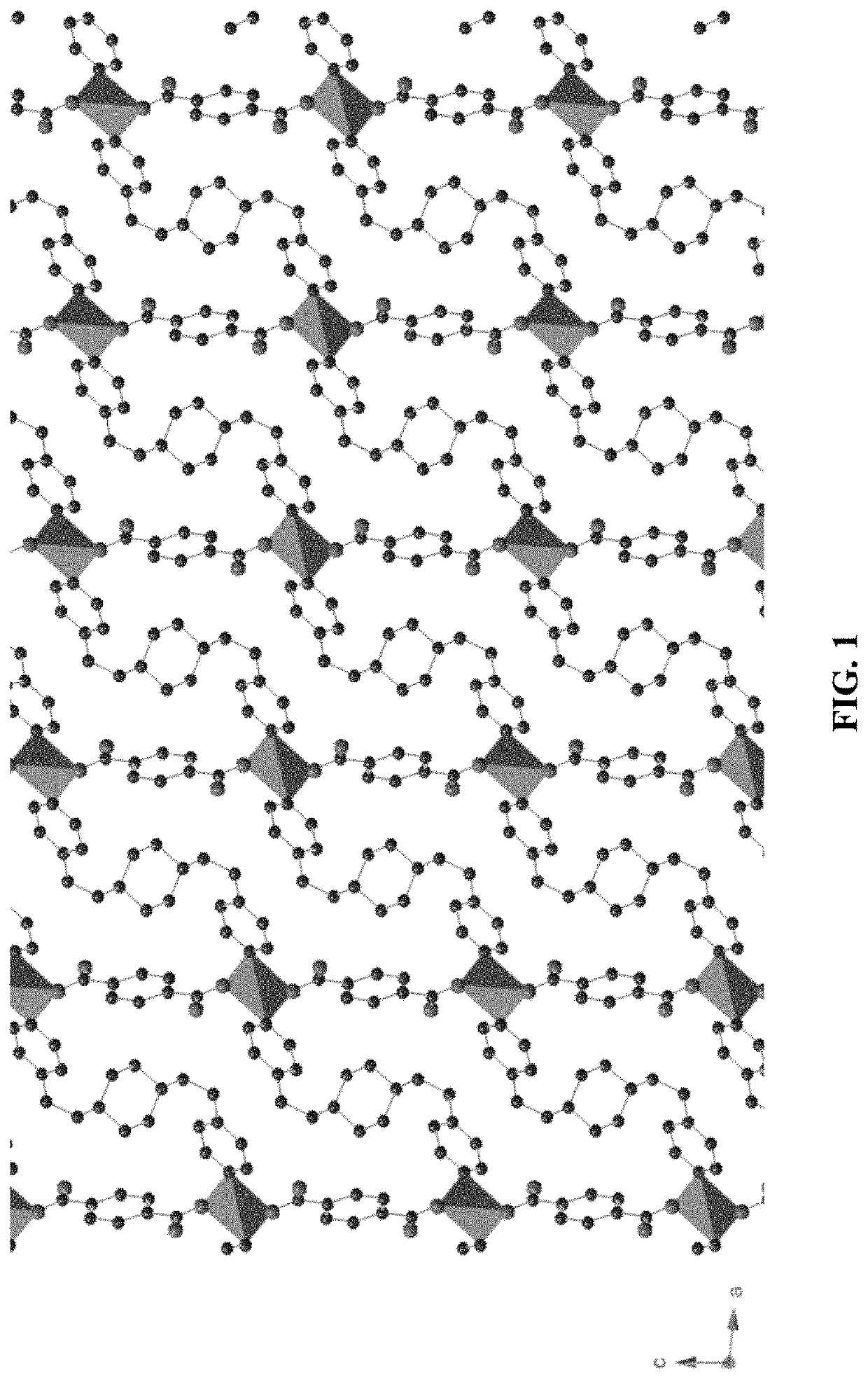
Water stable zinc-based metal organic framework and method of use
ActiveUS20200190114A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEnergy inputMetal-organic frameworkEngineering
A zinc-based metal organic framework and method of making is described. The zinc-based metal organic framework is in the form of an interpenetrating diamondoid framework where each Zn2+ ion center is linked with four other Zn2+ ion centers in a distorted tetrahedral geometry. The linking occurs through diamine and dicarboxylic acid linkers. The zinc-based metal organic framework may be deposited on a transparent conducting film and used as a photoelectrode for photoelectrochemical water splitting.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
