A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum capable of lowering cholesterol and promoting the production of intestinal short-chain fatty acids and its application
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and short-chain fatty acids, applied in Lactobacillus, applications, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low incidence of cardiovascular diseases, achieve the effects of lowering serum cholesterol levels, strong application potential, and alleviating liver pathological conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
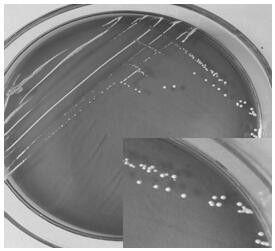
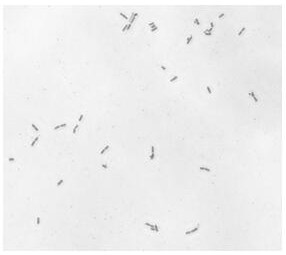
[0027] Isolation, Screening and Molecular Biological Identification of Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC 15463:
[0028] 1. Material preparation
[0029] Milk cake samples were provided by Kalong Village, Mula Township, Daocheng County, Sichuan Province;
[0030] The universal primer pair was synthesized by Invitrogen (Shanghai), and the 27F / 1492R sequence is as follows:
[0031] 27F: AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG
[0032] 1492R: TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT
[0033] MRS liquid medium: glucose 20.0 g, peptone 10.0 g, beef extract 10.0 g, yeast powder 6.0 g, Tween 80 1.0 mL, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.0 g, ammonium citrate 2.0 g, sodium acetate 5.0 g, magnesium sulfate 0.58 g, manganese sulfate 0.25 g, pure water 1 L, pH natural (add 1.5%-2.0% agar for solid medium).
[0034] 2. Specific ways
[0035]Weigh 10.0 g of the traditional yak milk cheese (milk cake) sample, stir it thoroughly in a conical flask filled with 90 mL of sterile water, and then shake it on a shaker for 60 min to co...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Detection of main fermentation characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC 15463
[0040] PBS buffer solution: Potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.20 g, disodium hydrogen phosphate 1.15 g, sodium chloride 8.0 g, potassium chloride 0.2 g, add 800 mL of pure water and stir to dissolve, adjust concentrated hydrochloric acid to the corresponding pH value, and dilute to 1 L.
[0041] DMEM complete medium: DMEM stock solution, 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% 100 U / ml double antibody.
[0042] 1. Acid resistance test: Inoculate the activated third-generation lactic acid bacteria into PBS buffer solution with pH 3.5, 2.5, and 2.0 at an inoculum amount of 1%, respectively, culture at 37°C for 3 hours, and measure the number of viable lactic acid bacteria by gradient dilution plate method.
[0043] 2. Bile salt resistance test: Inoculate the activated three-generation lactic acid bacteria into the MRS liquid medium containing 0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.3% bovine bile salt at an inoculation ...
Embodiment 3
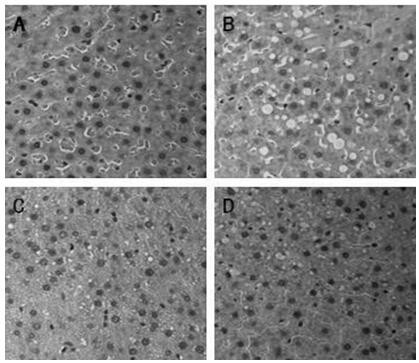
[0053] Determination of Cholesterol Degradation Ability of Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC 15463 in Vitro
[0054] MRS-cholesterol medium: MRS liquid medium (same as Example 2) was added with 0.1% ox bile salt, and cholesterol was added to make the final concentration 100 μg / mL.
[0055] The third-generation activated lactic acid bacteria were inoculated into MRS-cholesterol medium at an inoculum of 1% by the o-phthalaldehyde method, and cultured on a shaker at 120 r / min at 37°C for 24 h. Centrifuge at 10,000 g for 10 min at 4°C, take 1 mL of the supernatant into a stoppered colorimetric tube, add 1 mL of 33% KOH and 2 mL of absolute ethanol, vortex for 90 s, place in a water bath at 37°C for 15 min, and cool to At room temperature, add 2 mL of sterile water and 3 mL of n-hexane, vortex for 60 s, let stand for 10 min, take 1 mL of the upper layer liquid in a new test tube and evaporate to dryness in a water bath at 65°C, add 2 mL of o-phthalaldehyde-glacial acetic acid solution ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com