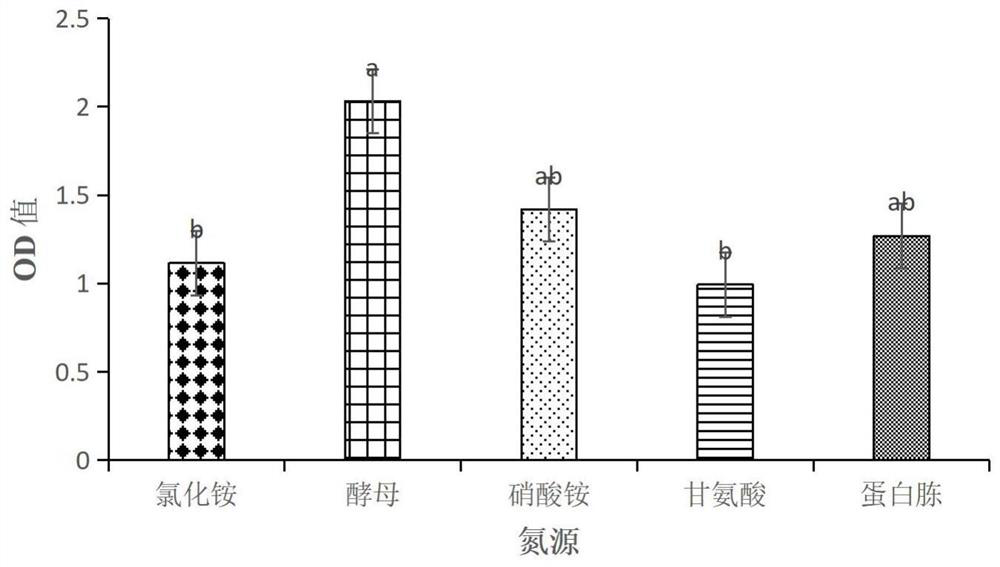
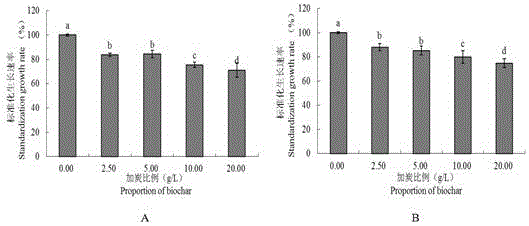
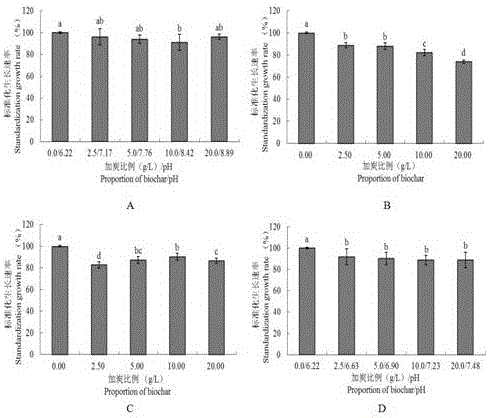
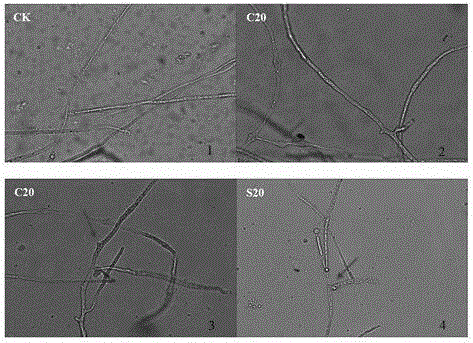
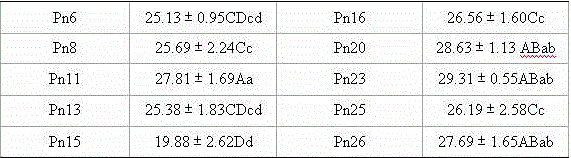
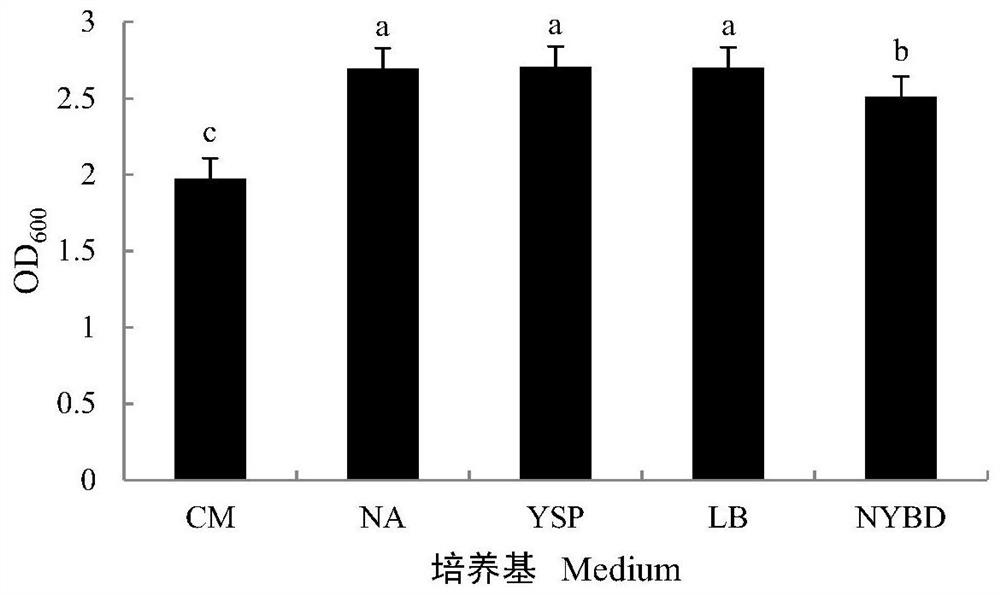
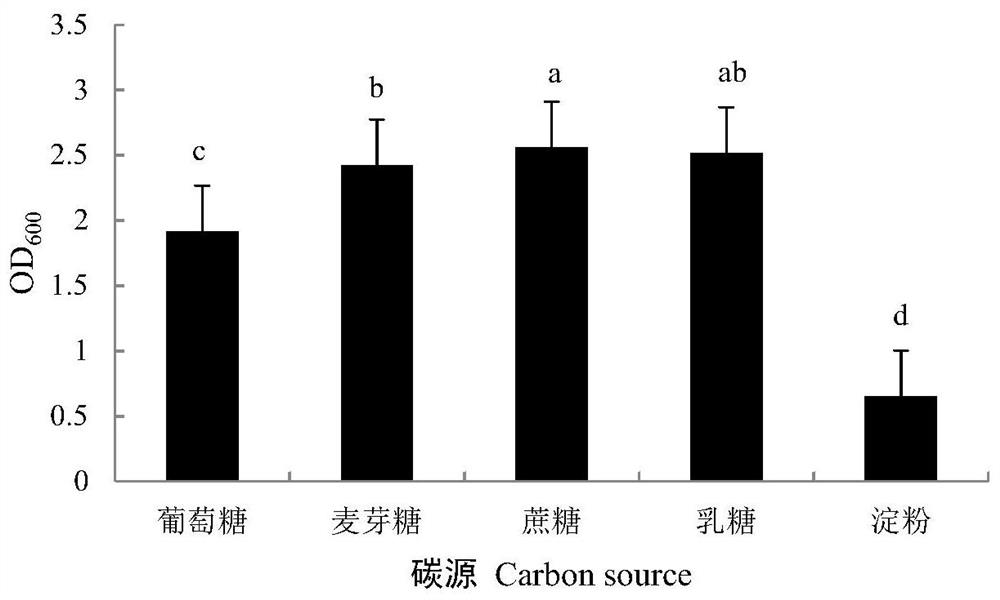
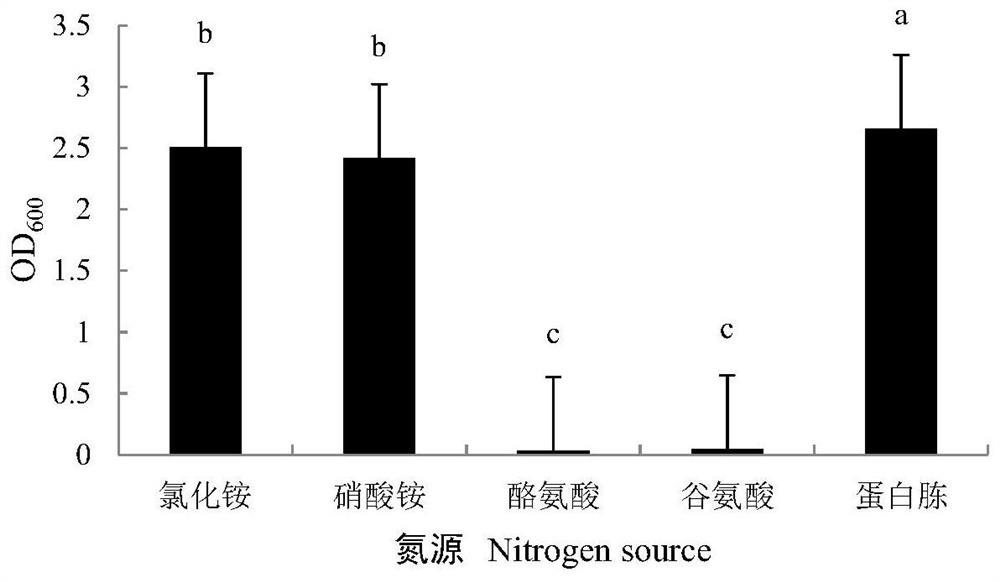
Patents
Literature
81 results about "Phytophthora nicotianae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phytophthora nicotianae or Black Shank is an oomycete belonging to the order Peronosprales and family Peronosporaceae.
