Patents
Literature
109 results about "Vitreous Humors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
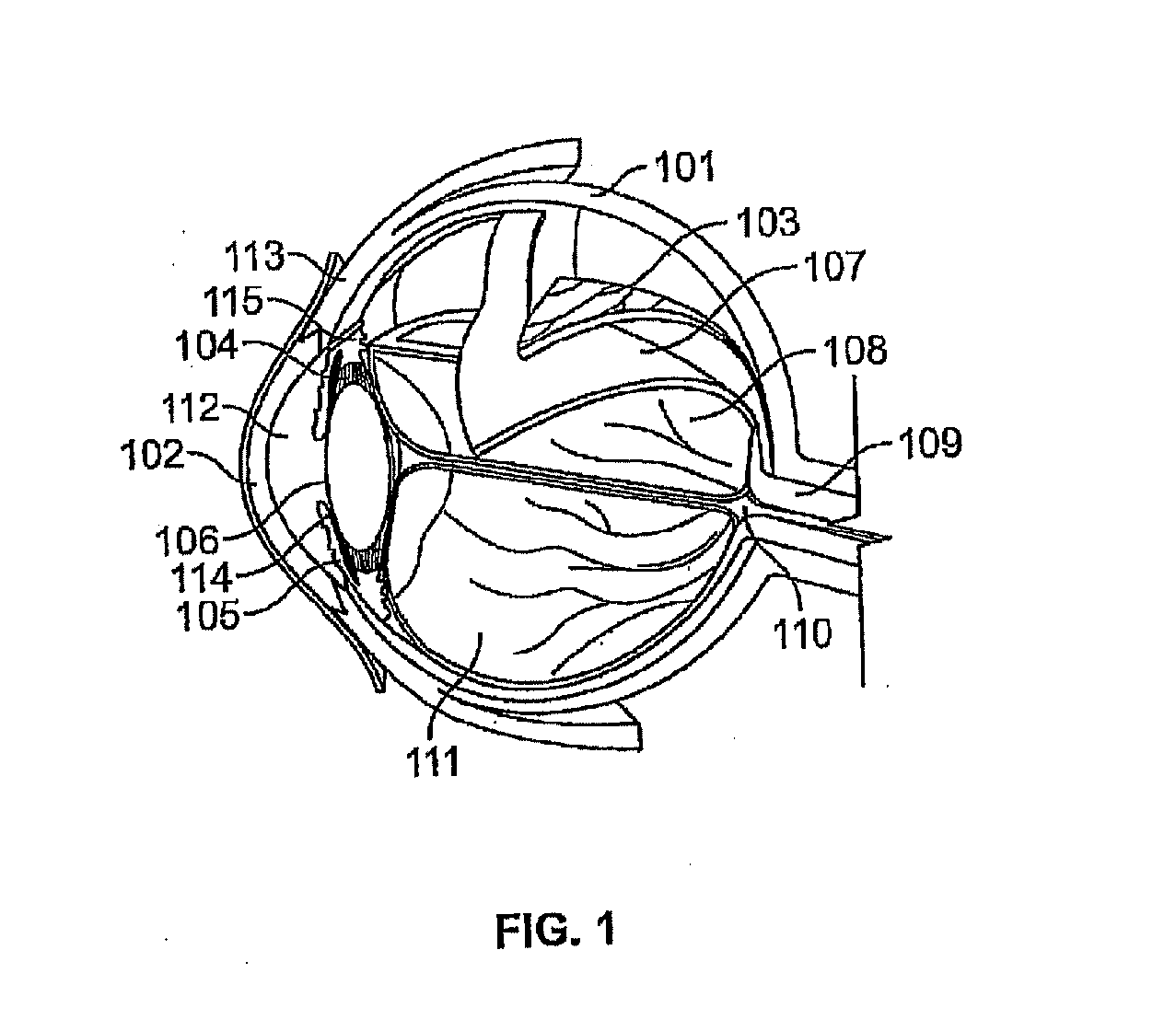
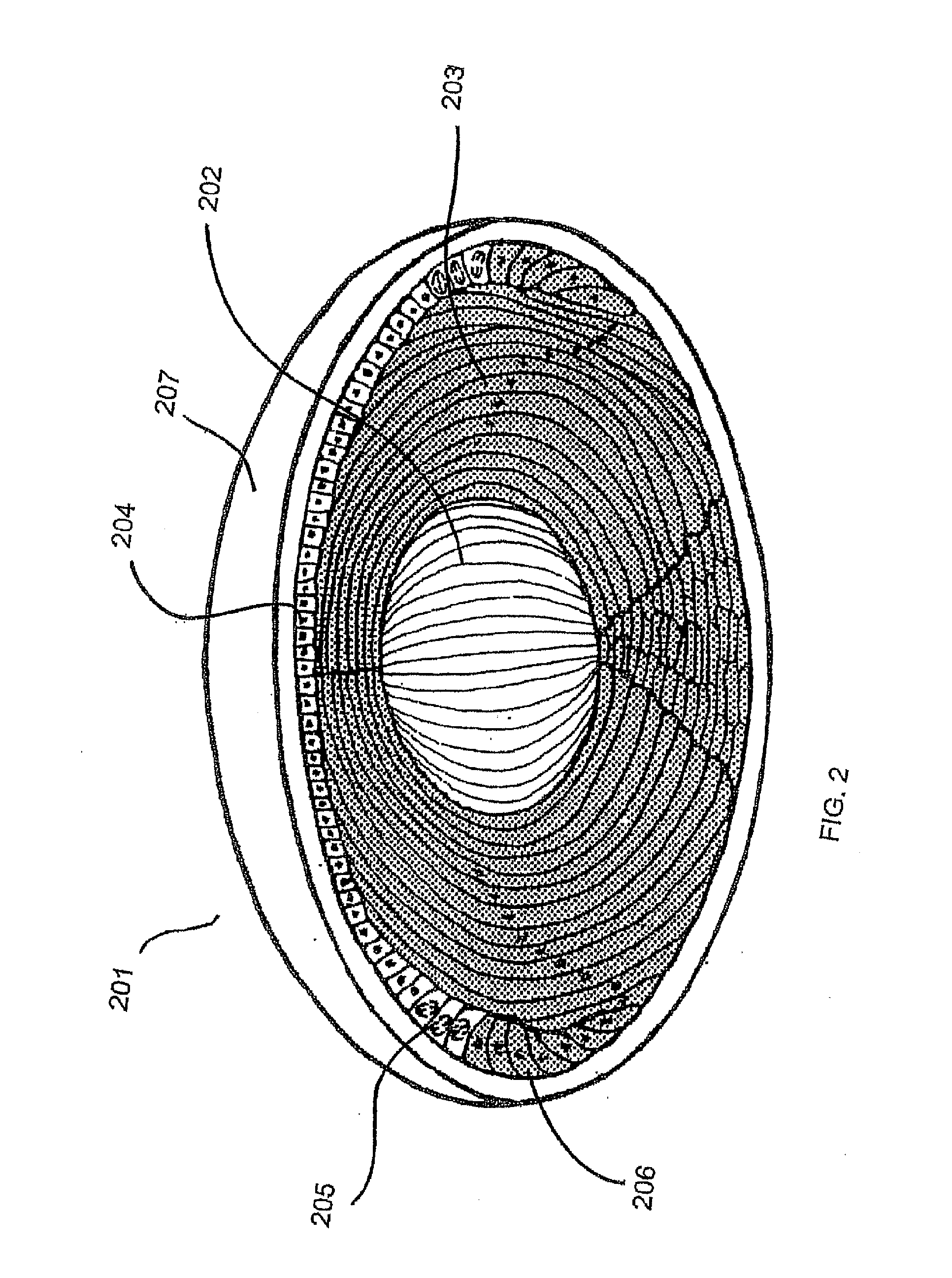
The vitreous body is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball of humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humour or simply the vitreous.
Fluidic intraocular lens systems and methods
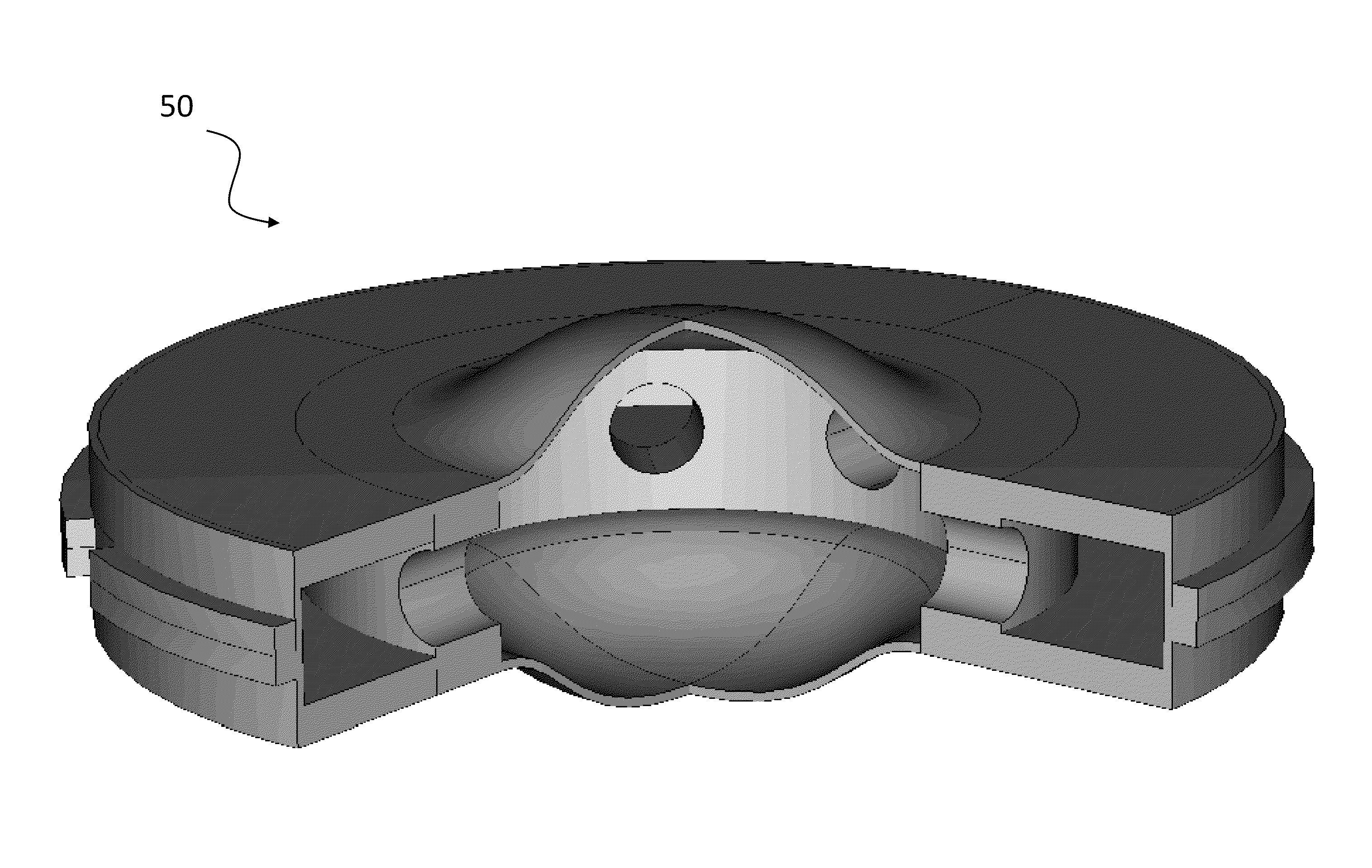
The present invention relates to a fluidic intraocular lens inserted into a capsular bag of an eye to replace a crystalline lens. The fluidic intraocular lens may be shaped by elastic membranes bonded to a support ring. The space inside the device may be filled with optically transparent fluid or gel having an index of refraction greater than the index of vitreous humor. The device may be such designed so that the focusing power of the lens can be changed by the deformation of the capsular bag, which may be subsequently controlled by a ciliary muscle.
Owner:RHEVISION TECH
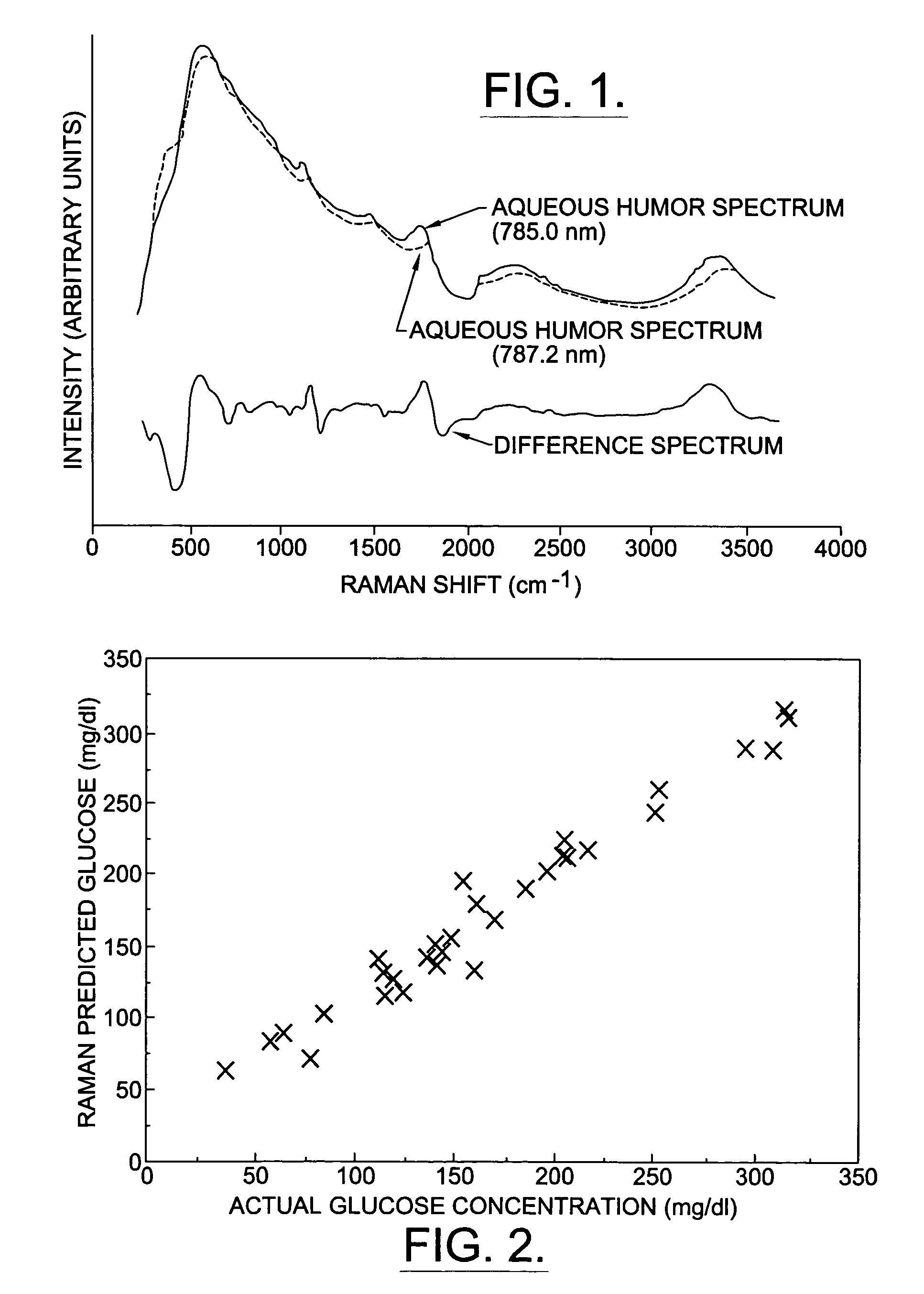
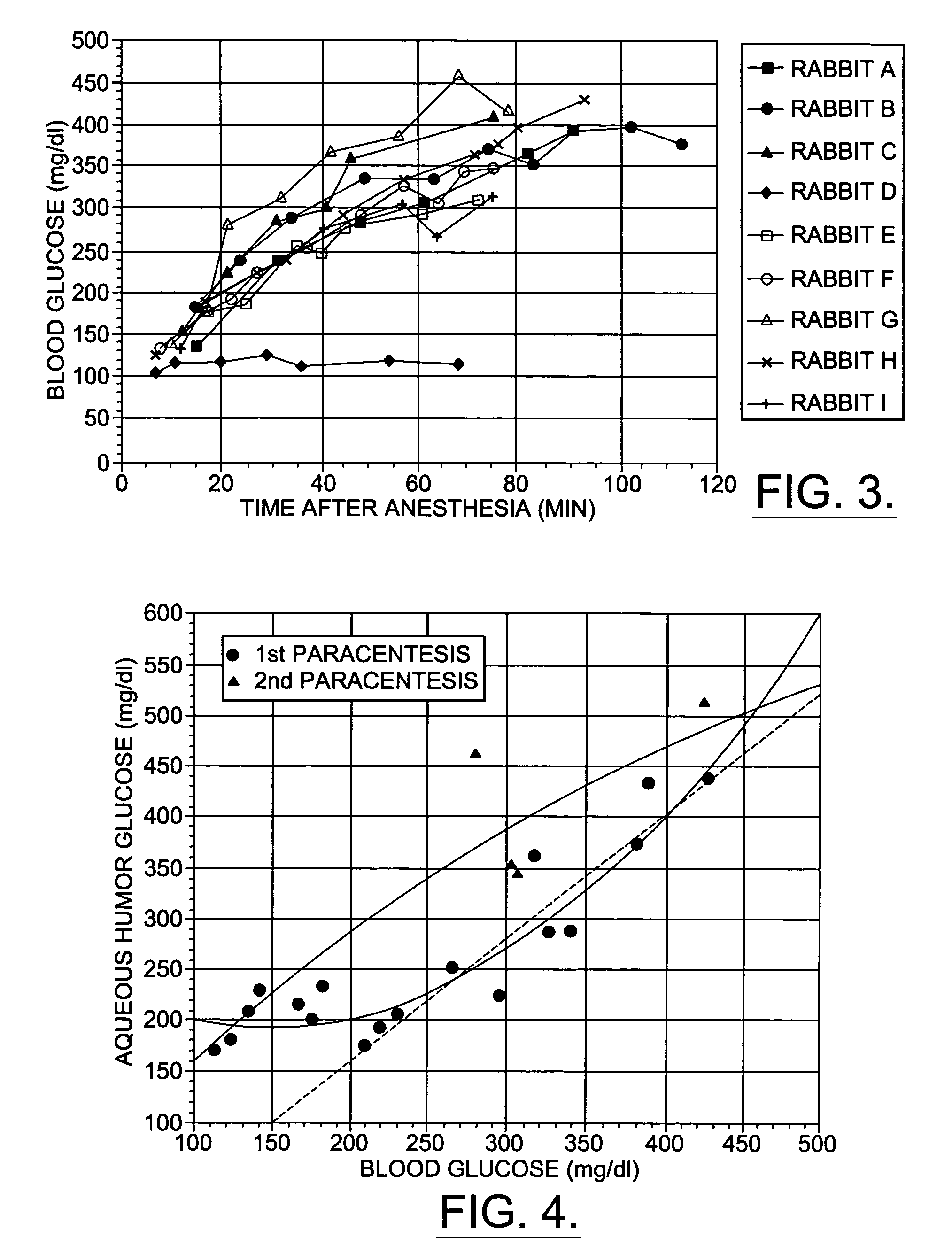
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances, including ethanol or toxins, in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals
InactiveUS7398119B2Fast “ triage ” assessmentReliable and faster treatment decisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationNon invasivePhysics
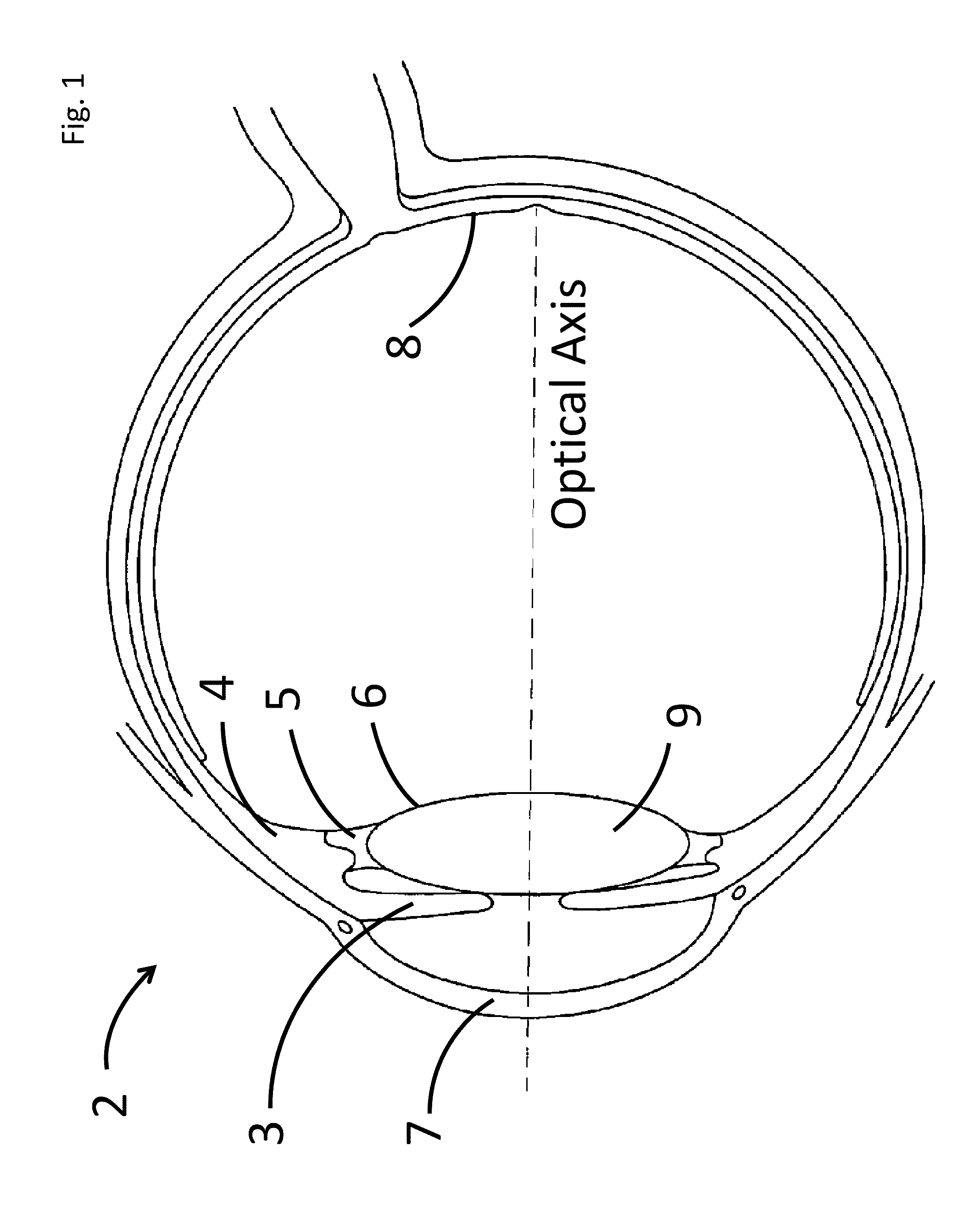
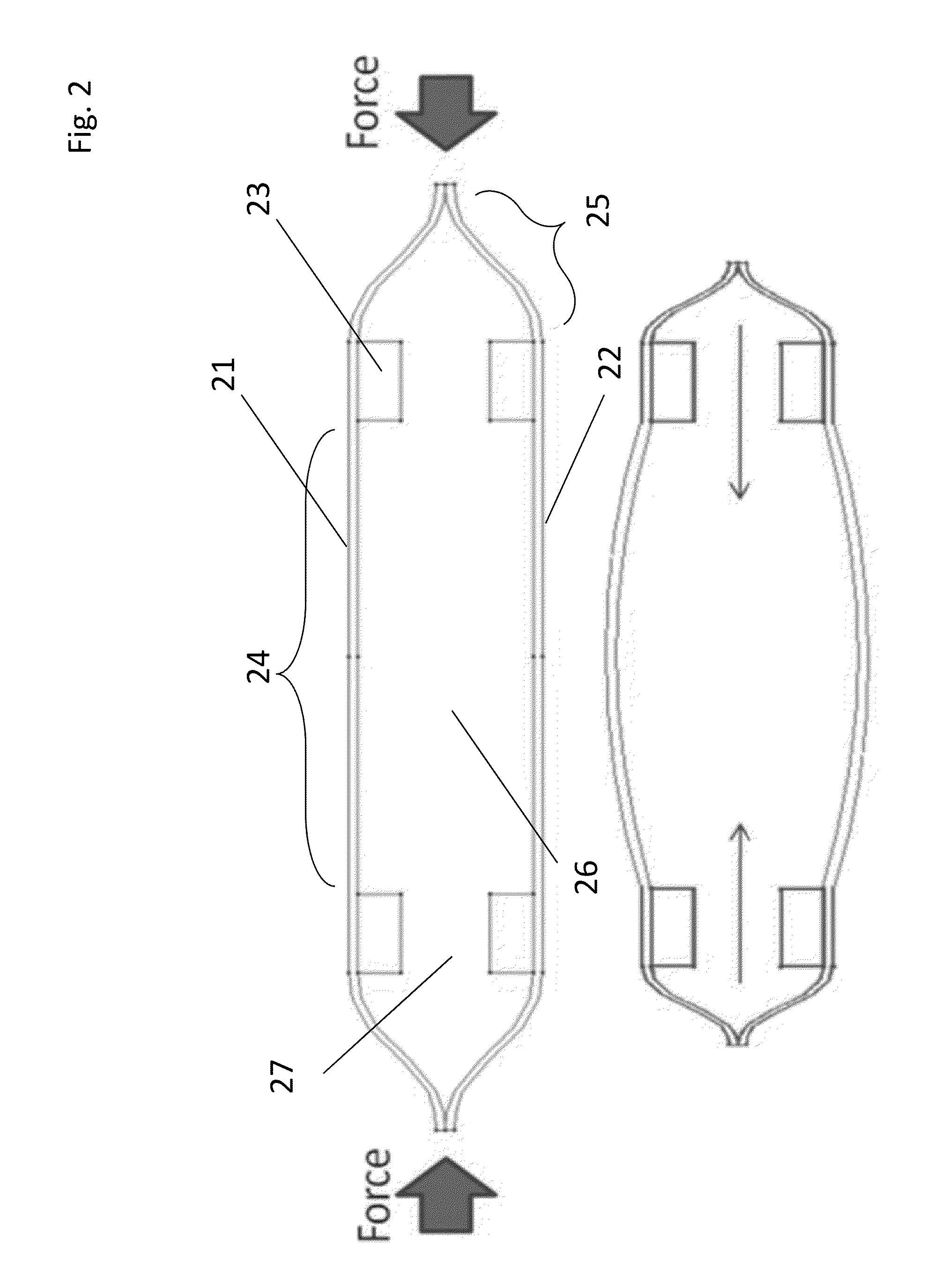
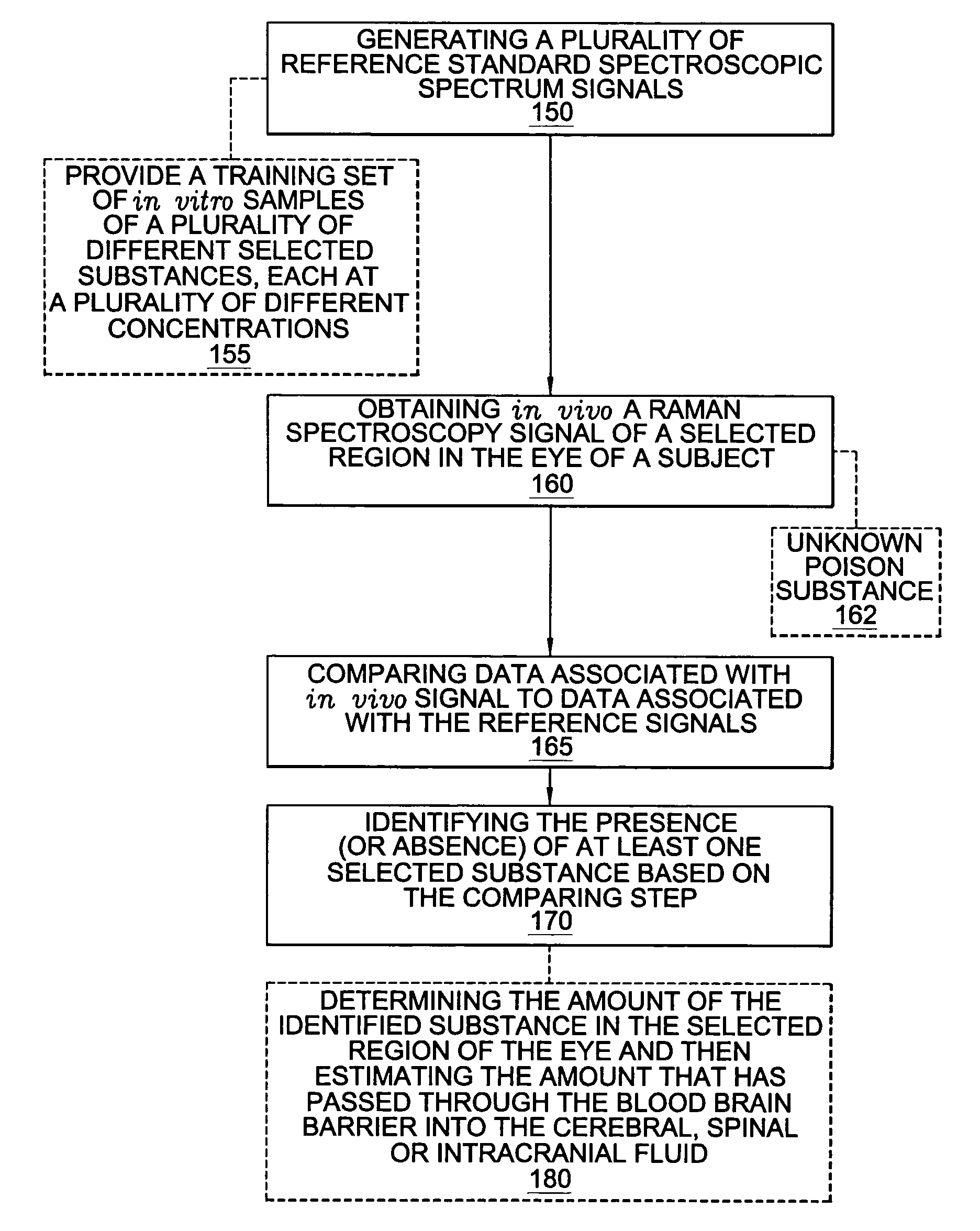
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier.Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam at a selected wavelength (e.g., at a wavelength of about 400 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Devices and Systems to Mitigate Traumatic Brain and Other Injuries Caused by Concussive or Blast Forces
ActiveUS20140343599A1Increase cerebral blood volumeDecrease intracranial complianceDevices for pressing relfex pointsTourniquetsSpinal columnInjury brain
