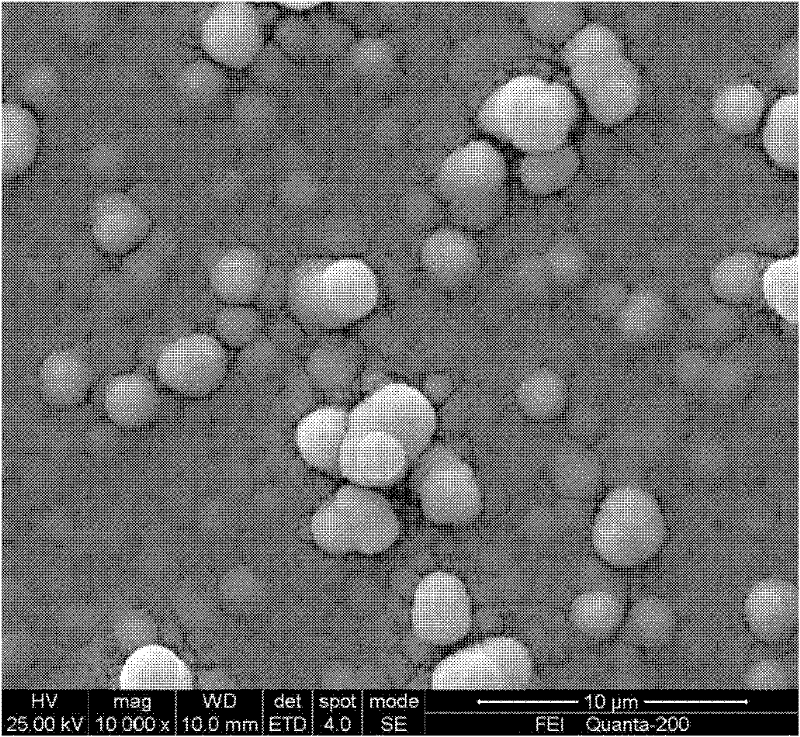
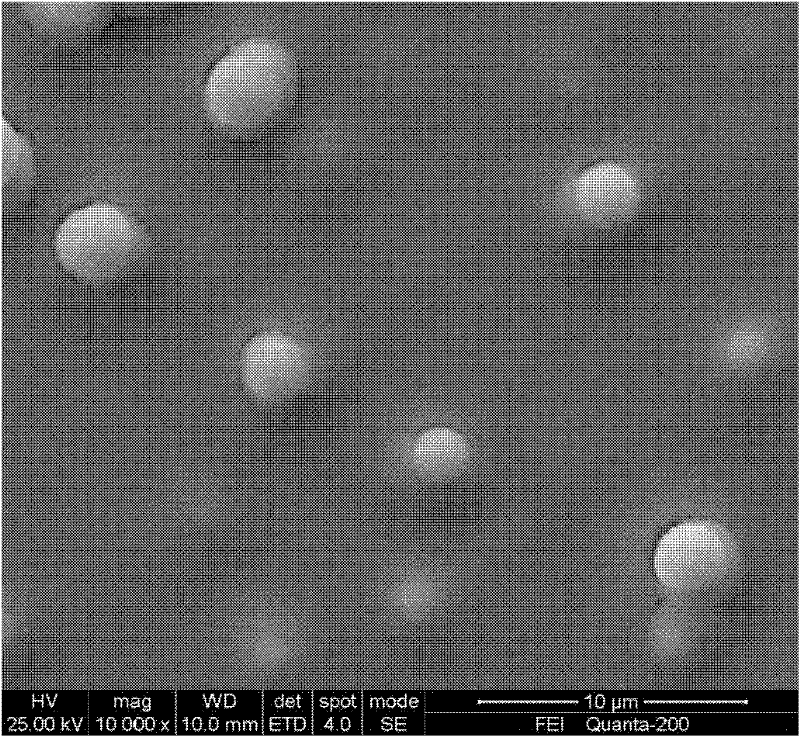
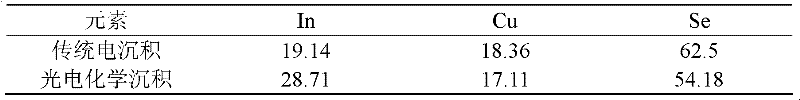
Preparation of Copper Indium Gallium Selenium Thin Films by Photoelectrochemical Deposition
A photoelectrochemical, copper indium gallium selenide technology, applied in the field of solar cell preparation, can solve the problems of poor morphology, difficult indium and gallium deposition, slow film growth rate, etc., achieves low cost, easy large-area deposition, and overcomes the growth rate slow effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] First, when the solute composition is 0.30mol / L H 2 SeO 3 , in the 500ml aqueous solution of 1mol / L Potassium chloride, adjust pH to 0.3 with dilute hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide; Adopt photoelectric cell, with stainless steel substrate as working electrode, large-area Pt net is counter electrode, saturated calomel electrode ( SCE) is the reference electrode; the following photoelectrochemical deposition parameters are adopted: the incident light is a monochromatic light source of 250 nm (the light intensity is 0.1 mW cm -2 ), the working electrode potential was 0.5V (vsSCE), the electrolyte temperature was 80°C, and the deposition time was 10 minutes. A thin film containing selenium with a thickness of 1-1.5 microns is pre-deposited on the cathode substrate. Then, when the solute composition is 0.15mol / L Cu(NO 3 ) 2 , 0.30mol / L InCl 3 , 0.5mol / L GaCl 3 , in 500ml aqueous solution of 1mol / L trisodium citrate, adjust the pH to 0.9 with dilute hydrochloric a...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The solute composition is 0.003mol / L CuCl 2 , 0.01mol / L InCl 3 , 0.001mol / L SeO 2 , 0.1mol / L lithium chloride, 0.2mol / L trisodium citrate in 500ml aqueous solution, adjust the pH to 1.8 with dilute hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide; use a photoelectric cell, with FTO glass substrate as the working electrode, large area The graphite sheet was used as the counter electrode, and the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was used as the reference electrode; the following photoelectrochemical deposition parameters were used: the incident light was a 500W xenon lamp light source (the light intensity was 10000mW cm -2 ) xenon lamp light source, working electrode potential -0.6V (vs SCE); deposit CuIn containing copper, indium and selenium with a thickness of 0.1 to 2 microns on the cathode substrate 1~2 Se 1~4 Thin films; the electrolyte temperature was 20°C, and the deposition time was 40 minutes. After testing, the obtained CuIn 1~2 Se 1~4 Film band gap E g =1.0eV, th...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The trisodium citrate in Example 2 is replaced by potassium cyanide or potassium pyrophosphate or nitrilotriacetic acid, the deposition potential is adjusted to 1.5V (vs SCE), and other conditions remain unchanged, finally CuIn with better morphology can be obtained 1~2 Se 1~4 Semiconductor thin film materials. After testing, the obtained CuIn 1~2 Se 1~4 Film band gap E g =1.1eV, the absorption coefficient is 10 5 cm -1 , the resistivity is 7.0Ωcm, and the carrier concentration is 7.9×10 18 cm -3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bandgap width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Absorption coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com