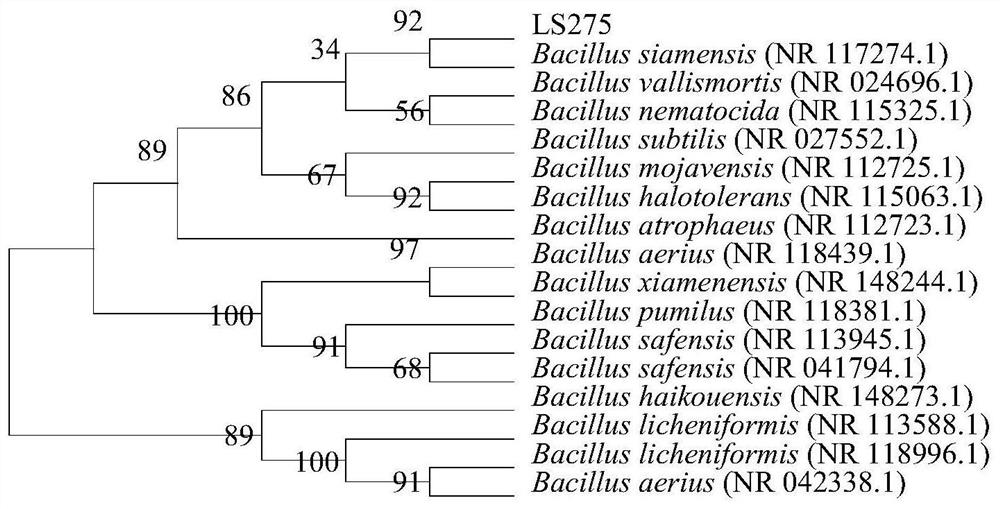
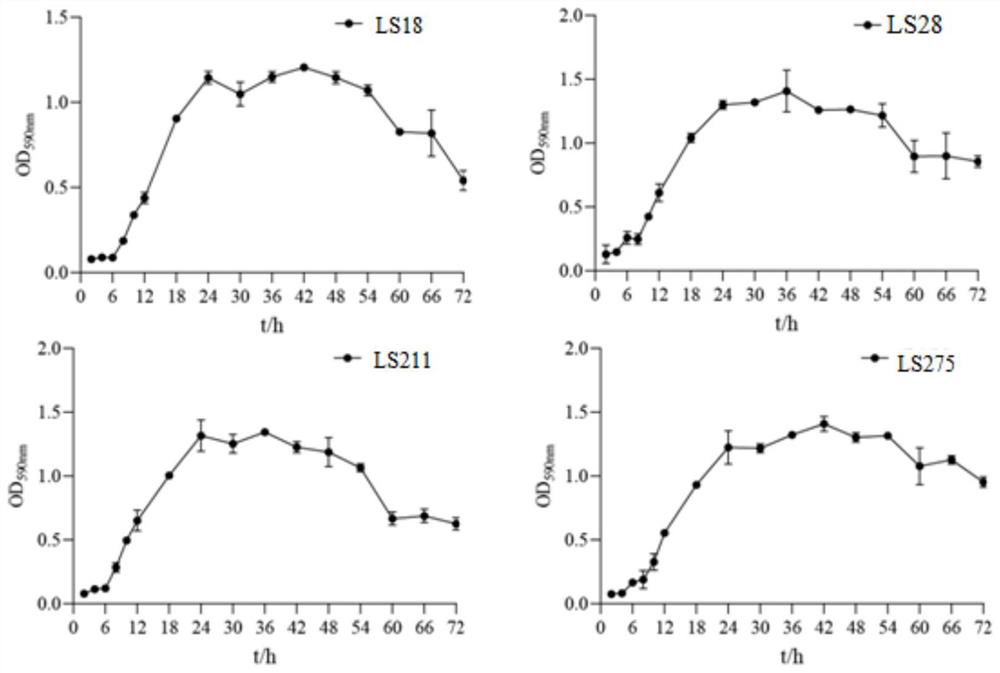
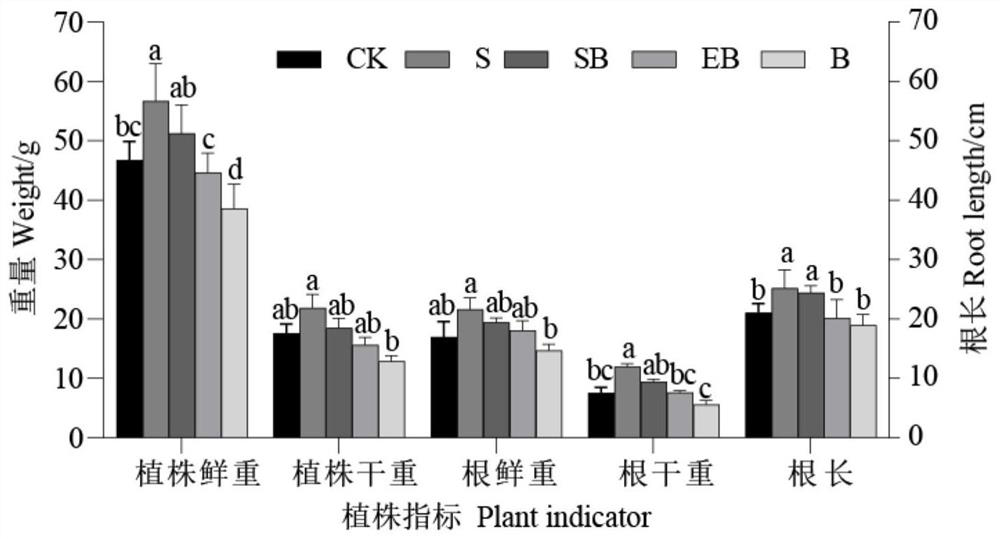
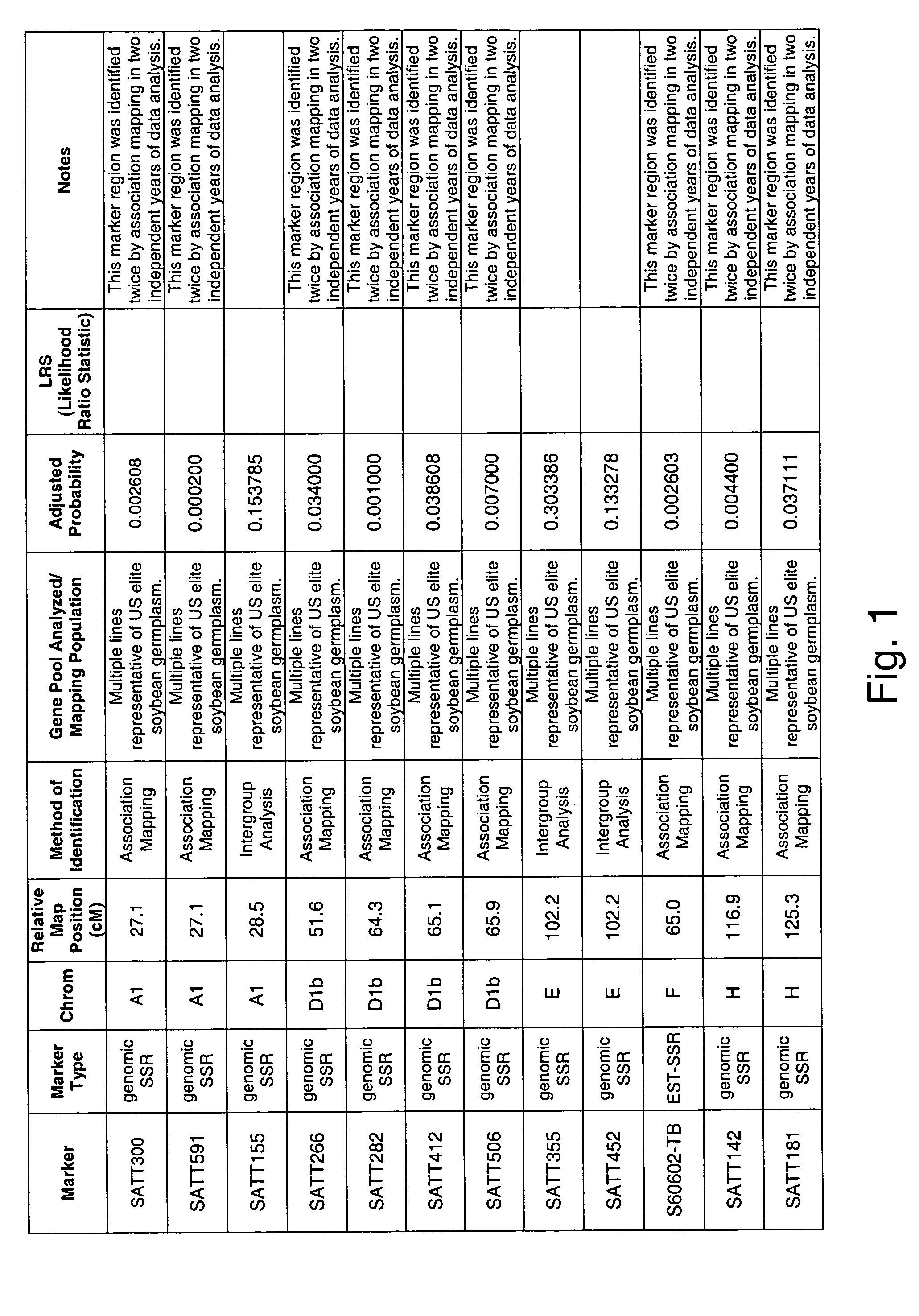
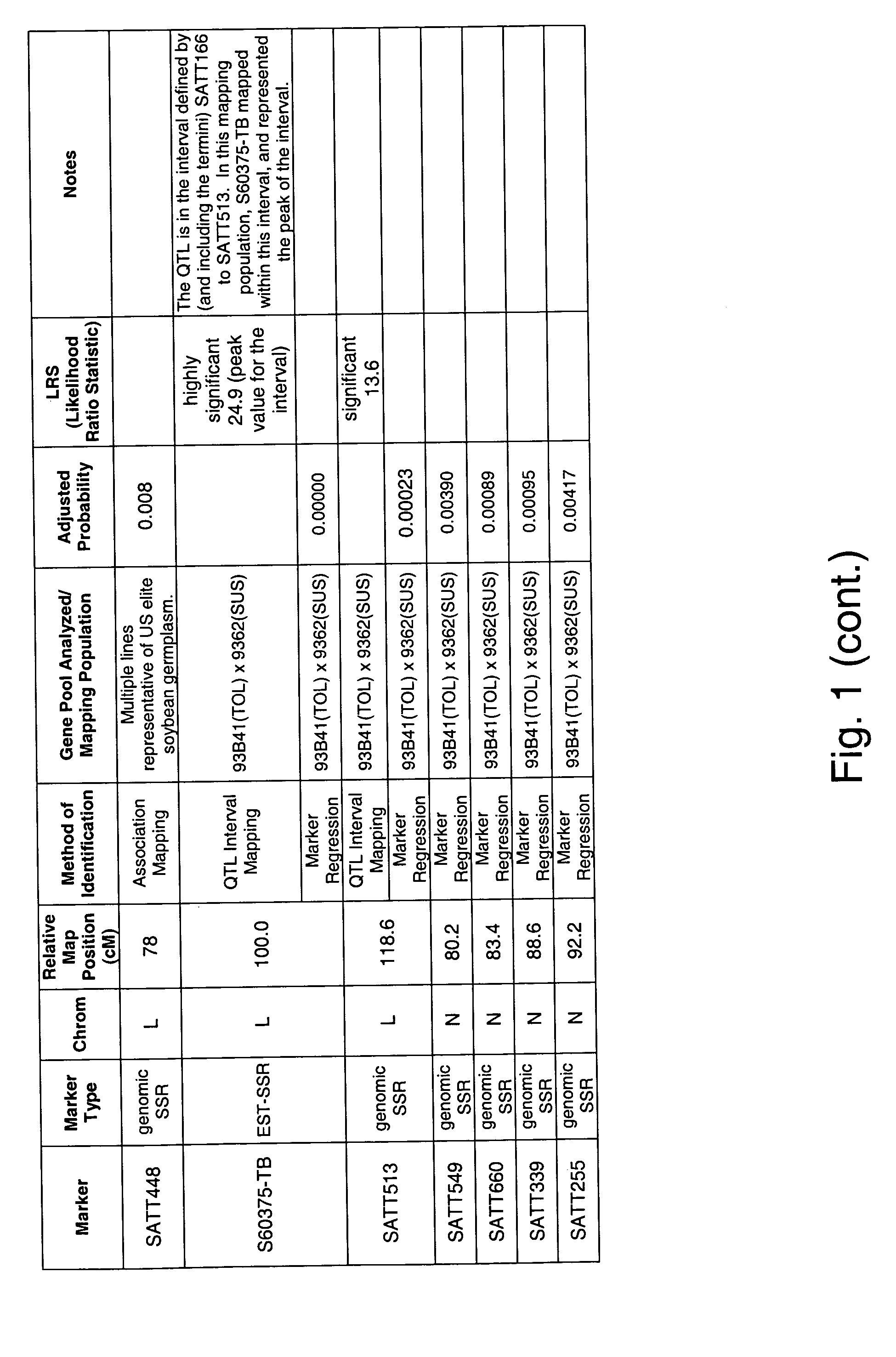
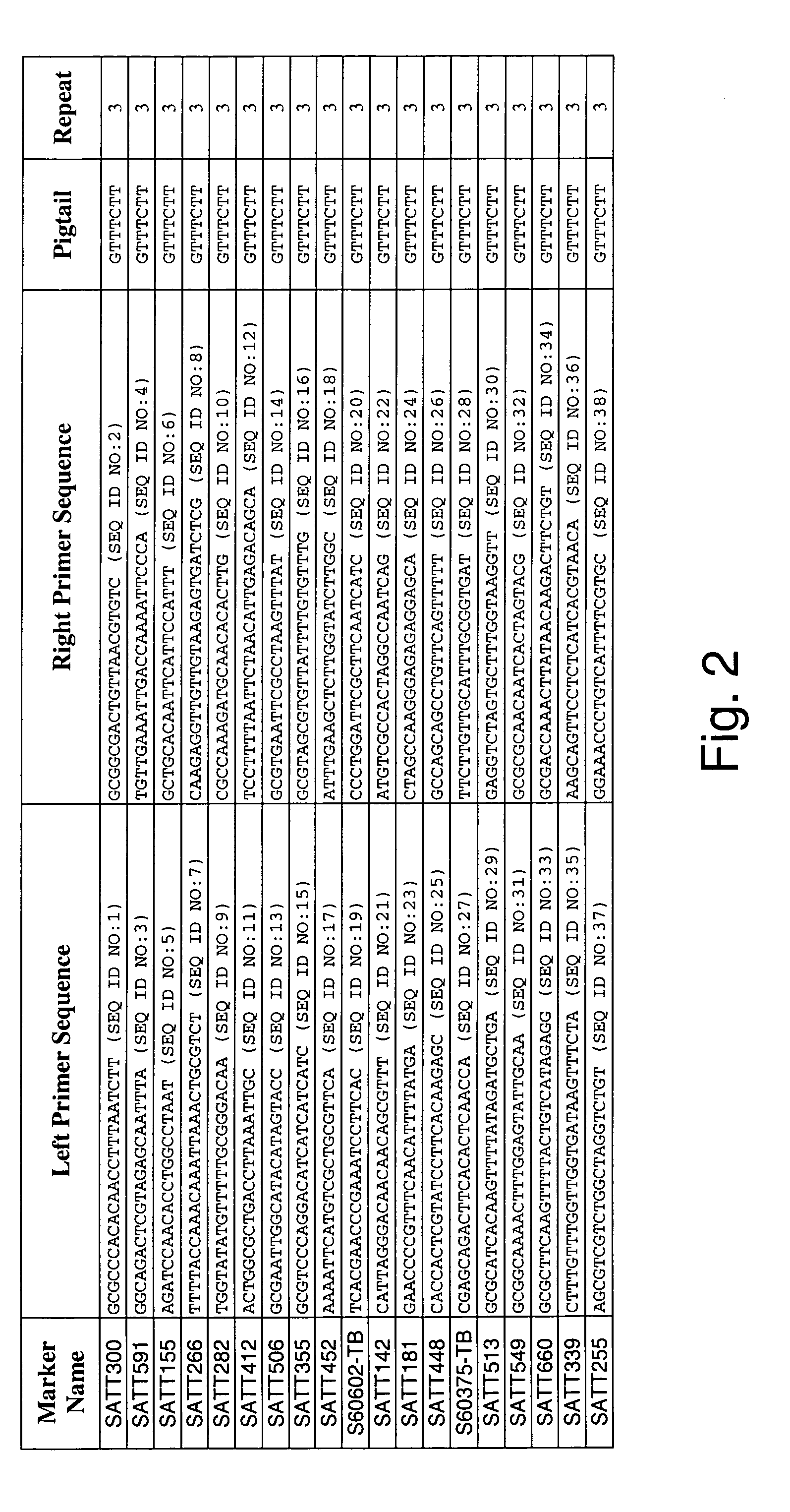
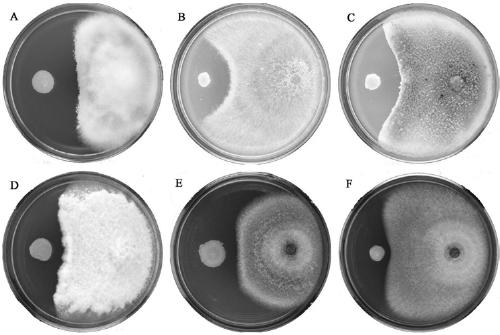
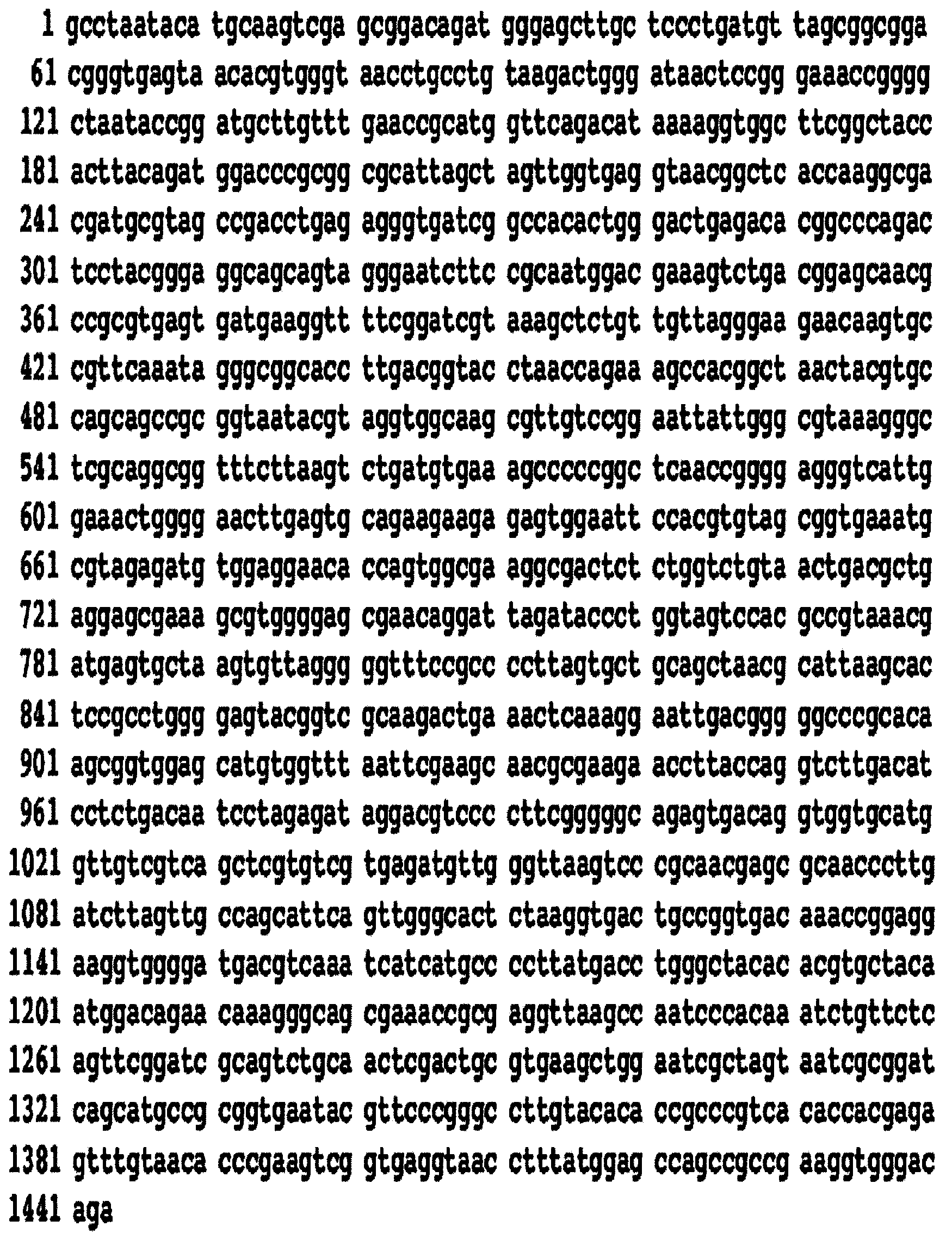Patents
Literature
225 results about "Fusarium solani" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fusarium solani is a species complex of at least 26 closely related filamentous fungi in the division Ascomycota, family Nectriaceae. It is the anamorph of Nectria haematococca. It is a common soil fungus and colonist of plant materials. Fusarium solani is implicated in plant disease as well as human disease notably infection of the cornea of the eye.
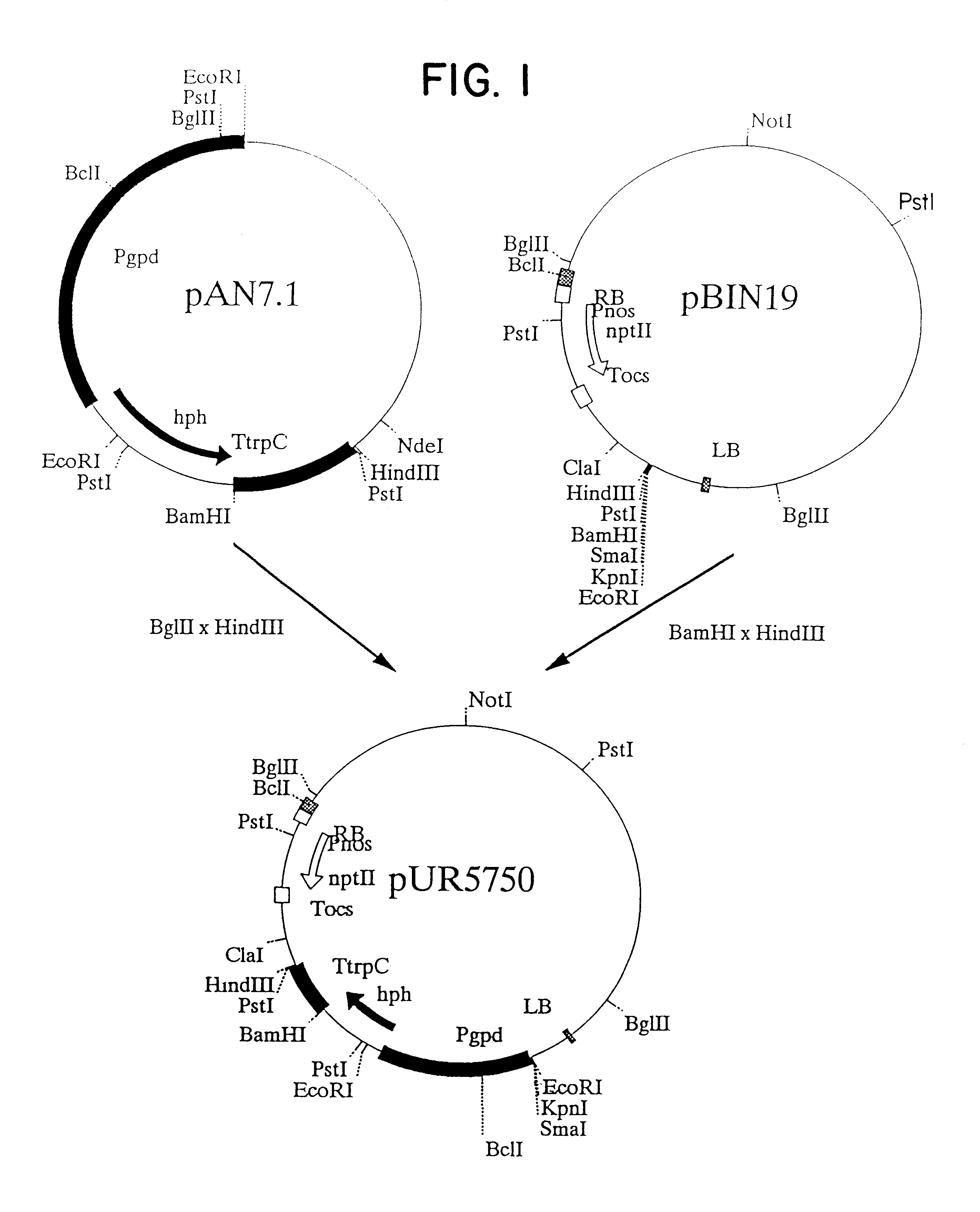
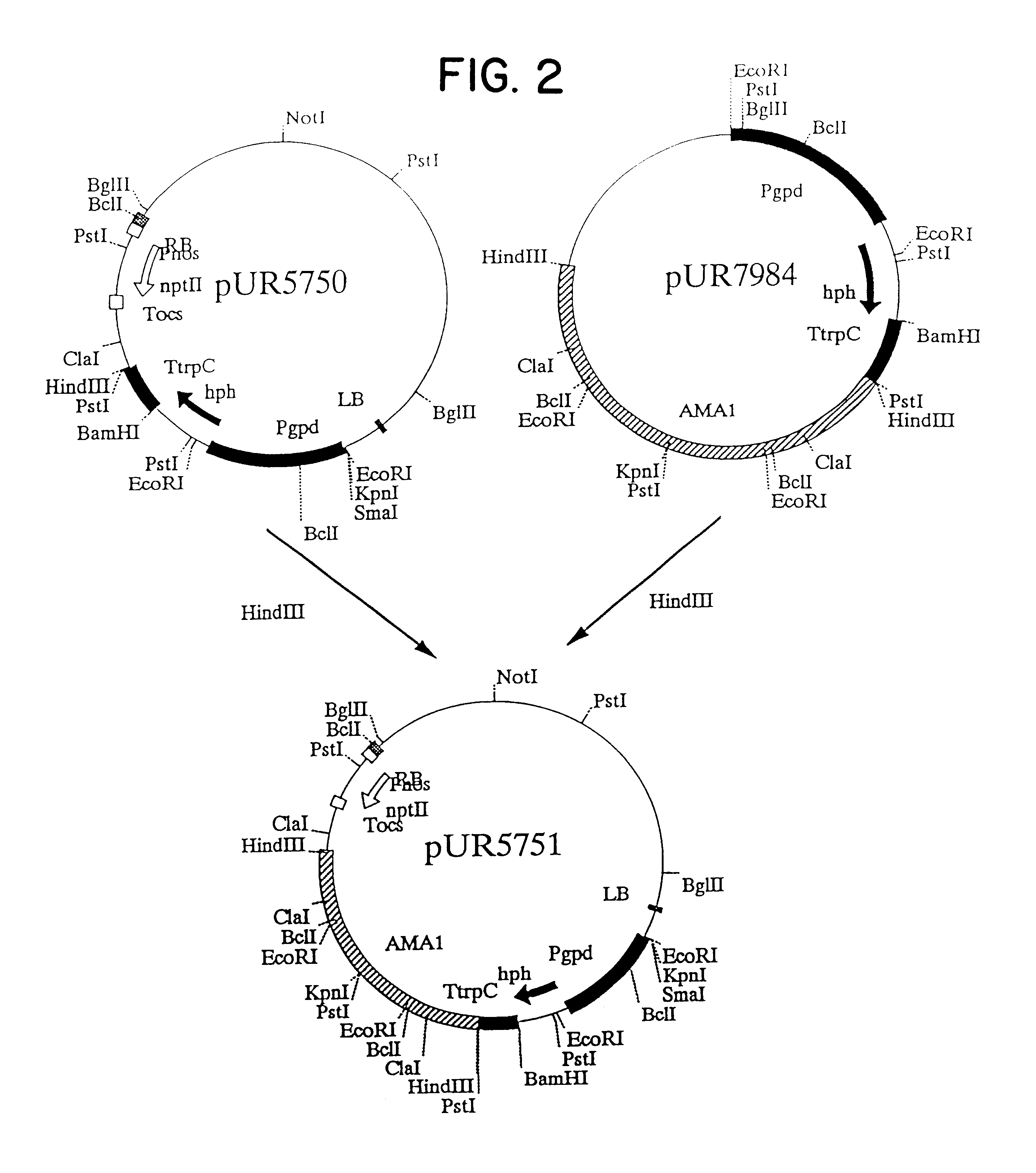
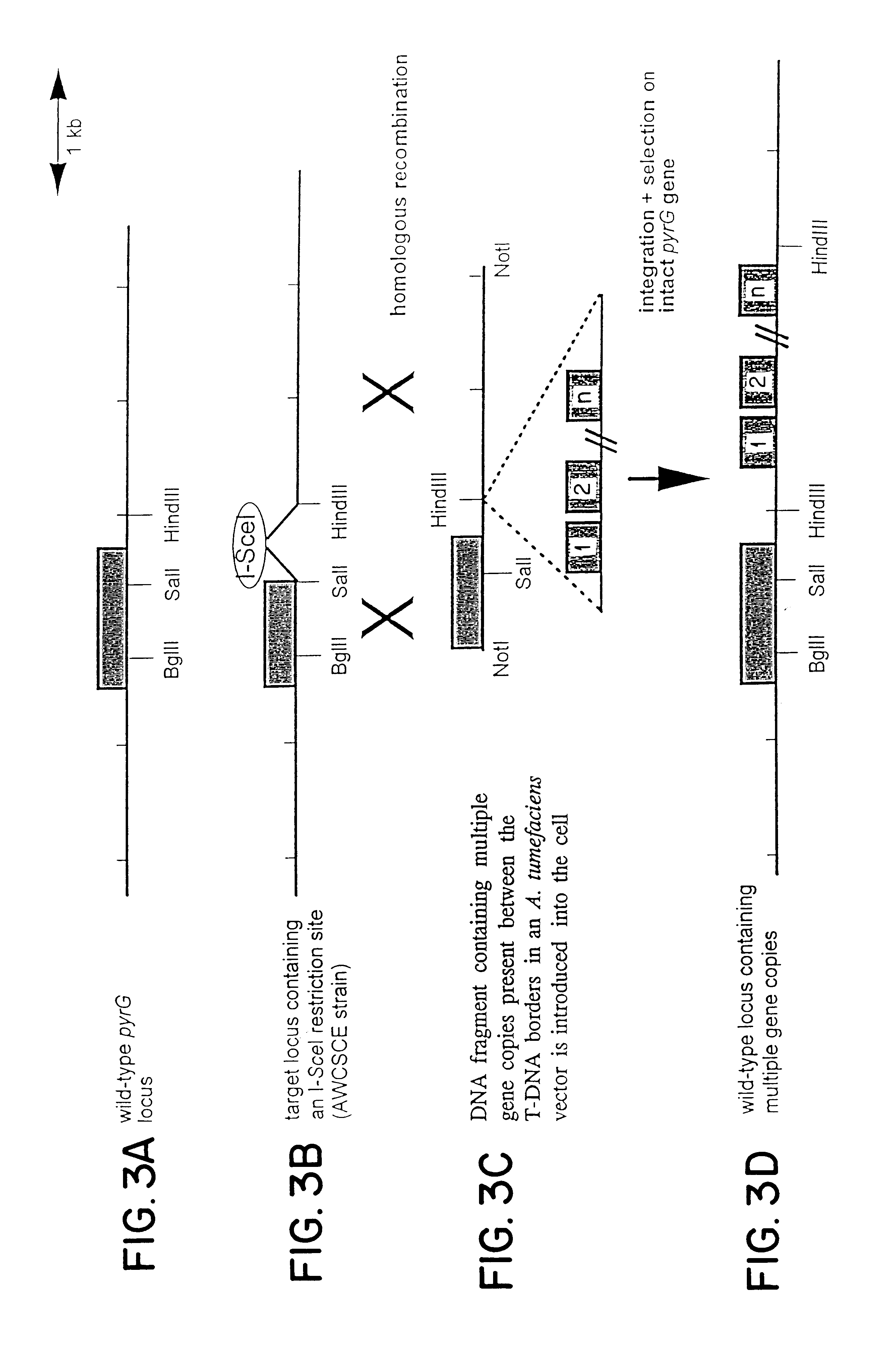
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
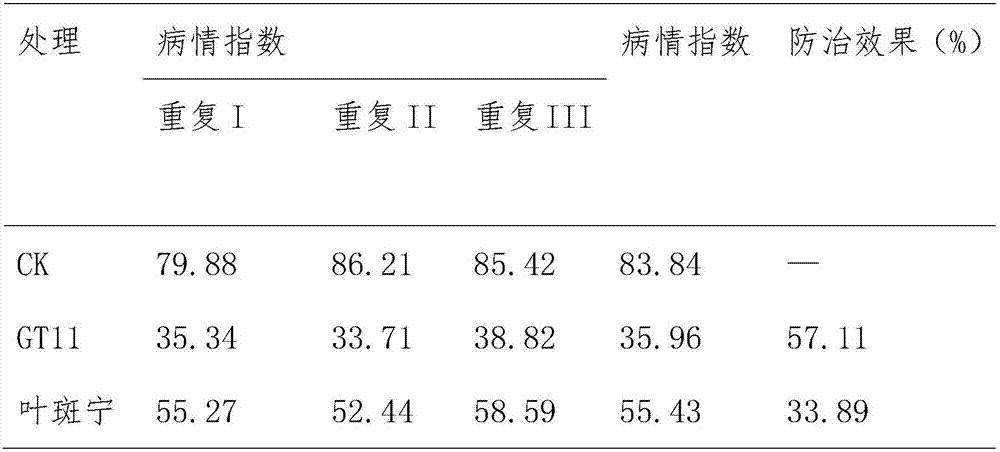
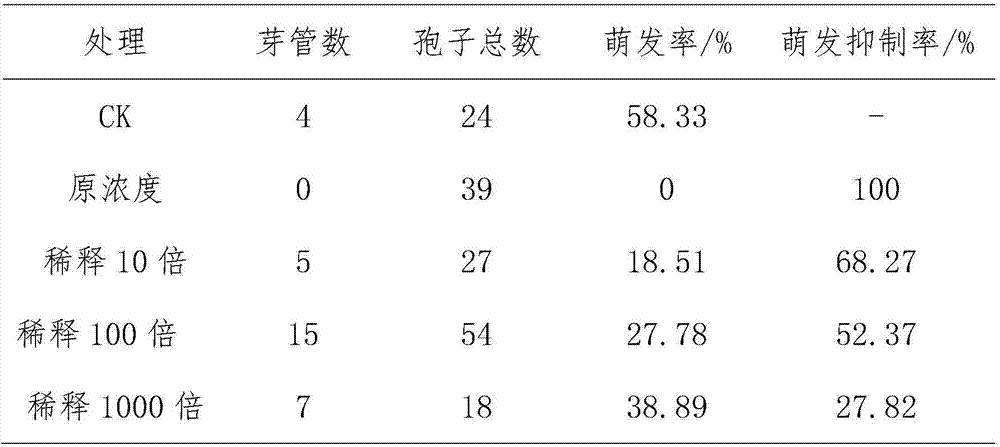
Bacillus belleus GT11 and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus belleus GT11 and application thereof. The bacillus belleus CT11 is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 13th, 2016; the collection number is CGMCC No.13446; the bacillus belleus CT11 can be prepared into water agent, wettable powder or coating material and can be used for preventing and controlling the root rot diseases of pseudo-ginseng and plukenetia volubilis and Chinese cabbage clubroot. The invention provides an efficient, nontoxic, safe, non-residual and conveniently used biological agent for preventing and controlling the diseases such as root rot and clubroot; the effective active ingredient is bacillus belleus CT11 strain; the strain can generate the secondary metabolite antimicrobial active matter, is capable of degrading the cell wall of pathogenic bacteria and has an excellent growth-promoting effect for the crops, such as, plukenetia volubilis, pseudo-ginseng and Chinese cabbage; besides, the bacillus belleus CT11 has a better antibacterial effect for pseudo-ginseng phytophthora sojae, pseudo-ginseng fusarium solani, plukenetia volubilis gray mold, paddy bacterial mycosphaerella, and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum and application thereof
ActiveCN105132336AGrowth inhibitionWide range of sterilization applicationsBiocideBacteriaFusarium oxysporumMicroorganism
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens and the microbial inoculum and application thereof. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is a Latin name, the strain number is HC200, and the accession number in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.10371. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens has a selective antagonism effect on biocontrol bacteria and pathogenic bacteria and has a strong inhibiting effect on fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, phytophthora nicotianae and ralstonia solanacearum, and has a good synergetic antagonism effect on pathogenic bacteria by being matched with trichoderma viride H06.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