A system for reducing the damaging effects of radiant energy, blast, or concussive events includes applying pressure to at least one jugular vein to reduce the egress of blood from the cranial cavity during or before the incidence of the imparting event. Reducing blood outflow from the cranial cavity increases intracranial volume and / or pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid to reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury and injuries to the spinal column. Reducing blood outflow further increases the intracranial pressure and volume, and thereby increases the pressure and volume of the cochlear fluid, the vitreous humor and the cerebrospinal fluid to thereby reduce the risk of injury to the inner ear, internal structure of the eye and of the spinal column. In addition, increasing intracranial pressure and volume reduces the likelihood of brain injury and any associated loss of olfactory function
Owner:TBI INNOVATIONS +1
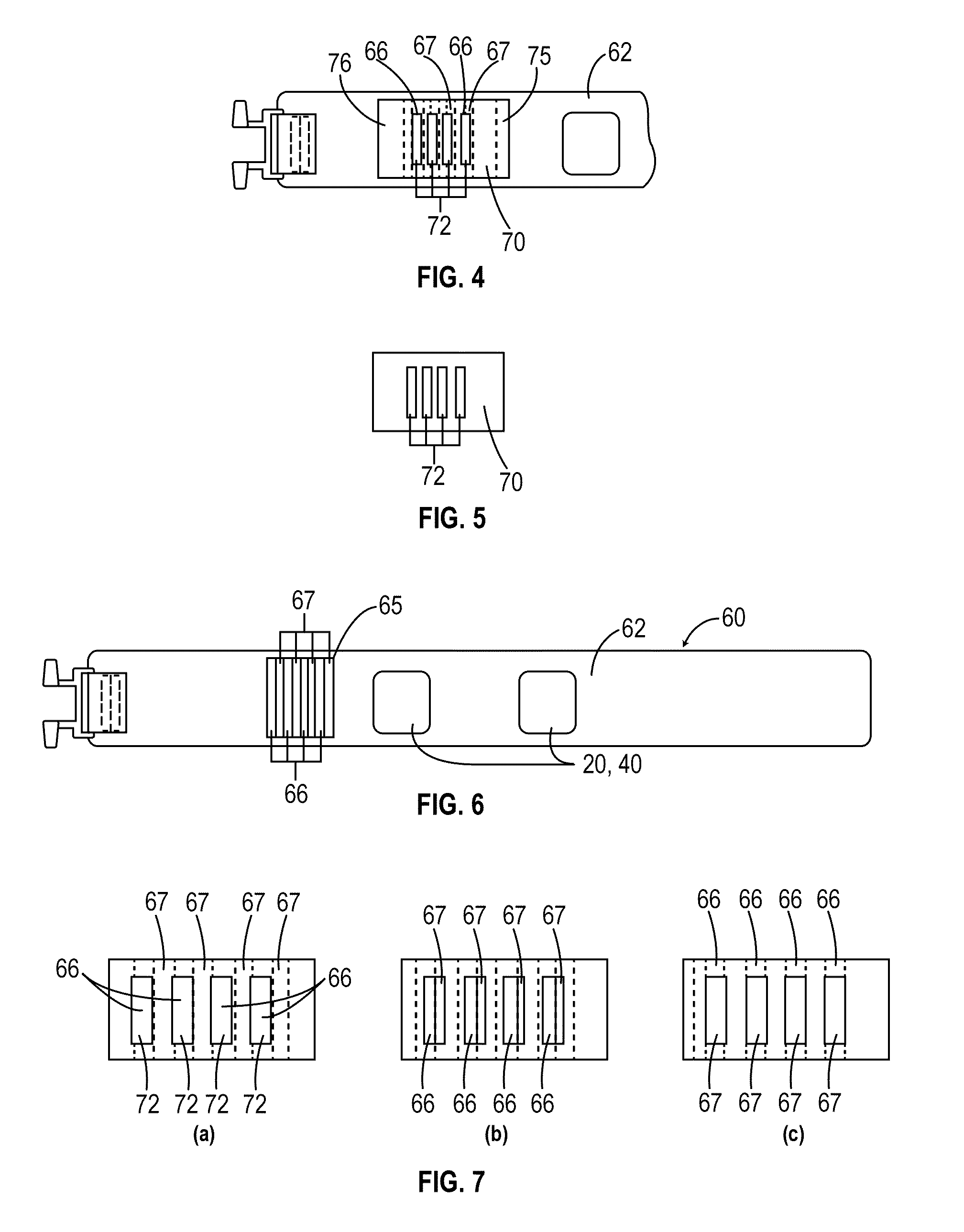
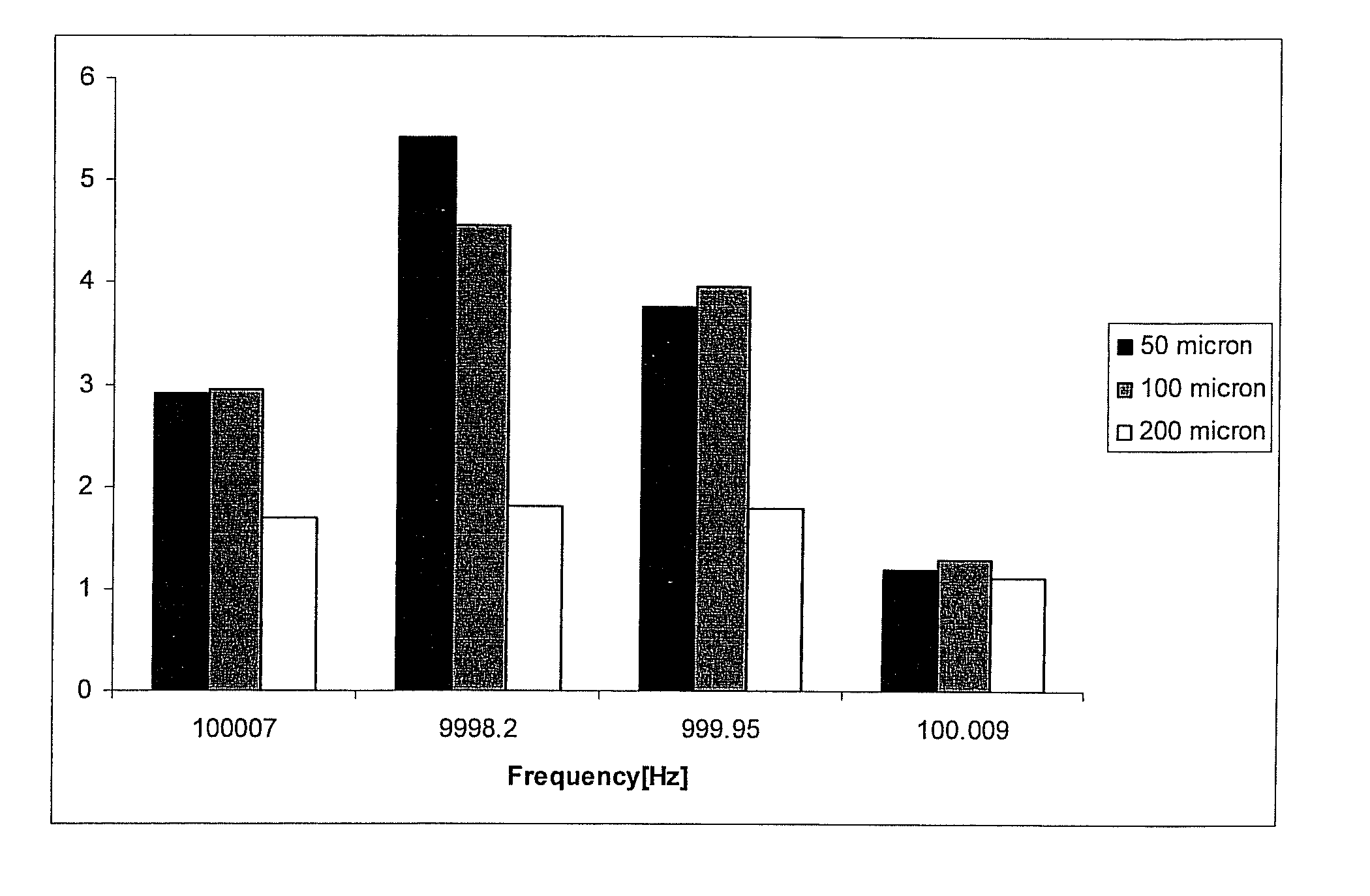
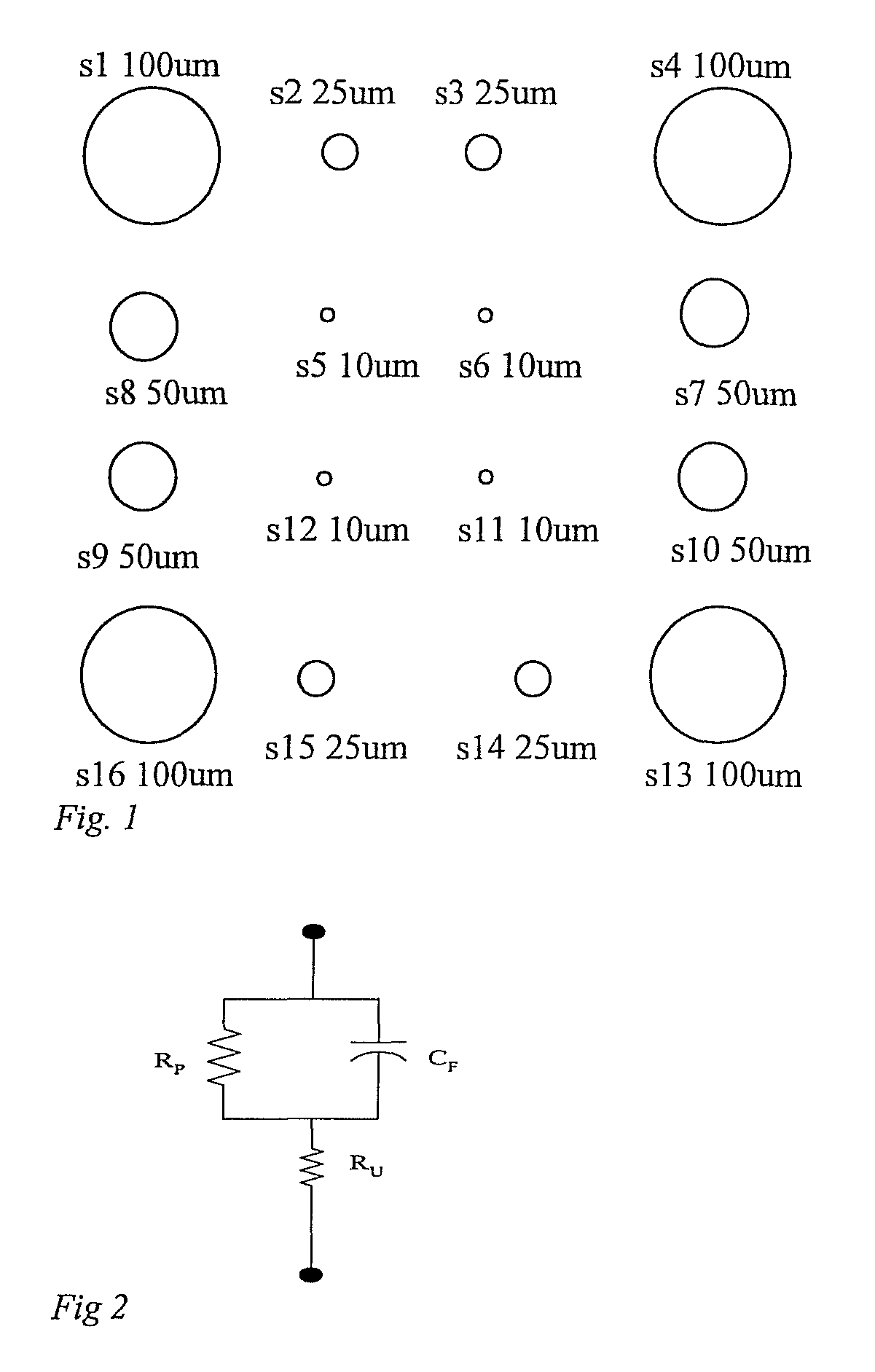
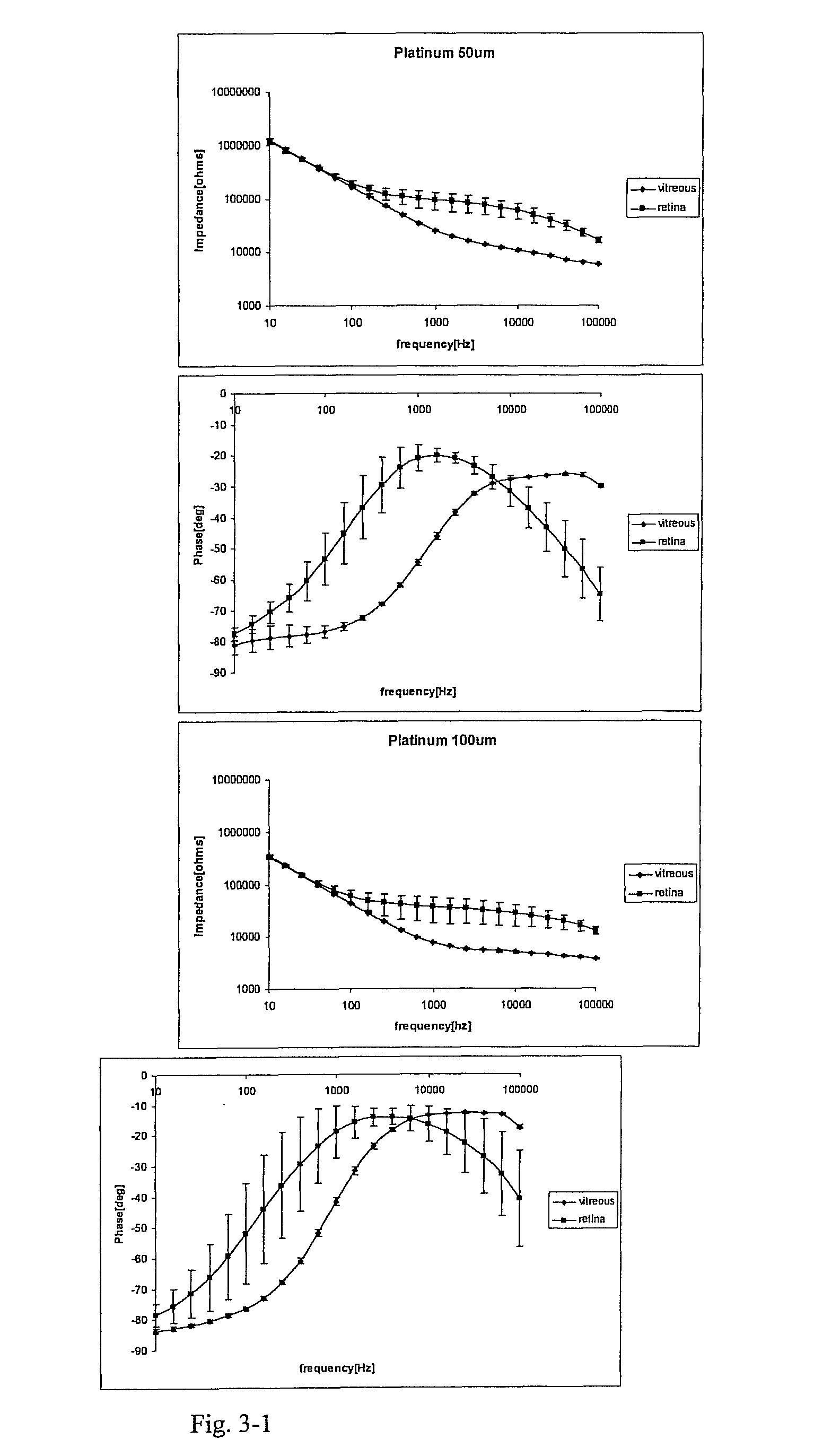
Method of improving electrode tissue interface
A critical element of a retinal prosthesis is the stimulating electrode array, which is placed in close proximity to the retina. It is via this interface that a retinal prosthesis electrically stimulates nerve cells to produce the perception of light. The impedance load seen by the current driver consists of the tissue resistance and the complex electrode impedance. The results show that the tissue resistance of the retina is significantly greater than that of the vitreous humor in the eye. Circuit models of the electrode-retina interface are used to parameterize the different contributors to the overall impedance.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +2
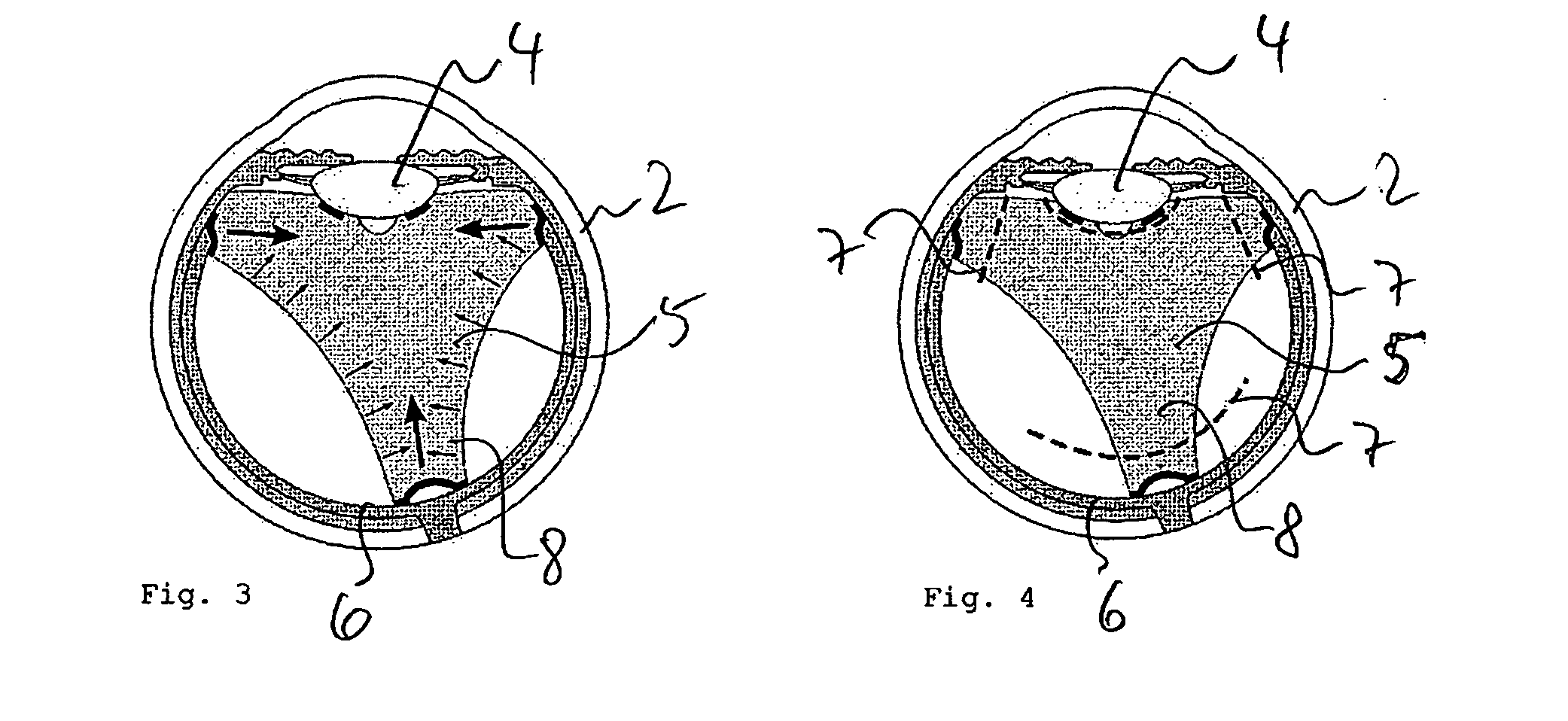
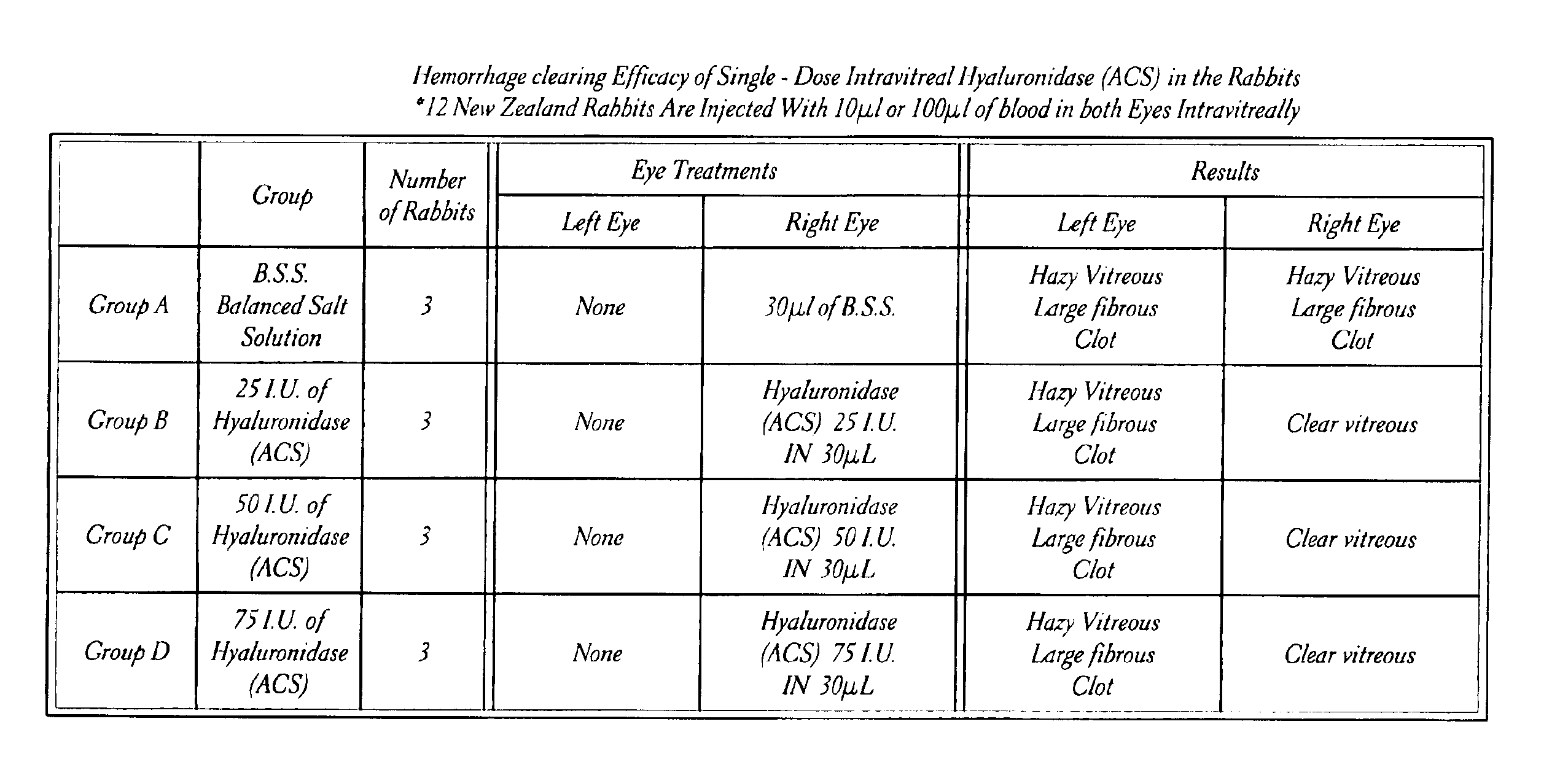
Use of hyaluronidase in the manufacture of an ophthalmic preparation for liquefying vitreous humor in the treatment of eye disorders
InactiveUS6863886B2Improve clearance rateIncreases rate of liquid exchangeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHyaluronidase
