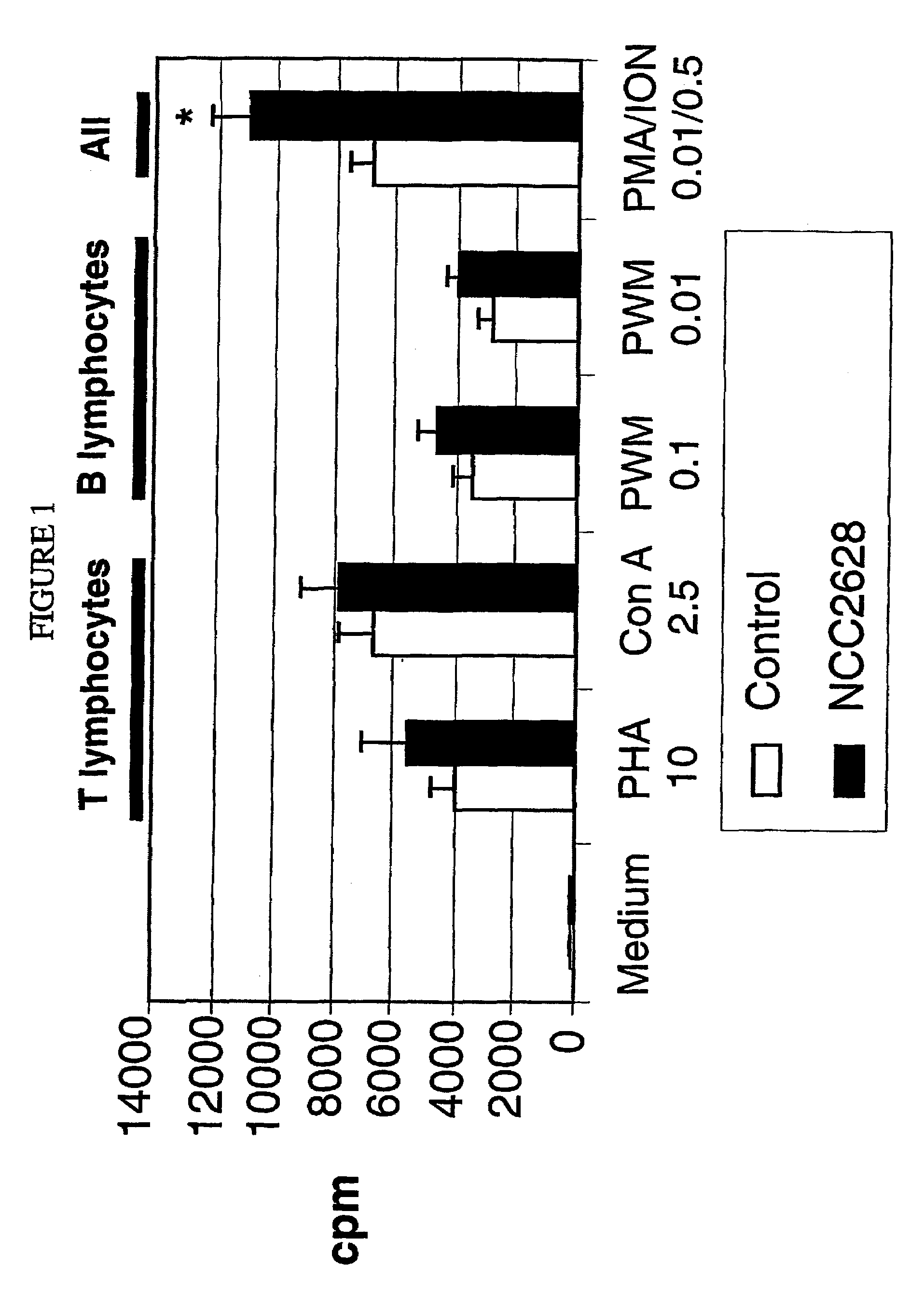
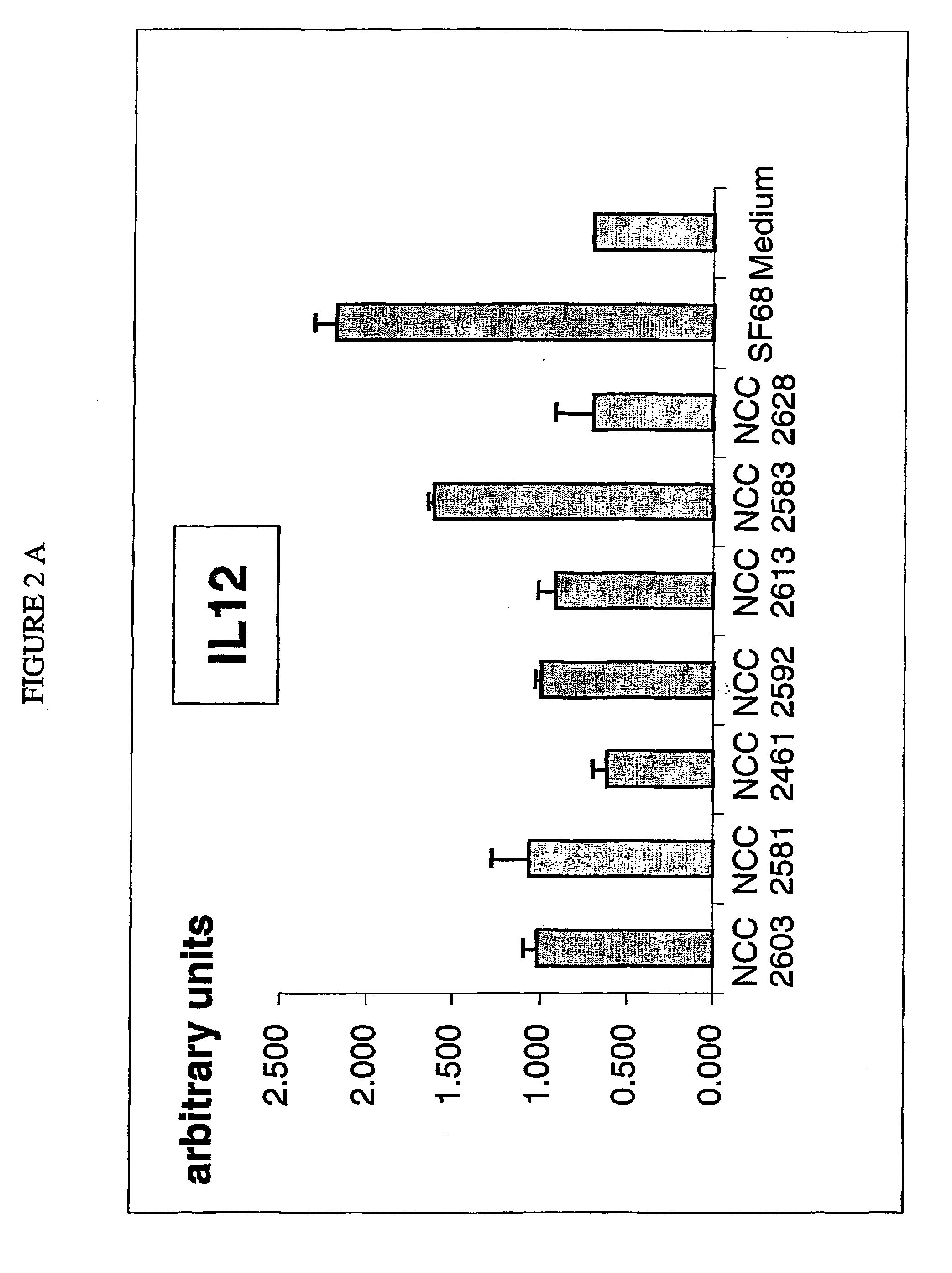
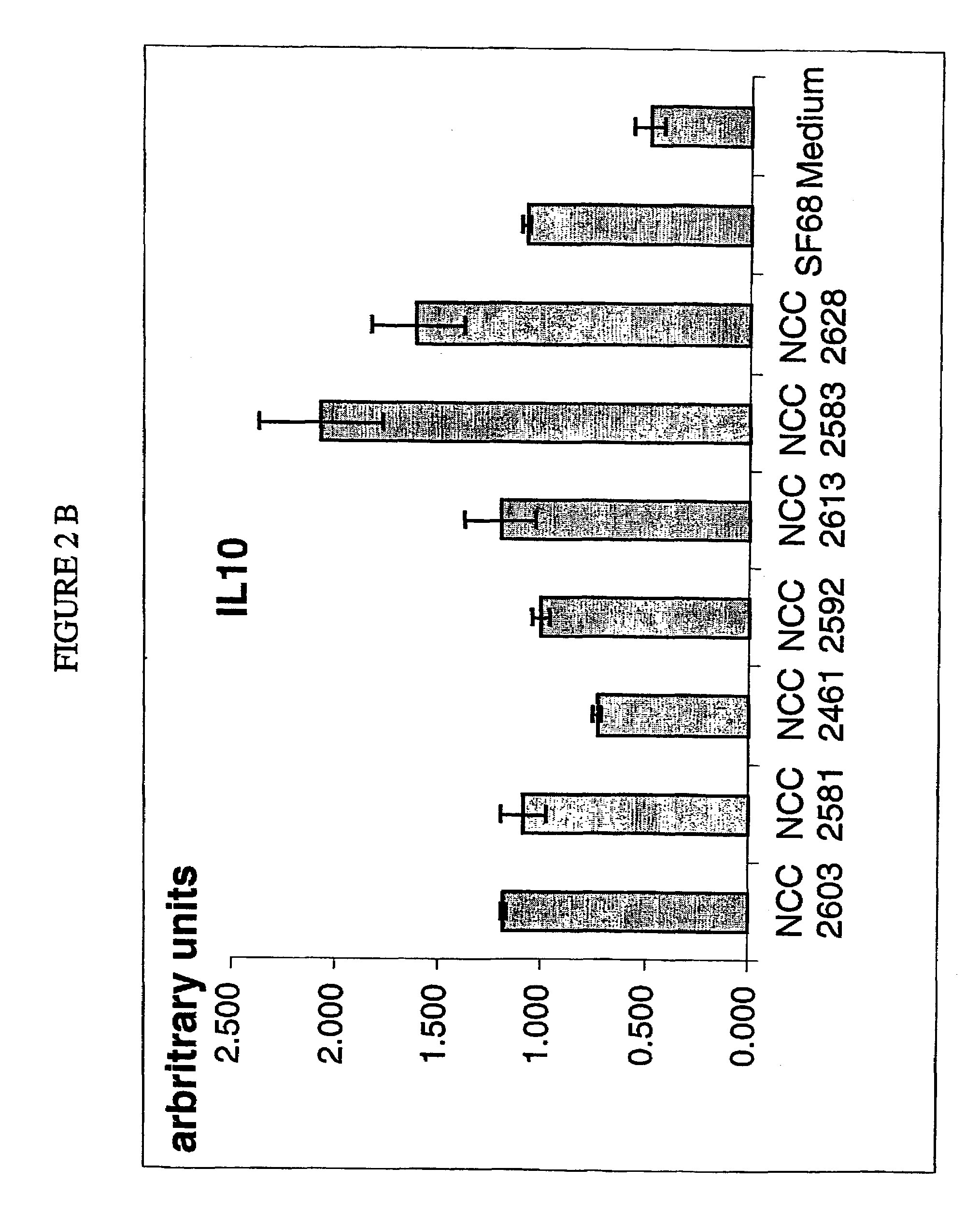
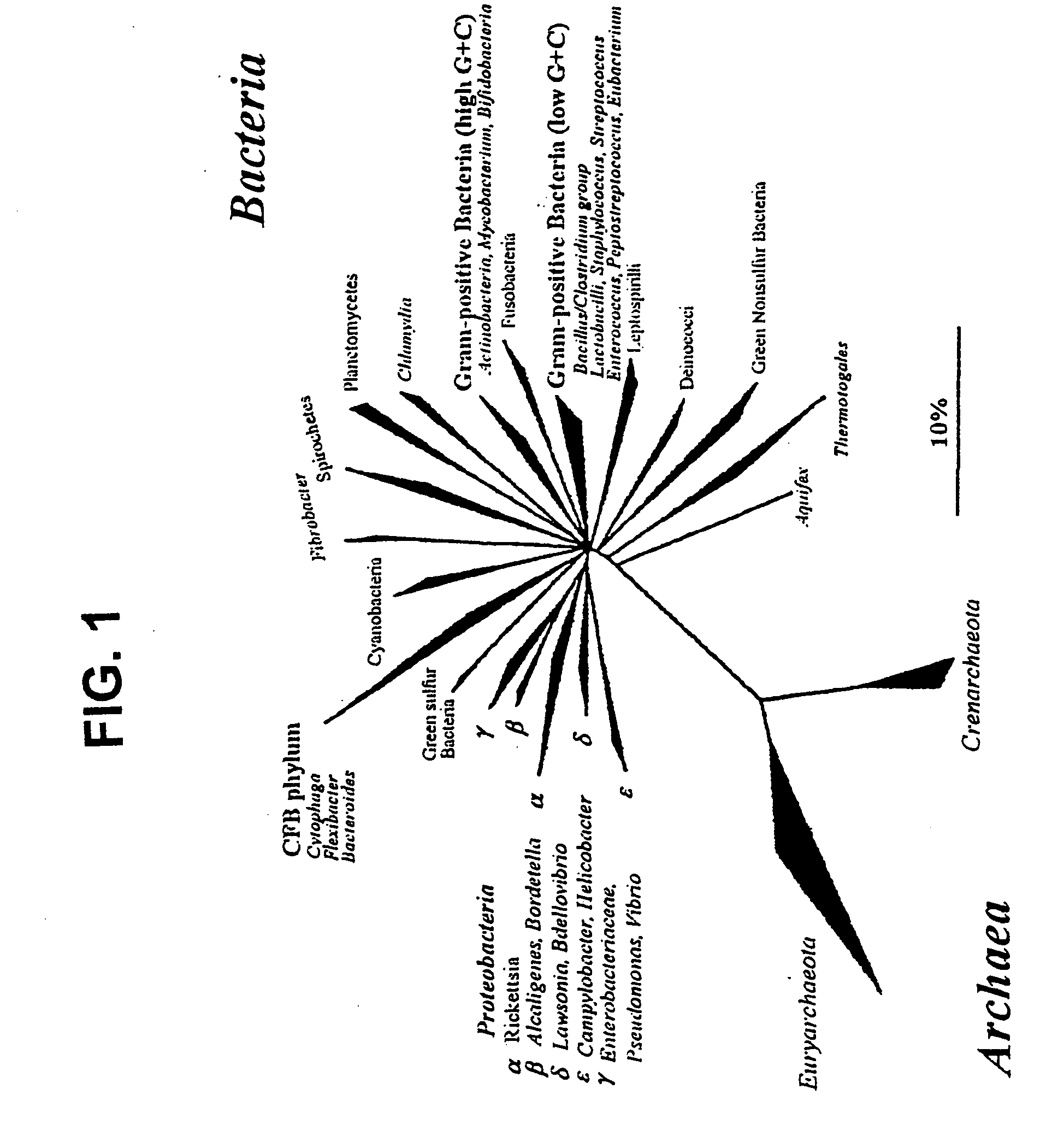
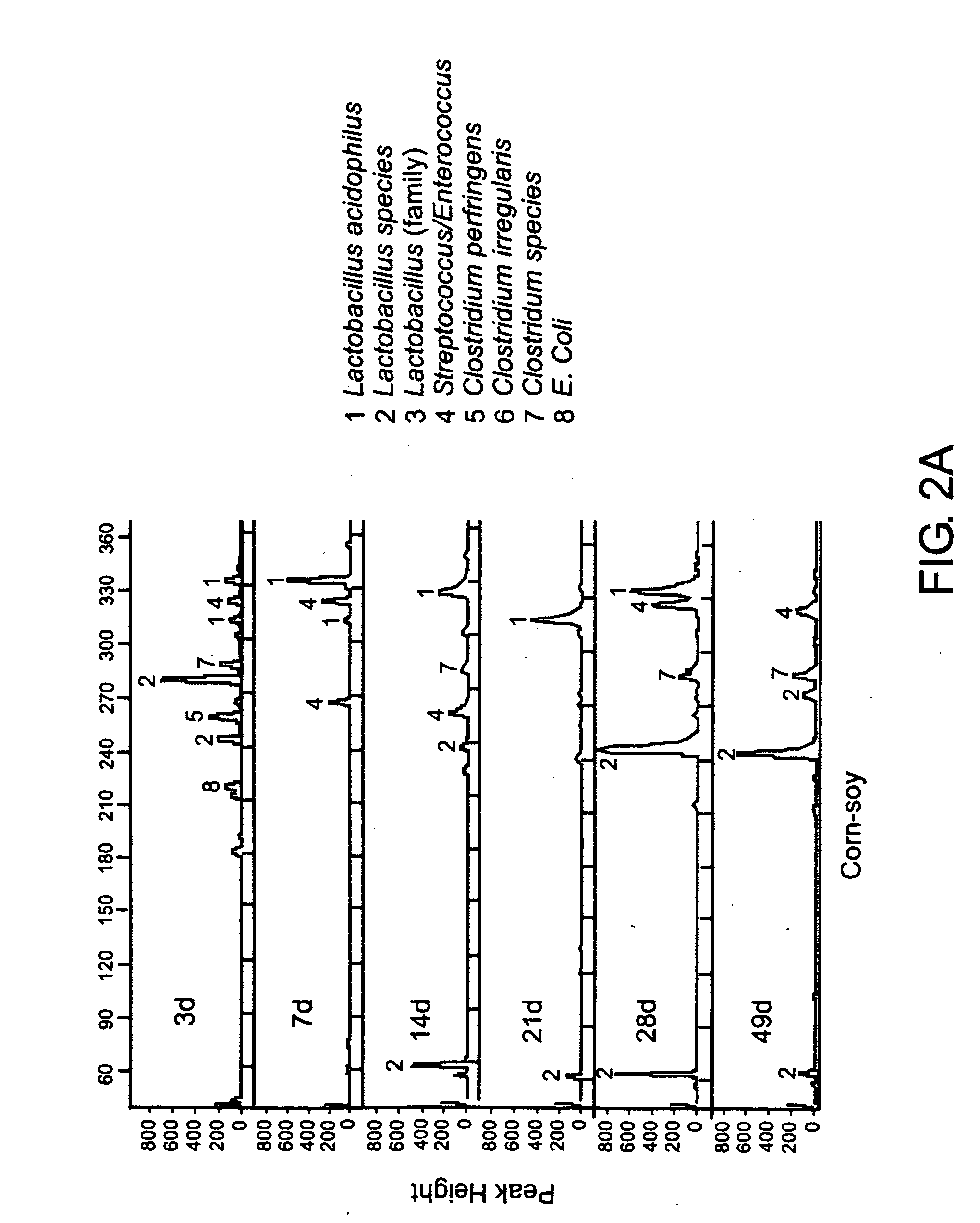
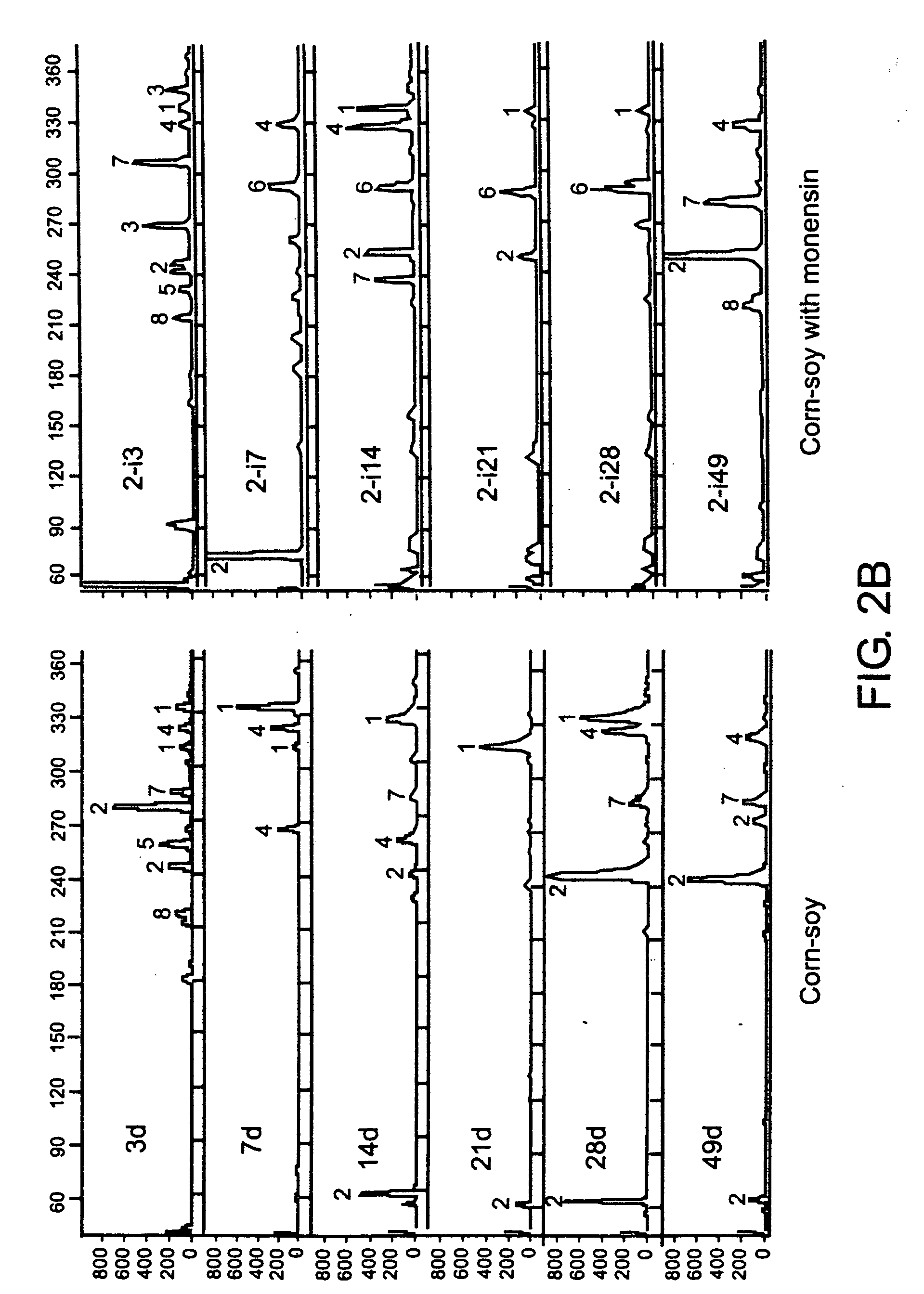
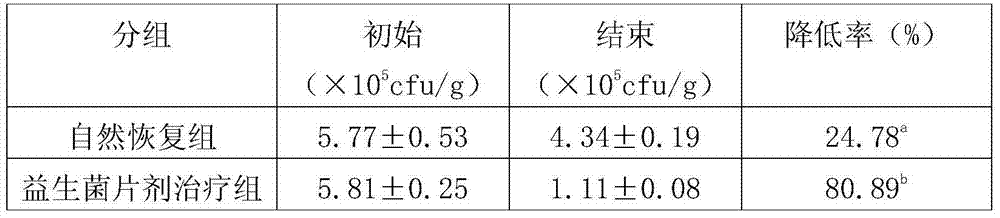
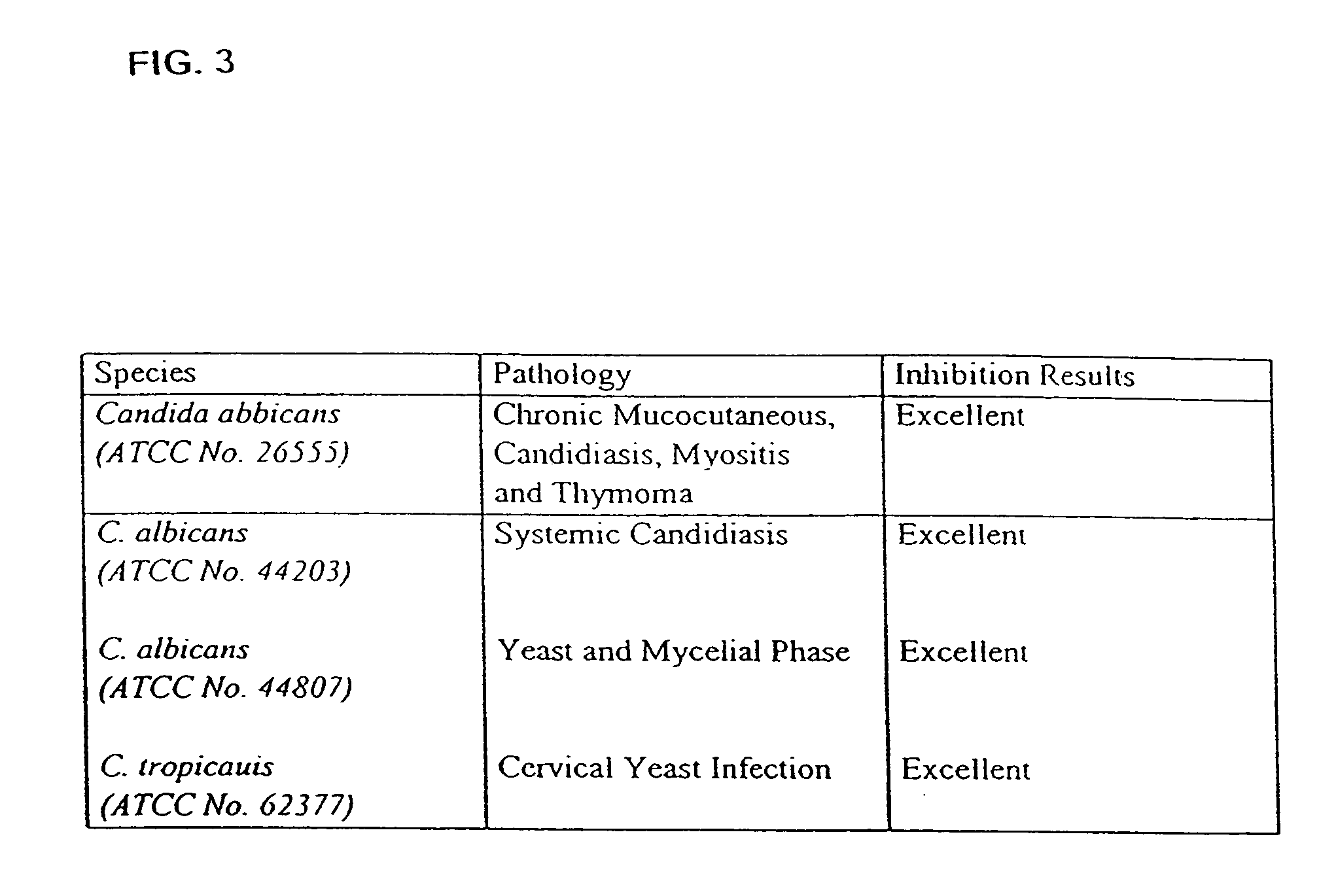
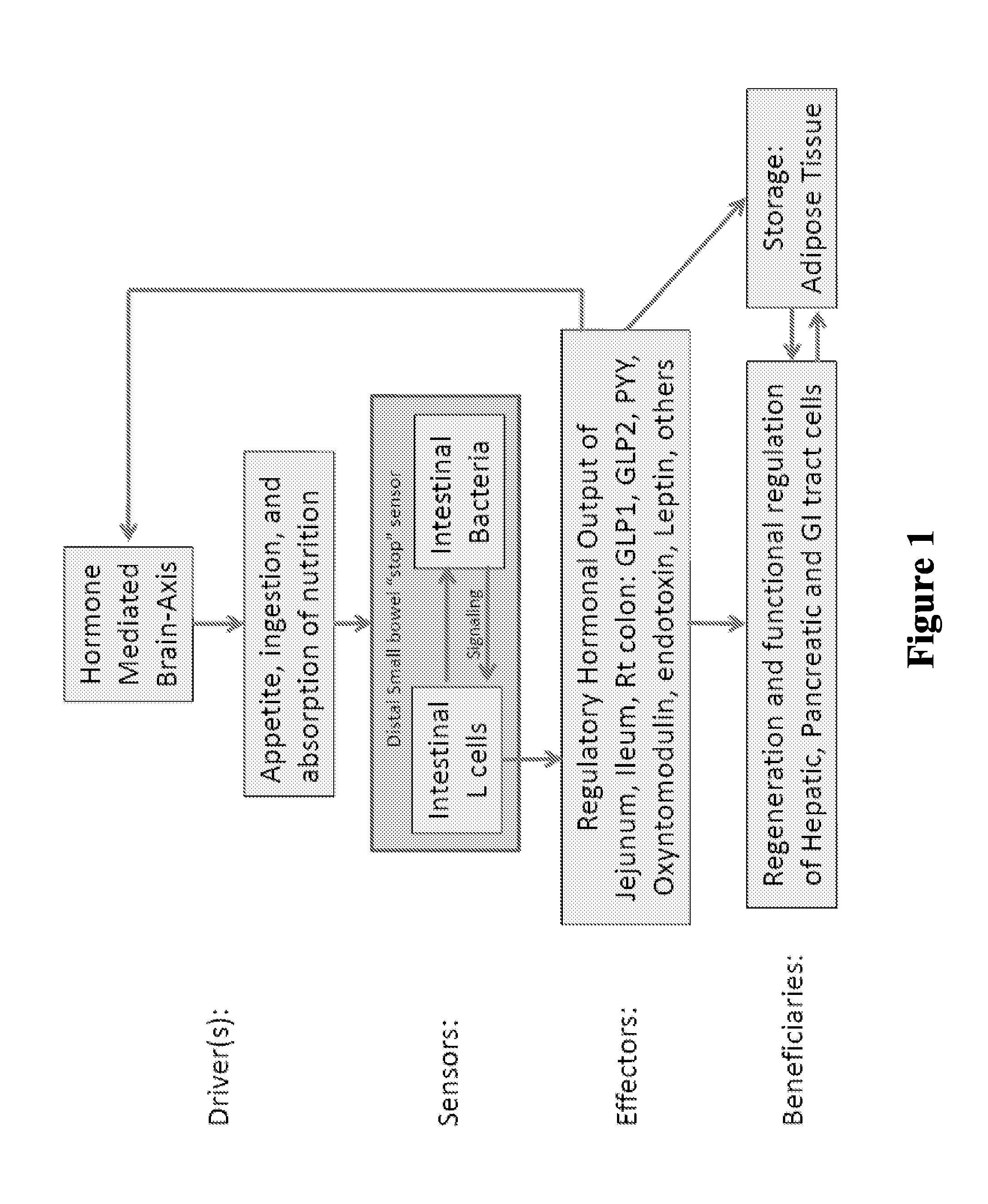
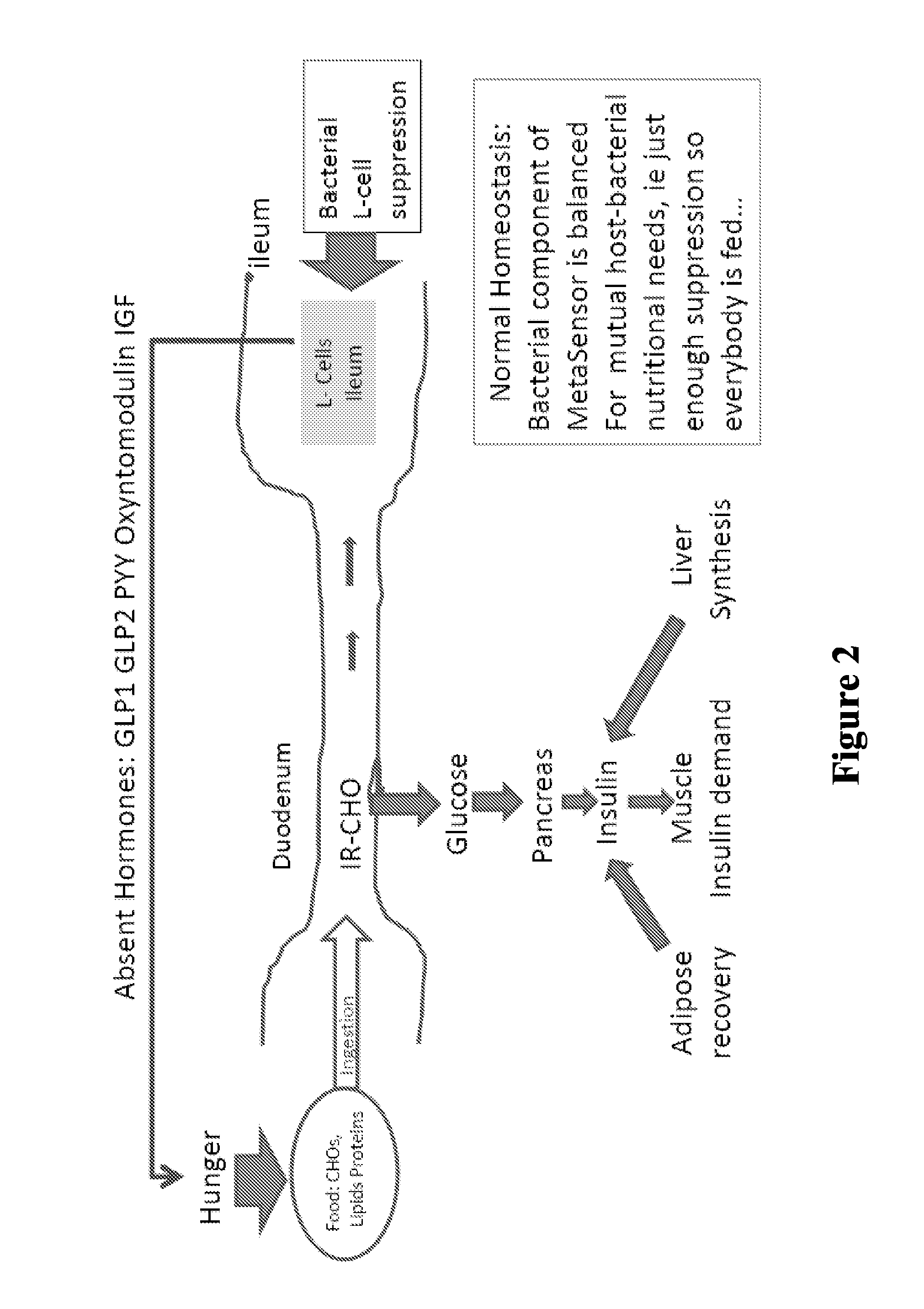
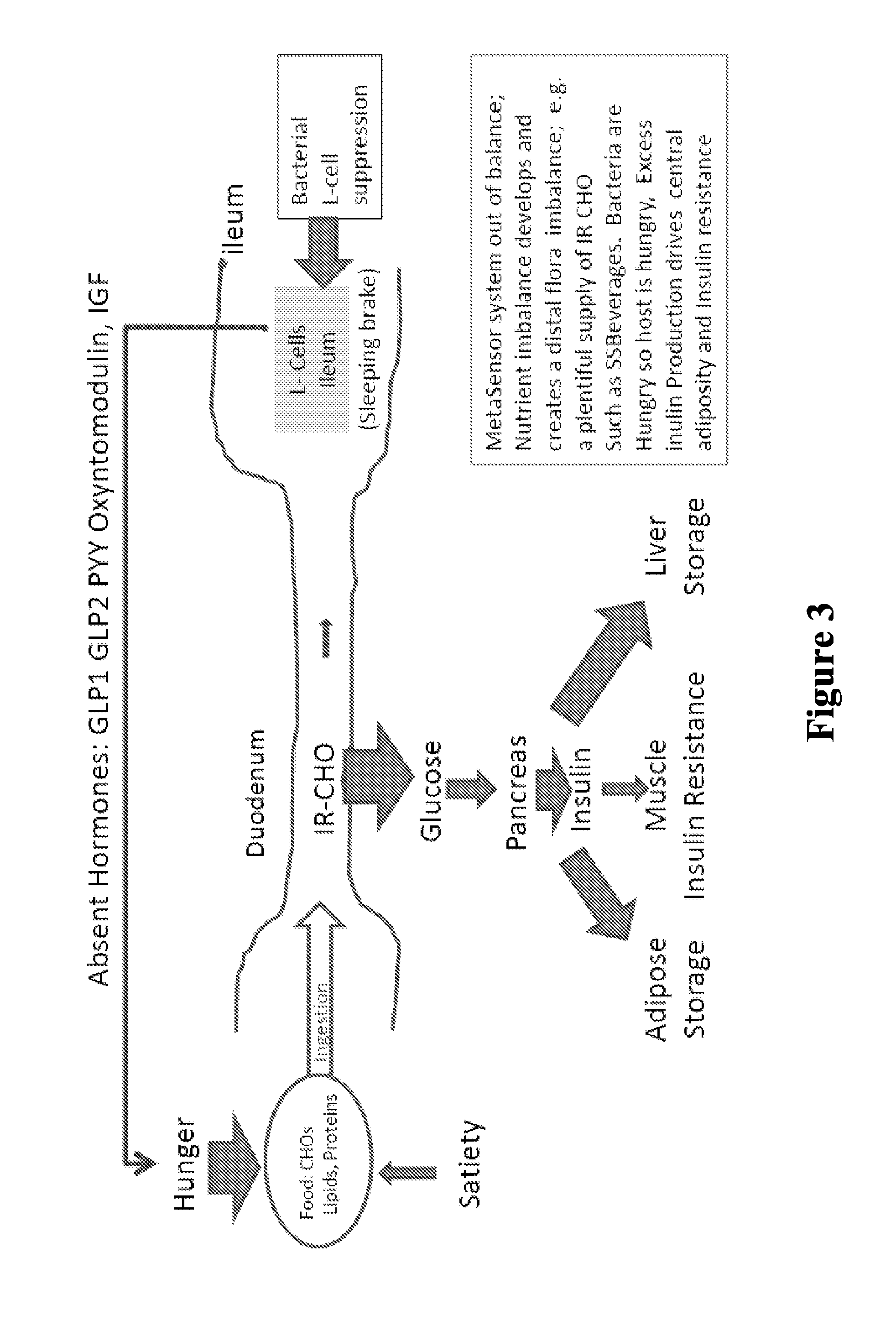
Patents
Literature
3481 results about "Probiotic bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Natural conditioning and nourishing ferment and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103844266AImprove comprehensivenessNo side effectsFood preparationSide effectEdible mushroom
The invention discloses a natural conditioning and nourishing ferment and a manufacturing method thereof. The ferment comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 1-80 parts of primarily fermented liquid, 1-30 parts of probiotics, 1-30 parts of enzymes, 1-10 parts of Chinese herbal medicines, 1-30 parts of fruits, 1-30 parts of vegetables, 1-30 parts of edible mushrooms, 1-30 parts of edible algae, 1-30 parts of maltose, and 1-30 parts of honey. The primarily fermented liquid comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 1-50 parts of corncobs, 1-15 parts of wheat, 1-30 parts of stem rice, 1-50 parts of brown rice, 1-50 parts of rice bran, 1-50 parts of black soya beans, 1-10 parts of black glutinous rice and 1-10 parts of semen sesami nigrum. The ferment is prepared by compounding the vegetables, the fruits, the edible mushrooms, the edible algae and the traditional Chinese medicinal materials with the enzymes and fermenting by the probiotics. By adopting the ferment, the integrated conditioning properties of a plurality of plants such as fruits and vegetables and traditional Chinese medicinal materials are compounded, and the natural conditioning and nourishing ferment is free of toxic and side effects. The ferment can be used as a food, also can be added to other foods and beverage, and the natural conditioning and nourishing effects are achieved.