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum and application thereof
ActiveCN105132336AGrowth inhibitionWide range of sterilization applicationsBiocideBacteriaFusarium oxysporumMicroorganism
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens and the microbial inoculum and application thereof. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is a Latin name, the strain number is HC200, and the accession number in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.10371. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens has a selective antagonism effect on biocontrol bacteria and pathogenic bacteria and has a strong inhibiting effect on fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, phytophthora nicotianae and ralstonia solanacearum, and has a good synergetic antagonism effect on pathogenic bacteria by being matched with trichoderma viride H06.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method of inducing phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria to generate sporangiums and release zoospores
ActiveCN103045529AShort induction periodNo pollution in the processSpore processesSnow moldNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant protection, and discloses a method of inducing phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria to generate sporangiums and release zoospores. The method comprises the following steps: activating the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria, preparing the induction liquid generating sporangiums and inducing to generate sporangiums and release zoospores. According to the invention, the used induction liquid is the Bache wild vegetable composite fruit and vegetable juice with the volume concentration of 15-25 percent and the compound fertilizer solution with the mass concentration of 0.05-0.20 percent, and when the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan is induced to generate the sporangiums, the continuous illumination culture is performed under the white fluorescent lamp. The method provided by the invention is simple, convenient, rapid and pollution-free, and can be used for the researches on virulence determination of the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria, the biological activity assay of the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria by the sterilizing agent, the evaluation of disease resistance of an epidemic disease by the luffa varieties and the like.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
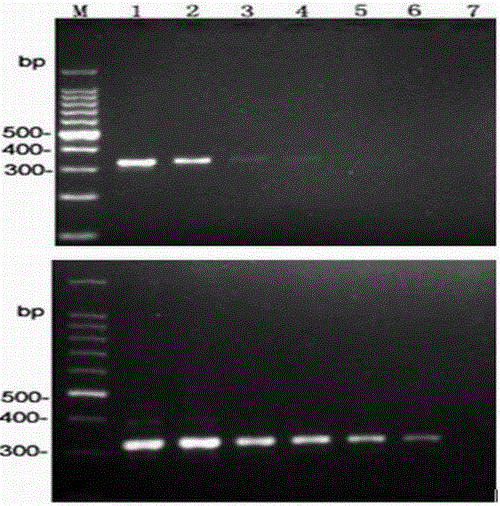
Phytophthora nicotianae molecule detection primer and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103555823AStrong specificityGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a Phytophthora nicotianae molecule detection primer and a detection method thereof, specially used for the specific molecule detection of Phytophthora nicotianae. A pair of specific primers of the Phytophthora nicotianae (comprising an upstream primer YhF:5'-GACATGATATCAACTGTTCTGCAG-3' and a downstream primer YhR:5'-CCTTGGATCTTCTCTCGATAAG-3') are mainly designed, and an amplified product having a fragment length of 342bp can be specially amplified on the pure DNA and bacteria bearing pathogenic tissues of the Phytophthora nicotianae through PCR amplification and agarose gel electrophoresis. The primer and the method can be used for the rapid, sensitive and specific detection of the Phytophthora nicotianae in Phytophthora nicotianae infected plant tissues in the production practices, can be used for the early stage diagnosis of field diseases and the monitoring and identification of pathogens, and provide reliable technologic and theoretic bases for the control of diseases caused by the Phytophthora nicotianae.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
LAMP detection kit and detection method for dendrobium officinale-phytophthora nicotianae
ActiveCN104561358AStrong specificityReduce false positive rateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumBuffer solution
The invention relates to an LAMP detection kit for dendrobium officinale-phytophthora nicotianae, which comprises a primer, a reaction buffer solution, a Bst DNA polymerase and a nucleic acid dye. The invention also relates to an LAMP detection method for dendrobium officinale-phytophthora nicotianae. After the kit disclosed by the invention is adopted for carrying out LAMP detection, the high-specificity, rapid, efficient, high-sensitivity and simple molecular detection on dendrobium officinale-phytophthora nicotianae can be realized.
Owner:SHANXI REALLY TECH
Method for genetic transformation and regeneration of eucalyptus urophylla
The invention belongs to a method for genetic transformation and regeneration of a eucalyptus, and particularly relates to the method for genetic transformation and regeneration by taking hypocotyledonary axis of an aseptic seedling of a eucalyptus urophylla as an explant. The hypocotyledonary axis of the seedling of the eucalyptus urophylla is taken as the explant, calluses are pre-cultured and induced, co-culture transformation is performed with agrobacterium tumefactions carrying exogenous genes, kanamycin is used for selection, and adventitious bud induction, bud proliferation, adventitious bud growth, rootage and transplantation are performed for getting a plant to be transformed. