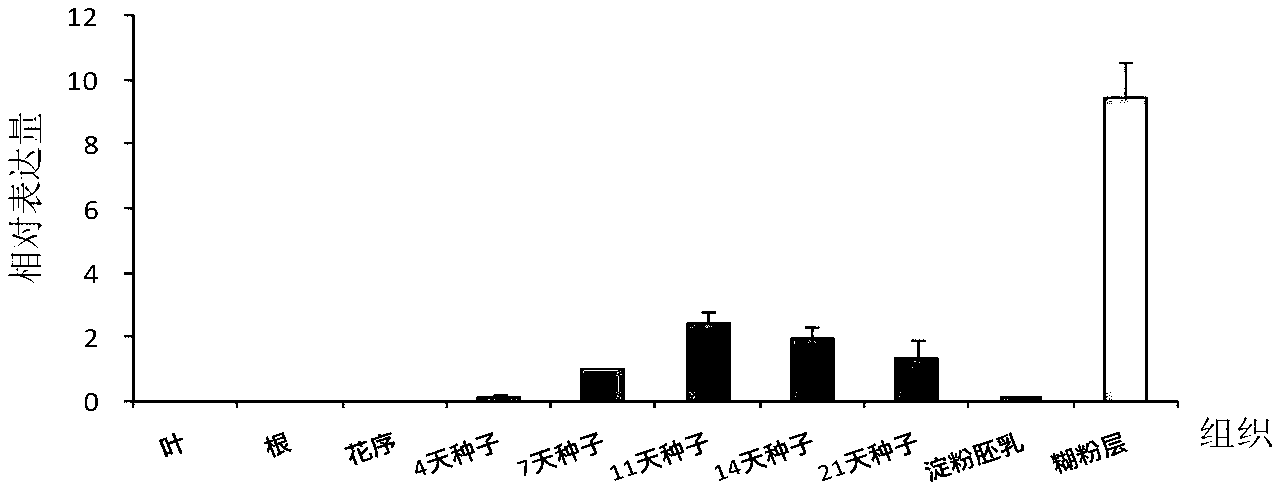Patents
Literature
247 results about "Glucuronidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glucuronidase may refer to several enzymes: Alpha-glucuronidase Beta-glucuronidase Glycyrrhizinate beta-glucuronidase Glucuronosyl-disulfoglucosamine glucuronidase
Modification of xylan
InactiveUS20130233501A1Low water solubilityReduce solubilityNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperSolubilityCellulose
The invention provides a method of modifying soluble xylan which contains glucuronic acid and / or arabinose side chains so that it can be adsorbed onto other substrates. The method includes the steps of enzymatically modifying the xylan by selectively removing glucuronic acid and / or arabinose side chains from the xylan with α-D-glucuronidase and / or α-L-arabinofuranosidase, and allowing the modified xylan to adsorb onto the substrate. The substrate may be a cellulosic substrate like pulp or paper or a non-cellulosic substrate. The enzymes are able to remove a sufficient number of the xylan side chains so as to decrease water solubility of the xylan, induce xylan precipitation and allow adsorption of the xylan onto other substrates. A pulping process which incorporates modification of xylan and adsorption onto cellulosic material is also provided, as are products which contain the modified xylan.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
Modified enzyme and treatment method
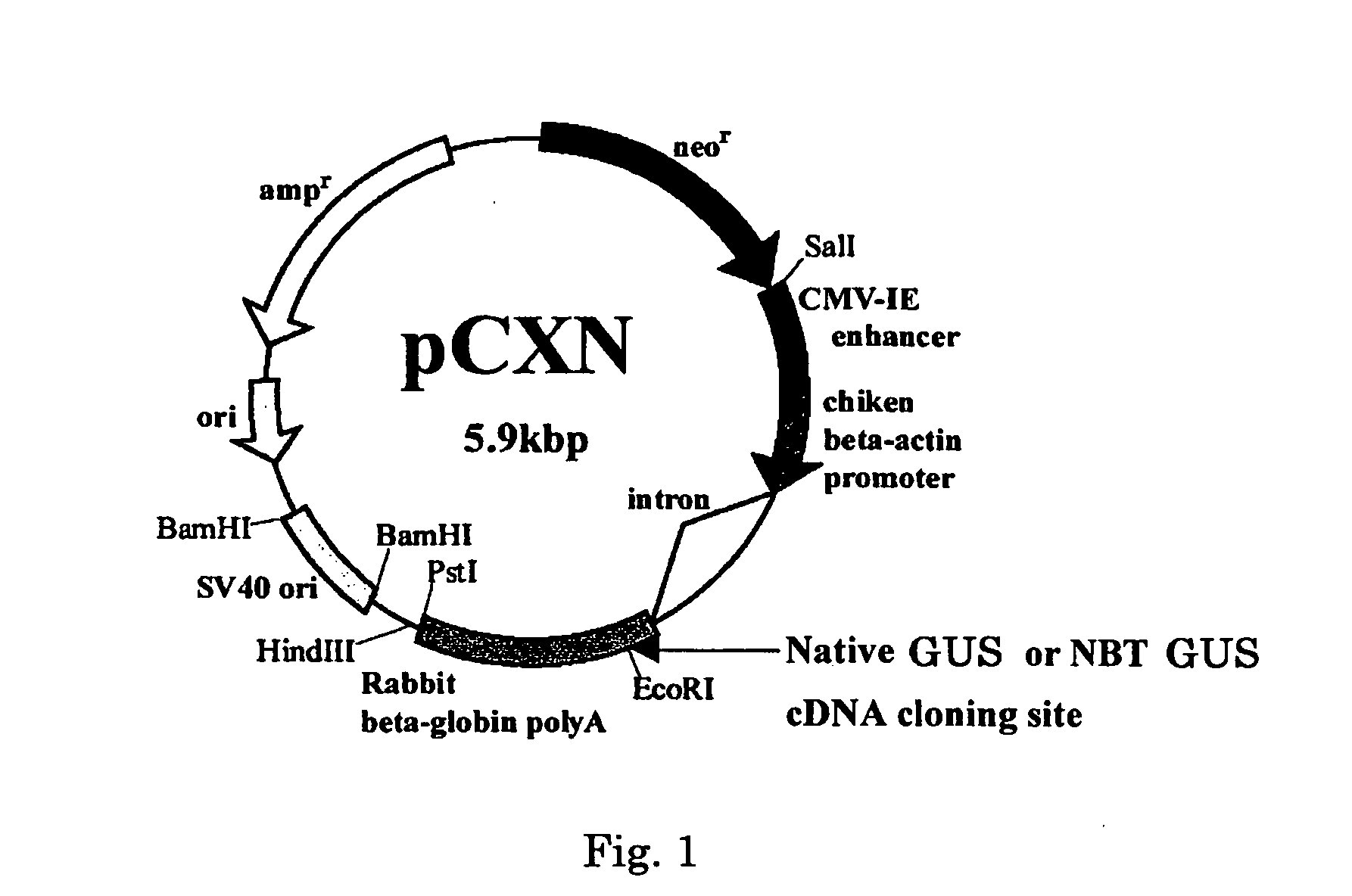
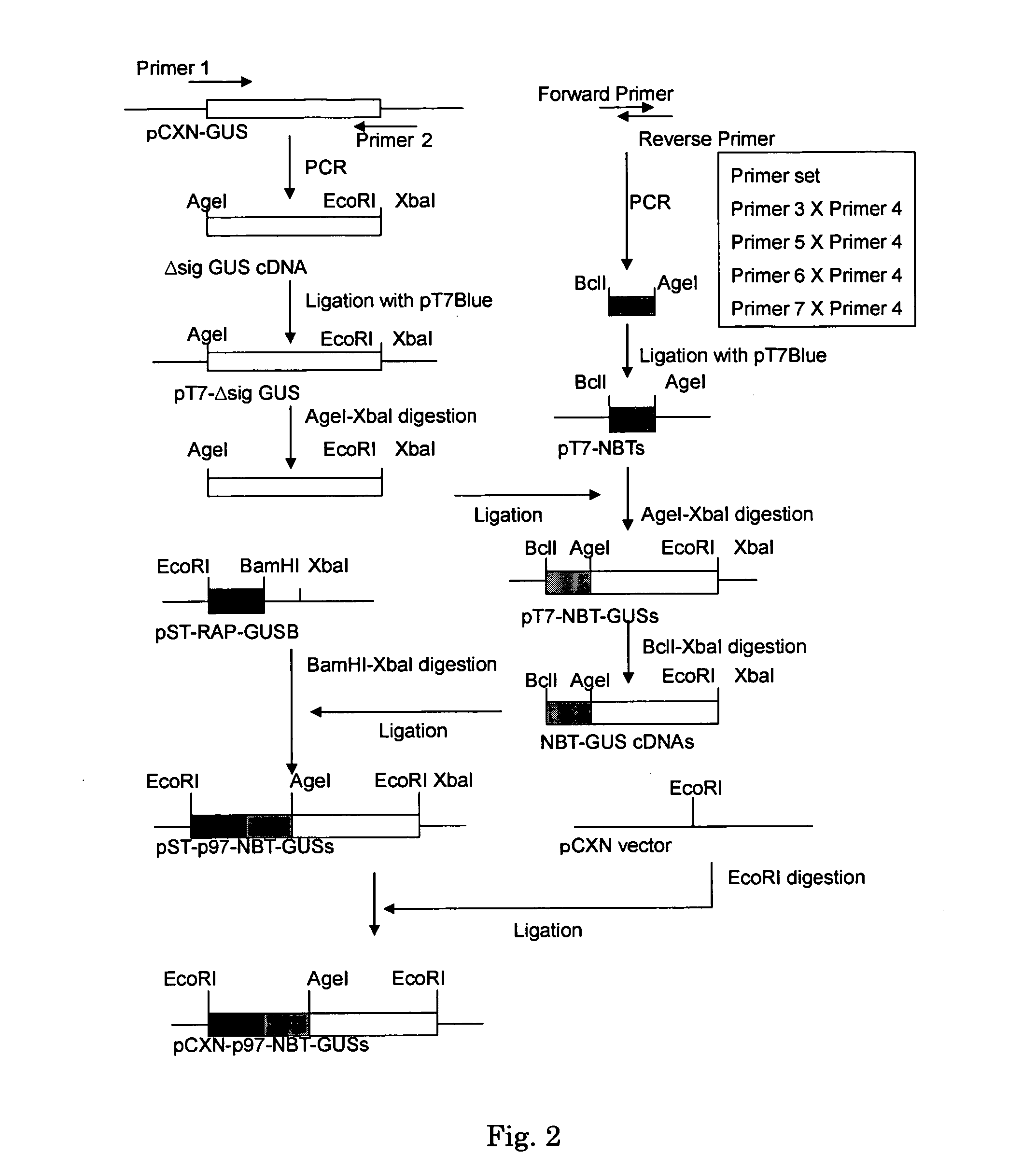
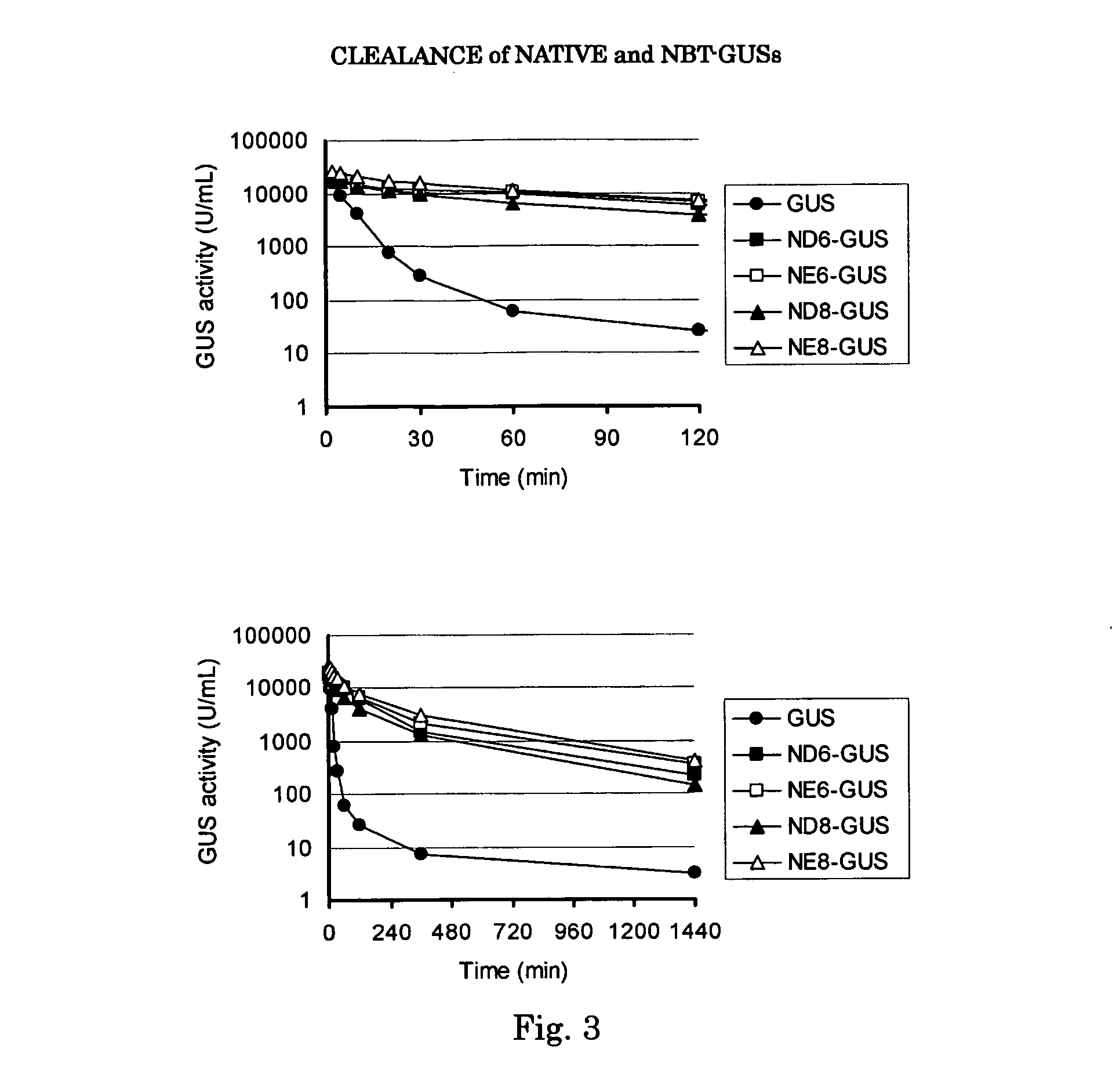
InactiveUS20090041741A1Extended half-lifeConvenient treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesLysosomeCompound (substance)
There is disclosed an isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase wherein the modification is having its carbohydrate moeties chemically modified so as to reduce its activity with respect to mannose and mannose 6-phosphate cellular delivery system while retaining enzymatic activity Also disclosed are methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage disease in mammals wherein the mammal is administered a therapeutically effective amount of isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase whereby said storage diseased is relieved in the brain and visceral organs of the mammal. Also disclosed are other lysosomal enzymes within the scope of the invention.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Probiotic propionibacterium
InactiveUS20050180963A1Promote growthGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBiocideAdjuvantPropanoic acid
The present invention relates to probiotic Propionibacterium strains and their use in the preparation of probiotic supplements and foods. The invention relates to the provision of Vitamin B12, propionic acid, folacin and bacteriocins by probiotic strains, stimulation of bifidobacteria growth, production of favourable effects on the lipid metabolism and on the immune system of hosts through immunostimulation, immunomodulation or use of a probiotic strain as an adjuvant, reduction of homocysteine and β glucuronidase and the prevention, treatment or amelioration of conditions associated with a need for these activities. The probiotic bacteria of the invention can be used in humans or other animals. In at least some applications, the bacteria can be used dead and parts rather than whole cells may be used. The present invention also relates to the preparation of vaccines for use in protecting patients from infectious diseases, in particular tuberculosis.