Owner:容瑜
Probiotic delivery system
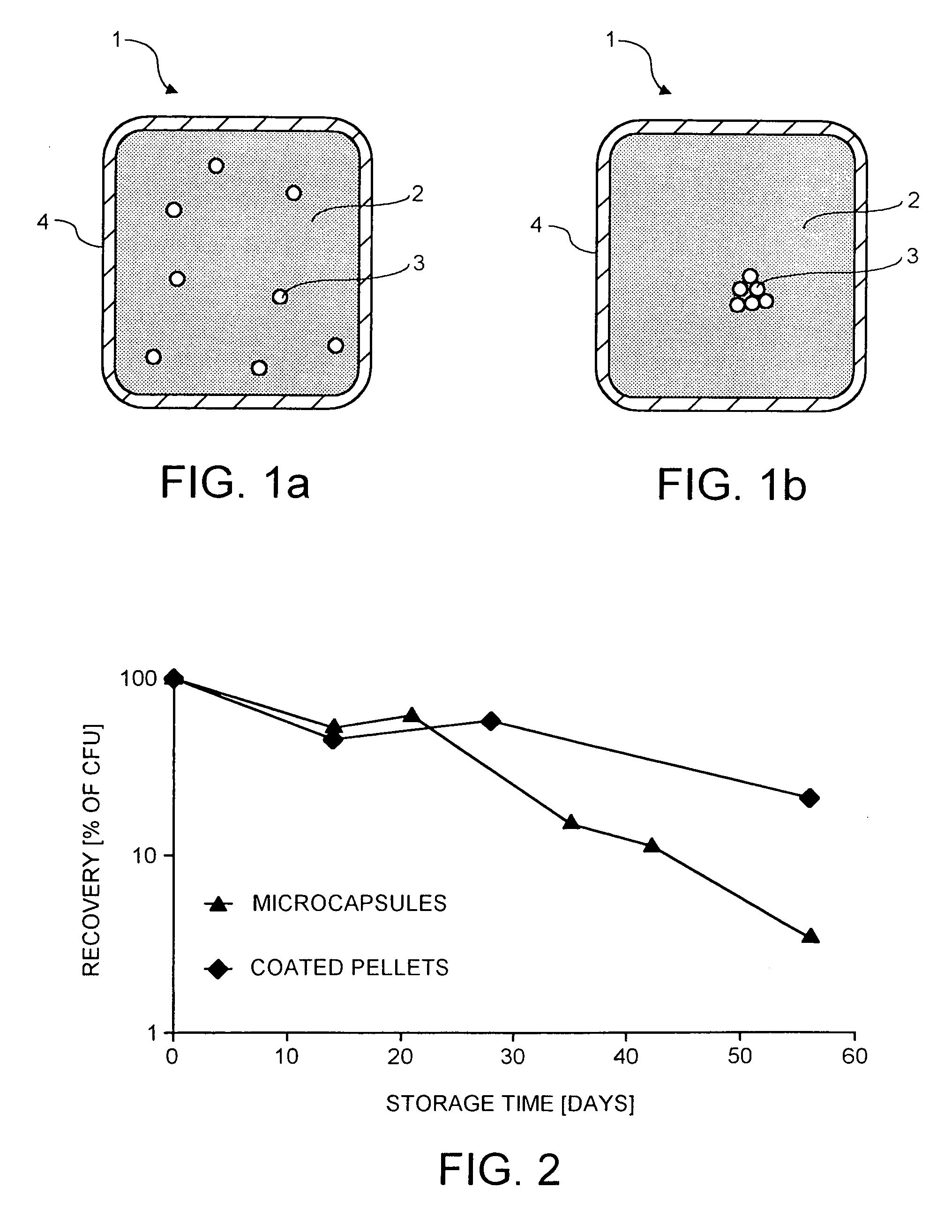
InactiveUS20050153018A1Improve stabilityProcessing is easy and straightforwardFood ingredient as barrier agentMicroorganism preservationMicroorganismBiotechnology
The present invention relates to a probiotic delivery system that is preferably added to a food product. In particular, the invention shows that compacted pellets having a volume of at least 0.02 cm3, that comprise, besides viable micro-organisms, arbitrary or eligible components, such as fillers, binder, plasticizer, other functional ingredients and a coating may be added to semi-moist, moist or semi-dry products. The micro-organisms remain viable for a longer time than commercially obtainable preparations of probiotics.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Alteration of microbial populations in the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS6348452B1Increase the number ofHigh activityBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsMicroorganismResistant starch
Method of enhancing a resident population of microorganism in a selected site of the gastrointestinal tract of an animal, the method comprising providing to the animal a selected modified or unmodified resistant starch or mixtures thereof in combination with one or more probiotic microorganisms such that upon ingestion the starch passes through the gastrointestinal tract substantially unutilized until it reaches the selected site where it is utilized by the resident and / or the probiotic microorganisms thereof causing an increase in number and / or activity of the microorganisms.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Method of hydration; infusion packet system(s), support member(s), delivery system(s), and method(s); with business model(s) and Method(s)
InactiveUS20020012689A1Constant deliveryUniform deliveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityDietary supplement
Liquid activated infusion packet(s) / system, promoting hydration, containing active and / or inactive ingredients and / or a support member(s). Infusion Packet(s) / System is one or more individual compartments, and / or group(s), whereby the enveloping material(s) may be totally or partially dissolvable, edible, transparent, opaque, decorated, etc. Further, including of one or more: color(s), flavor(s), aroma(s), pharmaceutical(s), nutraceutical(s), dietary supplement(s), enzyme(s), pre / pro-biotic(s), amino-acid(s), soluble-fiber(s), diagnostic agent(s) etc. regardless of form, + / - effervescence, + / - uniform / controlled-release encapsulations into liquid for humans and / or animals. Enveloping material may be in whole and / or in combination; non-synthetic / porous, and / or synthetic porous / non-porous with deliberate perforations. Infusion Packet(s) / System + / - tag, support member for assistance, consumer compliance: promotion, advertising, education, entertainment, (toy / game), etc. Manual and / or power operated parts, lights, noise, etc. Additionally incorporated; unique business modalities with test market opportunities and / or the ability to provide income and / or esteem for the health challenged.
Owner:STILLMAN SUZANNE JAFFE
Probiotic/prebiotic composition and delivery method
A prebiotic, composition comprising a probiotic and prebiotic, and method of delivering a probiotic, prebiotic or composition directly into the intestinal tract of a mammal are disclosed. The probiotic is any beneficial bacteria and the prebiotic is a substance beneficial to a probiotic. Most preferably, the prebiotic includes a mucopolysaccharide. The method preferably involves delivering the prebiotic, probiotic or composition via a delivery tube, such as an enteral feeding tube, directly to a position downstream of the stomach, most preferably to the jejunum.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome using probiotic composition
A method of treating irritable bowel syndrome using a probiotic composition including the bacilli (1) Bacillus subtilis, (2) Bacillus coagulans, and (3) Enterococcus faecium. The composition may further include a carrier medium, such as fructo-oligo-saccharides (FOS), as incorporated in a dose form such as a pill, capsule, powder or sachet. The compositions of the invention may be usefully employed as health or nutritional supplements, food additives, or therapeutic agents for combating a wide variety of physiological disorders.
Owner:COBB & ASSOCS
Categorization of microbial communities
ActiveUS20060172330A1Special deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismYeast
The present disclosure provides embodiments of a method for characterizing microbial populations. Exemplified by methods for characterizing microbiota in vaginal samples, the methods provided herein are widely applicable to the characterization of microbial communities. Also provided are probiotic regimens and methods for selecting appropriate probiotic regimens based on the normal vaginal microbiota of a subject. Reagents and kits for detecting normal vaginal microbiota and diagnosing pathogenic microorganisms in the vagina are also provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with SIDS
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Probiotics for pet food applications
InactiveUS7189390B2Ameliorating and reducing effectImprove probiotic activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismLactobacillus
The present invention relates to novel lactic acid bacterial micro-organisms that have been isolated and selected for their probiotic potential and their use for the preparation of petfood compositions intended to improve the health of pets, and to compositions containing the same.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Probiotic/Non-Probiotic Combinations
InactiveUS20080069861A1Improve Gut HealthWeight increasePeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderBiotechnologyIncreased carbohydrate
This invention pertains to a method of promoting gastrointestinal health by ingesting a composition comprising one or more probiotic microorganisms, one or more carbohydrate sources, and one or more resistant protein products. Large intestinal health is benefited by one or more of the following: increased fecal weight, lower fecal pH, increased carbohydrate fermentation, and amelioration of protein fermentation.