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection and RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) detection prove that, as for the obtained plant of the eucalyptus urophylla to be transformed, the exogenous genes are introduced into a genome of the eucalyptus urophylla and expressed; the transformed plant having better resistance to phytophthora nicotianae is found in the anti-disease detection of in vitro blades of the eucalyptus urophylla of a reverse radish-anti-fungal protein (RS-AFP2); and the relevant enzyme activity determination result of the resistance shows that, after inoculation of the transformed plant, the activities of L-phenylalanin ammo-nialyase (PAL), peroxidase (POD) and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) are enhanced.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof. The strain belongs to paenibacillus polymyxa strains YT9, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.15958.The separated strain not only has a strong inhibition effect on phytophthora sojae but also has a great antagonism effect on plant pathogenic oomycetes and phytopathogenic fungi, wherein the plant pathogenic oomycetes include phytophthora capsici, phytophthora nicotianae and the like, and phytopathogenic fungi include wheat sheath blight bacteria, wheat root rot bacteria, cercospora personata, cercospora arachidicola and the like; the bacteriostatic effect on phytophthora sojae is the strongest, wherein the bacteriostatic rate reaches 86.27%+ / -1.62%. In addition, the paenibacillus polymyxa strain YT9 is separated from healthy soybean rhizosphere soil and is free of ecological toxicity, high in safety, wide in bacteriostatic spectrum, stable and lasting in bacteriostatic activity and easy to culture. The strain has a broad application prospect in biological control over plant diseases.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Omega-3 desaturase from Phytophthora nicotianae, vector containing desaturase, recombinant microorganism and their application
The invention relates to a recombinant nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3 and used for encoding Omega-3 desaturase from Phytophthora nicotianae, a vector containing the Omega-3 desaturase, and a recombinant microorganism containing the vector, in particular recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and also relates to a construction method of the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as application of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing the desaturase in the biological synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae can catalyze C20:4<Delta5,8,11,14> into C20:5<Delta5,8,11,14,17> at normal temperature, with catalytic efficiency up to 65%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
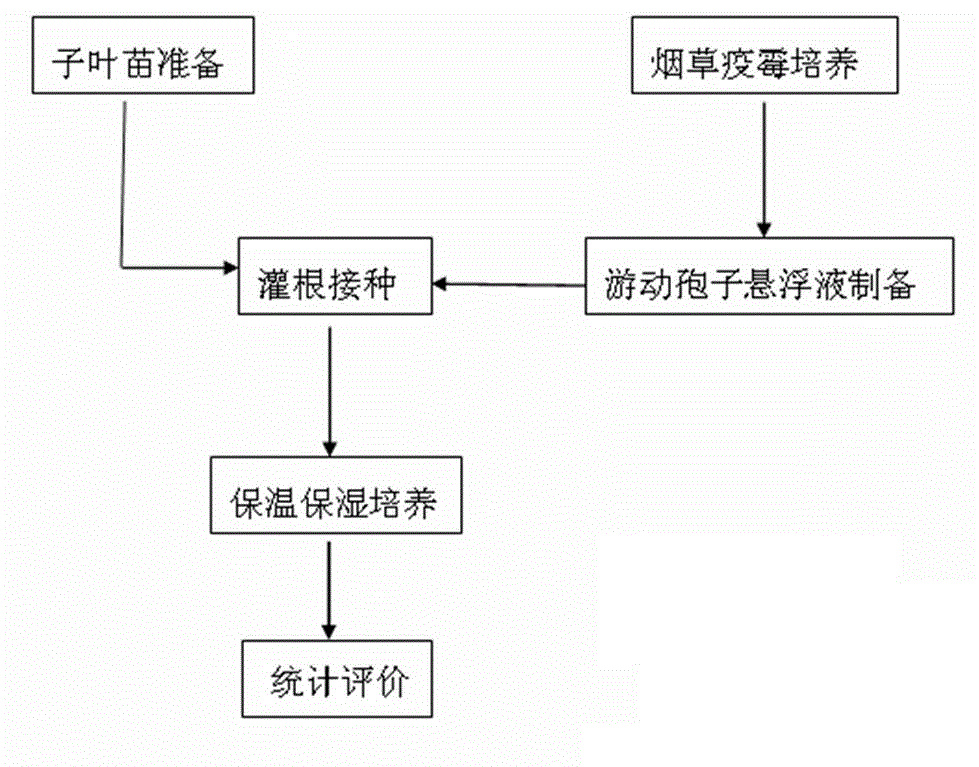
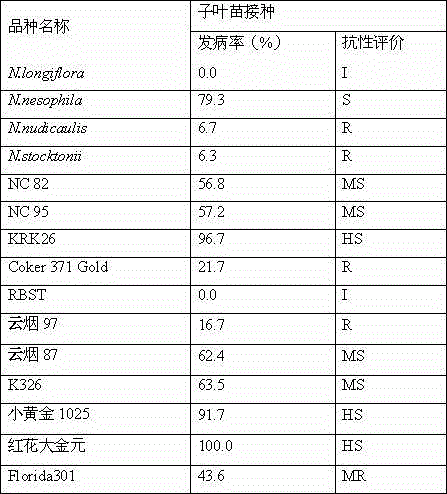
Method for phytophthora nicotianae inoculation of tobacco
InactiveCN104396599APrecise screeningEfficient screeningHorticulture methodsSporelingNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for phytophthora nicotianae inoculation of tobacco. The method for the phytophthora nicotianae inoculation of tobacco includes steps that (1) preparing for tobacco seed plantlets; (2) preparing phytophthora nicotianae zoospore suspension; (3) irrigating the roots to inoculate; (4) counting the morbidity situation, and evaluating the disease resistant result. The zoospore inoculated to the roots of the seed plantlets can be quantified rigidly, the resistant difference between the same variety due to excessive inoculation amount is avoided, and the resistance identification is more precise and effective; in the actual operation, the inoculation can be performed in quantities, the space usage is small, the labor cost is saved, and the experiment period is shortened. The method for the phytophthora nicotianae inoculation of tobacco is suitable for popularization.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Isoquinoline tricyclic alkaloid compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110483535AGood inhibitory effectHigh-efficiency new biopesticide molecular structureBiocideOrganic chemistryChromatographic separationSilica gel
The invention discloses an isoquinoline tricyclic alkaloid compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The compound is obtained by taking a whole plant of Thalictrum glandulosissimum as a raw material and by steps of extraction with ethyl acetate, silica gel column chromatography and high-pressure liquid chromatography separation and purification. The structural formula of the compound is C16H15NO2, and the compound has the following structural formula shown in the specification. The compound is named as 1-(2,2-dimethyl-2H-pyrano[2,3-g]isoquinolin-6-yl)ethanone. The inhibitory effect of the compound on Phytophthora nicotianae is remarkably superior to that of agricultural streptomycin, and the control effect on tobacco black shank reaches (71.5 + / - 3.2)%. The raw material is widely distributed, high in biological yield and high in alkaloid content. The compound preparation process is simple, the production cost is low and the compound is prone to industrial application.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Microbial insecticide and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a microbial insecticide, which is a concentrated cenobium composed of 18 microbial strains classified into three types. Characterized by strong insecticidal ability, fast insecticidal speed and wide insecticidal range, the microbial strains respectively are: Metarhizium anisopliae, Paecilomyces farinosus, Phytophthora nicotianae, Streptomyces amilatus, Streptomyces culicidicus, Streptomyces griseolus subsp.hangzhouensis, Streptomyces calvus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus sphaericus, Bacillus laterosporus, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.aisawai, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.merrisoni, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.galleriae, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.Israelensis, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.thuringiensis, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.berliner, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.dendrolimus, and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.sotto.