An enzymatic method is provided for treating ophthalmic disorders of the mammalian eye. Prevention of neovascularization and the increased rate of clearance from the vitreous of materials toxic to retina is accomplished by administering an amount of hyaluronidase effective to liquefy the vitreous humor of the treated eye without causing toxic damage to the eye. Liquefaction of the vitreous humor increases the rate of liquid exchange from the vitreal chamber. This increase in exchange removes those materials and conditions whose presence causes ophthalmological and retinal damage.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB PHARMA HLDG
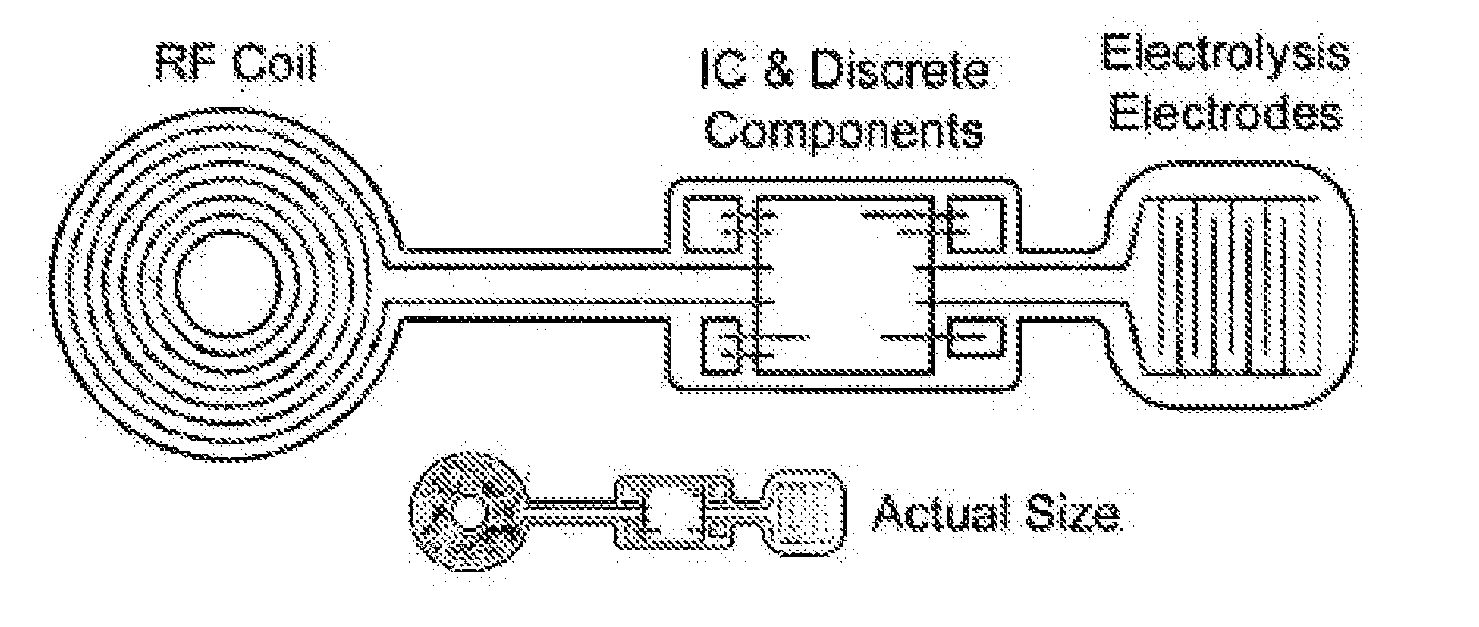
Method and apparatus for treating ischemic diseases
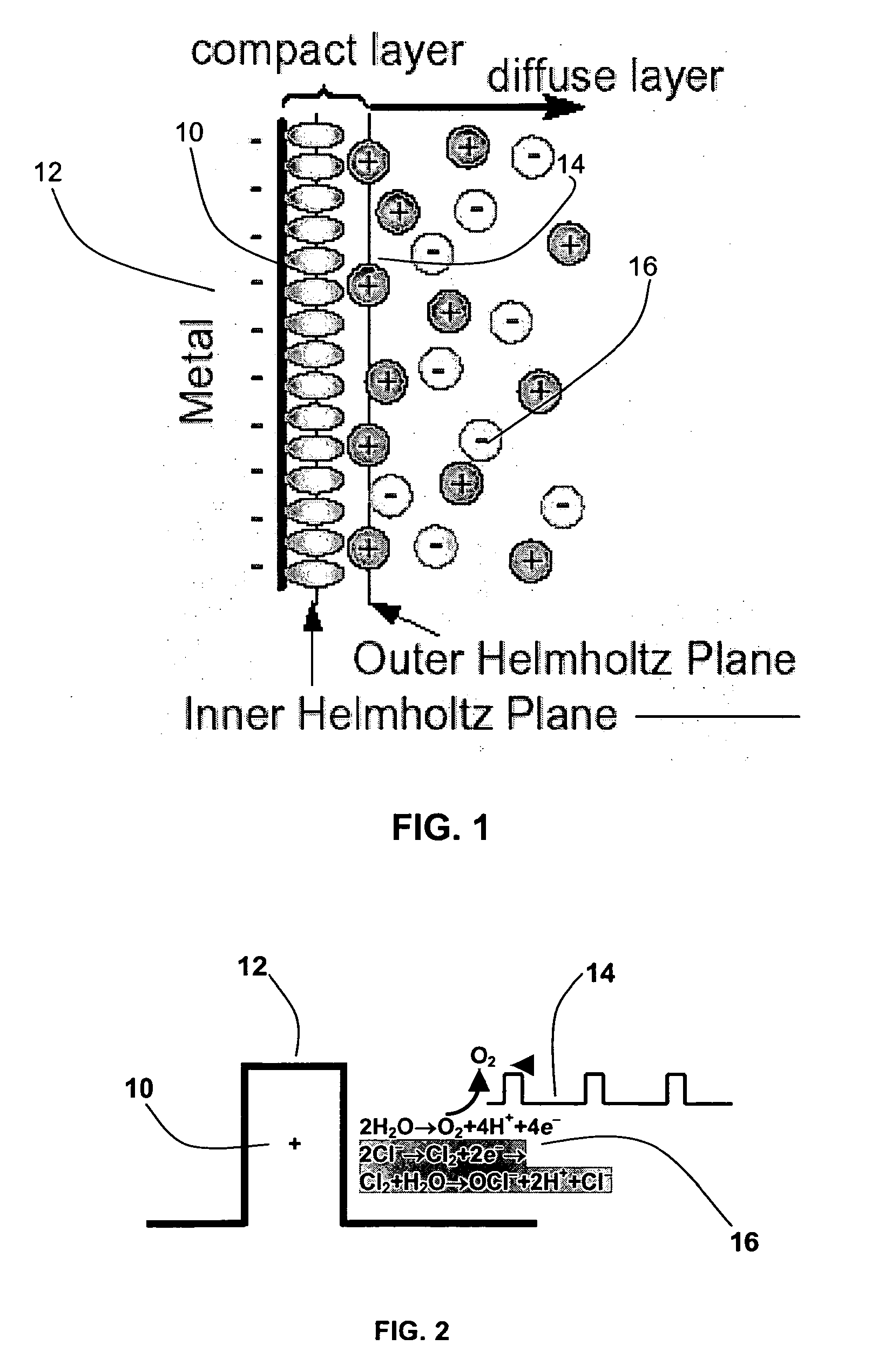
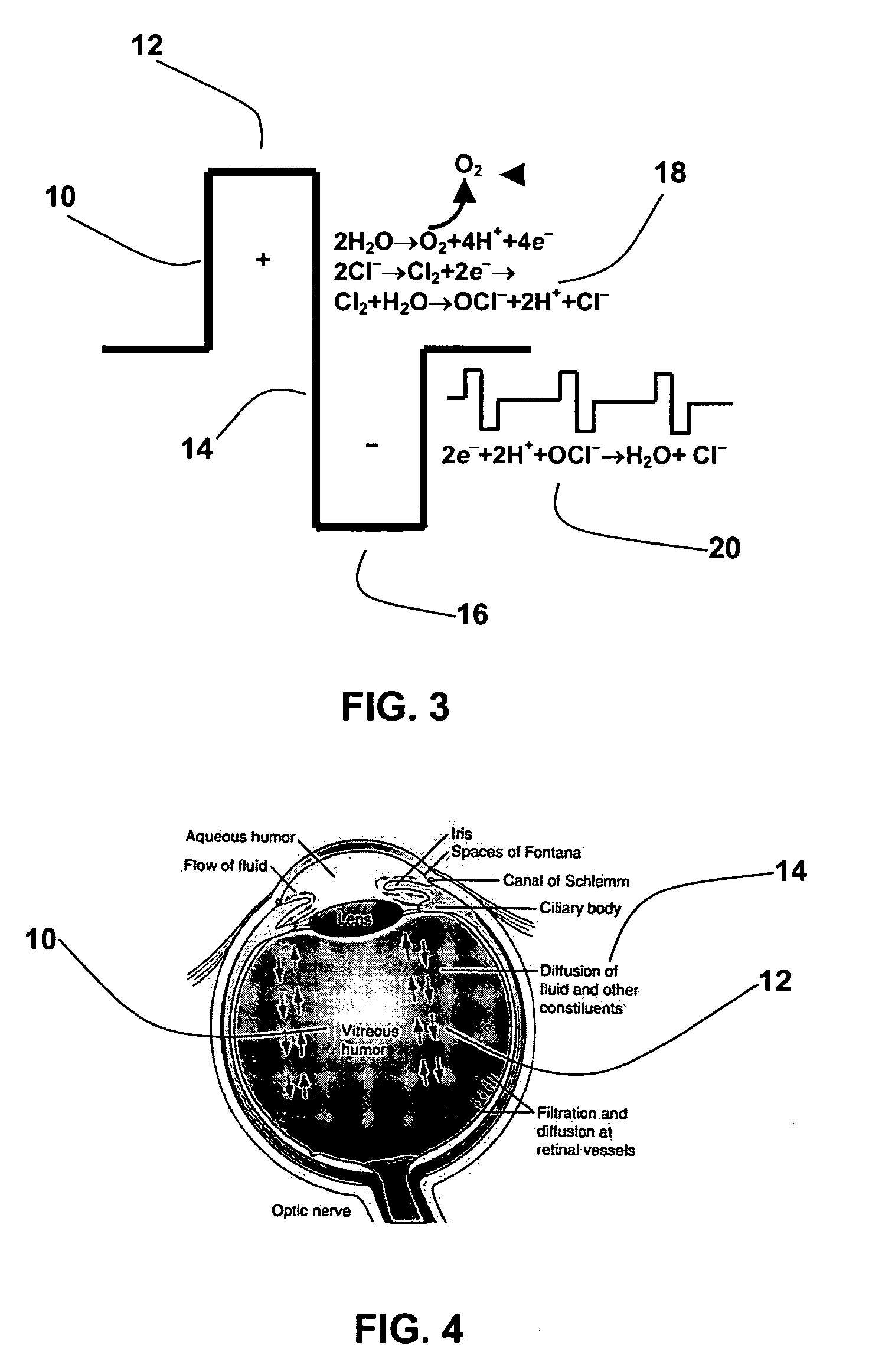
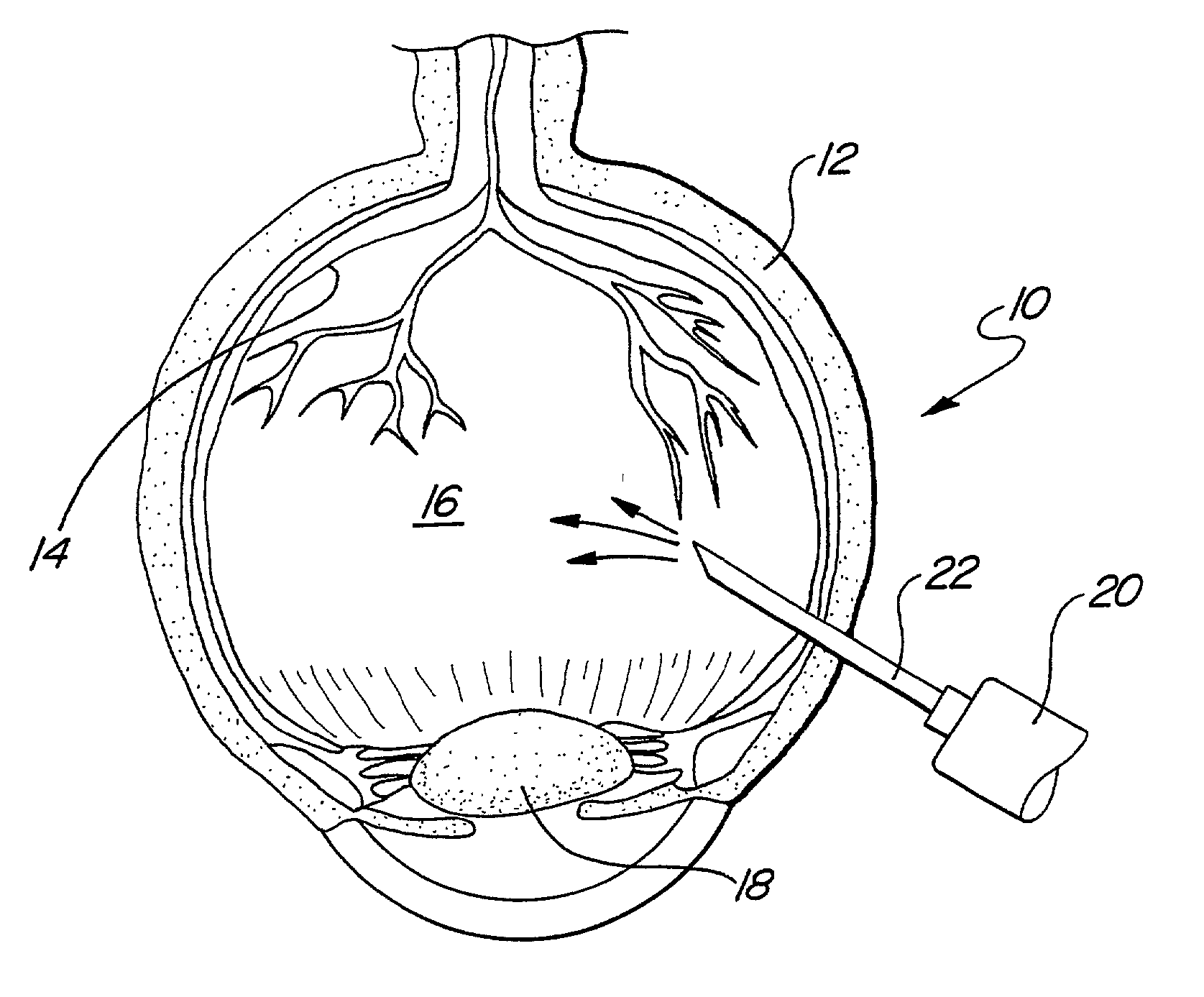
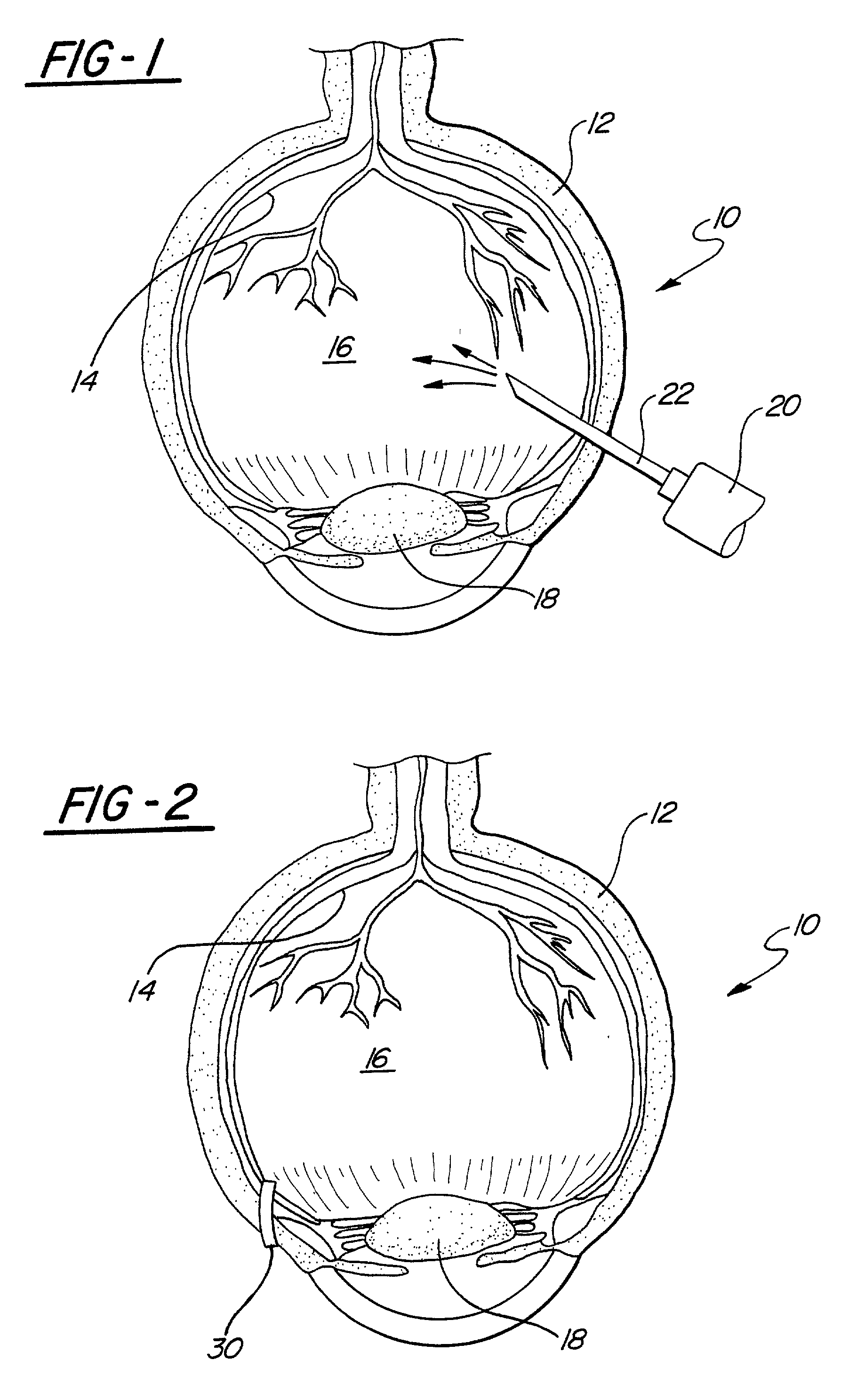
ActiveUS20100168646A1Formation of free chlorine is avoidedInhibition formationSenses disorderElectrotherapyDiabetic retinopathyRetinal Vascular Disorder
The present invention relates to the treatment of ischemic diseases, and more particularly, to treatment of diabetic retinopathy and ischemia of the retinal and choroidal tissues. The treatment, which will work in vitrectomized eyes as well as non-vitrectomized eyes, is based on selective and fractional electrolysis of the vitreous humor to produce oxygen and optionally active chlorine while simultaneously controlling pH. Oxygen or active chlorine can suppress or reverse the onset of diabetic retinopathy, other retinovascular diseases, and choroidal neovascularization.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Method for creating a separation of posterior cortical vitreous from the retina of the eye
InactiveUS20020139378A1Minimize and altogether eliminateMinimize or altogether eliminate the vitreoretinal tractionSenses disorderDiagnosticsVitreous HumorsRetina
A method is disclosed for creating a separation of posterior cortical vitreous from the retina of the eye. The method includes the step of introducing plasmin into the vitreous humor of the eye. The plasmin may be introduced either by injection or through a sustained release device. Optionally, other enzymes, polysaccharides, and / or glycoproteins are intermixed with the plasmin.