Owner:BRUNOB II BV
Microbial ecological traditional Chinese medicine preparation for livestock and poultry from fermentation production of multiple bacterials and fermentation method thereof
ActiveCN101401921ALow costImmunity exceedsFungiAnthropod material medical ingredientsHouttuyniaLactobacillus acidophilus
The invention relates to micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation for livestock and poultry by adoption of multi-strain fermentation production and a fermentation method. The compositions of traditional Chinese medicines in a culture medium of the fermentation preparation include: radix astragali, radix codonopsitis, Atractylodes macrocephala, Poria cocos, liquorice, medicated leaven, hawkthorn, angelica, Chinese rhubarb, Scutellaria baicalensis, radix isatidis, cordate houttuynia, sicklesenna seeds, Schisandra chinensis, Gynostemma pentaphylla, phellodendron, dried orange peel, radix bupleuri, curcuma, honeysuckle, Chinese gall, purslane and Quisqualis indica. The fermentation method is as follows: a multi-strain solid state fermentation strain is adopted for fermentation; bacillus subtilis, bacillus natto, bacillus licheniformis, beer yeast, Candida wtilis, Aspergillus niger, lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus acidophilus and bifidobacteria are purified and subjected to anaerobic fermentation under the conditions of a rotating speed of 180 revolutions per minute at a temperature is 32 DEG C for 48 to 72 hours till the pH value reaches 4.0. The micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation has the advantages that the micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation uses probiotics to ferment different Chinese medicine compositions, and is micro-ecological Chinese medicine preparation which completely replaces antibiotics and has the advantages of no residual medicine, disease prevention, growth promotion and low cost.
Owner:河南省龙腾高科实业有限公司
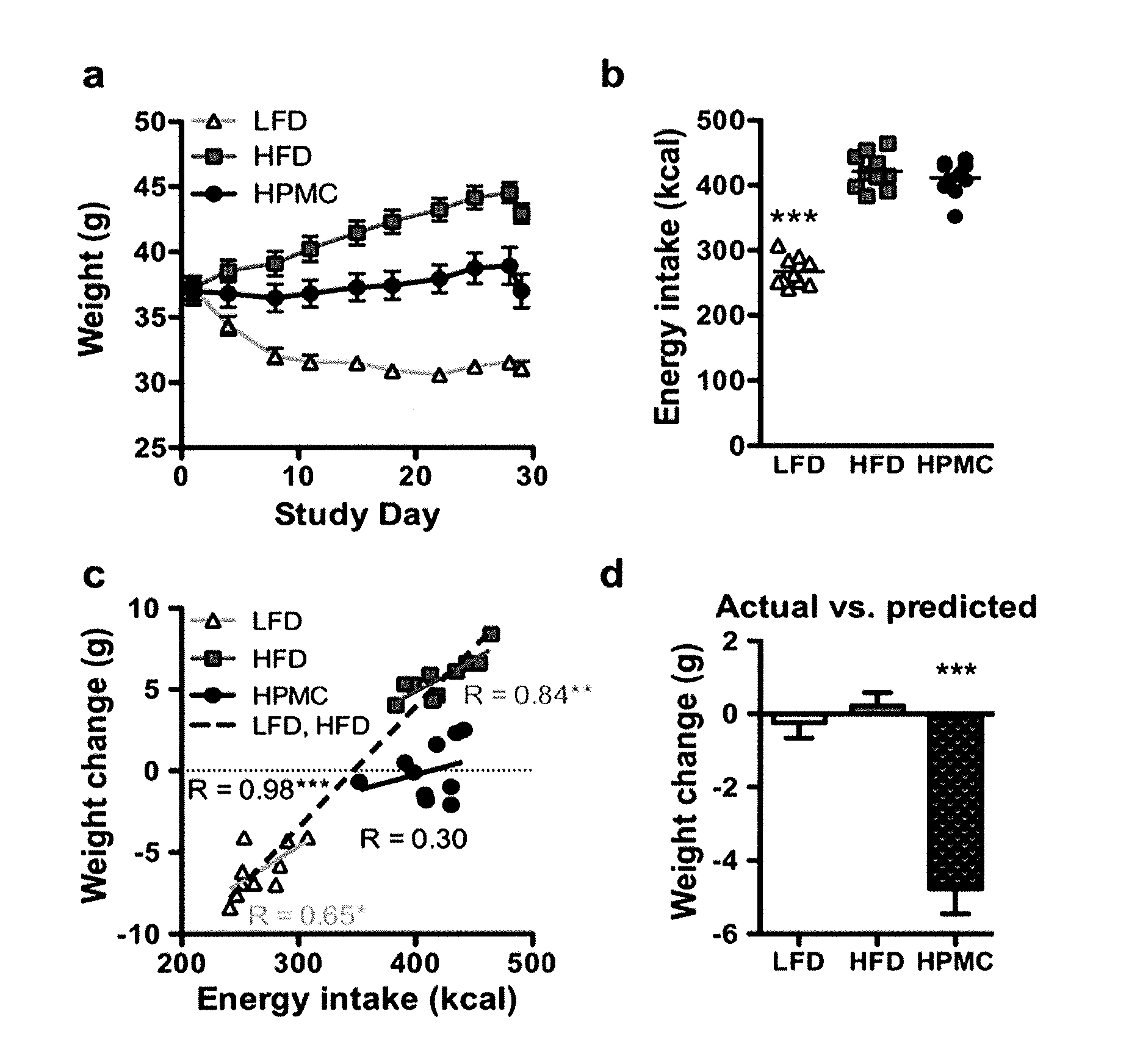
Compositions and methods for treating obesity and related disorders by characterizing and restoring mammalian bacterial microbiota
ActiveUS20120058094A1Good for weight lossReduce the populationBiocideMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyDisease
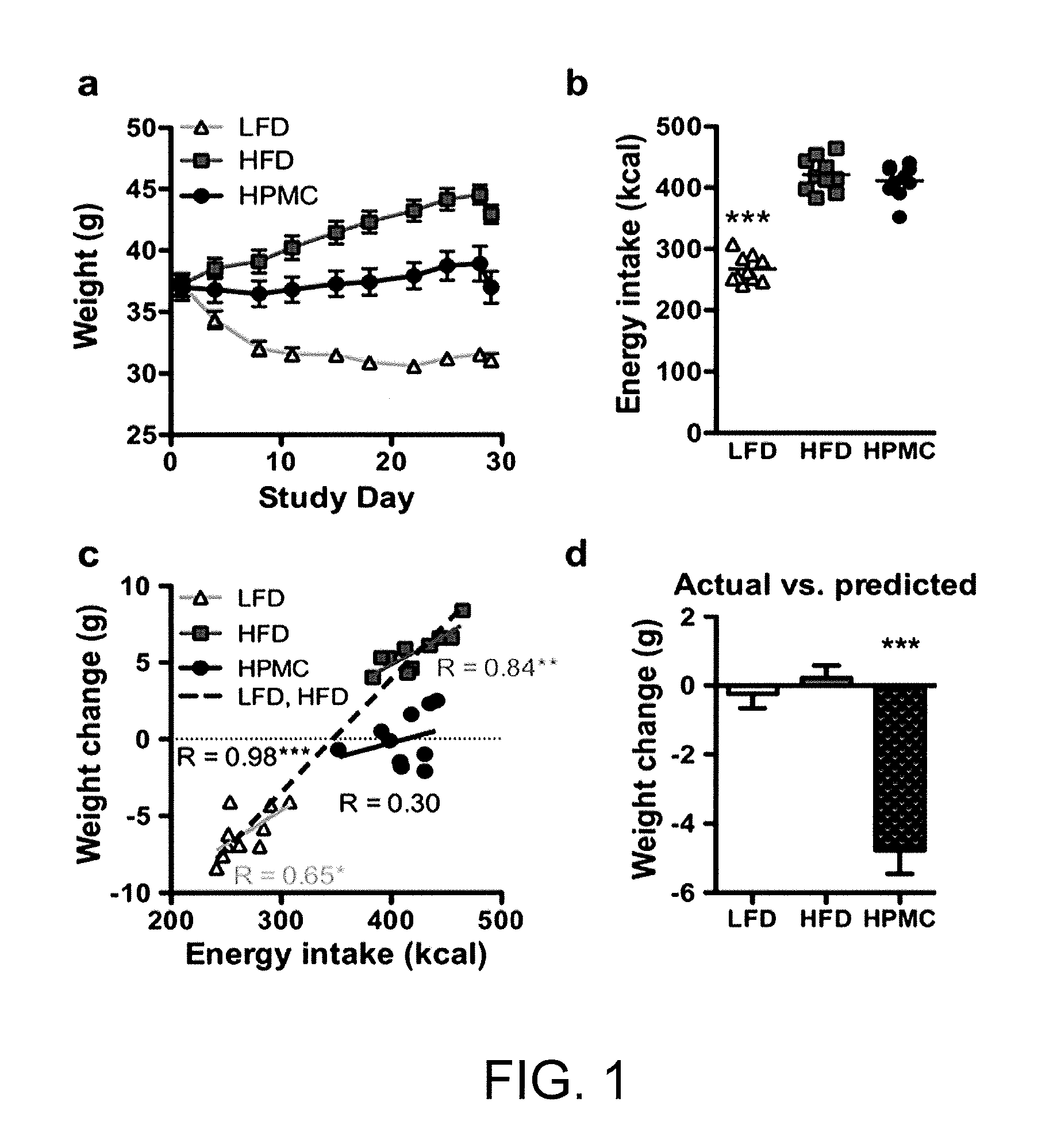
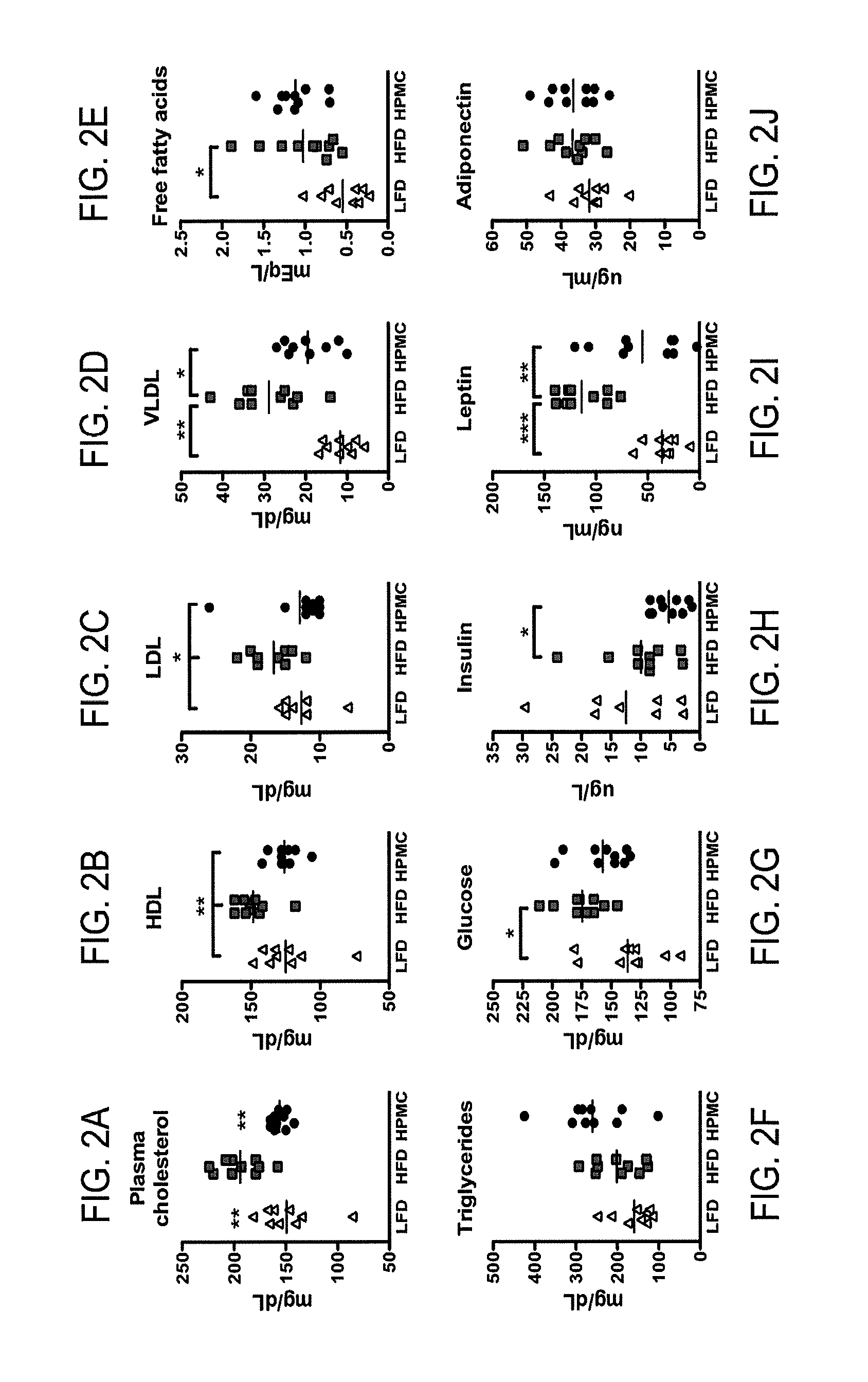
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian intestinal microbiota associated with associated with high-fat and low-fat diets and with diets containing hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) and related methods for diagnosing, preventing and treating obesity and related conditions such as metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of probiotics, and / or prebiotics, and / or narrow spectrum antibiotics / anti-bacterial agents that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial intestinal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Enteric-coated multilayer encapsulated probiotic microcapsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1969889AGrowth inhibitionPromote formationMetabolism disorderBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
The invention discloses an enteric-solubility multilayer encysted bacterium microcapsule and making method in the biological agent technical domain, which is characterized by the following: adopting sodium alginate, calcium chloride and chitose as clad material of microcapsule; making lactic acid bacteria or bifidobacteria as core-clad material; proceeding ionic exchange for sodium alginate and calcium chloride; forming second clad on the surface of calcium alginate through different isoelectric points of calcium alginate and chitose; freezing at low temperature to obtain the product.
