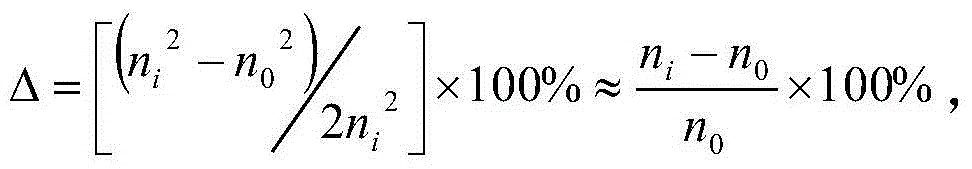Patents
Literature
583 results about "Glass matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antifouling coating composition
The antifouling composition of the present invention includes a glassy matrix formed by crosslinking a mixture of a silanol-terminated silicone and an alkoxy functionalized siloxane to provide an interpenetrating polymer network of glass and silicone and at least two materials capable of microphase separation, at least one of which is graftable to the glassy matrix.
Owner:MICROPHASE COATINGS
Solid oxide fuel cell sealant comprising glass matrix and ceramic fiber and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050147866A1Efficiently prevent and minimize viscous flowAccurate locationTime-programme switchesFinal product manufactureFiberFuel cells
Sealant compositions particularly suitable for solid oxide fuel cell sealant are provided and preferably comprise glass matrix and ceramic fiber, wherein glass matrix and ceramic fiber are mixed in an volume ratio of 25:75-75:25 in the sealant, and the ceramic fibers are preferably uniformly dispersed in the sealant to exhibit an orientation. Methods to manufacture the sealant compositions also are provided. Particularly preferred sealant compositions of the invention can efficiently avoid undesired viscous flow of glass matrix, precisely locate the stack of fuel cell on the region to be sealed, and maintain uniform sealing ability under various changes in size of the fuel cell stack.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
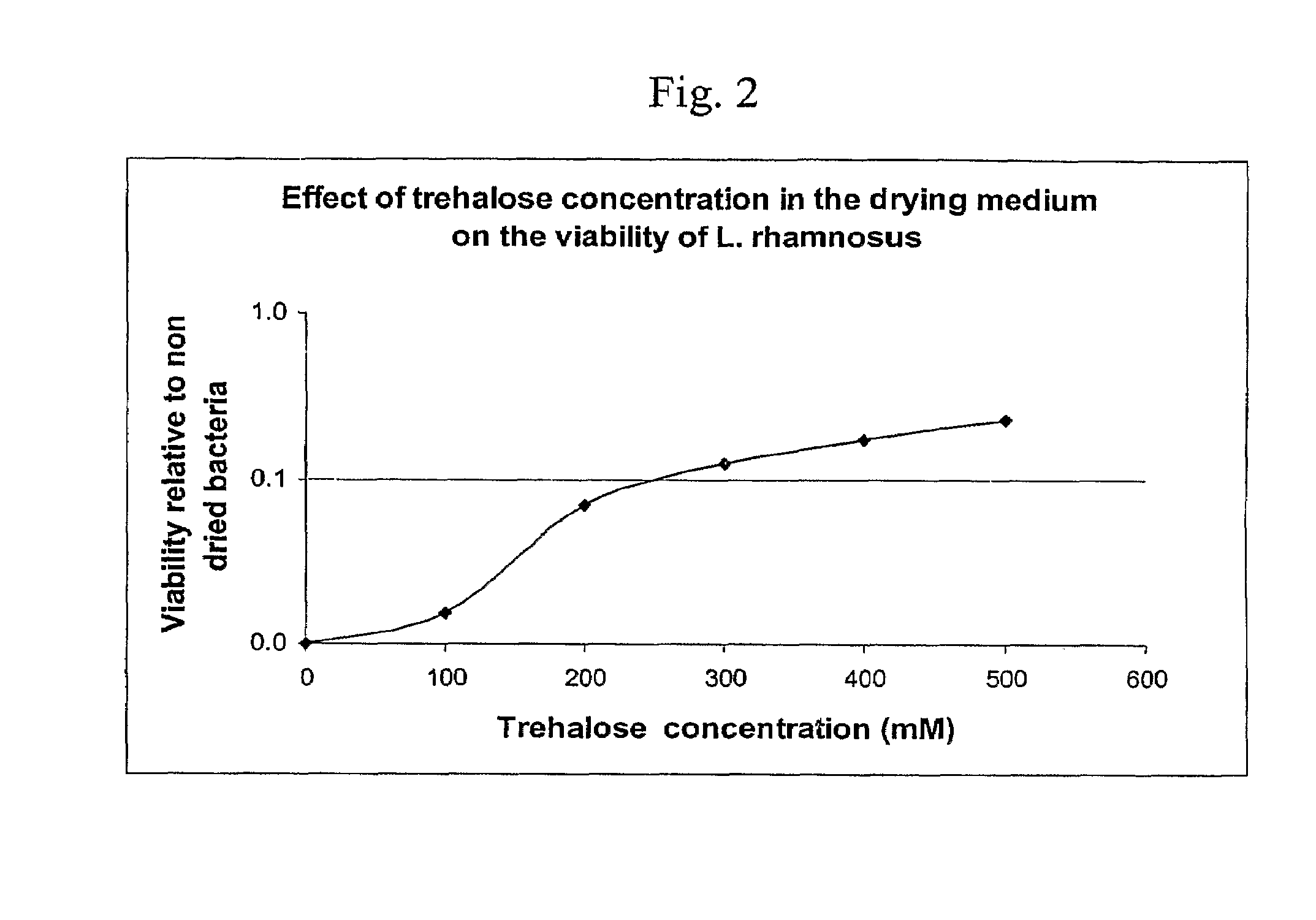
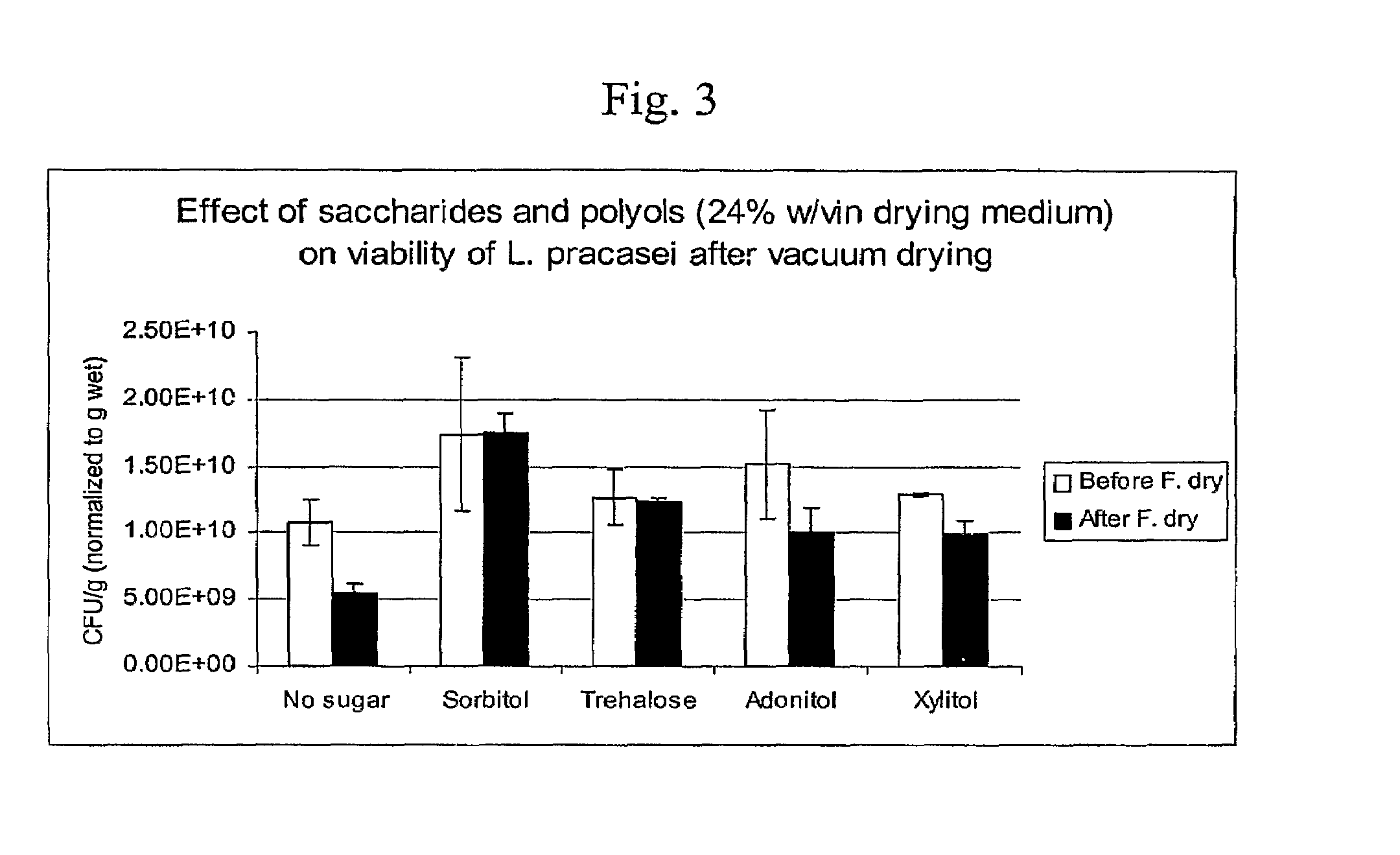
Delivery vehicle for probiotic bacteria comprising a dry matrix of polysaccharides, saccharides and polyols in a glass form and methods of making same
ActiveUS8097245B2Promote digestionOverall firmnessBiocideSugar food ingredientsPolyolDelivery vehicle
The disclosure relates to a solid glass matrix of polysaccharide, saccharides and polyols as delivery vehicle for preservation and post gastric administration of a probiotic. The delivery vehicle is capable of releasing the probiotic at their site of action. The present invention further includes methods of making and using the solid glass matrix delivery vehicle of the invention.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
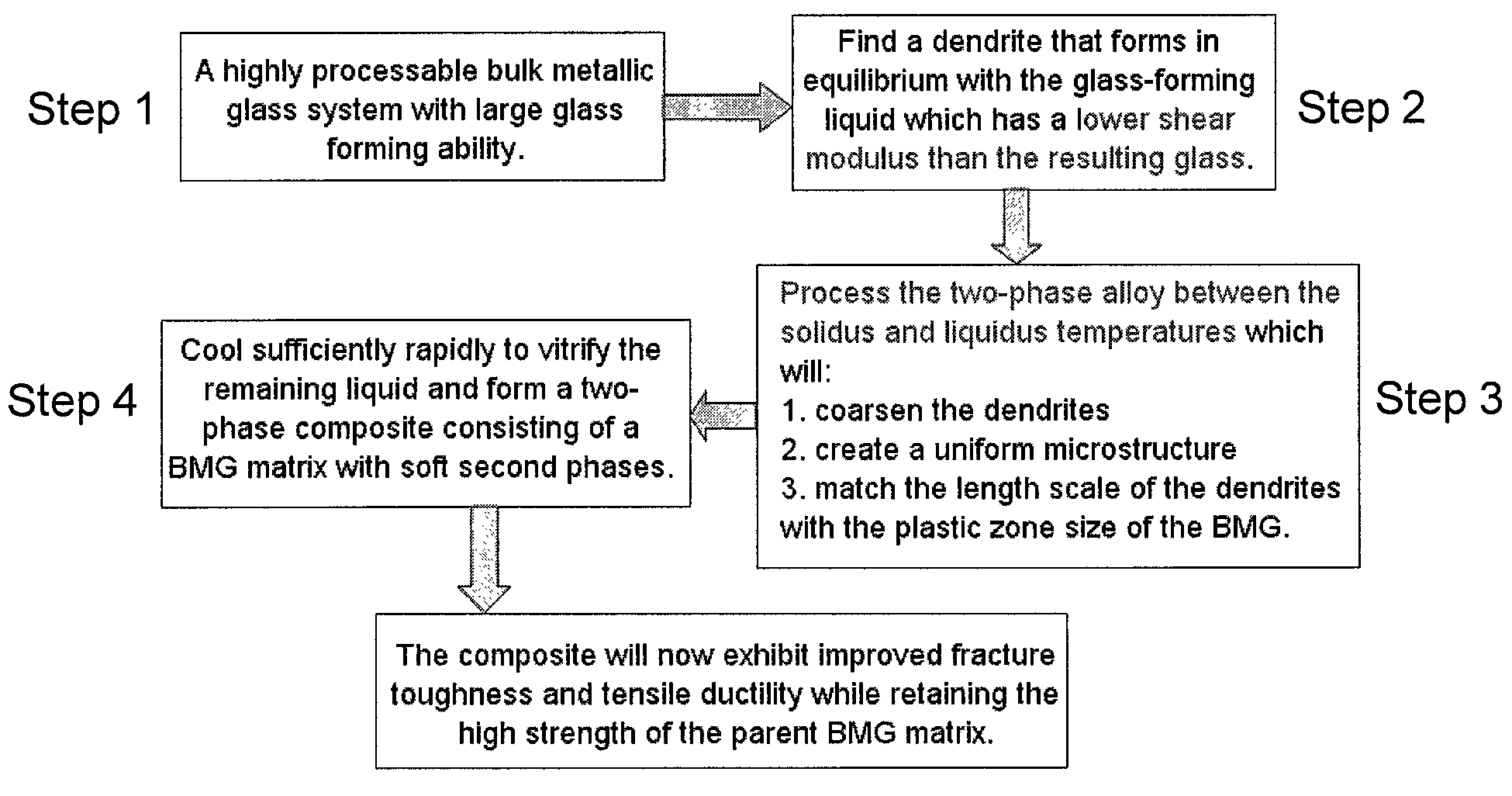
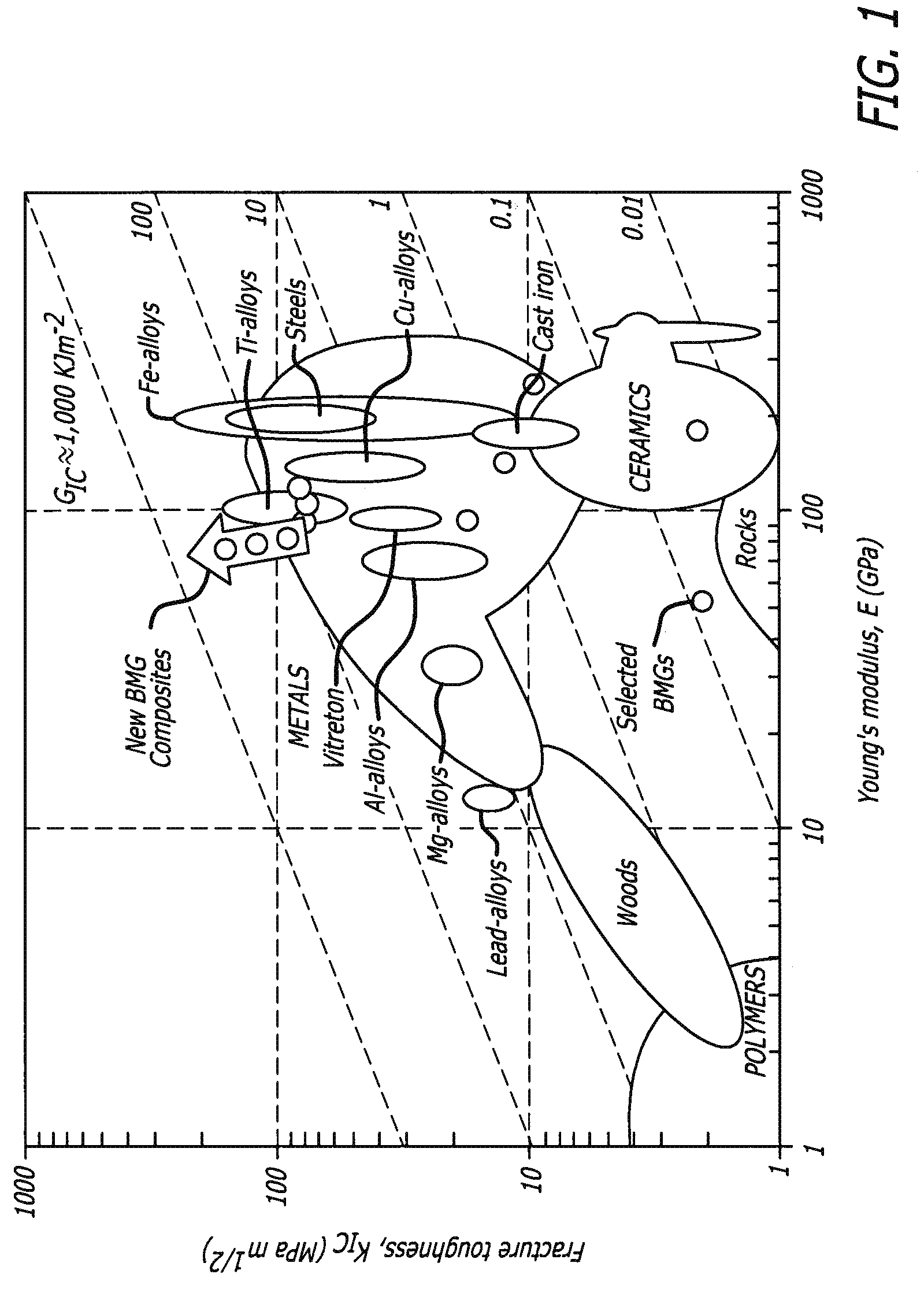
Semi-solid processing of bulk metallic glass matrix composites
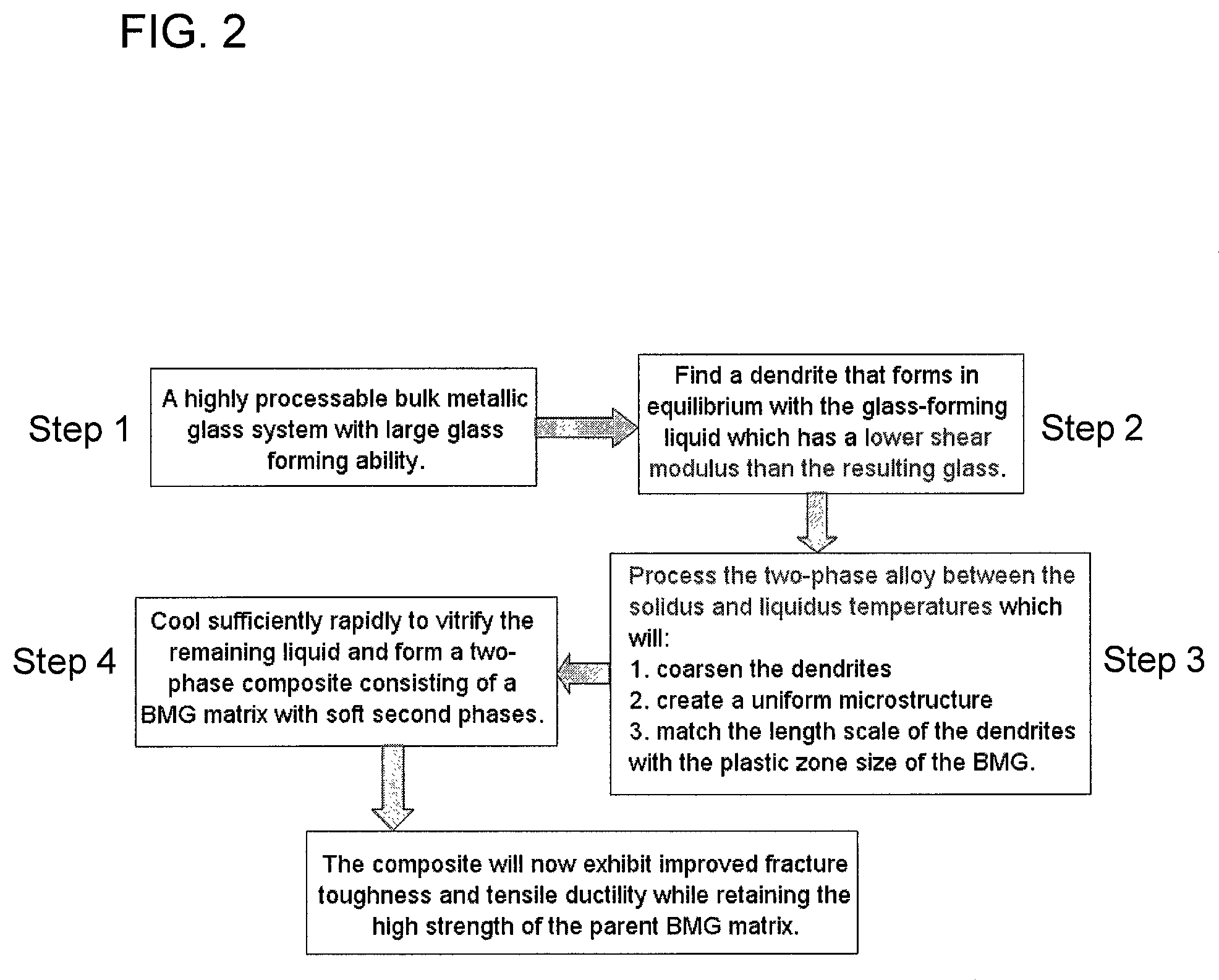
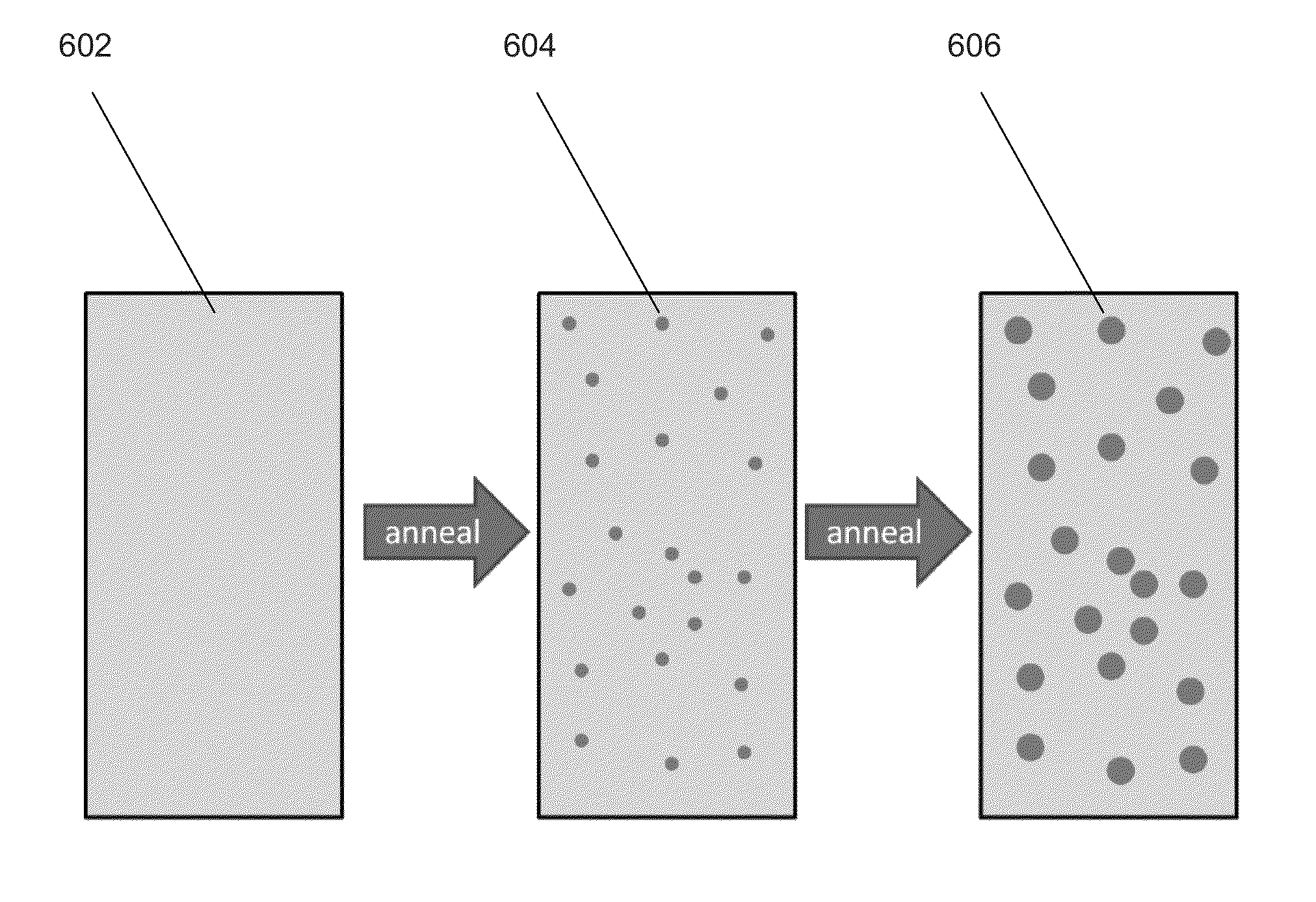
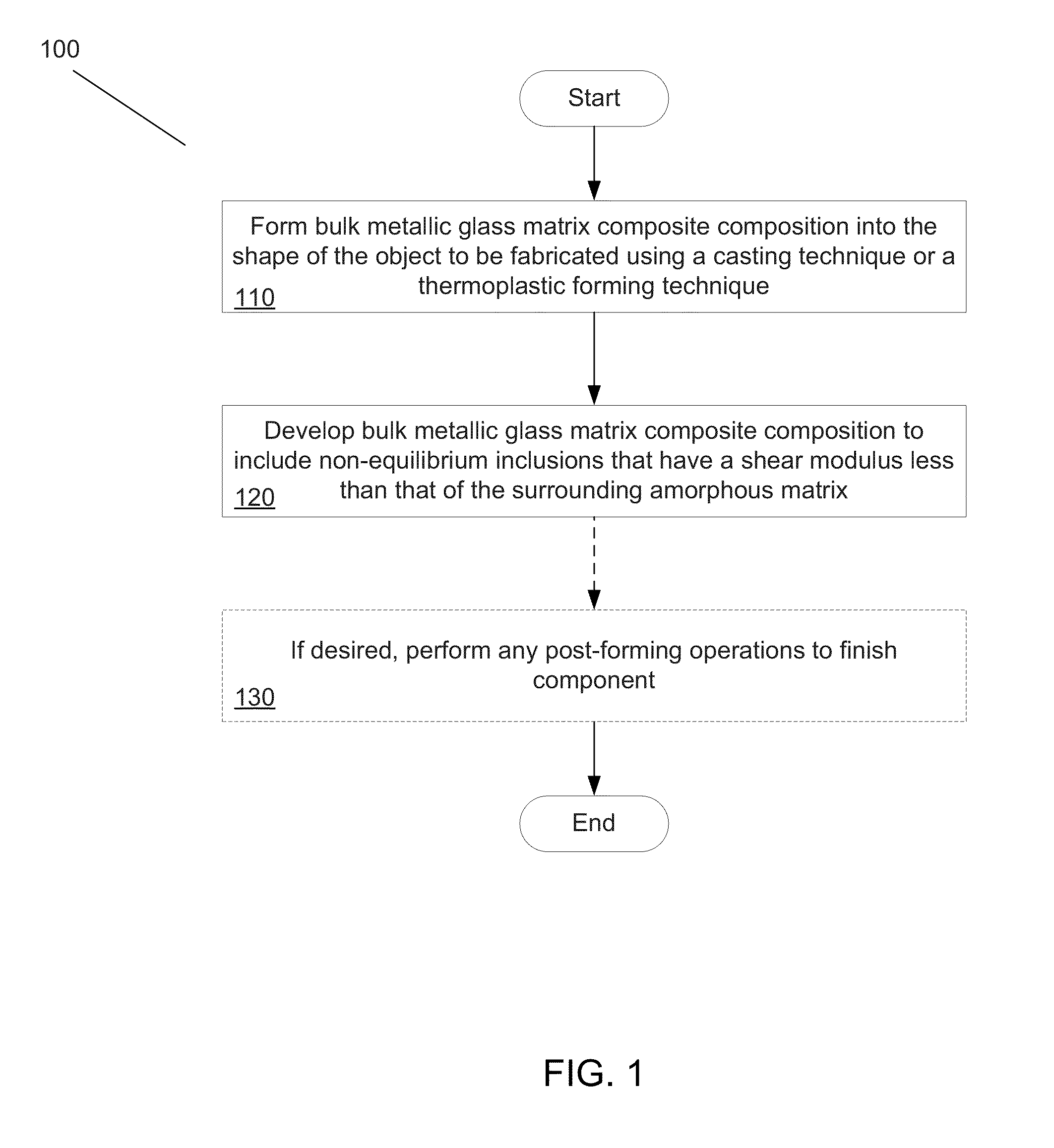