Owner:BEIJING CHENAO RUNZE TECH CO LTD
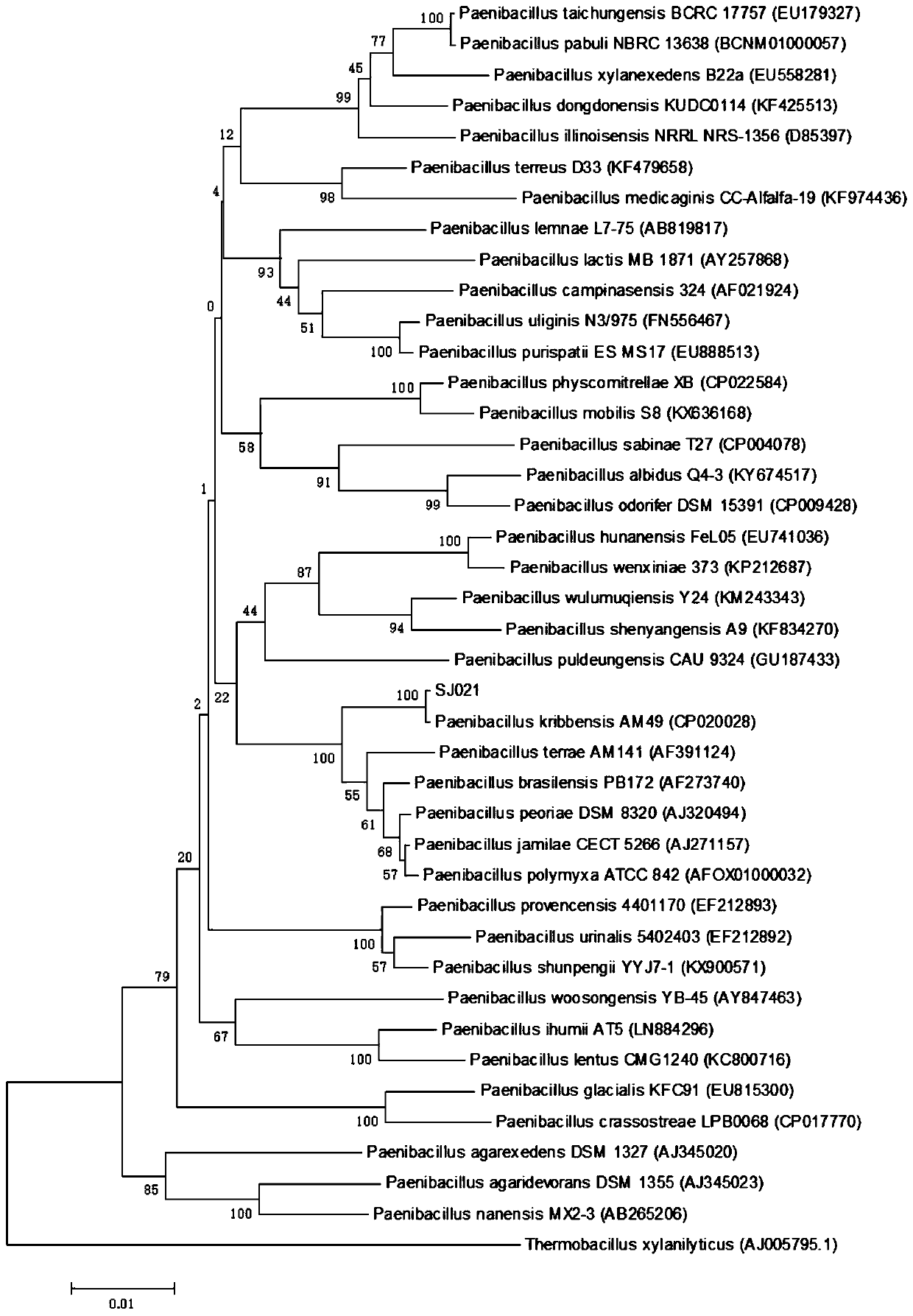
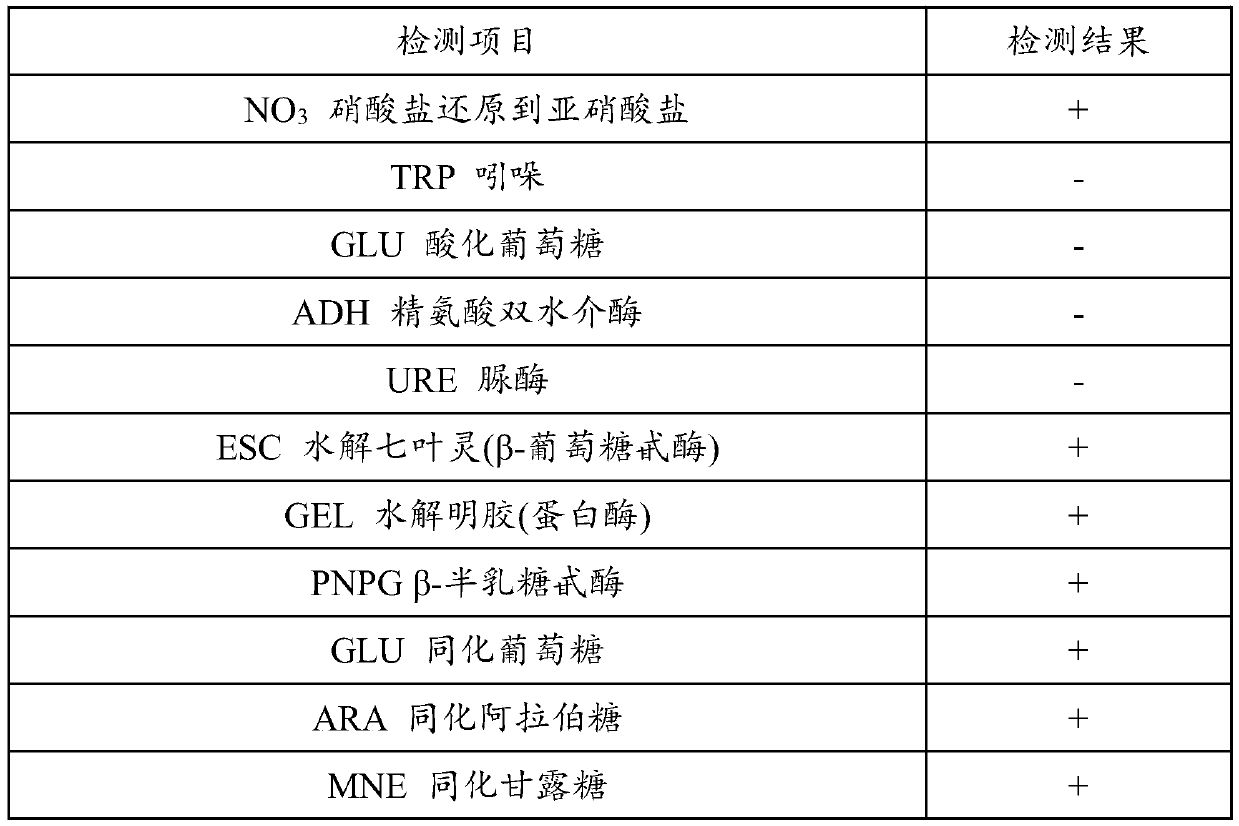
Paenibacillus kribbensis and preparation and application thereof
The invention provides a strain of paenibacillus kribbensis and a preparation and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of agricultural production and biocontrol microbial technology.The preservation number of the paenibacillus kribbensis is CGMCC No.17248. The provided paenibacillus kribbensis has a remarkable bacteriostatic activity on phytophthora nicotianae and fusarium, andthe bacteriostatic rates on phytophthora nicotianae and fusarium both exceed 70%. By applying the provided paenibacillus kribbensis to planting of tobacco, the growth of tobacco plants can be significantly promoted, and the yield and output value of the tobacco are increased.
Owner:漳州三炬生物技术有限公司
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primer for phytophthora capsici leonian, kit containing primer and application thereof
InactiveCN102643903AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPropagulePhytophthora sp.
The invention provides a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primer for phytophthora capsici leonian. The primer comprises Enl4s and Enl1a (as shown in Seq ID No.1 and 2). Four pairs of specific primers capable of quickly detecting phytophthora capsici leonian germs can be obtained based on the sequence difference between the Enl and Ypt genes of the phytophthora capsici leonian and other phytophthora nicotianaes: Enl2s / Enl3a, Enl4s / Enl1a, Ypt2s / Ypt3a and Ypt2s / Ypt5a, wherein the sensitivity of Enl4s / Enl1a is the highest. A PCR detection system is established on the basis, which is capable of quickly and accurately detecting the phytophthora capsici leonian from complex pathogenic bacteria environments in the tissues of plants having diseases and soil. A detection kit established according to the method is simple and convenient for operation, good in specificity and high in sensitivity; and the detection kit is capable of detecting the propagules in various forms of the phytophthora capsici leonian, such as hypha, oospore, zoospore and the like, thereby having great significance in the aspects of early warning on the epidemic situation of the phytophthora capsici leonian, pathogen supervision on the epidemic area and the like.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Screening method of biocontrol bacteria and dosage for tobacco black shank
InactiveCN102277408AAvoid missingAvoid screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for screening biocontrol bacteria and dosage thereof against tobacco black shank. The method comprises the following steps: a. cultivating sterile tobacco seedlings on filter paper in a petri dish; b. on the basis of step a , add bacterial culture solution with biocontrol potential in the petri dish; c, after the tobacco seedlings and the bacterial suspension with biocontrol potential are cultivated together for 24 hours, add the zoospore suspension of tobacco black shank bacteria to the petri dish d, on the basis of step c, give the tobacco seedlings normal growth conditions, detect the control effect of the bacteria with biocontrol potential added by observing the morbidity of the tobacco seedlings after 7 days, and screen out the biocontrol that can prevent and treat tobacco black shank bacteria. Compared with the traditional method, the present invention has many advantages. It is simple, fast, less workload, high efficiency, accurate and reliable screening result, and can screen bacteria with bio-control function from a large number of unknown bacteria in a short period of time.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI INST
Method for inducing phytophthora nicotianae to generate pathogenic secretory protein
InactiveCN102321711ASolve the problem of not producing pathogenic secreted proteinsMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyDiseased plant
The invention relates to a method for inducing phytophthora nicotianae to generate pathogenic secretory protein. The method comprises the following steps: taking a tobacco black shank sample back to a laboratory, flushing the surface of the diseased plant stem with tap water till the surface is clean; after drying, taking a 0.4 cm*0.4 cm pith tissue block at a juncture of the diseased and health tissue, placing the block in an oat medium, performing culture under a dark condition with a temperature of 28 DEG C for 3-4 days to form a large bacterial colony, transferring the mycelium block into 300 mL of secretory protein liquid induction medium, performing shaking culture at 28 DEG C and 120 rpm for 2 weeks, filtering the mycelia by a double-layer sterilization filter paper, centrifuging the filtrate at 5000 rpm for 10 min, adding ammonium sulfate into the supernatant, centrifuging the supernatant at 10000 rpm for 20 min, performing dialysis treatment of the precipitate, performing freeze drying to obtain secretory protein of phytophthora nicotianae, storing the protein at -20 DEG C. The method can induce phytophthora nicotianae to generate a lot of pathogenic secretory protein, fills the gap that secretory protein can not be obtained in phytophthora nicotianae pathogenesis research at home and abroad, and has great significance.