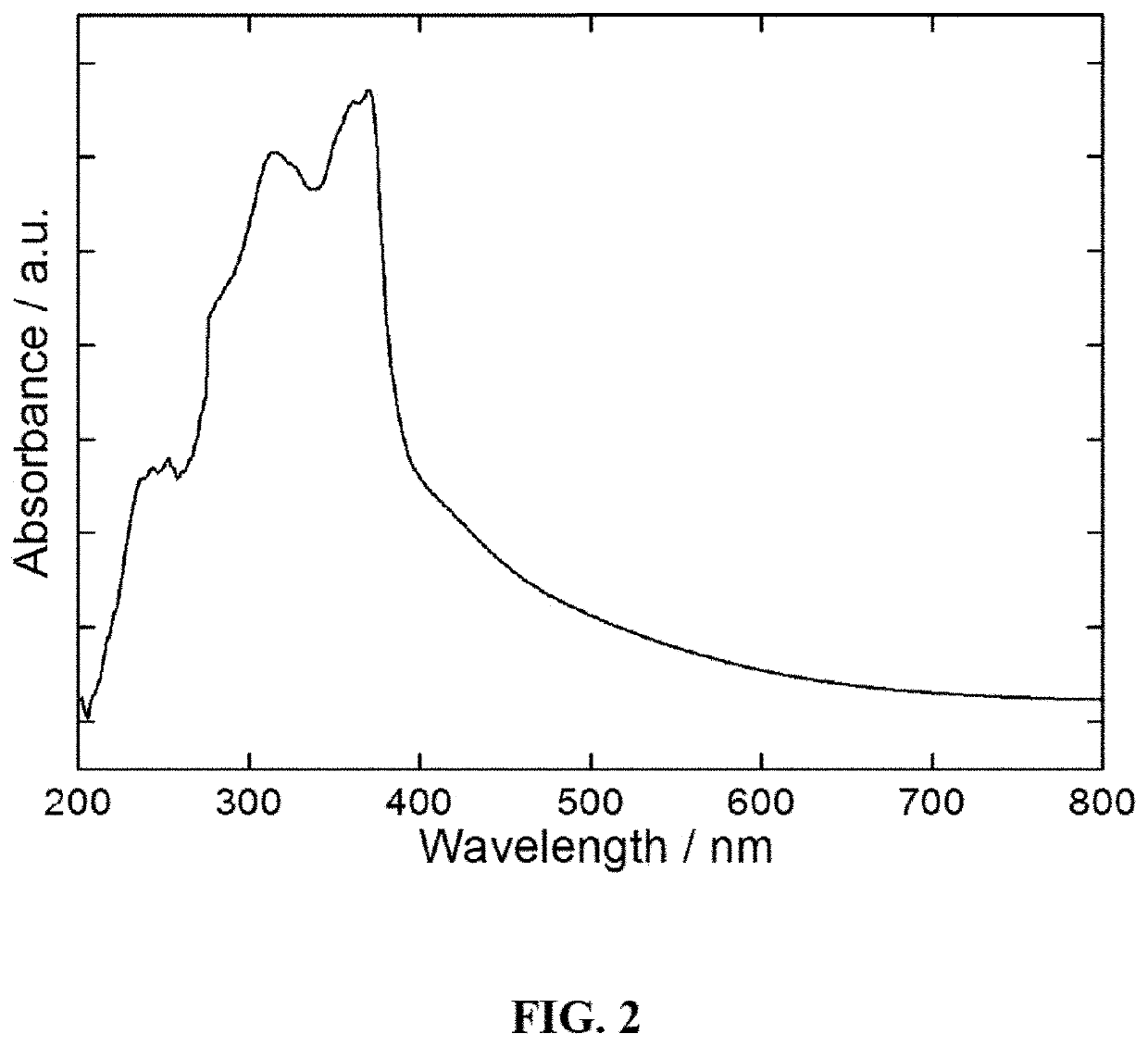
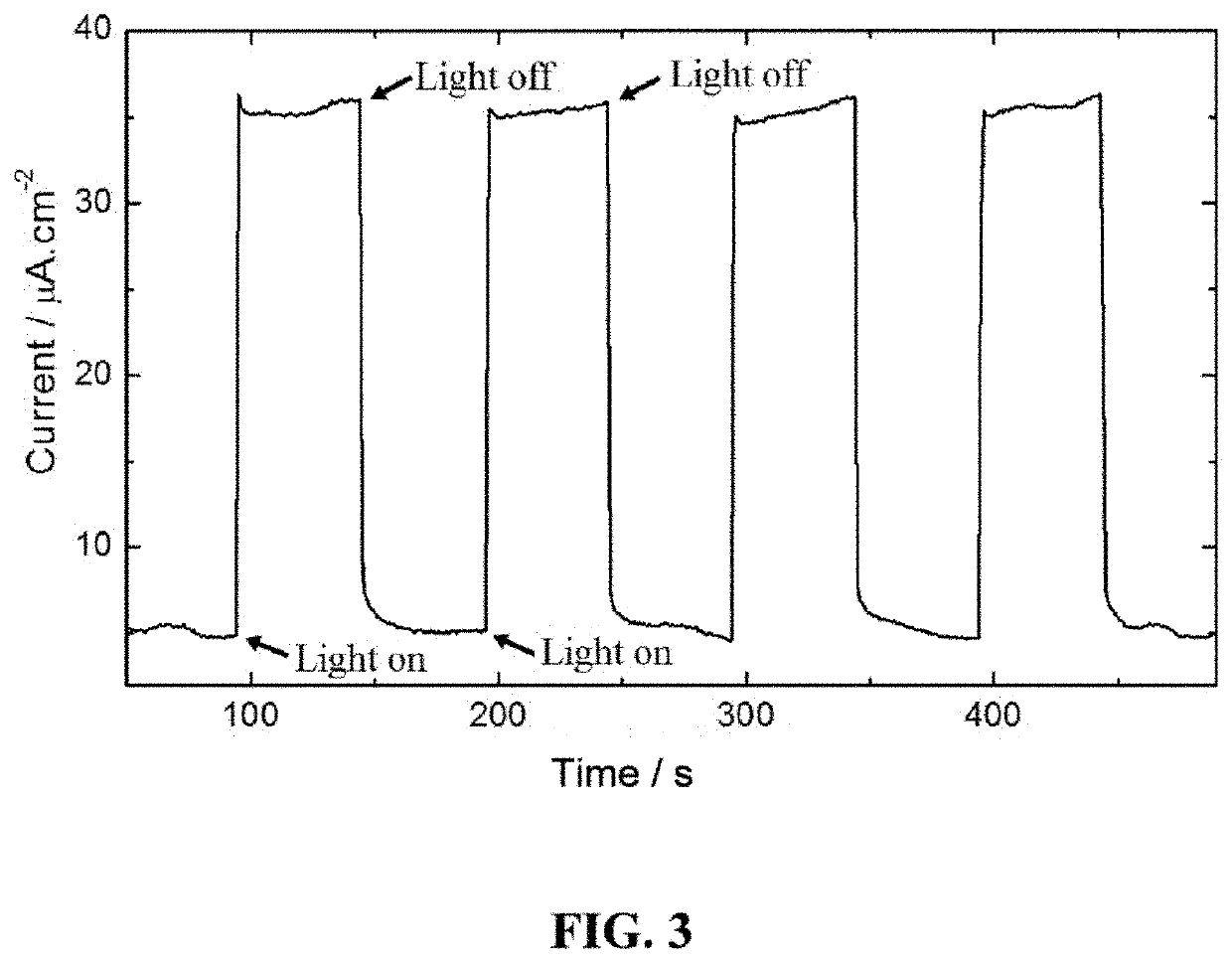
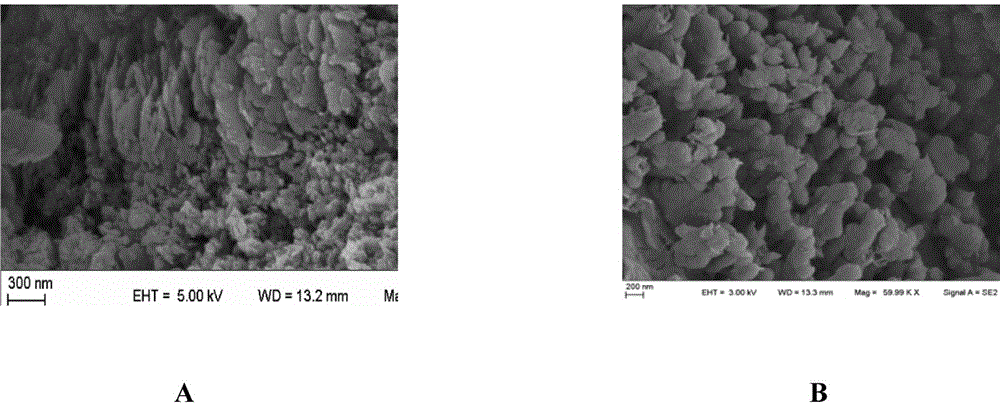
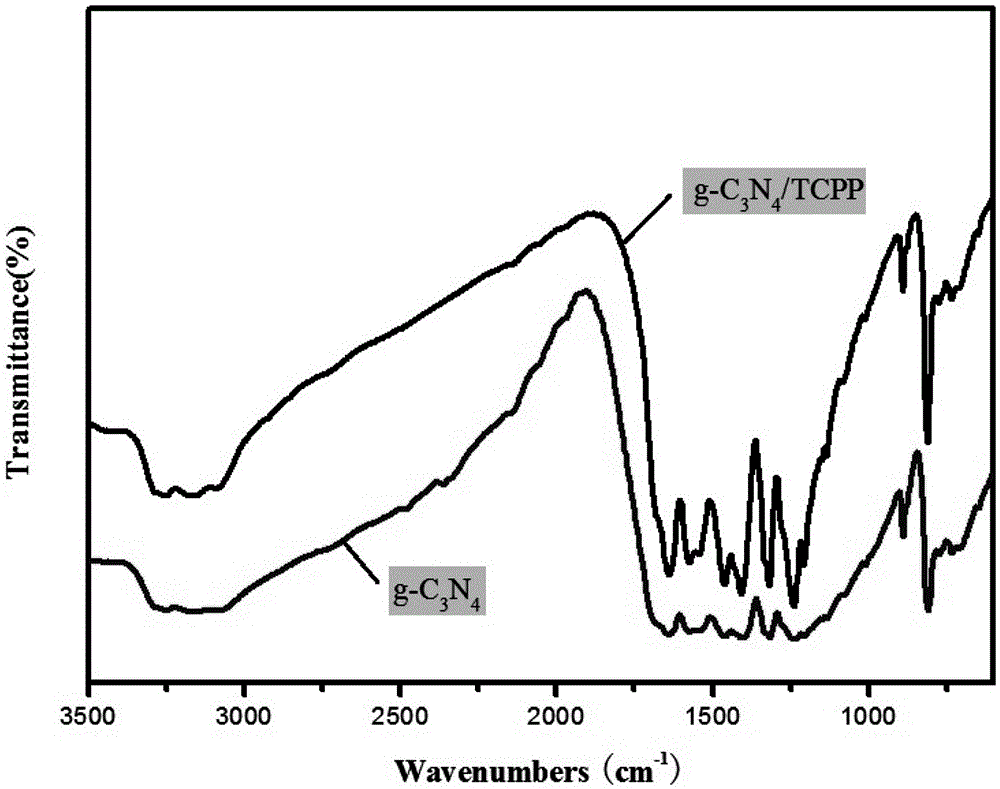
Graphite phase-like carbon nitride/tetracarboxylphenylporphyrin nano-composite material and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN105597820ASimple methodLow costWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsCarbon nitridePhotoelectrochemistry
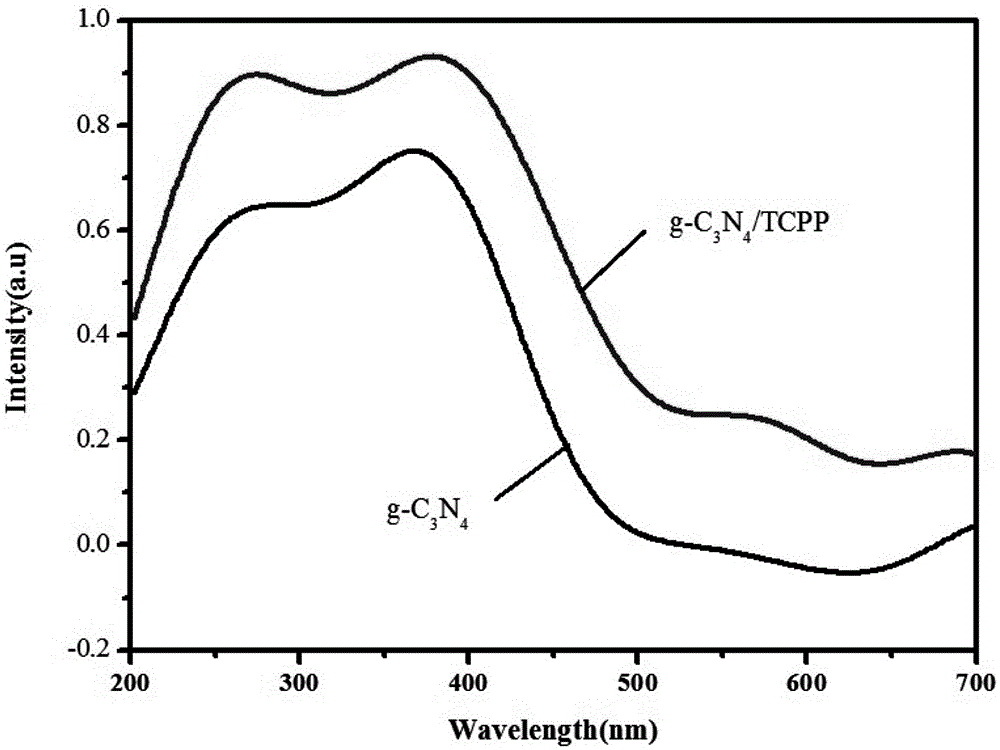
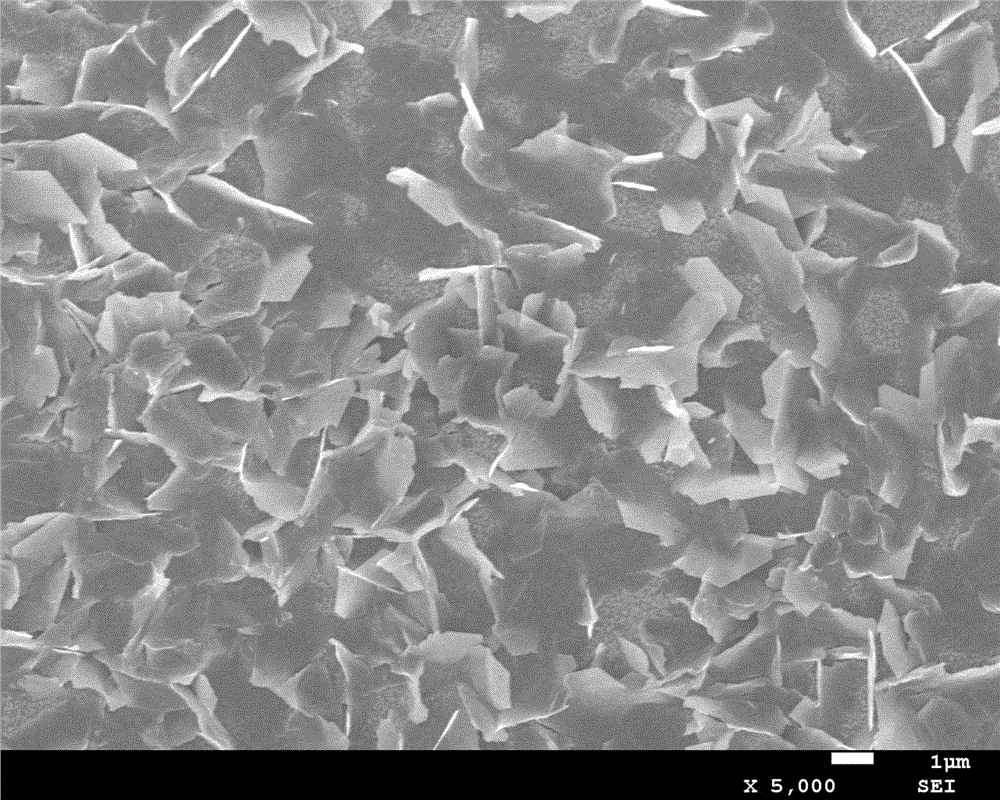
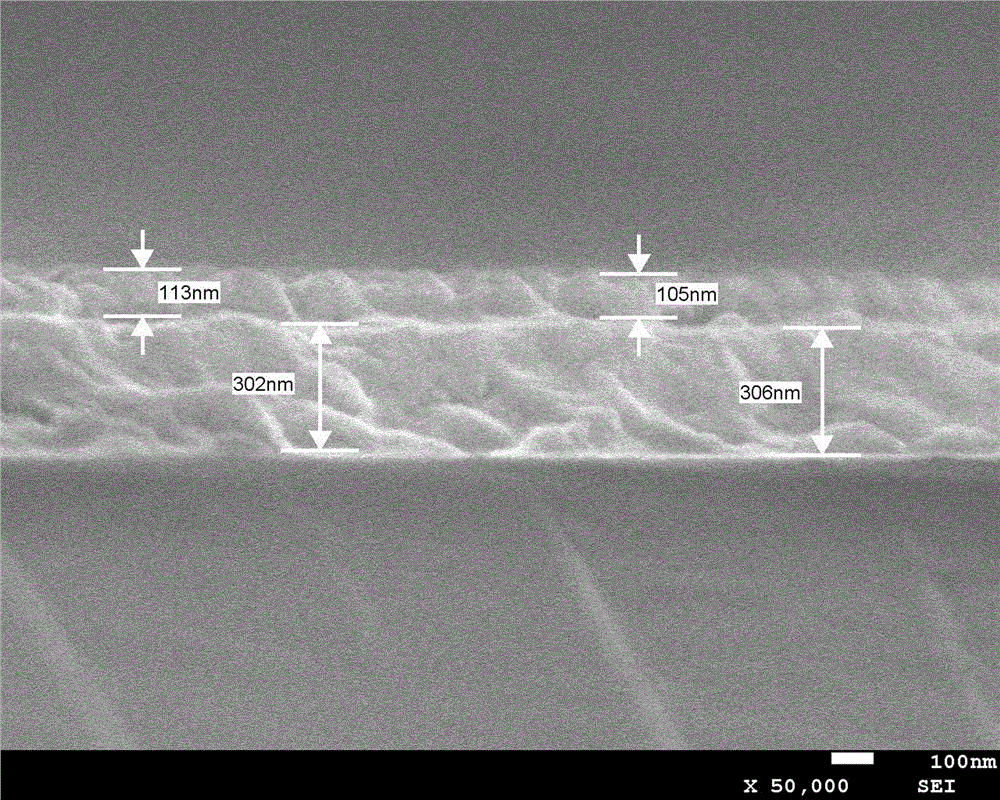
The invention provides a preparation method for a graphite phase-like carbon nitride / tetracarboxylphenylporphyrin nano-composite material. The nano-composite material is obtained with a solid-phase ball milling method. The invention furthermore provides an application of the graphite phase-like carbon nitride / tetracarboxylphenylporphyrin nano-composite material to the photocatalysis. The preparation method is simple, low in cost and easy to operate, and can shorten the reaction time to a very great extent. The nano-composite material has relatively good photoelectrochemical property, relatively good photocatalytic performance and good sensitization property and stability, and plays an important role in the aspects of organic pollutant degradation and dye photocatalytic degradation.