A method of forming bulk metallic glass engineering materials, and more particularly a method for forming coarsening microstructures within said engineering materials is provided. Specifically, the method forms ‘designed composites’ by introducing ‘soft’ elastic / plastic inhomogeneities in a metallic glass matrix to initiate local shear banding around the inhomogeneity, and matching of microstructural length scales (for example, L and S) to the characteristic length scale RP (for plastic shielding of an opening crack tip) to limit shear band extension, suppress shear band opening, and avoid crack development.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Process for preparing a glass-ceramic body
ActiveUS20140141960A1Improve distributionIncrease bodyDentistry preparationsMedical preparationsVitreous BodiesNucleation
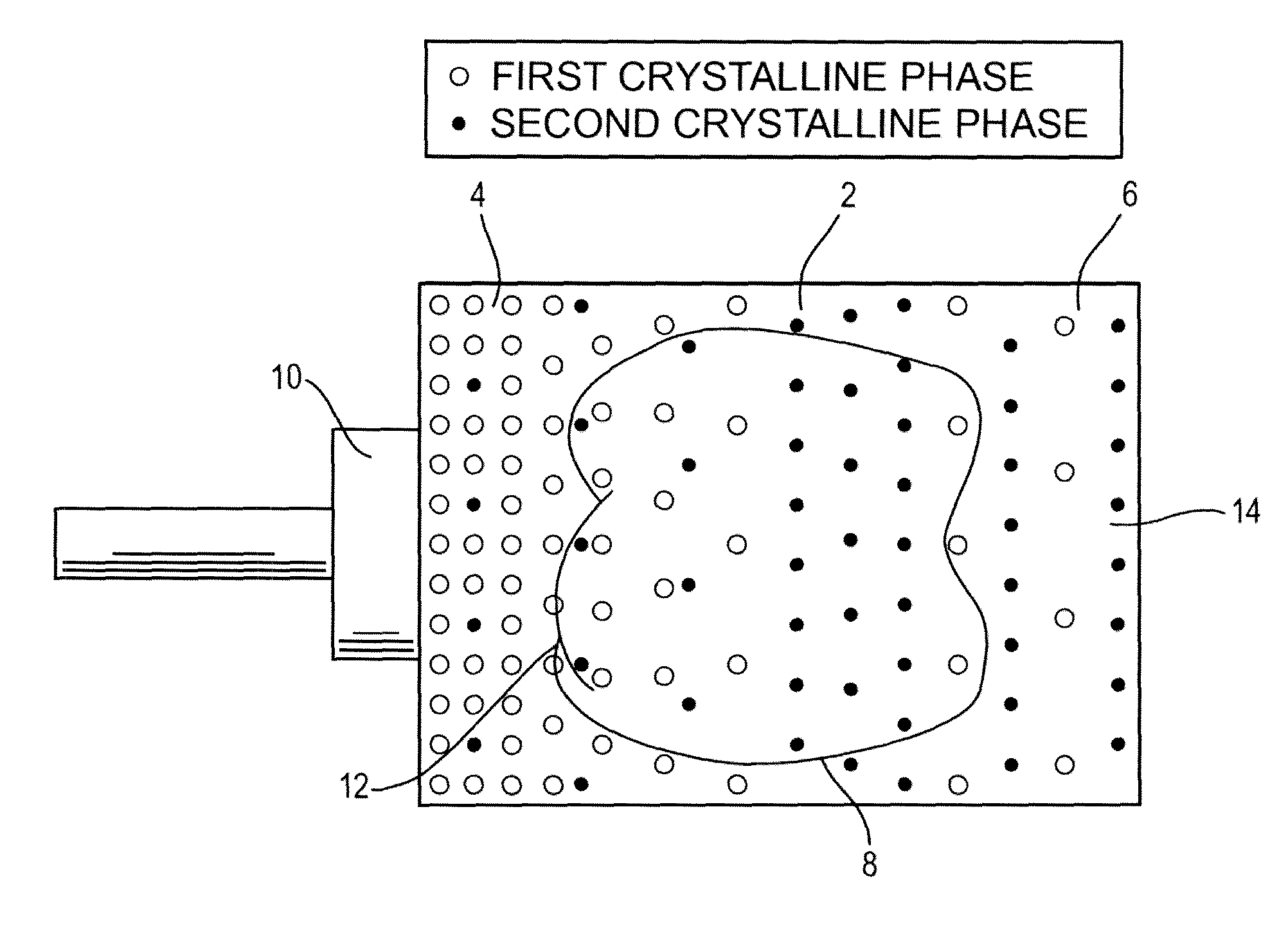
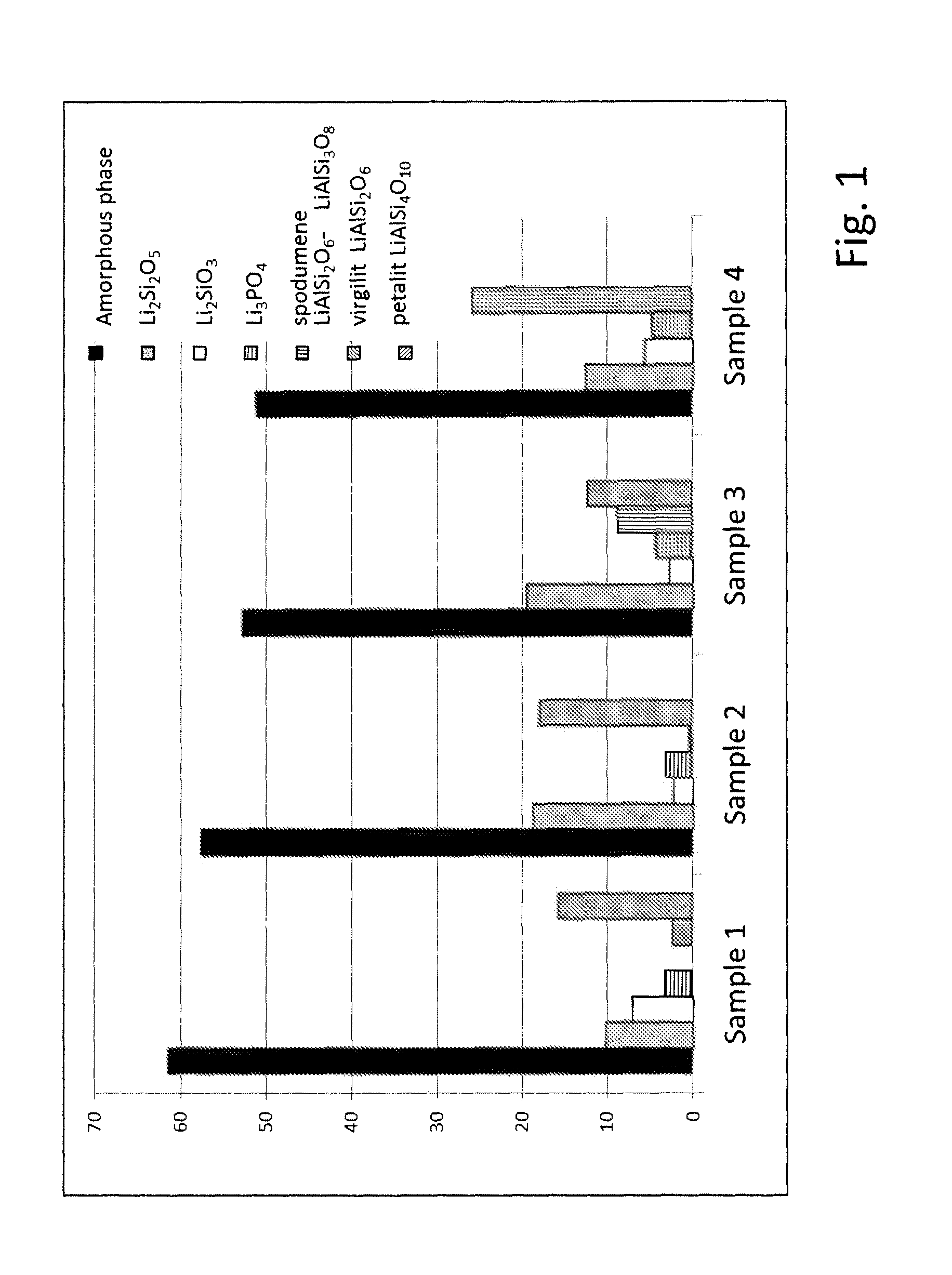
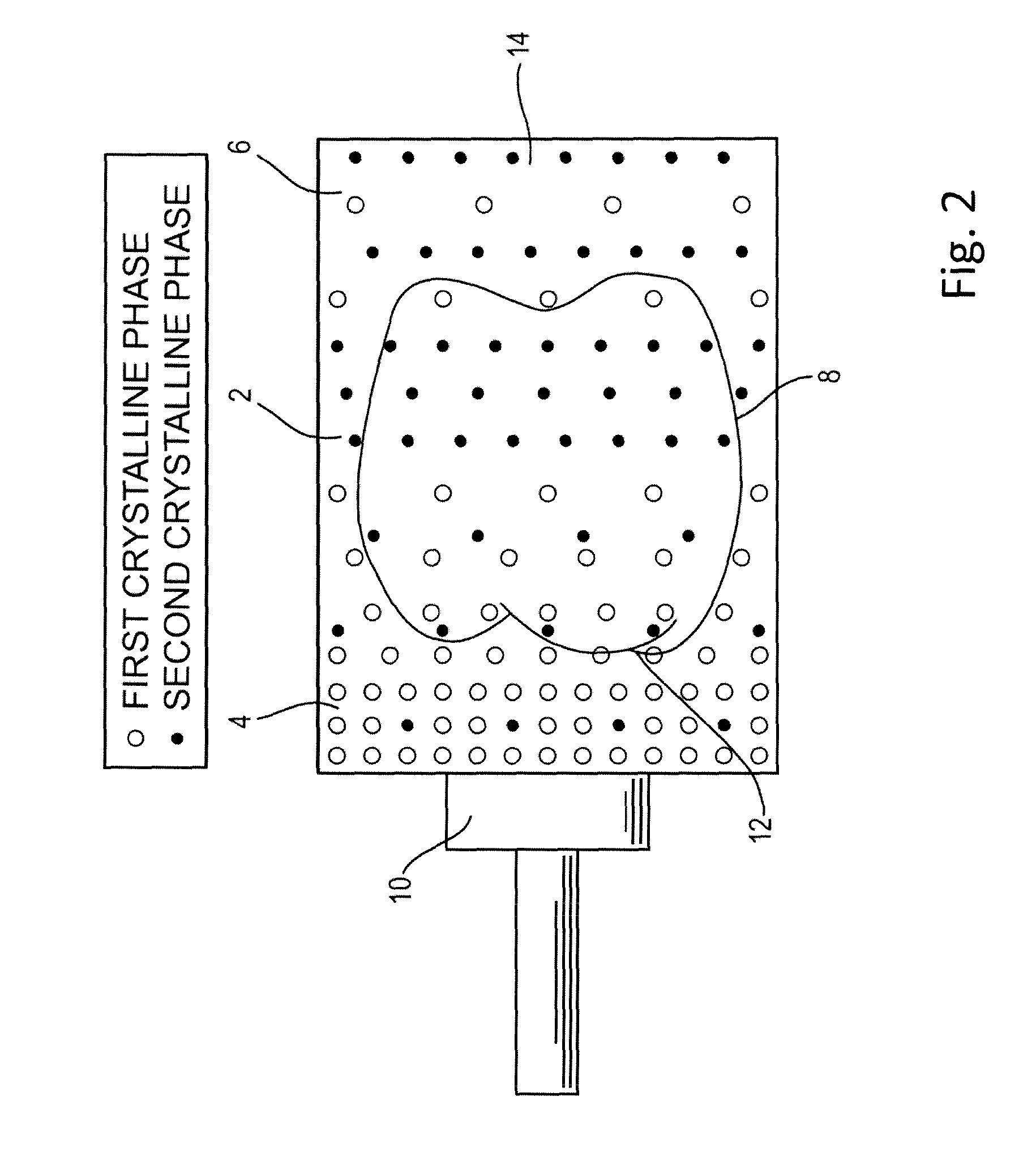
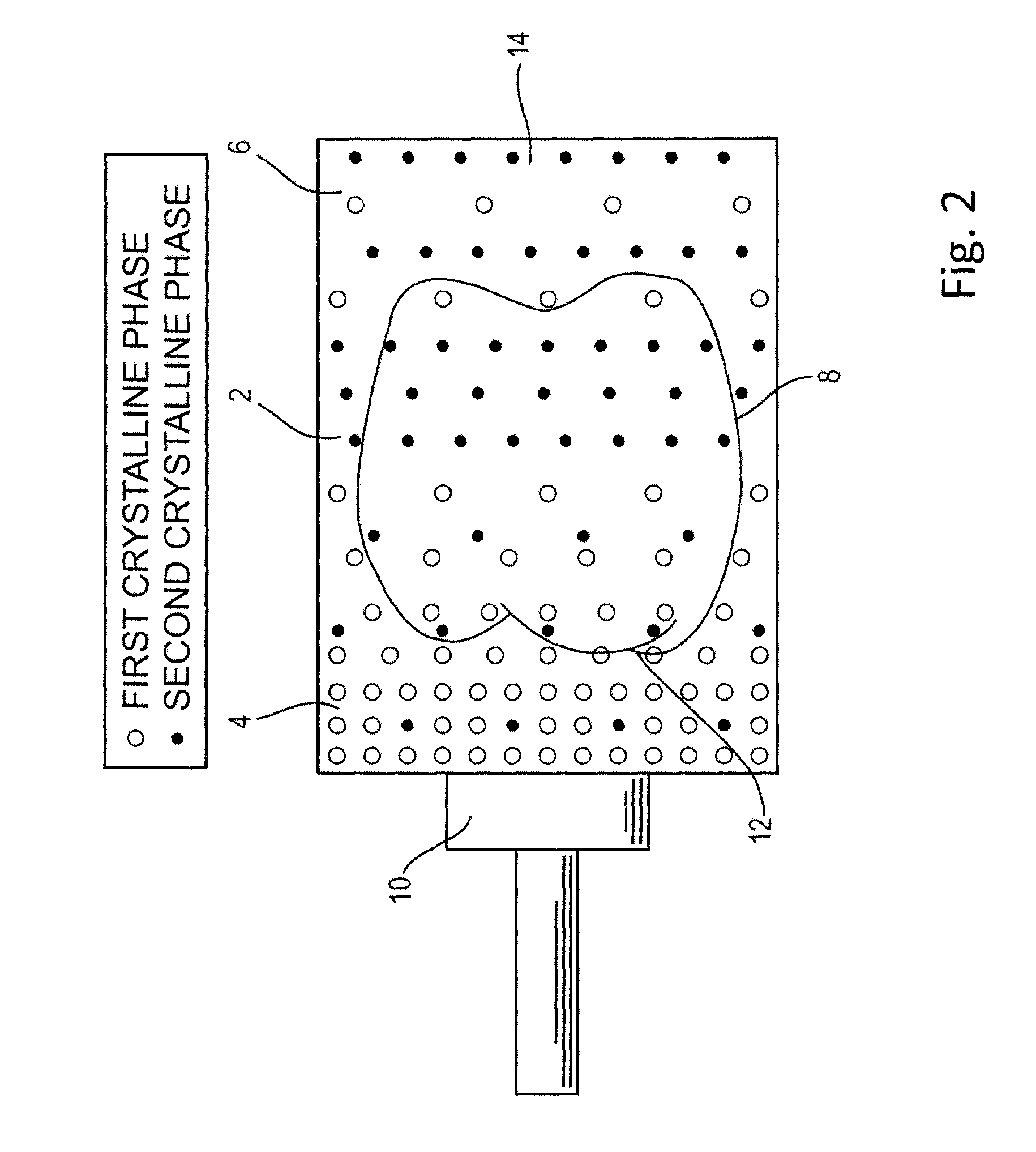
Process for preparing glass-ceramic body including the steps of providing a basic glass body and subjecting the basic glass body to a thermal treatment whereby a crystalline phase embedded in a glass matrix is formed. The basic glass body is made of a composition comprising 65 to 72 wt-% SiO2, at least 10.1 wt-% Li2O and at least 10.1 wt-% Al2O3 based on the total weight of the composition, the proportion of Li2O to Al2O3 being from 1:1 to 1.5:1. The thermal treatment involves a nucleation step followed by several crystallization steps at different temperatures, whereby at least two different crystalline phases are formed.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
Method for stably incorporating substances within dry, foamed glass matrices
Owner:QUADRANT DRUG DELIVERY
Method of forming inorganic pigments
The present invention provides a method of forming inorganic pigments using one or more metal alloys. Metal alloys used in the method of the invention are preferably milled to a mean particle size of less than about 10 microns, may be mixed with other metal oxides, and calcined in the presence of oxygen in a rotary kiln. Inorganic pigments formed in accordance with the method of the invention can be used in a wide variety of applications, including the coloration of glass matrixes, ceramic bodies, polymers, and paints.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Water-dispersible nanoparticles having high luminous efficiency and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20090315446A1High PL efficiencyImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensWater dispersibleOrganic solvent
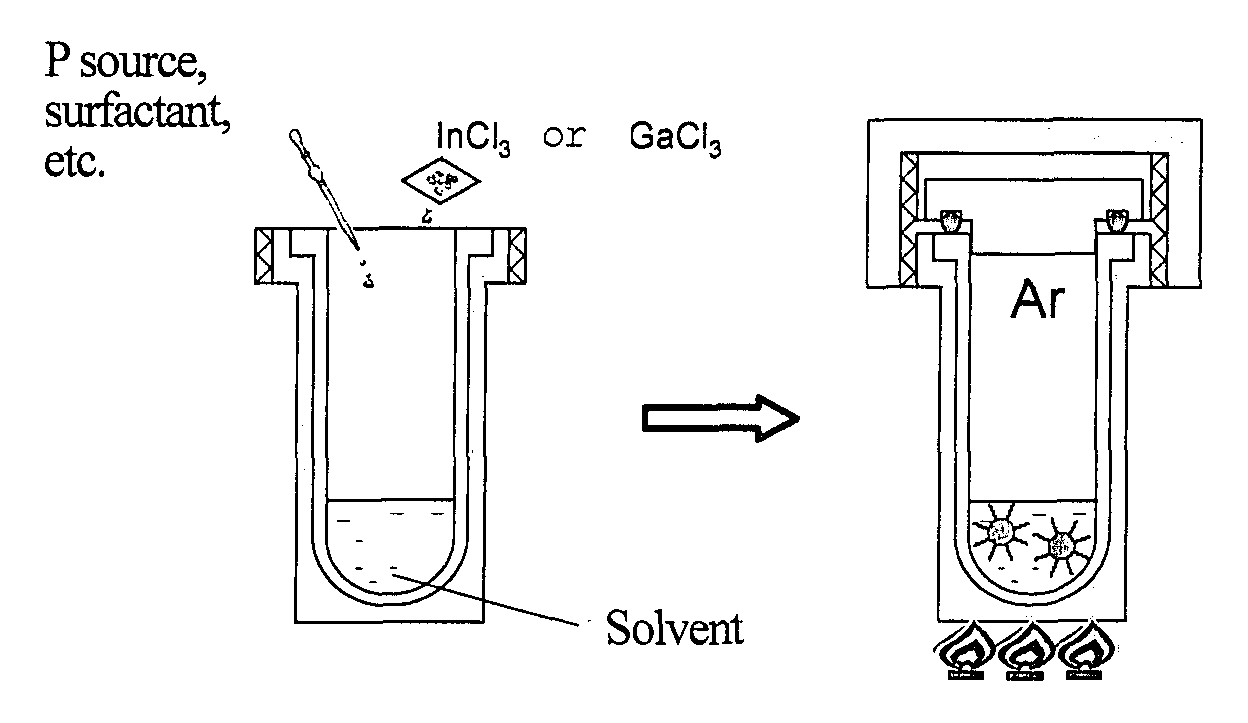
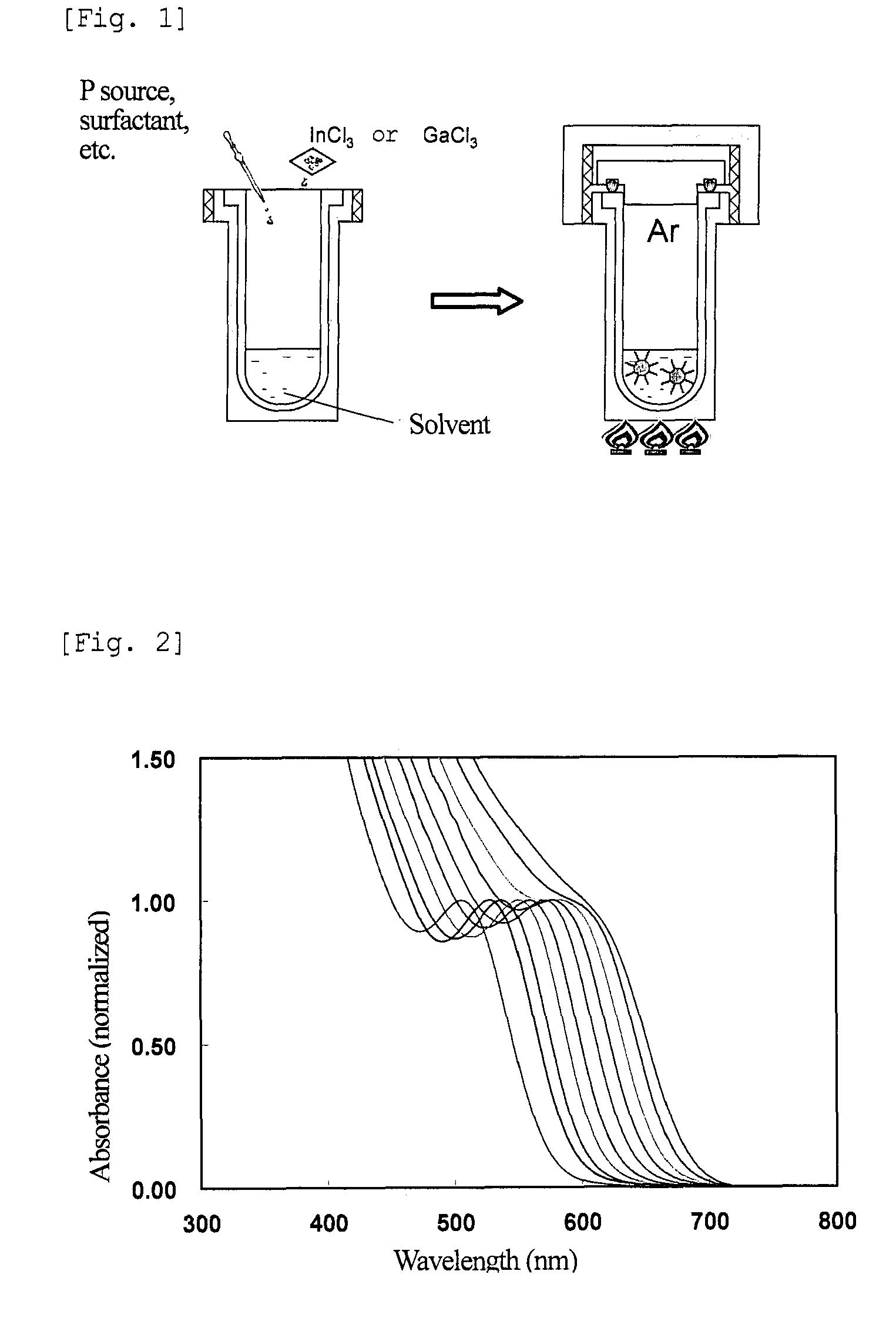
