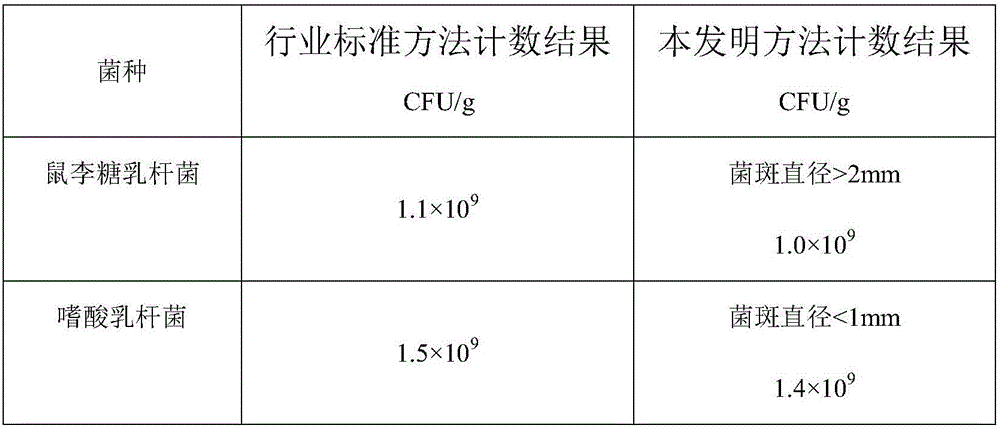
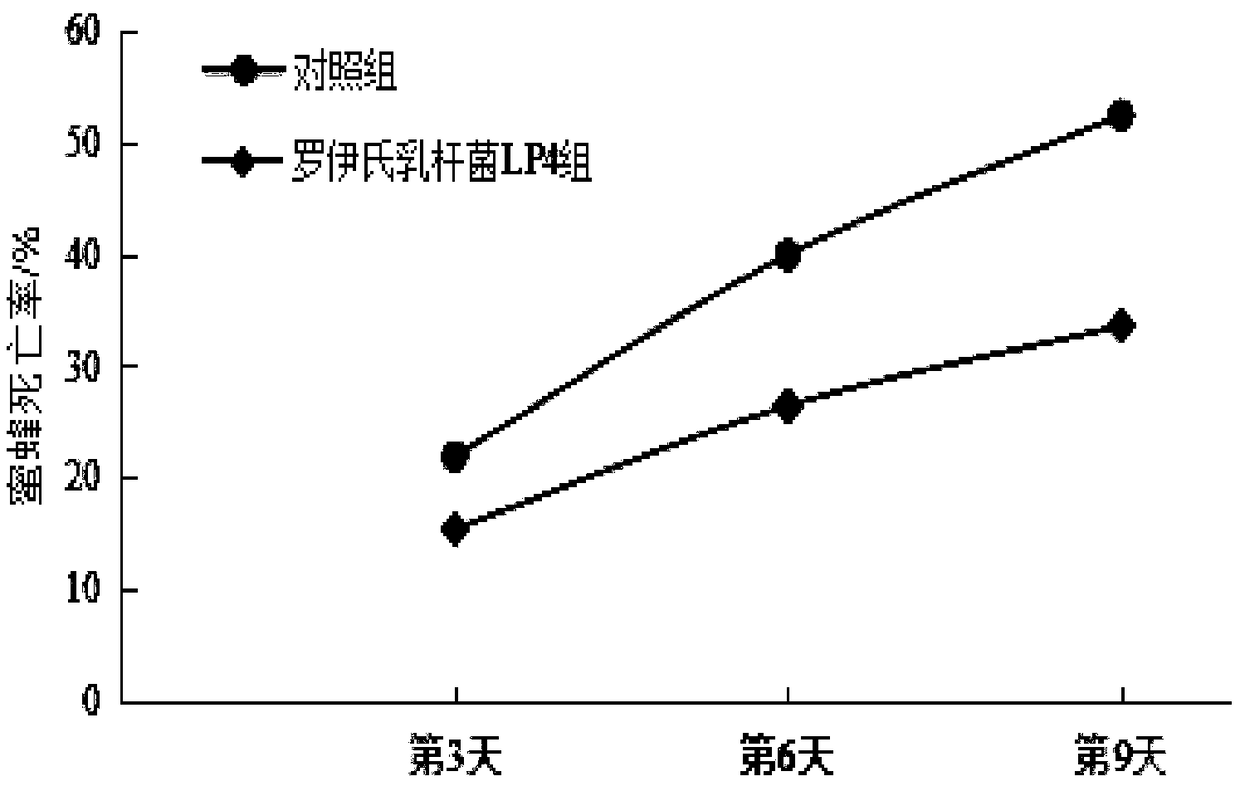
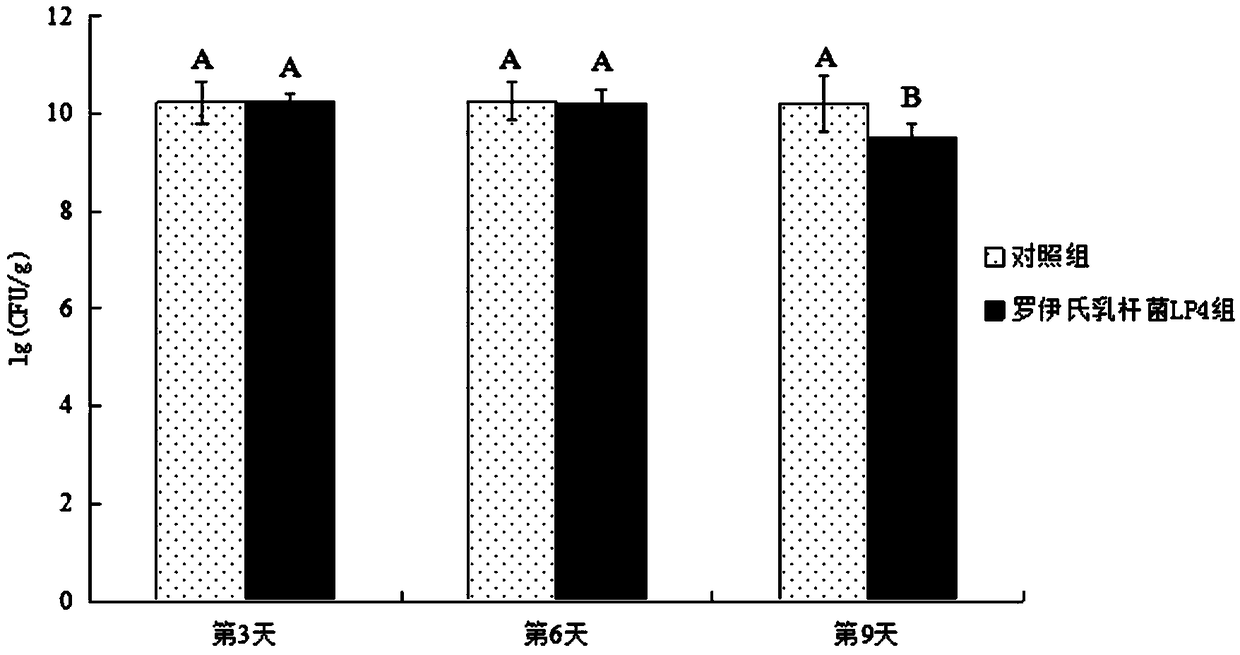
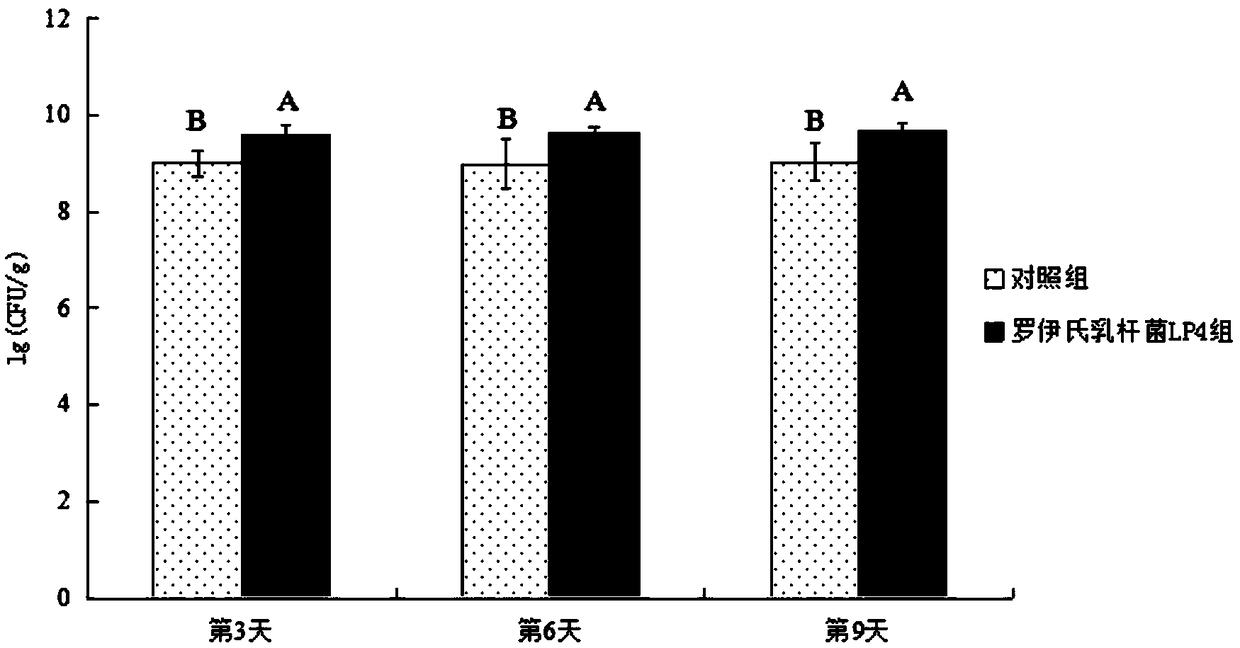
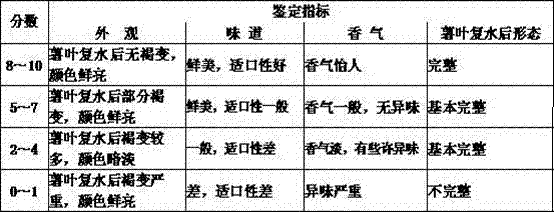
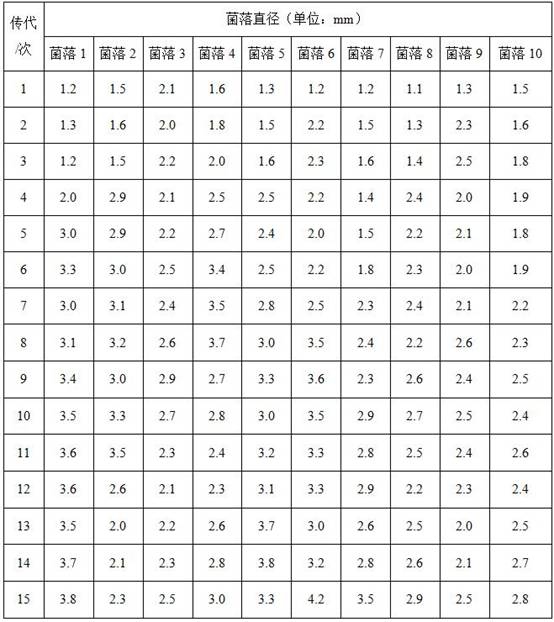
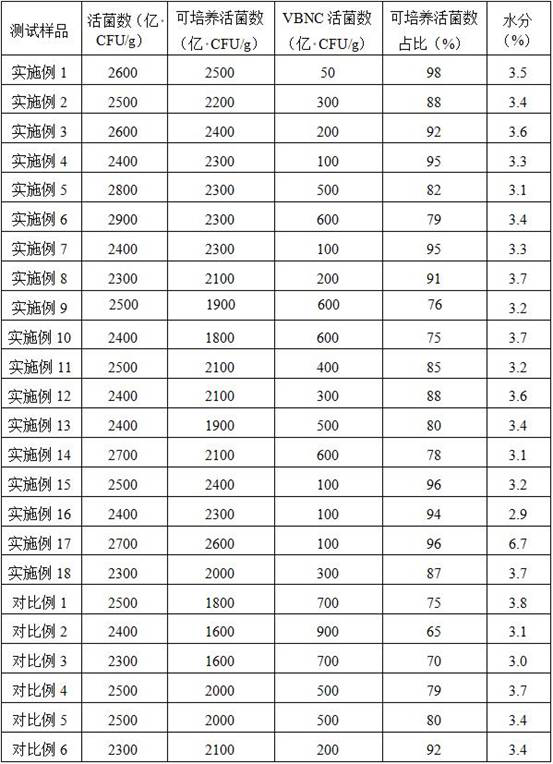
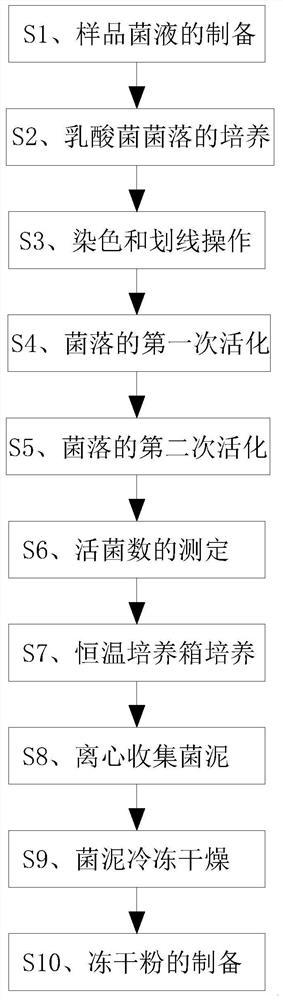
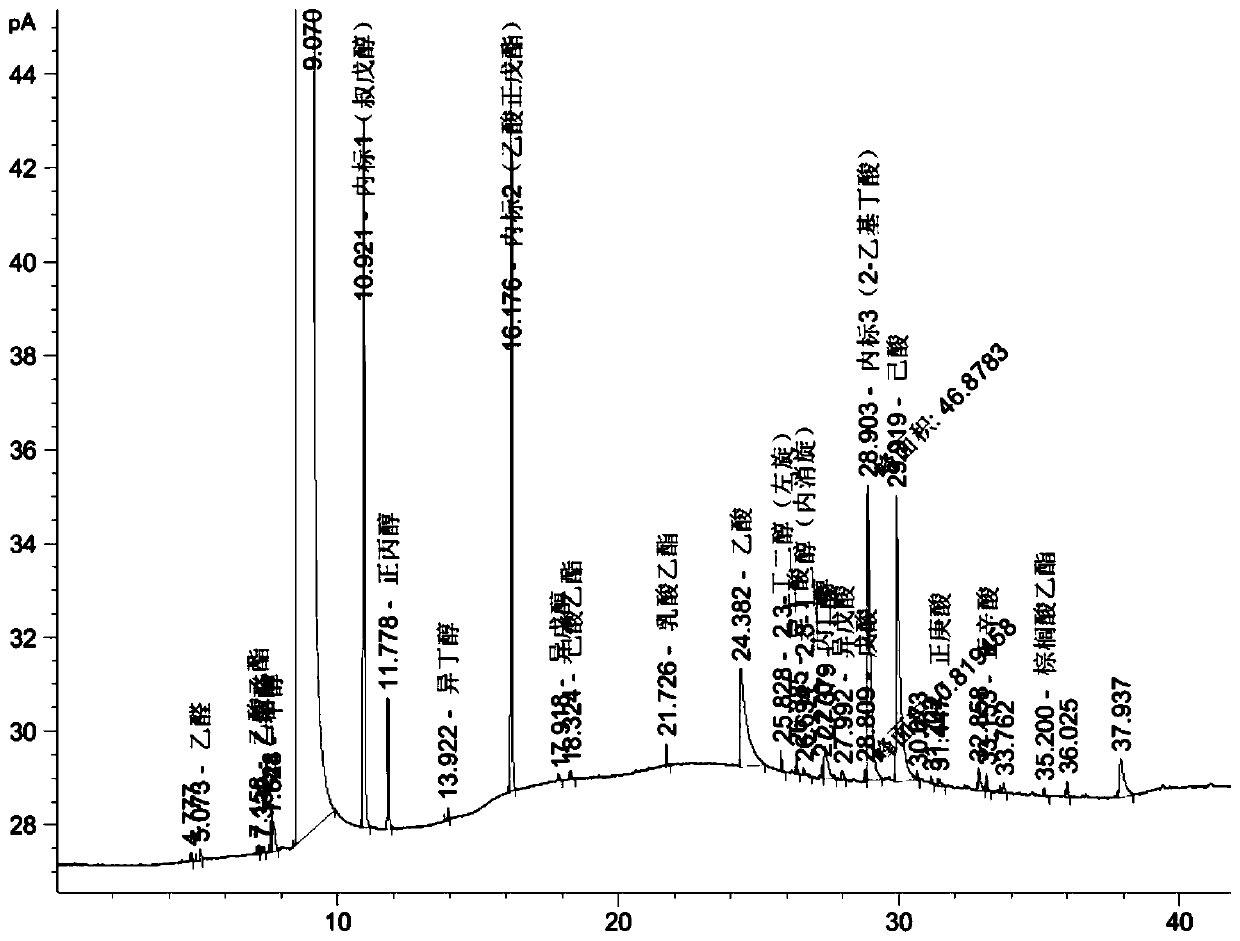
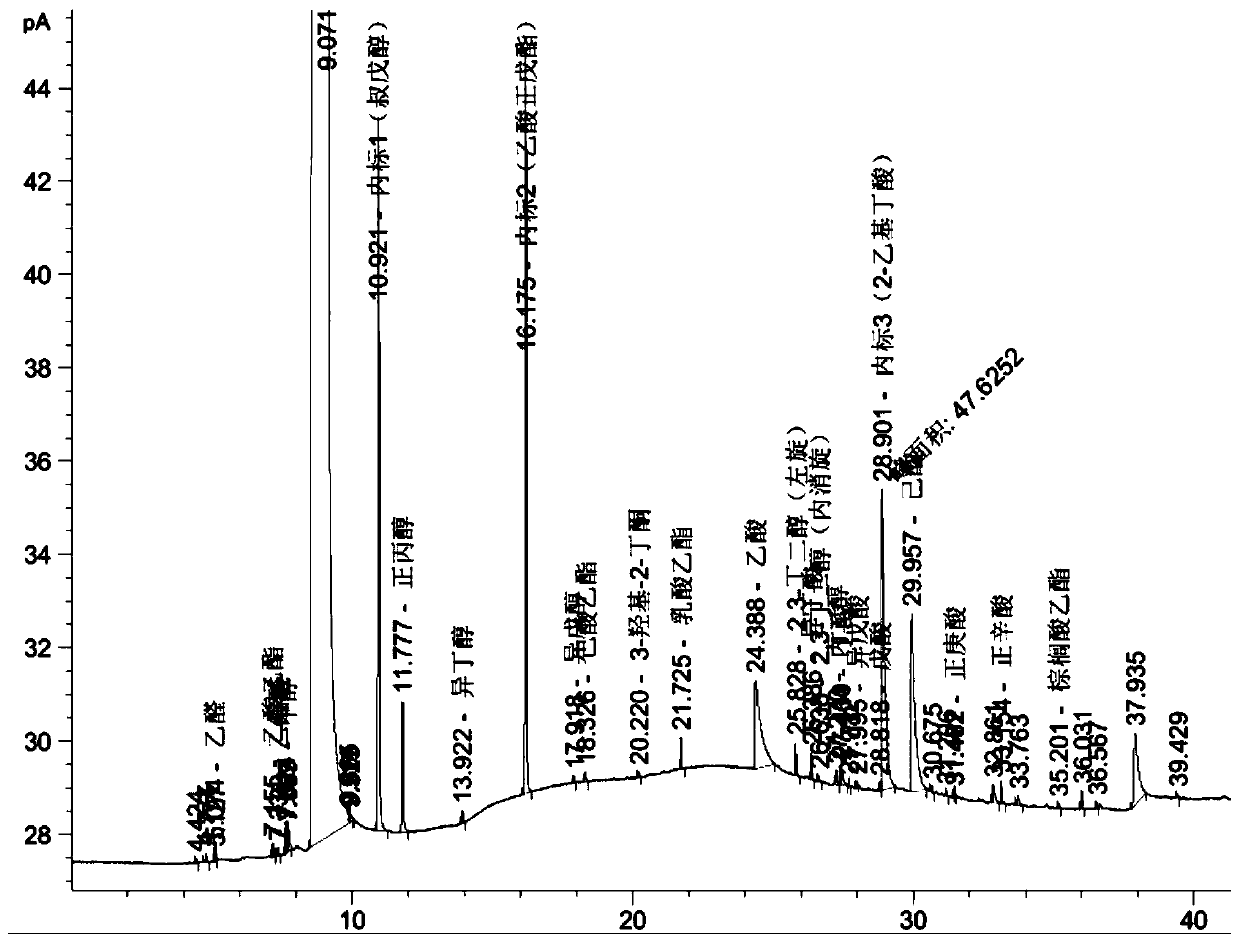
Patents
Literature
37 results about "MRS agar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
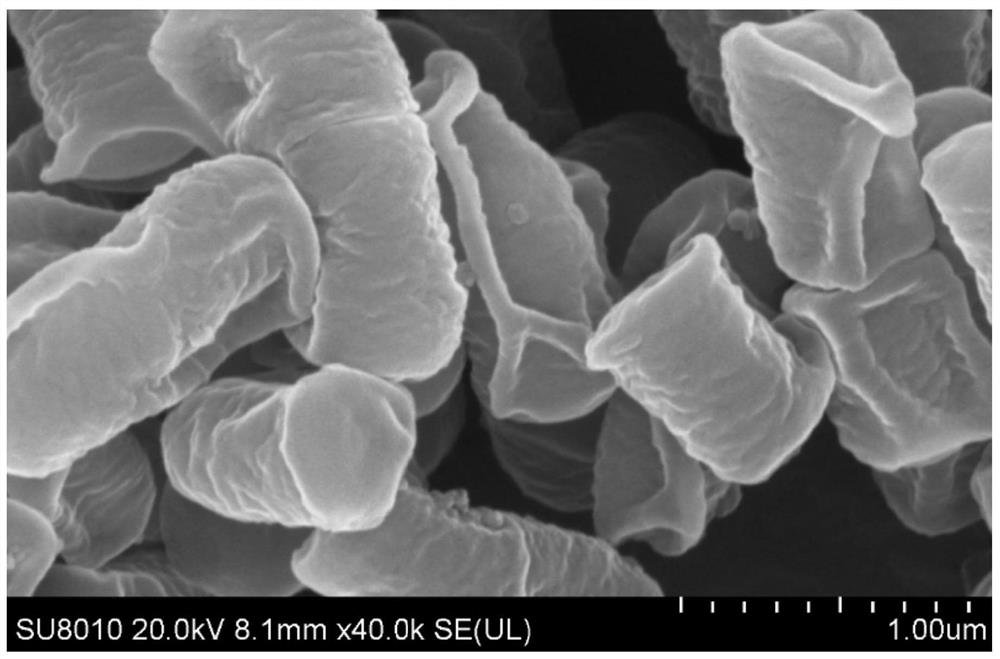
De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar, often abbreviated to MRS, is a selective culture medium designed to favour the luxuriant growth of Lactobacilli for lab study. Developed in 1960, this medium was named