Owner:UNIV OF NEWCASTLE RES ASSOCS
Beta-glucuronidase with an attached short peptide of acidic amino acids
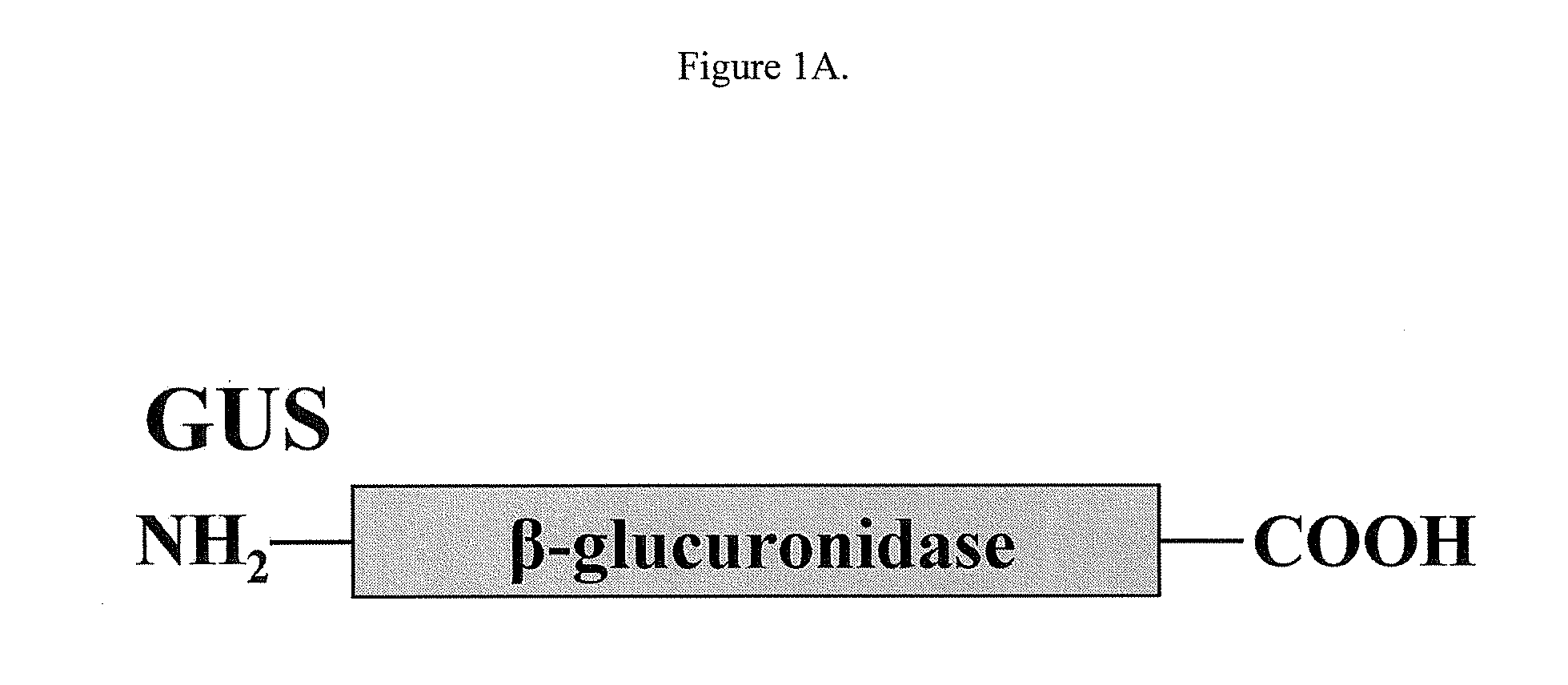
InactiveUS20070081986A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationBeta-glucuronidaseAcidic amino acids
Disclosed are a fusion protein comprising enzyme β-glucuronidase and short peptide consisting 4-15 acidic amino acids attached to the enzyme on its N-terminal side, pharmaceutical composition containing the fusion protein, and a method for treatment of type VII mucopolysaccharidosis using the fusion protein. Compared with the native enzyme, the fusion protein exhibits higher stability in the blood.
Owner:TOMATSU SHUNJI +5
Prodrug, medicinal utilization thereof and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20050203061A1High activityEfficient decompositionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSide effectGlucuronidase
A prodrug utilizes an enzyme whose enzymatic activity is different in between the target site of the drug and the site to express side effects, the prodrug having a substituent cleavable with the enzyme and being activated by cleaving the substituent with the enzyme. As the target site of the drug, for example, a respiratory organ can be mentioned and as the site to express side effects, for example, the heart can be mentioned. As the example of the drug, a bronchodilator can be mentioned and as the example of the enzyme, a glycosidase (for example, β-glucuronidase) can be mentioned. Furthermore, the substituent is, for example, a glycosyl group composed of a monosaccharide or an oligosaccharide. Use of the enzyme enables reducing the side effects of a drug of the type whose target site is different from the site to express side effects.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
Method For The Detection Of Coliforms And In Particular Escherichia Coli
InactiveUS20070196884A1Detectable amountReduction of background fluorescenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBacteria coliformsLarge intestine
The invention is relative to a novel method for the detection of coliforms, which is based on the use of a mixture of amino acids to promote the expression of inducible enzymes, in absence of cell growth. This enzyme-inducing solution can be used for the rapid detection of the enzymes β-glucuronidase and / or β-galactosidase in a very small number of E. coli and / or total coliforms.
Owner:ISRIM S CONS A R L
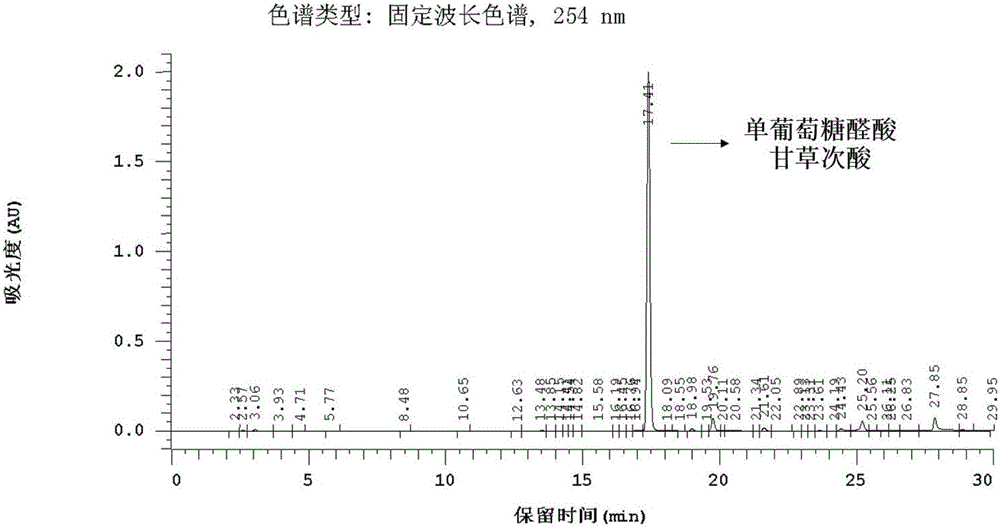
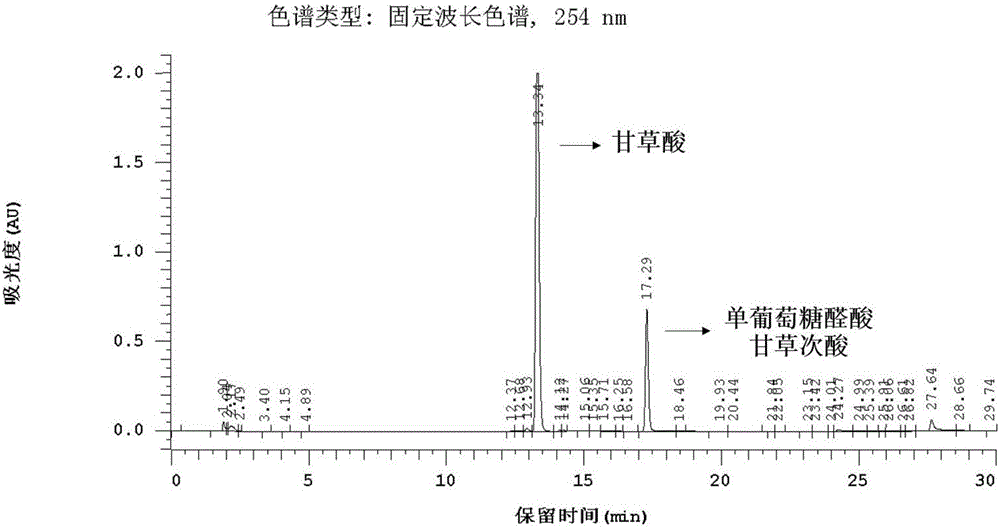
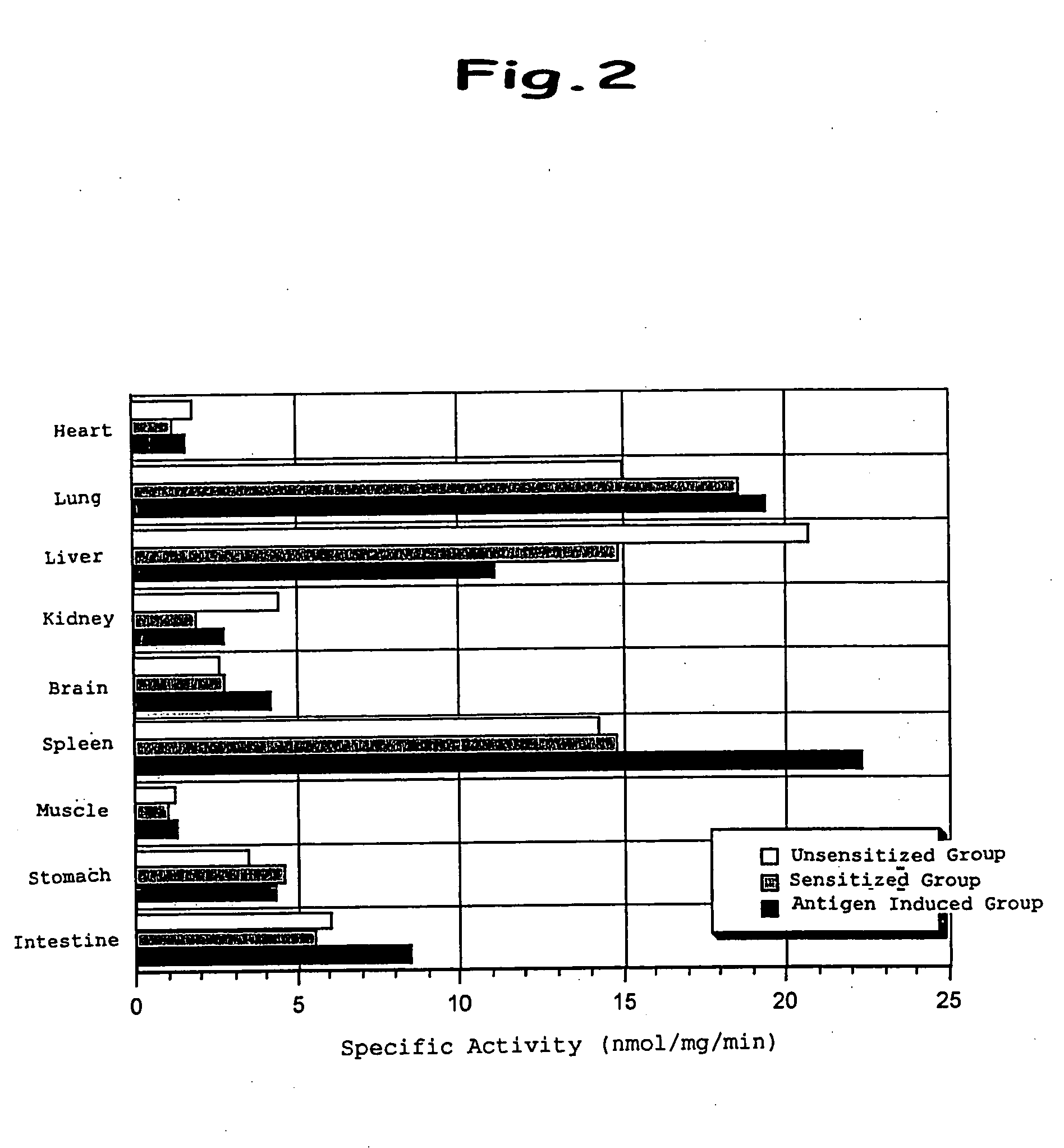
Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine
InactiveCN103063791AOptimizing enzymatic conditionsOptimizing Solid Phase Extraction ConditionsComponent separationChromatographic separationRotary evaporator
The invention discloses a method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine. The method comprises sequentially using beta-glucuronidase for enzymatic hydrolysis of samples, performing solid-phase extraction and purification, concentrating the samples with a vacuum rotary evaporator, and determining by using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer, thereby rapidly, accurately and simultaneously detecting contents of 1-hydroxy pyrene (1-OHP), 3-hydroxy benzo [a] pyrene (3-OHB [a] P) and 3-hydroxy benzo [a] anthracene (3-OHB [a] A) in the urine. The method uses deuterated standards as quantitative analysis substances of internal standards and thus can reduce errors in a pretreatment process for the samples; uses a tandem mass spectrometer to relatively improve selectivity and accuracy of the method; and selects a method of preparing standards by matrices, wherein, compared with a method of preparing the standards by pure water, the method of preparing standards by matrices is relatively good in accuracy and can eliminate interference from matrix effects. Through selecting and optimizing chromatographic columns and gradient elution conditions, the method relatively improves a chromatogram separating process and shortens a chromatographic analysis time.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
BNLEA3-1 promoter