Owner:黑龙江臻旸生物科技有限公司
Cobalt-nickel metal sulfide, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104616900AExcellent electrochemical performanceSimple preparation processLight-sensitive devicesNanotechnologyNickelElectrochemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dye-sensitized cell of a nanometer flake-like Cobalt-nickel metal sulfide. A nanometer flake-like cobalt-nickel metal sulfide counter electrode is in-situ grown on FTO conductive glass by a two-step hydrothermal method, and dye-sensitized cell counter electrodes with different morphologies and photoelectrochemical properties can be obtained by changing preparation parameters. A prepared transparent thin-film counter electrode obtains photoelectrochemical properties equivalent to Pt and excellent transparency; and the method is low in manufacturing cost, simple in technology and good in repeatability.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Method and device for treating cyanide-containing wastewater through photoelectrochemistry
InactiveCN102101708AWide concentration rangeImprove processing efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsElectrochemical responseElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for treating cyanide-containing wastewater through photoelectrochemistry, which comprises the following steps of: regulating the pH value of the cyanide-containing wastewater to be more than 10, adding NaCl, electrolyzing under the radiation of ultraviolet, and regulating the pH value of the effluent to be 7-9 to ensure that cyanides meet the standard. A device used for implementing the method comprises a reaction tank; the bottom on one side of the reaction tank is provided with a water inlet, and the bottom on the other side of the reaction tank is provided with a water outlet; anode plates and cathode plates are inserted in the reaction tank at intervals, all the anode plates are connected in series, and all cathode plates are connected in series; and an ultraviolet lamp is arranged between each anode plate and each cathode plate. The cyanides in water are effectively removed through functions such as electrochemical anode direct oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation, active chlorine oxidation, ultraviolet radiation of active chlorine to generate chlorine radicals and hydroxyl radicals and the like. Meanwhile, heavy metal ions in the cyanide-containing wastewater are deposited on cathodes in the electrochemical reaction process, and are removed and recycled; and organic matters in the cyanide-containing wastewater are effectively degraded and removed.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
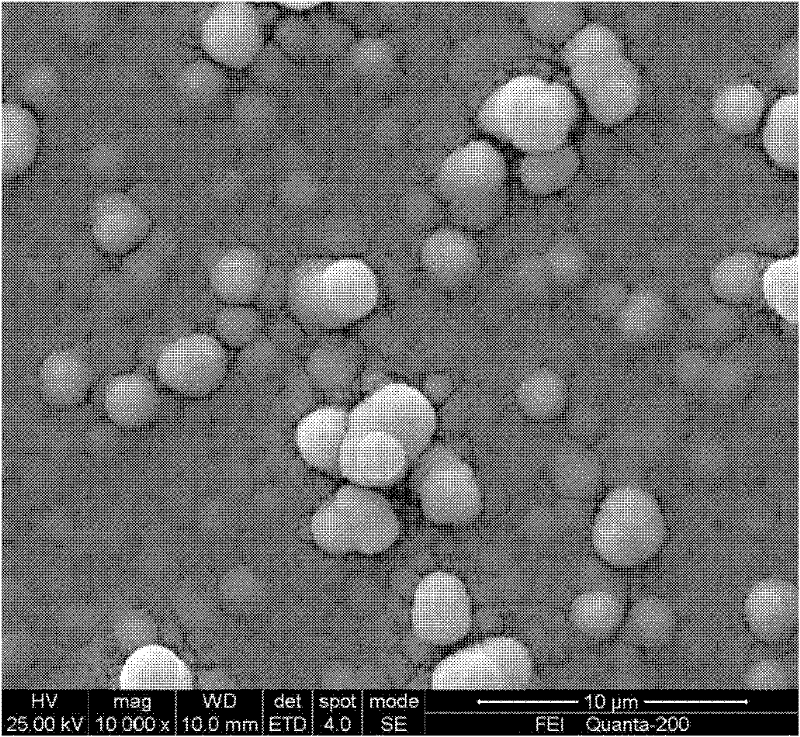
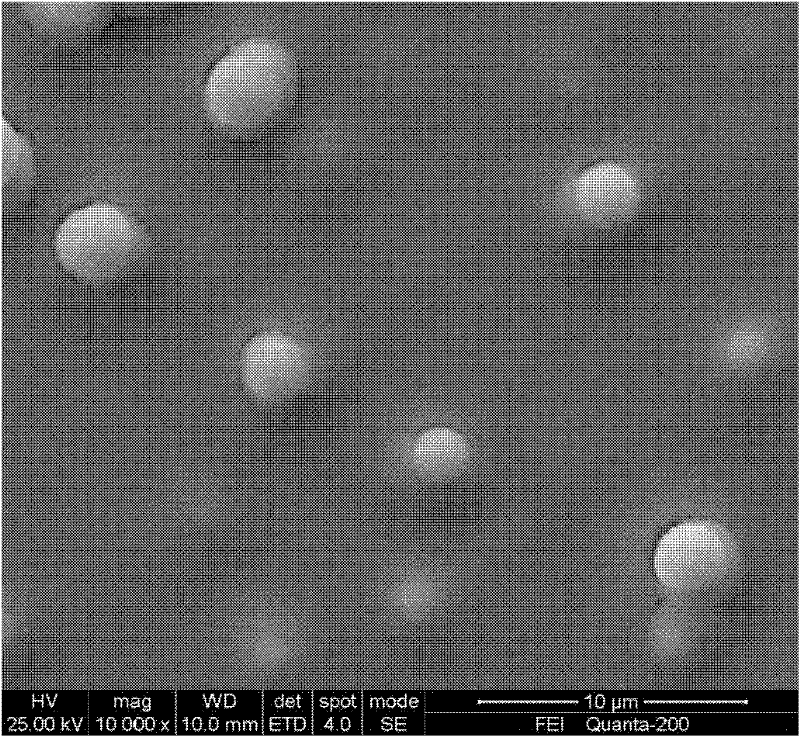
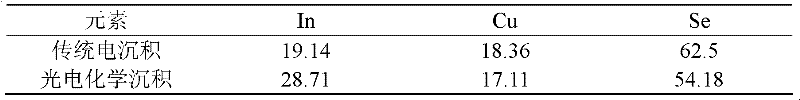
Preparation of Copper Indium Gallium Selenium Thin Films by Photoelectrochemical Deposition
InactiveCN102268702AOvercome speedOvercoming Indium and Gallium Deposition DifficultiesIndiumSlow growth