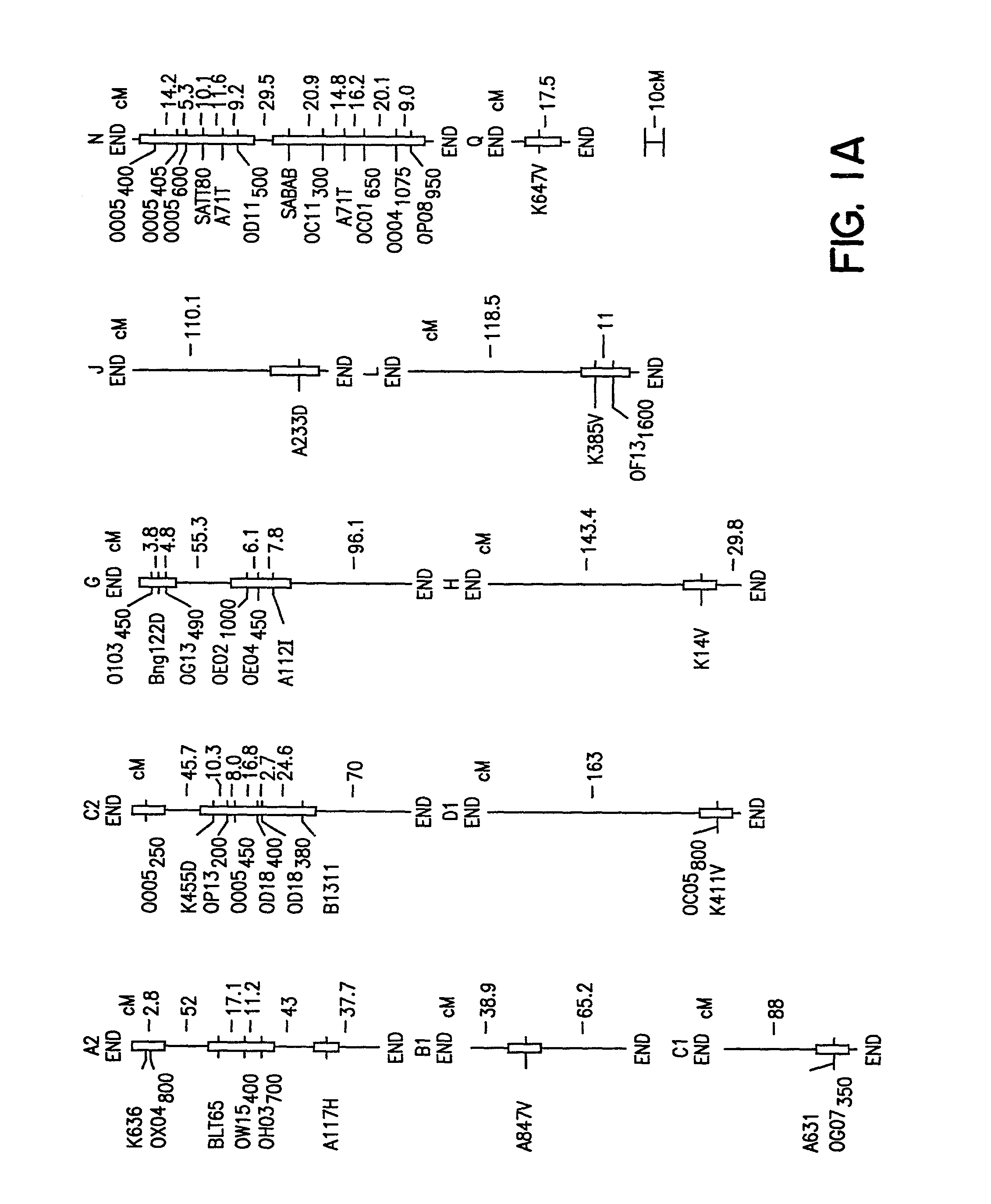
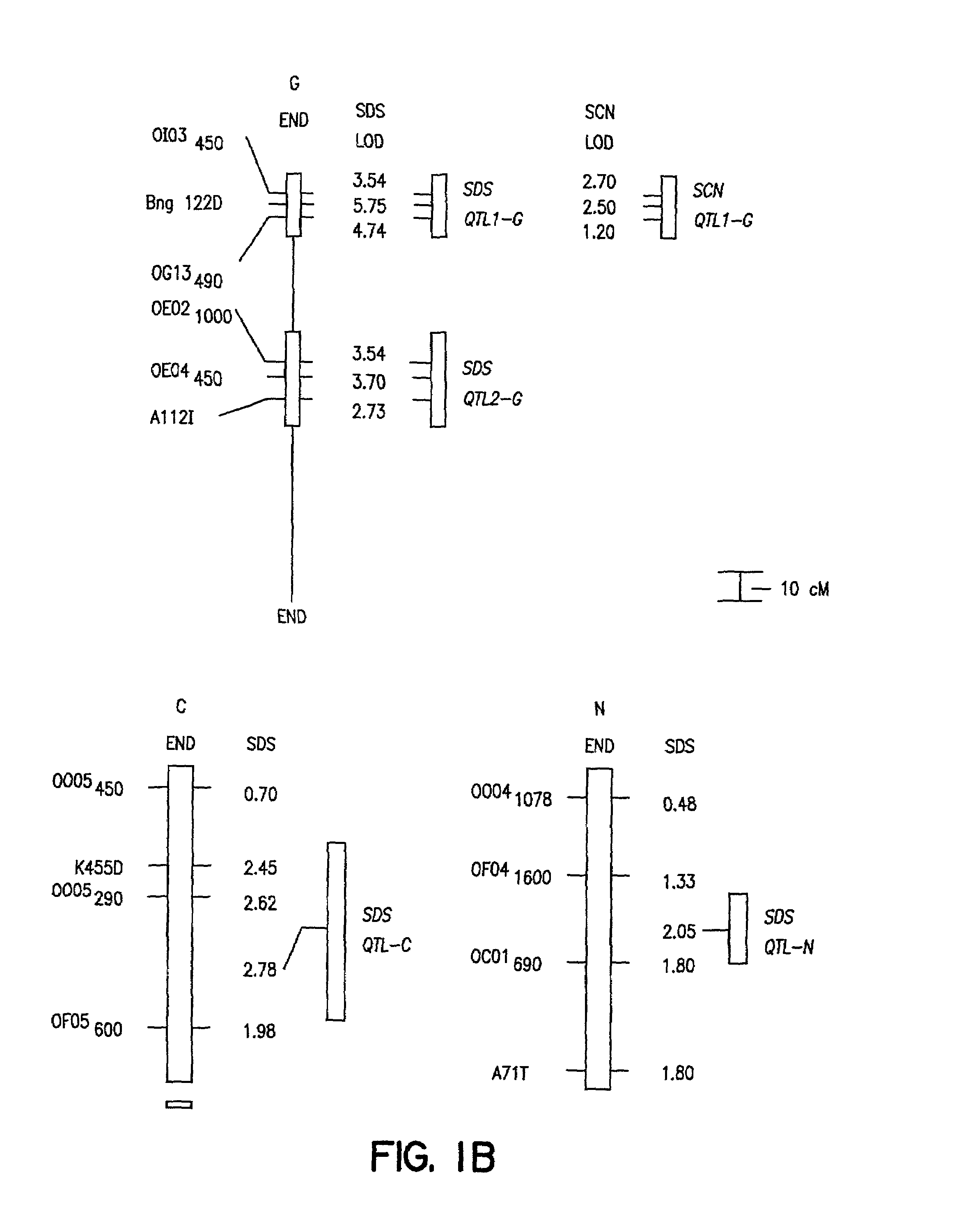
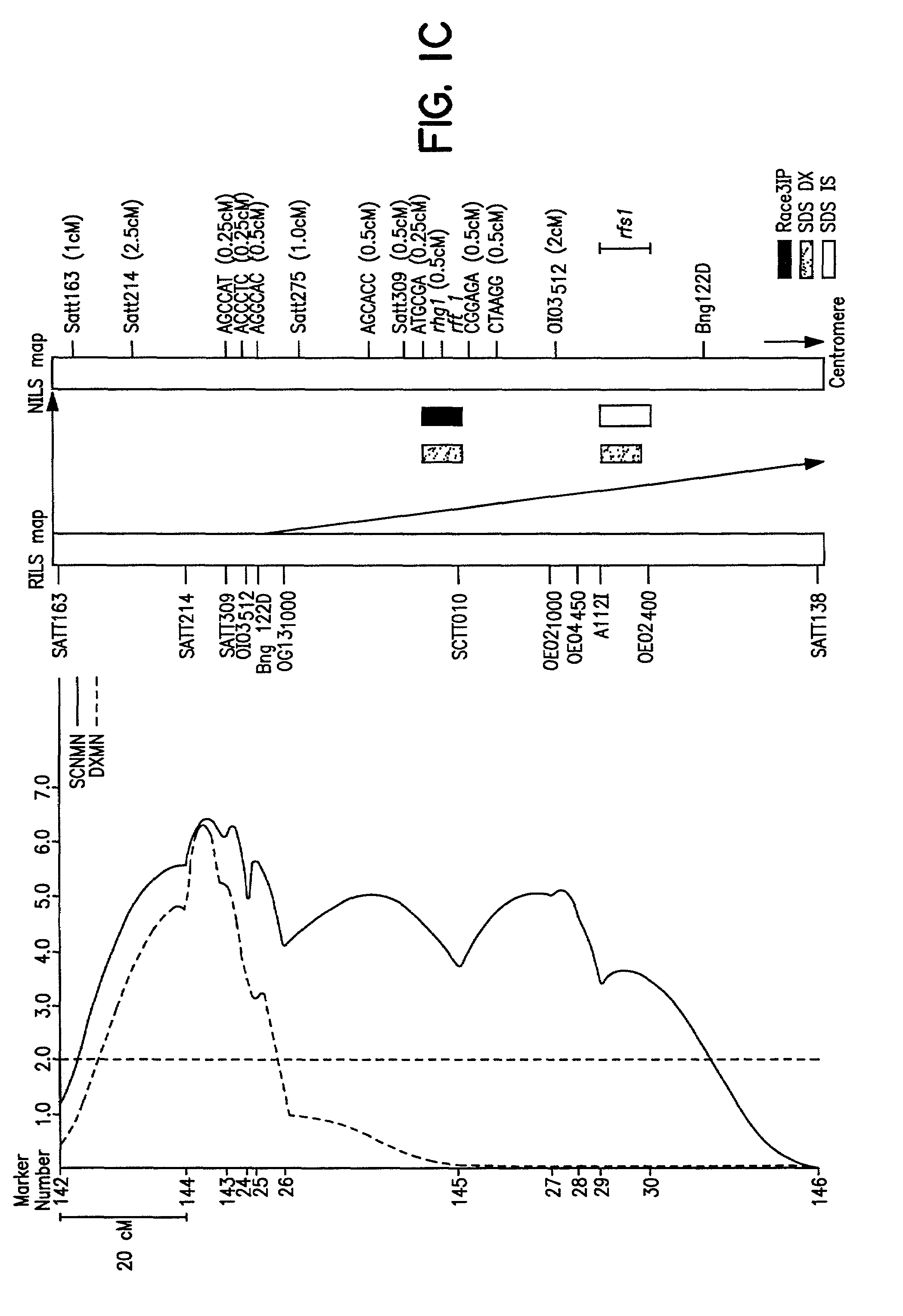
Method of determining soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in a soybean plant
InactiveUS7288386B2Solves the problem quickly and cheaply selecting resistant cultivarsImprove selection for SDS and SCN resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell culture mediaBacterial growth
A method of determining the presence of soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in the soybean plant in a greenhouse setting, the method comprising the steps of: (a) inoculating soil with a low density inoculum of Fusarium solani; (b) planting a soybean plant in said inoculated soil; (c) growing said plant in said soil in a greenhouse; (d) isolating Fusarium solani-infected tissue from said plant; (e) culturing said infected tissue for a period of time sufficient to allow for fungal colony forming unit growth; (f) scoring at least one of disease severity and infection severity in said plant using the number of said fungal colony forming units; and (g) correlating at least one of said disease severity and said infection severity to at least one of disease severity and infection severity data from genetic markers associated with soybean sudden death syndrome resistance to identify a correlation, wherein a statistically significant correlation indicates presence of soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in said soybean plant. Also provided is a method of characterizing resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in a soybean plant, the method comprising the steps of: (a) isolating roots from a soybean plant infected by Fusariurn solani; (b) culturing the root on a culture plate including a restrictive growth medium that provides for slow fungal growth and restricted bacterial growth; (c) determining root infection severity by statistically evaluating the number of Fusarium solani colony forming units on said culture plate; and (d) characterizing resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in said soybean plant based on said determined root infection severity.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Bacillus methylotrophicus and application thereof
InactiveCN105018386ABroad antibacterial spectrumEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaSclerotiniaScreening method
The invention provides bacillus methylotrophicus with a collection number of CCTCC M2015297. Bacillus methylotrophicus is named bacillus methylotrophicus XK-4. The invention further provides a screening method of bacillus methylotrophicus XK-4, an application of bacillus methylotrophicus XK-4 to inhibition of sclerotinia sclerotiorum, rhizoctonia solani, fusarium solani and fusarium oxysporum and a bacillus methylotrophicus XK-4 agent. Bacillus methylotrophicus XK-4 is a rape rhizosphere microorganism, is safe to human, livestock and crops, is environment-friendly, has a wider antibacterial spectrum, has better inhibitory effects on mycelial growth of common pathogenic bacteria, such