Owner:JINAN SYNBIOTICS BIOENG
Application of bacteroides fragilis in preparation of composition for treating inflammatory bowel diseases
InactiveCN103156888AEnhance pharmacological effectsGood treatment effectMilk preparationBacteria material medical ingredientsPharmacologic actionBowels diseases
The invention relates to the technical field of application of bacteroides fragilis, and in particular relates to application of bacteroides fragilis in preparation of a composition for treating inflammatory bowel diseases. The experiments show that bacteroides fragilis is safe and nontoxic and strong in pharmacologic action, and has good treating effect of treating inflammatory bowel diseases, thereby indicating that the bacteroides fragilis has good edible and medicinal prospects. According to the invention, a novel use of bacteroides fragilis is explored and a novel application field is developed. Bacteroides fragilis as a probiotic can be used for preparing foods or medical compositions for treating inflammatory bowel diseases so as to provide health-cared foods or treating medicines suitable for human body to take.
Owner:广东知光生物科技有限公司
Probiotic compositions
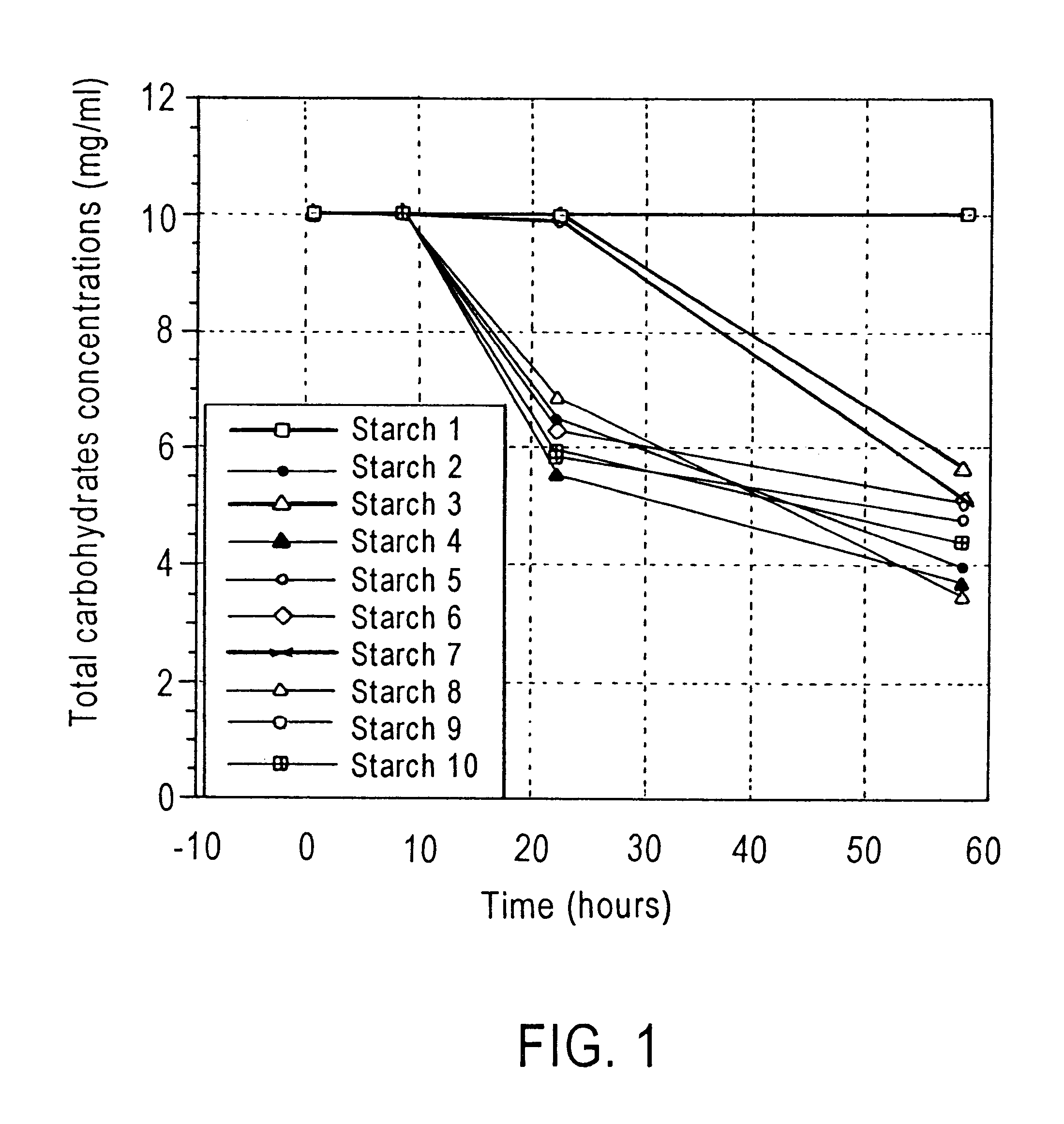
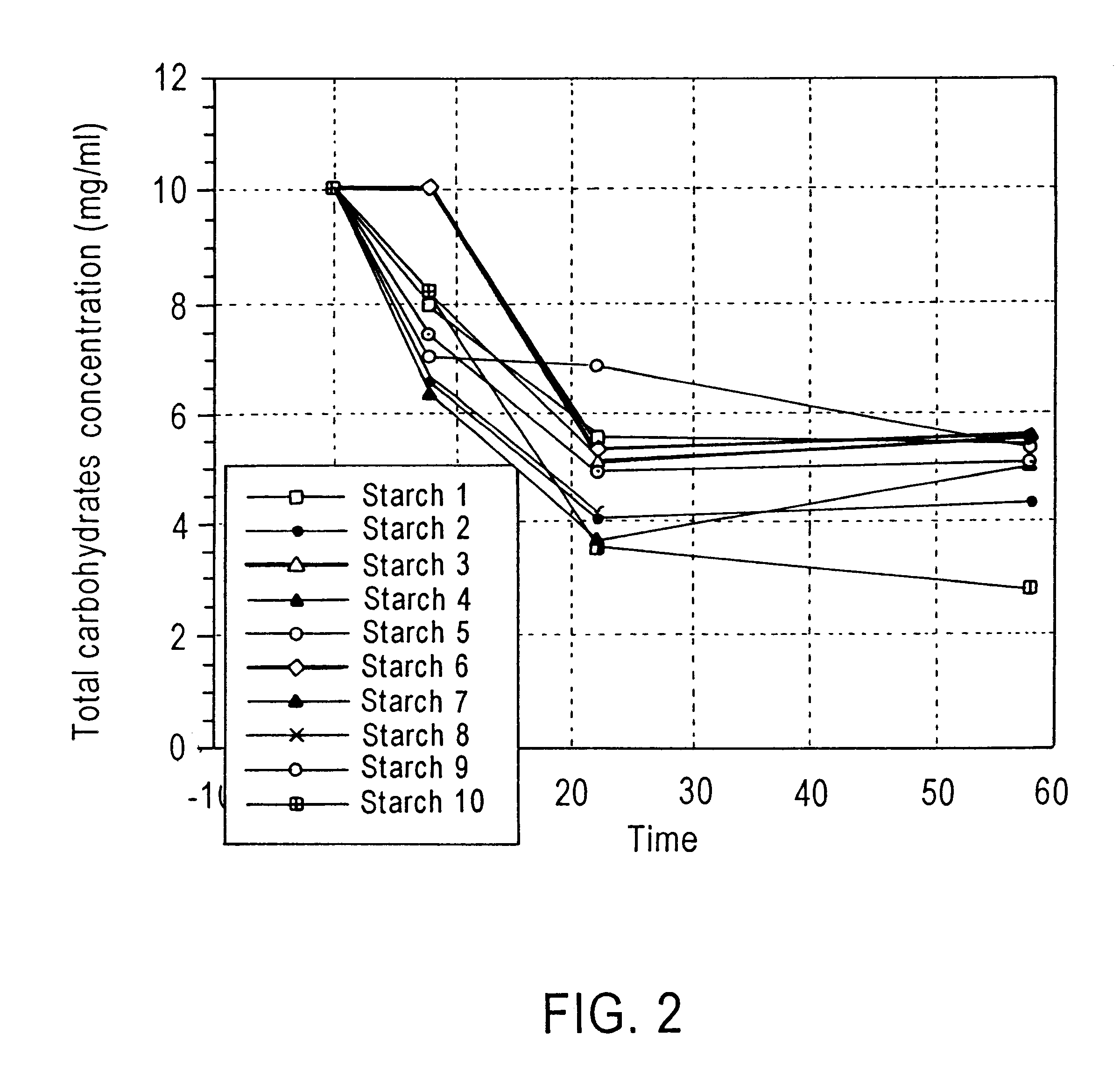
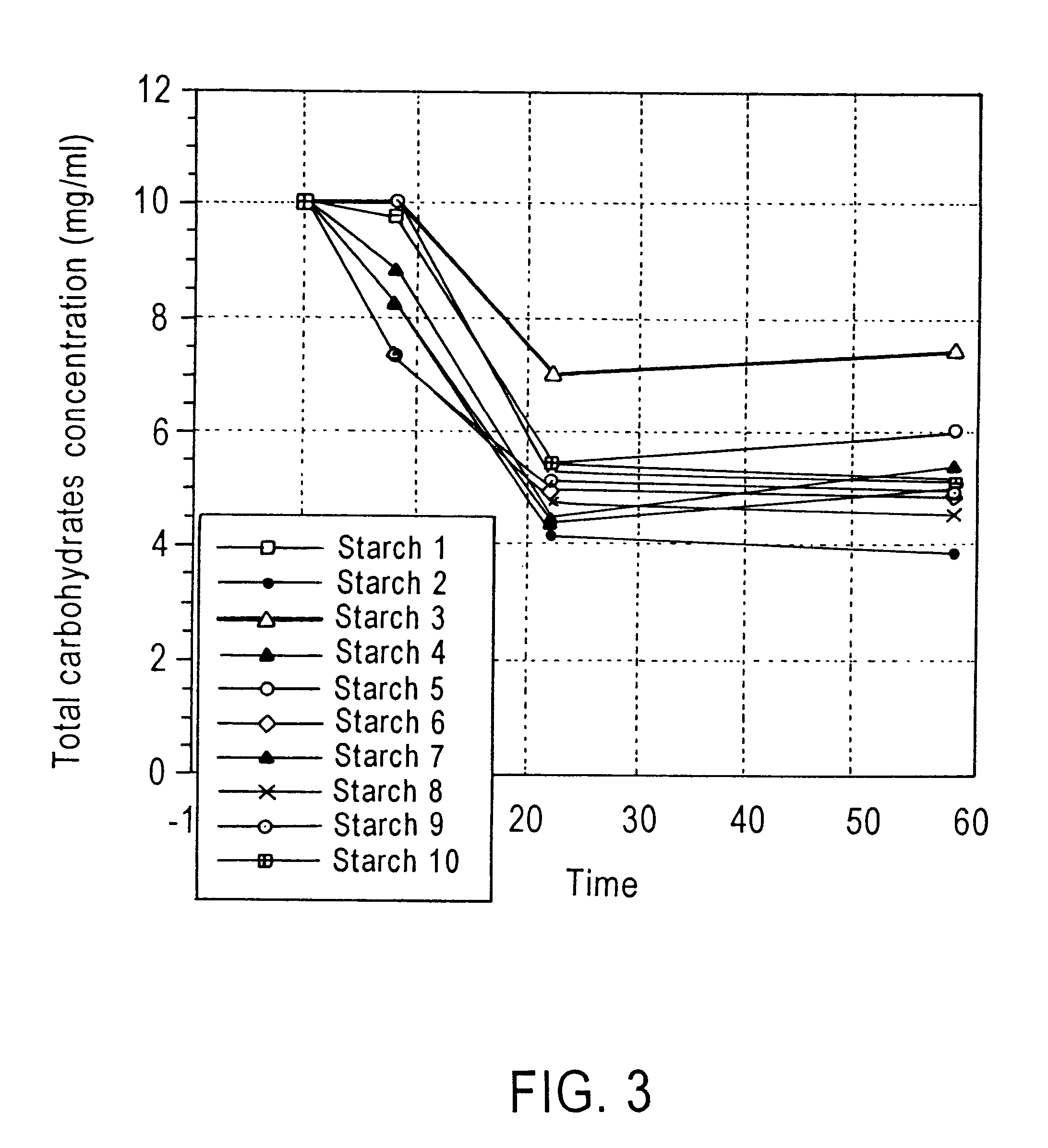
PCT No. PCT / AU95 / 00613 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 17, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 17, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 18, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 08261 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 21, 1996A probiotic composition is disclosed which is particularly useful for inclusion in food products to enhance their nutritional value. The composition comprises one or more probiotic microorganisms such as Bifidobacterium and a carrier to transport the microorganisms to the large bowel or other regions of the gastrointestinal tract. The carrier is a modified or unmodified resistant starch, particularly a high amylose starch, which acts as a growth or maintenance medium for microorganisms in the large bowel or other regions of the gastrointestinal tact.