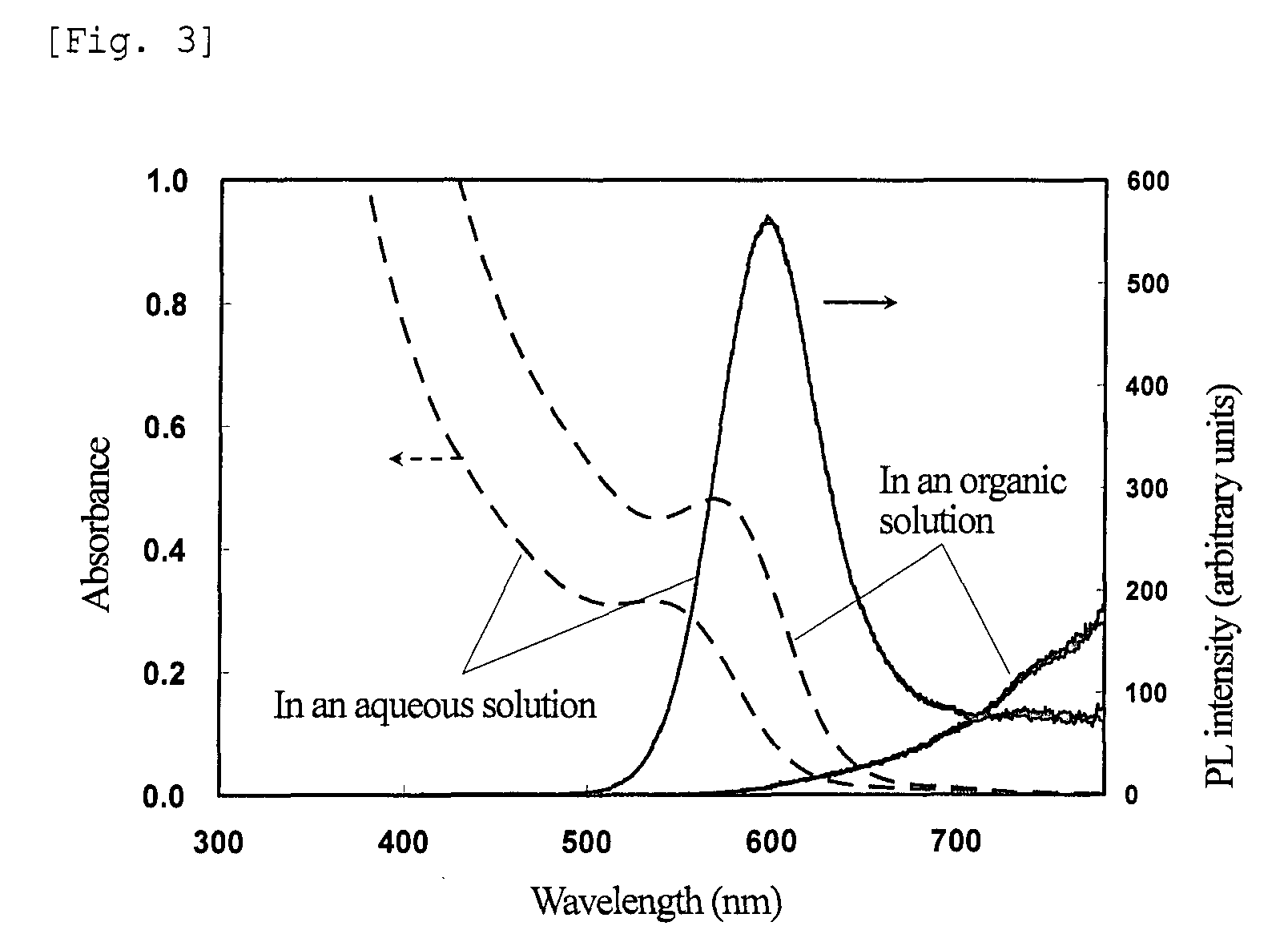
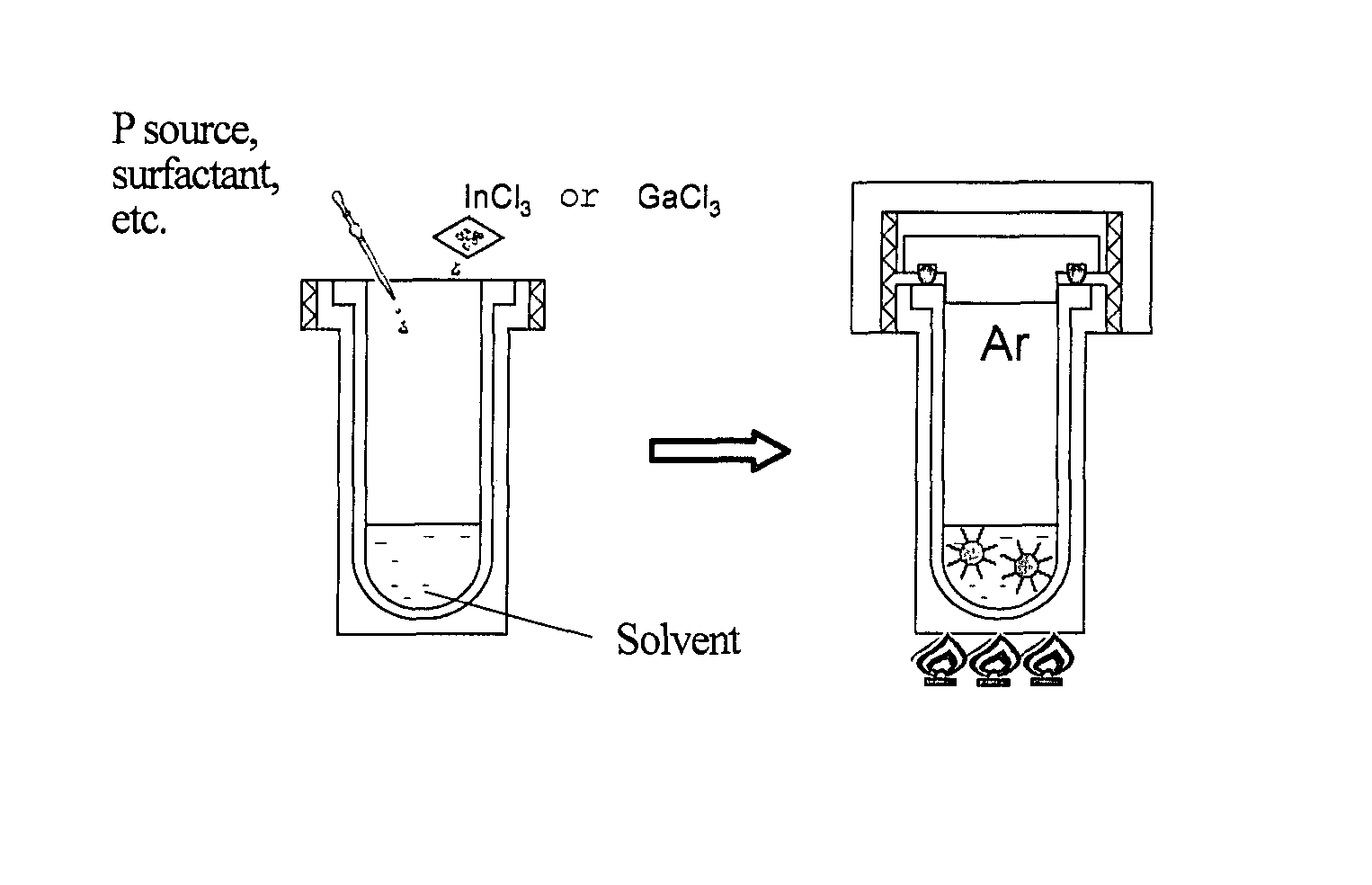
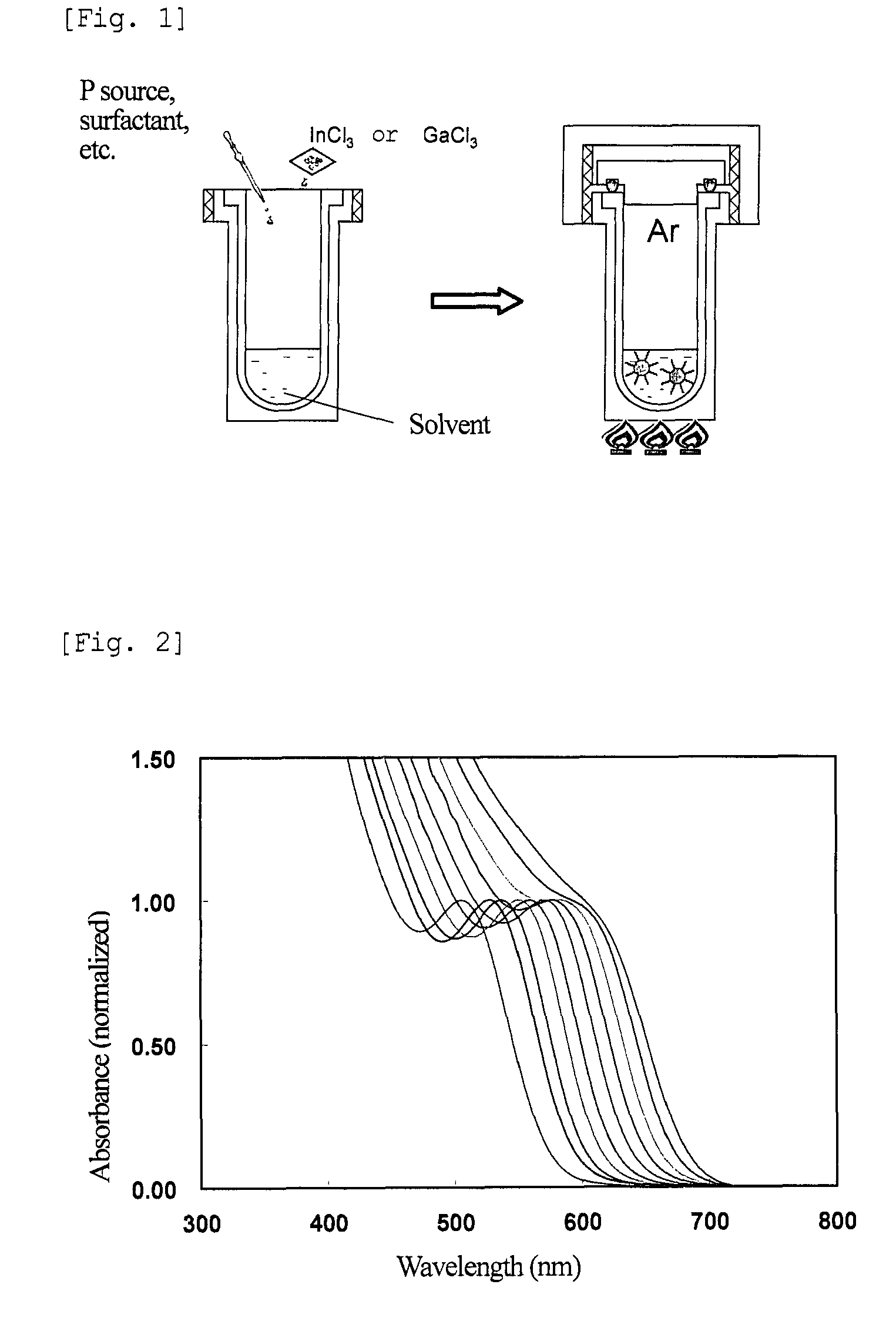
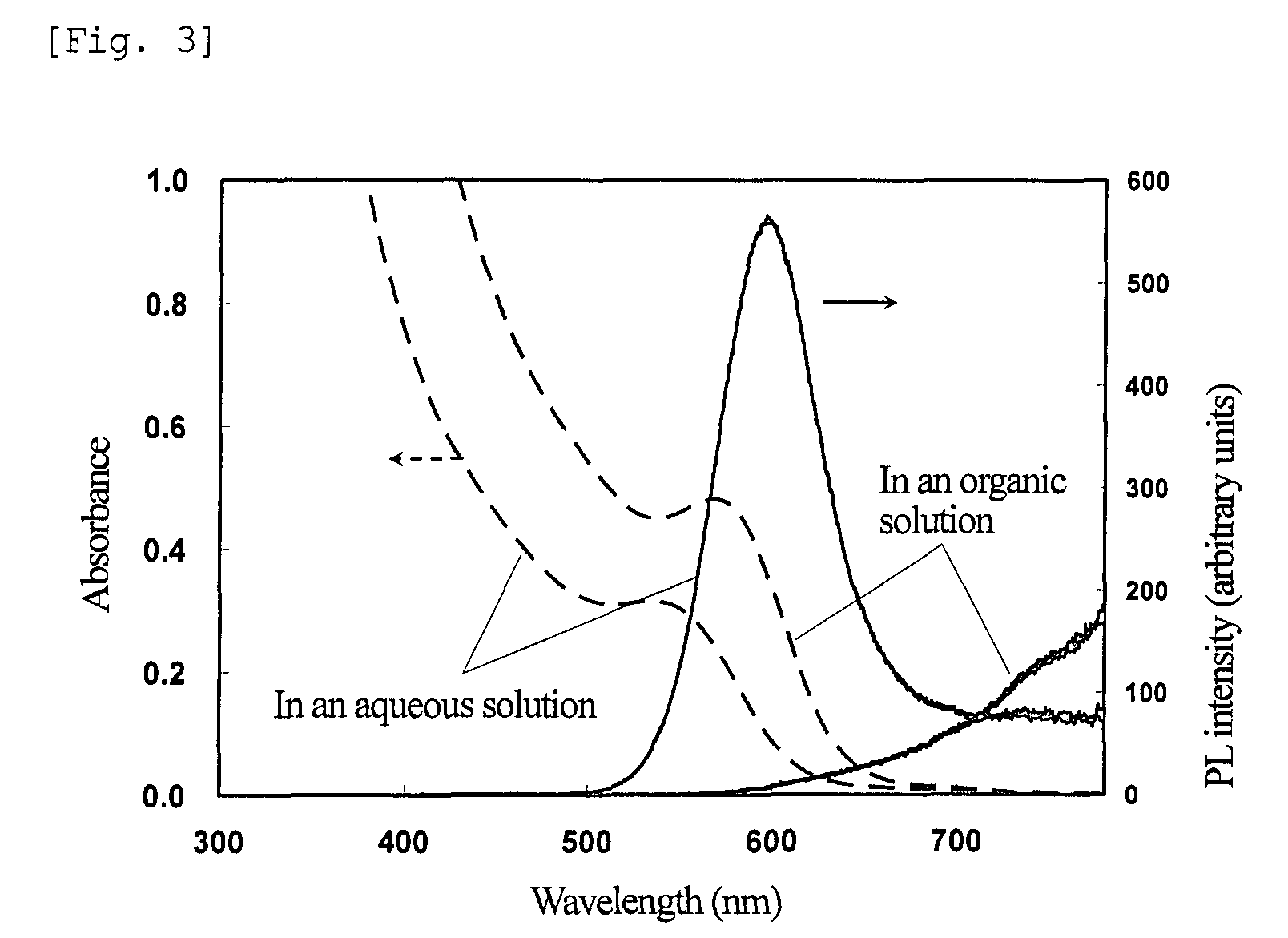
The present invention provides nanoparticles having a core / shell structure consisting of a core comprising a Group III element and a Group V element at a molar ratio of the Group III element to the Group V element in the range of 1.25 to 3.0, and a shell comprising a Group II element and a Group VI element and having a thickness of 0.2 nm to 4 nm, the nanoparticles having a photoluminescence efficiency of 10% or more and a diameter of 2.5 to 10 nm; a method of producing the water-dispersible nanoparticles comprising bringing a dispersion of III-V semiconductor nanoparticles in an organic solvent into contact with an aqueous solution of a Group II element-containing compound and a Group VI element-containing compound to thereby transfer the III-V semiconductor nanoparticles of the organic solvent dispersion to the aqueous solution, and then irradiating the aqueous solution with light; and a method of producing a glass matrix having the nanoparticles dispersed therein.The present invention provides III-V semiconductor nanoparticles having a high photoluminescence efficiency in an aqueous solution, and a method of producing the nanoparticles. The invention further provides a fluorescent material with high PL efficiency containing the III-V semiconductor nanoparticles retained in a glass matrix, a method of producing the fluorescent material, and a light-emitting device containing the fluorescent material.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Water-dispersible nanoparticles having high luminous efficiency and method of producing the same
ActiveUS8221651B2Improve efficiencyImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensWater dispersiblePhotoluminescence
Nanoparticles having a core / shell structure consisting of a core comprising a Group III element and a Group V element at a molar ratio of the Group III element to the Group V element in the range of 1.25 to 3.0, and a shell comprising a Group II element and a Group VI element and having a thickness of 0.2 nm to 4 nm, the nanoparticles having a photoluminescence efficiency of 10% or more and a diameter of 2.5 to 10 nm; a method of producing the water-dispersible nanoparticles and a method of producing a glass matrix having the nanoparticles dispersed therein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Glass plate, process for producing it, and process for producing TFT panel
ActiveUS20100129944A1Little influenceLow B2O contentGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusThermal expansionGlass sheet