as sclerotinia sclerotiorum, rhizoctonia solani, fusarium solani and fusarium oxysporum, has obvious inhibitory effects on mycelial growth of sclerotinia sclerotiorum and causes mycelia deformation. The further prepared agent has obvious control effects on sclerotinia rot of colza, is short in production cycle and has a very extensive application prospect in biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Multifunctional bacillus siamensis and application thereof
ActiveCN113151059AGood control effectEnhanced inhibitory effectFlowers cultivationPlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyRoot rot
The invention discloses a bacillus siamensis (bacillus siamensis), and the preservation number of the bacillus siamensis is CGMCC No.19505. The bacillus siamensis has a very high inhibition effect on root rot caused by fusarium solani, the bacterial liquid of the bacillus siamensis has a relatively good prevention and treatment effect on the root rot of oil peonies, the growth of oil peony plants can be promoted, so that the investment of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can be reduced, the environmental pollution can be alleviated, and the sustainable development of agriculture can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
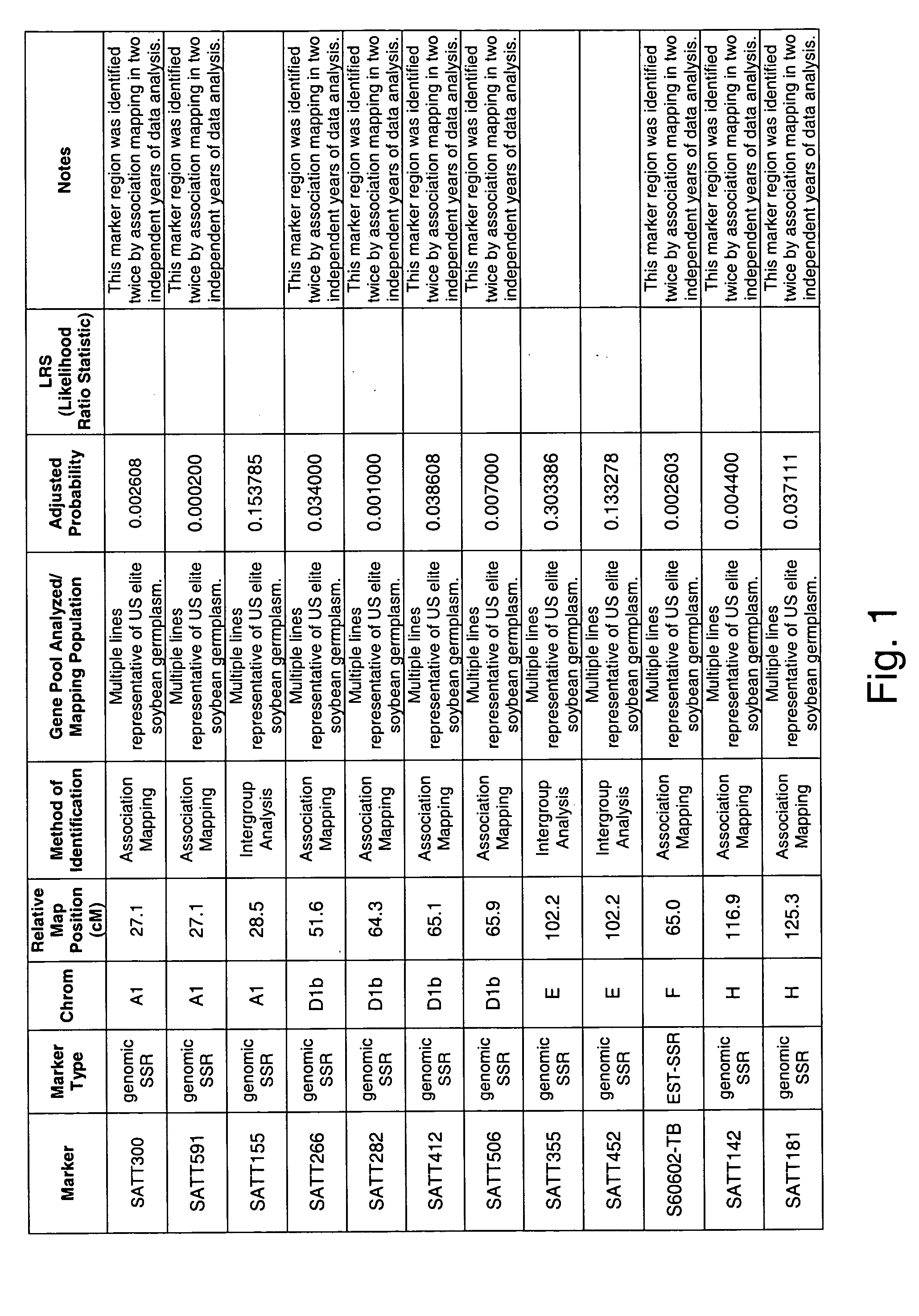
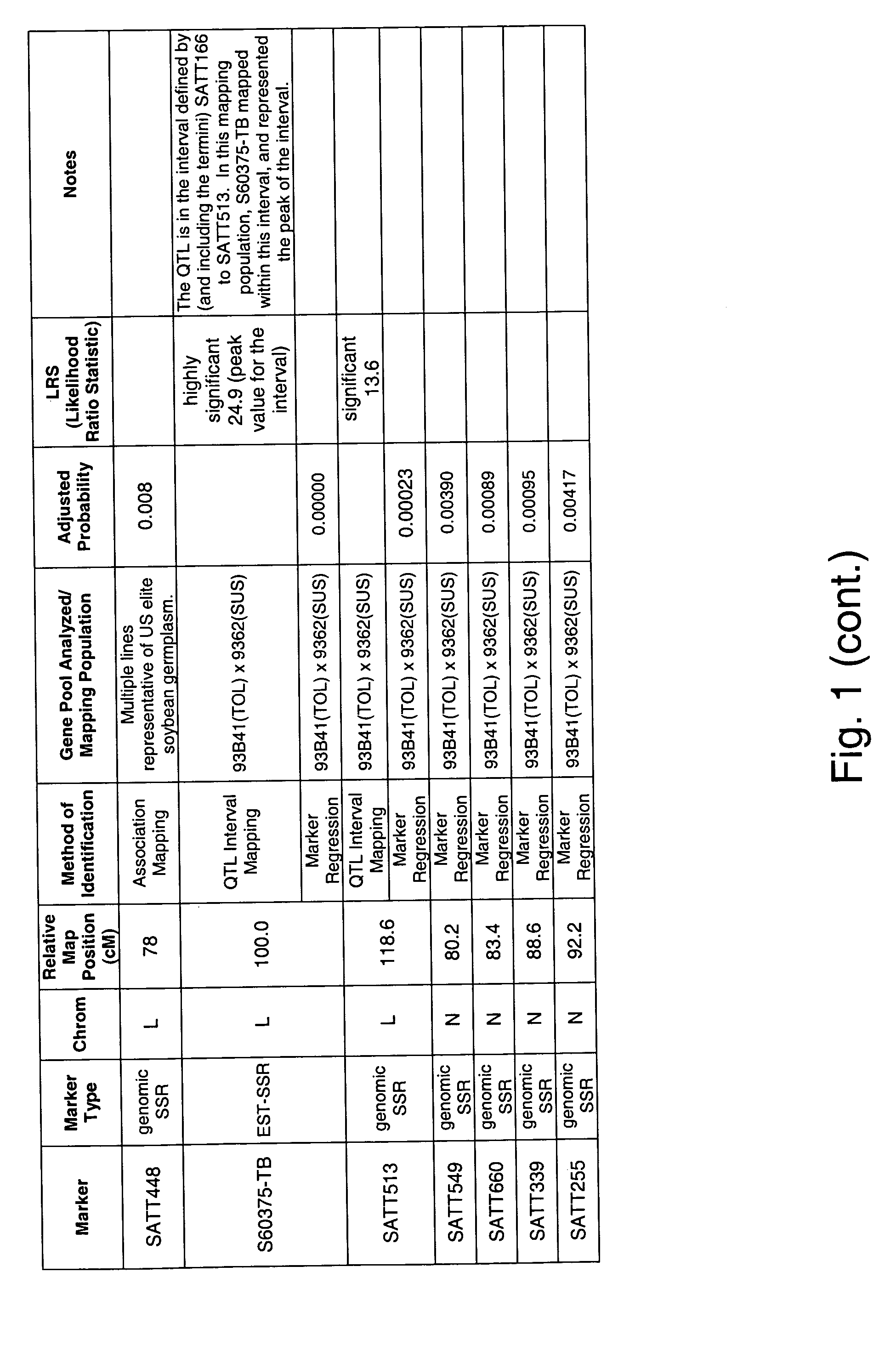
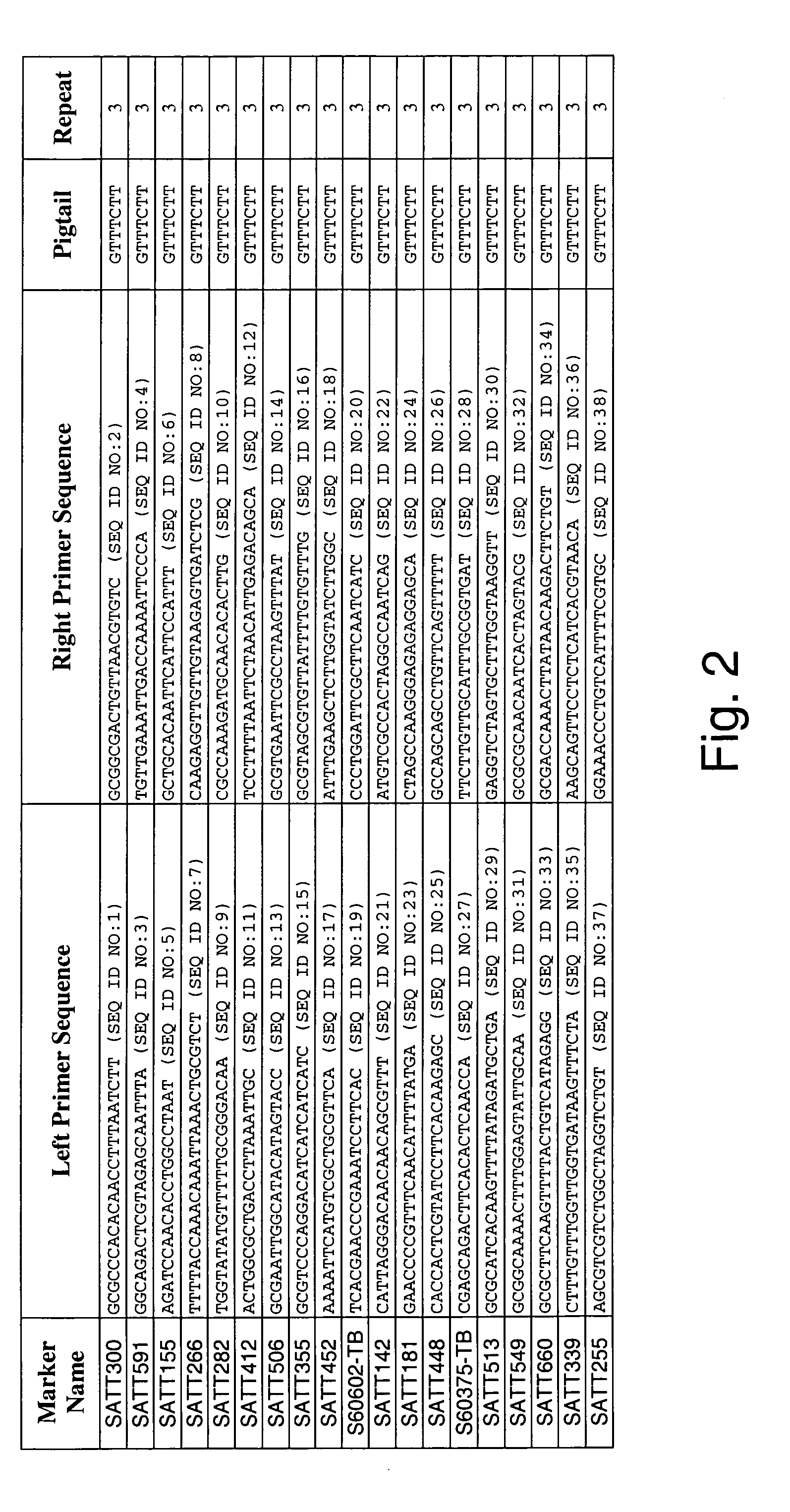
Genetic loci associated with Fusarium solani tolerance in soybean
ActiveUS7767882B2Rapid lossLosses in viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyFUSARIUM INFECTIONS
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying soybean plants that are tolerant, have improved tolerance or are susceptible to Fusarium solani infection (the causative agent of sudden death syndrome or SDS). The methods use molecular genetic markers to identify, select and / or construct disease-tolerant plants or identify and counterselect disease-susceptible plants. Soybean plants that display tolerance or improved tolerance to Fusarium solani infection that are generated by the methods of the invention are also a feature of the invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Panax notoginseng antimicrobial peptide gene PnSN1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105861517AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationGenomicsVerticillium species
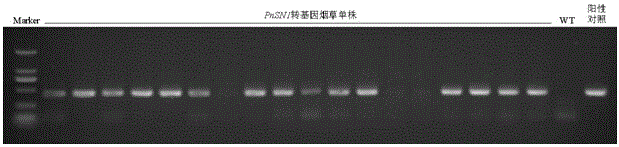
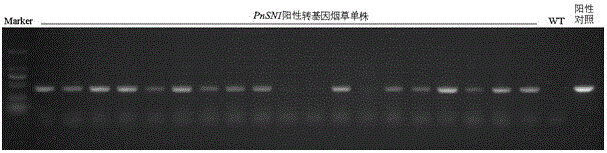
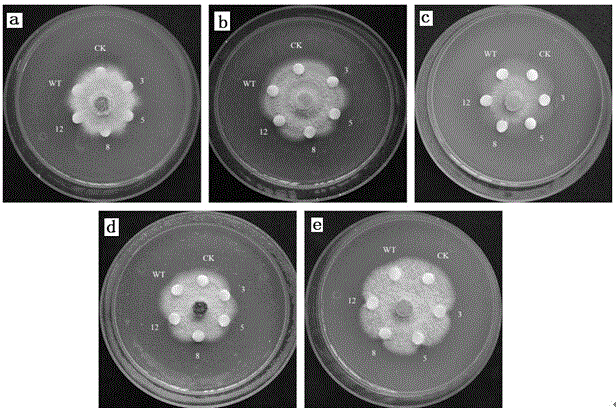
The invention discloses a panax notoginseng antimicrobial peptide gene PnSN1. The nucleotide sequence of the PnSN1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the PnSN1 gene is used for coding snakin antimicrobial peptide. The functional genomics correlation technique study proves that the PnSN1 gene has the function of improving the plant fungal infection resistance capability; the antifungal PnSN1 gene is built onto a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobaccos for overexpression; the transgenosis tobacco has high in vitro antifungal activity. The transgenosis tobacco subjected to PnSN1 overexpression has the strong inhibiting effect on the growth of fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, verticillium fusarium, botryosphaeria dothidea and beaded gibberella.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY11 and application thereof