for its inventors. It contains sodium acetate, which suppresses the growth of many competing bacteria (although some other Lactobacillales, like Leuconostoc and Pediococcus, may grow). This medium has a clear brown colour.
Enterococcus faecium for feeding and applications thereof
InactiveCN102304483AConducive to preservationLong storage timePowder deliveryBacteriaFreeze-dryingAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to enterococcus faecium for feeding as well as a freeze-drying fungicide and applications thereof, and discloses enterococcus faecium LAB12 CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4847 which is grampositive cocci, has no spores, grows well on an MRS agar plate, forms a round bacterial colony with the diameter of 0.5-1mm within 48 hours and is used for feeding, and the bacterial colony is round, smooth and upheaved, and is a shape of grey white dewdrop; the enterococcus faecium grows in a facultative anaerobic condition; the growth temperature range is 10 DEG C-45 DEG C; the optimum growth temperature is 30 DEG C-40 DEG C; and the growth pH value is 4-10, and the optimum pH value is 6.0. The freeze-drying fungicide formed by the bacterial strain is nontoxic and harmless, is gastric juice resistant, is cholate resistant, has a high inhibitory effect for multiple harmful bacteria, has a long quality guarantee period, can be widely applied to birds and livestock breeding to strengthen the animal disease-resistant capability, and is expected to be the substitution of antibiotics for feeding.