The invention relates to a method for preparing a copper indium gallium selenide film by photoelectrochemical deposition, which is to deposit a copper indium gallium selenide film on a substrate placed in an electrolyte by using a photoelectrochemical deposition method; the electrolyte is selected from aqueous solution, organic solution, ion Liquid or mixed solution, which contains at least one of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium ions; the photoelectrochemical deposition process parameters are: the working electrode potential is -6.0 ~ 1.5V (vs SCE); at least one single color The light is used as incident light, and the included angle between the incident direction of the incident light and the working electrode is 0-90°. Finally, heat treatment can be performed on the obtained film. The invention solves the problems of poor film morphology, difficulty in indium and gallium deposition, and slow film growth rate encountered in traditional electrodeposited copper indium gallium selenide films, and has the advantages of good film quality, fast growth rate, controllable composition and good shape etc., the preparation method is low in cost, easy to realize large-area deposition of copper indium gallium selenide thin film, and is conducive to its large-scale industrial promotion and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
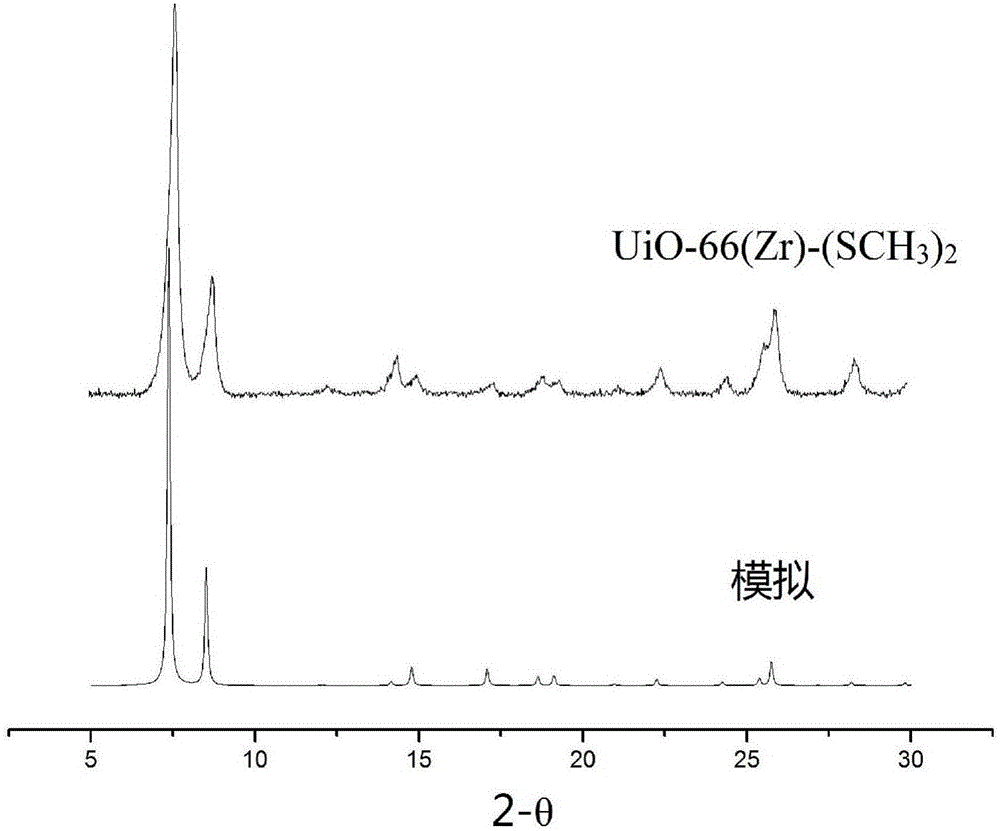
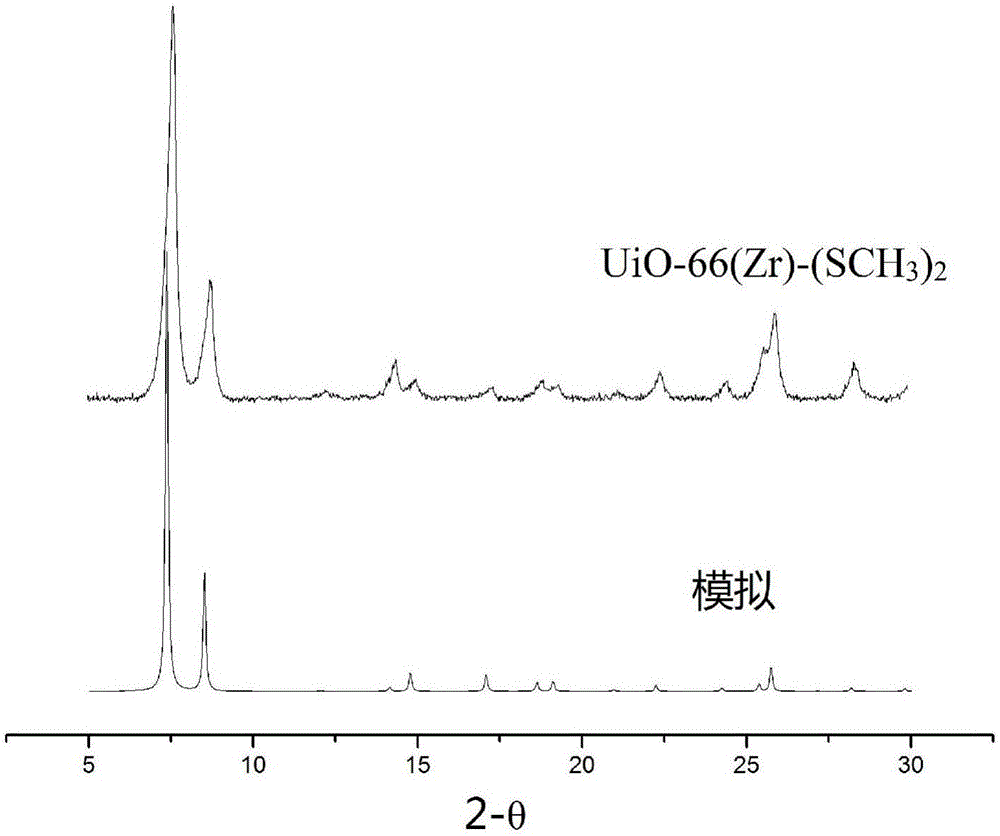
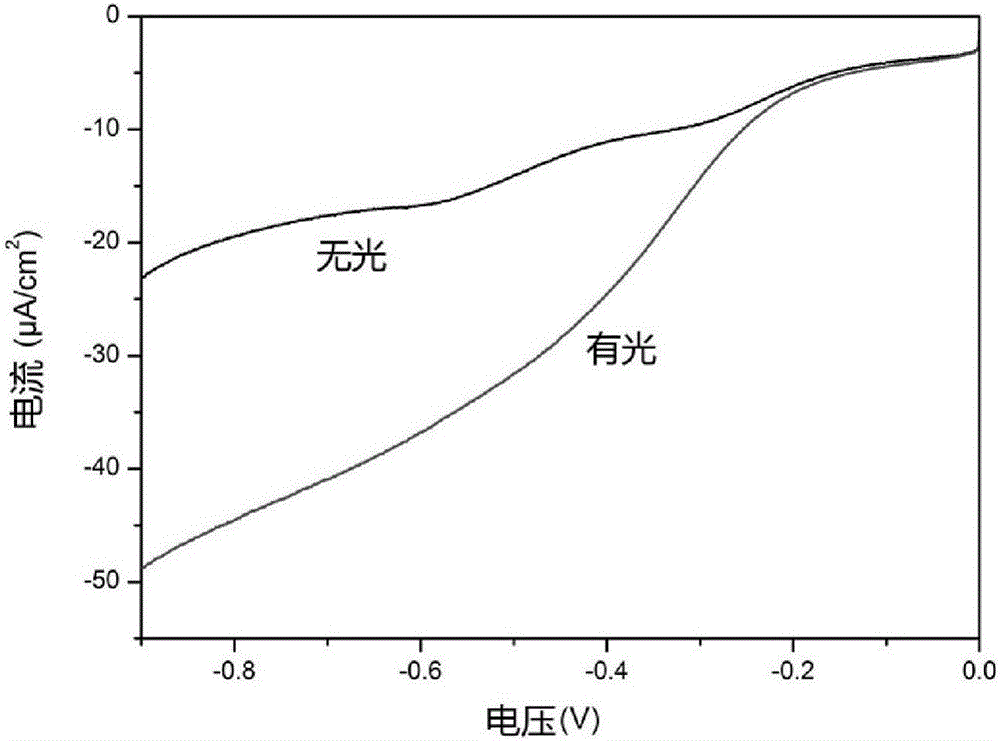
Zirconium organic frame material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106589398AStable structureImprove performanceHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionClean energyTerephthalic acid
The invention discloses a novel functionalized UiO-66 system zirconium organic frame catalyst material, a preparation method thereof and application of the catalyst material in the aspect of hydrogen generation through visible light catalytic water splitting. The preparation method of the zirconium organic frame catalyst material comprises the steps of 1 preparing a ligand 2,5-dimethyl sulfide terephthalic acid and 2 preparing a zirconium organic frame catalyst material (UiO-66(Zr)-(SCH3)2). The preparation method is simple and stable; the obtained zirconium organic frame catalyst material is stable in structure, can be used for the photoelectrode material for hydrogen generation through photoelectrochemical water splitting, and the performance is better than that of reported metal organic frame materials for hydrogen generation through photoelectrochemical water splitting. The material can be used for visible light catalytic hydrogen production, is excellent in performance and promotes application in clean energy and environment sustainable development.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
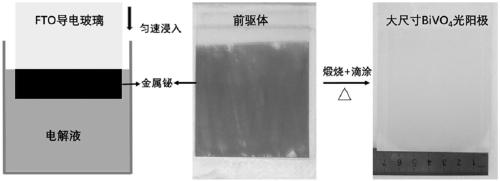
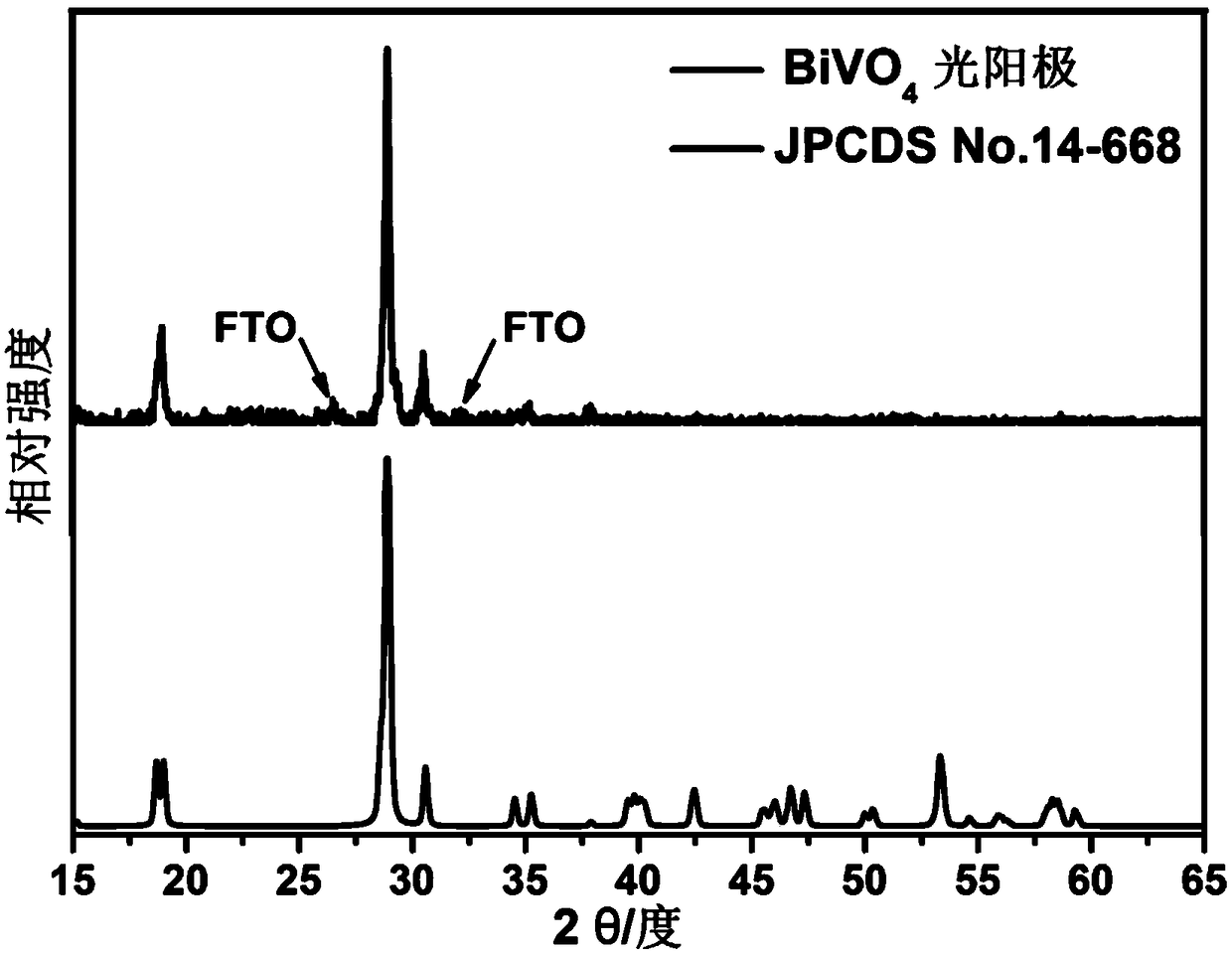
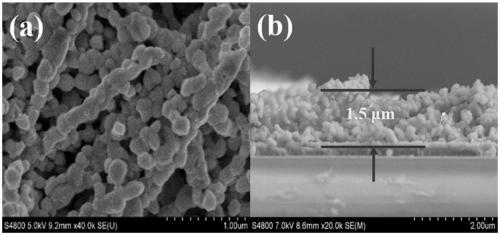