Owner:HONGYUN HONGHE TOBACCO (GRP) CO LTD +1
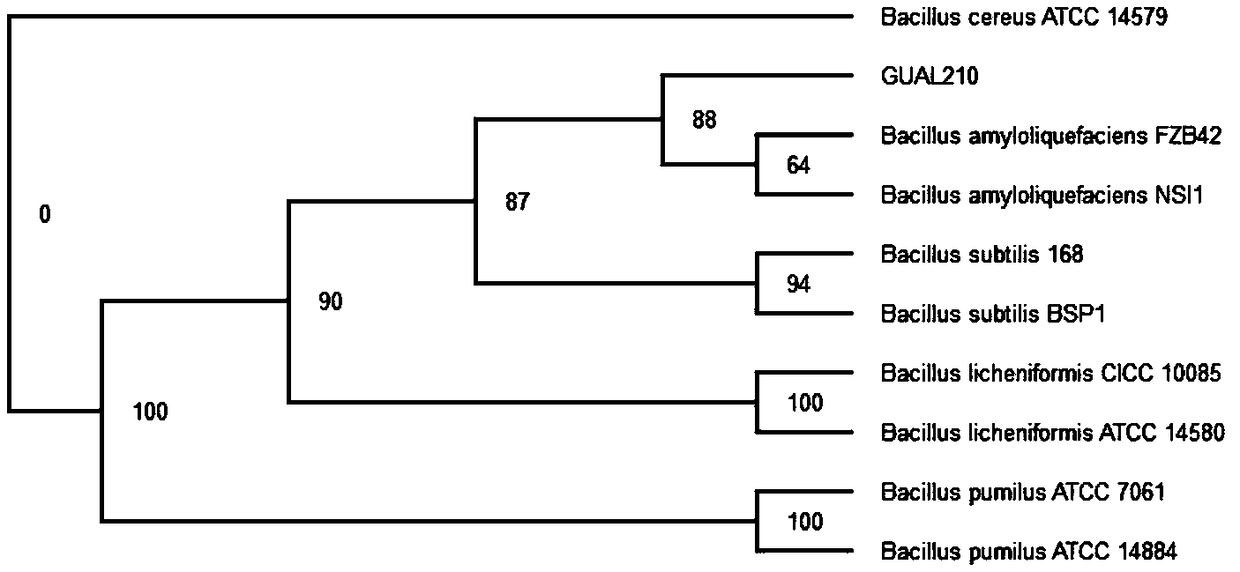
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210 and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210, which is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2018871. The invention furtherdiscloses application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210 to simultaneous control of tobacco black shank and tobacco bacterial wilt. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210 has an obvious ability of antagonizing both phytophthora nicotianae and ralatonia solanacearum simultaneously and the ability of antagonizing pepper anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
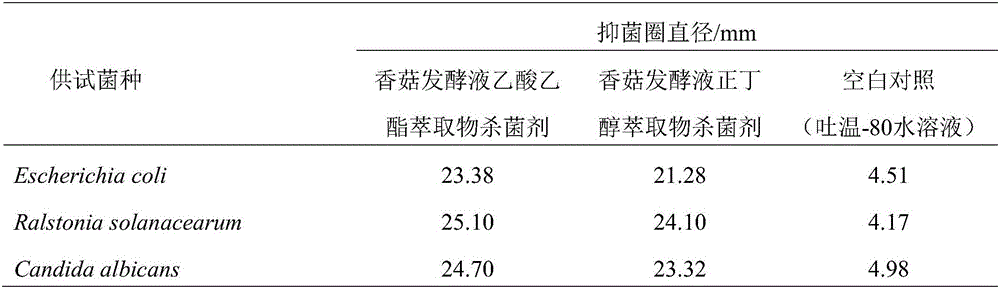
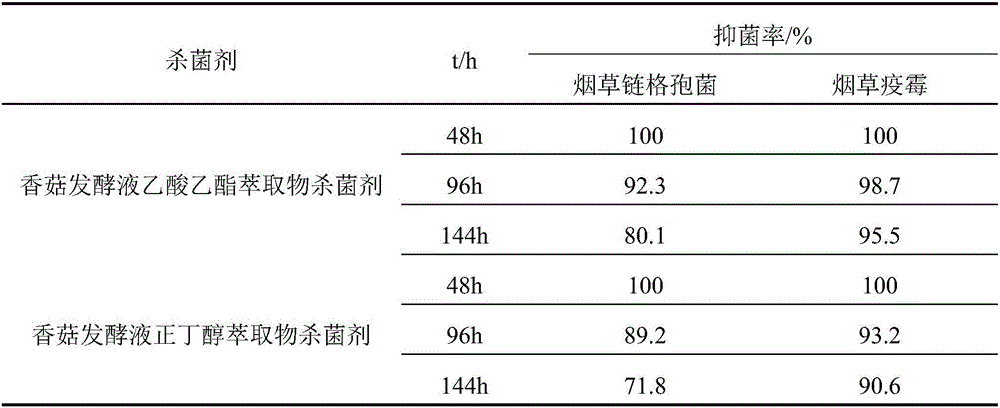
Microbial fungicide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106472572AWell mixedIncrease concentrationBiocideFood preservationEscherichia coliAlternaria
The invention relates to a microbial fungicide and a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a mushroom broth by an extractant, concentrating the material to a paste, and the paste and an auxiliary agent are used according to the mass volume ratio of 1g: 5mL to prepare the product. The mushroom broth extract fungicide contains natural antibacterial active metabolite, has wide-spectrum antibacterial and antifungal activities, can be used for inhibiting escherichia coli, pseudomonas solanacearum, tritirachium album, tobacco alternaria alternate and tobacco phytophthora, and can be used for preparing a food antiseptic or a biological pesticide. The preparation method is efficient, the obtained fungicide is the microbial source fungicide, and has the advantages of low toxicity and low residue.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Penicillium bilaiae MP6 with bacteriostatic action and application thereof
ActiveCN113403205AGrowth inhibitionSuppresses Fusarium WiltBiocideFungiBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
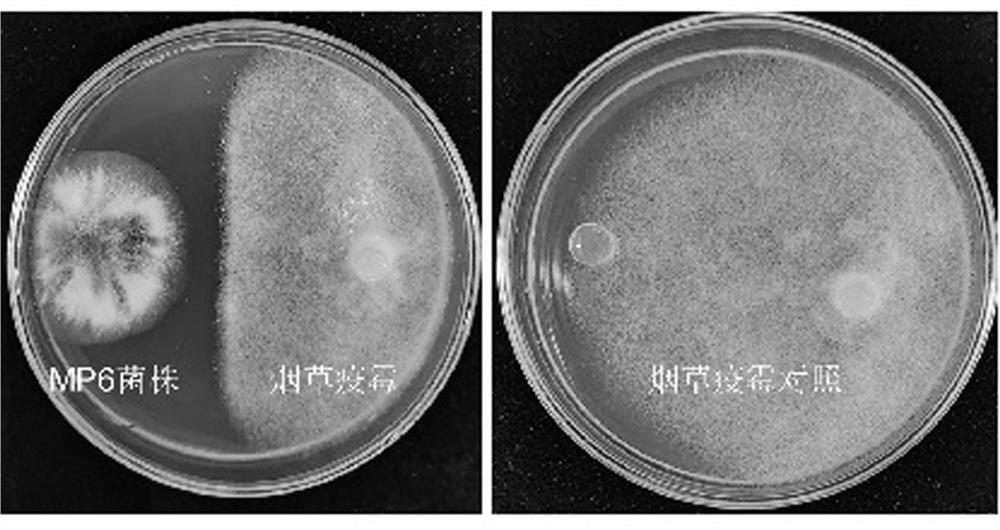
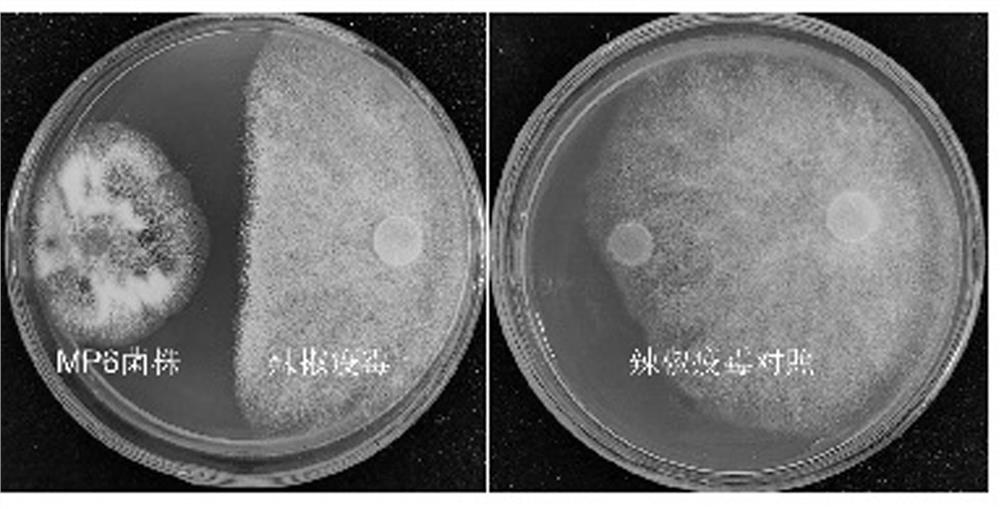
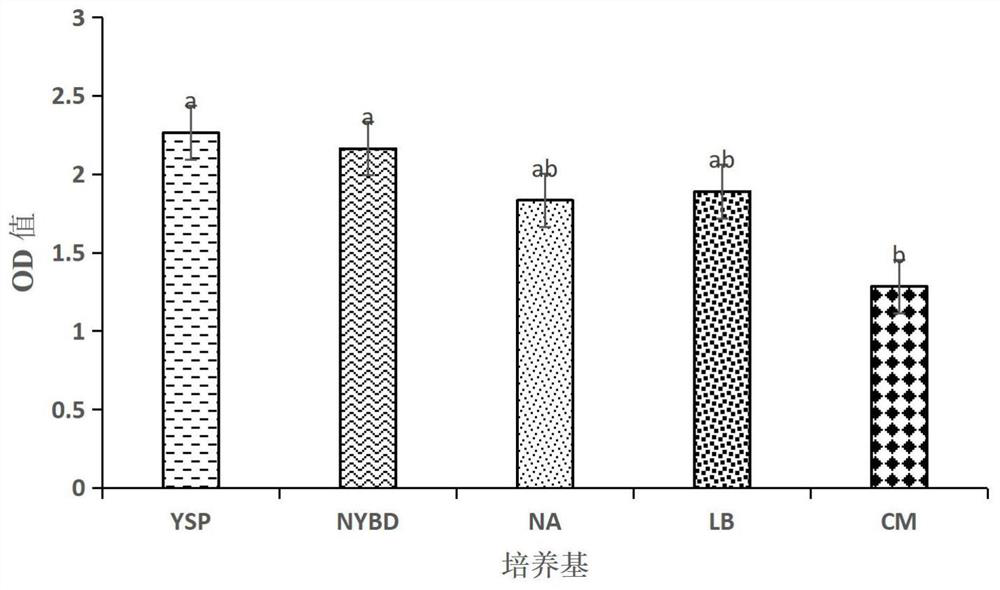
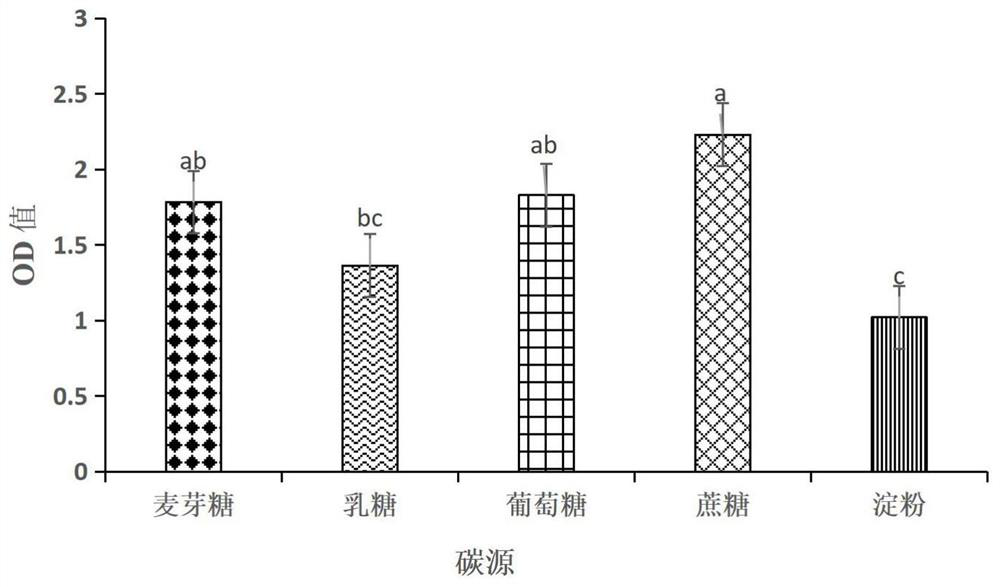
The invention discloses a Penicillium bilaiae MP6 with bacteriostatic action and application thereof. The Penicillium bilaiae MP6 is classified and named as Penicillium bilaiae, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2021612; the bacterial colony of the Penicillium bilaiae MP6 has developed hyphae and short length, and is felty; and the conidiophore head is broom-shaped, the conidium is chain-like, and the nucleotide sequence of ITS is shown as SEQ ID No. 5. The Penicillium bilaiae MP6 can be used for preparing a biocontrol agent for preventing and treating blight, phytophthora and / or bacterial wilt, and has obvious effects of inhibiting fusarium oxysporum, phytophthora sojae, phytophthora nicotianae, phytophthora capsici and ralstonia solanacearum, so that the resistance of plants to blight, phytophthora or bacterial wilt is increased, and the Penicillium bilaiae MP6 has good market application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Bacillus subtilis MC4-2 and application thereof