Owner:NUVUE TECH
Methods and devices to reduce the likelihood of injury from concussive or blast forces
ActiveUS20140276278A1Reduction of differential accelerationPrevent concussionEvaluation of blood vesselsGenitals massageSpinal columnInjury brain
A method and device for reducing the damaging effects of radiant energy, blast, or concussive events includes applying pressure to at least one jugular vein to reduce the egress of blood from the cranial cavity during or before the incidence of the imparting event. Reducing blood outflow from the cranial cavity increases intracranial volume and / or pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid to reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury and injuries to the spinal column. Reducing blood outflow further increases the intracranial pressure and volume, and thereby increases the pressure and volume of the cochlear fluid, the vitreous humor and the cerebrospinal fluid to thereby reduce the risk of injury to the inner ear, internal structure of the eye and of the spinal column. In addition, increasing intracranial pressure and volume reduces the likelihood of brain injury and any associated loss of olfactory function
Owner:TBI INNOVATIONS
Methods and devices to reduce the likelihood of injury from concussive or blast forces
A method and device for reducing the damaging effects of radiant energy, blast, or concussive events includes applying pressure to at least one jugular vein to reduce the egress of blood from the cranial cavity during or before the incidence of the imparting event. Reducing blood outflow from the cranial cavity increases intracranial volume and / or pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid to reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury and injuries to the spinal column. Reducing blood outflow further increases the intracranial pressure and volume, and thereby increases the pressure and volume of the cochlear fluid, the vitreous humor and the cerebrospinal fluid to thereby reduce the risk of injury to the inner ear, internal structure of the eye and of the spinal column. In addition, increasing intracranial pressure and volume reduces the likelihood of brain injury and any associated loss of olfactory function
Owner:TBI INNOVATIONS +1
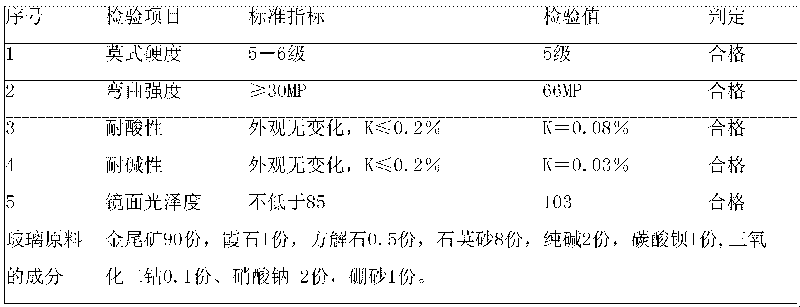
Black micro-crystalline glass plate made of gold ore tailings and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a black micro-crystalline glass plate made of gold ore tailings, which is prepared from the following raw materials in part by mass: gold ore tailings 60-90, quartz sand 8-20, calcite 0.5-2, nepheline 1-2, sodium carbonate 2-5, borax 1-2, barium carbonate 1-8, sodium nitrate 2-6 and cobalt oxide 0.1-0.5. A manufacturing method comprises: crushing and screening the gold ore tailings, the quartz sand, the calcite and the nepheline; removing cyanides from the gold ore tailings by an iron exchange method; weighing the raw materials in proportion and preparing a mixed material; melting the mixed material at 1,250 to 1,350 DEG C to form vitreous humour; allowing molten vitreous humour directly to flow into water to be quenched by water into glass grains; flatly spreading the glass grains in a refractory mould for crystallization; and grinding and cutting an obtained black crystalline glass sample. Compared with the traditional black crystalline glass, the product has more higher quality, and has the advantages of high Mohs' hardness, high bending strength, high chemical stability and pure color.
Owner:君达环保科技(宝鸡)有限公司
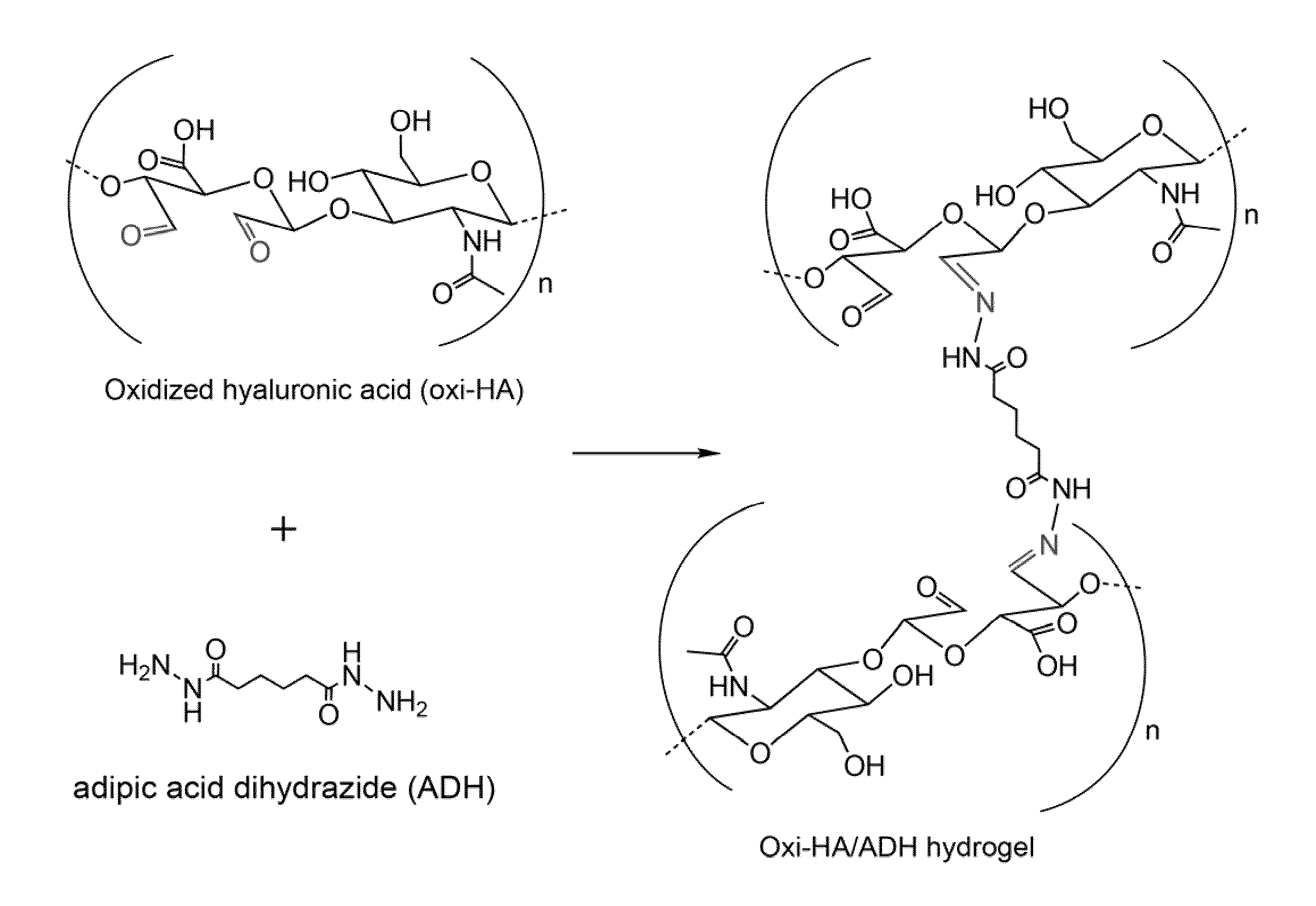
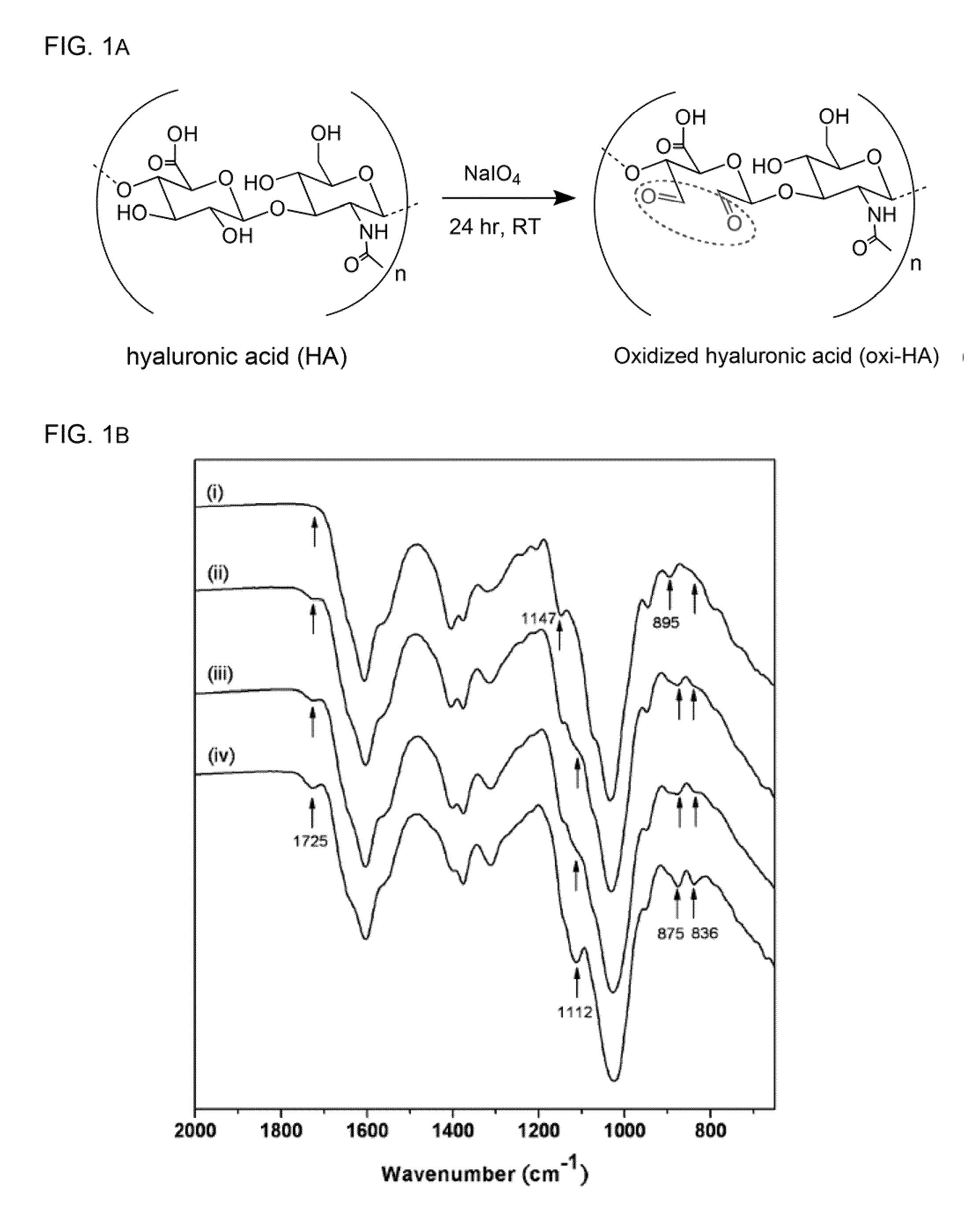
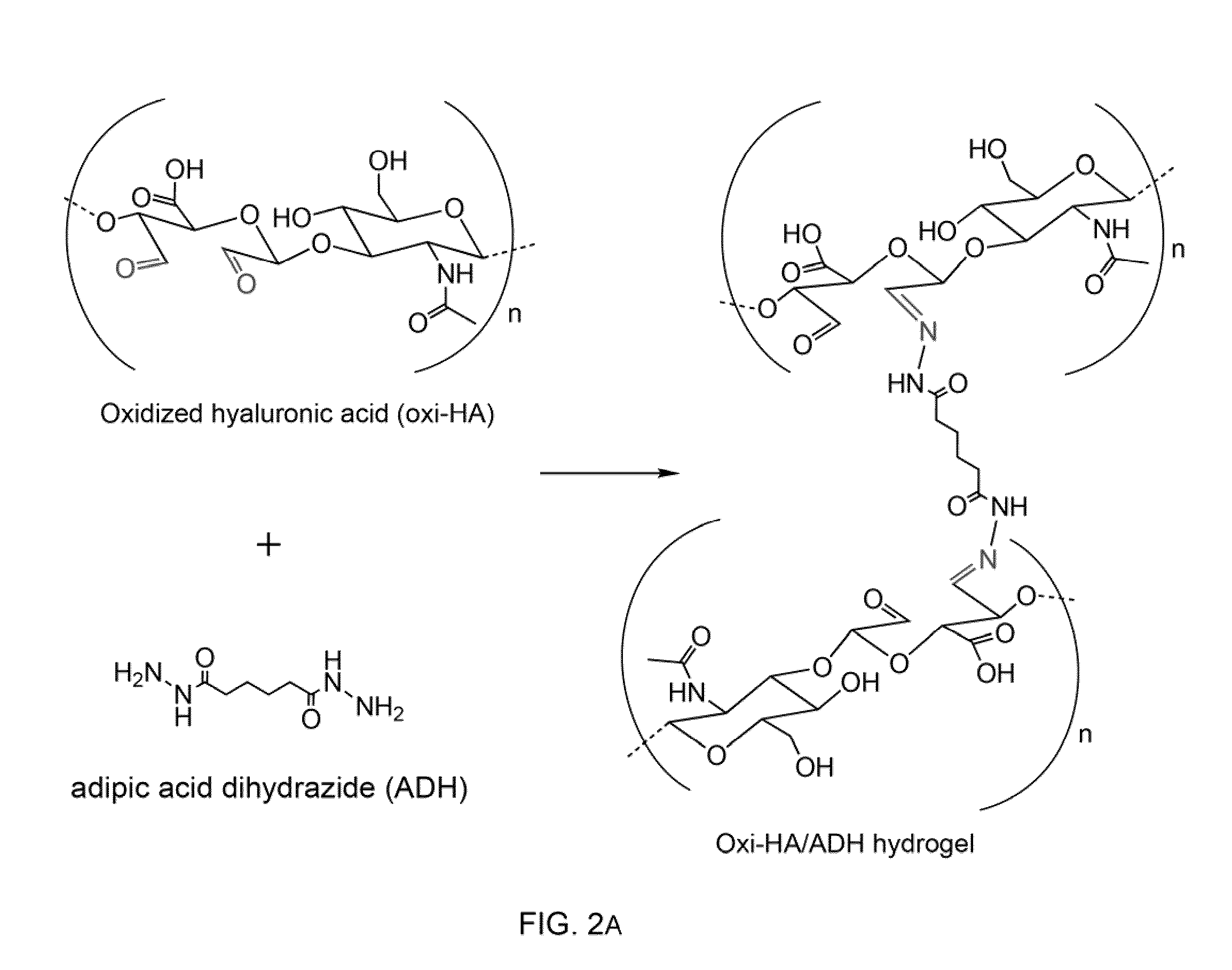
Cross-linked oxidated hyaluronic acid for use as a vitreous substitute
A composition comprising a polymer that comprises oxidated hyaluronic acid cross-linked by a dihydrazide is disclosed. The polymer is a hydrogel exhibiting the following properties: a) transparent and colorless; and b) transforming from a liquid state into a gel-matrix at 37° C. These characteristics make it useful as a vitreous humor substitute.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
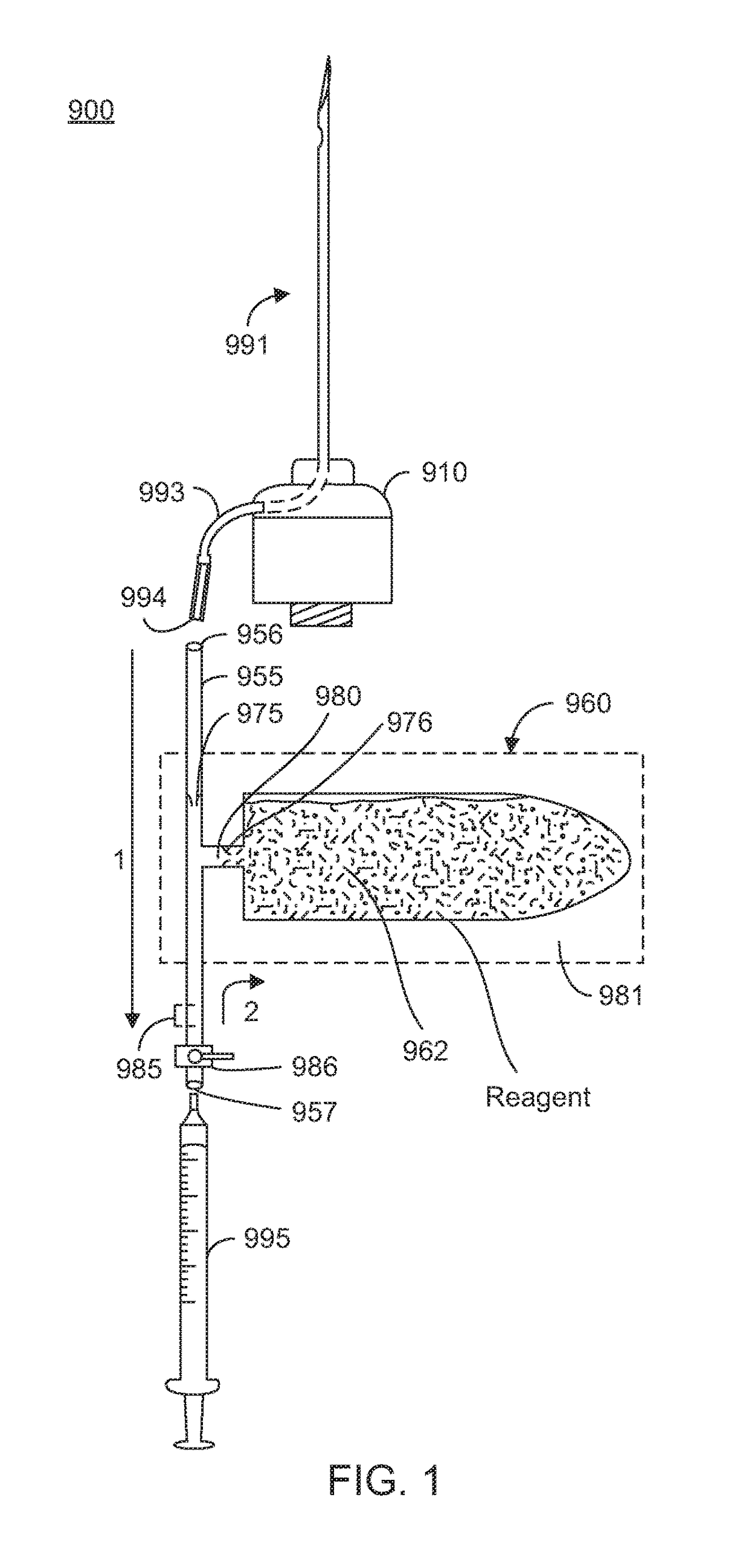
Device and method for vitreous humor surgery
ActiveUS20130131652A1Minimally invasiveReduce swellingLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFemto second laserLaser scanning
A device and a method for the femtosecond laser surgery of tissue, especially in the vitreous humor of the eye. The device of includes an ultrashort pulse laser with pulse widths in the range of approximately 10 fs-1 ps, especially approximately 300 fs, pulse energies in the range of approximately 5 nJ-5μJ, especially approximately 1-2 μJ and pulse repetition rates of approximately 10 kHz-10 MHz, especially 500 kHz. The laser system is coupled to a scanner system which allows the spatial variation of the focus in three dimensions (x, y and z). In addition to the therapeutic laser / scanner optical system the device includes a navigation system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Glass wool for dry vacuum insulated panel core material and production method thereof
The invention discloses a glass wool for a dry vacuum insulated panel core material and a production method thereof. The production method comprises the following steps of mixing the following components in parts by mass to form a mixture: 10.0-40.0 parts of quartz powder, 10.0-12.5 parts of feldspar, 9.0-11.0 parts of sodium borate, 1.5-3.5 parts of calcspar, 2.5-7.0 parts of dolomite, 7.0-15.0 parts of sodium carbonate and 15.0-60.0 parts of plate glass; adding the mixture into a melting tank of a kiln to melt and prepare vitreous humour; putting the vitreous humour into a bushing well and a centrifugal plate, and conveying to a centrifugal machine to spin and prepare the glass wool. The glass wool disclosed by the invention can be directly prepared into the dry vacuum insulated panel core material. Compared with the insulated panel core material produced by a wet process, the glass wool is short in production flow; and wet pulp is prepared without adding water or baking. Therefore, the production efficiency is improved; the energy source is greatly saved; the price of the insulated panel is reduced, and strong popularization and use of the market are facilitated.