Owner:北京金泰得生物科技股份有限公司
A Strain of Enterococcus Faecalis for Feed and Its Application
InactiveCN102277325AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove the living environmentAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseOptimal growth
The invention discloses an Enterococcus faecalis strain SBD, of which the collection number is CGMCC No.4848. The strain is a Gram positive strain and is spherical according to observation with microscope, and the strain does not form spores; the strain can well grow on a Mann, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) agar plate and can grow into a round, smooth and raised bacterial colony like a grey white dew and with a diameter of 0.5 to 1 millimeter within 48 hours; and the strain can grow in a facultatively anaerobic environment, the growth temperature range is from 10 to 50 DEG C, the optimal growth temperature is 30 to 40 DEG C, and the growth pH value range is from 4 to 10 and the optimal pH value is 6.5. The bacterial preparation made by the strain is nontoxic and safe, can resist gastric juice and cholate, has a strong inhibition effect on various harmful bacteria and can be widely used in livestock breeding industry (by directly adding into daily ration or drinking water of animals) to increase the disease resistance in animals; and the preparation is expected to replace antibiotic for feed purpose and can obviously improve average weight of weaned piglets, reduce a feed-to-meat ratio and improve living environment of livestock and therefore has a bright prospect.
Owner:北京金泰得生物科技股份有限公司
Lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of Sichuan sausages by fermentation
ActiveCN108587983AAdd flavorImprove securityBacteriaClimate change adaptationFood flavorFermentation starter
The invention relates to fermentation of microorganisms and meat food and specifically discloses lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in preparation of Sichuan sausages by fermentation. Theprovided lactobacillus plantarum 1-1 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is CGMCC NO. 15467, and the preservation date is March 20th, 2018. The strain is isolated from traditional sausages of Qingcheng Mountain in Dujiangyan City, Sichuan Province, grows well on an MRS agar culture medium, meets the requirements of meat fermenting agents due to main fermentation characteristics and is suitable for meat fermentation. The lactobacillus plantarum has the capability of degrading sarcoplasmic protein and biogenic amines in an in vitro simulation system, is used in production of the Sichuan sausages, can promote degradation of sarcoplasmic protein of the Sichuan sausages and significantly reduce the content of biogenic amines in the Sichuan sausages and have the potential to be used in actual production of the Sichuan sausages, so that it is ensured that the flavor, taste and safety of the Sichuan sausages are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Lactobacillus plantarum with abilities of reducing cholesterol and promoting intestinal short chain fatty acid generation ability and application of lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN108728382AImprove adhesionPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses lactobacillus plantarum N-1 with abilities of reducing cholesterol and promoting intestinal short chain fattyacid generation ability and application of the lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum N-1 was deposited in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center UNDER the accession number of CGMCC NO. 15463 with a deposit date of 20 Mar. 2018. The strain is separated from a traditional yak milk cheese product of Kalong Village, Mula Township, Daocheng County, Garze Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province, grows well on an MRS agar medium, has certain tolerance capacity on acid and bile salt, has high adhesion ability to human colon cancer cells Caco-2, has high cholesterol reducing ability, can remarkably improve generation of intestinal short chain fatty acids, is applied to the field of functional food, not only has actual production value, but also has quiteimportant significance on health of human bodies.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Caries resistant lactobacillus plantarum K41 and application thereof
ActiveCN108486022APromote growthEnhanced inhibitory effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a strain of caries resistant lactobacillus plantarum K41 and application thereof. Lactobacillus plantarum K41 provided by the invention is preserved in Common Microorganism Center of Chinese Microorganism Strain Preservation Management Committee, with preservation number of CGMCC No.15462, and preservation date of March 20, 2018. The strain is separated from farmyard self-made pickles in Yanan Road, Shunqing District, Nanchong, Sichuan, grows well on an MRS agar culture medium, can inhibit growth of streptococcus mutans UA159, forming of exopolysaccharide, degradation of hydroxyapatite, and forming of a biological film, has good auto-agglutination and copolymerization capability, is good in tolerance for antibiotics, salt and acid, and is easy to be planted in the oral cavity. Animal experiment shows that K41 can inhibit rat enamel demineralization and caries degree, can be applied to functional food, and has very important meaning for body health.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
ActiveCN101701201AReduce manufacturing costSave energyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationTyrosine
The invention relates to an enterococcus faecalis with the collection number of CGMCC No.3164. A bacterial colony is cultured on an MRS agar culture medium at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 24 hours to be gathered; the bacterial colony is white, thallus is ovate, extends along chain direction, is in pair or in short chain, is Gram-negative, generates lactic acid when fermenting glucose and is elliptic under a common microscope. When being applied, the bacterial colony is inoculated into a test tube filled with culture medium A to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for 24 hours; after being repeatedly activated five times, the bacteria solution is inoculated into a culture medium B to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for four days; the cultivated bacteria solution is decentralized at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes; and supernate is extracted to obtain high concentration tyramine solution. The culture medium A is an MRS liquid culture medium of 0.1% of tyrosine, and the culture medium B is an MRS liquid culture medium of 0.005% of pyridoxal phosphate and 0.1% of tyrosine.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