InactiveUS20080244793A1Weakly inducibleSugar derivativesPlant peptidesEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
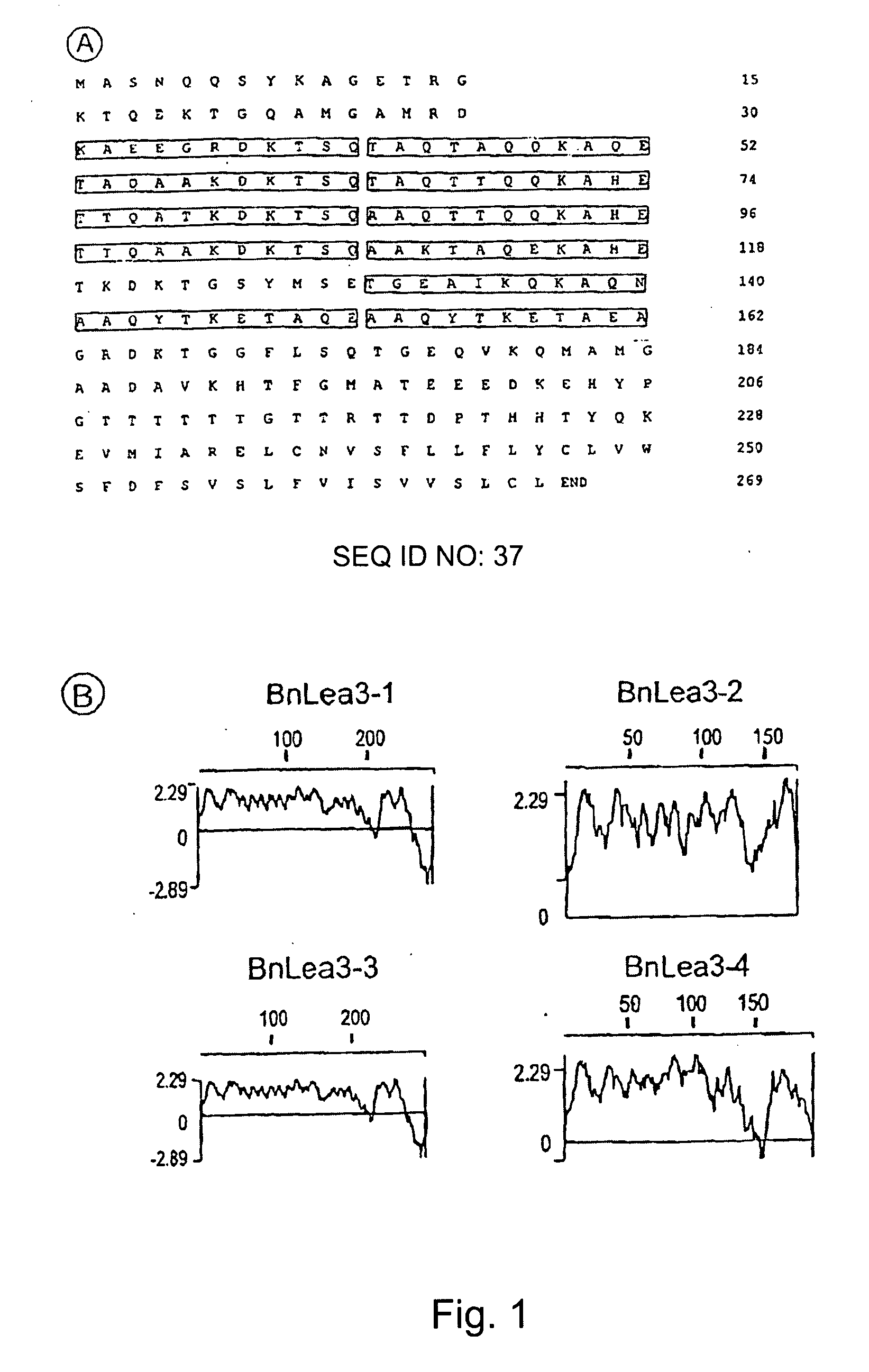
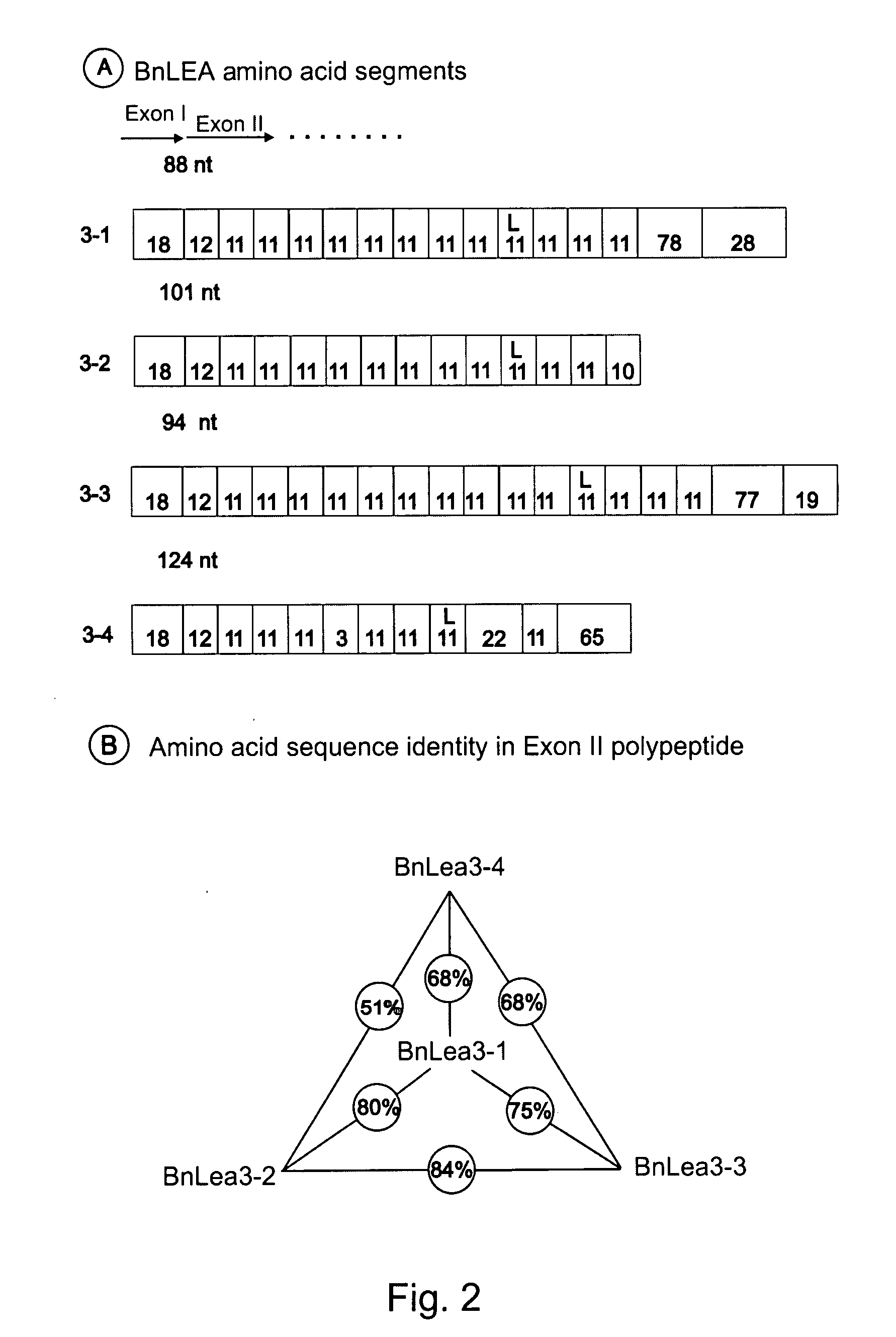
Late embryogenesis abundant (Lea) proteins accumulate in maturing seeds after many of the storage compounds have been synthesized, and they are considered relevant to maturation. We report here the molecular organization and expression of BnLea3-1, a novel Group 3 Lea gene from Brassica napus. BnLea3-1 contains a coding region of 798 bp, sharing 84.4% homology at the amino acid level with Lea76 of B. napus. Two tandem 11-mer repeats are truncated from the coding region of BnLea3-1, compared to the 13 conserved 11-mer repeats of Lea76. Substitutions of consensus residues are found at various positions within the 11-mer repeats. A 1561 bp 5′ flanking promoter fragment of BnLea3-1 fused to E. coli-glucuronidase (GUS) coding region conferred seed-specific GUS expression in stable transgenics of B. napus, tobacco and in transiently-transformed pea. A −137 bp minimal promoter preceding the first transcription start site, identified through progressive deletions from the upstream was sufficient for basal GUS expression in the seeds and in leaves treated with ABA. Deletion studies indicate the presence of enhancing elements located between −137 bp to −742 bp and suppressing elements located between −742 and −1561 bp. BnLea3-1 expression in seeds precedes that of Lea76. Unlike other Group 3 Lea members including HVA1 and Dc3, BnLea3-1 is active in seeds and responsive weakly in vegetative tissues to ABA and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) but not to stress treatments. Possible functions of BnLea3-1 and another member of the Group 3 Lea family BnLea3-2 in embryo development is discussed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
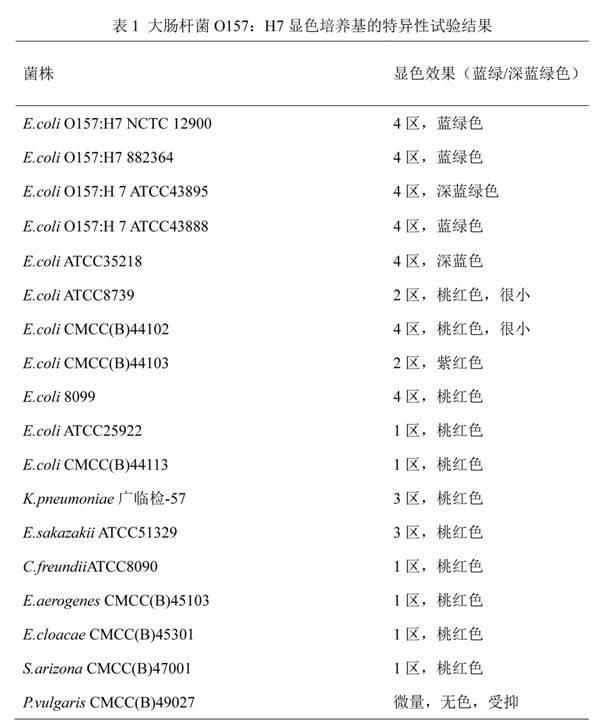
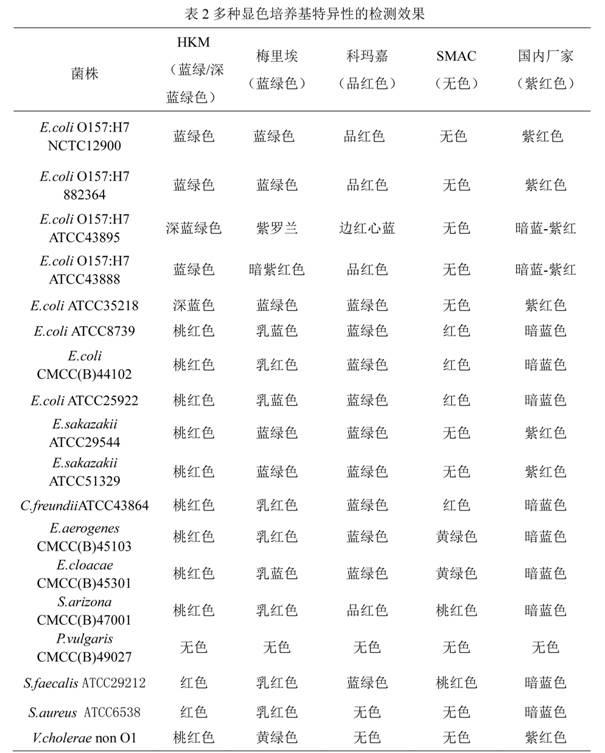
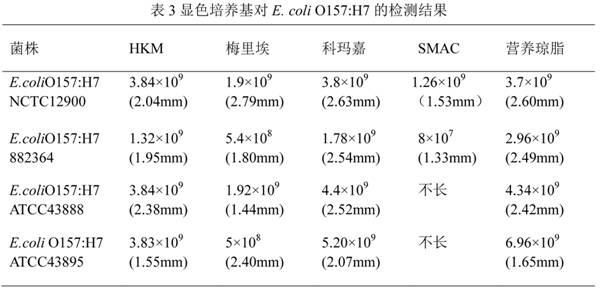
Chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7
ActiveCN102424832AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThio-
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7. The medium comprises agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, sorbitol, inositol, neutral red, beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, beta-glucuronidase chromogenic substrate, isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside, natrium taurocholicum, potassium tellurite and cefixime. The chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7 of the present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, direct bacterial strain discrimination according to colony color, short detection period and strong operationality, is suitable for treating high-reflux samples, is capable of comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and preliminarily identifying the esherichia coli O157:H7 in food production and environment, and provides a novel approach for rapidly detecting the microbes.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
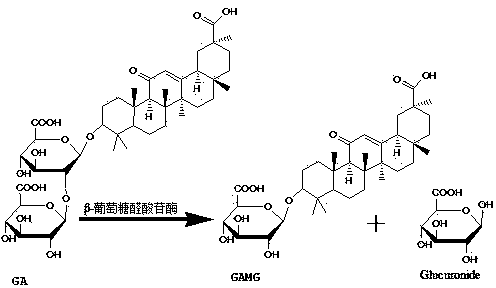
Method for high-yield preparation of glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide
InactiveCN103509843AIncrease productionImprove efficiencySugar derivativesSteroidsNegative feedbackBacterial strain
The invention provides a method for high-yield preparation of glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide, and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry. The method comprises the following steps: with a bacterial strain of generating specific glucuronidase as a catalyst and glycyrrhizic acid as a substrate, removing a glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide product by taking a macroporous resin as a separating medium in processes of continuous stirring and ventilating conversion reaction, releasing the substrate glycyrrhizic acid adsorbed in the resin, and discharging the glycyrrhizic acid out of a resin column together with unreacted glycyrrhizic acid in a fermentation liquor; and reflowing to a fermentation tank to continue to ferment. Simultaneous coupling of three processes of fermentation, material supplement and product separation is achieved; the problems of negative feedback inhibition and unfavourable fermentation caused by over-high viscosity of the product and a substrate fermented liquid are solved by maintaining proper substrate concentration and low product concentration in a fermentation process; the utilization efficiency of the substrate and the fermentation yield of the glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide are significantly improved; meanwhile, the automatic degree is high.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANSHENG PHARMA