Large-size nano-porous BiVO4 photo-anode as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109440130AEasy to prepareMild reaction conditionsEnergy inputElectrode shape/formsCapacitanceNew energy
The invention belongs to the technical fields of new energy and photoelectrochemistry, and specifically discloses a large-size nano-porous BiVO4 photo-anode as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. FTO conductive glass is taken as a substrate, bismuth nitrate is taken as a bismuth source, the FTO glass is immerged into a bismuth nitrate electrolyte at a certain speed, bismuth metal layer deposition and calcining are carried out to obtain bismuth oxide, then the surface of bismuth oxide is coated with DMSO solution containing vanadium(IV)oxy acetylacetonate (VO(acac)2) in a dripping manner, and finally calcining is carried out to obtain the photo-anode. The photo-anode prepared by the preparation method has the advantages of being simple in synthesis method, moderate in reaction conditions, pollution-free and the like, and good in prospect in the fields of photoinduction, capacitors, photoelectrocatalysis, photocatalysis and the like. Via experimental study, the photocurrent density of the nano-porous BiVO4 photo-anode in a photoelectrochemical test exceeds 1.4mA / cm<2>, the photon-to-electron conversion efficiency in a main light absorption area reaches 17%, and excellent stability is shown in the photoelectrochemical test.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for efficiently grinding and polishing GaN chips
InactiveCN106141900AHigh surface flatnessImprove polishing rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesHydrogen ion bindingHydrogen
The invention provides a method for efficiently grinding and polishing GaN chips, namely the photoelectrochemistry mechanical polishing method for efficiently grinding the GaN chips. The method includes the steps that under the effects of illumination and an external electric field, the to-be-polished surfaces of the GaN chips are oxidized to form gallium oxide, the gallium oxide and hydroxyl ions in a polishing solution are combined to form gallium hydroxide passivation layers, and the gallium oxide and hydrogen ions in the polishing solution are combined to form gallium ions; and under the protection of the gallium hydroxide passivation layers and the polishing solution rich in gallium ion, illumination and oxidation on concave parts of the to-be-polished surfaces are effectively restrained, high convex parts of the to-be-polished surfaces are mechanically removed, and new GaN surfaces are exposed and continue to be selectively removed through illumination and oxidation. The illumination intensity, voltage values and pressure applied to an upper tray are regulated and controlled, the oxidation speed of the to-be-polished surfaces of the chips is matched with the mechanical removing speed, and therefore the surface flatness and polishing efficiency of the GaN chips are improved, and high-quality polished GaN chips are obtained.