ActiveCN101701202AReduce manufacturing costSave energyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationTyrosine
The invention relates to an enterococcus faecalis with the collection number of CGMCC No.3165. A bacterial colony is cultured on an MRS agar culture medium at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 24 hours to be gathered; the bacterial colony is white, oval, is in short chain and Gram-negative, generates acid when fermenting glucose and is elliptic under a common microscope. When being applied, the bacterial colony is selected from a slope to be inoculated into a test tube filled with culture medium A to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for 24 hours; after being repeatedly activated five times, the finally activated bacteria solution is inoculated into a culture medium B to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for four days; inoculation amount is 106cfu / ml; cultured bacteria solution is decentralized at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes; and supernate is extracted to obtain high concentration tyramine solution. The culture medium A is an MRS liquid culture medium added with 0.1% of tyrosine, and the culture medium B is an MRS liquid culture medium added with 0.005% of pyridoxal phosphate and 0.1% of tyrosine.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compound micro-ecological preparation and application thereof to honey breeding process
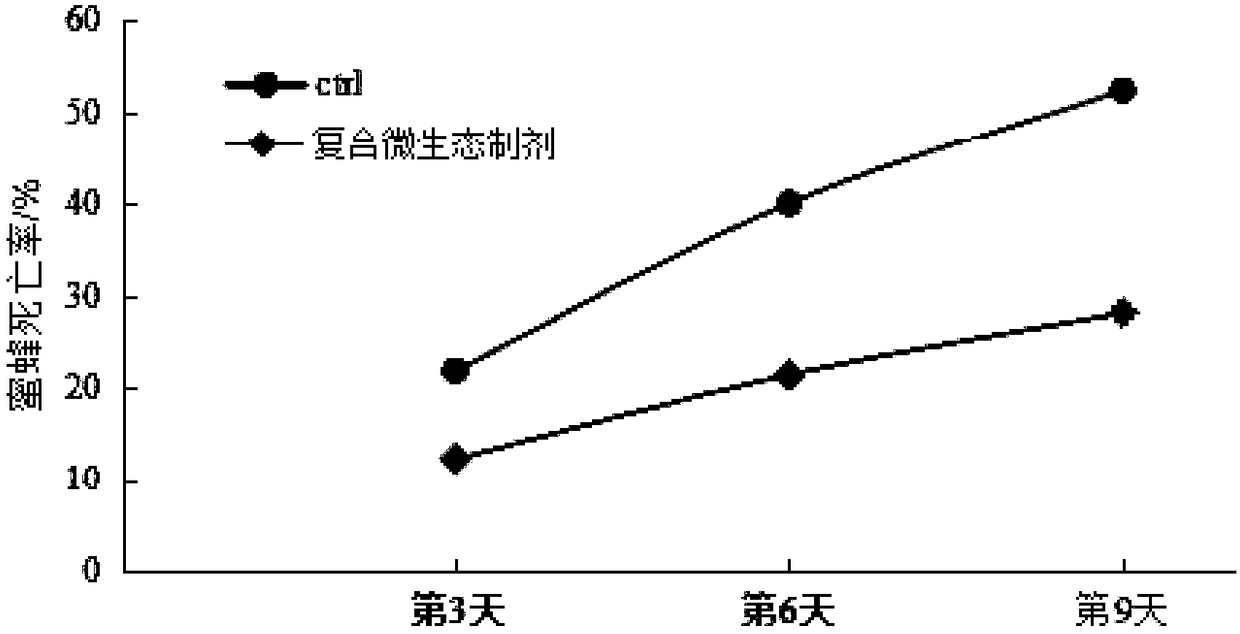
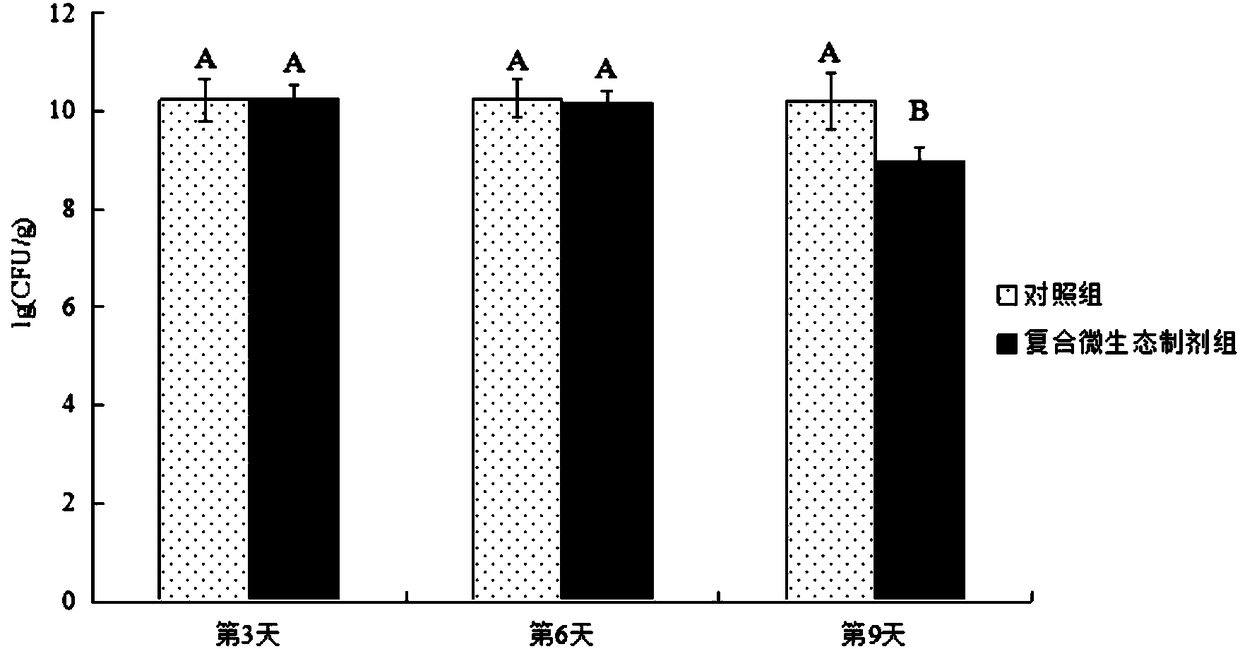
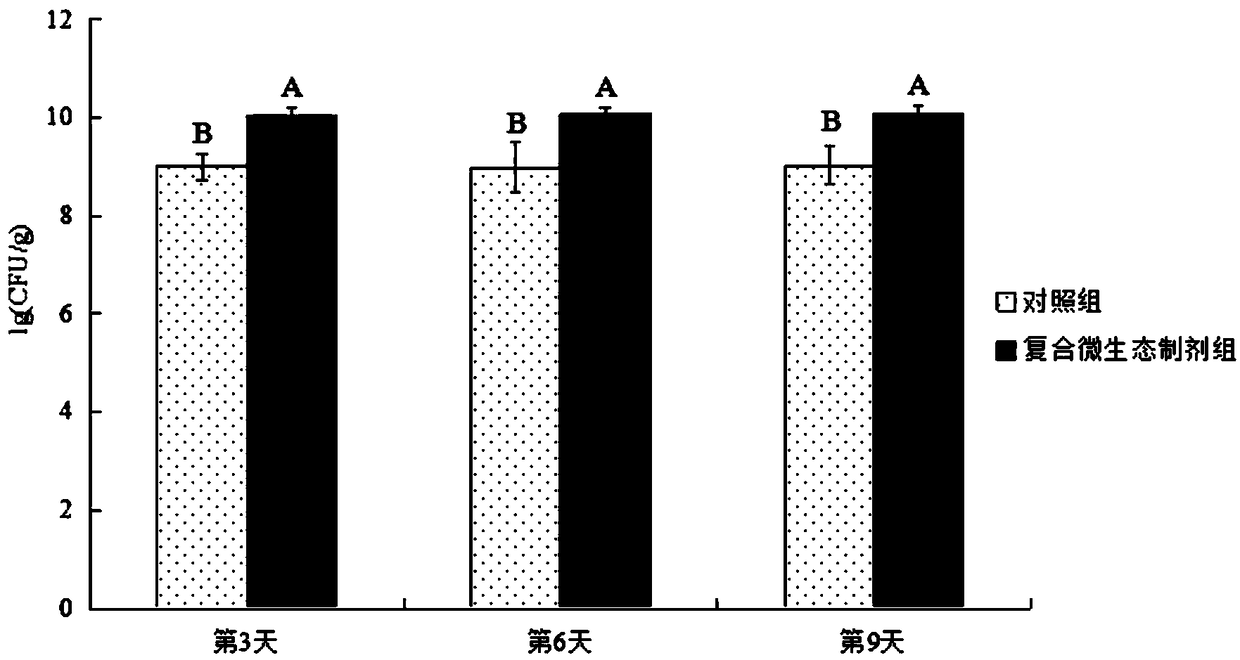
ActiveCN109055268AImprove survival rateImprove micro-ecological structureBacteriaLactobacillusAntibiotic YObserved Survival
The invention provides a compound micro-ecological preparation and application thereof to a honey breeding process. The compound micro-ecological preparation is prepared from two types of lactic acidbacteria including lactobacillus reuteri and lactobacillus helveticus. After the two strains are cultured through an MRS agar culture medium, bacterial colonies have round shapes, are milky white andhave ordered edges, and surfaces of the bacterial colonies are smooth and convex and are not transparent; the strains have relatively good bacterium-inhibition activity and are sensitive to various antibiotics; the lactobacillus reuteri LP4 and the lactobacillus helveticus KM7 are mixed at an equal ratio to prepare the micro-ecological preparation and the micro-ecological preparation is added intosyrup for feeding honeybees, so that a bacterial colony micro-ecological structure in intestinal tracts of the honeybees can be improved, the intestinal tract immunity of the honeybees is enhanced and the survival rate of the honeybees is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enterococcus faecium producing bacteriocin and application thereof
ActiveCN105779346AImprove toleranceImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaFood preservationSynechococcusAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to an Enterococcus faecium strain producing bacteriocin. The strain was preserved as a name Enterococcus faecium R1 by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 20, 2016, with preservation number CGMCC No.12085. A source of the strain is farm traditional fermented soybean paste and is presented as a circular or elliptic white smooth nontransparent colony smaller than 1mm in an MRS agar culture medium; uniform turbid growth is presented in an MRS liquid culture medium; thalli are spherical under an electron microscope and are arranged in pairs or in a chain, and gram staining is positive. The strain provided by the invention is sensitive to antibiotics, does not contain virulence genes and is a safe strain. The bacteriocin produced by the strain is enterococcin P, is stable under acidic conditions, has a very good thermal stability and has a good bacteriostatic effect on common enteropathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Lactobacillus strain and applications thereof
ActiveCN107904185AImprove filtration stabilitySuitable for industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismFlavor
The invention provides a Lactobacillus strain and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, wherein the Lactobacillus is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, has the preservation number of CCTCC M 2017450, and has the Latin name of Lactobacillus spicheri IZ. According to the present invention, the colony of the Lactobacillus strain is characterized in that the colony is milk white and round on an MRS agar plate, slightly projects, is wet, has the neat edge, the diameter is 2+ / -1 mm, the cell is rod-like, the suitable growth temperature is 25-35 DEG C, and the strain is a facultative anaerobic strain; the Lactobacillus is used for preparing corn sour spicy, wherein the main flavor of the corn sour spicy can be retained while the miscellaneous bacteria can be significantly inhibited, such that the defective rate of the corn sour spicy can be reduced to 0%; and the Lactobacillus is used for the industrial production of corn sour spicy.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Lactobacillus plantarum 550 with constipation relieving and sleep aiding functions and application of lactobacillus plantarum 550
PendingCN113462591APromote growthIncrease acidityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderBiotechnologyIntestino-intestinal
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum 550 with constipation relieving and sleep aiding functions and application of lactobacillus plantarum 550, belonging to the technical field of biology. The lactobacillus plantarum 550 provided by the invention is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 21, 2007, wherein the accession number of the lactobacillus plantarum 550 is CCTCC No. M 207202. The lactobacillus plantarum 550 provided by the invention is applied to preparation of functional food and medicines for relieving constipation, or / and helping sleep, or / and reducing cholesterol, or / and inhibiting pathogenic bacteria, or / and degrading nitrite. The lactobacillus plantarum 550 grows well and quickly on an MRS agar culture medium, is high in acid production capacity, has good gastric acid and cholate tolerance, and can be colonized in intestinal tracts. The lactobacillus plantarum 550 has a good bowel relaxing effect, strong capability of producing gamma-aminobutyric acid, the effect of reducing cholesterol in vitro, a good inhibition effect on common pathogenic bacteria, capability of rapidly degrading nitrite and the good safety.