To provide a glass plate which has a low B2O3 content and which can be used as a glass plate for e.g. an LCD panel.A glass plate which comprises, as a glass matrix composition as represented by mass % based on oxide, from 53 to 74 mass % of SiO2, from 15 to 23 mass % of Al2O3, from 0 to 3 mass % of B2O3, from 2 to 17 mass % of MgO, from 0 to 12 mass % of CaO, from 0 to 6 mass % of SrO, from 6 to 28 mass % of MgO+CaO+SrO, from 0 to 9 mass % of Na2O, from 0 to 6 mass % of K2O and from 0.8 to 11 mass % of Na2O+K2O, contains from 100 to 500 ppm of SO3, has an average coefficient of thermal expansion from 50 to 350° C. of at most 60×10−7 / ° C., and has a strain point of at least 600° C.
Material for conductor tracks made of copper alloy
ActiveCN1985014AMeet a wide range of requirementsLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceLanthanide
The invention relates to a material for conductor tracks made of copper alloy containing Cu > 90 At. %, whereby said material contains 0.5 to 10 At. % of one or more elements from the group consisting of Ca, Sr, Ba, Sc, Y, lanthanide, Cr, Ti, Zr, Hf, Si; and 0 to 5 At. % of one or more elements from the group consisting of Mg, V, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, Ag, Au, Fe, B. Said material has a low electrical resistance, good adhesion to the glass substrate, excellent oxidation resistance, and a low electromigration rate.
Owner:PLANSEE SE
Yb-doped fiber and manufacturing method thereof
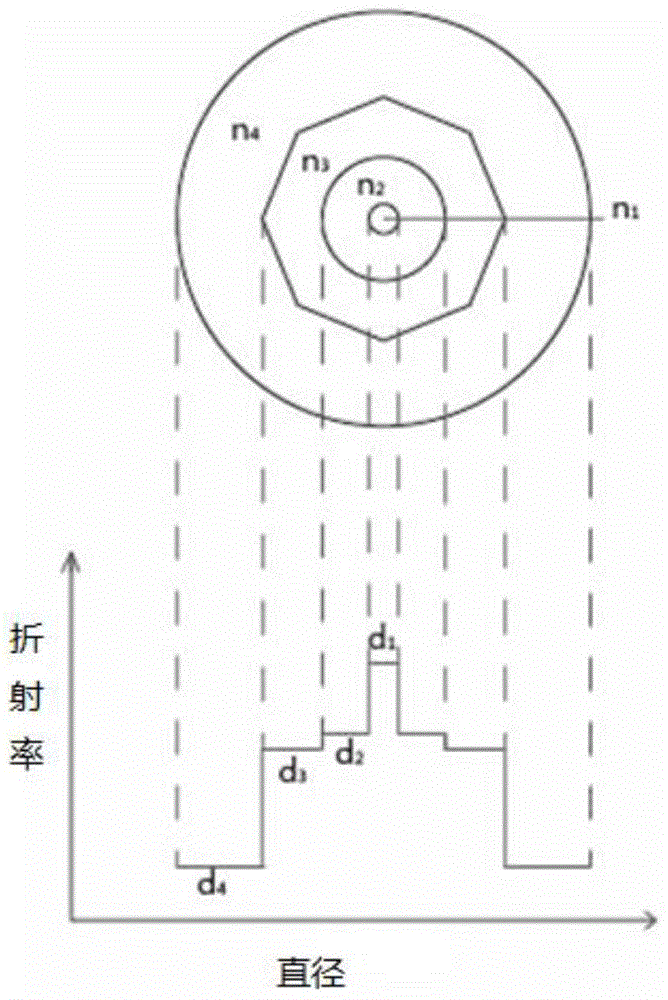
ActiveCN104865634AHigh refractive indexPromote absorptionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideGlass matrixHigh concentration
The invention discloses an Yb-doped fiber and a manufacturing method thereof. The Yb-doped fiber comprises a core layer at least containing Yb and Al, a glass matrix cladding surrounding the core layer, and a low-refractive index coating layer surrounding the glass matrix cladding. The glass matrix cladding comprises an inner cladding and an outer cladding. The refractive index of the inner cladding is lower than that of the core layer, and higher than that of the outer cladding. The inner cladding uses Ge, P, Al, and F as doping agents. The core layer is doped with F and P as doping agents. A MCVD method is used to manufacture a performing bar, fiber-drawing temperature is controlled, so optical fibers are drawn under relatively low tension, and required fibers are obtained. Through improving the refractive index of the inner cladding, relatively through reducing the difference between the refractive index of the core layer and the refractive index of the inner