ActiveCN110747202AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetics genomics
The invention discloses a Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY11. The Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY11 has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and encodes a protein having an amino acid sequences shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the invention, genomic studies have confirmed that the LrWRKY11 gene can improve anti-fungal functions of plants. Being constructed onto a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco so as to be subjected to overexpression, the anti-fungal LrWRKY11 gene disclosed by the invention is capable of endowing the transgenic tobacco with very strong resistance to fungal pathogens. Experimental results have shown that transgenic tobacco with overexpression of the LrWRKY11 gene has very high level of resistance to infection of Nigrospora oryzae, Fusarium verticillioides, Botryosphaeria dothidea, Fusarium solani and Alternaria panax.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Microbial agent for preventing and treating pinellia ternate root rot as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a microbial agent for preventing and treating pinellia ternate root rot as well as a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to bacillus velezensis MES861. According to the bacillus velezensis MES861, the preservation date is December 03, 2018, the name and the abbreviation of the preservation organization are China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the preservation number is CGMCC No.16857. According to the pinellia ternate root rot prevention and treatment microbial agent, fermentation liquor prepared through fermentation of the bacillus velezensis serves as the microbial agent for preventing and treating the pinellia ternate root rot. The preparation method for the microbial agent for preventing and treating the pinellia ternate root rot comprises the step that a liquid nutrient agar culture medium is inoculated with the bacillus velezensis, and shake culture is carried out so as to obtain the bacillus velezensis fermentation liquor. The bacillus velezensis has a strong inhibition effect on pathogenic bacteria such as fusarium graminearum, fusarium solani, fusarium oxysporum and F.moniliforlle, so that the occurrence of the pinellia ternate root rot is effectively prevented, and the stable yield and the income increase of pinellia ternate are promoted.
Owner:天津开发区坤禾生物技术有限公司
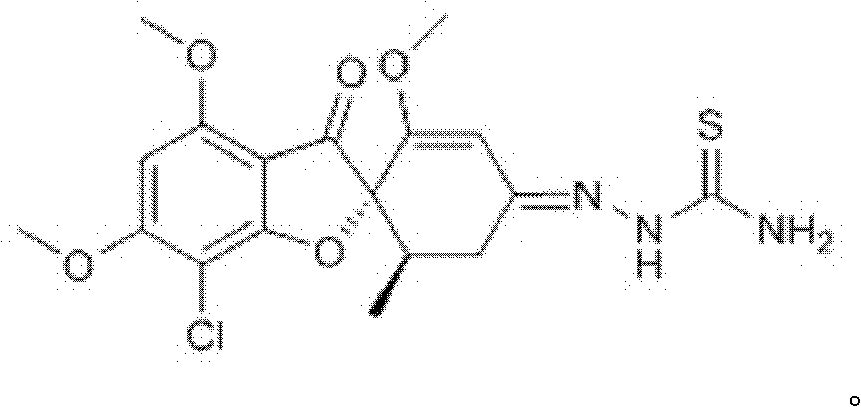
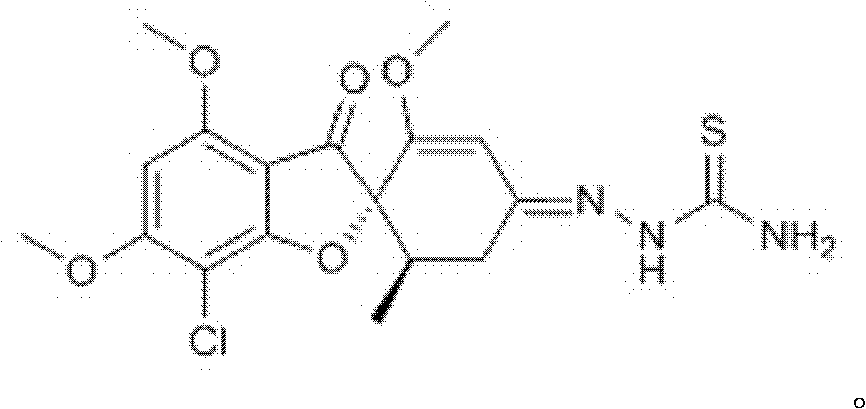
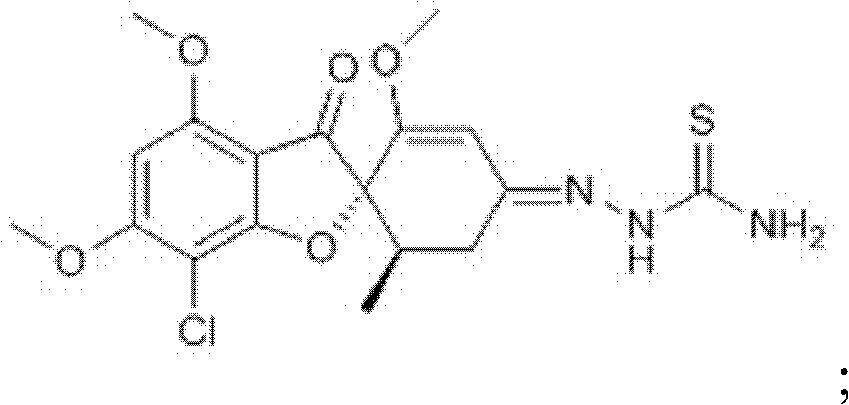
Novel thiosemicarbazone compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102219769AEasy to prepareEasy to operateOrganic chemistryFungicidesFusarium oxysporumColletotrichum acutatum