PendingCN112358993AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis MC4-2 and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and provides bacillus subtilis with the strain number of MC4-2and the preservation number of CGMCC (No.15975, and the bacillus subtilis MC42 is named as bacillus subtilis in a classified manner. The bacillus subtilis MC4-2 fermentation broth MC4-2 has a good inhibition effect on Phytophthora nicotianae, can be used as a living microbial agent and a metabolite dosage form for processing and development, is used for prevention and control of Phytophthora nicotianae, and is good in effect and low in cost.
Owner:YUNNAN TOBACCO CO LTD KUNMING BRANCH +1
Method of utilizing biomass charcoal to inhibit phytophthora nicotianae
InactiveCN106577049AEnhanced inhibitory effectSimple methodBiocideFungicidesNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention discloses a method of utilizing biomass charcoal to inhibit phytophthora nicotianae. The method includes the following steps: firstly, configuring and adding a biomass charcoal medium; secondly, adjusting pH with the added biomass charcoal medium to be original pH of the medium; and thirdly, configuring bacteria soil. The method is simple, is convenient to use, and has a great effect to inhibit phytophthora nicotianae. Two types of biomass charcoal different in proportion are added separately or added together to an oat medium, the influence of biomass charcoal on phytophthora nicotianae is determined through determination of relevant indexes, and relevant experiments are designed to conduct mechanism verification on the basis of the property of biomass charcoal. Brown soil is selected and rice husk charcoal with different proportions is added in a potted condition to verify an effect of biomass charcoal on phytophthora nicotianae prevention. Therefore, theoretical bases are provided for reasonable applications of biomass charcoal and related research and comprehensive control and treatment of phytophthora nicotianae.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
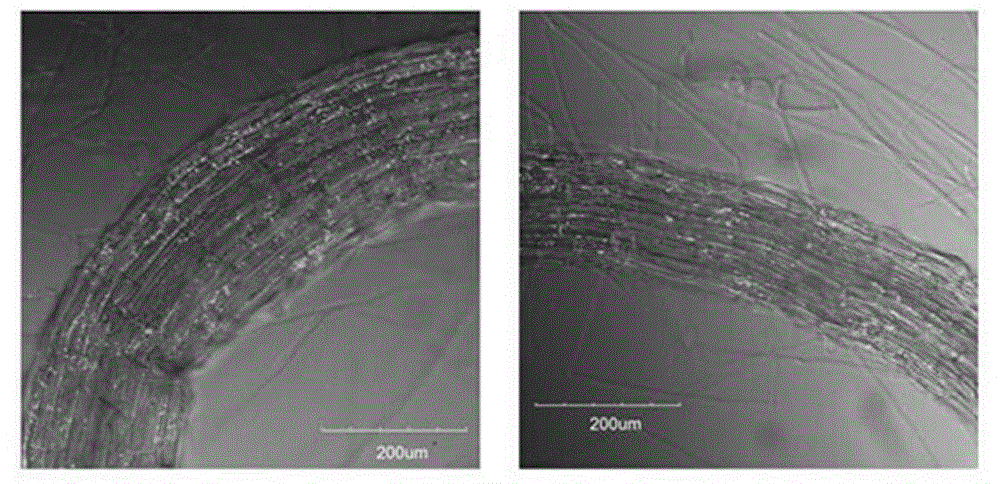
Real-time observation method for phytophthora nicotianae infection process
The invention discloses a real-time observation method for phytophthora nicotianae infection process. The real-time observation method for the phytophthora nicotianae infection process includes that preparing for tobacco seed plantlet, preparing phytophthora nicotianae zoospore suspension, irrigating the root to inoculate, dyeing and observing. According to the real-time observation method for the phytophthora nicotianae infection process, phytophthora nicotianae inoculation can be performed in a manual climatic box or a culture room by means of culture dish sponge and filter paper for preserving moisture, and the dyed and discolored seed plantlet radicle can be directly observed under a microscope. The real-time observation method for the phytophthora nicotianae infection process is convenient and easy to operate and suitable for observing the phytophthora nicotianae infection process of tobacco and detecting the resistance of different varieties.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Test method for inhibiting Phytophthora nicotianae