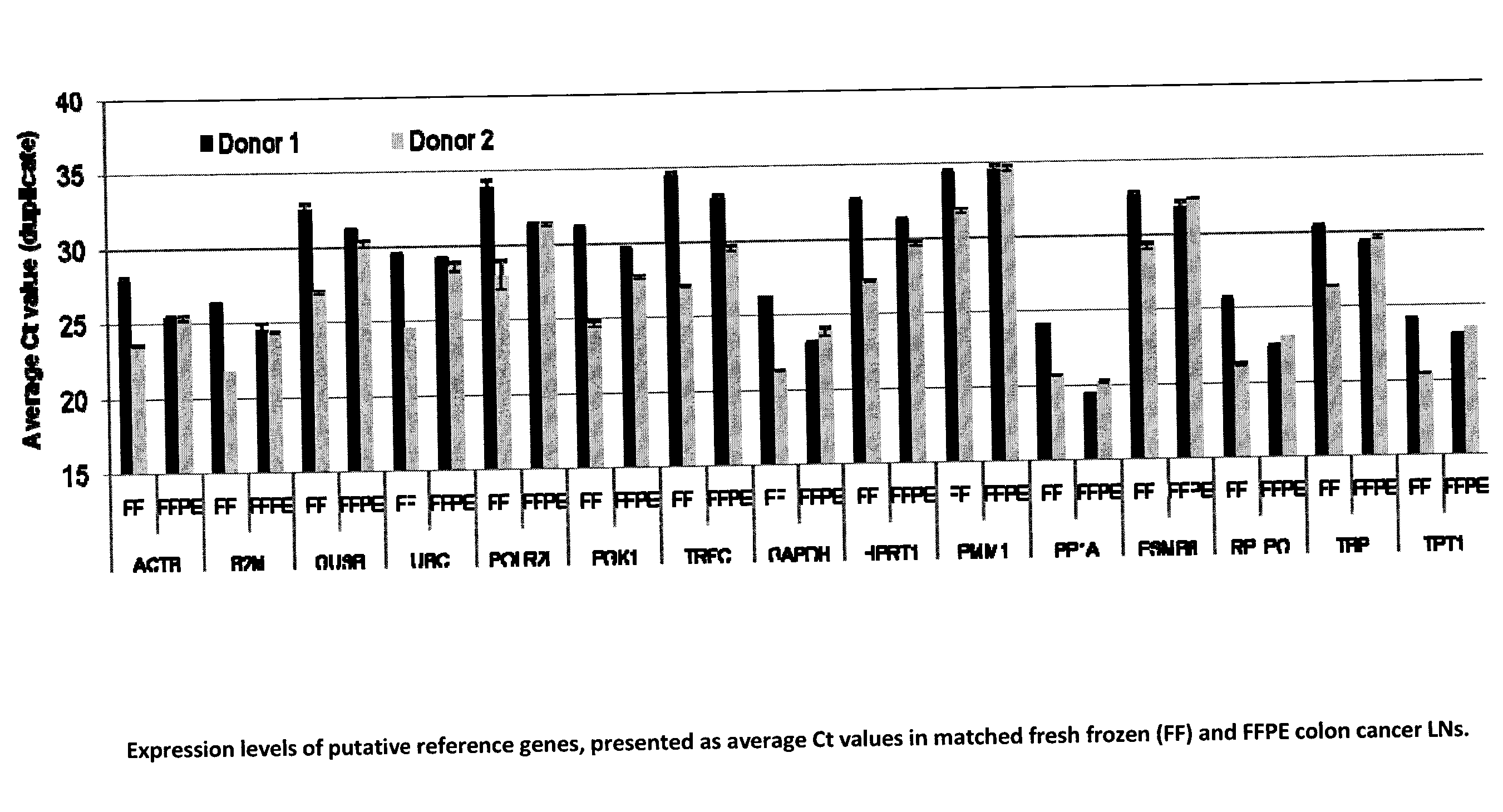
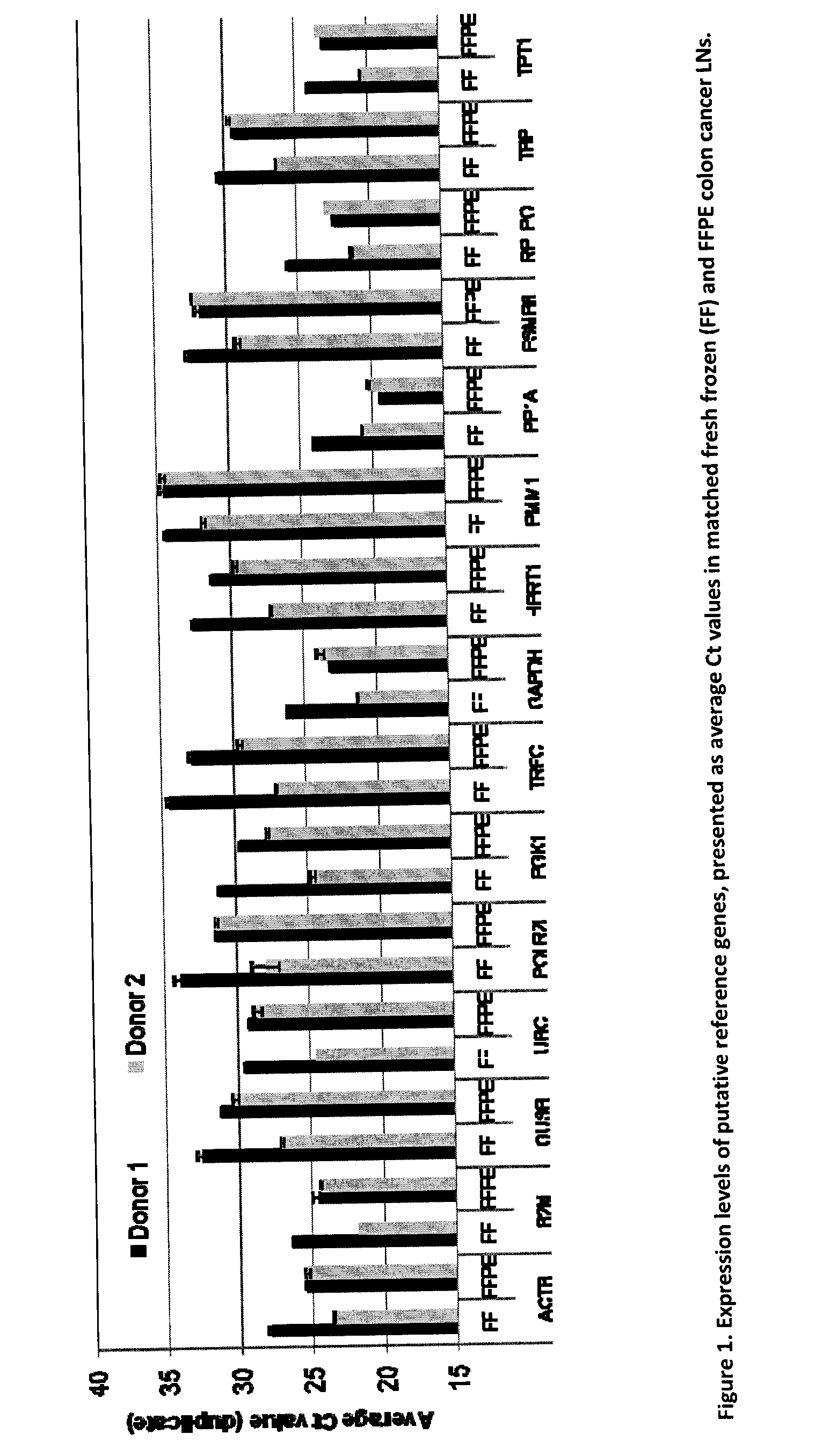
Method for Detecting Metastasis of GI Cancer
InactiveUS20110306055A1Reduce restrictionsAccurate layeringMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCyclaseLymphatic Spread
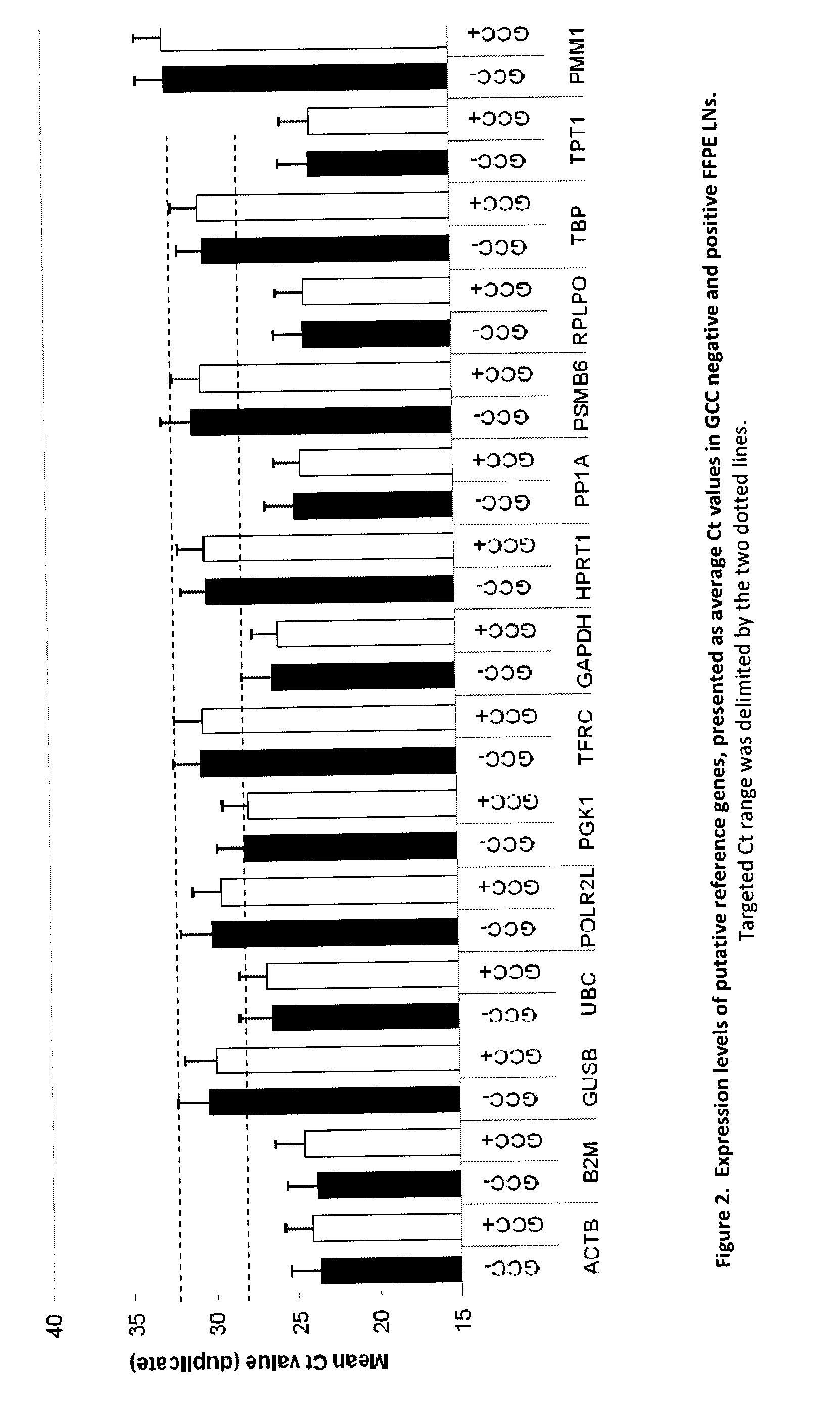
The present invention provides a novel method for diagnosing, monitoring, prognosing and staging Lymph Node (LN) status in colorectal cancer (CRC) that is more sensitive and accurate than conventional detection technologies such as histopathology. The Guanylyl Cyclase C (GCC) gene is specifically expressed in apical epithelial cells of the GI tract from the duodenum to the rectum and the detection of GCC mRNA in LNs is indicative of the presence of metastases. Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) detection of GCC mRNA to identify the presence of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in LNs has the potential to aid in CRC staging. When used in combination with glucuronidase B (GUSB), accurate quantification of GCC can be achieved with less than a 2-fold variation between intact and highly degraded RNA specimens. The invention also relates to a newly designed GCC / GUSB assay that uses relative quantification having improved prognostic value for time to recurrence and relapse-free survival in Stage I or II colon cancer patients. The GCC / GUSB assay also improves the statistical power of prognosis stratification for relative risk of recurrence and relapse-free survival.
Owner:DIAGNOCURE
Water-base chain lubricating agent
The invention relates to a lubricant which is used for high-speed conveyer apron production lines of PET bottles, glass bottles, ring-pull cans and the like and belongs to the filed of chemical lubricant. The proportion of the water-based chain lubricant is that oleic acid triethanolamine 3-8%, triethanolamine 4-9%, LF-131 2-5%, isothiazolin-ketone 1-3%, polymaleic acid 0.5-2%, glucuronidase 4-9%, EDTA-2Na 4-10%, benzotriazole 0.5-2%, sodium sulfonate xylene 0.5-2% and H2O 65-75%, wherein the water-based chain lubricant has high lubricating property and good solubility and is provided with a plurality of excellent performances as anti-hard water, sterilization, low-foam, non-corrosiveness, crack resistance, anti-coagulation and the like, when the lubricant is used in a lubricating system, the bottles inverting ratio can be effectively reduced, the workshop environment can be improved, and the service life of scraping belts cab be prolonged.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Biological wall breaking technology of pine pollen
The invention discloses a biological wall breaking technology of pine pollen. The process of the technology comprises the following two steps of: sterilizing pollen and enzymatically breaking the wall of the pollen, wherein the sterilizing time is 12-24 h, the pollen concentration in enzymolysis is 1-50 percent, the enzymatic wall breaking time is 0.5-36 h, and the enzymatic wall breaking temperature is 20-60 DEG C. One or more composite enzymes of the enzymic preparations, such as pepsin, trypsin, cathepsin, papain, subtilisin, lysozyme, Snail enzyme, amylase, arabinosidase, galactosidase, glucuronidase, acetyl xylan esterase, pectase, cellulose and hemicellulase, are used for enzymatic wall breaking. The process is simple and reliable, has less investment and high wall breaking rate, can fully obtain the active ingredients with no loss of activity and keep the original characteristics of the pine pollen.