The invention mainly provides a thiosemicarbazone compound which has an inhibition effect on fusarium oxysporum, fusarium moniliforme, fusarium solani and colletotrichum and a preparation method thereof. The chemical structural formula of the compound is shown in the specification. According to the invention, a novel way for preventing and controlling plant diseases caused by fusarium oxysporum, fusarium moniliforme, fusarium solani and colletotrichum is provided; and the preparation method is simple and convenient and has strong operability.
Owner:福建省农业科学院农业生物资源研究所
Lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY3 and application thereof
ActiveCN110818782AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY3 and a preparation method thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and a protein with an aminoacid sequence shown as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; according to the invention, functional genomics related technical researches prove that the LrWRKY3 gene has the function of improving the antifungal performance of plants; the antifungal LrWRKY3 gene disclosed by the invention is constructed on a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobacco for overexpression; the transgenic tobacco plantshave very strong fungus infection resistance, and experimental results show that transgenic tobacco leaves with over-expression of LrWRKY3 have very strong resistance to infection of five pathogenicfungi such as alternaria oryzae, Botryosphaeria dothidea, fusarium graminearum, Fusarium rotunda and fusarium solani.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bacterial strain for preventing potato blight and preparation method and application of preparation thereof
ActiveCN107603906APrevent Fusarium WiltPromote production increaseBiocideBacteriaEcological environmentBiological activation
The invention relates to a bacterial strain for preventing potato blight and a preparation method and the application of a preparation thereof. The bacterial strain is bacillus subtilis MES810, the preservation date is Aug, 10th, 2017, and the preservation number is CGMCCNo. 145154. The preparation method of the preparation corresponding to the bacterial strain comprises the following steps: activation of a culture; preparation of a primary seed solution; preparation of a secondary seed solution; fermentation in a fermentation tank, and discharging to obtain a bacillus subtilis liquid preparation. The bacillus subtilis has a strong inhibiting effect for fusarium pathogenic bacteria consisting of Fusarium solani, fusarium oxysporum, fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium nivale or elderberry fusarium and Eavenaceum, the occurrence of potato blight is prevented, the control efficiency is more than 80%, and the increase of both production and income for potato is promoted. The bacterial strain disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of no toxicity, no residue, no growth inhibition, small using amount and simple application method, and provides the possibility for the diversification of application schemes and the protection of ecological environment.