Owner:SINO NITRIDE SEMICON
Photoelectrochemical biofuel cell based on quantum dot, titanium dioxide and enzyme, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102231449AImprove output performanceEasy transferLight-sensitive devicesCell electrodesPlatinumFuel cells
The invention provides a photoelectrochemical biofuel cell based on quantum dot, titanium dioxide and enzyme, and a preparation method thereof. The photoelectrochemical biofuel cell comprises the following parts: an anode chamber containing an anode, a cathode chamber containing a cathode, a membrane material to separate the anode chamber and the cathode chamber, and an outer circuit. The anode and the cathode are formed by loading modifiers on basic materials; and the enzyme is immobilized on a quantum dot / titanium dioxide composite layer, and the quantum dot and titanium dioxide are connected through a coupling agent. The invention has following characteristics of high output performance, high utilization efficiency of incident light, cheap and easily available raw materials. In addition, nano platinum is employed as a catalyst to realize a maximum surface area and a maximum catalysis efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fluoropolymer film
Owner:SOLVAY SA +1
Optical anode used for hydrogen production by photoelectrochemistry decomposition water and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101575713AImprove photocatalytic activityImprove electrocatalytic activityCellsSemiconductor devicesIron saltsNickel salt
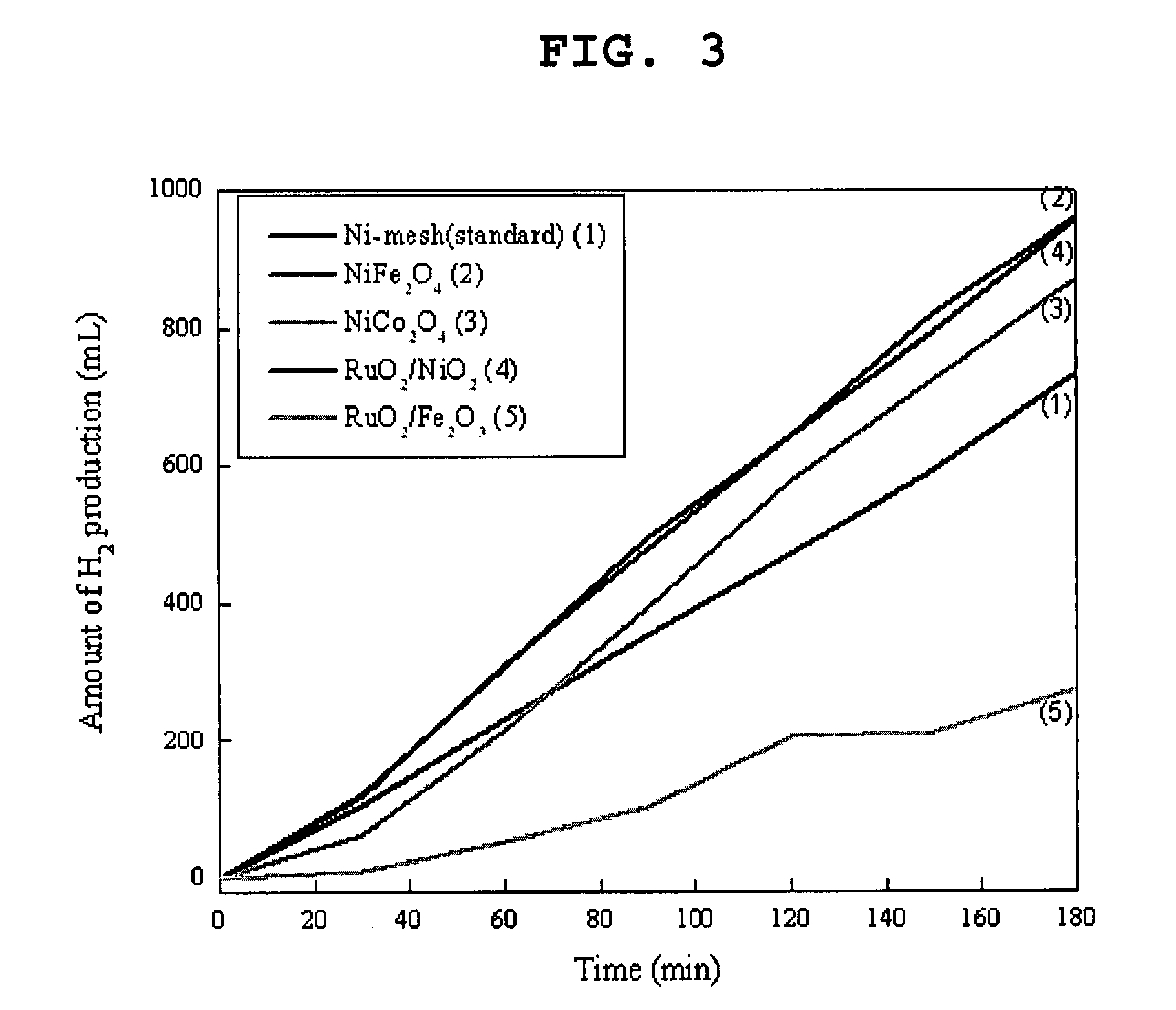
The invention provides an optical anode used for hydrogen production by photoelectrochemistry decomposition water and a preparation method thereof. The optical anode comprises: conductive glass (1); a sputtering layer (2) which is arranged on the conductive glass (1) and has bulges (3); and a Ni-Fe oxide film (4) arranged on the sputtering layer (2). The preparation method comprises the following steps: (a) sputtering coating the conductive glass (1), then sticking the silk screen onto the sputtering layer (2) and continuing for sputtering coating; and (b) immersing the conductive glass processed in step (a) into a dipping solution which contains nickel salt and iron salt for dip coating, then drying and heat processing the conductive glass. The optical anode prepared in the invention has higher photocatalytic activity and electrocatalytic activity, can save energy and improve the opto-electrical transformation efficiency of hydrogen production by photoelectrochemistry decomposition water.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
Photoelectrochemical sensor, and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN106501336APhotoresponse dropHigh photocurrent responseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectron injectionEngineering
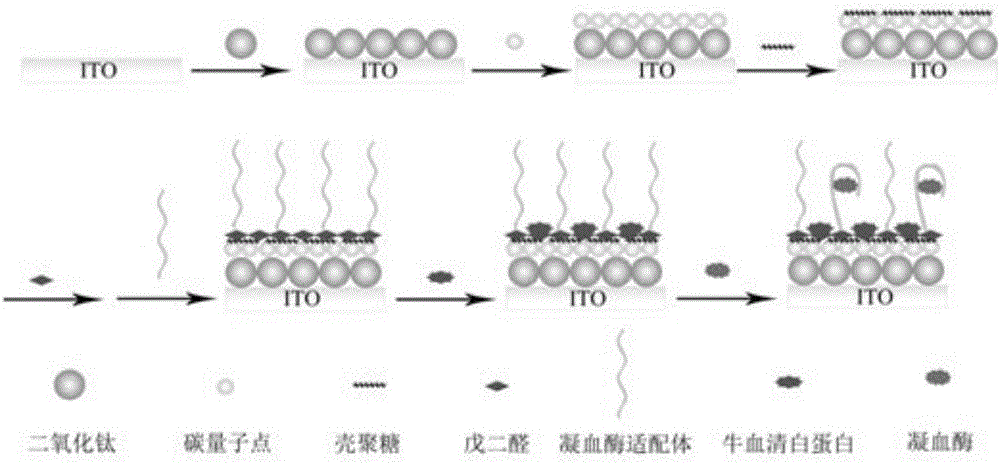
The invention relates to a photoelectrochemical sensor, and preparation and application thereof. A preparation method for the photoelectrochemical sensor comprises the following steps: S1, pretreating ITO electro-conductive glass; S2, adding TiO2 nanoparticles onto the ITO electro-conductive glass drop by drop to prepare an ITO / TiO2 electrode; S3, soaking the electrode in a carbon quantum dot solution for 10 h so as to obtain an ITO / TiO2 / CODs electrode; S4, adding chitosan onto the electrode drop by drop so as to obtain an ITO / TiO2 / CODs / CS electrode; S5, adding a glutaraldehyde solution onto the electrode drop by drop; and S6, dropwise adding thrombin aptamer drops, carrying out a reaction at 4 DEG C under a wet condition for 10 to 15 h, continuing adding bovine serum albumin onto the electrode drop by drop after leaching and blow-drying, and carrying out leaching and blow-drying again. The prepared photoelectrochemical sensor can be used for detection of thrombin. According to the invention, the carbon quantum dots with a wide visible light absorption range, good luminosity and high-efficiency electron injection capability are used as a photosensitizer for titanium dioxide, so the obtained composite structure has good response to photoelectric current under visible light. The prepared photoelectrochemical sensor has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, environment friendliness, high sensitivity and good selectivity.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Preparation method of aptamer photoelectrochemical sensor for high-sensitivity high-selectivity detection of MC-LR