Owner:SICHUAN GAOFUJI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Optimized process method for improving stability of lactic acid bacteria cells
ActiveCN113073068AGood storage stabilityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactic acid bacteriumMicrobiology
The invention relates to the technical field of lactic acid bacteria, and provides an optimized process method for improving the cell stability of lactic acid bacteria, which comprises the following steps: S1, culturing strains on an improved MRS agar culture medium solid plate, and screening thallus; S2, culturing the thallus seeds obtained in the step S1, then performing fermentation culture, and performing heat stress treatment on the fermentation liquid in the logarithmic later stage of fermentation; S3, centrifuging the fermentation liquid obtained in S2, and collecting bacterial sludge; S4, uniformly mixing the bacterial sludge obtained in S3 with the fermentation supernatant to obtain an emulsion; S5, freeze-drying the emulsion obtained in S4, and collecting bacterial powder; S6, repeating the operations of S1 to S5 on the bacterial powder obtained in S5 for 20-25 times to obtain stable bacterial powder; and S7, continuously culturing, centrifuging, emulsifying and freeze-drying the stable bacterial powder obtained in S6 to obtain final bacterial powder. According to the technical scheme, the problems that in the prior art, the viable count of lactic acid bacteria in the storage process is reduced, and the stability is not high are solved.
Owner:河北一然生物科技股份有限公司
Culture medium for simultaneously counting lactobacillus rhamnosus and lactobacillus acidophilus and application of culture medium
ActiveCN107523605AReduce human resource costsImprove work efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSurface layerLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention provides a culture medium for simultaneously counting lactobacillus rhamnosus and lactobacillus acidophilus, and application of the culture medium. The culture medium is formed by improving MRS agar through lincomycin hydrochloride, and the culture medium formed by improving MRS agar through lincomycin hydrochloride is initiatively applied to simultaneous counting of lactobacillus rhamnosus and lactobacillus acidophilus. The invention further provides a method for simultaneously counting lactobacillus rhamnosus and lactobacillus acidophilus by utilizing the culture medium. The method comprises the following steps: firstly laying and solidifying the culture medium, so as to obtain a base layer, adding a to-be-tested mixed sample and the culture medium onto the base layer, and performing laying and solidifying, so as to obtain a middle layer; then adding the culture medium to the middle layer, and performing laying and solidifying, so as to obtain a surface layer, ensuring that the base layer, the middle layer and the surface layer form an interlayer flat plate, finally performing anaerobic cultivation on the interlayer flat plate, and counting lactobacillus rhamnosus and lactobacillus acidophilus separately. The method reduces the costs of experiment vessels, experiment reagents and human resources.
Owner:完美(广东)日用品有限公司 +1
Lactobacillus reuteri and application thereof in bee breeding process
ActiveCN109182164AImprove survival rateImprove immunityBacteriaLactobacillusIntestinal structureApis cerana
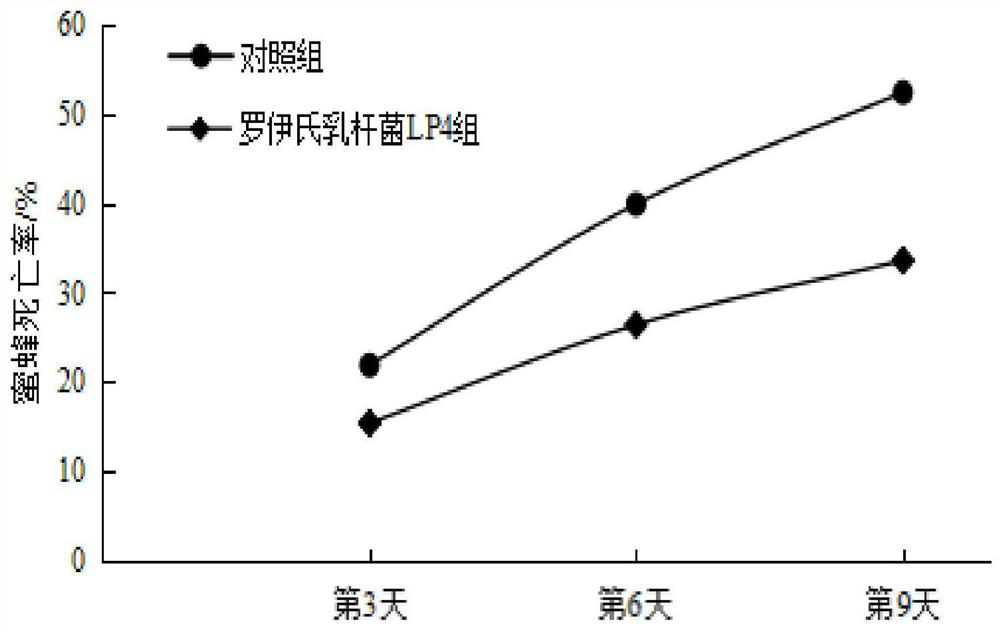
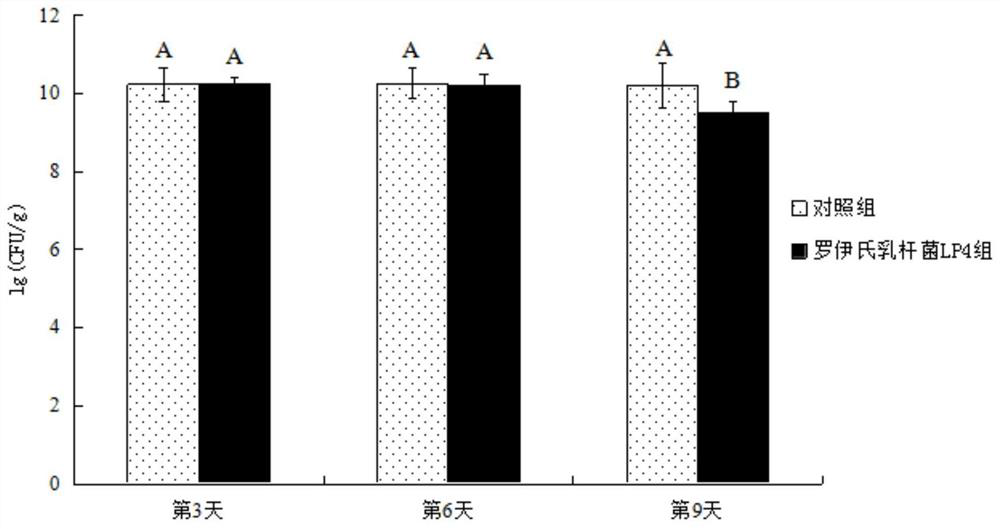
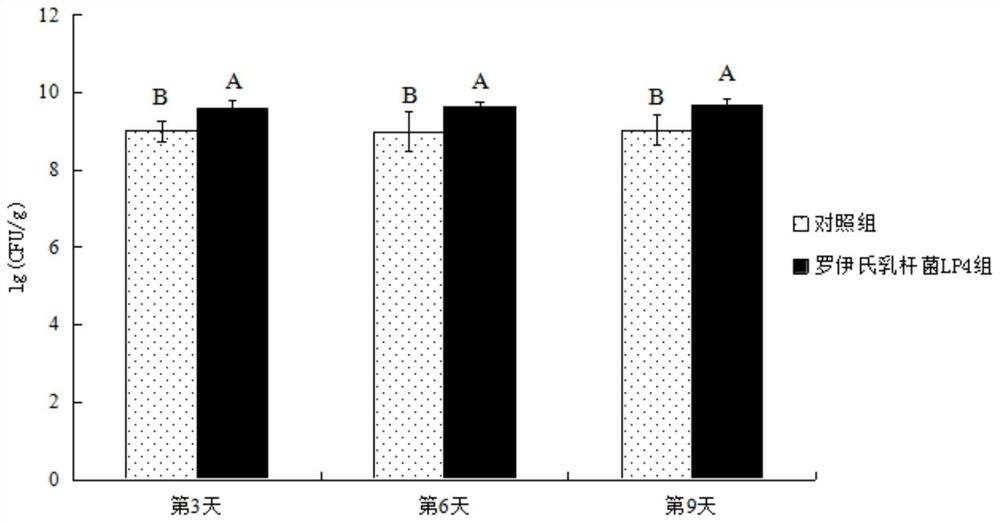
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides lactobacillus reuteri and application thereof in a bee breeding process. The lactobacillus reuteri is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 2, 2018, has a preservation number of CGMCC No.16043, and is classified and named as lactobacillus reuteri LP4. The lactobacillus reuteri is cultured in an MRS agar culture-medium, has round, milky white, neat-edged, smooth-faced, raised and non-transparent colonial form. The lactobacillus reuteri LP4 is spontaneously separated from intestines of Eastern worker bees which are bred by beekeepers in the Luoping County of Yunnan Province and freely digest rape flower honey in spring, has relatively good bacteriostatic activity, and is sensitiveto multiple antibiotics. The lactobacillus reuteri LP4 is added into syrup feeding bees in an amount of 108CFU / mL, so that the floral microecological structure in the intestines of bees can be improved, the intestinal immunity of bees can be enhanced, and the survival rate of bees can be improved.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Industrial production method for dried sweet potato leaf products
InactiveCN107981286AAdd flavorImprove palatabilityFood preservationFood ingredient as taste affecting agentBiotechnologyForced-air
The invention discloses an industrial production method for dried sweet potato leaf products. The method comprises the following operating steps: screening sweet potato leaves, rinsing with clean water, fixing green and protecting green, marinading and fermenting, separating the leaves and size, drying and dewatering. The method is technically characterized by comprising the steps: marinading andfermenting, namely inoculating lactobacillus plantarum onto an MRS agar medium to be activated, and culturing at a temperature of 33-37 DEG C for 2-3 days; inoculating the activated culture onto sweetpotato leaves in a fermentation tank according to an inoculum size of 3%, adding 3% of salt, uniformly stirring, and sealing the fermentation tank, wherein the fermentation temperature is 30-32 DEG C, and the fermentation time is 2-3 days; drying and dewatering, namely performing forced air drying at the temperature of 45-50 DEG C for 4-5 hours. Constitution water of the sweet potato leaves is not damaged as far as possible, and the original physical, chemical and biological properties and shapes invariable are kept unchanged. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the sweet potato leaves subjected to lactic acid fermentation are well flavored, contain favor components such as lactic acid, amino acids, fatty acids and the like, can achieve the effects of removing the own tannic acid and improving the product flavor and palatability, and are convenient to store, transport and sell after drying and dewatering.