Owner:天津开发区坤禾生物技术有限公司
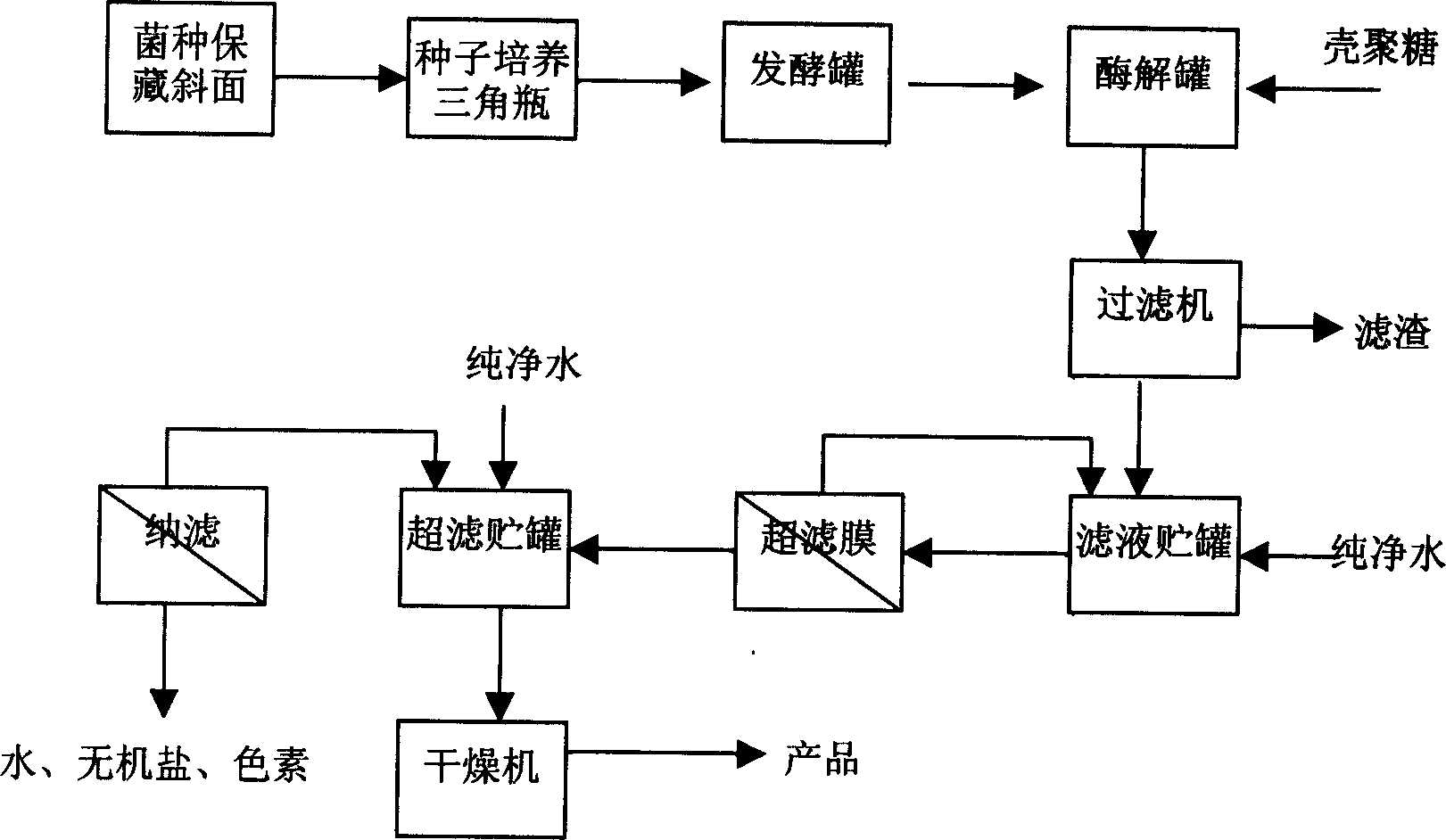
Production of chitose from fusarium solani
InactiveCN1680569AHigh activityReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationViscosityFusarium
A process of preparing chitosan used Fusarium Solami. Chitosan produced from Fusarium Solami is a kind of high efficient inscribed enzyme. Viscosity of chitosan solution can reduce to 90% in 2h between 37deg.C and 55deg.C. Producing field is bigger than 70% after 8h. Content of oligosaccharide below 10 is more than 90%. The process contains strain culture, ferment process, pre-process of material, filtering of enzymolysised solution, molecular weight assortment, decolour, desalting, concentrating and drying.
Owner:苏理
Genetic loci associated with fusarium solani tolerance in soybean
ActiveUS20060041954A1Rapid lossLosses in viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesTolerabilityFUSARIUM INFECTIONS
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying soybean plants that are tolerant, have improved tolerance or are susceptible to Fusarium solani infection (the causative agent of sudden death syndrome or SDS). The methods use molecular genetic markers to identify, select and / or construct disease-tolerant plants or identify and counterselect disease-susceptible plants. Soybean plants that display tolerance or improved tolerance to Fusaruim solani infection that are generated by the methods of the invention are also a feature of the invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Bacterial strain WXX-2 and bacterial agent for controlling peanut root rot
The invention relates to a bacterial strain WXX-2 and a bacterial agent for controlling peanut root rot. The bacterial strain is Bacillus pumilus with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 11540. The 16s rRNA base sequence of the bacterial strain is shown as SEQ ID No.1. Chitinase produced by the bacterial strain and used for degrading fungal hypha cell walls has higher activity ad has significant degradation capacity against fungal pathogen hyphae such as fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, blight bacteria, rhizoctonia and the like infecting roots of crops. The quantity of seed dressing with the bacterial agent is generally only 10-15 kg / mu, damage by the frequent peanut root rot in upland red soil can be effectively controlled, the control effect reaches 60% or higher, and the bacterial strain WXX-2 and the bacterial agent have the advantages of small application quantity, broad antibacterial spectrum, remarkable yield increasing effect and the like, and the influence of the root rot on the loss of peanut yield is effectively reduced.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel strain of Bacillus subtilis, and use thereof for preventing root rot disease in plants
The invention relates to a novel strain of Bacillus subtilis, and more particularly, to the B-5604 strain of Bacillus subtilis, which inhibits the growth of root rot pathogens, to a composition containing the strain or the culture medium thereof for controlling root rot pathogens, to a method for controlling ginseng root rot pathogens using the composition, and to a method for inhibiting the growth of Cylindrocarpon destructans or Fusarium solani using the strain. The microorganisms having antagonistic activity developed according to the present invention are not harmful to water and soil, and thus does not cause environmental pollution, and particularly, the microorganisms having antagonistic activity according to the invention may not only reduce root rot pathogens in farmland in which ginseng is repeatedly cultivated or recultivated, but also alleviate root rot disease in ginseng being cultivated, thus significantly contributing to ginseng cultivation.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Plant-derived pesticide as well as preparation method and application of plant-derived pesticide
ActiveCN103907650ANo side effectsGood insecticidal effectBiocideFungicidesSide effectPesticide residue
The invention discloses a plant-derived pesticide which consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 95-100 parts of dalmatian chrysan themum, 90-100 parts of bay leaves, 85-95 parts of black false hellebore, 85-90 parts of rhubarb, 80-90 parts of airpotato yam rhizome, 75-85 parts of pungent litse fruits, 75-80 parts of turnip seeds, 70-80 parts of sessile stemona roots, 65-75 parts of chaulmoogratree seeds, 65-70 parts of common fibraurea stem, 60-70 parts of amur corktree bark, 55-65 parts of pepper, 55-60 parts of garden balsam stems, 50-60 parts of China roses and 45-55 parts of rangoon creeper fruits. A preparation method of the plant-derived pesticide comprises the following steps: preparing each raw material; mixing; breaking walls and performing ultrafine smashing; sieving by using a 300-mesh sieve to obtain the plant-derived pesticide. The plant-derived pesticide has insecticidal and bactericidal functions, and has special effects on stubby root nematodes and fusarium solani (fusarium). The plant-derived pesticide has no side effect on soil and environments, is free from the side effects of pesticide residue, environment pollution and the like, and can be popularized and applied.
Owner:山东丰本生物科技股份有限公司
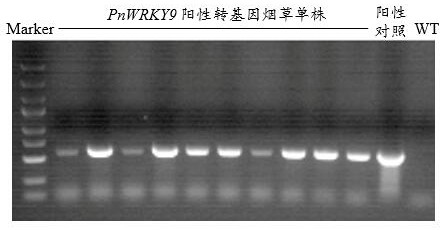
Pseudo-ginseng WRKY transcription factor gene PnWRKY9 and application thereof
ActiveCN112831504AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNigrospora oryzae
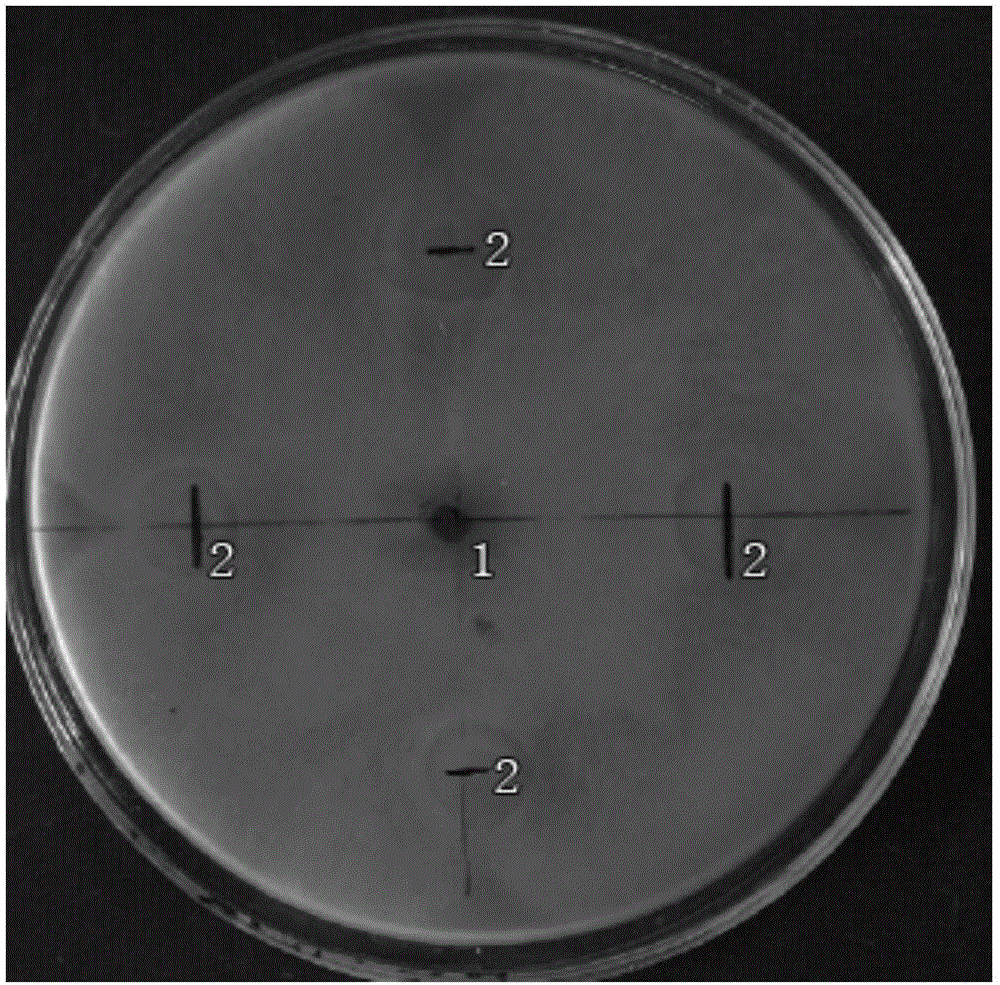
The invention discloses a pseudo-ginseng WRKY transcription factor gene PnWRKY9 and the application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the PnWRKY9 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the PnWRKY9 gene encodes a WRKY transcription factor; according to the application, molecular biology and functional genomics related technical researches prove that the PnWRKY9 gene has the function of improving the fungal disease resistance of plants, the antifungal gene PnWRKY9 is constructed on a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco for overexpression, and the transgenic tobacco plant has very strong in-vitro antifungal activity; according to the present invention, the PnWRKY9 overexpressed transgenic tobacco has the significant inhibition effect on the growth of Alternaria Compacta, Fusarium solani, and Nigrospora oryzae, and the PnWRKY9 overexpressed transgenic tobacco has the significant inhibition effect on the growth of the Alternaria Compacta, the Fusarium solani, and the Nigrospora oryzae, such that the PnWRKY9 overexpressed transgenic tobacco has the significant inhibition effect on the growth of the Nigrospora oryzae,.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
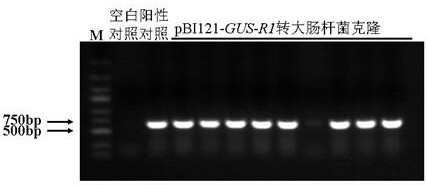
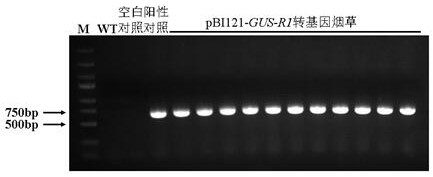
Pseudo-ginseng inducible promoter R1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a pseudo-ginseng inducible promoter R1 and application thereof, the nucleotide sequence of R1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and molecular biology and genetic engineering related technical researches prove that the pseudo-ginseng promoter R1 responds to several plant hormones, biological stress and abiotic stress; a fusion expression cassette constructed by the panax notoginseng promoter R1 and the beta-glucuronidase gene is transferred into tobacco for expression, and the activity of the glucuronidase of the transgenic tobacco is quantitatively detected through a fluorescence method. The result shows that after the transgenic tobacco is treated by fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, alternaria alternata, NaCl, AlCl3, gibberellin, methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, abscisic acid and ethephon, the activity of glucuronidase is obviously enhanced; the pseudo-ginseng promoter R1 is induced by several plant hormones and biological and abiotic stress factors, and can be used for plant disease-resistant gene engineering.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fusarium solani P-1 mycopremna and use in degradation of polychlorinated biphenyl thereof
The invention relates to a sort of new bacterial strain of Fusarium solani, namely P-1 CCTCC No: M207128, and also relates to the application of the Fusarium solani P-1 in degrading polychlorobiphenyl. The Fusarium solani P-1 can degrade polychlorobiphenyl effectively, in particular to aerobic condition, under which the Fusarium solani P-1 can degrade polychlorobiphenyl replaced by perchloricbiphenyl, and the average degrading rate of typical perchloricbiphenyl Aroclor 1245 can reach to 64.15 percent and the degrading rate of polychlorobiphenyl replaced by chlordane-lorobiphenyl of Aroclor 1245 can reach to 70.30 to 100 percent.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
New brevibacillus brevis strain, cultivation method and application of new brevibacillus brevis strain
InactiveCN104894006AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesPinellia
The invention relates to a strain which is separated and screened from pinellia ternate rhizosphere soil in Dafang county of Guizhou province and has the antagonism. Through authentication of the microbial taxonomy, the strain is named as the brevibacillus brevis strain GZDF3, and biological fungicide capable of preventing and treating pinellia ternate block stem rotten sickness is obtained by adopting fermentation liquor of the strain. The strain is obviously characterized in that the new brevibacillus brevis strain GZDF3 is provided; in addition, the antibiological inoculant prepared through the fermentation liquor of the strain has the obvious antagonism on pathogenic bacteria and pathogenic fungus, such as fusarium oxysporum and fusarium solani, of the pinellia ternate block stem rotten sickness; and the strain is an important microbial resource on the traditional Chinese medicinal material green planting industry.
Owner:GUIYANG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Paenibacillus terrae YC16-08 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses paenibacillus terrae YC16-08 and application thereof. A preservation number of the paenibacillus terrae YC16-08 is CGMCC No.16181. By virtue of test research, the paenibacillus terrae YC16-08 has an antagonism effect for phytophthora capsici, botryis cinerea, colletorichum acutatum, rhizoctonia solani, fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani and fusarium verticillioides. The paenibacillus terrae YC16-08 can generate siderophore, amylase, protease, pectinase, cellulase, IAA and NH3, and has nitrogen fixationcapacity and phosphorus dissolving capacity.
Owner:甘肃省农业科学院植物保护研究所
Chestnut preservation method
ActiveCN106070601AReduce the probability of mildewReduce browning rateEdible seed preservationFreeze-dryingInsect pest
The present invention discloses a chestnut preservation method and belongs to the technical field of chestnut preservations. The preservation method consists of the following steps: (1) fruit selecting: insect pest free, full and harmless chestnuts are selected; (2) preservative treating: the selected chestnuts are soaked with the preservative for 15-35 minutes; (3) clean water soaking: the treated chestnuts in the step (2) are soaked with the clean water at 40 to 50 DEG C for 20-40 minutes; (4) biological treating: the treated chestnuts in the step (3) are soaked with water solution containing endogenetic bacteria for 15-25 minutes, and the soaked chestnuts are air-dried; (5) water content controlling: the treated chestnuts in the step (4) are freeze-dried or cold-air dried to control the moisture content to be 38-44%; and (6) refrigerating: the treated chestnut in the step (5) are put into a cold storage to be preserved at a humidity of 85-95% and a temperature of -4 to 0 DEG C. The endogenetic bacteria are endogenetic bacteria separated from the chestnuts to be preserved and at least have both obvious inhibitions on fusarium solani and colletotrichum gloeosporioides.