Owner:安徽吉曜玻璃微纤有限公司
Use of hyaluronidase in the manufacture of an ophthalmic preparation for liquefying vitreous humor in the treatment of eye disorders
InactiveUS20050069531A1Improve clearance rateIncreases rate of liquid exchangePeptide/protein ingredientsDrug compositionsDiseaseHyaluronidase
An enzymatic method is provided for treating ophthalmic disorders of the mammalian eye. Prevention of neovascularization and the increased rate of clearance from the vitreous of materials toxic to retina is accomplished by administering an amount of hyaluronidase effective to liquefy the vitreous humor of the treated eye without causing toxic damage to the eye. Liquefaction of the vitreous humor increases the rate of liquid exchange from the vitreal chamber. This increase in exchange removes those materials and conditions whose presence causes ophthalmological and retinal damage.
Owner:KARAGEOZIAN HAMPAR +5
Methods and devices to reduce the likelihood of injury from concussive or blast forces
ActiveUS9173660B2Reduction of differential accelerationPrevent concussionTourniquetsSport apparatusSpinal columnInjury brain
A method and device for reducing the damaging effects of radiant energy, blast, or concussive events includes applying pressure to at least one jugular vein to reduce the egress of blood from the cranial cavity during or before the incidence of the imparting event. Reducing blood outflow from the cranial cavity increases intracranial volume and / or pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid to reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury and injuries to the spinal column. Reducing blood outflow further increases the intracranial pressure and volume, and thereby increases the pressure and volume of the cochlear fluid, the vitreous humor and the cerebrospinal fluid to thereby reduce the risk of injury to the inner ear, internal structure of the eye and of the spinal column. In addition, increasing intracranial pressure and volume reduces the likelihood of brain injury and any associated loss of olfactory function.
Owner:TBI INNOVATIONS +1
Processes and apparatus for preventing, delaying or ameliorating one or more symptoms of presbyopia
InactiveUS20110160622A1Preventing, delaying or ameliorating one or more symptoms of presbyopiaPromote formationUltrasound therapyLaser surgeryVitreous HumorsOphthalmology
The present invention generally relates to an apparatus and processes for preventing or delaying presbyopia. More particularly, the present invention relates to processes and apparatus for ablating epithelial cells in the germinative zone or the pregerminative zone of the crystalline lens of the eye so that onset or progression of presbyopia or one or more symptoms is de-layed or prevented. The present invention also relates to processes and apparatus for promoting formation of suture lines in the crystalline lens of the eye so that onset or progression of presbyopia or one or more symptoms is delayed or prevented. The present invention also relates to processes and apparatus for creating disruptions in the vitreous humor of the eye.
Owner:LENTICULAR RES GRP
Method for creating a separation of posterior cortical vitreous from the retina of the eye
InactiveUS20060024349A1Minimize or altogether eliminate the vitreoretinal tractionMinimize tractionSenses disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsVitreous HumorsBody fluid
A method is disclosed for creating a separation of posterior cortical vitreous from the retina of the eye. The method includes the step of introducing plasmin into the vitreous humor of the eye. The plasmin may be introduced either by injection or through a sustained release device. Optionally, other enzymes, polysaccharides, and / or glycoproteins are intermixed with the plasmin.
Owner:NUVUE TECH
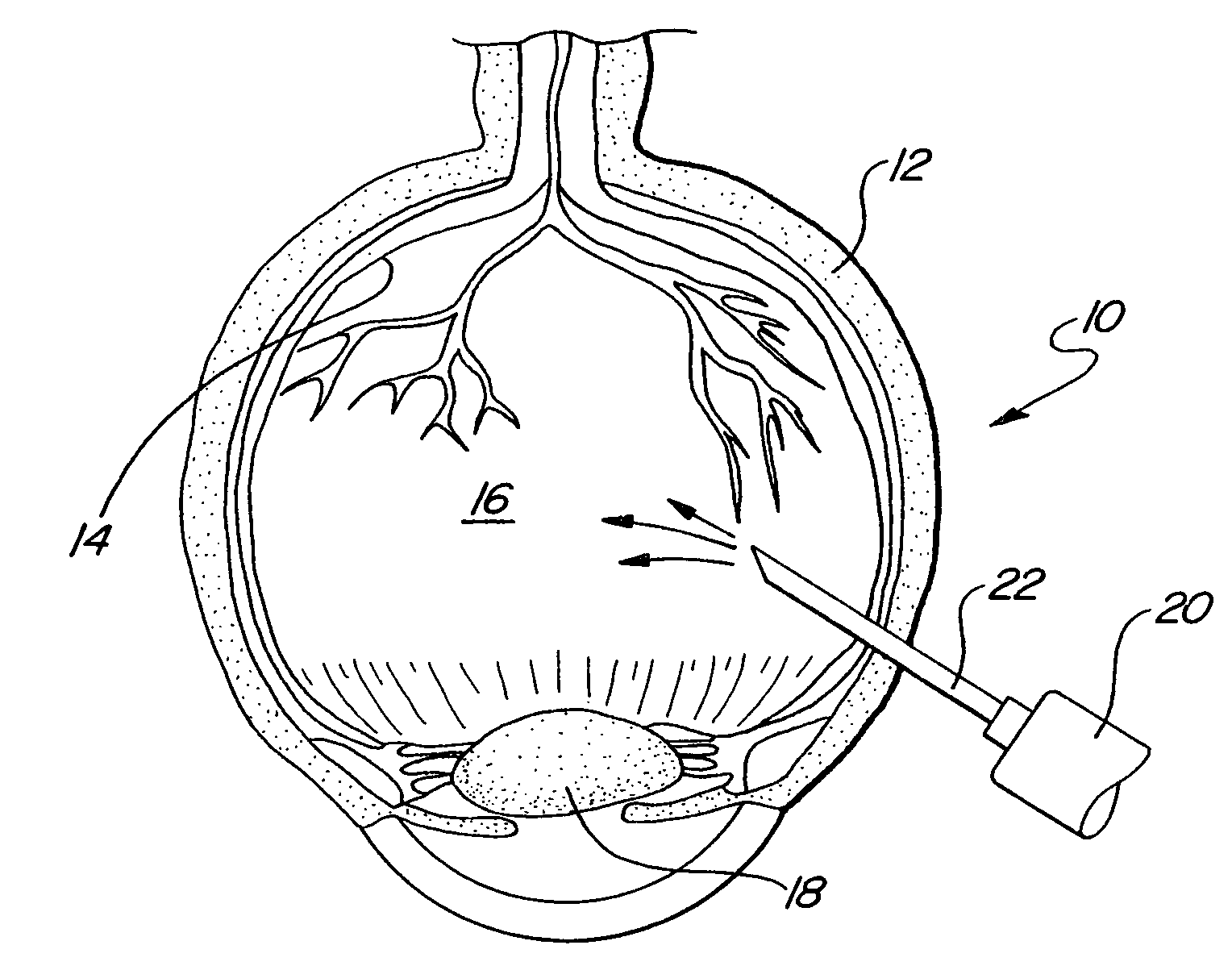
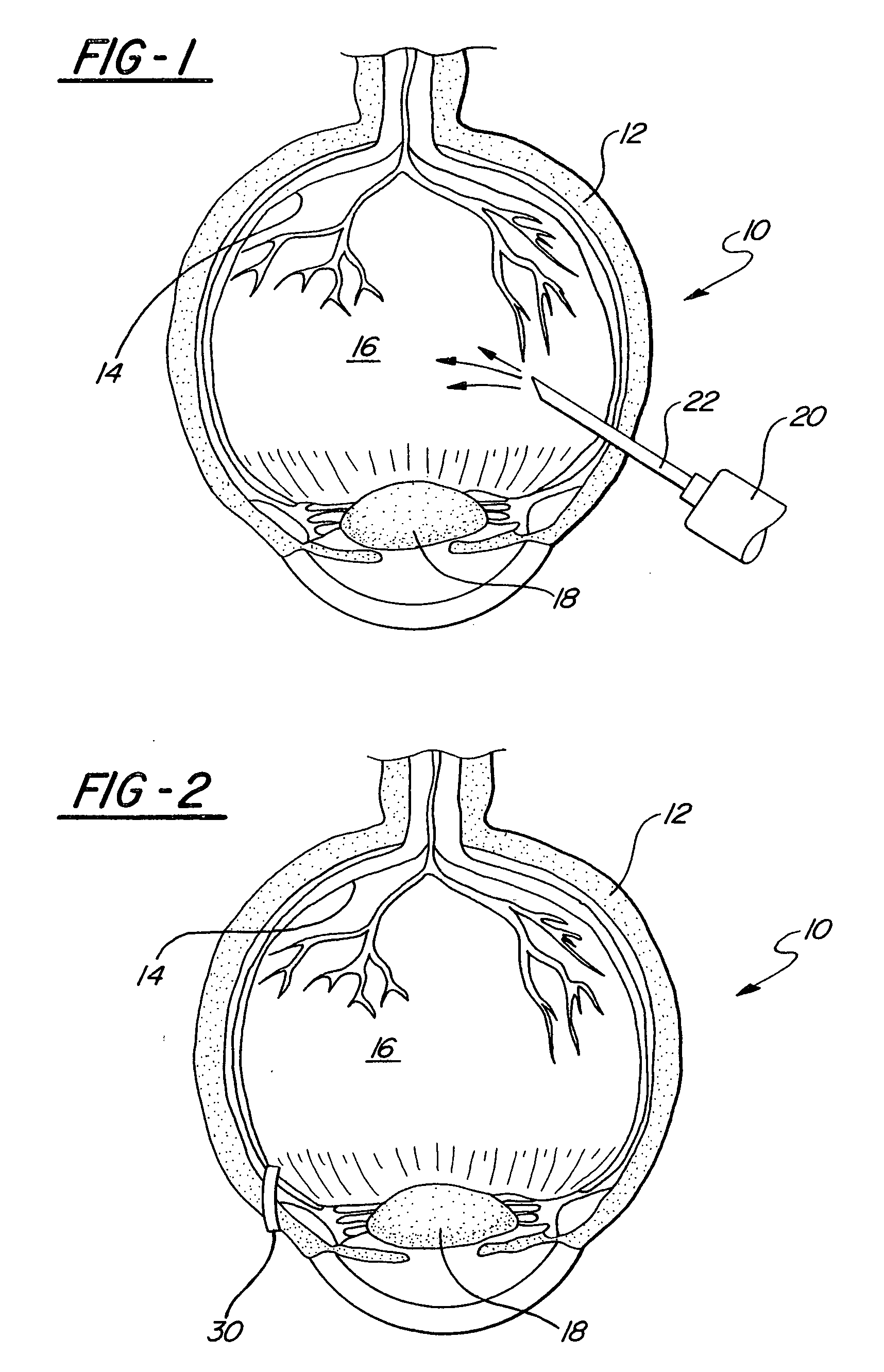
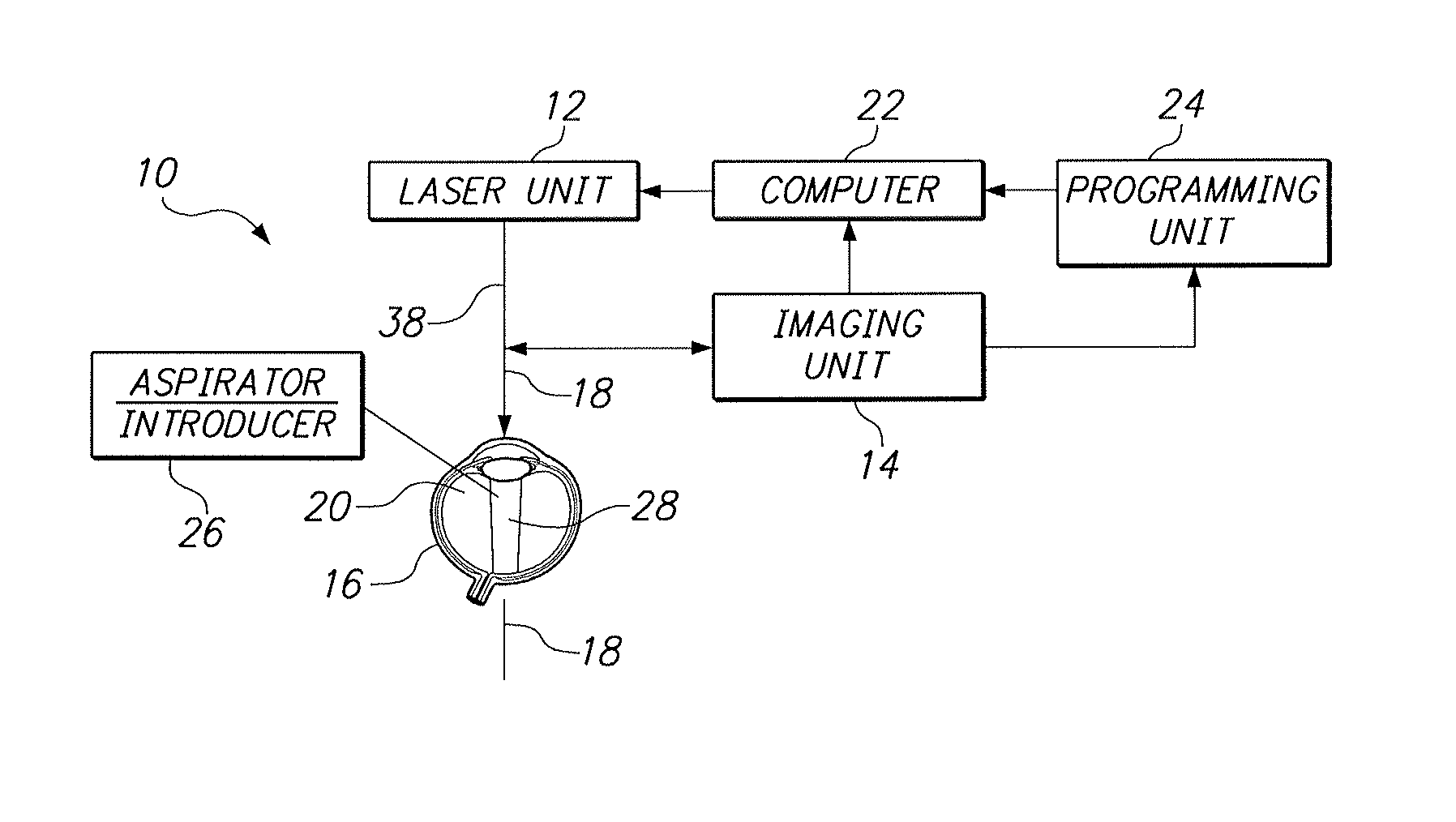
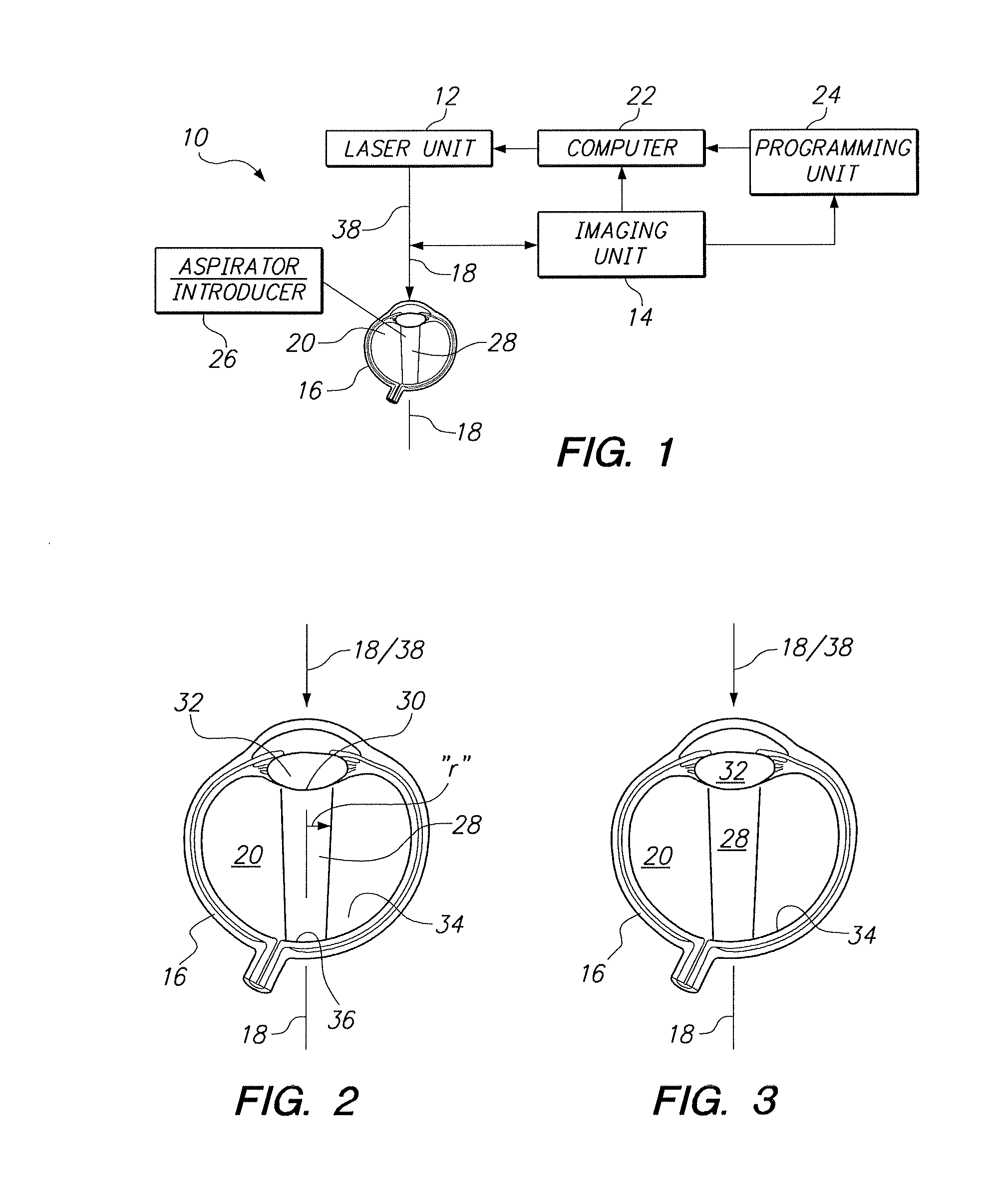
Treatment Systems for Vitreous Floaters
InactiveUS20150342782A1Efficient removalLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsVitreous FloaterVitreous Humors
In accordance with the present invention, a system and method are provided for using a computer-controlled, laser system to perform a partial vitrectomy of the vitreous humor in an eye. Operationally, an optical channel is first defined through the vitreous humor. Vitreous and suspended deposits (floaters) in the optical channel are then ablated and in some cases removed (e.g. aspirated) from the optical channel. In some instances, a clear liquid can be introduced into the optical channel to replace the ablated matter, and to thereby establish unhindered transparency in the optical channel.
Owner:STRATHSPEY CROWN HLDG
Methods and devices to reduce the likelihood of injury from concussive or blast forces
ActiveUS8900169B2Reduction of differential accelerationPrevent concussionEvaluation of blood vesselsGenitals massageSpinal columnInjury brain
A method and device for reducing the damaging effects of radiant energy, blast, or concussive events includes applying pressure to at least one jugular vein to reduce the egress of blood from the cranial cavity during or before the incidence of the imparting event. Reducing blood outflow from the cranial cavity increases intracranial volume and / or pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid to reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury and injuries to the spinal column. Reducing blood outflow further increases the intracranial pressure and volume, and thereby increases the pressure and volume of the cochlear fluid, the vitreous humor and the cerebrospinal fluid to thereby reduce the risk of injury to the inner ear, internal structure of the eye and of the spinal column. In addition, increasing intracranial pressure and volume reduces the likelihood of brain injury and any associated loss of olfactory function.