Owner:HUBEI GOLE BIO TECH DEV
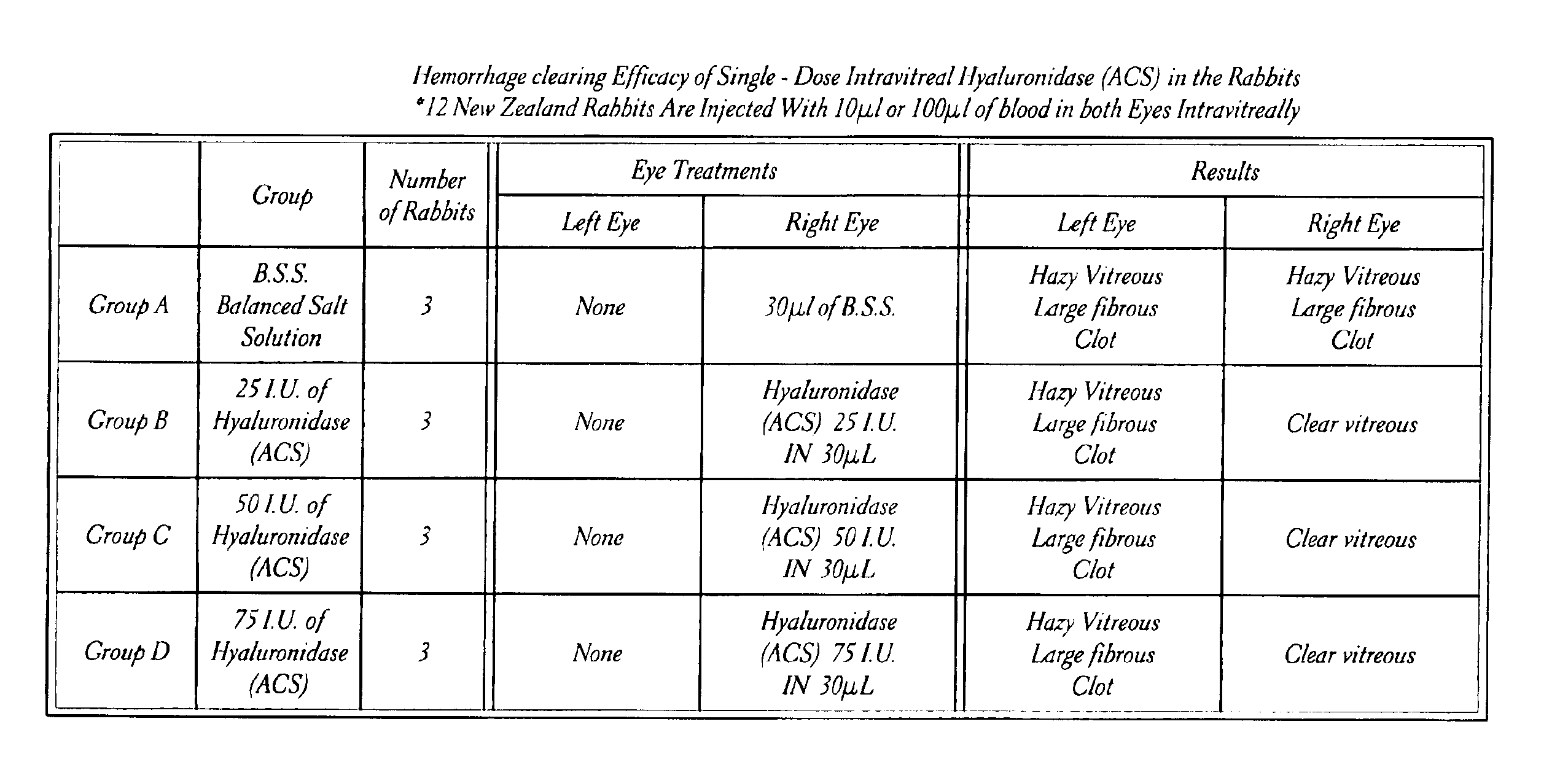
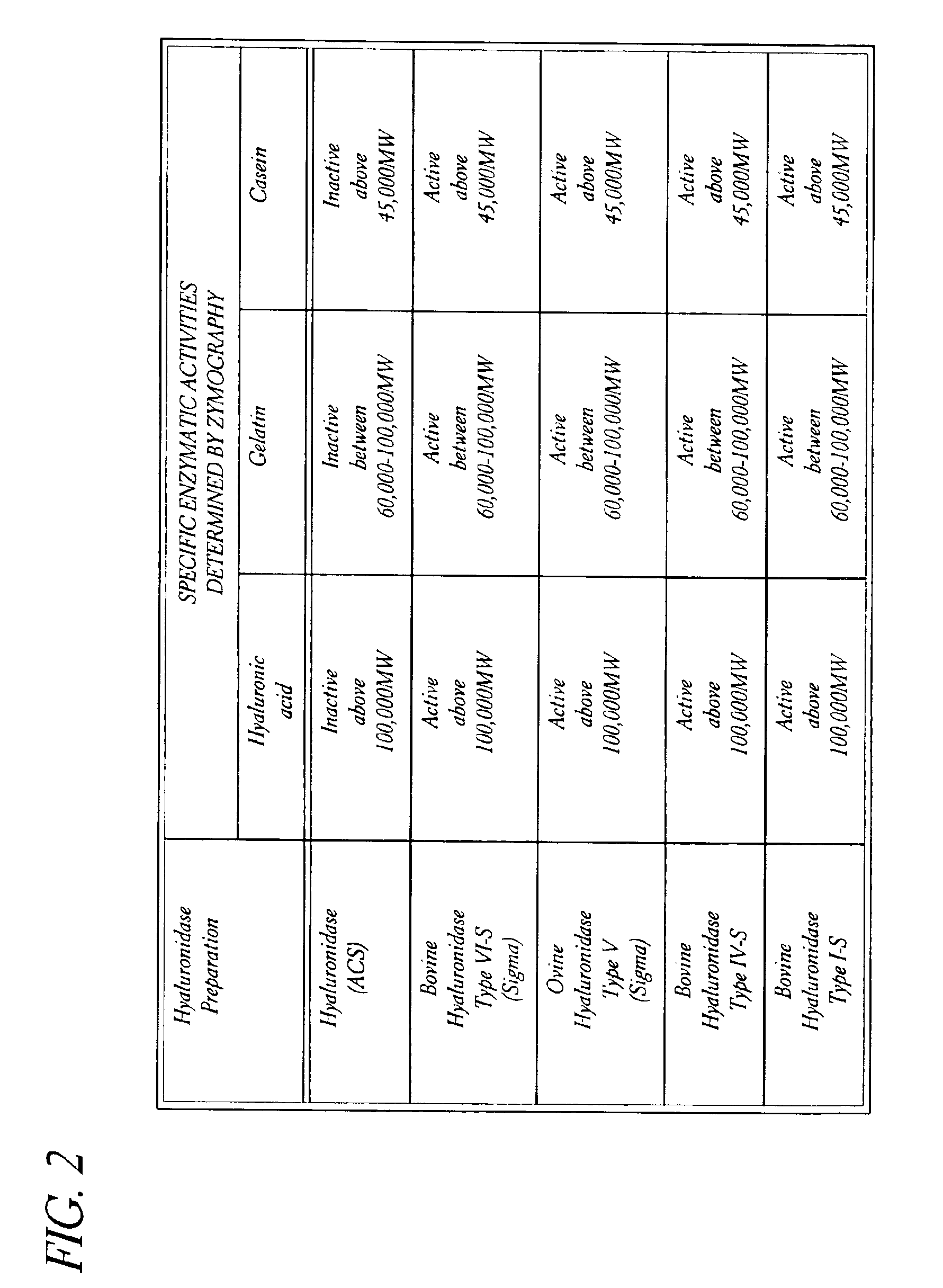
Hyaluronidase preparation for ophthalmic administration and enzymatic methods for accelerating clearance of hemorrhagic blood from the vitreous body of the eye
InactiveUS6939542B2Increase the gapOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderVitreous HumorsBody fluid
A thimerosal-free hyaluronidase preparation wherein the preferred hyaluronidase enzyme is devoid of molecular weight fractions below 40,000 MW, between 60-70,000 MW and above 100,000 MW. Also disclosed is a method for accelerating the clearance of hemorrhagic blood from the vitreous humor of the eye, said method comprising the step of contacting at least one hemorrhage-clearing enzyme (e.g., a β-glucuronidase, matrix metalloproteinase, chondroitinase, chondroitin sulfatase or protein kinase) with the vitreous humor in an amount which is effective to cause accelerated clearance of blood therefrom.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC +1
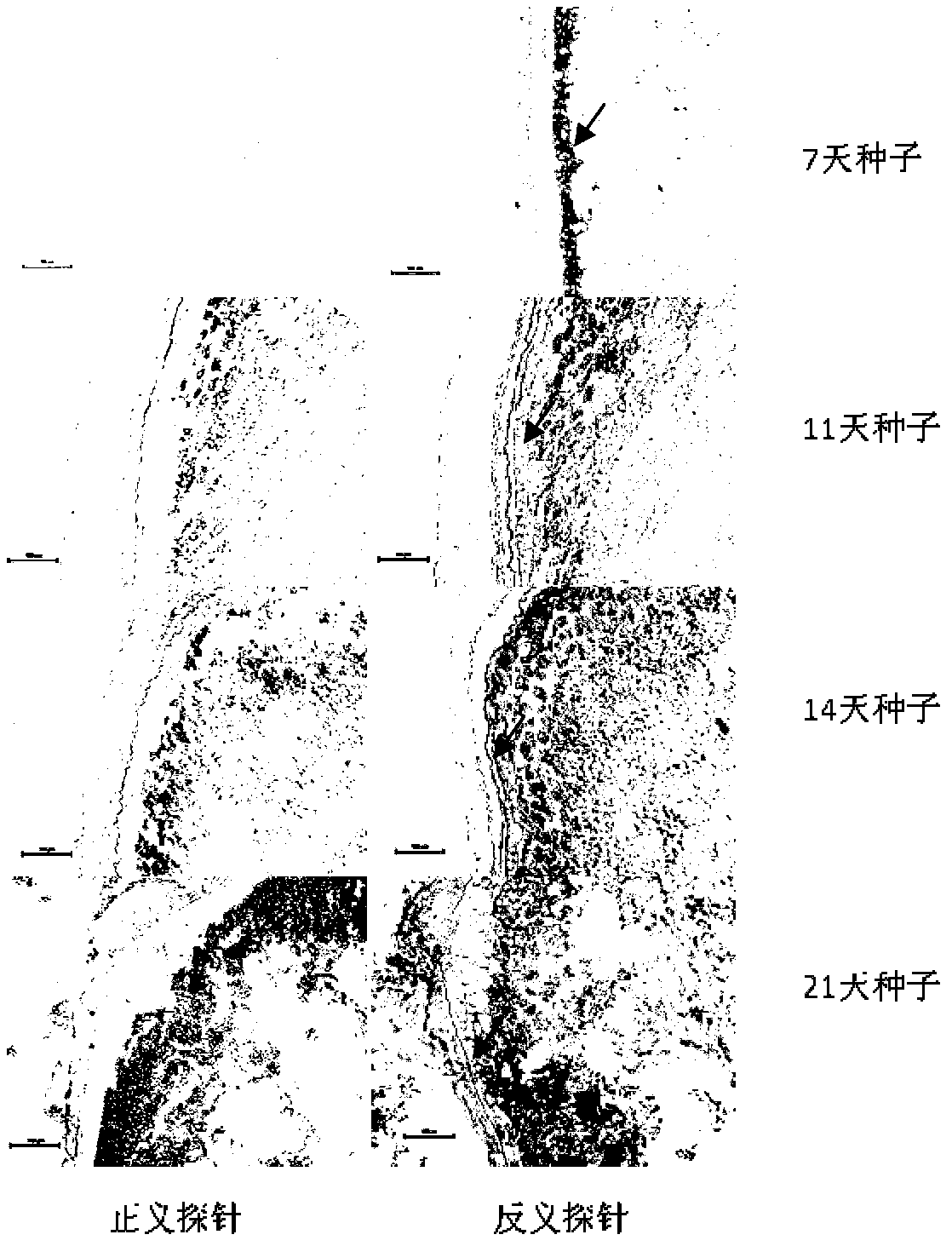
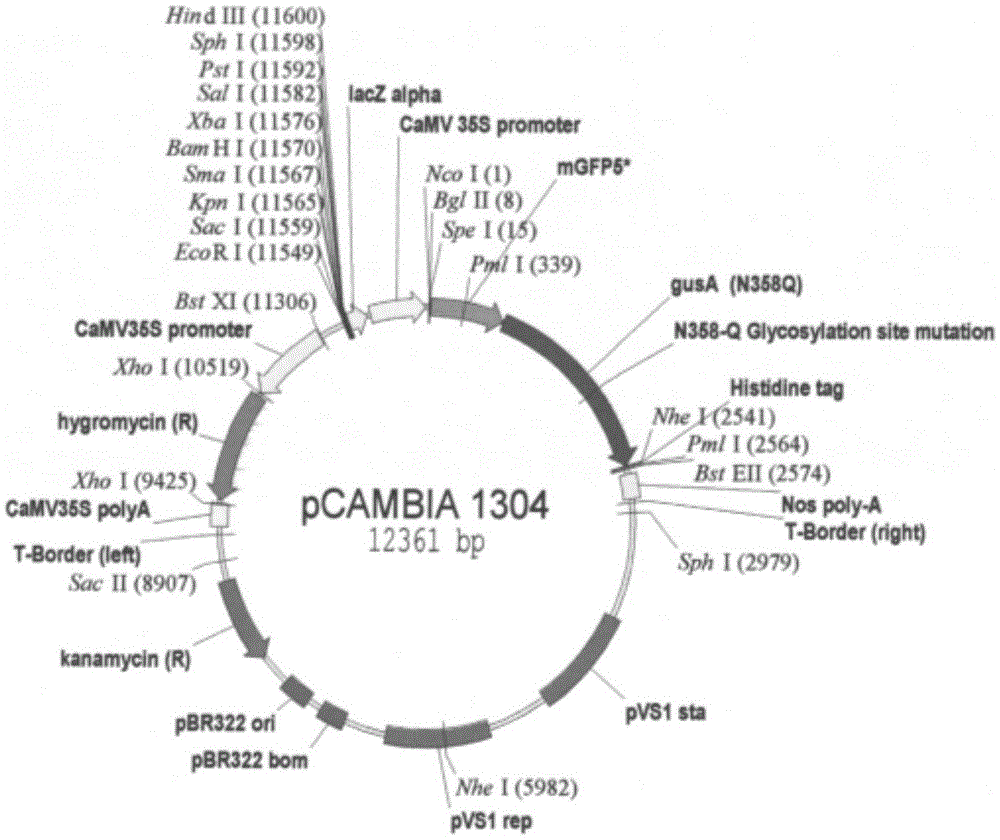
Method for improving instantaneous expression rate of agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated sugarcane glucuronidase (GUS)
InactiveCN102604986AIncreased transient expression rateOvercome the risk of transgenic lines being chimerasVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyTransgenic technology
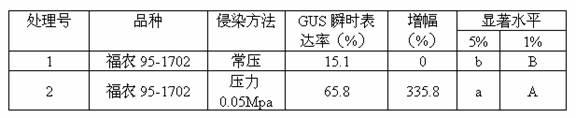
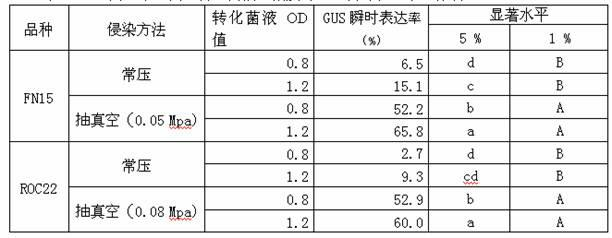
The invention relates to a method for improving the instantaneous expression rate of an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated sugarcane glucuronidase (GUS). The method comprises the following steps of: selecting materials, preparing conversion bacteria liquid, performing an infection method, performing cocultivation and selective cultivation, and chemically dyeing GUS active tissues. The method that the advantages and disadvantages of a transgenic technology method is measured by taking the degree of the GUS instantaneous expression rate as an index is nationally acknowledged. Therefore, the index which is nationally acknowledged is adopted to evaluate the technology method. By the method, the GUS instantaneous expression rate can be increased by 335.8 to 1,859.3 percent, the bottle neck problem about efficiently obtaining a transgenic sugarcane plant by using a agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated way can be effectively solved, a key technology method for introducing an exogenous gene into a sugarcane is provided for improving the variety of the sugarcane by using transgenic technology. Meanwhile, the method is also applied to the genetic transformation for other plants based on an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated way.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Pseudo-ginseng inducible promoter R1 and application thereof
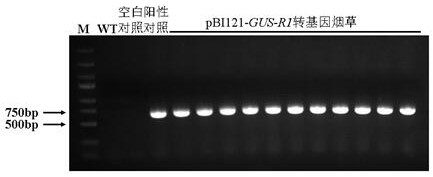
The invention discloses a pseudo-ginseng inducible promoter R1 and application thereof, the nucleotide sequence of R1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and molecular biology and genetic engineering related technical researches prove that the pseudo-ginseng promoter R1 responds to several plant hormones, biological stress and abiotic stress; a fusion expression cassette constructed by the panax notoginseng promoter R1 and the beta-glucuronidase gene is transferred into tobacco for expression, and the activity of the glucuronidase of the transgenic tobacco is quantitatively detected through a fluorescence method. The result shows that after the transgenic tobacco is treated by fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, alternaria alternata, NaCl, AlCl3, gibberellin, methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, abscisic acid and ethephon, the activity of glucuronidase is obviously enhanced; the pseudo-ginseng promoter R1 is induced by several plant hormones and biological and abiotic stress factors, and can be used for plant disease-resistant gene engineering.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
UPLC-MS/MS detecting method for detecting concentration of parabens preservatives in human urine
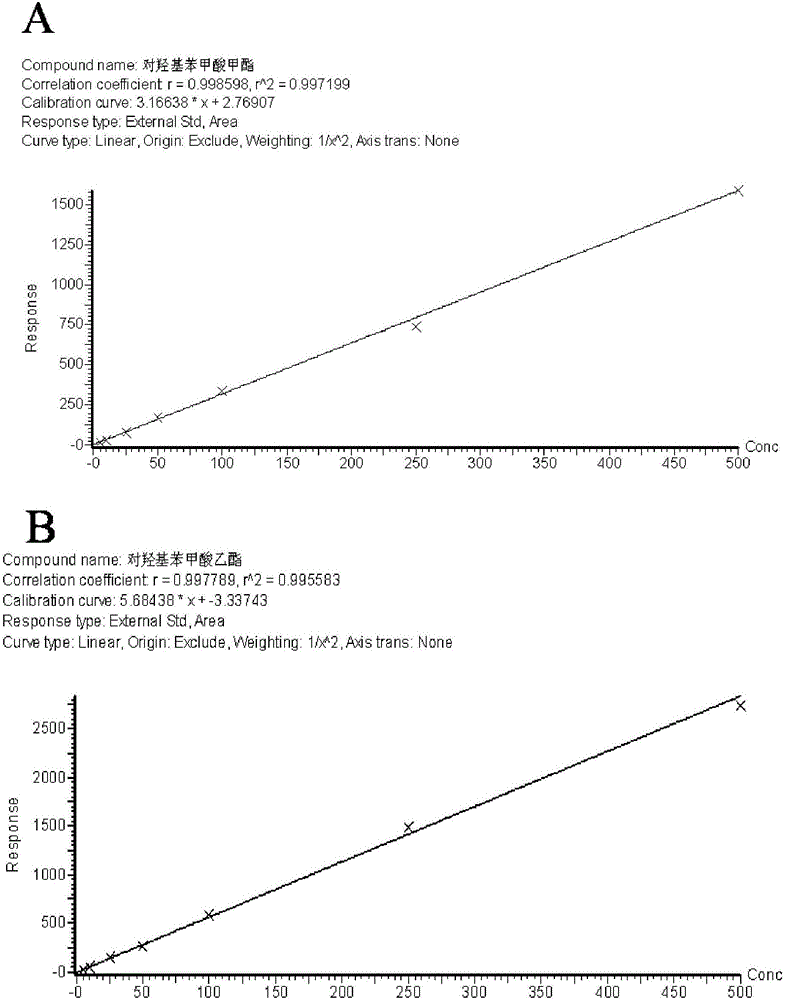
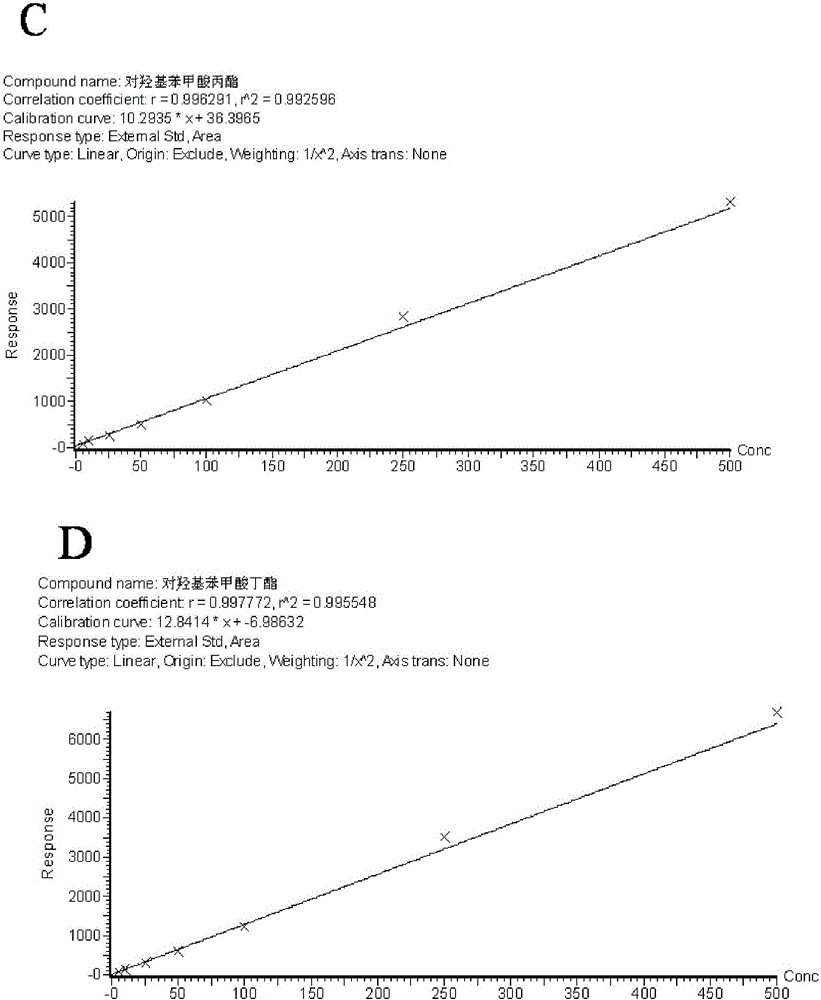
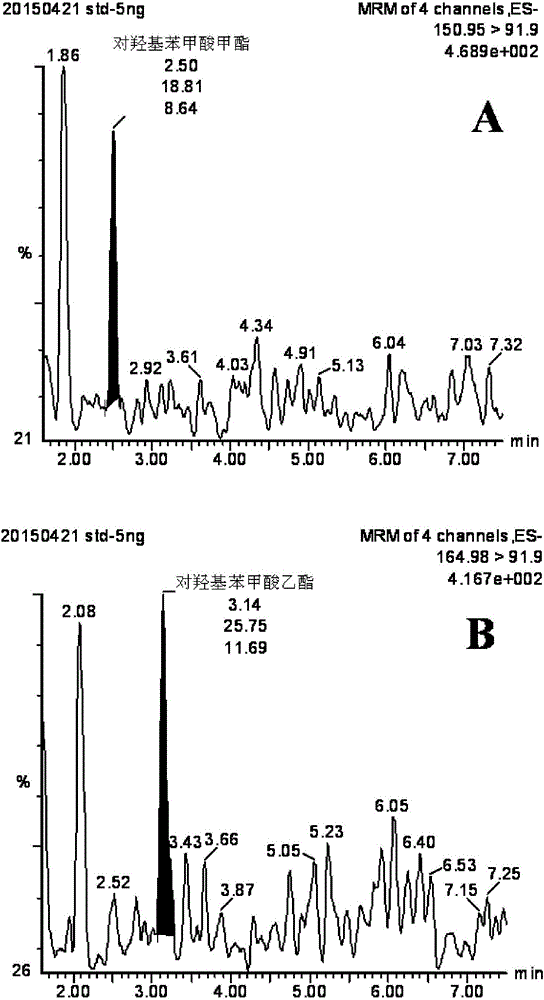
InactiveCN106248834AHigh sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityComponent separationBenzoic acidGlucuronidase