Owner:HUNAN TIANXIANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Preparation method of lactobacillus acidophilus powder capable of increasing culturable cell content
ActiveCN114686407APromote productionImproved to reduce the generation ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention provides a preparation method of lactobacillus acidophilus powder capable of increasing culturable cell content. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out streak isolation culture on lactobacillus acidophilus on an MRS agar culture medium until a bacterial colony with the diameter of at least 3-5mm appears in the MRS agar culture medium; (2) inoculating the cultured bacterial colony into an MRS liquid culture medium for gradient fermentation culture, mixing an osmotic pressure regulator and / or an enzyme substance into the MRS liquid culture medium after the culture is ended, and collecting to obtain thalli; and (3) mixing the thalli with a protective agent, and carrying out electrostatic drying to obtain the lactobacillus acidophilus powder. By improving the lactobacillus acidophilus strain and the production process, the number of thalli in a VBNC state in the bacterial powder is reduced while the initial viable count of the bacterial powder is ensured, the viable count and proportion of culturable thalli are increased, and the cost of industrial production is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU WECARE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Lactic acid bacterium separated from fulvic acid with probiotic activity
InactiveCN108220177AImprove balanceGood effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a lactic acid bacterium separated from fulvic acid with probiotic activity. The lactic acid bacterium is separated from a fulvic acid solution. The lactic acid bacterium is prepared through 48 hours of culture on a lactic acid bacterium MRS agar plate culture medium at 37 DEG C, the lactic acid bacterium is grown at a temperature of 25-45 DEG C, and the pH value is 6.0-8.0.The lactic acid bacterium is facultative anaerobic and resistant to acids, has antibacterial activity for pathogenic bacteria, and also has antibacterial activity for escherichia coli, staphylococcusaureus, salmonella typhimurium, bacillus cereus, listeria monocytogenes and proteus mirabilis. The invention further provides a composition with the lactic acid bacterium of an effective dosage. Thelactic acid bacterium has excellent acid-resistant antibacterial activity, and is an excellent candidate as a seed for producing various fermented milk products and other fermentation foods.
Owner:营口富里泥炭科技有限公司
Process for performing frozen separation on lactic acid bacteria and making dry powder
PendingCN112779195AEasy to useAffect activityBacteriaMicroorganism preservationBiotechnologyYeast extract
The invention discloses a process for performing frozen separation on lactic acid bacteria and making dry powder. The process comprises the following steps: S1, preparation of sample bacterial liquid: cutting a lactic acid bacteria source sample into pieces, performing grinding, performing transferring into a centrifugal tube filled with 9 mL of sterile water or normal saline, performing shaking by using a vortex or a shaking table, performing uniform mixing for 10-30 minutes, namely diluting 10 <-1 > sample liquid, and continuously diluting the sample to 10 <-3 >, 10 <-4 > and 10 <-5 >; and S2, culture of lactic acid bacteria colonies: respectively sucking 0.2 mL of the 10 <-3 >, 10 <-4 > and 10 <-5 > sample solutions in the step S1, coating an MRS agar culture medium with the sample solutions, performing operating according to three plates in each gradient, and performing culturing for 24-48 hours at the temperature of 37 DEG C to obtain required lactic acid bacteria colonies. According to the invention, the MRS agar culture medium is coated with the bacterial liquid, the MRS agar culture medium contains a specific content of a freeze-drying protective agent compounded by glucose, peptone, a yeast extract and the like, and in addition, a vacuum-nitrogen charging grinding and crushing technology after freeze-drying is combined, so that the freeze-dried powder can be effectively prevented from absorbing moisture in the environment in the crushing process.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
A kind of Lactobacillus plantarum and its application in the preparation of Sichuan sausage by fermentation
ActiveCN108587983BPromote growthHas protease activityBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyFermentation starter
The invention relates to microorganisms and meat food fermentation, and specifically discloses a plant lactobacillus and its application in fermenting and preparing Sichuan sausages. The Lactobacillus plantarum 1-1 provided by the present invention is preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, with a preservation number: CGMCC NO.15467, and a preservation date: March 20, 2018. The strain was isolated from traditional sausages in Mount Qingcheng, Dujiangyan City, Sichuan Province. It grew well on MRS agar medium. The main fermentation characteristics met the requirements of meat starter and were suitable for meat fermentation. It has the ability to degrade sarcoplasmic proteins and biogenic amines in an in vitro simulation system. Applied to the production of Sichuan sausage, it can promote the degradation of sarcoplasmic protein in Sichuan sausage and significantly reduce the content of biogenic amines in Sichuan sausage. It has the potential to be applied to the actual production of Sichuan sausage, thereby ensuring and improving the flavor, taste and safety of Sichuan sausage.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
ActiveCN101701201BReduce manufacturing costSave energyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationTyrosine
The invention relates to an enterococcus faecalis with the collection number of CGMCC No.3164. A bacterial colony is cultured on an MRS agar culture medium at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 24 hours to be gathered; the bacterial colony is white, thallus is ovate, extends along chain direction, is in pair or in short chain, is Gram-negative, generates lactic acid when fermenting glucose and is elliptic under a common microscope. When being applied, the bacterial colony is inoculated into a test tube filled with culture medium A to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for 24 hours; after being repeatedly activated five times, the bacteria solution is inoculated into a culture medium B to stand at the temperature of 37 DEG C to be cultured for four days; the cultivated bacteria solution is decentralized at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes; and supernate is extracted to obtain high concentration tyramine solution. The culture medium A is an MRS liquid culture medium of 0.1% of tyrosine, and the culture medium B is an MRS liquid culture medium of 0.005% of pyridoxal phosphate and 0.1% of tyrosine.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A strain of Lactobacillus reuteri and its application in bee breeding
ActiveCN109182164BGood probiotic propertiesImprove survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyApis cerana
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and provides a strain of Lactobacillus reuteri and its application in the bee breeding process. Lactobacillus reuteri was preserved on July 2, 2018 in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, the preservation number is CGMCC No.16043, and the classification is named Lactobacillus reuteri; the Lactobacillus reuteri After cultured on MRS agar medium, the colony was round, milky white, with neat edges, smooth surface and raised, opaque. The Lactobacillus reuteri LP4 was independently isolated from the intestines of worker bees of Apis mellifera Apis mellifera, which were raised by beekeepers in Luoping County, Yunnan Province, and freely fed on rapeseed nectar in spring. It has good antibacterial activity and is sensitive to various antibiotics. Press Lactobacillus reuteri LP4 by 10 8 The amount of CFU / mL added to the sugar water fed to bees can improve the micro-ecological structure of the flora in the bee intestines, enhance the intestinal immunity of bees, and increase the survival rate of bees.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Lactobacillus fermentum 9-4 and its application
ActiveCN110684685BReduce generationReduce accumulationMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
The invention discloses a strain of Lactobacillus fermentum 9-4 and its application. The strain was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection CCTCC on August 12, 2019, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2019619. The Lactobacillus fermentum is a lactic acid bacteria strain with purine-reducing ability screened from raw rice flour, a traditional food in Guangxi Zhuang area. The strain grows well on MRS agar medium and has strong acid resistance. The post-survival rate is 34%; it can grow slowly under 3% concentration of bile salt, and the survival rate is 65%. The strain has good acid resistance, bile salt resistance, and purine-reducing ability, and is suitable for the production of low-purine food and purine-reducing functional fermented food.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
A caries-resistant Lactobacillus plantarum and its application