InactiveCN110229868ABest antibacterial rateImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSnow moldNicotiana tabacum
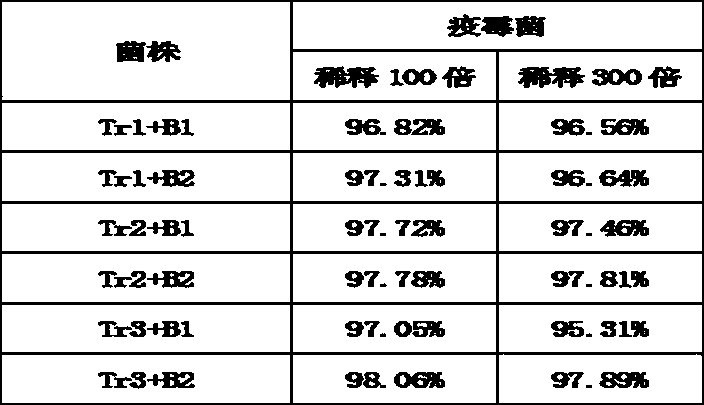
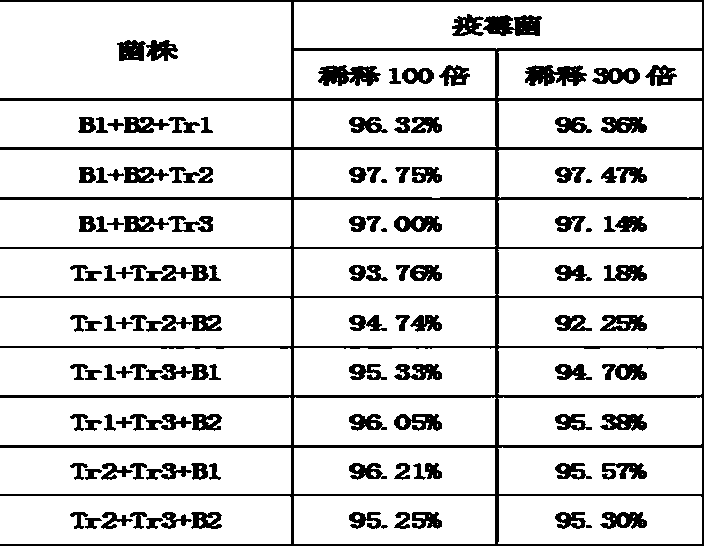
The invention relates to a test method for inhibiting Phytophthora nicotianae. A plate dilution coating method is adopted to separate rhizosphere soil microorganisms of healthy tobacco plants in the tobacco field with the tobacco black shank disease, and two antagonistic bacteria and three Trichoderma spp. are screened out from Phytophthora nicotianae by a plate confrontation test; and the numberof two antagonistic bacteria is B1 and B2 respectively, and the single-bacterium bacteriostatic rates of both of the bacteria are more than 80 percent, wherein the inhibition rate of the B1 to Phytophthora nicotianae is more than 90 percent, and both of the bacteria are identified to be paenibacillus polymyxa; the number of the three Trichoderma strains are YCS-Tr1, YCS-Tr2 and YCS-Tr3 respectively, the single-bacterium bacteriostatic rates of the strains are more that 94%, and the three strains are identified as green Trichoderma spp., Trichoderma paraviridescens and Trichoderma koningiopsisrespectively. The test data analysis obtains the strain combination mode with the optimal bacteriostatic rate, is beneficial to more accurately implementing the prevention and treatment work of inhibiting the Phytophthora nicotianae in the later field application, and provides a reference test method for acquiring a composition for efficiently and stably inhibiting the Phytophthora nicotianae.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High-yield paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof
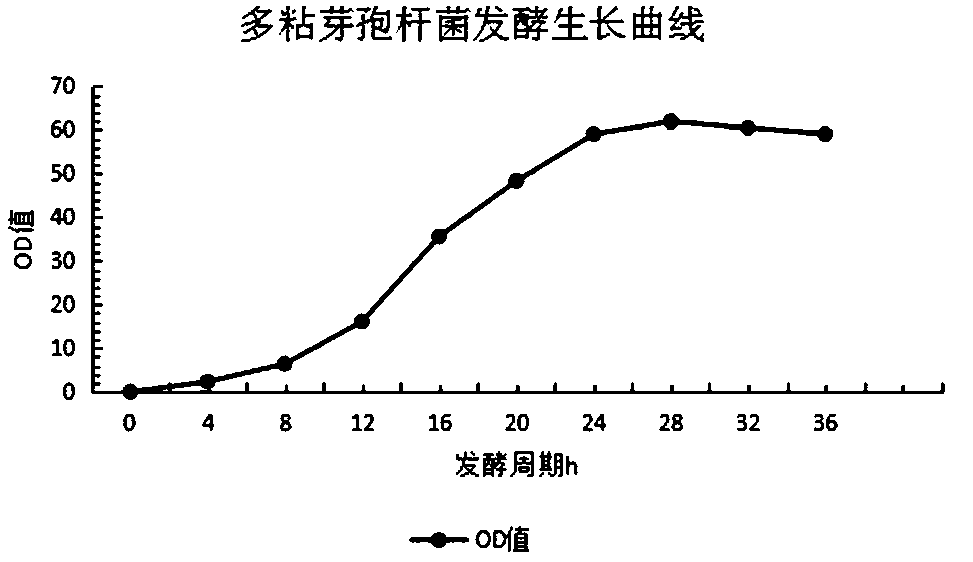
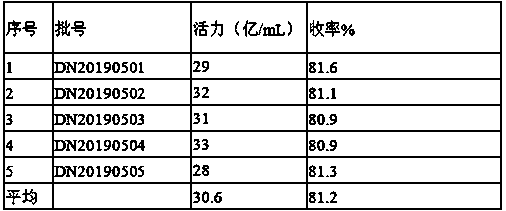
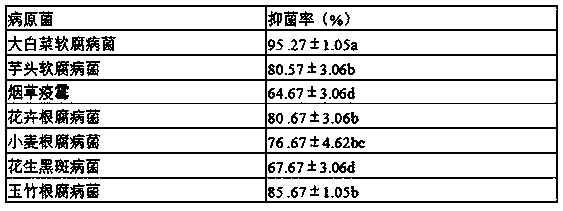
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological fermentation engineering, and specifically relates to a high-yield paenibacillus polymyxa strain and an application thereof. Paenibacillus polymyxa YSD7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 5, 2019, and a preservation number is CGMCC 19087. The paenibacillus polymyxa YSD7 can prevent and treaterwinia carotovora, taro soft rot bacteria, phytophthora nicotianae, flower root rot bacteria, bipolaris sorokiniana, cercospora personata, or polygonatum root rot bacteria. The inventors finally obtain the paenibacillus polymyxa strain YSD7 with relatively good growth vigor through the combination application of ultraviolet mutagenesis and diethyl sulfate mutagenesis technology, and qualitativescreening breeding based on the existing strain. Preliminary experimental results show that the highest fermentation activity of the YSD7 strain can reach 9.5 billion / mL, the YSD7 strain shows relatively good growth effects, and a good technical foundation for the preparation of paenibacillus polymyxa microbial preparation products can be laid.