The invention provides a UPLC-MS / MS detecting method for detecting concentration of parabens preservatives in human urine. The method includes the steps of firstly, processing samples, to be more specific, placing a to-be-detected urine sample into a test tube or a centrifugal tube, adding water with the volume being 1 / 10 times of the volume of the urine sample, adding beta-glucuronidase, shaking up and sealing, heating in water bath of 37 DEG C until complete reaction is achieved, taking a certain amount of reaction liquid, adding precipitator (methanol / acetonitrile=1:1) with the quantity being 3 times of the quantity of the reaction liquid to precipitate protein, well mixing in a vortex manner, centrifuging at 15000rpm for 10 minutes, and taking 5-10 microliters of supernate for sample analysis; secondly, injecting the sample, and performing the UPLC-MS / MS detection according to certain conditions; thirdly, calculating the concentration of the parabens preservatives in the human urine according to the peak area of the sample and the regression equations of standard curves. The UPLC-MS / MS detecting method has the advantages that the method is simple and fast, high in sensitivity, high in interference resistance and suitable for the simultaneous qualitative and quantitative detection of the preservatives in the urine, and food with excessive preservatives can be detected in the urine through metabolism.
Owner:HARMONIA TESTING TECH TIANJIN LTD
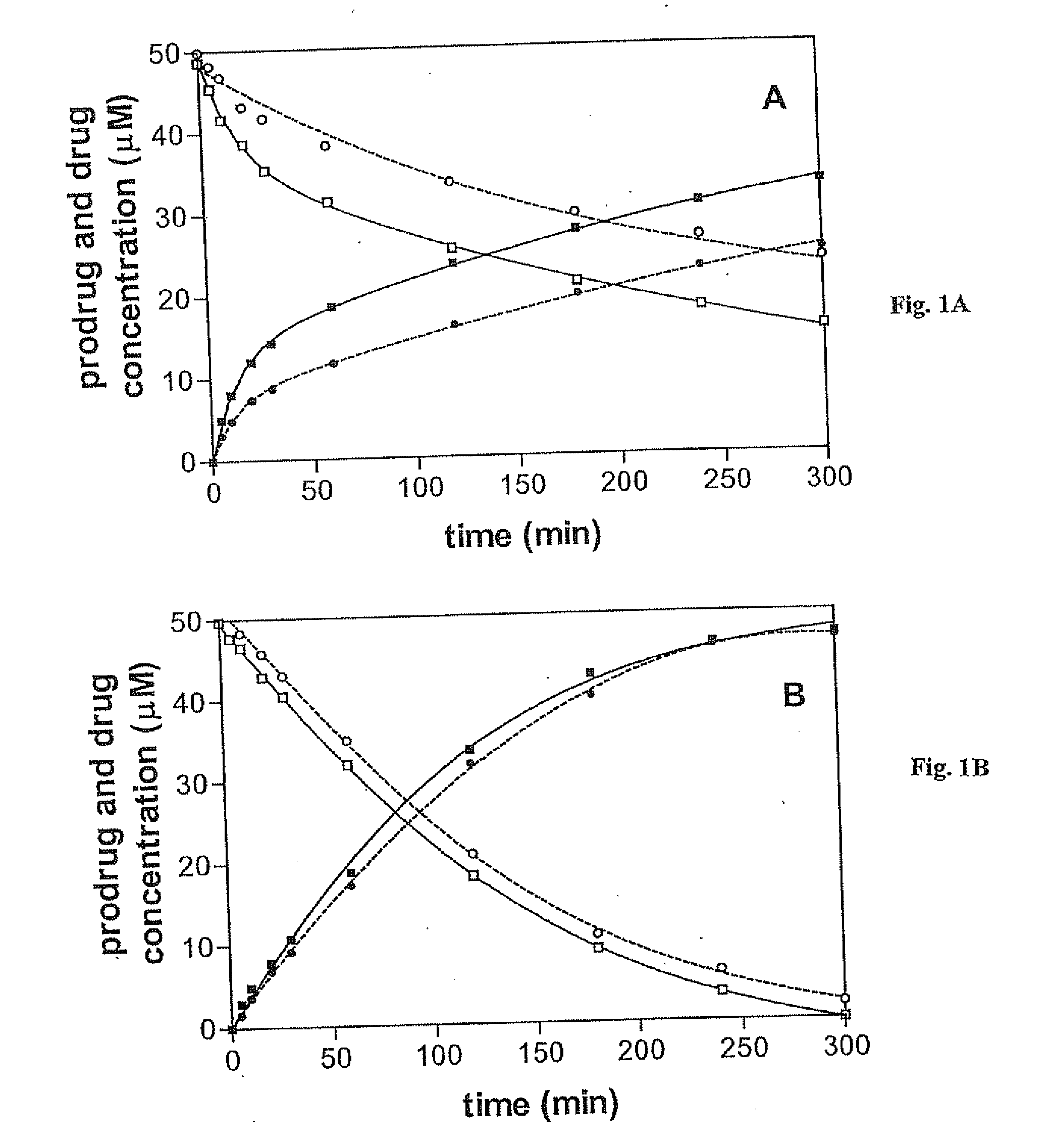
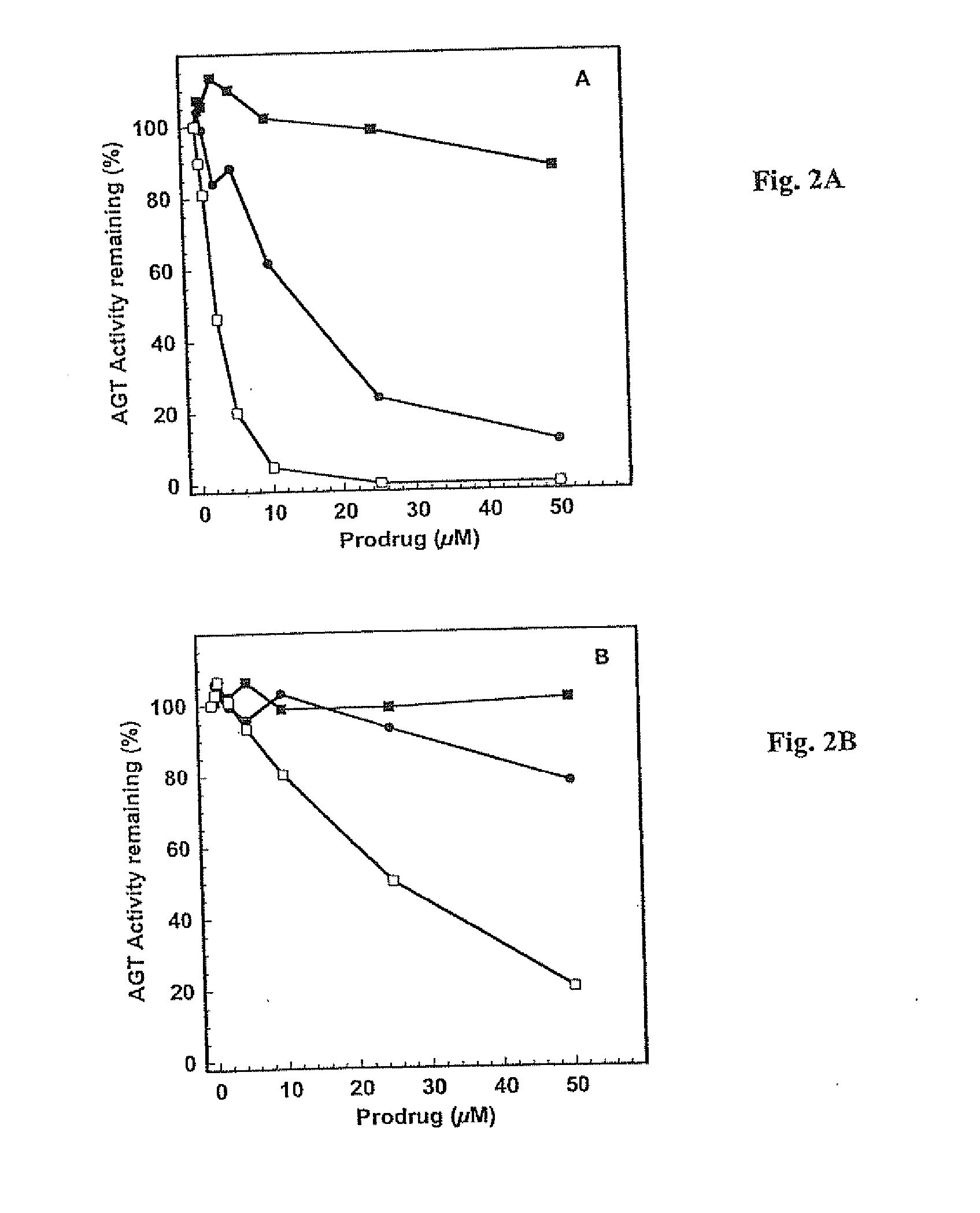
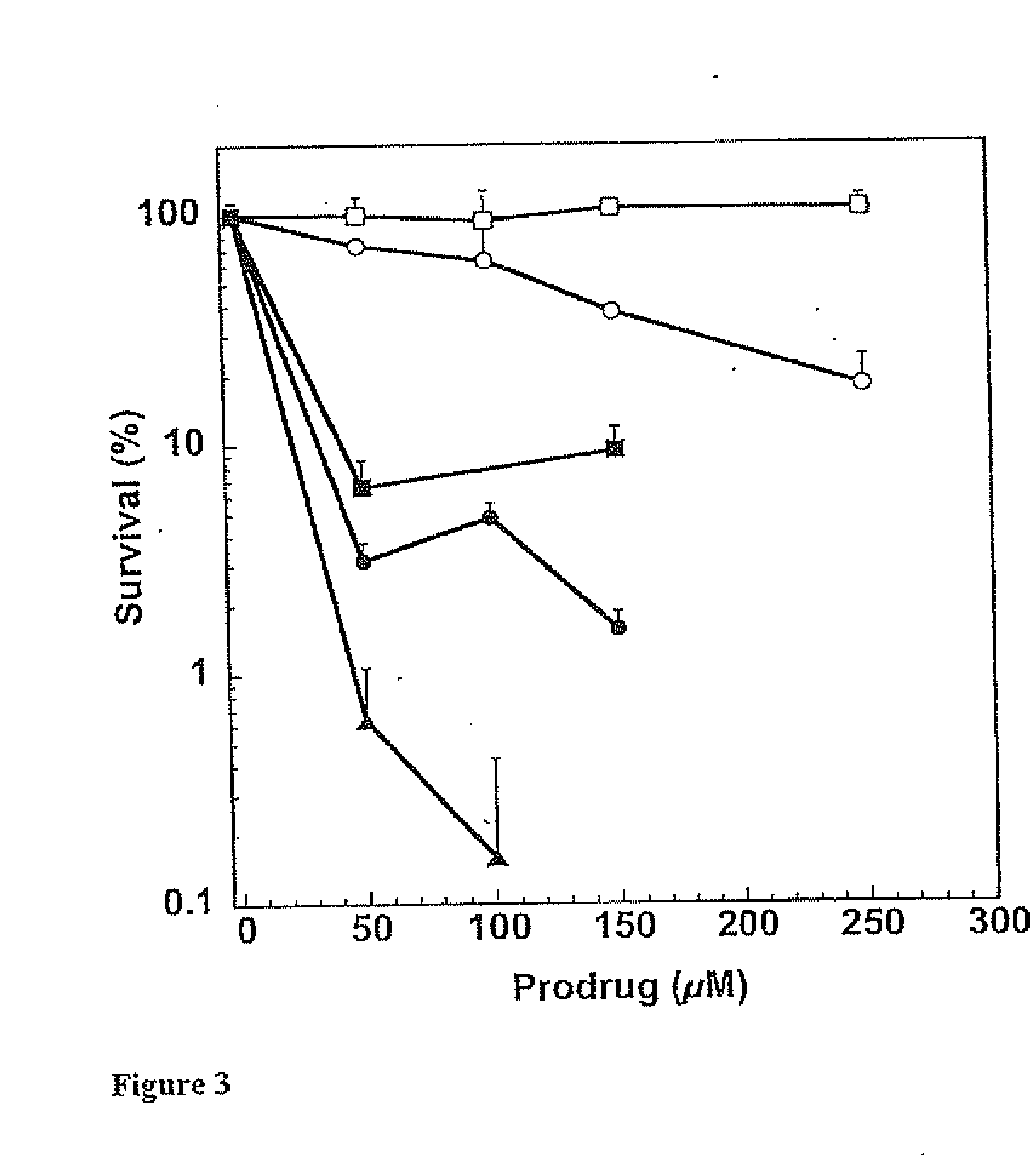
O6-alkylguanine-dna alkyltransferase inactivators and beta-glucuronidase cleavable prodrugs
Disclosed are prodrugs of inactivators of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT). The prodrugs are cleavable by the β-glucuronidase enzyme, which is either administered to the patient or produced by necrotic tumor cells. The prodrugs are represented by the formula A-B-C, wherein A is a glucuronosyl residue linked through its 1-oxygen to the phenyl ring of B; B is a benzyloxycarbonyl group, optionally ring-substituted with one or more electron withdrawing groups; and C is an inactivator of AGT, e.g., a substituted or unsubstituted O6-benzylguanine or O6-benzyl-2′-deoxyguanosine, Also disclosed are additional inactivators of AGT, pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inactivator or prodrug and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and a method of use of the inactivator or prodrug in enhancing the chemotherapeutic treatment of tumor cells in a mammal, e.g., a human, with an antineoplastic alkylating agent that causes cytotoxic lesions at the O6-position of guanine.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Dongxiang wild rice endophytic fungus strain capable of transforming glycyrrhizic acid to produce glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide
The invention provides a Dongxiang wild rice endophytic fungus strain capable of transforming glycyrrhizic acid to produce glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide. The strain is identified and named as Aspergillus flavus DX-SEL2 and preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2013686. The strain can induce generation of beta-glucuronidase in a transformation medium with a glycyrrhizic acid as an inductive agent, then hydrolysis is carried out so as to remove a glucuronyl group at the terminal of a glycyrrhizic acid molecule, so glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide is produced (secreted in fermentation broth). Organic solvent extraction, normal-phase silica gel column chromatography, reversed-phase silica gel column chromatography and the like are used for further separation and purification so as to obtain glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide. According to the invention, microbial catalytic conversion is employed, and the advantages of greenness, environmental protection, no pollution, simple transformation steps, a single product, a high transformation rate, etc. are obtained.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Specific expression promoter of rice seed aleurone layer and application thereof
The invention discloses a specific expression promoter of a rice seed aleurone layer and application of the rice seed aleurone layer, and provides a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) segment which is a DNA molecule shown in 1) or 2) or 3), wherein 1) is the DNA molecule shown in a sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) is the DNA molecule hybridized with a DNA sequence defined by 1) under a strict condition and having a promoter function; and 3) is the DNA molecule having homology of more than 70 percent with the DNA sequence defined by 1) and having a promoter function. The experiment shows that the promoter P-NF-YB1 is found, rice is introduced, and the expression of glucuronidase (GUS) gene is driven in the rice. The result shows that the rice seed aleurone layer specially expresses that the promoter is a tissue specificity promoter; and the promoter has wide application and market prospect in the field of agriculture.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
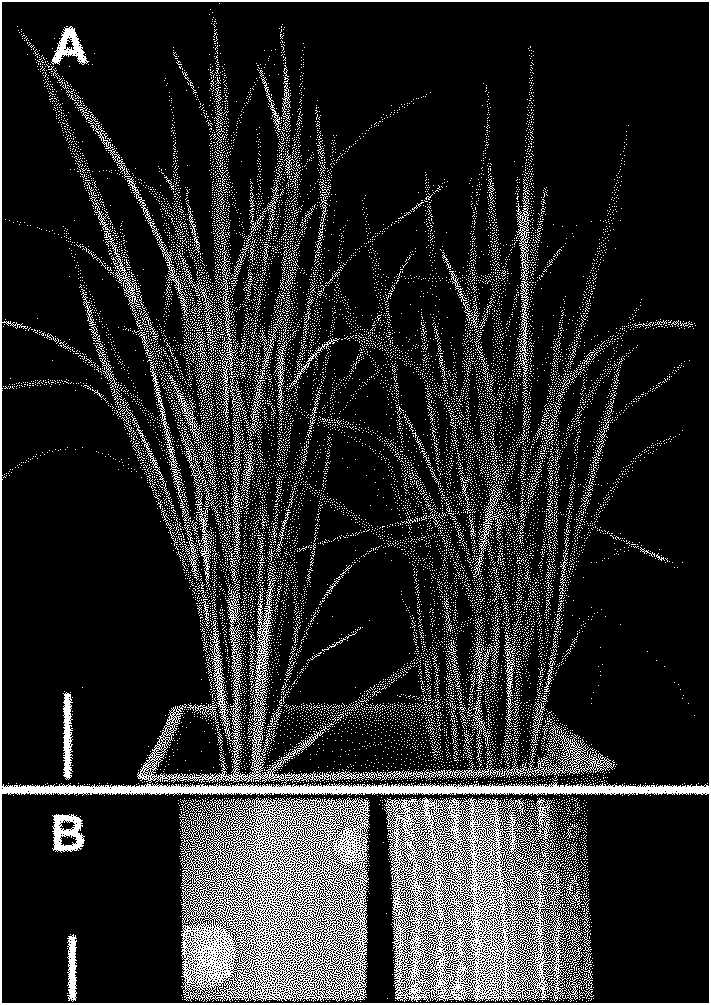
Method for culturing agrobacterium-mediated transgenic salix matsudana plants
InactiveCN103060372AShort induction timeShort training timeGenetic engineeringFermentationBudGlucuronidase
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for culturing transgenic plant with decreased wax
ActiveCN102168083AEnhanced effect of GUS stainingImprove dyeing effectPlant peptidesFermentationWaxCuticle