Owner:湖北大别山药业股份有限公司
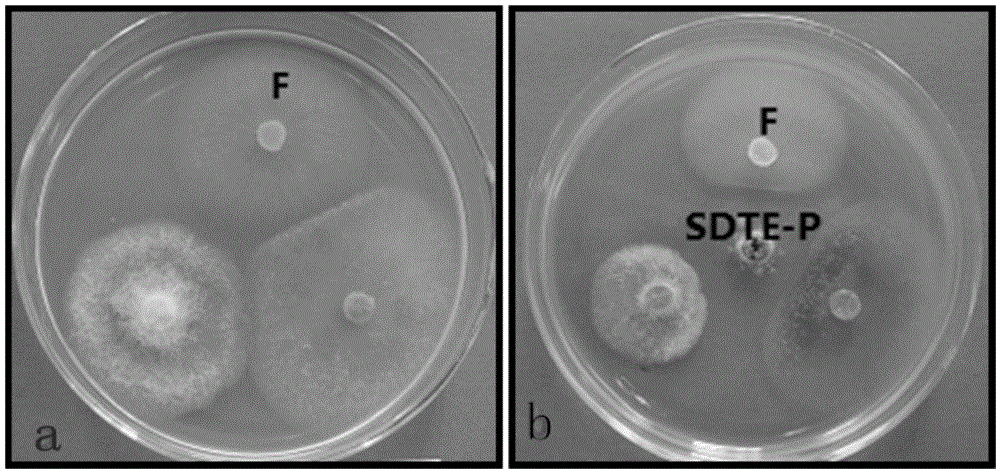
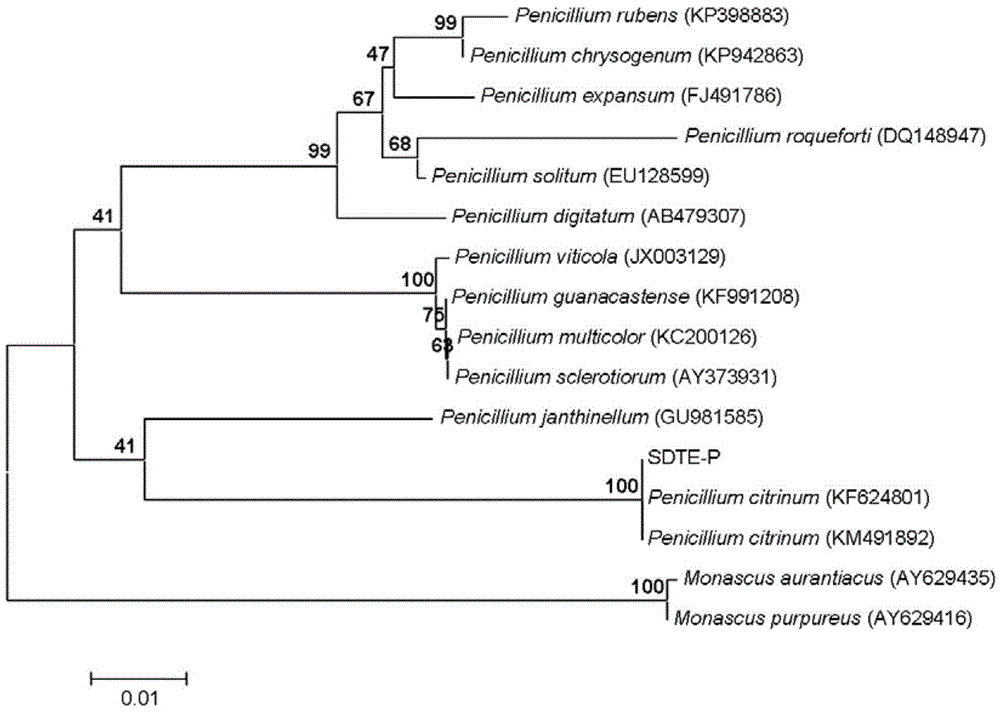
Application of sophora tonkinensis endophytic fungus SDTE-P in preventing and controlling panax notoginseng root rot
The invention discloses a sophora tonkinensis endophytic fungus SDTE-P. The sophora tonkinensis endophytic fungus SDTE-P is classified and named as Penicillium citrinum SDTE-P, wherein the ITS sequence of the strain is as described by SEQ ID NO.1, the depository authority is the General Microbiological Collection Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the depository address is Institute of Microbiology, Building 3, No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the depository date is 13 May 2015, and the depository number is CGMCC No.10808. According to the sophora tonkinensis endophytic fungus SDTE-P provided by the invention, a strain of endophytic fungus Penicillium citrinum SDTE-P is separated and screened from the root of a medicinal plant sophora tonkinensis for the first time, the Penicillium citrinum SDTE-P has a strong inhibiting effect on panax notoginseng fusarium solani, and a wide application prospect is created for the biological prevention and control field of panax notoginseng fungal diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
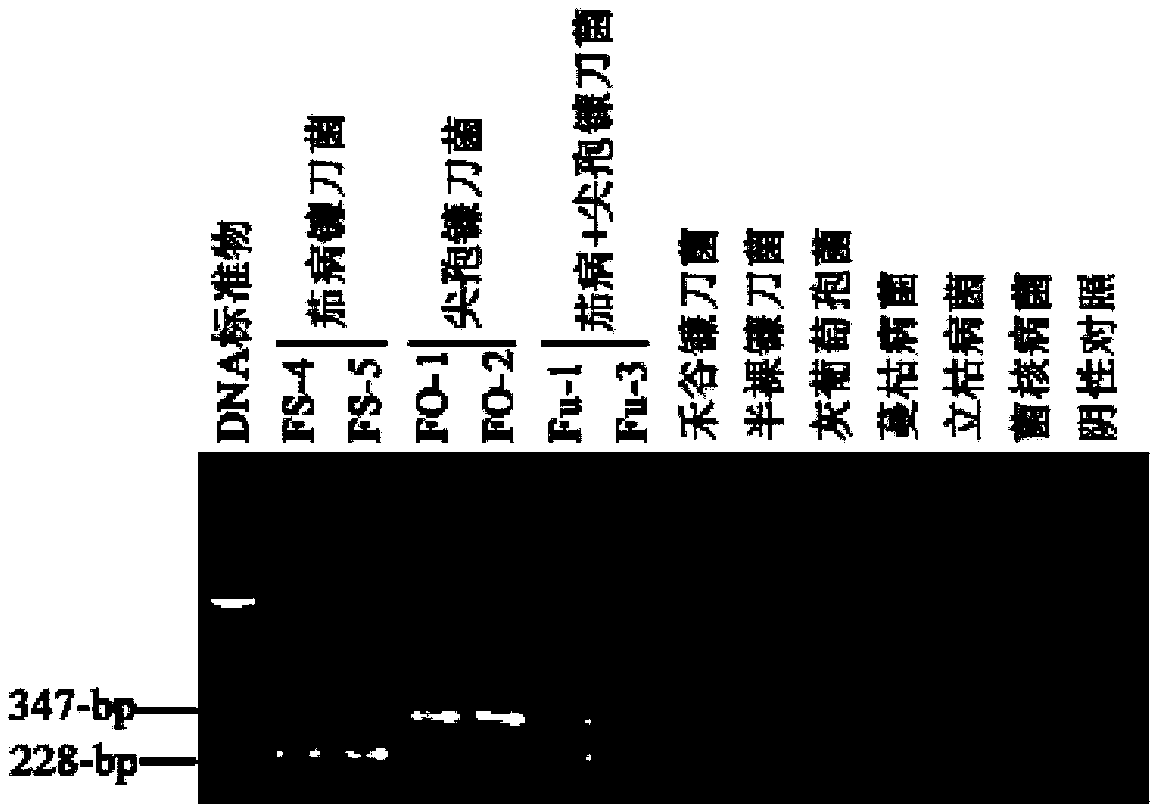
Sequences of primer for identifying fusarium solani and/or fusarium oxysporum, kit and method thereof
ActiveCN104263813AGenetically diverseGenetically stableMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFusarium oxysporumPathogenic bacteria
Sequences of primers for identifying fusarium solani and / or fusarium oxysporum, a kit and a molecular detection method thereof are disclosed. By verification, the primer sequences, the kit and the method have high specificity. By utilization of the group of the primers and the method, the fusarium solani and the fusarium oxysporum can be identified rapidly and accurately. Establishment of a system has important meaning for rapid early-phase detection of melon root rot and wilt, soil germ distribution and disease control. In addition, establishment of a molecular detection system based in TEF1-alpha as a target gene provides theoretical foundations and identification methods for complex systematic classification and identification of fusarium pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Lilium regale inducible promoter PD1 and application thereof
ActiveCN112852820ADon't waste energyEliminate damagePlant peptidesFermentationPlant hormoneNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a lilium regale inducible promoter PD1 and application thereof, the nucleotide sequence of the inducible promoter PD1 is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the lilium regale inducible promoter PD1 is proved to respond to several plant hormones, biological stress and abiotic stress through molecular biology and genetic engineering related technical research; a fusion gene expression cassette constructed by the lilium regale promoter PD1 and a [beta]-glucuronidase gene is transferred into tobacco for expression, and the glucuronidase activity of transgenic tobacco is quantitatively detected through adoption of a fluorescence method. Results show that after the transgenic tobacco is treated by abscisic acid, salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate, gibberellin, ethephon, fusarium solani, injury stress and sodium chloride, the activity of glucosidase is obviously enhanced; and the inducible promoter PD1 disclosed by the invention has a wide application prospect in genetic engineering for resisting biological or abiotic stress.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
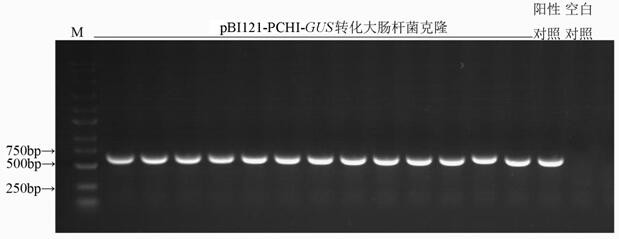
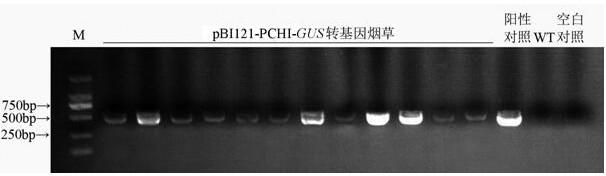
Inducible promoter PCHI and application thereof