Owner:TBI INNOVATIONS
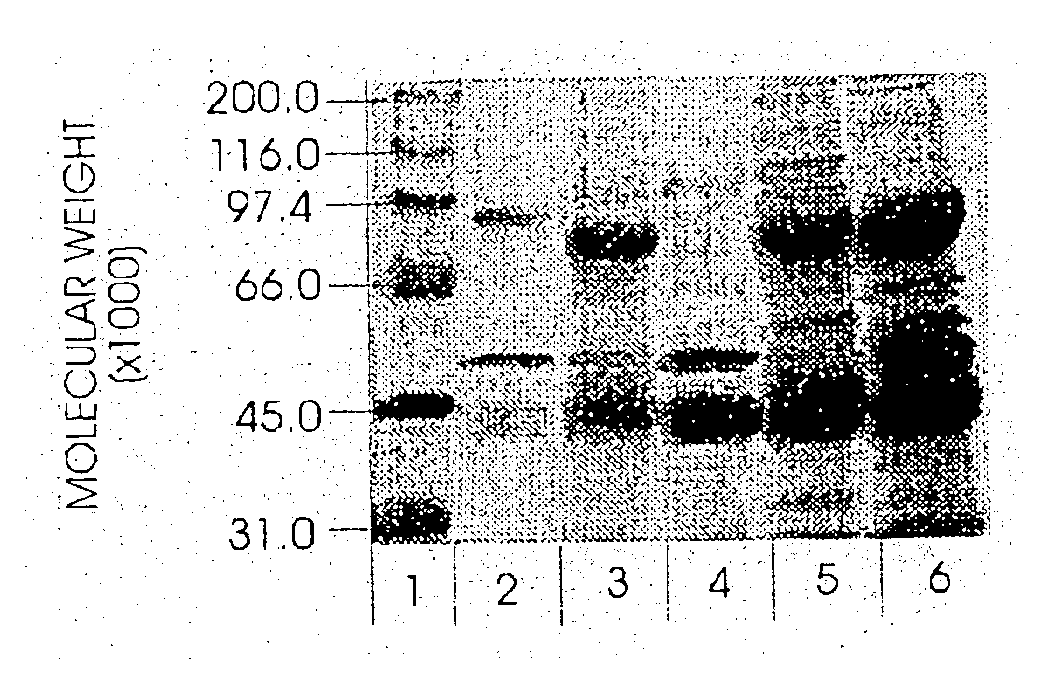
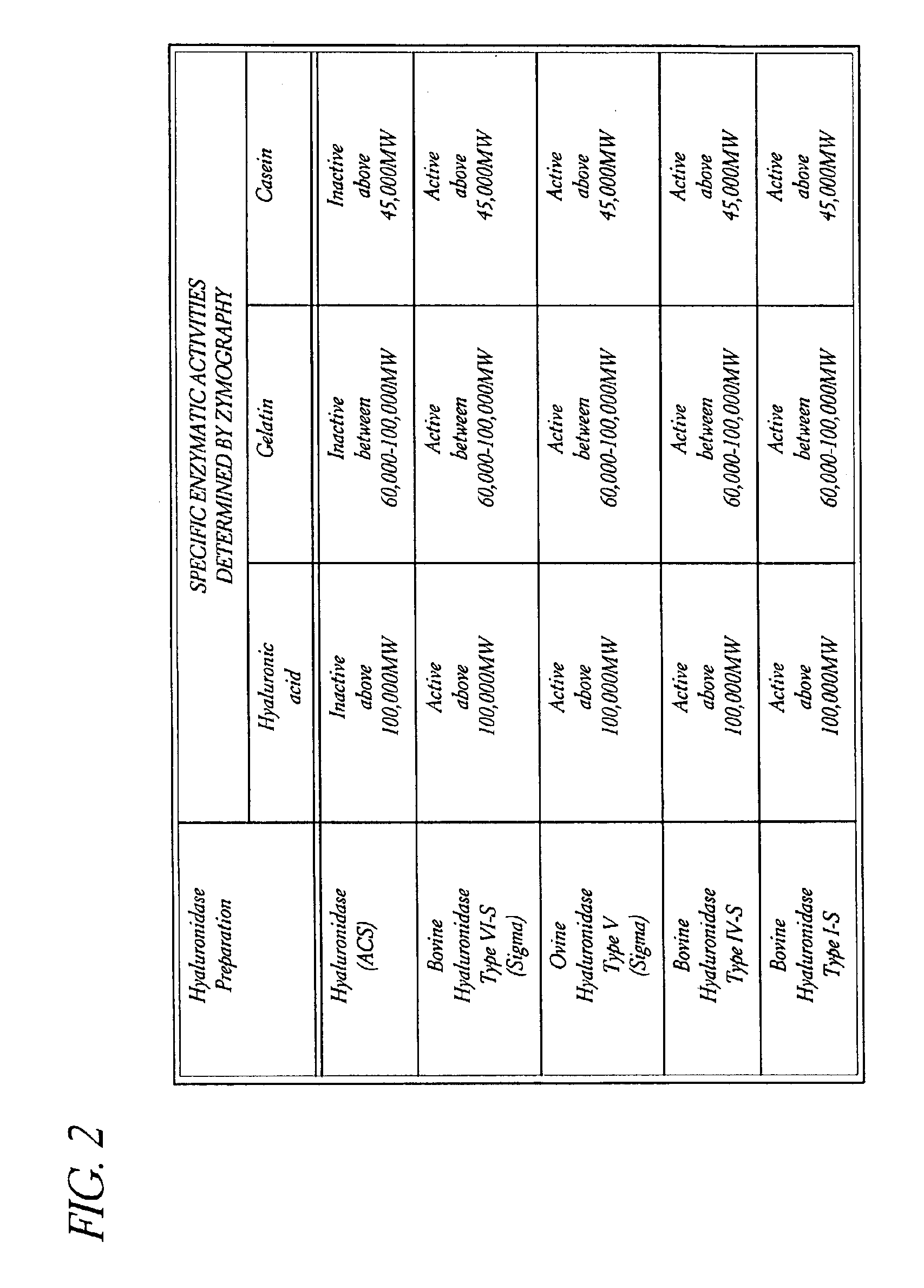
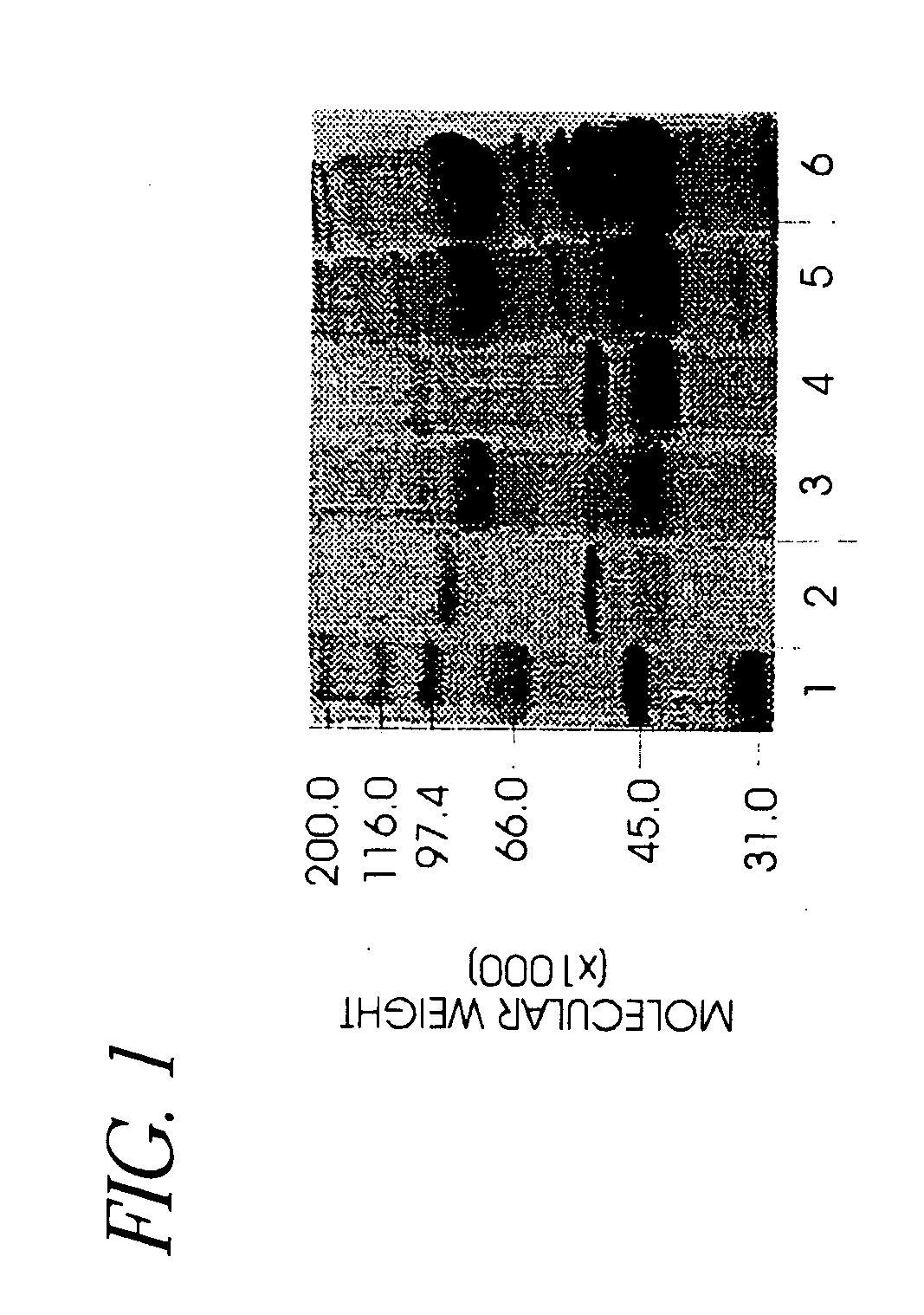
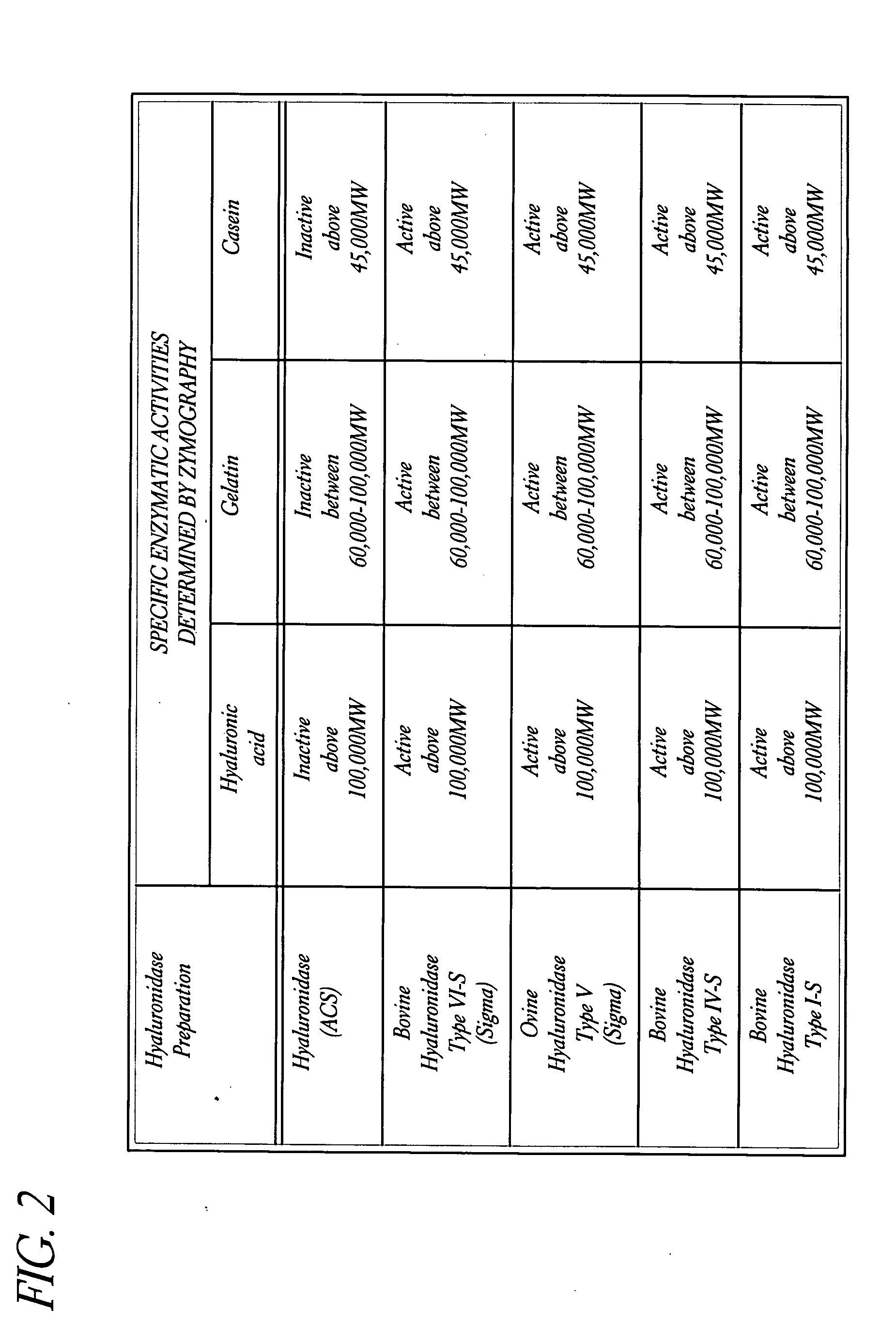
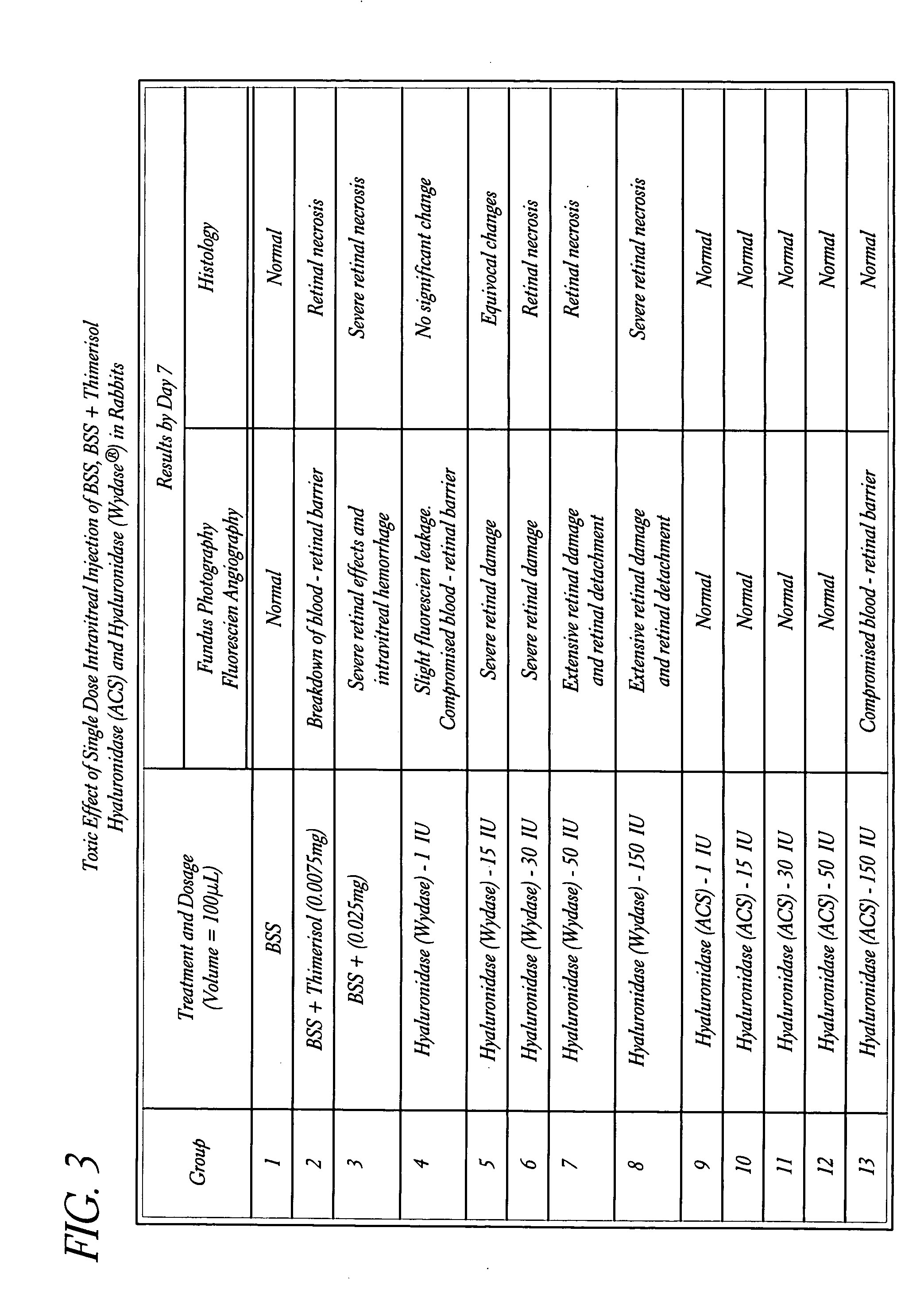
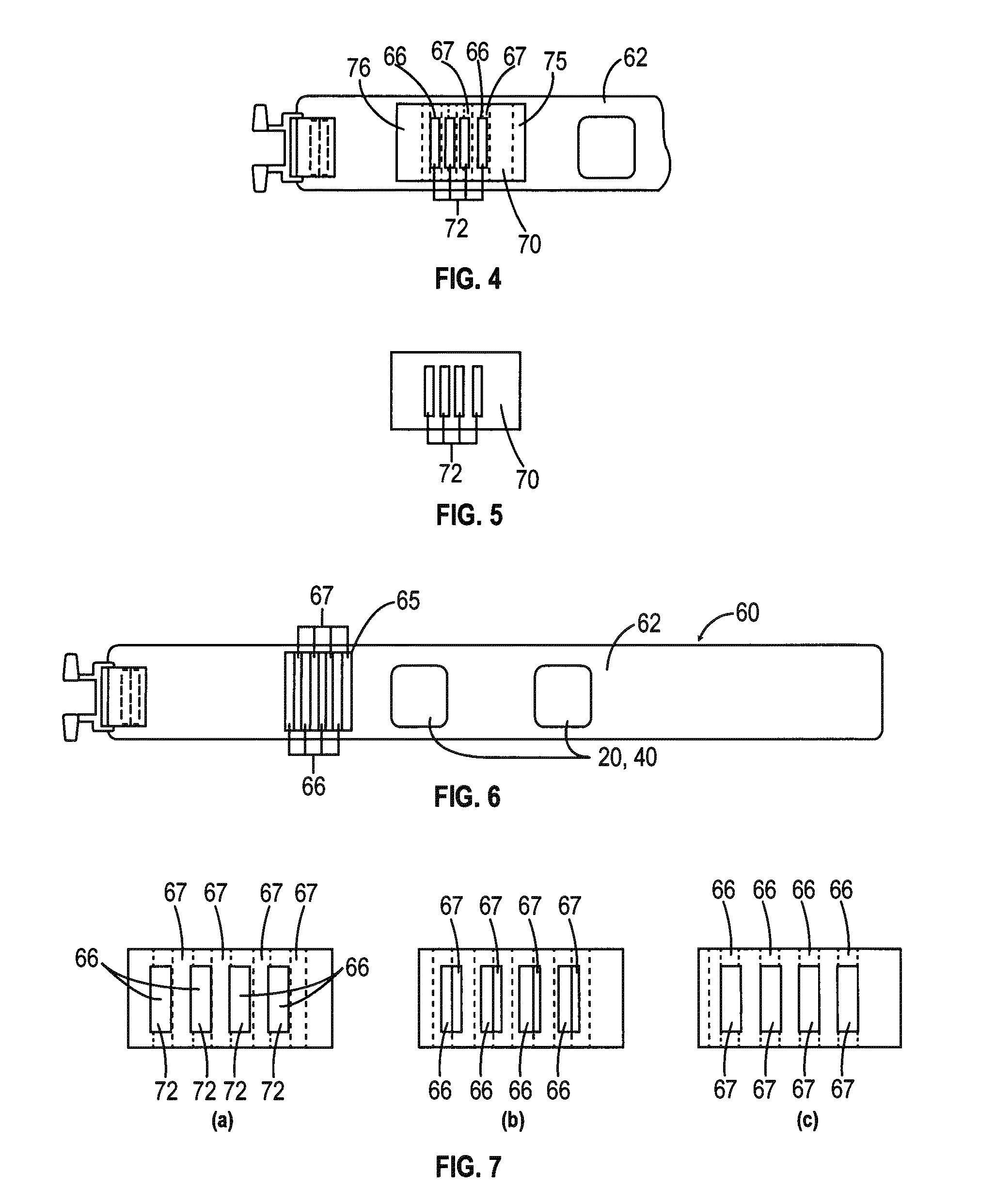
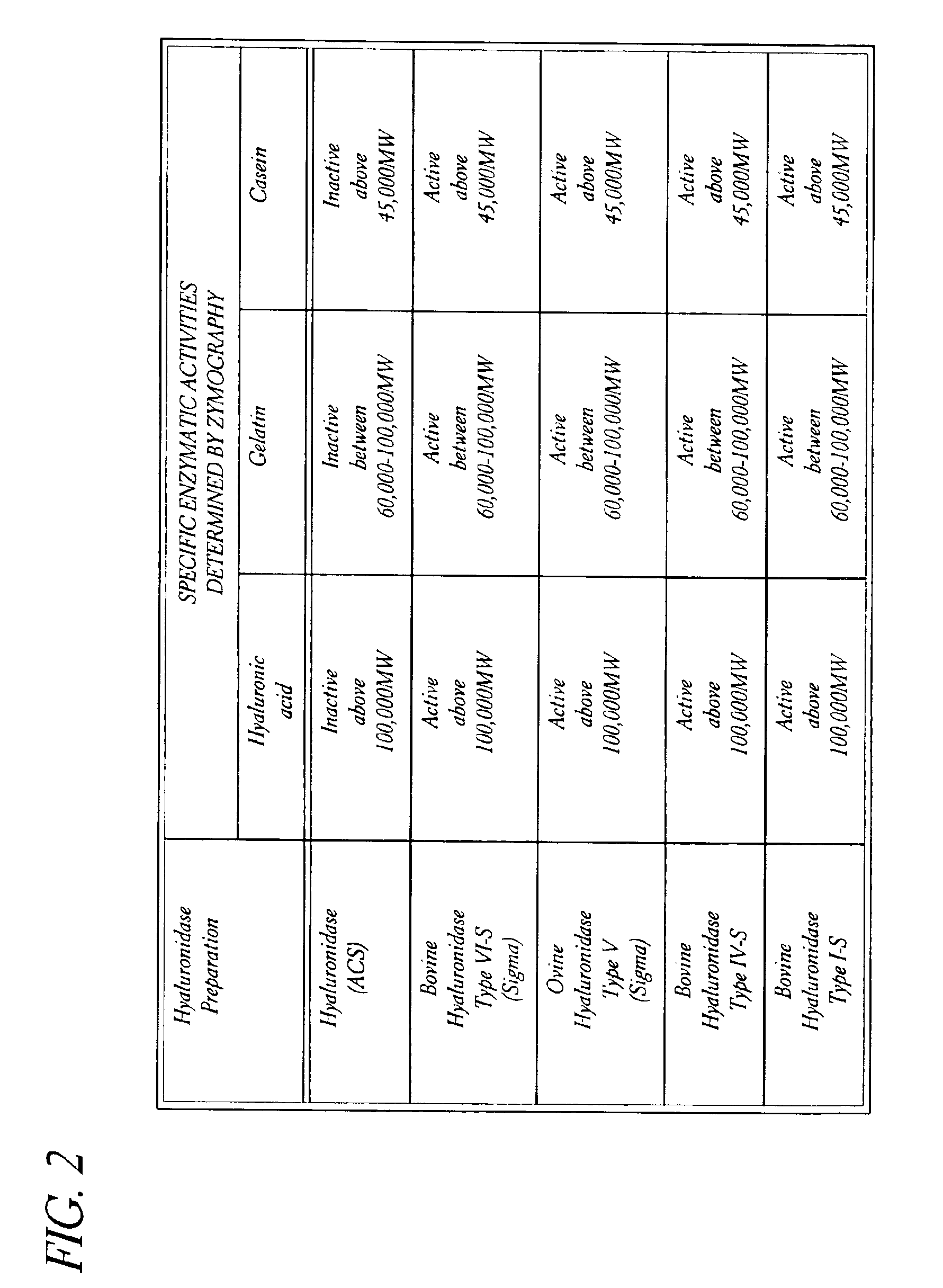
Hyaluronidase preparation for ophthalmic administration and enzymatic methods for accelerating clearance of hemorrhagic blood from the vitreous body of the eye
InactiveUS6939542B2Increase the gapOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderVitreous HumorsBody fluid
A thimerosal-free hyaluronidase preparation wherein the preferred hyaluronidase enzyme is devoid of molecular weight fractions below 40,000 MW, between 60-70,000 MW and above 100,000 MW. Also disclosed is a method for accelerating the clearance of hemorrhagic blood from the vitreous humor of the eye, said method comprising the step of contacting at least one hemorrhage-clearing enzyme (e.g., a β-glucuronidase, matrix metalloproteinase, chondroitinase, chondroitin sulfatase or protein kinase) with the vitreous humor in an amount which is effective to cause accelerated clearance of blood therefrom.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC +1
Reading enhancement device for preventing and treating presbyopia of the eye
Owner:READING ENHANCEMENT
Biomaker composition for detecting diabetic retinopathy and diagnostic kit therefor
InactiveUS20100179307A1Provide informationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsThyroxine-binding globulinDiabetic retinopathy
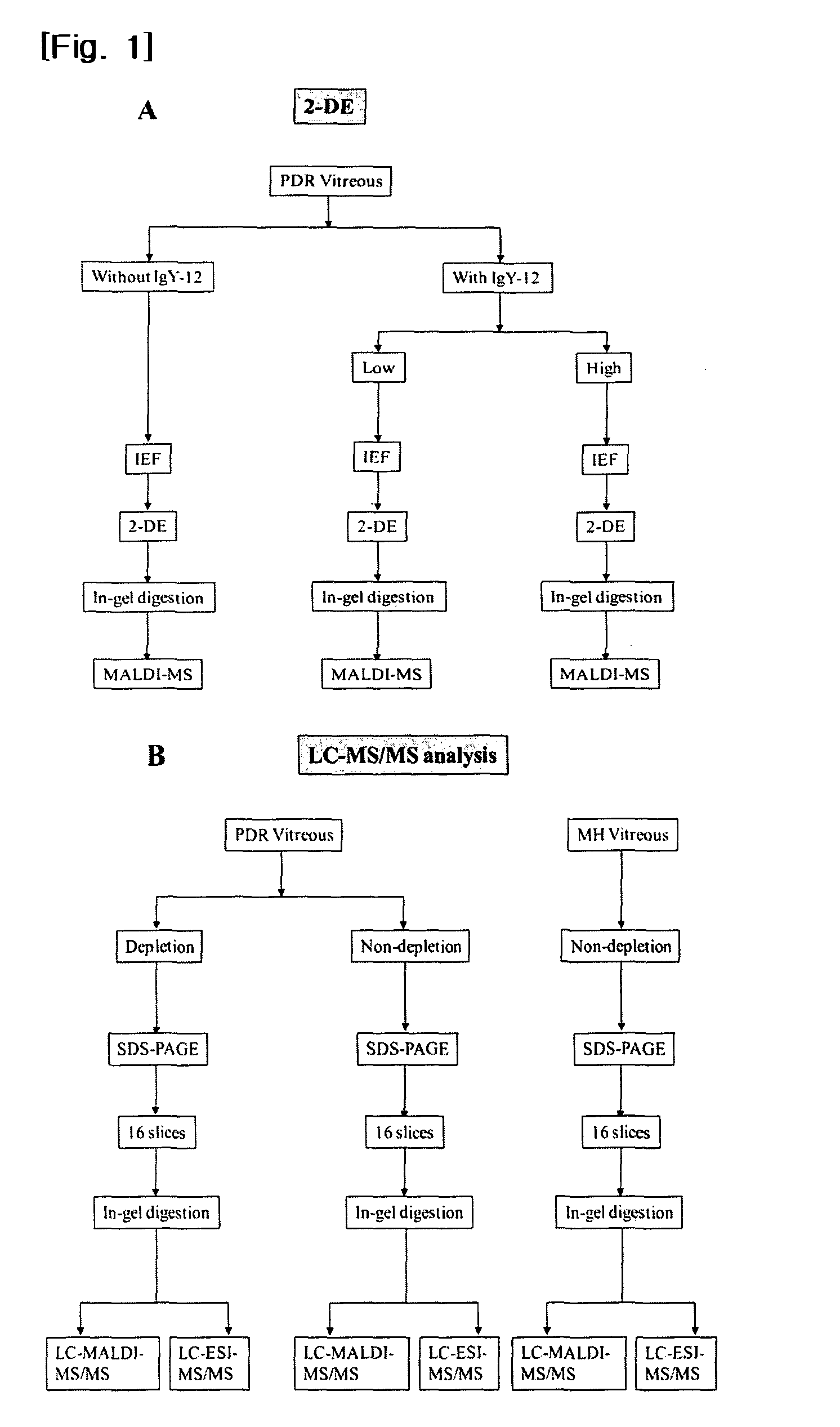
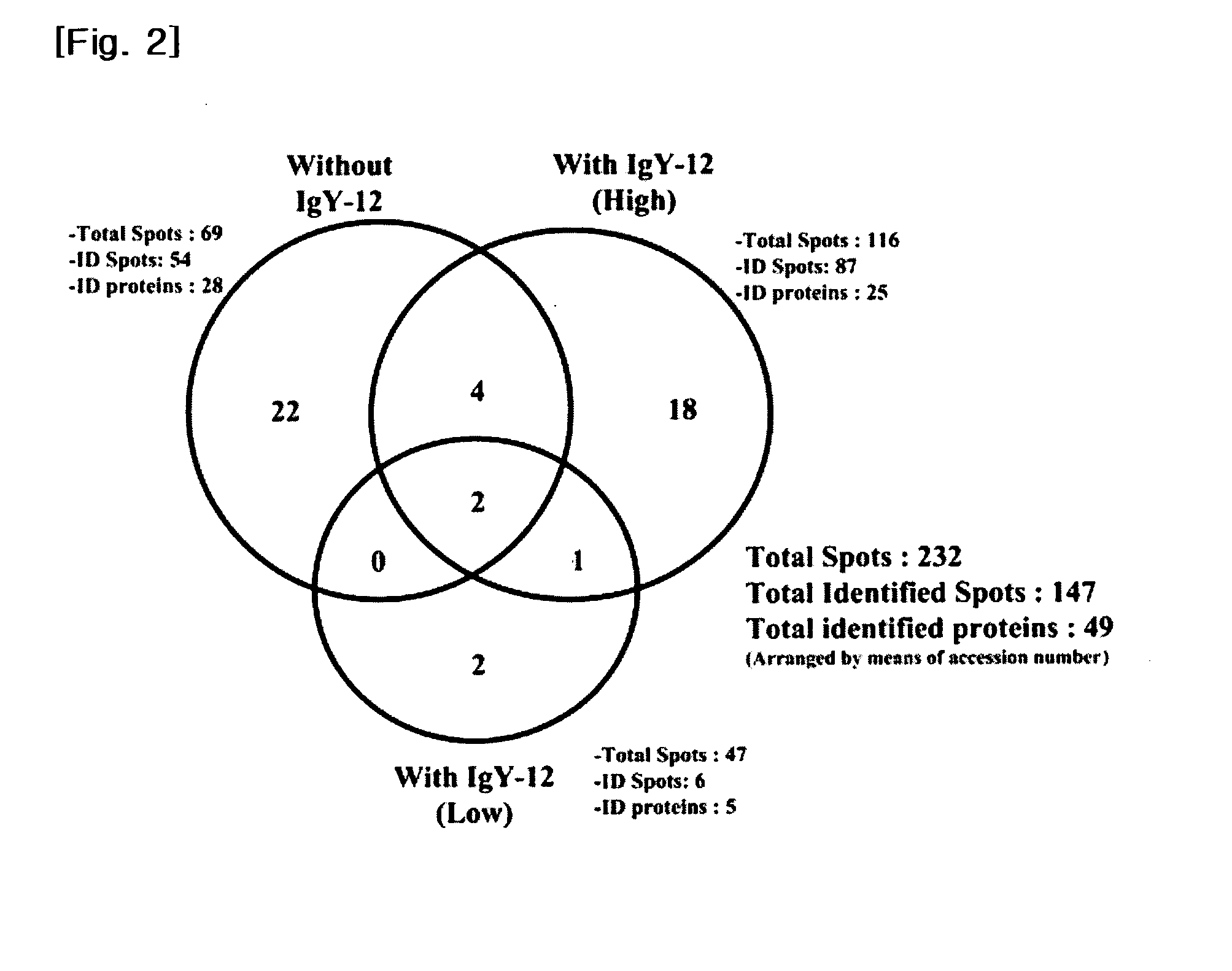
The present invention provides a biomarker composition for detecting diabetic retinopathy comprising at least one protein selected from the group consisting of proteins as set forth in SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 169. And also, the present invention provides a kit for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy, comprising a molecule specifically binding to at least one protein selected from the group consisting of proteins as set forth in SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 169. It has been newly found that 105 proteins as set forth in SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 105 are significantly over-expressed in the vitreous humors obtained from PDR patients, while 64 proteins as set forth in SEQ ID NOS: 106 to 169 are significantly over-expressed in those obtained from normal people. Therefore, the proteins can be used for biomarker capable of detecting diabetic retinopathy. The biomarker can provide fundamental information in researching vitreoretinal disorders, such as diabetic retinopathy. Especially, the newly found proteins may be applied to a kit for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy with a molecule specifically binding thereto, e.g., a monoclonal antibody. And also, it has been newly found that the levels of thyroxine-binding globulin precursor (TBG) in both vitreous and plasma of PDR and NPDR states and in plasma of diabetes mellitus state, are outstandingly higher than in non-diabetic control (MH or normal control). Therefore, TBG may be applied to a diabetes mellitus biomarker, and a kit for diagnosing diabetes mellitus with a molecule specifically binding thereto.