The invention discloses a method for culturing a transgenic plant with decreased wax. The method for culturing the transgenic plant with the decreasing wax comprises the following steps of: losing the gene coding function of proteins shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 of an initial plant so as to obtain the transgenic plant with the decreased wax. In the method, the gene affects the formation of leaf wax and is the gene for controlling leaf wax to form, and particularly, the gene can positively regulate the formation of leaf wax. The gene has important application value on the understanding of the mechanism of forming the leaf wax of paddy rice, and the gene can be used for breeding paddy rice to improve cuticular properties of paddy rice leaves by the gene engineering method so as to improve the drought control capacity. In addition, the gene and the protein can control the content of cuticular wax which may affect glucuronidase (GUS) staining effect of paddy rice leaves, and the GUS staining effect of paddy rice leaves can be enhanced by lowering the content of cuticular wax, so that the gene can be used to culture transgenic test materials for detecting expression conditions of exogenous gene on leaves.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
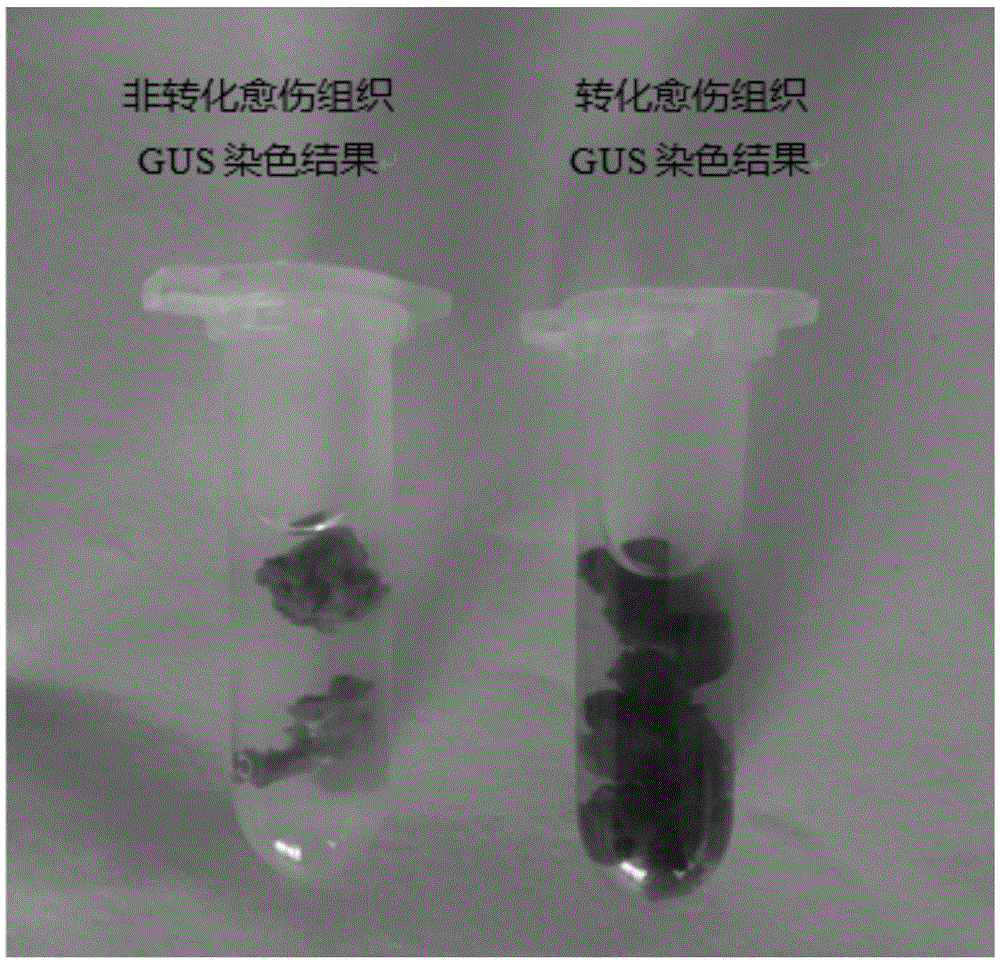
Dangshan pear genetic transformation method
ActiveCN105543278ACarries less germsReduce pollutionGenetic engineeringFermentationContamination rateGlucuronidase
The invention provides a Dangshan pear genetic transformation method. The Dangshan pear genetic transformation method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a genetic transformation receptor; (2) culturing agrobacterium tumefaciens and preparing infection solution; (3) carrying out infection and coculture; (4) carrying out sterilization culture and screening culture; and (5) carrying out resistant callus GUS (glucuronidase) staining identification. The Dangshan pear genetic transformation method has the advantages that Dangshan pear callus is taken as the receptor, NptII is taken as a marker gene, GUS gene is taken as a reporter gene, Dangshan pear genetic transformation is carried out by adopting an agrobacterium EHA105 mediated process for obtaining positive resistant callus, and then redifferentiation is carried out by virtue of the positive resistant callus for obtaining test-tube plantlets; meanwhile, a method for carrying out genetic transformation by firstly inducing resistant callus by virtue of fresh treetop, taken as an explant, grown the same year of Dangshan pear is firstly established, content of phenolic substances in fresh treetops of the Dangshan pear in spring is low, less germs are carried, both inoculation browning rate and contamination rate are low, materials are available, callus induction ratio is high, and demand of genetic transformation can be met.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
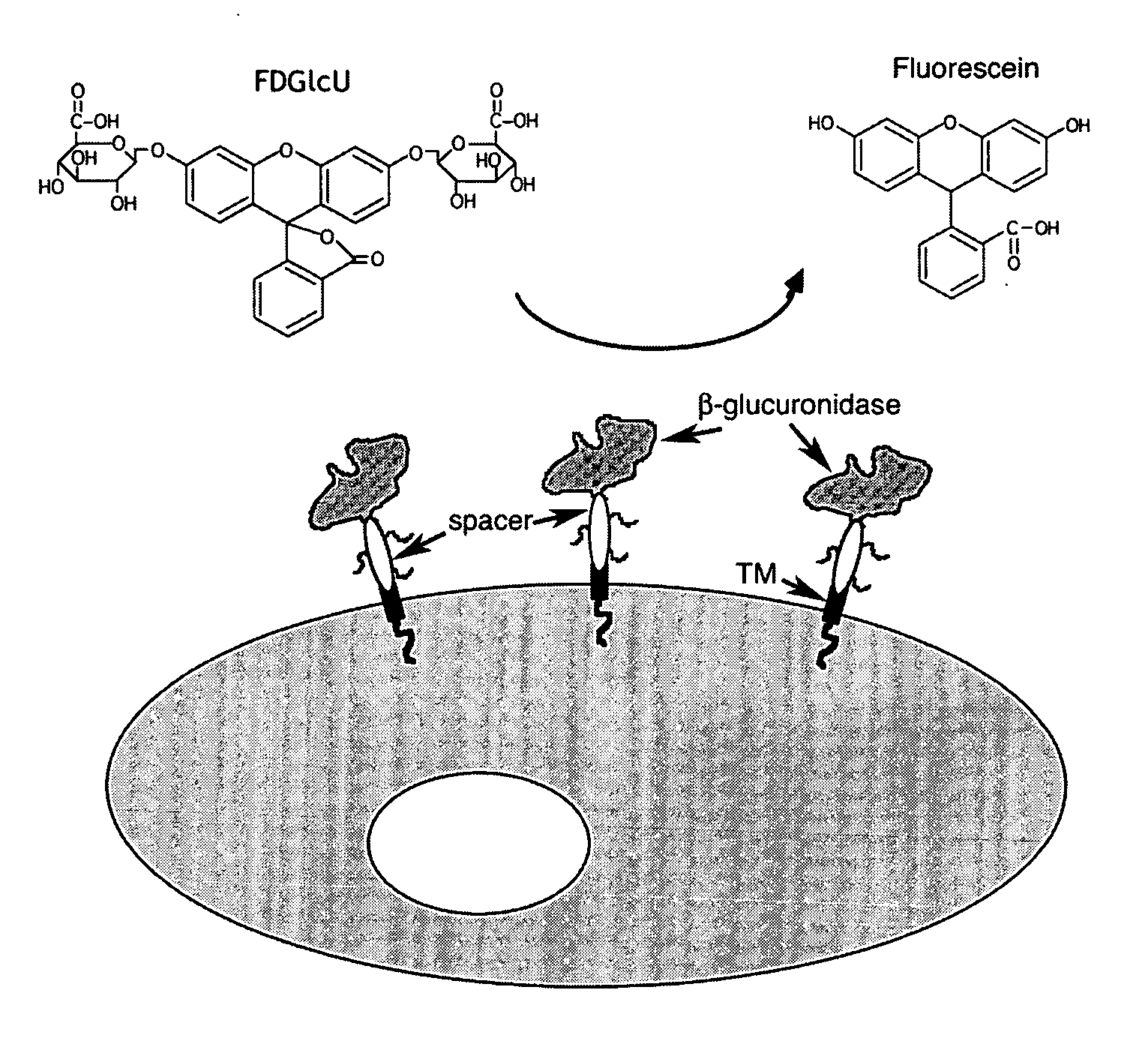
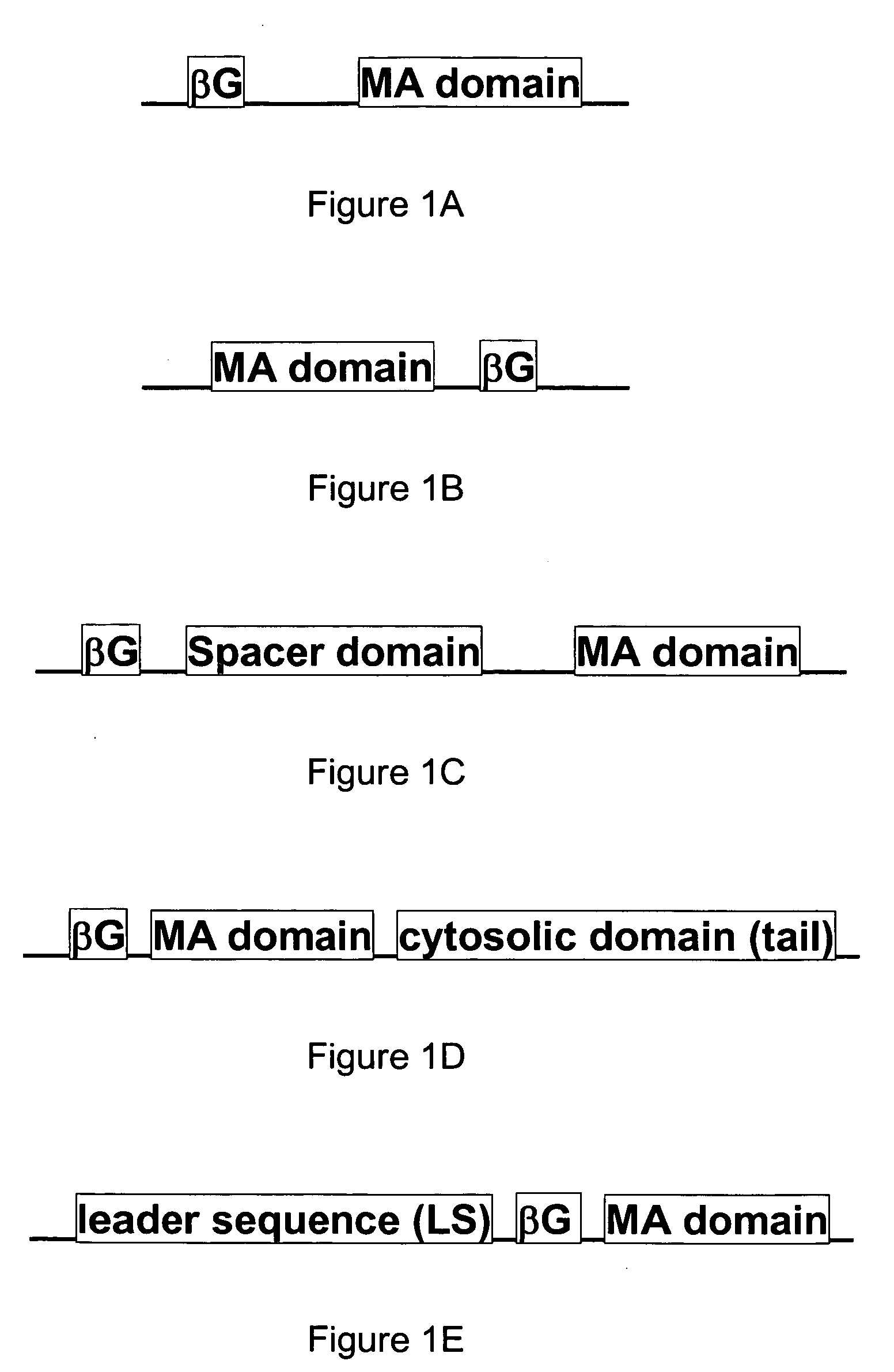
Membrane bound reporter gene system
InactiveUS20080176225A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA constructMembrane anchor
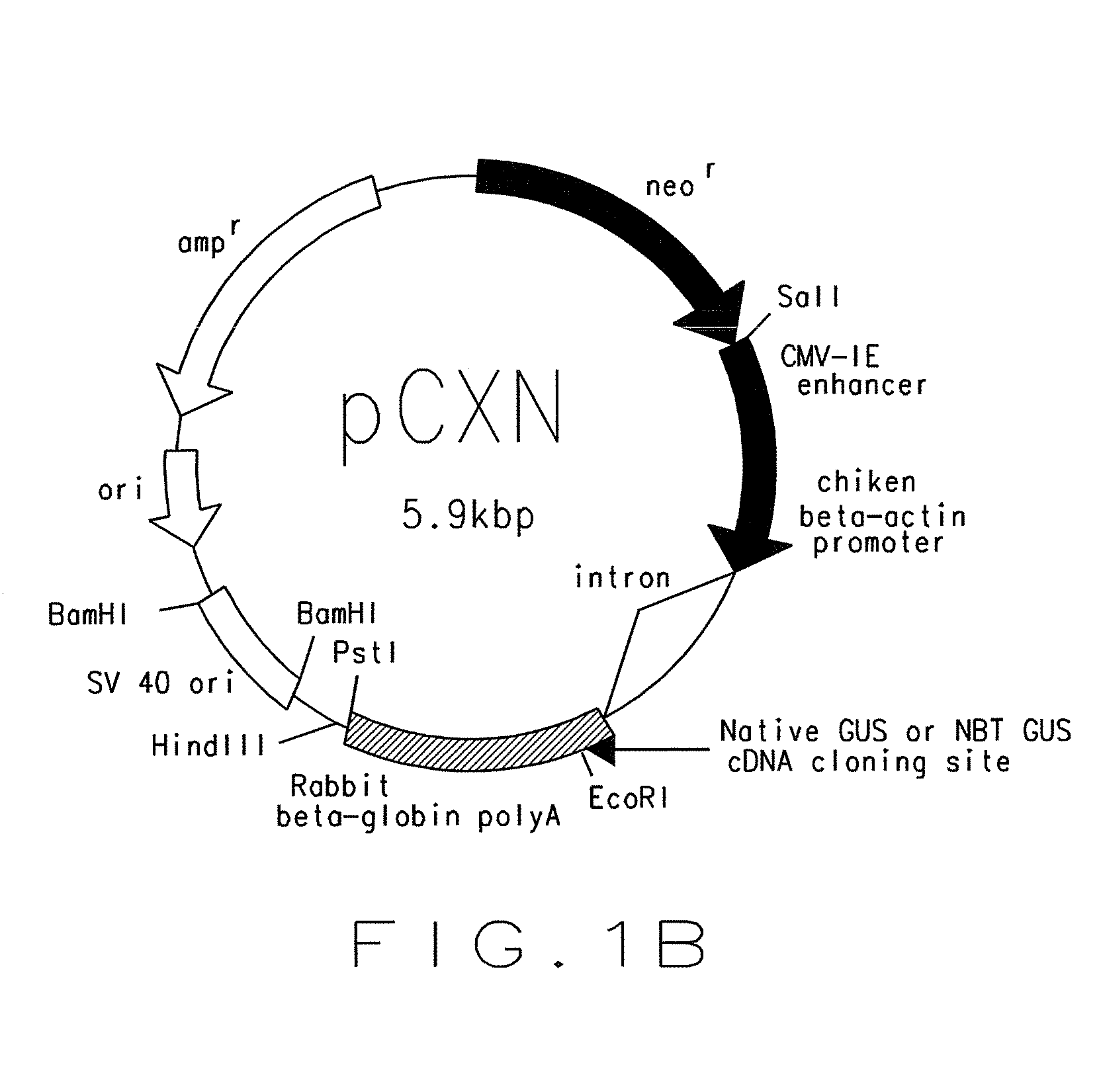
A recombinant DNA construct is provided and includes a first DNA fragment encoding a β-glucuronidase and a second DNA fragment encoding a membrane anchoring domain. The β-glucuronidase may be a human β-glucuronidase or a mouse β-glucuronidase. In one embodiment, an expression vector for delivering a gene of interest or portion thereof into a host cell includes a DNA sequence for the gene of interest, a first DNA fragment encoding a β-glucuronidase, and a second DNA fragment encoding a membrane anchoring domain. In another embodiment, a method of introducing a gene of interest or portion thereof into a host cell is provided, including introducing into the host cell a recombinant DNA construct.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Mutant staphylococcus beta-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity
ActiveUS20160237415A1Improve enzymatic activityImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycosylasesBenzodiazepineOpiate
Mutated Staphylococcus sp. RLH1 β-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity and thermostability as compared to wild type enzyme are provided. The enzymes of the invention advantageously allow for accurate analysis of bodily samples for the presence of drugs in 30 minutes or less, as compared to the several hours needed using prior enzyme preparations. Methods of using the mutated enzymes for hydrolysis of glucuronide substrates, including opiates and benzodiazepines, are also provided.
Owner:INTEGRATED MICRO CHROMATOGRAPHY SYST INC
Agrobacterium-mediated spirodela polyrhiza stable transformation system establishment method