InactiveCN104897746AHigh sensitivityHighly selective detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerNanoparticle
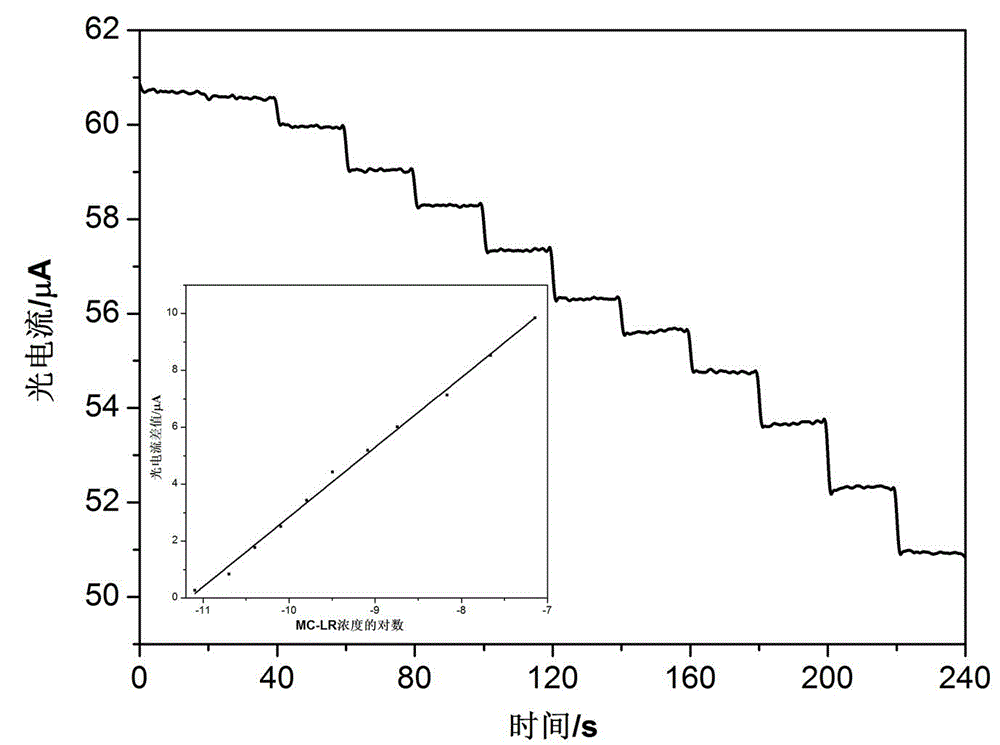
The invention relates to a preparation method of an aptamer photoelectrochemical sensor for high-sensitivity high-selectivity detection of MC-LR. The preparation method comprises preparing titanium dioxide nanotubes on a titanium matrix by an anodization method, carrying out modification with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, functionally assembling chitosan and glutaraldehyde to the surface of an electrode so that a photoelectric biological interface is built, and bonding a MC-LR aptamer with a specific base sequence to the surface of the base electrode by chemical bonding so that the MC-LR aptamer photoelectrochemical sensor is prepared. Through combination of a supersensitive photoelectric analysis technology and an aptamer technology with a MC-LR specific recognition function, the preparation method realizes high-sensitivity high-selectivity analysis detection of MC-LR, and has the MC-LR detection limit of 5.3*10<-12> mol / L and a linear detection range of 7.2*10<-8> to 8*10<-12> mol / L. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages of simple processes, fast response and low cost and can realize high-sensitivity high-selectivity analysis of MC-LR.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Phenazine oxazines dye and application of the same in dye sensitization of solar battery
InactiveCN101294004ASave raw materialsEasy to synthesizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron donorElectrical battery
The invention relates to a phenoxazine dye and a photoelectric converter using the dye, and belongs to the technology field of phenoxazine dyes. The technical proposal is that: the chemical structure of the dye contains substituted phenoxazine and the derivative thereof as electron donors and different conjugated groups as bridging chains, wherein one end of the bridging chains are connected with different electron-withdrawing groups. An electron-donating group on a nitrogen atom and lone-pair electrons on an oxygen atom interact with a chromophoric conjugated system, thereby resulting in more easier charge transfer of the excited state of molecules and generating unique photoelectric property. The phenoxazine dye has good application performance in dye-sensitized solar cells, and can replace expensive noble metal photosensitive dye in dye-sensitized solar cells.
Owner:ZHONGKE ENTERPRISE DEV NINGDE
Method and device for carrying out potential change detection through using photoelectrochemical method
ActiveCN110470722AHigh sensitivityImprove general performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesAuxiliary electrodePhysics
The invention relates to an electrochemical analysis technology, in particular to a method and device for carrying out potential change detection by utilizing a photoelectrochemical method. An electrode modified with a photosensitive material serves as a working electrode, an ion selective electrode serves as a reference electrode, and pt serves as an auxiliary electrode; the potential of the working electrode is adjusted through the potential of the reference electrode; and the quantitative / qualitative measurement of ions to be detected is realized according to current change outputted by theworking electrode before and after illumination. According to the method disclosed by the invention, with current adopted as output signals, the potential change of the ion selective electrode is measured through the photoelectrochemical method, and therefore, the method is different from a classical potential method. According to the method of the invention, the current method is utilized, ion activity detection can reach a pA level, and therefore, sensitivity is greatly improved.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com