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Novel polypeptide capable of inhibiting new vessels and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel polypeptide capable of inhibiting new vessels and an application thereof. The invention also relates to a polypeptide preparing method and an application thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing polypeptide. The polypeptide has a plurality of advantages that the molecular weight is little, polypeptide can penetrate through various ocular tissue barriers; water solubility is good, such that the polypeptides can maintain a high concentration in a neutral tear fluid, aqueous humor and vitreous humor; and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
New small peptides for inhibiting newborn blood vessels, and application thereof
The invention relates to polypeptides for preventing and inhibiting angiogenesis, and an application thereof. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the polypeptides, an application of the polypeptides, and a medicinal composition containing the polypeptides. The polypeptides have the advantages of small molecular weight, permeation of various eye tissue barriers, good water solubility, and maintenance of a high concentration in neutral tears, aqueous humor and vitreous humor.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Homogenous and heterogeneous assays and systems for determination of ocular biomarkers
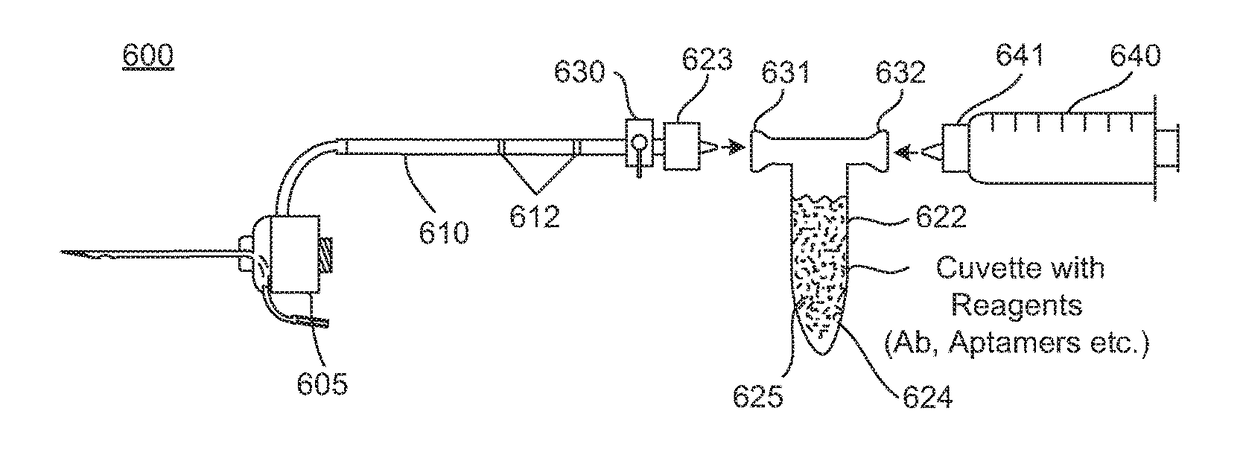
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for easy and rapid detection of ocular analytes in vitreous humor or aqueous humor. Specifically, exemplified are systems having a sample acquisition device that is in line with an analyte detection device. The system embodiments allow for the easy procurement and testing of samples. In a typical embodiment, the analyte detection assay device includes a housing that has a reaction chamber that is in fluid communication with a sample conduit and which contains reagents that specifically interact with the analyte. The reaction chamber is in fluid communication with a shunt that is in fluid communication with the sample conduit. The sample conduit has a sample conduit valve that is positioned distally to the shunt.
Owner:INSIGHT INSTR
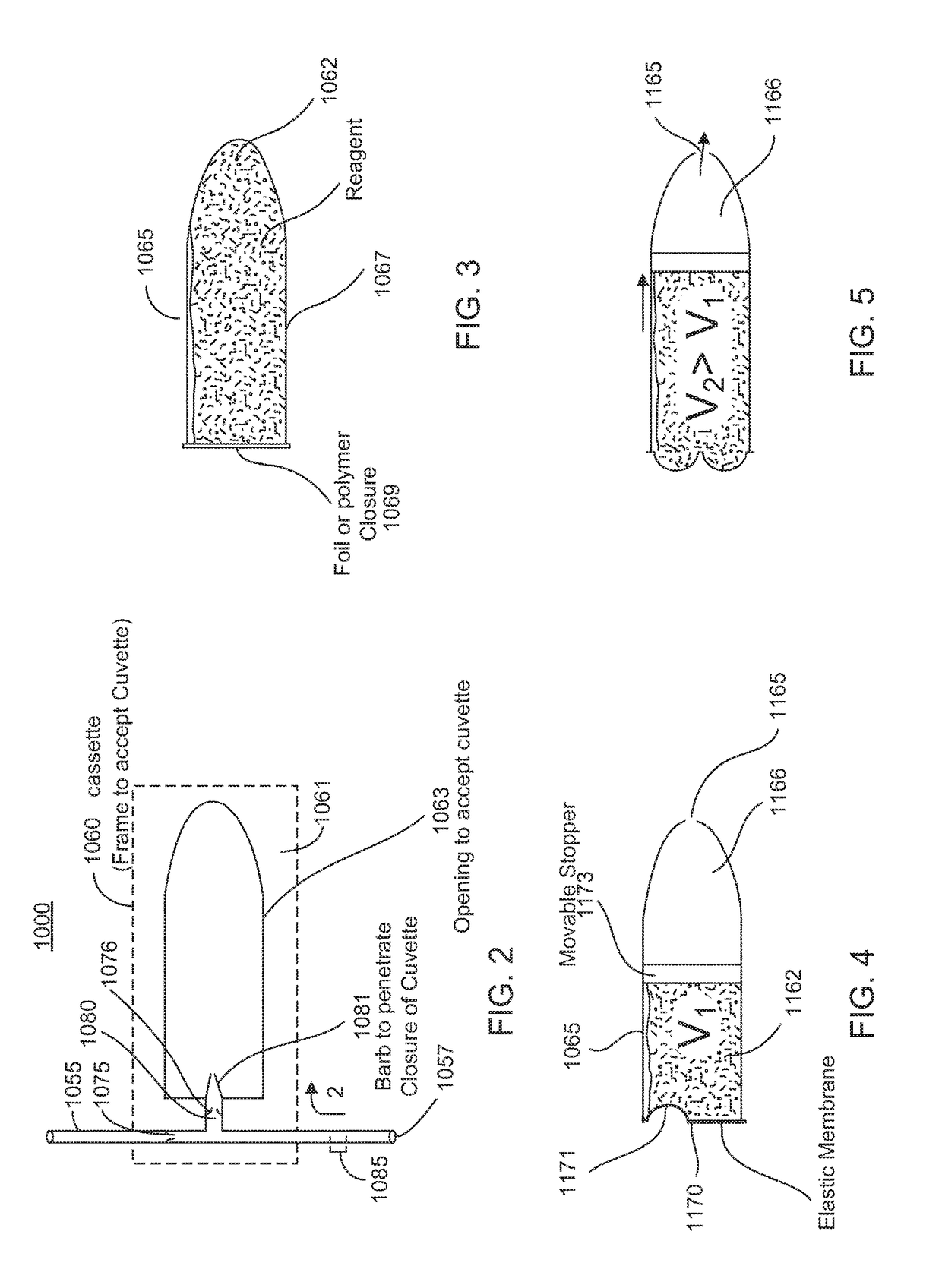
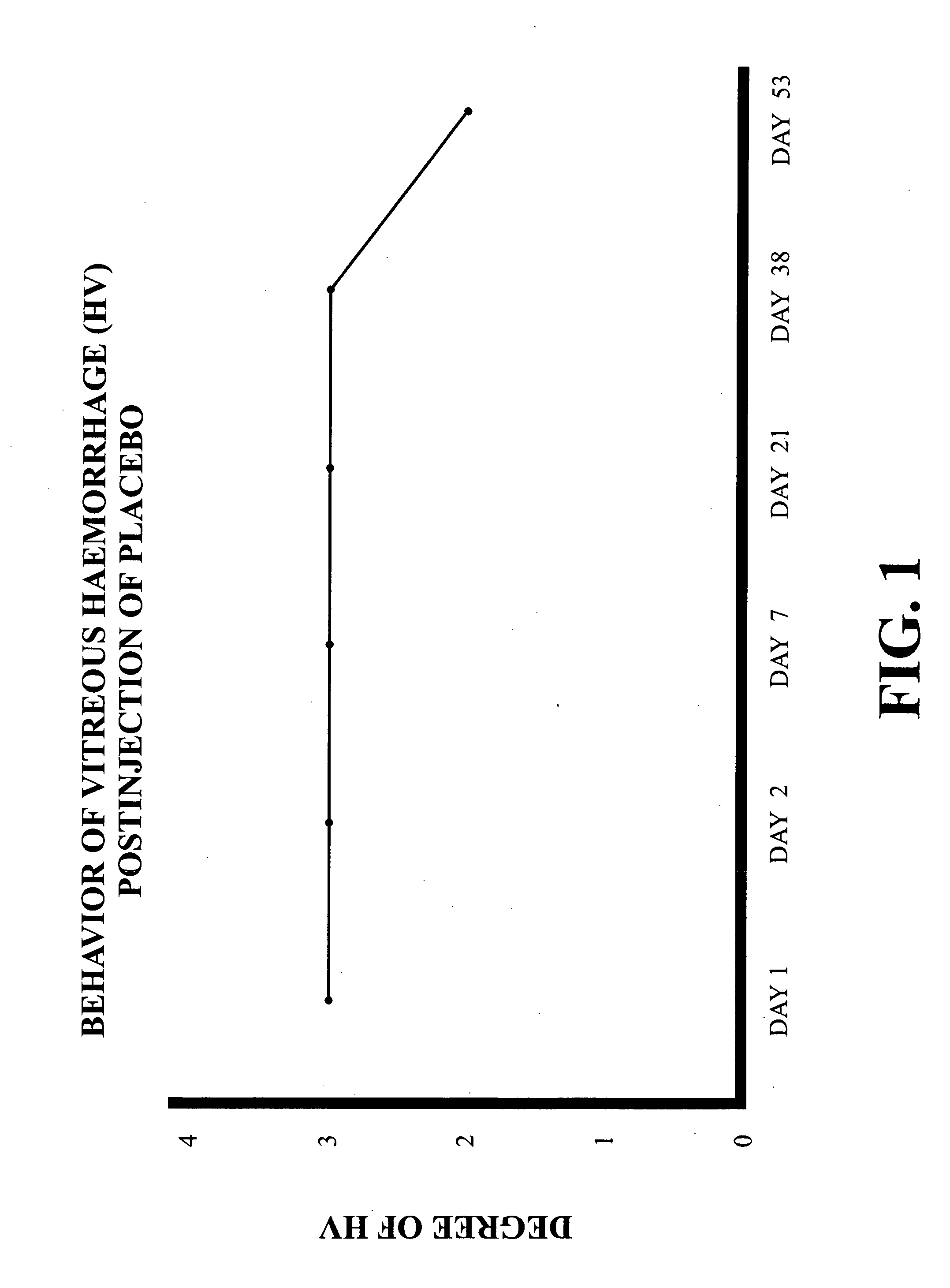
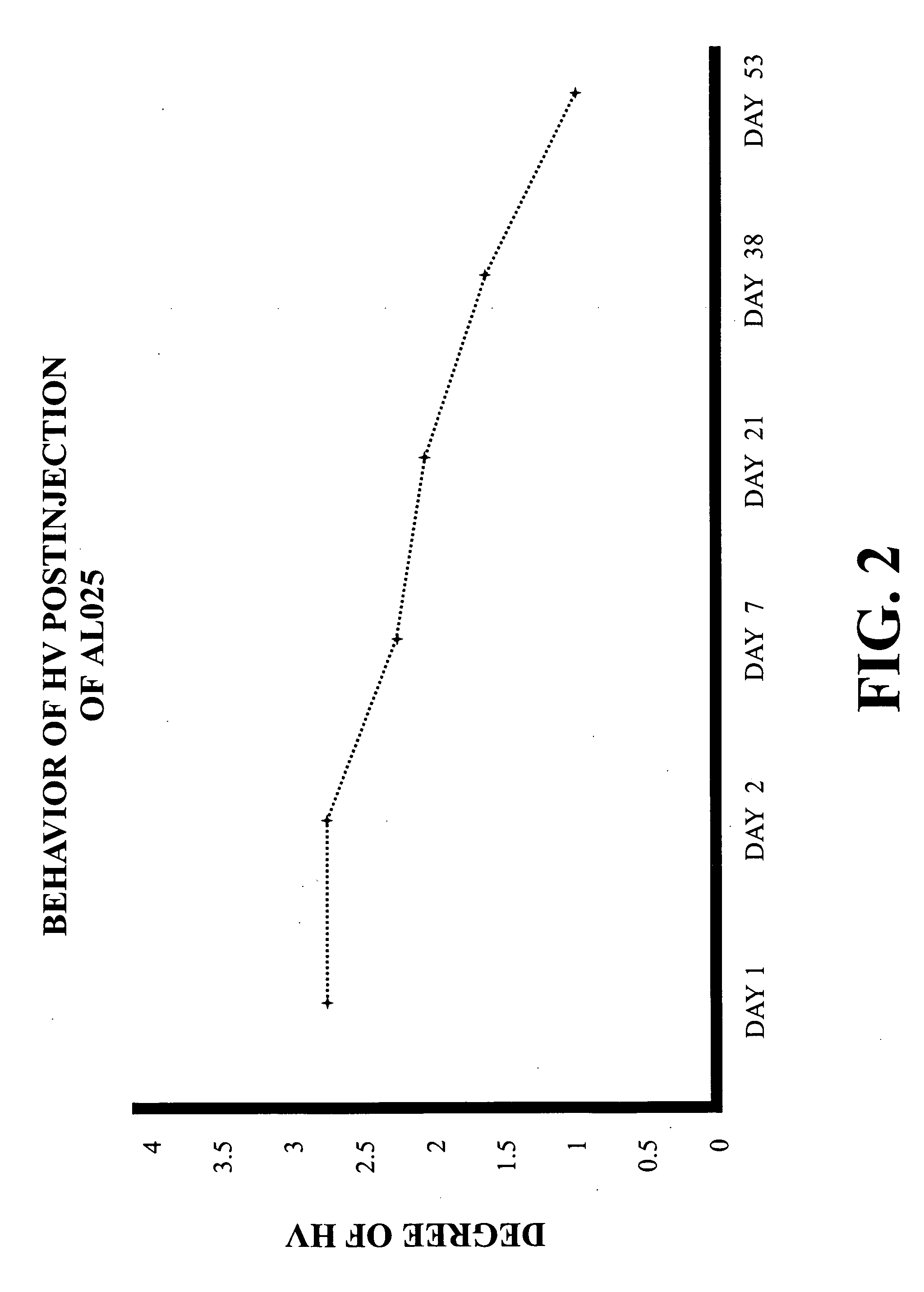
Intravitreally-injectable solution for the treatment of vitreous hemorrhages
InactiveUS20060116428A1Shorten clarification timeShorten the timeBiocideSenses disorderVitreous HumorsVitreous Bodies
The present invention relates to an ophthalmic solution for the clarification of vitreous hemorrhages. More specifically, it relates to a pharmaceutically acceptable intraocular injectable solution, for the treatment of vitreous hemorrhages, whereby the reabsorption of such hemorrhage is encouraged. It enables the clarification of the vitreous hemorrhage in a significantly short period of time to allow for the timely diagnosis of the lesion and the repair of the damage the hemorrhage has caused to the vitreous body. The ophthalmic solution of the present invention is injected at least once into the vitreous humor of the patient in a therapeutically effective dose to obtain the desired result.
