Degradable dynamics enhancement type bioglass radical porous composite material and preparation method thereof
A technology of bioglass and degradation mechanics, applied in medical science, bone implants, prostheses, etc., can solve problems such as low compressive strength, poor compatibility, and low interface bonding strength, and achieve improved machinability, Improvement of machinability and promotion of cell adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
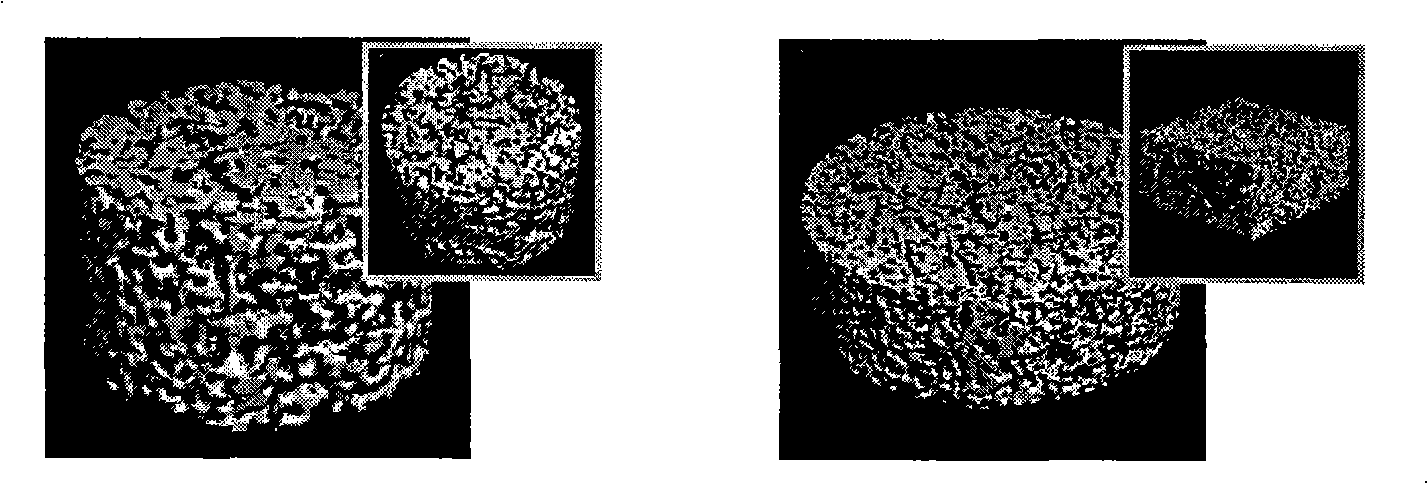
[0044] 1) Make a series of unequal diameters arranged along the diameter direction ( , 8, 10mm) cylindrical through-hole (honeycomb-shaped) polytetrafluoroethylene cylinder mold and a columnar through-hole mold with a length × width × height of 36 × 9 × 9mm, and placed in a pre-placed 0.22μm In the two suction funnels of pore filter paper, paraffin microspheres with a ball diameter of 150-280 μm are placed in the through holes of the mold to form a regular stacking array. After heat treatment at 40 ° C, the surfaces of adjacent microspheres are bonded to form a porous structure. template.