cladding, relatively high Al and Yb doping concentration in a fiber core is maintained, so as to reduce core layer NA under the condition that relatively high fiber cladding absorption coefficient is maintained, and single-mode output is realized, that is, fiber quality factor is proximity to one. The manufacturing method can manufacture a high-concentration Yb-doped fiber, and realizes relatively high cladding absorption coefficient.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Delivery vehicle for probiotic bacteria comprising a dry matrix of polysaccharides, saccharides and polyols in a glass form and methods of making same
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
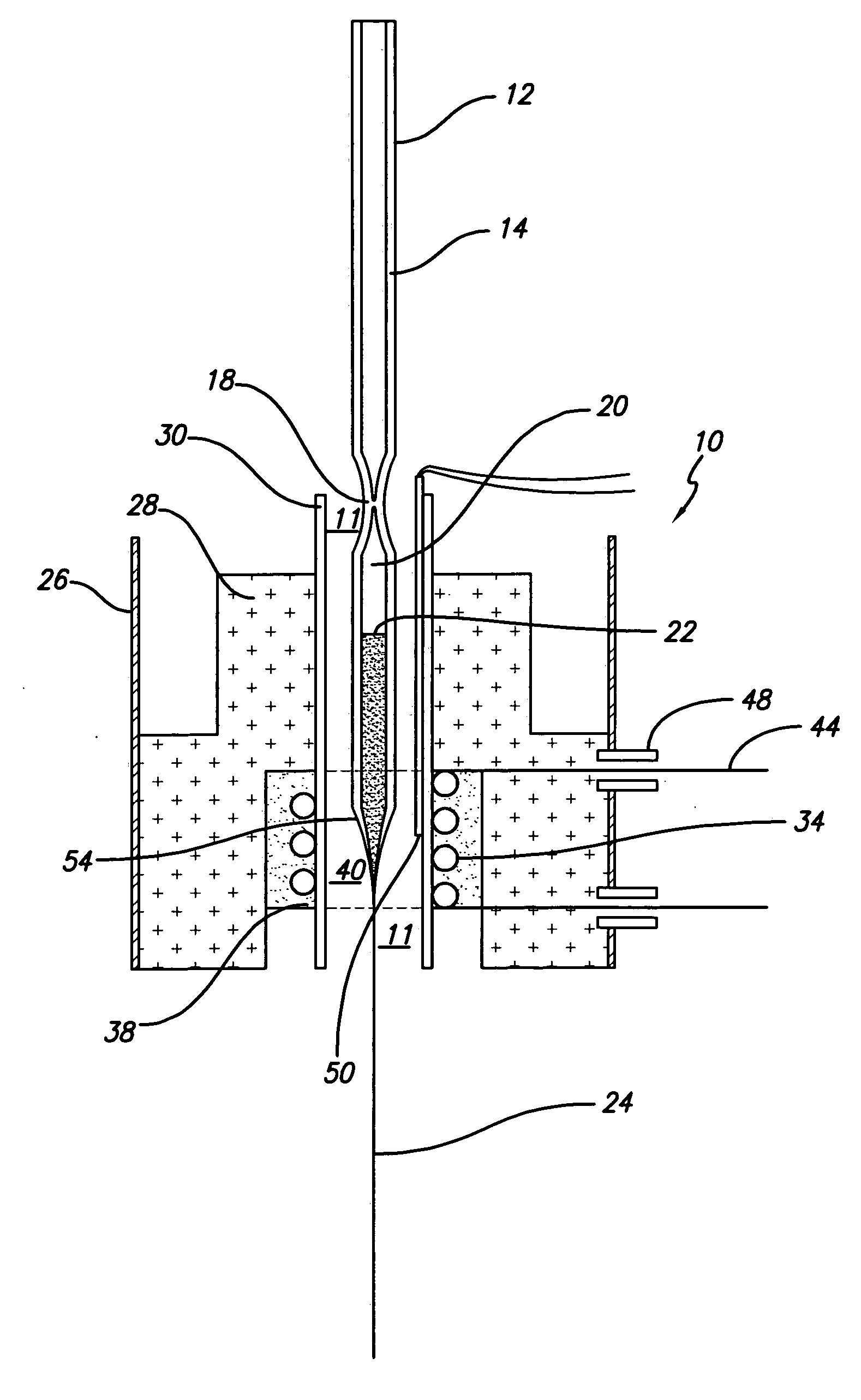
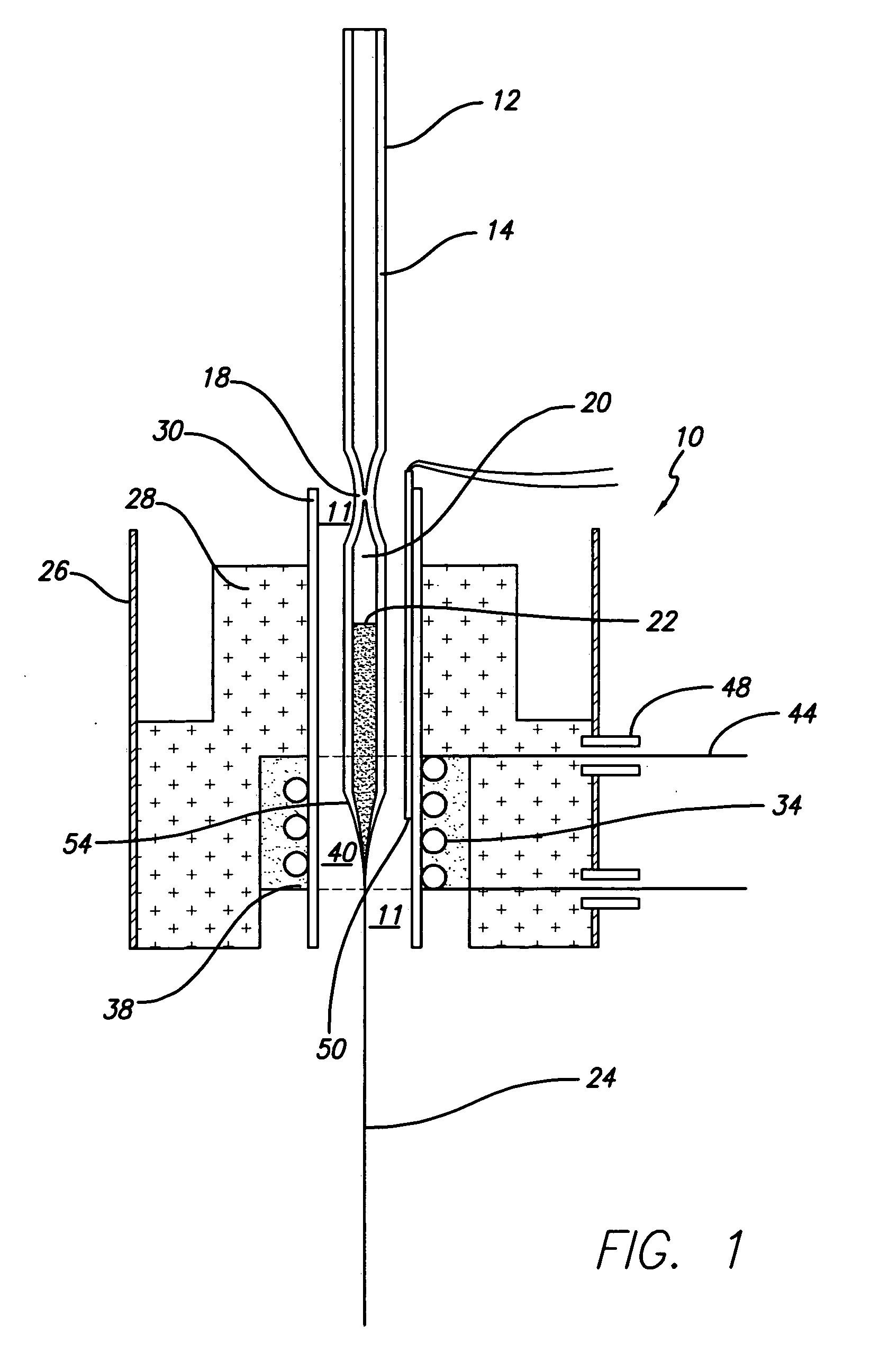
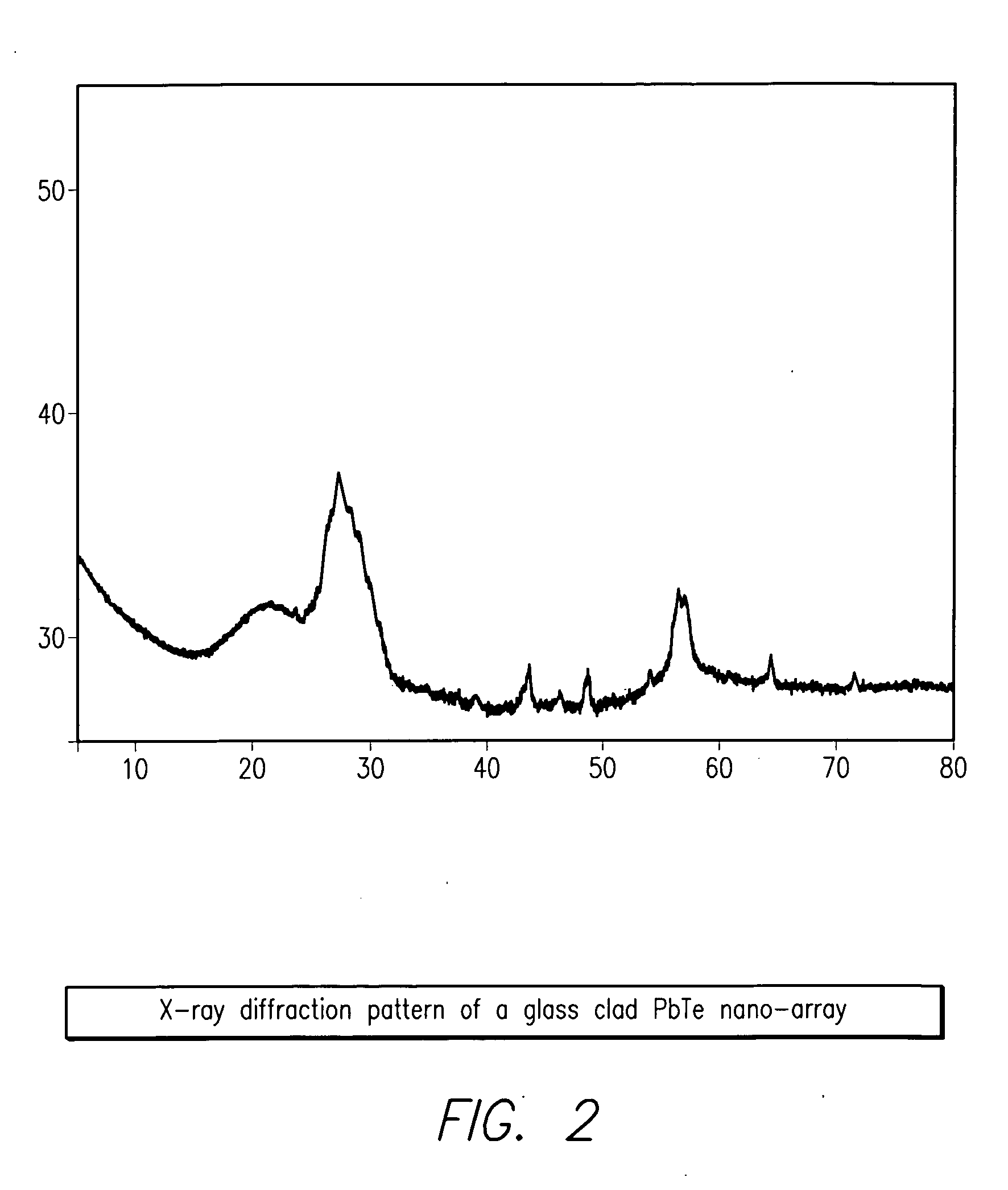
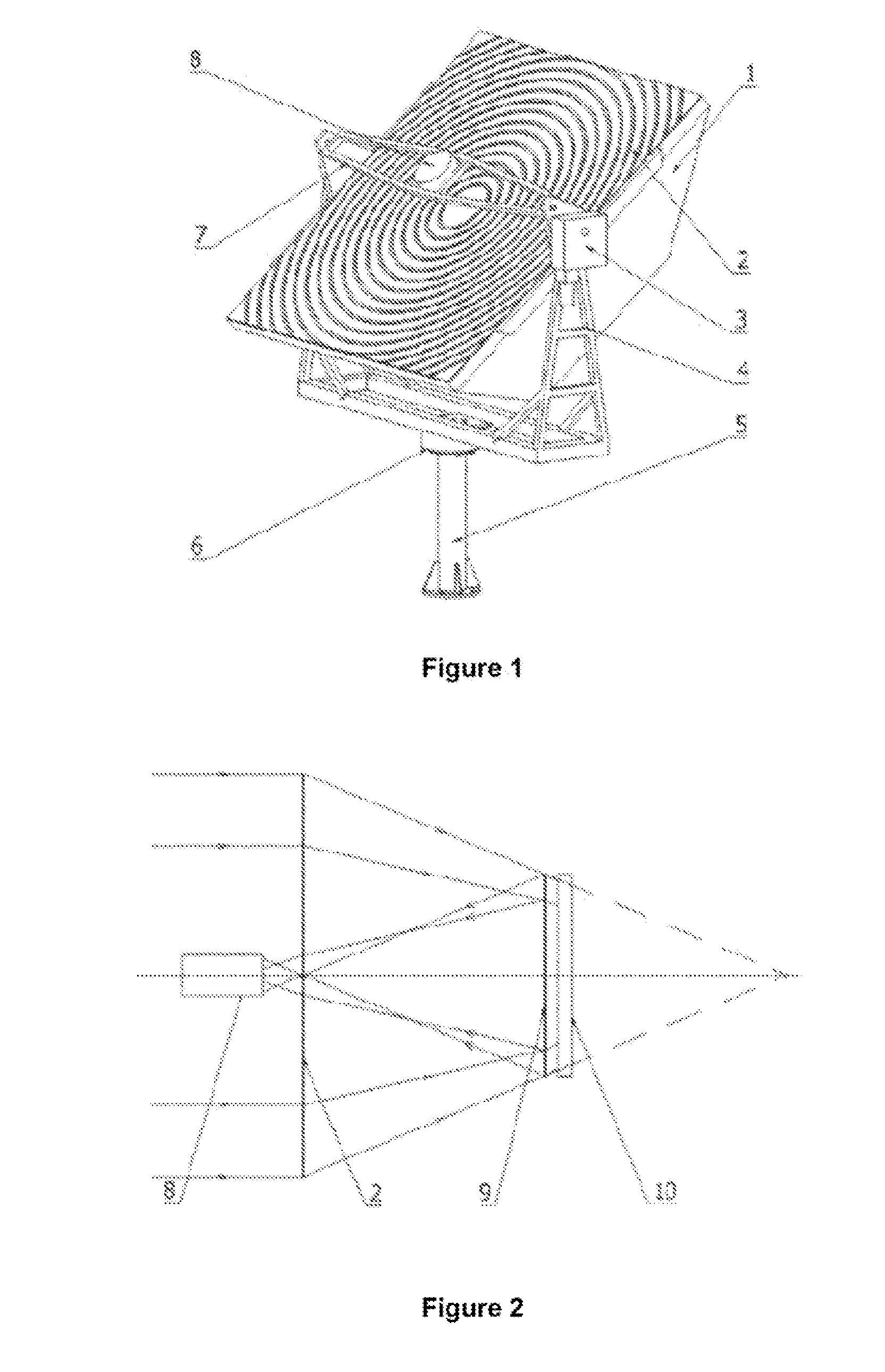
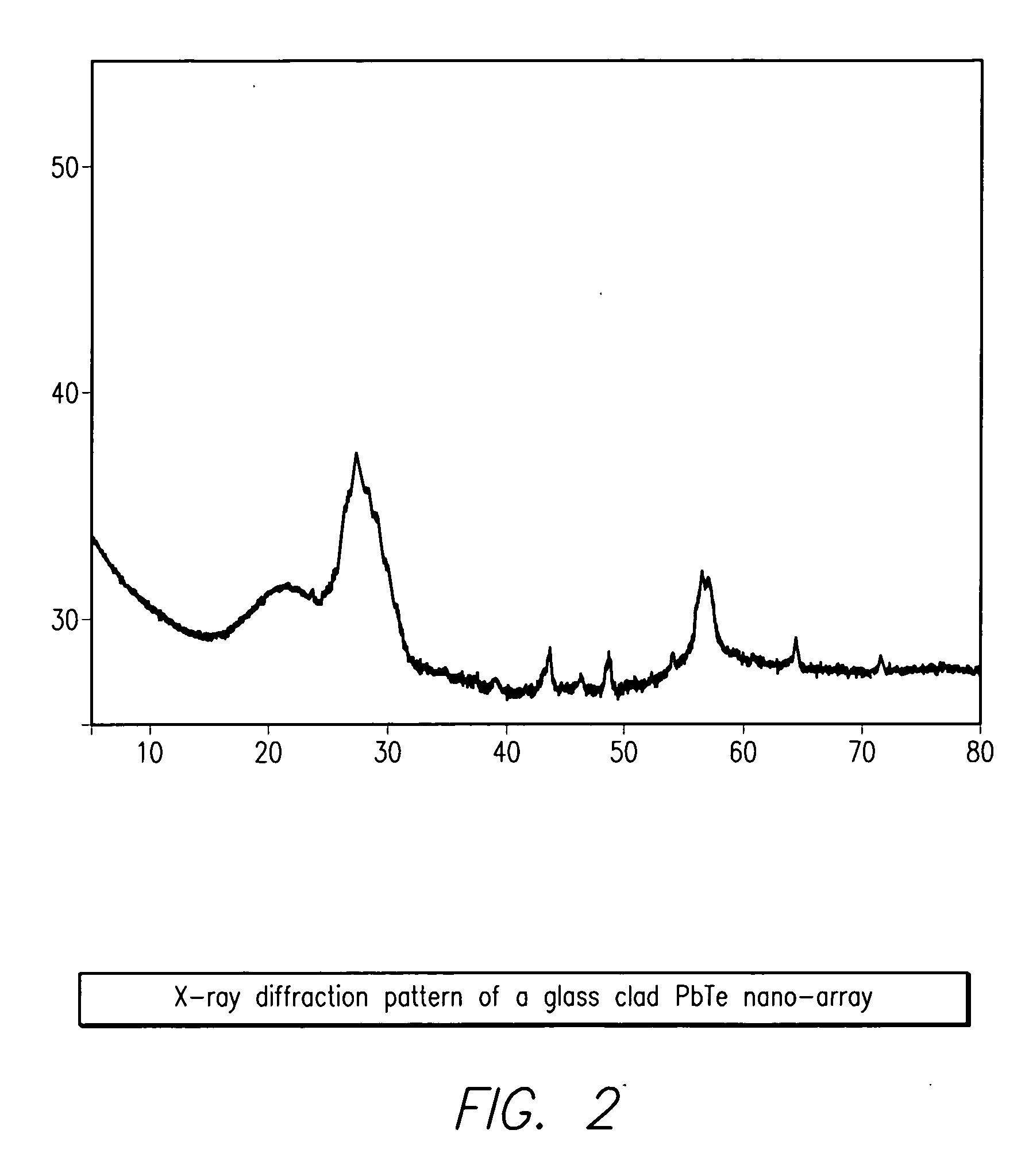
High density nanowire arrays in glassy matrix
InactiveUS20070131269A1Cost-effectivelySmall footprintThermoelectric device detailsThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsFiber
The present invention provides high density nanowire arrays in a glassy matrix comprising one or more thermoelectric fibers embedded in an electrically insulating material such that the thermoelectric material exhibits quantum confinement. According to the preferred embodiment of the invention, the thermoelectric material comprises PbTe and the glassy matrix comprises an electrically insulating material comprising a binary, ternary or higher component glass such as pyrex, borosilcate, aluminosilicate, quartz. The glass may also be formed from multiple constituents but not limited to lead oxide, tellurium dioxide and silicon dioxide, alumina, calcium oxide etc.
Owner:ZT3 TECH INC
Preparation method of fiber grating
ActiveCN104678486AImprove consistencyThe process is reasonable and simpleCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideGratingBare fiber
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fiber grating. The preparation method comprises the following steps: clamping a quartz glass matrix optical fiber performing bar on an optical fiber drawing tower to be molten and drawn, performing grating writing on the continuously descending bare fiber, coating the bare fiber with a coating, and performing ultraviolet curing, and at last reeling through a take-up reel, wherein the preparation method is characterized in that the grating writing adopts a phase-mask technique and uses a 193 nm excimer laser to perform monopulse exposure to write the bare fiber in the grating. The preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used for dynamically