ActiveCN112608924ADon't waste energyEliminate damagePlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention discloses an inducible promoter PCHI which is derived from lilium regale. The nucleotide sequence of the inducible promoter PCHI is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the invention, technical research related to molecular biology and genetic engineering proves that the lilium regale promoter PCHI responds to jasmonic acid methyl ester and biological stress. An expression cassette constructed by the lilium regale promoter PCHI and a beta-glucosidase gene is transferred into tobacco for expression, and the glucosidase activity of the obtained transgenic tobacco is quantitatively detected through a fluorescence method; and results show that after the transgenic tobacco is treated with jasmonic acid methyl ester, fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani and sporotrichum oryzae treatment, the glucosidase activity of the transgenic tobacco is obviously enhanced. The lilium regale promoter PCHI is induced by jasmonic acid methyl ester and biological stress factors and can be used in disease-resistant gene engineering of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
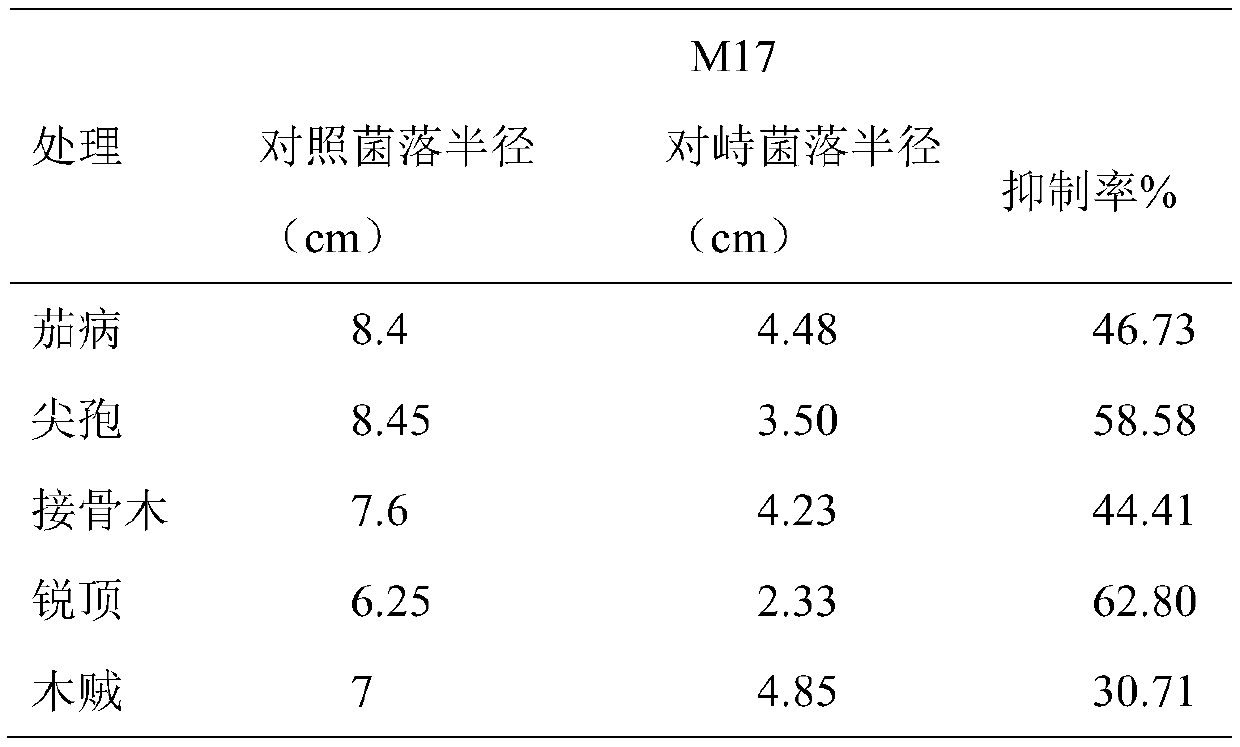
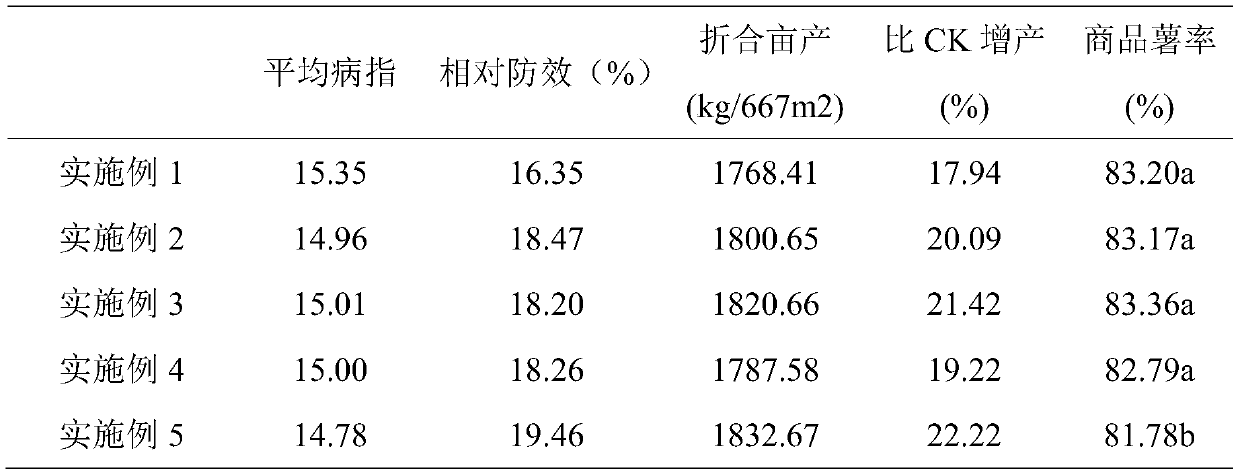
Solid fermentation of trichoderma harzianum and application of products of solid fermentation of trichoderma harzianum in potato fusarium root rots
The invention relates to solid fermentation of trichoderma harzianum. The solid fermentation of the trichoderma harzianum comprises the steps that trichoderma harzianum M-17 strains are inoculated into a solid culture medium for culture at 28 DEG C for 7-10 days, and according to the formula, the culture medium is prepared from the components of Chinese medicinal powder, potato flakes, corn flour,wood chips and potato skins. The trichoderma harzianum cultured by the method has a good inhibiting effect on pathogenic bacteria of potato root rots such as fusarium equiseti, fusarium sambucinum, fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani and fusarium acuminatum, and can be applied to the prevention and control process of the potato root rots, the occurrence of the potato root rots is reduced and prevented, the yield of potatoes is increased and the quality of the potatoes is improved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION NINGXIA ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI KEY LAB OF NINGXIA PLANT DISEASE & INSECT PESTS CONTROL
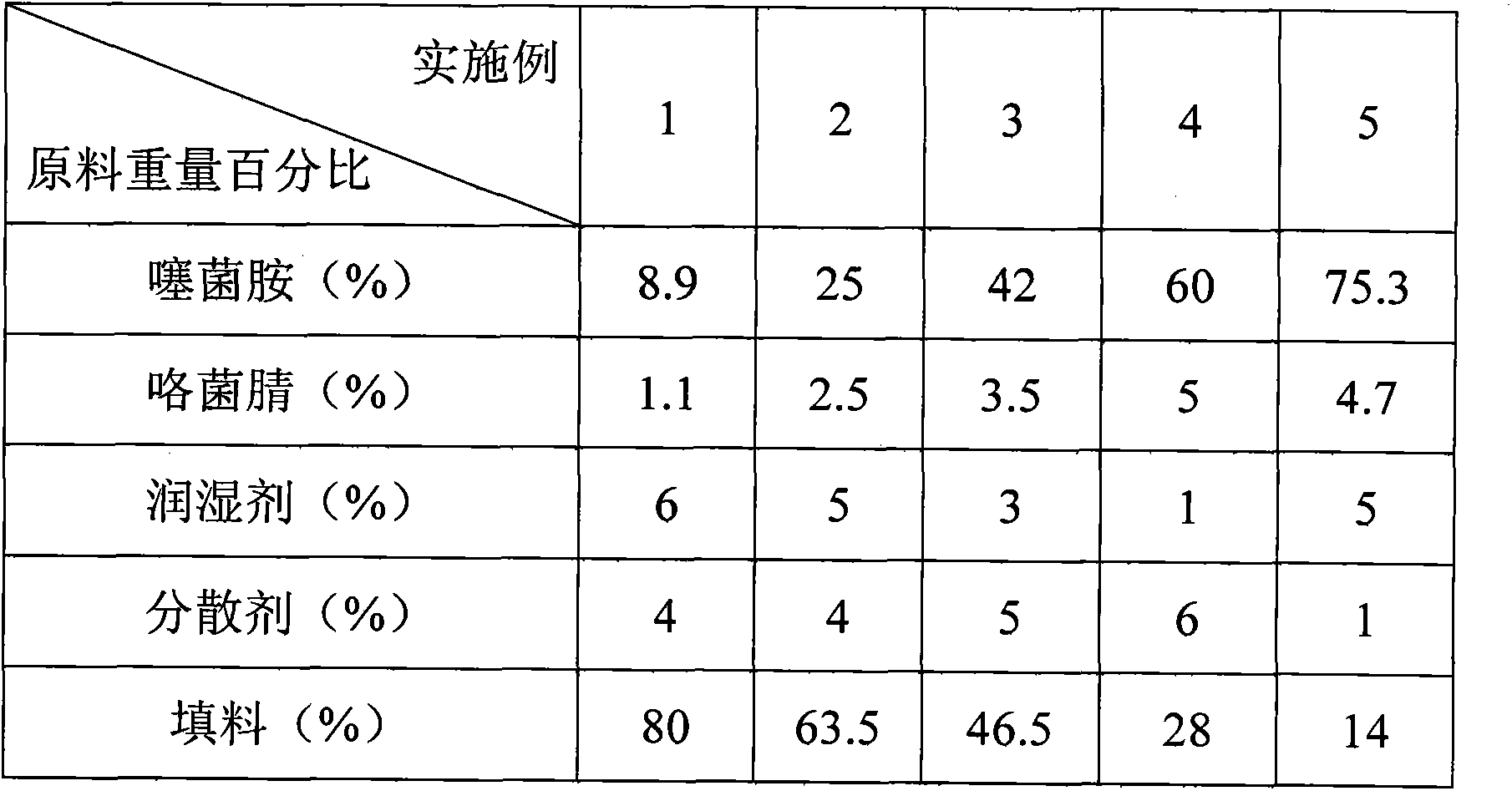
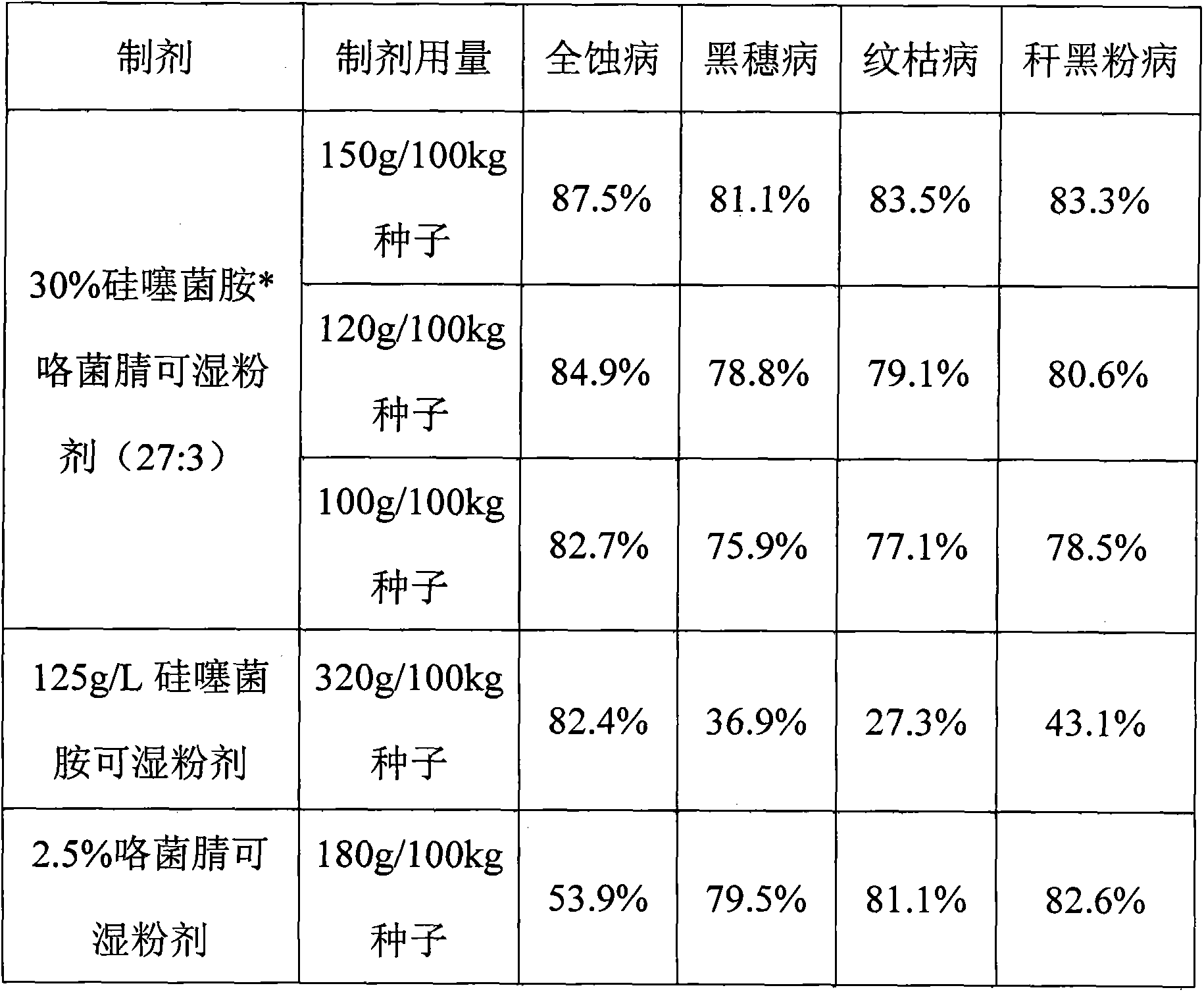
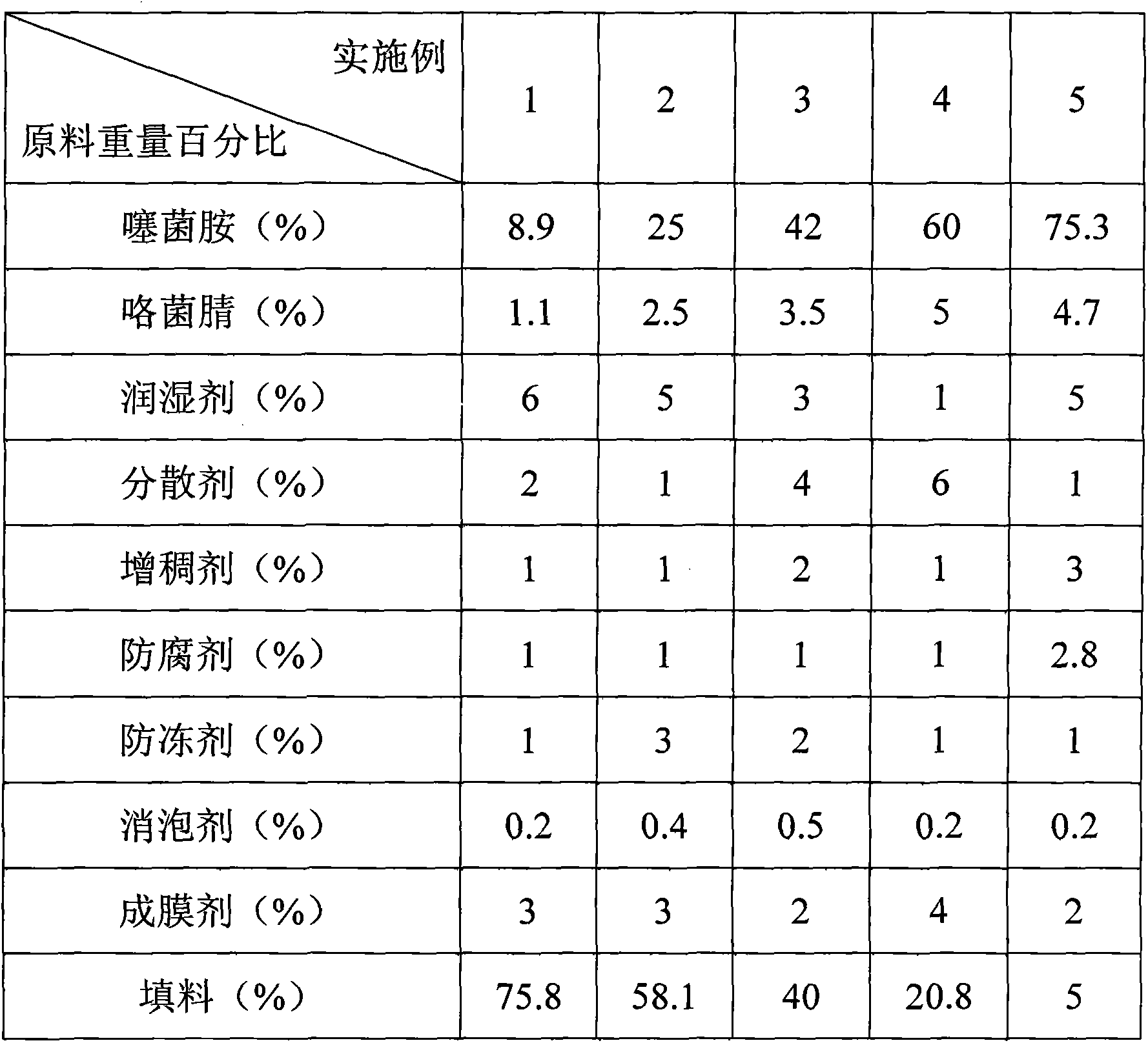
Wheat seed treating agent composition containing silthiopham
InactiveCN103300052AGood environmental compatibilityLow toxicityBiocideFungicidesSnow moldPlant disease
The invention discloses a wheat seed treating agent composition containing silthiopham, which solves the technical problems that a bactericidal spectrum is narrow, the usage amount per mu is high and the cost is high when silthiopham and fludioxonil are respectively used for preventing and treating wheat diseases. According to the technical scheme, the composition comprises the following components by weight percent: 10-80% of effective components, 5-15% of an auxiliary and 5-80% of fillers, wherein the effective components include silthiopham and fludioxonil by a weight ratio of (1:20)-(20:1). The wheat seed treating agent composition has the technical effects of being good in environment compatibility, low in toxicity and safe to humans and livestock; the composition is capable of preventing and treating the wheat diseases such as stinking smut, winter scald, snow mold, rhizoctonia solani kuhn, fusarium solani, septoria nodorum and flag smut which can be respectively prevented and treated by the silthiopham and the fludioxonil when the silthiopham and the fludioxonil are used respectively; besides, the composition has a remarkable synergism effect on gaeummanomyces; the usage amount per mu is lower than that when the silthiopham and the fludioxonil are used respectively, so that the usage amount is lowered and the cost is saved.
Owner:河北博嘉农业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com