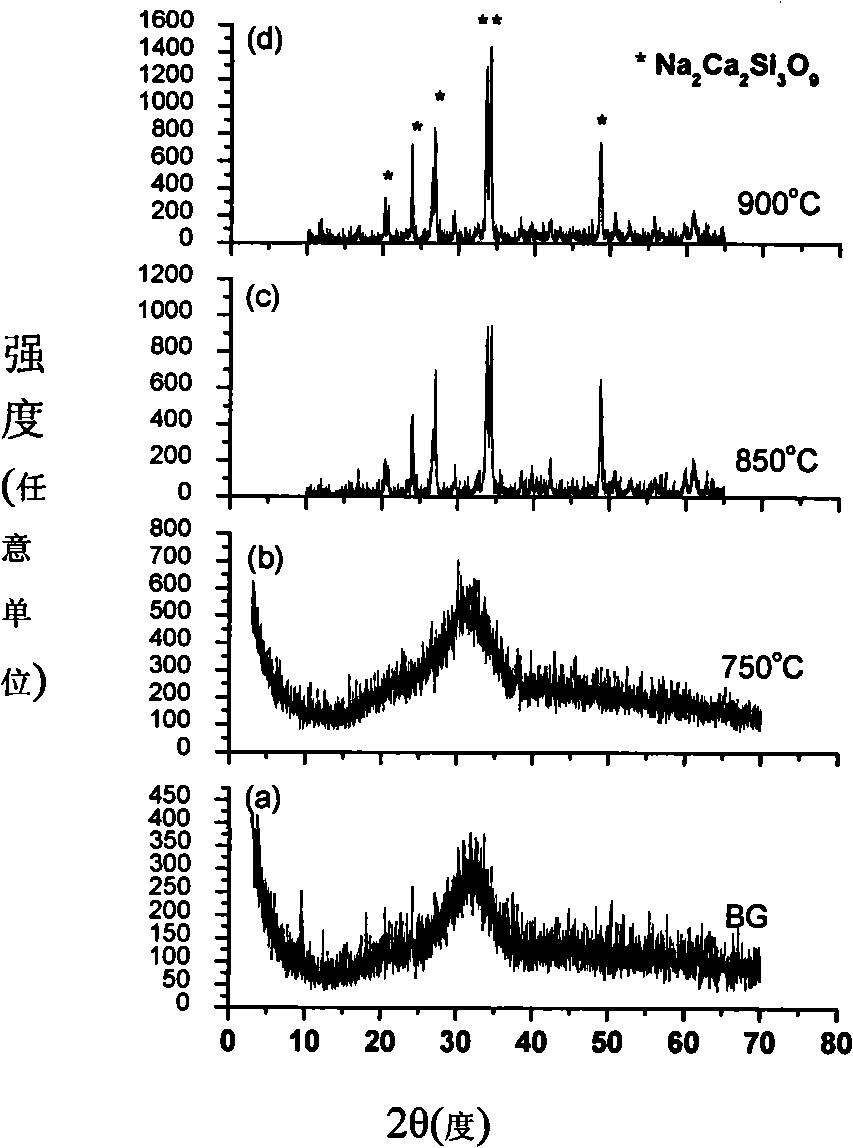
[0045] In 400mL absolute ethanol medium, add CaO22.5%, P 2 o 5 10%, SiO 2 45%, Na 2 O 22.5% of the mesoporous bioglass nanopowder to obtain the slurry, under vacuum conditions, the slurry is added dropwise in the porous template until the micropores of the template are completely filled by the slurry, let ethanol volatilize at room temperature, and dry; Sintered at 750°C to remove th...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1) Put paraffin microspheres with a ball diameter of 380-450 microns in a suction filter funnel to form a regular stacking array, and heat-treat at 40°C to bond the surfaces of adjacent microspheres to form a porous template;
[0051] Under vacuum conditions, will contain CaO38%, P 2 o 5 6.5%, SiO 2Add 55.5% ethanol slurry of mesoporous bioglass nanopowder dropwise into the porous template until the micropores of the template are completely filled with the slurry, let the ethanol evaporate at room temperature, and dry it; then sinter at 850°C to remove the paraffin microparticles. Spherical template, the bioglass porous scaffold with regular and interconnected pore structure is obtained, and the X-ray diffraction pattern of the porous material is as follows: figure 1 c, The spectrum shows that the porous material prepared by sintering at 850 °C crystallizes and precipitates Na 2 Ca 2 SiO 9 crystalline substance.
[0052] 2) Soak the bioglass porous scaffold in a ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] 1) Put paraffin microspheres with a ball diameter of 280-350 microns in a suction filter funnel to form a regular stacking array, and heat-treat at 45°C to bond the surfaces of adjacent microspheres to form a porous template;
[0057] Under vacuum conditions, will contain CaO16%, P 2 o 5 5.5%, SiO 2 Add the ethanol slurry of 78.5% mesoporous bioglass nanopowder dropwise into the porous template until the micropores of the template are completely filled with the slurry, let the ethanol evaporate at room temperature, and dry it; then sinter at 900°C to remove the paraffin microparticles. Spherical template, the bioglass porous scaffold with regular and interconnected pore structure is obtained, and the X-ray diffraction pattern of the porous material is as follows: figure 1 d, The spectrum shows that the porous material prepared by sintering at 900 °C crystallizes and precipitates Na 2 Ca 2 Si 3 o 9 crystalline substances;
[0058] 2) Soak the bioglass porous sca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com