and continuously preparing the fiber grating array online, is simple, convenient and reasonable in process, and high in manufacturing efficiency; the grating written by the phase-mask technique and the 193 nm excimer laser is stable in central wavelength, good in spectral form, and high in consistency of grating reflectivity; the method can be used for preparing the high-quality grating array and solves the problems that the grating prepared by the fiber drawing tower online is poor in stability, low in reliability, poor in grating quality and low in efficiency; the prepared fiber grating array can be used for long-distance detection and signal transmission.
Owner:武汉烽理光电技术有限公司
Systems and methods for fabricating objects from bulk metallic glass matrix composites using primary crystallization
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of the invention implement bulk metallic glass matrix composites in the fabrication of objects. In one embodiment, a method of fabricating an object including a bulk metallic glass matrix composite includes: forming a bulk metallic glass matrix composite composition into the shape of the object to be fabricated; and developing the bulk metallic glass matrix composite composition to include non-equilibrium inclusions that are softer than the surrounding matrix as measured by one of: the shear modulus, the elastic limit, and the hardness; where the bulk metallic glass matrix composite composition is such that the extent of the presence of the inclusions can be made to vary.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Large Tracking-Type Fresnel Lens Point-Focusing Solar System
The invention provides a large trailing-type Fresnel lens point-focusing solar power system, it comprises a box body, a point-focusing glass matrix Fresnel lens, a reflecting low-radiation glass, a photovoltaic component, a high-temperature heat accumulator and a tracker. The point-focusing glass Fresnel lens, the reflecting low-radiation glass and the photovoltaic component are arranged in proper sequence from up to down, and respectively arranged on the upper part, the middle part and the low part of the box body. The high-temperature heat accumulator is positioned on the point-focusing glass matrix Fresnel lens. The high-temperature heat accumulator is fixed and arranged on a transverse bracket connected with the box body. The box body is arranged on the tracker, and traces the sun by the drive of the tracker. The invention relates to a trailing and spotlighting technique and a sunlight selective transmission technique, it is a high-efficiency clean photoelectric and photothermic utilization method.