Owner:JIMENEZ BAYARDO ARTURO +4
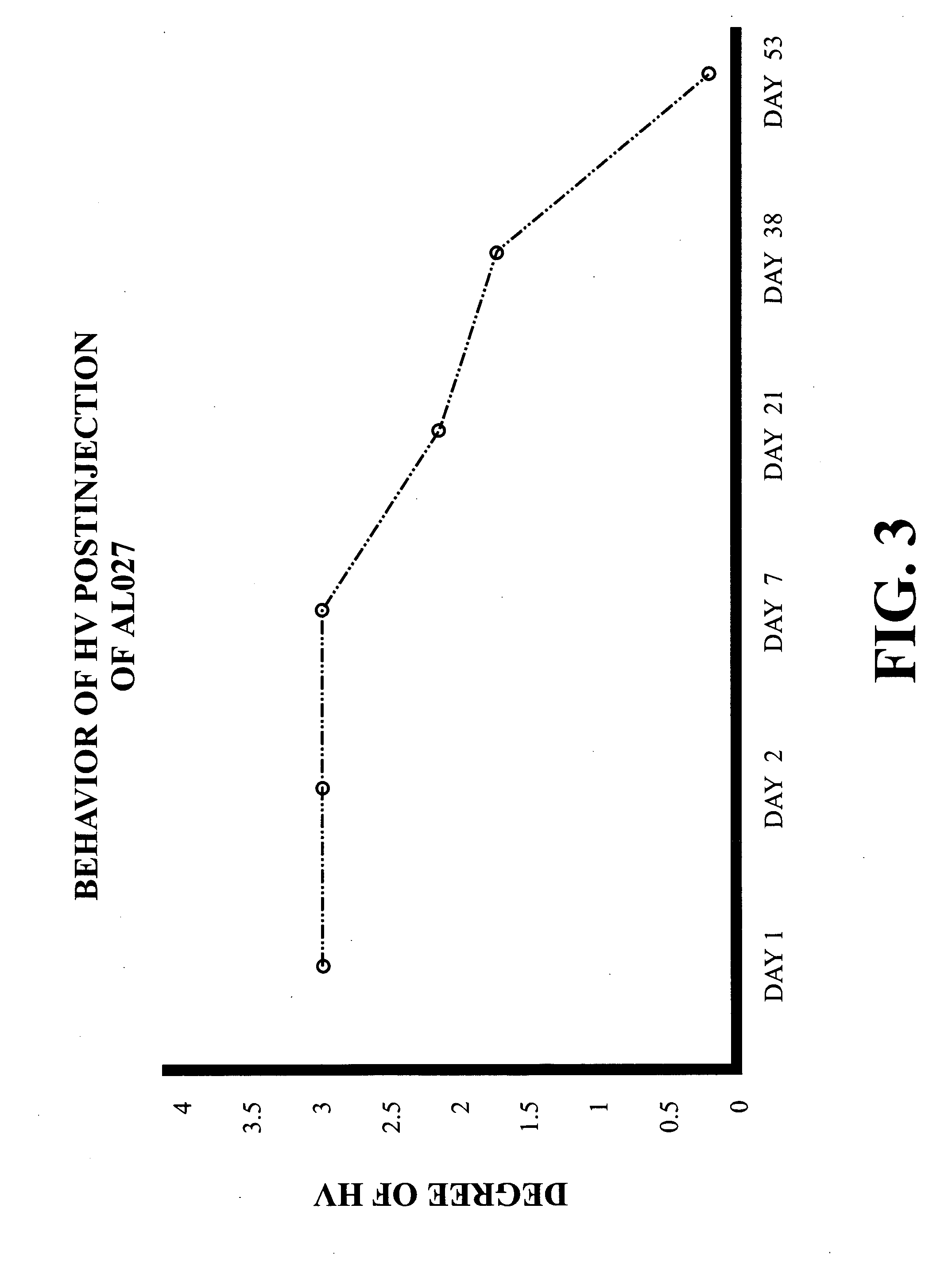
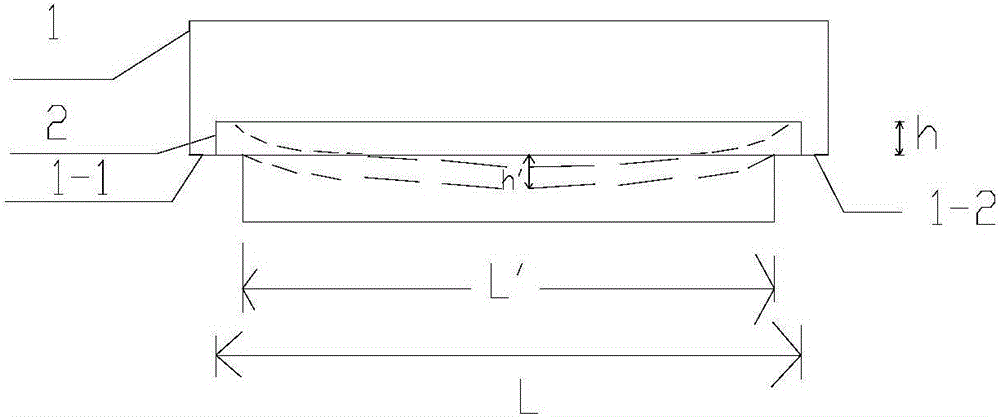
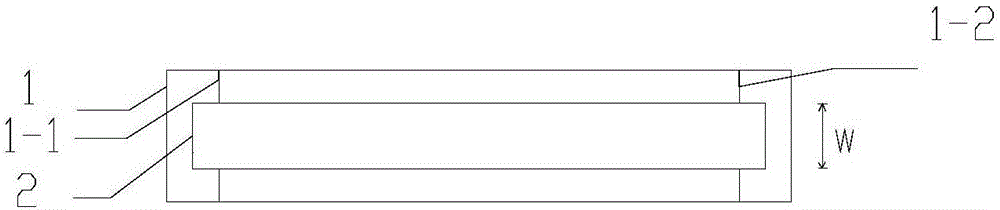
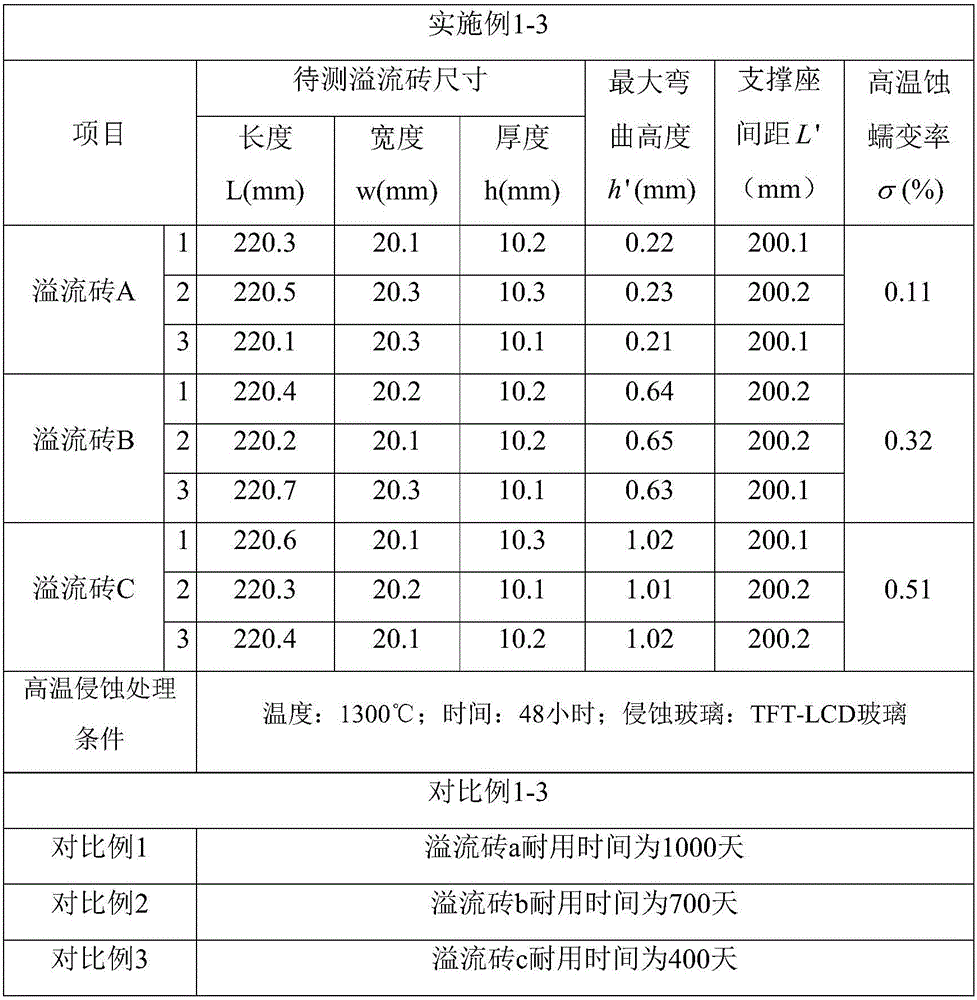
Method for deteting durability of overflow brick
ActiveCN106290130ASolve the problem that high temperature corrosion creep cannot be measuredImprove reliabilityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVitreous HumorsBrick
The invention discloses a method for detecting durability of an overflow brick. The detection method comprises the following steps of: horizontally placing a rectangular to-be-detected overflow brick into a high temperature resistant container in a manner of being vertical to the height direction, respectively placing two lengthwise ends of the to-be-detected overflow brick onto two supporting bases, so as to ensure that creep spaces are formed at the lower surface of the to-be-detected overflow brick and the bottom of the high temperature resistant container; performing high-temperature erosion treatment on the to-be-detected overflow brick in a vitreous humor so as to enable the overflow brick to creep downwards in the height direction, thereby obtaining the creep overflow brick; calculating the high temperature creep rate sigma of the overflow brick by use of a formula I, wherein the formula I is as shown in the description; the lower the high temperature creep rate sigma is, the better the durability of the to-be-detected overflow brick is. The detection method disclosed by the invention is capable of detecting the high temperature creep rate of the overflow brick so as to detect the durability of the overflow brick.
Owner:DONGXU OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Method for vitreous liquefaction
A process is disclosed for liquefying the vitreous humor of an eye. The process includes the steps of delivering plasmin into the vitreous of the eye and incubating the vitreous and plasmin together for a period of time. Plasmin may be introduced through injection or a sustained release device. Plasmin may be used to treat a pathological condition of the eye such as diabetic retinopathy, macular hole, macular pucker, intraocular infection, foreign intraocular material and retinal detachment.
Owner:THROMBOGENICS NV
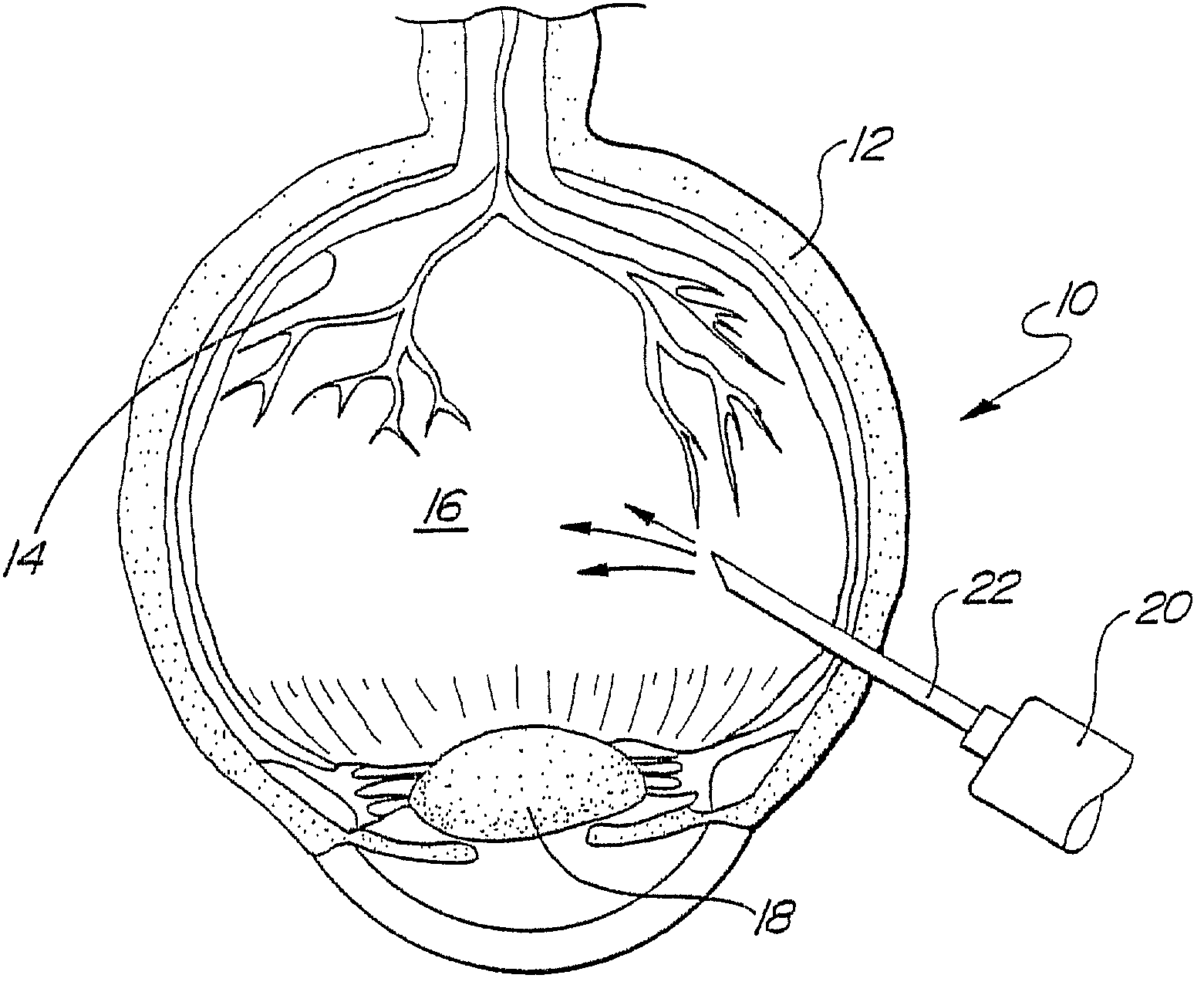
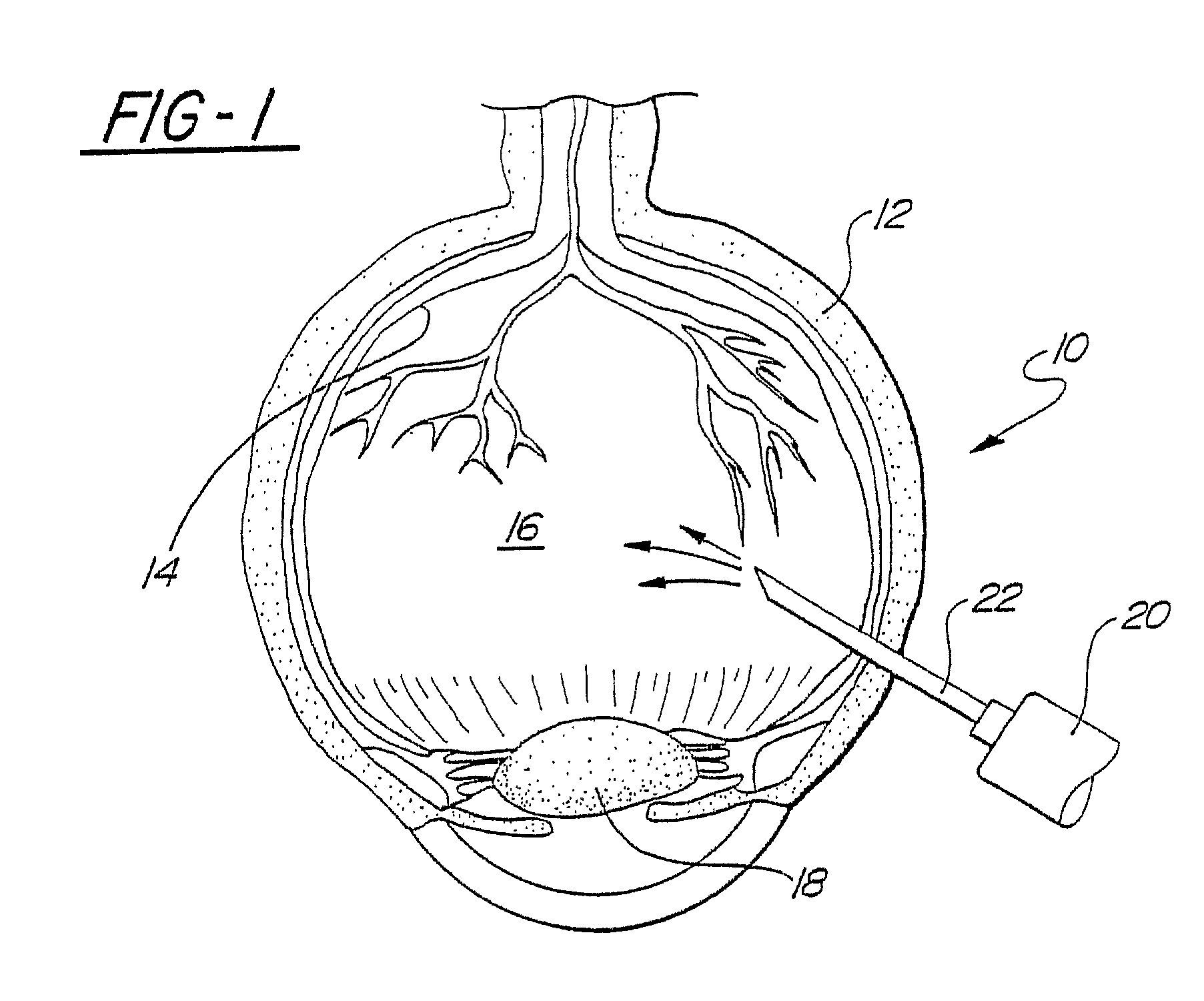
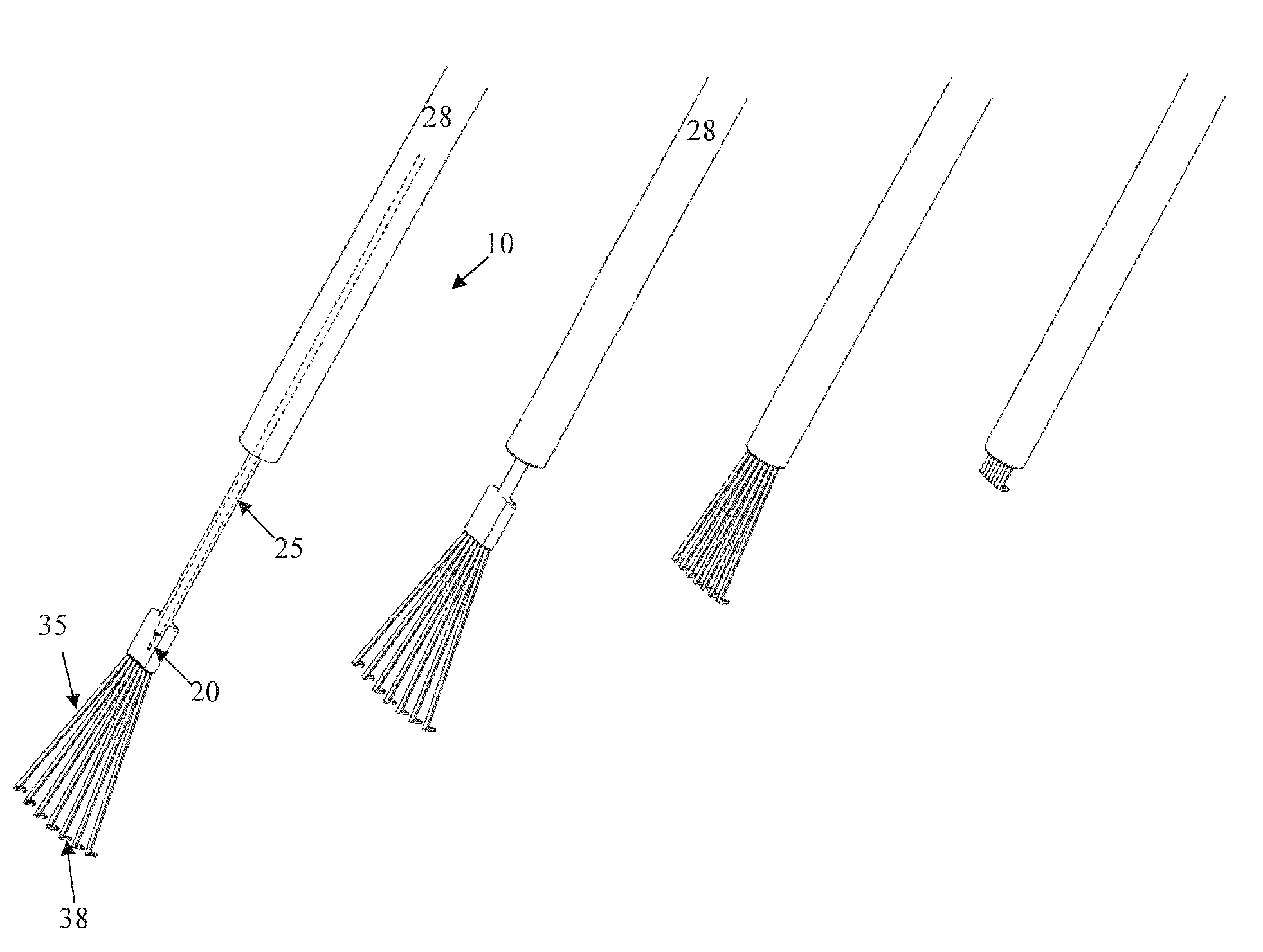
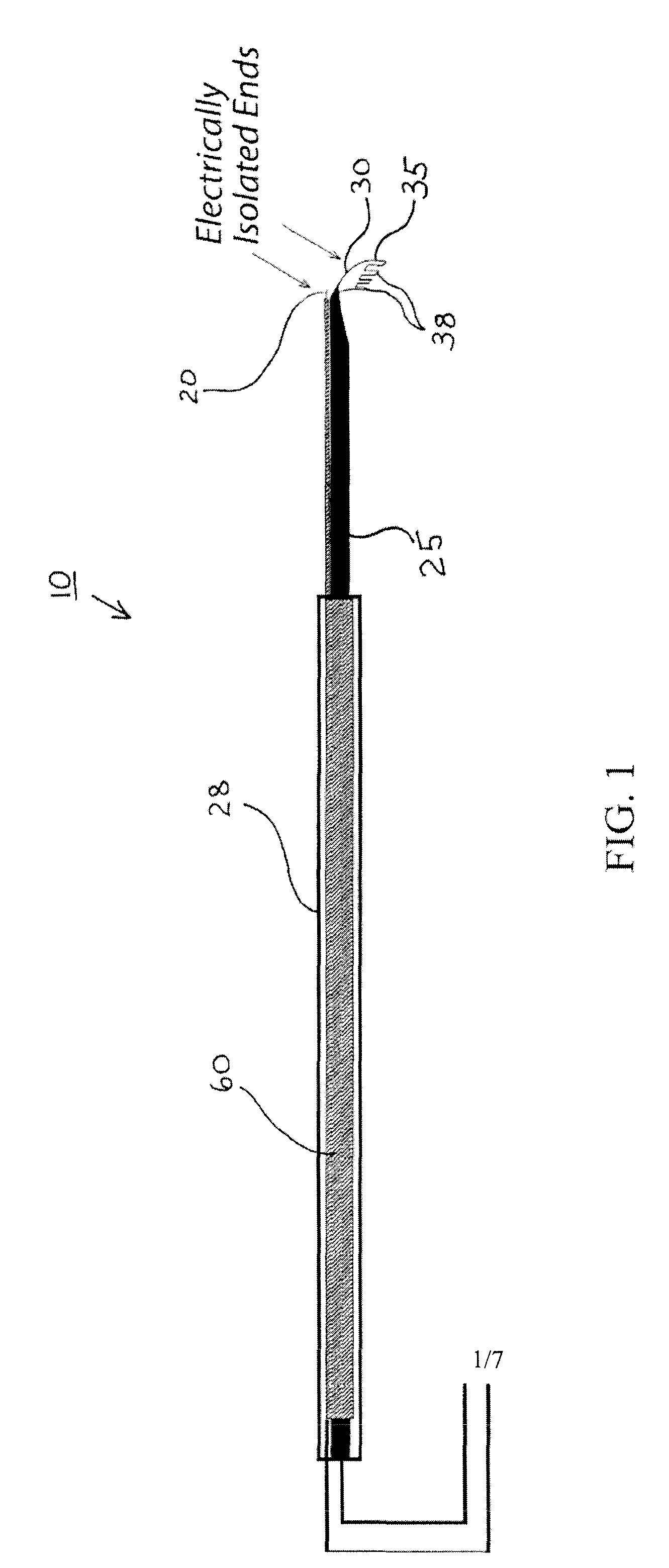
Methods and devices for differentiating between tissue types
The subject invention utilizes the characteristics of in vivo tissue impedances to provide an embodiment of a retinal rake capable of providing a visible and / or preferably an audible signal to a surgeon that more clearly indicates which type of tissue(s) is in contact with the retinal rake. A preferred embodiment comprises a handheld, battery operated retinal rake having two electrodes, wherein at least one electrode is the modified retinal rake. Upon contact with different optical tissues, e.g., epiretinal membranes, retinal tissue, vitreous humor, etc., the electrodes detect varying impedances which are translated by onboard circuitry into various signals that indicate what type of tissue, fluid, structure, etc. is in contact with the retinal rake.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Polypeptide for preventing and treating angiogenesis and application thereof
The invention relates to polypeptide for preventing and treating angiogenesis and application thereof. The invention also relates to the preparation and the application of the polypeptide and a medicinal composition containing the polypeptide. The polypeptide has a plurality of types of advantages, such as small molecular weight for permeating various eye tissue barriers, high water solubility for keeping high concentration in neutral tear, aqueous humor and vitreous humor, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com