Owner:PENFORD HLDG +1
Methods and Kits For Administering Probiotics
InactiveUS20080241226A1Improve tolerability and perception of benefitBiocideNervous disorderMedicineDrug loading dose
Methods for administering probiotics comprising the steps of: administering a loading dose of a loading probiotic for a loading time period; and administering a dose of a botanical and / or additional materials for the loading time period are disclosed. The methods also include administering a maintenance dose of a maintenance probiotic, and / or a botanical and / or an additional material for a maintenance time period. Also disclosed are kits for use in administering probiotics.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Probiotic bacteria and methods
InactiveUS20060067924A1Reduce colonizationAssess healthBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsMicroorganismAntibiotic Y
Provided herein are molecular methods for assessing the state of gastrointestinal microflora of an animal, especially a species of poultry, and methods for identifying probiotic bacteria by comparing certain bacteria present in animals fed a diet not containing antibiotics but absent or present in significantly lower numbers in animals fed a diet containing antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Treatment of autism using probiotic composition
A method of treating autism using a probiotic composition including the bacilli (1) Bacillus subtilis, (2) Bacillus coagulans, and (3) Enterococcus faecium. The composition may further include a carrier medium, such as fructo-oligo-saccharides (FOS), as incorporated in a dose form such as a pill, capsule, powder or sachet. The compositions of the invention may be usefully employed as health or nutritional supplements, food additives, or therapeutic agents for combating a wide variety of physiological disorders.
Owner:COBB & ASSOCS
Fruit and vegetable probiotic tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104489646AHigh survival rate of live bacteriaImprove stabilityNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsCelluloseDrug biological activity
The present invention discloses a fruit and vegetable probiotic tablet and a preparation method thereof. The fruit and vegetable probiotic tablet uses probiotic powders such as lactobacillus plantarum powder as the main raw material, and the preparation method scientifically mixes modified dietary fibers, fruit and vegetable powder, oligosaccharides, plant extracts, protein powder, tea leaf extracts and traditional Chinese medicine extracts and etc., thus improves the content of soluble celluloses which are of real significance for probiotic flora, enhances the physiological activity of celluloses, thereby increases the species of intestinal probiotic flora as well as significantly enhances the colonization ability and time of endogenous and exogenous probiotics in the human intestinal tracts, effectively inhibits the growth and reproduction of harmful intestinal bacteria, especially gram-negative bacteria, and fully regulates the composition of the intestinal probiotic flora. The prepared fruit and vegetable probiotic tablet has a high biological activity, a long human intestinal colonization time, and a significant weight loss effect, and is suitable for a wide range of people.
Owner:南京旭优食品技术有限公司
Encapsulation system for protection of probiotics during processing
Comestible products, for example beverage products, are disclosed containing encapsulated probiotic bacteria having resistance to subjection to at least thermal and acidic conditions. Beverage products include at least one aqueous liquid and capsules comprising a gelled mixture of alginate and denatured protein, and probiotic bacteria entrapped within the gelled mixture. The average particle size of the capsules is optionally less than 1000 microns (μm) in diameter, such as less than 500 μm in diameter. Methods are provided for making such encapsulated probiotics by providing a mixture comprising sodium alginate, denatured protein and active probiotic cells, and combining the mixture with a divalent cation to initiate cold gelation of the sodium alginate and denatured protein to form a second mixture. The second mixture is passed through an opening having a diameter of less than 1000 μm to form capsules. The weight ratio of protein to alginate is from 1:1 to 9:1.
Owner:PEPSI COLA TECHNICAL OPERATIONS INC +1
Probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacteria and uses thereof
InactiveUS7708988B2Good curative effectMitigating deleterious side-effectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseMicrobial agent
The present invention discloses compositions and methodologies for the utilization of probiotic organisms in therapeutic compositions. More specifically, the present invention relates to the utilization of one or more species or strains of lactic acid-producing bacteria, preferably strains of Bacillus coagulans, for the control of gastrointestinal tract pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant gastrointestinal tract pathogens, and their associated diseases by both a reduction in the rate of colonization and the severity of the deleterious physiological effects of the colonization of the antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In addition, the present invention relates to the utilization of therapeutic compounds comprised of lactic acid-producing bacteria and anti-microbial agents such as antibiotics, anti-fungal compounds, anti-yeast compounds, or anti-viral compounds. The present invention also discloses methodologies for: (i) the selective breeding and isolation of probiotic, lactic acid-producing bacterial strains which possess resistance or markedly decreased sensitivity to anti-microbial agents (e.g., antibiotics, anti-fungal agents, anti-yeast agents, and anti-viral agents); and (ii) treating or preventing bacteria-mediated infections of the gastrointestinal tract by use of the aforementioned probiotic bacterial strains with or without the concomitant administration of antibiotics. While the primary focus is on the treatment of gastrointestinal tract infections, the therapeutic compositions of the present invention may also be administered to buccal, vaginal, optic, and like physiological locations.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Targeted gastrointestinal tract delivery of probiotic organisms and/or therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20160022592A1Improve imbalanceAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to the development of a targeted delivery system for the oral delivery of probiotics or therapeutic agent for various indications, including and not limited to active and prophylaxis treatment of Clostridium difficile infection, antibiotic associated diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, intestinal flora replacement, supplemental flora treatments for patients taking antibiotics, and for restoration of balance and signaling between the intestinal microbiome and the intestinal cells in patients under treatment of metabolic syndrome manifestations, specifically diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, hyperlipidemia and hypertension.