ActiveCN108486022BPromote growthEnhanced inhibitory effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAnimal testing
The invention discloses a caries-resistant plant lactobacillus ( Lactobacillus plantarum ) K41 and its applications. The Lactobacillus plantarum K41 provided by the present invention was preserved in the General Microorganism Center of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 15462 and a preservation date of March 20, 2018. The strain was isolated from farmhouse-made kimchi in Yan'an Road, Shunqing District, Nanchong City, Sichuan Province. It grew well on MRS agar medium and could inhibit the growth of Streptococcus mutans UA159 cells, exopolysaccharide formation, hydroxyapatite degradation, and biofilm It has good self-polymerization and copolymerization ability, good tolerance to antibiotics, salt and acid, and is easy to colonize in the oral cavity. Animal experiments have shown that K41 can inhibit the demineralization of rat tooth enamel and the degree of dental caries, and its application in functional foods is of great significance to human health.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
A kind of Enterococcus faecium xc2 producing antibacterial substances and its screening method and application
InactiveCN108048352BGood antibacterial effectEnsure safetyAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyFeces
The invention discloses an Enterococcus faecium XC2 producing antibacterial substances and its screening method and application. The strain is named Enterococcus faecium XC2. The strain was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on May 31, 2016. ), its deposit number is CCTCC NO: M2016297. The strain was screened from pig feces samples. On the KF Streptococcus agar medium, it was a red, smooth and raised colony with a neat periphery. On the MRS agar medium, it was a milky white colony with a smooth edge and a diameter of 1 mm. It was oval in microscopic examination. , single, double or short chain arrangement, Gram stain blue. The bacterial strain of the present invention has obvious inhibitory effect on Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella and Escherichia coli, and it produces enterococcus B, which solves the problem of the disorder of intestinal flora of livestock and poultry caused by antibiotics, the decline of animal disease resistance and the unreasonable compliance with withdrawal period The problem of drug residues in animal products.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
ActiveCN101701202BReduce manufacturing costSave energyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationTyrosine
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of lactobacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN107904185BReduce defective rateImprove filtration stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFlavorMicroorganism
The invention provides a lactobacillus strain and its application, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. The lactobacillus is preserved in the China Center for Typical Culture Collection, the preservation number is: CCTCC M 2017450, and the Latin name is Lactobacillus spicheri IZ. The colony characteristics of the Lactobacillus strain are: MRS agar plate, colony milky white, round, colony diameter is 2 mm ± 1 mm, slightly raised, moist, with neat edges, cell shape is rod-shaped, and the suitable growth temperature is 25 ° C ~ 35 ° C , is a facultative anaerobic strain. The lactobacilli are used to prepare the glutaric acid pepper, can significantly inhibit miscellaneous bacteria while retaining the main flavor of the original glutatic acid pepper, and reduce the defective rate of the glutaric acid pepper to 0%, and are suitable for industrial production of the glutaric acid pepper.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Lactobacillus plantarum (L.plantarum) with capability of inhibiting kidney stone formation and application thereof
ActiveCN113308416AEasy to adaptEasy to colonizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStone formation
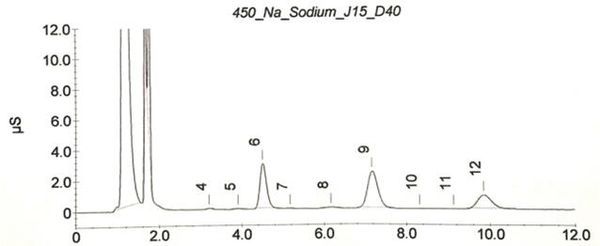
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses lactobacillus plantarum (L.plantarum) J-15 with the capability of inhibiting kidney stone formation and application thereof. The lactobacillus plantarum J-15 provided by the invention is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation number is CGMCC No.22140, and the preservation date is April 6, 2021. The strain is separated from excrement of healthy people in Chengdu of Sichuan province, grows well on an MRS agar culture medium, has certain endurance capacity to acid and cholate, is sensitive to various antibiotics, has certain oxalate degradation capacity and relatively strong renal crystallization inhibition capacity, and is shown by whole genome sequencing to have relatively strong carbohydrate metabolism capacity, membrane transport capacity and environmental adaptability, is applied to the field of functional foods and clinical kidney stone prevention and adjuvant therapy, has actual production value and has very important significance to human health.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum capable of lowering cholesterol and promoting the production of intestinal short-chain fatty acids and its application
ActiveCN108728382BImprove adhesionPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiological Techniques
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and specifically discloses a Lactobacillus plantarum ( Lactobacillus plantarum ) N‑1 and its applications. The Lactobacillus plantarum N-1 provided by the present invention is preserved in the General Microbiology Center of the China Microorganism Culture Collection Administration Committee, with the preservation number: CGMCC NO.15463, and the preservation date: March 20, 2018. The strain was isolated from traditional yak cheese products in Kalong Village, Mula Township, Daocheng County, Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province. It grows well on MRS agar medium, has a certain tolerance to acids and bile salts, and is resistant to human colon cancer cells. Caco‑2 has high adhesion ability, strong cholesterol-lowering ability, and can significantly increase the production of intestinal short-chain fatty acids. It is not only of practical production value, but also of great significance to human health when applied in the field of functional foods.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Method for detecting quantity of bacterium lacticum in mixed probiotic products
PendingCN111575337AAccurate detectionEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBifidobacterium
The invention discloses a method for detecting quantity of bacterium lacticum in mixed probiotic products. The method comprises the steps of (1) weighing mixed probiotic samples, adding bacteria-freenormal saline, and performing homogenizing; (2) taking sample homogenizing liquid, adding bacteria-free normal saline, and performing sequential and progressive diluting to an appropriate dilution degree; and (3) absorbing formed sample homogenizing liquid having the appropriate dilution degree to a bacteria-free culture dish, pouring an MRS agar culture medium into the culture dish, performing uniform mixing, performing aerobic culture at 35-37 DEG C for 70-72h, and after culture, counting the quantity of all colonies on a flat plate so as to obtain the quantity of bacterium lacticum. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a manner of performing aerobic culture on bacterium lacticum, only bacterium lacticum grow on a counting culture medium, growth of bifidobacteria is restrained, and interference of bifidobacteria on the detection of the quantity of bacterium lacticum is removed, so that the quantity of bacterium lacticum in the mixed probiotic products can be accuratelydetected, effective detection and control of the quantity of viable bacteria in bacterium lacticum in mixed probiotics can be realized, and the method can fill the blank of the detection of the quantity of bacterium lacticum in mixed probiotics containing bifidobacteria and bacterium lacticum.
Owner:BY HEALTH CO LTD
A kind of Enterococcus faecium producing bacteriocin and its application
ActiveCN105779346BImprove toleranceImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaFood preservationSynechococcusLiquid medium
The present invention relates to a bacteriocin-producing Enterococcus faecium strain. The preservation name of the strain is: Enterococcus faecium (Enterococcus faecium) R1. The preservation unit is: General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee. The preservation date is January 2016. 20th, deposit number: CGMCC No.12085. The source of the strain is the traditional fermented soy bean paste from farmers. In the MRS agar medium, it was a round or oval white smooth opaque colony smaller than 1 mm; in the MRS liquid medium, it grew uniformly turbid; under the electron microscope, the bacteria were spherical, Arranged in pairs or chains, Gram staining was positive. The bacterial strain of the invention is sensitive to antibiotics, does not contain virulence genes, and belongs to safe bacterial strains. The bacteriocin produced by it is enterococcin P, which is stable under acidic conditions, has good thermal stability, and has good antibacterial effect on common intestinal pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com