Owner:河南新仰韶生物科技有限公司
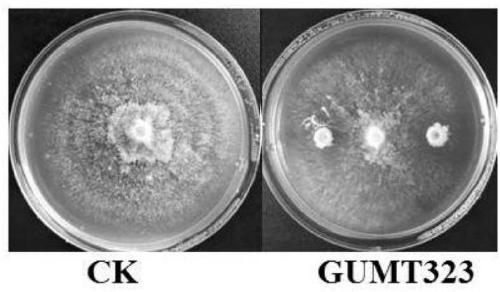
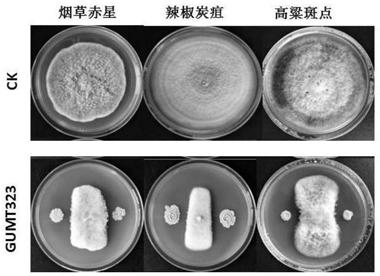
Bacillus subtilis GUMT323 and application thereof
ActiveCN109504640AAbility to significantly antagonize tobacco blackleg pathogen (Phytophthoranicotianae)BiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis GUMT323, which is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2018873. The invention further discloses application of the bacillus subtilis GUMT323 to control of tobacco black shank. The bacillus subtilis GUMT323 has an obvious ability of antagonizing both phytophthora nicotianae and the ability of antagonizing pepper anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Pseudomonas corrugata and its application
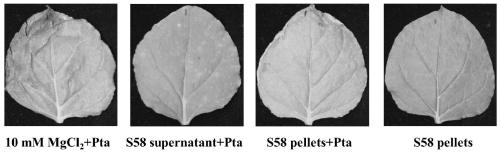
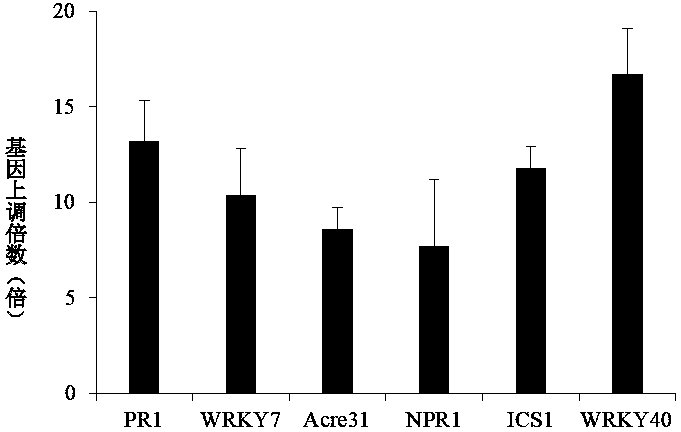
The invention discloses Pseudomonas corrugata and an application thereof. A strain number of Pseudomonas corrugata is S58, and a registration number is CGMCC No.17043 in the General Microbiology Center of the China Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee. The strain has stable perforamnce, high-efficiency, broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, and has the inhibitory effects for phytopathogenic fungi such as phytophthora nicotianae, phytophthora sojae, rhizoctonia solani and Magnaporthe oryzae, and acidovorax citrulli, Clavibacter, and flavimonas oryzihabitans and ralstonia solanacearum. The control effect of Pseudomonas corrugata S58 on ralstonia solanacearum is 76.2%, and the control effect against tobacco black shank is 60.5%. The Pseudomonas corrugata S58 is capable of producing ferritin and amylase, can cause programmed cell death in the surface immune response of plants, and can control the occurrence of tobacco wildfire by stimulating immune resistance. The Pseudomonas corrugata S58 is capable of hydrolyzing organic phosphorus and can be used for soil improvement.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Strawberry seedling cultivating method capable of resisting continuous cropping obstacle
InactiveCN106612726AImprove disease resistanceImprove survival rateSeed immunisationContinuous croppingFragaria
The invention relates to the technical field of fruits and vegetables seedling, and in particular relates to a strawberry seedling cultivating method capable of resisting a continuous cropping obstacle. The method comprises the steps of soaking strawberry seeds in a saturated salt water solution for soaking in a vacuum environment, soaking the strawberry seeds in scale mucus, sowing the strawberry seeds in garden soil of continuously cropping strawberry, and irrigating with a nitrobacteria solution; successively inoculating strawberry blonde monospora, fusarium oxysporum, phytophthora nicotianae, bacillus anthraci, sphaerotheca fuligine and botryis cinerea into young stems and leaves of the strawberry by stages, inoculating the fungi or viruses and timely spraying 5%-10% calamine water suspension, an allium caelureum extract liquid, a sweet pomegranate rind extract liquid, a lantern plant calyx extract liquid, 5% sodium sulfate solution and 0.05% hydrogen bromide water solution separately; and reserving the finally healthy strawberry seedlings. The treated strawberry seedlings are extremely high in disease resistance and can show relatively high disease resistance and high yield when planted into a continuous cropping field.
Owner:全椒县悠然自得果蔬种植专业合作社
Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 and application thereof
ActiveCN112391323AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. The strain number of the Bacillus tequilensis is D5-8, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 15973, and the Bacillus tequilensis is classified and named as Bacillus tequilensis. The Bacillus tequilensis D5-8 fermentation liquor D5-8 has a good inhibiting effect on Phytophthora nicotianae, can be used as a dosage form of a living microbial agent and a metabolite for processing and development, is used for preventing and controlling the Phytophthora nicotianae, and is good in effect and low in cost.
Owner:YUNNAN TOBACCO CO LTD KUNMING BRANCH +1
Method for determining phytophthora nicotianae virulence through in-vitro shoots
InactiveCN105861619APathogenicity stableGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumShoot
The invention discloses a method for determining phytophthora nicotianae virulence through in-vitro shoots. The method comprises the following steps of 1 preparing phytophthora nicotianae sclertium; 2, preparing in-vitro shoots; 3, performing inoculation; 4, determining and evaluating the virulence. The method is simple, convenient and easy to implement, the phytophthora nicotianae virulence is expressed stably, the repeatability is good, results are reliable, and the phytophthora nicotianae virulence and virulence intensity can be accurately reflected; in actual operation, determination can be performed in batches, the method has the advantages of being small in occupied space, saving the labor cost, and shortening the experimental period, and therefore the method is suitable for being applied and popularized.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
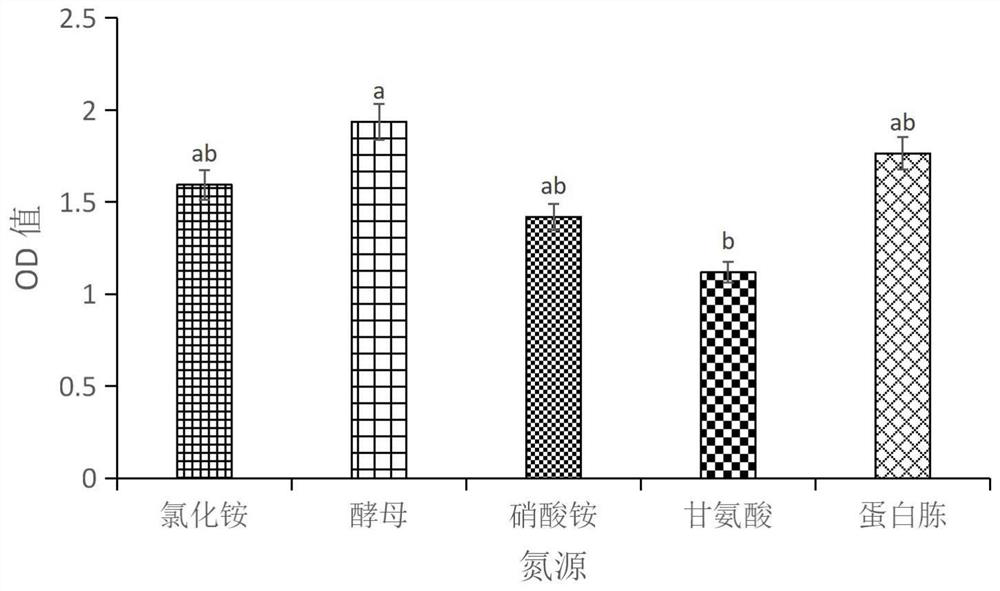
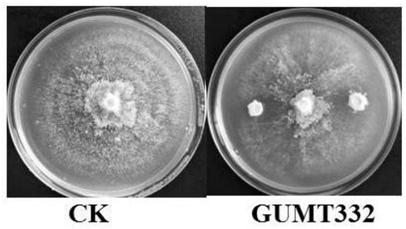
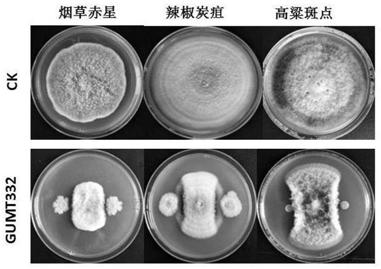
Bacillus subtilis GUMT332 and application thereof
ActiveCN109593682AAbility to significantly antagonize tobacco blackleg pathogen (Phytophthoranicotianae)BiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis GUMT332 collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), with the collection number of CCTCC NO:M 2018874. The invention also discloses an application of the bacillus subtilis GUMT332 in control of phytophthora nicotianae. The bacillus subtilis GUMT332 has obvious capacity for antagonizing the phytophthora nicotianae and chili anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for determining pathogenicity of phytophthora nicotianae through pumpkin chips
InactiveCN105861620APathogenicity stableGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumBatch operation
The invention discloses a method for determining pathogenicity of phytophthora nicotianae through pumpkin chips. The method comprises the following steps of 1, preparation of phytophthora nicotianae hypha blocks; 2, preparation of pumpkin chips; 3, inoculation; 4, pathogenicity determination and evaluation. The method is simple, convenient to use and easy to implement; pathogenic bacteria are stable in pathogenicity expression, repeatability is good, the result is reliable, and the pathogenicity and pathogenic strength of phytophthora nicotianae can be accurately reflected; during actual operation, batch operation can be conducted, the method has the advantages that the occupied space is small, labor cost is reduced, and the experimental period is shortened, and therefore the method is suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and application thereof
PendingCN113151097AReduce the disease indexGood control effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. The preservation number of the pseudomonas aeruginosa is CGMCC No.21856, the preservation time is March 9, 2021, and the preservation address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The pseudomonas aeruginosa is separated from digestive tracts of lepidoptera insect larvae, and fermentation liquor of the pseudomonas aeruginosa has a good inhibition effect on phytophthora nicotianae, so that the biological agent for preventing and controlling phytophthora nicotianae is prepared by taking living bodies or metabolites of the pseudomonas aeruginosa as main components, the effect is good, the cost is low, and the pseudomonas aeruginosa has important significance on prevention and control of phytophthora nicotianae.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com