Owner:THERABIOME
Novel compound microorganism living bacteria agent, method for preparing same and applications
The invention discloses a novel compound microorganism living bacteria agent. The agent comprises probiotics such as pediococcus, saccharomyces, bacillus and the like, wherein the total bacterial quantity is above 107 colony-forming units (cfu) / gram. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the novel compound microorganism living bacteria agent and applications of the novel compound microorganism living bacteria agent in preparation of organic sewage purification additives, deodorization fly dispelling agents, degreasing agents, pipeline blockage removing agents, feed additives and microorganism disease prevention agents. The novel compound microorganism living bacteria agent has the comprehensive effects of high removal rates to ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus, small sludge residues, energy saving, environmental friendliness and the like and the characteristics of convenience in use, safety and quickness in function, no secondary pollution, benefits to ecological protection, low treatment cost, good comprehensive profit and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI ECO WELL BIOSCI
Hygiene product with a probiotic composition
InactiveUS20040243076A1Simple preparation processExtended shelf lifeSanitary towelsBaby linensBacterial strainTampon
A hygiene product, such as a sanitary napkin, diaper, panty liner, tampon, incontinence guard, hygiene tissue and the like, includes a probiotic composition having a bacterial preparation of at least one lactic acid producing bacterial strain and a contact sorption drying carrier dispersed in a lipid phase. A method for producing a hygiene product with lactic acid producing bacteria, dried with the aid of contact sorption drying carriers, in a lipid phase is provided. The manufacturing process for the hygiene product has the advantages of economy, simplicity and bacterial survival during manufacturing and subsequent storage.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Infant milk powder added with biostime and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101449708AAdvantage maintenanceColonization fastMilk preparationFood preparationTreatment effectVegetable oil
The invention discloses an infant milk power added with synbiotics, comprising the following components: fresh milk 40-68 gram; demineralized whey powder 15-34 gram; granulated sugar3-6 graml; vegetable oil 4-8 gram; compound prebiotics 0.4-20 gram; compound probiotic 1.0*10<5>-1.0*10<11> cfu. The inventive infant milk power can be ysed for building advantages of beneficial bacterium when a newborn infant starts colony valuation. Through adding probiotic, the number of probiotic is advanced to increase in a short time, through adding prebiotics having selectively increasing effect on probiotic, the added probiotic is performed with fast field setting, thereby maintaining advantages of probiotic in intestinal flora. The invention also markedly relieves diarrhoetic symptoms, and has definite treatment effect on diarrhea caused by rotavirus.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGLIVE BIO TECH CO LTD
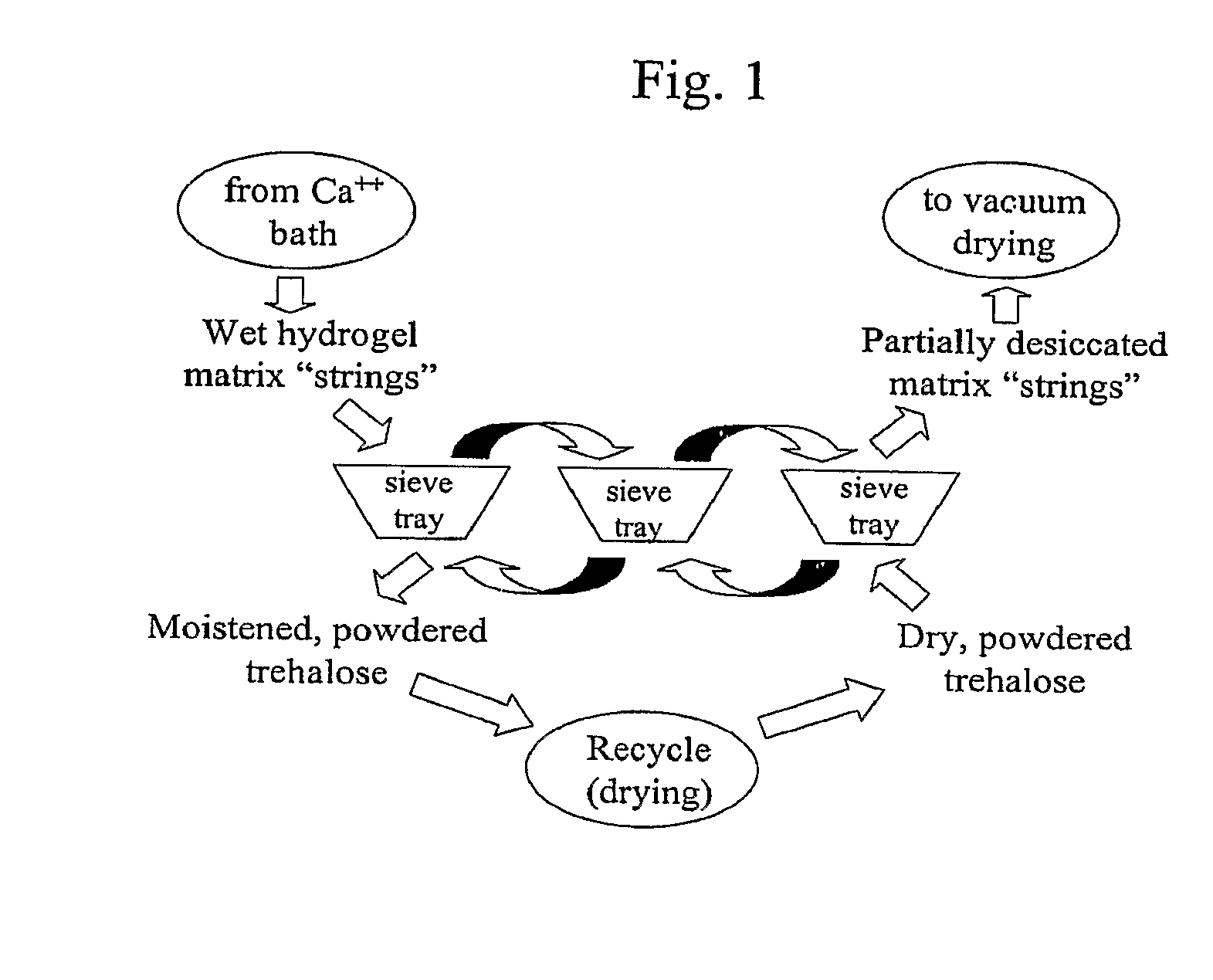
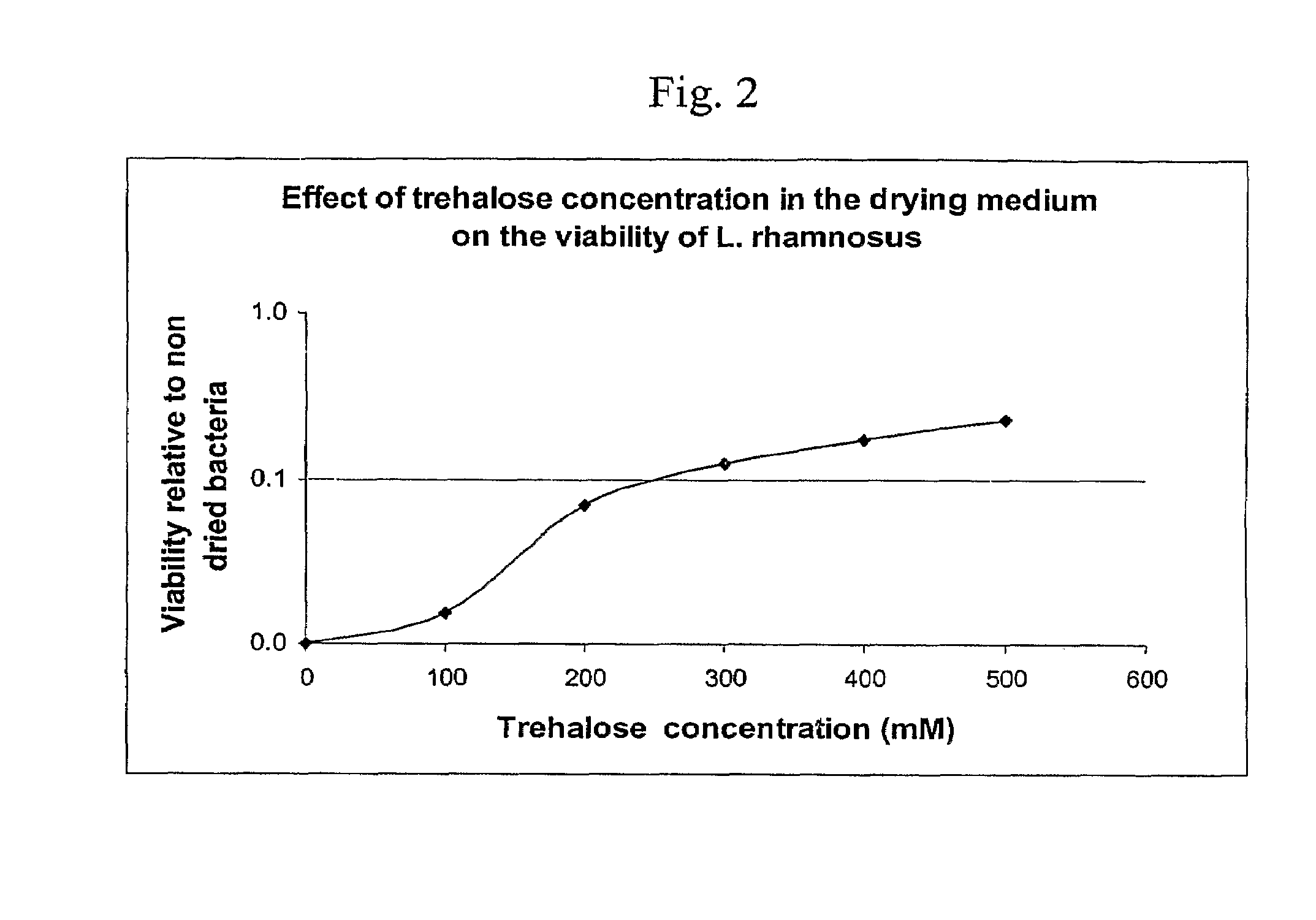
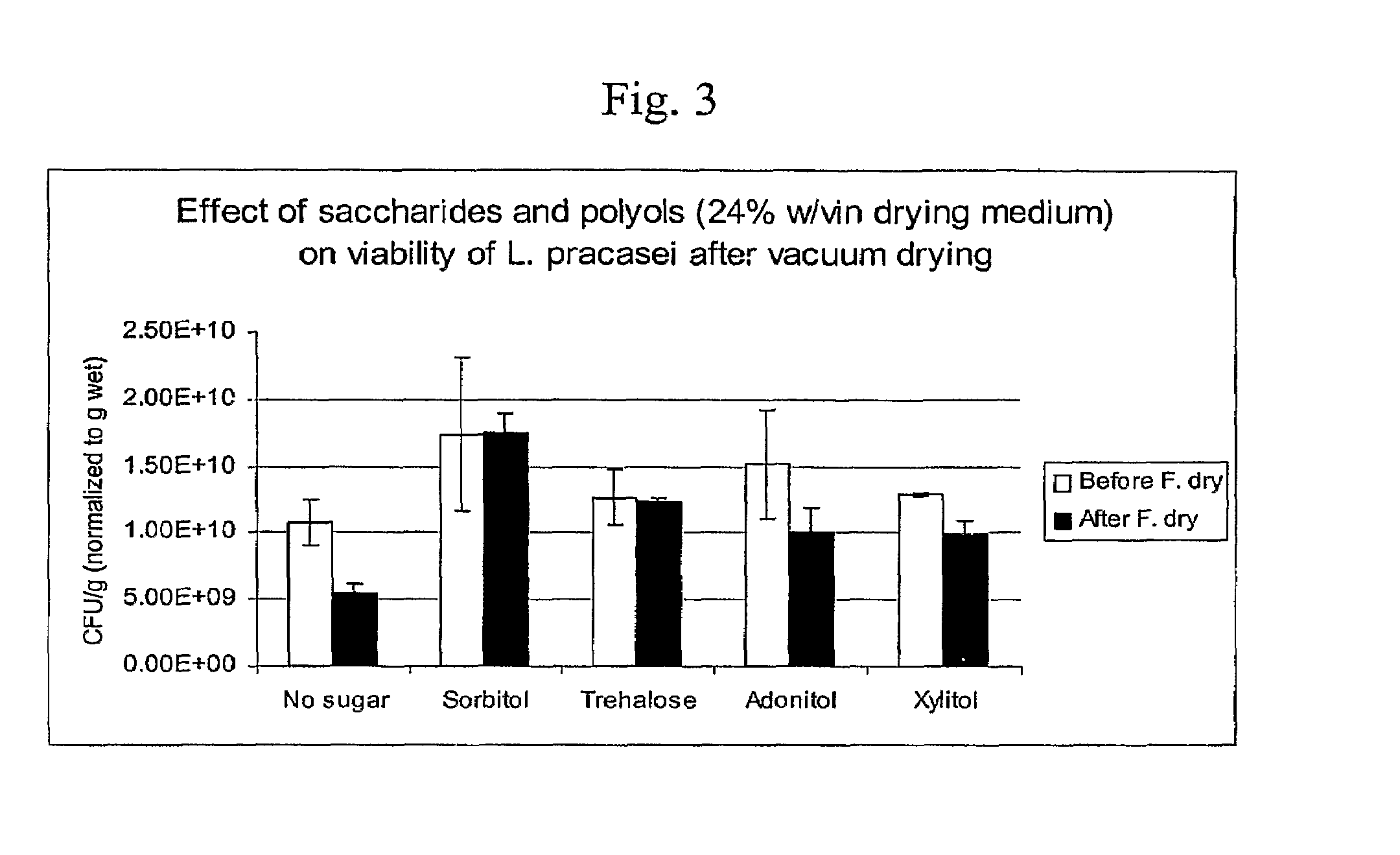
Delivery vehicle for probiotic bacteria comprising a dry matrix of polysaccharides, saccharides and polyols in a glass form and methods of making same
ActiveUS8097245B2Promote digestionOverall firmnessBiocideSugar food ingredientsPolyolDelivery vehicle
The disclosure relates to a solid glass matrix of polysaccharide, saccharides and polyols as delivery vehicle for preservation and post gastric administration of a probiotic. The delivery vehicle is capable of releasing the probiotic at their site of action. The present invention further includes methods of making and using the solid glass matrix delivery vehicle of the invention.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
Food Containing a Probiotic and an Isolated Beta-Glucan and Methods of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20080193485A1Reduce allergiesReduce colonizationAntibacterial agentsBiocideNatural sourceDisease
The invention features a food product containing a probiotic and β-glucan isolated from a natural source, methods of treating a disease or disorder by administering the food product, and a package containing separated components of the food product.
Owner:GORBACH SHERWOOD L +1
Heat resistant probiotic compositions and healthy food comprising them
Owner:DEGAMA PROBIOTICS +1
Synbiotic mixture
This invention relates to a preparation comprising a probiotic bacterial strain and a prebiotic mixture comprising 5-70 wt % of at least one N-acetylated oligosaccharide selected from the group comprising Ga1NAcα1,3Ga1β1,4G1c and Ga1β1,6Ga1NAcα1,3Ga1β1,4G1c, 20-95 wt % of at least one neutral oligosaccharide selected from the group comprising Ga1β1,6Ga1, Ga1β1,6Ga1β1,4G1c Ga1β1,6Ga1β1,6G1c, Ga1β1,3Ga1β1,3G1c, Ga1β1,3Ga1β1,4G1c, Ga1β 1,6Ga1β 1,6Ga1β 1,4G1c, Ga1β 1,6Ga1β 1,3Ga1β 1,4GIc Ga1β 1,3Ga1β 1,6Ga1β 1,4GIc and Ga1β1,3Ga1β1,3Ga1β1,4G1c and 2-50 wt % of at least one sialylated oligosaccharide selected from the group comprising NeuAcα2,3Ga1β1,4G1c and NeuAcα2,6Ga1β1,4G1c. The invention extends to food products comprising said preparation and to the use of the preparation in the prevention and treatment of infections.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com