InactiveCN106011169ALarge biomassImprove efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAsexual reproductionAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses an agrobacterium-mediated spirodela polyrhiza stable transformation system establishment method, which comprises the following steps: A, inducing calli of spirodela polyrhiza; B, connecting a target gene with a T vector; C, connecting the target gene with a plant expression vector; D, transforming the plant expression vector in agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404; E, preparing an infective bacteria solution; F, co-culturing the calli and the agrobacterium tumefaciens; G, performing regeneration and selective culturing: determining that the target gene is successfully integrated into a genome of the spirodela polyrhiza if a GUS (glucuronidase) staining result of thalli is blue, and determining that a part which is stained to be blue by thallus tissues is a part expressed by the target gene. The target gene is inserted into the plant expression vector and then transferred into the agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404 for callus infection, and the concentration of antibiotics is finally controlled to screen a positive plant to obtain transgenetic spirodela polyrhiza, and an established transformation system can still ensure continuous and stable inheritance after asexual reproduction of the spirodela polyrhiza, and has bio-safety and development and application value.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Probiotic propionibacterium
InactiveUS7427397B2Promote growthGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesPropanoic acid
The present invention relates to probiotic Propionibacterium strains and their use in the preparation of probiotic supplements and foods. The invention relates to the provision of Vitamin B12, propionic acid, folacin and bacteriocins by probiotic strains, stimulation of bifidobacteria growth, production of favourable effects on the lipid metabolism and on the immune system of hosts through immunostimulation, immunomodulation or use of a probiotic strain as an adjuvant, reduction of homocysteine and β glucuronidase and the prevention, treatment or amelioration of conditions associated with a need for these activities. The probiotic bacteria of the invention can be used in humans or other animals. In at least some applications, the bacteria can be used dead and parts rather than whole cells may be used. The present invention also relates to the preparation of vaccines for use in protecting patients from infectious diseases, in particular tuberculosis.
Owner:UNIV OF NEWCASTLE RES ASSOCS
Modified enzyme treatment method
InactiveUS20130011381A1Extended half-lifeConvenient treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug compositionsLysosomal enzyme defectCarbohydrate moiety
Disclosed is a method for the treatment of lysosomal storage disease in mammals wherein the mammal is administered a therapeutically effective amount of an isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase whereby said storage diseased disease is relieved in the brain and visceral organs of the mammal. There is also disclosed an isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase wherein the modification is having its carbohydrate moieties chemically modified so as to reduce its activity with respect to mannose and mannose 6-phosphate cellular delivery system while retaining enzymatic activity. Also disclosed are other lysosomal enzymes within the scope of the invention.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Method for producing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide by fermentation, and application
ActiveCN106636290ANo structural dissimilationSimple processMicroorganism based processesFermentationChemistryCarbon source
The invention discloses a method for producing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide by fermentation, and application, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, glycyrrhizinic acid is taken as a carbon source, a talaromyces fungus is introduced to produce beta-glucuronidase, and glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide can be prepared in large scale on the premise of being friendly to the environment. The method is simple in process and low in cost, the GAMG yield reaches 4.05g / L, the productivity is 88.00%, the purity is 80% or higher than 80% after purification by macroporous resin, the product purity is high, no structural alienation occurs, and the method has the advantages of being short in production cycle, easy to operate, low in energy consumption and the like, thereby being suitable for characteristics of later industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzyme replacement therapy for treating MPS vii related bone lesions using a chemically modified enzyme
The invention relates to a method of treating mucopolysaccharidoses using enzyme replacement therapy with chemically modified lysosomal enzymes. More specifically the method relates to administering chemically modified lysosomal enzymes intraperitoneal injection. In addition, the invention relates to treating type VII mucopolysaccharidoses or mucopolysaccharidoses type VII related bone lesions with a chemical modified β-glucuronidase, wherein the modified β-glucuronidase may be administered 5 weeks after birth, and or may be administered intraperitoneally.
Owner:CAROL ANN FOUND & INT MORQUIO ORG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ddef151-5fe8-4064-a572-cbb073af4b27/HDA00002539623800011.PNG)
![Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ddef151-5fe8-4064-a572-cbb073af4b27/HDA00002539623800012.PNG)
![Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ddef151-5fe8-4064-a572-cbb073af4b27/HDA00002539623800021.PNG)