Owner:CHENGDU ZSUN SCI & TECH DEVING
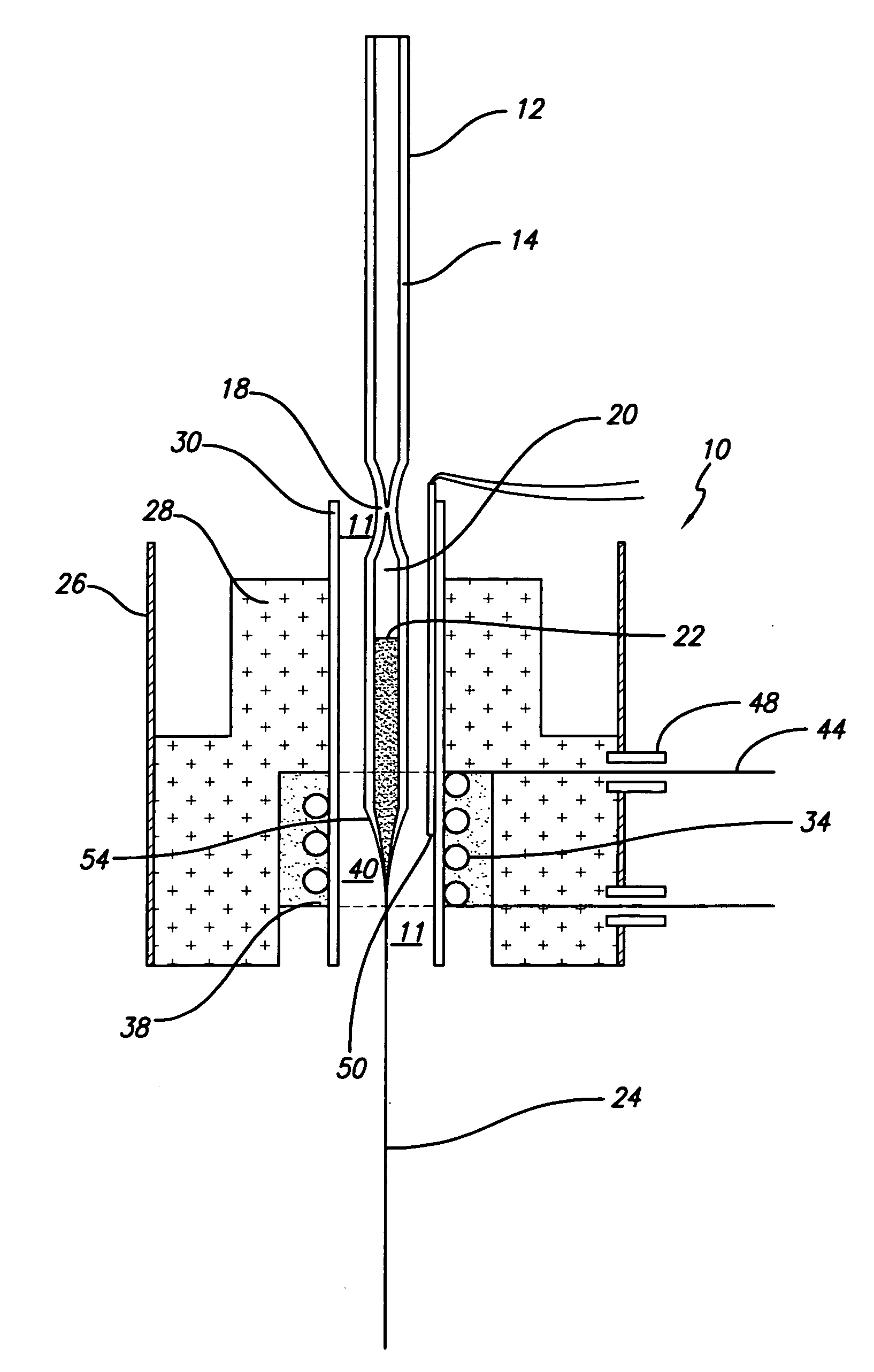
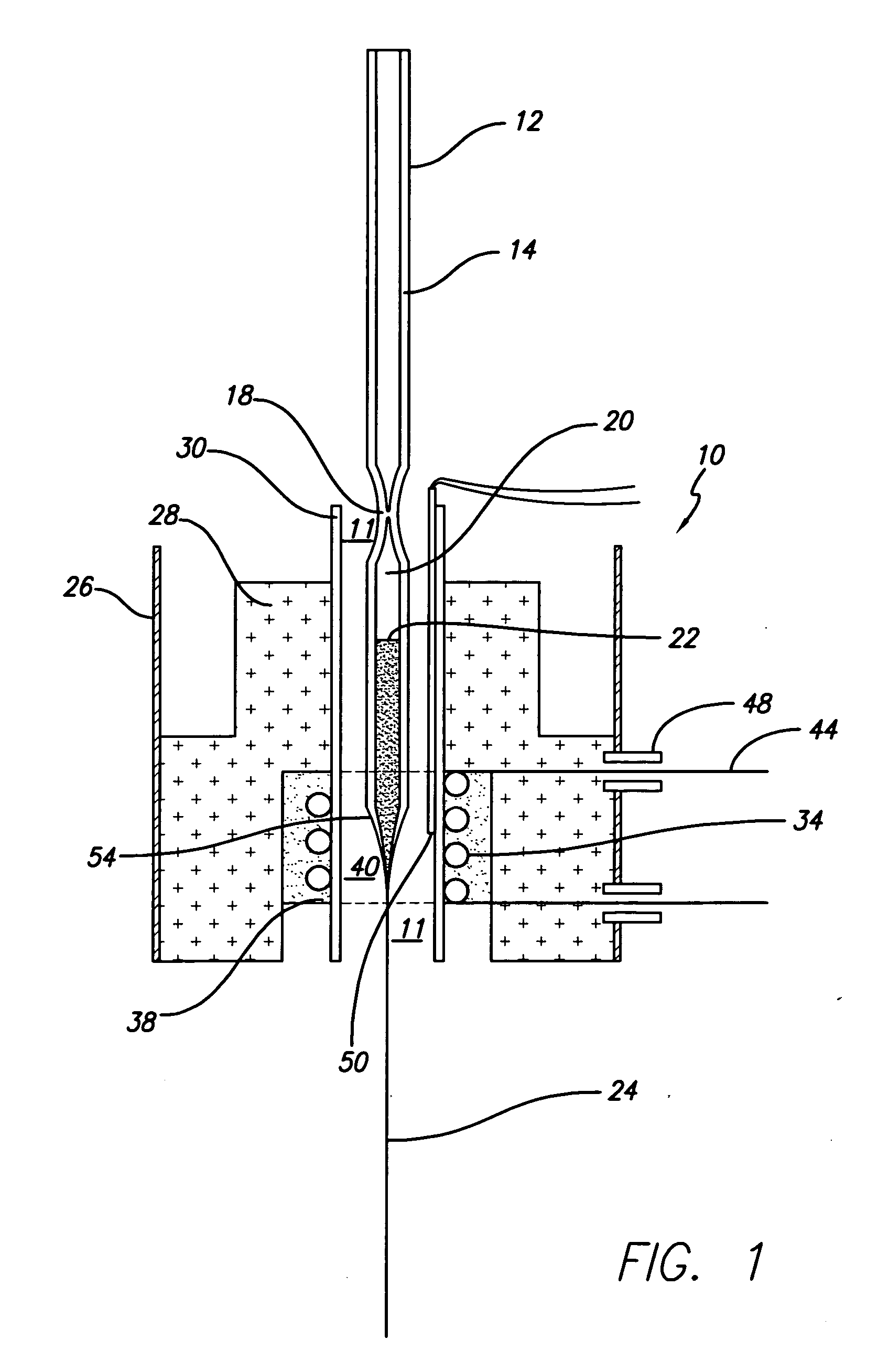
Methods of drawing high density nanowire arrays in a glassy matrix
InactiveUS20070131266A1Reduce variationExpand the populationGlass making apparatusThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric materialsFiber
The present invention provides a method of drawing a thermoelectrically active material in a glass cladding, comprising sealing off one end of a glass tube such that the tube has an open end and a closed end, introducing the thermoelectrically active material inside the glass tube and evacuating the tube by attaching the open end to a vacuum pump, heating a portion of the glass tube such that the glass partially melts and collapses under the vacuum such that the partially melted glass tube provides an ampoule containing the thermoelectric material to be used in a first drawing operation, introducing the ampoule containing the thermoelectric material into a heating device, increasing the temperature within the heating device such that the glass tube melts just enough for it to be drawn and drawing fibers of glass clad thermoelectrically active material. The invention further provides a method for bunching together such fibers and re-drawing them one or more times to produce arrays of thermoelectric nanowires clad in glass.
Owner:ZT3 TECH INC
Rare earth ion doped down-conversion luminescent transparent glass-ceramics
The invention discloses a rare earth ion doped down-conversion luminescence transparent microcrystalline glass, which is obtained by doping rare earth ion in an oxyfluoride microcrystalline glass substrate with the molar concentration of the rare earth ion to be 1-40% and the volume percent of the fluoride microcrystal in the glass matrix to be 1-50%. The down-conversion luminescence transparent microcrystalline glass of the invention has the advantages of low phonon energy of the fluoride, excellent machining characteristic and chemical stability of the oxide glass and quantum efficiency which is more than one; the glass slowly ages under the condition of outdoor long-term illumination and can also be machined into transparent plate shape or even ultrathin plate shape, therefore, the glass is one of the best selections which can be used in solar cells, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for stably incorporating substances within dry, foamed glass matrices and compositions obtained thereby
The invention provides methods for producing foamed glass and the compositions obtained thereby. The compositions are suitable for stable storage of a wide variety of substances, particularly biological and pharmaceutical.
Owner:QUADRANT DRUG DELIVERY
Degradable dynamics enhancement type bioglass radical porous composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101288780ARaise the sintering temperatureHigh compressive strengthBone implantStress concentrationCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to a biological glass base porous composite material of a degradable mechanical enhanced type and a preparation method thereof. The material takes a biological glass porous stent which comprises macroporous channels and mediated pore channels as matrix. Adjacent macroporous channels are mutually communicated. The internal and external surfaces of the macroporous channels and mediated pore channels are provided with gel layers which are assembled layer-to-layer by the biomolecules with positive and negative charges alternatively. The biological glass matrix is made from the components with the following weight percentage of 16-38 percent of CaO, 0-10 percent of P2O5, 45-80 percent of SiO2, 0-0.1 percent of SrO and 0-22.5 percent of Na2O. The releasing speed of the biological active ions of the biological glass base porous composite material which is similar to the extracellular matrix and is decorated by the layer-to-layer assembly of the charges of different polarity of the biomolecules can be effectively cut and controlled. The walls of the pore channels are beneficial to the adhesion growth of cells. The mechanical strength, the fracture toughness and the machinability are good. And the application of the regeneration treatment on the bone gear injury home position of a stress concentrated part can be satisfied.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glass plate for display panels, process for producing it, and process for producing TFT panel
InactiveUS20110003483A1Improve homogeneityImprove flatnessCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesGas discharge vessels/containersTO-18Glass sheet
To provide a glass plate for display panels which has a low 8203 content and a low compaction and which can be used as a glass substrate for large TFT panels.A glass plate for display panels, which comprises, as a glass matrix composition as represented by mass% based on oxide:SiO2 50.0 to 73.0,Al2O3 6.0 to 20.0,B2O3 0 to 2.0,MgO 4.2 to 9.0,CaO 0 to 6.0,SrO 0 to 2.0,BaO 0 to 2.0,MgO+CaO+SrO+BaO 6.5 to 11.3,Li2O 0 to 2.0,Na2O 2.0 to 18.0,K2O 0 to 13.0, andLi2O +Na2O+K2O 8.0 to 18.0,and has a heat shrinkage (C) of at most 20 ppm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Anti-corrosion composition
The present invention provides an anti-corrosion composition which can be applied to various substrates. The composition comprises a glass matrix formed by crosslinking a mixture of an amine-functionalized silane and an alkoxy-functionalized siloxane, an epoxy and a compatabilizing agent for coupling the epoxy and the alkoxy-functionalized siloxane of the glass matrix.
Owner:MICROPHASE COATINGS
Glass for manufacturing micro-channel plate glass matrix
The invention relates to glass for manufacturing micro-channel plate glass matrix. The glass comprises surface glass and core glass which are used together. The surface glass comprises the following components in part by weight: 47 to 50.0 parts of SiO2, 0.5 to 2.0 parts of Al2O3, 28 to 30.0 parts of PbO, 7.0 to 10.0 parts of Bi2O3, 5 to 6.5 parts of sigma (K2O+Rb2O+CS2O), 6 to 9.0 parts of sigma (BaO+CaO) and 0.5 to 1.0 part of sigma (As2O3+Sb2O3). The core glass comprises the following components in part by weight: 20 to 27.0 parts of SiO2, 12 to 18.0 parts of B2O3, 1 to 2.0 parts of Al2O3, 30 to 40 parts of sigma (BaO+CaO), 10 to 20 parts of La2O3, and 2 to 3 parts of sigma (ZnO+MgO). The glass has the advantages of deformation resistance of MCP, structural uniformity and good aperture precision.
Owner:杭州千盟光电科技有限公司
Large-mode-field ytterbium-doped optical fiber
InactiveCN105244741AReduce manufacturing difficultyNo reduction in doping concentrationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingActive medium shape and constructionLight beamRefractive index
The invention discloses a large-mode-field ytterbium-doped optical fiber. The optical fiber is provided with a core layer containing ytterbium at least, a glass substrate internal wrapping layer which surrounds the core layer, and a low-refractive-index coating layer which surrounds the glass substrate wrapping layer. Ytterbium concentration of the center of the optical fiber along any diameter direction of the core layer is the highest, and ytterbium concentration gradually reduces from the center to the two end points. Distribution of ytterbium concentration of the core layer along the diameter direction of the core layer meets Gaussian distribution. The optimized optical fiber output light beam quality is acquired by the design without reducing core layer doping concentration or changing bending property or increasing optical fiber preparation difficulty.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Process for preparing a glass-ceramic body
ActiveUS9260342B2The process is simple and clearImprove aestheticsImpression capsDentistry preparationsNucleationThermal treatment
Process for preparing glass-ceramic body including the steps of providing a basic glass body and subjecting the basic glass body to a thermal treatment whereby a crystalline phase embedded in a glass matrix is formed. The basic glass body is made of a composition comprising 65 to 72 wt-% SiO2, at least 10.1 wt-% Li2O and at least 10.1 wt-% Al2O3 based on the total weight of the composition, the proportion of Li2O to Al2O3 being from 1:1 to 1.5:1. The thermal treatment involves a nucleation step followed by several crystallization steps at different temperatures, whereby at least two different crystalline phases are formed.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
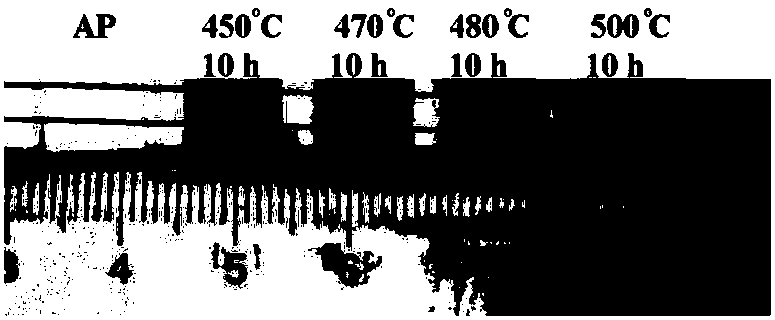
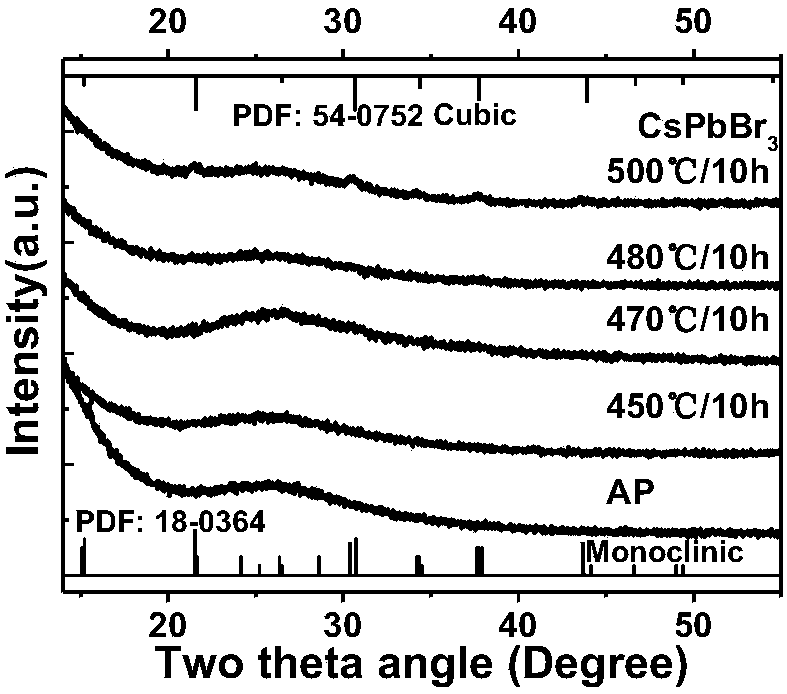
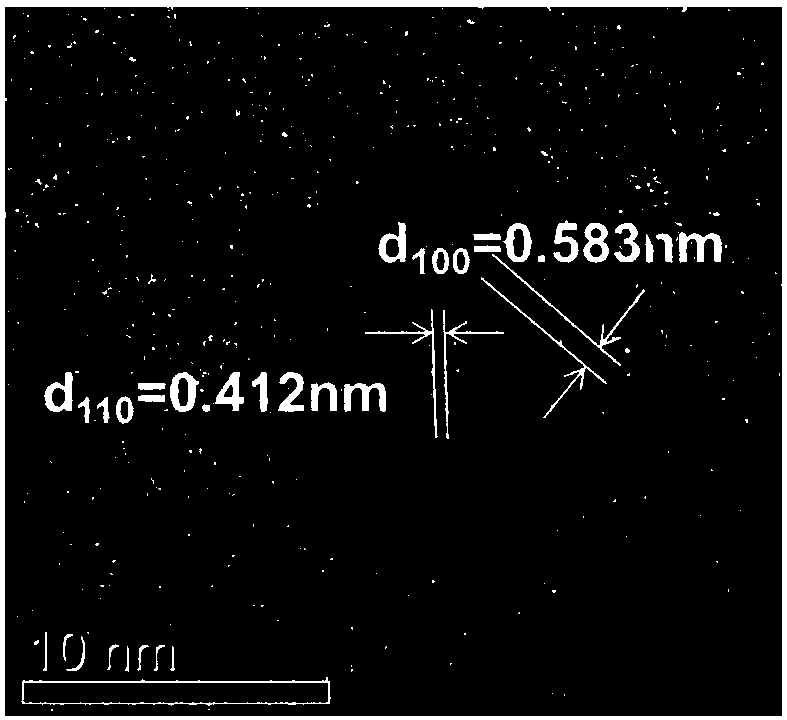
CsPbX3 nanocrystalline doped borogermanate glass, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides CsPbX3 nanocrystalline doped borogermanate glass, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The CsPbX3 nanocrystalline doped borogermanate glass is composed of the following components in mole percentages: 13.5 to 18.5% of Ge, 6.5 to 15.5% of B, 0 to 5.3 % of Zn, 0 to 2.5% of M, 0.3 to 2.3% of Pb, 1.3 to 4.6% of Cs, 2 to 7.9% of N, 1.6 to 6. 5% of X and 53 to 59%of O, wherein M is any one or a mixture of two or more selected from the group consisting of Ca, Sr or Ba; N is any one or a mixture of two or more selected from the group consisting of Li, Na or K; and X is any one or a mixture of two or more selected from the group consisting of Cl, Br or I. The CsPbX3 nanocrystalline doped borogermanate glass provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, easy operation, controllable nanocrystalline sizes, and capability of obtaining luminescence in a certain range of visible light wave bands; meanwhile, a glass substrate provides a stablesubstrate environment for nanocrystalline, so thermal stability and chemical stability of the nanocrystalline are significantly improved; and the CsPbX3 nanocrystalline doped borogermanate glass has broad application prospects.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Novel fluorescent glass and preparation method thereof
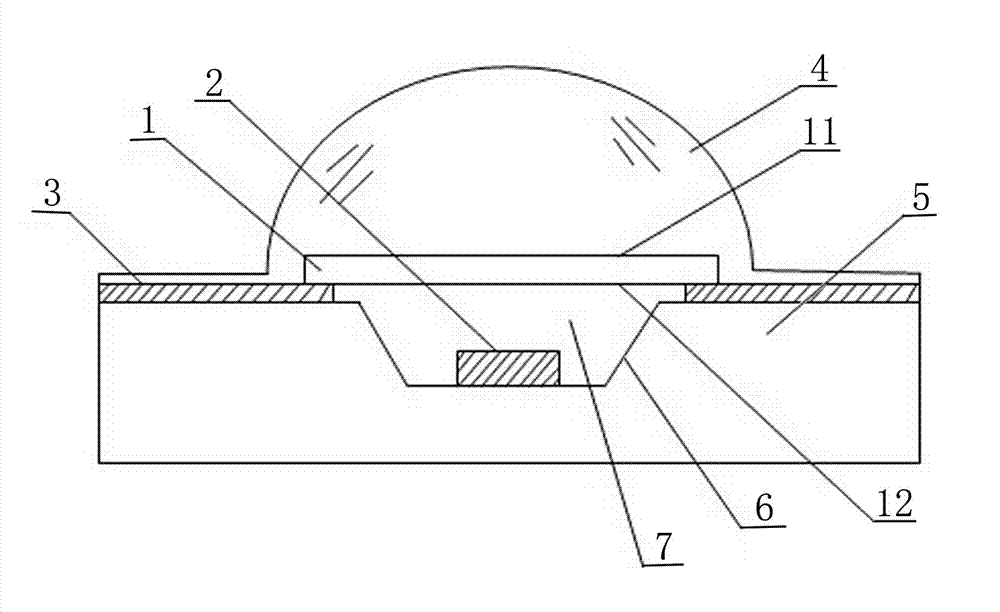
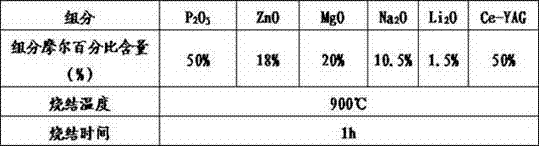
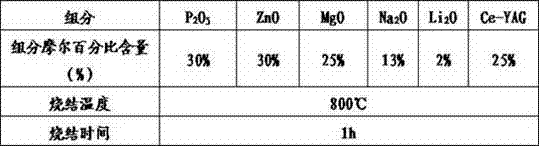
The invention discloses novel fluorescent glass and a preparation method thereof. The fluorescent glass is synthesized from a glass matrix prepared from 30%-50% of P2O5, 15%-30% of ZnO, 15%-25% of MgO, 5%-13% of Na2O and 0.5%-2% Li2O according to molar percentage, and a Ce-YAG fluorescent powder material accounting for 1%-50% of the total weight of the glass matrix. A fluorescent glass sheet is taken as an encapsulation material of a white light-emitting diode (LED), the shape and the thickness of the fluorescent glass sheet can be effectively controlled, and the uneven coating of the fluorescent powder is well avoided, so that the luminous efficiency, the service life and the spectrum stability of the white LED are improved. Furthermore, the novel fluorescent glass has the advantages that the preparation process is simple, the processing and shaping are easy, the raw materials are cheap, and the large-scale industrial production can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Upconversion luminescent material
An up-conversion fluorescent material disclosed by the invention contains rare earth ion and second-order nonlinear optical microlite with the scale of nanometer or micron in glass matrix, wherein, the molar concentration of the rare earth ion is 0.001-5 percent in the glass matrix, and the volume percent of the second-order nonlinear optical microlite is 0.1-50 percent in the glass matrix. The rare earth ion can absorb Lambada / 2 wavelength but not Lambada wavelength. A microcrystalline glass sample is focused by the laser of Lambada wavelength to produce ray rare earth ion of Lambada / 2 wavelength and produce visible light emitting through reabsorption. As the conversion efficiency of frequency multiplication is a plurality of orders of magnitude higher than multiphoton absorption up-conversion efficiency, the up-conversion efficiency is obviously increased. The up-conversion fluorescent material has broad application prospect in the fields of biomarkers and three-dimensional display, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Plant laser lighting fluorescent glass-ceramics and preparation method thereof
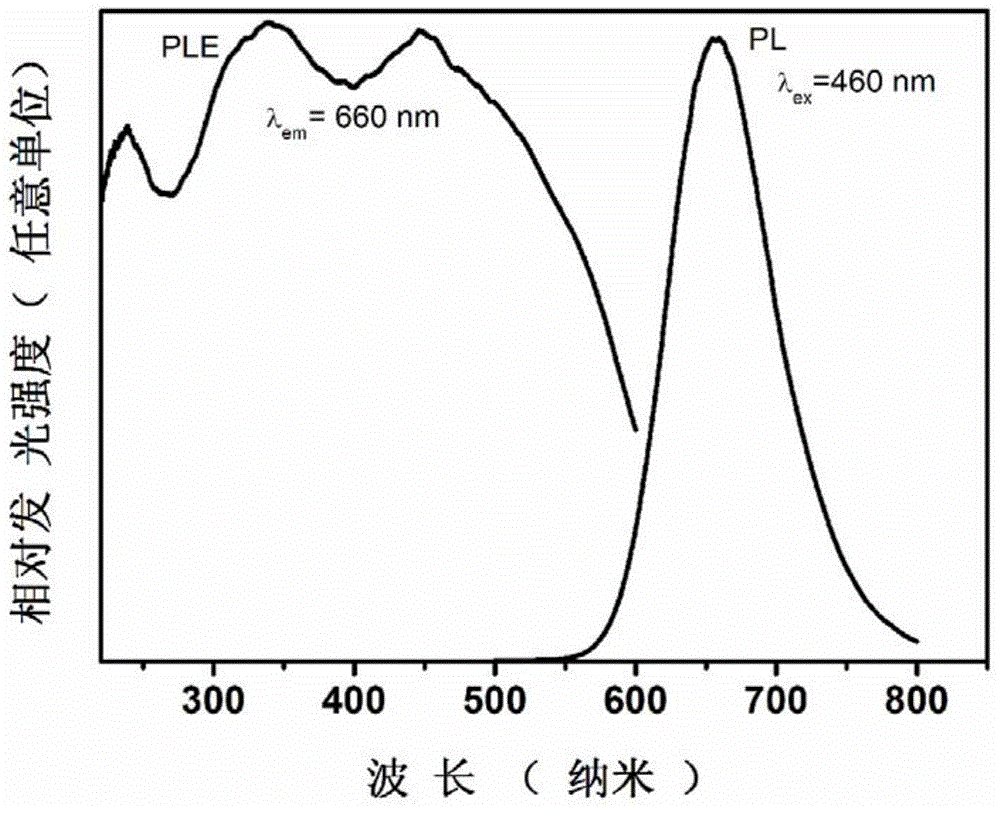
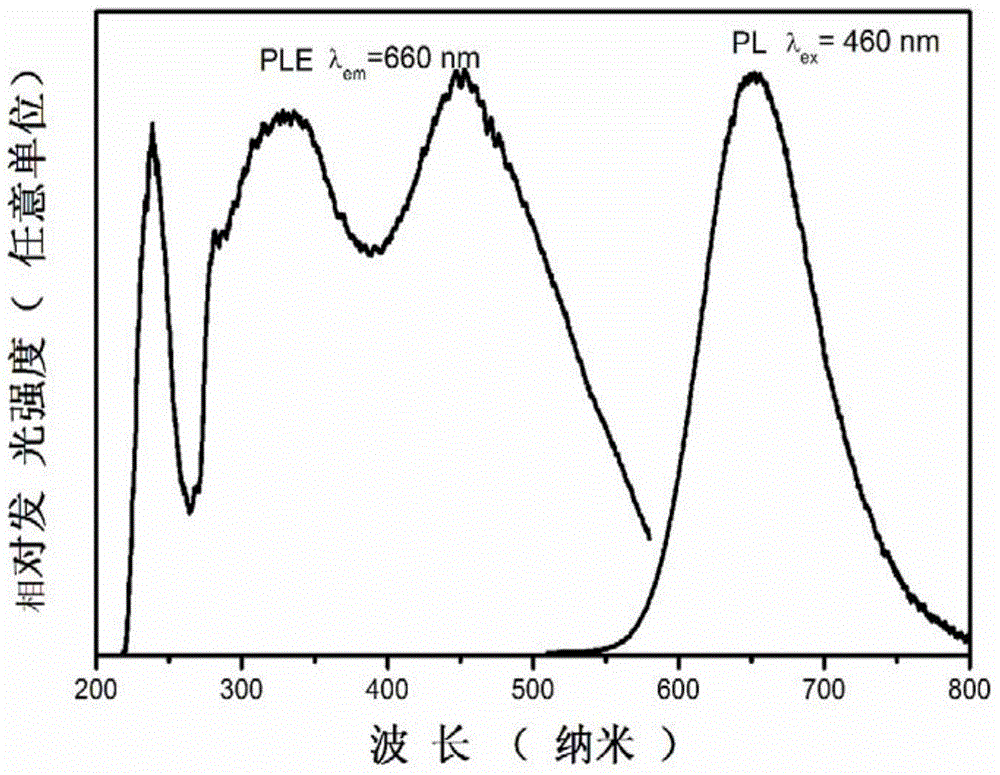
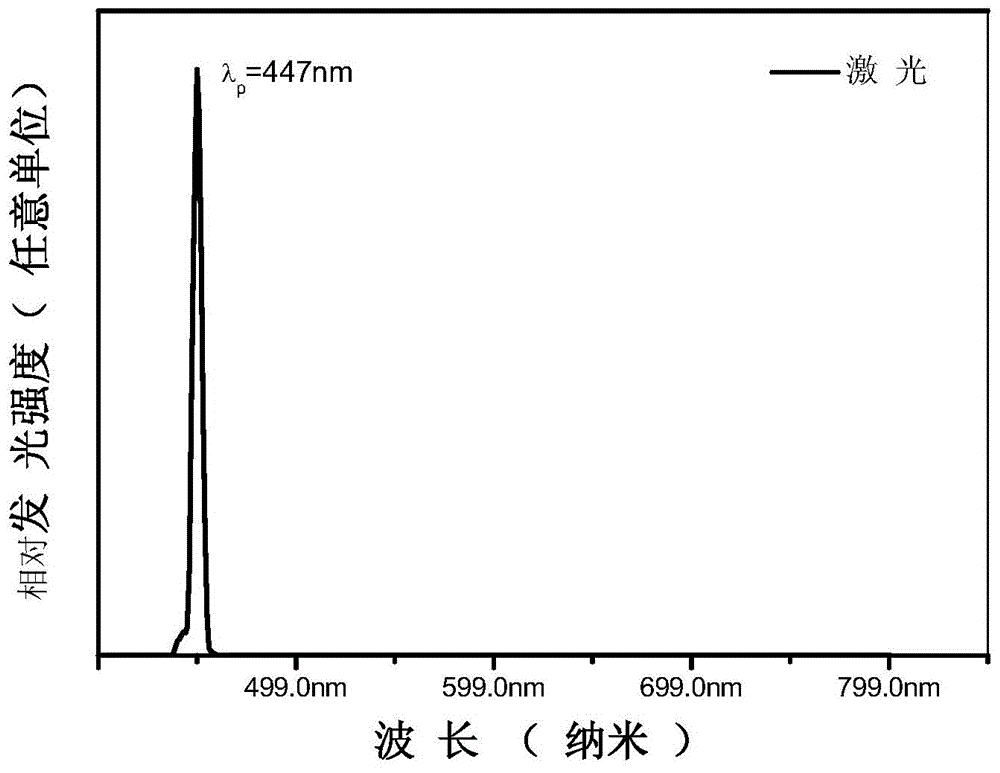
Plant laser lighting fluorescent glass-ceramics is composed of 5-30wt% of red fluorescent powder and the balance of a glass matrix; the red fluorescent powder emits 660nm wide spectrum deep red light under excitation of a blue laser light source, the full width at half maximum is wider than 60nm; and red fluorescent powder crystalline grains are uniformly embedded in the glass matrix. The advantages of the plant laser lighting fluorescent glass-ceramics are that: the fluorescent glass-ceramics emits high brightness 660nm wide spectrum red light under excitation of a blue semiconductor laser, partly-transmitted-out blue laser and the red light emitted by the fluorescent glass-ceramics are matched with effective spectrum of plant photosynthesis, at the same time, the plant laser lighting fluorescent glass-ceramics can obtain a high brightness plant laser lighting source under excitation of high energy density laser, and has potential application in the fields such as a plant factory, vertical planting, a greenhouse, a glass cultivation room, and the like.
Owner:深圳惠农智光科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com